
查询DS21352供应商
www.maxim-ic.com
3.3V DS21352 and 5V DS21552
T1 Single-Chip Transceivers
FEATURES
§ Complete DS1/ISDN–PRI/J1 transceiver functionality
§ Long and Short haul LIU
§ Crystal–less jitter attenuator
§ Generates DSX–1 and CSU line build-outs
§ HDLC controller with 64-byte buffers Configurable for
FDL or DS0 operation
§ Dual two–frame elastic store slip buffers that can
connect to asynchronous backplanes up to 8.192MHz
§ 8.192MHz clock output locked to RCLK
§ Interleaving PCM Bus Operation
§ Per-channel loopback and idle code insertion
§ 8-bit parallel control port muxed or nonmuxed buses
(Intel or Motorola)
§ Programmable output clocks for Fractional T1
§ Fully independent transmit and receive functionality
§ Generates/detects in-band loop codes from 1 to 8 bits
in length including CSU loop codes
§ IEEE 1149.1 JTAG-Boundary Scan
§ Pin compatible with DS2152/54/354/554 SCTs
§ 100-pin LQFP package (14 mm x 14 mm) 3.3V
(DS21352) or 5V (DS21552) supply; low power
CMOS
PIN ASSIGNMENT
DS21352
DS21552
100
1
ORDERING INFORMATION
DS21352L (0°C to +70°C)
DS21352LN (-40°C to +85°C)
DS21552L (0°C to +70°C)
DS21552LN (-40°C to +85°C)
DESCRIPTION
The DS21352/552 T1 single-chip transceiver contains all of the necessary functions for connection to T1
lines whether they are DS1 long haul or DSX–1 short haul. The clock recovery circuitry automatically
adjusts to T1 lines from 0 feet to over 6000 feet in length. The device can generate both DSX–1 line build
outs as well as CSU line build-outs of -7.5dB, -15dB, and -22.5dB. The onboard jitter attenuator
(selectable to either 32 bits or 128 bits) can be placed in either the transmit or receive data paths. The
framer locates the frame and multiframe boundaries and monitors the data stream for alarms. It is also
used for extracting and inserting robbed-bit signaling data and FDL data. The device contains a set of
internal registers which the user can access and control the operation of the unit. Quick access via the
parallel control port allows a single controller to handle many T1 lines. The device fully meets all of the
latest T1 specifications including ANSI T1.403-1995, ANSI T1.231-1993, AT&T TR 62411 (12–90),
AT&T TR54016, and ITU G.703, G.704, G.706, G.823, and I.431.
1 of 137 120501

DS21352/DS21552
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. LIST OF FIGURES .........................................................................................................................5
2. LIST OF TABLES ...........................................................................................................................6
3. INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................................7
3.1 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION..............................................................................................8
3.2 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY....................................................................................10
4. PIN DESCRIPTION ......................................................................................................................11
4.1 PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION..........................................................................................17
4.1.1 Transmit Side Pins ........................................................................................................17
4.1.2 Receive Side Pins ..........................................................................................................20
4.1.3 Parallel Control Port Pins............................................................................................23
4.1.4 JTAG Test Access Port Pins .........................................................................................25
4.1.5 Interleave Bus Operation Pins......................................................................................25
4.1.6 Line Interface Pins........................................................................................................26
4.1.7 Supply Pins....................................................................................................................27
5. PARALLEL PORT........................................................................................................................28
5.1 REGISTER MAP ...................................................................................................................28
6. CONTROL, ID, AND TEST REGISTERS .................................................................................32
6.1 POWER-UP SEQUENCE......................................................................................................32
6.2 DEVICE ID ............................................................................................................................32
6.3 PAYLOAD LOOPBACK.......................................................................................................37
6.4 FRAMER LOOPBACK .........................................................................................................38
6.5 PULSE DENSITY ENFORCER............................................................................................40
6.6 REMOTE LOOPBACK .........................................................................................................44
7. STATUS AND INFORMATION REGISTERS..........................................................................45
8. ERROR COUNT REGISTERS....................................................................................................52
8.1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER (LCVCR) ................................................53
8.2 PATH CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER (PCVCR) ...............................................54
8.3 MULTIFRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNT REGISTER (MOSCR)....................................55
9. DSO MONITORING FUNCTION...............................................................................................56
2 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
10. SIGNALING OPERATION..........................................................................................................58
10.1 PROCESSOR-BASED SIGNALING ....................................................................................58
10.2 HARDWARD-BASED SIGNALING ...................................................................................60
10.2.1 Receive Side.................................................................................................................60
10.2.2 Transmit Side...............................................................................................................61
11. PER-CHANNEL CODE (IDLE) GENERATION ......................................................................61
11.1 TRANSMIT SIDE CODE GENERATION ...........................................................................62
11.1.1 Fixed Per-Channel Idle Code Insertion ......................................................................62
11.1.2 Unique Per-Channel Idle Code Insertion....................................................................63
11.2 RECEIVE SIDE CODE GENERATION...............................................................................63
11.2.1 Fixed Per-Channel Idle Code Insertion ......................................................................64
11.2.3 Unique Per-Channel Idle Code Insertion....................................................................64
12. PER-CHANNEL LOOPBACK.....................................................................................................65
13. CLOCK BLOCKING REGISTERS ............................................................................................65
14. ELASTIC STORES OPERATION ..............................................................................................66
14.1 RECEIVE SIDE .....................................................................................................................66
14.2 TRANSMIT SIDE..................................................................................................................67
14.3 ELASTIC STORES INITIALIZATION................................................................................67
14.4 MINIMUM DELAY MODE..................................................................................................67
15. HDLC CONTROLLER.................................................................................................................68
15.1 HDLC FOR DS0S ..................................................................................................................68
15.1.1 Receive an HDLC Message .........................................................................................68
15.1.2 Transmit an HDLC Message .......................................................................................68
15.2 FDL/Fs EXTRACTION AND INSERTION .........................................................................69
15.3 HDLC and BOC CONTROLLER FOR THE FDL................................................................69
15.3.1 General Overview........................................................................................................69
15.3.2 Status Register for the HDLC......................................................................................70
15.3.3 Basic Operation Details ..............................................................................................71
15.3.4 HDLC/BOC Register Description ...............................................................................72
15.4 LEGACY FDL SUPPORT.....................................................................................................82
15.4.1 Overview......................................................................................................................82
15.4.2 Receive Section ............................................................................................................82
15.4.3 Transmit Section..........................................................................................................84
15.5 D4/SLC-96 OPERATION......................................................................................................84
3 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
16. LINE INTERFACE FUNCTION .................................................................................................85
16.1 RECEIVE CLOCK AND DATA RECOVERY ....................................................................85
16.2 TRANSMIT WAVE SHAPING AND LINE DRIVING.......................................................86
16.3 JITTER ATTNUATOR..........................................................................................................86
16.4 PROTECTED INTERFACES................................................................................................92
16.5 RECEIVE MONITOR MODE...............................................................................................95
17. PROGRAMMABLE IN-BAND LOOP CODE GENERATION AND DETECTION............96
18. TRANSMIT TRANSPARENCY ..................................................................................................99
19. JTAG-BOUNDARY SCAN ARCHITECTURE AND TEST ACCESS PORT .......................99
19.1 DESCRIPTION ......................................................................................................................99
19.2 TAP CONTROLLER STATE MACHINE ..........................................................................101
19.3 INSTRUCTION REGISTER ...............................................................................................103
19.4 TEST REGISTERS ..............................................................................................................105
20. INTERLEAVED PCM BUS OPERATION ..............................................................................109
20.1 CHANNEL INTERLEAVE .................................................................................................111
20.2 FRAME INTERLEAVE.......................................................................................................111
21. FUNCTIONAL TIMING DIAGRAMS .....................................................................................111
22. RECEIVE AND TRANSMIT DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS.....................................................123
23. OPERATING PARAMETERS...................................................................................................125
24. AC TIMING PARAMETERS AND DIAGRAMS....................................................................126
24.1 MULTIPLEXED BUS AC CHARACTERISTICS .............................................................126
24.2 NON-MULTIPLEXED BUS AC CHARACTERISTICS ...................................................129
24.3 RECEIVE SIDE AC CHARACTERISTICS .......................................................................132
24.4 TRANSMIT AC CHARACTERISTICS..............................................................................136
25. MECHANICAL DESCRIPTTION ............................................................................................139
4 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
1. LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 3-1 SCT BLOCK DIAGRAM.........................................................................................................9
Figure 16-1 EXTERNAL ANALOG CONNECTIONS ..........................................................................87
Figure 16-2 OPTIONAL CRYSTAL CONNECTIONS ..........................................................................88
Figure 16-3 TRANSMIT WAVEFORM TEMPLANE............................................................................89
Figure 16-4 JITTER TOLERANCE.........................................................................................................91
Figure 16-5 JITTER ATTENUATION ....................................................................................................91
Figure 16-6 PROTECTED INTERFACE EXAMPLE FOR THE DS21552...........................................93
Figure 16-7 PROTECTED INTERFACE EXAMPLE FOR TE DS21352..............................................94
Figure 16-8 TYPICAL MONITOR PORT APPLICATION....................................................................95
Figure 19-1 JTAG FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM......................................................................100
Figure 19-2 TAP CONTROLLER STATE DIAGRAM ........................................................................103
Figure 20-1 IBO BASIC CONFIGURATION USING 4 SCTS ............................................................110
Figure 21-1 RECEIVE SIDE D4 TIMING.............................................................................................111
Figure 21-2 RECEIVE SIDE ESF TIMING...........................................................................................112
Figure 21-3 RECEIVE SIDE BOUNDARY TIMING (with elastic store disabled)..............................113
Figure 21-4 RECEIVE SIDE 1.544 MHz BOUNDARY TIMING (with elastic store enabled) ...........113
Figure 21-5 RECEIVE SIDE 2.048 MHz BOUNDARY TIMING (with elastic store enabled) ...........114
Figure 21-6 RECEIVE SIDE INTERLEAVE BUS OPERATION, BYTE MODE ..............................115
Figure 21-7 RECEIVE SIDE INTERLEAVE BUS OPERATION, FRAME MODE ...........................116
Figure 21-8 TRANSMIT SIDE D4 TIMING .........................................................................................117
Figure 21-9 TRANSMIT SIDE ESF TIMING.......................................................................................118
Figure 21-10 TRANSMIT SIDE BOUNDARY TIMING (with elastic store disabled) ........................119
Figure 21-11 TRANSMIT SIDE 1.544 MHz BOUNDARY TIMING (with elastic store enabled)......119
Figure 21-12 TRANSMIT SIDE 2.048 MHz BOUNDARY TIMING (with elastic store enabled)......120
Figure 21-13 TRANSMIT SIDE INTERLEAVE BUS OPERATION, BYTE MODE.........................121
Figure 21-14 TRANSMIT SIDE INTERLEAVE BUS OPERATION, FRAME MODE .....................122
Figure 22-1 RECEIVE DATA FLOW ...................................................................................................123
Figure 22-2 TRANSMIT DATA FLOW................................................................................................124
Figure 24-1 INTEL BUS READ TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX=1) .............................................................127
Figure 24-2 INTEL BUS WRITE TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX=1) ...........................................................127
Figure 24-3 MOTOROLA BUS TIMING (BTS=1 / MUX=1)..............................................................128
Figure 24-4 INTEL BUS READ TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX=0) ..............................................................130
Figure 24-5 INTEL BUS READ TIMING (BTS=0 / MUX=0) .............................................................130
Figure 24-6 MOTOROLA BUS READ TIMING (BTS=1 / MUX=0)..................................................131
Figure 24-7 MOTOROLA BUS READ TIMING (BTS=1 / MUX=0)..................................................131
Figure 24-8 RECEIVE SIDE TIMING ..................................................................................................133
Figure 24-9 RECEIVE SIDE TIMING, ELASTIC STORE ENABLED...............................................134
Figure 24-10 RECEIVE LINE INTERFACE TIMING .........................................................................135
Figure 24-11 TRANSMIT SIDE TIMING.............................................................................................137
Figure 24-12 TRANSMIT SIDE TIMING, ELASTIC STORE ENABLED .........................................138
Figure 24-13 TRANSMIT LINE INTERFACE TIMING......................................................................138
5 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
2. LIST OF TABLES
Table 4-1 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN NUMBER................................................................11
Table 4-2 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN SYMBOL ................................................................14
Table 5-1 REGISTER MAP SORTED BY ADDRESS...........................................................................29
Table 6-1 DEVICE ID BIT MAP .............................................................................................................33
Table 6-2 OUTPUT PIN TEST MODES .................................................................................................36
Table 7-1 RECEIVE T1 LEVEL INDICATION .....................................................................................47
Table 7-2 ALARM CRITERIA ................................................................................................................49
Table 8-1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS ..............................................53
Table 8-2 PATH CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS.............................................54
Table 8-3 MULTIFRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNTING ARRANGMENTS .....................................55
Table 14-1 ELASTIC STORE DELAY AFTER INITIALIZATION......................................................67
Table 14-2 MINIMUM DELAY MODE CONFIGURATION................................................................67
Table 15-1 TRANSMIT HDLC CONFIGURATION...............................................................................68
Table 15-2 HDLC/BOC CONTROLLER REGISTERS..........................................................................70
Table 16-1 LINE BUILD OUT SELECT IN LICR .................................................................................86
Table16-2 TRANSMIT TRANSFORMER SELECTION .......................................................................87
Table 16-3 TRANSFORMER SPECIFICATIONS..................................................................................88
Table 16-4 PULSE TEMPLATE CORNER POINTS..............................................................................90
Table 16-5 RECEIVE MONITOR MODE GAIN....................................................................................95
Table 17-1 TRANSMIT CODE LENGTH...............................................................................................97
Table 17-2 RECEIVE CODE LENGTH ..................................................................................................97
Table 19-1 INSTRUCTION CODES FOR IEEE 1149.1 ARCHITECTURE .......................................104
Table 19-2 ID CODE STRUCTURE .....................................................................................................105
Table 19-3 DEVICE ID CODES............................................................................................................105
Table 19-4 BOUNDARY SCAN CONTROL BITS ..............................................................................106
Table 20-1 MASTER DEVICE BUS SELECT.....................................................................................110
6 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
3. INTRODUCTION
The DS21352/552 are 3.3V/5V superset versions of the popular DS2152 T1 single-chip transceiver
offering the new features listed below. All of the original features of the DS2152 have been retained and
software created for the original devices is transferable into the DS21352/552.
NEW FEATURES (after the DS2152)
§ Interleaving PCM Bus Operation
§ Integral HDLC controller with 64-byte buffers Configurable for FDL or DS0 operation
§ IEEE 1149.1 JTAG-Boundary Scan Architecture
§ 3.3V (DS21352 only) supply
FEATURES
§ option for non–multiplexed bus operation
§ crystal–less jitter attenuation
§ 3.3V I/O on all SCTs
§ additional hardware signaling capability including:
– receive signaling reinsertion to a backplane multiframe sync
– availability of signaling in a separate PCM data stream
– signaling freezing
– interrupt generated on change of signaling data
§ ability to calculate and check CRC6 according to the Japanese standard
§ ability to pass the F–Bit position through the elastic stores in the 2.048 MHz backplane mode
§ programmable in–band loop code generator and detector
§ per channel loopback and idle code insertion
§ RCL, RLOS, RRA, and RAIS alarms now interrupt on change of state
§ 8.192 MHz clock output synthesized to RCLK
§ HDLC controller can be configured for FDL
§ addition of hardware pins to indicate carrier loss & signaling freeze
§ line interface function can be completely decoupled from the framer/formatter to allow:
– interface to optical, HDSL, and other NRZ interfaces
– be able to “tap” the transmit and receive bipolar data streams for monitoring purposes
– be able corrupt data and insert framing errors, CRC errors, etc.
§ transmit and receive elastic stores now have independent backplane clocks
7 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
3.1 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The analog AMI/B8ZS waveform off of the T1 line is transformer coupled into the RRING and RTIP
pins of the DS21352/552. The device recovers clock and data from the analog signal and passes it
through the jitter attenuation mux to the receive side framer where the digital serial stream is analyzed to
locate the framing/multi-frame pattern. The DS21352/552 contains an active filter that reconstructs the
analog received signal for the nonlinear losses that occur in transmission. The device has a usable receive
sensitivity of 0 dB to –36 dB, which allows the device to operate on cables up to 6000 feet in length. The
receive side framer locates D4 (SLC–96) or ESF multiframe boundaries as well as detects incoming
alarms including, carrier loss, loss of synchronization, blue (AIS) and yellow alarms. If needed, the
receive side elastic store can be enabled in order to absorb the phase and frequency differences between
the recovered T1 data stream and an asynchronous backplane clock which is provided at the RSYSCLK
input. The clock applied at the RSYSCLK input can be either a 2.048 MHz clock or a 1.544 MHz clock.
The RSYSCLK can be a bursty clock with speeds up to 8.192 MHz.
The transmit side of the DS21352/552 is totally independent from the receive side in both the clock
requirements and characteristics. Data off of a backplane can be passed through a transmit side elastic
store if necessary. The transmit formatter will provide the necessary frame/multiframe data overhead for
T1 transmission. Once the data stream has been prepared for transmission, it is sent via the jitter
attenuation mux to the waveshaping and line driver functions. The DS21352/552 will drive the T1 line
from the TTIP and TRING pins via a coupling transformer. The line driver can handle both long haul
(CSU) and short haul (DSX–1) lines.
Reader’s Note: This data sheet assumes a particular nomenclature of the T1 operating environment. In
each 125 ms frame, there are 24 eight–bit channels plus a framing bit. It is assumed that the framing bit is
sent first followed by channel 1. Each channel is made up of eight bits, which are numbered, 1 to 8. Bit
number 1 is the MSB and is transmitted first. Bit number 8 is the LSB and is transmitted last. The term
“locked” is used to refer to two clock signals that are phase or frequency locked or derived from a
common clock (i.e., a 1.544 MHz clock may be locked to a 2.048MHz clock if they share the same 8 kHz
component). Throughout this data sheet, the following abbreviations will be used:
B8ZS Bipolar with 8 Zero Substitution
BOC Bit Oriented Code
CRC Cyclical Redundancy Check
D4 Superframe (12 frames per multiframe) Multiframe Structure
ESF Extended Superframe (24 frames per multiframe) Multiframe Structure
FDL Facility Data Link
FPS Framing Pattern Sequence in ESF
Fs Signaling Framing Pattern in D4
Ft Terminal Framing Pattern in D4
HDLC High Level Data Link Control
MF Multiframe
SLC–96 Subscriber Loop Carrier – 96 Channels (SLC–96 is an AT&T registered trademark)
8 of 137
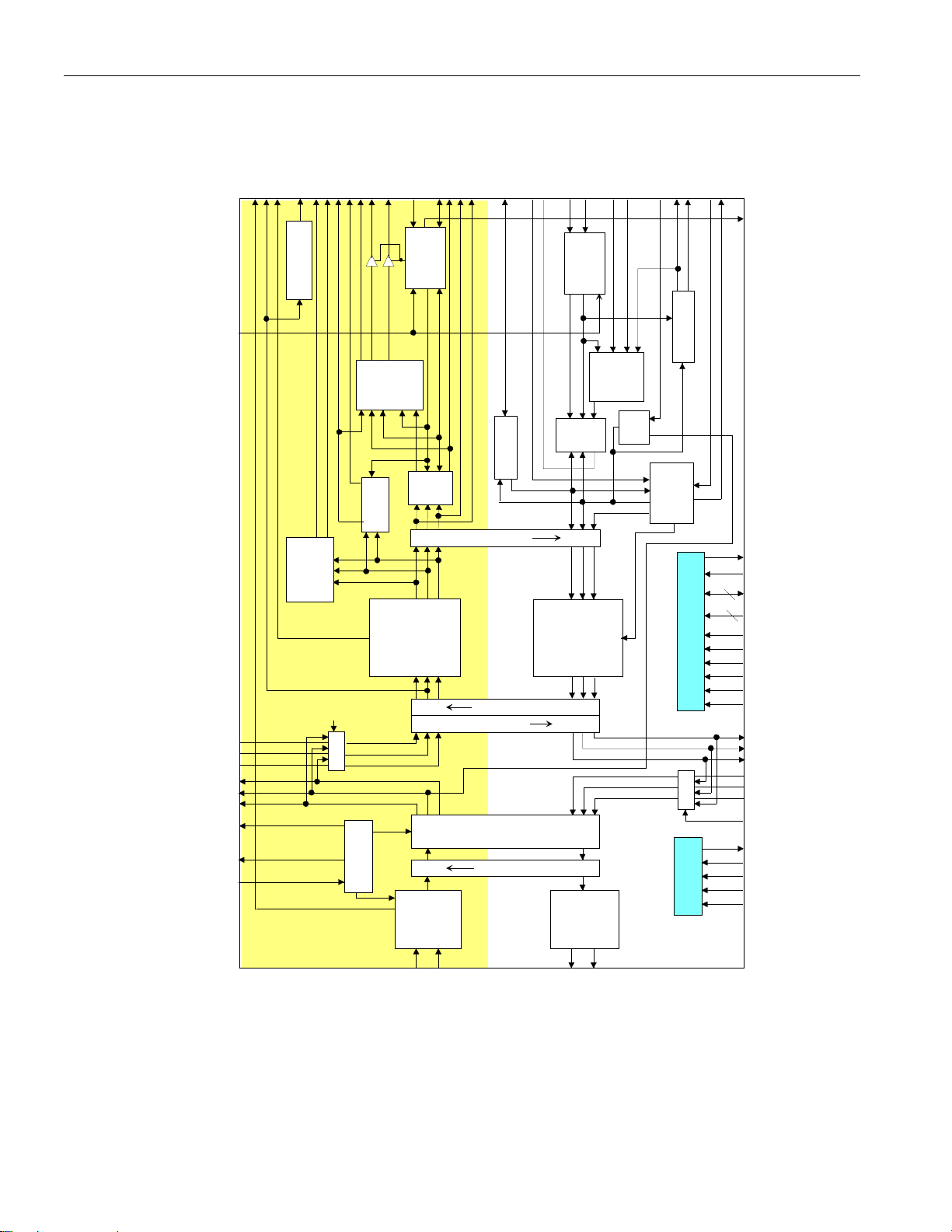
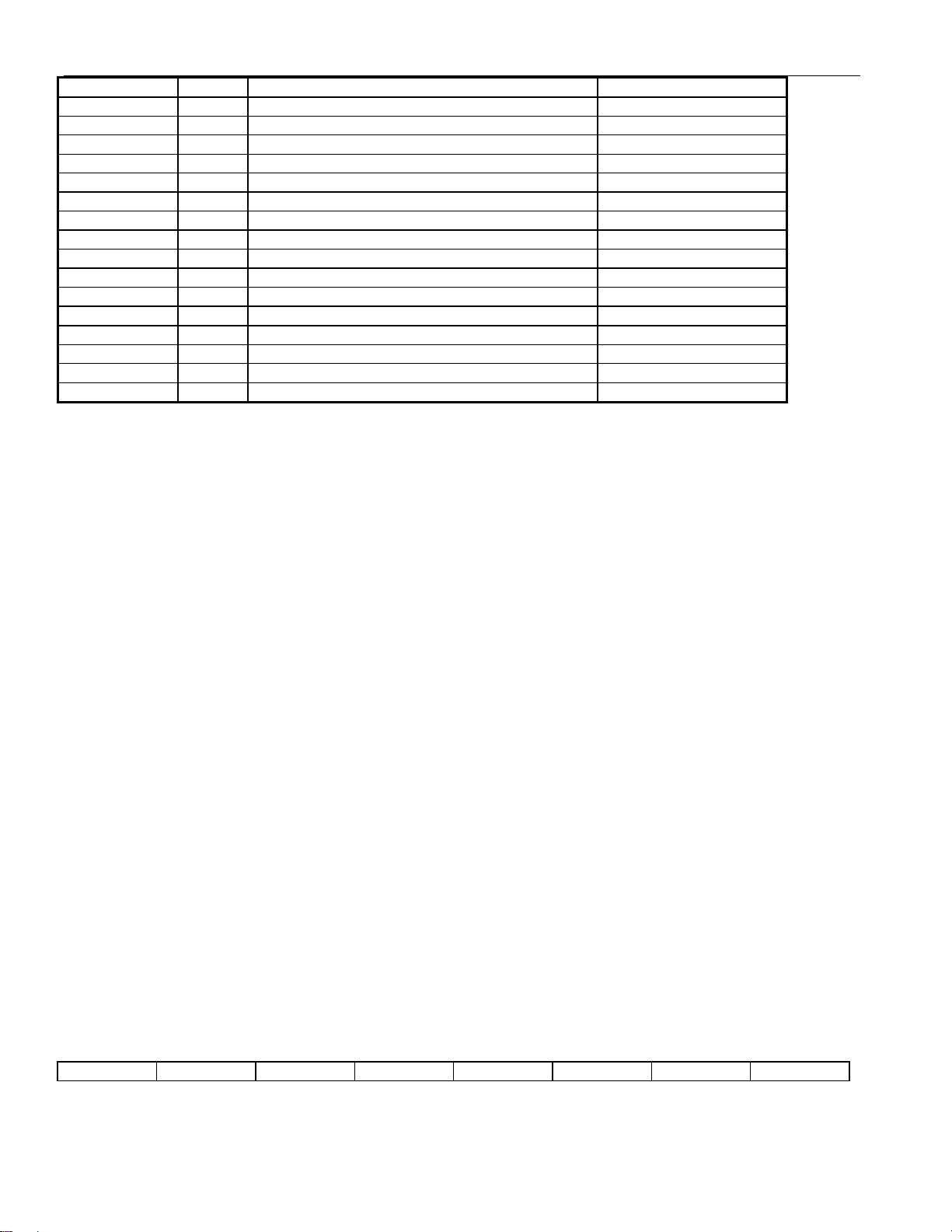
Figure 3-1 SCT BLOCK DIAGRAM
RSIGF
RCHCLK
RCL
RCHBLK
RLINK
RLOS/LOTC
RCLK
RLCLK
8MCLK
Synthesizer
8.192MHz Clock
RSER
RSIG
DS21352/DS21552
RMSYNC
RSYSCLK
RSYNC
RFSYNC
RDATA
Interleave
Bus
TSYNC
TESO
TDATA
TSSYNC
Interleave
TSYSCLK
Bus
TSER
TSIG
TCHBLK
TCLK
TCHCLK
TLINK
TLCLK
CO
RPOSI
RCLKI
RNEGI
RNEGO
RCLKO
RPOSO
8XCLK
XTALD
MCLK
Buffer
Signaling
Control
Framer
Receive Side
24.7MHz
Clock / Data
Recovery
RSYSCLK
Store
Elastic
Payload Loopback
DATA
SYNC
CLOCK
Framer Loopback
Remote Loopback
Jitter Attenuator
Either trans mit or receive pa th
Local Loopback
Receive
Line I/F
Timing Control
Hardware
Signaling
Insertion
LOTC
Store
Elastic
Sync C ontrol
SYNC
CLOCK
Formatter
Transmit Side
s
n
a
r
T
m
F
/
I
e
n
i
L
MUX
HDLC/BOC
Controller
FDL / DS0
INT*
FDL
DATA
(routed to all block s)
Parallel & Test Control Port
MUX
JTAG PORT
t
i
MUX
D0 to D7 /
AD0 to AD7
8
A0 to A6
7
ALE(AS) / A7
RD*(DS*)
WR*(R/W*)
BTS
CS*
TEST
TPOSO
TCLKO
TNEGO
TNEGI
TCLKI
TPOSI
LIUC
JTDO
JTDI
JTCLK
JTMS
J
R
S
T
CI
Timing
HDLC/BOC
Contr oller
FDL / DS0
LIUC
MUX
12.352 MHz
VCO / PLL
RTIP
RRING
9 of 137
TTIP
TRING

DS21352/DS21552
3.2 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY
Revision Notes
12-10-98 Initial Release
12-18-98 Add LIUODO (LIU Open Drain Output) to CCR7.0
Add CDIG (Customer Disconnect Indication Generator) to CCR7.1
Add LIUSI (Line Interface Unit Synchronization Interface) to CCR7.2
Correct IBO register bit functions order
Add bit level description to CCR3.6
1-4-99 Delete “The elastic stores can be forced to a known depth via the Elastic Store Reset bit (CCR3.6).
Toggling the CCR3.6 bit forces the read and write pointers into opposite frames” from section 12.0
1-18-99 Add receive IBO operation PCM timing diagram
1-18-99 Correct Device ID register bit definitions
1-28-99 Correct TSYSCLK and RSYSCLK AC timing and add 4.096 MHz and 8.192 MHz AC timing
2-2-99 Correct definition and label or TUDR bit in TPRM register
2-11-99 Correct format of register definitions in body of data sheet
4-1-99 Add Receive Monitor Mode section
4-15-99 Add section on Protected Interfaces
5-7-99 Correct FMS pin # and description in JTAG section
5-17-99 Correct name of status registers in section 15.3.2
5-19-99 Correct definition of RIR3.4
7-27-99 Correct Receive Monitor Mode section
8-16-99 Remove “Preliminary” notice from data sheet
10 of 137
4. PIN DESCRIPTION
Table 4-1 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN NUMBER
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
1 RCHBLK O Receive Channel Block
2 JTMS I IEEE 1149.1 Test Mode Select
3 8MCLK O 8.192 MHz Clock
4 JTCLK I IEEE 1149.1 Test Clock Signal
5 JTRST I IEEE 1149.1 Test Reset
6 RCL O Receive Carrier Loss
7 JTDI I IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Input
8 NC – No Connect
9 NC – No Connect
10 JTDO O IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Output
11 BTS I Bus Type Select
12 LIUC I Line Interface Connect
13 8XCLK O Eight Times Clock
14 TEST I Test
15 NC – No Connect
16 RTIP I Receive Analog Tip Input
17 RRING I Receive Analog Ring Input
18 RVDD – Receive Analog Positive Supply
19 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground
20 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground
21 MCLK I Master Clock Input
22 XTALD O Quartz Crystal Driver
23 NC – No Connect
24 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground
25 INT* O Interrupt
26 NC – No Connect
27 NC – No Connect
28 NC – No Connect
29 TTIP O Transmit Analog Tip Output
30 TVSS – Transmit Analog Signal Ground
31 TVDD – Transmit Analog Positive Supply
32 TRING O Transmit Analog Ring Output
33 TCHBLK O Transmit Channel Block
34 TLCLK O Transmit Link Clock
35 TLINK I Transmit Link Data
36 CI I Carry In
37 TSYNC I/O Transmit Sync
38 TPOSI I Transmit Positive Data Input
39 TNEGI I Transmit Negative Data Input
40 TCLKI I Transmit Clock Input
41 TCLKO O Transmit Clock Output
42 TNEGO O Transmit Negative Data Output
43 TPOSO O Transmit Positive Data Output
Table 4-1 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN NUMBER (cont.)
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
44 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply
45 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
46 TCLK I Transmit Clock
47 TSER I Transmit Serial Data
48 TSIG I Transmit Signaling Input
49 TESO O Transmit Elastic Store Output
DS21352/DS21552
11 of 137
50 TDATA I Transmit Data
51 TSYSCLK I Transmit System Clock
52 TSSYNC I Transmit System Sync
53 TCHCLK O Transmit Channel Clock
54 CO O Carry Out
55 MUX I Bus Operation
56 D0/AD0 I/O Data Bus Bit0/ Address/Data Bus Bit 0
57 D1/AD1 I/O Data Bus Bit1/ Address/Data Bus Bit 1
58 D2/AD2 I/O Data Bus Bit 2/Address/Data Bus 2
59 D3/AD3 I/O Data Bus Bit 3/Address/Data Bus Bit 3
60 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
61 DVDD - Digital Positive Supply
62 D4/AD4 I/O Data Bus Bit4/Address/Data Bus Bit 4
63 D5/AD5 I/O Data Bus Bit 5/Address/Data Bus Bit 5
64 D6/AD6 I/O Data Bus Bit 6/Address/Data Bus Bit 6
65 D7/AD7 I/O Data Bus Bit 7/Address/Data Bus Bit 7
66 A0 I Address Bus Bit 0
67 A1 I Address Bus Bit 1
68 A2 I Address Bus Bit 2
69 A3 I Address Bus Bit 3
70 A4 I Address Bus Bit 4
71 A5 I Address Bus Bit 5
72 A6 I Address Bus Bit 6
73 ALE (AS)/A7 I Address Latch Enable/Address Bus Bit 7
74 RD*(DS*) I Read Input(Data Strobe)
75 CS* I Chip Select
76 FMS I Framer Mode Select
77 WR*(R/W*) I Write Input(Read/Write)
78 RLINK O Receive Link Data
79 RLCLK O Receive Link Clock
80 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
81 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply
82 RCLK O Receive Clock
83 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply
84 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
85 RDATA O Receive Data
86 RPOSI I Receive Positive Data Input
87 RNEGI I Receive Negative Data Input
88 RCLKI I Receive Clock Input
Table 4-1 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN NUMBER (cont.)
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
89 RCLKO O Receive Clock Output
90 RNEGO O Receive Negative Data Output
91 RPOSO O Receive Positive Data Output
92 RCHCLK O Receive Channel Clock
93 RSIGF O Receive Signaling Freeze Output
94 RSIG O Receive Signaling Output
95 RSER O Receive Serial Data
96 RMSYNC O Receive Multiframe Sync
97 RFSYNC O Receive Frame Sync
98 RSYNC I/O Receive Sync
99 RLOS/LOTC O Receive Loss Of Sync/ Loss Of Transmit Clock
100 RSYSCLK I Receive System Clock
DS21352/DS21552
12 of 137
Table 4-1 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN SYMBOL
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
3 8MCLK O 8.192 MHz Clock
13 8XCLK O Eight Times Clock
66 A0 I Address Bus Bit 0
67 A1 I Address Bus Bit 1
68 A2 I Address Bus Bit 2
69 A3 I Address Bus Bit 3
70 A4 I Address Bus Bit 4
71 A5 I Address Bus Bit 5
72 A6 I Address Bus Bit 6
73 ALE (AS)/A7 I Address Latch Enable/Address Bus Bit 7
11 BTS I Bus Type Select
36 CI I Carry In
54 CO O Carry Out
75 CS* I Chip Select
56 D0/AD0 I/O Data Bus Bit0/ Address/Data Bus Bit 0
57 D1/AD1 I/O Data Bus Bit1/ Address/Data Bus Bit 1
58 D2/AD2 I/O Data Bus Bit 2/Address/Data Bus 2
59 D3/AD3 I/O Data Bus Bit 3/Address/Data Bus Bit 3
62 D4/AD4 I/O Data Bus Bit4/Address/Data Bus Bit 4
63 D5/AD5 I/O Data Bus Bit 5/Address/Data Bus Bit 5
64 D6/AD6 I/O Data Bus Bit 6/Address/Data Bus Bit 6
65 D7/AD7 I/O Data Bus Bit 7/Address/Data Bus Bit 7
44 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply
81 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply
45 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
60 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
80 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
84 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground
76 FMS I Framer Mode Select
61 DVDD - Digital Positive Supply
83 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply
25 INT* O Interrupt
4 JTCLK I IEEE 1149.1 Test Clock Signal
7 JTDI I IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Input
10 JTDO O IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Output
2 JTMS I IEEE 1149.1 Test Mode Select
5 JTRST I IEEE 1149.1 Test Reset
12 LIUC I Line Interface Connect
21 MCLK I Master Clock Input
55 MUX I Bus Operation
8 NC – No Connect
9 NC – No Connect
15 NC – No Connect
23 NC – No Connect
26 NC – No Connect
Table 4-1 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN SYMBOL (cont.)
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
27 NC – No Connect
28 NC – No Connect
1 RCHBLK O Receive Channel Block
92 RCHCLK O Receive Channel Clock
6 RCL O Receive Carrier Loss
82 RCLK O Receive Clock
DS21352/DS21552
13 of 137
88 RCLKI I Receive Clock Input
89 RCLKO O Receive Clock Output
74 RD*(DS*) I Read Input(Data Strobe)
85 RDATA O Receive Data
97 RFSYNC O Receive Frame Sync
79 RLCLK O Receive Link Clock
78 RLINK O Receive Link Data
99 RLOS/LOTC O Receive Loss Of Sync/ Loss Of Transmit Clock
96 RMSYNC O Receive Multiframe Sync
87 RNEGI I Receive Negative Data Input
90 RNEGO O Receive Negative Data Output
86 RPOSI I Receive Positive Data Input
91 RPOSO O Receive Positive Data Output
17 RRING I Receive Analog Ring Input
95 RSER O Receive Serial Data
94 RSIG O Receive Signaling Output
93 RSIGF O Receive Signaling Freeze Output
98 RSYNC I/O Receive Sync
100 RSYSCLK I Receive System Clock
16 RTIP I Receive Analog Tip Input
18 RVDD – Receive Analog Positive Supply
19 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground
20 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground
24 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground
33 TCHBLK O Transmit Channel Block
53 TCHCLK O Transmit Channel Clock
46 TCLK I Transmit Clock
40 TCLKI I Transmit Clock Input
41 TCLKO O Transmit Clock Output
50 TDATA I Transmit Data
49 TESO O Transmit Elastic Store Output
14 TEST I Test
34 TLCLK O Transmit Link Clock
35 TLINK I Transmit Link Data
39 TNEGI I Transmit Negative Data Input
42 TNEGO O Transmit Negative Data Output
38 TPOSI I Transmit Positive Data Input
43 TPOSO O Transmit Positive Data Output
32 TRING O Transmit Analog Ring Output
Table 4-1 PIN DESCRIPTION SORTED BY PIN SYMBOL (cont.)
47 TSER I Transmit Serial Data
48 TSIG I Transmit Signaling Input
52 TSSYNC I Transmit System Sync
37 TSYNC I/O Transmit Sync
51 TSYSCLK I Transmit System Clock
29 TTIP O Transmit Analog Tip Output
31 TVDD – Transmit Analog Positive Supply
30 TVSS – Transmit Analog Signal Ground
77 WR*(R/W*) I Write Input(Read/Write)
22 XTALD O Quartz Crystal Driver
DS21352/DS21552
14 of 137

4. PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
4.1.1 TRANSMIT SIDE PINS
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 1.544 MHz primary clock. Used to clock data through the transmit side formatter.
TCLK
Transmit Clock
Input
DS21352/DS21552
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Transmit NRZ serial data. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK when the transmit side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on
the falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is enabled.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 192 kHz clock which pulses high during the LSB of each channel. Synchronous with TCLK when the transmit side elastic
store is disabled. Synchronous with TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel to serial
conversion of channel data.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A user programmable output that can be forced high or low during any of the 24 T1 channels. Synchronous with TCLK when
the transmit side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous with TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is enabled. Useful
for blocking clocks to a serial UART or LAPD controller in applications where not all T1 channels are used such as Fractional
T1, 384 kbps (H0), 768 kbps or ISDN–PRI . Also useful for locating individual channels in drop–and–insert applications, for
external per–channel loopback, and for per–channel conditioning. See section 13 on page 76 for more information.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
1.544 MHz , 2.048 MHz , 4.096 MHz or 8.192 MHz clock. Only used when the transmit side elastic store function is enabled.
Should be tied low in applications that do not use the transmit side elastic store. See section 20 on page 129 for details on
4.096 MHz and 8.192 MHz operation using the Interleave Bus Option.
TSER
Transmit Serial Data
Input
TCHCLK
Transmit Channel Clock
Output
TCHBLK
Transmit Channel Block
Output
TSYSCLK
Transmit System Clock
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
4 kHz or 2 kHz (ZBTSI) demand clock for the TLINK input. See Section 15 for details. Transmit Link Data [TLINK].
TLCLK
Transmit Link Clock
Output
15 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
4.1.1 TRANSMIT SIDE PINS (cont.)
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
If enabled via TCR1.2, this pin will be sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data insertion into either the FDL stream
(ESF) or the Fs–bit position (D4) or the Z–bit position (ZBTSI). See Section 15 for details.
TLINK
Transmit Link Data
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A pulse at this pin will establish either frame or multiframe boundaries for the transmit side. Via TCR2.2, the DS21352/552
can be programmed to output either a frame or multiframe pulse at this pin. If this pin is set to output pulses at frame
boundaries, it can also be set via TCR2.4 to output double–wide pulses at signaling frames. See Section 20 for details.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Only used when the transmit side elastic store is enabled. A pulse at this pin will establish either frame or multiframe
boundaries for the transmit side. Should be tied low in applications that do not use the transmit side elastic store.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
When enabled, this input will sample signaling bits for insertion into outgoing PCM T1 data stream. Sampled on the falling
edge of TCLK when the transmit side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on the falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit
side elastic store is enabled.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of TCLK with data out of the transmit side elastic store whether the elastic store is enabled or not.
This pin is normally tied to TDATA.
TSYNC
Transmit Sync
Input / Output
TSSYNC
Transmit System Sync
Input
TSIG
Transmit Signaling Input
Input
TESO
Transmit Elastic Store Data Output
Output
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK with data to be clocked through the transmit side formatter. This pin is normally tied to
TESO.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of the transmit side formatter. Can be programmed to source
NRZ data via the Output Data Format (CCR1.6) control bit. This pin is normally tied to TPOSI.
TDATA
Transmit Data
Input
TPOSO
Transmit Positive Data Output
Output
16 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
4.1.1 TRANSMIT SIDE PINS (cont.)
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of the transmit side formatter. This pin is normally tied to
TNEGI.
TNEGO
Transmit Negative Data Output
Output
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Buffered clock that is used to clock data through the transmit side formatter (i.e., either TCLK or RCLKI). This pin is normally
tied to TCLKI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out onto the T1 line. Can be internally connected to TPOSO
by tying the LIUC pin high.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out onto the T1 line. Can be internally connected to TNEGO
by tying the LIUC pin high.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Line interface transmit clock. Can be internally connected to TCLKO by tying the LIUC pin high.
TCLKO
Transmit Clock Output
Output
TPOSI
Transmit Positive Data Input
Input
TNEGI
Transmit Negative Data Input
Input
TCLKI
Transmit Clock Input
Input
17 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
4.1.2 RECEIVE SIDE PINS
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated with either FDL data (ESF) or Fs bits (D4) or Z bits (ZBTSI) one RCLK before the start of a frame. See Section 20
for details.
RLINK
Receive Link Data
Output
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 4 kHz or 2 kHz (ZBTSI) clock for the RLINK output.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
1.544 MHz clock that is used to clock data through the receive side framer.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 192 kHz clock which pulses high during the LSB of each channel. Synchronous with RCLK when the receive side elastic
store is disabled. Synchronous with RSYSCLK when the receive side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel to serial
conversion of channel data.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A user programmable output that can be forced high or low during any of the 24 T1 channels. Synchronous with RCLK when
the receive side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous with RSYSCLK when the receive side elastic store is enabled. Useful for
blocking clocks to a serial UART or LAPD controller in applications where not all T1 channels are used such as Fractional T1,
384K bps service, 768K bps, or ISDN–PRI. Also useful for locating individual channels in drop–and–insert applications, for
external per–channel loopback, and for per–channel conditioning. See Section 13 page 76 for details.
RLCLK
Receive Link Clock
Output
RCLK
Receive Clock
Output
RCHCLK
Receive Channel Clock
Output
RCHBLK
Receive Channel Block
Output
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Received NRZ serial data. Updated on rising edges of RCLK when the receive side elastic store is disabled. Updated on the
rising edges of RSYSCLK when the receive side elastic store is enabled.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
An extracted pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin which identifies either frame (RCR2.4 = 0) or multiframe (RCR2.4 =
1) boundaries. If set to output frame boundaries then via RCR2.5, RSYNC can also be set to output double–wide pulses on
signaling frames. If the receive side elastic store is enabled via CCR1.2, then this pin can be enabled to be an input via RCR2.3
at which a frame or multiframe boundary pulse is applied. See Section 21 for details.
RSER
Receive Serial Data
Output
RSYNC
Receive Sync
Input/Output
18 of 137

4.1.2 RECEIVE SIDE PINS (cont.)
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
An extracted 8 kHz pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin which identifies frame boundaries.
RFSYNC
Receive Frame Sync
Output
DS21352/DS21552
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Only used when the receive side elastic store is enabled. An extracted pulse, one RSYSCLK wide, is output at this pin which
identifies multiframe boundaries. If the receive side elastic store is disabled, then this output will output multiframe boundaries
associated with RCLK.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of RCLK with the data out of the receive side framer.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
1.544 MHz , 2.048 MHz , 4.096 MHz or 8.192 MHz clock. Only used when the receive side elastic store function is enabled.
Should be tied low in applications that do not use the receive side elastic store. See section 20 on page 129 for details on 4.096
MHz and 8.192 MHz operation using the Interleave Bus Option.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Outputs signaling bits in a PCM format. Updated on rising edges of RCLK when the receive side elastic store is disabled.
Updated on the rising edges of RSYSCLK when the receive side elastic store is enabled.
RMSYNC
Receive Multiframe Sync
Output
RDATA
Receive Data
Output
RSYSCLK
Receive System Clock
Input
RSIG
Receive Signaling Output
Output
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A dual function output that is controlled by the CCR3.5 control bit. This pin can be programmed to either toggle high when the
synchronizer is searching for the frame and multiframe or to toggle high if the TCLK pin has not been toggled for 5 msec.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Set high when the line interface detects a carrier loss.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Set high when the signaling data is frozen via either automatic or manual intervention. Used to alert downstream equipment of
the condition.
RLOS/LOTC
Receive Loss of Sync / Loss of Transmit Clock
Output
RCL
Receive Carrier Loss
Output
RSIGF
Receive Signaling Freeze
Output
4.1.2 RECEIVE SIDE PINS (cont.)
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
An 8.192MHz clock output that is referenced to the clock that is output at the RCLK pin.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
8MCLK
8 MHz Clock
Output
RPOSO
Receive Positive Data Input
Output
19 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
Updated on the rising edge of RCLKO with bipolar data out of the line interface. This pin is normally tied to RPOSI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of RCLKO with the bipolar data out of the line interface. This pin is normally tied to RPOSI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Buffered recovered clock from the T1 line. This pin is normally tied to RCLKI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked through the receive side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied
together for a NRZ interface. Can be internally connected to RPOSO by tying the LIUC pin high.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked through the receive side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied
together for a NRZ interface. Can be internally connected to RNEGO by tying the LIUC pin high.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Clock used to clock data through the receive side framer. This pin is normally tied to RCLKO. Can be internally connected to
RCLKO by tying the LIUC pin high.
RNEGO
Receive Negative Data Input
Output
RCLKO
Receive Clock Output
Output
RPOSI
Receive Positive Data Input
Input
RNEGI
Receive Negative Data Input
Input
RCLKI
Receive Clock Input
Input
20 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
4.1.3 PARALLEL CONTROL PORT PINS
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Flags host controller during conditions and change of conditions defined in the Status Registers 1 and 2 and the HDLC Status
Register. Active low, open drain output
INT*
Interrupt
Output
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Selects the DS2152 mode when high or the DS21352/552 mode when low. If high, the JTRST is internally pulled low. If low,
JTRST has normal JTAG functionality. This pin has a 10k pull up resistor.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Set high to 3–state all output and I/O pins (including the parallel control port) when FMS = 1 or when FMS = 0 and JTRST* is
tied low. Set low for normal operation. Ignored when FMS = 0 and JTRST* = 1. Useful for board level testing.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Set low to select non–multiplexed bus operation. Set high to select multiplexed bus operation.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
In non–multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 0), serves as the data bus. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 1), serves as a 8–
bit multiplexed address / data bus.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
In non–multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 0), serves as the address bus. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 1), these pins
are not used and should be tied low.
FMS
Framer Mode Select
Input
TEST
3–State Control
Input
MUX
Bus Operation
Input
AD0 TO AD7
Data Bus [D0 to D7] or Address/Data Bus
Input
A0 TO A6
Address Bus
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Strap high to select Motorola bus timing; strap low to select Intel bus timing. This pin controls the function of the RD*(DS*),
ALE(AS), and WR*(R/W*) pins. If BTS = 1, then these pins assume the function listed in parenthesis ().
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
RD* and DS* are active low signals. DS active HIGH when MUX = 0. See bus timing diagrams.
BTS
Bus Type Select
Input
RD*(DS*)
Read Input - Data Strobe
Input
21 of 137

4.1.3 PARALLEL CONTROL PORT PINS (cont.)
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Must be low to read or write to the device. CS* is an active low signal.
CS*
Chip Select
Input
DS21352/DS21552
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
In non–multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 0), serves as the upper address bit. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 1), serves
to de-multiplex the bus on a positive–going edge.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
WR* is an active low signal.
ALE(AS)/A7
Address Latch Enable(Address Strobe) or A7
Input
WR*(R/W*)
Write Input(Read/Write)
Input
22 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
4.1.4 JTAG TEST ACCESS PORT PINS
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
If FMS = 1: JTAG functionality is not available and JTRST is held LOW internally.
If FMS = 0: JTAG functionality is available and JTRST is pulled up internally by a 10kΩ resistor.
If FMS = 0 and boundary scan is not used, this pin should be held low. This signal is used to asynchronously reset the test
access port controller. The device operates as a T1/E1 transceiver if JTRST is pulled low.
JTRST
IEEE 1149.1 Test Reset
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
This pin is sampled on the rising edge of JTCLK and is used to place the test access port into the various defined IEEE 1149.1
states. This pin has a 10k pull up resistor.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
This signal is used to shift data into JTDI on the rising edge and out of JTDO on the falling edge.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Test instructions and data are clocked into this pin on the rising edge of JTCLK. This pin has a 10k pull up resistor.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Test instructions and data are clocked out of this pin on the falling edge of JTCLK. If not used, this pin should be left
unconnected.
JTMS
IEEE 1149.1 Test Mode Select
Input
JTCLK
IEEE 1149.1 Test Clock Signal
Input
JTDI
IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Input
Input
JTDO
IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Output
Output
4.1.5 INTERLEAVE BUS OPERATION PINS
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A rising edge on this pin causes RSER and RSIG to come out of high Z state and TSER and TSIG to start sampling on the next
rising edge of RSYSCLK/TSYSCLK beginning an I/O sequence of 8 or 256 bits of data. This pin has a 10k pull up resistor.
CI
Carry In
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
CO
Carry Out
Output
An output that is set high when the last bit of the 8 or 256 IBO output sequence has occurred on RSER
and RSIG.
23 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
4.1.6 LINE INTERFACE PINS
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 1.544 MHz (50 ppm) clock source with TTL levels is applied at this pin. This clock is used internally for both clock/data
recovery and for jitter attenuation. A quartz crystal of 1.544 MHz may be applied across MCLK and XTALD instead of the
TTL level clock source.
MCLK
Master Clock Input
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A quartz crystal of 1.544 MHz may be applied across MCLK and XTALD instead of a TTL level clock source at MCLK.
Leave open circuited if a TTL clock source is applied at MCLK.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 12.352 MHz clock that is locked to the 1.544 MHz clock provided from the clock/data recovery block (if the jitter attenuator
is enabled on the receive side) or from the TCLKI pin (if the jitter attenuator is enabled on the transmit side). Can be internally
disabled by writing a 08h to TEST2.3 if not needed.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Tie low to separate the line interface circuitry from the framer/formatter circuitry and activate the
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/ RCLKI pins. Tie high to connect the line interface circuitry to the framer/formatter
circuitry and deactivate the TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins. When LIUC is tied high, the
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/ RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins should be tied low.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Analog inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins connect via a 1:1 transformer to the T1 line. See Section 16 for details.
XTALD
Quartz Crystal Driver
Output
8XCLK
Eight Times Clock
Output
LIUC
Line Interface Connect
Input
RTIP & RRING
Receive Tip and Ring
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Analog line driver outputs. These pins connect via a transformer to the T1 line. See Section 16 for details.
TTIP & TRING
Transmit Tip and Ring
Output
24 of 137

4.1.7 SUPPLY PINS
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
5.0 volts +/-5% (DS21552) or 3.3 volts +/-5% (DS21352). Should be tied to the RVDD and TVDD pins.
DVDD
Digital Positive Supply
Supply
DS21352/DS21552
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
5.0 volts +/-5% (DS21552) or 3.3 volts +/-5% (DS21352). Should be tied to the DVDD and TVDD pins.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
5.0 volts +/-5% (DS21552) or 3.3 volts +/-5% (DS21352). Should be tied to the RVDD and DVDD pins.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Should be tied to the RVSS and TVSS pins.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
0.0 volts. Should be tied to DVSS and TVSS.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
0.0 volts. Should be tied to DVSS and RVSS.
RVDD
Receive Analog Positive Supply
Supply
TVDD
Transmit Analog Positive Supply
Supply
DVSS
Digital Signal Ground
Supply
RVSS
Receive Analog Signal Ground
Supply
TVSS
Transmit Analog Signal Ground
Supply
25 of 137
DS21352/DS21552
5. PARALLEL PORT
The SCT is controlled via either a non–multiplexed (MUX = 0) or a multiplexed (MUX = 1) bus by an
external microcontroller or microprocessor. The SCT can operate with either Intel or Motorola bus timing
configurations. If the BTS pin is tied low, Intel timing will be selected; if tied high, Motorola timing will
be selected. All Motorola bus signals are listed in parenthesis (). See the timing diagrams in the A.C.
Electrical Characteristics in Section 24 for more details.
5.1 REGISTER MAP
Table 5-1 REGISTER MAP SORTED BY ADDRESS
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
00 R/W HDLC Control HCR
01 R/W HDLC Status HSR
02 R/W HDLC Interrupt Mask HIMR
03 R/W Receive HDLC Information RHIR
04 R/W Receive Bit Oriented Code RBOC
05 R Receive HDLC FIFO RHFR
06 R/W Transmit HDLC Information THIR
07 R/W Transmit Bit Oriented Code TBOC
08 W Transmit HDLC FIFO THFR
09 R/W Test 2 SEE NOTE 1 TEST2 (set to 00h)
0A R/W Common Control 7 CCR7
0B – not present –
0C – not present –
0D – not present –
0E – not present –
0F R Device ID IDR
10 R/W Receive Information 3 RIR3
11 R/W Common Control 4 CCR4
12 R/W In–Band Code Control IBCC
13 R/W Transmit Code Definition TCD
14 R/W Receive Up Code Definition RUPCD
15 R/W Receive Down Code Definition RDNCD
16 R/W Transmit Channel Control 1 TCC1
17 R/W Transmit Channel Control 2 TCC2
18 R/W Transmit Channel Control 3 TCC3
19 R/W Common Control 5 CCR5
1A R Transmit DS0 Monitor TDS0M
1B R/W Receive Channel Control 1 RCC1
1C R/W Receive Channel Control 2 RCC2
1D R/W Receive Channel Control 3 RCC3
1E R/W Common Control 6 CCR6
1F R Receive DS0 Monitor RDS0M
20 R/W Status 1 SR1
Table 5-1 REGISTER MAP SORTED BY ADDRESS (Cont.)
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
21 R/W Status 2 SR2
22 R/W Receive Information 1 RIR1
23 R Line Code Violation Count 1 LCVCR1
24 R Line Code Violation Count 2 LCVCR2
25 R Path Code Violation Count 1 SEE NOTE 3 PCVCR1
26 R Path Code violation Count 2 PCVCR2
26 of 137
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
27 R Multiframe Out of Sync Count 2 MOSCR2
28 R Receive FDL Register RFDL
29 R/W Receive FDL Match 1 RMTCH1
2A R/W Receive FDL Match 2 RMTCH2
2B R/W Receive Control 1 RCR1
2C R/W Receive Control 2 RCR2
2D R/W Receive Mark 1 RMR1
2E R/W Receive Mark 2 RMR2
2F R/W Receive Mark 3 RMR3
30 R/W Common Control 3 CCR3
31 R/W Receive Information 2 RIR2
32 R/W Transmit Channel Blocking 1 TCBR1
33 R/W Transmit Channel blocking 2 TCBR2
34 R/W Transmit Channel Blocking 3 TCBR3
35 R/W Transmit Control 1 TCR1
36 R/W Transmit Control 2 TCR2
37 R/W Common Control 1 CCR1
38 R/W Common Control 2 CCR2
39 R/W Transmit Transparency 1 TTR1
3A R/W
3B R/W Transmit Transparency 3 TTR3
3C R/W Transmit Idle 1 TIR1
3D R/W Transmit Idle 2 TIR2
3E R/W Transmit Idle 3 TIR3
3F R/W Transmit Idle Definition TIDR
40 R/W Transmit Channel 9 TC9
41 R/W Transmit Channel 10 TC10
42 R/W Transmit Channel 11 TC11
43 R/W Transmit Channel 12 TC12
44 R/W Transmit Channel 13 TC13
45 R/W Transmit Channel 14 TC14
46 R/W Transmit Channel 15 TC15
47 R/W Transmit Channel 16 TC16
48 R/W Transmit Channel 17 TC17
49 R/W Transmit Channel 18 TC18
4A R/W Transmit Channel 19 TC19
4B R/W Transmit Channel 20 TC20
4C R/W Transmit Channel 21 TC21
Transmit Transparency 2
TTR2
Table 5-1 REGISTER MAP SORTED BY ADDRESS (Cont.)
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
4D R/W Transmit Channel 22 TC22
4E R/W Transmit Channel 23 TC23
4F R/W Transmit Channel 24 TC24
50 R/W Transmit Channel 1 TC1
51 R/W Transmit Channel 2 TC2
52 R/W Transmit Channel 3 TC3
53 R/W Transmit Channel 4 TC4
54 R/W Transmit Channel 5 TC5
55 R/W Transmit Channel 6 TC6
56 R/W Transmit Channel 7 TC7
57 R/W Transmit Channel 8 TC8
58 R/W Receive Channel 17 RC17
59 R/W Receive Channel 18 RC18
27 of 137
DS21352/DS21552
5A R/W Receive Channel 19 RC19
5B R/W Receive Channel 20 RC20
5C R/W Receive Channel 21 RC21
5D R/W Receive Channel 22 RC22
5E R/W Receive Channel 23 RC23
5F R/W Receive Channel 24 RC24
60 R Receive Signaling 1 RS1
61 R Receive Signaling 2 RS2
62 R Receive Signaling 3 RS3
63 R Receive Signaling 4 RS4
64 R Receive Signaling 5 RS5
65 R Receive Signaling 6 RS6
66 R Receive Signaling 7 RS7
67 R Receive Signaling 8 RS8
68 R Receive Signaling 9 RS9
69 R Receive Signaling 10 RS10
6A R Receive Signaling 11 RS11
6B R Receive Signaling 12 RS12
6C R/W Receive Channel Blocking 1 RCBR1
6D R/W Receive Channel Blocking 2 RCBR2
6E R/W Receive Channel Blocking 3 RCBR3
6F R/W Interrupt Mask 2 IMR2
70 R/W Transmit Signaling 1 TS1
71 R/W Transmit Signaling 2 TS2
72 R/W Transmit Signaling 3 TS3
73 R/W Transmit Signaling 4 TS4
74 R/W Transmit Signaling 5 TS5
75 R/W Transmit Signaling 6 TS6
76 R/W Transmit Signaling 7 TS7
77 R/W Transmit Signaling 8 TS8
78 R/W Transmit Signaling 9 TS9
Table 5-1 REGISTER MAP SORTED BY ADDRESS (Cont.)
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
79 R/W Transmit Signaling 10 TS10
7A R/W Transmit Signaling 11 TS11
7B R/W Transmit Signaling 12 TS12
7C R/W Line Interface Control LICR
7D R/W Test 1 SEE NOTE 1 TEST1 (set to 00h)
7E R/W Transmit FDL Register TFDL
7F R/W Interrupt Mask Register 1 IMR1
80 R/W Receive Channel 1 RC1
81 R/W Receive Channel 2 RC2
82 R/W Receive Channel 3 RC3
83 R/W Receive Channel 4 RC4
84 R/W Receive Channel 5 RC5
85 R/W Receive Channel 6 RC6
86 R/W Receive Channel 7 RC7
87 R/W Receive Channel 8 RC8
88 R/W Receive Channel 9 RC9
89 R/W Receive Channel 10 RC10
8A R/W Receive Channel 11 RC11
8B R/W Receive Channel 12 RC12
8C R/W Receive Channel 13 RC13
8D R/W Receive Channel 14 RC14
8E R/W Receive Channel 15 RC15
28 of 137
DS21352/DS21552
DS21352/DS21552
8F R/W Receive Channel 16 RC16
90 R/W Receive HDLC DS0 Control Register 1 RDC1
91 R/W Receive HDLC DS0 Control Register 2 RDC2
92 R/W Transmit HDLC DS0 Control Register 1 TDC1
93 R/W Transmit HDLC DS0 Control Register 2 TDC2
94 R/W Interleave Bus Operation Register IBO
95 R/W Test 3 SEE NOTE 1 TEST3 (set to 00h)
96 R/W Test 4 SEE NOTE 1 TEST4 (set to 00h)
97 - not present -
98 - not present -
99 - not present 9A - not present 9B - not present 9C - not present 9D - not present 9E - not present -
9F - not present -
NOTES:
1. TEST1, TEST2, TEST3 and TEST4 registers are used by the factory; these registers must be cleared (set to 00h) on power–
up initialization to insure proper operation.
2. Register banks Axh, Bxh, Cxh, Dxh, Exh, and Fxh are not accessible.
3. Upper nibble of the PCVCR1 register is used for MOSCR1
6. CONTROL, ID, AND TEST REGISTERS
The operation of the DS21352/552 is configured via a set of eleven control registers. Typically, the
control registers are only accessed when the system is first powered up. Once the DS21352/552 has been
initialized, the control registers will only need to be accessed when there is a change in the system
configuration. There are two Receive Control Registers (RCR1 and RCR2), two Transmit Control
Registers (TCR1 and TCR2), and seven Common Control Registers (CCR1 to CCR7). Each of the eleven
registers are described in this section.
6.1 POWER-UP SEQUENCE
On power–up, after the supplies are stable the DS21352/552 should be configured for operation by
writing to all of the internal registers (this includes setting the Test Registers to 00h) since the contents of
the internal registers cannot be predicted on power–up. The LIRST (CCR7.7) should be toggled from
zero to one to reset the line interface circuitry (it will take the DS21352/552 about 40ms to recover from
the LIRST bit being toggled). Finally, after the TSYSCLK and RSYSCLK inputs are stable, the ESR bit
should be toggled from a zero to a one (this step can be skipped if the elastic stores are disabled).
6.2 DEVICE ID
There is a device IDentification Register (IDR) at address 0Fh. The MSB of this read–only register is
fixed to a zero indicating that a T1 device is present. The next 3 MSBs are used to indicate which T1
device is present; DS2152, DS21352, or DS21552. The E1 pin–for–pin compatible SCTs will have a
logic one in the MSB position with the following 3 MSBs indicating which E1 SCT is present; DS2154,
DS21354, or DS21554. Table 6-1 represents the possible variations of these bits and the associated SCT.
IDR: DEVICE IDENTIFICATION REGISTER (Address=0F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
T1E1 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
T1E1 IDR.7
T1 or E1 Chip Determination Bit.
29 of 137

Bit 6 IDR.6
DS21352/DS21552
0=T1 chip
1=E1 chip
Bit 6.
Bit 5 IDR.5
Bit 4 IDR.4
ID3 IDR.3 Chip Revision Bit 3. MSB of a decimal code that represents the chip revision.
ID2 IDR.1
ID1 IDR.2
Bit 5.
Bit 4.
Chip Revision Bit 2.
Chip Revision Bit 1.
30 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
Table 6-1 DEVICE ID BIT MAP
SCT T1/E1 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4
DS2152 0 0 0 0
DS21352 0 0 0 1
DS21552 0 0 1 0
DS2154 1 0 0 0
DS21354 1 0 0 1
DS21554 1 0 1 0
The lower four bits of the IDR are used to display the die revision of the chip.
RCR1: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=2B Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LCVCRF ARC OOF1 OOF2 SYNCC SYNCT SYNCE RESYNC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LCVCRF RCR1.7
ARC RCR1.6
OOF1 RCR1.5
OOF2 RCR1.4
SYNCC RCR1.3
SYNCT RCR1.2
SYNCE RCR1.1
RESYNC RCR1.0 Resync. When toggled from low to high, a resynchronization of the receive side framer
Line Code Violation Count Register Function Select.
0 = do not count excessive zeros
1 = count excessive zeros
Auto Resync Criteria.
0 = Resync on OOF or RCL event
1 = Resync on OOF only
Out Of Frame Select 1.
0 = 2/4 frame bits in error
1 = 2/5 frame bits in error
Out Of Frame Select 2.
0 = follow RCR1.5
1 = 2/6 frame bits in error
Sync Criteria.
In D4 Framing Mode.
0 = search for Ft pattern, then search for Fs pattern
1 = cross couple Ft and Fs pattern
In ESF Framing Mode.
0 = search for FPS pattern only
1 = search for FPS and verify with CRC6
Sync Time.
0 = qualify 10 bits
1 = qualify 24 bits
Sync Enable.
0 = auto resync enabled
1 = auto resync disabled
is initiated. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent resync.
31 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RCR2: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=2C Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RCS RZBTSI RSDW RSM RSIO RD4YM FSBE MOSCRF
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RCS RCR2.7
RZBTSI RCR2.6 Receive Side ZBTSI Support Enable. Allows ZBTSI information to be output on
RSDW RCR2.5 RSYNC Double–Wide. (note: this bit must be set to zero when RCR2.4 = 1 or when
RSM RCR2.4 RSYNC Mode Select. Selects frame or multiframe pulse when RSYNC pin is in output
Receive Code Select.
0 = idle code (7F Hex)
1 = digital milliwatt code (1E/0B/0B/1E/9E/8B/8B/9E Hex)
RLINK pin.
0 = ZBTSI disabled
1 = ZBTSI enabled
RCR2.3 = 1)
0 = do not pulse double wide in signaling frames
1 = do pulse double wide in signaling frames
mode. In input mode (elastic store must be enabled) multiframe mode is only useful
when receive signaling re-insertion is enabled. See the timing in Section 21.
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
RSIO RCR2.3 RSYNC I/O Select. (note: this bit must be set to zero when CCR1.2 = 0)
0 = RSYNC is an output
1 = RSYNC is an input (only valid if elastic store enabled)
RD4YM RCR2.2
FSBE RCR2.1
MOSCRF RCR2.0
Receive Side D4 Yellow Alarm Select.
0 = zeros in bit 2 of all channels
1 = a one in the S–bit position of frame 12
PCVCR Fs–Bit Error Report Enable.
0 = do not report bit errors in Fs–bit position; only Ft bit position
1 = report bit errors in Fs–bit position as well as Ft bit position
Multiframe Out of Sync Count Register Function Select.
0 = count errors in the framing bit position
1 = count the number of multiframes out of sync
32 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TCR1: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=35 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LOTCMC TFPT TCPT TSSE GB7S TFDLS TBL TYEL
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LOTCMC TCR1.7 Loss Of Transmit Clock Mux Control. Determines whether the transmit side
formatter should switch to RCLK if the TCLK input should fail to transition.
0 = do not switch to RCLK if TCLK stops
1 = switch to RCLK if TCLK stops
TFPT TCR1.6 Transmit F–Bit Pass Through. (see note below)
0 = F bits sourced internally
1 = F bits sampled at TSER
TCPT TCR1.5 Transmit CRC Pass Through. (see note below)
0 = source CRC6 bits internally
1 = CRC6 bits sampled at TSER during F–bit time
TSSE TCR1.4 Transmit Software Signaling Enable. (see note below)
0 = no signaling is inserted in any channel
1 = signaling is inserted in all channels from the TS1-TS12 registers (the TTR registers
can be used to block insertion on a channel by channel basis)
GB7S TCR1.3 Global Bit 7 Stuffing. (see note below)
0 = allow the TTR registers to determine which channels containing all zeros are to be
Bit 7 stuffed
1 = force Bit 7 stuffing in all zero byte channels regardless of how the TTR registers are
programmed
TFDLS TCR1.2 TFDL Register Select. (see note below)
0 = source FDL or Fs bits from the internal TFDL register (legacy FDL support mode)
1 = source FDL or Fs bits from the internal HDLC/BOC controller or the TLINK pin
TBL TCR1.1 Transmit Blue Alarm. (see note below)
0 = transmit data normally
1 = transmit an unframed all one’s code at TPOSO and TNEGO
TYEL TCR1.0 Transmit Yellow Alarm. (see note below)
0 = do not transmit yellow alarm
1 = transmit yellow alarm
NOTE: For a description of how the bits in TCR1 affect the transmit side formatter, see Figure 22-2
33 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TCR2: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=36 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TEST1 TEST0 TZBTSI TSDW TSM TSIO TD4YM TB7ZS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TEST1 TCR2.7 Test Mode Bit 1 for Output Pins. See Table 6-2..
TEST0 TCR2.6 Test Mode Bit 0 for Output Pins. See Table 6-2.
TZBTSI TCR2.5 Transmit Side ZBTSI Support Enable. Allows ZBTSI information to be input on
TLINK pin.
0 = ZBTSI disabled
1 = ZBTSI enabled
TSDW TCR2.4 TSYNC Double–Wide. (note: this bit must be set to zero when TCR2.3=1 or when
TCR2.2=0)
0 = do not pulse double–wide in signaling frames
1 = do pulse double–wide in signaling frames
TSM TCR2.3 TSYNC Mode Select. Selects frame or multiframe mode for the TSYNC pin. See the
timing in Section 21
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
TSIO TCR2.2
TD4YM TCR2.1
TB7ZS TCR2.0
TSYNC I/O Select.
0 = TSYNC is an input
1 = TSYNC is an output
Transmit Side D4 Yellow Alarm Select.
0 = zeros in bit 2 of all channels
1 = a one in the S–bit position of frame 12
Transmit Side Bit 7 Zero Suppression Enable.
0 = no stuffing occurs
1 = Bit 7 force to a one in channels with all zeros
Table 6-2 OUTPUT PIN TEST MODES
TEST 1 TEST 0 EFFECT ON OUTPUT PINS
0 0 operate normally
0 1 force all output pins into 3–state (including all I/O pins and parallel port pins)
1 0 force all output pins low (including all I/O pins except parallel port pins)
1 1 force all output pins high (including all I/O pins except parallel port pins)
34 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
CCR1: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=37 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TESE ODF RSAO TSCLKM RSCLKM RESE PLB FLB
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TESE CCR1.7
ODF CCR1.6
Transmit Elastic Store Enable.
0 = elastic store is bypassed
1 = elastic store is enabled
Output Data Format.
0 = bipolar data at TPOSO and TNEGO
1 = NRZ data at TPOSO; TNEGO = 0
RSAO CCR1.5 Receive Signaling All One’s. This bit should not be enabled if hardware signaling is
being utilized. See Section 10 for more details.
0 = allow robbed signaling bits to appear at RSER
1 = force all robbed signaling bits at RSER to one
TSCLKM CCR1.4
RSCLKM CCR1.3
RESE CCR1.2
PLB CCR1.1
FLB CCR1.0
TSYSCLK Mode Select.
0 = if TSYSCLK is 1.544 MHz
1 = if TSYSCLK is 2.048 MHz or IBO enabled (see section 20 for details on IBO
function)
RSYSCLK Mode Select.
0 = if RSYSCLK is 1.544 MHz
1 = if RSYSCLK is 2.048 MHz or IBO enabled (see section 20 for details on IBO
function)
Receive Elastic Store Enable.
0 = elastic store is bypassed
1 = elastic store is enabled
Payload Loopback.
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
Framer Loopback.
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
6.3 PAYLOAD LOOPBACK
Payload Loopback When CCR1.1 is set to a one, the DS21352/552 will be forced into Payload LoopBack
(PLB). Normally, this loopback is only enabled when ESF framing is being performed but can be enabled
also in D4 framing applications. In a PLB situation, the DS21352/552 will loop the 192 bits of pay-load
data (with BPVs corrected) from the receive section back to the transmit section. The FPS framing pattern, CRC6 calculation, and the FDL bits are not looped back, they are reinserted by the DS21352/552.
When PLB is enabled, the following will occur:
1. data will be transmitted from the TPOSO and TNEGO pins synchronous with RCLK instead of TCLK
2. all of the receive side signals will continue to operate normally
3. the TCHCLK and TCHBLK signals are forced low
4. data at the TSER, TDATA, and TSIG pins is ignored
5. the TLCLK signal will become synchronous with RCLK instead of TCLK.
6.4 FRAMER LOOPBACK
When CCR1.0 is set to a one, the DS21352/552 will enter a Framer LoopBack (FLB) mode. This
loopback is useful in testing and debugging applications. In FLB, the DS21352/552 will loop data from
the transmit side back to the receive side. When FLB is enabled, the following will occur:
1. An unframed all one’s code will be transmitted at TPOSO and TNEGO
2. Data at RPOSI and RNEGI will be ignored
35 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
3. All receive side signals will take on timing synchronous with TCLK instead of RCLKI.
Please note that it is not acceptable to have RCLK tied to TCLK during this loopback because this
will cause an unstable condition.
CCR2: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=38 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TFM TB8ZS TSLC96 TFDL RFM RB8ZS RSLC96 RZSE
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TFM CCR2.7
TB8ZS CCR2.6
TSLC96 CCR2.5 Transmit SLC–96 / Fs–Bit Insertion Enable. Only set this bit to a one in D4 framing
TFDL CCR2.4 Transmit FDL Zero Stuffer Enable. Set this bit to zero if using the internal
RFM CCR2.3
RB8ZS CCR2.2
RSLC96 CCR2.1 Receive SLC–96 Enable. Only set this bit to a one in D4/SLC–96 framing
RZSE CCR2.0 Receive FDL Zero Destuffer Enable. Set this bit to zero if using the internal
Transmit Frame Mode Select.
0 = D4 framing mode
1 = ESF framing mode
Transmit B8ZS Enable.
0 = B8ZS disabled
1 = B8ZS enabled
applications. Must be set to one to source the Fs pattern from the TFDL register. See
Section 15.5 for details.
0 = SLC–96/Fs–bit insertion disabled
1 = SLC–96/Fs–bit insertion enabled
HDLC/BOC controller instead of the legacy support for the FDL. See Section 15 for
details.
0 = zero stuffer disabled
1 = zero stuffer enabled
Receive Frame Mode Select.
0 = D4 framing mode
1 = ESF framing mode
Receive B8ZS Enable.
0 = B8ZS disabled
1 = B8ZS enabled
applications. See Section 15.5 for details.
0 = SLC–96 disabled
1 = SLC–96 enabled
HDLC/BOC controller instead of the legacy support for the FDL. See Section 15.4 for
details.
0 = zero destuffer disabled
1 = zero destuffer enabled
CCR3: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 3 (Address=30 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RESMDM TCLKSRC RLOSF RSMS PDE ECUS TLOOP TESMDM
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RESMDM CCR3.7 Receive Elastic Store Minimum Delay Mode. See Section 14.4 for details.
0 = elastic stores operate at full two frame depth
1 = elastic stores operate at 32–bit depth
TCLKSRC CCR3.6 Transmit Clock Source Select. This function allows the user to internally select
RCLK as the clock source for the transmit side formatter.
0 = Source of transmit clock determined by TCR1.7 (LOTCMC)
1 = Force transmitter to internally switch to RCLK as source of transmit clock. Signal
at TCLK pin is ignored
RLOSF CCR3.5
Function of the RLOS/LOTC Output.
0 = Receive Loss of Sync (RLOS)
36 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
1 = Loss of Transmit Clock (LOTC)
RSMS CCR3.4 RSYNC Multiframe Skip Control. Useful in framing format conversions from D4 to
ESF. This function is not available when the receive side elastic store is enabled.
0 = RSYNC will output a pulse at every multiframe
1 = RSYNC will output a pulse at every other multiframe note: for this bit to have any
affect, the RSYNC must be set to output multiframe pulses (RCR2.4=1 and
RCR2.3=0).
PDE CCR3.3
ECUS CCR3.2 Error Counter Update Select. See Section 8 for details.
TLOOP CCR3.1 Transmit Loop Code Enable. See Section 17 for details.
TESMDM CCR3.0 Transmit Elastic Store Minimum Delay Mode. See Section 14.4 for details.
Pulse Density Enforcer Enable.
0 = disable transmit pulse density enforcer
1 = enable transmit pulse density enforcer
0 = update error counters once a second
1 = update error counters every 42 ms (333 frames)
0 = transmit data normally
1 = replace normal transmitted data with repeating code as defined in TCD register
0 = elastic stores operate at full two frame depth
1 = elastic stores operate at 32–bit depth
37 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
6.5 PULSE DENSITY ENFORCER
The Framer always examines both the transmit and receive data streams for violations of the following rules which are
required by ANSI T1.403:
– no more than 15 consecutive zeros
– at least N ones in each and every time window of 8 x (N +1) bits where N = 1 through 23
Violations for the transmit and receive data streams are reported in the RIR2.0 and RIR2.1 bits
respectively. When the CCR3.3 is set to one, the DS21352 will force the transmitted stream to meet this
requirement no matter the content of the transmitted stream. When running B8ZS, the CCR3.3 bit should
be set to zero since B8ZS encoded data streams cannot violate the pulse density requirements.
38 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
CCR4: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 4 (Address=11 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RSRE RPCSI RFSA1 RFE RFF THSE TPCSI TIRFS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RSRE CCR4.7 Receive Side Signaling Re–Insertion Enable. See Section 10.2 for details.
0 = do not re–insert signaling bits into the data stream presented at the RSER pin
1 = reinsert the signaling bits into data stream presented at the RSER pin
RPCSI CCR4.6 Receive Per–Channel Signaling Insert. See Section 10.2 for more details.
0 = do not use RCHBLK to determine which channels should have signaling re–inserted
1 = use RCHBLK to determine which channels should have signaling re–inserted
RFSA1 CCR4.5 Receive Force Signaling All Ones. See Section 10.2 for more details.
0 = do not force extracted robbed–bit signaling bit positions to a one
1 = force extracted robbed–bit signaling bit positions to a one
RFE CCR4.4 Receive Freeze Enable. See Section 10.2 for details.
0 = no freezing of receive signaling data will occur
1 = allow freezing of receive signaling data at RSIG (and RSER if CCR4.7 = 1).
RFF CCR4.3 Receive Force Freeze. Freezes receive side signaling at RSIG (and RSER if
CCR4.7=1); will override Receive Freeze Enable (RFE). See Section 10.2 for details.
0 = do not force a freeze event
1 = force a freeze event
THSE CCR4.2 Transmit Hardware Signaling Insertion Enable. See Section 10.2 for details.
0 = do not insert signaling from the TSIG pin into the data stream presented at the
TSER pin
1 = insert signaling from the TSIG pin into data stream presented at the TSER pin
TPCSI CCR4.1 Transmit Per–Channel Signaling Insert. See Section 10.2 for details.
0 = do not use TCHBLK to determine which channels should have signaling inserted
from TSIG
1 = use TCHBLK to determine which channels should have signaling inserted from
TSIG
TIRFS CCR4.0 Transmit Idle Registers (TIR) Function Select. See Section 2.1 for timing details.
0 = TIRs define in which channels to insert idle code
1 = TIRs define in which channels to insert data from RSER (i.e., Per-Channel
Loopback function)
39 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
CCR5: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 5 (Address=19 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TJC LLB LIAIS TCM4 TCM3 TCM2 TCM1 TCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TJC CCR5.7
LLB CCR5.6 Local Loopback.
LIAIS CCR5.5
TCM4 CCR5.4 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that determines which
TCM3 CCR5.3
TCM2 CCR5.2
TCM1 CCR5.1
TCM0 CCR5.0 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode.
Transmit Japanese CRC6 Enable.
0 = use ANSI/AT&T/ITU CRC6 calculation (normal operation)
1 = use Japanese standard JT–G704 CRC6 calculation
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
Line Interface AIS Generation Enable.
0 = allow normal data from TPOSI/TNEGI to be transmitted at TTIP and TRING
1 = force unframed all ones to be transmitted at TTIP and TRING
transmit channel data will appear in the TDS0M register. See Section 9 for details.
Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 3.
Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 2.
Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 1.
40 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
CCR6: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 6 (Address=1E Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RJC RESA TESA RCM4 RCM3 RCM2 RCM1 RCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RJC CCR6.7
RESA CCR6.6 Receive Elastic Store Align. Setting this bit from a zero to a one will force the receive
TESA CCR6.5 Transmit Elastic Store Align. Setting this bit from a zero to a one will force the
RCM4 CCR6.4 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that determines which
RCM3 CCR6.3
RCM2 CCR6.2
RCM1 CCR6.1
RCM0 CCR6.0 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode.
Receive Japanese CRC6 Enable.
0 = use ANSI/AT&T/ITU CRC6 calculation (normal operation)
1 = use Japanese standard JT–G704 CRC6 calculation
elastic store’s write/read pointers to a minimum separation of half a frame. No action
will be taken if the pointer separation is already greater or equal to half a frame. If
pointer separation is less than half a frame, the command will be executed and the data
will be disrupted. Should be toggled after RSYSCLK has been applied and is stable.
Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent align. See section 14.3 for details.
transmit elastic store’s write/read pointers to a minimum separation of half a frame. No
action will be taken if the pointer separation is already greater or equal to half a frame.
If pointer separation is less than half a frame, the command will be executed and the
data will be disrupted. Should be toggled after TSYSCLK has been applied and is
stable. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent align. See section 14.3 for details.
receive channel data will appear in the RDS0M register. See Section 9 for details.
Receive Channel Monitor Bit 3.
Receive Channel Monitor Bit 2.
Receive Channel Monitor Bit 1.
41 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
CCR7: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 7 (Address=0A Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LIRST RLB RESR TESR – LIUSI CDIG LIUODO
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LIRST CCR7.7 Line Interface Reset. Setting this bit from a zero to a one will initiate an internal reset
that affects the clock recovery state machine and jitter attenuator. Normally this bit is
only toggled on power–up. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent reset.
RLB CCR7.6
RESR CCR7.5 Receive Elastic Store Reset. Setting this bit from a zero to a one will minimize the
TESR CCR7.4 Transmit Elastic Store Reset. Setting this bit from a zero to a one will maximize the
-CCR7.3Reserved. Must be set low for proper operation.
LIUSI CCR7.2 Line Interface Synchronization Interface Enable. This control bit determines whether
CDIG CCR7.1 Customer Disconnect Indication Generator. This control bit determines whether the
LIUODO CCR7.0 Line Interface Open Drain Option. This control bit determines whether the TTIP and
Remote Loopback.
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
delay through the receive elastic store. Should be toggled after RSYSCLK has been
applied and is stable. See section 14.3 for details. Do not leave this bit set HIGH.
delay through the transmit elastic store. Transmit data is lost during the reset. Should be
toggled after TSYSCLK has been applied and is stable. See section 14.3for details. Do
not leave this bit set HIGH.
the line receiver should handle a normal T1 signal or a 1.544MHz synchronization signal.
This control has no affect on the line interface transmitter.
0 = line receiver configured to support a normal T1 signal
1 = line receiver configured to support a synchronization signal
Line Interface will generate an unframed ...1010... pattern at TTIP and TRING instead of
the normal data pattern.
0 = generate normal data at TTIP & TRING as input via TPOSI & TNEGI
1 = generate a ...1010... pattern at TTIP and TRING
TRING outputs will be open drain or not. The line driver outputs can be forced open
drain to allow 6Vpeak pulses to be generated or to allow the creation of a very low power
interface.
0 = allow TTIP and TRING to operate normally
1 = force the TTIP and TRING outputs to be open drain
6.6 REMOTE LOOPBACK
When CCR7.6 is set to a one, the DS21352/552 will be forced into Remote LoopBack (RLB). In this
loopback, data input via the RPOSI and RNEGI pins will be transmitted back to the TPOSO and TNEGO
pins. Data will continue to pass through the receive side framer of the DS21352/552 as it would normally
and the data from the transmit side formatter will be ignored. Please see Figure 3-1 for more details.
42 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
7. STATUS AND INFORMATION REGISTERS
There is a set of nine registers that contain information on the current real time status of the device, Status
Register 1 (SR1), Status Register 2 (SR2), Receive Information Registers 1 to 3 (RIR1/RIR2/RIR3) and a
set of four registers for the onboard HDLC and BOC controller. The specific details on the four registers
pertaining to the HDLC controller are covered in Section 15.3.2 but they operate the same as the other
status registers in the DS21352/552 and this operation is described below.
When a particular event has occurred (or is occurring), the appropriate bit in one of these nine registers
will be set to a one. All of the bits in SR1, SR2, RIR1, RIR2, and RIR3 registers operate in a latched
fashion. This means that if an event or an alarm occurs and a bit is set to a one in any of the registers, it
will remain set until the user reads that bit. The bit will be cleared when it is read and it will not be set
again until the event has occurred again (or in the case of the RBL, RYEL, LRCL, and RLOS alarms, the
bit will remain set if the alarm is still present). There are bits in the four HDLC status registers that are
not latched and these bits are listed in Section 15.3.2.
The user will always proceed a read of any of the nine registers with a write. The byte written to the
register will inform the DS21352/552 which bits the user wishes to read and have cleared. The user will
write a byte to one of these registers, with a one in the bit positions he or she wishes to read and a zero in
the bit positions he or she does not wish to obtain the latest information on. When a one is written to a bit
location, the read register will be updated with the latest information. When a zero is written to a bit
position, the read register will not be updated and the previous value will be held. A write to the status
and information registers will be immediately followed by a read of the same register. The read result
should be logically AND’ed with the mask byte that was just written and this value should be written
back into the same register to insure that bit does indeed clear. This second write step is necessary
because the alarms and events in the status registers occur asynchronously in respect to their access via
the parallel port. This write–read– write scheme allows an external microcontroller or microprocessor to
individually poll certain bits without disturbing the other bits in the register. This operation is key in
controlling the DS21352/552 with higher–order software languages.
The SR1, SR2, and HSR registers have the unique ability to initiate a hardware interrupt via the INT
output pin. Each of the alarms and events in the SR1, SR2, and HSR can be either masked or unmasked
from the interrupt pin via the Interrupt Mask Register 1 (IMR1), Interrupt Mask Register 2 (IMR2), and
HDLC Interrupt Mask Register (HIMR) respectively. The HIMR register is covered in Section 15.3.2.
The interrupts caused by alarms in SR1 (namely RYEL, LRCL, RBL, and RLOS) act differently than the
interrupts caused by events in SR1 and SR2 (namely LUP, LDN, LOTC, RSLIP, RMF, TMF, SEC,
RFDL, TFDL, RMTCH, RAF, and RSC) and HIMR. The alarm caused interrupts will force the INT pin
low whenever the alarm changes state (i.e., the alarm goes active or inactive according to the set/clear
criteria in Table 7-2). The INT pin will be allowed to return high (if no other interrupts are present) when
the user reads the alarm bit that caused the interrupt to occur even if the alarm is still present. The event
caused interrupts will force the INT pin low when the event occurs. The INT pin will be allowed to return
high (if no other interrupts are present) when the user reads the event bit that caused the interrupt to
occur.
43 of 137
DS21352/DS21552
RIR1: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 1 (Address=22 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
COFA 8ZD 16ZD RESF RESE SEFE B8ZS FBE
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
COFA RIR1.7 Change of Frame Alignment. Set when the last resync resulted in a change of frame
or multiframe alignment.
8ZD RIR1.6 Eight Zero Detect. Set when a string of at least eight consecutive zeros (regardless of
the length of the string) have been received at RPOSI and RNEGI.
16ZD RIR1.5 Sixteen Zero Detect. Set when a string of at least sixteen consecutive zeros (regardless
of the length of the string) have been received at RPOSI and RNEGI.
RESF RIR1.4 Receive Elastic Store Full. Set when the receive elastic store buffer fills and a frame
is deleted.
RESE RIR1.3 Receive Elastic Store Empty. Set when the receive elastic store buffer empties and a
frame is repeated.
SEFE RIR1.2 Severely Errored Framing Event. Set when 2 out of 6 framing bits (Ft or FPS) are
received in error.
B8ZS RIR1.1 B8ZS Code Word Detect. Set when a B8ZS code word is detected at RPOSI and
RNEGI independent of whether the B8ZS mode is selected or not via CCR2.6. Useful
for automatically setting the line coding.
FBE RIR1.0 Frame Bit Error. Set when a Ft (D4) or FPS (ESF) framing bit is received in error.
RIR2: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 2 (Address=31 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RLOSC LRCLC TESF TESE TSLIP RBLC RPDV TPDV
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RLOSC RIR2.7 Receive Loss of Sync Clear. Set when the framer achieves synchronization; will
remain set until read.
LRCLC RIR2.6 Line Interface Receive Carrier Loss Clear. Set when the carrier signal is restored;
will remain set until read. See Table 7-2.
TESF RIR2.5 Transmit Elastic Store Full. Set when the transmit elastic store buffer fills and a frame
is deleted.
TESE RIR2.4 Transmit Elastic Store Empty. Set when the transmit elastic store buffer empties and a
frame is repeated.
TSLIP RIR2.3 Transmit Elastic Store Slip Occurrence. Set when the transmit elastic store has either
repeated or deleted a frame.
RBLC RIR2.2 Receive Blue Alarm Clear. Set when the Blue Alarm (AIS) is no longer detected; will
remain set until read. See Table 7-2.
RPDV RIR2.1 Receive Pulse Density Violation. Set when the receive data stream does not meet the
ANSI T1.403 requirements for pulse density.
TPDV RIR2.0 Transmit Pulse Density Violation. Set when the transmit data stream does not meet
the ANSI T1.403 requirements for pulse density.
RIR3: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER 3 (Address=10 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RL1 RL0 JALT LORC FRCL – – –
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RL1 RIR3.7 Receive Level Bit 1. SeeTable 7-1.
RL0 RIR3.6 Receive Level Bit 0. See Table 7-1.
JALT RIR3.5 Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip. Set when the jitter attenuator FIFO reaches to within 4
44 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
bits of its limit; useful for debugging jitter attenuation operation.
LORC RIR3.4 Loss of Receive Clock. Set when the RCLKI pin has not transitioned for at least 2 us (4
ms max).
FRCL RIR3.3 Framer Receive Carrier Loss. Set when 192 consecutive zeros have been received at
the RPOSI and RNEGI pins; allowed to be cleared when 14 or more ones out of 112
possible bit positions are received.
–RIR3.2Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
–RIR3.1Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
–RIR3.0Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
Table 7-1 RECEIVE T1 LEVEL INDICATION
RL1 RL0 TYPICAL LEVEL RECEIVED
0 0 +2 dB to –7.5 dB
0 1 –7.5 dB to –15 dB
1 0 –15 dB to –22.5 dB
1 1 less than –22.5 dB
45 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
SR1: STATUS REGISTER 1 (Address=20 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LUP LDN LOTC RSLIP RBL RYEL LRCL RLOS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LUP SR1.7 Loop Up Code Detected. Set when the loop up code as defined in the RUPCD register
is being received. See Section 16.5 for details.
LDN SR1.6 Loop Down Code Detected. Set when the loop down code as defined in the RDNCD
register is being received. See Section 16.5 for details.
LOTC SR1.5 Loss of Transmit Clock. Set when the TCLK pin has not transitioned for one channel
time (or 5.2 ms). Will force the RLOS/LOTC pin high if enabled via CCR1.6. Also will
force transmit side formatter to switch to RCLK if so enabled via TCR1.7.
RSLIP SR1.4 Receive Elastic Store Slip Occurrence. Set when the receive elastic store has either
repeated or deleted a frame.
RBL SR1.3 Receive Blue Alarm. Set when an unframed all one’s code is received at RPOSI and
RNEGI.
RYEL SR1.2 Receive Yellow Alarm. Set when a yellow alarm is received at RPOSI and RNEGI.
LRCL SR1.1 Line Interface Receive Carrier Loss. Set when a red alarm is received at RTIP and
RRING.
RLOS SR1.0 Receive Loss of Sync. Set when the device is not synchronized to the receive T1
stream.
46 of 137

Table 7-2 ALARM CRITERIA
ALARM SET CRITERIA CLEAR CRITERIA
Blue Alarm (AIS) (see note 1
below)
Yellow Alarm (RAI)
1. D4 bit 2 mode(RCR2.2=0)
when over a 3 ms window, 5 or
less zeros are received
when bit 2 of 256 consecutive
channels is set to zero for at least
254 occurrences
DS21352/DS21552
when over a 3 ms window, 6 or more zeros are
received
when bit 2 of 256 consecutive channels is set to
zero for less than 254 occurrences
2. D4 12th F–bit mode
(RCR2.2=1; this mode is also
referred to as the “Japanese
Yellow Alarm”)
3. ESF mode
Red Alarm (LRCL) (this alarm
is also referred to as Loss Of
Signal)
when the 12th framing bit is set
to one for two consecutive
occurrences
when 16 consecutive patterns of
00FF appear in the FDL
when 192 consecutive zeros are
received
when the 12th framing bit is set to zero for two
consecutive occurrences
when 14 or less patterns of 00FF hex out of 16
possible appear in the FDL
when 14 or more ones out of 112 possible bit
positions are received starting with the first one
received
NOTES:
1. The definition of Blue Alarm (or Alarm Indication Signal) is an unframed all ones signal. Blue alarm detectors should be
able to operate properly in the presence of a 10E–3 error rate and they should not falsely trigger on a framed all ones signal.
The blue alarm criteria in the DS21352/552 has been set to achieve this performance. It is recommended that the RBL bit be
qualified with the RLOS bit.
2. ANSI specifications use a different nomenclature than the DS21352/552 does; the following terms are equivalent:
RBL = AIS
RCL = LOS
RLOS = LOF
RYEL = RAI
47 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
SR2: STATUS REGISTER 2 (Address=21 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RMF TMF SEC RFDL TFDL RMTCH RAF RSC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RMF SR2.7 Receive Multiframe. Set on receive multiframe boundaries.
TMF SR2.6 Transmit Multiframe. Set on transmit multiframe boundaries.
SEC SR2.5 One Second Timer. Set on increments of one second based on RCLK; will be set in
increments of 999 ms, 999 ms, and 1002 ms every 3 seconds.
RFDL SR2.4 Receive FDL Buffer Full. Set when the receive FDL buffer (RFDL) fills to capacity
(8 bits).
TFDL SR2.3 Transmit FDL Buffer Empty. Set when the transmit FDL buffer (TFDL) empties.
RMTCH SR2.2 Receive FDL Match Occurrence. Set when the RFDL matches either RFDLM1 or
RFDLM2.
RAF SR2.1 Receive FDL Abort. Set when eight consecutive one’s are received in the FDL.
RSC SR2.0 Receive Signaling Change. Set when the DS21352/552 detects a change of state in
any of the robbed–bit signaling bits.
48 of 137

IMR1: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 1 (Address=7F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LUP LDN LOTC SLIP RBL RYEL LRCL RLOS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
DS21352/DS21552
LUP IMR1.7
LDN IMR1.6
LOTC IMR1.5
SLIP IMR1.4
RBL IMR1.3
RYEL IMR1.2
LRCL IMR1.1
RLOS IMR1.0
Loop Up Code Detected.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Loop Down Code Detected.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Loss of Transmit Clock.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Elastic Store Slip Occurrence.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Blue Alarm.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Yellow Alarm.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Line Interface Receive Carrier Loss.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Loss of Sync.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
49 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
IMR2: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 2 (Address=6F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RMF TMF SEC RFDL TFDL RMTCH RAF RSC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RMF IMR2.7
TMF IMR2.6
SEC IMR2.5
RFDL IMR2.4
TFDL IMR2.3
RMTCH IMR2.2
RAF IMR2.1
RSC IMR2.0
Receive Multiframe.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Transmit Multiframe.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
One Second Timer.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive FDL Buffer Full.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Transmit FDL Buffer Empty.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive FDL Match Occurrence.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive FDL Abort.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Signaling Change.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
8. ERROR COUNT REGISTERS
There are a set of three counters that record bipolar violations, excessive zeros, errors in the CRC6 code
words, framing bit errors, and number of multiframes that the device is out of receive synchronization.
Each of these three counters are automatically updated on either one second boundaries (CCR3.2=0) or
every 42 ms (CCR3.2=1) as determined by the timer in Status Register 2 (SR2.5). Hence, these registers
contain performance data from either the previous second or the previous 42 ms. The user can use the
interrupt from the one second timer to determine when to read these registers. The user has a full second
(or 42 ms) to read the counters before the data is lost. All three counters will saturate at their respective
maximum counts and they will not rollover (note: only the Line Code Violation Count Register has the
potential to over-flow but the bit error would have to exceed 10E-2 before this would occur).
50 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
8.1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER (LCVCR)
Line Code Violation Count Register 1 (LCVCR1) is the most significant word and LCVCR2 is the least
significant word of a 16–bit counter that records code violations (CVs). CVs are defined as Bipolar
Violations (BPVs) or excessive zeros. See Table 8-1 for details of exactly what the LCVCRs count. If the
B8ZS mode is set for the receive side via CCR2.2, then B8ZS code words are not counted. This counter is
always enabled; it is not disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS=1) conditions.
LCVCR1: LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER 1 (Address = 23 Hex)
LCVCR2: LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER 2 (Address = 24 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LCV15 LCV14 LCV13 LCV12 LCV11 LCV10 LCV9 LCV8 LCVCR1
LCV7 LCV6 LCV5 LCV4 LCV3 LCV2 LCV1 LCV0 LCVCR2
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LCV15 LCVCR1.7
MSB of the 16–bit code violation count
LCV0 LCVCR2.0
LSB of the 16–bit code violation count
Table 8-1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS
COUNT EXCESSIVE ZEROS
(RCR1.7)
no no BPVs
yes no BPVs + 16 consecutive zeros
no yes BPVs (B8ZS code words not counted)
yes yes BPV’s + 8 consecutive zeros
B8ZS ENABLED
(CCR2.2)
WHAT IS COUNTED
IN THE LCVCRs
51 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
8.2 PATH CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER (PCVCR)
When the receive side of a framer is set to operate in the ESF framing mode (CCR2.3=1), PCVCR will
automatically be set as a 12–bit counter that will record errors in the CRC6 code words. When set to
operate in the D4 framing mode (CCR2.3=0), PCVCR will automatically count errors in the Ft framing
bit position. Via the RCR2.1 bit, a framer can be programmed to also report errors in the Fs framing bit
position. The PCVCR will be disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS=1) conditions. See
Table 8-2 for a detailed description of exactly what errors the PCVCR counts.
PCVCR1: PATH VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER 1 (Address = 25 Hex)
PCVCR2: PATH VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER 2 (Address = 26 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
(note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) CRC/FB11 CRC/FB10 CRC/FB9 CRC/FB8 PCVCR1
CRC/FB7 CRC/FB6 CRC/FB5 CRC/FB4 CRC/FB3 CRC/FB2 CRC/FB1 CRC/FB0 PCVCR2
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CRC/FB11 PCVCR1.3 MSB of the 12–Bit CRC6 Error or Frame Bit Error Count (note #2)
CRC/FB0 PCVCR2.0 LSB of the 12–Bit CRC6 Error or Frame Bit Error Count (note #2)
NOTES:
1. The upper nibble of the counter at address 25 is used by the Multiframes Out of Sync Count Register
2. PCVCR counts either errors in CRC code words (in the ESF framing mode; CCR2.3=1) or errors in the framing bit position
(in the D4 framing mode; CCR2.3=0).
Table 8.2 PATH CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS
FRAMING MODE
(CCR2.3)
D4 no errors in the Ft pattern
D4 yes errors in both the Ft & Fs patterns
ESF don’t care errors in the CRC6 code words
COUNT Fs ERRORS
(RCR2.1)
WHAT IS COUNTED
IN THE PCVCRs
52 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
8.3 Multiframes Out Of Sync Count Register (MOSCR)
Normally the MOSCR is used to count the number of multiframes that the receive synchronizer is out of
sync (RCR2.0=1). This number is useful in ESF applications needing to measure the parameters Loss Of
Frame Count (LOFC) and ESF Error Events as described in AT&T publication TR54016. When the
MOSCR is operated in this mode, it is not disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS=1)
conditions. The MOSCR has alternate operating mode whereby it will count either errors in the Ft
framing pattern (in the D4 mode) or errors in the FPS framing pattern (in the ESF mode). When the
MOSCR is operated in this mode, it is disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS = 1)
conditions. See Table 8-3 for a detailed description of what the MOSCR is capable of counting.
MOSCR1: MULTIFRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNT REGISTER 1 (Address = 25
Hex) see note 1
MOSCR2: MULTIFRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNT REGISTER 2 (Address = 27
Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
MOS/FB11MOS/FB10MOS/FB9 MOS/FB8 (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) MOSCR1
CRC/FB7 CRC/FB6 CRC/FB5 CRC/FB4 CRC/FB3 CRC/FB2 CRC/FB1 CRC/FB0 MOSCR2
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
MOS/FB11 MOSCR1.7 MSB of the 12–Bit Multiframes Out of Sync or F–Bit Error Count (note #2)
MOS/FB0 MOSCR2.0 LSB of the 12–Bit Multiframes Out of Sync or F–Bit Error Count (note #2)
NOTES:
1. The lower nibble of the counter at address 25 is used by the Path Code Violation Count Register
2. MOSCR counts either errors in framing bit position (RCR2.0=0) or the number of multiframes out of sync (RCR2.0=1)
Table 8-3 MULTIFRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS
FRAMING MODE
(CCR2.3)
D4 MOS number of multiframes out of sync
D4 F–Bit errors in the Ft pattern
ESF MOS number of multiframes out of sync
ESF F–Bit errors in the FPS pattern
COUNT MOS OR F–BIT
ERRORS
(RCR2.0)
WHAT IS COUNTED
IN THE MOSCRs
53 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
9. DS0 MONITORING FUNCTION
The device has the ability to monitor one DS0 64kbps channel in the transmit direction and one DS0
channel in the receive direction at the same time. In the transmit direction the user will determine which
channel is to be monitored by properly setting the TCM0 to TCM4 bits in the CCR5 register. In the
receive direction, the RCM0 to RCM4 bits in the CCR6 register need to be properly set. The DS0 channel
pointed to by the TCM0 to TCM4 bits will appear in the Transmit DS0 Monitor (TDS0M) register and
the DS0 channel pointed to by the RCM0 to RCM4 bits will appear in the Receive DS0 (RDS0M)
register. The TCM4 to TCM0 and RCM4 to RCM0 bits should be programmed with the decimal decode
of the appropriate T1 channel. For example, if DS0 channel 6 in the transmit direction and DS0 channel
15 in the receive direction needed to be monitored, then the following values would be programmed into
CCR5 and CCR6:
TCM4 = 0 RCM4 = 0
TCM3 = 0 RCM3 = 1
TCM2 = 1 RCM2 = 1
TCM1 = 0 RCM1 = 1
TCM0 = 1 RCM0 = 0
CCR5: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 5 (Address=19 Hex)
[repeated here from section 6 for convenience]
(MSB) (LSB)
TJC LLB LIAIS TCM4 TCM3 TCM2 TCM1 TCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TJC CCR5.7
LLB CCR5.6 Local Loopback.
LIAIS CCR5.5
TCM4 CCR5.4 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that determines which
TCM3 CCR5.3
TCM2 CCR5.2
TCM1 CCR5.1
TCM0 CCR5.0 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode.
Transmit Japanese CRC6 Enable.
Line Interface AIS Generation Enable.
transmit channel data will appear in the TDS0M register. See Section 0 for details.
Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 3.
Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 2.
Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 1.
54 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TDS0M: TRANSMIT DS0 MONITOR REGISTER (Address=1A Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
B1 TDS0M.7 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 1. MSB of the DS0 channel (first bit to be transmitted).
B2 TDS0M.6
Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 2.
B3 TDS0M.5
B4 TDS0M.4
B5 TDS0M.3
B6 TDS0M.2
B7 TDS0M.1
B8 TDS0M.0 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 8. LSB of the DS0 channel (last bit to be transmitted).
Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 3.
Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 4.
Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 5.
Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 6.
Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 7.
CCR6: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 6 (Address=1E Hex)
[repeated here from section 6 for convenience]
(MSB) (LSB)
RJC RESA TESA RCM4 RCM3 RCM2 RCM1 RCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RJC CCR6.7
RESA CCR6.6
TESA CCR6.5
Receive Japanese CRC Enable.
Receive Elastic Store Align.
Transmit Elastic Store Align.
RCM4 CCR6.4 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that determines which
receive DS0 channel data will appear in the RDS0M register.
RCM3 CCR6.3
RCM2 CCR6.2
RCM1 CCR6.1 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 1.
RCM0 CCR6.0 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode that determines which
Receive Channel Monitor Bit 3.
Receive Channel Monitor Bit 2.
receive DS0 channel data will appear in the RDS0M register.
RDS0M: RECEIVE DS0 MONITOR REGISTER (Address=1F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
B1 RDS0M.7 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 1. MSB of the DS0 channel (first bit to be received).
B2 RDS0M.6
B3 RDS0M.5
B4 RDS0M.4
Receive DS0 Channel Bit 2.
Receive DS0 Channel Bit 3.
Receive DS0 Channel Bit 4.
55 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
B5 RDS0M.3
B6 RDS0M.2
B7 RDS0M.1
B8 RDS0M.0 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 8. LSB of the DS0 channel (last bit to be received).
Receive DS0 Channel Bit 5.
Receive DS0 Channel Bit 6.
Receive DS0 Channel Bit 7.
10. SIGNALING OPERATION
Processor based (i.e., software based) signaling access and hardware based access are available.
Processor based access and hardware based access can be used simultaneously if necessary. The
processor based signaling is covered in Section 10-1 and the hardware based signaling is covered in
Section 10-2.
10.1 PROCESSOR BASED SIGNALING
The robbed–bit signaling bits embedded in the T1 stream can be extracted from the receive stream and
inserted into the transmit stream by each framer. There is a set of 12 registers for the receive side (RS1 to
RS12) and 12 registers on the transmit side (TS1 to TS12). The signaling registers are detailed below.
The CCR1.5 bit is used to control the robbed signaling bits as they appear at RSER. If CCR1.5 is set to
zero, then the robbed signaling bits will appear at the RSER pin in their proper position as they are
received. If CCR1.5 is set to a one, then the robbed signaling bit positions will be forced to a one at
RSER. If hardware based signaling is being used, then CCR1.5 must be set to zero.
56 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RS1 TO RS12: RECEIVE SIGNALING REGISTERS (Address=60 to 6B Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
A(8) A(7) A(6) A(5) A(4) A(3) A(2) A(1) RS1 (60)
A(16) A(15) A(14) A(13) A(12) A(11) A(10) A(9) RS2 (61)
A(24) A(23) A(22) A(21) A(20) A(19) A(18) A(17) RS3 (62)
B(8) B(7) B(6) B(5) B(4) B(3) B(2) B(1) RS4 (63)
B(16) B(15) B(14) B(13) B(12) B(11) B(10) B(9) RS5 (64)
B(24) B(23) B(22) B(21) B(20) B(19) B(18) B(17) RS6 (65)
A/C(8) A/C(7) A/C(6) A/C(5) A/C(4) A/C(3) A/C(2) A/C(1) RS7 (66)
A/C(16) A/C(15) A/C(14) A/C(13) A/C(12) A/C(11) A/C(10) A/C(9) RS8 (67)
A/C(24) A/C(23) A/C(22) A/C(21) A/C(20) A/C(19) A/C(18) A/C(17) RS9 (68)
B/D(8) B/D(7) B/D(6) B/D(5) B/D(4) B/D(3) B/D(2) B/D(1) RS10 (69)
B/D(16) B/D(15) B/D(14) B/D(13) B/D(12) B/D(11) B/D(10) B/D(9) RS11 (6A)
B/D(24) B/D(23) B/D(22) B/D(21) B/D(20) B/D(19) B/D(18) B/D(17) RS12 (6B)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
D(24) RS12.7
A(1) RS1.0
Signaling Bit D in Channel 24
Signaling Bit A in Channel 1
Each Receive Signaling Register (RS1 to RS12) reports the incoming robbed bit signaling from eight
DS0 channels. In the ESF framing mode, there can be up to four signaling bits per channel (A, B, C, and
D). In the D4 framing mode, there are only two signaling bits per channel (A and B). In the D4 framing
mode, the framer will replace the C and D signaling bit positions with the A and B signaling bits from the
previous multiframe. Hence, whether the framer is operated in either framing mode, the user needs only
to retrieve the signaling bits every 3 ms. The bits in the Receive Signaling Registers are updated on
multiframe boundaries so the user can utilize the Receive Multiframe Interrupt in the Receive Status
Register 2 (SR2.7) to know when to retrieve the signaling bits. The Receive Signaling Registers are
frozen and not updated during a loss of sync condition (SR1.0=1). They will contain the most recent
signaling information before the “OOF” occurred. The signaling data reported in RS1 to RS12 is also
available at the RSIG and RSER pins.
A change in the signaling bits from one multiframe to the next will cause the RSC status bit (SR2.0) to be
set. The user can enable the INT pin to toggle low upon detection of a change in signaling by setting the
IMR2.0 bit. Once a signaling change has been detected, the user has at least 2.75 ms to read the data out
of the RS1 to RS12 registers before the data will be lost.
57 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TS1 TO TS12: TRANSMIT SIGNALING REGISTERS (Address=70 to 7B Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
A(8) A(7) A(6) A(5) A(4) A(3) A(2) A(1) TS1 (70)
A(16) A(15) A(14) A(13) A(12) A(11) A(10) A(9) TS2 (71)
A(24) A(23) A(22) A(21) A(20) A(19) A(18) A(17) TS3 (72)
B(8) B(7) B(6) B(5) B(4) B(3) B(2) B(1) TS4 (73)
B(16) B(15) B(14) B(13) B(12) B(11) B(10) B(9) TS5 (74)
B(24) B(23) B(22) B(21) B(20) B(19) B(18) B(17) TS7 (75)
A/C(8) A/C(7) A/C(6) A/C(5) A/C(4) A/C(3) A/C(2) A/C(1) TS7 (76)
A/C(16) A/C(15) A/C(14) A/C(13) A/C(12) A/C(11) A/C(10) A/C(9) TS8 (77)
A/C(24) A/C(23) A/C(22) A/C(21) A/C(20) A/C(19) A/C(18) A/C(17) TS9 (78)
B/D(8) B/D(7) B/D(6) B/D(5) B/D(4) B/D(3) B/D(2) B/D(1) TS10 (79)
B/D(16) B/D(15) B/D(14) B/D(13) B/D(12) B/D(11) B/D(10) B/D(9) TS11 (7A)
B/D(24) B/D(23) B/D(22) B/D(21) B/D(20) B/D(19) B/D(18) B/D(17) TS12 (7B)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
D(24) TS12.7
A(1) TS1.0
Signaling Bit D in Channel 24
Signaling Bit A in Channel 1
Each Transmit Signaling Register (TS1 to TS12) contains the Robbed Bit signaling for eight DS0
channels that will be inserted into the outgoing stream if enabled to do so via TCR1.4. In the ESF framing
mode, there can be up to four signaling bits per channel (A, B, C, and D). On multiframe boundaries, the
framer will load the values present in the Transmit Signaling Register into an outgoing signaling shift
register that is internal to the device. The user can utilize the Transmit Multiframe Interrupt in Status
Register 2 (SR2.6) to know when to update the signaling bits. In the ESF framing mode, the interrupt will
come every 3 ms and the user has a full 3ms to update the TSRs. In the D4 framing mode, there are only
two signaling bits per channel (A and B). However in the D4 framing mode, the framer uses the C and D
bit positions as the A and B bit positions for the next multiframe. The framer will load the values in the
TSRs into the outgoing shift register every other D4 multiframe.
10.2 HARDWARE BASED SIGNALING
10.2.1 RECEIVE SIDE
In the receive side of the hardware based signaling, there are two operating modes for the signaling
buffer; signaling extraction and signaling re–insertion. Signaling extraction involves pulling the signaling
bits from the receive data stream and buffering them over a four multiframe buffer and outputting them in
a serial PCM fashion on a channel–by–channel basis at the RSIG output. This mode is always enabled. In
this mode, the receive elastic store may be enabled or disabled. If the receive elastic store is enabled, then
the backplane clock (RSYSCLK) can be either 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz. In the ESF framing mode, the
ABCD signaling bits are output on RSIG in the lower nibble of each channel. The RSIG data is updated
once a multiframe (3 ms) unless a freeze is in effect. In the D4 framing mode, the AB signaling bits are
output twice on RSIG in the lower nibble of each channel. Hence, bits 5 and 6 contain the same data as
bits 7 and 8 respectively in each channel. The RSIG data is updated once a multiframe (1.5 ms) unless a
freeze is in effect. See the timing diagrams in Section 21 for some examples.
10.2.1.1 RECEIVE SIGNALING RE-INSERTION
The other hardware based signaling operating mode called signaling re–insertion can be invoked by
setting the RSRE control bit high (CCR4.7=1). In this mode, the user will provide a multiframe sync at
the RSYNC pin and the signaling data will be re–aligned at the RSER output according to this applied
58 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
multiframe boundary. In this mode, the elastic store must be enabled however the backplane clock can be
either 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz.
If the signaling re–insertion mode is enabled, the user can control which channels have signaling re–
insertion performed on a channel–by–channel basis by setting the RPCSI control bit high (CCR4.6) and
then programming the RCHBLK output pin to go high in the channels in which the signaling re–insertion
should not occur. If the RPCSI bit is set low, then signaling re–insertion will occur in all channels when
the signaling re–insertion mode is enabled (RSRE=1). How to control the operation of the RCHBLK
output pin is covered in Section 13.
10.2.1.2 RECEIVE SIGNALING ALL ONES
In both hardware based signaling operating modes, the user has the option to replace all of the extracted
robbed–bit signaling bit positions with ones. This option is enabled via the RFSA1 control bit (CCR4.5)
and it can be invoked on a per–channel basis by setting the RPCSI control bit (CCR4.6) high and then
programming RCHBLK appropriately just like the per–channel signaling re–insertion operates.
10.2.1.3 RECEIVE SIGNALING FREEZE
The signaling data in the four multiframe buffer will be frozen in a known good state upon either a loss of
synchronization (OOF event), carrier loss, or frame slip. This action meets the requirements of BellCore
TR– TSY–000170 for signaling freezing. To allow this freeze action to occur, the RFE control bit
(CCR4.4) should be set high. The user can force a freeze by setting the RFF control bit (CCR4.3) high.
The RSIGF output pin provides a hardware indication that a freeze is in effect. The four multiframe
buffer provides a three multiframe delay in the signaling bits provided at the RSIG pin (and at the RSER
pin if RSRE=1). When freezing is enabled (RFE=1), the signaling data will be held in the last known
good state until the corrupting error condition subsides. When the error condition subsides, the signaling
data will be held in the old state for at least an additional 9 ms (or 4.5 ms in D4 framing mode) before
being allowed to be updated with new signaling data.
10.2.2 TRANSMIT SIDE
Via the THSE control bit (CCR4.2), the framer can be set up to take the signaling data presented at the
TSIG pin and insert the signaling data into the PCM data stream that is being input at the TSER pin. The
user has the ability to control which channels are to have signaling data from the TSIG pin inserted into
them on a channel–by–channel basis by setting the TPCSI control bit (CCR4.1) high. When TPCSI is
enabled, channels in which the TCHBLK output has been programmed to be set high in, will not have
signaling data from the TSIG pin inserted into them. The signaling insertion capabilities of the framer are
available whether the transmit side elastic store is enabled or disabled. If the elastic store is enabled, the
backplane clock (TSYSCLK) can be either 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz.
11. PER–CHANNEL CODE (IDLE) GENERATION
Data can be replaced by an idle code on a channel–by–channel basis in the transmit and receive
directions. The transmit direction is from the backplane to the T1 line and is covered in Section11.1. The
receive direction is from the T1 line to the backplane and is covered in Section 11.2.
59 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
11.1 TRANSMIT SIDE CODE GENERATION
In the transmit direction there are two methods by which channel data from the backplane can be
overwritten with data generated by the framer. The first method which is covered in Section 11.1 was a
feature contained in the original DS2151 while the second method which is covered in Section 11.2 is a
new feature of the DS2152/352/552.
11.1.1 FIXED PER-CHANNEL IDLE CODE INSERTION
The first method involves using the Transmit Idle Registers (TIR1/2/3) to determine which of the 24 T1
channels should be overwritten with the code placed in the Transmit Idle Definition Register (TIDR).
This method allows the same 8–bit code to be placed into any of the 24 T1 channels. If this method is
used, then the CCR4.0 control bit must be set to zero.
Each of the bit position in the Transmit Idle Registers (TIR1/TIR2/TIR3) represent a DS0 channel in the
outgoing frame. When these bits are set to a one, the corresponding channel will transmit the Idle Code
contained in the Transmit Idle Definition Register (TIDR). Robbed bit signaling and Bit 7 stuffing will
occur over the programmed Idle Code unless the DS0 channel is made transparent by the Transmit
Transparency Registers.
TIR1/TIR2/TIR3: TRANSMIT IDLE REGISTERS (Address=3C to 3E Hex)
[Also used for Per–Channel Loopback]
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 TIR1 (3C)
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9 TIR2 (3D)
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17 TIR3 (3E)
SYMBOLS POSITIONS NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH1-24 TIR1.0-3.7
Transmit Idle Code Insertion Control Bits.
0 = do not insert the Idle Code in the TIDR into this channel
1 = insert the Idle Code in the TIDR into this channel
NOTE:
If CCR4.0=1, then a zero in the TIRs implies that channel data is to be sourced from TSER and a one
implies that channel data is to be sourced from the output of the receive side framer (i.e., Per–Channel
Loopback; see Figure 3-1.
TIDR: TRANSMIT IDLE DEFINITION REGISTER (Address=3F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TIDR7 TIDR6 TIDR5 TIDR4 TIDR3 TIDR2 TIDR1 TIDR0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TIDR7 TIDR.7 MSB of the Idle Code (this bit is transmitted first)
TIDR0 TIDR.0 LSB of the Idle Code (this bit is transmitted last)
11.1.2 UNIQUE PER-CHANNEL IDLE CODE INSERTION
The second method involves using the Transmit Channel Control Registers (TCC1/2/3) to determine which of the 24 T1
channels should be overwritten with the code placed in the Transmit Channel Registers (TC1 to TC24). This method is more
flexible than the first in that it allows a different 8–bit code to be placed into each of the 24 T1 channels.
60 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TC1 TO TC24: TRANSMIT CHANNEL REGISTERS (Address=50 to 57 and 40
to 4F Hex)
(for brevity, only channel one is shown; see Table 5-1 for other register address)
(MSB) (LSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 TC1 (50)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
C7 TC1.7 MSB of the Code (this bit is transmitted first)
C0 TC1.0 LSB of the Code (this bit is transmitted last)
TCC1/TCC2/TCC3: TRANSMIT CHANNEL CONTROL REGISTER (Address=16
to 18 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 TCC1 (16)
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9 TCC2 (17)
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17 TCC3 (18)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH24 TCC3.7
CH1 TCC1.0
Transmit Channel 24 Code Insertion Control Bit
0=do not insert data from the TC24 register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TC24 register into the transmit data stream
Transmit Channel 1 Code Insertion Control Bit
0=do not insert data from the TC1 register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TC1 register into the transmit data stream
11.2 RECEIVE SIDE CODE GENERATION
In the receive direction there are also two methods by which channel data to the backplane can be
overwritten with data generated by the framer. The first method which is covered in Section 11.2.1 was a
feature contained in the original DS2151 while the second method which is covered in Section 11.2.2 is a
new feature of the DS2152/352/552.
61 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
11.2.1 FIXED PER-CHANNEL IDLE CODE INSERTION
The first method on the receive side involves using the Receive Mark Registers (RMR1/2/3) to determine
which of the 24 T1 channels should be overwritten with either a 7Fh idle code or with a digital milliwatt
pattern. The RCR2.7 bit will determine which code is used. The digital milliwatt code is an eight byte
repeating pattern that represents a 1 kHz sine wave (1E/0B/0B/1E/9E/8B/8B/9E). Each bit in the RMRs,
represents a particular channel. If a bit is set to a one, then the receive data in that channel will be
replaced with one of the two codes. If a bit is set to zero, no replacement occurs.
RMR1/RMR2/RMR3: RECEIVE MARK REGISTERS (Address=2D to 2F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 RMR1(2D)
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9 RMR2(2E)
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17 RMR3(2F)
SYMBOLS POSITIONS NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH1-24 RMR1.0-3.7
Receive Channel Mark Control Bits
0 =do not affect the receive data associated with this channel
1 = replace the receive data associated with this channel with idle code or digital
milliwatt code (depends on the RCR2.7 bit)
11.2.2 UNIQUE PER-CHANNEL CODE INSERTION
The second method involves using the Receive Channel Control Registers (RCC1/2/3) to determine
which of the 24 T1 channels off of the T1 line and going to the backplane should be overwritten with the
code placed in the Receive Channel Registers (RC1 to RC24). This method is more flexible than the first
in that it allows a different 8–bit code to be placed into each of the 24 T1 channels.
RC1 TO RC24: RECEIVE CHANNEL REGISTERS (Address=80 to 8F and 58 to
5F Hex)
(for brevity, only channel one is shown; see Table 5-1 for other register address)
(MSB) (LSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 RC1 (80)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
C7 RC1.7 MSB of the Code (this bit is sent first to the backplane)
C0 RC1.0 LSB of the Code (this bit is sent last to the backplane)
62 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RCC1/RCC2/RCC3: RECEIVE CHANNEL CONTROL REGISTER
(ADDRESS=1B TO 1D Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 RCC1 (1B)
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9 RCC2 (1C)
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17 RCC3 (1D)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH24 RCC3.7
CH1 RCC1.0
Receive Channel 24 Code Insertion Control Bit
0 = do not insert data from the RC24 register into the receive data stream
1 = insert data from the RC24 register into the receive data stream
Receive Channel 1 Code Insertion Control Bit
0 = do not insert data from the RC1 register into the receive data stream
1 = insert data from the RC1 register into the receive data stream
12. PER–CHANNEL LOOPBACK
The Transmit Idle Registers (TIRs) have an alternate function that allows them to define a Per–Channel
LoopBack (PCLB). If the TIRFS control bit (CCR4.0) is set to one, then the TIRs will determine which
channels (if any) from the backplane should be replaced with the data from the receive side or in other
words, off of the T1 line. If this mode is enabled, then transmit and receive clocks and frame syncs must
be synchronized. One method to accomplish this would be to tie RCLK to TCLK and RFSYNC to
TSYNC.
13. CLOCK BLOCKING REGISTERS
The Receive Channel Blocking Registers (RCBR1/RCBR2/RCBR3) and the Transmit Channel Blocking Registers
(TCBR1/TCBR2/TCBR3) control the RCHBLK and TCHBLK pins respectively. The RCHBLK and TCHCLK pins are user
programmable outputs that can be forced either high or low during individual channels. These outputs can be used to block
clocks to a UART or LAPD controller in Fractional T1 or ISDN–PRI applications. When the appropriate bits are set to a one,
the RCHBLK and TCHCLK pins will be held high during the entire corresponding channel time. See the timing in Section 21
for an example.
RCBR1/RCBR2/RCBR3: RECEIVE CHANNEL BLOCKING REGISTERS
(Address=6C to 6E Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 RCBR1 (6C)
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9 RCBR2 (6D)
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17 RCBR3 (6E)
SYMBOLS POSITIONS NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH1-24 RCBR1.0-3.7
Receive Channel Blocking Control Bits.
0 = force the RCHBLK pin to remain low during this channel time
1 = force the RCHBLK pin high during this channel time
TCBR1/TCBR2/TCBR3: TRANSMIT CHANNEL BLOCKING REGISTERS
(Address=32 to 34 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 TCBR1 (32)
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9 TCBR2 (33)
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17 TCBR3 (34)
SYMBOLS POSITIONS NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH1-24 TCBR1.0-3.7
Transmit Channel Blocking Control Bits.
63 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
0 = force the TCHBLK pin to remain low during this channel time
1 = force the TCHBLK pin high during this channel time
14. ELASTIC STORES OPERATION
The device contains dual two–frame (386 bits) elastic stores, one for the receive direction, and one for the
transmit direction. These elastic stores have two main purposes. First, they can be used to rate convert the
T1 data stream to 2.048 Mbps (or a multiple of 2.048 Mbps) which is the E1 rate. Secondly, they can be
used to absorb the differences in frequency and phase between the T1 data stream and an asynchronous
(i.e., not locked) backplane clock (which can be 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz). The backplane clock
(TSYSCLK and/or RSYSCLK) can burst at rates up to 8.192 MHz. Both elastic stores contain full
controlled slip capability which is necessary for this second purpose. The receive side elastic store can be
enabled via CCR1.2 and the transmit side elastic store is enabled via CCR1.7. Both elastic stores are fully
independent and no restrictions apply to the sourcing of the various clocks that are applied to them. The
transmit side elastic store can be enabled whether the receive elastic store is enabled or disabled and vice
versa. Also, each elastic store can interface to either a 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz backplane without
regard to the backplane rate the other elastic store is interfacing.
14.1 RECEIVE SIDE
If the receive side elastic store is enabled (CCR1.2=1), then the user must provide either a 1.544 MHz
(CCR1.3=0) or 2.048 MHz (CCR1.3=1) clock at the RSYSCLK pin. The user has the option of either
providing a frame/multiframe sync at the RSYNC pin (RCR2.3=1) or having the RSYNC pin provide a
pulse on frame boundaries (RCR2.3=0). If the user wishes to obtain pulses at the frame boundary, then
RCR2.4 must be set to zero and if the user wishes to have pulses occur at the multiframe boundary, then
RCR2.4 must be set to one. The framer will always indicate frame boundaries via the RFSYNC output
whether the elastic store is enabled or not. If the elastic store is enabled, then multiframe boundaries will
be indicated via the RMSYNC output. If the user selects to apply a 2.048 MHz clock to the RSYSCLK
pin, then the data output at RSER will be forced to all ones every fourth channel and the F–bit will be
passed into the MSB of TS0. Hence channels 1(bits 1-7), 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, and 29 (timeslots 0(bits 1-
7), 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, and 28) will be forced to a one . Also, in 2.048 MHz applications, the RCHBLK
output will be forced high during the same channels as the RSER pin. See Section 13 for more details.
This is useful in T1 to CEPT (E1) conversion applications. If the 386–bit elastic buffer either fills or
empties, a controlled slip will occur. If the buffer empties, then a full frame of data (193 bits) will be
repeated at RSER and the SR1.4 and RIR1.3 bits will be set to a one. If the buffer fills, then a full frame
of data will be deleted and the SR1.4 and RIR1.4 bits will be set to a one.
64 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
14.2 TRANSMIT SIDE
The operation of the transmit elastic store is very similar to the receive side. The transmit side elastic
store is enabled via CCR1.7. A 1.544 MHz (CCR1.4=0) or 2.048 MHz (CCR1.4=1) clock can be applied
to the TSYSCLK input. If the user selects to apply a 2.048 MHz clock to the TSYSCLK pin, then the data
input at TSER will be ignored every fourth channel. Hence channels 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, and 29
(timeslots 0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, and 28) will be ignored. The user must supply an 8 kHz frame sync
pulse to the TSSYNC input. Also, in 2.048 MHz applications, the TCHBLK output will be forced high
during the channels ignored by the framer. See Section 21 for more details. Controlled slips in the
transmit elastic store are reported in the RIR2.3 bit and the direction of the slip is reported in the RIR2.5
and RIR2.4 bits.
14.3 ELASTIC STORES INITIALIZATION
There are two elastic store initializations that may be used to improve performance in certain
applications, Elastic Store Reset and Elastic Store Align. Both of these involve the manipulation of the
elastic store’s read and write pointers and are useful primarily in synchronous applications (RSYSCLK /
TSYSCLK are locked to RCLK / TCLK respectively). See table below for details.
Table 14-1 ELASTIC STORE DELAY AFTER INITIALIZATION
Initialization Register. Bit
Receive Elastic Store Reset
Transmit Elastic Store Reset
Receive Elastic Store Align
Transmit Elastic Store Align
CCR7.5
CCR7.4
CCR6.6
CCR6.5
Delay
8 Clocks < Delay < 1 Frame
1 Frame < Delay < 2 Frames
½ Frame < Delay < 1 ½ Frames
½ Frame < Delay < 1 ½ Frames
14.4 MINIMUM DELAY MODE
Elastic store minimum delay mode may be used when the elastic store’s system clock is locked to its
network clock (i.e., RCLK locked to RSYSCLK for the receive side and TCLK locked to TSYSCLK for
the transmit side). CCR3.7 and CCR3.0 enable the transmit and receive elastic store minimum delay
modes. When enabled the elastic stores will be forced to a maximum depth of 32 bits instead of the
normal 386 bits. This feature is useful primarily in applications that interface to a 2.048MHz bus.
Certain restrictions apply when minimum delay mode is used. In addition to the restriction mentioned
above, RSYNC must be configured as an output when the receive elastic store is in minimum delay mode
and TSYNC must be configured as an output when transmit minimum delay mode is enabled. In a
typical application RSYSCLK and TSYSCLK are locked to RCLK, and RSYNC (frame output mode) is
connected to TSSYNC (frame input mode). All of the slip contention logic in the framer is disabled
(since slips cannot occur). On power–up after the RSYSCLK and TSYSCLK signals have locked to their
respective network clock signals, the elastic store reset bits (CCR7.4 and CCR7.5) should be toggled
from a zero to a one to insure proper operation.
Table 14-2 MINIMUM DELAY MODE CONFIGURATION
Hardware Requirements Register Settings
Transmit
Receive
TSYSCLK can be 1.544MHz or 2.048MHz and must
be locked to TCLK (1.544MHz). TSYNC is an output
RSYSCLK can be 1.544MHz or 2.048MHz and must
be locked to RCLK (1.544MHz). RSYNC is an output.
CCR3.0 = 1, CCR1.7 = 1
TCR2.2 = 1
CCR3.7 = 1, CCR1.2 = 1
RCR2.3 = 0
15. HDLC CONTROLLER
This device has an enhanced HDLC controller configurable for use with the Facilities Data Link or DS0s.
There are 64 byte buffers in the transmit and receive paths. The user can select any DS0 or multiple
DS0s as well as any specific bits within the DS0(s) to pass through the HDLC controller. Note that
65 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TBOC.6 = 1 and TDC1.7 = 1 cannot exist without corrupting the data in the FDL. See Table 15-1 for
configuring the transmit HDLC controller.
Table 15-1 TRANSMIT HDLC CONFIGURATION
Function TBOC.6 TDC1.7 TCR1.2
DS0(s) 0 1 1 or 0
FDL 1 0 1
Disable 0 0 1 or 0
Note that the BOC controller is functional when the HDLC controller is used for DS0s. Section 15.3 contains all of the HDLC
and BOC registers and information on FDL/Fs Extraction and Insertion with and without the HDLC controller.
15.1 HDLC FORr DS0s
When using the HDLC controllers for DS0s, the same registers shown in section 15.3.2 will be used
except for the TBOC and RBOC registers and bits HDLC.7, HSR.7, and HIMR.7. As a basic guideline
for interpreting and sending HDLC messages and BOC messages, the following sequences can be
applied.
15.1.1 RECEIVE AN HDLC MESSAGE
1. Enable RPS interrupts.
2. Wait for interrupt to occur.
3. Disable RPS interrupt and enable either RPE, RNE, or RHALF interrupt.
4. Read RHIR to obtain REMPTY status.
a. If REMPTY=0, then record OBYTE, CBYTE, and POK bits and then read the FIFO.
a1. If CBYTE=0 then skip to step 5.
a2. If CBYTE=1 then skip to step 7.
b. If REMPTY=1, then skip to step 6.
5. Repeat step 4.
6. Wait for interrupt, skip to step 4.
7. If POK=0, then discard whole packet, if POK=1, accept the packet.
8. Disable RPE, RNE, or RHALF interrupt, enable RPS interrupt and return to step 1.
15.1.2 TRANSMIT AN HDLC MESSAGE
1. Make sure HDLC controller is done sending any previous messages and is current sending flags by checking that the FIFO
is empty by reading the TEMPTY status bit in the THIR register.
2. Enable either the THALF or TNF interrupt.
3. Read THIR to obtain TFULL status.
a. If TFULL=0, then write a byte into the FIFO and skip to next step (special case occurs when the last byte is to be
written, in this case set TEOM=1 before writing the byte and then skip to step 6).
b. If TFULL=1, then skip to step 5.
4. Repeat step 3.
5. Wait for interrupt, skip to step 3.
6. Disable THALF or TNF interrupt and enable TMEND interrupt.
7. Wait for an interrupt, then read TUDR status bit to make sure packet was transmitted correctly.
15.2 FDL/Fs EXTRACTION AND INSERTION
The device has the ability to extract/insert data from/ into the Facility Data Link (FDL) in the ESF
framing mode and from/into Fs–bit position in the D4 framing mode. Since SLC–96 utilizes the Fs–bit
position, this capability can also be used in SLC–96 applications. The device contains a complete HDLC
and BOC controller which can be used for the FDL or for DS0s. Using the HDLC controller for the FDL
is covered in Section 15.3.3. To allow for backward compatibility with earlier devices, legacy
functionality is maintained for the FDL, which is covered in Section 15.4. Section 15.5 covers D4 and
SLC–96 operation.
66 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
Firmware, which can be retrieved from the Web site (www.dalsemi.com/Prod_info
/Telecom/t1_e1_tools.html), was developed to implement the FDL. The code for the DS2151
incorporates the LAPD protocol and can be used with any of the 51/52/352/552 SCTs. The code for the
DS2152 can be used with the 52/352/552 SCTs.
15.3 HDLC AND BOC CONTROLLER FOR THE FDL
15.3.1 GENERAL OVERVIEW
The device contains a complete HDLC controller with 64–byte buffers in both the transmit and receive
directions as well as separate dedicated hardware for Bit Oriented Codes (BOC). The HDLC controller
performs all the necessary overhead for generating and receiving Performance Report Messages (PRM)
as described in ANSI T1.403 and the messages as described in AT&T TR54016. The HDLC controller
automatically generates and detects flags, generates and checks the CRC check sum, generates and
detects abort sequences, stuffs and destuffs zeros (for transparency), and byte aligns to the FDL data
stream. The 64–byte buffers in the HDLC controller are large enough to allow a full PRM to be received
or transmitted without host intervention. The BOC controller will automatically detect incoming BOC
sequences and alert the host. When the BOC ceases, the device will also alert the host. The user can set
the device up to send any of the possible 6–bit BOC codes.
There are thirteen registers that the host will use to operate and control the operation of the HDLC and
BOC controllers. A brief description of the registers is shown in Table 15-2.
67 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
Table 15-2 HDLC/BOC CONTROLLER REGISTERS
NAME FUNCTION
HDLC Control Register (HCR) general control over the HDLC and BOC controllers
HDLC Status Register (HSR) key status information for both transmit and receive directions
HDLC Interrupt Mask Register (HIMR) allows/stops status bits to/from causing an interrupt
Receive HDLC Register (RHIR) status information on receive HDLC controller
Receive BOC Register (RBOC) status information on receive BOC controller
Receive HDLC FIFO Register (RHFR) access to 64–byte HDLC FIFO in receive direction
Receive HDLC DS0 Control Register 1 (RDC1) controls the HDLC function when used on DS0 channels
Receive HDLC DS0 Control Register 2 (RDC2) controls the HDLC function when used on DS0 channels
Transmit HDLC Register (THIR) status information on transmit HDLC controller
Transmit BOC Register (TBOC) enables/disables transmission of BOC codes
Transmit HDLC FIFO Register (THFR) access to 64–byte HDLC FIFO in transmit direction
Transmit HDLC DS0 Control Register 1 (TDC1) controls the HDLC function when used on DS0 channels
Transmit HDLC DS0 Control Register 2 (TDC2) controls the HDLC function when used on DS0 channels
15.3.2 STATUS REGISTER FOR THE HDLC
Four of the HDLC/BOC controller registers (HSR, RHIR, RBOC, and THIR) provide status information.
When a particular event has occurred (or is occurring), the appropriate bit in one of these four registers
will be set to a one. Some of the bits in these four HDLC status registers are latched and some are real
time bits that are not latched. Section 15.3.2 contains register descriptions that list which bits are latched
and which are not. With the latched bits, when an event occurs and a bit is set to a one, it will remain set
until the user reads that bit. The bit will be cleared when it is read and it will not be set again until the
event has occurred again. The real time bits report the current instantaneous conditions that are occurring
and the history of these bits is not latched.
Like the other status registers, the user will always proceed a read of any of the four registers with a
write. The byte written to the register will inform the device which of the latched bits the user wishes to
read and have cleared (the real time bits are not affected by writing to the status register). The user will
write a byte to one of these registers, with a one in the bit positions he or she wishes to read and a zero in
the bit positions he or she does not wish to obtain the latest information on. When a one is written to a bit
location, the read register will be updated with current value and it will be cleared. When a zero is written
to a bit position, the read register will not be updated and the previous value will be held. A write to the
status and information registers will be immediately followed by a read of the same register. The read
result should be logically AND’ed with the mask byte that was just written and this value should be
written back into the same register to insure that bit does indeed clear. This second write step is necessary
because the alarms and events in the status registers occur asynchronously in respect to their access via
the parallel port. This write–read–write (for polled driven access) or write–read (for interrupt driven
access) scheme allows an external microcontroller or microprocessor to individually poll certain bits
without disturbing the other bits in the register. This operation is key in controlling the device with
higher–order software languages.
68 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
Like the SR1 and SR2 status registers, the HSR register has the unique ability to initiate a hardware
interrupt via the INT* output pin. Each of the events in the HSR can be either masked or unmasked from
the interrupt pin via the HDLC Interrupt Mask Register (HIMR). Interrupts will force the INT* pin low
when the event occurs. The INT pin will be allowed to return high (if no other interrupts are present)
when the user reads the event bit that caused the interrupt to occur.
15.3.3 BASIC OPERATION DETAILS
To allow the framer to properly source/receive data from/to the HDLC and BOC controller the legacy FDL circuitry (which is
described in Section 15.4) should be disabled and the following bits should be programmed as shown:
TCR1.2 = 1 (source FDL data from the HDLC and BOC controller)
TBOC.6 = 1 (enable HDLC and BOC controller)
CCR2.5 = 0 (disable SLC–96 and D4 Fs–bit insertion)
CCR2.4 = 0 (disable legacy FDL zero stuffer)
CCR2.1 = 0 (disable SLC–96 reception)
CCR2.0 = 0 (disable legacy FDL zero stuffer)
IMR2.4 = 0 (disable legacy receive FDL buffer full interrupt)
IMR2.3 = 0 (disable legacy transmit FDL buffer empty interrupt)
IMR2.2 = 0 (disable legacy FDL match interrupt)
IMR2.1 = 0 (disable legacy FDL abort interrupt).
As a basic guideline for interpreting and sending both HDLC messages and BOC messages, the following sequences can be
applied:
15.3.3.1 RECEIVE AN HDLC MESSAGE OR A BOC
1) Enable RBOC and RPS interrupts.
2) Wait for interrupt to occur.
3) If RBOC=1, then follow steps 5 and 6.
4) If RPS=1, then follow steps 7 through 13.
5) If LBD=1, a BOC is present, then read the code from the RBOC register and take action as needed.
6) If BD=0, a BOC has ceased, take action as needed and then return to step 1.
7) Disable RPS interrupt and enable either RPE, RNE, or RHALF interrupt.
8) Read RHIR to obtain REMPTY status.
a) If REMPTY=0, then record OBYTE, CBYTE, and POK bits and then read the FIFO.
i) If CBYTE=0 then skip to step 9.
ii) If CBYTE=1 then skip to step 11.
b) If REMPTY=1, then skip to step 10.
9) Repeat step 8.
10) Wait for interrupt, skip to step 8.
11) If POK=0, then discard whole packet.
12) If POK=1, accept the packet.
13) Disable RPE, RNE, or RHALF interrupt, enable RPS interrupt and return to step 1.
69 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
15.3.3.2 TRANSMIT AN HDLC MESSAGE
1) Make sure HDLC controller is done sending any previous messages and is current sending flags by checking that the
FIFO is empty by reading the TEMPTY status bit in the TPRM register.
2) Enable either the THALF or TNF interrupt.
3) Read THIR to obtain TFULL status.
a) If TFULL=0, then write a byte into the FIFO and skip to next step (special case occurs when the last byte is to be
written, in this case set TEOM=1 before writing the byte and then skip to step 6).
b) If TFULL=1, then skip to step 5.
4) Repeat step 3.
5) Wait for interrupt, skip to step 3.
6) Disable THALF or TNF interrupt and enable TMEND interrupt.
7) Wait for an interrupt, then read TUDR status bit to make sure packet was transmitted correctly.
15.3.3.3 TRANSMIT A BOC
1) Write 6–bit code into TBOC.
2) Set SBOC bit in TBOC=1.
15.3.4 HDLC/BOC Register Description
HCR: HDLC CONTROL REGISTER (Address=00 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RBR RHR TFS THR TABT TEOM TZSD TCRCD
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RBR HCR.7 Receive BOC Reset. A 0 to 1 transition will reset the BOC circuitry. Must be cleared
and set again for a subsequent reset.
RHR HCR.6 Receive HDLC Reset. A 0 to 1 transition will reset the HDLC controller. Must be
cleared and set again for a subsequent reset.
TFS HCR.5
THR HCR.4 Transmit HDLC Reset. A 0 to 1 transition will reset both the HDLC controller and the
TABT HCR.3 Transmit Abort. A 0 to 1 transition will cause the FIFO contents to be dumped and one
TEOM HCR.2 Transmit End of Message. Should be set to a one just before the last data byte of a
TZSD HCR.1 Transmit Zero Stuffer Defeat. Overrides internal enable.
TCRCD HCR.0
Transmit Flag/Idle Select.
0 = 7Eh
1 = FFh
transmit BOC circuitry. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent reset.
FEh abort to be sent followed by 7Eh or FFh flags/idle until a new packet is initiated by
writing new data into the FIFO. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent abort to
be sent.
HDLC packet is written into the transmit FIFO at TFFR. This bit will be cleared by the
HDLC controller when the last byte has been transmitted.
0 = enable the zero stuffer (normal operation)
1 = disable the zero stuffer
Transmit CRC Defeat.
0 = enable CRC generation (normal operation)
1 = disable CRC generation
HSR: HDLC STATUS REGISTER (Address=01 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RBOC RPE RPS RHALF RNE THALF TNF TMEND
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RBOC HSR.7 Receive BOC Detector Change of State. Set whenever the BOC detector sees a
change of state from a BOC Detected to a No Valid Code seen or vice versa. The setting
of this bit prompt the user to read the RBOC register for details.
70 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RPE HSR.6 Receive Packet End. Set when the HDLC controller detects either the finish of a valid
message (i.e., CRC check complete) or when the controller has experienced a message
fault such as a CRC checking error, or an overrun condition, or an abort has been seen.
The setting of this bit prompts the user to read the RPRM register for details.
RPS HSR.5 Receive Packet Start. Set when the HDLC controller detects an opening byte. The
setting of this bit prompts the user to read the RPRM register for details.
RHALF HSR.4 Receive FIFO Half Full. Set when the receive 64–byte FIFO fills beyond the half way
point. The setting of this bit prompts the user to read the RPRM register for details.
RNE HSR.3 Receive FIFO Not Empty. Set when the receive 64–byte FIFO has at least one byte
available for a read. The setting of this bit prompts the user to read the RPRM register
for details.
THALF HSR.2 Transmit FIFO Half Empty. Set when the transmit 64–byte FIFO empties beyond the
half way point. The setting of this bit prompts the user to read the TPRM register for
details.
TNF HSR.1 Transmit FIFO Not Full. Set when the transmit 64–byte FIFO has at least one byte
available. The setting of this bit prompts the user to read the TPRM register for details.
TMEND HSR.0 Transmit Message End. Set when the transmit HDLC controller has finished sending a
message. The setting of this bit prompts the user to read the TPRM register for details.
NOTE:
The RBOC, RPE, RPS, and TMEND bits are latched and will be cleared when read.
71 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
HIMR: HDLC INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER (Address=02 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RBOC RPE RPS RHALF RNE THALF TNF TMEND
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RBOC HIMR.7
RPE HIMR.6
RPS HIMR.5
RHALF HIMR.4
RNE HIMR.3
THALF HIMR.2
TNF HIMR.1
TMEND FIMR.0
Receive BOC Detector Change of State.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Packet End.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Packet Start.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive FIFO Half Full.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive FIFO Not Empty.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Transmit FIFO Half Empty.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Transmit FIFO Not Full.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Transmit Message End.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
72 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RHIR: RECEIVE HDLC INFORMATION REGISTER (Address=03 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RABT RCRCE ROVR RVM REMPTY POK CBYTE OBYTE
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RABT RHIR.7 Abort Sequence Detected. Set whenever the HDLC controller sees 7 or more ones in a
row.
RCRCE RHIR.6 CRC Error. Set when the CRC checksum is in error.
ROVR RHIR.5 Overrun. Set when the HDLC controller has attempted to write a byte into an already full
receive FIFO.
RVM RHIR.4 Valid Message. Set when the HDLC controller has detected and checked a complete
HDLC packet.
REMPTY RHIR.3 Empty. A real–time bit that is set high when the receive FIFO is empty.
POK RHIR.2 Packet OK. Set when the byte available for reading in the receive FIFO is the last byte of
a valid message (and hence no abort was seen, no overrun occurred, and the CRC was
correct).
CBYTE RHIR.1 Closing Byte. Set when the byte available for reading in the receive FIFO is the last byte
of a message (whether the message was valid or not).
OBYTE RHIR.0 Opening Byte. Set when the byte available for reading in the receive FIFO is the first byte
of a message.
NOTE:
The RABT, RCRCE, ROVR, and RVM bits are latched and will be cleared when read.
73 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RBOC: RECEIVE BIT ORIENTED CODE REGISTER (Address=04 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LBD BD BOC5 BOC4 BOC3 BOC2 BOC1 BOC0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LBD RBOC.7 Latched BOC Detected. A latched version of the BD status bit (RBOC.6). Will be
cleared when read.
BD RBOC.6 BOC Detected. A real–time bit that is set high when the BOC detector is presently
seeing a valid sequence and set low when no BOC is currently being detected.
BOC5 RBOC.5 BOC Bit 5. Last bit received of the 6–bit codeword.
BOC4 RBOC.4
BOC3 RBOC.3
BOC2 RBOC.2
BOC1 RBOC.1
BOC0 RBOC.0 BOC Bit 0. First bit received of the 6–bit codeword.
BOC Bit 4.
BOC Bit 3.
BOC Bit 2.
BOC Bit 1.
NOTE:
1. The LBD bit is latched and will be cleared when read.
2. The RBOC0 to RBOC5 bits display the last valid BOC code verified; these bits will be set to all ones on reset.
74 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RHFR: RECEIVE HDLC FIFO (Address=05 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RHFR7 RHFR6 RHFR5 RHFR4 RHFR3 RHFR2 RHFR1 RHFR0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RHFR7 RHFR.7 HDLC Data Bit 7. MSB of a HDLC packet data byte.
RHFR6 RHFR.6
RHFR5 RHFR.5
RHFR4 RHFR.4
RHFR3 RHFR.3
RHFR2 RHFR.2
RHFR1 RHFR.1
RHFR0 RHFR.0 HDLC Data Bit 0. LSB of a HDLC packet data byte.
HDLC Data Bit 6.
HDLC Data Bit 5.
HDLC Data Bit 4.
HDLC Data Bit 3.
HDLC Data Bit 2.
HDLC Data Bit 1.
THIR: TRANSMIT HDLC INFORMATION (Address=06 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
–––––TEMPTYTFULLTUDR
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
–THIR.7Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
–THIR.6Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
–THIR.5Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
–THIR.4Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
–THIR.3Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
TEMPTY THIR.2 Transmit FIFO Empty. A real–time bit that is set high when the FIFO is empty.
TFULL THIR.1 Transmit FIFO Full. A real–time bit that is set high when the FIFO is full.
TUDR THIR.0 Transmit FIFO Under-run. Set when the transmit FIFO empties out without the
TEOM control bit being set. An abort is automatically sent.
NOTE:
The TUDR bit is latched and will be cleared when read.
TBOC: TRANSMIT BOC REGISTER (Address=07 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
SBOC HBEN BOC5 BOC4 BOC3 BOC2 BOC1 BOC0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
SBOC TBOC.7 Send BOC. Rising edge triggered. Must be transitioned from a 0 to a 1 transmit the
BOC code placed in the BOC0 to BOC5 bits instead of data from the HDLC controller.
HBEN TBOC.6
Transmit HDLC & BOC Controller Enable.
75 of 137

0 = source FDL data from the TLINK pin
1 = source FDL data from the onboard HDLC and BOC controller
BOC5 TBOC.5 BOC Bit 5. Last bit transmitted of the 6–bit codeword.
DS21352/DS21552
BOC4 TBOC.4
BOC3 TBOC.3
BOC2 TBOC.2
BOC1 TBOC.1
BOC0 TBOC.0 BOC Bit 0. First bit transmitted of the 6–bit codeword.
BOC Bit 4.
BOC Bit 3.
BOC Bit 2.
BOC Bit 1.
THFR: TRANSMIT HDLC FIFO (Address=08 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
THFR7 THFR6 THFR5 THFR4 THFR3 THFR2 THFR1 THFR0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
THFR7 THFR.7 HDLC Data Bit 7. MSB of a HDLC packet data byte.
THFR6 THFR.6
THFR5 THFR.5
THFR4 THFR.4
HDLC Data Bit 6.
HDLC Data Bit 5.
HDLC Data Bit 4.
THFR3 THFR.3
THFR2 THFR.2
THFR1 THFR.1
THFR0 THFR.0 HDLC Data Bit 0. LSB of a HDLC packet data byte.
HDLC Data Bit 3.
HDLC Data Bit 2.
HDLC Data Bit 1.
RDC1: RECEIVE HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=90 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RDS0E - RDS0M RD4 RD3 RD2 RD1 RD0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RDS0E RDC1.7
-RDC1.6Not Assigned. Should be set to 0.
RDS0M RDC1.5
RD4 RDC1.4 DS0 Channel Select Bit 4. MSB of the DS0 channel select.
HDLC DS0 Enable.
0 = use the receive HDLC controller for the FDL.
1 = use the receive HDLC controller for one or more DS0 channels.
DS0 Selection Mode.
0 = utilize the RD0 to RD4 bits to select which single DS0 channel to use.
1 = utilize the RCHBLK control registers to select which DS0 channels to use.
RD3 RDC1.3
RD2 RDC1.2
DS0 Channel Select Bit 3.
DS0 Channel Select Bit 2.
76 of 137

RD1 RDC1.1
RD0 RDC1.0 DS0 Channel Select Bit 0. LSB of the DS0 channel select.
DS0 Channel Select Bit 1.
DS21352/DS21552
77 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RDC2: RECEIVE HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=91 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RDB8 RDB7 RDB6 RDB5 RDB4 RDB3 RDB2 RDB1
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RDB8 RDC2.7 DS0 Bit 8 Suppress Enable. MSB of the DS0. Set to one to stop this bit from being
used.
RDB7 RDC2.6 DS0 Bit 7 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
RDB6 RDC2.5 DS0 Bit 6 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
RDB5 RDC2.4 DS0 Bit 5 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
RDB4 RDC2.3 DS0 Bit 4 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
RDB3 RDC2.2 DS0 Bit 3 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
RDB2 RDC2.1 DS0 Bit 2 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
RDB1 RDC2.0 DS0 Bit 1 Suppress Enable. LSB of the DS0. Set to one to stop this bit from being
used.
78 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TDC1: TRANSMIT HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=92 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TDS0E - TDS0M TD4 TD3 TD2 TD1 TD0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TDS0E TDC1.7
-TDC1.6Not Assigned. Should be set to 0.
TDS0M TDC1.5
TD4 TDC1.4 DS0 Channel Select Bit 4. MSB of the DS0 channel select.
TD3 TDC1.3
TD2 TDC1.2
TD1 TDC1.1
TD0 TDC1.0 DS0 Channel Select Bit 0. LSB of the DS0 channel select.
HDLC DS0 Enable.
0 = use the transmit HDLC controller for the FDL.
1 = use the transmit HDLC controller for one or more DS0 channels.
DS0 Selection Mode.
0 = utilize the TD0 to TD4 bits to select which single DS0 channel to use.
1 = utilize the TCHBLK control registers to select which DS0 channels to use.
DS0 Channel Select Bit 3.
DS0 Channel Select Bit 2.
DS0 Channel Select Bit 1.
79 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
TDC2: TRANSMIT HDLC DS0 CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=93 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TDB8 TDB7 TDB6 TDB5 TDB4 TDB3 TDB2 TDB1
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TDB8 TDC2.7 DS0 Bit 8 Suppress Enable. MSB of the DS0. Set to one to stop this bit from
being used.
TDB7 TDC2.6 DS0 Bit 7 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
TDB6 TDC2.5 DS0 Bit 6 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
TDB5 TDC2.4 DS0 Bit 5 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
TDB4 TDC2.3 DS0 Bit 4 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
TDB3 TDC2.2 DS0 Bit 3 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
TDB2 TDC2.1 DS0 Bit 2 Suppress Enable. Set to one to stop this bit from being used.
TDB1 TDC2.0 DS0 Bit 1 Suppress Enable. LSB of the DS0. Set to one to stop this bit from
being used.
15.4 LEGACY FDL SUPPORT
15.4.1 OVERVIEW
In order to provide backward compatibility to the older DS2152 device, the DS21352/552 maintains the
circuitry that existed in the previous generation of the T1 Quad Framer. Sections 15.4.2 and 15.4.3 cover
the circuitry and operation of this legacy functionality. In new applications, it is recommended that the
HDLC controller and BOC controller described in Section 15.3 are used. On the receive side, it is
possible to have both the new HDLC/BOC controller and the legacy hardware working at the same time.
On the transmit side the HDLC/BOC controller can be assigned to a DSO while the legacy function
supports the FDL via software. Software for supporting the legacy functions is available from Dallas
Semiconductor.
15.4.2 RECEIVE SECTION
In the receive section, the recovered FDL bits or Fs bits are shifted bit–by–bit into the Receive FDL
register (RFDL). Since the RFDL is 8 bits in length, it will fill up every 2 ms (8 times 250 us). The framer
will signal an external microcontroller that the buffer has filled via the SR2.4 bit. If enabled via IMR2.4,
the INT pin will toggle low indicating that the buffer has filled and needs to be read. The user has 2 ms to
read this data before it is lost. If the byte in the RFDL matches either of the bytes programmed into the
RFDLM1 or RFDLM2 registers, then the SR2.2 bit will be set to a one and the INT pin will toggled low
if enabled via IMR2.2. This feature allows an external microcontroller to ignore the FDL or Fs pattern
until an important event occurs.
80 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
The framer also contains a zero destuffer which is controlled via the CCR2.0 bit. In both ANSI T1.403
and TR54016, communications on the FDL follows a subset of a LAPD protocol. The LAPD protocol
states that no more than 5 ones should be transmitted in a row so that the data does not resemble an
opening or closing flag (01111110) or an abort signal (11111111). If enabled via CCR2.0, the
DS21352/552 will automatically look for 5 ones in a row, followed by a zero. If it finds such a pattern, it
will automatically remove the zero. If the zero destuffer sees six or more ones in a row followed by a
zero, the zero is not removed. The CCR2.0 bit should always be set to a one when the DS21352/552 is
extracting the FDL. More on how to use the DS21352/552 in FDL applications in this legacy support
mode is covered in a separate Application Note.
RFDL: RECEIVE FDL REGISTER (Address=28 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RFDL7 RFDL6 RFDL5 RFDL4 RFDL3 RFDL2 RFDL1 RFDL0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RFDL7 RFDL.7 MSB of the Received FDL Code
RFDL0 RFDL.0 LSB of the Received FDL Code
The Receive FDL Register (RFDL) reports the incoming Facility Data Link (FDL) or the incoming Fs bits. The LSB is
received first.
RFDLM1: RECEIVE FDL MATCH REGISTER 1 (Address=29 Hex)
RFDLM2: RECEIVE FDL MATCH REGISTER 2 (Address=2A Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RFDL7 RFDL6 RFDL5 RFDL4 RFDL3 RFDL2 RFDL1 RFDL0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RFDL7 RFDL.7 MSB of the FDL Match Code
RFDL0 RFDL.0 LSB of the FDL Match Code
When the byte in the Receive FDL Register matches either of the two Receive FDL Match Registers (RFDLM1/RFDLM2),
SR2.2 will be set to a one and the INT will go active if enabled via IMR2.2.
81 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
15.4.3 TRANSMIT SECTION
The transmit section will shift out into the T1 data stream, either the FDL (in the ESF framing mode) or
the Fs bits (in the D4 framing mode) contained in the Transmit FDL register (TFDL). When a new value
is written to the TFDL, it will be multiplexed serially (LSB first) into the proper position in the outgoing
T1 data stream. After the full eight bits has been shifted out, the framer will signal the host
microcontroller that the buffer is empty and that more data is needed by setting the SR2.3 bit to a one.
The INT will also toggle low if enabled via IMR2.3. The user has 2 ms to update the TFDL with a new
value. If the TFDL is not updated, the old value in the TFDL will be transmitted once again. The framer
also contains a zero stuffer which is controlled via the CCR2.4 bit. In both ANSI T1.403 and TR54016,
communications on the FDL follows a subset of a LAPD protocol. The LAPD protocol states that no
more than 5 ones should be transmitted in a row so that the data does not resemble an opening or closing
flag (01111110) or an abort signal (11111111). If enabled via CCR2.4, the framer will automatically look
for 5 ones in a row. If it finds such a pattern, it will automatically insert a zero after the five ones. The
CCR2.0 bit should always be set to a one when the framer is inserting the FDL. More on how to use the
DS21352/552 in FDL applications is covered in a separate Application Note.
TFDL: TRANSMIT FDL REGISTER (Address=7E Hex)
[also used to insert Fs framing pattern in D4 framing mode; see Section 15.5]
(MSB) (LSB)
TFDL7 TFDL6 TFDL5 TFDL4 TFDL3 TFDL2 TFDL1 TFDL0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TFDL7 TFDL.7 MSB of the FDL code to be transmitted
TFDL0 TFDL.0 LSB of the FDL code to be transmitted
The Transmit FDL Register (TFDL) contains the Facility Data Link (FDL) information that is to be inserted on a byte basis
into the outgoing T1 data stream. The LSB is transmitted first.
15.5 D4/SLC–96 OPERATION
In the D4 framing mode, the framer uses the TFDL register to insert the Fs framing pattern. To allow the
device to properly insert the Fs framing pattern, the TFDL register at address 7Eh must be programmed to
1Ch and the following bits must be programmed as shown: TCR1.2=0 (source Fs data from the TFDL
register) CCR2.5=1 (allow the TFDL register to load on multiframe boundaries)
Since the SLC–96 message fields share the Fs–bit position, the user can access the these message fields
via the TFDL and RFDL registers. Please see the separate Application Note for a detailed description of
how to implement a SLC–96 function.
82 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
16. LINE INTERFACE FUNCTION
The line interface function in the DS21352/552 contains three sections; (1) the receiver which handles
clock and data recovery, (2) the transmitter which waveshapes and drives the T1 line, and (3) the jitter
attenuator. Each of the these three sections is controlled by the Line Inter-face Control Register (LICR)
which is described below.
LICR: LINE INTERFACE CONTROL REGISTER (Address=7C Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
L2 L1 L0 EGL JAS JABDS DJA TPD
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
L2 LICR.7 Line Build Out Select Bit 2. Sets the transmitter build out; see Table 16-1
L1 LICR.6 Line Build Out Select Bit 1. Sets the transmitter build out; see Table 16-1
L0 LICR.5 Line Build Out Select Bit 0. Sets the transmitter build out; see Table 16-1
EGL LICR.4 Receive Equalizer Gain Limit. 0 = –36 dB 1 = –30 dB
JAS LICR.3 Jitter Attenuator Select. 0 = place the jitter attenuator on the receive side 1 = place
the jitter attenuator on the transmit side
JABDS LICR.2 Jitter Attenuator Buffer Depth Select 0 = 128 bits 1 = 32 bits (use for delay
sensitive applications)
DJA LICR.1 Disable Jitter Attenuator. 0 = jitter attenuator enabled 1 = jitter attenuator disabled
TPD LICR.0 Transmit Power Down. 0 = normal transmitter operation 1 = powers down the
transmitter and 3-states the TTIP and TRING pins
16.1 RECEIVE CLOCK AND DATA RECOVERY
The DS21352/552 contains a digital clock recovery system. See Figure 3-1 and Figure 16-1 for more
details. The DS21352/552 couples to the receive T1 twisted pair via a 1:1 transformer. See for details.
The 1.544 MHz clock applied to the MCLK pin is internally multiplied by 16 via an internal PLL and fed
to the clock recovery system. The clock recovery system uses the clock from the PLL circuit to form a 16
times oversampler which is used to recover the clock and data. This oversampling technique offers
outstanding jitter tolerance (see Figure 16-4).
Normally, the clock that is output at the RCLKO pin is the recovered clock from the T1 AMI/B8ZS
waveform presented at the RTIP and RRING inputs. When no AMI signal is present at RTIP and RRING,
a Receive Carrier Loss (LRCL) condition will occur and the RCLKO will be sourced from the clock
applied at the MCLK pin. If the jitter attenuator is either placed in the transmit path or is disabled, the
RCLKO output can exhibit slightly shorter high cycles of the clock. This is due to the highly oversampled
digital clock recovery circuitry. If the jitter attenuator is placed in the receive path (as is the case in most
applications), the jitter attenuator restores the RCLK to being close to 50% duty cycle. Please see the
Receive AC Timing Characteristics in section 24 for more details.
83 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
16.2 TRANSMIT WAVE SHAPING AND LINE DRIVING
The DS21352/552 uses a set of laser–trimmed delay lines along with a precision Digital–to–Analog
Converter (DAC) to create the waveforms that are transmitted onto the T1 line. The waveforms created
by the DS21352/552 meet the latest ANSI, AT&T, and ITU specifications. See Figure 16-3. The user
will select which waveform is to be generated by properly programming the L2/L1/L0 bits in the Line
Interface Control Register (LICR). The DS21352/552 can set up in a number of various configurations
depending on the application. See Table 16-1.
Table 16-1 LINE BUILD OUT SELECT IN LICR
L2 L1 L0 LINE BUILD OUT APPLICATION
0 0 0 0 to133 feet/ DSX–1/0dB CSU
0 0 1 133 feet to266 DSX–1
0 1 0 266 feet to399 DSX–1
0 1 1 399 feet to533 DSX–1
1 0 0 533 feet to655 DSX–1
1 0 1 –7.5 dB CSU
1 1 0 –15 dB CSU
1 1 1 –22.5 dB CSU
Due to the nature of the design of the transmitter in the DS21352/552, very little jitter (less then 0.005
UIpp broad-band from 10 Hz to 100 kHz) is added to the jitter present on TCLKI. Also, the waveforms
that they create are independent of the duty cycle of TCLK. The transmitter in the DS21352/552 couples
to the T1 transmit twisted pair via a 1:1.15 or 1:1.36 step up transformer for the DS21552 or a 1:2 step up
transformer for the DS21352 as shown in Figure 16-1. In order for the devices to create the proper
waveforms, this transformer used must meet the specifications listed in Table 16-3.
16.3 JITTER ATTENUATOR
The DS21352/552 contains an onboard jitter attenuator that can be set to a depth of either 32 or 128 bits
via the JABDS bit in the Line Interface Control Register (LICR). The 128 bit mode is used in applications
where large excursions of wander are expected. The 32 bit mode is used in delay sensitive applications.
The characteristics of the attenuation are shown in Figure 16-4. The jitter attenuator can be placed in
either the receive or transmit path via the JAS bit in the LICR. Also, the jitter attenuator can be disabled
(in effect, removed) by setting the DJA bit in the LICR. In order for the jitter attenuator to operate
properly, a 1.544 MHz clock (+50 ppm) must be applied at the MCLK pin or a crystal with similar
characteristics must be applied across the MCLK and XTALD pins. If a crystal is applied across the
MCLK and XTALD pins, then the maximum effective series resistance (ESR) should be 40 Ohms and
capacitors should be placed from each leg of the crystal to the local ground plane as shown in Figure 16–
1. Onboard circuitry adjusts either the recovered clock from the clock/data recovery block or the clock
applied at the TCLKI pin to create a smooth jitter free clock which is used to clock data out of the jitter
attenuator FIFO. It is acceptable to provide a gapped/ bursty clock at the TCLKI pin if the jitter attenuator
is placed on the transmit side. If the incoming jitter exceeds either 120 UIpp (buffer depth is 128 bits) or
28 UIpp (buffer depth is 32 bits), then the DS21352/552 will divide the internal nominal 24.704 MHz
clock by either 15 or 17 instead of the normal 16 to keep the buffer from overflowing. When the device
divides by either 15 or 17, it also sets the Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip (JALT) bit in the Receive
Information Register (RIR3.5).
84 of 137

Figure 16-1 EXTERNAL ANALOG CONNECTIONS
0.47uF
(non-
T1 Transmit
Line
polarized)
Rt
Rt
N : 1
(see table below)
1 : 1
DS21352 / 552
TTIP
TRING
DVDD
DVSS
RVDD
RVSS
TVDD
TVSS
DS21352/DS21552
VDD
0.1uF
0.01uF
0.1uF
0.1uF
T1 Receive
RTIP
Line
RRING
50 50
0.1uF
XTALD
MCLK
NC
1.544MHz
Table 16-2 TRANSMIT TRANSFORMER SELECTION
DEVICE TRANSFORMER RESISTOR Rt
DS21552 1.15 : 1
1.36 : 1
DS21352 2 : 1 0 ohms
See separate application note on line interface design criteria for full details.
0 ohms Ideal, 2.2 ohms max
4.7 ohms Ideal
NOTES:
1. Resistor values are +/-1%.
2. The Rt resistors are used to protect the device from over–voltage.
3. See the Separate Application Note for details on how to construct a protected interface.
4. Normally a TTL level clock is applied MCLK and the XTAL pin is left as an NC. Optionally a crystal can be applied across
the MCLK and XTALD pins.
Table 16-3 TRANSFORMER SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATION RECOMMENDED VALUE
Turns Ratio DS21352 1:1(receive) and1:2(transmit) 5%
Turns Ratio DS21552 1:1(receive) and1:1.15 or1:1.36(transmit) 5%
Primary Inductance
Leakage Inductance
Intertwining Capacitance 40 pF maximum
DC Resistance 1.2 Ohms maximum
600mH minimum
1.0mH maximum
85 of 137

Figure 16-2 OPTIONAL CRYSTAL CONNECTIONS
DS21352/552
XTALD
MCLK
DS21352/DS21552
1.544MHz
C1
NOTES:
1. C1 and C2 should be 5 pF lower than two times the nominal loading capacitance of the crystal to adjust for the input
capacitance of the DS21352/552.
C2
86 of 137

Figure 16-3 TRANSMIT WAVEFORM TEMPLATE
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
DS21352/DS21552
NORMALIZED AMPLITUDE
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
-0.5
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
-500
T1.102/87, T1.403,
CB 119 (Oct. 79), &
I.431 Template
-300
-100 0 300 500 700-400 -200 200 400 600100
TIME (ns)
87 of 137

Table 16-4 PULSE TEMPLATE CORNER POINTS
TIME (ns) UI MAX CURVE MIN CURVE
-500 -0.77 0.05 -0.05
-255 -0.39 0.05
-175 -0.27 0.80
-175 -.027 1.15
-150 -0.23 -0.05
-150 -0.23 0.05
-100 0.95
-75 -0.12 1.15
0 0.00 1.05 0.95
DS21352/DS21552
100 0.15 0.90
150 0.23 0.50
150 0.23 -0.45
175 0.27 1.05
225 0.35 -0.07
300 0.46 -0.45
430 0.66 -0.20
600 0.93 0.05 -0.05
750 1.16 0.05 -0.05
88 of 137

Figure 16-4 JITTER TOLERANCE
K
1K
100
10
Mi mi mum Tol er ance
Level as per
UNIT INTERVALS (UIpp)
1
0.1
1
TR 62411 (Dec. 90)
10
100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
DS21352/DS21552
DS2152
Tol e r an ce
1K 10K 100
Figure 16-5 JITTER ATTENUATION
89 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
16.4 PROTECTED INTERFACES
In certain applications, such as connecting to the PSTN, it is required that the network interface be
protected from and resistant to certain electrical conditions. These conditions are divided into two
categories, surge and power line cross. A typical cause of surge is lightening strike. Power line cross
refers to accidental contact with high voltage power wiring. For protection against surges, additional
components and PCB layout considerations are required to reroute and dissipate this energy. In a surge
event, the network interface must not be damaged and continue to work after the event. In the event of a
power line contact, components such as fuses or PTCs that can “open” the circuit are required to prevent
the possibility of a fire caused by overheating the transformer. The circuit examples in this data sheet are
for “Secondary Over Voltage Protection” schemes for the line terminating equipment. Primary protection
is typically provided by the network service provide and is external to the equipment.
Figure 16-6 shows an example circuit for the 5 volt device and Figure 16-7 is an example for the 3.3
device. In both examples, fuses are used to provide protection against power line cross. 470 ohm input
resistors on the receive pair, a transient suppresser and a diode bridge on the transmit pair provide surge
protection. Resistors R1 – R4 provide surge protection for the fuse. Careful selection of the transformer
will allow the use of a fuse that requires no additional surge protection such as the circuit shown in Figure
16-7. The circuit shown in Figure 16-7 is required for 3.3 volt operation since additional resistance in the
transmit pair cannot be tolerated. For more information on line interface design, consult the T1 Line
Interface Design Criteria (note 353) and Secondary Over Voltage Protection (note 324) application notes.
These notes are available from Dallas Semiconductor’s web site.
90 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
Figure 16-6 PROTECTED INTERFACE EXAMPLE FOR THE DS21552
+VDD
Transmit
Line
Recei ve
Line
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
R1
R2
R3
R4
N:1
Rt
S
Rt
X1
1:1
X2
Rterm Rterm
D1
C2
D3 D4
470
470
0.1uF
C1
D2
DS21552
TTIP
TRING
RTIP
RRING
DVDD
DVSS
RVDD
RVSS
TVDD
TVSS
MCLK
0.01uF
+5V
0.1uF
0.1uF
0.1uF
1.544MHz
+
68uf
Note:
The 68uf cap is required to maintain VDD during a transient event.
COMPONET DESCRIPTION
D1 – D4 Schottky Diode, International Rectifier 11DQ04
C1 0.1uf ceramic in parallel with 10uf tantalum
C2 .47 uf, non polarized ceramic construction
S Semtech LC01-6, 6V low capacitance TVS
Fuse
Rt
Rterm
R1, R2, R3, R4
X1
X2
For more information on the selection of these components see the separate
application notes on Secondary Over Voltage Protection and T1 Network
Interface Design Criteria. These applications notes are available from Dallas
Semiconductor’s Web site at www.dalsemi.com
91 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
f
Figure 16-7 PROTECTED INTERFACE EXAMPLE FOR THE DS21352
+VDD
Transmit
Line
Recei ve
Line
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
2:1
X1
1:1
X2
50
D1
D2
DS21352
+3.3V
0.1uF
TTIP
S
C2
D3 D4
C1
TRING
DVDD
DVSS
RVDD
RVSS
TVDD
0.01uF
0.1uF
0.1uF
68u
+
TVSS
470
470
RTIP
MCLK
RRING
1.544MHz
50
0.1uF
Note:
The 68uf cap is required to maintain VDD levels during a transient event.
COMPONET DESCRIPTION
D1 – D4 Schottky Diode, International Rectifier 11DQ04
C1 0.1uf ceramic in parallel with 10uf tantalum
C2 .47 uf, non polarized ceramic construction
Fuse 1.25A slo-blo, Littlefuse V2301.25
S Semtech LC01-6, 6V low capacitance TVS
X1, X2 Transpower PT314, Low DCR
92 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
16.5 RECEIVE MONITOR MODE
When connecting to a monitor port a large resistive loss is incurred due to the voltage divider between the
T1 line termination resistors (Rt) and the monitor port isolation resistors (Rm) as shown below. The Rm
resistors are typically 470 ohm. This, along with the 100 ohm termination (Rt), produces 20dB of loss.
The receiver of the DS21352/552 can provide gain to overcome the resistive loss of a monitor connection.
This is a purely resistive loss/gain and should not be confused with the cable loss characteristics of a T1
transmission line. Via the TEST2 register as shown in the table below, the receiver can be programmed
to provide both 12dB and 20dB of gain.
Figure 16-8 TYPICAL MONITOR PORT APPLICATION
PRIMARY
T1 LINE
T1 TERMINATING
DEVICE
Rm Rm
MONITOR
PORT JACK
Table 16-5 RECEIVE MONITOR MODE GAIN
X
F
Rt
DS21X52
M
R
SECONDARY T1
TERMINATING
DEVICE
TEST2 (Address = 09 Hex) Register Value Gain
72 Hex
70 Hex 20dB
93 of 137
12dB
DS21352/DS21552
17. PROGRAMMABLE IN–BAND LOOP CODE GENERATION AND
DETECTION
Each framer in the DS21352/552 has the ability to generate and detect a repeating bit pattern that is from
one to eight bits in length. To transmit a pattern, the user will load the pattern to be sent into the Transmit
Code Definition (TCD) register and select the proper length of the pattern by setting the TC0 and TC1
bits in the In–Band Code Control (IBCC) register. Once this is accomplished, the pattern will be
transmitted as long as the TLOOP control bit (CCR3.1) is enabled. Normally (unless the transmit
formatter is programmed to not insert the F–bit position) the framer will overwrite the repeating pattern
once every 193 bits to allow the F–bit position to be sent. As an example, if the user wished to transmit
the standard “loop up” code for Channel Service Units which is a repeating pattern of ...10000100001...
then 80h would be loaded into TDR and the length would set to 5 bits.
Each framer can detect two separate repeating patterns to allow for both a “loop up” code and a “loop
down” code to be detected. The user will program the codes to be detected in the Receive Up Code
Definition (RUPCD) register and the Receive Down Code Definition (RDNCD) register and the length of
each pattern will be selected via the IBCC register. The framer will detect repeating pattern codes in both
framed and unframed circumstances with bit error rates as high as 10E–2. The code detector has a
nominal integration period of 48 ms. Hence, after about 48 ms of receiving either code, the proper status
bit (LUP at SR1.7 and LDN at SR1.6) will be set to a one. Normally codes are sent for a period of 5
seconds. it is recommend that the software poll the framer every 100 ms to 1000 ms until 5 seconds has
elapsed to insure that the code is continuously present.
IBCC: IN–BAND CODE CONTROL REGISTER (Address=12 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TC1 TC0 RUP2 RUP1 RUP0 RDN2 RDN1 RDN0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TC1 IBCC.7 Transmit Code Length Definition Bit 1. See Table 17-1
TC0 IBCC.6 Transmit Code Length Definition Bit 0. See Table 17-1
RUP2 IBCC.5 Receive Up Code Length Definition Bit 2. See Table 17-2
RUP1 IBCC.4 Receive Up Code Length Definition Bit 1. See Table 17-2
RUP0 IBCC.3 Receive Up Code Length Definition Bit 0. See Table 17-2
RDN2 IBCC.2 Receive Down Code Length Definition Bit 2. See Table 17-2
RDN1 IBCC.1 Receive Down Code Length Definition Bit 1. See Table 17-2
RDN0 IBCC.0 Receive Down Code Length Definition Bit 0. See Table 17-2
94 of 137

Table 17-1 TRANSMIT CODE LENGTH
TC1 TC0 LENGTH SELECTED
0 0 5 bits
0 1 6 bits / 3 bits
1 0 7 bits
1 1 8 bits / 4 bits / 2 bits / 1 bits
Table 17-2 RECEIVE CODE LENGTH
RUP2/ RDN2 RUP1/ RDN1 RUP0/ RDN0 LENGTH SELECTED
0001 bits
0012 bits
0103 bits
0114 bits
1005 bits
1016 bits
1107 bits
1118 bits
TCD: TRANSMIT CODE DEFINITION REGISTER (Address=13 Hex)
DS21352/DS21552
(MSB) (LSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
C7 TCD.7 Transmit Code Definition Bit 7. First bit of the repeating pattern.
C6 TCD.6
C5 TCD.5
C4 TCD.4
C3 TCD.3
C2 TCD.2 Transmit Code Definition Bit 2. A Don’t Care if a 5 bit length is selected.
C1 TCD.1 Transmit Code Definition Bit 1. A Don’t Care if a 5 or 6 bit length is selected.
C0 TCD.0 Transmit Code Definition Bit 0. A Don’t Care if a 5, 6 or 7 bit length is selected.
Transmit Code Definition Bit 6.
Transmit Code Definition Bit 5.
Transmit Code Definition Bit 4.
Transmit Code Definition Bit 3.
95 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
RUPCD: RECEIVE UP CODE DEFINITION REGISTER (Address=14 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
C7 RUPCD.7 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 7. First bit of the repeating pattern.
C6 RUPCD.6 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 6. A Don’t Care if a 1 bit length is selected.
C5 RUPCD.5 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 5. A Don’t Care if a 1 or 2 bit length is selected.
C4 RUPCD.4 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 4. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 3 bit length is selected.
C3 RUPCD.3 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 3. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 4 bit length is selected.
C2 RUPCD.2 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 2. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 5 bit length is selected.
C1 RUPCD.1 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 1. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 6 bit length is selected.
C0 RUPCD.0 Receive Up Code Definition Bit 0. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 7 bit length is selected.
RDNCD: RECEIVE DOWN CODE DEFINITION REGISTER (Address=15 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
C7 RDNCD.7 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 7. First bit of the repeating pattern.
C6 RDNCD.6 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 6. A Don’t Care if a 1 bit length is selected.
C5 RDNCD.5 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 5. A Don’t Care if a 1 or 2 bit length is selected.
C4 RDNCD.4 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 4. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 3 bit length is selected.
C3 RDNCD.3 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 3. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 4 bit length is selected.
C2 RDNCD.2 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 2. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 5 bit length is selected.
C1 RDNCD.1 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 1. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 6 bit length is selected.
C0 RDNCD.0 Receive Down Code Definition Bit 0. A Don’t Care if a 1 to 7 bit length is selected.
96 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
18. TRANSMIT TRANSPARENCY
Each of the 24 T1 channels in the transmit direction of the framer can be either forced to be transparent or
in other words, can be forced to stop Bit 7 Stuffing and/or Robbed Signaling from overwriting the data in
the channels. Transparency can be invoked on a channel by channel basis by properly setting the TTR1,
TTR2, and TTR3 registers.
TTR1/TTR2/TTR3: TRANSMIT TRANSPARENCY REGISTER (Address=39 to
3B Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 TTR1 (39)
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9 TTR2 (3A)
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17 TTR3 (3B)
SYMBOLS POSITIONS NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH1-24 TTR1.0-3.7
Transmit Transparency Registers.
0 = this DS0 channel is not transparent
1 = this DS0 channel is transparent
Each of the bit position in the Transmit Transparency Registers (TTR1/TTR2/TTR3) represent a DS0
channel in the outgoing frame. When these bits are set to a one, the corresponding channel is transparent
(or clear). If a DS0 is programmed to be clear, no robbed bit signaling will be inserted nor will the
channel have Bit 7 stuffing performed. However, in the D4 framing mode, bit 2 will be overwritten by a
zero when a Yellow Alarm is transmitted. Also the user has the option to prevent the TTR registers from
determining which channels are to have Bit 7 stuffing performed. If the TCR2.0 and TCR1.3 bits are set
to one, then all 24 T1 channels will have Bit 7 stuffing performed on them regardless of how the TTR
registers are programmed. In this manner, the TTR registers are only affecting which channels are to have
robbed bit signaling inserted into them.
19. JTAG-BOUNDARY SCAN ARCHITECTURE AND TEST ACCESS PORT
19.1 DESCRIPTION
The DS21352/552 IEEE 1149.1 design supports the standard instruction codes SAMPLE/PRELOAD,
BYPASS, and EXTEST. Optional public instructions included are HIGHZ, CLAMP, and IDCODE. See
Figure 19-1. The DS21352/552 contains the following as required by IEEE 1149.1 Standard Test Access
Port and Boundary Scan Architecture.
Test Access Port (TAP)
TAP Controller
Instruction Register
Bypass Register
Boundary Scan Register
Device Identification Register
97 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
The DS21352/552 are enhanced versions of the DS2152 and are backward pin-compatible. The JTAG
feature uses pins that had no function in the DS2152. When using the JTAG feature, be sure FMS (pin
76) is tied LOW enabling the newly defined pins of the DS21352/552. Details on Boundary Scan
Architecture and the Test Access Port can be found in IEEE 1149.1-1990, IEEE 1149.1a-1993, and IEEE
1149.1b-1994.
The Test Access Port has the necessary interface pins; JTRST, JTCLK, JTMS, JTDI, and JTDO. See the
pin descriptions for details.
Figure 19-1 JTAG FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Boundary Scan
Register
Identification
Register
Bypass
Register
Instruction
Register
Test Access Port
Controller
+V
10K 10K 10K
+V +V
JTDI JTMS JTCLK
MUX
Select
Output Enable
JTRST JTDO
98 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
19.2 TAP CONTROLLER STATE MACHINE
The TAP controller is a finite state machine that responds to the logic level at JTMS on the rising edge of
JTCLK. See Figure 19-1.
TEST-LOGIC-RESET
Upon power up, the TAP Controller will be in the Test-Logic-Reset state. The Instruction register will
contain the IDCODE instruction. All system logic of the device will operate normally.
RUN-TEST-IDLE
The Run-Test-Idle is used between scan operations or during specific tests. The Instruction register and
test registers will remain idle.
SELECT-DR-SCAN
All test registers retain their previous state. With JTMS LOW, a rising edge of JTCLK moves the
controller into the Capture-DR state and will initiate a scan sequence. JTMS HIGH during a rising edge
on JTCLK moves the controller to the Select-IR-Scan state.
CAPTURE-DR
Data may be parallel-loaded into the test data registers selected by the current instruction. If the
instruction does not call for a parallel load or the selected register does not allow parallel loads, the test
register will remain at its current value. On the rising edge of JTCLK, the controller will go to the ShiftDR state if JTMS is LOW or it will go to the Exit1-DR state if JTMS is HIGH.
SHIFT-DR
The test data register selected by the current instruction will be connected between JTDI and JTDO and
will shift data one stage towards its serial output on each rising edge of JTCLK. If a test register selected
by the current instruction is not placed in the serial path, it will maintain its previous state.
EXIT1-DR
While in this state, a rising edge on JTCLK will put the controller in the Update-DR state, which
terminates the scanning process, if JTMS is HIGH. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW will put
the controller in the Pause-DR state.
PAUSE-DR
Shifting of the test registers is halted while in this state. All test registers selected by the current
instruction will retain their previous state. The controller will remain in this state while JTMS is LOW.
A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS HIGH will put the controller in the Exit2-DR state.
EXIT2-DR
A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS HIGH while in this state will put the controller in the Update-DR
state and terminate the scanning process. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW will enter the ShiftDR state.
UPDATE-DR
A falling edge on JTCLK while in the Update-DR state will latch the data from the shift register path of
the test registers into the data output latches. This prevents changes at the parallel output due to changes
in the shift register.
99 of 137

DS21352/DS21552
SELECT-IR-SCAN
All test registers retain their previous state. The instruction register will remain unchanged during this
state. With JTMS LOW, a rising edge on JTCLK moves the controller into the Capture-IR state and will
initiate a scan sequence for the instruction register. JTMS HIGH during a rising edge on JTCLK puts the
controller back into the Test-Logic-Reset state.
CAPTURE-IR
The Capture-IR state is used to load the shift register in the instruction register with a fixed value. This
value is loaded on the rising edge of JTCLK. If JTMS is HIGH on the rising edge of JTCLK, the
controller will enter the Exit1-IR state. If JTMS is LOW on the rising edge of JTCLK, the controller will
enter the Shift-IR state.
SHIFT-IR
In this state, the shift register in the instruction register is connected between JTDI and JTDO and shifts
data one stage for every rising edge of JTCLK towards the serial output. The parallel register, as well as
all test registers, remain at their previous states. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS HIGH will move
the controller to the Exit1-IR state. A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW will keep the controller in
the Shift-IR state while moving data one stage thorough the instruction shift register.
EXIT1-IR
A rising edge on JTCLK with JTMS LOW will put the controller in the Pause-IR state. If JTMS is HIGH
on the rising edge of JTCLK, the controller will enter the Update-IR state and terminate the scanning
process.
PAUSE-IR
Shifting of the instruction shift register is halted temporarily. With JTMS HIGH, a rising edge on JTCLK
will put the controller in the Exit2-IR state. The controller will remain in the Pause-IR state if JTMS is
LOW during a rising edge on JTCLK.
100 of 137
 Loading...
Loading...