MCC 68AC430-100, 68AC430-100-4, 68AC430-100-2, 68AC430-100-5, 68AC430-100-6 Service Manual
...
T-353 Manual
OPERATION/SERVICE
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
for
68AC430-100
T-353
REV. 01/2013

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY SUMMARY Safety-1...............................................................
DESCRIPTION 1-1....................................................................
1.1 INTRODUCTION 1-1.......................................................
1.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 1-2...............................................
1.2.1 Rooftop Unit 1-2......................................................................
1.2.2 Condensing Section 1-2.................................................................
1.2.3 Evaporator Section 1-2..................................................................
1.2.4 BT-324 Microprocessor 1-3..............................................................
1.3 REFRIGERATION SYSTEM COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS 1-3.................
1.4 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS - MOTORS 1-3................................
1.5 SAFETY DEVICES 1-3......................................................
1.6 AIR CONDITIONING REFRIGERATION CYCLE 1-4............................
1.7 HEATING CYCLE 1-4.......................................................
OPERATION BT324 Controller 2-1.........................................................
2.1 STARTING, STOPPING AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS 2-1..................
2.1.1 Starting 2-1...........................................................................
2.1.2 Stopping 2-1..........................................................................
2.2 PRE-TRIP INSPECTION 2-1..................................................
2.3 SEQUENCE OF OPERATION BT324 2-2.......................................
2.3.1 Function of Keys when “Engine On” and controller active: 2-2...................................
2.3.2 Illuminating Indications (Display) 2-2.......................................................
2.4 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS BT324 2-2......................................
2.4.1 Display 2-2...........................................................................
2.4.2 Interior Temperature Control 2-2..........................................................
2.4.3 Ventilation 2-2........................................................................
2.4.4 Reheat (optional) 2-2....................................................................
2.4.5 Temperature Indication 2-2..............................................................
2.5 CHANGING BETWEEN °F (FAHRENHEIT) AND °C(CELCIUS) 2-2..............
TROUBLESHOOTING 3-1................................................................
3.1 System Will Not Cool 3-1................................................................
3.2 System Runs But Has Insufficient Cooling 3-1................................................
3.3 Abnormal Pressures 3-1.................................................................
3.4 Abnormal Noise Or Vibrations 3-1.........................................................
3.5 No Evaporator Air Flow Or Restricted Air Flow 3-2...........................................
3.6 Expansion Valve Malfunction 3-2..........................................................
3.7 Heating Malfunction 3-2.................................................................
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
i

TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
SERVICE 4-1........................................................................
4.1 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE 4-1.............................................
4.2 REMOVING COVER 4-1.....................................................
4.3 MANIFOLD GAUGE SET 4-1................................................
4.3.1 Installing R-134a Manifold Gauge/Hose Set 4-2..............................................
4.4 REMOVING THE REFRIGERANT CHARGE 4-3...............................
4.4.1 Removing Entire System Charge 4-3.......................................................
4.5 REFRIGERANT LEAK CHECK 4-3............................................
4.6 EVACUATION AND DEHYDRATION 4-3.....................................
4.6.1 General 4-3...........................................................................
4.6.2 Preparation 4-3........................................................................
4.6.3 Procedure for Evacuation and Dehydrating System 4-4.........................................
4.7 ADDING REFRIGERANT TO SYSTEM 4-4.....................................
4.7.1 Checking Refrigerant Charge 4-4..........................................................
4.7.2 Adding Full Charge 4-4.................................................................
4.8 CHECKING FOR NONCONDENSIBLES 4-4...................................
4.9 CHECKING AND REPLACING HIGH OR LOWPRESSURE CUTOUT SWITCH 4-4...
4.9.1 Replacing High Or Low Pressure Switches 4-4................................................
4.9.2 Checking High Pressure Switches 4-5......................................................
4.9.3 Checking Low Pressure Switches 4-5.......................................................
4.10 FILTER-DRIER 4-5.........................................................
4.10.1 To Check Filter-Drier 4-5................................................................
4.10.2 To Replace Filter-Drier Assembly 4-5......................................................
4.11 SERVICING THE HEAT VALVE 4-6..........................................
4.11.1 Coil Replacement 4-6...................................................................
4.11.2 Internal Part Replacement 4-6............................................................
4.11.3 Replace Entire Valve 4-6................................................................
4.12 SERVICE VALVES 4-7.......................................................
4.13 REPLACINGRETURNAIRFILTERS 4-7.......................................
4.14 THERMOSTATIC EXPANSION VALVE 4-8....................................
4.14.1 Valve Replacement 4-9..................................................................
4.14.2 Superheat Measurement 4-9..............................................................
ELECTRICAL 5-1......................................................................
5.1 INTRODUCTION 5-1.......................................................
Table 1-1 68AC430 Models 1-1.........................................................
Table 1-2 Additional Support Manuals 1-1................................................
Table 3-1 General System Troubleshooting Procedures 3-1...................................
Table 4-1 R-134a Temperature - Pressure Chart 4-11.........................................
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
LIST OF TABLES
ii

LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1-1 AC430 Rooftop Unit 1-2....................................................
Figure 1-2 Refrigerant/Heat Flow Diagram, AC430 1-5.....................................
Figure 1-3 AC430 With BT324 Control Board 1-6.........................................
Figure 3-1 BT324 Controller 2-1......................................................
Figure 4-1 Manifold Gauge Set (R-134a) 4-2..............................................
Figure 4-2 In-Line Service Connections 4-3..............................................
Figure 4-3 Checking High Pressure Switch 4-5............................................
Figure 4-4 Filter-Drier Removal 4-5....................................................
Figure 4-5 Heat Valve 4-7............................................................
Figure 4-6 Service Valve R134a (High Side) 4-7...........................................
Figure 4-7 Return Air Grill Assembly With Air Filter Showing 4-8.............................
Figure 4-8 Diffuser and Filter Element 4-8...............................................
Figure 4-9 Filter, Diffuser and Composite Frame 4-8.......................................
Figure 4-10 Return Air Grill Assembly With Diffuser And Composite Frame Showing 4-8..........
Figure 4-11 Thermostatic Expansion Valve 4-9...........................................
Figure 4-12 Thermostatic Expansion Valve Bulb and Thermocouple 4-9........................
Figure 5-2 Evaporator Motors 5-2.....................................................
Figure 5-3 Condenser Motors 5-3.....................................................
Figure 5-4 BT324 Controls With (1) Compressor 5-4.......................................
Figure 5-5 BT324 Control Circuit 5-5...................................................
Figure 5-6 AC430 With BT324 Control 5-6..............................................
Figure 5-7 AC430 With BT324 Control (Electrical Panel 91-62105-00) 5-7.......................
Figure 5-8 AC430 With BT324 Control (Electrical Panel 91-62105-00) 5-8.......................
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
iii

SAFETY SUMMARY
GENERAL SAFETY NOTICES
The following general safety notices supplement the specific warnings and cautions appearing elsewhere in this
manual. They are recommended precautions that must be understood and applied during operation and
maintenance of the equipment covered herein. A listing of the specific warnings and cautions appearing
elsewhere in the manual follows the general safety notices.
FIRST AID
An injury, no matter how slight, should never go unattended. Always obtain first aid or medical attention
immediately.
OPERATING PRECAUTIONS
Always wear safety glasses.
Keep hands, clothing and tools clear of the evaporator and condenser fans.
No workshouldbe performedon the unituntilall start-stop switchesare placed in the OFF position, and power
supply is disconnected.
Always work in pairs. Never work on the equipment alone.
In case of severe vibration or unusual noise, stop the unit and investigate.
MAINTENANCE PRECAUTIONS
Beware of unannounced starting of the evaporator and condenser fans. Do not open the unit cover before
turning power off.
Be sure power is turned off before working on motors, controllers, solenoid valves and electrical controls. Tag
circuit breaker and power supply to prevent accidental energizing of circuit.
Do not bypass any electrical safety devices, e.g. bridging an overload, or using any sort of jumper wires.
Problems with the system should be diagnosed, and any necessary repairs performed by qualified service
personnel.
When performing any arc welding on the unit, disconnect all wire harness connectors from the modules in the
control box. Do not remove wire harness from the modules unless you are grounded to the unit frame with a
static-safe wrist strap.
In case of electrical fire, open circuit switch and extinguish with CO2(never use water).
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
Safety--1

SPECIFIC WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING
Be sure to observe warnings listed in the safety summary in the front of this manual before
performing maintenance on the hvac system
WARNING
Read the entire procedure before beginning work. Park the vehicle on a level surface, with
parking brake applied. Turn main electrical disconnect switch to the off position.
WARNING
Do Not Use A Nitrogen Cylinder Without A Pressure Regulator
WARNING
Do Not Use Oxygen In Or Near A Refrigeration System As An Explosion May Occur.
WARNING
The Filter-drier May Contain Liquid Refrigerant. S lowly Loosen The Connecting Nuts And
AvoidContactWithExposedSkinOrEyes.
CAUTION
The AC430 Rooftop Systems has R134a serviceport couplings installed on the compressor and
on the unit piping.
CAUTION
To prevent trapping liquid refrigerant in the manifold gauge set be sure set is brought to
suction pressure before disconnecting.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
Safety--2
SECTION 1
DESCRIPTION
1.1 INTRODUCTION
This manual contains Operating Instructions,
Service Instructions and Electrical Data for the
Model 68AC430 Air Conditioning and Heating
equipment furnished by Mobile Climate Control as
showninTable1-1.
Model 68AC430 systems consists of a Rooftop unit
containing the condensing section, the evaporator
section and engine compartment mounted
compressor(s). To complete the system, the air
conditioning and heating equipment interfaces with
an optional drivers evaporator (dash-air), electrical
cabling, refrigerant piping, engine coolant piping (for
heating), duct work and other components
furnishedby Mobile Climate Control and/or the bus
manufacturer.
Additional support manuals are shown in Table 1-2.
Operation of the unit is controlled automatically by
an electronic thermostat. The controls maintain the
vehicle'sinterior temperature at the desired set point.
Table 1-1 68AC430 Models
Model Voltage Controller With Heat Dual Loop Single Loop Roof Radius
68AC430-100 12 VDC BT324 Yes X 4.6M
68AC430-100-2 12 VDC BT324 No X 4.6M
68AC430-100-4 12 VDC BT324 Yes X 4.6M
68AC430-100-5 12 VDC BT324 No X 4.6M
68AC430-100-6 12 VDC BT324 Yes X 7.8M
68AC430-100-7 12 VDC BT324 No X 7.8M
68AC430-100-8 * 12 VDC BT324 No X 7.8M
Table 1-2 Additional Support Manuals
MANUAL NUMBER EQUIPMENT COVERED TYPE OF MANUAL
T-353PL 68AC-430-100 Service Parts List
* Denotes Special Packaging
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
1--1
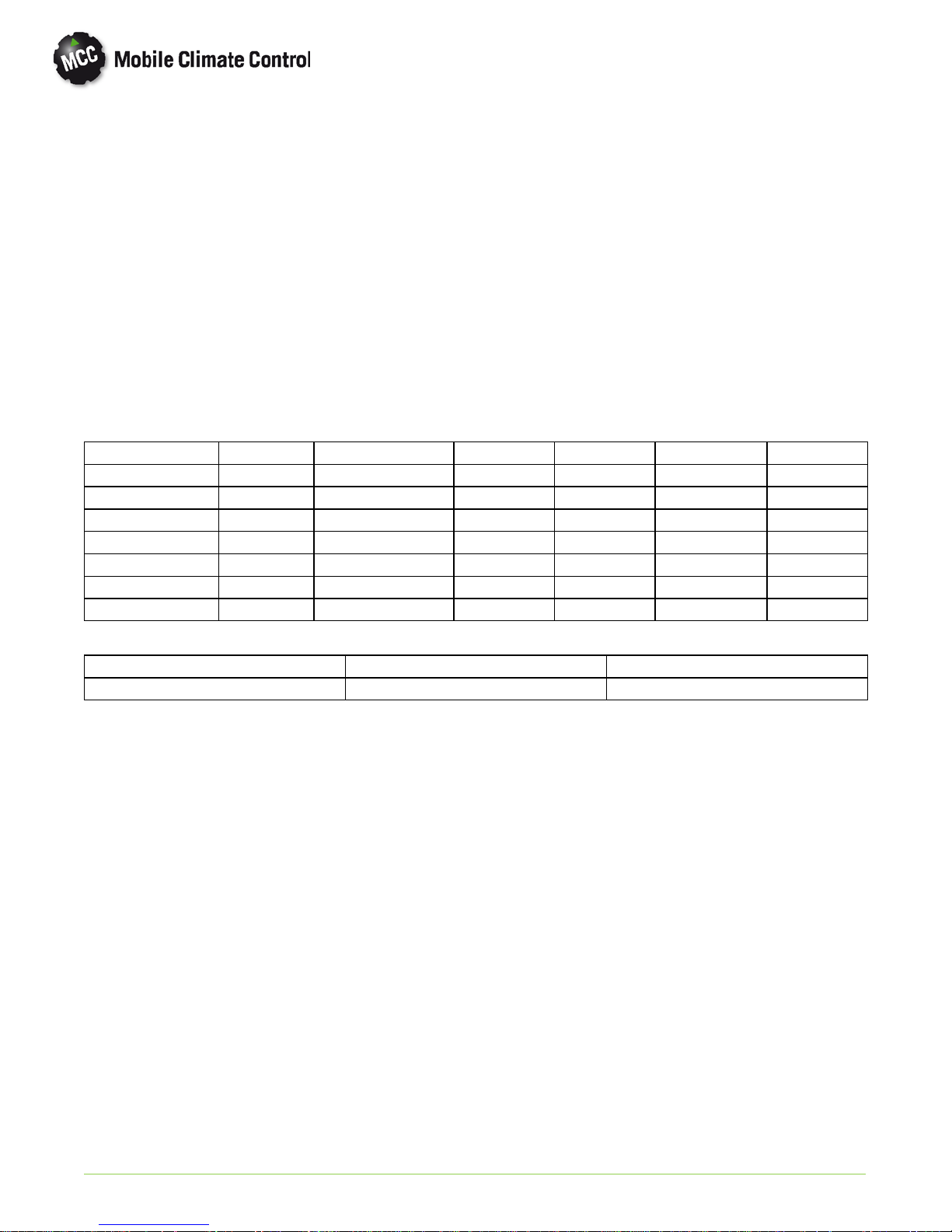
1.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
1.2.1 Rooftop Unit
The rooftop unit includes the condenser section and the evaporator section (See Figure 1-1).
Evaporator Section
Figure 1-1 AC430 Rooftop Unit
1.2.2 Condensing Section
The condensing section includes the condenser
coils, two (2)fan and mot or assemblies, receiver,
filter-drier and filter-drier service valves.
The condenser coils provide heat transfer surface for
condensing refrigerant gas at a high temperature and
pressure into a liquid at high temperature and
pressure. The condenser fans circulate ambient air
across the outside of the condenser tubes at a
temperature lower than refrigerant circulating inside
the tubes; this results in condensation of the
refrigerant into a liquid. The receiver collects and
stores liquid refrigerant. The receiver is also fitted
with a pressure relief valve which protects the system
from unsafe high pressure conditions. The
filter-drier removes moisture and debris from the
liquid refrigerant before it enters the thermostatic
expansion valve in the evaporator assembly. The
service valves enable isolation of the filter-drier for
service.
Condenser Section
1.2.3 Evaporator Section
The evaporatorsection includesthe evaporatorcoils,
two (2) single-shaftedblower/motor assemblies,two
(optional) heater coil assemblies, a thermostatic
expansion valve and condensate drain connections.
The evaporator coils provide heat transfer surface
for transferring heat from air circulating over the
outside of the coil to refrigerant circulating inside the
tubes; thus providing cooling. The heating coils (if
equipped) provide a heat transfer surface for
transferring heat from engine coolant water
circulating inside the tubes to air circulating over the
outside surface of the tubes, thus providing heating.
The fans circulate the air over the coils. The air filters
remove dirt particles from the air before it passes
over the coils. The thermostatic expansion valve
meters the flow of refrigerant entering the
evaporator coils. The heat valve controls the flow of
engine coolant to the heating co ils upon receipt of a
signal from the controller. The condensate drain
connections provide a means for connecting tubing
for disposing of condensate collected on the
evaporator coils during cooling operation.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
1--2
1.2.4 BT-324 Microprocessor
1.4 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS - MOTORS
This BT-324 controller has three (3) modes, Auto,
Vent (Cycle clutch type) and Heat.
In the auto mode the compressor is energized while
the evaporator and condenser fans are operated to
providerefrigerationas required. The compressor(s)
capacity is matched to the bus requirements. Once
interior temperature reaches the desired set po int,
the compressor(s) is de-energized.
In the heat mode the heat valves are opened to allow
a flow of engine coolant through the heat coils
located in the evaporator section. The evaporator
fans operate to circulate air over the heat coils in the
same manner as the cooling mode.
1.3 REFRIGERATION SYSTEM COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS
a. Refrigerant Charge R-134a (Approximate)
NOTE
Refrigerant charge will depend on hose
lengths and diameters; or if there is an InDash unit (front evaporator). The following
should only be used as a guideline.
AC430 Single Loop TM-21 Compressor
11 Pounds (5 kg)
b. Compressors
Compressor
Weight, (Dry) 7.5 Lbs. (3.4 kg)
Oil Charge 6.1 Oz. (180 cc) PAG
c. Thermostatic Expansion Valves:
TDEN 5.8 TR
Superheat Setting Factory Set at 12°F(±1.8°F)
6.7°C (±1°C)
TGEN 4.5
Superheat Setting Factory Set at 7.2°F(4°C)
MOP70psig(4.8bar)
TM-21
a. Evaporator Blower/Motor
Evaporator Motor
Horsepower (kW) .375 (.28)
Full Load Amps (FLA) 20.7
Operating Speed
High(RPM)
Bearing Lubrication
b. Condenser Fan Motor
Condenser Motor
Horsepower (kW) 1/4 (.18)
Full Load Amps (FLA) @
13.5 VDC
Operating Speed
High(RPM)
Bearing Lubrication
c. Return Air Sensor
Input Range: -40 to 176° F(-40to80°C)
Output: 20K ohms at 77° F(25°C)
d. Ambient Sensor (location chosen by Installer)
Input Range: -40 to 302° F (-40 to 150°C)
Output: 20K ohms at 77° F(25°C)
Opens at: 25° F(10°C)
Closes at: 35° F(1.7°C)
Brushless
12 VDC
3250
Factory Lubricated
(additional grease not required)
Permanent Magnet
12 VDC
14.4
3222
Factory Lubricated
(additional grease not required)
1.5 SAFETY DEVICES
System components are protected from damage
caused by unsafe operating conditions with safety
devices. Safety devices with Mobile Climate Control
supplied equipment include high pressure switch
(HPS), low pressure switch (LPS), circuit breakers
and fuses.
d. High Pressure Switch (HPS)
Opens at: 360 ±10 psig (20.41 ±0.68bar)
Closes at: 280 ±10 psig (13.61 ±0.68bar)
e. Low Pressure Switch (LPS)
Opens at: 6 ±3psig (0.41 ±0.20 bar)
Closes at: 25 ±3psig(1.7±0.20 bar)
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
Normally Closed
Normally Open
a. Pressure Switches
High Pressure Switch (HPS)
During the air co nditioning cycle, compressor clutch
operation will automatically stop if the HPS switch
contacts open due to an unsafe operating condition.
Opening HPS contacts de-energizes the compressor
clutch shutting down the compressor. The high
pressure switch (HPS) is installed in the condenser
section.
1--3

Low Pressure Switch (LPS)
The low pressure switch is installedin the evaporator
section and opens on a pressure drop to shut down
the system when a low pressure condition occurs.
b. Fuses and Circuit Breakers
The Relay Board is p ro tected against high current by
an OEM supplied circuit breaker or fuse located in
the bus battery compartment (150 Amp for 12 VDC
systems). Independen t 20 Amp, 12 VDC fuses
protect each condenser motor. Independent 25
Amp, 12 VDC fuses protect each evaporator motor.
Output circuits are pro tected by additional 2,3,5 and
10 Amp fuses according to circuit loads. During a
high current condition, the fuse may open.
1.6 AIR CONDITIONING REFRIGERATION CYCLE
When air conditioning (cooling) is selected by the
controller, the unit operates as a vapor compression
system using R-134a as a refrigerant (See Figure 1-2
refrigerant flow diagram). The main components of
the system are the A/C compressor, air-cooled
condenser coils, receiver, filter-drier, th ermo static
expansion valve, liquid line solenoid valve (if
equipped), and evaporator coils.
The compressor raises the pressure and the
temperature of the refrigerant and forces it into the
condenser tub es. The condenser fan circulates
surrounding air (which is at atemperature lower than
the refrigerant) over the outside of the condenser
tubes. Heat transfer is established from the
refrigerant (inside the tubes) to the condenser air
(flowing over the tubes). The condenser tubes have
fins designed to improve the transfer of heat from
the refrigerant gas to the air; this removal of heat
causes the refrigerant to liquefy, thus liquid
refrigerant leaves the condenser and flows to the
receiver.
The refrigerant leaves the receiver and passes
through the receiver outlet/service valve, th rou gh a
filter-drier where a desiccant keeps t h e refrigerant
clean and dry.
From the filter-drier, the liquidrefrigerant then flows
through the liquid line to the sight-glass and then to
the thermostatic expansion valve. The thermal
expansion valvereduces pressure and t em p erature of
the liquid and meters the flow of liquid refrigerant to
the evaporator to obtain maximum use of the
evaporator heat transfer surface.
The low pressure, low temperature liquid that flows
into the evaporator tubes is colder than the air that is
circulated over the evaporator tubes by the
evaporator fans (fans). Heat transfer is established
from the evaporator air (flowing over the tubes) to
the refrigerant (flowing inside the tubes). The
evaporator tubes have aluminum fins to increase
heat transfer from the air to the refrigerant;therefore
the cooler air is circulated to the interior of the bus.
The transfer of heat from the air to the low
temperature liquid refrigerant in the evaporator
causes the liquid to vaporize. This low temperature,
low pressure vapor passes through the suction line
and returns to the compressor where the cycle
repeats.
1.7 HEATING CYCLE
Heating circuit (See Figure 1-2) components
furnished by Mobile Climate Control include the
heater cores and solenoid operated heat valves.
Components furnished by the bus manufacturer
may include a water temperature switch (WTS) and
boost water pump.
The controller automatically controls the heat valves
during the heating mode to maintain required
temperatures inside the bus. Engine coolant (glycol
solution) is circulated through the heating circuit by
the engine and an auxiliary boost water pump. When
the heat valve solenoids are energized, the valves will
open to allow engine coolant to flow through the
heater coils. The valves are normally closed so that if
a failure occurs, the system will be able to cool.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
1--4
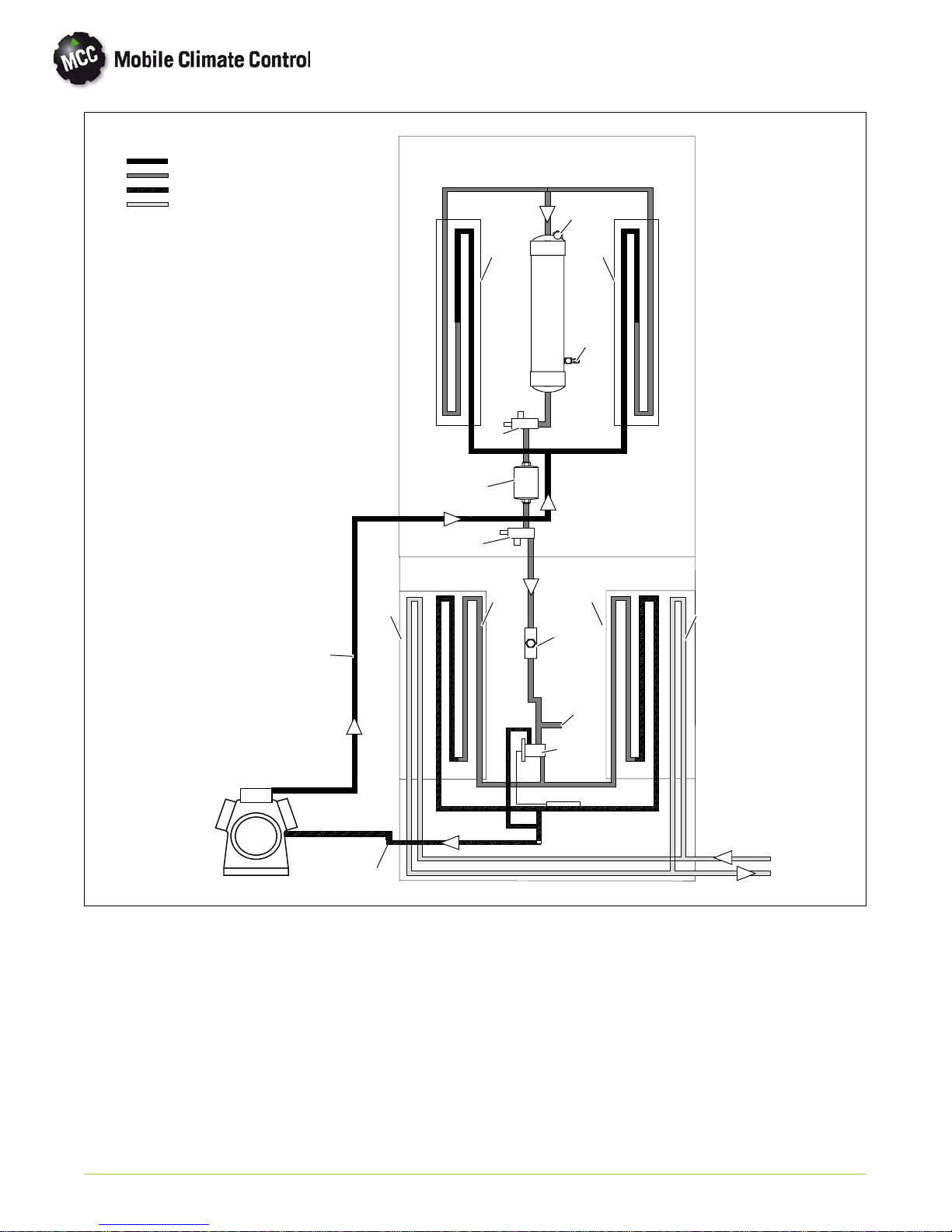
Discharge
Liquid
Suction
Coolant
14
11
11
13
3
10
12
CONDENSER
10
EVAPORATOR
8
77
8
2
6
9
Figure 1-2 Refrigerant/Heat Flow Diagram, AC430
1. Thermal Expansion Valve
2. Liquid Line Sight Glass
3. Fusible Plug
4. Dash Air Liquid Line
5. Suction Line
6. Discharge Line
7. Heater Coil
4
1
5
8. Evaporator Coil
9. Compressor
10. Service Valve
11. Condenser Coil
12. Filter-Drier
13. Receiver
14. Receiver Liquid Level Sight Glass
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
1--5
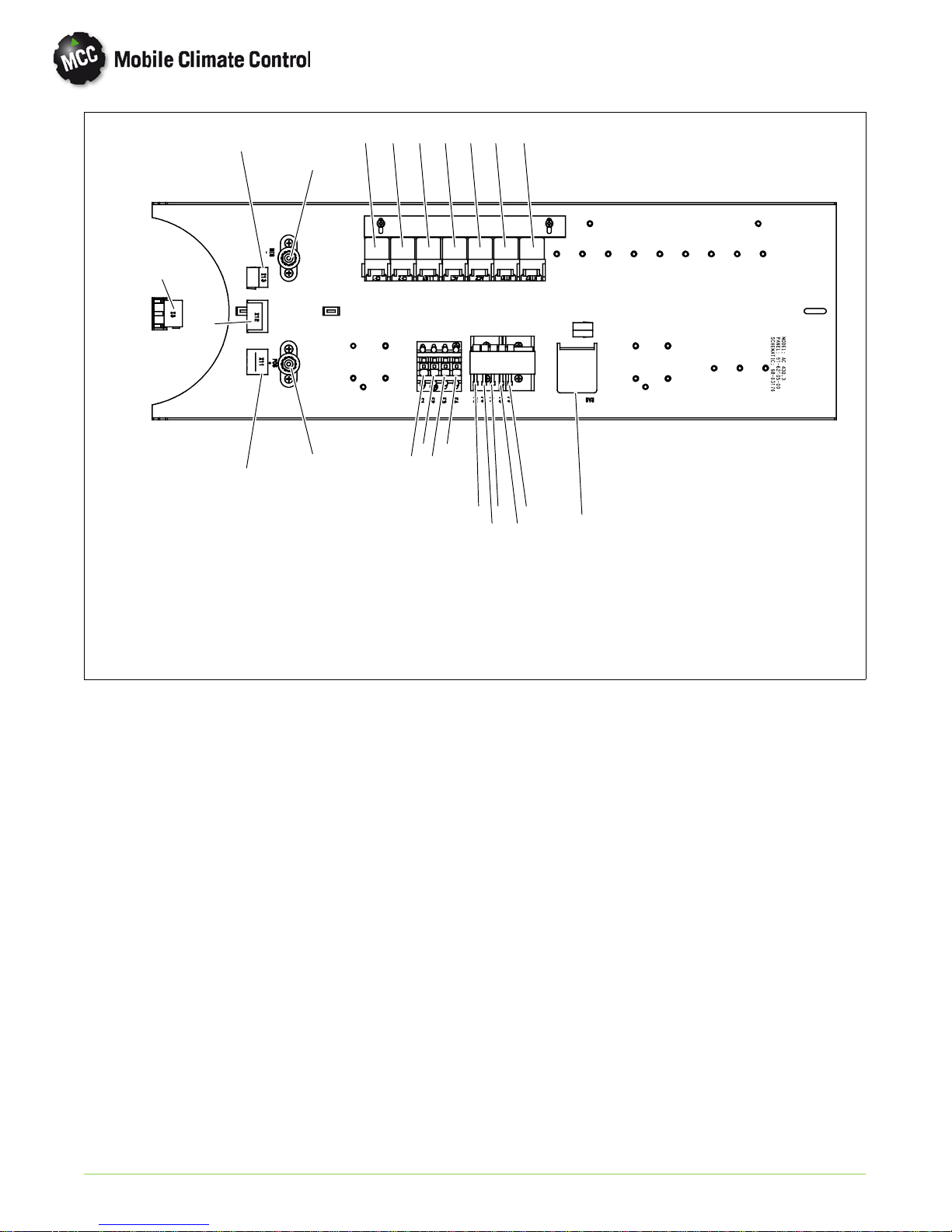
13
4
121110987
6
1
3
17
5
14
15
16
2
22
20
18
19
21
23
Figure 1-3 AC430 With BT324 Control Board
1. X3, Connector, Controller/Driver Display
2. X11, Connector, Evaporator Blower Motors
3. X12, Connector, Condenser Fan Motors/
High Pressure Switch
4. X13, Connector, Low Pressure Switch, Fresh
Air Flap
5. POS, 12VDCPower Connection
6. NEG, Ground Connection
7. CF1, Condenser Fan Relay 1
8. CF2, Condenser Fan Relay 2
9. LLSV, Liquid Line Solenoid Valve Relay
10. AC1, Condenser Fan On Relay
11. AC2, Condenser Fan On Relay
12. HTR1, Relay, Evaporator High Speed
13. HTR2, Relay, Evaporator Low Speed
14. F1, Fuse, Evaporator Motor
15. F2, Fuse, Evaporator Motor
16. F3, Fuse, Condenser Motor
17. F4, Fuse, Condenser Motor
18. F5, Fuse, LLSV
19. F6, Fuse, Condenser Fan Relay
20. F7, Fuse, Pressure Switch Relay
21. F8, Fuse, Heat Valve/ Pump Relay
22. F9, Fuse, Heat Valve/Floor Relay
23. RAS, Return Air Sensor
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
1--6

SECTION 2
OPERATION BT324 CONTROLLER
2.1 STARTING, STOPPING AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
The BT324 Digital Display is marked with
international symbols (See Figure 3-1).
2.1.1 Starting
a. If the engine is not running, start the engine.
b. When the 12VDC power is applied, the driver dis
play will illuminate and show return air set point.
Press the A/C key (Item 5 Figure 3-1) on the dis
play to trigger the start up sequence.
c. After the pre-trip inspection is completed, the
switches may be set in accordance with the desired
control modes.
1
6
Before starting, electrical power must be available
from the bus power supply.
A fuse located in the battery compartment passes
power for the clutch, evaporator and condenser
assemblies.
2.1.2 Stopping
Toggling the A/C key (Item 5 Figure 3-1) on the
display again will stop the system operation.
2.2 PRE-TRIP INSPECTION
After starting system, allow system to stabilize for ten
to fifteen minutes and check for the following:
a. Listen for abnormal noises in compressor or fan
motors.
b. Check refrigerant charge. (Refer to section 4.7.1 )
KEYS
1. Plus Key
2. Minus Key
3. Recirculate/Fresh Air Key
4. Blower Control Key
5. Automatic Climate Control (A/C)
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
5432
10987
Figure 3-1 BT324 Controller
LEDS
6. Display
7. Fresh Air Operation (Green)
8. Manual Blower Control 'ON' (Green)
9. Heating Mode (Green)
10. Malfunction Light (Red)
2--1

2.3 SEQUENCE OF OPERATION BT324
2.3.1 Function of Keys when “Engine On” and controller
active:
a. PlusKey - Increases interior temperature set point
by 1° per stroke or increasesmanual blower speed,
depending on displayed mode.
b. Minus Key - Decreases interior temp erature set
point by 1° per stroke or decreases manual b lower
speed, depending on displayed mode.
c. Recirculating Air/Fresh Air - Switches from Recir
culating Air to Fresh Air and vice-versa.
d. Blower Control - Switches on the manual blower
control.
e. Automatic Climate Con t ro l - Switches o n the Au
tomatic Temperature Control.
f. Temperature Indicator (Key2+Key3)- Shows
the inside temperature for 10 seconds. If pressed a
second time shows the outside temperature for 10
seconds (optional).
g. Reheat (optional) (Key3+Key5)- Starts Reheat
mode for 3 minutes (duration adjustable).
h. Controller Off (A/C Switch To Off) -Switches
off all control functions and the display.
NOTE
The following blower steps are disabled
when the automatic climate control is on:
2-, 3-step blower: Off
Continuously adjustable blower: Off
2.3.2 Illuminating Indications (Display)
With “Engine-On” and Controller active
2.4 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS BT324
When the engine is running, toggle the A/C Switch
to on to activate the Air Conditioning Unit.
2.4.1 Display
The temperature can be adjusted between 64° F(18°
C) and 82° F(28° C).
When the outside temperatures are below 35° F(2°
C) (adjustable parameter), the cooling function
remains disabled.
2.4.3 Ventilation
When the unit is operating in Automatic Climate
Control mode, the blower speed is controlled based
on the room temperature.
However, the blowers may be switched to manual
mode of operation by pressing the blower key.
Press the Plus o r Minus keys to select different
blower steps. The b lowers can not be switched OFF
when Automatic Climate Control is ON.
When Automatic Climate Control is OFF, the
blowers stop when the manual control is turned to
zero.
2.4.4 Reheat (optional)
The Reheat mode is used to remo ve air humidity and
to help defog the windshield. Press Key 3
(Recirculating Air/Fresh Air) and Key 5 (Automatic
Climate Control) at the same time to activate Reheat.
Heating and cooling will be energized on for 3
minutes (adjustable parameter). In addition, the
blowers are switched to maximum speed and the
fresh air flap is closed. At the end of the pre-set
duration of time, the functions return to the
previously selected settings.
Reheat mode is disabled with the outside
temperature is below 35° F(2° C) (adjustable
parameter), when the sensor is not installed, or when
there is a sensor failure.
2.4.5 Temperature Indication
Press key 2 (minus) and key 3 (Recirculating
Air/Fresh Air) at the same time to display the inside
temperature for 10 seconds.
Optionally, the outside temperature may be
displayed when pressing the keys a second time.
A sensor malfunction is displayed by “i --” or “o --”.
When the unit is ON, the display shows the interior
set point temperature. When selecting individual
functions, the display shows the corresponding
information for a short period of time. The display is
dark when the engine and control unit are OFF.
2.4.2 Interior Temperature Control
Press the Plus (1) or Minus (2) keys to set the desired
interior temperature.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
2.5 CHANGING BETWEEN °F (FAHRENHEIT) AND °C
(CELCIUS )
Procedures for changing the BT324 Controller
between Fahrenheit and Celsius is as follows:
a. Engine “OFF” & Ignition “ON”.
b. Press Key 1 (plus) an d Key 2 (minus) at the same
time until the display shows the word “Code”.
2--2

NOTE
After the display shows the word “Code”
you have 5 seconds to enter the correct ac
cess code.
c. Press Key 1 (Plus Key) one time and release.
e. Press Key 4 (blower control) one time and release.
The display will show the mode “Fah” for
temperatures in °F or the mode “Cel” for
temperatures in °C.
f. Press Key 1 (plus) or Key 2 (minus) to change the
temperature mode.
d. Press Key 3 (Recirculating Air/Fresh Air) one
time and release.
g. Press Key 5 (automatic climate control) one time
to end the program.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
2--3

SECTION 3
TROUBLESHOOTING
Table 3-1 General System Troubleshooting Procedures
INDICATION -
TROUBLE
POSSIBLE CAUSES
REFERENCE
SECTION
3.1 System Will Not Cool
Compressor will not run Drive-Belt loose or defective
Clutch coil defective
Clutch malfunction
Compressor malfunction
Electrical malfunction Coach power source defective
Circuit Breaker/safety device open
Check
Check/Replace
Check/Replace
See Table 1-2
Check/Repair
Check/Reset
3.2 System Runs But Has Insufficient Cooling
Compressor Drive-Belt loose or defective
Compressor valves defective
Refrigeration system Abnormal pressures
No or restricted evaporator air flow
Expansion valve malfunction
Restricted refrigerant flow
Low refrigerant charge
Service valves partially closed
Safety device open
Restricted air flow No evaporator air flow or restriction 3.5
Heating system Heat valve stuck open 3.7
Check
See Table 1-2
3.3
3.5
3.6
4.10
4.7
Open
1.5
3.3 Abnormal Pressures
High discharge pressure Refrigerant overcharge
Low discharge pressure Compressorvalve(s)wornorbroken
High suction pressure Compressorvalve(s)wornorbroken See Table 1-2
Low suction pressure Suction service valve partially closed
Suction and discharge pressures tend
to equalize when system is operating
Noncondensable in system
Condenser motor failure
Condenser coil dirty
Low refrigerant charge
Filter-drier inlet valve partially closed
Filter-drier partially plugged
Low refrigerant charge
Expansion valve malfunction
Restricted air flow
Compressor valve defective See Table 1-2
4.7.1
Check
Check
Clean
See Table 1-2
4.7
Open
Check/Open
4.10
4.7
3.6
3.5
3.4 Abnormal Noise Or Vibrations
Compressor Loose mounting hardware
Worn bearings
Worn or broken valves
Liquid slugging
Insufficient oil
Clutch loose, rubbing or is defective
Drive-Belt cracked, worn or loose
Dirt or debris on fan blades
Check/Tighten
See Table 1-2
SeeTable 1-2
3.6
1.3
Repair/Replace
Adjust/Replace
Clean
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
3--1

Table 3-1 General System Troubleshooting Procedures - Continued
INDICATION -
TROUBLE
POSSIBLE CAUSES
REFERENCE
SECTION
3.4 Abnormal Noise Or Vibrations - Continued
Condenser or evaporator fans Loose mounting hardware
Defective bearings
Blade interference
Blade missing or broken
Check/Tighten
Replace
Check
Check/Replace
3.5 No Evaporator Air Flow Or Restricted Air Flow
Air flow through coil blocked Coil frosted over
Dirty coil
Dirty filter
No or partial evaporator air flow Motor(s) defective
Motor brushes defective
Evaporator fan loose or defective
Fan damaged
Return air filter dirty
Icing of coil
Fan relay(s) defective
Safety device open
Fan rotation incorrect
Defrost coil
Clean
Clean/Replace
Repair/Replace
Replace
Repair/Replace
Repair/Replace
Clean/Replace
Clean/Defrost
Check/Replace
1.5
Check
3.6 Expansion Valve Malfunction
Low suction pressure with high super
heat
Low superheat and liquid slugging in
the compressor
Side to side temperature difference
(Warm Coil)
Low refrigerant charge
Wax, oil or dirt plugging valve orifice
Ice formation at valve seat
Power assembly failure
Loss of bulb charge
Broken capillary tube
Bulb is loose or not installed.
Superheat setting too low
Ice or other foreign material holding valve open
Wax, oil or dirt plugging valve orifice
Ice formation at valve seat
Power assembly failure
Loss of bulb charge
Broken capillary
4.7
Check
4.6
Replace
Replace
4.14
4.14
4.14
Check
4.6
Replace
Replace
4.14
3.7 Heating Malfunction
Insufficient heating Dirtyorpluggedheatercore
Coolant solenoid valve(s) malfunctioning or plugged
Low coolant level
Strainer(s) plugged
Hand valve(s) closed
Water pumps defective
Auxiliary Heater malfunctioning.
No Heating Coolant solenoid valve(s) malfunctioning or plugged
Controller malfunction
Pump(s) malfunctioning
Safety device open
Continuous Heating Coolant solenoid valve stuck open 4.11
Clean
Check/Replace
Check
Clean
Open
Repair/Replace
Repair/Replace
Check/Replace
Replace
Repair/Replace
1.5
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
3--2

SECTION 4
SERVICE
WARNING
Be sure to observe warnings listed in the safety summary in the front of this manual before per
forming maintenance on the hvac system
WARNING
Read the entire procedure before beginning work. Park the coach on a level surface, with park
ing brake applied. Turn main electrical d isconnect switch to the off position.
NOTE
To avoid damage to the earth's o zone layer, use a refrigerantreco very system whenever remo ving refrig
erant. When working with refrigerants you must comply with all local government environmental laws.
4.1 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
SYSTEM
ON OFF
a. Daily Maintenance
X
b. Weekly Inspection
X
c. Monthly Inspection and Maintenance
Pre-trip Inspection - after starting
X
Check tension and condition of drive belts.
X
Perform daily inspection
X
Check condenser, evaporator coils and air filters for cleanliness
X
Check refrigerant hoses, fittings and component connections for leaks
Feel filter-drier for excessive temperature drop across drier
X
Perform weekly inspection and maintenance
X
Clean evaporator drain pans and hoses
X
Check wire harnesses for chafing and loose terminals
X
Check fan motor bearings
X
Check compressor mounting bolts for tightness
SYSTEM
4.2 REMOVING COVER
To remove the cover do the following:
1. Turn all the 1/4 turn cam locks counterclockwise.
2. Using two people carefully grasp the cover under
the bottom edge and lift up.
REFERENCE
SECTION
2.2
None
See above
None
4.5
4.10
See above
None
Replace/Tighten
None
None
4.3 MANIFOLD GAUGE SET
A manifold gauge set can be used to determine
system operating pressures, add charge, equalize or
evacuate system.
When the suction pressure hand valve is front seated
(turned all the way in), th e suction (low) pressure can
be read. When the discharge pressure hand valve is
front seated, discharge (high) pressure can be read.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--1

When both valves are open (turned
counterclockwise),high pressure vapor willflow into
the low side. When only the low pressure valve is
open, the system can be charged or evacuated.
CAUTION
the manifold gauge set. Mid-seat both hand valves on
the manifold gauge set and allow the pressure in the
manifold gauge set to be drawn down to low side
pressure. This returns any liquid that may be in the
high side hose to the system.
The AC430 Rooftop Systems has R134a
service port couplings installed on the
unit piping.
4.3.1 Installing R-134a Manifold Gauge/Hose Set
An R-134a manifold gauge/hose set with self-sealing
hoses is pictured in Figure 4-1. The manifold
gauge/hose set is available from Mobile Climate
Control. (Mobile Climate Control P/N 07-00294-00,
which includes items 1 through 6, Figure 4-1). To
perform service using the manifold gauge/hose set,
do the following:
a. Preparing Manifold Gauge/Hose Set for use.
1. If the manifold gauge/hose set is new or was ex
posed to the atmosphere it will need to be evacu
ated to remove contaminants and air as follows:
2. Back-seat (turn counterclockwise) both field ser
vice couplers (see Figure 4-1) and mid-seat both
hand valves.
3. Connect the yellow hose to a vacuum pump and
an R-134a cylinder.
CAUTION
To prevent trapping liquid refrigerant in
the manifold gauge set be sure set is
brought to suction pressure before dis
connecting.
2. Back-seat the low side field service coupler and
front-seat both manifold set hand valves. Back
seat the in-line system access valves(if applicable).
Remove the coup lers from the in-line access
valves.
3. Install both in-line access valve caps.
SUCTION
PRESSURE
GAUGE
OPENED
(Backseated )
HAND VALVE
1.
DISCHARGE
PRESSURE
GAUGE
CLOSED
(Frontseated)
HAND VALVE
4. Evacuate to 10 inches of vacuum and then charge
with R134a to slightly positive pressure of 1.0
psig.
5. Front-seat both manifold gauge set hand valves
and disconnect from cylinder. The gauge set is
now ready for use.
b. Connecting the Manifold Gauge Gauge/Hose
Set.
To connect the manifold gauge/hose set for reading
pressures, do the following:
1. Connect the field service couplers (see
Figure 4-1) to the high and low in-line service ports.
2. Turn the field service coupling knobs clockwise,
which will open the system to the gauge set.
3. Read the system pressures.
c. Removing the Manifold Gauge Set.
1. While the compressor is still ON, backseat (coun
terclockwise) the high side field service coupler on
To Low Side
Access Valve
BLUE
6.
Blue Knob
3.
2.
4.
To Refrigerant Tank
or Vacuum Pump
2.
3.
YELLOW
Figure 4-1 Manifold Gauge Set (R-134a)
1. Manifold Gauge Set
2.. Hose Fitting (0.5-16 Acme)
3.. Refrigeration and/or Evacuation Hose
. (SAE J2196/R-134a)
4.. Hose Fitting w/O-ring (M14 x 1.5)
5.. High Side Field Service Coupling
6.. Low Side Field Service Coupling
To High Side
Access Valve
3.
RED
4.
5.
Red Knob
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--2

4.4 REMOVING THE REFRIGERANT CHARGE
NOTE
To avoid damage to the earth's ozone layer,
use a refrigerant recovery system whenever
removing refrigerant.
NOTE
It must be emphasized that only the correct
refrigerant should be used to pressurize the
system. Use of any other refrigerant will con
taminate the system, and require additional
evacuation.
4.4.1 Removing Entire System Charge
To remove the entire refrigerant charge, do the
following:
a. Connect a manifold gauge set to the system as
showninFigure4-2.
b. Con n ect a reclaimer to the center manifold gauge
set connection.
c. Recover refrigerant in accordance with reclaimer
manufacturers instructions.
1.
To Compressor
7.
D
2.
6.
3.
S
4.
5.
Figure 4-2 In-Line Service Connections
1. Discharge Service
Port
2. Suction Service
Port
3. Manifold Gauge
Set
4. Vacuum Pump
5. Reclaimer
6. Refrigerant Cylinder
7. Thermistor Vacuum
Gauge
a. Ensure filter drier service and solenoid valves(if
equipped) are open.
1. Filter drier service valves shou ld be back seated.
b. If system is without refrigerant, charge system
with refrigerant vapor to build up pressure be
tween 20 to 30 psig (1.36 to 2.04 bar).
c. Add sufficient nitrogen t o raise system pressure to
150 to 200 psig (10.21 to 13.61 bar).
d. Check for leaks. The recommended pro cedure for
finding leaks in a system is with an electronic leak
detector. Testing joints with soapsudsissatisfacto
ry only for locating large leaks.
e. Remove test gas and replace filter-drier.
f. Evacuate and dehydrate the system. (Refer to
paragraph 4.6.)
g. Charge the unit. (Refer to paragraph 4.7.)
4.6 EVACUATION AND DEHYDRATION
4.6.1 General
The presence of moisture in a refrigeration system
can have many undesirable effects. The most
common are copper plating, acid sludge formation,
“freezing-up” of metering devices by free water, and
formation of acids, resulting in metal corrosion. An
evacuation should take place after a system repair
(replacement of filter drier. expansion valve,
solenoid valve, etc).
4.6.2 Preparation
NOTE
Usinga compound gauge(manifold gauge) for
determination of vacuum level is not recom
mended because of its inherent inaccuracy.
4.5 REFRIGERANT LEAK CHECK
A refrigerant leak check should always be performed
after the system has been opened to replace or repair
a component.
To check for leaks in the refrigeration system,
perform the following procedure:
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
a. Evacuate and dehydrate only after pressure leak
test. (Refer to p aragraph 4.5)
b. Essential tools to properly evacuate and dehydrate
any system include a good vacuum pump with a
minimum of 5 cfm (8.5 m3/hr) volume displace
ment, (MCC P/N 07-00176-11), and a good mi
cron gauge (MCC P/N 07-00414-00).
4--3

c. Keep the ambient temperature above 60°F
(15.6°C) to speed evaporation o f moisture. If am
bient temperature is lower than 60°F (15.6°C),ice
may form before moisture removal is complete.
f. When correct charge has been added (refer to
paragraph1.3, refrigerantspecifications), close cyl
inder valve and front seat manifold discharge
valve.
4.6.3 Procedure for Evacuation and Dehydrating System
a. Remove refrigerant using a refrigerant recovery
system. Refer to paragraph 4.4.1
b. The recommended method is connecting 3/8”
OD refrigerant hoses designed for vacuum service
asshowninFigure5-1.
c. Make sure vacuum pump valve is open.
d. Start vacuum pump. Slowly open valves halfway
and then open vacuum gauge valve.
e. Evacuate unit until vacuum gauge indicates 500
microns Hg vacuum. Close gauge valve, vacuum
pump valve, and stop vacuum pump.
f. Wait five minutes to see if vacuum holds.
g. Charge system. Refer to paragraph 4.7.2
4.7 ADDING REFRIGERANT TO SYSTEM
4.7.1 Checking Refrigerant Charge
The following conditions must be met to accurately
check the refrigerant ch arge.
g. Prepare the cylinder as required to allow vapor
charging. Backseat the manifold suction valve and
charge vapor until the correct charge has been
added. Close cylinder valve and front seat suction
manifold set.
h. Check charge level in accordance with the proce
dures of paragraph 4.7.1.
4.8 CHECKING FOR NONCONDENSIBLES
To check for non co ndensibles, proceed as follows:
a. Stabilize system to equalize pressure between the
suction and discharge side of the system.
b. Check temperature at the condenser and receiver.
c. Check pressure at the discharge (in-line) service
port.
d. Check saturation pressure as it corresponds to the
condenser/receiver temperature. See tempera
ture-Pressure chart Table Table 4-1 for R134a.
a. Bus engine operating at high idle.
b. Unit operating in cool mode for 15 minutes.
c. Compressor discharge pressure at least 150 psig
(10.21 bar). (It may be necessary to block condens
er air flow to raise discharge pressure.)
d. Under the above conditions, the system is proper
ly charged when the float ball in the receiver tank
sight glass is showing ½ to ¾ level.
4.7.2 Adding Full Charge
a. Install manifold gauge set at the in-line suction and
discharge service ports.
b. Evacuate and dehydrate system. (Refer to para
graph 4.6)
c. Place appropriate refrigerant cylinder on scales.
Prepare to charge liquid refrigerant by connecting
charging hose from container to center connec
tion on gage manifold. Purge air from hoses.
d. Note weight of refrigerant and cylinder.
e. Open cylinder valve, backseat discharge valve on
gauge manifold and allow liquidrefrigerant to flow
into the high side of the system
e. If gauge reading is 3 psig or more than the calcu
lated P/T pressure in step d., non-condensables
are present.
f. Remove refrigerant using a refrigerant recovery
system.
g. Evacuate and dehydrate the system. (Refer to
paragraph 4.6.)
h. Charge the unit. (Refer to paragraph 4.7.2.)
4.9 CHECKING AND REPLACING HIGH OR LOWPRESSURE CUTOUT SWITCH
4.9.1 Replacing High Or Low Pressure Switches
a. The high and low pressure switches are equipped
with Schreader valves to allow removal and instal
lation without recovering the refrigerant charge.
b. Disconnect wiring from defective switch.
c. Installnew cutout switch after verifying switch set
tings.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--4

4.9.2 Checking High Pressure Switches
WARNING
Do not use a nitrogen cylinder without a
pressure regulator
WARNING
Do n o t use oxygen in or near a refrigeration
system as an explosion may occur.
a. Disconnect wiring and remove switch from sys
tem.
b. Connect an ohmmeter across switch terminals. If
the switch is good, the ohmmeter will indicate no
resistance, indicating that the contacts are closed.
c. Connect switch to a cylinder of dry nitrogen.
(SeeFigure 4-3).
1.
4.
2.
5.
point, the switch contacts should close, indicating
no resistance (continuity) on the ohmmeter.
g. Replace switch if it does not function as outlined
above.
4.9.3 Checking Low Pressure Switches
a. Disconnect wiring and remove switch from sys
tem.
b. Connect an ohmmeter across switch terminals. If
the switch is good, the ohmmeter will indicate an
infinite reading on an ohmmeter (no continuity).
c. Connect switch to a cylinder of dry nitrogen.
(SeeFigure 4-3).
d. Set nitrogen pressure regulator higher than switch
cutout setting. (refer to paragraph 1.3.)
e. Open cylinder valve. Slowly open the regulator
valve to increase the p ressure until it reaches cut in
point. The switch should close, which is indicated
by no resistance on an ohmmeter (continuity).
f. Close cylinder valve and release pressure through
the bleed-off valve. As p ressure drops to cut-out
point, the switch contacts should open, indicating
infinite resistance (no continuity) on the ohmme
ter.
4.10 FILTER-DRIER
6.
3.
Figure 4-3 Checking High Pressure Switch
1. Cylinder Valve and Gauge
2. Pressure Regulator
3. Nitrogen Cylinder
4. Pressure Gauge (0 to 400 psig = 0 to 27.22 bar)
5. Bleed-Off Valve
6. 1/4 inch Connection
d. Set nitrogen pressure regulator higher than switch
cutout setting. (refer to paragraph 1.3.)
e. Open cylinder valve. Slowly open the regulator
valve to increase the pressure until it reaches cut
out point. The switch should open, which is indi
cated by an infinite reading on an ohmmeter (no
continuity).
f. Close cylinder valve and release pressure through
the bleed-off valve. As pressure drops to cut-in
1.
2. 3. 4.
3.
2.
6.
5.
Figure 4-4 Filter-Drier Removal
1. Filter--Drier Inlet
Service Valve
2. Valve Service Port
3. Flare Nut
4. Filter--Drier
5. Liquid Line
Solenoid Valve
6. Filter--Drier Outlet
Service Valve
4.10.1 To Check Filter-Drier
The filter-drier (See Figure 4-4) mu st be ch anged if
the system has been opened, (for any reason), or the
filter drier is partially restricted. Restriction can be
identified by either the outlet frosting or a
temperature difference between the inlet and outlet.
4.10.2 To Replace Filter-Drier Assembly
Filter D rier replacement can be accomplished by
performing the following procedure.
a. Turn the driver's A/C switch to “OFF” position.
b. Front seat the filter-drier service valves on both
sides of the filter drier.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--5

c. Connect manifold gauge set and reclaimer to the
filter drier service valve access p o rts and reclaim
any refrigerant contained in the filter drier.
d. Place a new filter-drier near the unit for immediate
installation.
WARNING
The filter-drier may contain liquid refrig
erant. Slowly loosen the connecting nuts
and avoid contact with exposed skin or
eyes.
e. Using t wo open end wrenches, slowly crack open
the connecting nuts on each side of the filter-drier
assembly. Remove the filter-drier assembly.
f. Remove seal caps from the new filter-drier. Apply
a light coat of mineral oil to the filter-drier connec
tions.
g. Assemble th e new filter-drierto lines ensuring that
the arrow on the body of the filter-drier points in
the direction of the refrigerant flow (refrigerant
flows from the receiver to the evaporator). Finger
tighten the connecting nuts.
h. Tighten filter-drier connecting nuts using two
open end wrenches.
i. Connect vacuum pump to manifold gauge set and
evacuate filter to 500 microns. Close gauge valve,
vacuum pump valve, and stop vacuum pump.
j. Backseat (fully close) b o th service valve ports and
replace valve caps.
k. Remove Gauges.
4.11 SERVICING THE HEAT VALVE
The heat valve (Figure 4-5) requires no maintenance
unless a malfunction to the internal parts or coil
occurs. This may be caused by foreign material such
as: dirt, scale, or sludge in the coolant system, or
improper voltage to the coil.
NOTE
The OEM supplied heating (hot water) Sole
noid Valve is normally located outside of the
AC430 rooftop air conditioning system.
There are only three possiblevalvemalfunctions:coil
burnout, failure to open, or failure to close.
Coil burnout may be caused by the following:
1. Improper voltage
2. Continuous over-voltage, more than 10% or Un
der-voltageofmorethan15%.
3. Incomplete magnetic circuit due to the omission
of the coil housing or plunger.
4. Mechanical interference with movement of plung
er which m ay be caused by a deformed enclosing
tube.
Failure to open may be caused by the following:
1.Coil burned out or an open circuit to coil connec
tions.
2. Improper voltage.
3. Torn diaphragm.
4. Defective plunger or deformed valve b o dy assem
bly.
Failure to close may be caused by the following:
1. Defective plunger or deformed valve body as
sembly.
2. Foreign material in the valve.
3. Torn diaphragm.
4.11.1 Coil Replacement
a. It is not necessary to drain the coolant from the
system.
b. Place main battery disconnect switch in OFF posi
tion and lock.
c. Disconnect wire leads to coil.
d. Remove coil retaining screw and nameplate.
e. Lift burned-out coil from enclosing tube and re
place.
f. Connect wire leads and test operation.
4.11.2 Internal Part Replacement
a. Disconnect system from bus battery.
b. Open the vent fitting at the top of the outlet head
er of the heater coil.
c. Drain coil by opening the drain-cock on the inlet
tube.
d. Disassemble valve and replace defective parts.
e. Assemble valve, refill and bleed coolant lines.
4.11.3 Replace Entire Valve
a. Disconnect system from bus battery.
b. Drain coolant from lines as previously described
and disconnect hoses to valve .
c. Disconnect wire leads to coil.
d. Remove valve assembly from bracket.
e. Install new valve and re-connect hoses. It is not
necessary to disassemble the valve when installing.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--6

f. Refill and bleed coolant lines.
f
f
g. Connect wire leads and test operation.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
TO LIQUID LINE
TO FILTER/DRYER
Service Valve
Frontseated
(clockwise)
SERVICE
PORT
Service Valve
Backseated
(counterclockwise)
VALVE CAP
VALVE
STEM
Figure 4-5 Heat Valve
1. Coil Retaining Screw
2. Nameplate
3. Coil Housing
Assembly
4. Enclosing Tube &
Bonnet Assembly
5 . K i c k --- O
6. Plunger
7. Closing Spring
8. D iaphra gm
9. O ---Ring
10. Valve Body
Spring
4.12 SERVICE VALVES
The filter/drier (High Side) service valves
(Figure 4-6) are provided with a double seat and a
gauge port, which allows servicing of the filter drier
assembly.
Turning the valvestem counterclockwise (all the way
out) will backseat the valve to open the line to the
system and close off the gauge port. In normal
operation, the valve is backseated to allow full flow
through the valve. The valve should always be
backseated before removing the service port cap.
Turning the valve stem clockwise (all the way
forward) will frontseat the valve to isolate the system
and open the service port.
Figure 4-6 Service Valve R134a (High Side)
4.13 REPLACING RETURN AIR FILTERS
The return air filters are located behind the return air
grill, inside the vehicle.
The filters shou ld be checked for cleanliness
periodically depending on operating conditions. A
dirty filter will restrict air flow over the evaporator
coil which may cause insufficient cooling or heating
and possiblefrost buildupon the coil. To remove the
filters, do the following.
a. Insure air conditioning system is in the off posi
tion.
b. Remove the return air grille with the filter-diffuser
assembly, by turning the six 1/4 turn fasteners
counterclockwise.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--7

Composite Frame
Return Air Filter
Figure 4-7 Return Air Grill Assembly
With Air Filter Showing
c. Remove diffuser from the bus composite frame.
Diffuser
Diffuser
Air Filter
Composite Frame
Figure 4-9
Filter, Diffuser and Composite Frame
g. Place filter and diffuser into composite frame, with
filter element down (See Figure 4-9).
Return Air Filter
Figure 4-8 Diffuser and Filter Element
d. Remove and replace the filter element.
e. Center diffuser on filter element.
f. Pull filter element appro ximately 1/4 inch over
ends of the diffuser.
Captive 1/4 Fasteners
Figure 4-10 Return Air Grill Assembly
With Diffuser And Composite Frame Showing
h. Insert filter-diffuser assembly into composite
frame on bus with the six captive 1/4 fasteners.
(See Figure 4-10)
i. Lock the six captive 1/4 turns in place by rotating
clockwise.
4.14 THERMOSTATIC EXPANSION VALVE
The thermostat expansion valve (Figure 4-11) is an
automatic device which maintains constant
superheat of the refrigerant gas leaving the
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--8

evaporator regardless of suction pressure. The valve
functions are: (a) automatic control of refrigerant
flow to match the evaporator load and (b)
prevention of liquid refrigerant entering the
compressor. Unless the valve is defective, it seldom
requires any maintenance.
1.
2.
j. Run the coach for approximately 30 minutes on
fast idle.
k.Check refrigerant charge. (Refer to 4.7.1)
4.14.2 Superheat Measurement
NOTE
All readings must be taken from the TXV
bulb location and out of the direct air stream.
3.
Figure 4-11 Thermostatic Expansion Valve
1.. Power Head Assembly
2.. Equalizer Connection
3.. Bulb
4.14.1 Valve Replacement
a. Recover and recycle refrigerant from the sys
tem.(refer to 4.4.1)
b. Remove insulation from expansion valve bulb.
(See Figure 4-11 and Figure 4-12.)
c. Loosen retaining straps holding bulb to suction
line and detach bulb from the suction line.
d. Loosen flare nuts on equalizer line and disconnect
equalizer line from the expansion valve.
e. Check, clean and remove any foreign material
from the valve body, valve seat and mating sur
faces. I f required, replace the valve.
NOTE
R-134a valves are adjustable. Valves are pre
setatthefactory.
f. The thermal bulb is installed below the center of
the suction line (four or eight o'clock position).
This area must be clean to ensure positive bulb
contact. Strap thermal bulb to suction line. Ensure
that retaining straps are tight and renew insulation.
g. Fasten equalizer line to the expansion valve.
h. Leak check the new valve (Refer to paragraph 4.5)
i. Evacuate and recharge the system. (Refer to para
graph 4.6.)
3.
2.
1.
4.
5.
Figure 4-12 Thermostatic Expansion Valve Bulb and
Thermocouple
1.. Suction Line
(section view)
2.. TXV Bulb Clamp
3.. Nut & Bolt (clamp)
4.. Thermocouple
5.. TXV Bulb (Shown
in the 4’clock
position)
a. Open top cover.
b. Remove Presstite insulation from expansion valve
bulb and suction line.
c. Loosen one TXV bulb clamp and make sure area
under clamp is clean.
d. Place temperature thermocouple in contact with
the suction tube and parallel to the TXV bulb, and
then secure loosened clamp making sure b o t h
bulb and thermocouple are firmly secured to suc
tion line. (See Figure 4-12). Reinstall insulation
around the bulb.
e. Connect an accurate low p ressure gauge to t h e low
pressure port.
f. Close top cover being careful to ro u te thermocou
ple sensing wire and gauge hose outside the unit.
g. Start bus and run on fast idle until unit has stabi
lized, about 20 to 30 minutes.
NOTE
When conducting this test, the suction pres
sure must be at least 6 psig (0.41 bar) below
the expansion valve maximum operating
pressure (MOP). Refer to paragraph 1.3 for
MOP.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--9

h. From the temperature/pressure chart, determine
the saturation temperature corresponding to the
evaporator outlet pressure.
i. Note the temperature of the suction gas at the ex
pansion valve bulb. Subtract the saturation tem
perature from this temperature. The difference is
the superheat of the suction gas.
j. The superheat may cycle from a low to high read
ing. Monitor the superheat taking readings every
3-5 minutes for a total of 5-6 readings. Calculate
the superheats, add the readings and divide by the
number of readings taken to determine average su
perheat. The superheat should be 12 ± 1.8°F.
k. If superheat is not within tolerance, replace the
valve.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--10

Table 4-1 R-134a Temperature - Pressure Chart
Temperature Vacuum
°F °C
“/hg cm/hg kg/cm@ bar
-40 -40 14.6 49.4 37.08 0.49
.35 .37 12.3 41.6 31.25 0.42
-30 -34 9.7 32.8 24.64 0.33
-25 -32 6.7 22.7 17.00 0.23
-20 -29 3.5 11.9 8.89 0.12
-18 -28 2.1 7.1 5.33 0.07
-16 -27 0.6 2.0 1.52 0.02
Temperature Pressure
°F °C
psig kPa kg/cm@ bar
-14 -26 0.4 1.1 0.03 0.03
-12 -24 1.2 8.3 0.08 0.08
-10 -23 2.0 13.8 0.14 0.14
-8 -22 2.9 20.0 0.20 0.20
-6 -21 3.7 25.5 0.26 0.26
-4 -20 4.6 31.7 0.32 0.32
-2 -19 5.6 36.6 0.39 0.39
0 -18 6.5 44.8 0.46 0.45
2 -17 7.6 52.4 0.53 0.52
4 -16 8.6 59.3 0.60 0.59
6 -14 9.7 66.9 0.68 0.67
8 -13 10.8 74.5 0.76 0.74
10 -12 12.0 82.7 0.84 0.83
12 -11 13.2 91.0 0.93 0.91
14 -10 14.5 100.0 1.02 1.00
16 -9 15.8 108.9 1.11 1.09
18 -8 17.1 117.9 1.20 1.18
20 -7 18.5 127.6 1.30 1.28
22 -6 19.9 137.2 1.40 1.37
24 -4 21.4 147.6 1.50 1.48
26 -3 22.9 157.9 1.61 1.58
Temperature Pressure
°F °C
psig kPa kg/cm@ bar
28 -2 24.5 168.9 1.72 1.69
30 -1 26.1 180.0 1.84 1.80
32 0 27.8 191.7 1.95 1.92
34 1 29.6 204.1 2.08 2.04
36 2 31.3 215.8 2.20 2.16
38 3 33.2 228.9 2.33 2.29
40 4 35.1 242.0 2.47 2.42
45 7 40.1 276.5 2.82 2.76
50 10 45.5 313.7 3.20 3.14
55 13 51.2 353.0 3.60 3.53
60 16 57.4 395.8 4.04 3.96
65 18 64.1 441.0 4.51 4.42
70 21 71.1 490.2 5.00 4.90
75 24 78.7 542.6 5.53 5.43
80 27 86.7 597.8 6.10 5.98
85 29 95.3 657.1 6.70 6.57
90 32 104.3 719.1 7.33 7.19
95 35 114.0 786.0 8.01 7.86
100 38 124.2 856.4 8.73 8.56
105 41 135.0 930.8 9.49 9.31
110 43 146.4 1009 10.29 10.09
115 46 158.4 1092 11.14 10.92
120 49 171.2 1180 12.04 11.80
125 52 184.6 1273 12.98 12.73
130 54 198.7 1370 13.97 13.70
135 57 213.6 1473 15.02 14.73
140 60 229.2 1580 16.11 15.80
145 63 245.6 1693 17.27 16.93
150 66 262.9 1813 18.48 18.13
155 68 281.1 1938 19.76 19.37
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
4--11

SECTION 5
ELECTRICAL
5.1 INTRODUCTION
conditioning units which are fitted with two (2)
double-shafted evaporator blower/motor
This section includes electrical wiring schematics.
The schematics shown in this section provides
information for the AC430 model rooftop air
UNIT CONTROLLER FIGURE NUMBERS
68AC430 BT324 Figure 5-1 Thru Figure 5-6
68AC430 (Electrical Panel 91-62105-00) BT324 Figure 5-7 Thru Figure 5-8
assemblies and two (2) condenser fan motors.
Figure 5-2 thru Figure 5-6 shows the BT324
controller used with the AC430 system.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
5--1

98--67037--00
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
5--2
Figure 5-2 Evaporator Motors
T-353 Rev. 01/2013

© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
5--3
Figure 5-3 Condenser Motors
98--67037--00
T-353 Rev. 01/2013

98--67037--00
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
5--4
Figure 5-4 BT324 Controls With (1) Compressor
T-353 Rev. 01/2013

© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
5--5
Figure 5-5 BT324 Control Circuit
98--67037--00
T-353 Rev. 01/2013

98--67037--00
Figure 5-6 AC430 With BT324 Control
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
5--6
T-353 Rev. 01/2013

Figure 5-7 AC430 With BT324 Control (Electrical Panel 91-62105-00)
INDICATES RELAY CONTACTS (NORMALLY CLOSED)
INDICATES RELAY CONTACTS (NORMALLY OPEN)
INDICATES A CONNECTOR (VARIOUS STYLES)
INDICATES A TERMINAL CONNECTION
INDICATES A WIRE GROUND
INDICATES OPTIONAL WIRING OR FEATURE
INDICATES OPTIONAL UNIT WIRING O R FEATURE
INDICATES WIRING EXTERNAL TO UNIT
INDICATES WIRING INTERNAL TO UNIT
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
GRD
HIGHPRESSURESWITCH
FUSE,3AMP
FUSE,5AMP
A/CRELAY
ACR1--ACR2
CONDENSERFANRELAY
CFR1--CFR2
F1-- F2 FUSE,25AMP
ATS AMBIENTTEMPERATURESENSOR
DESCRIPTION
INDICATES AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (ATS)
INDICATES FUSE WITH MANUAL RESET
INDICATES FUSE
INDICATES ELECTRICAL COMPONENT
INDICATES RELAY COIL
86 85
ATS
SYMBOL
FUSE,10AMP
HPS
F5
F6-- F7
F8-- F9
F3-- F4 FUSE,20AMP
HTR1--HTR1 HEAT RELAY
5--7
RETURNAIRSENSOR
LOWPRESSURESWITCH
LIQUIDLINESOLENOIDVALVE
RAS
LPS
LLSV
LLSR LIQUIDLINESOLENOIDRELAY
T-353 Rev. 01/2013

POS
(+)
NEG
(--)
F7
F8
F9
ATS
OPTIONAL
DIMMER
12V(+)
IGNITION
12V (+)
ALTERNATOR
12V (+)
CHASSIS
GROUND
5AMP
10 AMP
10 AMP
GREY
LOOM
BLU
2AMP
3AMP
2AMP
BRN
WHT
30
30
30
ACR2
HTR1
HTR2
BT--7
BT--3
BT--5
BT--1
BT--9
LLSV
85
87
X12--5
HPS
B
X12--6
A
X13--1
X3--14
87
87
BT--13
BT--18
BT--10
BT--6
BT--15
BT--11
BT324CONTROLLER
BT--14
BT--8
BT--17
BT--4
X3--15
X3--16
X3--10 (NOT USED)
DRIVERCONTROLHARNESS
X3--11
X3--9
X3--6
X3--4
X3--3
X3--2
X3--1
X3--7
X3--8 (NOT USED)BT--2
86
X13--3
X13--4
86
HTR1
ACR1
A
B
X11--5
85
85
A
RETURN AIR
LPS
RAS
SENSOR
M1- -PWM
X13--2
B
COMP
CLUTCH
A B
HTR2
85
86
COOLANT
PUMP
RELAY
A B
COOLANT
VALVE
RELAY
A B
FRESH AIR
MOTOR
86
F1
25 AMP
F2
25 AMP
F3
20 AMP
F4
20 AMP
F5
3AMP
F6
5AMP
30
30
30
30
CFR1
87
CFR2
87
LSVR
87
ACR1
87
98--63176
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
X11--1
X11--3
X12--1
X12--7
5--8
M1- -1
M2- -PWM
M2- -1
M1- -A
M2- -AX12--2
LV --1
EVAP
MTR 1
EVAP
MTR 2
COND
MTR 1
COND
MTR 2
LLSV
86
86
86
ACR2
CFR1
CFR2
85
M1- -2
M2- -2
M1- -B
M2- -B
LV --1 2
85
85
X11--2
Figure 5-8 AC430 With BT324 Control (Electrical Panel 91-62105-00)
X11--4
T-353 Rev. 01/2013

INDEX
A
Air Filters, 4-7
Apex Unit, 1-2
C
Circuit Breaker, 1-4
Compressor, 1-3
Condenser Fan, 1-3
Condensing Section, 1-2
D
DESCRIPTION, 1-1
E
M
Maintenance Schedule, 4-1
Manifold Gauge Set, 4-2
N
Noncondensibles, 4-4
O
Operating Instructions, 2-1
OPERATION, 2-1
P
Pre-Trip Inspection, 2-1
Pump Down, 4-3
ELECTRICAL, 5-1
Evacuation, 4-3, 4-4
Evaporator, 1-2
Evaporator Fan, 1-3
F
Filter-Drier, 4-5
Fuse, 1-4
H
Heat Valve, 4-6
Heating Cycle, 1-4
High Pressure Switch, 1-3
L
R
Refrigerant Charge, 1-3, 4-3, 4-4
Refrigerant Removal, 4-3
Refrigeration Cycle, 1-4
S
SERVICE, 4-1
Starting, 2-1
Stopping, 2-1
Superheat, 4-9
T
Temperature Pressure Chart, 4-11
Temperature Sensor, 1-3
Thermostatic Expansion Valve, 1-3, 4-8
Low Pressure Switch, 1-3, 1-4
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control T-353 Rev. 01/2013
TROUBLESHOOTING, 3-1
Index --1

Every driver deserves the best possible
vehicle climate with MCC products
MCC provides exceptional performance in mobile climate comfort.
Specifications subject to change without notice. MCC is a registered trademark.
© 2012 Mobile Climate Control
Member of MCC Group S Certified ISO 9001 and ISO 1 4001.
www.mcc-hvac.com
3189 Farmtrail Road
York PA 17406 USA
Tel: 1--800--673--2431
Fax: 1--717--764--0401
T-353 Rev. 01/2013
 Loading...
Loading...