Page 1
y
www.maxim-ic.com
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DS2149 is a fully integrated LIU for longhaul or short-haul T1 applications over twistedpair installations. It interfaces to two twisted-pair
lines—one pair for transmit and one pair for
receive through an appropriate network
interface. The device can be configured for
control through software or hardware mode.
Software control is accomplished over a serial
port, in hardware mode; individual pin settings
allow standalone operation. The device provides
a precise, crystal-less jitter attenuator that can be
placed in either the transmit or receive path.
APPLICATIONS
Routers
Data Service Units (DSUs)
Channel Service Units (CSUs)
Muxes
Switches
Channel Banks
T1/E1 Test Equipment
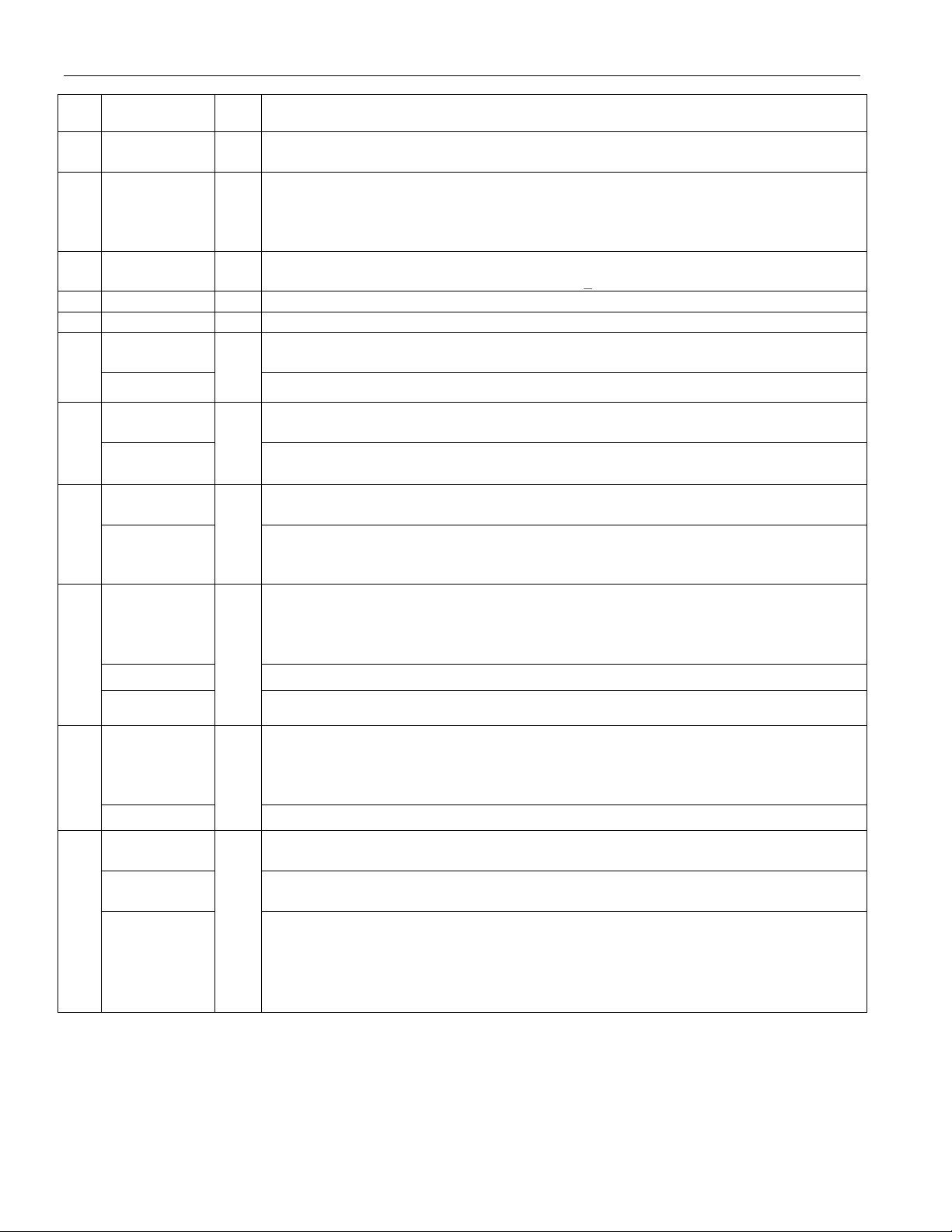
PIN CONFIGURATION
TOP VIEW
3 2 1
4
5
6
7
8
DS2149
9
10
11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18
28 27 26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
DEMO KIT AVAILABLE
DS2149
5V T1/J1 Line Interface Unit
FEATURES
§ Fully Integrated Line Interface Unit (LIU)
§ Pin Compatible with LevelOne LXT362
§ Supports Both Long Haul and Short Haul
§ Crystal-Less Jitter Attenuator
§ Jitter Attenuator Programmable for Transmit
or Receive Path
§ Meets ANSI T1.102, T1.403, T1.408, and
AT&T 62411
§ Usable Receive Sensitivity of 0dB to -36dB
That Allows the Device to Operate on
0.63mm (22AWG) Cables Up to 6k Feet in
Length
§ Five Line Build-Out Settings for Short-Haul
Applications
§ Four CSU Filters from 0dB to -22.5dB
§ Transmit/Receive Performance Monitors
with Driver-Fail, Monitor-Open, and Lossof-Signal Outputs
§ Bipolar or NRZ Interface
§ Programmable B8ZS Encoder/Decoder
§ QRSS Generator/Detector
§ Local, Remote, and Analog Loopbacks
§ Generates and Detects In-Band Loop-Up and
Loop-Down Codes
§ Serial Interface Provides Access to Control
Registers
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
DS2149Q 0°C to +70°C 28 PLCC
DS2149QN -40°C to +85°C 28 PLCC
PLCC
Note: Some revisions of this device may incorporate deviations from published specifications known as errata. Multiple revisions of any device
be simultaneously available through various sales channels. For information about device errata, click here: www.maxim-ic.com/errata.
ma
1 of 32 REV: 113004
Page 2

DS2149
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. DETAILED DESCRIPTION................................................................................................. 4
2. OPERATING MODES......................................................................................................... 5
3. INITIALIZATION AND RESET............................................................................................ 9
4. REGISTER DEFINITIONS .................................................................................................. 9
5. TRANSMITTER................................................................................................................... 15
5.1 TRANSMIT DIGITAL DATA INTERFACE ................................................................................... 15
5.2 TRANSMIT MONITORING ...................................................................................................... 15
5.3 TRANSMIT IDLE MODE......................................................................................................... 15
5.4 TRANSMIT PULSE SHAPE ....................................................................................................15
6. RECEIVER.......................................................................................................................... 15
6.1 RECEIVE EQUALIZER ..........................................................................................................15
6.2 RECEIVE DATA RECOVERY..................................................................................................15
6.3 RECEIVE DIGITAL-DATA INTERFACE ..................................................................................... 16
6.4 RECEIVE MONITOR MODE ...................................................................................................16
7. JITTER ATTENUATION .....................................................................................................16
8. HARDWARE MODE ...........................................................................................................16
9. SOFTWARE MODE ............................................................................................................ 17
9.1 INTERRUPT HANDLING ........................................................................................................17
10. DIAGNOSTIC MODE OPERATION.................................................................................... 19
10.1 LOOPBACK MODES............................................................................................................. 20
10.1.1 Local Loopback (LLB).................................................................................................................20
10.1.2 Analog Loopback (ALB)..............................................................................................................20
10.1.3 Remote Loopback (RLB) ............................................................................................................20
10.1.4 Network Loopback......................................................................................................................20
10.1.5 Dual Loopback ...........................................................................................................................20
10.2 INTERNAL PATTERN GENERATION AND DETECTION ............................................................... 21
10.2.1 Transmit Alarm-Indication Signal (TAIS).....................................................................................21
10.2.2 Quasirandom Signal Source (QRSS) .........................................................................................21
10.2.3 In-Band Network Loop-Up or Loop-Down Code Generator.........................................................22
10.3 E
10.3.1 Bipolar Violation Insertion (INSBPV)...........................................................................................22
10.3.2 Logic Error Insertion (INSLE)......................................................................................................22
10.3.3 Logic Error Detection (QPD).......................................................................................................22
10.3.4 Bipolar Violation Detection (BPV) ...............................................................................................22
10.4 A
10.4.1 Receive-Carrier Loss (RCL) .......................................................................................................23
10.4.2 Alarm-Indication-Signal Detection (AIS)......................................................................................23
10.4.3 Driver-Fail Monitor-Open (DFMO) ..............................................................................................23
10.4.4 Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip (JALT)...............................................................................................23
10.5 O
10.5.1 Receive Line-Attenuation Indication ...........................................................................................23
11. NETWORK INTERFACE ....................................................................................................24
12. DC CHARACTERISTICS.................................................................................................... 28
13. PACKAGE INFORMATION ................................................................................................ 32
RROR INSERTION AND DETECTION ..................................................................................... 22
LARM MONITORING........................................................................................................... 23
THER DIAGNOSTIC REPORTS ............................................................................................23
2 of 32
Page 3

DS2149
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram....................................................................................................................................... 4
Figure 2-1. Hardware Mode Pinout ........................................................................................................................ 6
Figure 2-2. Serial Port Mode Pinout....................................................................................................................... 6
Figure 9-1. Serial Data Port Operation for Read Access.................................................................................. 18
Figure 9-2. Serial Data Port Operation for Write Access.................................................................................. 18
Figure 10-1. Loopbacks in the DS2149 Block Diagram.................................................................................... 21
Figure 11-1. Basic Network Interface .................................................................................................................. 25
Figure 11-2. T1 Transmit Pulse Template .......................................................................................................... 26
Figure 11-3. Jitter Tolerance................................................................................................................................. 27
Figure 11-4. Jitter Attenuation............................................................................................................................... 27
Figure 12-1. Serial Bus Read Timing (MODE1 = 1).......................................................................................... 29
Figure 12-2. Serial Bus Write Timing (MODE1 = 1) .......................................................................................... 29
Figure 12-3. AC Characteristics for Receive Side ............................................................................................. 30
Figure 12-4. AC Characteristics for Transmit Side ............................................................................................ 31
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2-A. Operating Modes ................................................................................................................................... 5
Table 2-B. Control Pins for Hardware and Software Modes .............................................................................. 5
Table 2-C. Signal Descriptions ............................................................................................................................... 7
Table 4-A. Register Map.......................................................................................................................................... 9
Table 4-B. Register Bit Positions............................................................................................................................ 9
Table 4-C. Jitter Attenuator Selection.................................................................................................................. 10
Table 4-D. Line Code and Interface Selection ................................................................................................... 10
Table 4-E. Line Build-out Selection...................................................................................................................... 10
Table 4-F. Data Pattern Selection ........................................................................................................................ 11
Table 9-A. CLKE Pin Selection............................................................................................................................. 17
Table 9-B. Control and Operation Mode Selection............................................................................................ 19
Table 10-A. Diagnostic Modes.............................................................................................................................. 19
Table 11-A. Specifications for Receive Transformer......................................................................................... 24
Table 11-B. Specifications for Transmit Transformer........................................................................................ 24
Table 11-C. Transformer Turns Ratio vs. Series Resistance .......................................................................... 24
3 of 32
Page 4
DS2149
K
1. DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The DS2149 is a complete T1 line interface unit (LIU) for short-haul and long-haul applications. Receive
sensitivity adjusts automatically to the incoming signal and can be limited to -18dB, -26dB, or
-36dB. The device can generate the necessary DSX-1 line build-outs or CSU line build-outs of 0dB,
-7.5dB, -15dB, and -22.5dB. The on-board crystal-less jitter attenuator requires a 1.544MHz reference
clock. The jitter attenuator FIFO is selectable to either 32 bits or 128 bits in depth and can be placed in
either the transmit or receive data paths. The DS2149 has diagnostic capabilities such as loopbacks and
QRSS pattern generation and detection. The device can also generate and detect the in-band loop-up and
loop-down codes specified in AT&T 62411. The device can be configured for control using a serial
interface, or for hardware mode. The device fully meets all of the latest T1 specifications including ANSI
T1.102-1999, ANSI T1.403-1999, ANSI T1.408, and AT&T 62411.
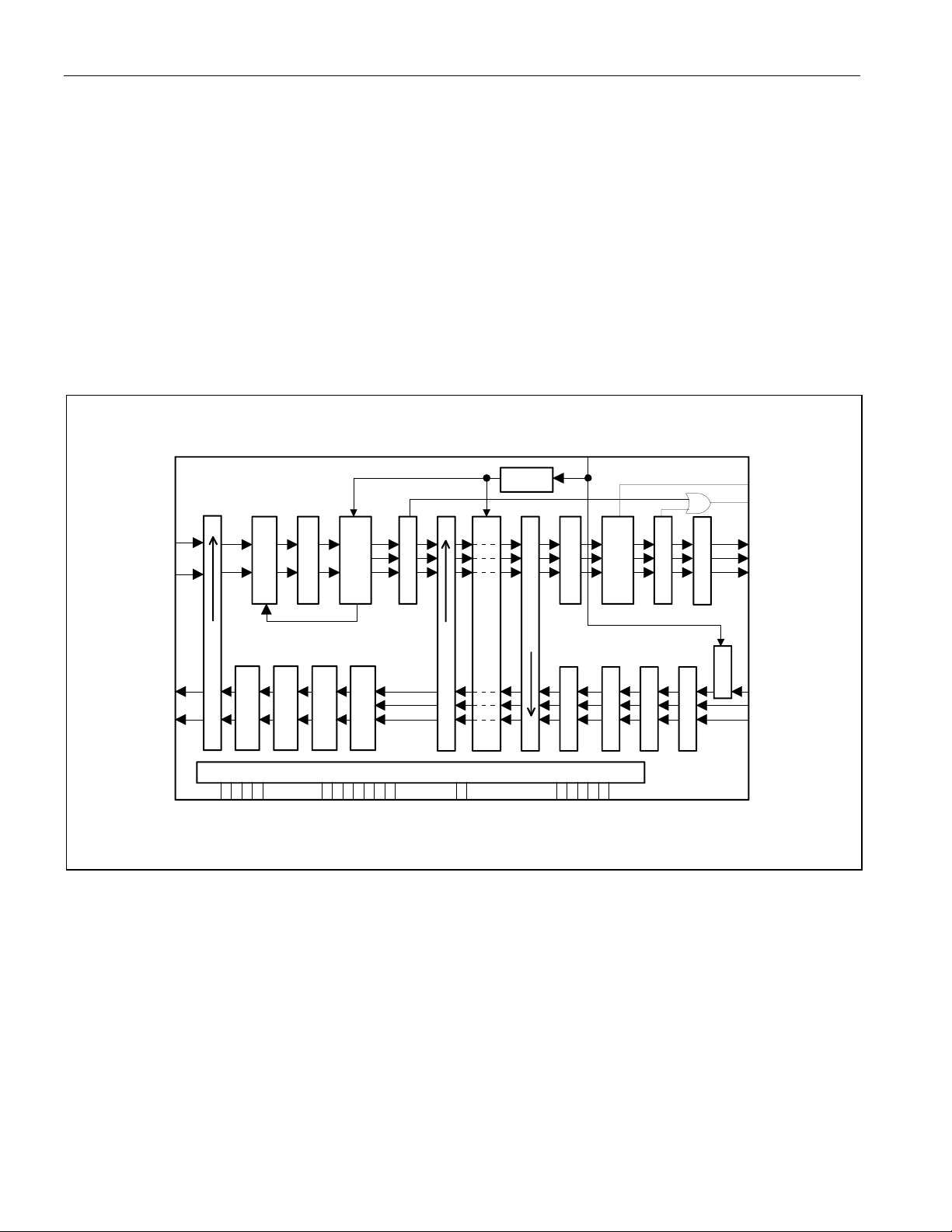
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram
L
C
M
L
L
P
C
/
O
V
t
a
t
c
R
N
R
G
I
R
T
P
I
k
c
a
b
p
o
o
L
s
r
g
e
o
l
T
N
R
G
I
T
T
P
I
v
i
a
r
n
D
A
e
n
i
L
e
t
r
e
e
t
D
l
i
k
F
a
e
P
s
r
e
t
l
i
F
U
S
C
y
a
D
/
k
c
o
l
C
g
n
i
p
a
h
S
e
v
a
W
r
r
o
e
t
v
c
o
e
t
c
e
e
D
R
L
C
R
k
c
Jitter Attenuator
a
b
p
o
o
S
I
A
t
i
m
s
a
n
r
T
L
l
a
c
o
L
r
e
p
d
o
o
o
c
L
e
d
D
k
c
a
b
p
o
o
L
e
t
o
m
e
R
n
a
S
B
Z
8
n
I
B
t
r
r
e
e
s
d
n
I
o
r
c
o
n
r
r
E
E
S
c
i
Z
g
8
o
B
L
r
r
o
t
o
c
t
c
e
t
e
t
e
e
D
D
S
e
S
d
R
o
Q
C
.
n
e
g
p
S
o
S
o
L
R
d
Q
n
a
B
n
I
NLOOP
RCL/QPD
t
c
RCLK
e
t
e
RPOS
d
S
I
RNEG
A
x
u
m
C
T
O
TCLK
L
TPOS
TNEG
Power connections Hardware Interface Serial Interface
L0L1L2
L3
LLB
VDD
VSM
GND
GND
TVDD
JASEL
RLB
TBL/QRSS
MODE0
MODE1
4 of 32
INT
CS
SDI
SDO
CLKE
SCLK
Page 5

DS2149
2. OPERATING MODES
The DS2149 has several pins with multiple functions and names according to the selected operating
mode. These operating modes are summarized in the tables below.
Table 2-A. Operating Modes
PIN
1 MCLK
2 TCLK
3 TPOS TDATA INSLER
4 TNEG INSBPV INSBPV
6 RNEG BPV RNEG BPV
7 RPOS RDATA RPOS RDATA
8 RCLK
13 TTIP
16 TRING
19 RTIP
20 RRING
Control pins are affected by serial port and hardware modes.
QRSS DISABLED QRSS ENABLED
BIPOLAR NRZ BIPOLAR NRZ
Table 2-B. Control Pins for Hardware and Software Modes
PIN
5 MODE1 MODE1
9 MODE0 MODE0
11 JASEL N.C.
12 RCL RCL/QPD RCL RCL/QPD
23 L0 INT
24 L1 SDI
25 L2 SDO
17 L3 N.C.
18 NLOOP NLOOP
26 RLB NLB CS
27 LLB ALB SCLK
28 TAIS QRSS CLKE
HARDWARE MODE SERIAL PORT MODE
NRZ QRSS NRZ QRSS
5 of 32
Page 6
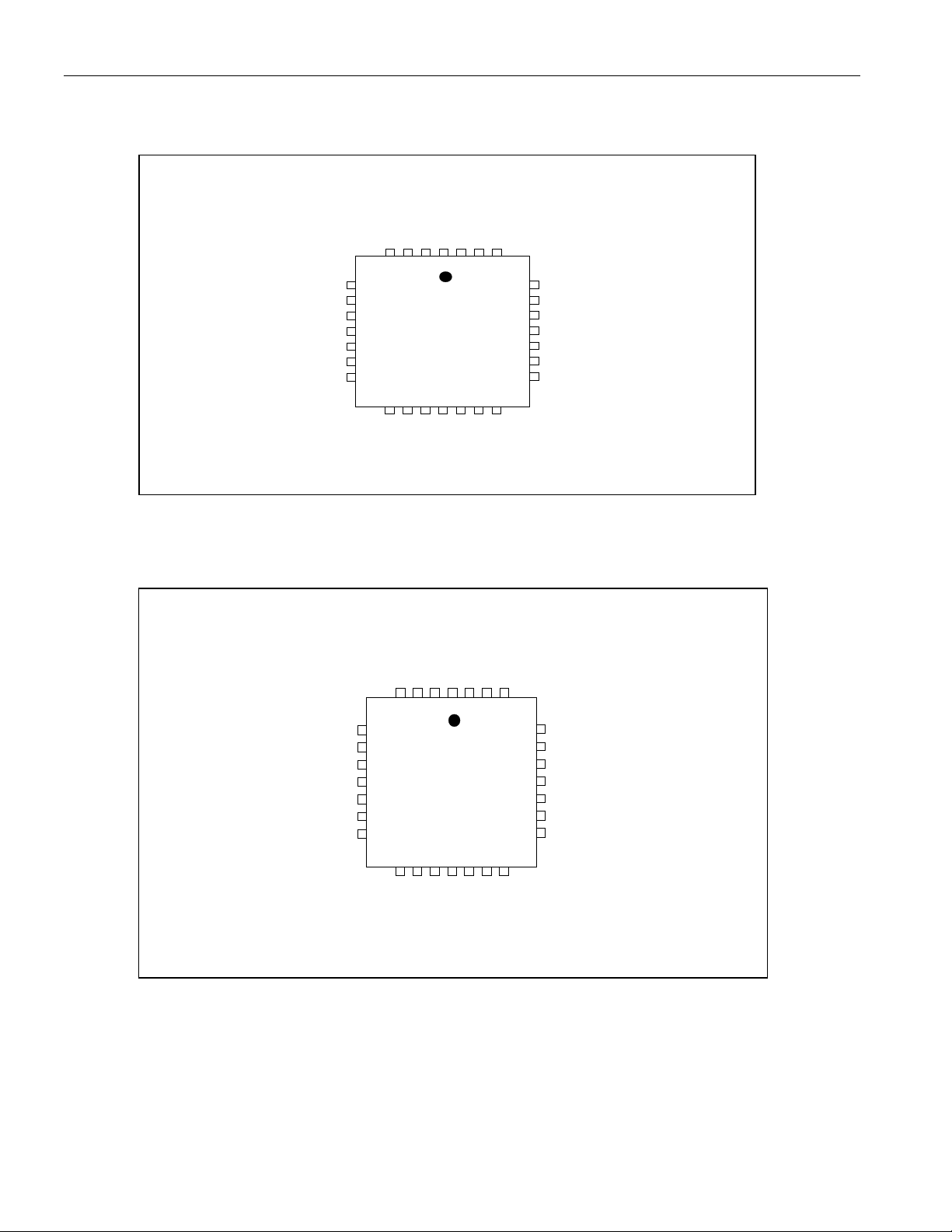
Figure 2-1. Hardware Mode Pinout
MODE1
RNEG
RPOS
RCLK
MODE0
VSM
JASEL
TNEG
TPOS
432
5
6
7
DS2149
8
9
10
11
12131415161718
TTIP
RCL/QPD
Figure 2-2. Serial Port Mode Pinout
TCLK
GND
MCLK
1
282726
TVDD
DS2149
TAIS/QRSS
LLB
RLB
L2
25
L1
24
L0
23
GND
22
VDD
21
RRING
20
RTIP
19
L3
TRING
NLOOP
TNEG
TPOS
TCLK
MCLK
CLKE
SCLK
CS
MODE1
RNEG
RPOS
RCLK
MODE0
VSM
N/C
432
5
6
7
DS2149
8
9
10
11
12131415161718
RCL/QPD
TTIP
1
GND
TVDD
282726
N/C
TRING
NLOOP
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
SDO
SDI
INT
GND
VDD
RRING
RTIP
6 of 32
Page 7
Table 2-C. Signal Descriptions
PIN NAME I/O FUNCTION
DS2149
1 MCLK I
2 TCLK I
TPOS
3
TDATA
INSLER
TNEG
4
INSBPV
5 MODE1 I
Master Clock. A 1.544MHz clock source with TTL levels is applied at this pin. This
clock is used internally for both clock/data recovery and for jitter attenuation.
Transmit Clock. A 1.544MHz primary clock. Used to clock data through the transmit
side formatter. Can be sourced internally by MCLK or RCLK.
Transmit Positive Data. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data to be
transmitted out onto the line.
Transmit NRZ Data. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data to be transmitted
I
onto the line.
Transmit Insert Logic Error. Rising edge on INSLER inserts a logic error into the
outbound QRSS pattern. Sampled on falling edge of TCLK.
Transmit Negative Data. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data to be
transmitted out onto the line.
I
Transmit Insert Bipolar Violation. INSBPV is sampled on the falling edge of TCLK.
Rising edge inserts one BPV.
Mode Select 1. Connect low to select hardware mode. Connect high to select serial
2
port mode. See also MODE0.
Receive Negative Data. Updated on the rising edge (CCR2.0 = 0) or the falling edge
RNEG
6
BPV
(CCR2.0 = 1) of RCLK with the bipolar data out of the line interface. Always valid
on rising edge of RCLK in hardware mode.
O
Receive Bipolar Violation. Transitions high for one clock cycle marking an inbound
bipolar violation. Valid on rising edge of RCLK.
Receive Positive Data. Updated on the rising edge (CCR2.0 = 0) or the falling edge
RPOS
(CCR2.0 = 1) of RCLK with bipolar data out of the line interface. Always valid on
rising edge of RCLK in hardware mode.
7
RDATA
O
Receive Data. RDATA is the NRZ output from the line interface. Set NRZE
(CCR1.6) to a 1 for NRZ applications. In NRZ mode, data is output on RPOS while a
received error causes a positive-going pulse synchronous with RCLK at RNEG
(Section 6
8
RCLK
9 MODE0 I
Receive Clock. Buffered recovered clock from the line. Synchronous to MCLK in
O
absence of signal at RTIP and RRING.
Mode Select 0. Set high to disable all output pins (including the serial control port).
2
Set low for normal operation. Useful in board level testing. See also MODE1.
).
1
10 VSM I
Voltage Supply Mode. Connect high for 5V operation. Has 10kW pullup.
Jitter Attenuator Select
0 = Place the jitter attenuator on the transmit side
11 JASEL I
2
1 = Place the jitter attenuator on the receive side
Float = Disable jitter attenuator
Not used in software mode
RCL Receive Carrier Loss. An output that toggles high during a receive carrier loss.
12
QPD
QPD. Output high when QRSS detector is searching for QRSS data pattern. Output
O
high for one-half clock cycle on bit error. Connect to external counter to count bit
errors.
13/
16
14 VSS —
15
TTIP/
TRING
TVDD
Transmit Tip and Ring. Analog line driver outputs. These pins connect through a
O
step-up transformer to the line (Section 5
Ground for Transmitter Block
— Positive Supply. 5.0V ±5% for the transmitter block. See also VSM pin 10.
7 of 32
).
Page 8
PIN NAME I/O FUNCTION
DS2149
17 L3 I
LBO3. LBO0 through LBO3 are used to select transmitter output pulse, and receiver
gain.
Network Loopback Active. Output high when RLB is activated by in-band loop-up
18 NLOOP O
command present for 5 seconds. Output is reset when RLP is deactivated by in-band
loop-down command present for 5 seconds. Activation of remote loopback through
hardware pin 26 or control bit RLB releases the NLOOP output.
19/
20
RTIP/
RRING
Receive Tip and Ring. Analog inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins connect
I
through a 1:1 transformer to the line (Section 6
21 VDD — Positive Supply. 5V ±5%. See also VSM pin 10.
22 VSS — Signal Ground
23
L0
INT
L1
24
SDI
L2
25
SDO
LBO0. LBO0 through LBO3 are used to select transmitter output pulse, and receiver
gain.
I/O
INT. Used to alert the host when one or more bits are set in the status register.
LBO1. LBO0 through LBO3 are used to select transmitter output pulse, and receiver
gain.
I
Serial Data Input. Input for serial address and data stream. Sampled on rising of
SCLK.
LBO2. LBO0 through LBO3 are used to select transmitter output pulse, and receiver
gain.
O
Serial Data Output. Updated on falling edge of SCLK if CLKE is connected high.
Updated on rising edge of SCLK if CLKE is connected low. SDO is high-Z during
write cycle or when CS is high.
Remote Loopback. Used to invoke remote loopback. When held high, the transmitter
RLB
26
inputs are ignored and inbound data received at RTIP and RRING is routed to the
transmitter outputs, TTIP and TRING and transmitted at the inbound recovered clock
2
rate.
I
NLB Network Loopback. Enables network loopback detection when RLB floats.
).
CS
Chip Select. Must be low to read or write to the device. CS is an active-low signal.
Local Loopback. Used to invoke local loopback. When held high, digital inputs
27
LLB
TPOS and TNEG are looped back to RPOS and RNEG, through the jitter attenuator
2
if enabled. Floating this input invokes analog loopback. The analog output signal at
I
TTIP and TRING is routed to the receive inputs RTIP and RRING.
SCLK
TAIS
QRSS
28
Serial Clock Input. Input clock to operate serial port. Max clock rate, 2.048MHz.
Transmit AIS. Input high forces transmitter to output unframed all ones. Unavailable
in remote loopback.
QRSS. Floating this pin enables QRSS pattern generator and detector. Input low
enables normal transmission of data.
2
I
Clock Edge Select
0 = Update RNEG/RPOS on falling edge of RCLK, SDO updated on rising edge of
CLKE
SCLK.
1 = Update RNEG/RPOS on rising edge of RCLK, SDO updated on falling edge of
SCLK.
Note 1: G.703 requires an accuracy of ±50ppm for T1. TR62411 and ANSI specifications require an accuracy of ±32ppm for T1 interfaces.
Note 2: Input pins have three operating modes.
8 of 32
Page 9
DS2149
3. INITIALIZATION AND RESET
During power-up, all control registers are cleared, disabling the transmitter outputs. The device requires a
master clock supplied to the MCLK input pin to operate the PLL. This master clock must be independent,
free-running, and jitter free.
A reset initializes the status and state machines for the RCL, AIS, NLOOP, and QRSS blocks. Under
software control, setting the RESET bit (CR2.7) clears all registers. Allow up to 100ms for the receiver to
recover from initialization.
4. REGISTER DEFINITIONS
The DS2149 contains eight registers for configuring the device and reading status. These are accessible
using the serial port. Table 4-A lists the register names and addresses.
Reading or writing to the internal registers requires writing one address/command byte prior to
transferring register data. The first bit written (LSb) of the address/command byte specifies whether the
access is a read (1) or a write (0). The next 6 bits identify the register address.
The last bit (MSb) of the address/command byte is the burst mode bit. When the burst bit is enabled (set
to 1) and a READ operation is performed, addresses 10h through 17h are read sequentially, starting at
address 10h. And when the burst bit is enabled and a WRITE operation is performed, addresses 10h
through 17h are written sequentially, starting at address 10h. Burst operation is stopped once address 17h
is read. All data transfers are initiated by driving the CS input low. All data transfers are terminated if the
CS input transitions high. Port control logic is disabled and SDO is tri-stated when CS is high.
Table 4-A. Register Map
REGISTER SYMBOL ADDRESS
Control Register 1 CR1 B010000
Control Register 2 CR2 B010001
Control Register 3 CR3 B010010
Interrupt Mask Register IMR B010011
Transition Status Register TSR B010100
Status Register SR B010101
Information Register IR B010110
Control Register 4 CR4 B010111
Table 4-B. Register Bit Positions
SYMBOL 7 (MSb) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 (LSb)
CR1 JASEL1 JASEL0 ENCENB UNIENB L3 L2 L1 L0
CR2 RESET PAT1 PAT0 TAIS ENLOOP ALB LLB RLB
CR3 JA6HZ TPD — EQZMON20 EQZMON26 JA128 LIRST TAOZ
IMR Z16D JALT DFMO B8ZSD QRSS AIS NLOOP RCL
TSR Z16D JALT DFMO B8ZSD QRSS AIS NLOOP RCL
SR — — DFMO — QRSS AIS NLOOP RCL
IR RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0 LUP LDN TSCD LOTC
CR4 — — — — — RCL2048 XFMR2 XFMR1
Note: Set unused bits to 0 for normal operation.
9 of 32
Page 10
CR1 (B010000): Control Register 1
MSb LSb
JASEL1 JASEL0 ENCENB UNIENB L3 L2 L1 L0
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
JASEL1 CR1.7 Jitter attenuator select (Table 4-C)
JASEL0 CR1.6 Jitter attenuator select (Table 4-C)
ENCENB CR1.5 B8ZS and NRZ control (Table 4-D)
UNIENB CR1.4 BPV and NRZ control (Table 4-D)
L3 CR1.3 Line build-out control (Table 4-E)
L2 CR1.2 Line build-out control (Table 4-E)
L1 CR1.1 Line build-out control (Table 4-E)
L0 CR1.0 Line build-out control (Table 4-E)
Table 4-C. Jitter Attenuator Selection
JASEL1 JASEL0 JITTER ATTENUATOR FUNCTION
0 1 Transmit path
1 1 Receive path
X 0 Disabled
Table 4-D. Line Code and Interface Selection
DS2149
UNIENB ENCENB LINE CODE INTERFACE
0 0 AMI Bipolar
1 0 AMI NRZ
X 1 B8ZS NRZ
Table 4-E. Line Build-out Selection
L3 L2 L1 L0 APPLICATION OUTPUT SIGNAL Rx GAIN (dB)
0 0 0 0 T1 Long Haul 0dB 36
0 0 1 0 T1 Long Haul -7.5dB 36
0 1 0 0 T1 Long Haul -15dB 36
0 1 1 0 T1 Long Haul -22.5dB 36
0 0 0 1 T1 Long Haul 0dB 26
0 0 1 1 T1 Long Haul -7.5dB 26
0 1 0 1 T1 Long Haul -15dB 26
0 1 1 1 T1 Long Haul -22.5dB 26
1 0 0 1 D4 Short Haul 6V 18
1 0 1 1 T1 Short Haul DSX-1 (0ft to 133ft) 18
1 1 0 0 T1 Short Haul DSX-1 (133ft to 266ft) 18
1 1 0 1 T1 Short Haul DSX-1 (266ft to 399ft) 18
1 1 1 0 T1 Short Haul DSX-1 (399ft to 533ft) 18
1 1 1 1 T1 Short Haul DSX-1 (533ft to 655ft) 18
10 of 32
Page 11

CR2 (B010001): Control Register 2
MSb LSb
RESET PAT1 PAT0 TAIS ENLOOP ALB LLB RLB
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
RESET CR2.7 Resets device states and clears all registers.
PAT1 CR2.6 Selects output data pattern (Table 4-F).
PAT0 CR2.5 Selects output data pattern (Table 4-F).
TAIS CR2.4
ENLOOP CR2.3
ALB CR2.2
LLB CR2.1
RLB CR2.0
0 = Transmit data normally
1 = Transmit unframed all ones
0 = Disable in-band loop-code detection
1 = Enable in-band loop-code detection
0 = Disable analog loopback
1 = Enable analog loopback
0 = Disable local loopback
1 = Enable local loopback
0 = Disable remote loopback
1 = Enable remote loopback
Table 4-F. Data Pattern Selection
DS2149
PAT0 PAT1 DATA SOURCE
0 0 TPOS/TNEG
0 1 Transmit QRSS
1 0 In-band loop-up 00001
1 1 In-band loop-down 001
CR3 (B010010): Control Register 3
MSb LSb
JA6HZ TPD — EQZMON20 EQZMON26 JA128 LIRST TAOZ
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
0 = Set bandwidth of jitter attenuator to 3Hz
JA6HZ CR3.7
TPD CR3.6
— CR3.5 —
EQZMON20 CR3.4
EQZMON26 CR3.3
JA128 CR3.2
LIRST CR3.1
TAOZ CR3.0
1 = Set bandwidth of jitter attenuator to 6Hz; not available if
JA128 = 1
0 = Enable transmitter outputs
1 = Disable transmitter outputs
0 = Normal receiver operation
1 = Add 20dB of resistive gain to inbound signal
0 = Normal receiver operation
1 = Add 26dB of resistive gain to inbound signal
0 = Jitter attenuator buffer depth = 32 bits
1 = Jitter attenuator buffer depth = 128 bits
0 = Normal operation
1 = Reset the receive LIU state machine
0 = Disable transmit alternate 1s and 0s
1 = Enable transmit alternate 1s and 0s
11 of 32
Page 12

IMR (B010011): Interrupt Mask Register
MSb LSb
Z16D JALT DFMO B8ZSD QRSS AIS NLOOP RCL
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
Z16D IMR.7
JALT IMR.6
DFMO IMR.5
B8ZSD IMR.4
QRSS IMR.3
AIS IMR.2
NLOOP IMR.1
RCL IMR.0
0 = Enable 16-zero detect interrupt
1 = Disable 16-zero detect interrupt
0 = Enable jitter-attenuator limit-trip interrupt
1 = Disable jitter-attenuator limit-trip interrupt
0 = Enable driver-open interrupt
1 = Disable driver-open interrupt
0 = Enable B8ZS-detect interrupt
1 = Disable B8ZS-detect interrupt
0 = Enable QRSS interrupt
1 = Disable QRSS interrupt
0 = Enable AIS interrupt
1 = Disable AIS interrupt
0 = Enable network-loopback interrupt
1 = Disable network-loopback interrupt
0 = Enable receive carrier-loss interrupt
1 = Disable receive carrier-loss interrupt
TSR (B010100): Transition Status Register
MSb LSb
Z16D JALT DFMO B8ZSD QRSS AIS NLOOP RCL
DS2149
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
Z16D TSR.7
JALT TSR.6
DFMO TSR.5 Set when SR.5 changes state; cleared when IMR.5 is cleared.
B8ZSD TSR.4
QRSS TSR.3 Set when SR.3 changes state; cleared when IMR.3 is cleared.
AIS TSR.2 Set when SR.2 changes state; cleared when IMR.2 is cleared.
NLOOP TSR.1 Set when SR.1 changes state; cleared when IMR.1 is cleared.
RCL TSR.0 Set when SR.0 changes state; cleared when IMR.0 is cleared.
Set when the receiver detects 16 consecutive 0s; cleared when
IMR.7 is cleared.
Set when the jitter attenuator FIFO reaches to within 4 bits of its
limit; cleared when IMR.6 is cleared.
Set when the receiver detects B8ZS codewords; cleared when
IMR.4 is cleared.
12 of 32
Page 13

SR (B010101): Status Register
MSb LSb
— — DFMO — QRSS AIS NLOOP RCL
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
— SR.7 —
— SR.6 —
DFMO SR.5 Set when transmitter detects open circuit.
— SR.4 —
QRSS SR.3 Set when the QRSS pattern is present at the receiver.
AIS SR.2 Set when the AIS pattern is present at the receiver.
NLOOP SR.1 Set when the in-band loop-up code is present at the receiver.
Set when receiver has detected consecutive s set forth by CR4.2.
RCL SR.0
Cleared when the receiver detects 14 1s in a window of 112 clock
cycles.
IR (B010110): Information Register
MSb LSb
RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0 LUP LDN TSCD LOTC
DS2149
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
RL3 IR.7 —
RL2 IR.6 —
RL1 IR.5 —
RL0 IR.4 —
LUP IR.3 Set when in-band loop-up code is being received.
LDN IR.2 Set when in-band loop-down code is being received.
TSCD IR.1 Set when transmitter detects a short circuit.
LOTC IR.0
Set when TCLK has not transitioned for approximately 5ms.
Receive Level Indication: RL0 is the LSB and RL3 is the MSB of a 4-bit nibble that is used to indicate the inbound
signal strength. Convert the binary to decimal and multiply by -2.5dB. The result indicates the approximate
attenuation seen at the receiver inputs.
13 of 32
Page 14

CR4 (B010111): Control Register 4
MSb LSb
— —
SYMBOL POSITION FUNCTION
— CR4.7 —
— CR4.6 —
— CR4.5 —
— CR4.4 —
— CR4.3 —
RCL2048 CR4.2
XFMR2 CR4.1
XFMR1 CR4.0
— — — RCL2048 XFMR2 XFMR1
0 = RCL threshold: 192 consecutive 0s
1 = RCL threshold: 2048 consecutive 0s
Set to 0 for use with standard transformers.
Set to 1 for use with alternate transformers (Table 11-C
Set to 0 for use with standard transformers.
Set to 1 for use with alternate transformers (Table 11-C
)
)
DS2149
14 of 32
Page 15

DS2149
5. TRANSMITTER
5.1 Transmit Digital Data Interface
Data is clocked into the device at the TCLK rate. In bipolar mode, TPOS and TNEG are the data inputs;
in NRZ mode, TDATA is the data input. Input data can pass through either the jitter attenuator or the
B8ZS encoder or both. In software mode, setting ENCENB enables B8ZS encoding. In hardware mode,
floating the MODE1 pin enables B8ZS encoding. With B8ZS encoding enabled, the L0 through L3 inputs
determine the coding and is listed in Table 4-E. TCLK supplies input synchronization. See Section 12 for
the TCLK and MCLK timing requirements.
5.2 Transmit Monitoring
In software mode, the DFMO bit in the status register is set when an open circuit in the transmitter path is
detected. A transition on this bit can provide an interrupt, and a transition sets the DFMO bit in the
transition status register. Setting CDFMO in the interrupt mask register, leaving a 1 in that bit location
masks the interrupt.
5.3 Transmit Idle Mode
Transmit idle mode allows multiple transceivers to be connected to a single line for redundant
applications. When TCLK is not present, transmit idle mode becomes active, and TTIP and TRING
change to high-impedance state. Remote loopback, dual loopback, TAIS, or detection of network loop-up
code in the receive direction temporarily disable the high-impedance state.
5.4 Transmit Pulse Shape
As shown in Table 4-E, line build-out control inputs (L0 through L3) determine the transmit pulse shape.
In software mode, these control inputs are located in control register 1; in hardware mode, these control
inputs are the L0 through L3 pins.
Shaped pulses meeting the various T1, DS1, and DSX-1 specifications are applied to the AMI line driver
for transmission onto the line at TTIP and TRING. The transceiver produces DSX-1 pulses for short-haul
T1 applications (settings from 0dB to 6dB of cable) and DS1 pulses for long-haul T1 applications
(settings from 0dB to -22.5dB). Refer to Table 4-E for pulse mask specifications.
6. RECEIVER
A 1:1 transformer provides the interface between the twisted pair and receiver inputs RTIP and RRING.
Recovered data is output at RPOS and RNEG (or RDATA in NRZ mode), and the recovered clock is
output at RCLK. See Section 12 for receiver timing specifications.
6.1 Receive Equalizer
The receiver can apply up to 36dB of gain. Control of the equalizer is accomplished by the L0 through L3
control inputs. These control signals are detailed in Table 4-E
and determine the maximum gain that is
applied. In software mode, these control signals are in Control Register 1; in hardware mode, these
control inputs are the L0 through L3 pins. With L0 low, up to 36dB of gain can be applied; when L0 is
high, 26dB can be applied in the gain limit to provide better noise immunity in shorter loop operations.
6.2 Receive Data Recovery
The clock and data recovery engine provides input jitter tolerance that exceeds the requirements of AT&T
62411. Inbound signal is filtered, equalized, and over-sampled 16 times. Then it is applied to the B8ZS
decoder if enabled.
15 of 32
Page 16

DS2149
6.3 Receive Digital-Data Interface
Recovered data is routed to the RCL monitor. In software mode, data also goes through the alarm
indication signal (AIS) monitor. The jitter attenuator can be enabled or disabled in the receive path or
transmit path. Received data can be routed to the B8ZS decoder or bypassed. Finally, the device can send
the digital data to the framer as either bipolar or NRZ data.
6.4 Receive Monitor Mode
The receive equalizer can be used in monitor-mode applications. Monitor-mode applications require
20dB of resistive attenuation of the signal, plus an allowance for cable attenuation (less than 20dB). In
software mode, setting CR3.4 (EQZMON20) enables the device to operate in monitor-mode applications
that require 20dB of resistive attenuation of the signal. Setting CR3.3 (EQZMON26) enables the device
to operate in monitor-mode applications that require 26dB of resistve attenuation. Setting both CR3.3 and
CR3.4 enables the device to operate in monitor-mode applications that require 32dB of resistive
attenuation. The monitor mode feature is not available in hardware mode.
7. JITTER ATTENUATION
The jitter attenuator only requires a jitter-free clock at 1.544MHz applied to the MCLK input. In
hardware mode, the jitter attenuator is a 32-bit FIFO buffer. Pulling the JASEL pin high places the jitter
attenuator in the receive path. Pulling the JASEL pin low places the jitter attenuator in the transmit path,
floating the JASEL pin disables the jitter attenuator. In software mode, clearing CR1.6 (JASEL0) disables
the jitter attenuator, setting CR1.6 enables the jitter attenuator. If enabled, clearing CR1.7 (JASEL1)
places the jitter attenuator in the transmit path, setting CR1.7 places the jitter attenuator in the receive
path. The jitter attenuator FIFO is 32 bits in length if CR3.2 (JA128) is cleared, 128 bits if set. The device
clocks data in the jitter attenuator using TCLK if placed in the transmit path, and RCLK if placed in the
receive path. Data is clocked out of the jitter attenuator using the dejittered clock produced by the internal
PLL. When the jitter attenuator is within two bits of overflowing or underflowing, the jitter attenuator
will adjust the output clock by one-eighth of a clock cycle. The jitter attenuator adds an average delay of
16 bits if the buffer depth is 32 bits in length, 64 bits if the buffer depth is 128 bits in length. In the event
of an RCL condition, if the jitter attenuator is in the receive path then RCLK is derived from MCLK.
Transition Status register bit TSR.6 (JALT) indicates that the jitter attenuator has adjusted the output
clock. This bit is latched, when set it remains set until the software reads the bit. The JALT can also
produce a hardware interrupt.
8. HARDWARE MODE
The DS2149 operates in hardware mode when the MODE1 pin is pulled low or floated. In hardware
mode, configuration of the device is under control of various input pins. RPOS, RNEG, and RDATA are
valid on the rising edge of RCLK only. Some functions such as INT, clock edge select, and some
diagnostic modes are not available.
16 of 32
Page 17

DS2149
9. SOFTWARE MODE
The DS2149 operates in software mode when the MODE1 pin is pulled high. In software mode, a
microprocessor controls the device and reads its status through the serial port, which provides access to
the internal registers. The host processor can completely configure the device as well as get diagnostics
and status reports through the serial port. In NRZ mode, bipolar violation insertions and logic error
insertions are controlled by the BPV and INSLER pins. Similarly, the recovered clock, data, and BPV
detection are available only at output pins. All other mode settings and diagnostic information are
available through the serial port. Figure 9-1 and Figure 9-2 show the serial port data structure. The
registers are accessible through a 16-bit word composed of an 8-bit command and address byte and a
subsequent 8-bit data byte. Software mode allows control of the output timing. The CLKE pin determines
when SDO is valid relative to SCLK and when receive data is valid relative to RCLK.
9.1 Interrupt Handling
In software mode, the DS2149 provides a latched interrupt output pin. When enabled, a change in any of
the status register bits generates an interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the INT output pin is driven low.
The INT output pin structure is an open-drain only. Each device that shares the INT line requires an
external pullup resistor. The interrupt is cleared when the interrupt condition no longer exists, and a 1 is
written to the appropriate bit in the interrupt mask register. Leaving a 1 in any of the bits in the interrupt
mask register masks that interrupt. Clearing that bit re-enables the interrupt.
Table 9-A. CLKE Pin Selection
CLKE PIN OUTPUT OUTPUT UPDATED ON
RPOS
LOW
HIGH
RNEG
RDATA
SDO Rising SCLK
RPOS
RNEG
RDATA
SDO Falling SCLK
Falling RCLK
Rising RCLK
17 of 32
Page 18

Figure 9-1. Serial Data Port Operation for Read Access
C
C
C
Read Access CLKE = 0
SCLK
SDI
SDO
Read Access CLKE = 1
SCLK
SDI
SDO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5
1
(lsb) (msb)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 0 B
1
(lsb) (msb)
B
0
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D0 D7
(lsb) (msb)
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6
D0
(lsb)
DS2149
D7
(msb)
Figure 9-2. Serial Data Port Operation for Write Access
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16SCLK
S
SDI
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 0 B
0
(lsb)
WRITE ACCESS ENABLED
SDO
(msb)
18 of 32
DO D6
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D7
(lsb) (msb)
Page 19

DS2149
Table 9-B. Control and Operation Mode Selection
MODE1 MODE0 HARDWARE SOFTWARE NRZ BIPOLAR AMI B8ZS
Low Low On Off Off On Off Off No
Low High On Off Off On Off Off Yes
Low Open On Off On Off On Off No
High Low Off On X X X X No
High High Off On X X X X Yes
High Open Off On X X X X No
Open Low On Off On Off Off On No
Open High On Off On Off Off On Yes
Open Open On Off On Off Off On No
OUTPUTS
DISABLED
10. DIAGNOSTIC MODE OPERATION
The DS2149 offers several diagnostic modes as listed in Table 10-A. Various diagnostic modes are only
available in software mode. In hardware mode, the diagnostic modes are selected by a combination of pin
settings. In software mode, the diagnostic modes are selected by setting appropriate bits in the diagnostic
control register.
Table 10-A. Diagnostic Modes
DIAGNOSTIC MODE
Local Loopback (LLB) Yes Yes No
Analog Loopback (ALB) Yes Yes No
Remote Loopback (RLB) Yes Yes No
In-Band Network Loopback (NLB) Yes Yes Yes
Dual Loopback (DLOOP) Yes Yes No
Internal Data Pattern Generation and Detection
Transmit AIS (TAIS) Yes Yes No
Quasirandom Signal Source (QRSS) Yes Yes Yes
In-Band Loop-Up/Down Code Generator No Yes No
Error Insertion and Detection
Bipolar Violation Insertion (INSBPV) Yes Yes No
Logic Error Insertion (INSLER) Yes Yes No
Bipolar Violation Detection (BPV) Yes Yes No
Logic Error Detection, QRSS (QPD) Yes Yes No
Alarm Condition Monitoring
Receive Carrier Loss (RCL) Monitoring Yes Yes Yes
Receive Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) Monitoring No Yes Yes
Transmit Driver Failure Monitoring (DFMO) No Yes Yes
Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip (JALT) No Yes Yes
Other Diagnostic Reports
Receive Line Attenuation Indicator (LATN) No Yes No
HARDWARE SOFTWARE MASKABLE
AVAILABILITY SOFTWARE MODE
19 of 32
Page 20

DS2149
10.1 Loopback Modes
10.1.1 Local Loopback (LLB)
When local loopback is enabled (set LLB in CR2, or pull the LLB pin high), inbound data at the receiver
inputs are ignored. TCLK and TPOS/TNEG pass through the jitter attenuator if enabled and are output at
RCLK and RPOS/RNEG. The transmit path is unaffected by LLB, and will continue to transmit data
normally (or AIS if TAIS is enabled).
10.1.2 Analog Loopback (ALB)
When analog loopback (ALB) is enabled (set ALB in CR2, or float the LLB pin), the receiver input pins
are disconnected from the clock and data recovery circuit and replaced by TTIP and TRING. This tests
the entire device including the jitter attenuator, transmitter, and receiver circuits.
10.1.3 Remote Loopback (RLB)
When remote loopback (RLB) is enabled (set RLB in CR2, or pull RLB pin high), inbound data at the
receiver inputs is looped back to the transmitter path. Data passes through the jitter attenuator if enabled.
The B8ZS encoder and decoder are not included in the loopback path. The receive path continues to
operate normally.
10.1.4 Network Loopback
When ENLOOP is enabled (set ENLOOP in CR2, or float the ENLOOP pin), the in-band loop code
detector is enabled. The receiver detects the in-band loop code patterns (00001 = loop up and
001 = loop down) present in the inbound data. The detectors detect both framed and unframed loop codes.
When the loop-up pattern is detected and present for 5 seconds, the device invokes remote loopback.
ENLOOP is dropped when:
1) The in-band loop-down pattern is present for 5 seconds.
2) RLB is activated.
3) ALB is activated.
10.1.5 Dual Loopback
Dual loopback is the simultaneous enabling of RLB and LLB. If the jitter attenuator is enabled and, when
both loopback paths are enabled, the jitter attenuator is placed in the local loopback path.
20 of 32
Page 21

DS2149
r
r
Figure 10-1. Loopbacks in the DS2149 Block Diagram
VCO/PLL
MCLK
NLOOP
RCL/QPD
RRING
RTIP
Filter
Recovery
Peak Detect
Clock / Data
RCL Detector
In-Band Loop
B8ZS Decoder
AIS Detector
Code Detector
QRSS Detector
RCLK
RPOS
RNEG
TRING
TTIP
Local Loopback
CSU Filters
Line Drivers
Wave Shaping
Transmit AIS
Remote Loopback
Jitter Attenuato
LOTC mux
TCLK
QRSS
B8ZS Encode
Logic Error Insert
In-Band Loop Gen.
TPOS
TNEG
10.2 Internal Pattern Generation and Detection
10.2.1 Transmit Alarm-Indication Signal (TAIS)
When TAIS is enabled (set TAIS in CR2, or pulling the TAIS pin high), the transmitter inputs
TPOS/TNEG and TDATA are ignored and the devices transmits unframed all ones at the transmitter
outputs at the TCLK frequency. If TCLK is not present, then the device uses MCLK to transmit. Both
TAIS and LLB can be enabled at the same time. The transmitter input data is looped back to the receiver
outputs through the jitter attenuator if enabled and the unframed all ones pattern is transmitted at TTIP
and TRING.
10.2.2 Quasirandom Signal Source (QRSS)
The QRSS data pattern is described in AT&T 62411. The pattern is represented by the polynomial 2
with the additional requirement that no more than 14 consecutive 0s be present in the pattern. When
QRSS is enabled (PAT0 = 0 and PAT1 = 1 in CR2 or float the QRSS pin), the data at the transmitter
inputs TPOS/TNEG or TDATA is ignored and replaced by the output of the QRSS pattern generator. In
addition, logic errors can be inserted into the data pattern with a rising edge on the INSLER input pin. If
no logic errors are to be inserted, then the INSLER pin must remain low. If the logic error occurs on the
same clock cycle as a 1 that has been inserted to suppress 15 0s, then the logic error is delayed until the
next clock cycle. The logic error insertion is available in both NRZ and bipolar data modes. Enabling the
QRSS pattern also enables the QRSS detector in the receiver. Pattern synchronization occurs when there
are no errors in 64 bits. When synchronized, the QPD output pin goes low. Once synchronized, an error
in the pattern causes the QPD output to go high for one-half RCLK cycle. In software mode, the level on
the CLKE pin determines the relationship between QPD and RCLK. When CLKE is low, QPD is high
when RCLK is high. When CLKE is high, QPD is high when RCLK is low. The QPD output can be used
to trigger an external bit error counter. When RCL is active or the receiver is not synchronized to the
QRSS pattern, then QPD maintains an output high.
20
- 1
21 of 32
Page 22

DS2149
In software mode, the device can generate an interrupt to indicate that the QRSS pattern synchronization
has been declared or lost. Clearing the QRSS bit in the interrupt mask register enables the interrupt. Use
the QPD output to increment an external bit error counter and use the interrupt to reset the counter. The
QRSS bit in the status register is set when the QRSS pattern is detected and cleared when pattern is lost
(more than 6 bit errors in a window of 64 bits). The QRSS bit in the transition status register indicates
that the QRSS status has changed since the last QRSS interrupt clear command.
10.2.3 In-Band Network Loop-Up or Loop-Down Code Generator
In-band network loop-up or loop-down transmission is available in software mode only. The loop-up
code is transmitted when PAT0 = 1 and PAT1 = 0 in CR2. Logic errors and bipolar violations can still be
inserted when loop codes are being transmitted.
10.3 Error Insertion and Detection
10.3.1 Bipolar Violation Insertion (INSBPV)
INSBPV is available in NRZ mode. Sampling occurs on the falling edge of TCLK. A rising edge on the
NSBPV pin inserts a BPV on the next available mark, except in the following conditions:
1) If the BPV would violate a B8ZS codeword.
2) When LLB and TAIS are both active. In this case, the BPV is looped back to the BPV pin and the line
driver transmits all ones with no violation.
3) When RLB is active.
4) When NLOOP is active.
BPVs can be inserted in both NRZ and bipolar data modes when the DS2149 is configured to transmit
internally generated data patterns (QRSS or in-band loop codes).
10.3.2 Logic Error Insertion (INSLE)
When transmitting QRSS or in-band loop codes, a logic error is inserted into the outbound data pattern on
a rising edge of the INSLER pin. Remember, when transmitting the QRSS pattern, logic error insertion is
inhibited if the error would replace a 1 with a 0 and result in a string of 15 or more consecutive 0s.
10.3.3 Logic Error Detection (QPD)
After QRSS pattern synchronization, logic errors are reported at the QPD output pin. If a logic error
occurs, the QPD pin goes high for one-half RCLK cycle. In software mode, the CLKE pin determines the
phase relationship between QPD and RCLK. When CLKE is low, QPD is high when RCLK is high.
When CLKE is high, QPD is high when RCLK is low. To count logic errors, use the QPD output to
increment an external error counter. A continuous output high indicates loss of synchronization to the
QRSS pattern or receive-carrier loss.
10.3.4 Bipolar Violation Detection (BPV)
When the B8ZS encoders and decoders are disabled or when configured for NRZ mode, bipolar
violations are reported at the BPV output pin. BPV goes high for a full clock cycle to indicate a bipolar
violation. When the B8ZS encoders and decoders are enabled, BPVs that are not part of codewords are
not reported.
22 of 32
Page 23

DS2149
10.4 Alarm Monitoring
10.4.1 Receive-Carrier Loss (RCL)
The receiver counts inbound 0s and declares RCL when the counter reaches 192. This applies to hardware
mode and software mode if the RCL2048 bit is cleared in CR4. In software mode, setting the RCL2048
bit changes the RCL counter to declare receive-carrier loss after 2048 consecutive 0s. Once set, the RCL
bit will remain set until the receiver detects a 12.5% density of 1s in a sliding window of 112 bits,
provided that there are no more than 98 consecutive 0s in that 112-bit window. When RCL is active,
RCLK is replaced by MCLK. RCL is indicated by an output high on the RCL pin and with a 1 in SR.0.
10.4.2 Alarm-Indication-Signal Detection (AIS)
AIS detection is only available in software mode. The receiver declares receipt of AIS when fewer than
six 0s are detected in 4632 bits (3ms). AIS is cleared when three or more 0s are received in 4632 bits. The
AIS bit in the status register (SR.2) indicates the presence of AIS. When the AIS status bit changes, the
AIS bit in the transition status register (TSR.2) is set. A change in the AIS status will generate an
interrupt if the AIS interrupt mask bit (IMR.2) bit is cleared.
10.4.3 Driver-Fail Monitor-Open (DFMO)
The DFMO bit is set in the status register when the transmitter outputs detect an open circuit. DFMO can
generate an interrupt if the DFMO interrupt mask bit (IMR.5) is cleared. This is not supported in
hardware mode.
10.4.4 Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip (JALT)
If the incoming jitter exceeds either 120 UIp-p (buffer depth is 128 bits) or 28 UIp-p (buffer depth is 32
bits), then the DS2149 will divide the internal nominal 24.704MHz (T1) clock by either 15 or 17 instead
of the normal 16 to keep the buffer from overflowing. When the device divides by either 15 or 17, it also
sets the jitter attenuator limit trip (JALT) bit in information register 1 (IR1).
10.5 Other Diagnostic Reports
10.5.1 Receive Line-Attenuation Indication
The device reports the approximate inbound signal strength in the status register (IR). The four most
significant bits indicate the signal strength in approximately 2.5dB increments.
23 of 32
Page 24

DS2149
11. NETWORK INTERFACE
Transformer specifications are listed in Table 11-A and Table 11-B. Table 11-C illustrates the series
resistance necessary for the basic interface and is associated with different transformer turns ratios.
Smaller turns ratios result in lower power-supply requirements. However, series resistance provides
added protection from potentially damaging voltages that can occur during lightning strikes. A basic
network interface is illustrated in Figure 11-1
. For a complete discussion of network interface design,
refer to Application Note 324: T1/E1 Network Interface Design.
Table 11-A. Specifications for Receive Transformer
SPECIFICATION RECOMMENDED VALUE
Turns Ratio (all applications) 1:1 ±2%
Primary Inductance
Leakage Inductance
Interwinding Capacitance 40pF maximum
Receive Transformer DC Resistance
Primary (Device Side)
Secondary
600mH minimum
1.0mH maximum
1.2Ω maximum
1.2Ω maximum
Table 11-B. Specifications for Transmit Transformer
SPECIFICATION RECOMMENDED VALUE
Turns Ratio, 5V 1:2 ±2%
Primary Inductance
Leakage Inductance
Interwinding Capacitance 40pF maximum
Transmit Transformer DC Resistance
Primary (Device Side)
Secondary
600mH minimum
1.0mH maximum
1.0Ω maximum
2.0Ω maximum
Table 11-C. Transformer Turns Ratio vs. Series Resistance
XFMR2
(CR4.1)
0 0 5.0
0 1 5.0
1 0 5.0
1 1 5.0
XFMR1
(CR4.0)
OPERATING
VOLTAGE
(V)
APPLICATION N Rt (Ω)
Long/Short 1:2 0
D4 1:2 0
Long/Short
D4 1:2 0
Long/Short
D4
Long/Short
D4 1:2 0
1:1.15 0
1:2 9.1
1:2 4:3
1:1.6 0
1:2 4.3
1:1.6 0
1:1.15 0
1:2 9.1
24 of 32
Page 25

Figure 11-1. Basic Network Interface
TRANSMIT
LINE
N:1
(larger winding
toward the network)
RECEIVE
LINE
1:1
R
R
r
0.1µF
Note 1: All resistor values are ±1%.
Note 2: The Rr resistors should be 50Ω each for T1 lines.
Note 3: C = 1mF if using a 1:2 transformer; C = 2mF if using a 1:3 transformer.
C
R
t
R
t
r
TTIP
TRING
DS2149
RTIP
RRING
(21)
V
DD
VSS (22)
VDD (15)
V
(14)
SS
MCLK
0.1µF
0.01µF
0.1µF
1.544MHz
+V
10µF
10µF
DS2149
DD
25 of 32
Page 26

Figure 11-2. T1 Transmit Pulse Template
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
NORMALIZED AMPLITUDE
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
0
T1.102/87, T1.403,
CB 119 (Oct. 79), &
I.431 Template
MAXIMUM CURVE
UI Time Amp.
0.05
-500
-0.77
-0.39
-0.27
-0.27
-0.12
0.00
0.27
0.35
0.93
1.16
-255
-175
-175
-75
0
175
225
600
750
0.05
0.80
1.15
1.15
1.05
1.05
-0.07
0.05
0.05
MINIMUM CURVE
UI Time Amp.
-0.05
-500
-0.77
-0.23
-0.23
-0.15
0.00
0.15
0.23
0.23
0.46
0.66
0.93
1.16
-150
-150
-100
0
100
150
150
300
430
600
750
-0.05
0.50
0.95
0.95
0.90
0.50
-0.45
-0.45
-0.20
-0.05
-0.05
DS2149
-0.4
-0.5
-400 -200 200 400 600100
-500 -300 -100 0 300 500 700
TIME (ns)
26 of 32
Page 27

Figure 11-3. Jitter Tolerance
UNIT INTERVALS (UIp-p)
1k
100
10
1
0.1
TR 62411 (DEC. 90)
1
10 100 1k 10k 100k
DS2149
DS2149
TOLERANCE
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 11-4. Jitter Attenuation
-20dB
-40dB
JITTER ATTENUATION (dB)
-60dB
0dB
C
u
r
v
e
1 10 100 1K 10K
Curve A
T1
B
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TR 62411 (Dec. 90)
Prohibited Area
100K
27 of 32
Page 28

DS2149
12. DC CHARACTERISTICS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Voltage Range on Any Pin Relative to Ground -1.0V to +6.0V
Operating Temperature Range for DS2149QN -40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range -55°C to +125°C
Soldering Temperature See IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020 Specification
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only,
and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is
not implied. Exposure to the absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
RECOMMENDED DC OPERATING CONDITIONS
(TA = -40°C to +85°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Logic 1 VIH 2.0 5.5 V
Logic 0 VIL -0.3 +0.8 V
Supply for 5V Operation (Note 1) VDD 4.75 5 5.25 V
CAPACITANCE
(TA = +25°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Input Capacitance CIN 5 pF
Output Capacitance C
7 pF
OUT
DC CHARACTERISTICS
(V
= 5V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.)
DD
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Input Leakage (Note 2) IIL -1.0 +1.0
Output Leakage (Note 3) ILO 1.0
Output Current (2.4V) IOH -1.0 mA
Output Current (0.4V) IOL +4.0 mA
Power Dissipation at 5V (Notes 4, 5) PDD 500 mW
Note 1: Applies to VDD.
Note 2: 0V < V
Note 3: Applied to INT when tri-stated
Note 4: TCLK = MCLK = 1.544MHz.
Note 5: Power dissipation for an all-ones data density.
IN
< V
DD.
mA
mA
28 of 32
Page 29

AC CHARACTERISTICS: SERIAL PORT (MODE1 = 1)
C
C
C
(VDD = 5.0V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 12-1 and Figure 12-2)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS
t
Setup Time CS to SCLK
Setup Time SDI to SCLK t
Hold Time SCLK to SDI t
SCLK High/Low Time t
SCLK Rise/Fall Time t
SCLK to CS Inactive
CS Inactive Time
SCLK to SDO Valid t
SCLK to SDO Tri-State t
CS Inactive or SCLK to SDO Tri-State
50 ns
CSS
50 ns
SSS
50 ns
SSH
200 ns
SLH
50 ns
SRF
t
50 ns
LSC
t
250 ns
CM
50 ns
SSV
100 ns
SSH
t
100 ns
CSH
Figure 12-1. Serial Bus Read Timing (MODE1 = 1)
CLKE = 0 CLKE = 1
S
SCLK
SDO
HIGH-Z
t
LSC
t
SSV
LSB MSB
S
SCLK
SDO
HIGH-Z
LSB
t
SSV
t
LSC
MSB
t
CSH
HIGH-Z
t
CSH
HIGH-Z
DS2149
Figure 12-2. Serial Bus Write Timing (MODE1 = 1)
t
CM
S
t
t
SRF
t
t
CSS
SSS
t
SSH
SCLK
SDI
SLH
MSB
29 of 32
LSBLSB
Data ByteControl Byte
t
LSC
MSB
Page 30

DS2149
AC CHARACTERISTICS: RECEIVE SIDE
(VDD = 5V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 12-3)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RCLK Period tCP 648 ns
t
RCLK Pulse Width (Note 6)
RCLK Pulse Width (Note 7)
CH
t
CL
t
CH
t
CL
200 ns
150 ns
Delay RCLK to RPOS, RNEG Valid tDD 50 ns
Note 6: Jitter attenuator enabled in the receive path.
Note 7: Jitter attenuator disabled or enabled in the transmit path.
Figure 12-3. AC Characteristics for Receive Side
RCLK
RPOS
RNEG
IN SOFTWARE MODE:
CLKE = 1
RPOS
RNEG
IN SOFTWARE AND
HARDWARE MODE:
=
t
DD
t
DD
t
CH
t
CP
t
CL
30 of 32
Page 31

DS2149
K
AC CHARACTERISTICS: TRANSMIT SIDE
(V
= 5V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 12-4)
DD
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS
TCLK Period tCP 648 ns
t
TCLK Pulse Width
CH
t
CL
75 ns
TPOS/TNEG Setup to TCLK Falling or Rising tSU 20 ns
TPOS/TNEG Hold from TCLK Falling or Rising tHD 20 ns
TCLK Rise and Fall Times tR, tF 25 ns
Figure 12-4. AC Characteristics for Transmit Side
TCL
TPOS
TNEG
t
CP
t
SU
t
CL
t
HD
t
R
t
CH
t
F
31 of 32
Page 32

DS2149
13. PACKAGE INFORMATION
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/DallasPackInfo
.)
32 of 32
 Loading...
Loading...