Page 1

Engine
CONTENTS
Workshop
Manual
SKYACTIV-G 2.5
FOREWORD
This manual explains the service points for
the above-indicated automotive system.
This manual covers all models with the
above-indicated automotive system, not any
one specific model.
In order to do these procedures safely,
quickly, and correctly, you must first read
this manual and any other relevant service
materials carefully.
All the contents of this manual, including
drawings and specifications, are the latest
available at the time of printing.
As modifications affecting repair or
maintenance occur, relevant information
supplementary to this volume will be made
available at Mazda dealers. This manual
should be kept up-to-date.
Title Section
GENERAL INFORMATION 00
ENGINE
© 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation
PRINTED IN U.S.A., DECEMBER 2012
Form No. 1A36–1U–12L
Part No. 9999–95–EWPY–14
01
Mazda Motor Corporation reserves the right
to alter the specifications and contents of
this manual without obligation or advance
notice.
All rights reserved. No part of this book may
be reproduced or used in any form or by any
means, electronic or mechanical—including
photocopying and recording and the use of
any kind of information storage and retrieval
system—without permission in writing.
Mazda Motor Corporation
HIROSHIMA, JAPAN
Page 2

Page 3
WARNING
Servicing a vehicle can be dangerous. If you have not received
service-related training, the risks of injury, property damage, and
failure of servicing increase. The recommended servicing procedures
for the vehicle in this workshop manual were developed with
Mazda-trained technicians in mind. This manual may be useful to
non-Mazda trained technicians, but a technician with our
service-related training and experience will be at less risk when
performing service operations. However, all users of this manual are
expected to at least know general safety procedures.
This manual contains "Warnings" and "Cautions" applicable to risks
not normally encountered in a general technician's experience.
They should be followed to reduce the risk of injury and the risk
that improper service or repair may damage the vehicle or render it
unsafe. It is also important to understand that the "Warnings" and
"Cautions" are not exhaustive. It is impossible to warn of all
the hazardous consequences that might result from failure to follow
the procedures.
The procedures recommended and described in this manual are
effective methods of performing service and repair. Some require tools
specifically designed for a specific purpose. Persons using procedures
and tools which are not recommended by Mazda Motor Corporation
must satisfy themselves thoroughly that neither personal safety nor
safety of the vehicle will be jeopardized.
The contents of this manual, including drawings and specifications, are
the latest available at the time of printing, and
reserves the right to change the vehicle designs and alter the contents
of this manual without notice and without incurring obligation.
Parts should be replaced with genuine Mazda replacement parts or
with parts which match the quality of genuine Mazda replacement
parts. Persons using replacement parts of lesser quality than that of
genuine Mazda replacement parts must satisfy themselves thoroughly
that neither personal safety nor safety of the vehicle will be
jeopardized.
Mazda Motor Corporation is not responsible for any problems which
may arise from the use of this manual. The cause of such problems
includes but is not limited to insufficient service-related training, use of
improper tools, use of replacement parts of lesser quality than that of
genuine Mazda replacement parts, or not being aware of any revision
of this manual.
Mazda Motor Corporation
Page 4

GENERAL INFORMATION
Toc of SC T
GENERAL INFORMATION . . . .00-00
Toc of SC T
00-00 GENERAL INFORMATION
00
SECTION
00-00
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL . . . . . . . . . 00-00–1
Range of Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–1
Service Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–2
Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–4
Advisory Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–4
UNITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–5
Conversion From SI Units (Système
International d'Unités) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–5
Number Of Digits For
Converted Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–5
Converted Value Rounding Off And
Rounding Up/down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–5
ABBREVIATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–6
FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES. . . . . . . 00-00–6
End of Toc
WM: GENERAL INFORMATION
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
Range of Topics
• This manual contains procedures for performing all required service operations. The procedures are divided
into the following basic operations:
— Removal/Installation
— Disassembly/Assembly
— Replacement
— Inspection
— Adjustment
• Simple operations which can be performed easily just by looking at the actual unit (i.e., removal/installation of
parts, cleaning of parts, and visual inspection) have been omitted.
Preparation of Tools and Measuring
Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–6
Special Service Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–6
Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–6
Inspection During Removal,
Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–7
Arrangement of Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–7
Cleaning of Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–7
Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–7
Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–8
Rubber Parts and Tubing . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–8
Torque Formulas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–8
Vise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-00–9
id000000000100
00-00–1
Page 5

GENERAL INFORMATION
Service Procedure
Inspection, adjustment
• Inspection and adjustment procedures are
divided into steps. Important points regarding the
location and contents of the procedures are
explained in detail and shown in the illustrations.
Fluid Pressure Inspection
1. Assemble the SSTs as shown in the figure.
49 1232 670A
SHOWS PROCEDURE ORDER
FOR SERVICE
Tightening torque
39—49 N·m {4.0—5.0 kgf·m, 29—36 ft·lbf}
49 H002 671
Caution
49 H032 322
Connect the gauge set from under
the vehicle to prevent contact with
the drive belt and the cooling fan.
SHOWS TIGHTENING
TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS
bpe2ue00000101
Repair procedure
1. Most repair operations begin with an overview illustration. It identifies the components, shows how the parts fit
together, and describes visual part inspection. However, only removal/installation procedures that need to be
performed methodically have written instructions.
2. Expendable parts, tightening torques, and symbols for oil, grease, and sealant are shown in the overview
illustration. In addition, symbols indicating parts requiring the use of special service tools or equivalent are also
shown.
3. Procedure steps are numbered and the part that is the main point of that procedure is shown in the illustration
with the corresponding number. Occasionally, there are important points or additional information concerning a
procedure. Refer to this information when servicing the related part.
00-00–2
Page 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
GREASE
GREASE
Procedure
"Removal/Installation"
Portion
"Inspection After
Installation" Portion
INSTALL THE PARTS BY
PERFORMING STEPS
—
1—3 IN REVERSE ORDER
SHOWS THERE
ARE REFERRAL
NOTES FOR SERVICE
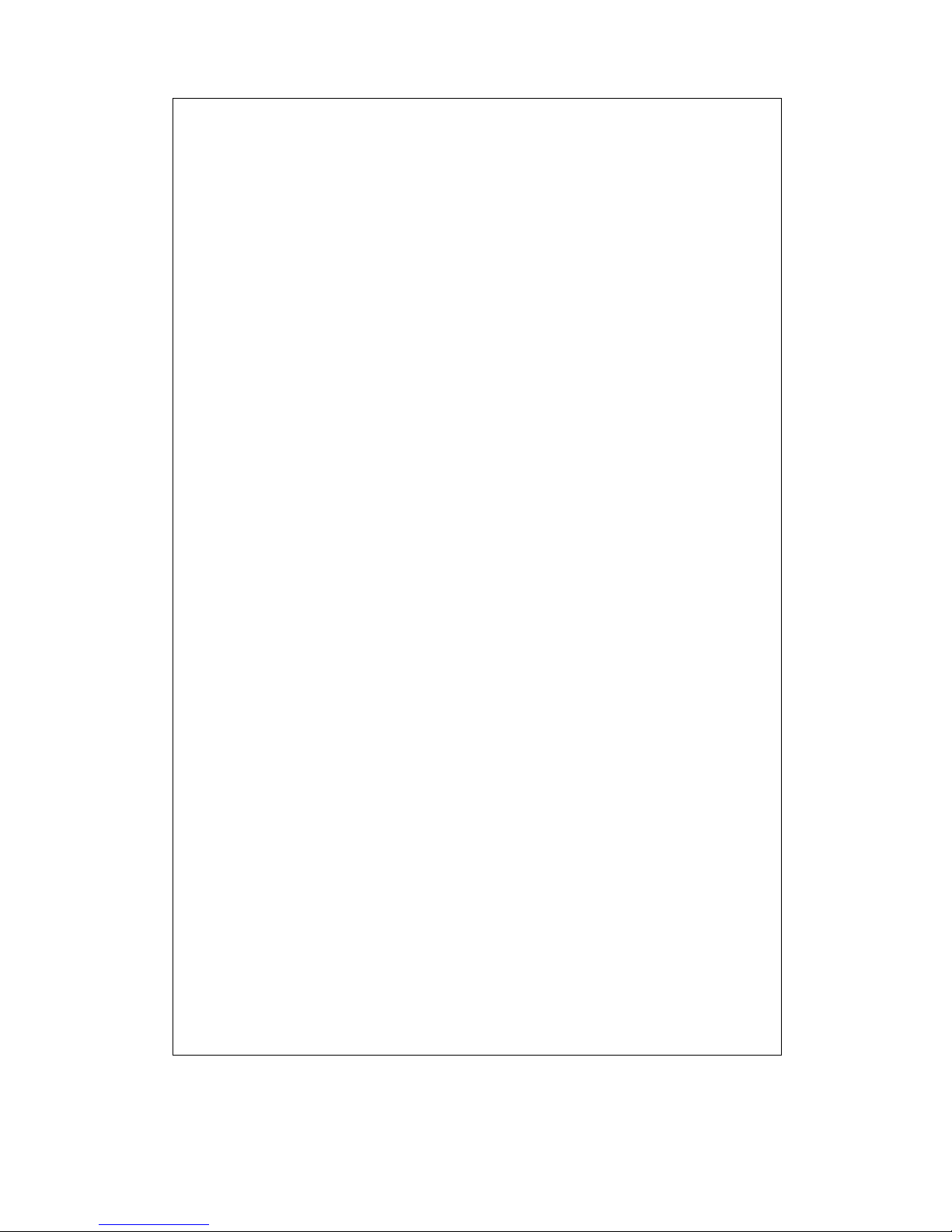
LOWER TRAILING LINK, UPPER TRAILING LINK REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
1
1. Jack up the rear of the vehicle and suppor t it with safety stands.
2. Remove the undercover. (See 01-10-4 Undercover Removal)
3. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
4. Install in the reverse order of removal.
5. Inspect the rear wheel alignment and adjust it if necessary.
2
11
SHOWS PROCEDURE ORDER
FOR SERVICE
10
44—60 {4.4—6.2, 32—44}
SHOWS TIGHTENING
TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS
SST
3
5
6
SST
4
94—116 {9.5—11.9, 69—86}
Split pin
1
Nut
2
Lower trailing link ball joint
3
(See 02-14-5 Lower Trailing Link Ball Joint Removal Note)
Bolt
4
Lower trailing link
5
Dust boot (lower trailing link)
6
GREASE
R
7
8 Nut
9 Upper trailing link ball joint
10
11
12
SHOWS SERVICE
ITEM (S)
INDICATES ANY RELEVANT
REFERENCES WHICH NEED
TO BE FOLLOWED DURING
INSTALLATION
SHOWS SPECIAL
SST
9
SST
12
43—56 {4.3—5.8, 32—41}
8
R
7
R
SERVICE TOOL (SST)
FOR SERVICE OPERATION
GREASE
SHOWS APPLICATION
POINTS OF GREASE, ETC.
SHOWS NON-REUSEABLE PARTS
SHOWS DETAILS
118—156 {12.0—16.0, 87—115}
2
R
1
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
Split pin
(See 02-14-5 Upper Trailing Link Ball Joint Removal Note)
Nut
Upper trailing link
Dust boot (upper trailing link)
00-00
SHOWS TIGHTENING
TORQUE UNITS
Lower Trailing Link Ball Joint, Upper Trailing Link
Ball Joint Removal Note
Remove the ball joint using the SSTs.
SHOWS REFERRAL
NOTES FOR
SERVICE
49 T028 304
49 T028 305
UPPER TRAILING LINK
LOWER TRAILING LINK
SHOWS SPECIAL
SERVICE TOOL (SST)
NO.
KNUCKLE
49 T028 303
bpe2ue00000001
00-00–3
Page 7
GENERAL INFORMATION
OIL
BRAKE
FLUID
ATF
GREASE
SEALANT
P
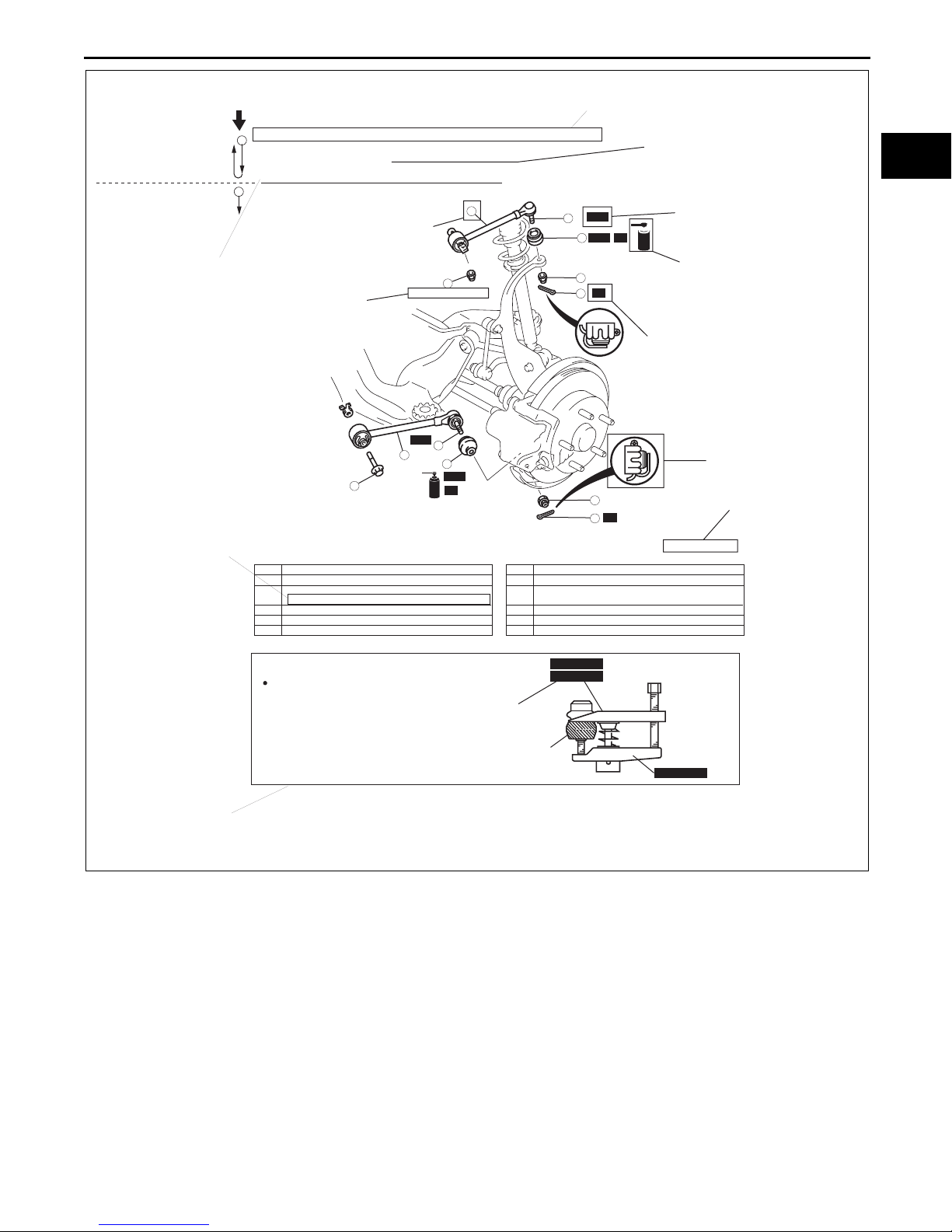
Symbols
• There are eight symbols indicating oil, grease, fluids, sealant, and the use of SST or equivalent. These symbols
show application points or use of these materials during service.
Symbol Meaning Kind
OIL
BRAKE
FLUID
ATF
GREASE
SEALANT
P
R
Apply oil New appropriate engine oil or gear oil
Apply brake fluid New appropriate brake fluid
Apply automatic transaxle/
transmission fluid
New appropriate automatic
transaxle/
transmission fluid
Apply grease Appropriate grease
Apply sealant
Apply petroleum jelly
Appropriate
sealant
Appropriate
petroleum jelly
Replace part O-ring, gasket, etc.
SST
Use SST or
equivalent
Appropriate tools
Advisory Messages
• You will find several Warnings, Cautions, Notes, Specifications and Upper and Lower Limits in this
manual.
Warning
• A Warning indicates a situation in which serious injury or death could result if the warning is ignored.
Caution
• A Caution indicates a situation in which damage to the vehicle or parts could result if the caution is ignored.
Note
• A Note provides added information that will help you to complete a particular procedure.
Specification
• The values indicate the allowable range when performing inspections or adjustments.
Upper and lower limits
• The values indicate the upper and lower limits that must not be exceeded when performing inspections or
adjustments.
End Of Sie
00-00–4
Page 8

GENERAL INFORMATION
UNITS
Electric current A (ampere)
Electric power W (watt)
Electric resistance ohm
Electric voltage V (volt)
Length
Negative pressure
Positive pressure
Number of revolutions rpm (revolutions per minute)
To r qu e
Volum e
Weight
mm (millimeter)
in (inch)
kPa (kilo pascal)
mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
inHg (inches of mercury)
kPa (kilo pascal)
2
kgf/cm
psi (pounds per square inch)
N·m (Newton meter)
kgf·m (kilogram force meter)
kgf·cm (kilogram force centimeter)
ft·lbf (foot pound force)
in·lbf (inch pound force)
L (liter)
US qt (U.S. quart)
Imp qt (Imperial quart)
ml (milliliter)
cc (cubic centimeter)
cu in (cubic inch)
fl oz (fluid ounce)
g (gram)
oz (ounce)
(kilogram force per square centimeter)
id000000100400
00-00
Conversion From SI Units (Système International d'Unités)
• All numerical values in this manual are based on SI units. Numbers shown in conventional units are converted
from these values.
Number Of Digits For Converted Values
• The number digits for converted values is the same as the number of significant figures
*1
of the SI unit.
• For the torque value, the number of significant figures is, in principle, is 2 digits, in consideration of market
practicalities. However, if the number of decimal places at the upper and lower limits of the converted value
differs, the one with least number of decimal places is used. In addition, if the integer part is 3 digits or more,
the integer part becomes the significant number of figures.
*1 : The number of significant figures is the number of digits from the left-most non-zero digit to the right-most digit
including 0. (Example: 0.12 is 2 digits, 41.0 is 3 digits)
Converted Value Rounding Off And Rounding Up/down
• If there is no tolerance in the SI unit value, after conversion, rounding off is to within the number of significant
digits.
• If there is tolerance in the SI unit value and the figure after conversion indicates the upper limit, the number of
digits is rounded down to within the number of significant figures. If it indicates the lower limit, they are rounded
up to within the number of significant figures.
• Even if the SI unit value is the same, the converted value may differ based on whether that value is the upper or
lower limit.
End Of Sie
00-00–5
Page 9
GENERAL INFORMATION
ABBREVIATIONS
ATX Automatic Transaxle
EX Exhaust
HLA Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
IN Intake
MTX Manual Transaxle
OCV Oil Control Valve
TDC Top Dead Center
SST Special Service Tool
End Of Sie
GAIHAN: -
FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES
Preparation of Tools and Measuring Equipment
• Be sure that all necessary tools and measuring
equipment are available before starting any work.
id000000010100
id000000750100
Special Service Tools
• Use special service tools or equivalent when they
are required.
Disassembly
• If the disassembly procedure is complex,
requiring many parts to be disassembled, all parts
should be marked in a place that will not affect
their performance or external appearance and
identified so that reassembly can be performed
easily and efficiently.
bpe2ue00000110
49 SE01 310
bpe2ue00000111
00-00–6
bpe2ue00000112
Page 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
Inspection During Removal, Disassembly
• When removed, each part should be carefully
inspected for malfunction, deformation, damage
and other problems.
Arrangement of Parts
• All disassembled parts should be carefully
arranged for reassembly.
• Be sure to separate or otherwise identify the parts
to be replaced from those that will be reused.
00-00
bpe2ue00000113
Cleaning of Parts
• All parts to be reused should be carefully and
thoroughly cleaned in the appropriate method.
Warning
• Using compressed air can cause dirt and
other particles to fly out causing injury to
the eyes. Wear protective eye wear
whenever using compressed air.
Reassembly
• Standard values, such as torques and certain
adjustments, must be strictly observed in the
reassembly of all parts.
• If removed, the following parts should be replaced
with new ones:
— Oil seals
— Gaskets
— O-rings
— Lockwashers
— Cotter pins
— Nylon nuts
bpe2ue00000114
bpe2ue00000002
bpe2ue00000115
00-00–7
Page 11
• Depending on location:
— Sealant and gaskets, or both, should be
applied to specified locations. When sealant
is applied, parts should be installed before
sealant hardens to prevent leakage.
— Oil should be applied to the moving
components of parts.
— Specified oil or grease should be applied at
the prescribed locations (such as oil seals)
before reassembly.
Adjustment
• Use suitable gauges and testers when making
adjustments.
bpe2ue00000116
Rubber Parts and Tubing
• Prevent gasoline or oil from getting on rubber
parts or tubing.
Torque Formulas
• When using a torque wrench-SST or equivalent
combination, the written torque must be
recalculated due to the extra length that the SST
or equivalent adds to the torque wrench.
Recalculate the torque by using the following
formulas. Choose the formula that applies to you.
Torque Unit Formula
N·m N·m × [L/(L+A)]
kgf·m kgf·m × [L/(L+A)]
kgf·cm kgf·cm × [L/(L+A)]
ft·lbf ft·lbf × [L/(L+A)]
in·lbf in·lbf × [L/(L+A)]
bpe2ue00000117
bpe2ue00000118
SST
A
L
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
bpe2ue00000119
A : The length of the SST past the torque wrench drive.
L : The length of the torque wrench.
Page 12

GENERAL INFORMATION
Vise
• When using a vise, put protective plates in the
jaws of the vise to prevent damage to parts.
End Of Sie
00-00
PROTECTIVE PLATES
bpe2ue00000120
00-00–9
Page 13

Page 14
ENGINE
Toc of SC T
MECHANICAL. . . . . . . . . . . . . .01-10
TECHNICAL DATA . . . . . . . . . . 01-50
Toc of SC T
01-10 MECHANICAL
01
SECTION
01-10
SERVICE TOOLS . . . . . . . . . . . 01-60
ELECTRIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING
MOTOR/DRIVER INSPECTION . . . . . . . 01-10–2
HYDRAULIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING
ACTUATOR INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–3
ELECTRIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING
ACTUATOR INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–3
OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV)
INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–4
Coil Resistance Inspection . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–4
Spool Valve Operation Inspection . . . . . 01-10–4
HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER (HLA)
INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–5
ROCKER ARM INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . 01-10–5
ENGINE OVERHAUL SERVICE
WARNING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–5
ENGINE MOUNTING/DISMOUNTING . . . 01-10–6
Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–6
Dismounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–6
TIMING CHAIN DISASSEMBLY. . . . . . . . 01-10–7
Water Pump Pulley
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–9
Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–10
Oil Pan Disassembly Note. . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–10
Engine Front Cover
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–10
Front Oil Seal Disassembly Note . . . . . 01-10–11
Chain Tensioner Disassembly Note . . . 01-10–11
Oil Pump Chain Disassembly Note. . . . 01-10–12
CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY (I) . . . 01-10–14
Electric Variable Valve Timing Actuator,
Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing
Actuator Disassembly Note. . . . . . . . . 01-10–16
Camshaft Cap Disassembly Note . . . . . 01-10–16
Rocker Arm Disassembly Note . . . . . . . 01-10–16
HLA Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–16
Cylinder Head Disassembly Note . . . . . 01-10–16
CYLINDER HEAD
DISASSEMBLY (II) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–17
Valve Keeper Disassembly Note . . . . . . 01-10–18
Valve Seal Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . 01-10–18
CYLINDER BLOCK
DISASSEMBLY (I) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–19
Dual-mass Flywheel (MTX)/ Drive
Plate (ATX) Installation Bolt
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–20
Dual-mass Flywheel
Disassembly Note (MTX) . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–21
Rear Oil Seal Disassembly Note . . . . . 01-10–21
CYLINDER BLOCK
DISASSEMBLY (II) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–22
Pilot Bearing Disassembly Note. . . . . . 01-10–23
Connecting Rod Cap
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–23
Connecting Rod Bearing
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–23
Piston, Connecting Rod
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–23
Snap Ring Disassembly Note. . . . . . . . 01-10–24
Lower Cylinder Block
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–24
Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Disassembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–25
Crankshaft Disassembly Note . . . . . . . 01-10–25
CYLINDER HEAD INSPECTION. . . . . . . 01-10–25
VALVE SEAT INSPECTION/REPAIR. . . . 01-10–26
VALVE, VALVE GUIDE
INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–27
VALVE GUIDE REPLACEMENT . . . . . . . 01-10–29
Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–29
Installation
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION . . . . . . . . 01-10–29
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–30
CYLINDER BLOCK INSPECTION . . . . . 01-10–32
OIL JET VALVE INSPECTION . . . . . . . . 01-10–32
PISTON INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–32
PISTON RING INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–33
PISTON PIN INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–34
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–35
CONNECTING ROD INSPECTION . . . . . 01-10–35
CONNECTING ROD CLEARANCE
INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–35
CRANKSHAFT INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . 01-10–36
DUAL-MASS FLYWHEEL
INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–37
Inspection Before Removal . . . . . . . . . 01-10–37
Inspection After Removal . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–38
PILOT BEARING INSPECTION . . . . . . . 01-10–39
BOLT INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–39
CYLINDER BLOCK ASSEMBLY (I) . . . . 01-10–40
Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–41
Plate Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–42
Lower Cylinder Block
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–29
01-10–1
Page 15

MECHANICAL
Piston Pin Assembly Note. . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–44
Snap Ring Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–44
Piston Ring Assembly Note. . . . . . . . . . 01-10–45
Connecting Rod Bearing
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–46
Piston, Connecting Rod
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–46
Connecting Rod Cap
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–47
Pilot Bearing Assembly Note . . . . . . . . 01-10–47
CYLINDER BLOCK ASSEMBLY (II) . . . . 01-10–48
Balancer Unit Assembly Note . . . . . . . . 01-10–49
Oil Pump Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–50
Water Pump Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . 01-10–51
Rear Oil Seal Assembly Note . . . . . . . . 01-10–52
End Plate Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–53
Dual-mass Flywheel (MTX)/ Drive
Plate (ATX) Installation Bolt
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–53
Knock Sensor (KS) Assembly Note . . . 01-10–54
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY (I) . . . . . . 01-10–55
Valve Seal Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–56
Valve Spring Assembly Note. . . . . . . . . 01-10–56
Valve Keeper Assembly Note . . . . . . . . 01-10–57
Thermostat Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . 01-10–58
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY (II) . . . . . 01-10–59
Cylinder Head Assembly Note . . . . . . . 01-10–61
Water Inlet Pipe Assembly Note. . . . . . 01-10–62
HLA Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–63
Rocker Arm Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . 01-10–63
Camshaft Assembly Note. . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–64
Electric Variable Valve Timing Actuator,
Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing
Actuator Assembly Note. . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–66
TIMING CHAIN ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–67
Oil Pump Chain Assembly Note. . . . . . 01-10–69
Timing Chain Assembly Note. . . . . . . . 01-10–71
Engine Front Cover Assembly Note . . . 01-10–74
Oil Pan Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–77
Electric Variable Valve Timing Motor/
Driver Assembly Note. . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–79
Front Oil Seal Assembly Note . . . . . . . 01-10–80
Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–80
Water Pump Pulley Assembly Note . . . 01-10–81
Oil Shower Pipe Assembly Note . . . . . 01-10–81
Cylinder Head Cover
Assembly Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-10–82
Water Outlet Assembly Note. . . . . . . . . 01-10–57
End of Toc
WM: -
ELECTRIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING MOTOR/DRIVER INSPECTION
id011000828100
Caution
• Do not disassemble the electric variable valve timing motor/driver because it is a precision unit.
• Do not apply excessive force when rotating the electric variable valve timing motor joint. If it is
rotated with excessive force, the electric variable valve timing motor could be damaged.
1. Rotate the electric variable valve timing motor joint to the left and right by your fingers and verify that it rotates
smoothly in 15° increments.
Note
• Rotate the joint area smoothly using only the tips of your fingers.
• The electric variable valve timing motor joint moves in 15° increments, and if the joint is moved 24 times, it
rotates one full rotation.
• If it does not rotate smoothly, replace the
electric variable valve timing motor/driver.
End Of Sie
WM: VARIABLE VALVE TIMING ACTUATOR
JOINT
ELECTRIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING MOTOR
am3uuw00009048
01-10–2
Page 16
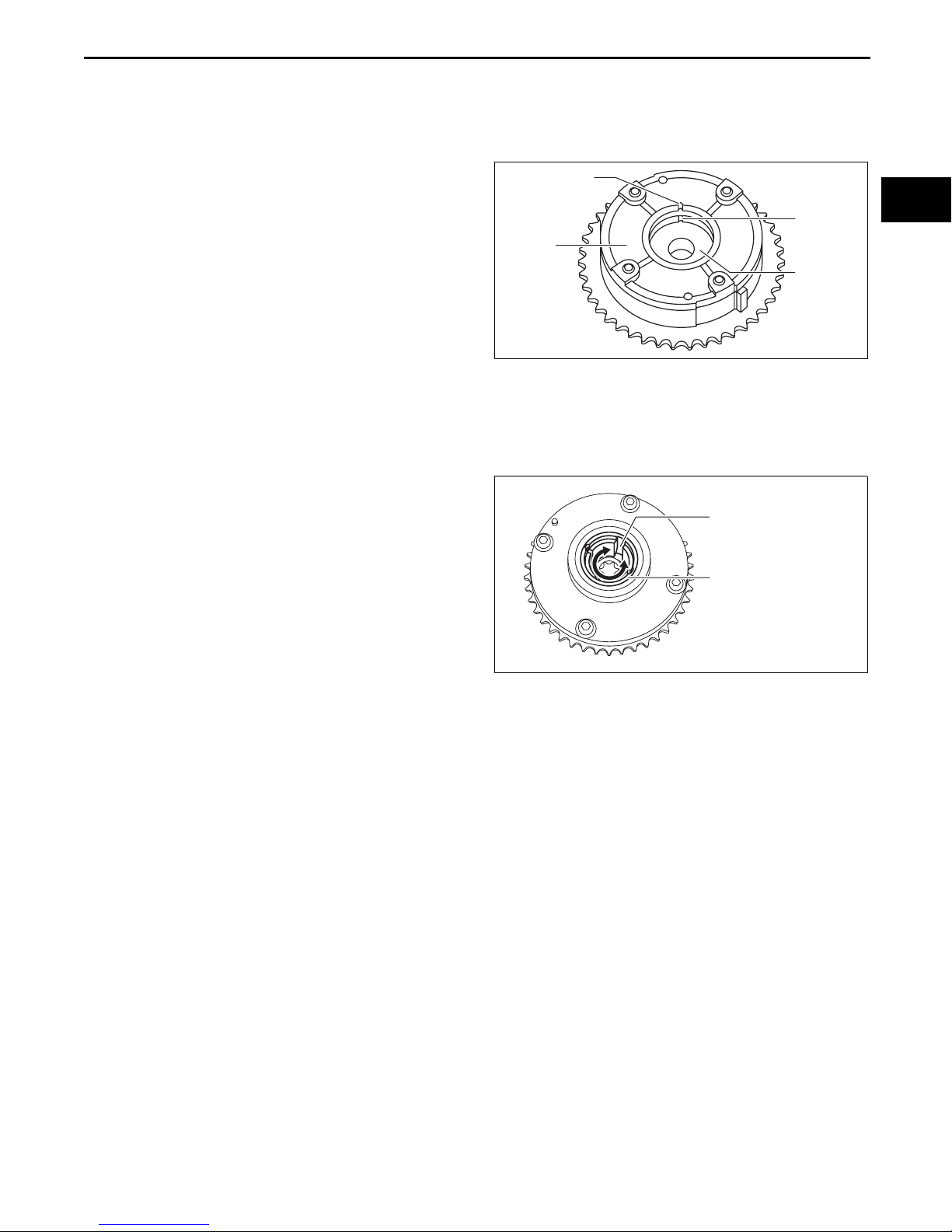
MECHANICAL
HYDRAULIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING ACTUATOR INSPECTION
Caution
• Do not disassemble the hydraulic variable valve timing actuator because it is a precision unit.
1. Verify that the notch of the rotor and projection of
the cover on the hydraulic variable valve timing
PROJECTION
actuator are aligned and fitted.
• If the projection and notch are not aligned,
rotate the rotor (camshaft installation) until a
click is heard and verify that they are aligned
COVER
and fixed in place.
— If the projection and notch are not aligned
or the rotor and cover are not secured
even if their projection and notch are
aligned, replace the hydraulic variable
valve timing actuator.
End Of Sie
ELECTRIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING ACTUATOR INSPECTION
Caution
• Do not disassemble the electric variable valve timing actuator because it is a precision unit.
1. Rotate the eccentric shaft of the electric variable
valve timing actuator to the left and right by hand
and verify that it rotates smoothly.
• If it does not rotate smoothly, replace the
electric variable valve timing actuator.
JOINT GROOVE
id011000126800
01-10
NOTCH
ROTOR
bpe2ue00000012
id011000555500
Note
ECCENTRIC SHAFT
• Hook a finger onto the joint groove of the
eccentric shaft to rotate the shaft easily.
• The eccentric shaft stops rotating at the
maximum retard position when it is rotated
counterclockwise as viewed from the front,
and at the maximum advance position when
rotated clockwise.
• The eccentric shaft rotates 15.8 turns from the maximum retard position to the maximum advance
position.
End Of Sie
WM: OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV)
bpe2ue00000097
01-10–3
Page 17
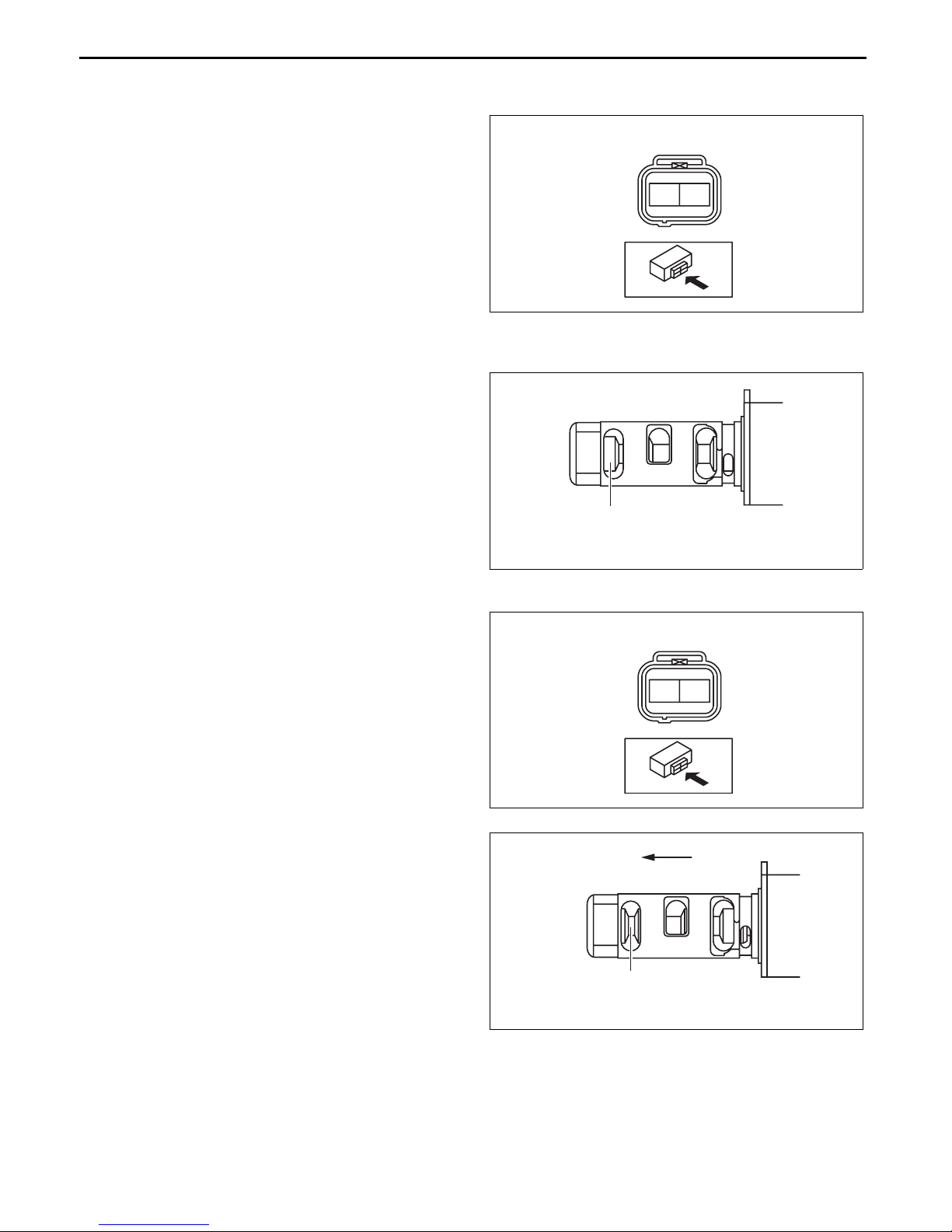
MECHANICAL
OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV) INSPECTION
Coil Resistance Inspection
1. Measure the resistance between terminals A and
B using an ohmmeter.
OCV coil resistance
6.9—7.5 ohms [20°C {68°F}]
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
OCV.
Spool Valve Operation Inspection
1. Verify that the spool valve in the OCV is in the
maximum valve timing advance position as
indicated in the figure.
• If there is any malfunction, replace the OCV.
Note
• When applying battery positive voltage
between the OCV terminals, the connection
can be either of the following:
— Positive battery cable to terminal A,
negative battery cable to terminal B
— Positive battery cable to terminal B,
negative battery cable to terminal A
id011000801400
OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV)
AB
bpe5ue00000015
SPOOL VALVE
(MAXIMUM VALVE TIMING
ADVANCE POSITION)
bpe1ze00000100
2. Apply battery positive voltage between the OCV
terminals and verify that the spool valve operates
and moves to the maximum valve timing retard
position.
• If there is any malfunction, replace the OCV.
3. Stop applying battery positive voltage and verify
that the spool valve returns to the maximum valve
timing advance position.
• If there is any malfunction, replace the OCV.
End Of Sie
WM: HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER (HLA)
OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV)
VALVE TIMING
RETARD
SPOOL VALVE
(MAXIMUM VALVE TIMING
RETARD POSITION)
AB
bpe5ue00000015
VALVE TIMING
ADVANCE
bpe1ze00000101
01-10–4
Page 18
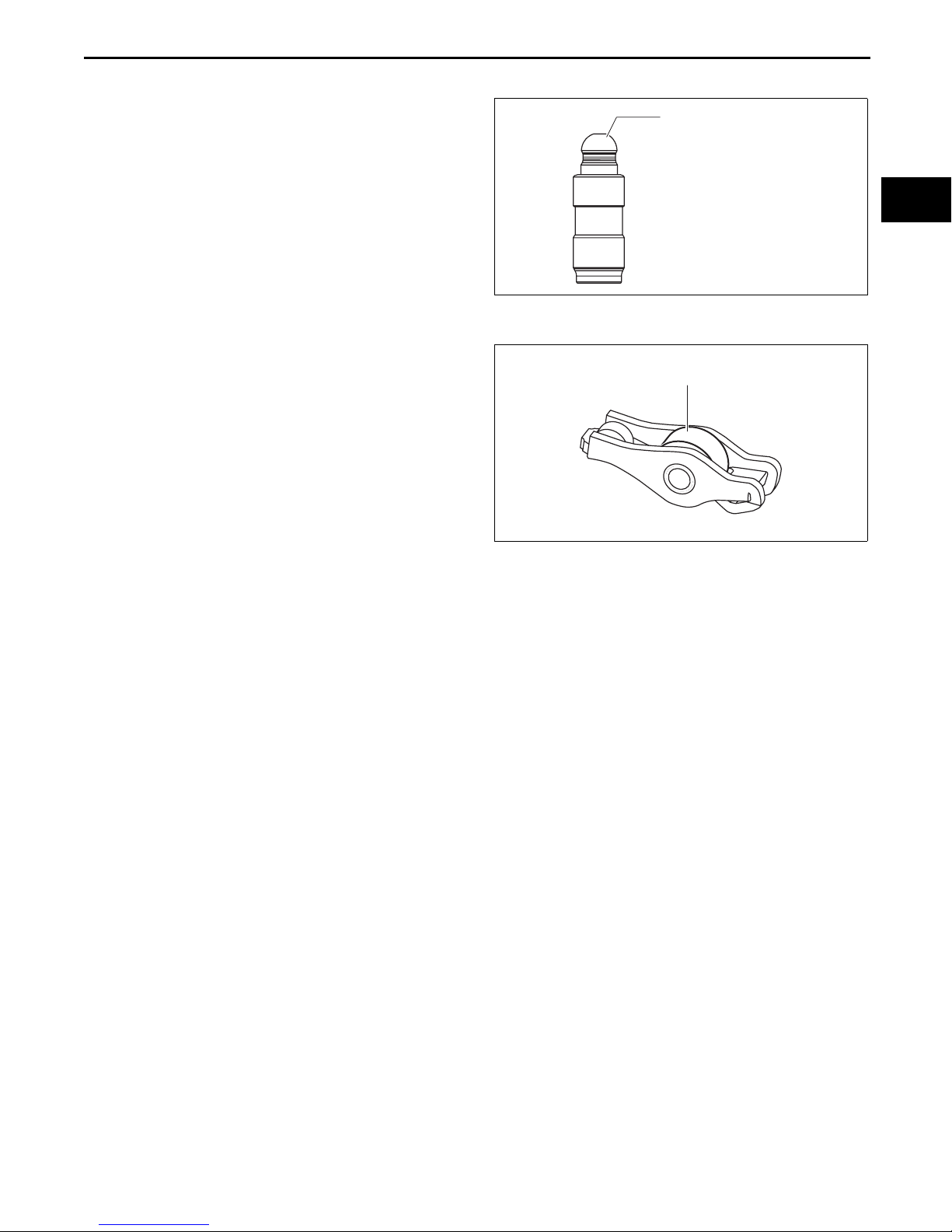
MECHANICAL
HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER (HLA) INSPECTION
1. Visually inspect the HLA surface where it contacts
the rocker arm for wear or damage.
• If there is any malfunction, replace the HLA.
End Of Sie
WM: ROCKER ARM
ROCKER ARM INSPECTION
1. Rotate the roller or the rocker arm by hand and
verify that rotates smoothly.
• If it does not rotate smoothly, replace the
rocker arm.
2. Visually inspect the rocker arm surface where it
contacts the HLA and valve stem for wear or
damage.
• If there is any malfunction, replace the rocker
arm.
End Of Sie
EN: ENGINE COMPLETE
id011000805000
ROCKER ARM
CONTACT SURFACE
01-10
am3uuw00008989
id011000904800
ROLLER
ENGINE OVERHAUL SERVICE WARNING
Warning
• Continuous exposure to USED engine oil has been shown to cause skin cancer in laboratory mice.
Protect your skin by washing with soap and water immediately after performing work.
End Of Sie
bpe2ue00000096
id011000503900
01-10–5
Page 19
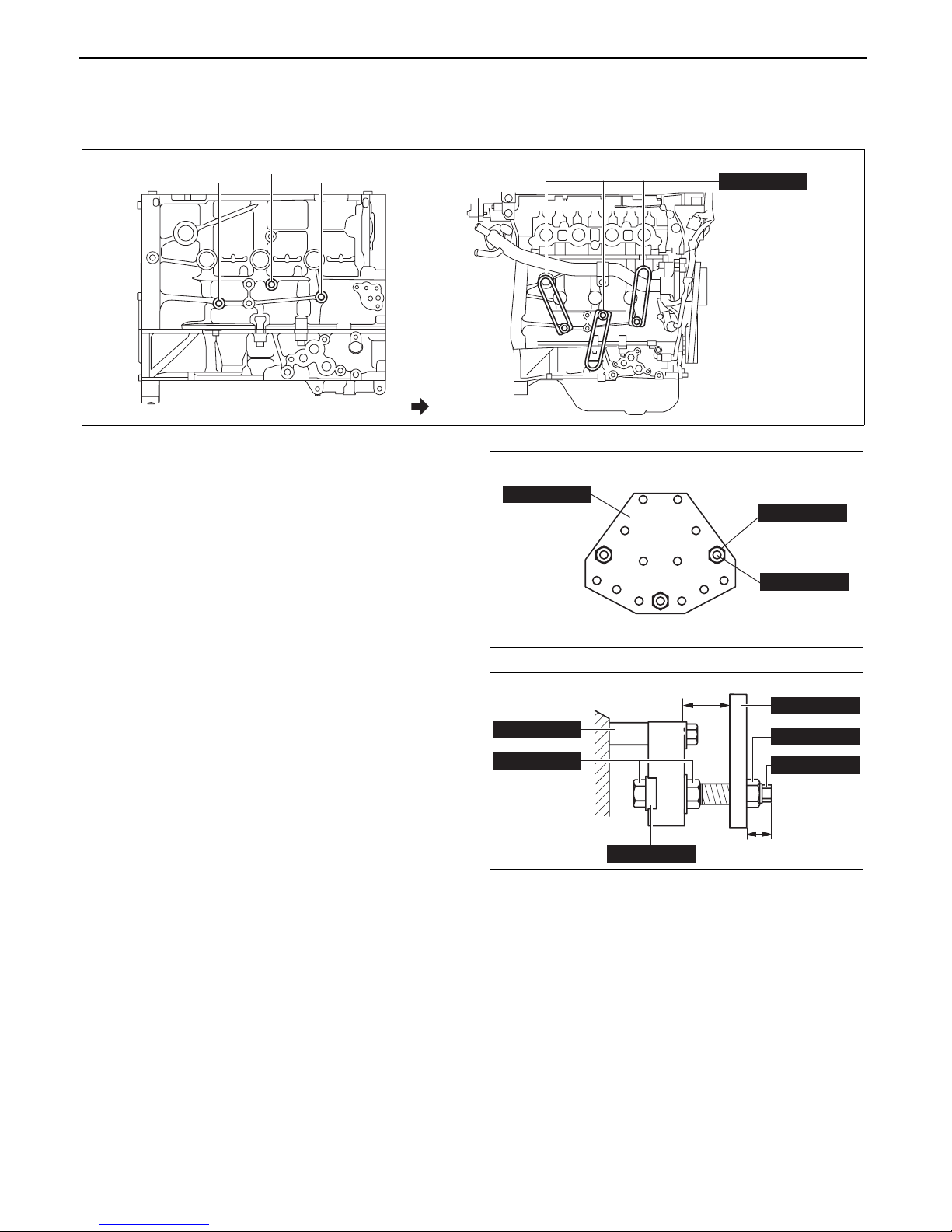
MECHANICAL
ENGINE MOUNTING/DISMOUNTING
id011000507000
Mounting
1. Install the SST (arms) to the three positions as shown in the figure and temporarily tighten the bolts (Part No.
9YA20-1003 or M10 × 1.5 length 90 mm {3.55 in}).
SST INSTALLATION HOLE
ENGINE FRONT
SST INSTALLED
49 L010 102
bpe1ze00000084
2. Install the SSTs (bolts and nuts) to the three
positions of the SST (plate) as shown in the
figure.
49 L010 101
49 L010 104
3. Install the SST (bolts, nuts and plate) set in Step 2
to the SST (arms) set in Step 1 using the SSTs
(hook and nuts).
4. Adjust the bolts so that approx. 20 mm {0.79 in}
of thread is exposed from the side of the plate.
5. Adjust the bolts and nuts so that the plate and
arms are parallel.
6. Tighten the SSTs (bolts and nuts) to affix the SST
firmly.
7. Install the engine to the SST (engine stand).
8. Remove the oil drain plug and drain the engine
oil.
9. Replace the gasket with a new one and install the
oil pan drain plug.
Tightening torque
30—41 N·m {3.1—4.1 kgf·m, 23—30 ft·lbf}
Dismounting
1. Dismount in the reverse order of mounting.
End Of Sie
49 L010 102
49 L010 104
ENGINE
PARALLEL
49 L010 103
49 L010 105
bp31je00000140
49 L010 101
49 L010 104
49 L010 105
APPROX. 20 mm {0.79 in}
bpe2ue00000089
01-10–6
Page 20
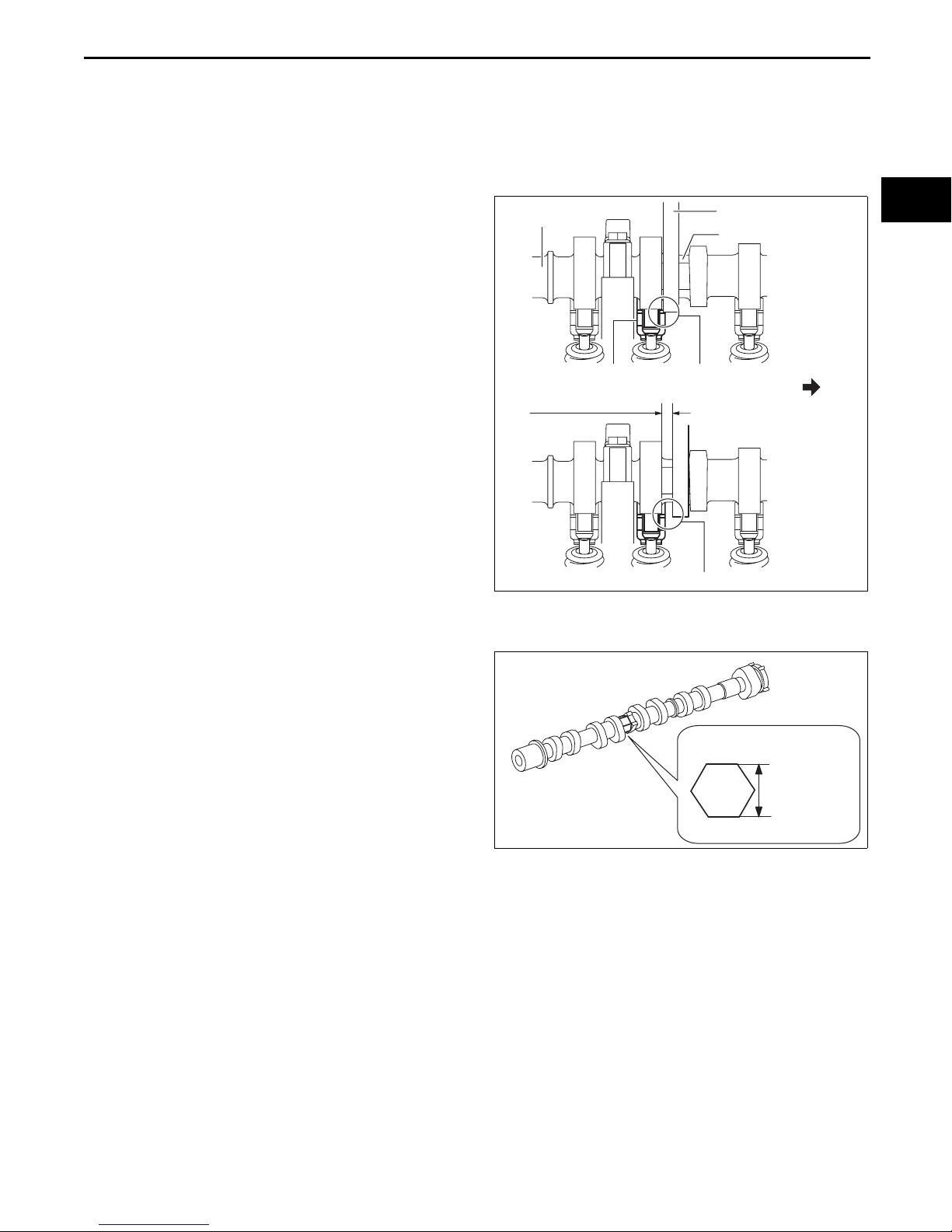
MECHANICAL
TIMING CHAIN DISASSEMBLY
Caution
• If the camshaft is rotated with the timing chain removed and the piston at the top dead center
position, the valve may contact the piston and the engine could be damaged. When rotating the
camshaft with the timing chain removed, rotate it after lowering the piston from the top dead
center position.
• When rotating the camshaft using a
wrench on the cast hexagon, the wrench
may contact the rocker arm and damage
CAMSHAFT
WRENCH
CAST HEXAGON
the rocker arm. To prevent damage to the
rocker arm when holding the camshaft on
the cast hexagon, use a wrench on the
rear side of the engine as shown in the
figure to secure a clearance between the
cam.
ROCKER ARM CONTACT
SECURE CLEARANCE
id011000505500
01-10
ENGINE REAR
Note
• Width at the cast hexagon of the camshaft is
22—24 mm {0.87—0.94 in}.
CAMSHAFT
DOES NOT CONTACT
CAST HEXAGON
22—24 mm
{0.87
am3uuw00008837
—0.94 in}
am3uuw00009029
01-10–7
Page 21
MECHANICAL
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
10
8
2
A
1
R
3
A
R
12
4
15
14
16
6
SST
R
5
7
11
R
13
22
24
23
17
18
9
21
SST SST
19
20
.
1 Dipstick
2 Cylinder head cover
3 Oil shower pipe
01-10–8
bpe1ze00000062
4 Spark plug
5 Water pump pulley
(See 01-10-9 Water Pump Pulley Disassembly Note.)
Page 22

MECHANICAL
6 Crankshaft pulley lock bolt
(See 01-10-10 Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt
Disassembly Note.)
7 Crankshaft pulley
8 Electric variable valve timing motor/driver
9Oil pan
(See 01-10-10 Oil Pan Disassembly Note.)
10 Engine front cover
(See 01-10-10 Engine Front Cover Disassembly
Note.)
11 Front oil seal
(See 01-10-11 Front Oil Seal Disassembly Note.)
12 Chain guide (No.1)
13 Chain tensioner
(See 01-10-11 Chain Tensioner Disassembly Note.)
14 Tensioner arm
15 Timing chain
16 Chain guide (No.2)
17 Crankshaft sprocket
18 Oil pump chain tensioner
(See 01-10-12 Oil Pump Chain Disassembly Note.)
19 Balancer shaft sprocket
(See 01-10-12 Oil Pump Chain Disassembly Note.)
20 Oil pump chain
(See 01-10-12 Oil Pump Chain Disassembly Note.)
21 Oil pump driven sprocket
(See 01-10-12 Oil Pump Chain Disassembly Note.)
22 Oil pump chain guide
23 Oil pump drive sprocket
24 Key
Water Pump Pulley Disassembly Note
Caution
• Be careful not to damage the belt groove and surface of the water pump pulley when using tools,
otherwise it will cause wear, breakage, abnormal noise of the drive belt (stretch belt), damage to
the pulley, and rust.
1. Align the water pump pulley hole with the water
pump hole as shown in the figure.
WATER PUMP
HOLEHOLE
01-10
2. Insert an appropriate bolt (length approx. 70 mm
{2.8 in}) into the water pump hole as shown in the
figure, and lock the water pump pulley against
rotation.
3. Remove the water pump pulley.
4. Remove the bolt used for locking the water pump
pulley against rotation.
WATER PUMP PULLEY
am3uuw00008841
WATER PUMP PULLEY
BOLT
am3uuw00008842
01-10–9
Page 23
MECHANICAL
Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt Disassembly Note
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Remove the crankshaft pulley lock bolt.
Oil Pan Disassembly Note
1. Remove the oil pan using a separator tool.
49 E011 1A0
bpe1ze00000063
Engine Front Cover Disassembly Note
1. Remove the engine front cover installation bolts.
2.
Using a screwdriver wrapped in a cloth, peel the
sealant away a little at a time, and remove the
engine front cover.
Caution
• Do not apply excessive force to the
screwdriver. Otherwise, the engine front
cover could be damaged.
• Be careful not to scratch or damage the
seal surface. Otherwise, it could cause
oil leakage.
CLOTH
adejjw00003946
CLOTH
am3uuw00008851
01-10–10
CLOTH
am3uuw00008852
Page 24

MECHANICAL
Front Oil Seal Disassembly Note
1. Remove the oil seal using a flathead screwdriver
with the tip protected by a clean cloth.
Chain Tensioner Disassembly Note
1. While moving the exhaust camshaft back and
forth in the direction of the arrow using a wrench
on the cast hexagon, press down the link plate of
the timing chain tensioner using a precision
screwdriver and release the plunger lock.
CLOTH
01-10
FRONT OIL SEAL
bpe2ue00000100
Note
• When moving the exhaust camshaft back
and forth, the timing chain pushes the
plunger in the chain tensioner making it
easier to operate the link plate.
2. Push back the plunger slowly in the direction
shown in the figure with the link plate still pushed
down.
3. Remove the screwdriver from the link plate with
the plunger still pushed down.
4. Release the force slightly from the plunger, and
move it back and forth 2—3 mm {0.08—0.11 in}.
bp31je00000104
LINK PLATE
PLUNGER
am3uuw00008854
am3uuw00008855
01-10–11
Page 25
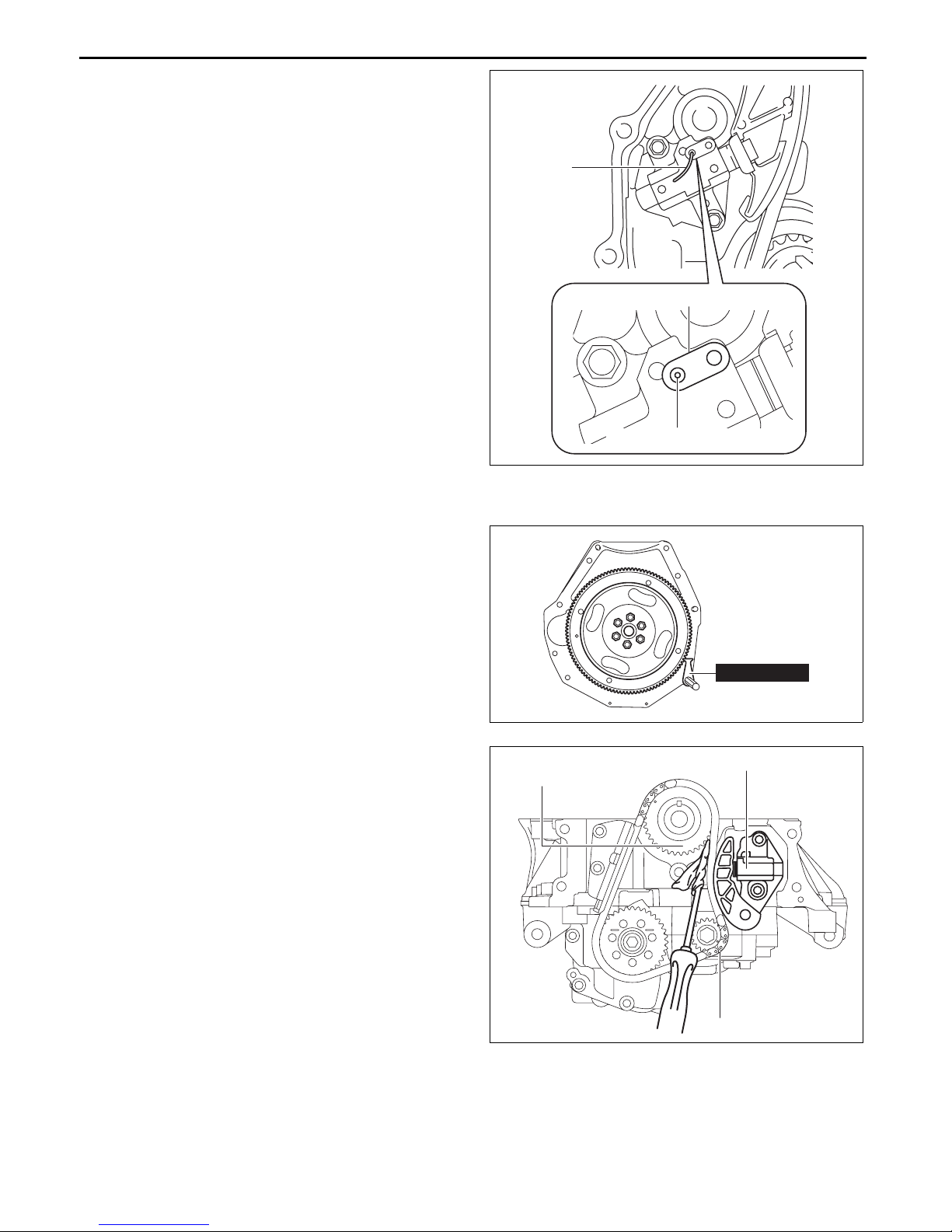
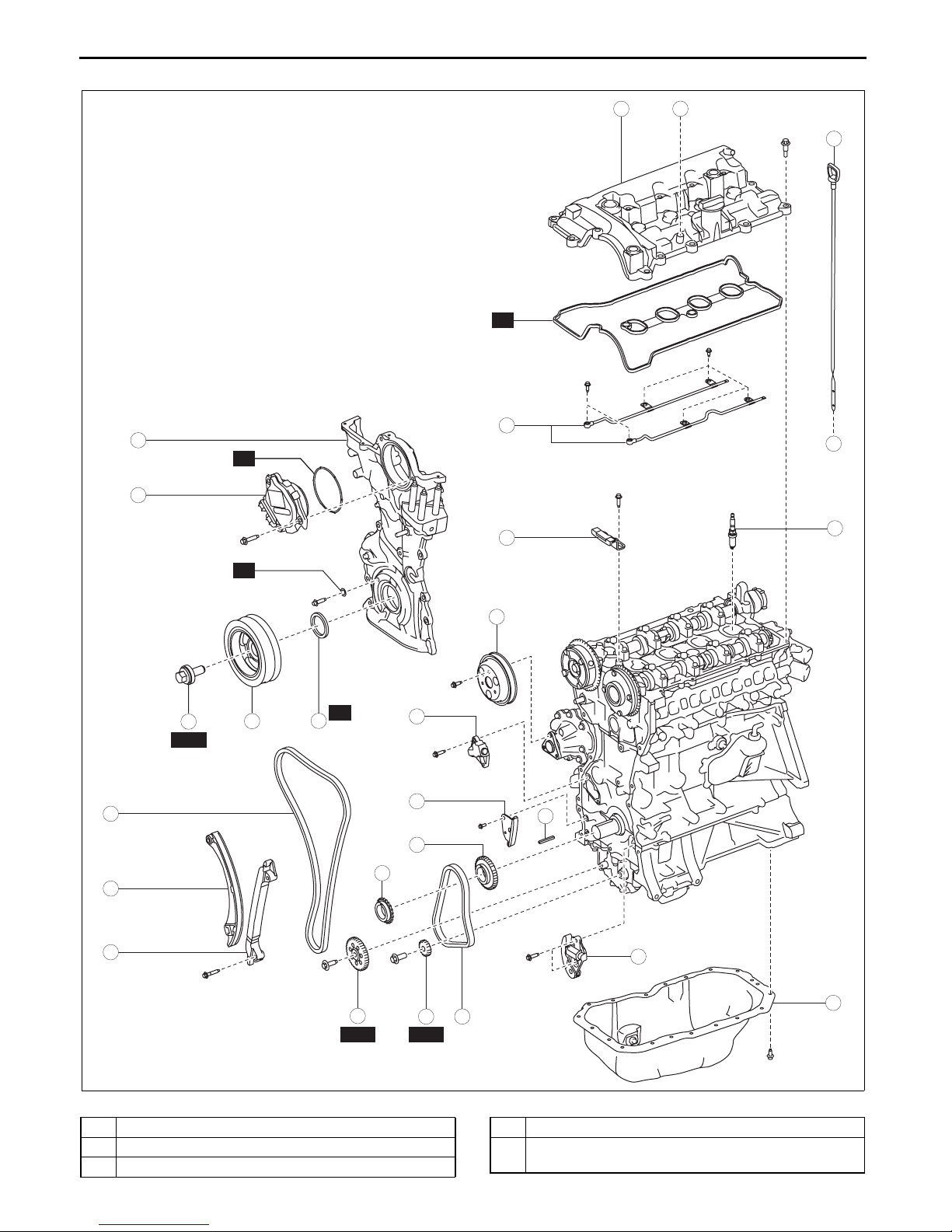
MECHANICAL
5. Insert a wire with an approx. diameter of 1.5 mm
{0.059 in} or a paper clip where the link plate hole
and the tensioner body hole overlap to secure the
link plate and lock the plunger.
6. Remove the chain tensioner.
WIRE OR
PAPER CLIP
LINK PLATE
TENSIONER BODY HOLE
am3uuw00008856
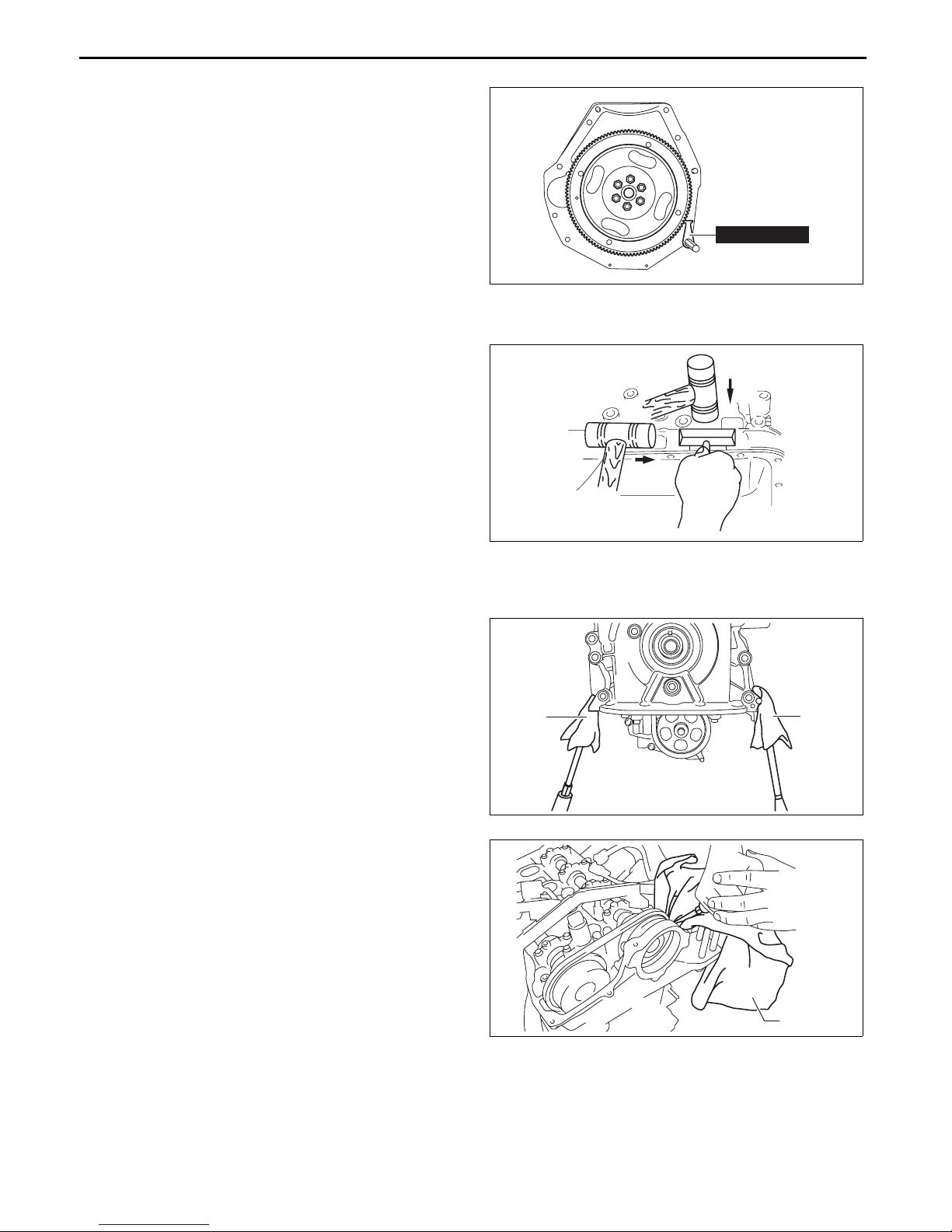
Oil Pump Chain Disassembly Note
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Slightly loosen the balancer shaft sprocket and oil
pump driven sprocket installation bolts.
Note
• At this stage, only loosen the installation
bolts, do not remove them. Remove the bolts
after removing the oil pump chain tensioner.
3. Set a cloth wrapped flathead screwdriver in the
gap between the oil pump drive sprocket and the
oil pump chain as shown in the figure.
OIL PUMP DRIVE
SPROCKET
49 E011 1A0
bpe1ze00000095
OIL PUMP CHAIN TENSIONER
01-10–12
OIL PUMP CHAIN
bpe1ze00000064
Page 26
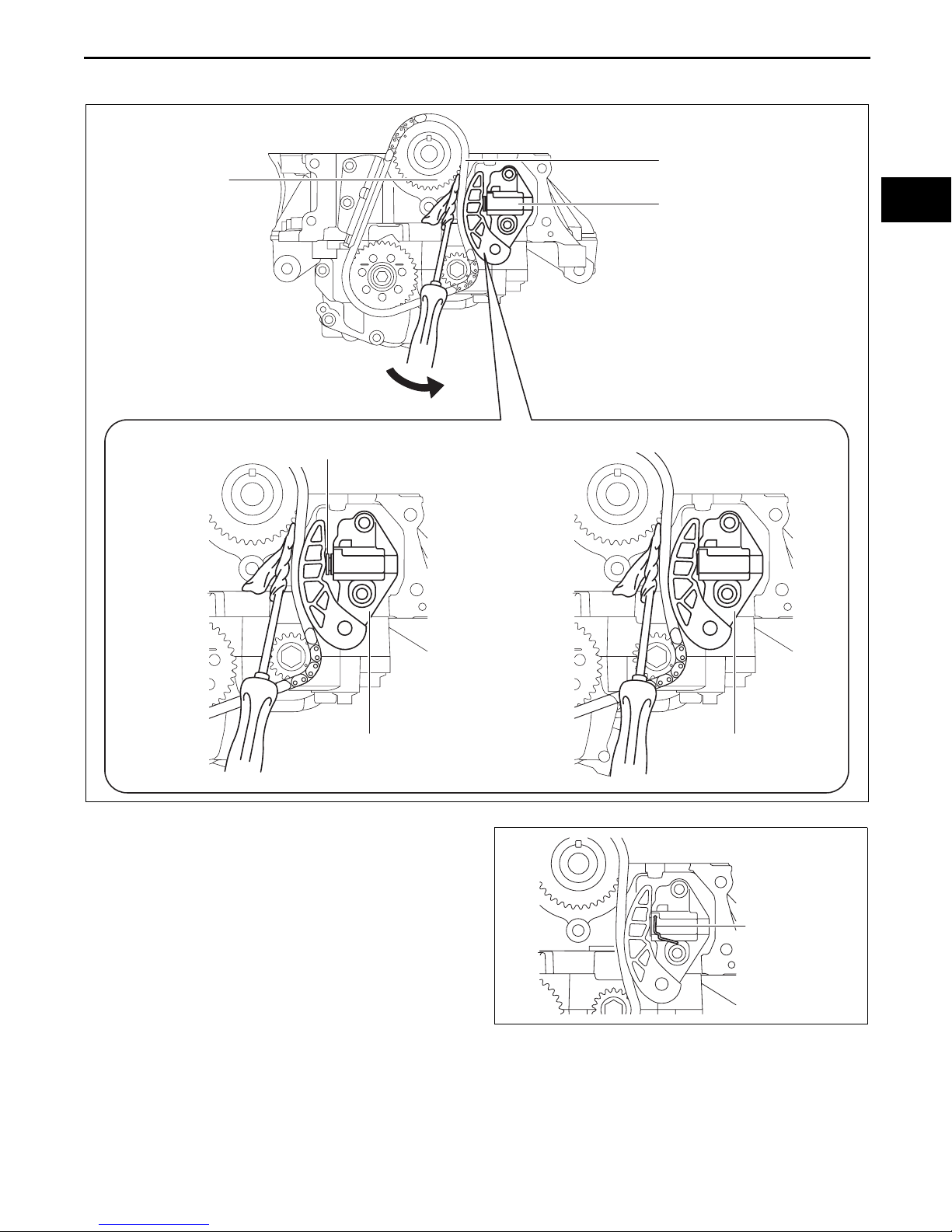
MECHANICAL
4. Move the screwdriver in the direction of the arrow and press the oil pump chain, and then press on the plunger
of the oil pump chain tensioner.
OIL PUMP CHAIN
OIL PUMP DRIVE
SPROCKET
OIL PUMP CHAIN TENSIONER
01-10
BEFORE PRESSING AFTER PRESSING
PLUNGER
OIL PUMP CHAIN TENSIONER
5. Insert a wire with an approx. diameter of 1.4 mm
{0.055 in} or a paper clip into the body hole of the
oil pump chain tensioner with the plunger
pressed.
OIL PUMP CHAIN TENSIONER
bpe1ze00000065
Note
• The wire or paper clip secures the plunger,
and the tension can be released.
6. Remove the oil pump chain tensioner.
7. Remove the oil pump chain and balancer shaft
sprocket as a single unit.
8. Remove the oil pump driven sprocket.
End Of Sie
WIRE OR
PAPER CLIP
bpe1ze00000066
01-10–13
Page 27
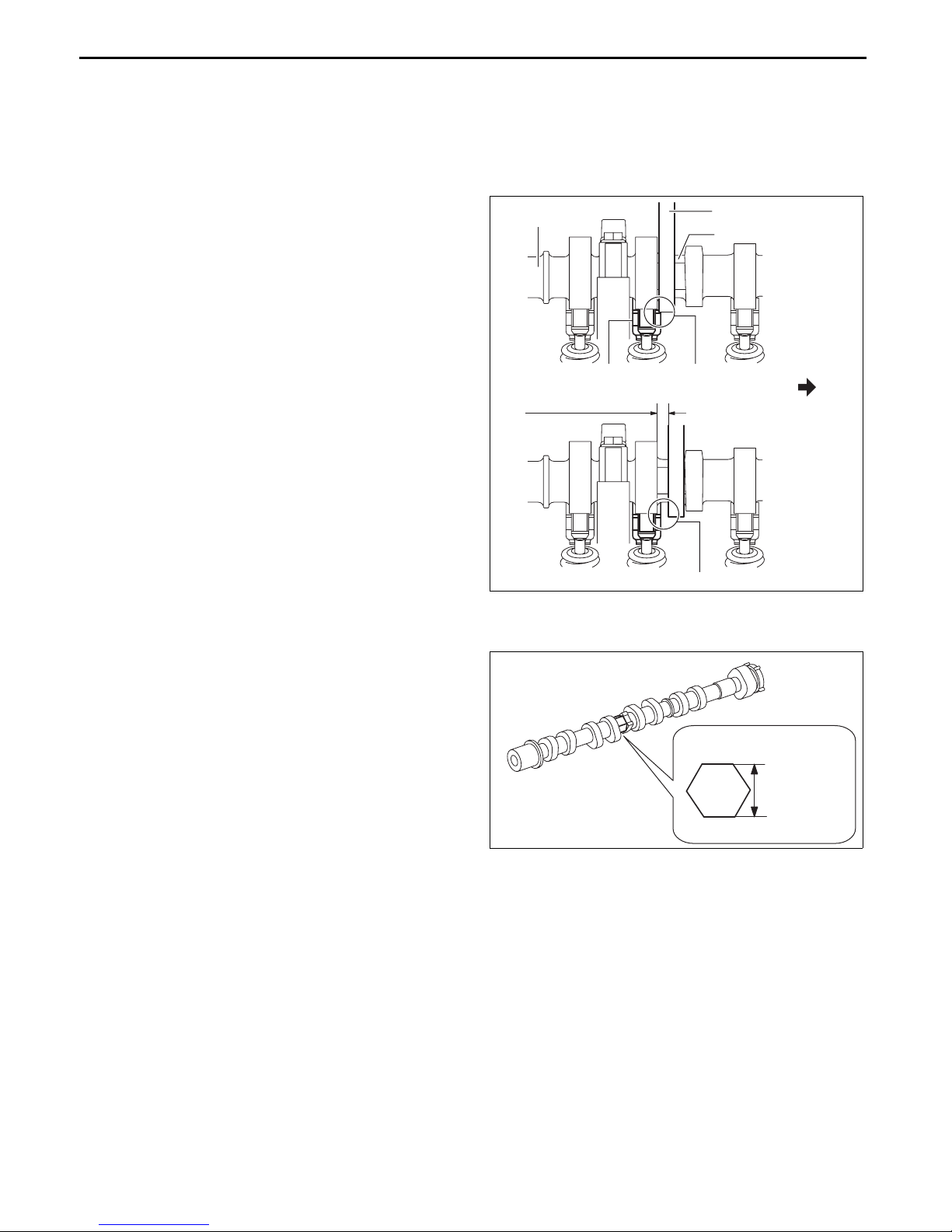
MECHANICAL
CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY (I)
Caution
• If the camshaft is rotated with the timing chain removed and the piston at the top dead center
position, the valve may contact the piston and the engine could be damaged. When rotating the
camshaft with the timing chain removed, rotate it after lowering the piston from the top dead
center position.
• When rotating the camshaft using a
wrench on the cast hexagon, the wrench
may contact the rocker arm and damage
CAMSHAFT
WRENCH
CAST HEXAGON
the rocker arm. To prevent damage to the
rocker arm when holding the camshaft on
the cast hexagon, use a wrench on the
rear side of the engine as shown in the
figure to secure a clearance between the
cam.
ROCKER ARM CONTACT
SECURE CLEARANCE
id011000500400
ENGINE REAR
Note
• Width at the cast hexagon of the camshaft is
22—24 mm {0.87—0.94 in}.
CAMSHAFT
DOES NOT CONTACT
CAST HEXAGON
22—24 mm
{0.87
am3uuw00008837
—0.94 in}
am3uuw00009029
01-10–14
Page 28
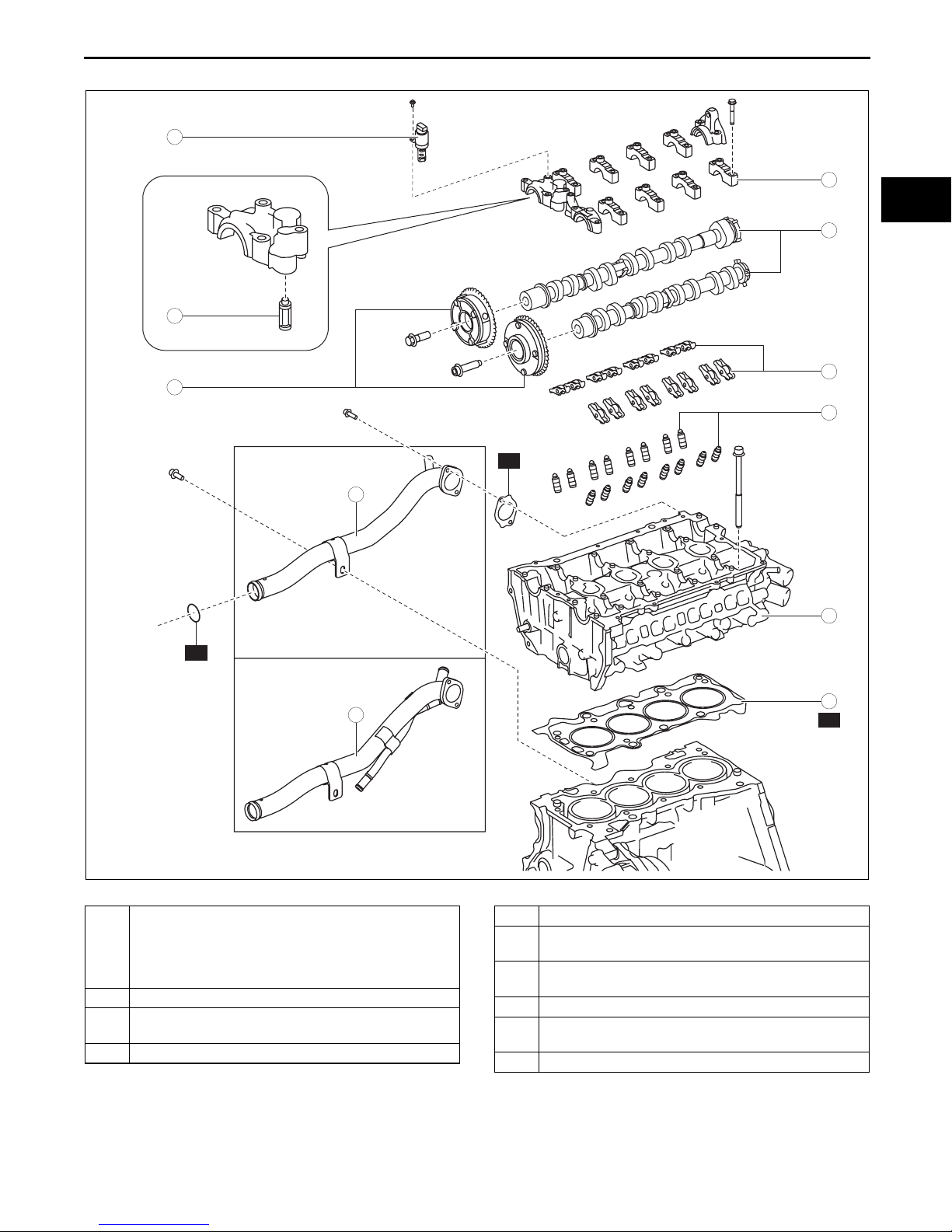
MECHANICAL
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
2
5
1
3
01-10
4
6
7
WITHOUT OIL COOLER
8
WATER
PUMP
R
WITH OIL COOLER
8
.
1 Electric variable valve timing actuator, hydraulic
variable valve timing actuator
(See 01-10-16 Electric Variable Valve Timing
Actuator, Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing Actuator
Disassembly Note.)
2OCV
3 Camshaft cap
(See 01-10-16 Camshaft Cap Disassembly Note.)
4 Camshaft
R
9
10
R
bpe5ue00000001
5 OCV oil filter
6 Rocker arm
(See 01-10-16 Rocker Arm Disassembly Note.)
7HLA
(See 01-10-16 HLA Disassembly Note.)
8 Water inlet pipe
9 Cylinder head
(See 01-10-16 Cylinder Head Disassembly Note.)
10 Cylinder head gasket
01-10–15
Page 29
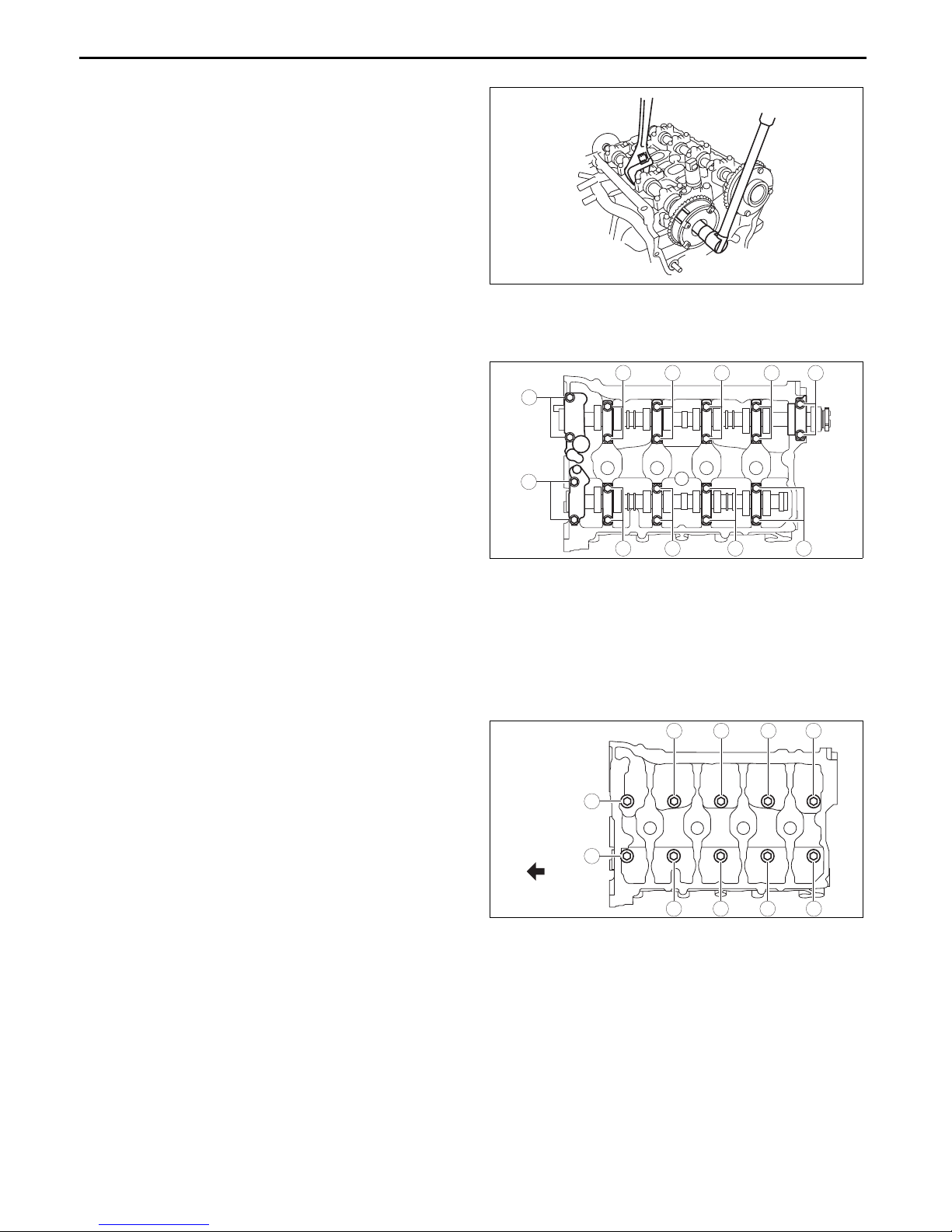
MECHANICAL
Electric Variable Valve Timing Actuator, Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing Actuator Disassembly Note
1. Hold the camshaft using a wrench on the cast
hexagon and loosen the actuator installation bolt.
bp31je00000161
Camshaft Cap Disassembly Note
1. Before removing the camshaft cap, Inspect the camshaft end play. (See 01-10-30 CAMSHAFT INSPECTION.)
2. Loosen the camshaft cap installation bolts in two
or three passes in the order shown in the figure
and remove the camshaft caps.
4 3
6
2
E2
E3
1
I2
I3
E4
I4
5
E5
I5
1
2
4
Rocker Arm Disassembly Note
1. Keep the rocker arms in the order of removal to enable reassembly in their original positions.
HLA Disassembly Note
1. Keep the HLAs in the order of removal to enable reassembly in their original positions.
Cylinder Head Disassembly Note
1. Loosen the cylinder head installation bolts in two
or three passes in the order shown in the figure
7
and remove them.
End Of Sie
3
4
ENGINE
FRONT
8
10
5
3
am3uuw00008985
26
159
bpe2ue00000014
01-10–16
Page 30
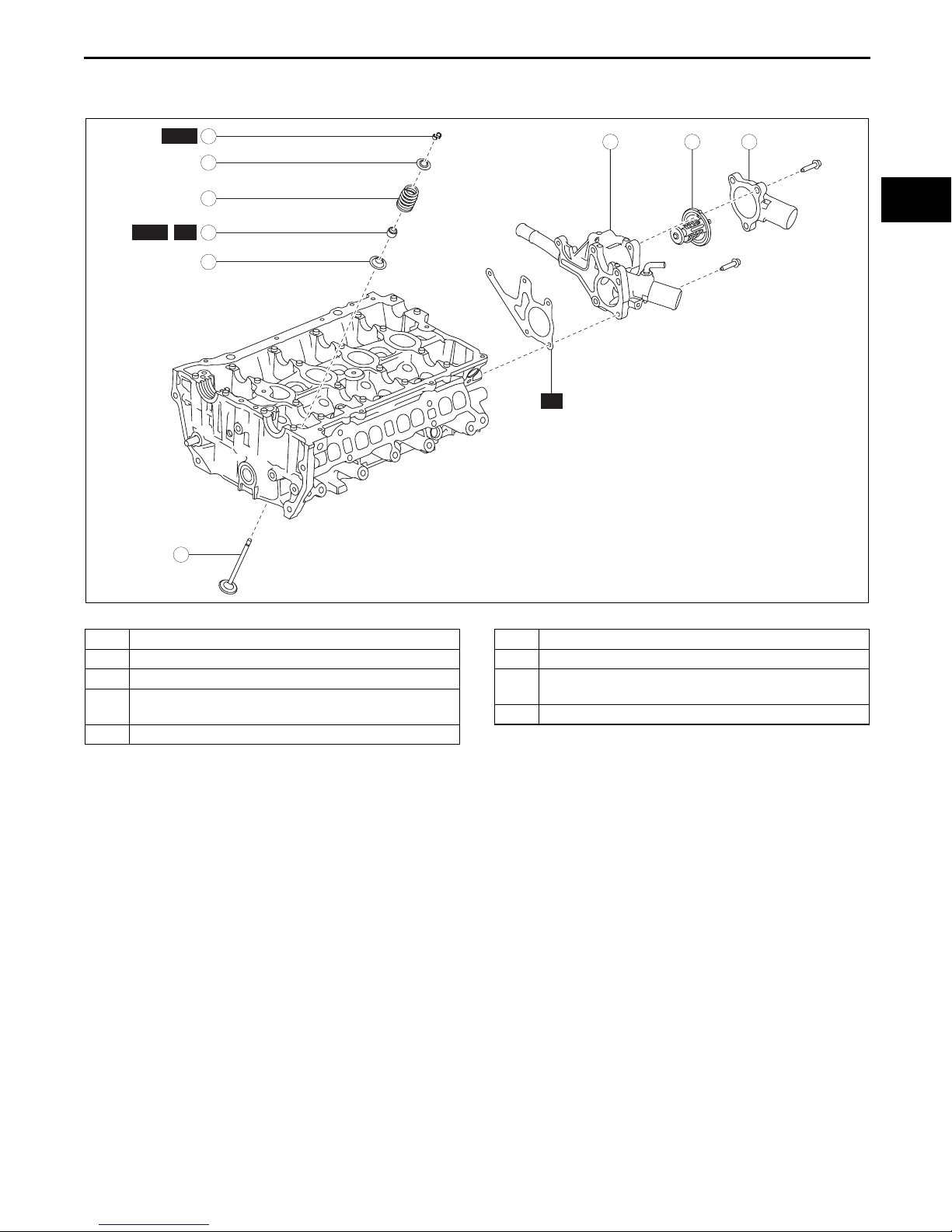
MECHANICAL
CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY (II)
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
SST
4
5
6
SST
R
8
9
id011000500500
3
2
1
01-10
R
7
.
1 Thermostat cover
2 Thermostat
3 Water outlet
4 Valve keeper
(See 01-10-18 Valve Keeper Disassembly Note.)
5 Upper valve spring seat
bpe1ze00000013
6Valve spring
7Valve
8 Valve seal
(See 01-10-18 Valve Seal Disassembly Note.)
9 Lower valve spring seat
01-10–17
Page 31

Valve Keeper Disassembly Note
1. Remove the valve keeper using the SSTs.
MECHANICAL
49 B012 0A2A
49 0636 100B
bpe1ze00000014
Valve Seal Disassembly Note
1. Remove the valve seal using the SST or pliers.
End Of Sie
49 S120 170
VALVE SEAL
VALVE GUIDE
bpe1ze00000015
VALVE SEAL
bpe1ze00000016
01-10–18
Page 32

MECHANICAL
CYLINDER BLOCK DISASSEMBLY (I)
Caution
• Do not disassemble the oil pump, water pump and balancer unit because it is a precision unit.
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
AT X
R
7 6
8
R
5
MTX
5
1
4
id011000500600
SST
R
3
SST
R
3
01-10
10
R
.
1 Knock sensor (KS)
2 Oil separator
3 Dual-mass flywheel (MTX)/ drive plate (ATX)
installation bolt
(See 01-10-20 Dual-mass Flywheel (MTX)/ Drive
Plate (ATX) Installation Bolt Disassembly Note.)
4 Backing plate (ATX)
5 Dual-mass flywheel (MTX), drive plate (ATX)
(See 01-10-21 Dual-mass Flywheel Disassembly
Note (MTX).)
11
R
2
9
bpe5ue00000002
6 End plate
7 Rear oil seal
(See 01-10-21 Rear Oil Seal Disassembly Note.)
8 Water pump
9Oil strainer
10 Oil pump
11 Balancer unit
01-10–19
Page 33

MECHANICAL
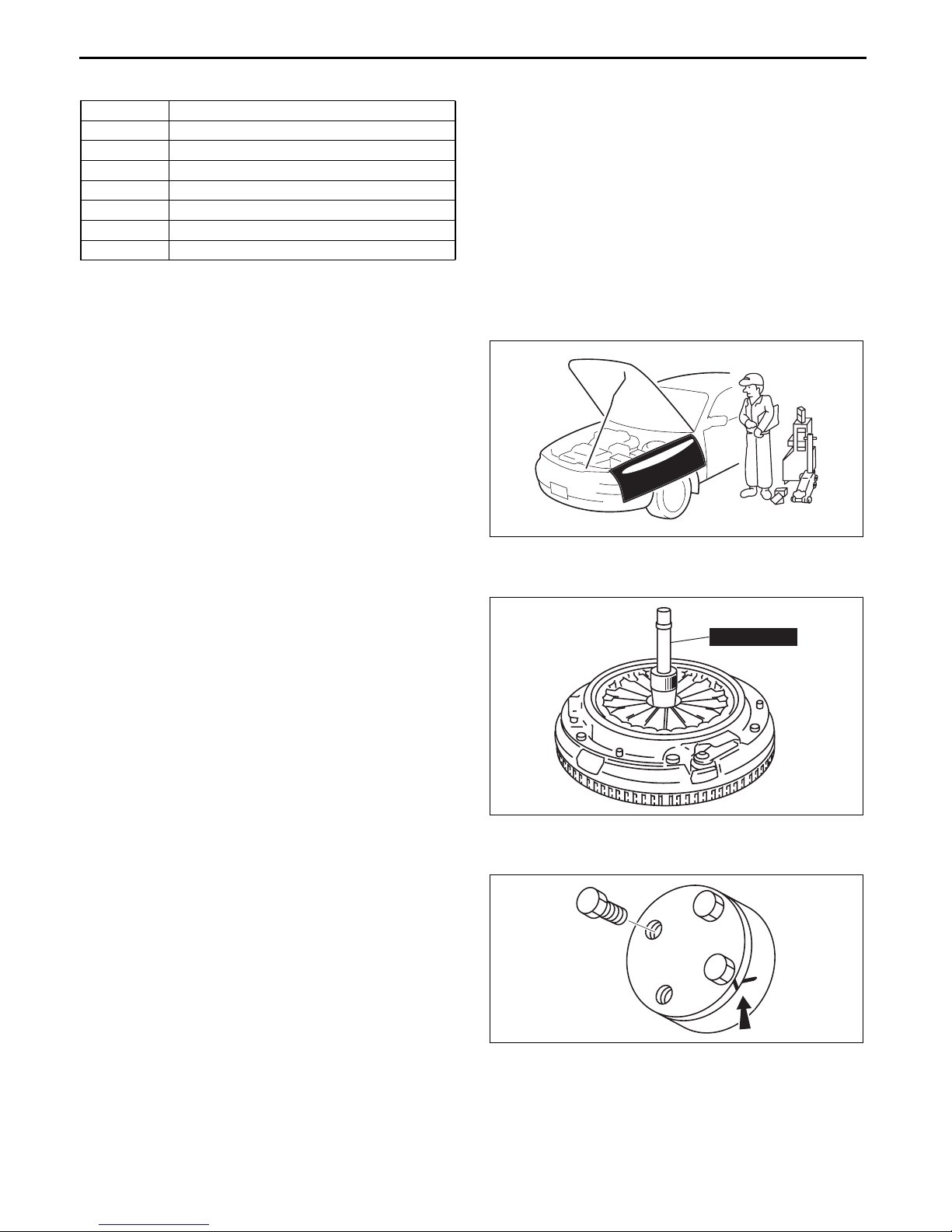
Dual-mass Flywheel (MTX)/ Drive Plate (ATX) Installation Bolt Disassembly Note
Dual-mass flywheel installation bolt (MTX)
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST (49 E011 1A0).
2. Loosen the bolts uniformly and gradually in the
order shown in the figure.
Note
• If the bolt installation holes are not
positioned properly, perform the following
procedure:
(1) Install the SST (49 S120 710) to the dual-
mass flywheel.
(2) Rotate the dual-mass flywheel (secondary
flywheel side) using the SST (49 S120 710).
(3) When the bolt installation holes are positioned
properly, hold the position and remove one of
the bolts.
(4) After removing the bolt, set up the SST (49
G033 102) to lock the dual-mass flywheel
(secondary flywheel side) against rotation.
49 E011 1A0
49 E011 1A0
49 E011 1A0
49 S120 710
8
1
3
5
6
4
2
7
ac5wzw00005660
am6xuw00005540
Warning
• If all of the bolts are removed without
locking the dual-mass flywheel
(secondary flywheel side) against
rotation, the dual-mass flywheel (primary
or secondary flywheel side) may rotate,
resulting in injury. Therefore, always set
up the SST (49 G033 102).
• When the bolts are removed from the
dual-mass flywheel, always cover the bolt
holes using tape. If the SST (49 G033 102) is removed while the operator’s finger is inserted in the
bolt hole, the dual-mass flywheel may rotate and the operator could be injured.
(5) Remove the remaining bolts.
Drive plate installation bolt (ATX)
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Loosen the bolts uniformly and gradually in the
order shown in the figure.
49 G033 102
49 S120 710
am6xuw00005541
49 E011 1A0
01-10–20
bpe1ze00000092
Page 34

MECHANICAL
Dual-mass Flywheel Disassembly Note (MTX)
Note
• When reusing the dual-mass flywheel, do not remove the SST (49 G033 102) locking the dual-mass
flywheel (secondary flywheel side) against rotation.
Rear Oil Seal Disassembly Note
1. Cut the oil seal lip using a utility knife.
2. Remove the oil seal using a flathead screwdriver
with the tip protected by a clean cloth to prevent
damage to the oil seal sliding part of the
crankshaft.
End Of Sie
01-10
REAR OIL
SEAL
CLOTH
bpe5ue00000003
01-10–21
Page 35

MECHANICAL
CYLINDER BLOCK DISASSEMBLY (II)
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
4
6
9
7
R
7
R
8
10
5
16
id011000500700
18
17
15
1
R
SST
13
3
2
.
1 Pilot bearing (MTX)
(See 01-10-23 Pilot Bearing Disassembly Note.)
2 Connecting rod cap
(See 01-10-23 Connecting Rod Cap Disassembly
Note.)
3 Lower connecting rod bearing
(See 01-10-23 Connecting Rod Bearing
Disassembly Note.)
4 Piston, connecting rod
(See 01-10-23 Piston, Connecting Rod Disassembly
Note.)
5 Upper connecting rod bearing
(See 01-10-23 Connecting Rod Bearing
Disassembly Note.)
12
11
14
bpe1ze00000038
6 Piston ring
7 Snap ring
(See 01-10-24 Snap Ring Disassembly Note.)
8 Piston pin
9Piston
10 Connecting rod
11 Lower cylinder block
(See 01-10-24 Lower Cylinder Block Disassembly
Note.)
12 Lower main bearing
(See 01-10-25 Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Disassembly Note.)
01-10–22
Page 36

MECHANICAL
13 Crankshaft
(See 01-10-25 Crankshaft Disassembly Note.)
14 Plate
15 Upper main bearing
(See 01-10-25 Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Disassembly Note.)
16 Thrust bearing
(See 01-10-25 Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Disassembly Note.)
17 Oil jet valve
18 Upper cylinder block
Pilot Bearing Disassembly Note
Note
• The pilot bearing does not need to be removed unless you are replacing it.
1. Use the SST to remove the pilot bearing.
49 1285 071
01-10
bpe2ue00000021
Connecting Rod Cap Disassembly Note
1. Before removing the connecting rod cap, inspect
the connecting rod side clearance. (See 01-10-35
CONNECTING ROD CLEARANCE
INSPECTION.)
2. The removed connecting rod caps are to be kept
so that they can be assembled to the same
positions and in the direction as before removal.
bp31je00000044
Connecting Rod Bearing Disassembly Note
1. The removed connecting rod bearings are to be kept so that they can be assembled to the same positions and
in the direction as before removal.
Piston, Connecting Rod Disassembly Note
1. Before removing the piston and connecting rod, remove the carbon in the cylinder.
2. Before removing the piston and connecting rod, inspect the oil clearance at the large end of the connecting rod.
(See 01-10-35 CONNECTING ROD CLEARANCE INSPECTION.)
01-10–23
Page 37

MECHANICAL
Snap Ring Disassembly Note
1. Before removing the snap ring, verify that the large end of connecting rod drops under its own weight with no
resistance. (See 01-10-35 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD INSPECTION.)
2. Remove the snap ring using a flathead
screwdriver.
SNAP RING
bpe2ue00000022
Lower Cylinder Block Disassembly Note
1. Before removing the lower cylinder block, inspect the crankshaft end play. (See 01-10-36 CRANKSHAFT
INSPECTION.)
2. Loosen the lower cylinder block installation bolts
B in two or three passes in the order shown in the
figure and remove them.
1
5
9
8
BBBBB
4
3. Loosen the lower cylinder block installation bolts
A in two or three passes in the order shown in the
figure and remove them.
ENGINE
FRONT
ENGINE
FRONT
2
1
2
6
10
5
6
9
10
7
AAAA
7
AAAA
3
BBBBB
bpe1ze00000039
A
48
3
A
bpe1ze00000040
01-10–24
Page 38

MECHANICAL
4. Using a screwdriver wrapped in a cloth, peel the
sealant away a little at a time, and remove the
LOWER CYLINDER BLOCK
lower cylinder block.
Caution
• Do not apply excessive force to the
screwdriver. Otherwise, the lower
cylinder block could be damaged.
• Be careful not to scratch or damage the
seal surface. Otherwise, it could cause
oil leakage.
CLOTH
bpe2ue00000025
Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing Disassembly Note
1. The removed thrust bearings and main bearings are to be kept so that they can be assembled to the same
positions and in the direction as before removal.
Crankshaft Disassembly Note
Caution
• Placing the crankshaft on a disassembly bench will deform or damage it because the plate for the
crankshaft position sensor signal detection installed to the crankshaft is larger than the
counterweight. Therefore, set wood blocks or similar objects on the both sides of the crankshaft
so that the plate does not contact the disassembly bench directly when placing the crankshaft on
the bench.
01-10
CLOTH
End Of Sie
CYLINDER HEAD INSPECTION
1. Inspect the cylinder head surface for cracks and other damage using a red dye penetrant.
• If there is a malfunction, replace the cylinder head.
2. Measure the combustion chamber side of the
cylinder head for distortion in six directions as
shown in the figure using a straight edge and
feeler gauge.
• If the distortion exceeds the maximum
specification, replace the cylinder head. Do
not attempt to repair the cylinder head by
milling or grinding.
Maximum distortion, head gasket side of the
cylinder head
0.05 mm {0.002 in}
id011000507100
bpe1ze00000003
01-10–25
Page 39

MECHANICAL
3. Inspect the contact surface of the exhaust
manifold and the intake manifold for distortion by
measuring as shown in the figure using a straight
edge and feeler gauge.
• If the distortion on the intake manifold side
exceeds the maximum specification, replace
the cylinder head.
• If the distortion on the exhaust manifold side
exceeds the maximum specification, grind the
surface or replace the cylinder head.
Maximum distortion, manifold side
IN: 0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
EX: 0.05 mm {0.002 in}
Maximum cutting length, manifold side
IN: Cutting not authorized
EX: 0.20 mm {0.0079 in}
End Of Sie
VALVE SEAT INSPECTION/REPAIR
1. Measure the contact width of the valve face and
the valve seat using the valve lapping compound.
• If it is not within the specification, resurface
the valve seat using the 45° valve seat cutter.
Standard valve seat contact width
1.37—1.84 mm {0.0540—0.0724 in}
IN
EX
bpe1ze00000004
id011000501300
SEAT CONTACT
WIDTH
Valve seat angle
45°
2. Verify that the area where the valve seat contacts
the valve face is centered.
• If the seating position is too high, correct the
valve seat using a 70° (IN) 70° (EX) valve seat
cutter and a 45° valve seat cutter.
• If the seating position is too low, correct as
follows:
— IN: Correct the valve seat using a 20°
valve seat cutter and then using a 45°
valve cutter.
— EX: Correct the valve seat using a 45°
valve seat cutter.
EX
45
bpe1ze00000102
IN
°
70
°
°
70
°
45
°
20
VALVE SEATVALVE SEAT
01-10–26
COMBUSTION CHAMBER
bpe1ze00000103
Page 40

MECHANICAL
3. Inspect the valve seat for sinkage. Measure the
protruding length (dimension L) of the valve stem
using a valve of standard length.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
cylinder head.
Standard valve seat sinkage amount
(Dimension L)
IN: 48.93—50.17 mm {1.927—1.975 in}
EX: 48.87—50.11 mm {1.925—1.972 in}
End Of Sie
VALVE, VALVE GUIDE INSPECTION
1. Measure the valve head margin thickness using a
vernier caliper.
• If it is less than the standard specification,
replace the valve.
Standard valve head margin thickness
IN: 1.75—1.95 mm {0.0689—0.0767 in}
EX: 1.95—2.15 mm {0.0768—0.0846 in}
2. Measure the length of the each valve using a
vernier caliper.
• If it is less than the minimum specification,
replace the valve.
IN : 34.0 mm {1.34 in}
EX : 29.0 mm {1.14 in}
MARGIN THICKNESS
L
01-10
bpe1ze00000104
id011000506200
bpe5ue00000012
Standard valve length
IN: 107.00—107.60 mm {4.2127—4.2362 in}
EX: 117.09—117.69 mm {4.6099—4.6334 in}
Minimum valve length
IN: 106.78 mm {4.2039 in}
EX: 116.87 mm {4.6012 in}.
3. Measure the valve stem diameter of each valve
using the micrometer. Measurement positions
total six and are in the X and Y directions, at three
points (A, B, and C) as shown in the figure.
• If it is less than the minimum specification,
replace the valve.
Standard valve stem diameter
IN: 5.470—5.485 mm {0.2154—0.2159 in}
EX: 5.465—5.480 mm {0.2152—0.2157 in}
Minimum valve stem diameter
IN: 5.424 mm {0.2135 in}
EX: 5.419 mm {0.2133 in}
bez0je00000017
X
Y
A
B
C
bpe2ue00000084
01-10–27
Page 41

MECHANICAL
4. Measure the inner diameter of each valve guide
using the caliper gauge. Measurement positions
total six and are in the X and Y directions, at three
points (A, B, and C) as shown in the figure.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
valve guide.
Standard valve guide inner diameter
IN: 5.510—5.530 mm {0.2170—0.2177 in}
EX: 5.510—5.530 mm {0.2170—0.2177 in}
5. Calculate the clearance between the valve stem
and the valve guide by subtracting the inner
diameter of the valve guide from the outer
diameter of the corresponding valve stem.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the valve or valve guide.
Standard clearance between valve stem and
guide
IN: 0.025—0.060 mm {0.0010—0.0023 in}
EX: 0.030—0.065 mm {0.0012—0.0025 in}
Maximum clearance between valve stem and
guide
0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
X
Y
A
B
C
bpe2ue00000085
VALVE STEM
VALVE GUIDE
CLEARANCE
bpe2ue00000086
6. Measure the projection height (dimension A) of
each valve guide using the vernier caliper.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
valve guide.
Standard valve guide projection height
IN: 16.4—17.0 mm {0.646—0.669 in}
EX: 16.4—17.0 mm {0.646—0.669 in}
End Of Sie
A
VALVE GUIDE
CYLINDER HEAD
bpe2ue00000087
01-10–28
Page 42

MECHANICAL
VALVE GUIDE REPLACEMENT
Removal
1. Tap the valve guide out from combustion chamber
side using the SST.
Installation
1. Apply clean engine oil to the valve guide.
2. Tap the valve guide from the camshaft side using
the SST so that the projection height (dimension
A) is within the specification.
Standard valve guide projection height
IN: 16.4—17.0 mm {0.646—0.669 in}
EX: 16.4—17.0 mm {0.646—0.669 in}
End Of Sie
id011000501200
49 B012 015
01-10
VALVE GUIDE
bpe2ue00000026
49 B012 015
A
VALVE GUIDE
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Caution
• The valve springs differ depending on the
IN and EX sides.Therefore, verify the free
length or identification paint beforehand
and inspect the valve springs.
CYLINDER HEAD
bpe2ue00000027
id011000501400
IN
48.96 mm {1.928 in}
PURPLE PAINT
EX
50.07 mm {1.971 in}
NOT PAINTED
bpe1ze00000041
01-10–29
Page 43

MECHANICAL
1. Measure the valve spring height using the spring
tester.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
valve spring.
Valve spring installation height
When pressurized with spring force of 228—
252 N {23.3—25.6 kgf, 51.3—56.6 lbf},
spring height is 38.0 mm {1.50 in}
2. Measure the amount of off-square on the valve
spring using a square.
(1) Rotate the valve spring one full turn and
measure A at the point where the gap is the
largest.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the valve spring.
Maximum valve spring off-square
IN: 2.0 ° (1.7 mm {0.067 in})
EX: 2.0 ° (1.7 mm {0.067 in})
End Of Sie
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION
1. Set the No.1 and No.5 journals of the camshaft on V-blocks.
2. Measure the camshaft runout using the dial
gauge.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the camshaft.
bp31je00000053
A
UPPER
LOWER
beltze00000017
id011000501500
Maximum camshaft runout
0.030 mm {0.0012 in}
3. Measure the cam height using the micrometer as
shown in the figure.
• If it is less than the minimum specification,
replace the camshaft.
Standard cam height
IN: 42.34 mm {1.667 in}
EX: 40.37 mm {1.589 in}
Minimum cam height
IN: 42.27 mm {1.664 in}
EX: 40.30 mm {1.587 in}
bpe2ue00000031
bp31je00000171
01-10–30
Page 44

4. Measure the journal diameter using the
micrometer. Measurement positions total four and
are in the X and Y directions, at two points (A and
B) as shown in the figure.
• If it is less than the minimum specification,
replace the camshaft.
MECHANICAL
A B
Standard camshaft journal diameter
24.96—24.98 mm {0.9827—0.9834 in}
Y
Minimum camshaft journal diameter
24.93 mm {0.9815 in}
5. Measure the camshaft journal oil clearance using
the following procedure:
(1) Clean the camshaft journal and the journal receptacle part.
(2) Put the camshaft on the cylinder head with the rocker arm detached.
(3) Cut the plastigauge to the same length as the
journal width and position it parallel to the
camshaft.
(4) Install the camshaft caps. (See 01-10-59
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY (II).)
(5) Remove the camshaft caps. (See 01-10-14
CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY (I).)
(6) Measure the camshaft journal oil clearance.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the cylinder head.
Standard camshaft journal oil clearance
0.035—0.080 mm {0.0014—0.0031 in}
Maximum camshaft journal oil clearance
0.090 mm {0.0035 in}
X
01-10
bp31je00000172
PLASTIGAUGE
bpe2ue00000032
6. Measure the camshaft end play using a dial
gauge.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the cylinder head or camshaft.
Standard camshaft end play
0.07—0.22 mm {0.003—0.008 in}
Maximum camshaft end play
0.23 mm {0.0091 in}
End Of Sie
bp31je00000173
01-10–31
Page 45

MECHANICAL
CYLINDER BLOCK INSPECTION
1. Measure the cylinder block for distortion in six
directions as shown in the figure using a straight
edge and feeler gauge.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the cylinder block.
Maximum distortion, head gasket side of the
cylinder block
0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
2. Measure the cylinder bore diameter using the
cylinder gauge. The measurement position is in
the X and Y directions at a point 43.9 mm {1.73
in} below the top surface of the cylinder as shown
in the figure.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
cylinder block.
Standard cylinder bore diameter
89.000—89.030 mm {3.5040—3.5051 in}
End Of Sie
OIL JET VALVE INSPECTION
1. Apply compressed air to oil jet valve A and verify
that air passes through oil jet valve B.
• If air does not flow, replace the oil jet valve.
• If there is air flow with air compressor of less
than 180 kPa {1.84 kgf/cm
replace the oil jet valve.
2
, 26.1 psi},
id011000507200
bp31je00000144
X
Y
43.9 mm {1.73 in}
bpe2ue00000098
id011000505900
B
A
Oil jet valve opening pressure
180—220 kPa {1.84—2.24 kgf/cm
2
, 26.2—
31.9 psi}
End Of Sie
PISTON INSPECTION
Caution
• If the piston is replaced, replace the piston, piston pin, and the snap ring as a single component.
1. Measure the piston outer diameter using the
micrometer. The measurement position is 8.0 mm
{0.31 in} from the lower end of the piston (area
with no coating on the piston skirt) and in the
thrust direction.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
piston.
Standard piston outer diameter
88.965—88.995 mm {3.5026—3.5037 in}
2. Measure the cylinder bore diameter. (See 01-1032 CYLINDER BLOCK INSPECTION.)
bp31je00000131
id011000502100
bpe1ze00000097
01-10–32
Page 46

MECHANICAL
3. Calculate the cylinder-to-piston clearance from the cylinder bore diameter and the piston outer diameter.
• If the clearance exceeds the maximum specification, replace the piston or cylinder block.
Standard clearance between piston and cylinder
0.025—0.045 mm {0.0010—0.0017 in}
Maximum clearance between piston and cylinder
0.066 mm {0.0026 in}
4. Measure the piston-to-ring groove clearance
along the perimeter using a feeler gauge. For the
O-ring, measure the clearance with the O-ring
assembled to the piston.
• If the clearance exceeds the maximum
specification, replace the piston or piston ring.
Standard clearance between piston ring and
ring groove
Top: 0.04—0.08 mm {0.002—0.003 in}
Second: 0.03—0.07 mm {0.0012—0.0027 in}
Oil: 0.04—0.12 mm {0.002—0.004 in}
Maximum clearance between piston ring and
ring groove
Top: 0.12 mm {0.0047 in}
Second: 0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
Oil: 0.17 mm {0.0067 in}
bpe1ze00000098
01-10
End Of Sie
PISTON RING INSPECTION
1. Using the piston, press the piston ring parallel into
the cylinder to 43.9 mm {1.73 in} from the upper
end of the cylinder block.
2. Measure the piston ring end gap using a feeler
gauge.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the piston ring.
Standard piston ring end gap
Top: 0.13—0.18 mm {0.0052—0.0070 in}
Second: 0.18—0.28 mm {0.008—0.011 in}
Oil (Rail): 0.10—0.35 mm {0.004—0.013 in}
Maximum piston ring end gap
Top: 0.35 mm {0.014 in}
Second: 0.45 mm {0.018 in}
Oil (Rail): 0.52 mm {0.020 in}
43.9 mm {1.73 in}
id011000592300
PISTON
CYLINDER BLOCK
PISTON RING
bpe2ue00000094
PISTON RING
bpe2ue00000095
End Of Sie
01-10–33
Page 47

MECHANICAL
C
PISTON PIN INSPECTION
Caution
• If the piston or piston pin is replaced, replace the piston, piston pin and the snap ring as a single
component.
1. Measure the piston pin outer diameter using the
micrometer. Measurement positions total eight
and are in the X and Y directions, at four points
(A, B, C, and D) as shown in the figure.
Standard piston pin outer diameter
20.995—21.000 mm {0.82658—0.82677 in}
2. Measure the piston pin hole diameter using the
caliper gauge. Measurement positions total eight
and are in the X and Y directions, at four points
X
(A, B, C, and D) as shown in the figure.
Standard piston pin hole diameter
21.004—21.008 mm {0.82693—0.82708 in}
A
B
3. Calculate the clearance between the piston pin
hole diameter and the piston pin outer diameter.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
piston or the piston pin.
C
D
Standard clearance between piston pin hole
diameter and piston pin outer diameter
0.004—0.013 mm {0.0002—0.0005 in}
id011000507500
X
Y
A
B
D
adj2224e255
Y
bpe1ze00000085
4. Measure the inner diameter on the small end of
the connecting rod using the caliper gauge in the
X and Y directions as shown in the figure.
Standard connecting rod small end inner
diameter
21.002—21.013 mm {0.82686—0.82728 in}
5. Calculate the clearance between the inner
diameter on the small end of the connecting rod
and the piston pin outer diameter.
• If it is not within the specification, replace the
CONNECTING ROD
connecting rod or the piston pin.
Standard clearance between connecting rod small end inner diameter and piston pin outer diameter
0.002—0.018 mm {0.00008—0.00070 in}
End Of Sie
X
Y
bpe2ue00000092
01-10–34
Page 48

MECHANICAL
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD INSPECTION
1. Check the oscillation torque as shown in the
figure. Verify that the large end drops under its
own weight with no resistance.
• If the piston shakes heavily or unsmoothly,
disassemble the piston and connecting rod,
then inspect the following: (See 01-10-34
PISTON PIN INSPECTION.)
— Clearance between piston pin outer
diameter and piston pin hole diameter.
— Clearance between piston pin outer
diameter and connecting rod small end
inner diameter.
End Of Sie
CONNECTING ROD INSPECTION
1. Inspect the connecting rod for bending and
distortion using the connecting rod aligner.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the connecting rod.
Maximum connecting rod bending
0.050 mm {0.0020 in}
Maximum connecting rod distortion
0.050 mm {0.0020 in}
id011000503100
01-10
bp31je00000061
id011000502800
Connecting rod center-to-center distance
154.8 mm {6.094 in}
End Of Sie
CONNECTING ROD CLEARANCE INSPECTION
1. Measure the side clearance at the large end of
the connecting rod using a feeler gauge.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the connecting rod or crankshaft.
Standard side clearance at the large end of
connecting rod
0.14—0.36 mm {0.006—0.014 in}
Maximum side clearance at the large end of
connecting rod
0.465 mm {0.0183 in}
2. Measure the oil clearance at the large end of the
connecting rod using the following procedure:
(1) Cut the plastigauge as wide as the connecting
rod bearing width, place it parallel to the
crankshaft, avoiding the oil hole.
(2) Install the lower connecting rod bearing and
connecting rod cap. (See 01-10-40
CYLINDER BLOCK ASSEMBLY (I).)
(3) Remove the connecting rod cap. (See 01-10-
22 CYLINDER BLOCK DISASSEMBLY (II).)
(4) Measure the oil clearance at the large end of
the connecting rod.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the bearing or grind the crank pin
and use oversize bearings so that the
specified clearance is obtained.
bpe2ue00000036
id011000507600
bp31je00000148
PLASTIGAUGE
bpe2ue00000093
01-10–35
Page 49

MECHANICAL
Standard bearing oil clearance at the large end of the connecting rod
0.026—0.052 mm {0.0011—0.0020 in}
Maximum bearing oil clearance at the large end of the connecting rod
0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
Connecting rod bearing size
STD: 1.502—1.519 mm {0.05914—0.05980 in}
OS 0.25: 1.628—1.631 mm {0.06410—0.06421 in}
OS 0.50: 1.753—1.756 mm {0.06902—0.06913 in}
End Of Sie
CRANKSHAFT INSPECTION
1. Measure the crankshaft end play using a dial
gauge.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the crankshaft or grind the thrust side
of crankshaft and use the oversize thrust
bearing so that the specified end play is
obtained.
Standard crankshaft end play
0.08—0.29 mm {0.004—0.011 in}
id011000502500
Maximum crankshaft end play
0.30 mm {0.012 in}
Thrust bearing size
STD: 2.500—2.550 mm {0.0985—0.1003 in}
OS 0.25: 2.625—2.675 mm {0.1034—0.1053
in}
2. Measure the runout of the main journal using a Vblock and dial gauge.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the crankshaft.
Maximum main journal runout
0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
3. Inspect the main journal diameter and crank pin
diameter. Measurement positions total four and
are in the X and Y directions, at two points (A and
B) as shown in the figure.
• If it is not within the specification or if it
exceeds the maximum off-round, grind the
journal with an oversized bearing.
bp31je00000217
bpe2ue00000035
AB
X
Y
Standard main journal diameter
49.980—50.000 mm {1.9678—1.9685 in}
Maximum main journal off-round
0.005 mm {0.0002 in}
Standard crank pin diameter
49.980—50.000 mm {1.9678—1.9685 in}
Maximum crank pin off-round
0.005 mm {0.0002 in}
01-10–36
b3e0110e085
Page 50

MECHANICAL
4. Inspect the main journal oil clearance using the following procedure:
(1) Install the thrust bearing, upper main bearing and crankshaft.
(2) Position a plastigauge on the journals.
(3) Install the lower main bearing and lower cylinder block. (See 01-10-40 CYLINDER BLOCK ASSEMBLY (I).)
(4) Remove the lower cylinder block. (See 01-10-22 CYLINDER BLOCK DISASSEMBLY (II).)
(5) Measure the main journal oil clearance.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the main bearing, or grind the
main journal and use oversized bearings
so that the specified oil clearance is
obtained.
Standard main journal oil clearance
0.016—0.039 mm {0.0007—0.0015 in}
Maximum main journal oil clearance
0.084 mm {0.0033 in}
Main bearing size
STD: 2.489—2.510 mm {0.0980—0.0988 in}
OS 0.25: 2.614—2.617 mm {0.10292—0.10303 in}
OS 0.50: 2.739—2.742 mm {0.10784—0.10795 in}
End Of Sie
DUAL-MASS FLYWHEEL INSPECTION
bp31je00000152
id011000501900
01-10
Caution
• Do not rework the dual-mass flywheel if it is distorted.
• Do not clean the dual-mass flywheel with any kind of fluid. Clean the dual-mass flywheel with a dry
cloth only.
• Do not clean the gap between the primary and secondary mass. Only clean the bolt connection
surface and the clutch surface.
Inspection Before Removal
1. Rotate the dual-mass flywheel or attempt to move
it up and down, and left and right to verify that the
center of the dual-mass flywheel does not move.
• If there is any movement as indicated by the
arrows in the figure, replace the dual-mass
flywheel.
2. Verify that the secondary mass does not rotate by
15 teeth or more.
• If it rotates by 15 teeth or more, replace the
dual-mass flywheel.
ac5wzw00005672
ac5wzw00005673
01-10–37
Page 51

MECHANICAL
3. Measure the amount of guide pin projection of the
dual-mass flywheel.
• If it exceeds the maximum amount, replace
the dual-mass flywheel.
Dual-mass flywheel guide pin projection
maximum amount
11.0—12.0 mm {0.434—0.472 in}
4. Using a dial indicator, measure the dual-mass
flywheel runout.
• If it exceeds the maximum runout, replace the
dual-mass flywheel.
Dual-mass flywheel maximum runout
1.5 mm {0.059 in}
ac5wzw00005674
ac5wzw00005675
Inspection After Removal
1. Visually inspect the dual-mass flywheel for crack.
• If there is any crack, replace the dual-mass flywheel.
2. Visually inspect the ring gear on the dual-mass flywheel for damage.
• If there is any damage, replace the dual-mass flywheel.
3. Visually inspect the surface that contacts the clutch disc for scratches, nicks, and discoloration.
• If there is any malfunction, replace the dual-mass flywheel.
Note
• Correct slight scratches and discoloration
using sandpaper.
4. Visually inspect for grease leakage between the
primary mass and secondary mass.
• If there is grease leakage, replace the dualmass flywheel.
End Of Sie
ac5wzw00005676
01-10–38
ac5wzw00005677
Page 52

MECHANICAL
PILOT BEARING INSPECTION
1. Without removing the pilot bearing, turn the
bearing while applying force in the axial direction.
• If there is any malfunction, replace the pilot
bearing.
End Of Sie
BOLT INSPECTION
1. Measure the length of the each bolt.
• If it exceeds the maximum specification,
replace the bolt.
Standard cylinder head bolt length
145.2—145.8 mm {5.717—5.740 in}
Maximum cylinder head bolt length
146.5 mm {5.768 in}
Standard connecting rod bolt length
43.7—44.3 mm {1.73—1.74 in}
Maximum connecting rod bolt length
45.0 mm {1.77 in}
id011000505200
01-10
am3uuw00002078
id011000503300
L
beltze00000026
End Of Sie
01-10–39
Page 53

MECHANICAL
OIL
OIL
SEALANT
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
CYLINDER BLOCK ASSEMBLY (I)
id011000504000
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
15
OIL
13
OIL
10
12
R
12
R
OIL
OIL
11
3
9
OIL
4
OIL
14
1
2
8—11 N·m
{82—112 kgf·cm,
71—97 in·lbf}
R
18
OIL
6
OIL
16
17
26—32 {2.7—3.2, 20—23}
+80—100
.
°
1 Upper cylinder block
38—42 {3.9—4.2, 29—30}
LOOSEN ALL THE BOLTS (UNTIL
BOLTS ARE TORQUE-FREE)
OIL
+30—34 {3.1—3.4, 23—25}
+57.5—62.5
2 Oil jet valve
3 Thrust bearing
(See 01-10-41 Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Assembly Note.)
4 Upper main bearing
(See 01-10-41 Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Assembly Note.)
5Plate
(See 01-10-42 Plate Assembly Note.)
6 Crankshaft
01-10–40
20—26
{2.1—2.6,
15—19}
°
OIL
7
5
19—25
{2.0—2.5,
15—18}
8
SEALANT
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
bpe5ue00000004
7 Lower main bearing
(See 01-10-41 Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing
Assembly Note.)
8 Lower cylinder block
(See 01-10-42 Lower Cylinder Block Assembly
Note.)
9 Connecting rod
10 Piston
11 Piston pin
(See 01-10-44 Piston Pin Assembly Note.)
12 Snap ring
(See 01-10-44 Snap Ring Assembly Note.)
Page 54

MECHANICAL
13 Piston ring
(See 01-10-45 Piston Ring Assembly Note.)
14 Upper connecting rod bearing
(See 01-10-46 Connecting Rod Bearing Assembly
Note.)
15 Piston, connecting rod
(See 01-10-46 Piston, Connecting Rod Assembly
Note.)
16 Lower connecting rod bearing
(See 01-10-46 Connecting Rod Bearing Assembly
Note.)
17 Connecting rod cap
(See 01-10-47 Connecting Rod Cap Assembly
Note.)
18 Pilot bearing (MTX)
(See 01-10-47 Pilot Bearing Assembly Note.)
Thrust Bearing And Main Bearing Assembly Note
Caution
• If the thrust bearings and main bearings are reused, assemble the bearings to the same positions
and in the direction as before removal to prevent engine damage due to seizure or burning of the
bearing.
• To prevent engine damage due to seizure or burning of the bearing, apply engine oil to the sliding
part when assembling.
Thrust bearing
1. Apply clean engine oil to the thrust bearings.
2. Assemble the bearings with the oil groove of the
thrust bearing pointed toward the sliding surface.
THRUST BEARING
01-10
Main bearing
1. Apply clean engine oil to the main bearings.
2. Align the positioning tab of the main bearing with
the positioning groove of the lower and upper
cylinder block, and assemble the bearings.
MAIN BEARING
AFTER INSTALLATION
OIL GROOVE
bpe1ze00000043
GROOVE
TA B
CYLINDER BLOCK
bpe1ze00000044
01-10–41
Page 55

MECHANICAL
Plate Assembly Note
Caution
• Placing the crankshaft on a disassembly bench will deform or damage it because the plate for the
crankshaft position sensor signal detection installed to the crankshaft is larger than the
counterweight. Therefore, set wood blocks or similar objects on the both sides of the crankshaft
so that the plate does not contact the disassembly bench directly when placing the crankshaft on
it bench.
1. Install the plate using the following procedure:
(1) Install the groove of the plate tooth to the
position shown in the figure and temporarily
tighten bolt A.
(2) Temporarily tighten the bolt B.
(3) Install bolt C and tighten the bolts to the
specified tightening torque in the order of C,
B, and A.
Tightening torque
20—26 N·m {2.1—2.6 kgf·m, 15—19 ft·lbf}
Lower Cylinder Block Assembly Note
1. Completely clean and remove any oil, dirt, sealant or other foreign matter that may be adhering to the lower
cylinder block and cylinder block.
2. When reusing the lower cylinder block installation bolts, clean any old sealant from the bolts.
A
PLATE
C
GROOVE
B
CRANKSHAFT
bpe2ue00000038
Caution
• Apply silicon sealant in a single, unbroken line.
• To prevent silicon sealant from hardening, adhere the engine front cover and the cylinder block
firmly within 10 min. after applying silicon sealant. After adhering them, tighten the installation
bolts immediately.
• Using bolts with the old seal adhering
could cause cracks in the cylinder block.
DAMAGE
OLD SEALANT
bpe2ue00000039
01-10–42
Page 56

MECHANICAL
SEALANT
SEALANT
SEALANT
SEALANT
3. Apply silicon sealant to the lower cylinder block shown in the figure.
ENGINE FRONT
A
01-10
SEALANT
LESS THAN
4 mm {0.2 in}
A
SEALANT
LOWER CYLINDER
BLOCK
SECTION A-A
0.5—1.5 mm
{0.02—0.05 in}
SEALANT
Bead thickness
2—6 mm {0.1—0.2 in}
4. Install the lower cylinder block.
5. Tighten the lower cylinder block installation bolts using the following procedure:
(1) Apply clean engine oil to the seating surface and thread of lower cylinder block installation bolts A.
LESS THAN
4 mm {0.2 in}
SEALANT
bpe1ze00000046
01-10–43
Page 57

MECHANICAL
(2) Tighten lower cylinder block installation bolts
A in the order shown in the figure using the
following procedure:
Tightening procedure
Step 1: 38—42 N·m {3.9—4.2 kgf·m, 29—30
ft·lbf}
Step 2: Loosen all the bolts (until bolts are
torque-free).
Step 3: 30—34 N·m {3.1—3.4 kgf·m, 23—25
ft·lbf}
Step 4: 57.5—62.5°
(3) Tighten the lower cylinder block installation
bolts B in the order shown in the figure.
Tightening torque
19—25 N·m {2.0—2.5 kgf·m, 15—18 ft·lbf}
6. After verifying that silicone sealant protrudes to
the rear oil seal press-in part, wipe away the
excess silicone sealant.
• If silicone sealant does not protrude to the
rear oil seal press-in part, remove the lower
cylinder block and apply silicone sealant
again.
ENGINE
FRONT
ENGINE
FRONT
10
10
A
6
2
1
6
A
3
4 89 5
A
B BB B B
2
3
AA A
7
AA A A
bpe2ue00000041
7
1
Piston Pin Assembly Note
1. Apply clean engine oil to the piston pin.
2. Insert the piston pin to the piston and connecting rod.
Note
• When assembling the piston to the connecting rod, each one can be assembled in either direction.
Snap Ring Assembly Note
Caution
• Do not compress the outer diameter of the snap ring more than necessary when assembling the
snap ring (20.66 mm {0.8134 in} or less).
1. Insert a new snap ring using a thin plier.
4
B BB BB
89 5
bpe2ue00000042
01-10–44
Page 58

MECHANICAL
Piston Ring Assembly Note
Note
• It is not required to position the end gap between the top ring and second ring.
1. Assemble the oil ring so that the end gap of each
oil ring rail does not overlap as shown in the
figure.
2. Assemble so that the identification paint marks on
the top and second rings are visible to the right
side of each end gap.
Note
• If there are no identification paint marks on
the top and second rings, place the ring with
the bigger inner circumference at the top as
shown in the figure.
UPPER OIL RING RAIL
OIL RING SPACER
IDENTIFICATION PAINT MARK
END GAP
30° 30°
PISTON PIN AXIS
LOWER OIL RING RAIL
bpe2ue00000043
TOP RING
SECOND RING
bpe1ze00000047
TOP RING
NOTCH
01-10
SECOND RING
NOTCH
bpe2ue00000044
01-10–45
Page 59

MECHANICAL
Connecting Rod Bearing Assembly Note
Caution
• If a connecting rod bearing is reused, assemble it to the same position and in the direction as
before removal to prevent engine damage due to seizure or burning of the bearing.
• To prevent engine damage due to seizure or burning of the bearing, apply engine oil to the sliding
part when assembling.
1. Apply engine oil to the connecting rod bearings.
2. Align the positioning tab of the connecting rod
bearing with the positioning groove of the
connecting rod and connecting rod cap, and
assemble the bearings.
TA B
GROOVE
Piston, Connecting Rod Assembly Note
1. Insert the piston into the cylinder with the mark on
top of the piston facing the intake side.
CONNECTING ROD
BEARING
INSTALLED
ENGINE
FRONT
CONNECTING ROD CAP
bpe1ze00000048
EX
6TN
G
2
01-10–46
MARKED
IN
bpe2ue00000045
Page 60

MECHANICAL
Connecting Rod Cap Assembly Note
Caution
• When assembling the connecting rod caps, align the broken, rough faces of the connecting rods
and connecting rod caps.
• If the following condition is met, replace the connecting rod cap bolts.
— Length exceeds maximum
specification
Standard connecting rod cap bolt length
43.7—44.3 mm {1.73—1.74 in}
01-10
Maximum connecting rod cap bolt length
45.0 mm {1.77 in}
1. Position so that the broken, rough faces of the
connecting rods and connecting rod caps are
aligned exactly, and assemble the connecting rod
caps.
2. Tighten the connecting rod cap bolts in the
following two steps.
Tightening procedure
Step 1: 26—32 N·m {2.7—3.2 kgf·m, 20—23 ft·lbf}
Step 2: 80—100°
Pilot Bearing Assembly Note
1. Install new pilot bearing to the specified position
using the following tools.
Tool
Snap-on brand millimeter size bushing
driver set (A160M) adapter A160M7 (20—
22 mm {0.79—0.86 in})
• Use the adapter with the 20 mm {0.79 in}
side of the A160M7 (20—22 mm {0.79—
0.86 in}) facing the pilot bearing side.
Substitution tool
Outer diameter: 21 mm {0.83 in}
Inner diameter: 19 mm {0.75 in}
L
adejjw00001214
bpe2ue00000046
Standard pilot bearing position
Distance A of pilot bearing from crankshaft
end: 1.5—2.5 mm {0.060—0.098 in}
End Of Sie
CRANKSHAFT
PILOT BEARING
A
bpe2ue00000047
01-10–47
Page 61

MECHANICAL
OIL
OIL
CYLINDER BLOCK ASSEMBLY (II)
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
4
20—26 {2.1—2.6, 15—19}
R
id011000504100
R
OIL
SST
5 6
AT X
7 8
108—116
{11.1—11.8,
80—85}
SST
R
9
MTX
7
11
17—23
{1.8—2.3,
13—16}
R
152—160
{15.5—16.3,
113—118}
SST
R
9
1
2
20—26 {2.1—2.6, 15—19}
*1: 8—11 N·m {82—112 kgf·m, 71—97 ft·lbf}
.
1 Balancer unit
(See 01-10-49 Balancer Unit Assembly Note.)
2 Oil pump
(See 01-10-50 Oil Pump Assembly Note.)
3 Oil strainer
4 Water pump
(See 01-10-51 Water Pump Assembly Note.)
5 Rear oil seal
(See 01-10-52 Rear Oil Seal Assembly Note.)
6 End plate
(See 01-10-53 End Plate Assembly Note.)
16—22 {1.7—2.2, 12—16}
+30—36 {3.1—3.6, 23—26}
20—26 {2.1—2.6, 15—19}
*1
3
OIL
R
10
*1
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
bpe5ue00000005
7 Dual-mass flywheel (MTX), drive plate (ATX)
8 Backing plate (ATX)
9 Dual-mass flywheel (MTX)/ drive plate (ATX)
installation bolt
(See 01-10-53 Dual-mass Flywheel (MTX)/ Drive
Plate (ATX) Installation Bolt Assembly Note.)
10 Oil separator
11 Knock sensor (KS)
(See 01-10-54 Knock Sensor (KS) Assembly Note.)
01-10–48
Page 62

MECHANICAL
Balancer Unit Assembly Note
1. Assemble the balancer unit using the following procedure:
(1) Tighten the bolts in the order shown in the
figure.
BALANCER UNIT
2
3
01-10
5
6
Tightening torque
Installation position Tightening torque
1—4 16—22 N·m {1.7—2.2 kgf·m, 12—16 ft·lbf}
5, 6 20—26 N·m {2.1—2.6 kgf·m, 15—19 ft·lbf}
(2) Retighten the bolts in the order of the
numbers indicated in the figure.
Tightening torque
30—36 N·m {3.1—3.6 kgf·m, 23—26 ft·lbf}
4
BALANCER UNIT
2
4
1
ENGINE
FRONT
bpe1ze00000051
3
1
ENGINE
FRONT
bpe1ze00000052
01-10–49
Page 63

MECHANICAL
Oil Pump Assembly Note
1. Install the oil pump using the following procedure:
(1) Temporarily tighten the three bolts shown in
the figure.
BOLT
OIL PUMP
(2) Tighten the two bolts shown in the figure to
the specified torque.
Note
• The tightening order for the two bolts is
optional.
Tightening torque
20—26 N·m {2.1—2.6 kgf·m, 15—19 ft·lbf}
(3) Finally, tighten the bolt shown in the figure to
the specified torque.
BOLT
ENGINE FRONT
BOLT
OIL PUMP
BOLT
ENGINE FRONT
BOLT
bpe1ze00000053
bpe1ze00000054
Tightening torque
20—26 N·m {2.1—2.6 kgf·m, 15—19 ft·lbf}
01-10–50
OIL PUMP
BOLT
ENGINE FRONT
bpe1ze00000055
Page 64

MECHANICAL
Water Pump Assembly Note
Caution
• Assemble the water pump gasket to the correct direction shown in the figure. Otherwise, it could
leak engine coolant and damage the engine.
WATER PUMP GASKET GROOVE WATER PUMP
1. Insert a new water pump gasket into the water pump groove.
2. Install the water pump.
3. Tighten the bolts in the order shown in the figure.
Tightening torque
20—26 N·m {2.1—2.6 kgf·m, 15—19 ft·lbf}
WATER PUMP
01-10
bpe2ue00000053
1
3
2
bpe2ue00000054
01-10–51
Page 65

MECHANICAL
Rear Oil Seal Assembly Note
1. Apply clean engine oil to the inner surface of a new rear oil seal.
2. Insert the rear oil seal into the cylinder block by hand.
3. Tap the oil seal in evenly using the SST and a
hammer.
Rear oil seal press on amount
0—0.5 mm {0—0.019 in}
49 S033 101
VIEW FROM A
HAMMER
49 S033 101
REAR OIL SEAL
A
CYLINDER BLOCK
bpe1ze00000056
B
SECTION B-B
CYLINDER BLOCK
B
0—0.5 mm
{0—0.019 in}
REAR OIL SEAL
bpe5ue00000006
01-10–52
Page 66

MECHANICAL
End Plate Assembly Note
1. After end plate assembly, crimp the parts A and B shown in the figure.
B
10 {0.39}
END PLATE
A
45
10 {0.39}
45
TUBULAR PIN
°
45
10 {0.39}
45
°
Crimp procedure
Crimp depth: 0.1—1.0 mm {0.004—0.039 in}
Crimp width: 0.5—10.0 mm {0.02—0.39 in}
Crimp locations: Part A is 1 or more on one-side within shaded area and part B is 2 or more within
shaded areas
2. After crimping, verify that there is no damage and removal of the end plate.
Dual-mass Flywheel (MTX)/ Drive Plate (ATX) Installation Bolt Assembly Note
Dual-mass flywheel installation bolt (MTX)
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST (49 E011 1A0).
2. Temporarily tighten the new bolts.
°
TUBULAR
PIN
°
01-10
mm {in}
bpe2ue00000055
Note
• If the dual-mass flywheel (secondary flywheel side) is not positioned properly, perform the following
procedure to install it:
(1) Temporarily tighten the new bolts to the
position as shown in the figure.
49 G033 102
49 E011 1A0
am6zzw00011777
01-10–53
Page 67

MECHANICAL
(2) Install the SST (49 S120 710) to the dual-
mass flywheel.
(3) Rotate the dual-mass flywheel (secondary
flywheel side) using the SST (49 S120 710),
and then temporarily tighten the remaining
new bolt after removing the SST (49 G033
102).
3. Tighten the new bolts in two or three passes in
the order shown in the figure.
Tightening torque
152—160 N·m {15.5—16.3 kgf·m, 113—118
ft·lbf}
49 E011 1A0
49 E011 1A0
1
3
5
49 G033 102
49 S120 710
am6xuw00005541
8
6
4
2
7
ac5wzw00005664
Drive plate installation bolt (ATX)
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Tighten the new bolts in two or three passes in
the order shown in the figure.
Tightening torque
108—116 N·m {11.1—11.8 kgf·m, 80—85
ft·lbf}
1
3
5
2
Knock Sensor (KS) Assembly Note
• Verify that there is no foreign matter caught between the KS unit and cylinder block.
• The direction of the knock sensor connector must
be within the range shown in the figure.
End Of Sie
60º
6
4
49 E011 1A0
bpe1ze00000093
01-10–54
KS
am6zzw00008568
Page 68

MECHANICAL
OIL
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY (I)
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
SST
6
5
4
SST
2
R
1
id011000504300
7
8
9
01-10
8—11
{82—112,
71—97}
R
OIL
3
.
1 Lower valve spring seat
2 Valve seal
(See 01-10-56 Valve Seal Assembly Note.)
3Valve
4 Valve spring
(See 01-10-56 Valve Spring Assembly Note.)
5 Upper valve spring seat
N·m {kgf·cm, in·lbf}
bpe1ze00000017
6 Valve keeper
(See 01-10-57 Valve Keeper Assembly Note.)
7 Water outlet
(See 01-10-57 Water Outlet Assembly Note.)
8 Thermostat
(See 01-10-58 Thermostat Assembly Note.)
9 Thermostat cover
01-10–55
Page 69

MECHANICAL
Valve Seal Assembly Note
1. Press on the valve seal to the valve guide using
the SST by hand.
Valve seal identification color
IN: GREEN
EX: GRAY
Valve Spring Assembly Note
Caution
• The valve springs differ depending on IN
and EX sides. Therefore, verify the free
length or identification paint beforehand
and assemble the valve springs correctly.
9.52 mm
{0.375 in}
49 B012 016
3.5 mm
{0.14 in}
VALVE SEAL
49 B012 016
VALVE SEAL
bpe1ze00000057
IN
48.96 mm {1.928 in}
1. Assemble the valve spring with the small diameter
side of the valve spring facing upward.
PURPLE
PAINT
EX
50.07 mm {1.971 in}
NOT
PAINTE
bpe1ze00000094
01-10–56
Page 70

Valve Keeper Assembly Note
1. Install the valve keeper using the SST.
MECHANICAL
Water Outlet Assembly Note
1. Install the water outlet gasket with the bead of the
gasket facing the direction shown in the figure.
2. Temporarily tighten the water outlet installation
bolts.
49 0636 100B
49 B012 0A2A
01-10
bpe1ze00000020
B
SECTION B-B
CYLINDER HEAD WATER OUTLET
WATER OUTLET
GASKET
BEAD
bpe1ze00000021
01-10–57
Page 71

MECHANICAL
3. Tighten bolt A of the 5 bolts shown in the figure to
the specified torque first.
Tightening torque
8—11 N·m {82—112 kgf·cm, 71—97 in·lbf}
Note
• The tightening order for the remaining 3
bolts is optional.
Thermostat Assembly Note
1. Install the thermostat with the jiggle pin aligned
with the notch of the water outlet.
End Of Sie
BOLT
A
WATER OUTLET
A
BOLT
bpe1ze00000022
NOTCH
JIGGLE-PIN
THERMOSTAT
bpe1ze00000023
01-10–58
Page 72

MECHANICAL
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY (II)
Caution
• If the camshaft is rotated with the timing chain removed and the piston at the top dead center
position, the valve may contact the piston and the engine could be damaged. When rotating the
camshaft with the timing chain removed, rotate it after lowering the piston from the top dead
center position.
• When rotating the camshaft using a
wrench on the cast hexagon, the wrench
may contact the rocker arm and damage
CAMSHAFT
WRENCH
CAST HEXAGON
the rocker arm. To prevent damage to the
rocker arm when holding the camshaft on
the cast hexagon, use a wrench on the
rear side of the engine as shown in the
figure to secure a clearance between the
cam.
ROCKER ARM CONTACT
SECURE CLEARANCE
id011000504400
01-10
ENGINE REAR
Note
• Width at the cast hexagon of the camshaft is
22—24 mm {0.87—0.94 in}.
CAMSHAFT
DOES NOT CONTACT
CAST HEXAGON
22—24 mm
{0.87
am3uuw00008968
—0.94 in}
am3uuw00009029
01-10–59
Page 73

1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
MECHANICAL
6
10
12—16 N·m
{123—163 kgf·cm,
107—141 in·lbf}
20—26
{2.1—2.6,
15—19}
8—11 N·m
{82—112 kgf·cm,
71—97 in·lbf}
9
75—85 {7.7—8.6, 56—62}
102—114 {10.5—11.6, 76—84}
WITHOUT OIL COOLER
3
3.0—6.0 N·m
8
R
{31—61 kgf·cm,
27—53 in·lbf}
+8—11 N·m
{82—112 kgf·cm,
71—97 in·lbf}
OIL
13—17 N·m
{133—173 kgf·cm,
116—150 in·lbf}
+43—47
{4.4—4.7, 32—34}
+85—95
+85—95°
OIL
7
OIL
5
OIL
4
°
WATER
PUMP
R
.
1 Cylinder head gasket
2 Cylinder head
(See 01-10-61 Cylinder Head Assembly Note.)
3 Water inlet pipe
(See 01-10-62 Water Inlet Pipe Assembly Note.)
4HLA
(See 01-10-63 HLA Assembly Note.)
5 Rocker arm
(See 01-10-63 Rocker Arm Assembly Note.)
6 OCV oil filter
WITH OIL COOLER
2
R
1
3
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
bpe5ue00000007
7 Camshaft
(See 01-10-64 Camshaft Assembly Note.)
8 Camshaft cap
(See 01-10-64 Camshaft Assembly Note.)
9OCV
10 Electric variable valve timing actuator, hydraulic
variable valve timing actuator
(See 01-10-66 Electric Variable Valve Timing
Actuator, Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing Actuator
Assembly Note.)
01-10–60
Page 74

MECHANICAL
Cylinder Head Assembly Note
Caution
• If the following condition is met, replace the cylinder head bolts.
— Length exceeds maximum
specification
Standard cylinder head bolt length L
145.2—145.8 mm {5.717—5.740 in}
Maximum cylinder head bolt length L
146.5 mm {5.767 in}
1. When a cylinder head bolt is reused, apply engine
oil to any part of the following:
• Bolt seating surface
• Cylinder head seating surface
2. Tighten the cylinder head bolts in the order shown
in the following four steps.
Tightening procedure
Step 1: 13—17 N·m {133—173 kgf·cm, 116—
150 in·lbf}
Step 2: 43—47 N·m {4.4—4.7 kgf·m, 32—34
ft·lbf}
Step 3: 85—95°
Step 4: 85—95°
ENGINE
FRONT
01-10
L
adejjw00001214
4 1 5 9
8
7
3 2 6
10
am3uuw00008818
01-10–61
Page 75

MECHANICAL
Water Inlet Pipe Assembly Note
Caution
• Do not apply oil (such as engine oil, ATF) to the O-ring of the water inlet pipe. Otherwise, the O-
ring could swell causing a seal malfunction.
1. Clean away the sealant adhering to the bolt hole on the cylinder block side of the water inlet pipe stay.
2. Apply engine coolant to the O-ring.
3. Install the O-ring to the water inlet pipe.
4. Insert the water inlet pipe into the water pump being careful not to damage the O-ring.
5. Install the water inlet pipe gasket with the gasket
projection facing the direction shown in the figure.
R
PROJECTION
6. Tighten the bolts in the order shown in the figure.
1
12—16 N·m
{123—163 kgf·cm,
107—141 in·lbf}
STAY
bpe2ue00000065
WATER INLET PIPEWATER OUTLET
20—26
{2.1—2.6,
15—19}
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
bpe5ue00000008
01-10–62
Page 76

MECHANICAL
OIL
HLA Assembly Note
1. Perform HLA air bleeding using the following procedure:
(1) Put the HLA in a container filled with engine oil.
Caution
• Do not insert the round bar firmly because the check ball spring force is extremely weak.
(2) While lightly pressing the check ball using a
round bar (approx. 1.0 mm {0.039 in}
diameter), bleed air by moving the plunger up
and down.
(3) Press the end of the plunger in the oil and
verify that there is no rebounding feel.
• If rebounding feel cannot be eliminated,
replace the HLA.
2. Install the HLAs to their original positions as
before removal.
Rocker Arm Assembly Note
1. Apply engine oil to the HLAs and the end of the
valve stems.
2. Install the rocker arms to their original positions
as before removal.
CONTAINER
FILLED WITH
ENGINE OIL
PLUNGER
CHECK
BALL
01-10
ROUND
BAR
1
ROUND BAR
(APPROX. 1.0
2
mm {0.039 in}
DIAMETER)
bpe2ue00000067
OIL
VALVE STEM
HLA
VALV E
bpe2ue00000068
01-10–63
Page 77

MECHANICAL
OIL
Camshaft Assembly Note
1. As shown in the figure, apply gear oil (SAE No. 90 or equivalent) or engine oil to the center area of each journal
of the cylinder head.
Caution
• Apply 0.05 ml {0.05 cc, 0.003 in
3
} or less of oil to journal No.6.
JOURNAL NO.6
OIL
2. Apply gear oil (SAE No. 90 or equivalent) or engine oil to the following locations of each camshaft.
• Thrust surface of front journal
3. As shown in the figure, align the cam position of
cylinder No.1 around top dead center (TDC) and
EXHAUST CAMSHAFT
INTAKE CAMSHAFT
place the camshafts on the cylinder head.
CYLINDER HEAD
bpe2ue00000069
bpe2ue00000070
01-10–64
Page 78

MECHANICAL
OIL
4. As shown in the figure, apply gear oil (SAE No. 90 or equivalent) or engine oil to the center area of each journal
of the camshaft.
OIL
01-10
5. Apply adhesive agent (Loctite 962T) around
journal No.6 of the cylinder head or the exhaustside rear camshaft cap.
Caution
• Verify that there is no adhesive agent on
the journal.
Adhesive agent bead width
0.5—1.5 mm {0.02—0.05 in}
6. Install the camshaft caps in the marked number
order, and temporarily tighten the camshaft cap
installation bolts in two or three passes evenly.
CYLINDER HEAD
AROUND
JOURNAL NO.6
EXHAUST-SIDE REAR
CAMSHAFT CAP
GROOVE
bpe1ze00000011
ADHESIVE
ADHESIVE
bpe2ue00000071
01-10–65
Page 79

MECHANICAL
7. Tighten the camshaft cap installation bolts in two steps in the order shown in the figure.
3
1
2
4
6
5
E2
E3
E4
5
I2
I3
4
2
I4
1
E5
MARKED NUMBER
MARKED NUMBER
I5
3
am3uuw00008996
Tightening torque
Step 1: 3.0—6.0 N·m {31—61 kgf·cm, 27—53 in·lbf}
Step 2: 8—11 N·m {82—112 kgf·cm, 71—97 in·lbf}
Electric Variable Valve Timing Actuator, Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing Actuator Assembly Note
1. Align the knock pin on the end of the camshaft
with the notch on the actuator (intake side) or
ELECTRIC VARIABLE VALVE
TIMING ACTUATOR
knock pin installation hole (exhaust side), then
install the actuator to the camshaft.
INTAKE
CAMSHAFT
NOTCH
HYDRAULIC VARIABLE VALVE
TIMING ACTUATOR
KNOCK PIN
INSTALLATION HOLE
KNOCK PIN
EXHAUST
CAMSHAFT
KNOCK PIN
bpe2ue00000072
01-10–66
Page 80

MECHANICAL
2. Hold the camshaft using a wrench on the cast
hexagon, and tighten the actuator installation bolt.
Tightening torque
Electric variable valve timing actuator
(intake side): 102—114 N·m {10.5—11.6
kgf·m, 76—84 ft·lbf}
Hydraulic variable valve timing actuator
(exhaust side): 75—85 N·m {7.7—8.6 kgf·m,
56—62 ft·lbf}
01-10
End Of Sie
TIMING CHAIN ASSEMBLY
Caution
• If the camshaft is rotated with the timing chain removed and the piston at the top dead center
position, the valve may contact the piston and the engine could be damaged. When rotating the
camshaft with the timing chain removed, rotate it after lowering the piston from the top dead
center position.
• When rotating the camshaft using a
wrench on the cast hexagon, the wrench
may contact the rocker arm and damage
the rocker arm. To prevent damage to the
rocker arm when holding the camshaft on
the cast hexagon, use a wrench on the
rear side of the engine as shown in the
figure to secure a clearance between the
cam.
CAMSHAFT
ROCKER ARM CONTACT
SECURE CLEARANCE
WRENCH
CAST HEXAGON
bpe2ue00000073
id011000505600
ENGINE REAR
Note
• Width at the cast hexagon of the camshaft is
22—24 mm {0.87—0.94 in}.
CAMSHAFT
DOES NOT CONTACT
CAST HEXAGON
22—24 mm
{0.87
01-10–67
am3uuw00008968
—0.94 in}
am3uuw00009029
Page 81

1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
SEALANT
OIL
SEALANT
SEALANT
SEALANT
SEALANT
MECHANICAL
SEALANT
14
16
20—26
{2.1—2.6,
15—19}
19
SST
90—110
{9.2—11,
67—81}
+55—65
4.5—7.0 N·m
{46—71 kgf·m,
40—61 ft·lbf}
A
24
23
R
8.0—9.0 N·m
R
9—12 N·m
{92—122 kgf·m,
80—106 ft·lbf}
{82—91 kgf·m,
71—79 ft·lbf}
22
A
R
*1
11
SEALANT
SEALANT
15—20
21
{1.6—2.0,
12—14}
20
*1
R
SST
OIL
SEALANT
13
*1
18
17
°
10
12
9
*1
*1: 8—11 N·m {82—112 kgf·m, 71—97 ft·lbf}
.
1Key
20—30
{2.1—3.0,
15—22}
2 Oil pump drive sprocket
3 Oil pump chain guide
4
SST SST
01-10–68
3
*1
2
1
8
7
SEALANT
15
6
5
38—46 {3.9—4.6, 29—33}
*1
4 Oil pump driven sprocket
(See 01-10-69 Oil Pump Chain Assembly Note.)
*1
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
bpe1ze00000068
Page 82

MECHANICAL
5Oil pump chain
(See 01-10-69 Oil Pump Chain Assembly Note.)
6 Balancer shaft sprocket
(See 01-10-69 Oil Pump Chain Assembly Note.)
7 Oil pump chain tensioner
(See 01-10-69 Oil Pump Chain Assembly Note.)
8 Crankshaft sprocket
9 Chain guide (No.2)
10 Timing chain
(See 01-10-71 Timing Chain Assembly Note.)
11 Chain guide (No.1)
(See 01-10-71 Timing Chain Assembly Note.)
12 Tensioner arm
(See 01-10-71 Timing Chain Assembly Note.)
13 Chain tensioner
(See 01-10-71 Timing Chain Assembly Note.)
14 Engine front cover
(See 01-10-74 Engine Front Cover Assembly Note.)
Oil Pump Chain Assembly Note
1. Verify that the key and knock pin are aligned to
the positions shown in the figure.
• If they are not in the positions shown in the
figure, rotate the crankshaft and balancer
shaft (No.1) to set cylinder No.1 to top dead
center (TDC).
2. Temporarily assemble the oil pump driven
sprocket.
3. Temporarily tighten the oil pump driven sprocket
installation bolt.
15 Oil pan
(See 01-10-77 Oil Pan Assembly Note.)
16 Electric variable valve timing motor/driver
(See 01-10-79 Electric Variable Valve Timing Motor/
Driver Assembly Note.)
17 Front oil seal
(See 01-10-80 Front Oil Seal Assembly Note.)
18 Crankshaft pulley
19 Crankshaft pulley lock bolt
(See 01-10-80 Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt Assembly
Note.)
20 Water pump pulley
(See 01-10-81 Water Pump Pulley Assembly Note.)
21 Spark plug
22 Oil shower pipe
(See 01-10-81 Oil Shower Pipe Assembly Note.)
23 Cylinder head cover
(See 01-10-82 Cylinder Head Cover Assembly Note.)
24 Dipstick
KEY
01-10
4. Align the oil pump chain alignment mark with the
balancer shaft sprocket alignment mark.
BALANCER SHAFT
(NO.1)
KNOCK PIN
bpe1ze00000070
BALANCER SHAFT
SPROCKET
ALIGNMENT MARK
OIL PUMP CHAIN
ALIGNMENT
MARK (ORANGE)
bpe1ze00000071
01-10–69
Page 83

MECHANICAL
5. Install the oil pump chain and balancer shaft sprocket as a single unit while aligning the alignment marks on
each sprocket and oil pump chain as shown in the figure.
OIL PUMP CHAIN
ALIGNMENT
MARK (YELLOW)
OIL PUMP DRIVE
SPROCKET
ALIGNMENT MARK
BALANCER SHAFT
SPROCKET
ALIGNMENT MARK
OIL PUMP CHAIN ALIGNMENT
MARK (ORANGE)
KEY
6. Temporarily tighten the balancer shaft sprocket installation bolt.
7. Install the oil pump chain tensioner.
Caution
• At this stage, do not remove the wire or paper clip installed to the oil pump chain tensioner.
8. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
9. Tighten the oil pump driven sprocket installation
bolt.
Tightening torque
20—30 N·m {2.1—3.0 kgf·m, 15—22 ft·lbf}
10. Tighten the balancer shaft sprocket installation
bolt.
Tightening torque
38—46 N·m {3.9—4.6 kgf·m, 29—33 ft·lbf}
11. Remove the wire or paper clip installed to the oil
pump chain tensioner and apply tension to the oil pump chain.
• If a new oil pump chain tensioner is used, remove the installed stopper.
bpe1ze00000072
49 E011 1A0
bpe1ze00000096
01-10–70
Page 84

MECHANICAL
Timing Chain Assembly Note
1. Verify that the timing marks and the key are aligned to the position shown in the figure.
TIMING CHAIN ALIGNMENT MARK
PIN
CYLINDER
HEAD
UPPER
SURFACE
01-10
TIMING MARK
KEY
bpe5ue00000009
Note
• The timing mark of SKYACTIV-G 2.5 is not completely parallel with the upper surface of the cylinder head.
• If they are not in the position shown in the figure, rotate the camshaft and crankshaft to set the cylinder No.1
top dead center (TDC).
01-10–71
Page 85

MECHANICAL
2. Install the timing chain while aligning the marks on each sprocket and the timing chain as shown in the figure.
TIMING CHAIN
ALIGNMENT MARK
(ORANGE)
PIN
CYLINDER
HEAD
UPPER
SURFACE
HYDRAULIC VARIABLE VALVE TIMING
ACTUATOR TIMING CHAIN ALIGNMENT MARK
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
TIMING CHAIN
ALIGNMENT MARK
TIMING MARK
TIMING CHAIN
ALIGNMENT MARK
(YELLOW)
bpe1ze00000075
3. Install the tensioner arm.
4. Install the chain tensioner.
5. After installing the chain tensioner, remove the installed wire or paper clip, and then apply tension to the timing
chain.
• If a new chain tensioner is used, remove the
installed stopper.
6. Install the chain guide (No.1).
7. Verify that there is no looseness in the timing
chain, and re-verify that each sprocket is in the
specified location.
01-10–72
STOPPER
LINK PLATE
am3uuw00008861
Page 86

MECHANICAL
8. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise two turns and inspect the valve timing.
CYLINDER
HEAD
UPPER
SURFACE
PIN
01-10
TIMING MARK
KEY
bpe5ue00000010
Note
• The timing mark of SKYACTIV-G 2.5 is not completely parallel with the upper surface of the cylinder head.
01-10–73
Page 87

MECHANICAL
Engine Front Cover Assembly Note
Note
• For a new engine front cover, the positioning
pins in the two locations shown in the figure
project to the outside of the engine.
1. If the engine front cover is newly replaced, tap the
positioning pins in the two locations to the seal
surface side.
2. Completely clean and remove any oil, dirt, sealant
or other foreign matter that may be adhering to
the engine front cover, cylinder head, and cylinder
block.
3. When reusing the engine front cover installation
bolts, clean any old sealant from the bolts.
VIEW FROM A
ENGINE OUTSIDE
POSITIONING
PIN
SEAL SIDE
POSITIONING PIN
A
bpe1ze00000006
Caution
• Apply the silicon sealant in a single,
unbroken line.
• To prevent silicone sealant from
hardening, adhere the engine front cover
to the cylinder block within 10 min. after
silicone sealant is applied. Tighten the
installation bolts completely soon after
adhering.
• Using bolts with the old seal adhering
could cause cracks in the cylinder head
and cylinder block.
POSITIONING
PIN
WOOD SLAB
OLD SEALANT
ENGINE OUTSIDE
SEAL SIDE
POSITIONING PIN
0—1 mm
0.03 in}
{0—
bpe1ze00000007
DAMAGE
bpe1ze00000008
01-10–74
Page 88

MECHANICAL
SEALANT
SEALANT
4. Apply silicone sealant to the engine front cover as shown in the figure.
A
10 {0.39}
10 {0.39}
SEALANT
01-10
B
C
B
10 {0.39}
B
C
10 {0.39}
B
90°
B
C
B
10 {0.39}
Bead thickness
A: 2—6 mm {0.1—0.2 in}
B: 4—6 mm {0.16—0.23 in}
C: 4—8 mm {0.2—0.3 in}
A
SECTION D-D
0.5—1.5 mm
{0.02
—0.05 in}
B
10 {0.39}
SEALANT
C
B
32.5 {1.28}
10 {0.39}
ENGINE FRONT
COVER
mm {in}
bpe1ze00000078
01-10–75
Page 89

MECHANICAL
SEALANT
SEALANT
5. Apply silicone sealant to the areas shown in the
figure.
Caution
• Apply the silicone sealant so that it goes
into the cylinder head gasket.
6. Install the engine front cover to the engine.
A
Note
• Temporarily install an appropriate bolt to the
drive belt auto tensioner installation bolt hole
to prevent:
— A silicone sealant adhesion malfunction
in the drive belt auto tensioner
installation bolt hole.
— A bolt mis-installation due to silicone
sealant hardening.
7. Prepare an appropriate M8 X 1.25 bolt (length 40
mm {1.6 in}).
Caution
• For the number 10 bolt of the tightening
order, install the bolts with new washer.
CYLINDER HEAD
SEALANT
CYLINDER BLOCK
DRIVE BELT AUTO
TENSIONER
INSTALLATION BOLT HOLE
VIEW FROM A
SEALANT
CYLINDER
HEAD
GASKET
am3uuw00008866
01-10–76
am3uuw00008867
Page 90

MECHANICAL
8. Tighten the engine front cover installation bolts in the order shown in the figure.
15 19 2016
11
7
4
3
10
6
14
M8 x 1.25, LENGTH
9
40 mm {1.6 in}
1822
21
1
12
8
5
2
13
17
10
WASHER
R
bpe1ze00000079
Tightening torque
20—26 N·m {2.1—2.6 kgf·cm, 15—19 in·lbf}
9. Remove the bolt installed to the drive belt auto tensioner installation bolt hole when installing the drive belt auto
tensioner.
Oil Pan Assembly Note
1. Completely clean and remove any oil, dirt, sealant or other foreign matter that may be adhering to the cylinder
block and oil pan.
2. When reusing the oil pan installation bolts, clean any old sealant from the bolts.
01-10
Caution
• Apply the silicon sealant in a single, unbroken line around the whole perimeter.
• To prevent silicone sealant from hardening, adhere the oil pan to the cylinder block within 10 min.
after silicone sealant is applied. Tighten the installation bolts completely soon after adhering.
• Using bolts with the old seal adhering
could cause cracks in the cylinder block.
DAMAGE
OLD SEALANT
am6zzw00002304
01-10–77
Page 91

MECHANICAL
SEALANT
SEALANT
3. Apply silicone sealant to the oil pan along the inside of the bolt holes as shown in the figure.
A-A SECTIONAL VIEW
A
A
Thickness
3.0—7.0 mm {0.12—0.27 in}
4. Install the oil pan using the following procedure:
(1) Install the oil pan to the cylinder block.
(2) Temporarily tighten the two bolts shown in the
figure.
SEALANT
CYLINDER BLOCK
0.5—1.5 mm {0.02—0.05 in}
SEALANT
OIL PAN
bpe5ue00000011
(3) Tighten the bolts in the order shown in the
figure.
Tightening torque
8—11 N·m {82—112 kgf·cm, 71—97 in·lbf}
17
19
20
18
BOLT
16 12
1115
7
BOLT
bpe1ze00000081
3
6
2
10
14
13
9
8
4
5
1
bpe1ze00000082
01-10–78
Page 92

MECHANICAL
Electric Variable Valve Timing Motor/Driver Assembly Note
1. Install a new O-ring to the O-ring installation groove of the engine front cover.
Caution
• To prevent damage to the electric
variable valve timing motor/driver, do not
apply excessive force (force of 100 N
{10.2 kgf, 22.5 lbf} or more) to the shaded
areas shown in the figure.
2. Install the electric variable valve timing motor/
driver using the following procedures.
Note
• The eccentric shaft on the electric variable
valve timing actuator side can be rotated to
the left and right.
• The electric variable valve timing motor/
driver can be assembled with the joint
groove of the eccentric shaft in any position,
and it will not lead to vehicle damage or
performance reduction.
01-10
bpe1ze00000009
JOINT GROOVE
ECCENTRIC
SHAFT
(1) Before installation, rotate the joint on the end
of the electric variable valve timing motor so
that it is aligned to the joint groove on the
electric variable valve timing actuator side.
(2) Engage the joint on the end of the electric
variable valve timing motor with the joint
groove on the electric variable valve timing
actuator side.
(3) Attach the seal surface.
(4) Tighten the electric variable valve timing
motor/driver installation bolts.
Tightening torque
20—26 N·m {2.1—2.6 kgf·m, 15—19 ft·lbf}
ELECTRIC VALIABLE VALVE TIMING ACTUATOR
JOINT
ELECTRIC VARIABLE
VALVE TIMING
MOTOR/DRIVER
ELECTRIC VARIABLE
VALVE TIMING ACTUATOR
am3uuw00009042
JOINT GROOVE
am3uuw00009043
01-10–79
Page 93

MECHANICAL
Front Oil Seal Assembly Note
1. Apply clean engine oil to the inner surface of a new front oil seal.
2. Insert the front oil seal into the engine front cover by hand.
3. Tap the oil seal in evenly using the SST and a
hammer.
Front oil seal press on amount
0—0.5 mm {0—0.019 in}
49 G028 205
VIEW FROM A
HAMMER
49 G028 205
FRONT OIL SEAL
A
ENGINE FRONT COVER
am3uuw00008830
B
Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt Assembly Note
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Tighten the crankshaft pulley lock bolt in the order
shown in the following two steps.
Tightening procedure
Step 1: 90—110 N·m {9.2—11 kgf·m, 67—81
ft·lbf}
Step 2: 55—65°
B
SECTION B-B
ENGINE FRONT
COVER
0—0.5 mm
{0—0.019 in}
FRONT OIL SEAL
am3uuw00008831
49 E011 1A0
bpe1ze00000069
01-10–80
Page 94

MECHANICAL
Water Pump Pulley Assembly Note
Caution
• Be careful not to damage the belt groove and surface of the water pump pulley when using tools,
otherwise it will cause wear, breakage, abnormal noise of the drive belt (stretch belt), damage to
the pulley, and rust.
1. Install the water pump pulley to the water pump and temporarily tighten the bolt.
2. Align the water pump pulley hole with the water
pump hole as shown in the figure.
WATER PUMP
HOLEHOLE
WATER PUMP PULLEY
3. Insert an appropriate bolt (length 70 mm {2.8 in})
into the water pump hole shown in the figure and
WATER PUMP PULLEY
lock the water pump pulley against rotation.
4. Completely tighten the water pump pulley bolt to
the specified torque.
Tightening torque
8—11 N·m {82—112 kgf·cm, 71—97 in·lbf}
01-10
bpe2ue00000081
5. Remove the bolt used for locking the water pump
pulley against rotation.
Oil Shower Pipe Assembly Note
1. Install the oil shower pipe in the order shown in
the figure.
BOLT
am3uuw00008874
2 3
1
1
2 3
OIL SHOWER
PIPE
am3zzw00012759
01-10–81
Page 95

MECHANICAL
Tightening torque
Installation position Tightening torque
1 9—12 N·m {92—122 kgf·cm, 80—106 in·lbf}
2, 3 8.0—9.0 N·m {82—91 kgf·cm, 71—79 in·lbf}
Cylinder Head Cover Assembly Note
Caution
• To assure the sealing performance of the cylinder head cover, be careful of the following:
— Verify that the cylinder head cover gasket is inserted into the cylinder head cover groove and
install the cylinder head cover.
— Completely clean and remove any oil, dirt, sealant or other foreign matter from the seal
surface.
• To prevent silicone sealant from hardening, adhere the cylinder head cover and the cylinder head
within 10 min. after silicone sealant is applied. Tighten the installation bolts completely soon after
adhering.
1. Insert a new cylinder head cover gasket into the cylinder head cover groove.
01-10–82
Page 96

MECHANICAL
SEALANT
SEALANT
SEALANT
2. Apply silicone sealant to the areas shown in the figure.
ENGINE FRONT SIDE
SEALANT
2—6 mm
{0.1—0.2 in}
ENGINE FRONT COVER
4—5 mm
{0.16—0.19 in}
CYLINDER HEAD
VIEW FROM A
3—13 mm
{0.2—0.5 in}
01-10
3—13 mm
{0.2—0.5 in}
SEALANT
2—6 mm
{0.1—0.2 in}
ENGINE REAR SIDE
4—5 mm
{0.16—0.19 in}
4—5 mm
{0.16—0.19 in}
SEALANT
ENGINE
FRONT
CYLINDER
HEAD
COVER
ENGINE FRONT
COVER MATCHING
SURFACE
A
EXHAUST-SIDE REAR
CAMSHAFT CAP
VIEW FROM B
B
2—6 mm
{0.1—0.2 in}
2—6 mm
{0.1—0.2 in}
EXHAUST-SIDE
REAR CAMSHAFT
CAP
2—6 mm
{0.1—0.2 in}
3. Tighten the cylinder head cover bolts in the order
shown in the figure.
Tightening torque
4.5—7.0 N·m {46—71 kgf·cm, 40—61 in·lbf}
End Of Sie
CYLINDER HEAD
14
13
12
15
CYLINDER HEAD
bpe2ue00000082
38 7 4
9
10
11
6 2 51
am3uuw00008879
01-10–83
Page 97

Page 98

TECHNICAL DATA
01-50 TECHNICAL DATA
ENGINE TECHNICAL DATA . . . . . . . . . . 01-50–1
End of Toc
WM: ENGINE
ENGINE TECHNICAL DATA
Item Specification
OCV coil resistance 6.9—7.5 ohms [20°C {68°F}]
Maximum distortion, head gasket side of the cylinder
head
Maximum distortion, manifold side
Maximum cutting length, manifold side
Standard valve seat contact width 1.37—1.84 mm {0.0540—0.0724 in}
Valve seat angle 45°
Standard valve seat sinkage amount (Dimension L)
Standard valve head margin thickness
Standard valve length
Minimum valve length
Standard valve stem diameter
Minimum valve stem diameter
Standard valve guide inner diameter
Standard clearance between valve stem and guide
Maximum clearance between valve stem and guide 0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
Standard valve guide projection height
Valve spring installation height
Maximum valve spring off-square
Maximum camshaft runout 0.030 mm {0.0012 in}
Standard cam height
Minimum cam height
Standard camshaft journal diameter 24.96—24.98 mm {0.9827—0.9834 in}
Minimum camshaft journal diameter 24.93 mm {0.9815 in}
Standard camshaft journal oil clearance 0.035—0.080 mm {0.0014—0.0031 in}
Maximum camshaft journal oil clearance 0.090 mm {0.0035 in}
Standard camshaft end play 0.07—0.22 mm {0.003—0.008 in}
Maximum camshaft end play 0.23 mm {0.0091 in}
Maximum distortion, head gasket side of the cylinder
block
Standard cylinder bore diameter 89.000—89.030 mm {3.5040—3.5051 in}
Oil jet valve opening pressure
Standard piston outer diameter 88.965—88.995 mm {3.5026—3.5037 in}
Standard clearance between piston and cylinder 0.025—0.045 mm {0.0010—0.0017 in}
Maximum clearance between piston and cylinder 0.066 mm {0.0026 in}
When pressurized with spring force of 228—252 N {23.3—25.6 kgf,
IN: 48.93—50.17 mm {1.927—1.975 in}
EX: 48.87—50.11 mm {1.925—1.972 in}
IN: 1.75—1.95 mm {0.0689—0.0767 in}
EX: 1.95—2.15 mm {0.0768—0.0846 in}
IN: 107.00—107.60 mm {4.2127—4.2362 in}
EX: 117.09—117.69 mm {4.6099—4.6334 in}
IN: 5.470—5.485 mm {0.2154—0.2159 in}
EX: 5.465—5.480 mm {0.2152—0.2157 in}
IN: 5.510—5.530 mm {0.2170—0.2177 in}
EX: 5.510—5.530 mm {0.2170—0.2177 in}
IN: 0.025—0.060 mm {0.0010—0.0023 in}
EX: 0.030—0.065 mm {0.0012—0.0025 in}
IN: 16.4—17.0 mm {0.646—0.669 in}
EX: 16.4—17.0 mm {0.646—0.669 in}
51.3—56.6 lbf}, spring height is 38.0 mm {1.50 in}
180—220 kPa {1.84—2.24 kgf/cm
0.05 mm {0.002 in}
IN: 0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
EX: 0.05 mm {0.002 in}
IN: Cutting not authorized
EX: 0.20 mm {0.0079 in}
IN: 106.78 mm {4.2039 in}
EX: 116.87 mm {4.6012 in}.
IN: 5.424 mm {0.2135 in}
EX: 5.419 mm {0.2133 in}
IN: 2.0 ° (1.7 mm {0.067 in})
EX: 2.0 ° (1.7 mm {0.067 in})
IN: 42.34 mm {1.667 in}
EX: 40.37 mm {1.589 in}
IN: 42.27 mm {1.664 in}
EX: 40.30 mm {1.587 in}
0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
2
, 26.2—31.9 psi}
id015000800100
01-50
01-50–1
Page 99

TECHNICAL DATA
Item Specification
Standard clearance between piston ring and ring
groove
Maximum clearance between piston ring and ring
groove
Standard piston ring end gap
Maximum piston ring end gap
Standard piston pin outer diameter 20.995—21.000 mm {0.82658—0.82677 in}
Standard piston pin hole diameter 21.004—21.008 mm {0.82693—0.82708 in}
Standard clearance between piston pin hole diameter
and piston pin outer diameter
Standard connecting rod small end inner diameter 21.002—21.013 mm {0.82686—0.82728 in}
Standard clearance between connecting rod small end
inner diameter and piston pin outer diameter
Maximum connecting rod bending 0.050 mm {0.0020 in}
Maximum connecting rod distortion 0.050 mm {0.0020 in}
Connecting rod center-to-center distance 154.8 mm {6.094 in}
Standard side clearance at the large end of
connecting rod
Maximum side clearance at the large end of
connecting rod
Standard bearing oil clearance at the large end of the
connecting rod
Maximum bearing oil clearance at the large end of the
connecting rod
Connecting rod bearing size
Standard crankshaft end play 0.08—0.29 mm {0.004—0.011 in}
Maximum crankshaft end play 0.30 mm {0.012 in}
Thrust bearing size
Maximum main journal runout 0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
Standard main journal diameter 49.980—50.000 mm {1.9678—1.9685 in}
Maximum main journal off-round 0.005 mm {0.0002 in}
Standard crank pin diameter 49.980—50.000 mm {1.9678—1.9685 in}
Maximum crank pin off-round 0.005 mm {0.0002 in}
Standard main journal oil clearance 0.016—0.039 mm {0.0007—0.0015 in}
Maximum main journal oil clearance 0.084 mm {0.0033 in}
Main bearing size
Dual-mass flywheel guide pin projection maximum
amount
Dual-mass flywheel maximum runout 1.5 mm {0.059 in}
Standard cylinder head bolt length 145.2—145.8 mm {5.717—5.740 in}
Maximum cylinder head bolt length 146.5 mm {5.768 in}
Standard connecting rod bolt length 43.7—44.3 mm {1.73—1.74 in}
Maximum connecting rod bolt length 45.0 mm {1.77 in}
Rear oil seal press on amount 0—0.5 mm {0—0.019 in}
Front oil seal press on amount 0—0.5 mm {0—0.019 in}
Top: 0.04—0.08 mm {0.002—0.003 in}
Second: 0.03—0.07 mm {0.0012—0.0027 in}
Oil: 0.04—0.12 mm {0.002—0.004 in}
Top: 0.12 mm {0.0047 in}
Second: 0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
Oil: 0.17 mm {0.0067 in}
Top: 0.13—0.18 mm {0.0052—0.0070 in}
Second: 0.18—0.28 mm {0.008—0.011 in}
Oil (Rail): 0.10—0.35 mm {0.004—0.013 in}
Top: 0.35 mm {0.014 in}
Second: 0.45 mm {0.018 in}
Oil (Rail): 0.52 mm {0.020 in}
0.004—0.013 mm {0.0002—0.0005 in}
0.002—0.018 mm {0.00008—0.00070 in}
0.14—0.36 mm {0.006—0.014 in}
0.465 mm {0.0183 in}
0.026—0.052 mm {0.0011—0.0020 in}
0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
STD: 1.502—1.519 mm {0.05914—0.05980 in}
OS 0.25: 1.628—1.631 mm {0.06410—0.06421 in}
OS 0.50: 1.753—1.756 mm {0.06902—0.06913 in}
STD: 2.500—2.550 mm {0.0985—0.1003 in}
OS 0.25: 2.625—2.675 mm {0.1034—0.1053 in}
STD: 2.489—2.510 mm {0.0980—0.0988 in}
OS 0.25: 2.614—2.617 mm {0.10292—0.10303 in}
OS 0.50: 2.739—2.742 mm {0.10784—0.10795 in}
11.0—12.0 mm {0.434—0.472 in}
End Of Sie
01-50–2
Page 100

SERVICE TOOLS
01-60 SERVICE TOOLS
ENGINE SST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 01-60–1
End of Toc
SOKYU_WM: ENGINE
ENGINE SST
1: Mazda SST number
2: Global SST number
Example
1: 49 E011 1A0
2: –
Ring gear brake
set
id016000119200
01-60
1: 49 L010 1A0
2: –
Engine hanger
set
1: 49 0636
100B
2: –
Valve spring
lifter arm
1: 49 S120 710
2: –
Coupling flange
holder
1: 49 B012 015
2: –
Valve guide
installer
1: 49 G028 205
2: –
Oil seal installer
1: 49 0107
680A
2: –
Engine stand
1: 49 B012
0A2A
2: –
Pivot
1: 49 G033 102
2: –
Handle
1: 49 S033 101
2: –
Dust cover
installer
1: 49 E011 1A0
2: –
Ring gear brake
set
1: 49 S120 170
2: –
Valve seal
remover
1: 49 1285 071
2: –
Bearing puller
1: 49 B012 016
2: –
Attachment
——
End Of Sie
01-60–1
 Loading...
Loading...