Page 1

Operation Maintenance Manual OM 756-2
MicroTech II® Unit Ventilator Controls
for AAF®-HermanNelson® Classroom Unit Ventilators
Group: Applied Systems
Part Number: 106506329
Date: April 2010
4-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling and Hydronic Heat-
Software Model UV13 (Valve Control)
Software Model UV14 (F&BP Damper Control)
Used with AAF-HermanNelson Classroom Unit Ventilator
Model AVS, AVV, AVR - Floor Mounted
Model AHV, AHF, AHR - Ceiling Mounted
IMPORTANT
Before unit commissioning, please read this publication in its entirety.
Develop a thorough understanding before starting the commissioning procedure.
This manual is to be used by the commissioner as a guide. Each installation is unique, only general topics are covered.
The order in which topics are covered may not be those required for the actual commissioning.
© 2010 McQuay International
Page 2

Introduction 3
Acronyms/Abbreviations 5
Getting Started 7
Using the Keypad/Display 7
Display Format 7
Keypad Functions 7
Using the Keypad/Display 9
Menu Reference 9
Description of Operation 12
State Programming 12
UVC Unit Modes 13
OFF Mode (State 9) 14
Night Purge Mode (State 8) 15
Fan Only Mode (State A) 15
Emergency Heat Mode (Super State) 16
Auto Mode 17
Cool Mode (Super State) 19
Special Purpose Unit Modes 23
Unit Mode Priority 25
Occupancy Modes 26
Occupied Mode 26
Unoccupied Mode 26
Standby Mode 26
Bypass Mode 27
Additional Occupancy Features 27
Networked Occupancy Sensor Capability 27
Unit-Mounted Time-Clock 27
Unit-Mounted Tenant Override Switch 27
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor Tenant Override Switch 27
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor Status LED 27
Space Temperature Set Points 28
Networked Set Point Capability 28
Networked Set Point Offset Capability 28
Networked Set Point Shift Capability 28
Networked Space Temperature Sensor Capability 28
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor with +/–3°F
Adjustment (optional) 29
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor with 55°F to 85°F
Adjustment (optional) 29
Effective Set Point Calculations 29
Proportional Integral (PI) Control Loops 31
Discharge Air Temperature Control 31
PI Control Parameters 32
Proportional Band 32
Integral Time 33
Indoor Air Fan Operation 33
Auto Mode 33
Occupied, Standby, and Bypass Operation 33
Unoccupied Operation 34
Cycle Fan 34
Off Delay 34
Outdoor Air Damper Operation 34
Minimum Position 34
Economizer Operation 34
Networked Space Humidity Sensor Capability 36
Networked Outdoor Humidity Sensor Capability 36
CO2 Demand Controlled Ventilation (optional) 36
Networked Space CO2 Sensor Capability 36
ASHRAE Cycle II 37
Valve Control (software model 13) 37
Face and Bypass Damper Control (software model 14) 37
End-of-Cycle Valve Control (software model 14) 37
Passive Dehumidification (optional, software model 14) 37
Active Dehumidification State (optional with reheat units, software
model 13) 38
Floating-Point Actuator Auto-Zero, Overdrive and Sync 38
Water Coil Leaving Air Thermostat (Freeze-stat) 38
Valve Control (software model 13) 38
Face & Bypass Damper Control (software model 14) 39
External Binary Inputs 39
External Binary Input 1 39
External Binary Input 2 39
External Binary Input 3 40
External Binary Outputs 40
External Binary Output 1 40
External Binary Output 2 41
External Binary Output 3 41
UVC Input and Output Table 42
Diagnostics and Service 43
Alarm and Fault Monitoring 43
Space Temp Sensor Failure () 44
Condensate Overflow Indication (optional) () 44
Outdoor Temp Sensor Failure () 44
Discharge Air Temp Sensor Failure () 44
Space Humidity Sensor Failure (optional) () 45
Outdoor Humidity Sensor Failure (optional) () 45
Space CO2 Sensor Failure (optional) () 45
Change Filter Indication () 45
EPROM Memory Indicator () 45
Configuration Display () 45
Troubleshooting Temperature Sensors 45
Troubleshooting Humidity Sensors 46
Troubleshooting Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensors 47
UVC Configuration Parameters 48
1 McQuay IM 708-2
Page 3
Introduction
Introduction
This manual provides information on the MicroTech II® control system used in the AAF®-
®
HermanNelson
Unit Ventilator product line. It describes the MicroTech II components, input/
output configurations, field wiring options and requirements, and service procedures.
For installation and general information on the MicroTech II Unit Ventilator Controller, refer
to IM 747, MicroTech II Unit Ventilator Controller.
For installation, commissioning instructions, and general information on a particular unit
ventilator model, refer to the appropriate manual (Table 1), as well as accompanying software
operating instruction manual (T able 4), and possible accessory manuals that may pertain to the
unit (Table 3).
For installation and maintenance instructions on a plug-in communications card, refer to the
appropriate protocol-specific installation and maintenance manual (Table 2). For a description
of supported network variables for each protocol, refer to Protocol Data Packet bulletin ED
15065.
Copies of the latest version of these manuals are available for download on our website at
www. mcquay.com or from your local McQuay Representative.
Table 1: Model-spe c ific unit ventilator installation literature
Description Manual #
Vertical IM 817 X X X X
Horizontal IM 830 X X X X
Vertical Self-Contained IM 789 X X X X X X
AHF
AHB
AHV
AHR
AVS
AVB
AVV
AVR
AZB
AZR
AZS
AZU
AZV
AZQ
Table 2: Protocol-specific communication card installation literature and protocol data
Description Manual #
Unit Ventilator Unit Controller LonWorks® Communications Module IM 729
Unit Ventilator Unit Controller JCI N2 Open® Communications Module IM 730
Unit Ventilator Unit Controller BACnet® Communications Module IM 731
Protocol Data Packet ED-15065
Table 3: Accessory-specific installation literature
Description Manual #
MTII Unit Ventilator Controls Installation IM 747
Room Temperature Sensors Installation IM 629
ATS Service Cable Installation for Unit Ventilators IM 762
McQuay OM 756 3
Page 4

Introduction
Table 4: Software program literature
Description Manual #
Air Source Heat Pump with Electric Heat (Software Model 00) OM 748
Water Source Heat Pump with Electric Heat (Software Model 02)
Water Source Heat Pump without Electric Heat (Software Model 03)
DX Cooling with Electric Heat (Software Model 04) OM 750
DX Cooling Only (Software Model 05) OM 751
Electric Heat Only (Software Model 06) OM 752
DX Cooling with Hydronic Heat - Valve Control (Software Model 07)
DX Cooling with Hydronic Heat - F&BP Damper Control (Software Model 08)
2-Pipe Hydronic Heat Only - Valve Control (Software Model 09)
2-Pipe Hydronic Heat Only - F&BP Damper Control (Software Model 10)
2-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling and Hot Water Heat - Valve Control (Software Model 11)
2-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling and Hot Water Heat - F&BP Damper Control (Software
Model 12)
4-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling and Hydronic Heat - Valve Control (Software Model 13)
4-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling and Hydronic Heat - F&BP Damper Control (Software
Model 14)
2-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling Only - Valve Control (Software Model 15)
2-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling Only - F&BP Damper Control (Software Model 16)
2-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling with Electric Heat - Valve Control (Software Model 17)
2-Pipe Chilled Water Cooling with Electric Heat - F&BP Damper Control (Software
Model 18)
OM 749
OM 753
OM 754
OM 755
OM 756
OM 757
OM 758
NOTICE
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with this instruction manual, may cause interference to radio
communications. It has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against detrimental interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
detrimental interference in which case users are required to correct the interference at their
own expense. McQuay International disclaims any liability resulting from any
interference or for the correction thereof.
WARNING
Electric shock hazard. Can cause personal injury or equipment damage.
This equipment must be properly grounded. Connections and service to the MicroTech II
control panel must be performed only by personnel that are knowledgeable in the operation
of the equipment being controlled.
CAUTION
Extreme temperature can damage system components.
The MicroTech II controller is designed to operate in ambient temperatures from -20°F to
125°F. It can be stored in ambient temperatures from -40°F to 140°F. It is designed to be
stored and operated in relative humidity up to 95% (non-condensing).
CAUTION
Static sensitive components. A static discharge while handling electronic circuit
boards can damage components.
Discharge any static electrical charge by touching the bare metal inside the main control
panel before performing any service work. Never unplug any cables, circuit board terminal
blocks, relay modules, or power plugs while power is applied to the panel.
4 McQuay OM 756
Page 5
Introduction
Acronyms/Abbreviations
The following table list acronyms and abbreviations that may or may not be used within this
manual. Other abbreviations for keypad displays and parameters can be found in Table 7 on
page 10 and Table 26 on page 48.
Table 5: Acronyms and abbre v iations
Description
Air Fan AF
Auxiliary Heat End Differential AHED
Auxiliary Heat Start Differential AHSD
American Standard Code for Information Interchange ASCII
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air
Conditioning Engineers, Inc
Compressorized Cooling Lockout CCLO
Spac e CO
Chilled Water CW
Chilled Water Valve Position CWVP
Discharge Air DA
Discharge Air High Limit DAHL
Discharge Air Temperature DAT
Discharge Air Temperature Setpoint DATS
Demand Controlled Ventilation
DX Cooling Discharge Air Low Limit DXLL
Economizer Compare Differential ECD
Economizer IA/OA Enthalpy Differential EED
Economizer OA Enthalpy Setpoint EES
Emergency Heat Setpoint EHS
Exhaust Interlock OAD Min Position Setpoint EOAD
Outdoor Air Temperature Setpoint EOAT
End-of-Cycle EOC
EOC OAT Low Setpoint EOCS
Outdoor Air Humidity Output EORH
Space Humidity Setpoint ERH
Economizer IA/OA Temp Differential ETD
Economizer OA Temp Setpoint ETS
Source (water in) Temperature EWIT
Face and Bypass Damper Position FBDP
Federal Communications Commission FCC
Face and Bypass F & BP
Heating, Ventilating, Air Conditioning Refrigeration HVACR
Heating EOC Valve Setpoint HEOC
Hot Water HW
Indoor Air IA
Indoor Air Fan IAF
Indoor Air Temperature IAT
Light Emitting Diode LED
Local User Interface LUI
Mixed Air Low Limit MALL
Mechanical Cooling Low Limit Setpoint MCLL
National Electric Code NEC
Outside Air OA
Outside Air Dampers OAD
Energize Exhaust Fan OAD Setpoint OADE
OAD Min Position High-Speed Setpoint OADH
OAD Min Position Low-Speed Setpoint OADL
OAD Min Position Med-Speed Setpoint OADM
Outdoor Air Damper Position OADP
OAD Lockout Setpoint OALS
OAD Max Position Setpoint OAMX
Outside Air Temperature OAT
Setpoint CO2S
2
Acronym/
ASHRAE
DCV
Abr.
McQuay OM 756 5
Page 6

Introduction
Description
Occupied Cooling Setpoint OCS
Occupied Heating Setpoint OHS
Occupancy Override Input OOI
Occupancy Sensor Input OSI
Proportional Integral PI
Parts Per Million PPM
Positive Temperature Coefficient PTC
Relative Humidity RH
Space Humidity Setpoint
Read Only RO
Read Write RW
Standby Cooling Setpoint SCS
Standby Heating Setpoint SHS
Thermal Expansion Valve TXV
Unoccupied Cooling Setpoint UCS
Unoccupied Heating Setpoint UHS
Unit Ventilator UV
Unit Ventilator Controller UVC
UVC (Heat/Cool) Mode Output UVCM
UVC State Output UVCS
Wet Heat Valve Position VALP
Ventilation Cooling Low Limit Setpoint VCLL
Ventilation Cooling Lockout VCLO
Ventilation Cooling Setpoint VCS
Wet Heat WH
Source (water in) Temperature Differential WITD
Acronym/
RHS
Abr.
6 McQuay OM 756
Page 7

Getting Started
Getting Started
The MicroTech II Unit Vent Controller (UVC) is a self-contained device that is capable of
complete, stand-alone operation. Information in the controller can be displayed and modified
by using the keypad/display (local user interface). The following sections describe how to use
the keypad/display.
Note – Many UVC parameters are accessible both through the keypad/display and the network
interface. The shared keypad/display and the network interface variables have a “lastchange-wins” relationship.
Using the Keypad/Display
The keypad/display shown in Figure 1 is provided with all MicroTech II Applied Unit
Ventilator unit controllers. With the keypad/display, operating conditions, system alarms, and
control parameters can be monitored. Set points and other parameters also can be modified.
Figure 1: Keypad/display
MicroTechTMII
FAN ONLY
COOL
HEAT
AUTO
MODE FAN
HIGH
MED
LOW
AUTO
FUNC
ON /
STOP
Display Format
The keypad/display’s 2-digit, 7-segment display normally shows the effective heating or
cooling temperature set point (Effective Set Point Output). The display also is used to view
and modify UVC parameters as explained in the following sections.
Note – When the UVC is in the OFF mode, the effective heating set point appears in the display.
All other LEDs are switched off.
Keypad Functions
Security Levels
The keypad/display provides a 4-level password security feature that can be used to restrict
access. The available security levels are shown in Table 6.
Note – All unit ventilator controllers ship with the lowest security (level 0) enabled. To change
security levels, see Figure 2. Once a security level is changed, the keypad/display
remains at that security level until the next time it is changed.
Why can’t I use the MODE or FAN key or adjust Set Point Offset?
Most likely this is due to the security feature being used. If the security feature is set higher
than level 0, then some keypad/display functionality is locked out. To ensure this is not the
problem, enter the level 0 password then try to use the keypad/display again.
McQuay OM 756 7
Page 8

Getting Started
Table 6: Keypad/display security levels
Level Display What is restricted? Password
0
1
2
3
Default level (access all) 10
Does not allow set point offset changes;
also locks out keypad/display menu
access.
Does not allow set point offset changes
nor MODE key changes; also locks out
keypad/display menu access.
Does not allow set point offset changes
nor MODE and FAN key changes; also
locks out keypad/display menu access.
21
32
43
Figure 2: Changing keypad/display security levels
ON/STOP Key and LED
Use the ON/STOP key to toggle the UVC between OFF mode and running (Application Mode
Input). The ON/STOP LED is off when the UVC is in the OFF mode.
Note – When the UVC is in the OFF mode, the effective heating set point appears in the display.
All other LEDs are switched off.
– The UVC archives each change to the keypad/display FAN and MODE keys. When the
ON/STOP key is used to bring the unit out of OFF mode, the UVC implements the last
active fan and unit modes.
– Each time the UVC power cycles, the UVC is in the auto fan and auto unit modes when
power is returned.
WARNING
Off mode is a “stop” state for the unit ventilator. It is not a “power
off” state. Power may still be provided to the unit.
FAN Key
Use the F AN key to toggle through each of the fan speeds (Fan Speed Command Input): Auto,
Low, Medium, and High.
MODE Key
Use the MODE key to toggle through the keypad/display accessible unit modes (Heat/Cool
Mode Input): Auto, Heat, Cool, and Fan Only.
Arrow Keys
Use the arrow keys to scroll between parameters and to adjust parameters.
FUNC Key
Use the Func key to view the actual space temperature or to confirm selection and changes to
user-adjustable parameters.
8 McQuay OM 756
Page 9
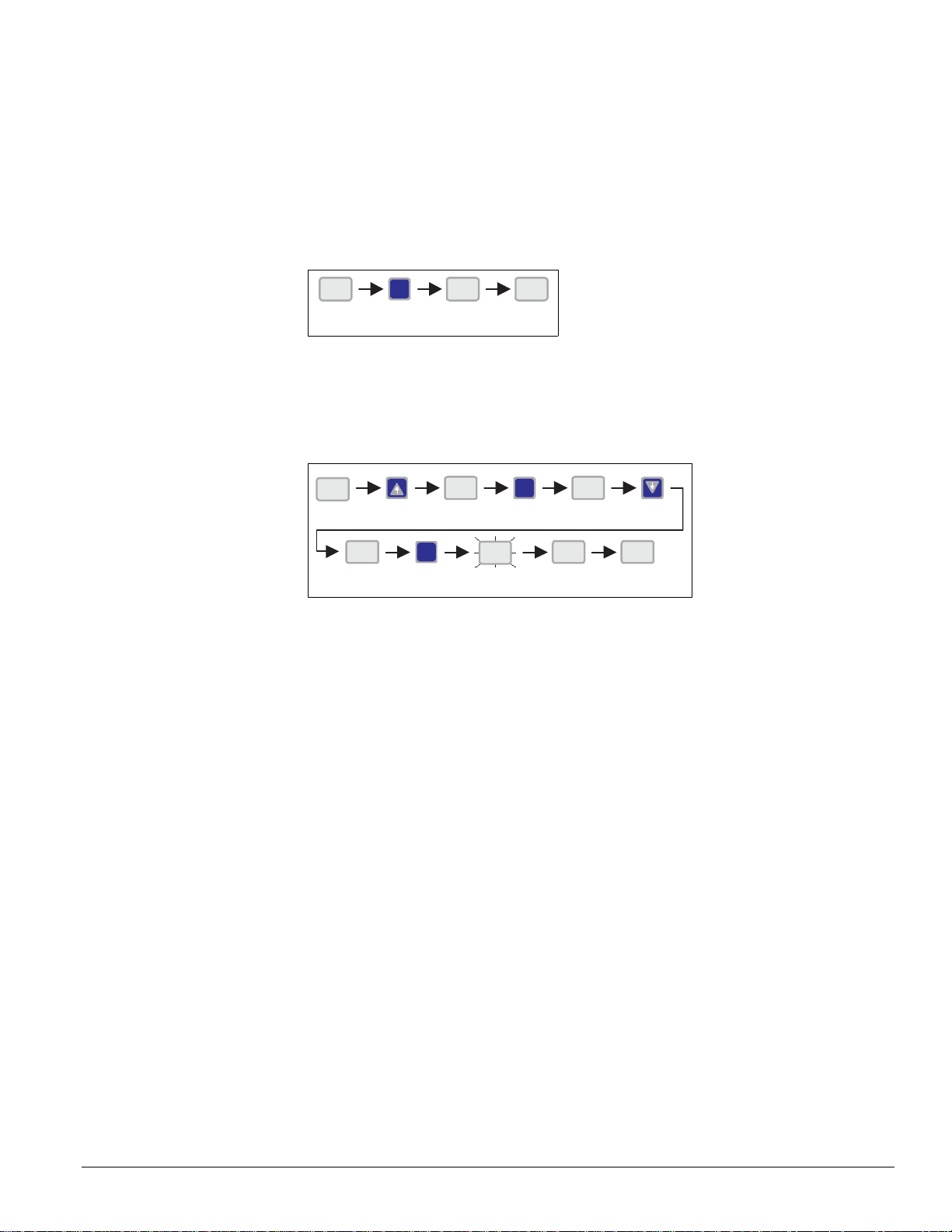
Getting Started
Using the Keypad/Display
Viewing Actual Indoor Air Temperature (IAT)
Normally, the effective set point temperature appears on the keypad/display. You also can use
the keypad/display to view the indoor air temperature (IAT). See Figure 3.
Note – When the actual indoor air temperature (Effective Space Temp Output) equals the
effective set point temperature (Effective Set Point Output), you there is no change to the
keypad/display when you view space temperature.
Figure 3: Viewing indoor air temperature
70 71 70
Effective
set point
Changing Set Points
The keypad/display can be used to make a +/–5°F (+/–3°C) offset adjustment to the effective
temperature set point. See Figure 4. Also see “Space Temperature Set Points” on page 28 to
learn more about temperature set points.
Figure 4: Adjusting the set point offset
FUNC
Enter
(5-sec)
Actual space
temperature
Effective
set point
-1
Flash
value
FUNC
Enter
0
0
Current
offset
So 69
Effective
set point
70
Effective
set point
-1
Adjusted
offset
FUNC
Save
change
So
Set point
offset
Note – The set point offset clears whenever UVC power is cycled. When you change the set point
offset after a power cycle, or for the very first time, this cleared value shows as the highest
allowed value (5°F/3°C) but is not an actual offset value.
– When using the +/–3°F (+/–1.7°C) remote wall sensor, any set point offset adjustment
made at the keypad/display causes the UVC to override and ignore the remote wall
sensor set point adjustment knob. To use the remote wall sensor set point adjustment
knob after you changed the set point offset on the keypad/display, clear the keypad/
display set point offset by cycling UVC power.
– When using the 55°F to 85°F remote wall sensor, the UVC ignores any LUI set point offset
adjustments.
Menu Reference
The keypad/display menu eases troubleshooting and simplifies UVC configuration. The user
can access the most common parameters and system status values without a PC or network
interface.
The keypad/display menu is accessed via an unmarked, hidden key. This hidden key is located
approximately behind the letter “h” in the MicroTech II logo on the keypad/display face.
The keypad/display menu consists of two levels. The first level is the keypad/display Menu
Item List containing alphanumeric characters representing each parameter. The second level is
where the parameter’s value is viewed and adjusted if the parameter is adjustable. After 15seconds, an inactivity timer automatically causes the display to back out of the menu levels,
returning to the effective set point display.
McQuay OM 756 9
Page 10

Getting Started
Figure 5: Changing a keypad/display menu item
Table 7: Keypad/display menu item list
Display Keypad menu item list Abr. Description
Reset Alarm Input
UVC (Heat/Cool) Mode
Output
UVC State Output UVCS
Discharge Air Temp Set
point Output
Discharge Air Temp Output DAT Display current DA temperature. RO x x
Ventilation Cooling Low
Limit set point
Mechanical Cooling Low
Limit set point
Slave Type Configuration
Valve Override Input
Effective Occupancy Output Display current occupancy. RO x x
Occupancy Override Input
Occupied Cooling set point OCS Adjust occupied cooling set point. RW x x
Standby Cooling Set point SCS Adjust standby cooling set point. RW x x
Unoccupied Cooling Set
point
Occupied Heating Set point OHS Adjust occupied heating set point. RW x x
Standby Heating Set point SHS Adjust standby heating set point. RW x x
Unoccupied Heating Set
point
Wall Sensor Type Set wall sensor type: 0 = +/–3F, 1 = 55°F to 85°F. RW x x 0
Outside Air Damper Position
Output
OAD Min Position High-
Speed Set point
OAD Min Position Med-
Speed Set point
OAD Min Position Low-
Speed Set point
Enter 1 to clear alarms (clears all inactive alarms, except filter alarm). To enable
the alarm again, enter 0.
Display current UVC mode. 1 = Heat, 3 = Cool, 4 = Night Purge, 6 = Off, 8 =
UVCM
Emerg. Heat, 9 = Fan Only
Display current UVC state. 1 = EconMech, 2 = Mech, 3 = Econ, 4 = DA Heat, 5
= Heat, 6 = ActiveDehum, 7 = Full Heat, 8 = Night Purge, 9 = Off, 10 = Fan Only,
11 = Heat Mode Cant Heat, 12 = CantCool, 13 = Emerg Heat Mode Cant Heat,
14 = Heat Mode Low Limit, 15 = Cool Mode Low Limit
DATS Display current DA temperature set point. RO x x
VCLL Adjust economizer cooling DA temperature low limit. RW x x
MCLL Adjust mechanical cooling DA temperature low limit. RW x x
Set slave type: 0 = Independent (slave uses own sensors), 1 = Dependent
(slave follows master). This feature requires a network over which the master
and slave UVCs can communicate.
Override valve position: 0 = normal operation, 20 = fully open all heating valves,
21 = fully close all heating valves. Adjusting this variable is intended only for
troubleshooting and hydronic system balancing. Once you are done, set this
variable to 0 or cycle unit power to return the UVC to normal operation.
Set occupancy: 0 = occupied, 1 = unoccupied, 2 = bypass, 3 = standby.
Adjusting this variable is intended only for troubleshooting. Once you are done,
cycle unit power to clear this variable and return the UVC to normal operation.
UCS Adjust unoccupied cooling set point. RW x x
UHS Adjust unoccupied heating set point. RW x x
OADP Display OA damper position. RO x x
Adjust OA damper minimum position with IAF at high speed. (This variable is
OADH
factory set to 5% open when the unit is ordered with optional
Adjust OA damper minimum position with IAF at medium speed. (This variable
OADM
is not used when the optional
OA damper minimum regardless of fan speed.)
Adjust OA damper minimum position with IAF at low speed. (This variable is not
OADL
used when the optional
damper minimum regardless of fan speed.)
CO2 DCV i s en abled . On ly OAD H is a cti ve as the
CO2 DCV is enabled. Only OADH is active as the OA
CO2 DCV.)
RO
13 14
1
RW
RW x x
RO x x
RO x x
RW x x 0
RW x x 0
RW x x
RW x x 20%
RW x x 25%
RW x x 30%
Default
54°F
(12°C)
45°F
(7°C)
73°F
(23°C)
77°F
(25°C)
82°F
(28°C)
70°F
(21°C)
66°F
(19°C)
61°F
(16°C)
2
10 McQuay OM 756
Page 11
Display Keypad menu item list Abr. Description
Exhaust Interlock OAD Min
Position Set point
Energize Exhaust Fan OAD
Set point
OAD Max Position Set point OAMX Adjust OA damper maximum position. RW x x 99%
OAD Lockout Enable
OAD Lockout Set point OALS
Economizer Enable Set economizer status: 0 = disable, 1 = enable. RW x x 1
Economizer OA Temp Set
point
Economizer IA/OA Temp
Differential
Economizer OA Enthalpy
Set point
Economizer IA/OA Enthalpy
Differential
Space Humidity Output ERH Display room humidity (optional). 00 = No sensor connected. RO x x
Space Humidity Set point RHS Adjust room humidity set point for active dehumidification (optional). RW x 60%
Outdoor Air Humidity Output EORH Display OA humidity (optional). 00 = No sensor connected. RO x x
Outdoor Air Temp Output EOAT Display OA temperature. RO x x
Emergency Heat Enable Set emergency heat status: 0 = disable, 1 = enable. RW x x 1
Emergency Heat Set point EHS Adjust emergency heat set point. RW x x
Emergency Heat Shutdown
Configuration
Auxiliary Heat Start
Differential
Auxiliary Heat End
Differential
Auxiliary Heat Configuration Set auxiliary heat type: 0 = N.O. device, 1 = N.C. device. RW x 0
External BI-1 Configuration
External BI-3 Configuration
External BO-3 Configuration
Fan Cycling Configuration
Filter Alarm Enable Set filter alarm status: 0 = disable, 1 = enable. RW x x 0
Reset Filter Alarm Input Enter 1 to clear filter alarm. RW x x
F&BP Damper Position
Output
WH or CW/HW Valve
Position Output
CW Valve Position Output CWVP Display CW valve position. RO x
Space Temp Sensor Offset Adjust this setting to bias the UVC measured space temperature. RW x x 0
Keypad/display
Temperature Units
1. RW = read and write capable, RO = read only.
2. If a menu value is greater than 2-digits (higher than 99), then
3. Additional UVC field configuration is required if the dewpoint/humidity binary input is used. Consult the factory.
Adjust OA damper position above which the exhaust fan output will be
EOAD
energized. There is a fixed –5% differential associated with this set point.
OADE Adjust OA damper minimum position when exhaust interlock input is energized. RW x x 12%
Set OA damper lockout feature status: 0 = disable, 1 = enable. (This variable is
factory set to 1 when the unit is ordered as a recirc unit with no OAD.)
Adjust OA temperature below which the OA damper closes if the OA damper
lockout is enabled. (This variable is factory set to –99°C when the unit is
ordered as a recirc unit with no OAD.)
Adjust economizer OA temperature set point. DO NOT lower this set point
ETS
below CCLO or you risk creating a deadband where no cooling occurs.
ETD Adjust economizer IA/OA temperature differential. RW x x
EES Adjust economizer OA enthalpy set point. RW x x
EED Adjust economizer IA/OA enthalpy differential. RW x x
Set emergency heat operation during shutdown, 0 = no emergency heat during
shutdown: 1 = allow emergency heat during shutdown.
AHSD Adjust auxiliary heat start differential. RW x
AHED Adjust auxiliary heat stop differential. RW x
Set the function of external binary input 1: 0 = unoccupied, 1 = dewpoint/
humidity switch
Set the function external binary Input 3: 0 = ventilation lockout, 1 = exhaust
interlock.
Set the function of external binary output 3: 0 = exhaust fan on/off signal, 1 =
auxiliary heat.
Set space fan cycles (switches off) during occupied, bypass, and standby
mode: 2 = continuous, 3 = cycling.
FBDP Display F&BP damper position. RO x
VALP Display WH or CW/HW valve position. RO x
Set keypad/display temperature units in English or SI. This set point also effects
which unit types displayed over Metasys N2 and BACnet MS/TP networks
using the appropriate optional communications modules.
3
.
will be displayed on the keypad/display.
Getting Started
RO
13 14
1
RW
RW x x 99%
RW x x 0
RW x x
RW x x
RW x x 0
RW x 0
RW x x 0
RW x 0
RW x x 2
Default
35.6°F
(2°C)
68°F
(20°C)
1.8°F
(1°C)
25 Btu/lb
(58 kJ/kg)
1.3 Btu/lb
(3 kJ/kg)
53.6°F
(12°C)
1.8°F
(1°C)
1.8°F
(1°C)
RW x x F
2
McQuay OM 756 11
Page 12

Description of Operation
Description of Operation
State Programming
The MicroTech II UVC takes advantage of “state” machine programming to define and
control unit ventilator operation. “State” defines specific states or modes of operation for each
process within the unit ventilator (e.g., heating, cooling, etc.) and contain the specific logic for
each state. This eliminates some of the most common problems associated with control
sequences such as the possibility of simultaneous heating and cooling, rapid cycling, etc.
State machine programming, and the unique nature of state diagrams, can be easily used to
describe operation. It can simplify sequence verification during unit commissioning, as well as
simplify troubleshooting. With the unique combination of state machine programming and the
keypad/display’s ability to allow a technician to easily determine the active UVC state,
troubleshooting the UVC can be very simple.
The state diagrams presented in the following sections consist of several “elements” including
super states, states, conditional jumps (also called transitions) and transition points. Super
states are used as a means to group two or more related states into a single control function
such as cooling, or heating, etc. States are where all the actual work takes place, within each
state the UVC enables PI-loops and other logic sequences required to control unit ventilator
operation within that particular state, while other functions and PI-loops not needed durin g
that state may be disabled. Conditional jumps, or transitions, are the logic paths used by the
UVC to determine which state should be made active, these are the “questions” the UVC
continually considers. The transition point is simply a point through which a number of
conditional jumps meet. Think of it as a point where a number of questions must be
considered from which the UVC then determines which path is followed and which state is
then made active.
The UVC states and super states are used to define the “normal” unit modes, such as Off,
Night Purge, Fan Only , Emergency Heat, Auto, Cool, Heat, and Active Dehum. The UVC also
supports several “special purpose” unit modes such as Purge, Pressurize, De-pressurize, and
Shutdown, which can be forced via a network connection and override typical UVC operation.
Note – Not all states or modes are available for all UV configurations, and some states (such as
Active Dehum) are optional.
– In the state descriptions below the terms, saturated high and saturated low, indicate that
the heating or cooling function being described has reached 100% or 0%, respectively.
12 McQuay OM 756
Page 13
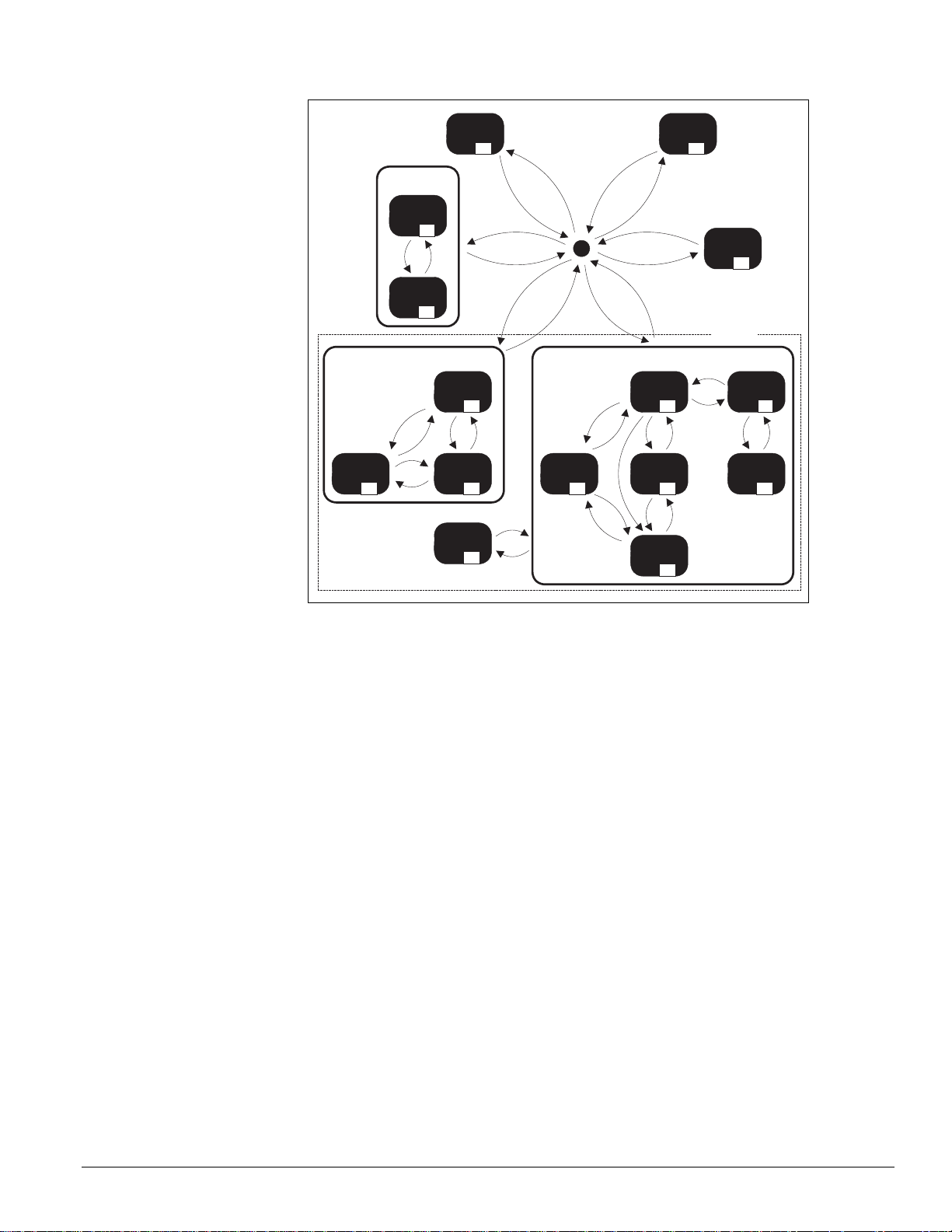
Figure 6: Complete UVC—state diagram
EmergencyHeat
ModeSuperState
FullHeat
CantHeat
Heat
LowLimit
7
D
5
E
FanOnly
A
NightPurge
8
Off
9
HeatMode
SuperState
AutoMo de
Econ
EconMech
Mech
3
1
2
CantCool
C
DAHeat
LowLimit
4
F
Active
Dehum
6
CoolMode
SuperState
CantHeat
B
Description of Operation
UVC Unit Modes
The UVC provides several “normal” modes of unit operation. These include: Off, Night
Purge, Fan Only, Cool, Emergency Heat, Auto, Heat, and Cool.
Normal UVC modes can contain a single state or several states depending upon the
functionality required for each particular mode. Each UVC state is assigned a number, which
can be very helpful when trying to understand which state is currently active within the UVC.
To view the current UVC state number, use the keypad/display.
McQuay OM 756 13
Page 14
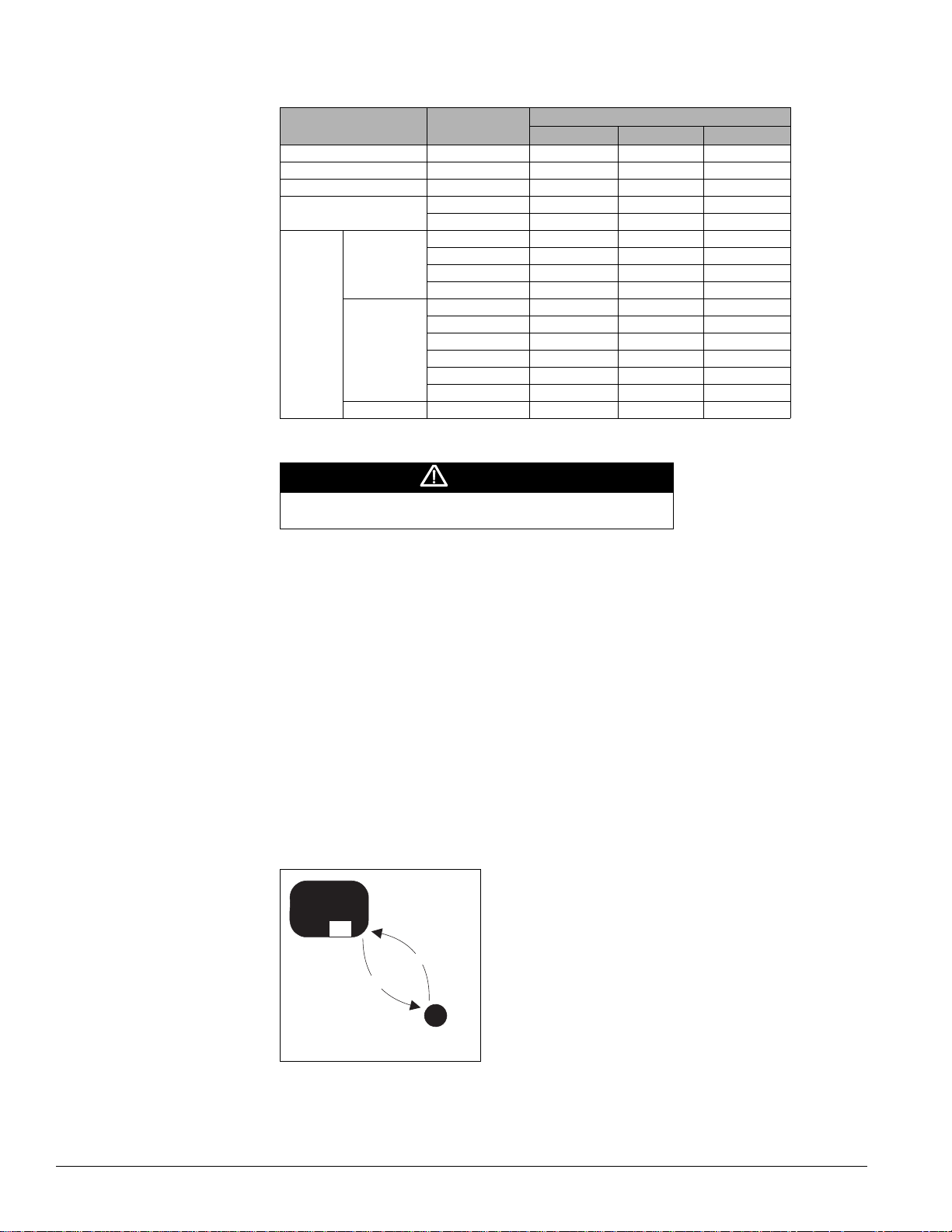
Description of Operation
OFF
9
F
Table 8: UVC st a t e na mes and numbers
Normal UVC modes State names
OFF OFF 9 9 57
Night purge Night Purge 8 8 56
Fan only Fan Only 10 A 65
Emergency heat
Heat
Auto
Cool
Dehumidify
1. Optional (software model 13 only).
Full Heat 7 7 55
Cant Heat 13 D 68
Heat 5 5 53
Cant Heat 11 B 66
Low Limit 14 E 69
Defrost 17 H 72
EconMech 1 1 49
Mech 2 2 50
Econ 3 3 51
DA Heat 4 4 52
Cant Cool 12 C 67
Low Limit 15 F 70
1
Active Dehum 6 6 54
Decimal ASCII Hex
State numbers
WARNING
Off mode is a “stop” state for the unit ventilator. It is not a “power
off” state. Power may still be provided to the unit.
OFF Mode (State 9)
Off mode is provided so that the UVC can be forced into a powered OFF condition. OFF mode
is a “stop” state for the unit ventilator; it is not a power off state. OFF mode consists of a
single UVC state: OFF [9].
When OFF mode becomes active, the UVC stops all normal heating, cooling, and ventilatio n
(OA damper is closed), and fan operation ends. The UVC continues to monitor space
conditions, indicate faults, and provide network communications (if connected to a network)
in the OFF mode while power is maintained to the unit.
While in OFF mode, the UVC does not maintain DA temperatures. If the space temperature
drops below EHS while in the OFF mode, the UVC is forced into the Emergency Heat mode
(see “Emergency Heat Mode (Super State)” on page 16).
Note – Special purpose unit modes such as Purge, Pressurize, and De-pressurize can force the
UVC to perform “special” functions during which the display appears to be in the OFF
mode.
Figure 7: Off state diagram
UVC Mode
UVC Mode OFF
OF
Transition
point
14 McQuay OM 756
Page 15
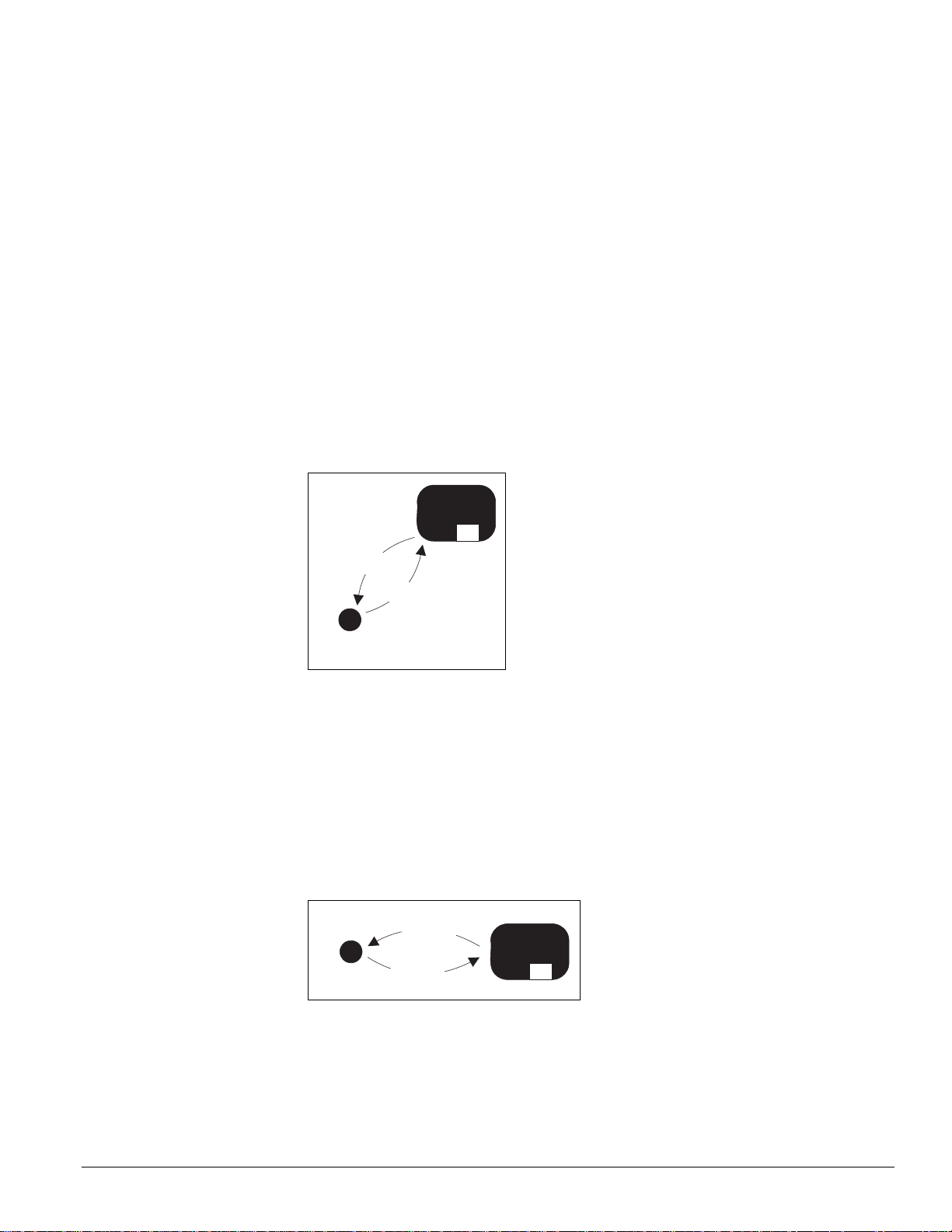
Description of Operation
Night Purge
8
UVC Mode
Night purge
UVC Mode
Night purge
Transition
point
Fan Only
A
UVC Mode
Fan Only
UVC Mode
Fan Only
Transition
point
Night Purge Mode (State 8)
Night Purge mode is provided as a means to more easily and quickly ventilate a space. Night
purge can be useful in helping to remove odor build up at the end of each day, or after
cleaning, painting, or other odor generating operations occur within the space. Night Purge
mode consists of a single UVC state: Night Purge [8].
Night Purge is a full ventilation with exhaust mode, during which room comfort is likely to be
compromised. Therefore, McQuay strongly recommends using Night Purge only when the
space is unoccupied.
When Night Purge mode becomes active, the UVC stops all normal heating and cooling. Since
any new energy used to treat the incoming air would be wasted in the purge process. In the
Night Purge mode, the space fan is set to high speed, the OA damper is set to 100% open, and
the Exhaust Fan binary output (see “External Binary Outputs” on page 40) is set to ON. If the
UVC is not set to another mode within 1 hour (fixed), the UVC automatically switches to the
Fan Only mode (see “Fan Only Mode (State A)” on page 15).
While in Purge mode, the UVC does not maintain DA temperatures. If the space temperature
drops below the EHS, the UVC is forced into the Emergency Heat mode (see “Emergency
Heat Mode (Super State)” on page 16).
Figure 8: Night purge state diagram
Fan Only Mode (State A)
The Fan Only mode is provided so that the UVC can be forced into a Fan Only operation via a
keypad/display or a network connection. Fan Only mode consists of a single UVC state: Fan
Only [A].
When Fan Only mode becomes active, the UVC stops all normal heating and cooling.
While in Fan Only mode, the UVC does not maintain DA temperatures. If the space
temperature drops below the EHS, the UVC is forced into the Emergency Heat mode (see
“Emergency Heat Mode (Super State)”).
Figure 9: Fan only state diagram
McQuay OM 756 15
Page 16

Description of Operation
Full Heat
Cant Heat
7
D
Emergency Heat Mode (Super State)
The Emergency Heat mode is provided for situations where the UVC is in a mode that does
not normally allow heating, such as OFF, Cool, Night Purge, or Fan Only. If Emergency Heat
mode is enabled, the UVC can automatically force itself into the Emergency Heat mode from
OFF, Cool, Night Purge, Fan Only, Purge, Pressurize, De-pressurize, and Shutdown.
Emergency Heat mode consists of UVC states: Full Heat [7] and Cant Heat [D].
When the Emergency Heat mode becomes active, the UVC automatically determines which
state to make active, Full Heat [7], or Cant Heat [D], based on the transitions for each of those
states.
Figure 10: Emergency heat state diagram
Emergency Heat Mode
Super State
Transition
point
Heat
Available
Heat
Available
UVC Mode
Emergency Heat
UVC Mode
Emergency Heat
Full Heat State (State 7)
The Full Heat [7] state is the “normal” state that the UVC goes into when Emergency Heat
mode is active. It is activated when the space temperature is lower than the EHS.
When Emergency Heat mode becomes active, the UVC goes into 100% heating until the space
temperature raises to the EHS plus a fixed differential (5.4°F/3°C). In the Emergency Heat
mode, the space fan is set to high speed, and the OA damper operates normally.
If the UVC automatically forces itself into the Emergency Heat mode from another mode
(e.g., Cool, Fan Only, etc.), then the UVC returns to the appropriate unit mode once the space
temperature rises to the EHS plus a fixed differential (5.4°F/3°C).
The UVC monitors the DAT to ensure it does not exceed DAHL. If the DAT does exceed
DAHL, then heating is set to 0% for a minimum of 2-minutes (fixed) and until the DAT drops
36°F (20°C) fixed differential below DAHL.
Cant Heat State (State D)
The Cant Heat [D] state is a “non-normal” state that the UVC can go into when Emergency
Heat mode is active. An IAT or DAT sensor fault during Emergency Heat mode causes the
UVC to make this state active.
When the Cant Heat state becomes active, the space fan remains at high speed as set during
the Full Heat state.
The UVC will remain in the Cant Heat state until heat becomes available.
16 McQuay OM 756
Page 17

Description of Operation
Heat
Low Limit
Cant Heat
5
E
B
Transition
point
Heat Mode
Super State
UVC Mode Heat AND
UVC Mode
Auto
OR
UVC Mode
Auto AND Space =
Warm AND Heat Pl = Sat Low
UVC Mode = Heat
OR
UVC Mode
Auto AND
Space
Warm
Heat Pl = Sat Hi
(2 minutes)
AND
DAT<VCLL
LLPl = Sat Lo
(2 minutes)
AND
DAT<(VCLL + 1.8F)
Heat = Available
AND
Low Limit = Inactive
Heat = Available
AND
Low Limit = Inactive
Heat
Available
Heat
Available
Auto Mode
Auto mode is provided so that the UVC can be set to automatically determine if heating or
cooling is required. Auto mode is the default power-up UVC mode. Auto mode is made up of
the Heat, Cool, and Active Dehum (optional, software model 13) modes. When the UVC is set
to auto mode, the UVC automatically determines which mode (Heat, Cool, or Active Dehum)
to use.
Heat Mode (Super State)
When in Heat mode, the UVC will use primary heat as needed to maintain the effective
heating setpoint (see “Space Temperature Set Points” on page 28). The keypad/display or a
network connection can be used to force the unit into the Heat mode. Additionally, the UVC
when set to Auto mode can automatically force the unit into the Heat mode as needed. When
the UVC is in Auto mode, it is “normal” for the UVC to “idle” in Heat mode when there is no
need to switch to another mode.
The Heat mode super state consists of UVC states: Heat [5], Low Limit [E], and Cant Heat
[B].
When the Heat mode super state becomes active, the UVC automatically determines which of
the Heat Mode states to make active based upon the transitions for each state.
Figure 11: Heat mode super state diagram
Heat State (State 5)
The Heat state is the “normal” state during Heat mode. When the Heat state becomes active,
the UVC will (within State) continually calculate the DATS (“Discharge Air Temperature
McQuay OM 756 17
Control” on page 31) required to maintain the effective heat setpoint (see “Space Temperature
Set Points” on page 28). The calculated DATS will not be allowed to go above DAHL. The
UVC will use primary heat as needed to maintain the current DATS. The Heat Timer (3minutes fixed) will begin counting. The CO
active, if the unit is equipped for CO
2
demand controlled ventilation function will be
2
control (see “CO2 Demand Controlled Ventilation
(optional)” on page 36), and the OA damper will be adjusted as needed to maintain the CO
setpoint. The UVC will remain in this state until one of the transition out conditions become
true, or until one of the super state transition out conditions becomes true.
2
Page 18

Description of Operation
Note – The OAD is considered to be in “alarm” when the OAD is forced below the active minimum
position in the Low Limit state. This is not an actual unit “alarm” or “fault” condition, but
only a condition used for the purpose of transition arguments.
Figure 12: Heat state operation (occupied mode and auto fan)
Figure 13: Heat state operation (occupied mode and auto fan)
Low Limit State (State E)
The Low Limit state is a “non-normal” state the UVC can go into while Heat mode is active
when the unit reaches 100% heating and still cannot meet the current DATS (see “Discharge
Air T emperature Control” on page 31) required to maintain the effective heating set point (see
“Space Temperature Set Points” on page 28). This is likely to occur only if the OA
temperature is very cold, the OA damper minimum position is set too high, the unit ventilator
is oversized for the application, or if the primary heating has failed.
When the Low Limit state becomes active, the Low Limit PI-loop can override the OA
damper position (see “Outdoor Air Damper Operation” on page 34) and adjust the OA damper
toward closed as necessary to maintain the current DATS (see “Discharge Air Temperature
Control” on page 31).
18 McQuay OM 756
Page 19

Description of Operation
Econ
EconMech
Mech
3
1
2
CantCool
C
Active
Dehum
6
CoolMode
SuperState
DAHeat
LowLimit
4
F
LLPI=SatLow (2 min)
AND
DAT>(VCLL+1.8F)
HeatPI=SatHi (2 min)
AND DAT<VCLL
SpaceHighCO2
AND
HeatPI=SatLow
AND
DAT>VCLL
Space=HighCO2
OR
DAT<VCLL
Space=High%RH
AND
Cool=Available
AND
%RH=Reliable
SpaceHigh%RH
OR
Cool
Available
OR
%RH
Reliable
UVCModeCool AND UVCModeAuto
OR
UVCMode=Auto AND Space=Cold AND
MechPI=SatLow (3 min) AND
EconPI=SatLow
UVCMode=Cool
OR
UVCMode=Auto AND Space=Warm
EconAvailable
AND
MechCool
Available
Econ = Available
AND
MechCool
Available
EconAvailable
AND
MechCool=Available
MechPI=SatLow (3 min) AND
EconMechTimer=Expired
(3 min OR
MechCool
Available
EconAvailable
Econ=Available
MechCoolAvailable
EconAvailable
AND
MechCool=Available
Transition
Point
EconTimer=Expired
(3 min) AND
EconPI=SatHi AND
MechCool=Available
Cant Heat State (State B)
The Cant Heat state is a “non-normal” state the UVC can go to when Heat mode is active. An
IAT or DAT sensor fault during the Heat mode causes the UVC to make this state active.
When the Cant Heat state becomes active, no heating or ventilation takes place. The OA
damper goes to the minimum position unless it is forced closed by other functions such as
freezestat (T6) or morning warm-up.
Cool Mode (Super State)
When in Cool mode the UVC uses primary cooling (economizer) and secondary cooling
(mechanical, hydronic) as needed to maintain the effective cooling set point (see “Space
Temperature Set Points” on page 28). The keypad/display or network connection can be used
to force the unit into the Cool mode. When the UVC is in Auto mode, it is “normal” for the
UVC to “idle” in Cool mode when there is no need to switch to another mode. The Cool mode
super state consists of the following UVC states: Econ Mech [1], Mech [2], Econ [3], DA Heat
[4], Low Limit [F], Cant Cool [C], and Active Dehum [6] (optional).
When the Cool mode super state becomes active, the UVC will automatically determine which
UVC state to make active based upon the transitions for each state.
If the space temperature drops below EHS, and the Emergency Heat function is enabled, the
UVC will be forced into the Emergency Heat mode (see “Emergency Heat Mode (Super
State)” on page 16).
Figure 14: Cool mode super state diagram
McQuay OM 756 19
Page 20

Description of Operation
Econ State (State 3)
The Econ state is a “normal” state during Cool mode. The Econ state typically is active in the
Cool mode when primary cooling (economizer) is available and adequate to meet the cooling
requirements.
When the Econ state becomes active, the UVC uses economizer cooling (see “Economizer
Operation” on page 34) as needed to maintain the effective cooling set point (see “Space
Temperature Set Points” on page 28). If cooling is not required while in the Econ state, the
UVC can “idle” in the Econ state until cooling is required or until there is a call to switch to
another mode or state.
The UVC monitors the DAT to ensure it does not fall below VCLL.
The CO
Controlled Ventilation (optional)” on page 36) and the OA damper is adjusted as needed to
maintain the CO
Figure 15: Econ state operation (occupied mode and auto fan)
demand controlled ventilation function (optional) will be active (see “CO2 Demand
2
set point.
2
Econ Mech State (State 1)
The Econ Mech state is a “normal” state during Cool mode. The Econ Mech state typically is
active in the Cool mode when primary cooling (economizer) alone is not adequate to meet the
cooling requirements and both primary cooling and secondary cooling (compressor) are
available.
When the Econ Mech state becomes active, the OA damper is set to 100% open, and the UVC
uses the units mechanical cooling capabilities as needed to maintain the effective cooling set
point (see “Space Temperature Set Points” on page 28).
The UVC monitors the DAT to ensure it does not fall below MCLL.
20 McQuay OM 756
Page 21

Description of Operation
Figure 16: Econ mech state operation (occupied mode and auto fan - valve control)
Figure 17: Econ mech state operation (occupied mod e and auto fan - F&BP damper)
Mech State (State 2)
The Mech state is a “normal” state during Cool mode. The Mech state typically is active in the
Cool mode when primary cooling (economizer) is not available.
When the Mech state becomes active, the UVC uses the unit’s mechanical cooling capabilities
as needed to maintain the effective cooling set point (see “Space Temperature Set Points” on
page 28). If cooling is not required while in the Mech state, the UVC can “idle” in the Mech
state until cooling is required or until there is a call to switch to another mode or state.The
UVC monitors the DAT to ensure it does not fall below MCLL.
The CO
demand controlled ventilation function (optional) is active (see “CO2 Demand
2
Controlled Ventilation (optional)” on page 36), and the OA damper is adjusted as needed to
maintain the CO
set point.
2
Passive dehumidification (optional software model 14) can be used during unoccupied mode.
The UVC can use the Passive Dehumidification Temp Setpoint in place of the Unoccupied
Cooling Setpoint when dehumidification is required (see “Passive Dehumidification (optional,
software model 14)” on page 37).
McQuay OM 756 21
Page 22

Description of Operation
Figure 18: Mech state operation (occupied mode and auto fan - valve control)
Figure 19: Mech state operation (occupied mode and auto fan - F&BP damper)
Discharge Air (DA) Heat State (State 4)
The DA Heat state is a “normal” state during Cool mode. The DA Heat state typically is active
when reheat is required to maintain DATS while maintaining the required OA damper
position. The DA Heat state can also be made active if the optional CO
provided and CO
levels are high, requiring the OA damper to open beyond what is required
2
DCV feature is
2
for economizer cooling.
When DA Heat state is active, the UVC uses the units heating capability as needed to maintain
VCLL. The CO
demand controlled ventilation function (optional) is active (see “CO2
2
Demand Controlled Ventilation (optional)” on page 36), and the OA damper is adjusted as
needed to maintain the CO
22 McQuay OM 756
set point.
2
Page 23

Description of Operation
Low Limit State (State F)
The Low Limit state is a “non-normal” state during Cool mode. The Low Limit state typically
follows the DA Heat state when the UVC reaches 100% heat and still cannot maintain VCLL.
When the Low Limit state becomes active, the Low Limit PI-loop overrides the OAD
minimum position (see “Outdoor Air Damper Operation” on page 34) and adjusts the OAD
toward closed as necessary to maintain the DAT set point (see “Discharge Air Temperature
Control” on page 31).
Cant Cool State (State C)
The Cant Cool state is a “non-normal” state during Cool mode. The Cant Cool state typically
becomes active when both primary and secondary cooling are not available (or they are
disabled) or when an IAT, DAT or OAT sensor failure occurs.
When the Cant Cool state becomes active, no cooling is available.
Active Dehum State (optional, software model 13)
The Active Dehum state is a “normal” state that the UVC can go into when Cool mode is
active and when the unit is equipped for active dehumidification (optional).
When the Active Dehum state becomes active, the UVC captures the current IAT and uses this
as the temporary set point during dehumidification. The unit’s mechanical cooling capabilities
initially are set to 100% (cooling valve 100% open) and the heat PI maintains the captured set
point. If the heat PI saturates high (100% heat) for 2-minutes or more (e.g., heating cannot
keep up with cooling), the cooling is disabled until the heat PI saturates low (heat valve 0%
open). The UVC uses a 5% RH fixed differential below the RHS to determine when active
dehumidification is complete. The UVC monitors the DAT to ensure it does not fall below
MCLL, nor goes above DAHL.
The space fan is forced to low speed when the Active Dehum state is active.
The optional Active Dehum state is available during all occupancy modes.
The CO
demand controlled ventilation function (optional) will be available (see “CO2
2
Demand Controlled Ventilation (optional)” on page 36), and the OA damper is adjusted as
needed to maintain the CO
Note – When the Active Dehum state becomes active (high humidity) the UVC captures the
current IAT and uses this value as the temporary effective set point. While this set point
change is often very minimal, and is likely to go unnoticed, this can be a source of
confusion when switching from unoccupied-to-occupied mode. For example, when
switching from unoccupied-to-occupied, it is likely the UVC will need to reduce the space
temperature a considerable amount. During this cooling process it is possible that the
space humidity will go above the humidity set point forcing the UVC into Active Dehum. If
this occurs, it is possible that the UVC will temporarily hold a set point somewhere
between the unoccupied and occupied cooling set points as it dehumidifies the space,
after which the UVC will continue to lower the space temperature to the occupied cooling
set point.
set point.
2
Special Purpose Unit Modes
There are some additional UVC modes that are considered special purpose unit modes. These
special purpose modes include Pressurize, Depressurize, Purge, Shutdown, and Energy Hold
Off. These modes force the UVC to perform very specific and limited functions. Use these
with caution and only for short periods as needed.
In each of these special purpose UVC modes, if the space temperature drops below EHS and
the Emergency Heat function is enabled, the UVC is forced into the Emergency Heat mode
(see “Emergency Heat Mode (Super State)” on page 16) and then return once the Emergency
Heat function is satisfied.
McQuay OM 756 23
Page 24

Description of Operation
Table 9: Actions during special purpose unit modes
Action
Pressurize High 100% Open Off
Depressurize Off Closed On
Purge High 100% Open On
Shutdown Off Closed Off
Energy hold off Off Closed Off
Indoor air fan
(IAF)
Outdoor air
damper (OAD)
Exhaust fan
output
Pressurize Mode
When in Pressurize mode, the UVC uses the IAF, OAD, and exhaust output as needed to
pressurize the space. The UVC stops all normal heating and cooling but does allow emergency
heat if required. The pressurize mode can only be accessed via a network connection.
Depressurize Mode
When in Depressurize mode the UVC will use the IAF, OAD, and exhaust output as needed to
depressurize the space. The UVC stops all normal heating and cooling but does allow
emergency heat if required. The de-pressurize mode can only be accessed via a network
connection or with ServiceTools for MicroTech II Applied Terminal Unit Controllers (ATS).
Purge Mode
When in Purge mode, the UVC uses the IAF, OAD, and exhaust output as needed to purge the
space. The UVC stops all normal heating and cooling but does allow emergency heat if
required. The purge mode can only be accessed via a network connection or with ServiceTools
for MicroTech II Applied Terminal Unit Controllers (ATS).
Shutdown Mode
Shutdown mode is the equivalent of the Off mode, but is an Off mode forced by a network
connection. When in Shutdown mode, the UVC stops all normal heating, cooling, ventilation
(OA damper is closed), and fan operation. By default emergency heat is not be used during the
shutdown mode, however, the UVC can be configured (Emergency Heat Shutdown
Configuration) to allow emergency heat operation during shutdown mode. The shutdown
mode can be accessed via a network connection, a binary input to the UVC, or with
ServiceTools for MicroTech II Applied Terminal Unit Controllers (ATS).
WARNING
Shutdown mode and energy hold off mode are a “stop” state for
the unit ventilator. It is not a “power off” state.
Energy Hold Off Mode
The UVC supports an energy hold off state, which when active forces the UVC to stop all
normal heating, cooling and ventilation. Typically used by a network connection to force the
UVC to cease heating, cooling and ventilation when conditions exist where heating, cooling
and ventilation are not required or desired. Energy hold off mode is very similar to shutdown
mode except that energy hold off always allows emergency heat if required. The energy hold
off mode can only be accessed via a network connection or with ServiceTools for
MicroTech II Applied Terminal Unit Controllers (ATS).
24 McQuay OM 756
Page 25

Description of Operation
Unit Mode Priority
The UVC uses the network variables and binary inputs listed in Table 10 and Table 11 to
determine the current unit mode. Special purpose UVC unit modes have higher priority than
the normal UVC unit modes as shown in the tables.
Each table lists the highest priority items on the left to the lower priority items to the right. The
right-most columns indicate unit operation as a result of the left-most columns. The term
“Don’t care” in these tables implies that another network variable or binary input to the left
has a higher priority.
Table 10: Special purpose UVC unit mod e prio ri ty
Priority result
Emergency override
input
Normal
1
3
Pressurize Don’t care Don’t care Don’t care Off Pressurize
De-pressurize Don’t care Don’t care Don’t care Off De-pressurize
Purge Don’t care Don’t care Don’t care Off Purge
Shutdown Don’t care Don’t care Don’t care Off Off
1. Network input.
2. Network output.
3. Normal indicates the UVC power-up condition.
4. De-energized indicates that the contacts connected to this binary input are open.
5. Energized indicates that the contacts connected to this binary input are closed.
Remote shutdown
binary input
De-energized
Energized
4
5
Energy hold
off input
1
Normal Normal
Energy hold
off output
2
Unit mode
2
output
See the normal
UVC mode priority (Table 11)
Energy hold off Energy hold off Off Off
Don’t care Energy hold off Off Off
Actual UVC action
Table 11: Normal UVC mode priority
Priority result
Application override
input
1
Normal (Auto)
Heat Don’t care Heat
Cool Don’t care Cool
Night purge Don’t care Night purge
Off Don’t care Off
Emergency heat Don’t care Emergency heat
Fan only Don’t care Fan only
1. Network input.
2. Network output.
3. Normal (Auto) is the normal UVC power-up state.
Unit mode override
Normal (Auto)
3
Night purge Night purge
Emergency heat Emergency heat
input
1
Unit mode output
3
Heat
Cool
Emergency heat
Heat Heat
Cool Cool
Off Off
Fan only Fan only
2
McQuay OM 756 25
Page 26

Description of Operation
Occupancy Modes
The UVC is provided with four occupancy modes: Occupied, Standby, Unoccupied, and
Bypass. The occupancy mode affects which heating and cooling temperature set points are
used, affects IAF operation, and affects OAD operation. The Manual Adjust Occupancy and
Networked Occupancy Sensor network variables, along with the Unoccupied and Tenant
Override binary inputs, are used to determine the Effective Occupancy. The term “Don’ t care”
in Table 12 implies that another network variable or binary input to the left has a higher
priority.
Note – The Occupancy Override Input is provided as a way for a network connection to manually
force the UVC into a particular occupancy mode. The Occupancy Override Input can
override the tenant override feature. For example, if the network uses the Occupancy
Override Input to force the unit into unoccupied mode, then the tenant override switch
does not operate as expected. Therefore, McQuay strongly recommends using the
Occupancy Sensor Input to control occupancy modes over a network and only using the
Occupancy Override Input if there is reason to ensure tenant override does not occur.
Table 12: Occupan cy mode pr iority
Priority result
Occupancy
Override input
Occupied Don’t care Don’t care Occupied
Unoccupied Don’t care Don’t care Unoccupied
Bypass
Standby Don’t care Don’t care Standby
Null (default)
1. Network input.
2. Network output.
3. Typical operation is defined in this row of the table.
4. The tenant override switch (unit or wall sensor mounted) can be used here to force the UVC
into bypass.
Occupancy
sensor input
Occupied Don’t care Occupied
Unoccupied Don’t care Bypass
Null (default)
Occupied Don’t care Occupied
Unoccupied Don’t care Unoccupied
3
Null (default)
Unoccupied binary input
1
Contacts open (Occupied) Occupied
Contacts Closed (Unoccupied) Bypass
Contacts open (Occupied) Occupied
Contacts closed (Unoccupied) Unoccupied
Effective
occupancy
output
2
4
4
Occupied Mode
The occupied mode is the normal day time mode of UVC operation. During occupied mode
the UVC uses the occupied heating and cooling set points, the OAD operates normally, and by
default the IAF remains on.
Unoccupied Mode
The unoccupied occupancy mode is the normal night time mode of UVC operation. During
unoccupied mode the UVC uses the unoccupied heating and cooling set points, the OAD
remains closed, and the IAF cycles as needed for heating or cooling. The IAF remains off
when there is no need for heating or cooling.
Standby Mode
The standby mode is a special purpose daytime mode of UVC operation. During standby,
mode the UVC uses the standby heating and cooling set points, the OAD remains closed, and
by default the IAF remains on.
26 McQuay OM 756
Page 27

Description of Operation
Bypass Mode
The bypass mode (also called Tenant Override) is the equivalent of a temporary occupied
mode. Once the bypass mode is initiated, it remains in effect for a set period of time (120
minutes, default). During the bypass mode, the UVC uses the occupied heating and cooling set
points, the OAD operates normally, and by default the IAF remains on.
Additional Occupancy Features
Networked Occupancy Sensor Capability
A networked occupancy sensor can be interfaced with the Occupancy Sensor Input variable to
select occupancy modes. When the Occupancy Sensor Input variable is used, it automatically
overrides any hard-wired unoccupied binary input signal.
Unit-Mounted Time-Clock
An optional unit-mounted factory-installed electronic 24-hour/7-day time clock can be
provided on stand-alone unit ventilator configurations. It is factory wired to the UVC
unoccupied binary input and can be set to automatically place the unit into occupied and
unoccupied modes based upon its user configured schedule.
Unit-Mounted Tenant Override Switch
A tenant override switch is factory installed in all floor mounted units and is located near the
LUI on the unit. This switch provides a momentary contact closure that can be used by room
occupants to temporarily force the UVC into the bypass occupancy mode from unoccupied
mode.
Note – The Occupancy Override Input can override the tenant override feature. For example, if
the network uses the Occupancy Override Input to force the unit into unoccupied mode,
then the unit-mounted tenant override switch does not operate as expected. Therefore,
McQuay strongly recommends using the Occupancy Sensor Input to control occupancy
modes over a network and only using the Occupancy Override Input if there is reason to
ensure tenant override does not occur.
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor Tenant Override Switch
The optional remote wall-mounted sensors include a tenant override switch. This switch
provides a momentary contact closure that can be used by room occupants to temporarily force
the UVC into the bypass occupancy mode from unoccupied mode.
Note – The Occupancy Override Input can override the tenant override feature. For example, if
the network uses the Occupancy Override Input to force the unit into unoccupied mode,
then the wall sensor tenant override switch does not operate as expected. Therefore,
McQuay strongly recommends using the Occupancy Sensor Input to control occupancy
modes over a network and only using the Occupancy Override Input if there is reason to
ensure tenant override does not occur.
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor Status LED
The optional remote wall-mounted sensors each include a UVC status LED. This status LED
aids diagnostics by indicating the UVC occupancy mode and fault condition.
Table 13: Remote wall-mounted sensor status LED
Indication LED operation
Occupied On continually
Unoccupied On 1 second/off 9 seconds
Bypass On continually
Standby On 9 seconds/off 1 second
Fault On 5 seconds/off 5 seconds
McQuay OM 756 27
Page 28
Description of Operation
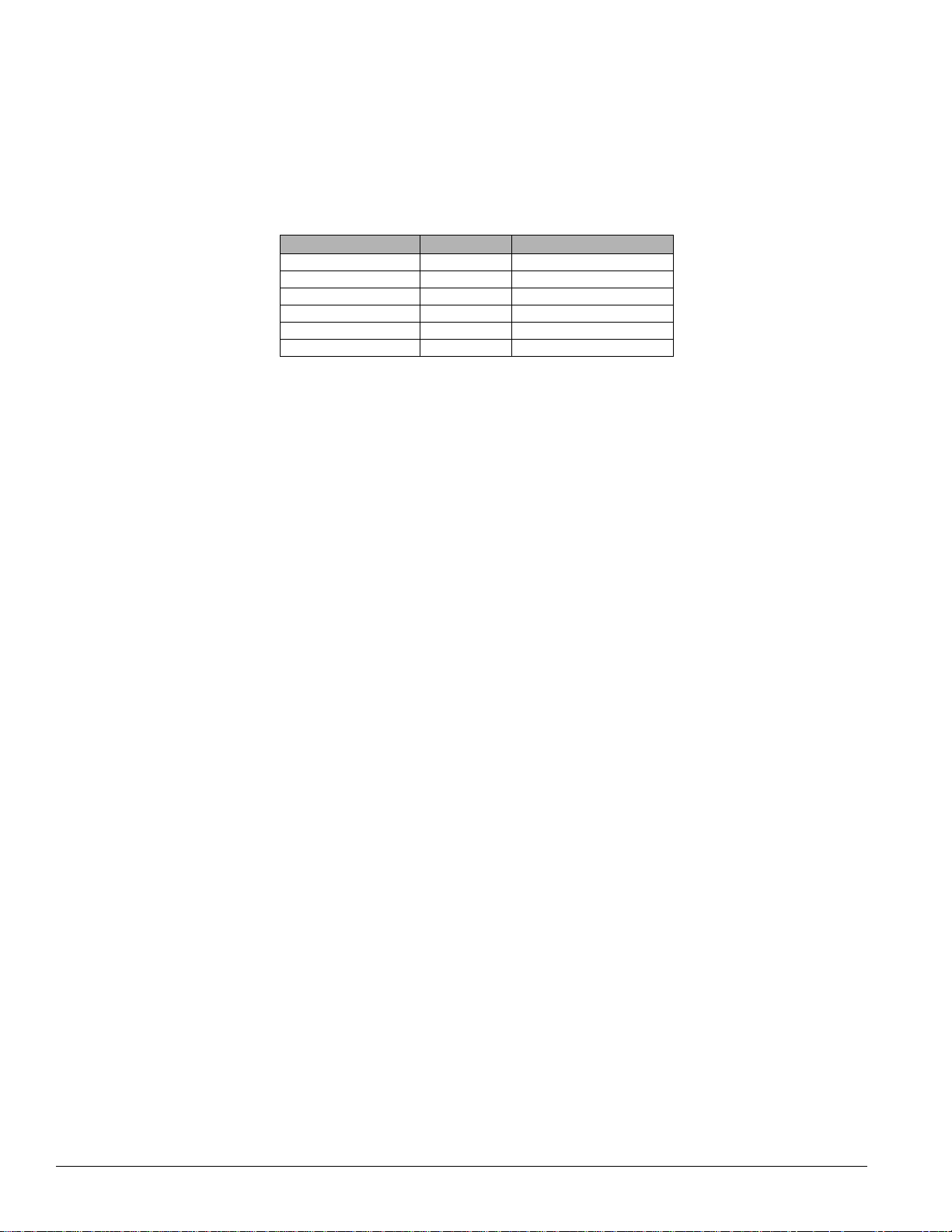
Space Temperature Set Points
The UVC uses the six occupancy-based temperature set points as the basis to determine the
Effective Set point Output. The effective set point is calculated based on the unit mode, the
occupancy mode, and the values of several network variables. The effective set point then is
used as the temperature set point that the UVC maintains.
Table 14: Default occupancy-based temperature set points
Temperature set point Abbreviation Defaults
Unoccupied cool UCS 82.4°F (28.0°C)
Standby cool SCS 77.0°F (25.0°C)
Occupied cool OCS 73.4°F (23.0°C)
Occupied heat OHS 69.8°F (21.0°C)
Standby heat SHS 66.2°F (19.0°C)
Unoccupied heat UHS 60.8°F (16.0°C)
Networked Set Point Capability
The Space Temp Setpoint Input variable is used to allow the temperature set points for the
occupied and standby modes to be changed via the network; the unoccupied set points are not
affected by this variable.
Networked Set Point Offset Capability
The Networked Set Point Offset Input variable is used to shift the effective occupied and
standby temperature set points by adding the value of the Setpoint Offset Input variable to the
current set points; the unoccupied points are not affected by this variable. This variable is
typically set bound to a supervisory network controller or to a networked wall module having
a relative set point knob.
Use the keypad/display to make adjustments to the value of the Setpoint Offset Input variable.
See “Changing Set Points” on page 9.
Note – The keypad/display and the network both affect the Set Point Offset Input variable. Keep
in mind that changes to this variable are last-one-wins.
Networked Set Point Shift Capability
The Set Point Shift Input variable is used to shift the effective heat/cool set points. It typically
is bound to a networked supervisory controller or system that provides functions such as
outdoor air temperature compensation. All occupied, standby, and unoccupied set points are
shifted upward (+) or downward (
–) by the corresponding value of the Set Point Shift Input
variable.
Note – The Set Point Shift Input capability is not available through the BACnet® interface.
Networked Space Temperature Sensor Capability
A networked space temperature sensor can be interfaced with the Space Temp Input variable.
When the Space Temp Input variable is used (valid value), it automatically overrides the hardwired space temperature sensor.
28 McQuay OM 756
Page 29

Description of Operation
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor with +/–3°F Adjustment (optional)
When the optional remote wall-mounted sensor with +/–3°F adjustment dial is used, the UVC
effectively writes the value of the set point adjustment dial to the Set Point Offset Input
variable.
Note – If a network connection is used to adjust the Set Point Offset Input variable, you must not
use the optional remote wall-mounted sensor with +/–3°F adjustment.
– If the keypad/display is used by room occupants to adjust the Set Point Offset, do not use
the optional remote wall-mounted sensor with +/–3°F adjustment.
If you have the optional remote wall-mounted sensor with +/–3°F adjustment and an
occupant uses the keypad to make Set Point Offset adjustments, this overrides any
+/–3°F adjustment on the optional remote wall-mounted sensor since the keypad/display
has higher priority. If you find that changes to the +/–3°F adjustment on the remote wallmounted sensor have no effect, it is likely that an occupant used the keypad/display to
make a Set Point Offset change. Cycle unit power to clear this situation and restore the
ability to change the Set Point Offset from the +/–3°F adjustment on the remote
wall-mounted sensor.
Remote Wall-Mounted Sensor with 55°F to 85°F Adjustment (optional)
When the optional remote wall-mounted sensor with 55°F to 85°F adjustment dial is used, the
UVC will effectively write the value of the set point dial to the Space Temp Set Point Input
variable.
Note – If a network connection is using the Space Temp Set Point Input variable, do not use the
optional remote wall-mounted sensor with 55°F to 85°F adjustment.
– If it is intended that the LUI will be used by room occupants to adjust the Setpoint Offset,
then you must not use the optional remote wall-mounted sensor with 55
adjustment. When using the optional remote wall-mounted sensor with 55
adjustment, the UVC will ignore any Setpoint Offset changes made at the LUI.
°F to 85°F
°F to 85°F
Effective Set Point Calculations
The UVC calculates the effective set point (Effective Set Point Output) based on several
factors. These factors include the six occupancy set points for heating and cooling (Occupancy
Temperature Set Point), occupancy mode, the value of the network variables Space Temp Set
Point Input, Set Point Offset Input, and the Set Point Shi ft Input as well as the optional wallmounted sensor’s set point adjustment knob. As always, network inputs have priority over
hardwired connections.
The UVC determines if heating or cooling is required based on the current unit mode (Heat/
Cool Mode Output) and then calculates the required set point for heating or cooling. After
calculating, the Effective Set Point Output network variable is set equal to the calculated set
point. The Effective Set Point Output is the temperature set point that the UVC maintains,
which normally appears on the keypad/display.
McQuay OM 756 29
Page 30

Description of Operation
Set Point
Offset Input
(network input)
WallSensorType
Config. Value
1
+3°F/–3°F
Wall Sensor
Network Value
Space Temp
Set Point Input
(network input)
0
55°F/85°F
Wall Sensor
Network Value
Set Point
SetptOffset
Occupied Cooling Set Point (OCS)
Standby Cooling Set Point (SCS)
Unoccupied Cooling Set Point (UCS)
Occupied Heating Set Point (OHS)
Standby Heating Set Point (SHS)
Unoccupied Heating Set Point (UHS)
Occupied Cooling Set Point Shift (OCSS)
Standby Cooling Set Point Shift (SCSS)
Unoccupied Cooling Set Point Shift (UCSS)
Occupied Heating Set Point Shift (OCSS)
Standby Heating Set Point Shift (SHSS)
Unoccupied Heating Set Point Shift (UHSS)
SetptShift (network inputs)
Occupancy Temperature Setpoints
(network configuration variables)
Local User
Interface
+5°F/–5°F
AbsOffsetOccupied = Setpoint - (OCS + OHS)/2
AbsOffsetStandby = Setpoint - (SCS + SHS)/2
Occupied and Bypass Modes
EffectiveCoolSetpoint = OCS + AbsOffsetOccupied + SetptOffset + OCSS
EffectiveHeatSetpoint = OHS + AbsOffsetOccupied + SetptOffset + OHSS
Standby Mode
EffectiveCoolSetpoint = SCS + AbsOffsetStandby + SetptOffset + SCSS
EffectiveHeatSetpoint = SHS + AbsOffsetStandby + SetptOffset + SHSS
Unoccupied Mode
EffectiveCoolSetpoint = UCS + UCSS
EffectiveHeatSetpoint = UHS + UHSS
If both entering paths have
valid values, then the network
value has priority.
Effective Set Point Calculations for each Occupancy Mode
If both entering paths have
valid values, then the keypad/display value
has priority.
Figure 20: Effective set point calculations
Table 15: Set point calculation examples
30 McQuay OM 756
Given
OccupancyMode = Occupied or BypassHeat/CoolMode = Heat
SpaceTempSetpoint = (not used)
SetpointOffset = (not used) = 0.0°F
SetpointShift = (not used) = 0.0°F
OHS = 69.8°F
Example A
Effective set point calculations
EffectiveSetpoint = OHS + SetpointOffset + SetpointShift = 69.8 + 0.0 + 0.0 = 69.8°F
Given
OccupancyMode = Occupied or BypassHeat/CoolMode = Heat
SpaceTempSetpoint = 71.0°F
SetpointOffset = -1.0°F (occupant adjustment on remote wall sensor, or LUI)
SetpointShift = (not used) = 0.0°F
OCS = 73.4°F, OHS = 69.8F
Effective set point calculations
Example B
AbsoluteOffset = (OCS – OHS) / 2 =(73.4°F – 69.8°F) / 2 = 1.8°F
EffectiveSetpoint = SpaceTempSetpoint – AbsoluteOffset + SetpointOffset + SetpointShift = 71.0 -
1.0 - 1.0 + 0.0 = 68.2°F
Page 31

Proportional Integral (PI) Control Loops
The MicroTech II UVC uses PI-loop control for heating, cooling and ventilation pro cesses
within the unit ventilator. Numerous PI algorithms can be used depending upon the unit
ventilator configuration. The UVC uses “single” and “cascading” PI loops where needed.
Table 16: PI loop list
PI loops PI loop type Set point
PI-1 Space Temperature
PI-2 Primary Cooling (Economizer)
PI-3 Secondary Cooling
PI-4 Primary Heating
PI-5
PI-6 Low Limit Single
CO2 (optional) Single Effective CO2 Setpoint Space CO
Cascading
Effective Heating or Cooling
Temperature Setpoint
Calculated Discharge Air Temperature
Setpoint Output
Calculated Discharge Air Temperature
Setpoint Output
Calculated Discharge Air Temperature
Setpoint Output
Calculated Discharge Air Temperature
Setpoint
Feedback
(controlled
variable)
Space Temperature
Discharge Air
Temperature
Discharge Air
Temperature
Discharge Air
Temperature
2
Discharge Air
Temperature
Description of Operation
Output
Calculated Discharge Air
Temperature Setpoint Output
Position the OA Damper
Operate the Compressor
Position the Wet Heat Valve or
F&BP Damper
Position the OA Damper
Position the OA Damper
Figure 21: PI loop graphic for CO
2
Discharge Air Temperature Control
The UVC uses two “cascading” PI loops to aid in providing very stable space temperature
control. The Space Temperature PI-loop is used to calculate the Discharge Air Temperature
Setpoint Output required to meet the Effective Temperature Setpoint Output. A second PI-loop
(Primary Cooling, Secondary Cooling, or Primary Heating) is then activated to control the
heating or cooling device required to achieve the calculated Discharge Air Temperature
Setpoint Output.
Figure 22: Cascading PI loop graphic 1 (software model 14—primary heat)
Figure 23: Cascading PI loop graphic 2 (primary cool—economizer)
McQuay OM 756 31
Page 32

Description of Operation
PI Control Parameters
Associated with each PI loop is a set of two adjustable parameters: Proportional Band and
Integral Time. When the unit ventilator is properly sized for the space, the factory settings for
these parameters provides the best and most robust control action (see Figure 24).
If field problems arise, first ensure these parameters are set back to the factory default settings.
If adjustment is required, only make small adjustments to one parameter at a time. After each
adjustment, allow enough time for the system to stabilize before making further adjustments.
If you do not have the means to graph the space performance, record the actual measured
value and set point for several minutes and then plot the results using a spreadsheet to
determine the correct action to change the PI parameter.
CAUTION
Adjusting PI parameters can cause erratic unit operation,
and potentially damage the equipment.
PI control parameters should only be adjusted by trained
personnel having a complete understanding of how these
parameters affect system operation. Generally these parameters
do not need to be adjusted from the factory default settings.
Figure 24: Optimized PI loop control
Proportional Band
The proportional band, or proportional action, causes the controlled output to changes in
proportion to the magnitude of the difference between the sensor value and set point.
A proportional band setting that is too small (see Figure 25) causes control oscillations that go
fully above and below the set point.
Figure 25: Proportional bands
A proportional band setting that is too large (see Figure 25) causes an offset between the actual
measured oscillation center and the set point. A small offset is not necessarily a problem since
most systems have a small “natural” offset and the integral function automatically works to
eliminate or reduce this effect.
32 McQuay OM 756
Page 33

Description of Operation
Area Under The Curve
Too Small
In general, it is best to start with a relatively large proportional band setting (the factory
default setting is best) and adjust to smaller values.
If you want the system to respond strongly to small changes in the space, adjust the
proportional band to a higher setting.
If you want the system to react weakly to small changes in the space, adjust the proportional
band to a higher setting.
Integral Time
The integral time, or integral action, causes the controlled output to change in proportion to
time difference between the sensor value and set point. The difference over time between the
actual value and set point forms an “area under the curve” (see Figure 26). The integral action
works to reduce this “area under the curve” and to eliminate any natural system offset.
Figure 26: Integral time
The smaller the integral time, the faster the output ramps up or down with small changes in the
space. The smaller the integral time, the quicker the system reacts to small changes in the
space. If the Integral Time is set too small, long oscillations occur (see Figure 26).
In general, it is best to start with a relatively large integral time setting (the factory default
setting is best) and adjust to smaller values. If you want the system respond strongly to small
changes in the space, lower the integral time. If you want the system to react weakly to small
changes in the space, adjust the integral time to a higher setting.
Indoor Air Fan Operation
The UVC supports a three-speed indoor air (IA) fan; low, medium, and high. The UVC
calculates the effective fan speed and operation bas ed on the unit mode, the occupancy mode,
and the values of several network variables.
Auto Mode
The UVC is provided with a user selectable auto fan mode feature. When in auto fan mode,
the UVC uses the space temperature PI loop to automatically adjust the fan speed as needed to
maintain space temperature. This ensures that the UVC maintains the lowest and quietest fan
speeds whenever possible. When in auto fan mode, a maximum of six fan speed changes per
hour is allowed (by default). This prevents frequent automatic fan speed changes from
disturbing room occupants.
Occupied, Standby, and Bypass Operation
During occupied standby and bypass modes, the IA fan, by default, remains On.
McQuay OM 756 33
Page 34

Description of Operation
Unoccupied Operation
During unoccupied mode, the IA fan typically remains off and cycles with calls for heating
and cooling.
Cycle Fan
The UVC is provided with a Fan Cycling Configuration variable that can be used to force the
IA fan to cycle with calls for heating and cooling during the occupied, standby, and bypass
occupancy modes. When the fan is off, the OA damper is closed. McQuay recommends using
this feature only when it is acceptable that normal ventilation is not required.
When the IA fan is set to cycle, the UVC is configured to continue fan operation for a time
period after heating or cooling is complete.
Off Delay
When the UVC is placed into off mode or shutdown mode, the UVC is configured to continue
fan operation for a short time period and then shutdown.
Outdoor Air Damper Operation
The UVC is configured for an OA damper operated by a floating-point actuator. The OA
damper actuator contains a spring that ensures the OA damper is closed upon loss of power.
The floating-point actuator is driven by the UVC using two binary (Triac) outputs. The OA
damper typically is open to the current minimum position during the occupied and bypass
occupancy modes and closed during the unoccupied and standby occupancy modes.
A Triac output is best tested under load using a 24 V relay for verification. To verify:
1 Put a relay across the Triac outputs.
2 Cycle the power.
3 Verify the relay’s closed contacts during calibration.
Minimum Position
The UVC is configured to maintain three OA damper minimum positions based on the
operation of the IAF fan. This allows each unit to be field configured to provide the amount of
fresh air required to the space at each of the three IA fan speeds.
Table 17: Default OA damper minimum positions
IAF speed Without CO
High 20% 5%
Medium 25% 5%
Low 30% 5%
Note – If the CO2 Demand Controlled Ventilation (DCV) option is used, the UVC only uses the IA
fan high speed OA damper minimum position regardless of fan speed. The DCV function
adjusts the OA damper above this minimum as needed to maintain CO
2
With CO
2
set point.
2
Economizer Operation
The economizer function is used by the UVC to determine if the OA is adequate for
economizer (primary) cooling. When both the economizer and mechanical cooling are
available, the economizer is used as primary cooling and the UVC adds mechanical cooling
only if the economizer is not adequate to meet the current cooling load (e.g., the OA damper
reaches 100% and cooling is still required).
The UVC supports three economizer functions:
• Basic (default)—Temperature Comparison Economizer
34 McQuay OM 756
Page 35

Description of Operation
• Expanded (optional)—Temperature Comparison with OA Enthalpy Setpoint Economizer
(Strategy 1)
• Leading Edge (optional)—Temperature Comparison with Enthalpy Comparison Economizer
(Strategy 2)
Temperature Comparison Economizer (default)
If the default Basic economizer function is selected, the unit ventilator is provided from the
factory without the optional IA and OA humidity sensors. In this case, the UVC is factory set
for Economizer Strategy 1—the UVC automatically detects that no OA humidity sensor is
present and adjusts to use the T emperature Comparison Economizer function.
Temperature Comparison with OA Enthalpy Setpoint Economizer (optional)
If the optional Expanded economizer function is selected, the unit ventilator is provided from
the factory with the optional OA humidity sensor, which is used along with the OA
temperature sensor to calculate OA enthalpy. In this case, the UVC is factory set for
Economizer Strategy 1 and uses the Temperature Comparison with OA Enthalpy Setpoint
Economizer function.
Note – Temperature Comparison with OA Enthalpy Setpoint Economizer requires an optional OA
humidity sensor.
Temperature Comparison with Enthalpy Comparison Economizer (optional)
If the optional Leading Edge economizer function is selected, the unit ventilator is provided
from the factory with both the IA humidity and OA humidity sensors, which are used along
with the IA temperature and OA temperature sensors to calculate IA enthalpy and OA
enthalpy. In this case, the UVC is factory set for Economizer Strategy 2 and uses the
Temperature Comparison with Enthalpy Comparison Economizer function.
Note – Temperature Comparison with Enthalpy Comparison requires both an optional OA
humidity sensor and an optional IA humidity sensor.
Table 18: Economizer enable/disable tests defined
Economizer
Tests
enable/disable tests
A OA temp set point EffectiveOATemp < (EconOATempSetpt – EconTempDiff) EffectiveOATemp >= EconOATempSetpt
B IA/OA differential temp EffectiveOATemp < (EffectiveSpaceTemp – 3.6°F – EconTempDiff) EffectiveOATemp >= (EffectiveSpaceTemp – 3.6°F)
C OA enthalpy set point
IA/OA differential
D
enthalpy
EffectiveOAEnthalpy < (EconOAEnthalpySetpt –
EffectiveOAEnthalpy < (EffectiveSpaceEnthalpy –
Table 19: How economizer enable/disable tests are selected
Economizer
strategy
All
Basic
Expanded Reliable Reliable Don’t care Reliable
Leading Edge
Space temp sensor OA temp sensor
Unreliable Don’t care Don’t care Don’t care OA damper closed
Don’t care Unreliable Don’t care Don’t care OA damper closed
Reliable Reliable Don’t care Unreliable Test B
Reliable Reliable Don’t care Reliable Test C
Reliable Reliable Reliable Reliable Test D and Test B
Reliable Reliable Unreliable Reliable Test B
Reliable Reliable Reliable Unreliable Test B
Reliable Reliable Unreliable Unreliable Test B
Note: The hard-wired sensor and the equivalent input must both be unreliable for the value to be considered
unreliable.
Enable test Disable test
EconEnthalpyDiff)
EconEnthalpyDiff)
Space humidity
sensor
EffectiveOAEnthalpy >= EconOAEnthalpySetpt
EffectiveOAEnthalpy >= EffectiveSpaceEnthalpy
OA humidity sensor
Economizer enable/
disable tests
Test C and Either
Tes t B o r Te st A
McQuay OM 756 35
Page 36

Description of Operation
Networked Space Humidity Sensor Capability
A networked space humidity sensor can be network interfaced with the Space Humidity Input
variable. When the Space Humidity Input variable is used (valid value), it automatically
overrides the hard-wired space humidity sensor (if present).
Networked Outdoor Humidity Sensor Capability
A networked outdoor humidity sensor can be network interfaced with the Outdoor Humidity
Input variable. When the Outdoor Humidity Input variable is used (valid value), it
automatically overrides the hard-wired outdoor humidity sensor (if present).
CO2 Demand Controlled Ventilation (optional)
Ventilation equipment typically uses fixed damper positions to determine the amount of OA
for proper ventilation within the space. Most commonly, the fixed position of the OA damper
is based on the maximum number of occupants the space is designed to accommodate.
However, this fixed OA damper operation ignores the fact that most spaces during the day
have varying occupancy levels and may only rarely reach maximum design occupancy levels.
This type of fixed damper control for ventilation is energy wasteful since you are treating OA
not actually needed for ventilation during low occupancy levels.
People produce CO
when they breath; the CO2 level within the space has a direct relationship
2
with the number of people within that space.
The UVC can optionally be factory configured to provide CO
Ventilation (DCV). The CO
DCV function is useful in saving the energy typically wasted in
2
-based Demand Controlled
2
treating OA not actually needed for ventilation within a space during occupancy levels below
maximum design. The CO
above the minimum position as needed to maintain the Space CO
DCV function uses a PI-loop control to adjust the OA damper
2
Setpoint (1200 PPM
2
default).
The minimum damper position used with CO
minimum position that would be used without CO
damper position typically is 20% then when using CO
DCV typically can be set at ~20% of the
2
DCV. For example, if the minimum OA
2
DCV, you could set the new minimum
2
OA damper position as low as 4% (e.g., 20% × 0.20 = 4%). This new, smaller minimum OA
damper position then should provide enough ventilation to keep odors in check with in the
space for most applications.
Note – The CO2 DCV function can increase the OA damper position past that required by the
economizer and vice versa.
– If odors within the space become a problem, increase the OA damper minimum position
as needed to eliminate these odors. It may be necessary with new construction or after
renovation to raise the minimum position for some time period to help reduce odor buildup due to the out-gassing of new construction material and then return the minimum OA
damper position at a later date.
– If the CO
fan high speed OA damper minimum position regardless of fan speed. The DCV function
adjusts the OA damper above this minimum as needed. In this case, the IA fan high speed
OA damper minimum position is factory set at 5%.
Demand Controlled Ventilation (DCV) option is used, the UVC only uses the IA
2
Networked Space CO2 Sensor Capability
A networked space CO2 sensor can be network interfaced with the Space CO2 Input variable.
When the Space CO
wired space CO
36 McQuay OM 756
Input variable is used (valid value), it automatically overrides the hard-
2
sensor (if present).
2
Page 37

Description of Operation
ASHRAE Cycle II
The UVC supports ASHRAE Cycle II operation. The basis of ASHRAE Cycle II is to
maintain the required minimum amount of ventilation whenever possible, which can be
increased during normal operation for economizer cooling or CO
DCV control or reduced to
2
prevent excessively cold discharge air temperatures.
A discharge air temperature sensor is installed in all unit ventilators. If necessary, the
ASHRAE II control algorithm overrides room control and modifies the heating, ventilating,
and cooling functions (as available) to prevent the discharge air temperature from falling
below the VCLL set point.
Valve Control (software model 13)
The UVC is configured for a modulating wet heat valve and a modulating chilled water valve
both operated by separate floating-point actuators. The modulating valve actuator contains a
spring that ensures that the wet heat valve is open and that the chilled water valve is closed
upon loss of power. Each floating-point actuator is driven by the UVC using two binary
(Triac) outputs.
Face and Bypass Damper Control (software model 14)
The UVC is configured for a face and bypass damper operated by a floating-point actuator.
The floating-point actuator is driven by the UVC using two binary (Triac) outputs.
End-of-Cycle Valve Control (software model 14)
The UVC is configured for a two-position wet heat end-of-cycle (EOC) valve. The twoposition valve actuator contains a spring that ensures that the wet heat valve is open upon loss
of power. The two-position actuator is driven by the UVC using one binary (Triac) output.
.
CAUTION
Both a wet-heat end-of-cycle (EOC) valve and a chilled water
end-of-cycle (EOC) valve are strongly recommended by
McQuay. If an EOC valve is not installed, it is likely that
overheating of the space will occur.
Passive Dehumidification (optional, software model 14)
The term “Passive Dehumidification” is meant to convey that “reheat” is not used as part of
the passive dehumidification process. Passive Dehumidification is used only during the
unoccupied mode. During unoccupied mode, when humidity is high, and when the UVC is in
the auto or cool modes, and the source (water-in) temperature is acceptable for cooling, the
UVC uses passive dehumidification. When passive dehumidification is active, the Effective
Set Point changes from the normal Unoccupied Cooling set point (82°F , default) to the Passive
Dehumidification Temp set point (72°F, default). For proper passive dehumidification
operation, set the Passive Dehumidification Temp set point below the Unoccupied Cooling set
point. During passive dehumidification, the UVC uses the Passive Dehumidification F&BP
Damper Max setting to restrict the F&BP damper from opening the coil face greater that 20%face (default); the space fan remains in low speed during cooling. This restricted F&BP
damper cooling at low fan speed is how passive dehumidification is achieved during the
unoccupied mode. The UVC uses a 5% RH fixed differential below the RHS to determine
when passive dehumidification is comp lete.
McQuay OM 756 37
Page 38

Description of Operation
Active Dehumidification State (optional with reheat units, software model 13)
The Active Dehum state is a “normal” state that the UVC can go into when Cool mode is
active and when the unit is equipped for optional active dehumidification (see Active
Dehumidification).
When the Active Dehum state becomes active, the UVC will capture the current IAT and use
this as the temporary setpoint during dehumidification. The units mechanical cooling
capabilities will initially be set to 100% (full open chilled water valve) and the heat PI will
maintain the captured setpoint. If the heat PI saturates high (100% full open wet heat valve)
for 2-minutes or more (i.e. heating cannot keep up with cooling), mechanical control will be
disabled until the heat PI saturates low (0% heat). The UVC uses a 5%RH fixed differential
below the RHS to determine when active dehumidification is complete. The UVC will
control
2
2
monitor the DAT to ensure it does not fall below MCLL, nor goes above DAHL. The CO
demand controlled ventilation function will be active, if the unit is equipped for CO
(see “CO2 Demand Controlled Ventilation (optional)” on page 36), and the OAD will be
adjusted as needed to maintain the CO
humidity is not high, mechanical cooling is not available or the relative humidity sensor is not
reliable.
setpoint. The UVC will remain in this state until space
2
Floating-Point Actuator Auto-Zero, Overdrive and Sync
The UVC at power-up auto-zeros all floating-point actuators (OA damper) before going into
normal operation to ensure proper positioning. During auto-zero, the unit remains off. The
actuators all open approximately 30% and then are driven full closed. The overdrive feature
then is used to continue forcing the actuators closed for one full stroke period. Once the
zeroing process is complete, normal unit operation begins.
The UVC is configured such that whenever a floating-point actuator is commanded to go to
0% or 100%, the UVC overdrives the actuator one full stroke period past the 0% or 100%
position to ensure proper positioning.
Additionally, the UVC is configured to sync all floating-point actuators once every six hours
of operation. T o do this, the UVC forces the actuator to the closest rail position (0% or 100%),
uses the overdrive feature, and then returns to the required position. For example, if the
actuator is at 20% when the six-hour limit is reached, the UVC then forces the actuator to 0%,
overdrive for one full stroke and then returns to the 20% position.
Water Coil Leaving Air Thermostat (Freeze-stat)
A normally-closed low temperature thermostat is factory provided to detect low leaving air
temperature conditions on the indoor air coil. This thermostat is mounted on the discharge air
side of the unit’s water coil. The low temperature thermostat cut-out is 38°F +/–2°F (3°C +/–
1°C) and the cut-in is 45°F +/–2°F (7°C +/–1°C). When the low temperature thermostat
detects low leaving air temperatures (contacts open), the following occurs.
Valve Control (software model 13)
When the freeze-stat cuts-out:
1 The OA damper closes immediately.
2 The space fan stops.
3 The wet heat and chilled water valve minimums are set to 50%.
4 If heating is required, the wet heat valve modulates above 50%, as needed. auxiliary heat
may be used as needed.
When the freeze-stat cuts-in, the UVC returns to normal operation.
38 McQuay OM 756
Page 39

Description of Operation
Binary Inputs
3 sets of dry contacts to signal UVC
Input 1: Unoccupied (default)
Input 2: Remote shutdown
Input 3: Ventilation lockout (default)
or
Exhaust interlock system
Face & Bypass Damper Control (software model 14)
When the freeze-stat cuts-out:
1 The OA damper closes immediately.
2 The wet heat and chilled water EOC valves open immediately.
3 If heating is required, the F&BP damper modulates normally to main tain room
temperature. Auxiliary heat may be used as needed.
When the freeze-stat cuts-in, the UVC returns to normal operation.
External Binary Inputs
The UVC is provided with three binary inputs that provide the functions described below.
Figure 27: Binary inputs
These inputs each allow a single set of dry contacts to be used as a signal to the UVC. Multiple
units can be connected to a single set of dry contacts. For wiring examples, see MicroTech II
Unit Ventilator Controller IM 747.
Note – Not all of the functions listed can be used at the same time. The UVC is provided with
configuration parameters that can be adjusted to select which function is used for these
inputs where multiple functions are indicated below.
External Binary Input 1
This input can be configured as an unoccupied (default) or dew point/humidity signal.
Unoccupied Input Signal
This input allows a single set of dry contacts to be used to signal the UVC to go into
unoccupied or occupied mode. When the contacts close, the UVC goes into unoccupied mode.
When the contacts open, the UVC goes into occupied mode. Additional variables can effect
occupancy mode and override this binary input. See “Occupancy Modes” on page 26.
Dewpoint/Humidity Input Signal (optional, software models 13 and 14)
This input allows a single set of dry contacts to be used to signal the UVC to go into
dehumidification. See“Active Dehum State (optional, software model 13)” on page 23 “Active
Dehum State (optional, software model 13)” on page 23, “Passive Dehumidification (optional,
software model 14)” on page 37, and “Mech State (State 2)” on page 21. When the contacts
close (high humidity), the UVC goes into active dehumidification. When the contacts open
(low humidity), the UVC stops dehumidification. The device used must incorporate its own
differential dewpoint or differential humidity. See “Cool Mode (Super State)” on page 19.
McQuay OM 756 39
External Binary Input 2
This input can only be used for remote shutdown.
Page 40

Description of Operation
Binary Outputs
3 relay type outputs w/signal voltage
Output 1: Relay output for light signal
Output 2: Fault signal
Output 3: Exhaust fan operation (default)
or
Auxiliary heat device
Remote Shutdown Input Signal
This input allows a single set of dry contacts to be used to signal the UVC to go into shutdown
mode. When the contacts close (shutdown), the UVC goes into shutdown mode. When the
contacts open. the UVC returns to normal operation. See “Active Dehumidification State
(optional with reheat units, software model 13)” on page 38.
External Binary Input 3
This input can be configured as a ventilation lockout (default) or exhaust interlock signal.
Ventilation Lockout Input Signal
This input allows a single set of dry contacts to be used to signal the UVC to close the OA
damper. When the contacts close (ventilation lockout signal), the UVC closes the OA damper.
When the contacts open, the UVC returns to normal OA damper operation.
Exhaust Interlock Input Signal
This input allows a single set of dry contacts to be used to signal the UVC that an exhaust fan
within the space is energized. The UVC repositions the OA damper to a user adjustable
minimum position (Exhaust Interlock OA Damper Min Position Setpoint). When the contacts
close (exhaust fan on signal), the UVC uses the value defined by the Exhaust Interlock OA
Damper Min Position Setpoint as the new minimum OA damper position regardless of IA fan
speed. When the contacts open, the UVC returns to normal OA damper operation.
External Binary Outputs
The UVC is provided with three binary outputs that provide the functions described below.
Figure 28: Binary outputs
These outputs are relay type outputs that are intended to be used with signal level voltages (24
VAC maximum) only. For wiring examples, see MicroTech II Unit Ventilator Controller IM
747.
Note – Not all of the functions listed can be used at the same time. The UVC is provided with
configuration parameters that can be adjusted to select which function will be used for
these outputs when multiple functions are indicated below.
External Binary Output 1
This output can only be used as a signal for space lights.
40 McQuay OM 756
Page 41

Description of Operation
Lights On/Off Signal
This relay output provides one set of Normally Open dry contacts that can be used to signal
the operation of the space lights. When the UVC is in occupied, standby, or bypass occupancy
modes, the relay output signals the lights ON (contacts closed). When the UVC is in
unoccupied occupancy mode, the relay output signals the lights OFF (contacts open).
External Binary Output 2
This output can only be used as a fault signal.
Fault Signal
This relay output provides Normally Open, Normally Closed, and Common connections that
can be used to signal a fault condition. When a fault exists, the UVC energizes this relay
output. When the fault or faults are cleared, the UVC de-energizes this relay output.
External Binary Output 3
This output can only be used to signal exhaust fan operation (default) or operate an auxiliary
heat device.
Exhaust Fan ON/OFF Signal
This relay output provides one set of Normally Open dry contacts that can be used to signal
the operation of an exhaust fan. When the OA damper opens more than the Energize Exhaust
Fan OA Damper set point, then the relay output signals the exhaust fan ON (contacts closed).
When the OA damper closes below this set point, the relay output signals the exhaust fan OFF
(contacts open).
Auxiliary Heat Signal
This relay output provides one set of Normally Open dry contacts that can be used to operate
an auxiliary heat device. The UVC by default is configured to operate a Normally Open
auxiliary heat device (de-energize when heat is required), such as a wet heat valve actuator
with a spring setup to open upon power failure. However, the Auxiliary Heat Configuration
variable can be used to set the UVC to use a Normally Closed auxiliary heat device (energize
when heat is required), such as electric heat.
Table 20: Auxiliary heat start/stop calculation
Start/Stop Calculation
Auxiliary heat
starts when:
Auxiliary heat
stops when:
Primary Heat PI-Loop = saturated high (100%) for
more than two minutes
AND
EffectiveSpaceTemp
AuxiliaryHeatStartDifferential
EffectiveSpaceTemp (EffectiveSetpoint –
AuxiliaryHeatStartDifferential) +
AuxiliaryHeatStopDifferential
EffectiveSetpoint –
McQuay OM 756 41
Page 42

UVC Input and Output Table
UVC Input and Output Table
All UVC input and output connections and their corresponding unit ventilator usage are shown
in the following table.
Table 21: Input s an d outputs, software models 13 and 14
I/O Model 13—4-pipe heat/cool - valve control
Model 14—4-pipe heat/cool - F&BP damper
control
BO-1 Inside Fan High Inside Fan High
BO-2 Inside Fan Medium Inside Fan Medium
BO-3
BO-4
BO-5
External Output Option 2:
BO-6
Fault Indication
1
BO-7 Cool Valve Open Wet Heat EOC Valve (NO)
External Output Option 2:
Fault Indication
1
2
BO-8 Cool Valve Close
BO-9
BI-1 Condensate Overflow Condensate Overflow
BI-2
BI-3 Low Air Temperature Thermostat (NC) Low Air Temperature Thermostat (NC)
External Input Option 3:
BI-4
Ventilation Lockout (default) or Exhaust
3
Interlock
External Input Option 2:
BI-5
Remote Shutdown
External Input Option 1:
BI-6
Unoccupied (default) or Dewpoint/Humidity
3
External Input Option 3:
Ventilation Lockout (default) or Exhaust
3
Interlock
External Input Option 2:
Remote Shutdown
External Input Option 1:
3
Unoccupied (default) or Dewpoint/Humidity
3
BI-7
BI-8
BI-9
BI-10
BI-11
BI-12
AI-1 IA Temp. Sensor + T.O. IA Temp. Sensor + T.O.
AI-2 Remote Setpt. Adjust. Pot. Remote Setpt. Adjust. Pot.
AI-3
AI-4 OA Temp Sensor OA Temp Sensor
AI-5
AI-6 DA Temp Sensor DA Temp Sensor
Expansion board
xBO-1
xBO-2
External Output Option 1:
Lights On/Off
1
External Output Option 3:
Exhaust Fan On/Off (default) or Auxiliary Heat
External Output Option 1:
Lights On/Off
External Output Option 3:
1
Exhaust Fan On/Off (default) or Auxiliary Heat
1
xBO-3 OA Damper Open OA Damper Open
xBO-4 OA Damper Close OA Damper Close
xBO-5 Wet Heat Valve Open F&BP Damper Open Face
xBO-6 Wet Heat Valve Close F&BP Damper Close Face
xBO-7
xBO-8 Inside Fan Low Inside Fan Low
xAI-1 IA Humidity Sensor
xAI-2 OA Humidity Sensor
xAI-3 Indoor CO2 Sensor
4
4
4
IA Humidity Sensor
OA Humidity Sensor
Indoor CO2 Sensor
4
4
4
xAI-4
1. Field selectable external output options (all possible options are shown).
2. End of Cycle (EOC) valve is required for proper unit operation and space control.
3. Field selectable external input options (all possible options are shown).
4. Optional.
3
1
42 McQuay OM 756
Page 43
Diagnostics and Service
Diagnostics and Service
The most important aspect of troubleshooting unit ventilator controls is to isolate the source of
the problem into one of two categories:
1 The problem resides within the UVC.
2 The problem is external to the UVC. Under most circumstances the problem is external to
the UVC.
Alarm and Fault Monitoring
The UVC is programmed to monitor the unit for specific alarm conditions. If an alarm
condition exists, a fault occurs. When a fault exists, the following occurs:
• The UVC indicates the fault condition by displaying the fault code on the keypad/display.
• The remote wall-mounted sensor (optional) LED flashes a pattern indicating that a fault
condition exists.
• The fault signal binary output energizes.
• The fault performs the appropriate control actions as described for each fault.
Manual reset faults can be reset in one of three ways:
• By cycling the unit power.
• Via the keypad/display menu.
• Via the network interface.
Table 22: Alarm and fault code summary
Priority Fault description Reset
1 Space Temp Sensor Failure Auto
2 Not used
3 Not used
4 Not used
5 Condensate Overflow Indication Auto
6 Not used
7 Outdoor Temp Sensor Failure Auto
8 Discharge Air Temp Sensor Failure Auto
9 Not used
10 Not used
11 Space Humidity Sensor Failure Auto
12 Outdoor Humidity Sensor Failure Auto
13 Space CO2 Sensor Failure Auto
14 Not Used
15 Not Used
16 Change Filter Indication Manual
17 EPROM Memory Indicator Replace conroller board
18 Configuration Display Download file
Keypad/
display fault
codes
McQuay OM 756 43
Page 44

Diagnostics and Service
Space Temp Sensor Failure ()
The Space Temp Sensor Failure fault occurs when the UVC detects open or short conditions
from the sensor.
Effect:
• Space fan de-energizes (unless in emergency heat mode).
• Outside air damper is forced closed.
• Heating valve is fully opened to the coil (software model 13).
• Chilled water valve is fully opened to the coil (so ftware model 13).
• F&BP damper is positioned to 100% face (software model 14).
• Heating EOC valve is opened (software model 14).
• Cooling EOC valve is closed (software model 14).
• Electric heat stages are de-energized.
• Fault is indicated.
Condensate Overflow Indication (optional) ()
The Condensate Overflow Indication fault will occur when the UVC detects high condensate
levels within the units indoor coil drain pan.
Effect:
• Chilled water valve is forced closed (software model 13).
• Cooling EOC valve is closed (software model 14).
• Fault is indicated.
Outdoor Temp Sensor Failure ()
The Outdoor Temp Sensor Failure fault occurs when the UVC detects open or short conditions
from the sensor.
Effect:
• Outside air damper is forced closed.
• EOC valve control due to OA temperature is disabled. EOC valve(s) will operate based upon
space temperature only (software model 14).
• Fault is indicated.
Discharge Air Temp Sensor Failure ()
The Discharge Air Temp Sensor Failure fault occurs when the UVC detects open or short
conditions from the sensor. Emergency heat mode is available during this fault condition.
Effect:
• Space fan is immediately de-energized (unless in emergency heat mode).
• Outside air damper is forced closed.
• Heating valve is fully opened to the coil (software model 13).
• Chilled water valve is fully opened to the coil (so ftware model 13).
• F&BP damper is positioned to 100% face (software model 14).
• Heating EOC valve is opened (software model 14).
• Cooling EOC valve is closed (software model 14).
• Fault is indicated.
44 McQuay OM 756
Page 45

Diagnostics and Service
Space Humidity Sensor Failure (optional) ()
The Space Humidity Sensor Failure fault occurs when the UVC detects open or short
conditions from the sensor.
Effect:
• IA/OA Enthalpy comparison economizer (if used) is disabled.
• Dehumidification function (optional) is disabled.
• Fault is indicated.
Outdoor Humidity Sensor Failure (optional) ()
The Outdoor Humidity Sensor Failure fault occurs when the UVC detects open or short
conditions from the sensor.
Effect:
• IA/OA Enthalpy comparison or OA Enthalpy economizer (if used) is disabled.
• Fault is indicated.
Space CO2 Sensor Failure (optional) ()
The Space CO2 Sensor Failure fault occurs when the UVC detects open or short conditions
from the sensor.
Effect:
• CO
Demand Controlled Ventilation function is disabled.
2
• Fault is indicated.
Change Filter Indication ()
The Change Filter Indication fault occurs when the UVC calculates that the total fan run time
has exceeded the allowed number of hours since the last filter change.
Effect:
• Fault is indicated.
EPROM Memory Indicator ()
The EPROM Memory Indicator occurs when an unusual electrical event has scrambled the
EPROM memory within the controller board. In the event that this happens, the controller
board must be replaced.
Configuration Display ()
The Configuration Display occurs when the display file “**.cfg” is incorrect or has not been
downloaded with the appropriate file from service tools.
Troubleshooting Temperature Sensors
The UVC is configured to use passive positive temperature coefficient (PTC) sensor whose
resistance increases with increasing temperature. The element has a reference resistance of
1035 ohms at 77°F (25°C). Each element is calibrated according to the tables shown.
Use the following procedure to troubleshoot a suspect sensor.
1 Disconnect both sensor leads from the UVC.
2 Using some other calibrated temperature sensing device, take a temperature reading at the
sensor location.
McQuay OM 756 45
Page 46

Diagnostics and Service
3
Use the temperature reading from Step 2 to determine the expected sensor resistance from
Table 23.
4 Using a calibrated ohmmeter, measure the actual resistance across the two sensor leads.
5 Compare the expected resistance to the actual resistance.
6 If the actual resistance value deviates substantially (more than 10%) from the expected
resistance, replace the sensor.
Table 23: Temperature versus resistance
°F (°C) Resistance in ohms °F (°C) Resistance in ohms
–40 (–40) 613 113 (45) 1195
–31 (–35) 640 122 (50) 1237
–22 (–30) 668 131 (55) 1279
–13 (–25) 697 140 (60) 1323
–4 (–20) 727 149 (65) 1368
5 (–15) 758 158 (70) 1413
14 (–10) 789 167 (75) 1459
23 (–5) 822 176 (80) 1506
32 (0) 855 185 (85) 1554
41 (5) 889 194 (90) 1602
50 (10) 924 203 (95) 1652
59 (15) 960 212 (100) 1702
68 (20) 997 221 (105) 1753
77 (25) 1035 230 (110) 1804
86 (30) 1074 239 (115) 1856
95 (35) 1113 248 (120) 1908
104 (40) 1153
Troubleshooting Humidity Sensors
The UVC is configured to use a 0–100% RH, 0–5 VDC, capacitive humidity sensor. Each
sensor is calibrated according to the table shown.
CAUTION
The humidity sensor is not protected against reversed polarity.
Check carefully when connecting the device or damage can
result.
Use the following procedure to troubleshoot a suspect sensor:
1 Disconnect the sensors output voltage lead from the UVC analog input.
2 Using some other calibrated humidity sensing device, take a humidity reading at the sensor
location.
3 Use the humidity reading from Step 2 determine the expected sensor voltage from
Table 24.
4 Using a calibrated multi-meter, measure the actual voltage across the yellow and white
sensor leads.
Wire color definitions:
White = ground
Yellow = output VDC
Blue = supply VDC
5 Compare the expected voltage to the actual voltage.
6 If the actual voltage value deviates substantially (more than 10%) from the expected
voltage, replace the sensor.
46 McQuay OM 756
Page 47

Diagnostics and Service
Table 24: Humidity versus voltage.
RH (%) VDC (mV) RH (%) VDC (mV)
10 1330 55 2480
15 1475 60 2600
20 1610 65 2730
25 1740 70 2860
30 1870 75 2980
35 1995 80 3115
40 2120 85 3250
45 2235 90 3390
50 2360 95 3530
Troubleshooting Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensors
The UVC is configured to use a 0–2000 PPM, 0–10 VDC, single beam absorption infrared gas
sensor. Each sensor is calibrated according to the table shown.
Use the following procedure to troubleshoot a suspect sensor.
1 Disconnect the sensors output voltage lead from the UVC analog input (xAI-3).
2 Using some other calibrated CO
3 Use the CO
reading from Step 2 to determine the expected sensor voltage from Table 25.
2
4 Using a calibrated multi-meter, measure the actual voltage across the lead removed from
xAI-3 and ground.
5 Compare the expected voltage to the actual voltage.
6 If the actual voltage value deviates substantially (more than 10%) from the expected
voltage, replace the sensor.
sensing device, take a CO2 reading at the sensor location.
2
In the unlikely event that the CO
sensor requires calibration, consult the factory for
2
information on obtaining calibration equipment and instructions.
Table 25: CO2 versus voltage table
CO2 (PPM) VDC (V) CO2 (PPM) VDC (V)
300 1.5 1200 6.0
400 2.0 1300 6.5
500 2.5 1400 7.0
600 3.0 1500 7.5
700 3.5 1600 8.0
800 4.0 1700 8.5
900 4.5 1800 9.0
1000 5.0 1900 9.5
McQuay OM 756 47
Page 48

UVC Configuration Parameters
UVC Configuration Parameters
The UVC is been provided with a number of configuration variables as listed in the following
table. These configuration variables are stored in UVC non-volatile memory. For a description
of supported network variables for each protocol, refer to Protocol Data Packet bulletin ED
15065.
Table 26: UVC configuration parameters (OM 756)
Configuration Parameter Name Abr. Notes Default 13 14
Occupied Cooling Setpoint
Standby Cooling Setpoint
Unoccupied Cooling Setpoint
Occupied Heating Setpoint
Standby Heating Setpoint
Unoccupied Heating Setpoint
Local Bypass Time tenant override
Spac e CO
Space Humidity Setpoint
Emergency Heat Enable 0 = disable, 1 = enable (uses auxiliary heat where primary
Emergency Heat Setpoint
Emergency Heat Shutdown
Configuration
Wall Sensor Type
Slave Type Configuration
OAD Min Position High-Speed Setpoint
OAD Min Position Med-Speed Setpoint
OAD Min Position Low-Speed Setpoint
Exhaust Interlock OAD Min Position
Setpoint
Energize Exhaust Fan OAD Setpoint
OAD Max Position Setpoint
OAD Lockout Enable 0 = disable, 1 = enable (this variable will be factory set to 1
OAD Lockout Setpoint
Economizer Enable 0 = disable, 1 = enable
Economizer OA Temp Setpoint
Economizer IA/OA Temp Differential
Economizer OA Enthalpy Setpoint
Economizer IA/OA Enthalpy Differentia l
External BI-1 Configuration 0 = Unoccupied, 1 = Dewpoint/Humidity
External BI-3 Configuration 0 = Ventilation Lockout, 1 = Exhaust Interlock
External B0-3 Configuration 0 = Auxiliary Heat 1 = Exhaust Fan On/Off
Filter Alarm Enable 0 = disable, 1 = enable
Setpoint
2
2
2
2
2
OCS 73°F (23°C) x x
SCS 77°F (25°C) x x
UCS 82 °F (28°C) x x
OHS 70°F (21°C) x x
SHS 66°F (19°C) x x
UHS 61 °F (16°C) x x
120 min x x
CO2S 1200 PPM x x
used with both active (reheat) and passive dehumidification
RHS
sequences
heat is not applicable)
EHS 54°F (12°C) x x
0 = no emergency heat during shutdown, 1 = emergency
heat available during shutdown
0 = +/- 3°F, 1 = 55°F to 85°F
0 = independent slave, 1 = dependent slave
(this variable will be factory set to 5% open when the unit is
OADH
ordered with optional CO
(this variable is ignored when the unit is ordered with
OADM
optional CO
(this variable is ignored when the unit is ordered with
OADL
optional CO
OA damper minimum position when the exhaust interlock
EOAD
input is energized
defines position above which exhaust fan output will be
OADE
energized
OAMX 99 % open x x
when the unit is ordered as a recirc unit with no OAD)
OA temperature below which the OA damper will remain
OALS
closed (this variable will be factory set to –99°C when the
unit is ordered as a recirc unit with no OAD)
ETS 68°F (20°C) x x
ETD 2°F (1°C) x x
EES 25 btu/lb (58 kJ/kg) x x
EED 1.3 btu/lb (3 kJ/kg) x x
DCV)
2
DCV)
2
DCV)
2
60% RH x x
1 x x
0 x x
0 x x
0 x x
20% open x x
25% open x x
30% open x x
99% open x x
12% open x x
0 x x
36°F (2°C) x x
1 x x
0 x x
0 x x
0 x x
0 x x
LUI Menu
1
Item
48 McQuay OM 756
Page 49

UVC Configuration Parameters
Configuration Parameter Name Abr. Notes Default 13 14
Filter Change Hours Setpoint fan run hours between filter change alarms
Primary Cool Proportional Band
Primary Cool Integral Time
Secondary Cool Proportional Band
Secondary Cool Integral Time
Primary Heat Proportional Band
Primary Heat Integral Time
Discharge Air Temp Proportional Band
Discharge Air Temp Integral Time
Proportional Band
CO
2
Integral Time
CO
2
Ventilation Cooling Low Limit Setpoint
Mechanical Cooling Low Limit Setpoint
Discharge Air High Limit
Passive Dehum Temp Setpoint
Passive Dehum F&BP Damper Max
Space Fan Off Delay
Fan Cycling Configuration space fan operation during occupied, standby and bypass
Space Fan Speed Changes Per Hour example: 6/60min = 10 min (maximum of 1 fan speed
Space Fan Run Time Reset reset total run time: 1 = reset (you must return the variable
EOC OAT Low Setpoint
Auxiliary Heat Start Differential
Auxiliary Heat End Differential
Auxiliary Heat Configuration 0 = normally open heat device (hot water valve, etc.), 1 =
Space Humidity Sensor Enable 0 = disable, 1 = enable (this variable will be factory set to 1
Outdoor Humidity Sensor Enable
OAD Stroke Time
F&BP Damper Stroke Time
WH or CW/HW Valve Stroke Time
Application Name and Version Label
1. Indicates parameters accessible through the keypad/display.
2. Requires optional equipment.
2
2
discharge air low limit during ventilation or economizer
VCLL
cooling
discharge air low limit during mechanical (compressor or
MCLL
hydronic) cooling
DAHL 14 0°F (60°C) x x
2
2
2
cooling setpoint used during passive dehumidification
maximum F&BP damper face position during passive
dehumidification
occupancy modes: 2 = continuous, 3 = cycle
change every 10 min when fan in auto)
back to 0 after reset)
OA temperature below which the EOC valve will remain
EOCS
open
degrees below effective heating setpoint where auxiliary
AHSD
heat starts
degrees above auxiliary heat start point where auxiliary heat
AHED
ends
normally closed heat device (electric heat, etc.)
when the unit is ordered with optional humidity sensor)
0 = disable, 1 = enable (this variable will be factory set to 1
when the unit is ordered with optional humidity sensor)
700 hrs x x
18°F (10°C) x x
180 sec x x
11°F (6°C) x x
600 sec x x
54°F (30°C) x x
300 sec x x
3.996°F (2.2°C) x x
300 sec x x
100 PPM x x
600 sec x x
54°F (12°C) x x
45°F (7°C) x x
72°F (22°C) x
20% face x
30 sec x x
2 x x
6 x x
0 x x
39°F (4°C) x
2°F (1°C) x x
2°F (1°C) x x
0 x x
0 x x
0 x x
90 sec x x
95 sec x
26 sec x
x x
LUI Menu
1
Item
Table 27:
McQuay OM 756 49
Page 50

McQuay Training and Development
Now that you have made an investment in modern, efficient McQuay equipment, its care should be a high priority.
For training information on all McQuay HVAC products, please visit us at www.mcquay.com and click on training, or
call 540-248-9646 and ask for the Training Department.
Warranty
All McQuay equipment is sold pursuant to its standard terms and conditions of sale, including Limited Product
Warranty. Consult your local McQuay Representative for warranty details. Refer to Form 933-43285Y. To find your
local McQuay Representative, go to www.mcquay.com.
This document contains the most current product information as of this printing. For the most up-to-date product
information, please go to www.mcquay.com.
© 2010 McQuay International • www.mcquay.com • 800-432-1342
 Loading...
Loading...