
查询DS21448供应商
www.maxim-ic.com
3.3V E1/T1/J1 Quad Line Interface
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DS21448 is a quad-port E1 or T1 line interface
unit (LIU) for short-haul and long-haul applications. It
incorporates four independent transmitters and four
independent receivers in a single 144-pin PBGA or
128-pin LQFP package.
The transmit drivers generate the necessary G.703
E1 waveshapes in 75W or 120W applications and the
DSX-1 or CSU line build-outs of 0dB, -7.5dB, -15dB,
and -22.5dB for T1 applications.
The DS21448 has a usable receiver sensitivity of
0 to -43dB for E1 applications and 0 to -36dB for T1
that allows it to operate on 0.63mm (22AWG) cables
up to 2.5km (E1) and 6000ft (T1) in length. The user
has the option to use internal receive termination,
software selectable for 75W, 100W, and 120W
applications, or external termination.
The on-board crystal-less jitter attenuator can be
placed in either the transmit or the receive data path,
and requires only a 2.048MHz MCLK for both E1 and
T1 applications (with the option of using a 1.544MHz
MCLK in T1 applications).
The DS21448 has diagnostic capabilities such as
loopbacks and PRBS pattern generation and
detection. 16-bit loop-up and loop-down codes can
be generated and detected. A single input pin can
power down all transmitters to allow the
implementation of hitless protection switching (HPS)
for 1+1 redundancy without the use of relays.
The device can be controlled through an 8-bit parallel
port (muxed or nonmuxed) or a serial port, and it can
be used in hardware mode. A standard boundary
scan interface supports board-level testing.
APPLICATIONS
Integrated Multiservice Access Platforms
T1/E1 Cross-Connects, Multiplexers, and Channel
Banks
Central-Office Switches and PBX Interfaces
T1/E1 LAN/WAN Routers
Wireless Base Stations
DS21448
FEATURES
§ Four Complete E1, T1, or J1 LIUs
§ Supports Long- and Short-Haul Trunks
§ Internal Software-Selectable Receive-Side
Termination for 75W/100W/120W
§ 3.3V Power Supply
§ 32-Bit or 128-Bit Crystal-Less Jitter Attenuator
Requires Only a 2.048MHz Master Clock for E1
and T1, with the Option to Use 1.544MHz for T1
§ Generates the Appropriate Line Build-Outs With
and Without Return Loss for E1, and DSX-1 and
CSU Line Build-Outs for T1
§ AMI, HDB3, and B8ZS Encoding/Decoding
§ 16.384MHz, 8.192MHz, 4.096MHz, or 2.048MHz
Clock Output Synthesized to Recovered Clock
§ Programmable Monitor Mode for Receiver
§ Loopbacks and PRBS Pattern Generation/
Detection with Output for Received Errors
§ Generates/Detects In-Band Loop Codes, 1 to 16
Bits, Including CSU Loop Codes
§ 8-Bit Parallel or Serial Interface with Optional
Hardware Mode
§ Muxed and Nonmuxed Parallel Bus Supports
Intel or Motorola
§ Detects/Generates Blue (AIS) Alarms
§ NRZ/Bipolar Interface for Tx/Rx Data I/O
§ Transmit Open-Circuit Detection
§ Receive Carrier Loss (RCL) Indication (G.775)
§ High-Z State for TTIP and TRING
§ 50mA
§ JTAG Boundary Scan Test Port per IEEE 1149.1
§ Meets Latest E1 and T1 Specifications Including
ANSI.403-1999, ANSI T1.408, AT&T TR 62411,
ITU G.703, G.704, G.706, G.736, G.775, G.823,
I.431, O.151, O.161, ETSI ETS 300 166,
JTG.703, JTI.431, TBR12, TBR13, and CTR4
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART TEMP RANGE
DS21448 0°C to +70°C 3.3 144 BGA
DS21448N -40°C to +85°C 3.3 144 BGA
DS21448L 0°C to +70°C 3.3 128 LQFP
DS21448LN -40°C to +85°C 3.3 128 LQFP
Pin Configurations appear in Section 11.
Transmit Current Limiter
RMS
VOLTAGE
(V)
PINPACKAGE
Note: Some revisions of this device may incorporate deviations from published specifications known as errata. Multiple revisions of any device
may be simultaneously available through various sales channels. For information about device errata, click here: www.maxim-ic.com/errata
1 of 60
REV: 012104
.

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. BLOCK DIAGRAMS...................................................................................................................... 5
2. PIN DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................................................... 7
3. DETAILED DESCRIPTION...........................................................................................................13
3.1 DS21448 AND DS21Q348 DIFFERENCES ....................................................................................13
4. PORT OPERATION......................................................................................................................13
4.1 HARDWARE MODE.......................................................................................................................13
4.2 SERIAL PORT OPERATION............................................................................................................15
4.3 PARALLEL PORT OPERATION .......................................................................................................17
4.3.1 Device Power-Up and Reset.................................................................................................................17
4.3.2 Register Map.........................................................................................................................................18
4.3.3 Control Registers ..................................................................................................................................19
5. STATUS REGISTERS..................................................................................................................23
6. DIAGNOSTICS ............................................................................................................................27
6.1 IN-BAND LOOP-CODE GENERATION AND DETECTION.....................................................................27
6.2 LOOPBACKS ................................................................................................................................31
6.2.1 Remote Loopback (RLB) ......................................................................................................................31
6.2.2 Local Loopback (LLB) ...........................................................................................................................31
6.2.3 Analog Loopback (LLB) ........................................................................................................................31
6.2.4 Dual Loopback (DLB)............................................................................................................................31
6.3 PRBS GENERATION AND DETECTION ...........................................................................................31
6.4 ERROR COUNTER........................................................................................................................31
6.5 ERROR COUNTER UPDATE...........................................................................................................32
6.6 ERROR INSERTION.......................................................................................................................32
7. ANALOG INTERFACE.................................................................................................................33
7.1 RECEIVER...................................................................................................................................33
7.2 TRANSMITTER .............................................................................................................................33
7.3 JITTER ATTENUATOR ...................................................................................................................34
7.4 G.703 SYNCHRONIZATION SIGNAL ...............................................................................................34
8. JTAG BOUNDARY SCAN ARCHITECTURE AND TEST ACCESS PORT..................................43
8.1 JTAG TAP CONTROLLER STATE MACHINE ...................................................................................43
8.2 INSTRUCTION REGISTER ..............................................................................................................45
8.3 TEST REGISTERS ........................................................................................................................46
9. OPERATING PARAMETERS.......................................................................................................48
10. AC TIMING PARAMETERS AND DIAGRAMS ............................................................................49
11. PIN CONFIGURATIONS ..............................................................................................................56
11.1 144-PIN BGA ..........................................................................................................................56
11.2 128-PIN LQFP.........................................................................................................................57
12. PACKAGE INFORMATION..........................................................................................................58
13. THERMAL INFORMATION ..........................................................................................................60
14. REVISION HISTORY....................................................................................................................60
2 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram....................................................................................................................... 5
Figure 1-2. Receive Logic Detail.............................................................................................................. 6
Figure 1-3. Transmit Logic Detail............................................................................................................. 6
Figure 4-1. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 1 ........................................................15
Figure 4-2. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 2 ........................................................16
Figure 4-3. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 3 ........................................................16
Figure 4-4. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 4 ........................................................16
Figure 4-5. Serial Port Operation for Write Access (R = 0) Modes 1 and 2 .............................................17
Figure 4-6. Serial Port Operation for Write Access (R = 0) Modes 3 and 4 .............................................17
Figure 7-1. Basic Interface......................................................................................................................36
Figure 7-2. Protected Interface Using Internal Receive Termination.......................................................37
Figure 7-3. Protected Interface Using External Receive Termination......................................................38
Figure 7-4. Dual Connector-Protected Interface Using Receive Termination ..........................................39
Figure 8-5. E1 Transmit Pulse Template ................................................................................................40
Figure 8-6. T1 Transmit Pulse Template.................................................................................................41
Figure 7-7. Jitter Tolerance.....................................................................................................................42
Figure 7-8. Jitter Attenuation ..................................................................................................................42
Figure 8-1. JTAG Block Diagram............................................................................................................43
Figure 8-2. TAP Controller State Diagram ..............................................................................................44
Figure 10-1. Intel Bus Read Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 0) ......................................................................49
Figure 10-2. Intel Bus Write Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 0) ......................................................................50
Figure 10-3. Motorola Bus Timing (PBTS = 1, BIS0 = 0) ........................................................................50
Figure 10-4. Intel Bus Read Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 1) ......................................................................51
Figure 10-5. Intel Bus Write Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 1) ......................................................................52
Figure 10-6. Motorola Bus Read Timing (PBTS = 1, BIS0 = 1)...............................................................52
Figure 10-7. Motorola Bus Write Timing (PBTS = 1, BIS0 = 1) ...............................................................52
Figure 10-8. Serial Bus Timing (BIS1 = 1, BIS0 = 0)...............................................................................53
Figure 10-9. Receive-Side Timing ..........................................................................................................54
Figure 10-10. Transmit-Side Timing .......................................................................................................55
3 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2-A. Bus Interface Selection .......................................................................................................... 7
Table 2-B. Pin Assignments .................................................................................................................... 7
Table 2-C. Parallel Interface Mode Pin Description ................................................................................. 9
Table 2-D. Serial Interface Mode Pin Description ...................................................................................10
Table 2-E. Hardware Interface Mode Pin Description.............................................................................11
Table 3-A. DS21448 vs. DS21Q348 Pin Differences ..............................................................................13
Table 4-A. Loopback Control in Hardware Mode ....................................................................................14
Table 4-B. Transmit Data Control in Hardware Mode .............................................................................14
Table 4-C. Receive Sensitivity Settings in Hardware Mode ....................................................................14
Table 4-D. Monitor Gain Settings in Hardware Mode..............................................................................14
Table 4-E. Internal Rx Termination Select in Hardware Mode ................................................................14
Table 4-F. MCLK Selection in Hardware Mode.......................................................................................14
Table 4-G. Parallel Port Mode Selection.................................................................................................18
Table 4-H. Register Map ........................................................................................................................18
Table 4-I. Receive Sensitivity Settings....................................................................................................22
Table 4-J. Backplane Clock Select .........................................................................................................22
Table 4-K. Monitor Gain Settings............................................................................................................22
Table 4-L. Internal Rx Termination Select...............................................................................................22
Table 5-A. Received Alarm Criteria ........................................................................................................25
Table 5-B. Receive Level Indication .......................................................................................................27
Table 6-A. Transmit Code Length...........................................................................................................29
Table 6-B. Receive Code Length............................................................................................................29
Table 6-C. Definition of Received Errors.................................................................................................32
Table 6-D. Function of ECRS Bits and RNEG Pin ..................................................................................32
Table 7-A. Line Build-Out Select for E1 in Register CCR4 (ETS = 0)......................................................34
Table 7-B. Line Build-Out Select for T1 in Register CCR4 (ETS = 1)......................................................34
Table 7-C. Line Build-Out Select for E1 in Register CCR4 (ETS = 0) Using Alternate Transformer
Configuration ...................................................................................................................................35
Table 7-D. Transformer Specifications (3.3V Operation) ........................................................................35
Table 8-A. Instruction Codes for IEEE 1149.1 Architecture.....................................................................45
Table 8-B. ID Code Structure .................................................................................................................46
Table 8-C. Device ID Codes...................................................................................................................46
Table 8-D. Boundary Scan Control Bits ..................................................................................................47
Table 10-A. AC Characteristics—Multiplexed Parallel Port (BIS0 = 0)....................................................49
Table 10-B. AC Characteristics—Nonmultiplexed Parallel Port (BIS0 = 1) .............................................51
Table 10-C. AC Characteristics—Serial Port (BIS1 = 1, BIS0 = 0)..........................................................53
Table 10-D. AC Characteristics—Receive Side......................................................................................54
Table 10-E. AC Characteristics—Transmit Side .....................................................................................55
Table 13-A. Thermal Characteristics—BGA ...........................................................................................60
Table 13-B. Theta-JA (qJA) vs. Airflow—BGA..........................................................................................60
Table 13-C. Thermal Characteristics—LQFP..........................................................................................60
Table 13-D. Theta-JA (qJA) vs. Airflow—LQFP........................................................................................60
4 of 60
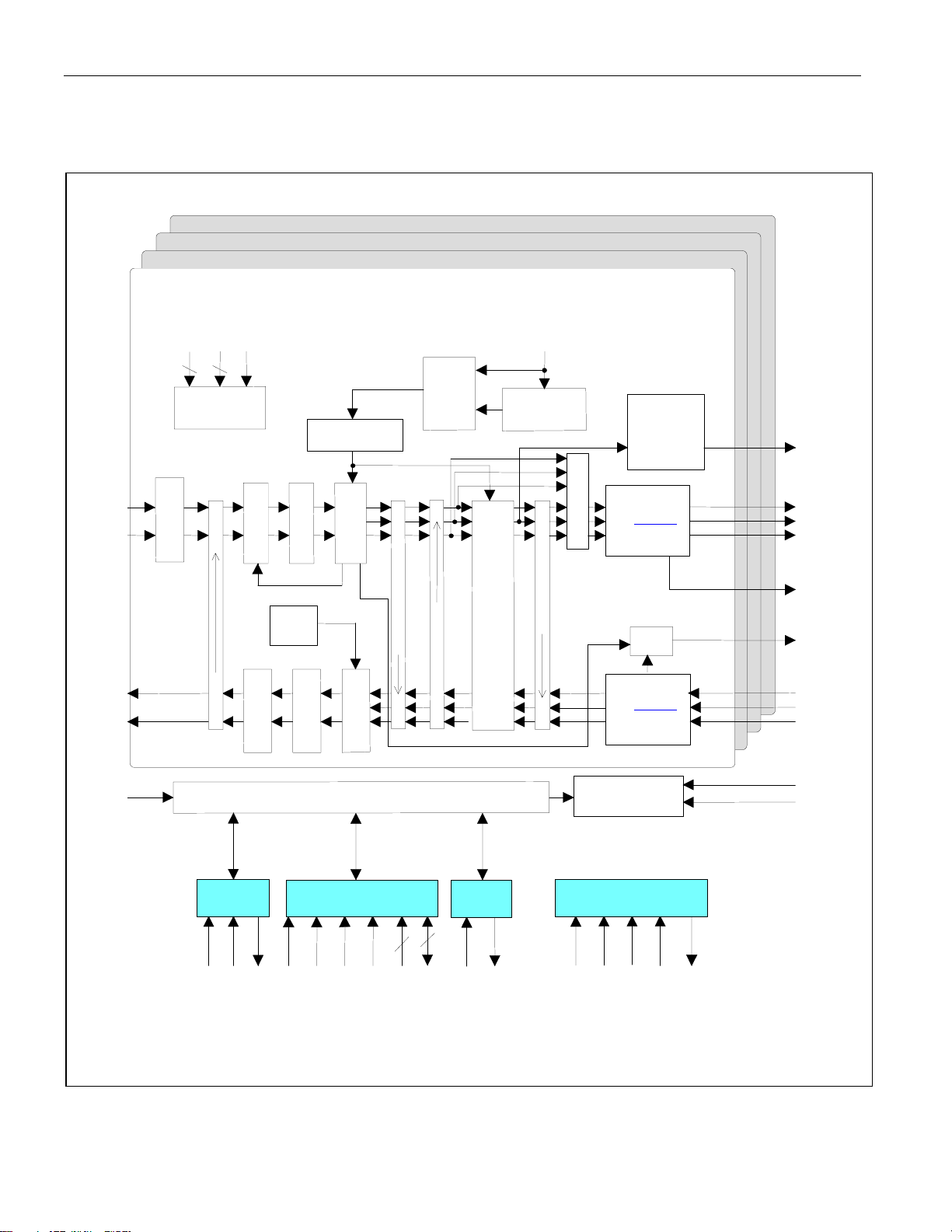
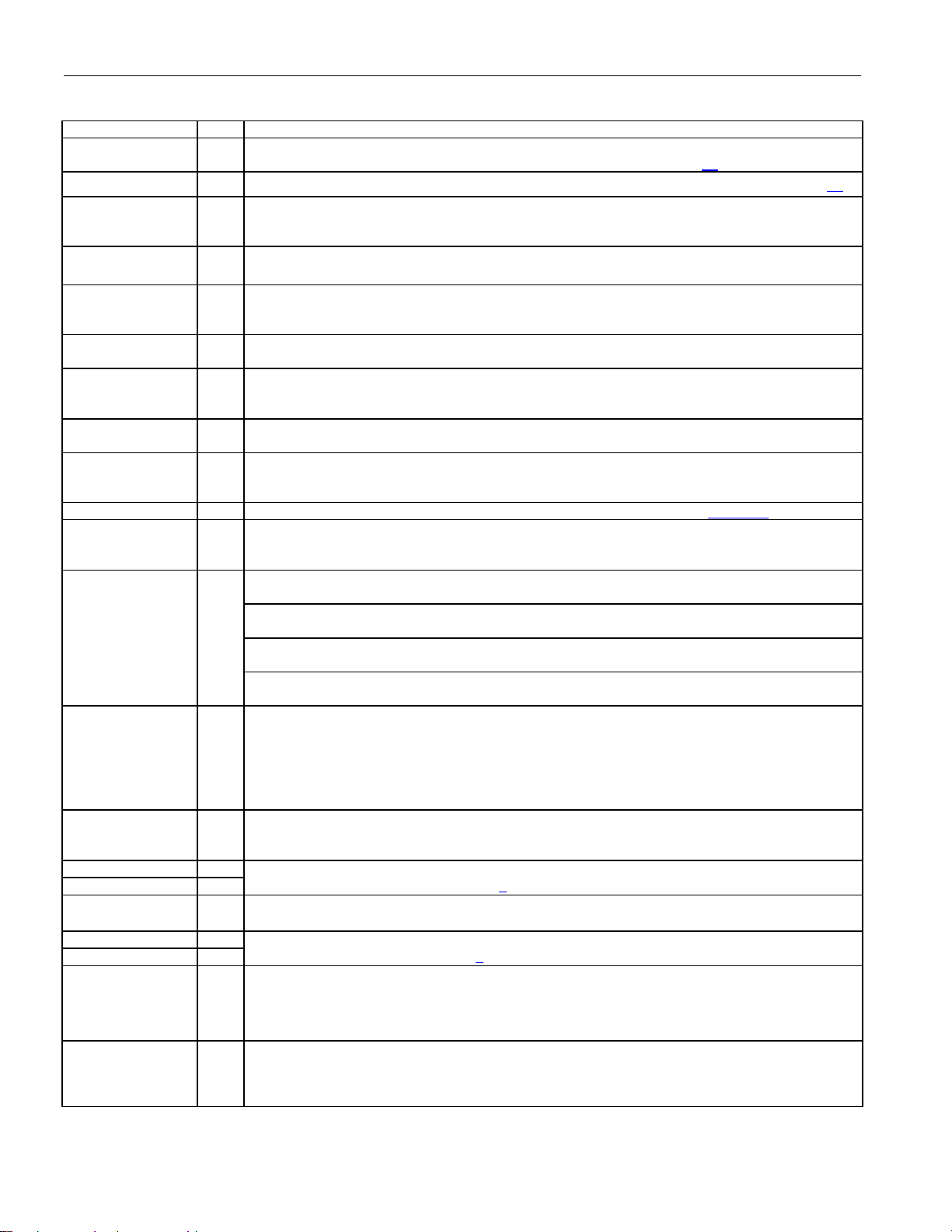
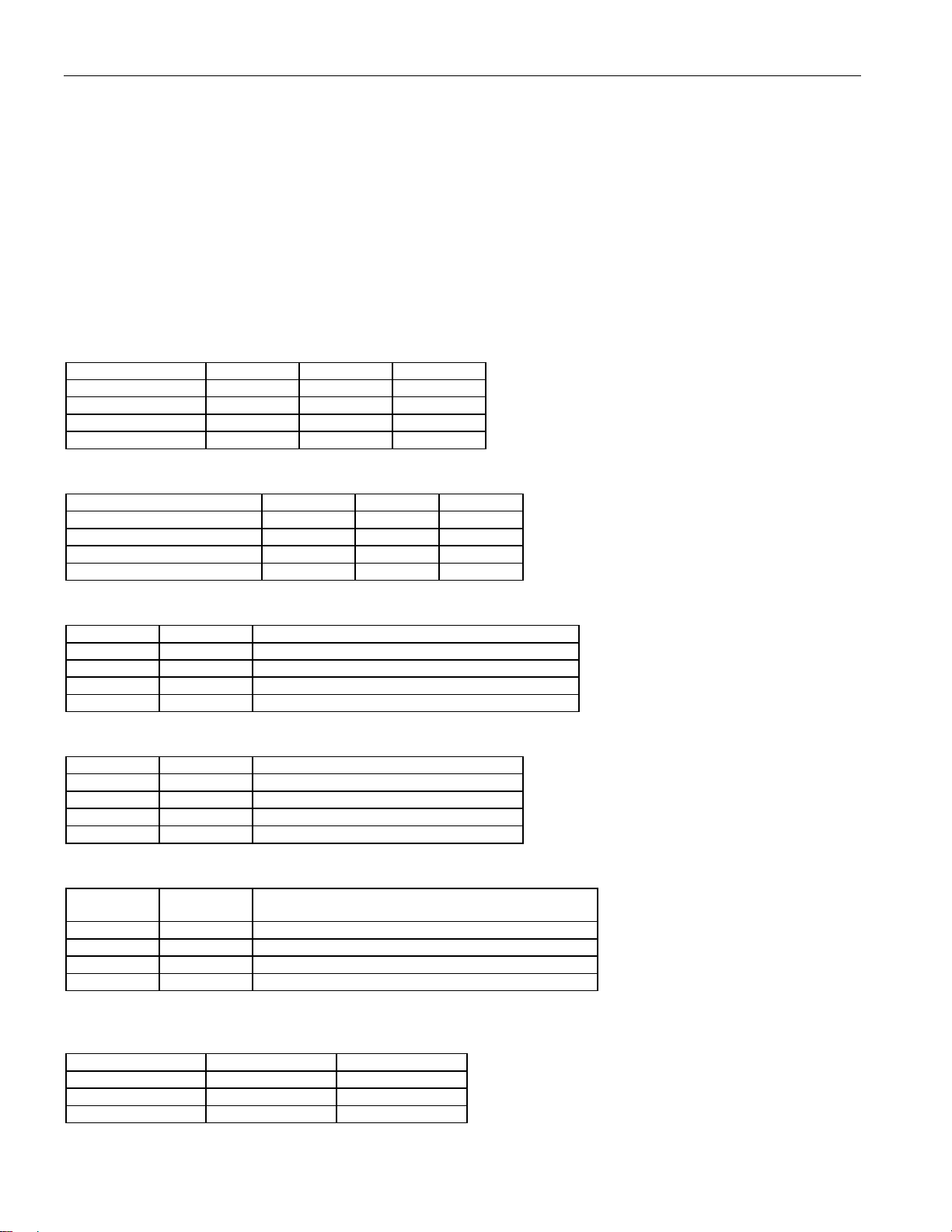
1. BLOCK DIAGRAMS
H
K
T
K
SDI
WR
(R/
W
)
RD(DS
)
(
S)
A0 TO A4
(
)
K
RECEIVE PATH)
K
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
RRING
RTIP
TRING
TTIP
CHANNEL 4
CHANNEL 3
CHANNEL 2
CHANNEL 1
2
OPTIONAL
TERMINANATION
DD
SS
V
V
2
POWER
CONNECTIONS
ANALOG LOOPBACK
VSM
FILTER
UNFRAMED
ALL-ONES
INSERTION
LINE DRIVERS
PEAK DETECT
CSU FILERS
VCO/PLL
RECOVERY
CLOCK/DATA
WAVESHAPING
JACLK
TYPICAL OF ALL FOUR CHANNELS
MCLK
MUX
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
DUAL MODE
n
2.048MHz TO
1.544MHz PLL
16.384MHz OR
8.192MHz OR
4.096MHz OR
2.048MHz
SYNTHESIZER
MUX
See Figure 1-2
REMOTE LOOPBAC
BPCLK
RPOS
RCLK
RNEG
PBEO
REMOTE LOOPBACK
JITTER ATTENUATION
LOCAL LOOPBAC
(CAN BE PLACED IN EITHER TRANSM IT OR
MUX
See Figure 1-3
RCL/LOTC
TPOS
TCLK
TNEG
Dallas
RST
TXDIS/TEST
BIS0
MUX (THE SERIAL, PARALLEL, AND HARDWARE INTERFACES
SERIAL
INTERFACE
SHARE DEVICE PINS)
PARALLEL INTERFACE
8
5
SCL
SDO
PBTS
A
ALE
CONTROL AND
(ROUTED TO
ALL BLOCKS)
CS
IN
CONTROL AND TEST
PORT (ROUTED TO
ALL BLOCKS)
JTAG PORT
JTMS
JRST
JTDI
JTCL
JTDO
Semiconductor
DS21448
D0 TO D7/AD0
TO AD7
5 of 60
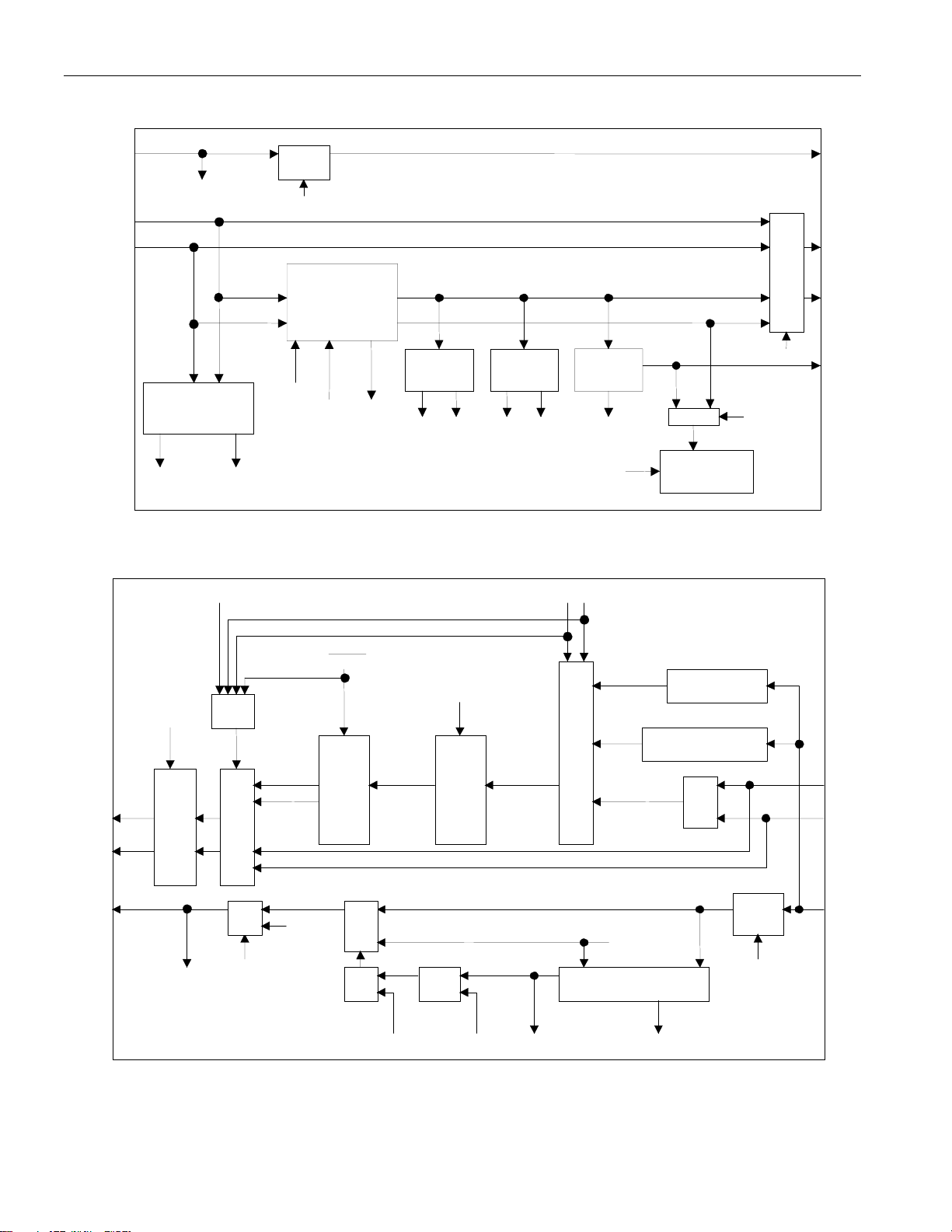
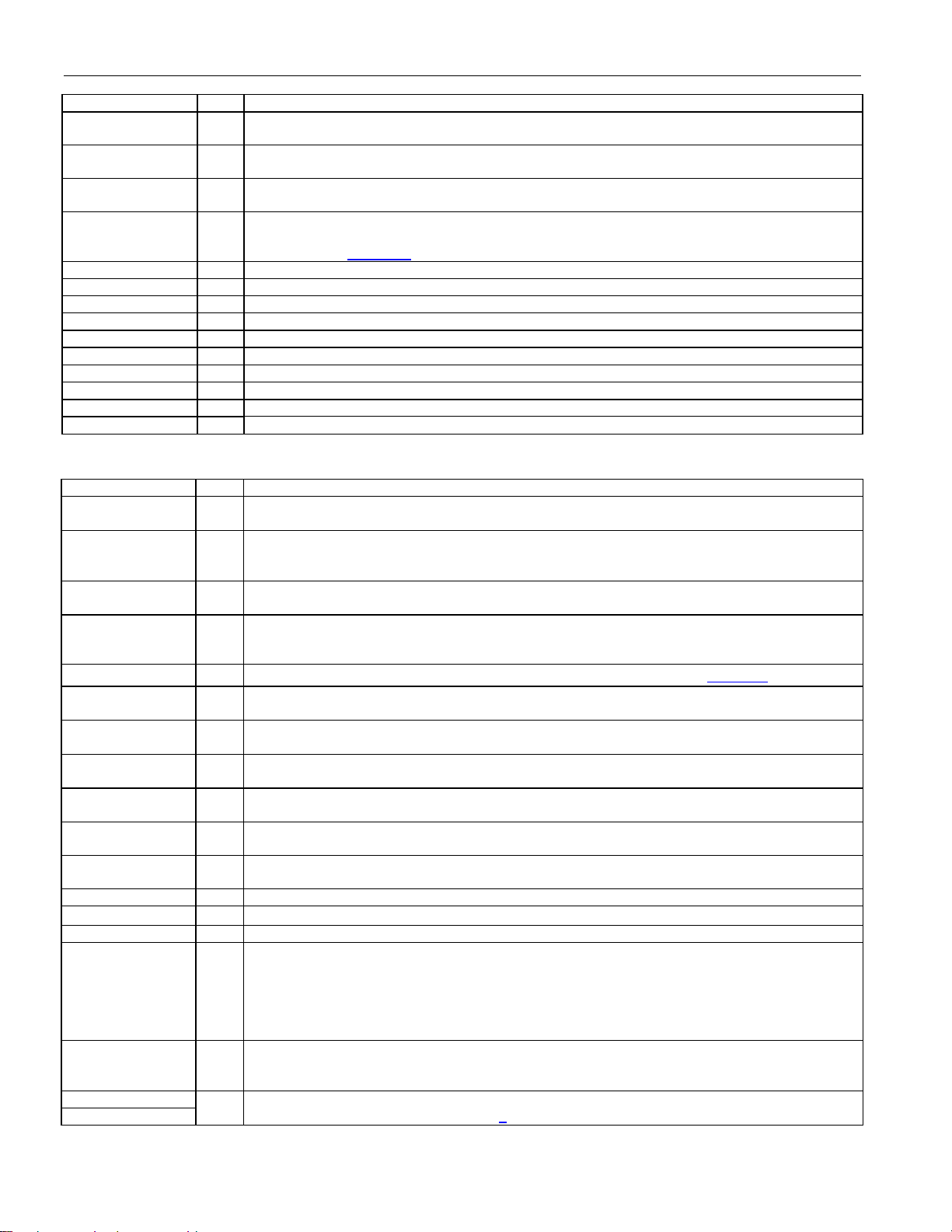
Figure 1-2. Receive Logic Detail
A
K
A
A
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
CLOCK
INVERT
FROM
REMOTE
LOOPBACK
ROUTED TO
LL BLOCKS
4 OR 8 ZERO DETECT
16 ZERO DETECT
RIR1.7 RIR1.6
CCR2.0
B8ZS/HDB3
DECODER
CCR2.3
CCR6.2/
CCR6.0/
CCR6.1
Figure 1-3. Transmit Logic Detail
CCR1.6
RIR1.5
ALL-ONES
DETECTOR
NRZ DATA
BPV/CV/EXZ
LOOP CODE
DETECTOR
SR.6 SR.7SR.4 RIR1.3
CCR3.3
PRBS
DETECTOR
SR.0
CCR1.4
CCR3.4
MUX
16-BIT ERROR
COUNTER (ECR)
MUX
CCR1.6
CCR6.0
RCLK
RPOS
RNEG
PBEO
TO REMOTE
LOOPBAC
CCR3.1
BPV
INSERT
ROUTED TO
LL BLOCKS
OR
GA TE
MUX
MUX
CCR1.1
CCR2.2
CCR3.0
PRBS
GENERATOR
MUX
1
B8ZS/
HDB3
CODER
LOGIC
ERROR
INSERT
0
0
1
RCLK
MUX
OR
GA TE
CCR1.2
0
1
ND
GATE
CCR1.0
TO LOTC OUTPUT PIN
JACLK
(FROM MCLK)
LOSS-OF-TRANSMIT
CLOCK DETECT
LOOP CODE
GENERATOR
SR.5
OR
GATE
CLOCK
INVERT
CCR2.1
TPOS
TNEG
TCLK
6 of 60
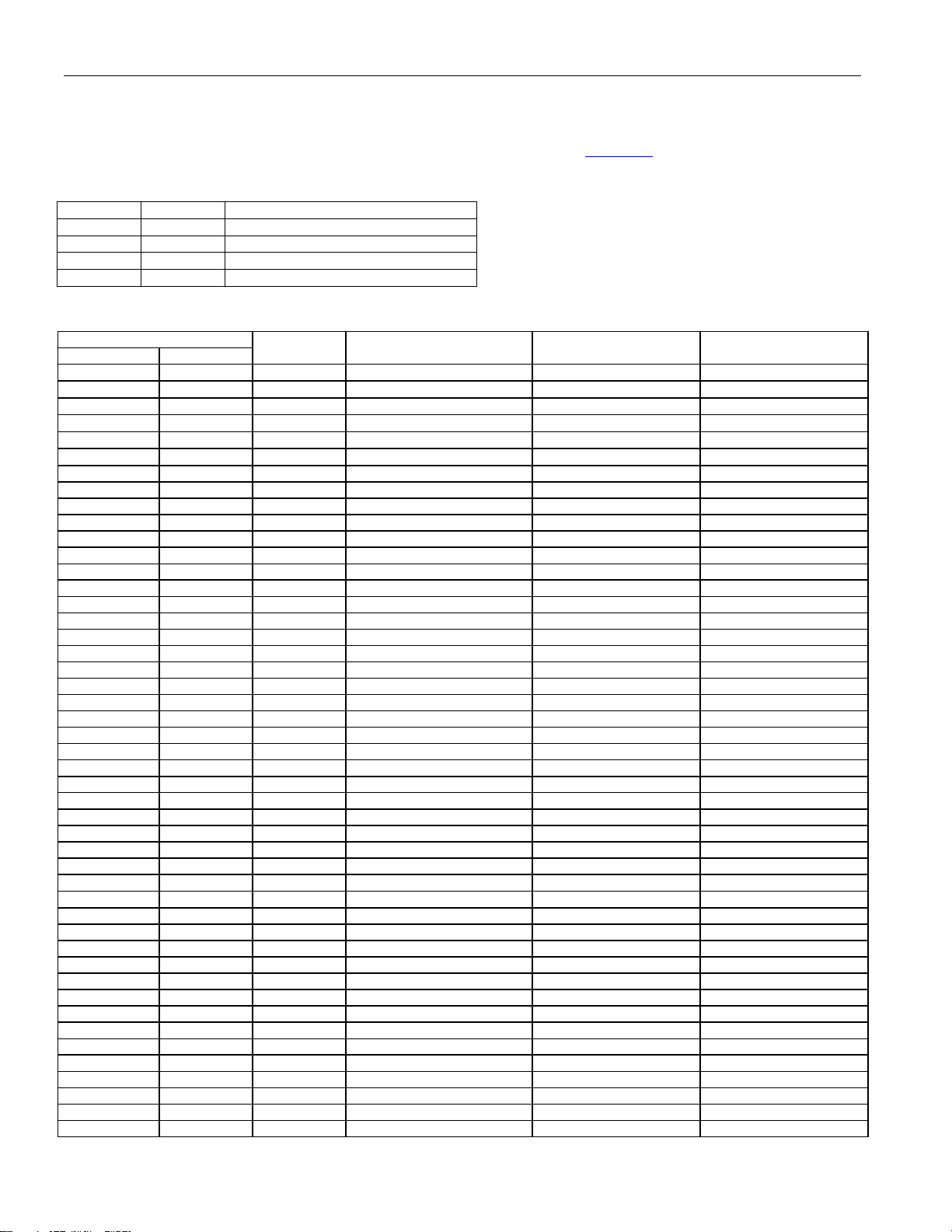
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
2. PIN DESCRIPTION
The DS21448 can be controlled in parallel port mode, serial port mode, or hardware mode. The bus interface select
bits 0 and 1 (BIS0, BIS1) determine the device mode and pin assignments (Table 2-A
Table 2-A. Bus Interface Selection
BIS1 BIS0 BUS INTERFACE TYPE
0 0 Parallel Port Mode (multiplexed)
0 1 Parallel Port Mode (nonmultiplexed)
1 0 Serial Port Mode
1 1 Hardware Mode
Table 2-B. Pin Assignments
PIN
BGA LQFP
J3 18 I
D3 57 I
D10 84 I
K10 114 I
J2 91 I
H1 92 I
K2 95 I ALE (AS) N/A SCLKE
J1 35 I N/A SCLK L2
K3 36 I N/A SDI L1
K1 62 I/O A4 SDO L0
L1 63 I A3 ICES DJA
H11 64 I A2 OCES JAMUX
H12 65 I A1 N/A JAS
G12 66 I A0 N/A HBE
J10 75 I/O D7/AD7 N/A CES
H10 76 I/O D6/AD6 N/A TPD
G11 77 I/O D5/AD5 N/A TX0
J9 78 I/O D4/AD4 N/A TX1
E3 79 I/O D3/AD3 N/A LOOP0
D4 80 I/O D2/AD2 N/A LOOP1
F3 81 I/O D1/AD1 N/A MM0
D5 82 I/O D0/AD0 N/A MM1
— 3 I VSM VSM VSM
L5 115–117 — VDD1 VDD1 VDD1
E4 19–21 — VDD2 VDD2 VDD2
D8 49–51 — VDD3 VDD3 VDD3
J8 85–87 — VDD4 VDD4 VDD4
M4 118–120 — VSS1 VSS1 VSS1
F4 22–24 — VSS2 VSS2 VSS2
D9 52–54 — VSS3 VSS3 VSS3
H9 88–90 — VSS4 VSS4 VSS4
K9 97 I/O
K5 110 O PBEO1 PBEO1 PBEO1
G3 111 O PBEO2 PBEO2 PBEO2
E10 121 O PBEO3 PBEO3 PBEO3
K8 123 O PBEO4 PBEO4 PBEO4
L6 126 O RCL1/LOTC1 RCL1/LOTC1 RCL1
D7 128 O RCL2/LOTC2 RCL2/LOTC2 RCL2
F9 1 O RCL3/LOTC3 RCL3/LOTC3 RCL3
J7 2 O RCL4/LOTC4 RCL4/LOTC4 RCL4
K7 98 I TXDIS/TEST TXDIS/TEST TXDIS/TEST
A1 124 I RTIP1 RTIP1 RTIP1
A4 28 I RTIP2 RTIP2 RTIP2
A7 60 I RTIP3 RTIP3 RTIP3
A10 93 I RTIP4 RTIP4 RTIP4
B2 125 I RRING1 RRING1 RRING1
B5 29 I RRING2 RRING2 RRING2
I/O PARALLEL PORT MODE SERIAL PORT MODE HARDWARE MODE
CS1 CS1
CS2 CS2
CS3 CS3
CS4 CS4
RD (DS)
WR (R/W)
INT INT
N/A ETS
N/A NRZE
7 of 60
).
EGL1
EGL2
EGL3
EGL4
RT1
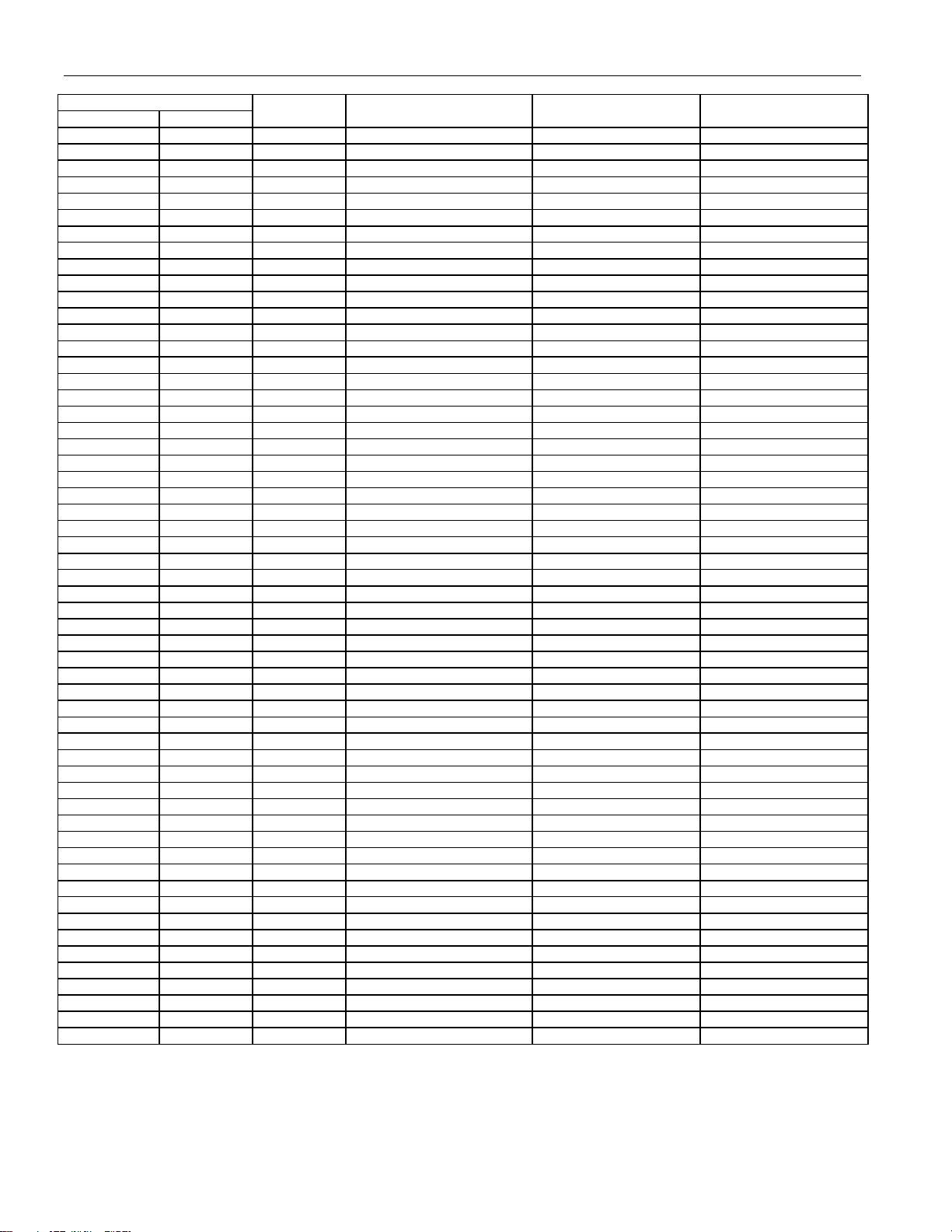
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
PIN
BGA LQFP
B8 61 I RRING3 RRING3 RRING3
B11 94 I RRING4 RRING4 RRING4
L9 106 I
J6 109 I MCLK MCLK MCLK
H4 122 O BPCLK1 BPCLK1 BPCLK1
D6 47 O BPCLK2 BPCLK2 BPCLK2
F10 56 O BPCLK3 BPCLK3 BPCLK3
L8 112 O BPCLK4 BPCLK4 BPCLK4
L7 107 I BIS0 BIS0 BIS0
M8 68 I BIS1 BIS1 BIS1
A2 6 O TTIP1 TTIP1 TTIP1
A5 38 O TTIP2 TTIP2 TTIP2
A8 71 O TTIP3 TTIP3 TTIP3
A11 102 O TTIP4 TTIP4 TTIP4
J4 7 — TVSS1 TVSS1 TVSS1
D1 39 — TVSS2 TVSS2 TVSS2
E9 72 — TVSS3 TVSS3 TVSS3
L10 103 — TVSS4 TVSS4 TVSS4
J5 8 — TVDD1 TVDD1 TVDD1
D2 40 — TVDD2 TVDD2 TVDD2
G9 73 — TVDD3 TVDD3 TVDD3
M9 104 — TVDD4 TVDD4 TVDD4
B3 9 O TRING1 TRING1 TRING1
B6 41 O TRING2 TRING2 TRING2
B9 74 O TRING3 TRING3 TRING3
B12 105 O TRING4 TRING4 TRING4
K4 10 O RPOS1 RPOS1 RPOS1
E1 12 O RPOS2 RPOS2 RPOS2
D11 14 O RPOS3 RPOS3 RPOS3
K11 16 O RPOS4 RPOS4 RPOS4
G2 11 O RNEG1 RNEG1 RNEG1
E2 13 O RNEG2 RNEG2 RNEG2
F11 15 O RNEG3 RNEG3 RNEG3
M10 25 O RNEG4 RNEG4 RNEG4
H3 127 O RCLK1 RCLK1 RCLK1
F1 31 O RCLK2 RCLK2 RCLK2
E11 58 O RCLK3 RCLK3 RCLK3
L11 96 O RCLK4 RCLK4 RCLK4
G1 26 I TPOS1 TPOS1 TPOS1
F2 30 I TPOS2 TPOS2 TPOS2
E12 33 I TPOS3 TPOS3 TPOS3
M11 55 I TPOS4 TPOS4 TPOS4
H2 27 I TNEG1 TNEG1 TNEG1
M1 32 I TNEG2 TNEG2 TNEG2
D12 34 I TNEG3 TNEG3 TNEG3
K12 59 I TNEG4 TNEG4 TNEG4
M2 17 I TCLK1 TCLK1 TCLK1
L2 43 I TCLK2 TCLK2 TCLK2
F12 83 I TCLK3 TCLK3 TCLK3
L12 113 I TCLK4 TCLK4 TCLK4
M12 108 I PBTS N/A RT0
L3 42 I JTRST JTRST JTRST
M3 48 I JTMS JTMS JTMS
M5 44 I JTCLK JTCLK JTCLK
M6 45 I JTDI JTDI JTDI
M7 46 O JTDO JTDO JTDO
Note 1: The VSM signal is not available with the BGA package option.
Note 2: The LQFP no-connect pin numbers are 4, 5, 37, 67, 69, 70, and 99–101.
Note 3: The BGA no-connect pin numbers are A3, A6, A9, A12, B1, B4, B7, B10, C1–C12, E5–E8, F5–F8, G4–G8, G10, H5–H8, J11, J12, K6,
and L4.
I/O PARALLEL PORT MODE SERIAL PORT MODE HARDWARE MODE
HRST HRST HRST
8 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 2-C. Parallel Interface Mode Pin Description
PIN I/O FUNCTION
Read Input (Data Strobe). RD and DS are active-low signals. DS is active low when in
RD (DS)
WR (R/W)
ALE (AS) I
A4–A0 I
D7/AD7–D0/AD0 I/O
INT
TXDIS/TEST I
HRST
MCLK I
BIS0/BIS1 I Bus Interface Select Bit 0 and 1. Used to select bus interface option. See Table 2-A for details.
PBTS I
CS1–CS4
PBEO1–PBEO4 O
RCL1/LOTC1–
RCL4/LOTC4
RTIP1–RTIP4 I
RRING1–RRING4 I
BPCLK1–BPCLK4 O
TTIP1–TTIP4 O
TRING1–TRING4 O
RPOS1–RPOS4 O
RNEG1–RNEG4 O
I
nonmultiplexed, Motorola mode. See the bus timing diagrams in Section 10
I
Write Input (Read/Write). WR is an active-low signal. See the bus timing diagrams in Section 10.
Address Latch Enable (Address Strobe). When using multiplexed bus mode (BIS0 = 0), this pin
serves to demultiplex the bus on a positive-going edge. In nonmultiplexed bus mode (BIS0 = 1),
ALE should be wired low.
Address Bus. In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS0 = 1), these pins serve as the address bus.
In multiplexed bus operation (BIS0 = 0), these pins are not used and should be wired low.
Data Bus/Address/Data Bus. In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS0 = 1), these pins serve as the
data bus. In multiplexed bus operation (BIS0 = 0), these pins serve as an 8-bit multiplexed
address/data bus.
Interrupt (INT). The interrupt flags the host controller during conditions and change of conditions
O
defined in the status register. It is an active-low, open-drain output.
Tri-State Control, Multifunctional. Set this pin high, with all CS1–CS4 inputs inactive, to tri-state
TTIP1–TTIP4 and TRING1–TRING4. Set this pin high with any of the CS1–CS4 inputs active to
tri-state all outputs and I/O pins (including the parallel control port). Set low for normal operation.
Hardware Reset. Bringing HRST low resets the DS21448, setting all control bits to the all-zeros
I
default state.
Master Clock. A 2.048MHz (±50ppm) clock source with TTL levels is applied at this pin. This
clock is used internally for both clock/data recovery and for jitter attenuation. Use of a T1
1.544MHz clock source is optional (Note 1).
Parallel Bus Type Select. When using the parallel port, set PBTS high to select Motorola bus
timing; set low to select Intel bus timing. This pin controls the function of the RD (DS), ALE (AS),
and WR (R/W) pins.
Chip Select 1. Must be low to read or write to channel 1 of the device. CS1 is an active-low
signal.
Chip Select 2. Must be low to read or write to channel 2 of the device. CS2 is an active-low
signal.
I
Chip Select 3. Must be low to read or write to channel 3 of the device. CS3 is an active-low
signal.
Chip Select 4. Must be low to read or write to channel 4 of the device. CS4 is an active-low
signal.
PRBS Bit-Error Output. The receiver constantly searches for a 215 - 1 (E1) or a QRSS (T1)
PRBS, depending on the ETS bit setting (CCR1.7). It remains high if it is out of synchronization
with the PRBS pattern. It goes low when synchronized to the PRBS pattern. Any errors in the
received pattern after synchronization cause a positive-going pulse (with same period as E1 or
T1 clock) synchronous with RCLK. PRBS bit errors can also be reported to the ECR1 and ECR2
registers by setting CCR6.2 to logic 1.
Receive Carrier Loss/Loss-of-Transmit Clock. An output that toggles high during a receive carrier
O
loss (CCR2.7 = 0) or toggles high if the TCLK pin has not been toggled for 5ms ± 2ms (CCR2.7 =
1). CCR2.7 defaults to logic 0 when in hardware mode.
Receive Tip and Ring. Analog inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins connect through a
1:1 transformer to the line. See Section 7 for details.
Backplane Clock. A 16.384MHz, 8.192MHz, 4.096MHz, or 2.048MHz clock output that is
referenced to RCLK selectable through CCR5.7 and CCR5.6.
Transmit Tip and Ring. Analog line-driver outputs. These pins connect through a step-up
transformer to the line. See Section 7 for details.
Receive Positive Data. These bits are updated on the rising edge (CCR2.0 = 0) or the falling
edge (CCR2.0 = 1) of RCLK with bipolar data out of the line interface. Set NRZE (CCR1.6) to 1
for NRZ applications. In NRZ mode, data is output on RPOS, and a received error (BPV, CV, or
EXZ) causes a positive-going pulse synchronous with RCLK at RNEG.
Receive Negative Data. Updated on the rising edge (CCR2.0 = 0) or the falling edge (CCR2.0 =
1) of RCLK with the bipolar data out of the line interface. Set NRZE (CCR1.6) to 1 for NRZ
applications. In NRZ mode, data is output on RPOS, and a received error (BPV, CV, or EXZ)
causes a positive-going pulse synchronous with RCLK at RNEG.
.
9 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
PIN I/O FUNCTION
RCLK1–RCLK4 O
TPOS1–TPOS4 I
TNEG1–TNEG4 I
TCLK1–TCLK4 I
JTRST I JTAG Reset
JTMS I JTAG Mode Select
JTCLK I JTAG Clock
JTDI I JTAG Data In
JTDO O JTAG Data Out
VSM I Voltage Supply Mode (LQFP only). Should be wired low for correct operation.
TVDD1–TVDD4 — 3.3V, ±5% Transmitter Positive Supply
VDD1–VDD4 — 3.3V, ±5% Positive Supply
TVSS1–TVSS4 — Transmitter Signal Ground
VSS1–VSS4 — Signal Ground
Receive Clock. Buffered recovered clock from the line. Synchronous to MCLK in absence of
signal at RTIP and RRING.
Transmit Positive Data. Sampled on the falling edge (CCR2.1 = 0) or the rising edge
(CCR2.1 = 1) of TCLK for data to be transmitted out onto the line.
Transmit Negative Data. Sampled on the falling edge (CCR2.1 = 0) or the rising edge
(CCR2.1 = 1) of TCLK for data to be transmitted out onto the line.
Transmit Clock. A 2.048MHz or 1.544MHz primary clock. It is used to clock data through the
transmit-side formatter. It can be sourced internally by MCLK or RCLK. See Common Control
Register 1 and Figure 1-3
.
Table 2-D. Serial Interface Mode Pin Description
PIN I/O FUNCTION
Interrupt (INT). Flags host controller during conditions and change of conditions defined in the
INT
TXDIS/TEST I
HRST
MCLK I
BIS0/BIS1 I Bus Interface Select Bit 0 and 1. Used to select bus interface option. See Table 2-A for details.
CS1
CS2
CS3
CS4
ICES I
OCES I
SCLK I Serial Clock. Serial interface clock.
SDI I Serial Data Input. Serial interface data input.
SDO O Serial Data Output. Serial interface data output.
PBEO1–PBEO4 O
RCL1/LOTC1–
RCL4/LOTC4
RTIP1–RTIP4
RRING1–RRING4
I/O
status register. Active-low, open-drain output.
Tri-State Control, Multifunctional. Set this pin high with all CS1–CS4 inputs inactive to tri-state
TTIP1–TTIP4 and TRING1–TRING4. Set this pin high with any of the CS1–CS4 inputs active to
tri-state all outputs and I/O pins (including the parallel control port). Set low for normal operation.
Hardware Reset. Bringing HRST low resets the DS21448, setting all control bits to the all-zeros
I
default state.
Master Clock. A 2.048MHz (±50ppm) clock source with TTL levels is applied at this pin. This
clock is used internally for both clock/data recovery and for jitter attenuation. A T1 1.544MHz
clock source is optional (Note 1).
Chip Select 1. Must be low to read or write to channel 1 of the device. CS1 is an active-low
I
signal.
Chip Select 2. Must be low to read or write to channel 2 of the device. CS2 is an active-low
I
signal.
Chip Select 3. Must be low to read or write to channel 3 of the device. CS3 is an active-low
I
signal.
Chip Select 4. Must be low to read or write to channel 4 of the device. CS4 is an active-low
I
signal.
Input Clock-Edge Select. Selects whether the serial interface data input (SDI) is sampled on the
rising (ICES = 0) or falling edge (ICES = 1) of SCLK.
Output Clock-Edge Select. Selects whether the serial interface data output (SDO) changes on
the rising (OCES = 1) or falling edge (OCES = 0) of SCLK.
PRBS Bit-Error Output. The receiver constantly searches for a 215 - 1 (E1) or a QRSS (T1)
PRBS, depending on the ETS bit setting (CCR1.7). It remains high if it is out of synchronization
with the PRBS pattern. It goes low when synchronized to the PRBS pattern. Any errors in the
received pattern after synchronization cause a positive-going pulse (with same period as E1 or
T1 clock) synchronous with RCLK. PRBS bit errors can also be reported to the ECR1 and ECR2
registers by setting CCR6.2 to logic 1.
Receive Carrier Loss/Loss-of-Transmit Clock. An output that toggles high during a receive carrier
O
loss (CCR2.7 = 0) or toggles high if the TCLK pin has not been toggled for 5ms ± 2ms
(CCR2.7 = 1). CCR2.7 defaults to logic 0 when in hardware mode.
Receive Tip and Ring. Analog inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins connect through a
I
1:1 transformer to the line. See Section 7
for details.
10 of 60
PIN I/O FUNCTION
BPCLK1–BPCLK4 O
TTIP1–TTIP4 O
TRING–TRING4 O
RPOS1–RPOS4 O
RNEG1–RNEG4 O
RCLK1–RCLK4 O
TPOS1–TPOS4 I
TNEG1–TNEG4 I
TCLK1–TCLK4 I
JTRST I JTAG Reset
JTMS I JTAG Mode Select
JTCLK I JTAG Clock
JTDI I JTAG Data In
JTDO O JTAG Data Out
VSM I Voltage Supply Mode (LQFP only). VSM should be wired low for correct operation.
TVDD1–TVDD4 — 3.3V, ±5% Transmitter Positive Supply
VDD1–VDD4 — 3.3V, ±5% Positive Supply
TVSS1–TVSS4 — Transmitter Signal Ground for Transmitter Outputs
VSS1–VSS4 — Signal Ground
Backplane Clock. A 16.384MHz, 8.192MHz, 4.096MHz, or 2.048MHz clock output that is
referenced to RCLK selectable through CCR5.7 and CCR5.6.
Transmit Tip and Ring. Analog line-driver outputs. These pins connect through a step-up
transformer to the line. See Section 7
Receive Positive Data. Updated on the rising edge (CCR2.0 = 0) or the falling edge (CCR2.0 = 1)
of RCLK with bipolar data out of the line interface. Set NRZE (CCR1.6) to 1 for NRZ applications.
In NRZ mode, data is output on RPOS, and a received error (BPV, CV, or EXZ) causes a
positive-going pulse synchronous with RCLK at RNEG.
Receive Negative Data. Updated on the rising edge (CCR2.0 = 0) or the falling edge (CCR2.0 =
1) of RCLK with the bipolar data out of the line interface. Set NRZE (CCR1.6) to 1 for NRZ
applications. In NRZ mode, data is output on RPOS, and a received error (BPV, CV, or EXZ)
causes a positive-going pulse synchronous with RCLK at RNEG.
Receive Clock. Buffered recovered clock from the line. Synchronous to MCLK in absence of
signal at RTIP and RRING.
Transmit Positive Data. Sampled on the falling edge (CCR2.1 = 0) or the rising edge (CCR2.1 =
1) of TCLK for data to be transmitted out onto the line.
Transmit Negative Data. Sampled on the falling edge (CCR2.1 = 0) or the rising edge (CCR2.1 =
1) of TCLK for data to be transmitted out onto the line.
Transmit Clock. A 2.048MHz or 1.544MHz primary clock used to clock data through the transmit
side formatter. They can be sourced internally by MCLK or RCLK. See Common Control Register
1 and Figure 1-3.
for details.
Table 2-E. Hardware Interface Mode Pin Description
PIN I/O FUNCTION
E1/T1 Select
ETS I
NRZE I
SCLKE I
DJA I
JAMUX I
JAS I
HBE I
L0/L1/L2 I
0 = E1
1 = T1
NRZ Enable
0 = bipolar data at RPOS/RNEG and TPOS/TNEG
1 = NRZ data at RPOS and TPOS or TNEG; RNEG outputs a positive-going pulse when the
device receives a BPV, CV, or EXZ.
Receive and Transmit Synchronization Clock Enable. SCLKE combines RSCLKE (CCR5.3) and
TSCLKE (CCR5.2).
0 = disable 2.048MHz synchronization transmit and receive mode
1 = enable 2.048MHz synchronization transmit and receive mode
Disable Jitter Attenuator
0 = jitter attenuator enabled
1 = jitter attenuator disabled
Jitter Attenuator Clock Mux. Controls the source for JACLK.
0 = JACLK sourced from MCLK (2.048MHz or 1.544MHz at MCLK).
1 = JACLK sourced from internal PLL (2.048 MHz at MCLK).
Jitter Attenuator Path Select
0 = place the jitter attenuator on the receive side
1 = place the jitter attenuator on the transmit side
Receive and Transmit HDB3/B8ZS Enable. HBE combines RHBE (CCR2.3) and THBE
(CCR2.2).
0 = enable HDB3 (E1)/B8ZS (T1)
1 = disable HDB3 (E1)/B8ZS (T1)
Line Build-Out Select Bits 0,1, and 2. These pins set the transmitter build-out; see (Table 7-A
(E1) and Table 7-B
(T1).
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
11 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
PIN I/O FUNCTION
Receive and Transmit Clock Select. Selects which RCLK edge to update RPOS and RNEG and
CES I
TPD I
TX0/TX1 I
LOOP0/LOOP1 I Loopback Select Bits 0 and 1. These inputs determine the active loopback mode (Table 4-A).
MM0/MM1 I
RT1/RT0 I
TEST I
HRST
MCLK I
BIS0/BIS1 I Bus Interface Select Bit 0 and 1. Used to select bus interface option (Table 2-A).
EGL1–EGL4 I
PBEO1–PBEO4 O
RCL1–RCL4 O Receive Carrier Loss. An output that toggles high during a receive carrier loss.
RTIP1–RTIP4 I
RRING1–RRING4 I
BPCLK1–BPCLK4 O Backplane Clock. A 16.384MHz clock output that is referenced to RCLK.
TTIP1–TTIP4
TRING1–TRING4
RPOS1–RPOS4 O
RNEG1–RNEG4 O
RCLK1–RCLK4 O
TPOS1–TPOS4 I
TNEG1–TNEG4 I
TCLK1–TCLK4 I
JTRST I JTAG Reset
JTMS I JTAG Mode Select
JTCLK I JTAG Clock
JTDI I JTAG Data In
JTDO O JTAG Data Out
VSM I Voltage Supply Mode (LQFP only). VSM should be wired low for correct operation.
TVDD1–TVDD4 – 3.3V, ±5% Transmitter Positive Supply
VDD1–VDD4 — 3.3V, ±5% Positive Supply
which TCLK edge to sample TPOS and TNEG. CES combines TCES and RCES.
0 = update RPOS/RNEG on rising edge of RCLK; sample TPOS/TNEG on falling edge of TCLK
1 = update RPOS/RNEG on falling edge of RCLK; sample TPOS/TNEG on rising edge of TCLK
Transmit Power-Down
0 = normal transmitter operation
1 = powers down the transmitter and tri-states TTIP and TRING pins
Transmit Data Source Select Bits 0 and 1. These inputs determine the source of the transmit
).
).
).
).
15
- 1 PRBS (ETS = 0) or a
for details.
for details.
.
data (Table 4-B
Monitor Mode Select Bits 0 and 1. These inputs determine if the receive equalizer is in a monitor
mode (Table 4-D
Receive LIU Termination Select Bits 0 and 1. These inputs determine the receive termination
(Table 4-E
Tri-State Control. Set high to tri-state all outputs and I/O pins (including the parallel control port).
Set low for normal operation. Useful in board-level testing.
Hardware Reset. Bringing HRST low resets the DS21448, setting all control bits to the all-zero
I
default state.
Master Clock. A 2.048MHz (±50ppm) clock source with TTL levels is applied at this pin. This
clock is used internally for both clock/data recovery and for jitter attenuation. A T1 1.544MHz
clock source is optional (Note 1). See Table 4-F for details.
Receive Equalizer Gain-Limit Select. These bits control the sensitivity of the receive equalizers
(Table 4-C
PRBS Bit-Error Output. The receiver constantly searches for a 2
QRSS PRBS (ETS = 1). The pattern is chosen automatically by the value of the ETS pin. It
remains high if it is out of synchronization with the PRBS pattern. It goes low when synchronized
to the PRBS pattern. Any errors in the received pattern after synchronization cause a positivegoing pulse (with same period as E1 or T1 clock) synchronous with RCLK.
Receive Tip and Ring. Analog inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins connect through a
1:1 transformer to the line. See Section 7
Transmit Tip and Ring. Analog line-driver outputs. These pins connect through a step-up
O
transformer to the line. See Section 7
Receive Positive Data. Updated on the rising edge (CES = 0) or the falling edge (CES = 1) of
RCLK with bipolar data out of the line interface. In NRZ mode (NRZE = 1), data is output on
RPOS, and a received error (BPV, CV, or EXZ) causes a positive-going pulse synchronous with
RCLK at RNEG.
Receive Negative Data. Updated on the rising edge (CES = 0) or the falling edge (CES = 1) of
RCLK with bipolar data out of the line interface. In NRZ mode (NRZE = 1), data is output on
RPOS, and a received error (BPV, CV, or EXZ) causes a positive-going pulse synchronous with
RCLK at RNEG.
Receive Clock. Buffered recovered clock from the line. Synchronous to MCLK in absence of
signal at RTIP and RRING.
Transmit Positive Data. Sampled on the falling edge (CES = 0) or the rising edge (CES = 1) of
TCLK for data to be transmitted out onto the line.
Transmit Negative Data. Sampled on the falling edge (CES = 0) or the rising edge (CES = 1) of
TCLK for data to be transmitted out onto the line.
Transmit Clock. A 2.048MHz or 1.544MHz primary clock used to clock data through the transmit
side formatter. It can be sourced internally by MCLK or RCLK. See Common Control Register 1
and Figure 1-3
12 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
PIN I/O FUNCTION
TVSS1–TVSS4 — Transmitter Signal Ground for Transmitter Outputs
VSS1–VSS4 — Signal Ground
Note 1: G.703 requires an accuracy of ±50ppm for T1 and E1. TR62411 and ANSI specs require ±32ppm accuracy for T1 interfaces.
3. DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The DS21448 contains four independent LIUs that share a common interface for configuration and status. The user
can choose between three different means of accessing the device: a parallel microprocessor interface, a serial
interface, and a hardwired mode, which configures the device by setting levels on the device’s pins. The
DS21448’s four chip selects (
CS1, CS2, CS3, and CS4) determine which LIU is accessed when using the parallel
or serial interface modes. Four sets of identical register maps exist, one for each channel. Using the appropriate
chip select accesses a channel’s register map.
The analog AMI/HDB3 waveform off the E1 line or the AMI/B8ZS waveform off the T1 line is transformer-coupled
into the RTIP and RRING pins of the DS21448. The user has the option to use internal termination, software
selectable for 75W/100W/120W applications, or external termination. The device recovers clock and data from the
analog signal and passes it through the jitter attenuation mux, outputting the received line clock at RCLK and
bipolar or NRZ data at RPOS and RNEG. The DS21448 contains an active filter that reconstructs the analogreceived signal for the nonlinear losses that occur in transmission. The receive circuitry is also configurable for
various monitor applications. The device has a usable receive sensitivity of 0 to -43dB for E1 and 0 to -36dB for T1
that allows the device to operate on 0.63mm (22AWG) cables up to 2.5km (E1) and 6k feet (T1) in length. Data
input at TPOS and TNEG is sent through the jitter attenuation mux to the waveshaping circuitry and line driver. The
DS21448 drives the E1 or T1 line from the TTIP and TRING pins through a coupling transformer. The line driver
can handle both CEPT 30/ISDN-PRI lines for E1 and long-haul (CSU) or short-haul (DSX-1) lines for T1.
3.1 DS21448 and DS21Q348 Differences
The DS21448 BGA is a monolithic quad-port LIU that is a replacement for the DS21Q348. The additional features
of JTAG, transmit driver disable, and the serial interface in the DS21448 have changed the function of several pins,
as shown in Table 3-A
.
Table 3-A. DS21448 vs. DS21Q348 Pin Differences
PIN DS21Q348 DS21448
G4 VSM N.C.
J1 VSS SCLK
K1 A4 A4/SDO
K3 VSS SDI
K7 TEST TXDIS/TEST
L3 N.C. JTRST*
M3 N.C. JTMS*
M5 N.C. JTCLK
M6 N.C. JTDI*
M7 N.C. JTDO
*DS21448 pin is internally pulled up.
4. PORT OPERATION
4.1 Hardware Mode
The DS21448 supports a hardware configuration mode that allows the user to configure the device by setting levels
on the device’s pins. This mode allows the DS21448 configuration without the use of a microprocessor, simplifying
designs. Not all of the device features are supported in the hardware mode.
In hardware mode (BIS0 = 1, BIS1 = 1) several pins have been redefined so they can be used for initializing the
DS21448. Refer to Table 2-B
and Table 2-E for pin assignment and definition. Because of limited pin count, several
13 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
functions have been combined and affect all four channels in the device and/or treat the receive and transmit paths
as one block. Restrictions when using the hardware mode include the following:
· BPCLK pins only output a 16.384MHz signal.
· The RCL/LOTC pins are designated to RCL.
· The RHBE and THBE control bits are combined and controlled by HBE.
· RSCLKE and TSCLKE bits are combined and controlled by SCLKE.
· TCES and RCES are combined and controlled by CES.
· The transmitter functions are combined and controlled by TX1 and TX0.
· Loopback functions are controlled by LOOP1 and LOOP0.
· JABDS defaults to 128-bit buffer depth.
· All other control bits default to logic 0.
Table 4-A. Loopback Control in Hardware Mode
LOOPBACK SYMBOL LOOP1 LOOP0
Remote Loopback RLB 1 1
Local Loopback LLB 1 0
Analog Loopback ALB 0 1
No Loopback — 0 0
Table 4-B. Transmit Data Control in Hardware Mode
TRANSMIT DATA SYMBOL TX1 TX0
Unframed All Ones TUA1 1 1
Alternating Ones and Zeros TAOZ 1 0
TPOS and TNEG — 0 0
PRBS
TPRBSE
0 1
Table 4-C. Receive Sensitivity Settings in Hardware Mode
EGL ETS RECEIVE SENSITIVITY (dB)
0 0 (E1) -12 (short haul)
1 0 (E1) -43 (long haul)
1 1 (T1) -30 (limited long haul)
0 1 (T1) -36 (long haul)
Table 4-D. Monitor Gain Settings in Hardware Mode
MM1 MM0 INTERNAL LINEAR GAIN BOOST (dB)
0 0 Normal operation (no boost)
0 1 20
1 0 26
1 1 32
Table 4-E. Internal Rx Termination Select in Hardware Mode
RT1 RT0
0 0 Internal receive-side termination disabled
0 1 Internal receive-side 120Ω enabled
1 0 Internal receive-side 100Ω enabled
1 1 Internal receive-side 75Ω enabled
INTERNAL RECEIVE
TERMINATION CONFIGURATION
Table 4-F. MCLK Selection in Hardware Mode
MCLK (MHz) JAMUX ETS
2.048 0 0
2.048 1 1
1.544 0 1
14 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
C
(
)
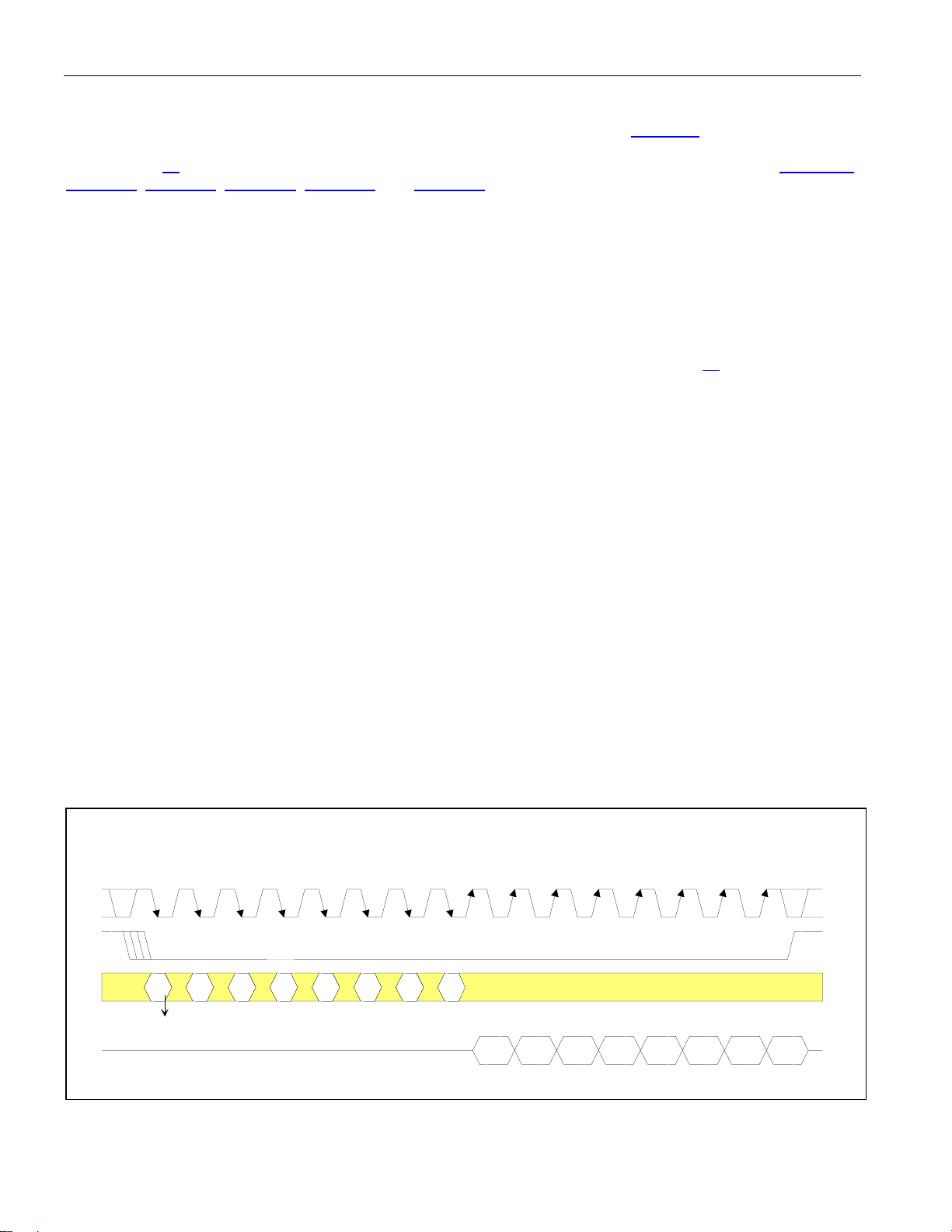
4.2 Serial Port Operation
Setting BIS1 = 1 and BIS0 = 0 enables the serial bus interface on the DS21448 (Table 2-A). Serial port read/write
timing is unrelated to the system transmit and receive timing, allowing asynchronous reads or writes by the host.
See Section 10
Figure 4-2
for the AC timing of the serial port. All serial port accesses are LSB first. See Figure 4-1,
, Figure 4-3, Figure 4-4, Figure 4-5, and Figure 4-6 for additional details.
A serial bus access requires the use of four signals: serial clock (SCLK), one of the four chip selects (
CS), serial
data input (SDI), and serial data output (SDO). The DS21448 uses SCLK to sample data that is present on SDI and
output data onto SDO. Input clock-edge select (ICES) allows the user to choose which SCLK edge input data is
sampled on. Output clock-edge select (OCES) allows the user to choose which SCLK edge output data changes
on. When ICES is low, input data is latched on the rising edge of SCLK, and when ICES is high, input data is
latched on the falling edge of SCLK. When OCES is low, data is output on the falling edge of SCLK, and when
OCES is high, data is output on the rising edge of SCLK. Data is held until the next falling or rising edge of SCLK.
All data transfers are initiated by driving the appropriate port’s
must go inactive between data transfers. See the serial bus timing information in Section 10
transfers are terminated if the port’s
when all
CS pins are inactive.
CS input transitions high. Port control logic is disabled, and SDO is tri-stated
CS input low and ends with CS going inactive. CS
for details. All data
Reading from or writing to the internal registers requires writing one address/command byte prior to the transferring
register data. Two types of serial bus transfers exist, standard and burst. The standard serial bus access always
consists of two bytes, an address/command byte that is always supplied by the user on SDI, and a data byte that
can either be written to the DS21448 using SDI (write operation) or output by the DS21448 on SDO (read
operation). The burst serial bus access consists of a single address/command byte followed either by 22 read or 22
write data bytes.
The first bit written (LSB) of the address/command byte specifies whether the access is to be a read (1) or a write
(0). The next 5 bits identify the register address. Valid register addresses are 00h through 15h. Bit 7 is reserved
and must be set to 0 for proper operation. Bit 8, the last bit (MSB) of the address/command byte, is the burst modeenable bit. When the burst bit is enabled (set to 0) and a READ operation is performed, the DS21448 automatically
outputs the contents of registers 00h through 15h sequentially, starting with register address 00h. When the burst
bit is enabled and a WRITE operation is performed, data supplied on SDI is sequentially written into the DS21448’s
register space starting at address 00h. Burst operation is stopped once address 15h is read or
CS goes inactive.
For both burst read and burst write transfers, the address/command byte’s register address bits must be set to 0.
The user can broadcast register write accesses to multiple ports simultaneously by enabling the desired channels’
chip selects at the same time. However, only one port can be read at a time. Any attempt to read multiple ports
simultaneously results in invalid data being returned on SDO.
Figure 4-1. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 1
ICES = 1 (SAMPLE SDI ON THE FALLING EDGE OF SCLK)
OCES = 1 (UPDATE SDO ON RISING EDGE OF SCLK)
SCLK
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
SDI
(LSB)
SDO
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 0 B
1
READ ACCESS ENABLED
(MSB)
D0
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6
LSB
D7
(MSB)
15 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
C
(
)
C
C
Figure 4-2. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 2
ICES = 1 (SAMPLE SDI ON THE FALLING EDGE OF SCLK)
OCES = 0 (UPDATE SDO ON FALLING EDGE OF SCLK)
SCLK
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
SDI
SDO
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 0 B
1
(LSB)
(MSB)
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6
D0
LSB
Figure 4-3. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 3
ICES = 0 (SAMPLE SDI ON THE RISING EDGE OF SCLK)
OCES = 0 (UPDATE SDO ON FALLING EDGE OF SCLK)
SCLK
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
SDI
(LSB)
SDO
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 0 B
1
(MSB)
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6
D0
(LSB)
Figure 4-4. Serial Port Operation for Read Access (R = 1) Mode 4
ICES = 0 (SAMPLE SDI ON THE RISING EDGE OF SCLK)
OCES = 1 (UPDATE SDO ON RISING EDGE OF SCLK)
SCLK
SDI
SDO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5
1
(LSB) (MSB)
B
0
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D0 D7
(LSB)
D7
(MSB)
D7
(MSB)
(MSB)
16 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
C
C
)
Figure 4-5. Serial Port Operation for Write Access (R = 0) Modes 1 and 2
ICES = 1 (SAMPLE SDI ON THE FALLING EDGE OF SCLK)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16SCLK
S
SDI
(LSB)
WRITE ACCESS ENABLED
SDO
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 0 B
0
(MSB)
DO D6
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D7
(LSB)
(MSB)
Figure 4-6. Serial Port Operation for Write Access (R = 0) Modes 3 and 4
ICES = 0 (SAMPLE SDI ON THE RISING EDGE OF SCLK
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16SCLK
S
SDI
(LSB)
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 0 B
0
(MSB)
DO D6
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D7
(LSB) (MSB)
WRITE ACCESS ENABLED
SDO
4.3 Parallel Port Operation
The option for either multiplexed bus operation (BIS0 = 0) or nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS0 = 1) is available
when using the parallel interface. The DS21448 can operate with either Intel or Motorola bus timing configurations.
If the PBTS pin is wired low, Intel timing is selected; if wired high, Motorola timing is selected. All Motorola bus
signals are listed in parentheses (). Four sets of identical register maps exist, one for each channel. See Table 4-H
for register names and addresses. Use the appropriate chip select (
register map. See the timing diagrams in Section 10
for more details. Hardware and serial port modes are not
CS1, CS2, CS3, or CS4) to access a channel’s
supported when using parallel port operation.
4.3.1 Device Power-Up and Reset
The DS21448 resets itself upon power-up, setting all writeable registers to 00h and clearing the status and
information registers. CCR3.7 (TUA1) = 0 results in the LIU transmitting unframed all ones. After the power
supplies have settled, initialize all control registers to the desired settings, then toggle the LIRST bit (CCR3.2). The
DS21448 can at any time be reset to the default settings by bringing
down and powering up again.
HRST low (level triggered) or by powering
17 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 4-G. Parallel Port Mode Selection
PBTS BIS0 PROCESSOR BUS INTERFACE TYPE
0 0 Intel Parallel Port Mode (Multiplexed)
0 1 Intel Parallel Port Mode (Nonmultiplexed)
1 0 Motorola Parallel Port Mode (Multiplexed)
1 1 Motorola Parallel Port Mode (Nonmultiplexed)
4.3.2 Register Map
Table 4-H shows the typical register map for all four ports. Use the appropriate chip select (CS1, CS2, CS3, or CS4)
to access a channel’s register map.
Table 4-H. Register Map
NAME R/W ADDRESS FUNCTION
CCR1 R/W 00h Common Control Register 1
CCR2 R/W 01h Common Control Register 2
CCR3 R/W 02h Common Control Register 3
CCR4 R/W 03h Common Control Register 4
CCR5 R/W 04h Common Control Register 5
CCR6 R/W 05h Common Control Register 6
SR R 06h Status Register
IMR R/W 07h Interrupt Mask Register
RIR1 R 08h Receive Information Register 1
RIR2 R 09h Receive Information Register 2
IBCC R/W 0Ah In-Band Code Control Register
TCD1 R/W 0Bh Transmit Code Definition Register 1
TCD2 R/W 0Ch Transmit Code Definition Register 2
RUPCD1 R/W 0Dh Receive-Up Code Definition Register 1
RUPCD2 R/W 0Eh Receive-Up Code Definition Register 2
RDNCD1 R/W 0Fh Receive-Down Code Definition Register 1
RDNCD2 R/W 10h Receive-Down Code Definition Register 2
ECR1 R 11h Error Count Register 1
ECR2 R 12h Error Count Register 2
TEST1 R/W 13h Test 1
TEST2 R/W 14h Test 2
TEST2 R/W 15h Test 3
— — (Note 1) —
Note 1: Register addresses 16h–1Fh do not exist.
18 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
4.3.3 Control Registers
CCR1 (00H): Common Control Register 1
(MSB)
ETS NRZE RCLA ECUE JAMUX TTOJ TTOR LOTCMC
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
ETS CCR1.7
NRZE CCR1.6
RCLA CCR1.5
ECUE CCR1.4
JAMUX CCR1.3
TTOJ CCR1.2
TTOR CCR1.1
LOTCMC CCR1.0
E1/T1 Select
0 = E1
1 = T1
NRZ Enable
0 = bipolar data at RPOS/RNEG and TPOS/TNEG
1 = NRZ data at RPOS and TPOS or TNEG; RNEG outputs a positive-going pulse when the
device receives a BPV, CV, or EXZ
Receive-Carrier-Loss Alternate Criteria
0 = RCL declared upon 255 (E1) or 192 (T1) consecutive zeros
1 = RCL declared upon 2048 (E1) or 1544 (T1) consecutive zeros
Error Counter Update Enable. A 0-to-1 transition forces the next receive clock cycle to load the
error counter registers with the latest counts and reset the counters. The user must wait a
minimum of two clock cycles (976ns for E1 and 1296ns for T1) before reading the error count
registers to allow for a proper update. See Section 6
Jitter Attenuator Clock Mux. Controls the source for JACLK (Figure 1-1
0 = JACLK sourced from MCLK (2.048MHz or 1.544MHz at MCLK)
1 = JACLK sourced from internal PLL (2.048MHz at MCLK)
TCLK to JACLK. Internally connects TCLK to JACLK (Figure 1-3
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
TCLK to RCLK. Internally connects TCLK to RCLK (Figure 1-3
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Loss-of-Transmit Clock Mux Control. Determines whether the transmit logic should switch to
JACLK if the TCLK input should fail to transition (Figure 1-3).
0 = do not switch to JACLK if TCLK stops
1 = switch to JACLK if TCLK stops
for details.
).
).
).
(LSB)
19 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
CCR2 (01H): Common Control Register 2
(MSB)
RLPIN — SCLD CLDS RHBE THBE TCES RCES
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
RLPIN CCR2.7
— CCR2.6 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
SCLD CCR2.5
CLDS CCR2.4
RHBE CCR2.3
THBE CCR2.2
TCES CCR2.1
RCES CCR2.0
RCL/LOTC Pin Function Select. Forced to logic 0 in hardware mode.
0 = toggles high during a receive-carrier loss condition
1 = toggles high if TCLK does not transition for at least 5ms
Short Circuit-Limit Disable (ETS = 0). Controls the 50mA (RMS) current limiter.
0 = enable 50mA current limiter
1 = disable 50mA current limiter
Custom Line-Driver Select. Setting this bit to 1 redefines the operation of the transmit line
driver. When this bit is set to 1 and CCR4.5 = CCR4.6 = CCR4.7 = 0, the device generates a
square wave at the TTIP and TRING outputs instead of a normal waveform. When this bit is
set to 1 and CCR4.5 = CCR4.6 = CCR4.7 ¹ 0, the device forces TTIP and TRING outputs to
become open-drain drivers instead of their normal push-pull operation. This bit should be set
to 0 for normal operation of the device. Contact the factory for more details about how to use
this bit.
Receive HDB3/B8ZS Enable
0 = enable HDB3 (E1)/B8ZS (T1)
1 = disable HDB3 (E1)/B8ZS (T1)
Transmit HDB3/B8ZS Enable
0 = enable HDB3 (E1)/B8ZS (T1)
1 = disable HDB3 (E1)/B8ZS (T1)
Transmit Clock-Edge Select. Selects which TCLK edge to sample TPOS and TNEG.
0 = sample TPOS and TNEG on falling edge of TCLK
1 = sample TPOS and TNEG on rising edge of TCLK
Receive Clock-Edge Select. Selects which RCLK edge to update RPOS and RNEG.
0 = update RPOS and RNEG on rising edge of RCLK
1 = update RPOS and RNEG on falling edge of RCLK
(LSB)
20 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
CCR3 (02H): Common Control Register 3
(MSB)
TUA1 ATUA1 TAOZ TPRBSE TLCE LIRST IBPV IBE
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
TUA1 CCR3.7
ATUA1 CCR3.6
TAOZ CCR3.5
TPRBSE CCR3.4
TLCE CCR3.3
LIRST CCR3.2
IBPV CCR3.1
IBE CCR3.0
Transmit Unframed All Ones. The polarity of this bit is set such that the device transmits an allones pattern on power-up or device reset. This bit must be set to 1 to allow the device to transmit
data. The transmission of this data pattern is always timed off JACLK (Figure 1-1
0 = transmit all ones at TTIP and TRING
1 = transmit data normally
Automatic Transmit Unframed All Ones. Automatically transmit an unframed all-ones pattern at
TTIP and TRING during an RCL condition.
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Transmit Alternate Ones and Zeros. Transmit a …101010… pattern at TTIP and TRING. The
transmission of this data pattern is always timed off TCLK.
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Transmit PRBS Enable. Transmit a 215 - 1 (E1) or a QRSS (T1) PRBS at TTIP and TRING.
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Transmit Loop-Code Enable. Enables the transmit side to transmit the loop-up code in the transmit
code definition registers (TCD1 and TCD2). See Section 6 for details.
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Line Interface Reset. Setting this bit from 0 to 1 initiates an internal reset that resets the clock
recovery state machine and recenters the jitter attenuator. Normally this bit is only toggled on
power-up. It must be cleared and set again for a subsequent reset.
Insert Bipolar Violation (BPV). A 0-to-1 transition on this bit causes a single bipolar violation to be
inserted into the transmit data stream. Once this bit has been toggled from 0 to 1, the device waits
for the next occurrence of three consecutive 1s to insert the BPV. This bit must be cleared and set
again for a subsequent error to be inserted (Figure 1-3
Insert Bit Error. A 0-to-1 transition on this bit causes a single logic error to be inserted into the
transmit data stream. This bit must be cleared and set again for a subsequent error to be inserted
(Figure 1-3
).
).
).
(LSB)
CCR4 (03H): Common Control Register 4
(MSB)
L2 L1 L0 EGL JAS JABDS DJA TPD
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
L2 CCR4.7 Line Build-Out Select Bit 2. Sets the transmitter build-out (Table 7-A for E1, Table 7-B for T1).
L1 CCR4.6 Line Build Out Select Bit 1. Sets the transmitter build-out (Table 7-A for E1, Table 7-B for T1).
L0 CCR4.5 Line Build Out Select Bit 0. Sets the transmitter build-out (Table 7-A for E1, Table 7-B for T1).
EGL CCR4.4 Receive Equalizer Gain Limit. This bit controls the sensitivity of the receive equalizer (Table 4-I).
JAS CCR4.3
JABDS CCR4.2
DJA CCR4.1
TPD CCR4.0
Jitter Attenuator Path Select
0 = place the jitter attenuator on the receive side
1 = place the jitter attenuator on the transmit side
Jitter Attenuator Buffer Depth Select
0 = 128 bits
1 = 32 bits (use for delay-sensitive applications)
Disable Jitter Attenuator
0 = jitter attenuator enabled
1 = jitter attenuator disabled
Transmit Power-Down
0 = normal transmitter operation
1 = powers down the transmitter and tri-states the TTIP and TRING pins
(LSB)
21 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 4-I. Receive Sensitivity Settings
EGL
(CCR4.4)
0 0 (E1) -12 (short haul)
1 0 (E1) -43 (long haul)
1 1 (T1) -30 (limited long haul)
0 1 (T1) -36 (long haul)
CCR5 (04H): Common Control Register 5
(MSB)
BPCS1 BPCS0 MM1 MM0 RSCLKE TSCLKE RT1 RT0
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
BPCS1 CCR5.7 Backplane Clock Frequency Select 1. See Table 4-J for details.
BPCS0 CCR5.6 Backplane Clock Frequency Select 0. See Table 4-J for details.
MM1 CCR5.5 Monitor Mode Gain Select 1 (Table 4-K. )
MM0 CCR5.4 Monitor Mode Gain Select 0. See (Table 4-K.
RSCLKE CCR5.3
TSCLKE CCR5.2
RT1 CCR5.1 Receive Termination Select 1. See Table 4-L for details.
RT0 CCR5.0 Receive Termination Select 0. See Table 4-L for details.
ETS
(CCR1.7)
RECEIVE SENSITIVITY
(dB)
(LSB)
Receive Synchronization Clock Enable
0 = disable 2.048MHz synchronization receive mode
1 = enable 2.048MHz synchronization receive mode
Transmit Synchronization Clock Enable
0 = disable 2.048MHz transmit synchronization clock
1 = enable 2.048MHz transmit synchronization clock
Table 4-J. Backplane Clock Select
BPCS1
(CCR5.7)
0 0 16.384
0 1 8.192
1 0 4.096
1 1 2.048
BPCS0
(CCR5.6)
BPCLK FREQUENCY (MHz)
Table 4-K. Monitor Gain Settings
MM1
(CCR5.5)
0 0 Normal operation (no boost)
0 1 20
1 0 26
1 1 32
MM0
(CCR5.4)
INTERNAL LINEAR GAIN
BOOST (dB)
Table 4-L. Internal Rx Termination Select
RT1
(CCR5.1)
0 0 Internal receive-side termination disabled
0 1
1 0
1 1
RT0
(CCR5.0)
INTERNAL RECEIVE
TERMINATION CONFIGURATION
Internal receive-side 120W enabled
Internal receive-side 100W enabled
Internal receive-side 75W enabled
22 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
CCR6 (05H): Common Control Register 6
(MSB)
LLB RLB ARLBE ALB RJAB ECRS2 ECRS1 ECRS0
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
LLB CCR6.7
RLB CCR6.6
ARLBE CCR6.5
ALB CCR6.4
RJAB CCR6.3
ECRS2 CCR6.2 Error Count Register Select 2. See Section 6.4 for details.
ECRS1 CCR6.1 Error Count Register Select 1. See Section 6.4 for details.
ECRS0 CCR6.0 Error Count Register Select 0. See Section 6.4 for details.
Local Loopback. In local loopback, transmit data is looped back to the receive path, passing
through the jitter attenuator if it is enabled. Data in the transmit path acts as normal. See
Section 6.2
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
Remote Loopback. In remote loopback, data output from the clock/data recovery circuitry is
looped back to the transmit path, passing through the jitter attenuator if it is enabled. Data in
the receive path acts as normal, while data presented at TPOS and TNEG is ignored. See
Section 6.2
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
Automatic Remote Loopback Enable and Reset. When this bit is set high, the device
automatically goes into remote loopback when it detects loop-up code programmed into the
receive loop-up code definition registers (RUPCD1 and RUPCD2) for a minimum of 5
seconds; it also sets the RIR2.1 status bit. Once it is in an RLB state, the bit remains in this
state until it has detected the loop code programmed into the receive loop-down code
definition registers (RDNCD1 and RDNCD2) for a minimum of 5 seconds, at which point it
forces the device out of RLB and clears RIR2.1. Toggling this bit from 1 to 0 resets the
automatic RLB circuitry. The action of the automatic remote loopback circuitry is logically
ORed with the RLB (CCR6.6) control bit (i.e., either one can cause a RLB to occur).
Analog Loopback. In analog loopback, signals at TTIP and TRING are internally connected to
RTIP and RRING. The incoming line signals at RTIP and RRING are ignored. The signals at
TTIP and TRING are transmitted as normal. See Section 6.2
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
RCLK Jitter Attenuator Bypass. This control bit allows the receive-recovered clock and data to
bypass the jitter attenuation, while still allowing the BPCLK output to use the jitter attenuator.
See Section 7.3
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
for details.
for details.
for more details.
for details.
(LSB)
5. STATUS REGISTERS
The three registers that contain information about the device’s real-time status are the status register (SR) and
receive information registers 1 and 2 (RIR1/RIR2). When a particular event has occurred (or is occurring), the
appropriate bit in one of these registers is set to 1. Some bits in SR, RIR1, and RIR2 are latched bits and some are
real-time bits (denoted in the following register descriptions). For latched status bits, when an event or an alarm
occurs, the bit is set to 1 and remains set until the user reads that bit. The bit is cleared when it is read, and it is not
set until the event has occurred again. Two of the latched status bits (RUA1 and RCL) remain set after reading if
the alarm is still present.
The user always precedes a read of any of the three status registers with a write. The byte written to the register
informs the DS21448 which bits the user wishes to read and have cleared. The user writes a byte to one of these
registers with a 1 in the bit positions to be read and a 0 in the other bit positions. When a 1 is written to a bit
location, that location is updated with the latest information. When a 0 is written to a bit position, that bit position is
not updated, and the previous value is held. A write to the status and information registers is immediately followed
by a read of the same register. The read result should be logically ANDed with the mask byte that was just written,
and this value should be written back into the same register to ensure that bit does indeed clear. This second write
step is necessary because the alarms and events in the status registers occur asynchronously with respect to their
access through the parallel port. This write-read-write scheme allows an external microcontroller or microprocessor
to individually poll certain bits without disturbing the other bits in the register. This operation is key in controlling the
DS21448 with higher-order software languages.
23 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
The bits in the SR register have the unique ability to initiate a hardware interrupt through the
INT output pin. Each
of the alarms and events in the SR can be either masked or unmasked from the interrupt pin through the interrupt
mask register (IMR). The interrupts caused by the RCL, RUA1, and LOTC bits in the SR act differently than the
interrupts caused by the other status bits in the SR. The RCL, RUA1, and LOTC bits forces the
whenever they change state (i.e., go active or inactive). The
INT pin is allowed to return high (if no other interrupts
INT pin low
are present) when the user reads the alarm bit that caused the interrupt to occur, even if the alarm is still present.
The other status bits in the SR can force the
INT pin low when they are set. The INT pin is allowed to return high (if
no other interrupts are present) when the user reads the event bit that caused the interrupt to occur.
The host can quickly determine which of the four LIU channels is generating an interrupt by reading one of the
unused addresses in the 16h–1Fh range in any LIU channel. See the following LIU channel interrupt status
description for additional information.
LIU Channel Interrupt Status
(MSB)
— — — — LIU4 LIU3 LIU2 LIU1
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
N/A 7 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
N/A 6 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
N/A 5 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
N/A 4 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
LIU4 3
LIU3 2
LIU2 1
LIU1 0
LIU4 Status Register. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the status register (SR) in channel 4 is
asserting an interrupt.
LIU3 Status Register. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the status register (SR) in channel 3 is
asserting an interrupt.
LIU2 Status Register. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the status register (SR) in channel 2 is
asserting an interrupt.
LIU1 Status Register. A 1 in this bit position indicates that the status register (SR) in channel 1 is
asserting an interrupt.
(LSB)
SR (06H): Status Register
(MSB)
LUP LDN LOTC RUA1 RCL TCLE TOCD PRBSD
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
LUP
(Latched)
LDN
(Latched)
LOTC
(Real Time)
RUA1
(Latched)
RCL
(Latched)
TCLE
(Real Time)
TOCD
(Real Time)
PRBSD
(Real Time)
SR.7
SR.6
SR.5
SR.4
SR.3
SR.2
SR.1
SR.0
Loop-Up Code Detected. This bit is set when the loop-up code defined in registers RUPCD1 and
RUPCD2 is being received. See Section 6.1
Loop-Down Code Detected. This bit is set when the loop-down code defined in registers
RDNCD1 and RDNCD2 is being received. See Section 6.1
Loss-of-Transmit Clock. This bit is set when the TCLK pin has not transitioned for 5ms (±2ms),
forcing the LOTC pin high.
Receive Unframed All Ones. This bit is set when an unframed all-ones code is received at RRING
and RTIP (Table 5-A
Receive Carrier Loss. This bit is set when an RCL condition exists at RRING and RTIP. See
(Table 5-A
Transmit Current-Limit Exceeded. This bit is set when the 50mA (RMS) current limiter is activated
whether or not the current limiter is enabled.
Transmit Open-Circuit Detect. This bit is set when the device detects that the TTIP and TRING
outputs are open circuited.
PRBS Detect. This bit is set when the receive side detects a 2
pseudorandom bit sequence (PRBS).
) for details.
).
for details.
for details.
15
- 1 (E1) or a QRSS (T1)
(LSB)
24 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 5-A. Received Alarm Criteria
ALARM E1/T1 SET CRITERIA CLEAR CRITERIA
RUA1 E1 Fewer than two 0s in two frames (512 bits) More than two 0s in two frames (512 bits)
RUA1 T1
RCL
(Note 1)
RCL
(Note 1)
Note 1: RCL is also known as a loss of signal (LOS) or Red Alarm in T1.
Note 2: See CCR1.5 for details.
E1
T1
Over a 3ms window, five or fewer 0s are
received.
255 (or 2048) consecutive 0s received
(G.775) (Note 2)
192 (or 1544) consecutive 0s are received
(Note 2)
IMR (07H): Interrupt Mask Register
(MSB)
LUP LDN LOTC RUA1 RCL TCLE TOCD PRBSD
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
LUP IMR.7
LDN IMR.6
LOTC IMR.5
RUA1 IMR.4
RCL IMR.3
TCLE IMR.2
TOCD IMR.1
PRBSD IMR.0
Loop-Up Code Detected
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Loop-Down Code Detected
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Loss-of-Transmit Clock
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Unframed All Ones
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Carrier Loss
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Transmit Current-Limiter Exceeded
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Transmit Open-Circuit Detect
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
PRBS Detection
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Over a 3ms window, six or more 0s are
received.
In 255-bit times, at least 32 1s are
received.
14 or more 1s out of 112 possible bit
positions are received, starting with the
first 1 received.
(LSB)
25 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
RIR1 (08H): Receive Information Register 1
(MSB)
ZD 16ZD HBD RCLC RUA1C JALT — —
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
ZD
(Latched)
16ZD
(latched)
HBD
(Latched)
RCLC
(Latched)
RUA1C
(Latched)
JALT
(Latched)
N/A RIR1.1 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
N/A RIR1.0 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
Zero Detect. This bit is set when a string of at least four (ETS = 0) or eight (ETS = 1)
RIR1.7
RIR1.6
RIR1.5
RIR1.4
RIR1.3
RIR1.2
consecutive 0s (regardless of the length of the string) have been received. This bit is cleared
when read.
16 Zero Detect. This is set when at least 16 consecutive 0s (regardless of the length of the
string) have been received. This bit is cleared when read.
HDB3/B8ZS Word Detect. This is set when an HDB3 (ETS = 0) or B8ZS (ETS = 1) codeword
is detected independently of the receive HDB3/B8ZS mode (CCR4.6) being enabled. This bit
is cleared when read. It is useful for automatically setting the line coding.
RCL Clear. Set when the RCL alarm has met the clear criteria defined in Table 5-A
is cleared when read.
Receive Unframed All-Ones Clear. This bit is set when the unframed all-ones signal is no
longer detected. This bit is cleared when read (Table 5-A
Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip. This bit is set when the jitter attenuator FIFO reaches within 4 bits
of its useful limit. This bit is cleared when read and is useful for debugging jitter attenuation
operation.
).
(LSB)
. This bit
RIR2 (09H): Receive Information Register 2
(MSB)
RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0 — — ARLB SEC
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
RL3
(Real Time)
RL2
(Real Time)
RL1
(Real Time)
RL0
(Real Time)
N/A RIR2.3 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
N/A RIR2.2 Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
ARLB
(Real Time)
SEC
(Latched)
RIR2.7 Receive Level Bit 3 (Table 5-B
RIR2.6
RIR2.5 Receive Level Bit 1 (Table 5-B
RIR2.4
RIR2.1
RIR2.0
Receive Level Bit 2
Receive Level Bit 0
Automatic Remote Loopback Detected. This bit is set to 1 when the automatic remote
loopback circuitry has detected the presence of a loop-up code for 5 seconds. It remains set
until the automatic RLB circuitry has detected the loop-down code for 5 seconds. See
Section 11
disabled (CCR6.5 = 0).
One-Second Timer. This bit is set to 1 on one-second boundaries as timed by the device,
based on the RCLK. It is cleared when read.
for more details. This bit is forced low when the automatic RLB circuitry is
(Table 5-B)
(Table 5-B)
)
)
(LSB)
26 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 5-B. Receive Level Indication
RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0 RECEIVE LEVEL (dB)
0 0 0 0 Greater than -2.5
0 0 0 1 -2.5 to -5.0
0 0 1 0 -5.0 to -7.5
0 0 1 1 -7.5 to -10.0
0 1 0 0 -10.0 to -12.5
0 1 0 1 -12.5 to -15.0
0 1 1 0 -15.0 to -17.5
0 1 1 1 -17.5 to -20.0
1 0 0 0 -20.0 to -22.5
1 0 0 1 -22.5 to -25.0
1 0 1 0 -25.0 to -27.5
1 0 1 1 -27.5 to -30.0
1 1 0 0 -30.0 to -32.5
1 1 0 1 -32.5 to -35.0
1 1 1 0 -35.0 to -37.5
1 1 1 1 -37.5 to -40.0
6. DIAGNOSTICS
6.1 In-Band Loop-Code Generation and Detection
The DS21448 can generate and detect a repeating bit pattern from 1 to 8 or 16 bits in length. To transmit a pattern,
the user loads the pattern into the transmit code definition (TCD1 and TCD2) registers and selects the proper
length of the pattern by setting the TC0 and TC1 bits in the in-band code control (IBCC) register. When generating
a 1-, 2-, 4-, 8-, or 16-bit pattern, the transmit code registers (TCD1 and TCD2) must be filled with the proper code.
Generation of a 1-, 3-, 5-, or 7-bit pattern only requires TCD1 to be filled. Once this is accomplished, the pattern is
transmitted, as long as the TLCE control bit (CCR3.3) is enabled. For example, if the user wished to transmit the
standard loop-up code for CSUs, which is a repeating pattern of ...10000100001..., then 80h would be loaded into
TCD1, and the length would set using TC1 and TC0 in the IBCC register to 5 bits.
The DS21448 can detect two separate repeating patterns to allow for a loop-up code and a loop-down code to be
detected. The user programs the codes in the receive-up code definition (RUPCD1 and RUPCD2) registers and the
receive-down code definition (RDNCD1 and RDNCD2) registers; the length of each pattern is selected through the
IBCC register. The DS21448 detects repeating pattern codes with bit-error rates as high as 1 x 10
detector has a nominal integration period of 48ms, so after approximately 48ms of receiving either code, the proper
status bit (LUP at SR.7 and LDN at SR.6) is set to 1. Normally codes are sent for a period of 5 seconds. It is
recommended that the software poll the DS21448 every 100ms to 1000ms until 5 seconds has elapsed to ensure
the code is continuously present.
-2
. The code
27 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
IBCC (0AH): In-Band Code Control Register
(MSB)
TC1 TC0 RUP2 RUP1 RUP0 RDN2 RDN1 RDN0
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
TC1 IBCC.7 Transmit Code Length Definition Bit 1 (Table 6-A)
TC0 IBCC.6 Transmit Code Length Definition Bit 0. (Table 6-A)
RUP2 IBCC.5 Receive Up Code Length Definition Bit 2 (Table 6-B)
RUP1 IBCC.4 Receive-Up Code Length Definition Bit 1 (Table 6-B)
RUP0 IBCC.3 Receive-Up Code Length Definition Bit 0 (Table 6-B)
RDN2 IBCC.2 Receive-Down Code Length Definition Bit 2 (Table 6-B)
RDN1 IBCC.1 Receive-Down Code Length Definition Bit 1 (Table 6-B)
RDN0 IBCC.0 Receive-Down Code Length Definition Bit 0 (Table 6-B)
(LSB)
28 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 6-A. Transmit Code Length
TC1 TC0
0 0 5
0 1 6/3
1 0 7
1 1 16/8/4/2/1
LENGTH SELECTED
(BITS)
Table 6-B. Receive Code Length
RUP2/RDN2 RUP1/RDN1 RUP0/RDN0
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 2
0 1 0 3
0 1 1 4
1 0 0 5
1 0 1 6
1 1 0 7
1 1 1 16/8
TCD1 (0BH): Transmit Code Definition Register 1
(MSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
C7 TCD1.7 Transmit Code Definition Bit 7. First bit of the repeating pattern.
C6 TCD1.6 Transmit Code Definition Bit 6
C5 TCD1.5 Transmit Code Definition Bit 5
C4 TCD1.4 Transmit Code Definition Bit 4
C3 TCD1.3 Transmit Code Definition Bit 3
C2 TCD1.2 Transmit Code Definition Bit 2. A don’t care if a 5-bit length is selected.
C1 TCD1.1 Transmit Code Definition Bit 1. A don’t care if a 5-bit or 6-bit length is selected.
C0 TCD1.0 Transmit Code Definition Bit 0. A don’t care if a 5-, 6-, or 7-bit length is selected.
TCD2 (0CH): Transmit Code Definition Register 2
(MSB)
C15 C14 C13 C12 C11 C10 C9 C8
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
C15 TCD2.7 Transmit Code Definition Bit 15
C14 TCD2.6 Transmit Code Definition Bit 14
C13 TCD2.5 Transmit Code Definition Bit 13
C12 TCD2.4 Transmit Code Definition Bit 12
C11 TCD2.3 Transmit Code Definition Bit 11
C10 TCD2.2 Transmit Code Definition Bit 10
C9 TCD2.1 Transmit Code Definition Bit 9
C8 TCD2.0 Transmit Code Definition Bit 8
LENGTH SELECTED
(BITS)
(LSB)
(LSB)
29 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
RUPCD1 (0DH): Receive-Up Code Definition Register 1
(MSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
C7 RUPCD1.7 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 7. First bit of the repeating pattern.
C6 RUPCD1.6 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 6. A don’t care if a 1-bit length is selected.
C5 RUPCD1.5 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 5. A don’t care if a 1-bit or 2-bit length is selected.
C4 RUPCD1.4 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 4. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 3-bit length is selected.
C3 RUPCD1.3 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 3. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 4-bit length is selected.
C2 RUPCD1.2 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 2. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 5-bit length is selected.
C1 RUPCD1.1 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 1. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 6-bit length is selected.
C0 RUPCD1.0 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 0. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 7-bit length is selected.
(LSB)
RUPCD2 (0EH): Receive-Up Code Definition Register 2
(MSB)
C15 C14 C13 C12 C11 C10 C9 C8
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
C15 RUPCD2.7 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 15
C14 RUPCD2.6 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 14
C13 RUPCD2.5 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 13
C12 RUPCD2.4 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 12
C11 RUPCD2.3 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 11
C10 RUPCD2.2 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 10
C9 RUPCD2.1 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 9
C8 RUPCD2.0 Receive-Up Code Definition Bit 8
(LSB)
RDNCD1 (0FH): Receive-Down Code Definition Register 1
(MSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
C7 RDNCD1.7 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 7. First bit of the repeating pattern.
C6 RDNCD1.6 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 6. A don’t care if a 1-bit length is selected.
C5 RDNCD1.5 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 5. A don’t care if a 1-bit or 2-bit length is selected.
C4 RDNCD1.4 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 4. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 3-bit length is selected.
C3 RDNCD1.3 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 3. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 4-bit length is selected.
C2 RDNCD1.2 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 2. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 5-bit length is selected.
C1 RDNCD1.1 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 1. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 6-bit length is selected.
C0 RDNCD1.0
Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 0. A don’t care if a 1-bit to 7-bit length is selected.
(LSB)
RDNCD2 (10H): Receive-Down Code Definition Register 2
(MSB)
C15 C14 C13 C12 C11 C10 C9 C8
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
C15 RDNCD2.7 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 15
C14 RDNCD2.6 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 14
C13 RDNCD2.5 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 13
C12 RDNCD2.4 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 12
C11 RDNCD2.3 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 11
C10 RDNCD2.2 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 10
C9 RDNCD2.1 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 9
C8 RDNCD2.0 Receive-Down Code Definition Bit 8
(LSB)
30 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
6.2 Loopbacks
6.2.1 Remote Loopback (RLB)
When RLB (CCR6.6) is enabled, the DS21448 is placed into remote loopback. In this loopback, data from the
clock/data recovery state machine is looped back to the transmit path, passing through the jitter attenuator if it is
enabled. The data at the RPOS and RNEG pins is valid, while data presented at TPOS and TNEG is ignored. See
Figure 1-1
If the automatic RLB enable (CCR6.5) is set to 1, the DS21448 automatically goes into remote loopback when it
detects the loop-up code programmed in the receive-up code definition registers (RUPCD1 and RUPCD2) for a
minimum of 5 seconds. When the DS21448 detects the loop-down code programmed in the receive loop-down
code definition registers (RDNCD1 and RDNCD2) for a minimum of 5 seconds, the DS21448 comes out of remote
loopback. Setting ARLBE to 0 can also disable the ARLB.
for more details.
6.2.2 Local Loopback (LLB)
When LLB (CCR6.7) is set to 1, the DS21448 is placed into local loopback. In this loopback, data on the transmit
side is transmitted as normal. TCLK and TPOS/TNEG pass through the jitter attenuator (if enabled) and are output
at RCLK and RPOS/RNEG. Incoming data from the line at RTIP and RRING is ignored. If transmit unframed all
ones (CCR3.7) is set to 1 while in LLB, TTIP and TRING transmit all ones while TCLK and TPOS/TNEG are looped
back to RCLK and RPOS/RNEG. See Figure 1-1
for more details.
6.2.3 Analog Loopback (LLB)
Setting ALB (CCR6.4) to 1 puts the DS21448 in analog loopback. Signals at TTIP and TRING are internally
connected to RTIP and RRING. The incoming signals at RTIP and RRING are ignored. The signals at TTIP and
TRING are transmitted as normal. See Figure 1-1
for more details.
6.2.4 Dual Loopback (DLB)
Setting CCR6.7 and CCR6.6 (LLB and RLB, respectively) to 1 puts the DS21448 into dual loopback operation. The
TCLK and TPOS/TNEG signals are looped back through the jitter attenuator (if enabled) and output at RCLK and
RPOS/RNEG. Clock and data recovered from RTIP and RRING are looped back to the transmit side and output at
TTIP and TRING. This mode of operation is not available when implementing hardware operation. See Figure 1-1
more details.
6.3 PRBS Generation and Detection
Setting TPRBSE (CCR3.4) = 1 enables the DS21448 to transmit a 215 - 1 (E1) or a QRSS (T1) PRBS, depending
on the ETS bit setting in CCR1.7. The DS21448’s receive side always searches for these PRBS patterns
independently of CCR3.4. The PRBS bit-error output (PBEO) remains high until the receiver has synchronized to
one of the two patterns (64 bits received without an error), at which time PBEO goes low, and the PRBSD bit in the
SR is set. Once synchronized, any bit errors received cause a positive-going pulse at PBEO, synchronous with
RCLK. This output can be used with external circuitry track bit-error rates during the PRBS testing. Setting CCR6.2
(ECRS2) = 1 allows the PRBS errors to be accumulated in the 16-bit counter in registers ECR1 and ECR2. The
PRBS synchronizer remains in sync until it experiences six bit errors or more within a 64-bit span. Both PRBS
patterns comply with the ITU-T O.151 specifications.
6.4 Error Counter
Error count register 1 (ECR1) is the most significant word and ECR2 is the least significant word of a userselectable 16-bit counter that records incoming errors, including BPVs, code violations (CVs), excessive zero
violations (EXZs), and/or PRBS errors. See Table 6-C
, Table 6-D, and Figure 1-2 for details.
31 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 6-C. Definition of Received Errors
ERROR E1 OR T1 DEFINITION OF RECEIVED ERRORS
BPV E1/T1
CV E1
EXZ E1 When four or more consecutive zeros are detected.
EXZ T1
PRBS E1/T1 A bit error in a received PRBS pattern. See Section 6.3 for details. ITU-T O.151.
Two consecutive marks with the same polarity. Ignores BPVs because of HDB3 and B8ZS zero
suppression when CCR2.3 = 0. Typically used with AMI coding (CCR2.3 = 1). ITU-T O.161.
When HDB3 is enabled (CCR2.3 = 0) and the receiver detects two consecutive BPVs with the same
polarity. ITU-T O.161.
When receiving AMI-coded signals (CCR2.3 = 1), detection of 16 or more 0s or a BPV. ANSI T1.403
1999.
When receiving B8ZS-coded signals (CCR2.3 = 0), detection of eight or more 0s or a BPV. ANSI
T1.403 1999.
Table 6-D. Function of ECRS Bits and RNEG Pin
E1 or T1
(CCR1.7)
0 0 0 0 X CVs
0 0 0 1 X BPVs (HDB3 codewords not counted)
0 0 1 0 X CVs + EXZs
0 0 1 1 X BPVs + EXZs
1 0 X 0 0 BPVs (B8ZS codewords not counted)
1 0 X 1 0 BPVs + 8 EXZs
1 0 X 0 1 BPVs
1 0 X 1 1 BPVs + 16 EXZs
X 1 X X X PRBS Errors (Note 2)
Note 1: RNEG outputs error data only when in NRZ mode (CCR1.6 = 1).
Note 2: PRBS errors are always output at PBEO, independent of ECR control bits and NRZ mode, and are not present at RNEG.
ECRS2
(CCR6.2)
ECRS1
(CCR6.1)
ECRS0
(CCR6.0)
RHBE
(CCR2.3)
FUNCTION OF ECR COUNTERS/RNEG
(Note 1)
6.5 Error Counter Update
A 0-to-1 transition of the ECUE (CCR1.4) control bit updates the ECR registers with the current values and resets
the counters. ECUE must be set back to 0 and another 0-to-1 transition must occur for subsequent reads/resets of
the ECR registers. Note that the DS21448 can report errors at RNEG when in NRZ mode (CCR1.6 = 1) by
outputting a pulse for each error occurrence. The counter saturates at 65,535 and does not roll over.
ECR1 (11H): Upper Error Count Register 1/ECR2 (12H): Lower Error Count Register 2
(MSB)
E15 E14 E13 E12 E11 E10 E9 E8 ECR1
E7 E6 E5 E4 E3 E2 E1 E0 ECR2
NAME POSITION FUNCTION
E15 ECR1.7 MSB of the 16-bit error count.
E0 ECR2.0 LSB of the 16-bit error count.
(LSB)
6.6 Error Insertion
When IBPV (CCR3.1) is transitioned from 0 to 1, the device waits for the next occurrence of three consecutive 1s
to insert a BPV. IBPV must be cleared and set again for another BPV error insertion. See Figure 1-3
the insertion of the BPV into the data stream.
When IBE (CCR3.0) is transitioned from 0 to 1, the device inserts a logic error. IBE must be cleared and set again
for another logic error insertion. See Figure 1-2
and Figure 1-3 for details about the logic error insertion into the
data steam.
for details on
32 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
7. ANALOG INTERFACE
7.1 Receiver
The DS21448 contains a digital clock recovery system. The DS21448 couples to the receive E1 or T1 twisted pair
(or coaxial cable in 75W E1 applications) through a 1:1 transformer. See Table 7-C
Figure 7-1
, Figure 7-2, Figure 7-3, and Table 4-L show the receive termination requirements. The DS21448 has the
option of using internal termination resistors.
The DS21448 is designed to be fully software selectable for E1 and T1 without the need to change any external
resistors for the receive side. The receive side allows user configuration for 75W, 100W, or 120W receive
termination by setting the RT1 (CCR5.1) and RT0 (CCR5.0) bits. When using the internal termination feature, the
resistors should be 60W each. See Figure 7-1 for details. If external termination is required, RT1 and RT0 should
R
r
be set to 0, and both R
resistors (Figure 7-1) should be 37.5W, 50W, or 60W each, depending on the line
r
impedance.
The resultant E1 or T1 clock derived from the 2.048/1.544 PLL (JACLK in Figure 1-1
through another internal PLL and fed to the clock recovery system. The clock recovery system uses the clock from
the PLL circuit to form a 16-times oversampler used to recover the clock and data. This oversampling technique
offers outstanding performance to meet jitter tolerance specifications, as shown in Figure 7-7
Normally, the clock that is output at the RCLK pin is the recovered clock from the E1 AMI/HDB3 or T1 AMI/B8ZS
waveform presented at the RTIP and RRING inputs. When no signal is present at RTIP and RRING, an RCL
condition occurs, and the RCLK is derived from the JACLK source. See Figure 1-1
attenuator is placed in the receive path (as is the case in most applications), the jitter attenuator restores the RCLK
to an approximate 50% duty cycle. If the jitter attenuator is either placed in the transmit path or is disabled, the
RCLK output can exhibit slightly shorter high cycles of the clock. This is because of the highly oversampled digital
clock recovery circuitry. See the receive-side AC timing characteristics in Section 10
The receive-side circuitry also contains a clock synthesizer that outputs a user-configurable clock (up to
16.384MHz) synthesized from RCLK at BPCLK (pin 31). See Table 4-J
for details about output clock frequencies at
BPCLK. In hardware mode, BPCLK defaults to a 16.384MHz output.
The DS21448 has a bypass mode for the receive-side clock and data. This allows the BPCLK to be derived from
RCLK after the jitter attenuator, while the clock and data presented at RCLK, RPOS, and RNEG go unaltered. This
is intended for applications where the receive-side jitter attenuation is done after the LIU. Setting RJAB (CCR6.3) to
logic 1 enables the bypass. Ensure the jitter attenuator is in the receive path (CCR4.3 = 0). See Figure 1-1
details.
The DS21448 reports the signal strength at RTIP and RRING in 2.5dB increments through RL3–RL0 located in the
receive information register 2. This feature is helpful when troubleshooting line performance problems (Table 5-B
E1 and T1 monitor applications require various flat-gain settings for the receive-side circuitry. The DS21448 can be
programmed to support these applications through the monitor mode control bits MM1 and MM0. When the monitor
modes are enabled, the receiver tolerates normal line loss up to -6dB (Table 4-K
).
7.2 Transmitter
The DS21448 uses a set of laser-trimmed delay lines with a precision digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to create
the waveforms that are transmitted onto the E1 or T1 line. The waveforms meet the latest ETSI, ITU, ANSI, and
AT&T specifications. The user selects which waveform to generate by setting the ETS bit (CCR1.7) for E1 or T1
operation, then programming the L2/L1/L0 bits in common control register 4 for the appropriate application. See
Table 7-A
A 2.048MHz or 1.544MHz TTL clock is required at TCLK for transmitting data at TPOS and TNEG. ITU
specification G.703 requires ±50ppm accuracy for T1 and E1. TR62411 and ANSI specs require ±32ppm accuracy
for T1 interfaces. The clock can be sourced internally by RCLK or JACLK. See CCR1.2, CCR1.1, CCR1.0, and
Figure 1-3
and Table 7-B for the proper L2/L1/L0 settings.
for details. Because of the transmitter’s design, very little jitter (less than 0.005UI
for transformer details.
) is internally multiplied by 16
.
for more details. If the jitter
for more details.
for more
broadband from
P-P
).
33 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
10Hz to 100kHz) is added to the jitter present on TCLK. Also, the waveforms created are independent of the duty
cycle of TCLK. The transmitter couples to the E1 or T1 transmit-twisted pair (or coaxial cable in some E1
applications) through a 1:2 step-up transformer. For the device to create the proper waveforms, the transformer
used must meet the specifications listed in Table 7-C
.
The DS21448 has an automatic short-circuit limiter that limits the source current to 50mA (RMS) into a 1Ω load.
This feature can be disabled by setting the SCLD bit (CCR2.5) = 1. When the current limiter is activated, TCLE
(SR.2) is set even if the short-circuit limiter is disabled. The TPD bit (CCR4.0) powers down the transmit-line driver
and tri-states the TTIP and TRING pins. The DS21448 can also detect when the TTIP or TRING outputs are open
circuited. When an open circuit is detected, TOCD (SR.1) is set.
7.3 Jitter Attenuator
The DS21448 contains an on-board jitter attenuator that can be set to a depth of either 32 or 128 bits through the
JABDS bit (CCR4.2). The 128-bit mode is used in applications where large excursions of wander are expected.
The 32-bit mode is used in delay-sensitive applications. Figure 7-8
shows the attenuation characteristics. The jitter
attenuator can be placed in either the receive path or the transmit path by appropriately setting or clearing the JAS
bit (CCR4.3). Also, setting the DJA bit (CCR4.1) can disable the jitter attenuator (in effect, remove it). For the jitter
attenuator to operate properly, a 2.048MHz or 1.544MHz clock must be applied at MCLK. ITU specification G.703
requires ±50ppm accuracy for T1 and E1. TR62411 and ANSI specs require ±32ppm accuracy for T1 interfaces.
An on-board PLL for the jitter attenuator converts the 2.048MHz clock to a 1.544MHz rate for T1 applications.
Setting JAMUX (CCR1.3) to logic 0 bypasses this PLL. On-board circuitry adjusts either the recovered clock from
the clock/data recovery block or the clock applied at the TCLK pin to create a smooth jitter-free clock, which is used
to clock data out of the jitter attenuator FIFO. It is acceptable to provide a gapped/bursty clock at the TCLK pin if
the jitter attenuator is placed on the transmit side. If the incoming jitter exceeds either 120UI
bits) or 28UI
(buffer depth is 32 bits), the DS21448 divides the internal nominal 32.768MHz (E1) or 24.704MHz
P-P
(buffer depth is 128
P-P
(T1) clock by either 15 or 17 instead of the normal 16 to keep the buffer from overflowing. When the device divides
by either 15 or 17, it also sets the JALT bit in the receive information register 1 (RIR1).
7.4 G.703 Synchronization Signal
The DS21448 can receive a 2.048MHz square-wave synchronization clock, as specified in Section 10 of ITU
G.703. To use the DS21448 in this mode, set the receive-synchronization-clock enable (CCR5.3) = 1. The
DS21448 can also transmit the 2.048MHz square-wave synchronization clock, as specified in Section 10 of G.703.
To transmit the 2.048MHz clock, set the transmit-synchronization-clock enable (CCR5.2) = 1.
Table 7-A. Line Build-Out Select for E1 in Register CCR4 (ETS = 0)
L2 L1 L0 APPLICATION N RETURN LOSS
0 0 0
0 0 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
75W normal
120W normal
75W with high return loss
120W with high return loss
1:2 N.M. 0
1:2 N.M. 0
1:2 21dB 6.2
1:2 21dB 11.6
R
(W)
t
Table 7-B. Line Build-Out Select for T1 in Register CCR4 (ETS = 1)
L2 L1 L0 APPLICATION N RETURN LOSS
0 0 0 DSX-1 (0 to 133ft)/0dB CSU 1:2 N.M. 0
0 0 1 DSX-1 (133 to 266f) 1:2 N.M. 0
0 1 0 DSX-1 (266 to 399ft) 1:2 N.M. 0
0 1 1 DSX-1 (399 to 533ft) 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 0 DSX-1 (533 to 655ft) 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 1 -7.5dB CSU 1:2 N.M. 0
1 1 0 -15dB CSU 1:2 N.M. 0
1 1 1 -22.5dB CSU 1:2 N.M. 0
Note: See Figure 7-1, Figure 7-2, and Figure 7-3.
N.M. = Not meaningful.
(W)
R
t
34 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 7-C. Line Build-Out Select for E1 in Register CCR4 (ETS = 0) Using Alternate
Transformer Configuration
L2 L1 L0 APPLICATION N RETURN LOSS
0 0 0
0 0 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
Note: See Figure 7-4.
75W normal
120W normal
75W with high return loss
120W with high return loss
0.8:1:1CT N.M. 0
0.8:1:1CT N.M. 0
0.8:1:1CT 21dB 11.6
0.8:1:1CT 21dB 11.6
R
(W)
t
Table 7-D. Transformer Specifications (3.3V Operation)
SPECIFICATION RECOMMENDED VALUE
Turns Ratio 1:1 (receive) and 1:2 (transmit) ±2%
Primary Inductance
Leakage Inductance
Interwinding Capacitance 40pF (max)
TRANSMIT TRANSFORMER DC RESISTANCE
Primary (Device Side)
Secondary
RECEIVE TRANSFORMER DC RESISTANCE
Primary (Device Side)
Secondary
600mH (min)
1.0mH (max)
1.0W (max)
1.5W (max)
1.2W (max)
1.2W (max)
35 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
m
m
r
Figure 7-1. Basic Interface
TRANSMIT LINE
2:1
(LARGER WINDING
TOWARD THE NETWORK)
R
t
1.0mF
(NONPOLARIZED)
R
t
TTIP
TRING
Dallas
Semiconducto
DS21448
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
0.1
0.01mF 0.01mF
RECEIVE LINE
1:1
R
RTIP
RRING
R
r
r
0.1mF
V
SS
MCLK
2.048MHz
(THIS CAN ALSO BE 1.544MHz
FOR T1 ONLY OPERATION)
NOTE 1: ALL RESISTOR VALUES ARE ±1%.
NOTE 2: IN E1 APPLICATIONS, THE R
(Table 7-A
NOTE 3: THE RR RESISTORS SHOULD EACH BE SET TO 60W IF THE INTERNAL RECEIVE-SIDE TERMINATION FEATURE IS ENABLED. WHEN THIS
FEATURE IS DISABLED, R
NOTE 4: SEE Table 7-A
). NO RETURN LOSS IS REQUIRED FOR T1 APPLICATIONS.
AND Table 7-B FOR THE APPROPRIATE TRANSMIT TRANSFORMER TURNS RATIO (N).
RESISTORS ARE USED TO INCREASE THE TRANSMITTER RETURN LOSS
T
= 37.5W FOR 75W OR 60W FOR 120W E1 SYSTEMS, OR 50W FOR 100W T1 LINES.
R
V
DD
F
10
F0.1mF
+
68mF
36 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
r
m
m
Figure 7-2. Protected Interface Using Internal Receive Termination
S
S
60
R
t
R
t
1.0mF
(NONPOLARIZED)
60
0.1mF
TTIP
TRING
Semiconducto
DS21448
RTIP
RRING
Dallas
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
MCLK
TRANSMIT
LINE
RECEIVE
LINE
NOTE 1: ALL RESISTOR VALUES ARE ±1%.
NOTE 2: S IS A SIDACTOR.
NOTE 3: THE FUSES ARE OPTIONAL TO PREVENT AC POWER LINE CROSSES FROM COMPROMISING THE TRANSFORMERS.
NOTE 4: THE R
NOTE 5: THE 68mF IS USED TO KEEP THE LOCAL POWER PLANE POTENTIAL WITHIN TOLERANCE DURING A SURGE.
NOTE 6: REFER TO APPLICATION NOTE 324 FOR SIDACTOR AND FUSE DETAILS.
FUSE
S
FUSE
(LARGER WINDING TOWARD
FUSE
S
FUSE
RESISTORS ARE USED TO INCREASE THE TRANSMITTER RETURN LOSS (Table 7-A). NO RETURN LOSS IS REQUIRED
T
FOR T1 APPLICATIONS.
S
S
2:1
THE NETWORK)
S
S
1:1
V
DD
F
0.1
0.01mF 0.01mF
F0.1mF
10
2.048MHz
(THIS CAN ALSO BE 1.544MHz
FOR T1 ONLY OPERATION)
+
68mF
37 of 60
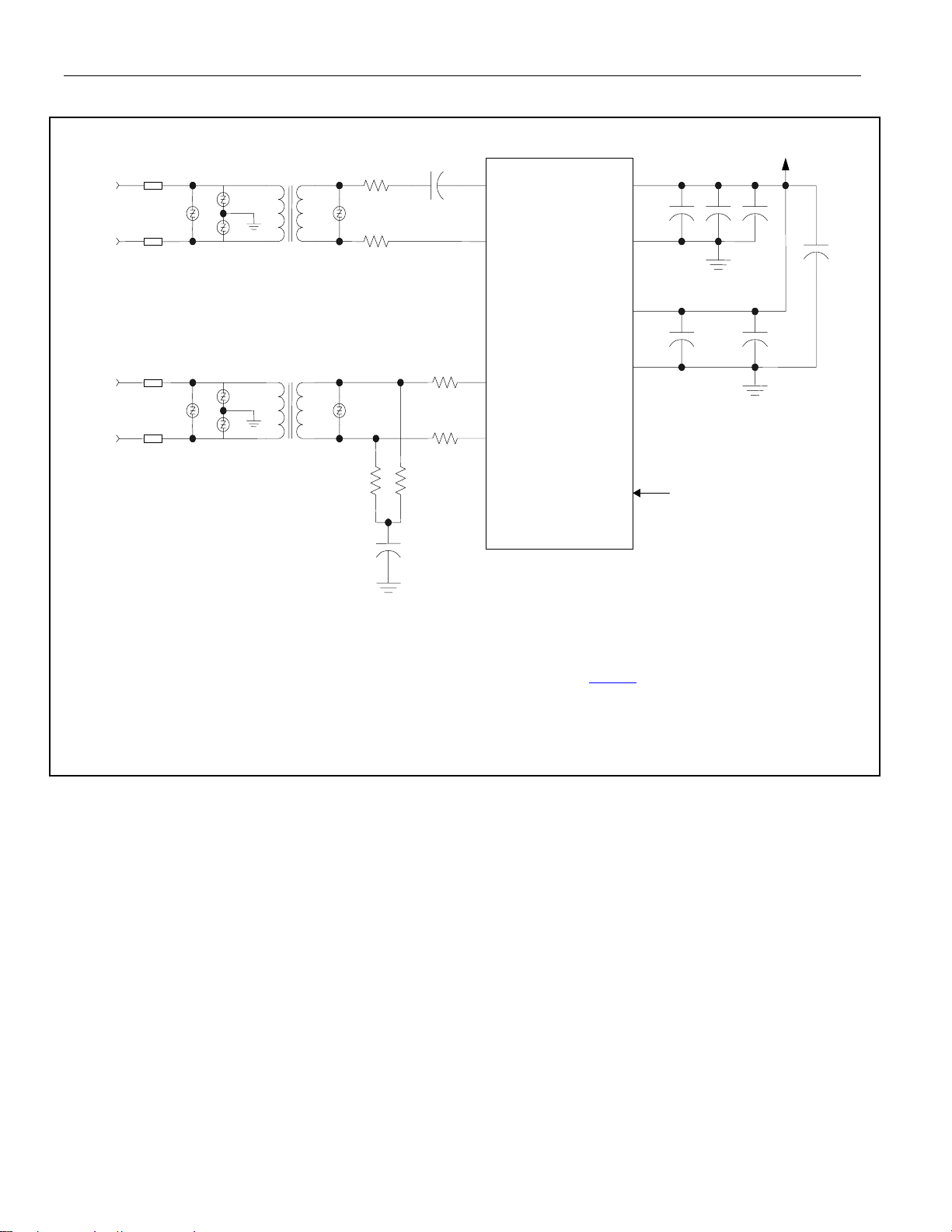
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
r
m
m
m
Figure 7-3. Protected Interface Using External Receive Termination
TRANSMIT
LINE
FUSE
S
FUSE
S
S
2:1
(LARGER WINDING TOWARD
THE NETWORK)
RECEIVE
LINE
FUSE
S
FUSE
S
S
1:1
NOTE 1: ALL RESISTOR VALUES ARE ±1%.
NOTE 2: S IS A SIDACTOR.
NOTE 3: THE FUSES ARE OPTIONAL TO PREVENT AC POWER LINE CROSSES FROM COMPROMISING THE TRANSFORMERS.
NOTE 4: R
NOTE 5: THE R
NOTE 6: THE 68mF IS USED TO KEEP THE LOCAL POWER PLANE POTENTIAL WITHIN TOLERANCE DURING A SURGE.
NOTE 7: REFER TO APPLICATION NOTE 324 FOR SIDACTOR AND FUSE DETAILS.
= 37.5W FOR 75W OR 60W FOR 120W E1 SYSTEMS, OR 50W FOR 100W T1 LINES.
r
RESISTORS ARE USED TO INCREASE THE TRANSMITTER RETURN LOSS (Table 7-A). NO RETURN LOSS IS REQUIRED FOR
T
T1 APPLICATIONS.
S
S
R
t
R
t
R
r
1.0mF
(NONPOLARIZED)
470
470
R
r
0.1mF
TTIP
TRING
Dallas
Semiconducto
DS21448
RTIP
RRING
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
MCLK
0.01mF 0.01mF
V
DD
0.1
F
10
F0.1mF
2.048MHz
(THIS CAN ALSO BE 1.544MHz
FOR T1 ONLY OPERATION)
+
68
F
38 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Figure 7-4. Dual Connector-Protected Interface Using Receive Termination
FUSE
0.22mF
0.8:1:1CT
UNBALANCED
LINE (75W)
BALANCED LINE
(100W/120W)
UNBALANCED
LINE (75W)
BALANCED LINE
(100W/120W)
FUSE
FUSE
FUSE
51.1
FUSE
FUSE
S
L1
S
S
S
0.22mF
1.6:1
0.22mF
2:1
0.8:1:1CT
V
TTIP
R
1.0mF
S
t
TRING
R
t
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
0.1mF
0.01mF 0.01mF
10mF0.1mF
DD
+
68mF
RTIP
V
S
0.8:1
SS
Dallas
Semiconductor
S
L1
0.22mF
S
S
1:1
S
DS21448
MCLK
2.048MHz (THIS CAN ALSO
BE 1.544MHz FOR T1 ONLY
OPERATION)
RRING
60 60
0.1mF
NOTE 1: REFER TO APPLICATION NOTE 384 FOR A COMPLETE DISCUSSION OF THIS CIRCUIT.
NOTE 2: ALL RESISTOR VALUES ARE ±1%.
NOTE 3: THE FUSES ARE OPTIONAL TO PREVENT AC POWER LINE CROSSES FROM COMPROMISING THE TRANSFORMERS.
NOTE 4: S IS A SIDACTOR.
NOTE 5: THE R
NOTE 6: THE 68mF IS USED TO KEEP THE LOCAL POWER PLANE POTENTIAL WITHIN TOLERANCE DURING A SURGE.
RESISTORS ARE USED TO INCREASE THE TRANSMITTER RETURN LOSS (Table 7-C). NO RETURN LOSS IS REQUIRED
T
FOR T1 APPLICATIONS.
39 of 60

Figure 7-5. E1 Transmit Pulse Template
1.2
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
1.1
269ns
1.0
0.9
0.8
in 120Ω SYSTEMS, 1.0 ON
PEAK
)
PEAK
0.7
0.6
194ns
G.703
TEMPLATE
0.5
0.4
219ns
0.3
SCALED AMPLITUDE
THE SCALE = 3.00V
0.2
0.1
0
-0.1
-0.2
(IN 75W SYSTEMS, 1.0 ON THE SCALE = 2.37V
0
50 100 150 200 250 -50-100-150 -200 -250
TIME (ns)
40 of 60

Figure 7-6. T1 Transmit Pulse Template
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
NORMALIZED AMPLITUDE
-0.1
T1.102/87, T1.403,
-0.2
CB 119 (OCT ‘79), AND
I.431 TEMPLATE
-0.3
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
MAXIMUM CURVE
UI TimeAmp.
-500
-0.77
-255
-0.39
-175
-0.27
-175
-0.27
-75
-0.12
0
0.00
175
0.27
225
0.35
600
0.93
750
1.16
0.05
0.05
0.80
1.15
1.15
1.05
1.05
-0.07
0.05
0.05
MINIMUM CURVE
UI Time Amp.
-500
-0.77
-0.23
-0.23
-0.15
0.00
0.15
0.23
0.23
0.46
0.66
0.93
1.16
-150
-150
-100
0
100
150
150
300
430
600
750
-0.05
-0.05
0.50
0.95
0.95
0.90
0.50
-0.45
-0.45
-0.20
-0.05
-0.05
-0.4
-0.5
-500 -300 -100 0 300 500 700 -400 -200 200 400 600 100
TIME (ns)
41 of 60

Figure 7-7. Jitter Tolerance
1k
100
)
P-P
10
1
UNIT INTERVALS (UI
0.1
1
Figure 7-8. Jitter Attenuation
0
-20
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
TR 62411 (DEC ‘90)
ITU-T G.823
10 100 1k 10k 100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TBR12
PROHIBITED
AREA
CURVE A
DS21448 TOLERANCE
ITU G.7XX
PROHIBITED AREA
T1E1
-40
JITTER ATTENUATION (dB)
-60
10 100 1k 10k
1
CURVE B
FREQUENCY (Hz)
42 of 60
TR 62411 (DEC 90)
PROHIBITED AREA
100k

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
8. JTAG BOUNDARY SCAN ARCHITECTURE AND TEST ACCESS PORT
The DS21448 IEEE 1149.1 design supports the standard instruction codes SAMPLE/PRELOAD, BYPASS, and
EXTEST. Optional public instructions included are HIGHZ, CLAMP, and IDCODE (Table 8-A
contains the following items, which meet the requirements set by the IEEE 1149.1 Standard Test Access Port
(TAP) and Boundary Scan Architecture:
Test Access Port
TAP Controller
Instruction Register
The TAP has the necessary interface pins JTRST, JTCLK, JTMS, JTDI, and JTDO. See the pin descriptions in
Section 1
1149.1-1990, IEEE 1149.1a-1993, and IEEE 1149.1b-1994.
for details. Details on Boundary Scan Architecture and the Test Access Port can be found in IEEE
Bypass Register
Boundary Scan Register
Device Identification Register
Figure 8-1. JTAG Block Diagram
VDD
10kW 10kW 10kW
JTDI JTMS JTCLK
V
DD
BOUNDRY SCAN
REGISTER
IDENTIFICATION
REGISTER
BYPASS
REGISTER
INSTRUCTION
REGISTER
TEST ACCESS PORT
CONTROLLER
MUX
SELECT
OUTPUT ENABLE
V
DD
JTRST JTDO
8.1 JTAG TAP Controller State Machine
This section covers the operation of the TAP controller state machine. See Figure 8-2 for details on each of the
states described below. The TAP controller is a finite state machine that responds to the logic level at JTMS on the
rising edge of JTCLK (Table 8-B
Test-Logic-Reset. Upon power-up, the TAP controller is in test-logic-reset state. The instruction register contains
the IDCODE instruction. All system logic of the device operates normally.
Run-Test-Idle. The run-test-idle is used between scan operations or during specific tests. The instruction register
and test registers remain idle.
Select-DR-Scan. All test registers retain their previous state. With JTMS LOW, a rising edge of JTCLK moves the
controller into the capture-DR state and initiates a scan sequence. JTMS HIGH during a rising edge on JTCLK
moves the controller to the select-IR-scan state.
).
43 of 60
). The DS21448

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Figure 8-2. TAP Controller State Diagram
Capture-DR. Data can be parallel-loaded into the test data registers selected by the current instruction. If the
instruction does not call for a parallel load or the selected register does not allow parallel loads, the test register
remains at its current value. On the rising edge of JTCLK, the controller goes to the shift-DR state if JTMS is LOW,
or it goes to the exit1-DR state if JTMS is HIGH.
Shift-DR. The test data register selected by the current instruction is connected between JTDI and JTDO, and
shifts data one stage toward its serial output on each rising edge of JTCLK. If a test register selected by the current
instruction is not placed in the serial path, it maintains its previous state.
Exit1-DR. While in this state, a rising edge on JTCLK puts the controller in the update-DR state, which terminates
the scanning process, if JTMS is HIGH. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW puts the controller in the pauseDR state.
Pause-DR. Shifting of the test registers is halted while in this state. All test registers selected by the current
instruction retain their previous state. The controller remains in this state while JTMS is LOW. A rising edge on
JTCLK with JTMS HIGH puts the controller in the exit2-DR state.
Exit2-DR. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS HIGH while in this state puts the controller in the update-DR state
and terminates the scanning process. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW enters the shift-DR state.
Update-DR. A falling edge on JTCLK while in the update-DR state latches the data from the shift register path of
the test registers into the data output latches. This prevents changes at the parallel output due to changes in the
shift register.
Test Logic
1
Reset
0
0
Run Test/
Idle
1
Select
DR-Scan
11
Select
IR-Scan
00
Capture DR
Shift DR
Exit DR
Pause DR
0
Exit2 DR
0
1
0
1
11
Capture IR
0
0
Shift IR
0
1
1
Exit IR
1
0
Pause IR
00
1
0
Exit2 IR
11
Update DR
11
Update IR
00
44 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Select-IR-Scan. All test registers retain their previous state. The instruction register remains unchanged during this
state. With JTMS LOW, a rising edge on JTCLK moves the controller into the capture-IR state and initiates a scan
sequence for the instruction register. JTMS HIGH during a rising edge on JTCLK puts the controller back into the
test-logic-reset state.
Capture-IR. The capture-IR state is used to load the shift register in the instruction register with a fixed value. This
value is loaded on the rising edge of JTCLK. If JTMS is HIGH on the rising edge of JTCLK, the controller enters the
exit1-IR state. If JTMS is LOW on the rising edge of JTCLK, the controller enters the shift-IR state.
Shift-IR. In this state, the shift register in the instruction register is connected between JTDI and JTDO and shifts
data one stage for every rising edge of JTCLK toward the serial output. The parallel register and all test registers
remain at their previous states. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS HIGH moves the controller to the exit1-IR state.
A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW keeps the controller in the shift-IR state while moving data one stage
through the instruction shift register.
Exit1-IR. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW puts the controller in the pause-IR state. If JTMS is HIGH on the
rising edge of JTCLK, the controller enters the update-IR state and terminates the scanning process.
Pause-IR. Shifting of the instruction shift register is halted temporarily. With JTMS HIGH, a rising edge on JTCLK
puts the controller in the exit2-IR state. The controller remains in the pause-IR state if JTMS is LOW during a rising
edge on JTCLK.
Exit2-IR. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS HIGH puts the controller in the update-IR state. The controller loops
back to shift-IR if JTMS is LOW during a rising edge of JTCLK in this state.
Update-IR. The instruction code shifted into the instruction shift register is latched into the parallel output on the
falling edge of JTCLK as the controller enters this state. Once latched, this instruction becomes the current
instruction. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW puts the controller in the run-test-idle state. With JTMS HIGH,
the controller enters the select-DR-scan state.
8.2 Instruction Register
The instruction register contains a shift register, as well as a latched parallel output, and is 3 bits in length. When
the TAP controller enters the shift-IR state, the instruction shift register is connected between JTDI and JTDO.
While in the shift-IR state, a rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW shifts the data one stage toward the serial
output at JTDO. A rising edge on JTCLK in the exit1-IR state or the exit2-IR state with JTMS HIGH moves the
controller to the update-IR state. The falling edge of that same JTCLK latches the data in the instruction shift
register to the instruction parallel output. Table 8-A
shows the instructions supported by the DS21448 and its
respective operational binary codes.
Table 8-A. Instruction Codes for IEEE 1149.1 Architecture
INSTRUCTION SELECTED REGISTER INSTRUCTION CODES
SAMPLE/PRELOAD Boundary Scan 010
BYPASS Bypass 111
EXTEST Boundary Scan 000
CLAMP Bypass 011
HIGHZ Bypass 100
IDCODE Device Identification 001
SAMPLE/PRELOAD. This is a mandatory instruction for the IEEE 1149.1 specification that supports two functions.
The digital I/Os of the device can be sampled at the boundary scan register without interfering with the normal
operation of the device by using the capture-DR state. SAMPLE/PRELOAD also allows the device to shift data into
the boundary scan register through JTDI using the shift-DR state.
BYPASS. When the BYPASS instruction is latched into the parallel instruction register, JTDI connects to JTDO
through the 1-bit bypass test register. This allows data to pass from JTDI to JTDO without affecting the device’s
normal operation.
45 of 60
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
EXTEST. This allows testing of all interconnections to the device. When the EXTEST instruction is latched in the
instruction register, the following actions occur. Once enabled through the update-IR state, the parallel outputs of
all digital output pins are driven. The boundary scan register is connected between JTDI and JTDO. The captureDR samples all digital inputs into the boundary scan register.
CLAMP. All digital outputs of the device are output data from the boundary scan parallel output while connecting
the bypass register between JTDI and JTDO. The outputs do not change during the CLAMP instruction.
HIGHZ. All digital outputs of the device are placed in a high-impedance state. The BYPASS register is connected
between JTDI and JTDO.
IDCODE. When the IDCODE instruction is latched into the parallel instruction register, the identification test
register is selected. The device identification code is loaded into the identification register on the rising edge of
JTCLK following entry into the capture-DR state. Shift-DR can be used to shift the identification code out serially
through JTDO. During test-logic-reset, the identification code is forced into the instruction register’s parallel output.
The ID code always has a 1 in the LSB position. The next 11 bits identify the manufacturer’s JEDEC number and
number of continuation bytes followed by 16 bits for the device and 4 bits for the version Table 8-B
the device ID code for the SCT devices.
. Table 8-C lists
Table 8-B. ID Code Structure
MSB LSB
Version
(Contact Factory)
4 bits 16 bits 00010100001 1
Device ID JEDEC 1
Table 8-C. Device ID Codes
DEVICE 16-BIT ID
DS21448 0018
8.3 Test Registers
IEEE 1149.1 requires a minimum of two test registers—the bypass register and the boundary scan register. An
optional test register, the identification register, has been included with the DS21448 design. It is used with the
IDCODE instruction and the test-logic-reset state of the TAP controller.
Bypass Register
The bypass register is a single 1-bit shift register used with the BYPASS, CLAMP, and HIGHZ instructions that
provides a short path between JTDI and JTDO.
Identification Register
The identification register contains a 32-bit shift register and a 32-bit latched parallel output. This register is
selected during the IDCODE instruction and when the TAP controller is in the test-logic-reset state. See Table 8-B
and Table 8-C
Boundary Scan Register
The boundary scan register contains a shift register path and a latched parallel output for all control cells and digital
I/O cells, and is n bits in length. See Table 8-D
for more information about bit usage.
for all cell bit locations and definitions.
46 of 60

Table 8-D. Boundary Scan Control Bits
BIT
— A1 124 RTIP1 I
— A2 6 TTIP1 O
— A4 28 RTIP2 I
— A5 38 TTIP2 O
— A7 60 RTIP3 I
— A8 71 TTIP3 O
— A10 93 RTIP4 I
— A11 102 TTIP4 O
— B2 125 RRING1 I
— B3 9 TRING1 O
— B5 29 RRING2 I
— B6 41 TRING2 O
— B8 61 RRING3 I
— B9 74 TRING3 O
— B11 94 RRING4 I
— B12 105 TRING4 O
— D1 39 TVSS2 —
— D2 40 TVDD2 —
64 D3 57
48 D4 80 D2/AD2 I/O
46 D5 82 D0/AD0 I/O
67 D6 47 BPCLK2 O
22 D7 128 RCL/LOTC2 O
— D8 49–51 VDD3 —
— D9 52–54 VSS3 —
44 D10 84
15 D11 14 RPOS3 O
3 D12 34 TNEG3 I
17 E1 12 RPOS2 O
16 E2 13 RNEG2 O
49 E3 79 D3/AD3 I/O
— E4 19–21 VDD2 —
— E9 72 TVSS3 —
27 E10 121 PBEO3 O
63 E11 58 RCLK3 O
4 E12 33 TPOS3 I
6 F1 31 RCLK2 O
7 F2 30 TPOS2 I
47 F3 81 D1/AD1 I/O
— F4 22–24 VSS2 —
21 F9 1 RCL/LOTC3 O
65 F10 56 BPCLK3 O
14 F11 15 RNEG3 O
45 F12 83 TCLK3 I
9 G1 26 TPOS1 I
18 G2 11 RNEG1 O
31 G3 111 PBEO2 O
— G9 73 TVDD3 —
51 G11 77 D5/AD5 I/O
PIN
BGA LQFP
NAME I/O
CS2
CS3
I
I
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
PIN BIT
54
(Note 1)
56 G12 66 A0 I
42 H1 92
8 H2 27 TNEG1 I
23 H3 127 RCLK1 O
26 H4 122 BPCLK1 O
— H9 88–90 VSS4 —
52 H10 76 D6/AD6 I/O
58 H11 64 A2 I
57 H12 65 A1 I
2 J1 35 SCLK I
43 J2 91
11 J3 18
— J4 7 TVSS1 —
— J5 8 TVDD1 —
33 J6 109 MCLK I
20 J7 2 RCL/LOTC4 O
— J8 85–87 VDD4 —
50 J9 78 D4/AD4 I/O
53 J10 75 D7/AD7 I/O
60 K1 62 A4 I
41 K2 95 ALE (AS) I
1 K3 36 SDI I
19 K4 10 RPOS1 O
32 K5 110 PBEO1 O
37 K7 98 TXDIS/TEST I
25 K8 123 PBEO4 O
39
(Note 2)
38 K9 97
28 K10 114
13 K11 16 RPOS4 O
62 K12 59 TNEG4 I
59 L1 63 A3 I
0 L2 43 TCLK2 I
— L3 42 JTRST I
— L5 115–117 VDD1 —
24 L6 126 RCL/LOTC1 O
35 L7 107 BIS0 I
30 L8 112 BPCLK4 O
36 L9 106
— L10 103 TVSS4 —
40 L11 96 RCLK4 O
29 L12 113 TCLK4 I
5 M1 32 TNEG2 I
12 M2 17 TCLK1 I
— M3 48 JTMS I
— M4 118–120 VSS1 —
— M5 44 JTCLK I
BGA LQFP
— BUScntl —
—
NAME I/O
WR (R/W)
RD (DS)
CS1
INTcntl
INT
CS4
HRST
I
I
I
—
I/O
I
I
47 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
BIT
— M6 45 JTDI I
— M7 46 JTDO O
55 M8 68 BIS1 I
— M9 104 TVDD4 —
Note 1: 0 = Dn/ADn are inputs; 1 = Dn/ADn are outputs.
Note 2: 0 = INT is an input; 1 = INT is an output.
PIN
BGA LQFP
NAME I/O
10 M10 25 RNEG4 O
61 — — ADRScntl —
66 M11 55 TPOS4 I
34 M12 108 PBTS I
PIN BIT
BGA LQFP
NAME I/O
9. OPERATING PARAMETERS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Voltage on Any Pin Relative to Ground -1.0V to +6.0V
Operating Temperature for DS21448TN -40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature See IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020A Specification
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only,
and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is
not implied. Exposure to the absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device.
RECOMMENDED DC OPERATING CONDITIONS
(TA = -40°C to +85°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Logic 1 VIH 2.2 5.5 V
Logic 0 VIL -0.3 +0.8 V
Supply for 3.3V Operation VDD (Note 1) 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
CAPACITANCE
(TA = +25°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Input Capacitance CIN 5 pF
Output Capacitance C
7 pF
OUT
DC CHARACTERISTICS
(VDD = 3.3V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Input Leakage IIL (Note 2) -1.0 +1.0
Output Leakage ILO (Note 3) +1.0
Output Current (2.4V) IOH -1.0 mA
Output Current (0.4V) IOL +4.0 mA
Supply Current at 3.3V IDD (Notes 4, 5) 320 400 mA
Power Dissipation at 3.3V PDD (Notes 4, 5) 1.06 1.32 W
Note 1: Applies to VDD.
Note 2: 0.0V < V
Note 3: Applied to INT when tri-stated.
Note 4: TCLK = MCLK = 2.048MHz.
Note 5: Power dissipation with all ports active, TTIP and TRING driving a 30W load, for an all-ones data density.
< VDD.
IN
mA
mA
48 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
C
RD W
R
10. AC TIMING PARAMETERS AND DIAGRAMS
Table 10-A. AC Characteristics—Multiplexed Parallel Port (BIS0 = 0)
(VDD = 3.3V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 10-1, Figure 10-2, and Figure 10-3)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Cycle Time t
Pulse Width, DS Low or RD High
Pulse Width, DS High or RD Low
Input Rise/Fall Times tR, tF 20 ns
R/W Hold Time
R/W Setup Time Before DS High
CS Setup Time Before DS, WR, or RD Active
CS Hold Time
Read Data Hold Time t
Write Data Hold Time t
Muxed Address Valid to AS or ALE Fall t
Muxed Address Hold Time t
Delay Time DS, WR, or RD to AS or ALE Rise
Pulse Width AS or ALE High PW
Delay Time, AS or ALE to DS, WR, or RD
Output Data Delay Time from DS or RD
Data Setup Time t
Figure 10-1. Intel Bus Read Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 0)
ALE
S
AD0–AD7
t
ASD
PW
t
ASD
EL
t
ASL
PW
ASH
200 ns
CYC
100 ns
PW
EL
100 ns
PW
EH
10 ns
t
RWH
50 ns
t
RWS
t
20 ns
CS
0 ns
t
CH
10 50 ns
DHR
5 ns
DHW
15 ns
ASL
10 ns
AHL
20 ns
t
ASD
30 ns
ASH
10 ns
t
ASED
20 80 ns
t
DDR
50 ns
DSW
t
CYC
t
ASED
PW
EH
t
CS
t
AHL
t
DDR
t
CH
t
DHR
49 of 60

Figure 10-2. Intel Bus Write Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 0)
C
RD W
W C
AD0–AD7
ALE
R
S
t
ASD
t
ASD
PW
t
PW
EL
ASL
ASH
t
t
t
AHL
ASED
CS
t
CYC
Figure 10-3. Motorola Bus Timing (PBTS = 1, BIS0 = 0)
PW
ASH
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
PW
EH
t
CH
t
DHW
t
DSW
AS
DS
R/
AD0–AD7
(READ)
S
AD0–AD7
(WRITE)
PW
EL
t
ASD
t
ASL
t
ASL
t
t
AHL
AHL
PW
EH
t
CH
t
DHR
t
DHW
t
RWH
t
ASED
t
CYC
t
RWS
t
DDR
t
CS
t
DSW
50 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
WR C
R
Table 10-B. AC Characteristics—Nonmultiplexed Parallel Port (BIS0 = 1)
(VDD = 3.3V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 10-4, Figure 10-5, Figure 10-6, and Figure 10-7)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Setup Time for A0 to A4, Valid to CS
Active
Setup Time for CS Active to Either RD,
WR, or DS Active
Delay Time from Either RD or DS Active
to Data Valid
Hold Time from Either RD, WR, or DS
Inactive to
CS Inactive
Hold Time from CS Inactive to Data Bus
Tri-State
Wait Time from Either WR or DS Active to
Latch Data
Data Setup Time to Either WR or DS
Inactive
Data Hold Time from Either WR or DS
Inactive
Address Hold from Either WR or DS
Inactive
t1 0 ns
t2 0 ns
t3 75 ns
t4 0 ns
t5 5.0 20 ns
t6 75 ns
t7 10 ns
t8 10 ns
t9 10 ns
Figure 10-4. Intel Bus Read Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 1)
A0–A4
D0–D7
S
t1
0ns (MIN)
0ns (MIN)
t2 t3 t4
D
ADDRESS VALID
75ns (MAX)
DATA VALID
5ns (MIN) / 20ns (MAX)
t5
0ns (MIN)
51 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
RD CS W
W CS D
W C
D
Figure 10-5. Intel Bus Write Timing (PBTS = 0, BIS0 = 1)
A0–A4
ADDRESS VALID
D0–D7
t1
t7 t8
10ns
(MIN)
0ns (MIN)
0ns (MIN)
R
t2 t6 t4
75ns (MIN)
Figure 10-6. Motorola Bus Read Timing (PBTS = 1, BIS0 = 1)
A0–A4
ADDRESS VALID
D0–D7
5ns (MIN) / 20ns (MAX)
DATA VALID
R/
t1
0ns (MIN)
S
0ns (MIN)
t2 t3 t4
75ns (MAX)
Figure 10-7. Motorola Bus Write Timing (PBTS = 1, BIS0 = 1)
10ns
(MIN)
0ns (MIN)
t5
0ns (MIN)
A0–A4
ADDRESS VALID
D0–D7
R/
t1
0ns (MIN)
S
0ns (MIN)
t2 t6 t4
75ns (MIN)
S
52 of 60
10ns
(MIN)
t7
t8
10ns
(MIN)
0ns (MIN)

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
C
Table 10-C. AC Characteristics—Serial Port (BIS1 = 1, BIS0 = 0)
(VDD = 3.3V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 10-8)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Setup Time CS to SCLK
Setup Time SDI to SCLK t
Hold Time SCLK to SDI t
SCLK High/Low Time t
SCLK Rise/Fall Time t
SCLK to CS Inactive
CS Inactive Time
SCLK to SDO Valid t
SCLK to SDO Tri-State t
CS Inactive to SDO Tri-State
CSS
50 ns
SSS
50 ns
SSH
200 ns
SLH
50 ns
SRF
t
LSC
t
CM
50 ns
SSV
100 ns
SST
t
CSH
50 ns
50 ns
250 ns
t
Figure 10-8. Serial Bus Timing (BIS1 = 1, BIS0 = 0)
S
t
CSS
SCLK
(Note 1)
SCLK
(Note 2)
SDI
t
SSS
LSB MSB
SDO
NOTE 1: OCES =1 AND ICES = 0.
NOTE 2: OCES = 0 AND ICES = 1.
t
SSH
HIGH-Z
t
t
SRF
SLH
MSB
LSB
LSB
t
SSV
100 ns
t
CM
t
LSC
t
CSH
t
SST
HIGH-Z
MSB
53 of 60

Table 10-D. AC Characteristics—Receive Side
(VDD = 3.3V ± 5%, TA =-40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 10-9)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RCLK Period tCP
(Note 1) 488
(Note 2) 648
RCLK Pulse Width
RCLK Pulse Width
Delay RCLK to RPOS, RNEG,
PBEO, RBPV Valid
Note 1: E1 mode.
Note 2: T1 or J1 mode.
Note 3: Jitter attenuator enabled in the receive path.
Note 4: Jitter attenuator disabled or enabled in the transmit path.
tCH
t
CL
tCH
t
CL
t
50.0 ns
DD
(Note 3) 200
(Note 4) 150
Figure 10-9. Receive-Side Timing
RCLK
(Note 1)
RCLK
(Note 2)
RPOS, RNEG
PBEO
RNEG
(Note 3)
NOTE 1: RCES = 1 (CCR2.0) OR CES = 1.
NOTE 2: RCES = 0 (CCR2.0) OR CES = 0.
NOTE 3:
RNEG IS IN NRZ MODE (CCR1.6 = 1).
t
DD
t
DD
BIT
ERROR
BPV/
EXZ/
CV
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
ns
t
CL
PRBS DETECTOR OUT OF SYNC
t
CP
t
CH
ns
ns
BPV/
EXZ/
CV
54 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
Table 10-E. AC Characteristics—Transmit Side
(VDD = 3.3V ±5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C.) (Figure 10-10)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
TCLK Period tCP
(Note 5) 488
(Note 6) 648
ns
tCH 75
TCLK Pulse Width
TPOS/TNEG Setup to TCLK
Falling or Rising
TPOS/TNEG Hold from TCLK
Falling or Rising
t
75
CL
t
20 ns
SU
t
20 ns
HD
ns
TCLK Rise and Fall Times tR, tF 25 ns
Note 5: E1 mode.
Note 6: T1 or J1 mode.
Figure 10-10. Transmit-Side Timing
TCLK
(Note 1)
t
R
t
F
t
CL
t
CP
t
CH
TCLK
(Note 2)
TPOS, TNEG
NOTE 1: TCES = 0 (CCR2.1) OR CES = 0.
NOTE 2: TCES = 1 (CCR2.1) OR CES = 1.
t
SU
t
HD
55 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
11. PIN CONFIGURATIONS
11.1 144-Pin BGA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
A
RTIP1 TTIP1 N.C. RTIP2 TTIP2 N.C. RTIP3 TTIP3 N.C. RTIP4 TTIP4 N.C.
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
N.C. RRING1 TRING1 N.C. RRING2 TRING2 N.C. RRING3 TRING3 N.C. RRING4 TRING4
N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C.
TVSS2 TVDD2
RPOS2 RNEG2
RCLK2 TPOS2
TPOS1 RNEG1 PEBO2 N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. TVDD3 N.C.
WR
(R/W)
SCLK
A4/
SDO
TNEG1 RCLK1 BPCLK1 N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. VSS4
RD
(DS)
ALE
(AS)
CS2
D3/
AD3
D1/
AD1
CS1
SDI RPOS1 PEBO1 N.C.
D2/
AD2
VDD2 N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. TVSS3 PEBO3 RCLK3 TPOS3
VSS2 N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C.
TVSS1 TVDD1 MCLK
D0/
AD0
BPCLK2
RCL/
LOTC2
RCL/
LOTC4
TXDIS/
TEST
VDD3 VSS3
LOTC3
VDD4
PEBO4
CS3
RCL/
AD4
BPCLK3 RNEG3 TCLK3
D6/
AD6
D4/
INT CS4
D7/
AD7
RPOS3 TNEG3
D5/
AD5
A2/
OCES
N.C. N.C.
RPOS4 TNEG4
A0
A1
L
M
A3/
ICES
TNEG2 TCLK1 JTMS VSS1 JTCLK JTDI JTDO BIS1 TVDD4 RNEG4 TPOS4 PBTS
TCLK2 JTRST N.C. VDD1
RCL/
LOTC1
56 of 60
BIS0 BPCLK4
HRST
TVSS4 RCLK4 TCLK4

11.2 128-Pin LQFP
C
C
A
A
A
A
X
C
3
R
DS
W
/
W
A
I
T
HRST
CS4
N.C.
N.C.
TTIP4
N.C.
DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
)/NRZE
)/ETS
RT1
/
N
TXDIS/TEST
RCLK4
(R
R
LE (AS)/SCLKE
RRING4
D
VSS4
VSS4
RTIP4
VSS4
/EGL3
S
D0/AD0/MM1
VDD4
VDD4
VDD4
TCLK3
D4/AD4/TX1
D1/AD1/MM0
D3/AD3/LOOP0
D2/AD2/LOOP1
TRING3
D5/AD5/TX0
D6/AD6/TPD
TVSS3
TVDD3
D7/AD7/CES
N.C.
TTIP3
N.C.
A1/JAS
A0/HBE
N.C.
BIS1
TVSS4
TVDD4
TRING4
BIS0
PBTS/RT0
MCLK
PBEO1
PBEO2
BPCLK4
TCLK4
/EGL4
VDD1
VDD1
VDD1
VSS1
VSS1
VSS1
PBEO3
BPCLK1
PBEO4
RTIP1
RRING1
RCL1/LOTC1
RCLK1
RCL2/LOTC2
708090 100
60
110
Dallas Semiconductor
DS21448
50
120
40
1
RCL3/LOTC3
RCL4/LOTC4
N.C.
N.C.
TTIP1
VSM
10 20 30
TVSS1
TVDD1
TRING1
RPOS1
RNEG1
RPOS2
RNEG2
RPOS3
RNEG3
RPOS4
TCLK1
VDD2
VDD2
VDD2
VSS2
VSS2
S1/
EGL1
VSS2
RNEG4
TPOS1
TNEG1
RTIP2
TPOS2
RRING2
RCLK2
TNEG2
TPOS3
SCLK/L2
TNEG3
SDI/L1
TTIP2
N.C.
2/OCES/JAMU
3/ICES/DJ
4/SD0/L0
RRING3
RTIP3
TNEG4
RCLK3
/EGL2
S2
BPCLK3
TPOS4
VSS3
VSS3
VSS3
VDD3
VDD3
VDD3
JTMS
BPCLK2
JTDO
JTDI
JTCLK
TCLK2
JTRST
TRING2
TVDD2
TVSS2
57 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
12. PACKAGE INFORMATION
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package
outline information, go to www.maxim-ic.com/DallasPackInfo
.)
58 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
PACKAGE INFORMATION (continued)
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package
outline information, go to www.maxim-ic.com/DallasPackInfo
.)
59 of 60

DS21448 3.3V T1/E1/J1 Quad Line Interface
13. THERMAL INFORMATION
Table 13-A. Thermal Characteristics—BGA
PARAMETER MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Ambient Temperature (Note 1) -40 +85 °C
Junction Temperature +125 °C
Theta-JA (qJA) in Still Air (Note 2)
+24
°C/W
Table 13-B. Theta-JA (qJA) vs. Airflow—BGA
FORCED AIR (m/s)
0 24°C/W
1 21°C/W
2.5 19°C/W
THETA-JA (q
JA
)
Table 13-C. Thermal Characteristics—LQFP
PARAMETER MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Ambient Temperature (Note 1) -40 +85 °C
Junction Temperature +125 °C
Theta-JA (qJA) in Still Air (Note 2)
Theta-JC (qJC) in Still Air (Note 3)
+27.8
+0.1
°C/W
°C/W
Table 13-D. Theta-JA (qJA) vs. Airflow—LQFP
FORCED AIR (m/s)
THETA-JA (q
0 27.8°C/W
1 23.5°C/W
2.5 21.6°C/W
Note 1: The package is mounted on a four-layer JEDEC-standard test board.
Note 2: Theta-JA (q
Note 3: While Theta-JC (q
the average temperature on top center of the LQFP package (TC), the proper term is Psi-JT. It is defined by: (Tj - TC) / overall package
power.
Note 4: The method of measurement for the thermal parameters is defined in the EIA/JEDEC-standard document EIA-JESD51-2.
) is the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, when the package is mounted on a four-layer JEDEC-standard test board.
JA
) is commonly used as the thermal parameter that provides a correlation between the junction temperature (Tj) and
JC
JA
)
14. REVISION HISTORY
REVISION DESCRIPTION
042303 New product release.
Table 5-B. Receive Level Indication: Changed “-12.5 to -5.0” to “-12.5 to -15.0”. Adjusted steps
after -17.5 dB to be in -2.5dB decrements.
012104
Section 9, Operating Parameters: Updated supply current and power dissipation values in the DC
Characteristics table to reflect latest characterization data. Updated Note 5 to show that values are for all ports
active.
Maxim/Dallas Semiconductor cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim/Dallas Semiconductor product.
No circuit patent licenses are implied. Maxim/Dallas Semiconductor reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2004 Maxim Integrated Products · Printed USA
60 of 60
 Loading...
Loading...