Page 1

Quickstart Guide
English ( 2 – 13 )
Guía de inicio rápido
Español ( 14 – 27 )
Guide d’utilisation rapide
Français ( 28 – 41 )
Guida rapida
Italiano ( 42 – 55 )
Schnellstart-Anleitung
Deutsch ( 56 – 70 )
Appendix
English ( 71 )
Page 2

Quickstart Guide (English)
Introduction
Box Contents
Oxygen Pro 49
USB Cable
Software Download Card
Quickstart Guide
Safety & Warranty Manual
Support
For the latest information about this product (system requirements, compatibility information, etc.)
and product registration, visit m-audio.com.
For additional product support, visit m-audio.com/support.
Setup
To start using your Oxygen Pro 49, you need to connect your equipment, get your software properly
configured, and then set the keyboard’s operation Mode.
To connect Oxygen Pro 49 to your computer, use the included USB cable. Plug the USB-B end of
the cable into the keyboard and the USB-A end of the cable into your computer (or into a USB hub
connected to your computer).
Note: In addition to sending data, the USB cable powers the keyboard. If you will be connecting
Oxygen Pro 49 to a USB hub that has other devices connected to it, then we recommend using a
powered USB hub.
To configure your DAW to work with Oxygen Pro 49, enable Oxygen Pro 49 as a MIDI control
surface in the appropriate settings menu within the DAW (Preferences, Options, Device Setup,
etc.).
If you will be using Oxygen Pro 49 with the included MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition
or Ableton Live Lite software, see Installing Your Included Software for more specific instructions
on configuring your DAW with Oxygen Pro 49. If you will be using a different DAW, consult the user
manual provided with the DAW for additional help with this step.
If you will be using Oxygen Pro 49 with a hardware synth rather than your computer, connect
Oxygen Pro 49’s MIDI Out port to a synth with a standard 5-pin MIDI cable. Then make sure that
Oxygen Pro 49 is set to operate with one of its custom presets selected (as instructed in Setting the
Keyboard’s Operation Mode) and that the Oxygen Pro 49 is set to send MIDI data from the 5-pin
MIDI out port in the Global Settings. In order to use an external hardware synth, you will need to
connect Oxygen Pro 49 to a computer, laptop, or to a powered USB hub.
2
Page 3

Installing Your Included Software
We've included MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition, and Ableton Live Lite with Oxygen Pro 49
so you can get started making music with professional software right out of the box. Additionally, we’ve
included a set of Expansion Packs and AIR virtual instrument plugins for you to use with your DAW.
To download the included MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition, or Ableton Live Lite
software, register your Oxygen Pro 49 on m-audio.com and follow the installation instructions in your User
Account. If you will be using Ableton Live Lite, we recommend visiting ableton.com to check for any
available software updates. For help configuring either DAW with Oxygen Pro 49, see Pro Tools | First
M-Audio Edition Setup or Ableton Live Lite Setup below.
To download the included AIR virtual instrument plugins, follow the instructions on the software
download card in the box. After installation, most DAWs will not load virtual instrument plugins
automatically; you may need to manually choose a plug-in folder for your software to scan. The plugin
folders for Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition and Ableton Live Lite depend on your operating system, as
indicated below.
Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition/AAX plugin folders:
• Windows (32-bit): C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• Windows (64-bit): C:\Program Files\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Application Support/Avid/Audio/Plug-Ins
Ableton/VST Plugins:
• Windows (32-bit): C:\Program Files (x86)\VSTplugins
• Windows (64-bit): C:\Program Files\VSTplugins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Plugins/VST
To set your plugin folder in Ableton Live Lite:
1. Go to the Preferences menu.
2. Select the File Folder tab. Under Plug-In Sources, click Browse and select the appropriate plugin
folder (as indicated above).
3. After making your selection, the Use VST Custom Plug-In Folder button should be ON. If it is not, click
the button to turn it on. You can then exit the Preferences menu.
Ableton Live Lite Setup
1. First, connect Oxygen Pro 49 to your computer. Then launch Ableton Live Lite.
2. Open the Ableton Live Lite Preferences window. If you are using a Mac, go to Live > Preferences. If
you are using a PC, go to Options > Preferences.
3. Select the Link / MIDI tab on the left. Under the MIDI Ports section, adjust the settings as follows:
Under Control Surfaces, for Input and Output select Oxygen Pro 49.
Next to Input: Oxygen Pro 49, select On in the Track and Remote columns.
Next to Output: Oxygen Pro 49, select On in the Track and Remote columns.
4. Close the Preferences window.
5. To add an instrument or plugin to trigger with Oxygen Pro 49, select Instruments or Plug-ins in the
Categories column.
6. In the Name column to the right of the Categories column, locate the Instrument or Plug-in of your
choice. Click-and-drag the instrument to a MIDI track in Ableton Live Lite to load the instrument.
The Instrument can now be triggered with Oxygen Pro 49.
3
Page 4

Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition Setup
1. Connect Oxygen Pro 49 to your computer. Then launch Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition.
2. Open or Create a Project.
3. Select the Setup pulldown menu and open MIDI Input Devices. Enable MIDI Input from the Oxygen
Pro 49 by clicking the box next to Oxygen Pro 49.
4. Create a new instrument track by selecting the Track pulldown menu and clicking New.
5. In the New pulldown menu, select Stereo and then Instrument Track.
6. In the newly created track, add an Insert to your track by clicking in your track's Inserts A-E and
selecting Multichannel Plugin > Instrument. Select the instrument you would like to use, such as
Xpand!2 (Stereo).
The plugin can now be triggered with Oxygen Pro 49.
Preset Editor
To download the included Preset Editor software, follow the instructions on the software download card
in the box. This software can be used to create custom MIDI mappings for you to load onto Oxygen Pro 49.
For more information on operating the keyboard with one of the custom presets selected, see the following
section and Operation > Using Custom Mappings. The Preset Editor also comes with its own Editor User
Guide.
Setting the Keyboard’s Operation Mode
Once you’ve set up Oxygen Pro 49 to work with your DAW, it’s time to set the keyboard’s operation Mode.
By choosing the operation Mode, you can set the keyboard to automatically coordinate with your DAW’s
features or set it to work as a personally customized controller. With these two Modes, Oxygen Pro 49 gives
you the option to quickly switch between controlling a plugin to controlling your DAW with just the touch of
a button.
The two operation Modes determine the function of the MIDI keyboard’s editable controls:
• DAW: In DAW Mode, the keyboard’s controls will be automatically mapped to sliders, buttons, knobs,
and pads in your DAW.
• Preset: In Preset Mode, the keyboard’s editable controls can be set to functions that you design
yourself. A number of individual preset mappings can be created and then saved to the keyboard’s
internal memory for you to load at a later time.
To set the keyboard to operate in DAW Mode, press the DAW Button. The button will be lit to show that
DAW Mode is selected.
To change which DAW your keyboard is set to control:
1. Press and hold the DAW Button to open the DAW Select menu on the Display.
2. Turn the Select/Scroll Encoder to cycle through the available DAWs on the Display. As you turn the
encoder, the currently selected DAW will update on the Display. The User option enables you to map
custom DAW controls to the keyboard, as described in Operation > Using Custom Mappings.
3. When the DAW you want is shown on the Display, press the Select/Scroll Encoder to confirm your
selection.
Note: To exit out of DAW Mode without changing the currently selected DAW, press the Back Button.
To set the keyboard to operate in Preset Mode, press the Preset Button. The button will be lit to show
that Preset Mode is selected.
To change the currently selected preset:
1. Press and hold the Preset Button to open the Preset Select menu on the Display.
2. Turn the Select/Scroll Encoder to cycle through the available Presets on the Display. As you turn the
encoder, the currently selected Preset will update on the Display.
3. When the preset you want is shown on the Display, press the Select/Scroll Encoder to confirm your
selection. See Operation > Using Custom Mappings for more information on mapping Presets.
4
Page 5
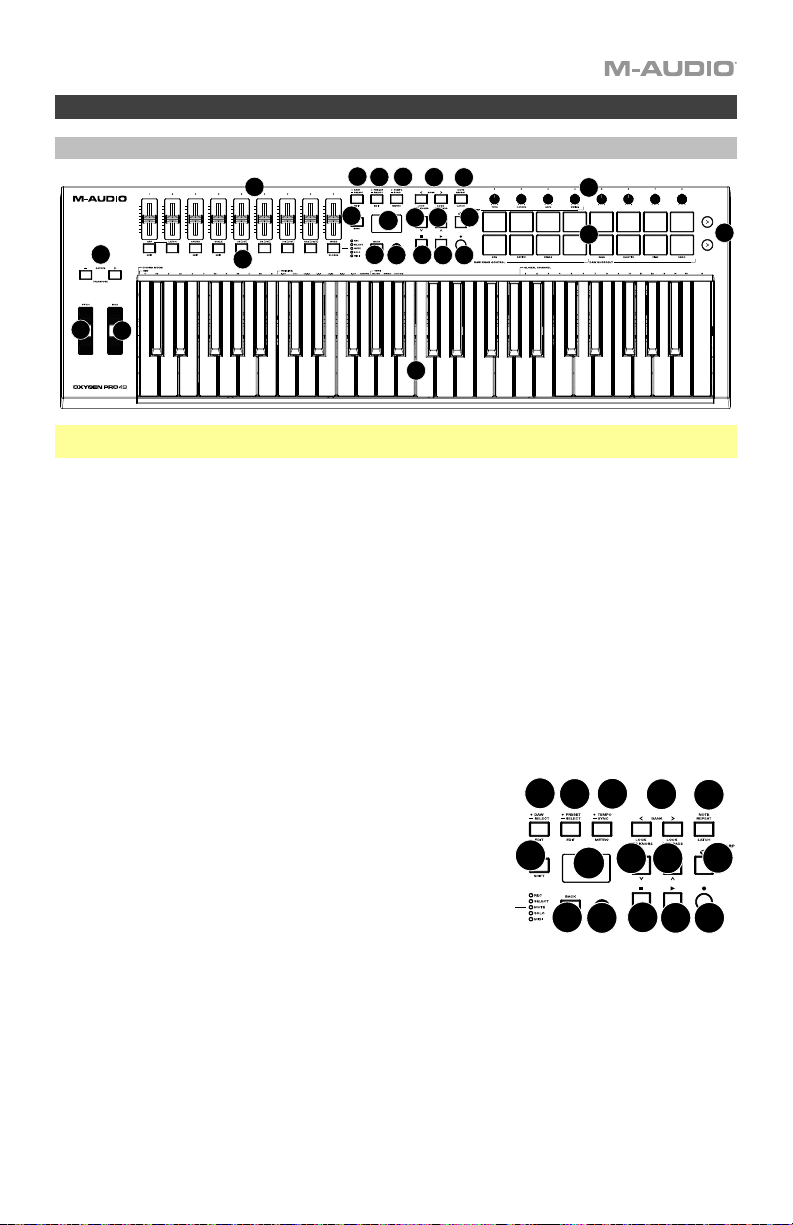
Features
Top Panel
18
17
11 12
14
1
19
15 16
13
10
5
9
6
23
20
7
18
11 12
8
14
17
15 16
21
19
13
5
10
6
7
9
8
22
2
3
4
Note: Text accompanying keyboard controls indicates secondary functions that can be accessed by
pressing Shift while using the control.
1. Keybed: This velocity-sensitive keybed is the primary method of sending Note On/Off MIDI data. In
addition to being velocity sensitive, the keybed also includes channel aftertouch, which means you can
affect the sound a virtual instrument plugin makes by varying how much pressure you apply on the key
after initially pressing the key.
Hold Shift and press keys C2–Bb3 to edit Chord Mode settings. See Operation > Using the
Keyboard’s Internal Functions to learn more about this feature.
2. Octave Buttons: Press these buttons to adjust the pitch range of the keys up or down one octave.
Hold Shift and press these buttons to adjust the pitch range of the keys up or down one semitone. The
keyboard can be raised up to four octaves or lowered down to three octaves from its default octave
range and a total of twelve semitones from its default transposition.
To reset Oxygen Pro 49 to its default octave range and transposition (C2–C6 on the keybed), press the
Octave - and Octave + Buttons simultaneously.
3. Pitch Bend Wheel: Roll this wheel up and down from the center position to bend the pitch of the
keyboard while playing. The default range of the pitch-bend will vary between software synths. The
wheel is spring mounted and will return to the center position when released.
4. Modulation Wheel: Move this wheel to send continuous controller data—MIDI CC #01 (modulation), by
default.
5. DAW Button: Press this button to set Oxygen Pro 49 to operate
in DAW Mode. Press and hold the button to open the DAW Select
menu on the Display.
Hold Shift and press this button to edit and create your own
DAW preset. After editing the User DAW, press the button again
to Save your changes to the User DAW.
See Setup > Setting the Keyboard’s Operation Mode for more
information on DAW Mode. See Operation > Using Custom
Mappings for
6. Preset Button: Press this button to set Oxygen Pro 49 to operate in Preset Mode. Press and hold the
button to open the Preset Select menu on the Display.
Hold Shift and press this button to edit a preset. After editing one of the presets, press the button again
to save your changes to the current Preset.
See Setup > Setting the Keyboard’s Operation Mode for more information on Preset Mode. See
Operation > Using Custom Mappings for information on mapping presets.
7. Display: The main Display screen shows the status of the last used control. Use this screen to monitor
parameter levels as you adjust controls on the keyboard. Also, use the Display along with the
Select/Scroll Encoder to view and edit keyboard settings. See Operation > Display Overview for
more information on the Display.
information on mapping the User preset.
25
5
Page 6

8. Select/Scroll Encoder: If you are entered into one of the Display’s Edit menus, turn this encoder to
change settings/parameters and press the encoder to confirm a selection.
If you are not viewing any of the edit menus, turning the encoder and pressing the encoder will each
function as separate MIDI controls. When operating with a DAW, the assigned controls will be
predetermined. When operating with a preset or the User DAW selected, the controls can be edited.
9. Back Button: If entered into one of the Display’s Edit menus, press this button to go back to the main
Display screen.
If you are not viewing one of the Edit menus, this button will be assigned to control. When operating
with a DAW, the assigned control will be predetermined. When operating with a preset or the User
DAW selected, the control can be edited. When editing a Preset or DAW name press the Shift button
and the Back button to delete a letter.
10. Shift Button: Hold the Shift Button while moving or pressing controls or buttons on the keyboard to
access their secondary functions.
11. << Button: Depending on what screen is selected in your DAW, this button will either rewind the open
song or move down in the active window.
12. >> Button: Depending on what screen is selected in your DAW, this button will either fast forward the
open song or move up in the active window.
13. Loop Button: Press this button to activate/deactivate the loop function in your DAW.
14. Stop Button: Press this button to stop the open song in your DAW. Double-press this button to stop
the open song and return the playhead to the beginning of the song. Press Shift and this button to send
a MIDI panic message to turn off all Note messages and return all controls to zero.
15. Play Button: Press this button to play the song in your DAW.
16. Record Button: Press this button to activate recording in your DAW.
17. Bank Buttons: If operating in DAW Mode or one of the custom presets, use these buttons to switch the
currently selected bank for the Sliders, Knobs, Pads, and Function Buttons. There are four banks for
these controls, giving you the equivalent of 36 sliders, 32 knobs, and 64 pads.
Press Shift and the Bank < button will lock the Shift modifier ARP knob controls. This is useful for
changing ARP parameters during a live performance. Press Shift and the
Bank > button will lock the
Shift modifier Pad controls. This is useful for making edits while mixing a song. To return the knobs or
pads to their normal mode, press the Shift button and the Bank < or Bank > button.
18. Tempo Button: Tap this button to set Oxygen Pro 49’s tempo or press and hold it to pull up the Tempo
Edit menu on the Display, where you can use the Select/Scroll Encoder to manually enter the tempo
and choose to sync Oxygen Pro 49’s tempo with your DAW. The tempo setting affects the keyboard’s
arpeggiator and note repeat functions. See Operation > Using the Keyboard’s Internal Functions for
more details.
Hold Shift and press this button to turn your DAW’s metronome on/off.
19. Note Repeat Button: Press this button to activate the note repeat function for the Pads. To latch the
note repeat function, hold Shift and then press this button. While Note Repeat is active the
Select/Scroll Encoder can be used to change the current Time Division setting of the Arpeggiator
and pad Note Repeat. See Operation > Using the Keyboard’s Internal Functions for more details on
note repeat.
20. Pads (1–16): Use these velocity-sensitive pads to send MIDI Note On/Off messages or perform other
MIDI assignments (if using a preset or the User DAW). Hold Shift while pressing Pads 9–11 to reassign
the function of the Knobs, and hold shift while pressing Pads 13–16 to use the DAW shortcuts (see
Operation > Using Secondary Controls in DAW Mode to learn more).
21. Pad Row Play: Press this button to play through the audio clips assigned to each pad in the
corresponding row of pads. Depending on the DAW, these buttons will have different functions.
22. Sliders (1–9): Push these sliders up/down to perform their assigned controls. When operating with a
DAW, the assigned controls will be predetermined. When operating with a preset or the User DAW
selected, the controls can be edited.
6
Page 7

23. Knobs (1–8): Turn these knobs left/right to perform their assigned controls. When operating with a
DAW, the assigned controls will be predetermined. When operating with a preset or the User DAW
selected, the controls can be edited.
See Operation > Using Secondary Controls in DAW Mode to learn how to change the predetermined
assignments of the Knobs when operating in DAW Mode with a DAW selected.
Hold Shift while turning Knobs 1–4 to edit arpeggiator settings. See Using the Keyboard’s Internal
Functions to learn more about the arpeggiator.
Important: Both the Sliders and Knobs are enabled with “soft takeover.” This means that if you switch
banks, a slider or knob will not work until it is positioned at the current value of the newly selected
software control. For example, if you move Slider 1 in Bank 1 and then switch to Bank 2, physical
Slider 1 will not affect software Slider 10 until the physical slider is positioned at the current value of
software Slider 10. This feature allows you to make changes in one bank and then switch banks without
making unwanted changes to the new bank’s controls. The Display will show a checkered value meter
if a Slider or Knob needs to be moved before it can “take over” its assigned control (see Display
Overview for an illustration).
Important: In Avid Pro Tools, stereo tracks have two panning controls: left and right. Press the Shift
button to switch the knobs between the left channel and right channel. If the pan controls aren't moving
on a mono track, press the Shift button to change pan knob back to controlling the pan control
normally.
24. Mode button (with LEDs): Press the Mode Button to activate one of the secondary Modes for the
Function Buttons. When the keyboard is set to operate in DAW Mode, the available secondary Modes
for the Function Buttons are Rec, Select, Mute, and Solo; in these Modes, the buttons perform
predetermined DAW channel Record Arm, Track Select, Mute, and Solo functions (see Operation >
Using Secondary Controls in DAW Mode to learn more). When the keyboard is set to operate in
Preset Mode, the available secondary Mode for the Function Buttons is MIDI, in which the buttons
perform MIDI controls that are predetermined in one of the custom presets.
The LEDs to the right of the Mode Button indicate which Mode the Function Buttons are in.
Hold Shift and press the Mode Button to access the keyboard’s Global Settings menu.
25. Function Buttons (1–8): When the Function Buttons are set to their primary Mode, they will control
the keyboard’s internal functions, as described below:
ARP Button: Press this button to activate the arpeggiator. Hold Shift and press this button to edit
the arpeggiator’s settings.
Latch Button: Press this button to toggle the arpeggiator between momentary and latch Mode.
Chord Button: Press this button to activate Chord Mode. Hold Shift and press this button to edit the
Chord Mode settings.
Scale Button: Press this button to activate Scale Mode. Hold Shift and press this button to edit the
Scale Mode settings.
1/4–1/32T (Time Division Buttons): Use these buttons to select the keyboard’s time division setting
for the note repeat and arpeggiator functions. Each press of one of these buttons alternates between
the standard timing listed above the button and the triplet timing listed beneath the button. A solid
red LED shows that a standard timing is selected, while a flashing LED shows that a triplet timing is
selected.
See Operation > Using the Keyboard’s Internal Functions to learn more about the features
mentioned above.
7
Page 8

Rear Panel
1. Power Switch: Use this switch to power Oxygen Pro 49
on or off.
2. Sustain Pedal Input: This input accepts a momentarycontact foot pedal (not included). When pressed, the
pedal by default will sustain the sound you are playing
without you having to keep your fingers pressed down on
the keys. The sustain pedal input can be remapped to
perform a custom MIDI assignment.
Note: The polarity of the sustain pedal is determined by the keyboard upon startup. When an Oxygen
Pro 49 keyboard is powering up, the sustain pedal is assumed to be in the "up" (Off) position. It is
important that the sustain pedal is not in the down position before starting up the keyboard, as the
pedal will then operate in reverse, and notes will sustain when the pedal is not pressed.
3. USB Port: When connected to a computer, the USB port delivers power to the keyboard and transmits
MIDI data.
4. MIDI Out: Use a standard 5-pin MIDI cable to connect this port to a hardware synth or other MIDI
device.
Note: The MIDI output port can send MIDI from the Oxygen Pro 49, your connected computer, or both.
Go into the Global Settings to set what is sent to the MIDI Out.
5. Kensington
security cables for theft protection.
®
Lock Connector: This connector is compatible with standard laptop-style Kensington
2
345
1
Operation
Display Overview
Main Display Screen
As you use the keyboard’s Sliders, Knobs, Pads, and Function Buttons
while performing, the Display will update with the current bank for the last
used control, the name/number of the control, the current level applied by
the control (00–127, if applicable), and a graphical meter illustrating the
level (if applicable). While performing, the Display screen will have a black
background with white text.
Note: The Display shows the number of the software control, which does not always match the number of
the hardware control on your keyboard. For example, if the keyboard is set to Bank 3, and you turn Knob 1
on the keyboard, the Display will read Knob 20, since hardware Knob 1 controls software Knob 20 when
the keyboard is set to Bank 3.
As described in Features > Top Panel, the Sliders and Knobs are
enabled with soft takeover. If you switch banks and a Slider or Knob
needs to be moved before it can take over its assigned control, the
Display illustrates this by showing a checkered, gray meter underneath
the control level. As pictured in the example to the right, the bank has just
been switched to Bank 2, and Slider 1 needs to be pushed all the way up
in order for it to begin controlling software Slider 10.
8
Page 9

Edit Menus
In addition to showing last used controls while performing, the Display (along with the Select/Scroll
Encoder) is your main tool for editing various keyboard settings, including the MIDI assignments for editable
controls, the settings for the keyboard’s internal functions (such as the arpeggiator), as well as global
hardware settings.
When you enter into an Edit menu for any keyboard function, the Display
will show the name of the Edit menu, a setting field highlighted for editing,
a parameter field showing the setting’s current status, and graphical
blocks at the bottom of the screen to indicate how many other settings
are available in the Edit menu. While entered into an Edit menu, the
Display will have a white background with black text.
To scroll through settings in an Edit menu, turn the Select/Scroll Encoder while the setting field is
highlighted.
To select a setting to edit, press the Select/Scroll Encoder while the setting field is highlighted. The
parameter field will then be highlighted.
To edit the setting parameter, select the setting to edit as described above. Then turn the Select/Scroll
Encoder while the parameter field is highlighted. Once the desired parameter is highlighted, press the
Select/Scroll Encoder to confirm the edit. The Display will then go back to highlighting the setting field.
To exit the Edit menu without saving changes, press the Back Button. To exit the Edit menu and save
changes, press the DAW Button (if editing the User DAW), or the Preset Button (if editing a Preset).
Note: The settings that are available in the Edit menu may change depending on what parameters you
select. For example, the Arpeggiator Edit menu varies depending on the selected parameter for the
Arpeggiator Type setting.
Using Secondary Controls in DAW Mode
While DAW Mode is designed so that complex mapping is not necessary to use Oxygen Pro 49 with your DAW,
some of the keyboard’s controls still have multiple features that you can switch between in DAW Mode.
Modes for the Function Buttons
When the keyboard is set to operate in DAW Mode and a DAW is selected, the Function Buttons can be toggled
between five different Modes.
To toggle the Mode for the Function Buttons, press the Mode Button to the right of the Function Buttons. With
each press, the Mode Button LED will change to indicate which Mode is currently selected. The following Modes
are available:
Primary (No LED): When no LED is lit, the Function Buttons are set to their primary assignments (printed
above/below each button). These assignments relate to the keyboard’s internal functions: the arpeggiator, note
repeat, Chord Mode, and Scale Mode. For more information on using the Function Buttons with these features, see
Using the Keyboard’s Internal Functions.
Rec (Red LED): When set to Record Mode, each button will activate/deactivate recording for the corresponding
track in your DAW (track 1–32, depending on which button is pressed and which bank is selected).
Select (Green LED): In this Mode, each button will bring into focus the corresponding software track (track 1–32,
depending on which button is pressed and which bank is selected).
Mute (Blue): In this Mode, each button will mute/unmute the corresponding software track (track 1–32, depending
on which button is pressed and which bank is selected).
Solo (Yellow LED): In this Mode, each button will solo or unsolo the corresponding software track (track 1–32,
depending on which button is pressed and which bank is selected).
Note: MIDI Mode is intended either for custom MIDI mapping. This Mode is only available when the keyboard is set
to operate in Preset Mode.
9
Page 10

Changing the Function of the Knobs in DAW Mode
Note: Not all parameters are available in every DAW.
When operating in DAW Mode, the knobs can perform one of three functions.
To change how the knobs work, hold the Shift Button and press Pad 9, 10, or 11. The following functions are
available:
Pan (Pad 9): Each knob will pan the corresponding software track (track 1–32, depending on which knob is turned
and which bank is selected).
Device (Pad 10): Each knob will control device controls of the corresponding software track (track 1–32, depending
on which knob is turned and which bank is selected).
Sends (Pad 11): Each knob will control the level of the aux sends for the corresponding software track (track 1–32,
depending on which knob is turned and which bank is selected).
Accessing DAW Shortcuts with the Pads
Note: Not all parameters are available in every DAW.
In DAW Mode, pressing a pad will send a Note On message so that you can trigger a synth or sample in your
software. However, you can hold Shift and press Pads 13, 14, 15, or 16 to perform the following commands:
Save (Pad 13): Save changes to the currently open file in your DAW.
Quantize (Pad 14): Quantize the currently selected audio region in your DAW.
Undo (Pad 15): Undo the last change made to the file in your DAW.
View (Pad 16): Toggle between different windows (e.g. Mix, or Edit) for your DAW.
Important: In order for these shortcuts to work with your DAW, PC needs to be set to Win (Windows) or Mac in
Oxygen Pro 49’s Global Settings menu. To access the Global Settings menu on the Display, hold Shift and press
the Mode Button. Use the Select/Scroll Encoder to adjust the setting according to your PC type, and then press
the Back Button to exit the menu.
Using Custom Mappings
Oxygen Pro 49 has many fully customizable controls, and with the ability to create and save keyboard
mappings, you can store different mappings for different DAWs, plugins, or performance scenarios that can
be changed on the fly.
When operating in Preset Mode, there are 16 presets available on the keyboard (1–16). A preset is a group
of MIDI assignments for Oxygen Pro 49’s controls that can be saved to the keyboard’s internal memory and
loaded at a later time. Presets can be edited when the keyboard is in Preset Edit Mode. In addition to having
these 16 presets on the keyboard, you can use the included Editor software to store an unlimited number of
presets on your computer and modify which 16 are currently saved to the keyboard’s internal memory.
When operating in DAW Mode, the User setting allows you create a custom mapping for the keyboard that
includes not only MIDI messages but also Mackie or Mackie/HUI messages. This allows you to map
keyboard controls with commands for the DAW itself (such as “Save” or “Mute”) in addition to mapping
keyboard controls with MIDI assignments for instrument/plug-in parameters within the DAW. The User DAW
setting can be edited when the keyboard is in DAW Edit Mode. In addition to having the User DAW on the
keyboard, you can use the included Editor software to store an unlimited number of User DAWs on your
computer and modify which one is currently saved to the keyboard’s internal memory.
To enter Preset Edit Mode, first select the preset you want to edit (as described in Setup > Setting the
Keyboard’s Operation Mode). Then press and hold Shift and press the Preset Button.
To enter DAW Edit Mode, press and hold Shift and press the DAW Button.
To exit Edit Mode and save your changes, press the Preset Button (if you were editing presets) or the
DAW BUTTON (if you were editing the User DAW setting).
If you made changes, the Display screen will ask if you would like to save them. Use the Select/Scroll
Encoder to choose between Cancel, Replace, and Save As. Selecting Cancel will take you back to Edit
Mode, while selecting Replace will save the preset without changing its name. Select Save As to be able to
rename and change the preset location number of the preset using the Select/Scroll Encoder. If you need
to delete a character while editing the name, press and hold the Shift Button and the Back Button.
For help using the Preset Editor, see the Editor User Guide that comes with the software.
10
Page 11

Using the Keyboard’s Internal Functions
The following keyboard functions can be used when the keyboard is set to operate in either DAW or Preset
Mode.
Note: In order to control the arpeggiator, Chord Mode, or Scale Mode functions described in the following
sections, the Function Buttons underneath the Sliders have to be set to their primary Mode. The Function
Buttons are set to their primary Mode when no LED to the right of the Mode Button is lit. If the Function
Buttons are not set to their primary Mode, press the Mode Button as many times as necessary until no
LED to the right of the Mode Button is lit.
In the following sections, the described LED operation for the Function Buttons assumes that they are set
to their primary Mode.
Note Repeat
When this feature is activated, any pressed Performance Pad will repeat its Note message in rhythm with
the keyboard’s current tempo and time division settings. Each repeated note will be the length selected for
the time division setting. For more help changing the tempo and time division settings, see Keyboard
Tempo and Time Division.
The note repeat feature can be activated momentarily or it can be latched.
To use note repeat momentarily, press and hold the Note Repeat Button and then press a pad. As long
as you are holding the Note Repeat Button, the note played by the pad will repeat.
To latch the note repeat feature, hold Shift and press the Note Repeat Button. Pressing any pad will
cause its assigned note to repeat without you having to hold down the Note Repeat Button.
To turn off the Toggle/Latch feature, press the Note Repeat Button again.
Note: While Note Repeat is active, the Select/Scroll Encoder can be used to change the current Time
Division setting of the Arpeggiator and pad Note Repeat.
Arpeggiator
When the arpeggiator is activated, the keyboard will repeatedly play pressed keys in sequence. The
arpeggiator’s timing and rhythm is based on the keyboard’s time division setting and either the keyboard’s
or your DAW’s tempo setting. Each note in the arpeggio will be the length you’ve selected for the time
division setting; for example, if you select 1/4, each note in the arpeggio will be a quarter note. See
Keyboard Tempo and Time Division for help editing these settings.
The arpeggiator can be operated in one of two Modes:
• Momentary: the arpeggiator will play notes only as long as the keys are pressed down; when you
release the keys, the arpeggiator will stop.
• Latch: the arpeggiator will play notes when you press down the keys, and it will continue to play even
after you release your fingers from the keys.
To activate or deactivate the arpeggiator, press the Arp Button. When the arpeggiator is activated, the
button LED will be lit.
To toggle between momentary and latch Mode, press the Latch Button. When latch is activated, the
button LED will be lit.
To start an arpeggio, press any keys while the arpeggiator is activated.
To start a new latched arpeggio while a previously latched arpeggio is still playing, press a new
combination of keys.
To add notes to a latched arpeggio while it is still playing, hold down the same keys you previously
pressed for the arpeggio while pressing the keys for the new notes you want to add.
To edit the arpeggiator’s settings, hold Shift and press the Arp Button. The Display will then enter the
menu for editing the Arpeggiator. Use the Select/Scroll Encoder to adjust settings (as described in Display
Overview). When you’re done editing settings, press the Back Button to exit the Arpeggiator Edit menu.
11
Page 12

Alternatively, you can hold Shift or press Shift and Bank < to lock the Shift modifier ARP knob controls
while turning Knobs 1–4 to edit some but not all of the settings. The Display will show the new settings as
you change them.
Note: While Note Repeat is active, the Select/Scroll Encoder can be used to change the current Time
Division setting of the Arpeggiator and pad Note Repeat.
Keyboard Tempo and Time Division
Oxygen Pro 49’s tempo and time division settings determine the timing and rhythm for the note repeat and
arpeggiator features. When Clock is set to Internal in the Tempo Edit screen on the Display, the keyboard’s tempo
can be tapped in or it can be entered exactly from within the Tempo Edit screen. When Clock is set to External, the
keyboard’s tempo will automatically sync with your DAW’s tempo.
To tap in the keyboard’s tempo, tap the Tempo Button two or more times at the desired BPM. The Display will
update with the new tempo as you tap the button.
Note: In order to tap in the keyboard’s menu, the keyboard’s Clock setting in the Tempo Edit menu must be on
Internal. If set to External, the keyboard’s tempo will sync with your DAW.
To enter the Tempo Edit menu on the Display, press and hold the Tempo Button. Use the Select/Scroll
Encoder to change the Clock setting or enter in an internal keyboard tempo (20.0–240.0). When you’re done editing
settings, press the Back Button to exit the Tempo Edit menu. See Display Overview for more help on using the
Select/Scroll Encoder with the Display’s Edit menus.
To set the keyboard’s time division, press the Time Division Button for the desired setting (as printed
above/below the button). Double-press the button if you want to use a triplet setting. When a standard time division
is selected, the corresponding button will be lit. When a triplet time division is selected, the corresponding button
will flash.
Note: While Note Repeat is active the Select/Scroll Encoder can be used to change the current Time Division
setting of the Arpeggiator and pad Note Repeat.
Chord Mode
When you activate Chord Mode, pressing a single key or pad will play a full chord rather than only one note. The key
or pad you press will determine the root note in the chord, and the type of chord selected will depend on the current
settings.
The chord feature can be operated by turning the Select/Scroll Encoder to one of two Modes that will determine
the exact chord assigned to each key:
• Smart Mode: In this Mode, you will first assign the keyboard to a musical key (e.g. D minor). Then you will
assign the desired voicing for the chords (what intervals will be included in the chord, e.g. 1-3-5). Each key’s
chord voicing will then be automatically enharmonic to the selected key.
• Custom: In this Mode, you can determine the chord structure that will be assigned to each key by manually
playing it. For example, if you select this Mode, and play a 1-b3-5-b7 chord, every key will then be assigned to
play this chord structure. The note of the key you press will serve as the root of the chord.
To activate or deactivate Chord Mode, press the Chord Button. While Chord Mode is activated, the Chord
Button will be lit.
To edit the Chord Mode settings, first hold Shift while pressing the Chord Button to enter the Chord Edit menu on
the Display. Then use the Select/Scroll Encoder to adjust settings (as described in Display Overview). When
you’re done editing settings, press the Back Button to exit the Chord Edit menu.
Alternatively, you can hold Shift while pressing keys C2–Bb3 if you are using the Smart chord Mode.
Note: By default, the keys are setup to play chords when Chord Mode is activated. However, in the Global Settings
menu this can be changed so that when Chord Mode is active, chords will play on the keys or pads or both.
12
Page 13

Scale Mode
With Scale Mode, you can set the keybed so that keys outside the notes of a selected musical scale are disabled.
This allows you to play within a chosen scale without the risk of playing any “wrong” notes. You can choose from 16
different options when assigning a scale to the keyboard.
To activate or deactivate Scale Mode, press the Scale Button. While Scale Mode is activated, the Scale Button
will be lit.
To determine what musical scale the keybed is set to, enter the Scale Edit menu on the Display by holding Shift
and pressing the Scale Button. Then use the Select/Scroll Encoder to adjust settings (as described in Display
Overview). When you’re done editing settings, press the Back Button to exit the Scale Edit menu.
Global Settings Menu
Use the Global Settings Menu on the Display to customize some of the keyboard’s default controls. These settings
apply to the keyboard in both DAW and Preset Mode, and any changes made from the Global Settings Menu will be
saved after the keyboard is turned off.
To enter the Global Settings Menu, hold Shift and press the Mode Button. Use the Select/Scroll Encoder to
adjust settings (as described in Display Overview).
To exit the Global Settings Menu, press the Back Button.
13
Page 14

Guía del usuario (Español)
Introducción
Contenido de la caja
Oxygen Pro 49
Cable USB
Tarjeta de descarga de software
Guía del usuario
Manual sobre la seguridad y garantía
Soporte
Visite m-audio.com para ver y descargar la documentación más reciente, los requisitos del
sistema y demás información relativa a su producto.
Para obtener soporte adicional del producto, visite m-audio.com/support.
Instalación
Para comenzar a utilizar su Oxygen Pro 49, debe conectar su equipo, configurar su software
correctamente y luego ajustar el modo de funcionamiento de su teclado.
Para conectar el Oxygen Pro 49 a su ordenador, utilice el cable USB incluido. Conecte el
extremo del cable con el conector USB-B al teclado y el extremo USB-A del cable a su
ordenador (o un concentrador USB conectado a su ordenador).
Nota: Además de enviar datos, el cable USB alimenta el teclado. Si planea utilizar el Oxygen
Pro 49 conectado a un concentrador USB que tiene otros dispositivos conectados a él,
recomendamos utilizar un concentrador USB alimentado.
A fin de configurar su DAW para que funcione con el Oxygen Pro 49, habilite el Oxygen
Pro 49 como una superficie de control MIDI en el menú de configuración correspondiente del
DAW [Preferences (Preferencias), Options (Opciones), Device Setup (Ajustes del dispositivo),
etc.].
Si planea utilizar el Oxygen Pro 49 con el software MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio
Edition, o Ableton Live Lite incluido, consulte Instalación de su software incluido para
obtener instrucciones específicas sobre cómo configurar su DAW con el Oxygen Pro 49. Si
planea utilizar una DAWdiferente, consulte el manual del usuario provisto con la DAW para
obtener ayuda adicional sobre este paso.
Si planea utilizar el Oxygen Pro 49 con un sintetizador de hardware en lugar de su ordenador,
conecte el puerto MIDI Out del Oxygen Pro 49 a un sintetizador con un cable MIDI estándar
de 5 patillas. Luego asegúrese de que el Oxygen Pro 49 esté configurado para funcionar con
uno de sus presets personalizados seleccionados (como se indica en Ajuste del modo de
funcionamiento del teclado) y que el Oxygen Pro 49 esté configurado para enviar datos MIDI
desde el puerto de salida MIDI de 5 patillas en el menú de Ajuste globales. A fin de utilizar un
sintetizador de hardware externo, deberá conectar el Oxygen Pro 49 a un ordenador,
ordenador portátil o concentrador USB alimentado.
14
Page 15

Instalación de su software incluido
Hemos incluido MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition, y Ableton Live Lite junto con el Oxygen
Pro 49 para que pueda comenzar a hacer música con software profesional ni bien lo saque de su caja.
Adicionalmente, hemos incluido un conjunto de paquetes de expansión y plugins de instrumentos virtuales
de AIR para que los utilice con su DAW.
Para descargar el software MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition, o Ableton Live Lite incluido,
registre su Oxygen Pro 49 en m-audio.com y siga las instrucciones de instalación en su Cuenta de usuario.
Si planea utilizar Ableton Live Lite, la recomendamos visitar ableton.com para comprobar si existen
actualizaciones de software disponibles. Para obtener ayuda sobre cómo configurar cualquiera de esas
DAW con Oxygen Pro 49, consulte Configuración de Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition o Configuración
de Ableton Live Lite Setup a continuación.
Para descargar los plugins de instrumentos virtuales de AIR, siga las instrucciones que se encuentran
en la tarjeta de descarga del software en la caja. Tras la instalación, la mayoría de las DAW no cargarán los
plugins de instrumento virtual automáticamente; es posible que tenga que seleccionar una carpeta que
contenga plugins manualmente para que su software la escanee. Las carpetas de plugins del Pro Tools |
First M-Audio Edition y el Ableton Live Lite dependen de su sistema operativo, como se indica a
continuación.
Carpetas de plugins Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition/AAX:
• Windows (32 bits): C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• Windows (64 bits): C:\Program Files\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Application Support/Avid/Audio/Plug-Ins
Plugins de Ableton/VST:
• Windows (32 bits): C:\Program Files (x86)\VSTplugins
• Windows (64-bits): C:\Program Files\VSTplugins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Plugins/VST
Cómo establecer su carpeta de plugins en Ableton Live Lite:
1. Vaya al menú Preferences (Preferencias).
2. Seleccione la pestaña File Folder (Carpeta de archivos). Bajo Plug-In Sources (Fuentes de plugin)
haga clic en Browse (Explorar) y seleccione la carpeta de plugins apropiada (tal como se indica más
arriba).
3. Después de hacer su selección, el botón Use VST Custom Plug-In Folder (Usar carpeta de plugins
VST personalizada) debe estar en ON (encendido). Si no lo está, haga clic en el botón para encenderlo.
Luego podrá salir del menú Preferences.
15
Page 16

Configuración de Ableton Live Lite
1. Primero conecte el Oxygen Pro 49 a su ordenador. Luego abra Ableton Live Lite.
2. Abra la ventana Preferences
Preferences
> Preferencias).
3. Seleccione la pestaña Link / MIDI (Enlace / MIDI) del lado izquierdo. Dentro de la sección MIDI Ports
(Puertos MIDI) configure los ajustes de la siguiente manera:
Dentro de Control Surfaces (Superficies de control), para Input (entrada) y Output (salida) seleccione
Oxygen Pro 49.
Junto a Input: Oxygen Pro 49, seleccione On (activado) en las columnas Track y Remote (Pista y
Remoto).
Junto a Output: Oxygen Pro 49, seleccione On (activado) en las columnas Track y Remote (Pista y
Remoto).
4. Cierre la ventana Preferences (Preferencias).
5. Para añadir un instrumento o plugin a fin de ejecutarlo desde el Oxygen Pro 49, seleccione
Instruments (Instrumentos) o Plug-ins en la columna Categories (Categorías).
6. En la columna Name (Nombre) justo a la derecha de la columna Categorías, localice el Instrumento o
Plugin de su elección. Haga clic y arrastre el instrumento sobre una pista
cargarlo.
El instrumento ahora puede ejecutarse con el Oxygen Pro 49.
(Vivo > Preferencias). Si está utilizando una PC, vaya a Options > Preferences (Opciones
de Ableton Live Lite. Si está utilizando una Mac, vaya a Live >
MIDI en Ableton Live Lite para
Configuración de Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition
1. Conecte el Oxygen Pro 49 a su ordenador. Luego ejecute Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition.
2. Abra o cree un proyecto.
3. Seleccione el menú desplegable Setup y abra MIDI Input Devices (Dispositivos de entrada MIDI).
Habilite MIDI Input (Entrada MIDI) desde Oxygen Pro 49 haciendo clic en la casilla junto al Oxygen Pro
49.
4. Cree una pista de instrumento nuevo, seleccionando el menú desplegable Track (pista) y haciendo clic
en New (Nueva).
5. En el menú desplegable New (Nuevo), seleccione Stereo y luego Instrument Track (Pista de
instrumento).
6. En la pista recientemente creada, añada un inserto en su pista haciendo clic en Inserts A-E (Insertos A-
E) y seleccionando Multichannel Plugin > Instrument (Plugin multicanal > Instrumento). Seleccione el
instrumento que desea utilizar, como por ejemplo Xpand!2 (estéreo).
El plugin ahora puede ejecutarse con el Oxygen Pro 49.
Editor de presets
Para descargar el software de edición de presets
de descarga del software en la caja. Este software se puede utilizar para crear mapeos MIDI personalizados
para cargar en el Oxygen Pro 49. Para obtener más información sobre cómo operar el teclado con uno de
los presets personalizados seleccionados, consulte la siguiente sección y Funcionamiento > Uso de
mapeos personalizados. El editor de presets también viene con su propia Guía del usuario del Editor.
, siga las instrucciones que se encuentran en la tarjeta
16
Page 17

Ajuste del modo de funcionamiento del teclado
Una vez que haya configurado el Oxygen Pro 49 para que funcione con su DAW, llegó el momento de
configurar el modo de funcionamiento del teclado. Al seleccionar el modo de funcionamiento, puede ajustar
el teclado para que se coordine automáticamente con las características de su DAW o ajustarlo para que
funcione como un controlador personalizado. Con estos dos modos, el Oxygen Pro 49 le da la opción de
conmutar rápidamente entre el control de un plugin y el control de su DAW con solo tocar un botón.
Los dos modos de funcionamiento determinan la función de los controles editables de su teclado MIDI:
• DAW: En modo de DAW, los controles del teclado se mapean automáticamente a los deslizadores,
botones, perillas y pads de su DAW.
• Preset: En modo de preset, los controles editables de su teclado se pueden ajustar a funciones
diseñadas por usted mismo. Se pueden crear una cantidad de mapeos de presets individuales y luego
guardarse en la memoria interna del teclado para poder cargarlos más tarde.
Para ajustar el teclado a fin de que funcione en modo de DAW, pulse el botón
iluminará para mostrar que está seleccionado el modo de DAW.
Para cambiar la DAW que su teclado está configurado para controlar:
1. Mantenga pulsado el botón DAW para abrir el menú de selección de DAW en la pantalla.
2. Gire el codificador Select/Scroll para recorrer las DAW disponibles por la pantalla. A medida que gira
el codificador, la DAW actualmente seleccionada se actualizará en la pantalla. La opción User
(Usuario) le permite mapear controles de DAW personalizados al teclado, tal como se describe en
Funcionamiento > Uso de mapeos personalizados.
3. Cuando la DAW que desea aparezca en la pantalla, pulse el codificador Select/Scroll para confirmar
su selección.
Nota: Para salir del modo de DAW sin modificar la DAW actualmente seleccionada, pulse el botón
Back.
Para ajustar el teclado a fin de que funcione en modo de preset, pulse el botón Preset. El botón se
iluminará para mostrar que está seleccionado el modo de preset.
Para modificar el preset actualmente seleccionado:
1. Mantenga pulsado el botón Preset para abrir el menú de selección de
2. Gire el codificador Select/Scroll para conmutar entre las DAW disponibles a través de la pantalla
medida que gira el codificador, la DAW actualmente seleccionada se actualizará en la pantalla.
3. Cuando el preset que desea aparezca en la pantalla, pulse el codificador Select/Scroll para confirmar
su selección. Consulte Funcionamiento > Uso de mapeos personalizados para obtener más
información sobre cómo mapear Presets.
Preset en la pantalla.
DAW. El botón se
. A
17
Page 18
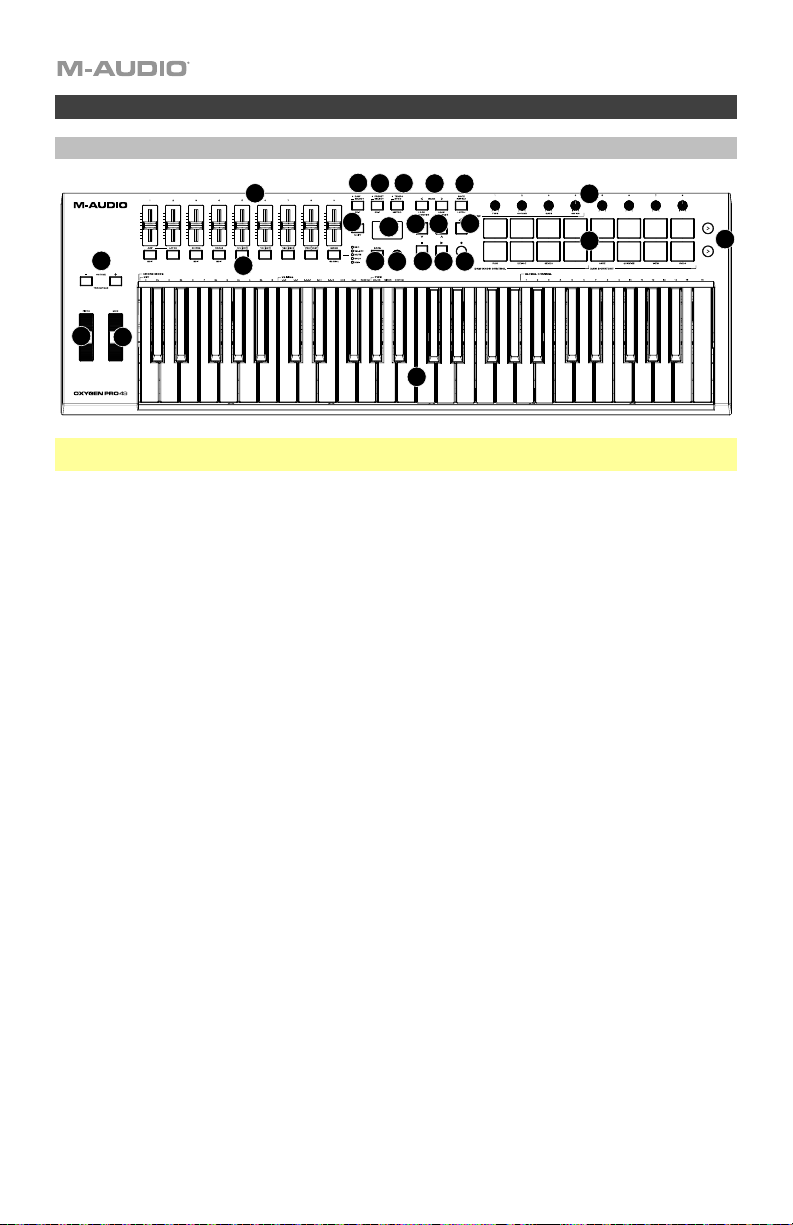
Características
Panel superior
18
17
11 12
14
1
19
15 16
13
23
20
21
5
10
6
7
9
8
22
2
3
4
25
Nota: El texto entre corchetes junto a los controles del teclado indica las funciones secundarias que se
pueden ejecutar pulsando Shift mientras se utiliza el control.
1. Placa del teclado: Esta placa del teclado sensible la velocidad es el método principal para enviar
datos de activación/desactivación de nota MIDI. Además de ser sensible a la velocidad, la placa del
teclado también incluye postpulsación de canal, lo que significa que se puede afectar el sonido emitido
por un plugin de instrumento virtual al variar la cantidad de presión que se aplica sobre la tecla tras
pulsarla inicialmente.
Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse las teclas C2–Bb3 para editar los ajustes del modo de acorde.
Consulte Funcionamiento > Cómo utilizar las
más sobre esta característica.
2. Botones de octava: Pulse estos botones para ajustar el rango de tono de las teclas en una octava
hacia arriba o hacia abajo. Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse estos botones para ajustar el rango de tono
de las teclas en un semitono hacia arriba o hacia abajo. El teclado puede subirse hasta cuatro octavas
y bajarse hasta tres octavas desde su rango de octavas predeterminado y un total de 12 semitonos
desde su transposición predeterminada.
Para regresar al Oxygen Pro 49 a sus rangos de octavas y transposición predeterminados (C2–C4 en la
placa del teclado), pulse los botones Octave - y Octave + simultáneamente.
3. Rueda de inflexión de tono: Gire esta rueda hacia arriba y hacia abajo desde la posición central para
flexionar el tono del teclado mientras toca. El rango predeterminado de la inflexión de tono varía en
función de los sintetizadores de software. La rueda está montada mediante resortes y regresará a su
posición central al soltarse.
4. Rueda de modulación: Mueva esta rueda para enviar datos de controlador continuo—MIDI CC #01
(modulación), por defecto.
18
de las funciones internas del teclado para aprender
Page 19

5. Botón DAW: Pulse este botón para configurar al Oxygen Pro 49
para que funcione en modo de DAW. Mantenga pulsado el botón
para abrir el menú de selección de DAW en la pantalla.
Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse este botón para editar y crear su
propio preset de DAW. Tras editar la DAW de usuario, pulse el
botón nuevamente para guardar sus cambios en la DAW de
usuario.
Consulte Configuración > Ajuste del modo de funcionamiento
del teclado para obtener más información sobre el modo DAW.
Consulte Funcionamiento > Uso de mapeos personalizados
para obtener más información sobre cómo mapear los presets de
usuario.
6. Botón de preset: Pulse este botón para configurar al Oxygen Pro 49 para que funcione en modo de
preset. Mantenga pulsado el botón para abrir el menú de selección de preset en la pantalla.
Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse este botón para entrar al modo de vista general. Tras editar uno de los
presets, pulse el botón nuevamente para guardar sus cambios en el preset actual.
Consulte Configuración > Ajuste del modo de funcionamiento del teclado para obtener más
información sobre el modo de preset. Consulte Funcionamiento > Uso de mapeos personalizados
para obtener más información sobre cómo mapear un preset.
7. Pantalla: La pantalla principal muestra el estado del último control utilizado. Utilice esta pantalla para
monitorear los niveles del parámetro a medida que ajusta los controles del teclado. Además, utilice la
pantalla junto con el codificador Select/Scroll para ver y editar los ajustes del teclado. Consulte
Funcionamiento > Vista general de la pantalla para obtener más información sobre la pantalla.
8. Codificador Select/Scroll: Si se encuentra dentro de uno de los menús de edición de la pantalla, gire
este codificador para modificar los ajustes/parámetros y pulse el codificador para confirmar una
selección.
Si no está visualizando ninguno de los menús de edición, tanto girar como impulsar el codificador
funcionarán como controles MIDI separados. Al operar con una DAW, los controles asignados serán
predeterminados. Al operar con un preset o con la DAW de usuario seleccionada, los controles se
pueden editar.
9. Botón Volver: Si se encuentra dentro de uno de los menús de edición de la pantalla, pulse este botón
para volver a la pantalla principal.
Si no está visualizando ninguno de los menús de edición, este botón estará asignado un control. Al
operar con una DAW, el control asignado será predeterminado. Al operar con un preset o con la DAW
de usuario seleccionada, el control se puede editar. Al editar un Preset o nombre de DAW, pulse el
botón
Shift (función secundaria) y el botón Back (volver) para borrar una letra.
10. Botón de función secundaria: Mantenga pulsado el botón Shift mientras mueve o pulsa controles o
botones en el teclado para acceder a sus funciones secundarias.
11. Botón <<: En función de la pantalla seleccionada en su DAW, este botón rebobinará la canción abierta
o se desplazará hacia abajo en la ventana activa.
12. Botón >>: En función de la pantalla seleccionada en su DAW, este botón hará un avance rápido de la
canción abierta o se desplazará hacia arriba en la ventana activa.
13. Botón de bucle: Pulse este botón para activar/desactivar la función de bucle en su DAW.
14. Botón Parar: Pulse este botón para detener la canción abierta en su DAW. Pulse el botón dos veces
para parar la canción abierta y regresar el cabezal de reproducción al comienzo de la misma. Pulse
Shift junto con este botón para enviar un mensaje de pánico MIDI a fin de desactivar todos los
mensajes de notas y regresar todos los controles a cero.
15. Botón de reproducción: Pulse este botón para reproducir una canción en su DAW.
16. Botón de grabación: Pulse este botón para activar la grabación en su DAW.
5
10
9
6
7
18
11 12
8
14
17
15 16
19
13
19
Page 20

17. Botones de banco: Si está operando en modo de DAW o alguno de los presets personalizados, utilice
estos botones para conmutar el banco actualmente seleccionado para los deslizadores, perillas, pads
y botones de función. Existen cuatro bancos para los controles, brindándole el equivalente a 36
deslizadores, 32 perillas, y 64 pads. Pulse Shift y el botón Bank < (banco) para bloquear los controles
de las perillas de ARP del modificador Shift. Esto resulta útil para modificar los parámetros de ARP
durante una actuación en vivo. Pulse Shift y el botón Bank > para bloquear los controles de Pad del
modificador Shift. Eso resulta útil para realizar ediciones mientras se mezcla una canción. Para
regresar las perillas o pads a su modo normal, pulse el botón Shift y el botón Bank < o Bank >.
18. Botón tempo: Toque este botón para ajustar el tempo del Oxygen Pro 49 o manténgalo pulsado para
desplegar el menú de edición de tempo en la pantalla, en donde podrá utilizar el codificador
Select/Scroll para introducir manualmente el tempo y seleccionar si desea sincronizar el tempo del
Oxygen Pro 49 con su DAW. El ajuste del tempo afecta al arpegiador y a las funciones de repetición de
nota del teclado. Consulte Funcionamiento > Cómo utilizar las
de las funciones internas del
teclado para obtener más detalles.
Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse este botón para encender o apagar el metrónomo de su DAW.
19. Botón de repetición de nota: Pulse este botón para activar la función de repetición de nota para los
pads. Para usar la función de repetición de nota en comportamiento permanente, mantenga pulsado
Shift y luego pulse este botón. Mientras Note Repeat (repetición de nota) esté activo, utilice el
codificador Select/Scroll para modificar el ajuste actual de la división de tiempo del arpegiador y la
característica Note Repeat del pad. Para usar la función de repetición de nota en comportamiento
momentáneo o permanente, mantenga pulsado Shift y luego pulse este botón. Consulte
Funcionamiento > Cómo utilizar las
de las funciones internas del teclado para obtener más
detalles sobre la repetición de notas.
20. Pads (1-16): Utilice estos pads sensibles la velocidad para enviar mensajes de
activación/desactivación de nota MIDI o efectuar otras asignaciones MIDI (si está utilizando un preset o
la DAW de usuario). Mantenga pulsado Shift mientras pulsa los pads 9–11 para reasignar la función de
las perillas, y mantenga pulsado Shift mientras pulsa los pads 13–16 para utilizar los accesos directos
de la DAW (consulte Funcionamiento > Uso de los controles secundarios en el modo de DAW para
aprender más).
21. Reproducción de filas de pads: Pulse este botón para reproducir todos los clips de audio asignados a
cada pad en la correspondiente fila de pads. Dependiendo de la DAW, estos botones tendrán
diferentes funciones.
22. Deslizadores (1–9): Mueva estos deslizadores hacia arriba y hacia abajo para efectuar sus controles
asignados. Al operar con una DAW, los controles asignados serán predeterminados. Al operar con un
preset o con la DAW de usuario seleccionada, los controles se pueden editar.
23. Perillas (1-8): Gire estas perillas hacia la izquierda y hacia la derecha para efectuar sus controles
asignados. Al operar con una DAW, los controles asignados serán predeterminados. Al operar con un
preset o con la DAW de usuario seleccionada, los controles se pueden editar.
Consulte Funcionamiento > Uso de los controles secundarios en modo de DAW para aprender a
modificar las asignaciones predeterminadas de las perillas al operar en modo de DAW con una DAW
seleccionada.
Mantenga pulsado Shift mientras gira las perillas 1–4 para evitar los ajustes del arpegiador. Consulte
Cómo utilizar las
de las funciones internas del teclado para aprender más sobre el arpegiador.
Importante: Tanto los deslizadores como las perillas cuentan con "relevo suave". Esto significa que,
si cambia de bancos, un deslizador o perilla no funcionará hasta que se lo ubique en el valor actual del
control de software recientemente seleccionado. Por ejemplo, si mueve el deslizador 1 del banco 1 y
luego cambia al banco 2, el deslizador 1 físico no afectará el deslizador 10 del software hasta que el
deslizador físico se coloque en el valor actual del deslizador 10 del software. Esta característica le
permite realizar cambios en un banco y luego cambiar de bancos sin realizar cambios involuntarios en
los controles del nuevo banco. La pantalla mostrará un medidor de valores cuadriculado si algún
deslizador o perilla debe moverse antes de que pueda "relevar" a su control asignado (consulte la
ilustración en Vista general de la pantalla).
Importante: En Avid Pro Tools, las pistas estéreo tienen dos controles de balance (panning): izquierdo
y derecho. Pulse el botón Shift para conmutar las perillas entre el canal izquierdo y el derecho. Si los
controles de balance no se están moviendo es una pista monoaural, pulse el botón Shift para que la
perilla de balance vuelva a controlar el balance normalmente.
20
Page 21

24. Botón de modo (con LED): Pulse el botón Mode para activar uno de los modos secundarios para los botones
de función. Cuando el teclado se configura para funcionar en modo de DAW, los modos secundarios
disponibles para los botones de función son Rec, Select, Mute y Solo (grabar, seleccionar, silenciar y solo);
en estos modos, los botones llevan a cabo las funciones predeterminadas de DAW de preparar canal para
grabación, seleccionar pista, silenciar y sólo (consulte Funcionamiento > Uso de los controles secundarios
en modo de DAW para aprender más). Cuando el teclado se configura para funcionar en modo de preset, el
modo secundario disponible para los botones de función es el de MIDI, en el cual los botones desempeñan
controles de MIDI que están predeterminados en uno de los presets personalizados.
Los LED que se encuentran a la derecha del botón Mode indican el modo en el que se encuentran los botones
de función.
Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse el botón Mode para acceder al menú de ajustes globales del teclado.
25. Botones de función (1-8): Cuando los botones de función se ajustar a su modo principal, controlarán las
funciones internas del teclado, tal como se describen a continuación:
Botón ARP: Pulse este botón para activar el arpegiador. Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse este botón para
editar los ajustes del arpegiador.
Botón de comportamiento permanente: Pulse este botón para conmutar el arpegiador entre
comportamiento momentáneo y comportamiento permanente.
Botón de acorde: Pulse este botón para activar el modo de acorde. Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse este
botón para editar los ajustes del modo de acorde.
Botón de escala: Pulse este botón para activar el modo de escala. Mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse este
botón para editar los ajustes del modo de escala.
1/4–1/32T (Botones de división de tiempo): Utilice estos botones para seleccionar el ajuste de división de
tiempo del teclado para las funciones de repetición de nota y arpegiador. Cada pulsación de uno de estos
botones conmuta entre la sincronización estándar indicada arriba del botón y la sincronización en tresillos
indicada debajo del mismo. Un LED rojo encendido constantemente indica que está seleccionada una
sincronización estándar, mientras que un LED intermitente indica que está seleccionada una sincronización
basada en tresillos.
Consulte Funcionamiento > Cómo utilizar las de las funciones internas del teclado para aprender más
sobre las características anteriormente mencionadas.
Panel trasero
1. Interruptor de encendido: Utilice este interruptor para
encender y apagar el Oxygen Pro 49.
2. Entrada para pedal de sostenido: Esta entrada acepta
pedales de sostenido de contacto momentáneo (no incluido).
Cuando se lo presiona, el pedal por defecto sostiene las
notas que está tocando sin que tenga que mantener sus
dedos pulsando las teclas. La entrada del pedal sostenido se
puede reprogramar para efectuar una asignación de MIDI
personalizada.
Nota: La polaridad del pedal de sostenido está determinada por el teclado al momento del encendido. Cuando
el teclado Oxygen Pro 49 se está encendiendo, se asume que el pedal de sostenido está la posición "hacia
arriba" (desactivado). Es importante que el pedal de sostenido no esté en la posición hacia abajo durante el
encendido, de lo contrario el pedal invertirá su funcionamiento y sostendrá las notas cuando no está pisado.
3. Puerto USB: Al conectarlo a un ordenador, el puerto USB suministra energía al teclado y transmite los datos
de MIDI.
4. Salida MIDI: Utilice un cable MIDI estándar de 5 patillas para conectar este puerto a un sintetizador de
hardware u otro dispositivo MIDI externo.
Nota: El puerto de salida MIDI puede enviar MIDI desde el Oxygen Pro 49, su ordenador conectado, o ambos.
Vaya a los ajustes globales para configurar lo que se envía por la salida MIDI.
5. Conector de bloqueo Kensington
roboKensington estándar de tipo ordenador portátil.
®
: Este conector es compatible con los cables de seguridad anti
2
345
1
21
Page 22

Funcionamiento
Descripción general de la pantalla
Vista general de la pantalla principal
A medida que utiliza los deslizadores, perillas, pads y botones de
función mientras toca, la pantalla se actualizará con el banco actual para
el último control utilizado, el nombre/número del control, el nivel
actualmente aplicado por el control (00
indicador gráfico que indica el nivel (si corresponde). Mientras toca, la
pantalla tendrá texto blanco con fondo negro.
Nota: La pantalla muestra el número de control de software, el cual no siempre coincide con el número de
control de hardware de su teclado. Por ejemplo, si el teclado está configurado para el banco 3 y gira la
perilla 1 del teclado, la pantalla mostrará perilla 20, dado que la perilla 1 del hardware controla la perilla
20 del software cuando el teclado se configura para el banco 3.
Tal como se describe en Características > Panel superior, los
deslizadores y perillas cuentan con relevo suave. Si cambia de banco y
un deslizador o perilla debe moverse antes de poder relevar a su control
asignado, la pantalla ilustra esto mostrando un indicador gris
cuadriculado debajo del nivel de control. Como se muestra en el ejemplo
de la derecha, el banco acaba de ser cambiado al banco 2 y el
deslizador 1 debe desplazarse hasta arriba de todo para que pueda
comenzar a controlar el deslizador 10 del software.
Menús de edición
Además de mostrar los últimos controles utilizados al tocar, la pantalla (junto con el codificador
Select/Scroll) es su principal herramienta para editar diversos ajustes del teclado, incluyendo las
asignaciones de MIDI para los controles editables y los ajustes de las funciones internas del teclado (tales
como el arpegiador), así como los ajustes globales de hardware.
Cuando entra a un menú de edición para cualquier función del teclado, la
pantalla muestra el nombre del menú de edición, el campo del ajuste
resaltado a editar, un campo de parámetro que muestra el estado actual
del ajuste y un gráfico de bloques en la parte inferior de la pantalla que
indican cuántos otros ajustes están disponibles en el menú de edición.
Una vez adentro de un menú de edición, la pantalla tendrá texto negro
con fondo blanco.
Para recorrer los ajustes en un menú de edición, gire el codificador Select/Scroll mientras el campo del
ajuste está resaltado.
Para seleccionar el ajuste a editar, pulse el codificador Select/Scroll mientras el campo del ajuste está
resaltado. El campo del parámetro quedará entonces resaltado.
Para editar el parámetro, seleccione el ajuste a editar como se describió anteriormente. Luego gire el
codificador Select/Scroll mientras el campo del parámetro se encuentra resaltado. Una vez que el
parámetro deseado se encuentre resaltado, pulse el codificador Select/Scroll para confirmar la edición. La
pantalla volverá entonces a resaltar el campo del ajuste.
Para salir del menú de edición sin guardar los cambios, pulse el botón Back. Para salir del menú de
edición y guardar los cambios, pulse el botón DAW (si está editando la DAW de usuario) o el botón Preset
(si está editando un Preset).
Nota: Los ajustes que están disponibles en el menú de edición podrían cambiar función de los parámetros
que seleccione. Por ejemplo, el menú de edición del arpegiador varía en función del parámetro
seleccionado para el ajuste Type (tipo) del arpegiador.
22
–127, si corresponde) y un
Page 23

Uso de los controles secundarios en modo de DAW
Si bien el modo de DAW está diseñado de manera que no se requiere un mapeo complejo para utilizar el Oxygen
Pro 49 con su DAW, algunos de los controles del teclado siguen teniendo múltiples características que se pueden
conmutar en modo de DAW.
Modos de los botones de función
Cuando el teclado está configurado para funcionar en modo de DAW y se selecciona una DAW, los botones de
función se pueden conmutar entre cinco modos diferentes.
Para conmutar el modo de los botones de función, pulse el botón Mode, el cual se encuentra a la derecha de
los botones de función. Con cada pulsación, el LED del botón Mode cambiará para indicar el modo actualmente
seleccionado. Los siguientes modos están disponibles:
Principal (sin LED): Cuando ninguno de los LED está iluminado, los botones de función están configurados para
realizar sus asignaciones principales (impresas arriba/debajo de cada botón). Estas asignaciones se relacionan las
funciones internas del teclado: arpegiador, repetición de nota, modo de acorde y modo de escala. Para obtener
más información sobre cómo utilizar los botones de función con estas características, consulte Cómo utilizar las
de las funciones funciones internas del teclado.
Rec (Grabar) (LED rojo): Cuando se ajustan a modo de grabación, cada botón activará/desactivará la grabación
para la pista correspondiente en su DAW (pista 1–32, en función del botón pulsado y el banco seleccionado).
Select (Seleccionar) (LED verde): En este modo, cada botón pondrá en foco la pista correspondiente del software
(pista 1–32, en función del botón pulsado y el banco seleccionado).
Mute (Silenciar) (LED azul): En este modo, cada botón silenciar/anulará el silenciamiento de la pista correspondiente
del software (pista 1–32, en función del botón pulsado y el banco seleccionado).
Solo (LED amarillo): En este modo, cada botón conmutará la aplicación de un solo en la pista correspondiente del
software (pista 1–32, en función del botón pulsado y el banco seleccionado).
Nota: El modo MIDI está pensado para mapeo MIDI personalizado. Este modo solo está disponible cuando el
teclado está ajustado para funcionar en modo de preset.
Cómo cambiar la función de las perillas en modo de DAW
Nota: No todos los parámetros están disponibles en todas las DAW.
Al operar en modo de DAW, las perillas pueden desempeñar una de tres funciones.
Para cambiar la forma en la que funcionan las perillas, mantenga pulsado el botón Shift y pulse el pad 9, 10 o
11. Las siguientes funciones están disponibles:
Balance (pad 9): Cada perilla controlará el balance de la pista correspondiente del software (pista 1–32, en función
de la perilla pulsada y el banco seleccionado).
Dispositivo (pad 10): Cada perilla controlará los controles del dispositivo de la pista correspondiente del software
(pista 1–32, en función de la perilla pulsada y el banco seleccionado).
Envíos (pad 11): Cada perilla controlará el nivel de los envíos auxiliares de la pista correspondiente del software
(pista 1–32, en función de la perilla pulsada y el banco seleccionado).
Cómo acceder a los accesos directos de la DAW con los pads
Nota: No todos los parámetros están disponibles en todas las DAW.
En modo de DAW, al pulsar un pad se envía un mensaje de activación de nota para que pueda ejecutar un sonido
sintetizado o muestra en su software. Sin embargo, puede pulsar Shift y pulsar los pads 13, 14, 15 o 16 para llevar
a cabo los siguientes comandos:
Save (Guardar) (pad 13): Guarda los cambios realizados al archivo actualmente abierto en su DAW.
Quantize (Cuantificar) (pad 14): Cuantifica la región de audio actualmente seleccionada en su DAW.
Undo (Deshacer) (pad 15): Vuelve atrás el último cambio realizado al archivo en su DAW.
View (Vista) (pad 16): Conmuta entre diferentes ventanas (por ej., Mezcla o Edición) de su DAW.
Importante: Para que estos tres accesos directos funcionen con su DAW, el PC debe ajustarse a Win (Windows) o
Mac en el menú de ajustes globales del Oxygen Pro 49’s. Para acceder al menú de ajustes globales en la pantalla,
mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse el botón Mode. Utilice el codificador Select/Scroll para modificar el ajuste en
función del tipo de su PC, y luego pulse el botón Back para salir del menú.
23
Page 24

Uso de mapeos personalizados
El Oxygen Pro 49 cuenta con numerosos controles completamente personalizados, y con la habilidad de
crear y guardar mapeos de teclado, es posible almacenar diferentes mapeos para diferentes DAW, plugins
o escenarios de actuación que se pueden modificar sobre la marcha.
Al operar en modo de presets, hay 16 presets disponibles en el teclado (1-16). Un preset es un grupo de
asignaciones MIDI para los controles del Oxygen Pro 49 que se pueden almacenar en la memoria interna
del teclado y recuperarse posteriormente. Los presets se pueden editar cuando el teclado está en modo de
edición de preset. Además de contar con estos 16 presets en el teclado, puede utilizar el software de
edición incluido para almacenar un número ilimitado de presets en su ordenador y elegir los 16 que desee
almacenar en la memoria interna del teclado.
Al operar en modo de DAW, el ajuste usuario le permite crear un mapeo personalizado para el teclado que
no solo incluye mensajes MIDI sino también mensajes Mackie o Mackie/HUI. Esto le permite mapear
controles del teclado con comandos para la DAW misma (tales como "Guardar" o "Silenciar") además de
mapear controles del teclado con asignaciones MIDI para parámetros de instrumentos/plugins dentro de la
DAW. El ajuste de DAW de usuario se puede editar cuando el teclado se encuentra en modo de edición de
DAW. Además de contar con la DAW de usuario en el teclado, puede utilizar el software de edición incluido
para almacenar un número ilimitado de DAW de usuario en su ordenador y modificar la que desee
almacenar en la memoria interna del teclado.
Para entrar al modo de edición de preset, seleccione primero el preset que desea editar (tal como se
describe en Funcionamiento > Ajuste del modo de funcionamiento del teclado). Luego mantenga
pulsado Shift y pulse el botón Preset.
Para entrar al modo de edición de DAW, mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse el botón DAW.
Para salir del modo de edición y guardar sus cambios, pulse el botón Preset (si estaba editando
presets) o el botón DAW (si estaba editando un ajuste de DAW de usuario).
Si realizó cambios, la pantalla le preguntará si desea guardarlos. Utilice el codificador Select/Scroll para
seleccionar entre Cancel (cancelar), Replace (reemplazar) y Save As (guardar como). Si selecciona Cancel,
regresará al modo de edición, mientras que, si selecciona Replace, se guardará el preset sin modificar su
nombre. Seleccione Save As para guardar y poder renombrar el preset y modificar su número de ubicación
utilizando el codificador Select/Scroll. Si necesita eliminar un carácter al editar el nombre, mantenga
pulsado el botón Shift y el botón Back.
Para obtener ayuda sobre cómo usar el editor de presets, consulte la Guía del usuario del editor que viene
junto con el software.
24
Page 25

Cómo utilizar las funciones internas del teclado
Las siguientes funciones del teclado se pueden utilizar cuando el mismo se ajusta para funcionar tanto en
modo de DAW como en modo de preset.
Nota: A fin de controlar las funciones del arpegiador, modo de acorde o modo de escala descritas en las
siguientes secciones, los botones de función que se encuentran debajo de los deslizadores tienen que
ajustarse para funcionar en su modo principal. Los botones de función están ajustados para funcionar en
su modo principal cuando no hay ningún LED encendido a la derecha del botón de modo. Si los botones
de función no están ajustados a su modo principal, pulse el botón de modo tantas veces como sea
necesario hasta que no quede ningún LED iluminado a la derecha del botón de modo.
En las siguientes secciones, el funcionamiento descrito de los LED para los botones de función supone
que están ajustados a su modo principal.
Repetición de nota
Cuando esta característica se activa, cualquier pad de actuación pulsado repetirá su mensaje de
activación de nota según el ritmo del tempo y los ajustes de división de tiempo actuales del teclado. Cada
nota repetida tendrá la longitud seleccionada en el ajuste de división de tiempo. Para obtener más ayuda
sobre cómo modificar el tiempo y los ajustes de división de tiempo, consulte Tempo y división de tiempo
del teclado.
La característica de repetición de nota puede tener un comportamiento momentáneo (se activa
momentáneamente) o permanente.
Para utilizar la repetición de nota momentáneamente, mantenga pulsado el botón Note Repeat y luego
pulse un pad. Siempre y cuando mantenga pulsado el botón Note Repeat, la nota reproducida por el pad
se repetirá.
Para que la característica de repetición de nota tenga comportamiento permanente, mantenga
pulsado Shift y pulse el botón Note Repeat. Al pulsar cualquier pad, se hará repetir su nota signada sin
tener que mantener pulsado el botón Note Repeat.
Para desactivar la característica de comportamiento permanente/trabado, pulse nuevamente el botón
Note Repeat.
Nota: Mientras Note Repeat (repetición de nota) esté activo, utilice el codificador Select/Scroll para
modificar el ajuste actual de la división de tiempo del arpegiador y la característica Note Repeat del pad.
Arpegiador
Cuando se activa el arpegiador, el teclado reproducirá las teclas pulsadas repetidamente en secuencia. La
sincronización y ritmo del arpegiador se basa en el ajuste de división de tiempo del teclado y el ajuste de
tempo ya sea de su teclado o su DAW. Cada nota del arpegio tendrá la longitud que haya seleccionado en
el ajuste de división de tiempo; por ejemplo, si seleccionó 1/4, cada nota del arpegio será una negra.
Consulte Tempo y división de tiempo del teclado para obtener ayuda sobre cómo editar estos ajustes.
El arpegiador se puede operar en dos maneras:
• Momentáneo: el arpegiador reproducirá las notas siempre y cuando las teclas estén pulsadas; cuando
suelte las teclas, el arpegiador se detendrá.
• Permanente: el arpegiador reproducirá las notas cuando pulse las teclas y seguirá reproduciéndolas
incluso después de haber levantado sus dedos del teclado.
Para activar o desactivar el arpegiador, pulse el botón Arp. Cuando el arpegiador se activa, se ilumina el
LED del botón.
Para conmutar entre el modo momentáneo y permanente, pulse el botón Latch. Cuando el modo
permanente se activa, se ilumina el LED del botón.
Para comenzar un arpegio, pulse cualquiera de las teclas con el arpegiador activado.
Para comenzar un arpegio en modo permanente nuevo mientras otro arpegio en modo permanente
anterior se sigue reproduciendo, pulse una nueva combinación de teclas.
25
Page 26

Para añadir notas a un arpegio en modo permanente mientras se sigue reproduciendo, mantenga
pulsadas las mismas teclas que pulsó previamente para el arpegio al mismo tiempo que pulsa las teclas de
las notas nuevas que desea añadir.
Para editar los ajustes del arpegiador, mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse el botón Arp. Luego, la pantalla
entrará al menú de edición del arpegiador. Utilice el codificador Select/Scroll para modificar los ajustes
(tal como se describe en Descripción general de la pantalla). Una vez que haya terminado de editar los
ajustes, pulse el botón Back para salir del menú de edición del arpegiador.
Como alternativa, puede mantener presionada la tecla Shift o presionar Shift y Bank < para bloquear los
controles de la perilla ARP del modificador Shift mientras gira las Perillas 1–4 para editar algunos pero no
todos los ajustes. La pantalla mostrará los nuevos ajustes a medida que los modifica.
Nota: Mientras Note Repeat (repetición de nota) esté activo, utilice el codificador Select/Scroll para
modificar el ajuste actual de la división de tiempo del arpegiador y la característica Note Repeat del pad.
Tempo y división de tiempo del teclado
Los ajustes del tempo y división de tiempo del Oxygen Pro 49 determinan la sincronización y el ritmo de las
características de repetición de nota y el arpegiador. Cuando Clock (reloj) se ajusta a Internal (interno) en la
pantalla de edición del tempo, el tempo del teclado puede introducirse tocándolo con el dedo siguiendo el
ritmo o indicando su valor exacto dentro de la pantalla de edición del tempo. Cuando Clock se ajusta a
External (externo) el tempo del teclado se sincronizará automáticamente con el tempo de su DAW.
Para introducir el tempo del teclado tocándolo con el dedo, toque el botón Tempo dos o más veces a
la velocidad de los BPM deseados. La pantalla se actualizará con el tempo nuevo a medida que toca el
botón.
Nota: A fin de poder marcar el tempo mediante toques en el menú del teclado, el ajuste Clock del teclado
en el menú edición del tempo debe ser Internal. Si se lo ajusta a External, el tempo del teclado se
sincronizará con su DAW.
Para entrar al menú de edición del tempo en la pantalla, mantenga pulsado el botón Tempo. Utilice el
codificador Select/Scroll para modificar el ajuste Clock o introducir un tempo interno del teclado (20,0
240,0). Una vez que haya terminado de editar los ajustes, pulse el botón Back para salir del menú de
edición del tempo. Consulte Descripción general de la pantalla para obtener más información sobre
cómo utilizar el codificador Select/Scroll con los menús de edición de la pantalla.
Para ajustar la división de tiempo del teclado, pulse el botón Time Division (división de tiempo) para
obtener el ajuste deseado (tal como está impreso arriba/debajo del botón). Pulse el botón dos veces si
desea utilizar un ajuste basado en tresillos. Cuando se selecciona una división de tiempo estándar, se
ilumina el botón correspondiente. Cuando se selecciona una división de tiempo basada en tresillos, el botón
parpadeará.
Nota: Mientras Note Repeat (repetición de nota) esté activo, utilice el codificador Select/Scroll para
modificar el ajuste actual de la división de tiempo del arpegiador y la característica Note Repeat del pad.
–
26
Page 27

Modo de acordes
Cuando activa el modo de acordes, al pulsar una sola tecla o almohadillas se reproducirá un acorde
completo en lugar de una sola nota. La tecla o almohadillas que pulse determinará la nota raíz del acorde y
el tipo de acorde seleccionado dependerá de los ajustes actuales.
La característica de acorde puede funcionar en dos modos girando el codificador Select/Scroll que
determinarán el acorde exacto asignado a cada tecla:
• Modo Smart (inteligente): En este modo, primero debe asignar el teclado a una nota musical (por ej.,
D menor). Luego debe asignar la armonización deseada para los acordes (qué intervalos se incluirán
en el acorde), por ej., 1-3-5). La armonización del acorde de cada nota será automáticamente
enarmónica a la nota seleccionada.
• Custom (Personalizado): En este modo se puede determinar la estructura del acorde que se asignará
a cada nota tocándolo manualmente. Por ejemplo, si selecciona este modo y toca el acorde 1-b3-5-b7,
cada tecla se programará para tocar esta estructura de acorde. La nota de la tecla que pulse servirá
como la raíz del acorde.
Para activar o desactivar el modo de acorde, pulse el botón Chord. Mientras el modo de acorde esté
activado, el botón Chord permanecerá iluminado.
Para editar los ajustes del modo de acorde, primero mantenga pulsado Shift mientras pulsa el botón
Chord para entrar al menú de edición de acorde en la pantalla. Luego utilice el codificador Select/Scroll
para modificar los ajustes (tal como se describe en Descripción general de la pantalla). Una vez que haya
terminado de editar los ajustes, pulse el botón Back para salir del menú de edición de acorde.
Como alternativa, puede mantener pulsado Shift mientras pulsa las notas C2
modo de acorde Smart.
Nota: Por defecto, las teclas están configuradas para reproducir acordes cuando el modo de acorde está
activado. Sin embargo, esto se puede modificar en el menú de ajustes globales de manera que cuando
dicho modo está activado, los acordes se reproducirán en las teclas, los pads o ambos.
–Bb3 si está utilizando el
Modo de escala
Con el modo de escala, puede configurar la placa del teclado de forma que las teclas que caigan fuera de
una escala musical seleccionada queden deshabilitadas. Esto le permite tocar dentro de una escala
seleccionada sin correr el riesgo de tocar notas "incorrectas". Puede elegir entre 16 opciones diferentes
para asignar una escala al teclado.
Para activar o desactivar el modo de escala, pulsado el botón Scale. Mientras el modo de escala esté
activado, el botón Scale permanecerá iluminado.
Para determinar en qué escala musical está configurado el teclado, entre al menú Scale Edit (edición
de teclado) en la pantalla manteniendo pulsado Shift y pulsando el botón Scale. Luego utilice el
codificador Select/Scroll para modificar los ajustes (tal como se describe en Descripción general de la
pantalla). Una vez que haya terminado de editar los ajustes, pulse el botón Back para salir del menú de
edición de escala.
Menú de ajustes globales
Utilice el menú de ajuste globales en la pantalla para personalizar algunos de los controles
predeterminados del teclado. Estos ajustes se aplican al teclado tanto en modo de DAW como modo de
preset y cualquier cambio realizado desde el menú de ajustes globales quedará guardado al apagar el
teclado.
Para entrar al menú de ajustes globales, mantenga pulsado Shift y pulse el botón Mode. Utilice el
codificador Select/Scroll para modificar los ajustes (tal como se describe en Descripción general de la
pantalla).
Para salir del menú de ajuste globales, pulse el botón Back.
27
Page 28

Guide d’utilisation (Français)
Présentation
Contenu de la boîte
Oxygen Pro 49
Câble USB
Carte de téléchargement de logiciel
Guide d’utilisation
Consignes de sécurité et informations concernant la garantie
Assistance
Veuillez visiter m-audio.com pour consulter et télécharger la documentation la plus récente, la
configuration requise et les autres informations sur le produit.
Pour de l’assistance supplémentaire, veuillez visiter m-audio.com/support.
Installation
Pour commencer à utiliser l'Oxygen Pro 49, vous devez brancher votre équipement, configurer
correctement votre logiciel, puis définir le mode de fonctionnement du clavier.
Pour relier l’Oxygen Pro 49 à votre ordinateur, utilisez le câble USB fourni. Reliez l'extrémité USBB du câble au clavier et l'extrémité USB-A du câble à l'ordinateur ou dans un concentrateur USB
branché à l’ordinateur.
Remarque : En plus de transmettre des données, le câble USB sert à alimenter le clavier. Si vous
reliez l’Oxygen Pro 49 à un concentrateur USB auquel d'autres appareils sont connectés, nous vous
recommandons d'utiliser un concentrateur USB branché à une alimentation secteur.
Pour configurer votre station audionumérique (DAW) afin de pouvoir l’utiliser avec l’Oxygen
Pro 49, vous devez activer l’Oxygen Pro 49 comme surface de contrôle MIDI dans le menu des
réglages approprié du DAW (Preferences, Options, Device Setup, etc.).
Si vous souhaitez utiliser le logiciel MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition ou Ableton Live
Lite avec l’Oxygen Pro 49, veuillez consulter la section Installation des logiciels fournis pour des
instructions plus spécifiques à la configuration du logiciel que vous souhaitez installer. Si vous
souhaitez utiliser un autre logiciel audionumérique, veuillez consulter son guide d'utilisation afin
d’obtenir de l'aide pour cette étape.
Si vous souhaitez utiliser l’Oxygen Pro 49 avec un synthétiseur matériel plutôt qu'avec un ordinateur,
reliez le port de sortie MIDI de l’Oxygen Pro 49 à un synthétiseur avec un câble MIDI standard à 5
broches. Assurez-vous ensuite que l'Oxygen Pro 49 est configuré pour fonctionner avec l'un de ses
préréglages personnalisés sélectionnés (comme indiqué dans la section Réglage du mode de
fonctionnement du clavier) et qu’il est configuré pour transmettre des données MIDI à partir du
port de sortie MIDI à 5 broches dans le menu des réglages principaux. Pour utiliser un synthétiseur
matériel externe, vous devez connecter l’Oxygen Pro 49 à un ordinateur, un ordinateur portable ou
un concentrateur USB alimenté.
28
Page 29

Installation des logiciels fournis
Nous avons inclus les logiciels MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition et Ableton Live Lite avec
l’Oxygen Pro 49 afin que vous puissiez commencer à créer de la musique avec un logiciel de qualité
professionnelle dès sa sortie de l'emballage. De plus, nous avons inclus des modules d'extension et des
plug-ins d'instruments virtuels AIR que vous pouvez utiliser avec votre DAW.
Pour télécharger le logiciel MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition ou Ableton Live Lite, veuillez
enregistrer l’Oxygen Pro 49 sur le site m-audio.com et suivre les instructions d’installation à partir de votre
compte utilisateur. Si vous utilisez Ableton Live Lite, nous vous recommandons de visiter le site
ableton.com afin de vérifier s’il y a des mises à jour disponibles. Veuillez consulter la section Installation
Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition ou Installation Ableton Live Lite ci-dessous pour des instructions plus
spécifiques sur la configuration des ces logiciels audionumériques.
Pour télécharger les plug-ins d'instruments virtuels AIR, veuillez suivre les instructions sur la carte de
téléchargement de logiciel. La plupart des logiciels audionumériques ne chargent pas automatiquement les
plug-ins d'instruments virtuels après l’installation, il est possible que vous ayez à sélectionner manuellement
un dossier de plug-in. Les dossiers de plug-ins pour Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition et Ableton Live
Lite varient en fonction de votre système d'exploitation, comme indiqué ci-dessous.
Dossiers de plug-ins Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition/AAX :
• Windows (32 bits) : C:\Program Files(x86)\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• Windows (64 bits) : C:\Program Files\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• MacOS : Macintosh HD/Library/Application Support/Avid/Audio/Plug-Ins
Plug-ins Ableton/VST :
• Windows (32 bits) : C:\Program Files(x86)\VSTplugins
• Windows (64 bits) : C:\Program Files\VSTplugins
• MacOS : Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Plugins/VST
Pour définir le dossier de plug-ins dans Ableton Live Lite :
1. Allez dans le menu Preferences.
2. Cliquez sur l’onglet File Folder. Sous Plug-In Sources, cliquez sur Browse et sélectionnez le dossier
des plug-ins approprié, comme indiqué ci-dessus.
3. Après avoir effectué votre sélection, le bouton Use VST Custom Plug-In Folder devrait être activé. Si
ce n’est pas le cas, cliquez sur le bouton pour l’activer. Vous pouvez ensuite quitter le menu
Preferences.
29
Page 30

Installation de Ableton Live Lite
1. Commencez par relier l’Oxygen Pro 49 à votre ordinateur. Lancez ensuite Ableton Live Lite.
2. Ouvrez la fenêtre Preferences dans Ableton Live Lite. Si vous utilisez un Mac, cliquez sur Live
Preferences. Si vous utilisez un PC, cliquez sur Options > Preferences.
3. Sélectionnez l'onglet Link/MIDI à gauche. Sous la section MIDI Ports, ajustez les réglages comme
indiqué ci-dessous :
Sous Control Surfaces, pour Input et Output, sélectionnez Oxygen Pro 49.
À côté de Input : Oxygen Pro 49, sélectionnez le bouton On dans les colonnes Track et Remote.
À côté de Output : Oxygen Pro 49, sélectionnez le bouton On dans les colonnes Track et Remote.
4. Fermez la fenêtre Preferences.
5. Pour ajouter un instrument ou un plug-in qui pourra être déclenché avec l'Oxygen Pro 49, sélectionnez
Instruments ou Plug-ins dans la colonne Categories.
6. Dans la colonne Name à droite de la colonne Categories, recherchez l'instrument ou le plug-in que
vous souhaitez ajouter. Cliquez et glissez l'instrument sur une piste MIDI dans Ableton Live Lite pour
charger l'instrument.
L'instrument peut maintenant être déclenché par l’Oxygen Pro 49.
>
Installation de Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition
1. Reliez l’Oxygen Pro 49 à votre ordinateur. Lancez ensuite Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition
2. Ouvrez ou créez un projet.
3. À partir du menu déroulant Setup, sélectionnez l’option MIDI Input Devices. Activez MIDI Input de
l’Oxygen Pro 49 en cochant la case à côté d’Oxygen Pro 49.
4. Pour créer une nouvelle piste d'instrument, sélectionnez l’option New à partir du menu déroulant
Track.
5. À partir du menu déroulant New, sélectionnez l’option Stereo, puis Instrument Track.
6. Dans la nouvelle piste, ajoutez un insert en cliquant sur les Inserts A-E de la piste et en sélectionnant
l’option Multichannel Plugin > Instrument. Sélectionnez ensuite l'instrument que vous souhaitez
utiliser, comme Xpand!2 (stéréo).
Le plug-in peut maintenant être déclenché par l’Oxygen Pro 49.
Logiciel de modification des préréglages
Pour télécharger le logiciel Preset Editor, veuillez suivre les instructions sur la carte de téléchargement
de logiciel fournie. Ce logiciel peut être utilisé pour créer des mappages MIDI personnalisés qui pourront
ensuite être chargés sur l’Oxygen Pro 49. Afin d’en savoir plus sur l'utilisation du clavier avec l'un des
préréglages personnalisés, veuillez consulter la section suivante, ainsi que la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation
de mappages personnalisés. Le logiciel Preset Editor est également livré avec son propre guide
d'utilisation.
30
Page 31

Réglage du mode de fonctionnement du clavier
Une fois que vous avez configuré l’Oxygen Pro 49 pour qu’il fonctionne avec votre DAW, il est temps de
définir le mode de fonctionnement du clavier. En sélectionnant le mode de fonctionnement, vous pouvez
configurer le clavier pour qu'il mappe automatiquement les fonctionnalités de votre DAW ou l’utiliser comme
un contrôleur personnalisé. Avec ces deux modes, l
rapidement entre commander un plug-in et commander votre DAW en appuyant sur une seule touche.
Les deux modes de fonctionnement déterminent la fonction des commandes modifiables du clavier MIDI :
• DAW : En mode DAW, les commandes du clavier seront automatiquement mappées aux curseurs,
touches, boutons et pads de votre DAW.
• Preset : En mode Preset, les commandes modifiables du clavier peuvent être réglées sur des fonctions
que vous déterminez. Un certain nombre de mappages prédéfinis individuels peuvent être créés puis
sauvegardés dans la mémoire interne du clavier pour que vous puissiez les charger ultérieurement.
Pour configurer le clavier pour qu'il fonctionne en mode DAW, appuyez sur la touche DAW. La touche
s’allumera afin d’indiquer que le mode DAW est sélectionné.
Pour modifier le DAW commandé par le clavier :
1. Maintenez la touche DAW enfoncée afin d’afficher le menu DAW.
2. Tournez l'encodeur Select/Scroll afin de parcourir les DAW disponibles. Lorsque vous tournez
l'encodeur, l’écran s’actualise afin d’afficher le DAW sélectionné. L'option User vous permet de
mapper des commandes DAW personnalisées au clavier, comme décrit dans Fonctionnement >
Utilisation de mappages personnalisés.
3. Lorsque le DAW souhaité s'affiche, appuyez sur l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour confirmer votre
sélection.
Remarque : Pour quitter le mode DAW sans changer de DAW, appuyez sur la touche Back.
Pour configurer le clavier pour qu'il fonctionne en mode Preset, appuyez sur la touche Preset. La
touche s’allume afin d’indiquer que le mode Preset est sélectionné.
Pour changer de préréglage :
1. Maintenez la touche Preset enfoncée afin d’afficher le menu Preset Select.
2. Tournez l'encodeur Select/Scroll afin de parcourir les préréglages disponibles à l’écran. Lorsque vous
tournez l'encodeur, l’écran s’actualise afin d’afficher le préréglage sélectionné.
3. Lorsque le préréglage souhaité s'affiche à l'écran, appuyez sur l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour
confirmer votre sélection. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation de mappages
personnalisés afin d’en savoir plus sur le mappage des préréglages.
'Oxygen Pro 49 vous donne la possibilité de basculer
31
Page 32

Caractéristiques
Panneau supérieur
18
17
11 12
14
1
19
15 16
13
23
20
21
5
10
6
7
9
8
22
2
3
4
Remarque : Le texte entre crochets accompagnant les commandes du clavier indique les fonctions
secondaires accessibles en appuyant simultanément sur la touche Shift et la touche de commande.
1. Plateau de clavier : Sensible à la dynamique, le clavier est la principale méthode de transmission des
données d'activation et de désactivation des notes MIDI. En plus d'être sensible à la dynamique, le
clavier dispose de la fonction aftertouch de canal, ce qui signifie que vous pouvez modifier le son
produit par un plug-in d'instrument virtuel en faisant varier la pression appliquée après avoir appuyé
initialement sur la touche.
Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée, puis appuyer sur les touches C2–Bb3 permet de modifier les
réglages du mode Chord. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation des fonctions
internes du clavier pour en savoir plus sur cette fonctionnalité.
2. Touches de sélection de l'octave : Ces touches permettent d'augmenter ou de diminuer la plage de
hauteur tonale des touches d'une octave. Maintenir la touche Shift et appuyer sur une de ces touches
permet d'augmenter ou de diminuer la plage de hauteur tonale des touches d’un demi-ton. La plage de
hauteur tonale du clavier peut être transposée jusqu'à quatre octaves plus hautes ou trois octaves plus
basses, et jusqu’à douze demi-tons à partir de sa transposition par défaut.
Appuyer simultanément sur les touches Octave - et Octave + permet de réinitialiser la plage de
hauteur tonale et la transposition par défaut (C2–C4 sur le clavier) de l’Oxygen Pro 49.
3. Molette de la hauteur tonale : Faire rouler cette molette de haut en bas à partir de la position centrale
permet de modifier la hauteur tonale du clavier en jouant. La plage de modification de hauteur tonale
par défaut varie selon le synthétiseur logiciel. Cette molette est équipée d'un ressort et revient à sa
position initiale lorsqu'elle est relâchée.
4. Molette de modulation : Cette molette transmet des données de contrôleur en continu — MIDI CC #01
(modulation), par défaut.
32
25
Page 33

5. Touche DAW : Cette touche permet de configurer l’Oxygen Pro
49 pour qu'il fonctionne en mode DAW. Maintenir cette touche
enfoncée permet d’accéder au menu DAW Select.
Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée puis appuyer sur cette touche
permet de créer des préréglages personnalisés pour le logiciel
audionumérique. Appuyer de nouveau sur la touche après avoir
modifié le User DAW permet de sauvegarder les modifications
apportées.
Veuillez consulter la section Installation > Réglage du mode de
fonctionnement du clavier afin d’en savoir plus sur le mode
DAW. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation
de mappages personnalisés afin d’en savoir plus sur le
mappage du User DAW.
6. Touche Preset : Cette touche permet de configurer l’Oxygen Pro 49 pour qu'il fonctionne en mode
Preset. Maintenir cette touche enfoncée permet d’afficher le menu Preset Select.
Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée puis appuyer sur cette touche permet de modifier un préréglage.
Appuyer de nouveau sur la touche après avoir modifié un préréglage permet de sauvegarder les
modifications apportées.
Veuillez consulter la section Installation > Réglage du mode de fonctionnement du clavier afin d’en
savoir plus sur le mode Preset. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation de
mappages personnalisés afin d’en savoir plus sur le mappage des préréglages.
7. Écran : La fenêtre principale affiche l'état de la dernière commande utilisée. Il permet de contrôler le
niveau des paramètres lorsque vous ajustez les commandes sur le clavier. L'encodeur Select/Scroll
permet d’afficher et de modifier les réglages du clavier. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement >
Présentation de l’écran afin d’en savoir plus.
8. Encodeur Select/Scroll : Lorsqu’un des menus de modification est affiché, tourner l’encodeur permet
de modifier les réglages/paramètres et l’enfoncer permet de confirmer la sélection.
Si aucun menu de modification n’est affiché, tourner l'encodeur et appuyer sur l'encodeur
fonctionnent comme des commandes MIDI distinctes. En mode DAW, les commandes assignées sont
prédéterminées. Lorsqu’un préréglage ou le User DAW est sélectionné, les commandes assignées sont
modifiables.
9. Touche Back : Lorsqu’un menu de modification est affiché, appuyer sur cette touche permet de revenir
à la fenêtre principale.
Si aucun menu de modification n’est affiché, cette touche sera assignée à une commande. Lorsqu’un
DAW est sélectionné, les commandes assignées sont prédéterminées. Lorsqu’un préréglage ou le User
DAW est sélectionné, les commandes assignées sont modifiables. Lors de la modification d'un nom de
préréglage ou de DAW, appuyez sur la touche Shift et la touche Back pour supprimer une lettre.
10. Touche Shift : Maintenir la touche Shift
touches permet d’accéder aux fonctions secondaires des touches.
11. Touche << : En fonction de la fenêtre sélectionnée dans votre DAW, cette touche permet de faire un
retour arrière sur la piste sélectionnée ou de déplacer le curseur dans le bas de la fenêtre.
12. Touche >> : En fonction de la fenêtre sélectionnée dans DAW, cette touche permet de faire une avance
rapide sur la piste sélectionnée ou de déplacer le curseur dans le haut de la fenêtre.
13. Touche de bouclage : Cette touche permet d’activer ou de désactiver la fonction de bouclage dans
votre DAW.
14. Touche d’arrêt de lecture : Cette touche permet d’arrêter la lecture de la piste dans votre DAW.
Enfoncer cette touche deux fois permet d’arrêter la lecture de la piste sélectionnée et de repositionner
le curseur de lecture au début de la piste. Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée, puis enfoncez cette
touche permet de transmettre un message de désactivation de toutes les notes (MIDI Panic/All Notes
Off) et de remettre le réglage de toutes les commandes à zéro.
15. Touche de lecture : Cette touche permet de faire jouer la piste sélectionnée dans votre DAW.
16. Touche d’enregistrement : Cette touche permet de lancer l’enregistrement dans votre DAW.
17. Touches des banques : Ces touches permettent de changer la banque sélectionnée pour les
curseurs, les boutons, les pads et les touches de fonction. Il y a quatre banques pour ces
commandes, soit l'équivalent de 36 curseurs, 32 boutons, et 64 pads.
enfoncée tout en utilisant une des commandes ou des
5
10
9
6
7
18
11 12
8
14
17
15 16
19
13
33
Page 34

Appuyez sur la touche
bouton
ARP. Ceci s’avère utile pour modifier les paramètres ARP pendant une prestation en direct.
Appuyez sur la touche
Shift et sur la touche Bank < pour verrouiller les fonctions secondaires du
Shift et sur la touche Bank < pour verrouiller les fonctions secondaires des
pads. Ceci s’avère utile pour effectuer des modifications lors du mixage d'une chanson. Pour ramener
les boutons ou les pads à leur mode de fonctionnement normal, appuyez sur la touche Shift et la
touche Bank < ou Bank >.
18. Touche Tempo : Taper cette touche permet de définir le tempo de l'Oxygen Pro 49, alors que le
maintenir enfoncer permet d’afficher le menu de modification du tempo, à partir duquel il est possible
d’entrer manuellement le tempo et de choisir de synchroniser le tempo de l'Oxygen Pro 49 à celui du
DAW. Le réglage du tempo affecte les fonctions de l'arpégiateur et de répétition de la note du clavier.
Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation des fonctions internes du clavier pour en
savoir plus sur cette fonctionnalité.
Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyer sur cette touche permet d’activer et de désactiver
l’arpégiateur de votre DAW.
19. Touche de répétition de la note : Cette touche permet d’activer la fonction de répétition de notes des
pads. Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée puis appuyer sur cette touche permet de verrouiller et de
déverrouiller la fonction de répétition de la note. Lorsque la fonction Note Repeat est active, utilisez
l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour changer le réglage de la division temporelle de l'arpégiateur et de la
fonction Note Repeat du pad. Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée puis appuyer sur cette touche permet
de verrouiller et de déverrouiller la fonction Note Repeat. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement
> Utilisation des fonctions internes du clavier pour en savoir plus sur la fonction de répétition de la
note.
20. Pads (1–16) : Ces pads sensibles à la dynamique permettent de transmettre des messages d'activation
et de désactivation des notes MIDI ou d’effectuer d'autres affectations MIDI (lors de l’utilisation d’un
préréglage ou du User DAW). Maintenir la touche Shift tout en appuyant sur les pads 9–11 permet de
réassigner la fonction des boutons, et maintenir la touche Shift tout en appuyant sur les pads 13–16
permet d’utiliser les raccourcis de votre DAW. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement >
Utilisation des commandes secondaires en mode DAW afin d’en savoir plus.
21. Lecture d'une rangée de pads : Ces touches permettent de lancer la lecture de tous les clips audio
assignés aux pads de la rangée correspondante. Selon le DAW, ces touches auront des fonctions
différentes.
22. Curseurs (1–9) : Pousser ces curseurs vers le haut ou vers le bas permet d’effectuer les commandes
qui leur sont assignées. Lorsqu’un DAW est sélectionné, les commandes assignées sont
prédéterminées. Lorsqu’un préréglage ou le User DAW est sélectionné, les commandes assignées sont
modifiables.
23. Boutons (1–8) : Tourner ces boutons vers la gauche et vers la droite permet d’effectuer les commandes
qui leur sont assignées. Lorsqu’un DAW est sélectionné, les commandes assignées sont
prédéterminées. Lorsqu’un préréglage ou le User DAW est sélectionné, les commandes assignées sont
modifiables.
Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation des commandes secondaires en mode
DAW afin d’en savoir plus sur la réassignation des fonctions des boutons en mode DAW lorsqu’un
DAW est sélectionné.
Maintenir la touche Shift tout en tournant les boutons 1-4 permet de modifier les réglages de
l'arpégiateur. Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation des fonctions internes du
clavier afin d’en savoir plus sur l'arpégiateur.
Important : Les curseurs et les boutons sont activés avec une « prise de commande en douceur ».
Cela signifie que si vous changez de banque, un curseur ou un bouton ne fonctionnera pas tant qu'il ne
sera pas positionné sur la valeur actuelle de la commande logicielle nouvellement sélectionnée. Par
exemple, si vous déplacez le curseur 1 dans la banque 1, puis passez à la banque 2, le curseur
matériel 1 n'affectera pas le curseur logiciel 10 tant que le curseur matériel n'est pas positionné à la
valeur actuelle du curseur logiciel 10. Cette fonction vous permet d'effectuer des modifications dans
une banque, puis de changer de banque sans apporter de modifications indésirables aux contrôles de
la nouvelle banque. L'écran affiche un indicateur de valeur à damier si un curseur ou un bouton doit
être déplacé avant de pouvoir commander la fonction assignée (veuillez consulter la section
Présentation de l’écran pour une illustration).
Important : Dans Avid Pro Tools, les pistes stéréo ont deux commandes de panoramique : gauche et
droit. Appuyez sur la touche Shift pour interchanger les boutons entre le canal gauche et le canal droit.
Si les commandes de panoramique ne se déplacent pas sur une piste mono, appuyez sur la touche
Shift pour ramener le bouton de panoramique à son mode de fonctionnement normal.
34
Page 35

24. Touche Mode (avec indicateurs DEL) : Appuyer sur la touche Mode permet d’activer un des modes
secondaires des touches de fonction. Lorsque le mode DAW est sélectionné, les modes secondaires
accessibles pour les touches de fonction sont enregistrement, sélection, mise en sourdine et mise
en solo. Lorsque ces modes sont utilisés, les touches exécutent les fonctions de chargement pour
l’enregistrement, de sélection de piste, de mise en sourdine et de mise en solo prédéterminées du
canal DAW (veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation des commandes secondaires
en mode DAW afin d’en savoir plus). Lorsque le mode Preset est sélectionné, le mode secondaire
accessible pour les touches de fonction est MIDI, dans lequel les touches exécutent les fonctions de
commande MIDI prédéterminées selon le préréglage personnalisé sélectionné.
Les DEL situées à droite de la touche Mode indiquent le mode des touches de fonction.
Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée tout en appuyant sur la touche Mode permet d’afficher le menu des
paramètres principaux du clavier.
25. Touches de fonction (1–8) : Lorsque les touches de fonction sont définies sur leur mode principal,
elles peuvent commander les fonctions internes du clavier, comme décrit ci-dessous :
Touche ARP : Cette touche permet d'activer l'arpégiateur. Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée puis
appuyer sur cette touche permet de modifier les réglages de l'arpégiateur.
Touche de verrouillage : Cette touche permet d’alterner entre le mode de fonctionnement
momentané et verrouillé de l’arpégiateur.
Touche Chord : Cette touche permet d’activer le mode Chord. Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée
puis appuyer sur cette touche permet de modifier les réglages du mode Chord.
Touche Scale : Cette touche permet d’activer le mode Scale. Maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée
puis appuyer sur cette touche permet de modifier les réglages du mode Scale.
1/4–1/32T (touches de division temporelle) : Ces touches permettent de sélectionner le réglage de
division temporelle du clavier pour les fonctions de répétitions de la note et l’arpégiateur. Chaque
pression sur l'une de ces touches alterne entre la division standard indiquée au-dessus de la touche
et la division ternaire indiquée sous la touche. Une DEL rouge fixe indique qu’une division standard
est sélectionnée, alors qu'une DEL clignotante indique qu'une division ternaire est sélectionnée.
Veuillez consulter la section Fonctionnement > Utilisation des fonctions internes du clavier afin d’en
savoir plus sur les fonctionnalités ci-dessus.
Panneau arrière
1. Interrupteur d'alimentation : Cette touche permet de mettre
l’Oxygen Pro 49 sous et hors tension.
2. Entrée pour pédale de sustain : Cette entrée prend en charge
une pédale à contact momentané (non fournie). Lorsque cette
pédale est enfoncée, le son joué est maintenu sans avoir à
garder les doigts sur les touches. L'entrée pour pédale de
sustain peut être remappée afin d’effectuer une commande MIDI
personnalisée.
Remarque : La polarité de la pédale de sustain est déterminée par le clavier au démarrage. Lorsque
l’Oxygen Pro 49 est mis sous tension, la pédale de sustain est supposée être en position « relevée »
(désactivée). Il est important que la pédale de sustain ne soit pas en position abaissée avant de mettre
le clavier sous tension, car la pédale fonctionnera alors en sens inverse et les notes seront maintenues
lorsque la pédale n'est pas enfoncée.
3. Port USB : Lorsque relié à un ordinateur, ce port permet d’alimenter le clavier et de transmettre des
données MIDI.
4. Sortie MIDI : Utilisez un câble MIDI à cinq broches standard afin de brancher cette sortie à l’entrée
5. Connecteur de verrouillage Kensington
synthétiseur matériel ou d’un autre appareil MIDI.
d’un
Remarque : La sortie MIDI peut transmettre des données MIDI depuis l’Oxygen Pro 49, votre
ordinateur ou les deux. Accédez au menu des réglages principaux pour définir ce qui est transmis à
la sortie MIDI.
Kensington standard pour ordinateur portable pour la protection contre le vol.
®
: Ce connecteur est compatible avec les câbles de sécurité
2
345
1
35
Page 36

Fonctionnement
Présentation de l'écran
Fenêtre principale
Au fur et à mesure que vous utilisez les curseurs, les boutons, les pads
et les touches de fonction du clavier, l'écran s’actualise en affichant la
banque sélectionnée, le nom/numéro de la dernière commande utilisée, le
niveau appliqué par la commande (00-127, le cas échéant) et l’indicateur
graphique illustrant le niveau (le cas échéant). Pendant l'exécution des
commandes, l’arrière-plan de l'écran est noir et le texte est blanc.
Remarque : L'écran affiche le numéro de la commande logicielle, qui ne correspond pas toujours au
numéro de commande matériel sur le clavier. Par exemple, si le clavier est réglé sur la banque 3 et que vous
tournez le bouton 1 sur le clavier, l'écran affichera le bouton 20, car le bouton matériel 1 commande le
bouton logiciel 20 lorsque le clavier est réglé sur la banque 3.
Comme décrit dans la section Fonctionnalités > Panneau supérieur, les
curseurs et les boutons sont activés avec une « prise de commande en
douceur ». Si vous changez de banque et qu'un curseur ou un bouton
doit être déplacé avant de pouvoir commander la fonction qui lui est
assignée, l'écran affiche un indicateur de valeur à damier gris sous le
niveau de de la commande. Comme illustré dans l'exemple de droite, la
banque 2 vient d’être sélectionnée et le curseur 1 doit être déplacé au
maximum avant qu'il puisse commander le curseur logiciel 10.
Menus Edit
En plus d'afficher les dernières commandes utilisées lors de l'exécution, l'écran (ainsi que l'encodeur
Select/Scroll) est votre principal outil pour modifier divers réglages du clavier, y compris les assignations
MIDI pour les commandes modifiables, les réglages des fonctions internes du clavier (comme l’arpégiateur),
ainsi que les réglages matériels principaux.
Lorsque vous accédez au menu de modification pour n'importe quelle
fonction du clavier, l'écran affiche le nom du menu de modification, un
champ des réglages en surbrillance, un champ des paramètres indiquant
l'état actuel du réglage et des blocs graphiques en bas de l'écran pour
indiquer combien d'autres réglages sont accessibles dans le menu de
modification.
Dans les menus de modification, l’arrière-plan de l'écran est blanc et le texte est noir.
Pour parcourir les réglages d’un menu de modification, tournez l’encodeur Select/Scroll alors que le
champ des réglages est en surbrillance. Pour sélectionner un réglage à modifier, enfoncez l’encodeur
Select/Scroll alors que le champ des réglages est en surbrillance. Le champ des paramètres sera en
surbrillance.
Pour modifier le paramètre du réglage, sélectionnez le réglage à modifier comme décrit ci-dessus, puis
tournez l’encodeur Select/Scroll alors que le champ des paramètres est en surbrillance. Une fois que le
paramètre souhaité est en surbrillance, enfoncez l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour confirmer la modification.
L’écran affiche à niveau le champ des réglages en surbrillance.
Pour quitter le menu de modification sans sauvegarder les modifications, appuyez sur la touche Back.
Pour quitter le menu de modification et sauvegarder les modifications, appuyez sur la touche DAW
(lors du réglage du User DAW), ou la touche Preset (lors du réglage d’un préréglage).
Remarque : Les réglages disponibles dans les menus de modification peuvent changer en fonction des
paramètres que vous sélectionnez. Par exemple, le menu de modification pour l’arpégiateur change selon le
paramètre sélectionné pour le réglage Type.
36
Page 37

Utilisation des commandes secondaires en mode DAW
Bien que le mode DAW soit conçu de sorte qu'aucun mappage complexe ne soit nécessaire pour utiliser votre DAW
avec l’Oxygen Pro 49, certaines commandes du clavier disposent tout de même de plusieurs fonctionnalités qui
vous permettent de passer d’une fonction à une autre.
Modes des touches de fonction
Lorsque le mode DAW est activé et qu'un DAW est sélectionné, les touches de fonction permettent d’alterner entre
cinq modes différents.
Pour modifier le mode des touches de fonction, appuyez sur la touche Mode à droite des touches de fonction.
À chaque pression, l’indicateur DEL de la touche Mode change afin d’indiquer le mode sélectionné. Les cinq
modes suivants sont disponibles :
Principal (aucune DEL) : Lorsqu'aucune DEL n'est allumée, les touches de fonction sont définies sur leurs
assignations principales (indiquée au-dessus/en dessous de chaque touche). Ces assignations concernent les
fonctions internes du clavier : l'arpégiateur, la répétition de la note, le mode Chord et le mode Scale. Veuillez
consulter la section Utilisation des fonctions internes du clavier afin d’en savoir plus sur l’utilisation des touches
de fonction avec ces fonctionnalités.
Rec (DEL rouge) : Lorsque le mode Record est activé, chaque touche permet d’activer et de désactiver
l'enregistrement de la piste correspondante dans le DAW (piste 1–32, selon la touche enfoncée et la banque
sélectionnée).
Select (DEL verte) : Lorsque ce mode est activé, chaque touche permet de mettre en surbrillance la piste logicielle
correspondante (piste 1–32, selon la touche enfoncée et la banque sélectionnée).
Mute (DEL bleue) : Lorsque ce mode est activé, chaque touche permet de mettre en sourdine la piste logicielle
correspondante (piste 1–32, selon la touche enfoncée et la banque sélectionnée).
Solo (DEL jaune) : Lorsque ce mode est activé, chaque touche permet de mettre en solo la piste logicielle
correspondante (piste 1–32, selon la touche enfoncée et la banque sélectionnée).
Remarque : Le mode MIDI est destiné au mappage MIDI personnalisé. Ce mode est disponible uniquement lorsque
le clavier est en mode Preset.
Modification des fonctions des boutons en mode DAW
Remarque : Certains réglages ne sont disponibles que dans certains DAW.
En mode DAW, les boutons peuvent exécuter l'une de trois fonctions.
Pour modifier le fonctionnement des boutons, maintenez la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur le pad 9, 10
ou 11. Les fonctions suivants sont disponibles :
Pan (Pad 9) : Chaque bouton permet de régler le panoramique de la piste logicielle correspondante (piste 1–32,
selon le bouton tourné et la banque sélectionnée).
Device (Pad 10) : Chaque bouton permet de commander des fonctions appareils pour la piste logicielle
correspondante (piste 1–32, selon le bouton tourné et la banque sélectionnée).
Sends (Pad 11) : Chaque bouton permet de commander les niveaux des départs auxiliaires pour la piste logicielle
correspondante (piste 1–32, selon le bouton tourné et la banque sélectionnée).
Utilisation de raccourcis DAW avec les pads
Nota: No todos los parámetros están disponibles en todas las DAW.
En mode DAW, appuyer sur un pad transmet un message d’activation des notes afin que vous puissiez déclencher
un synthétiseur ou un échantillon dans votre logiciel. Cependant, vous pouvez également maintenir la touche Shift
enfoncée et appuyer sur les pads 13, 14, 15 ou 16 pour exécuter les commandes suivantes :
Save (Pad 13) : Ce pad permet de sauvegarder les modifications au fichier ouvert dans votre DAW.
Quantize (Pad 14) : Ce pad permet de quantifier la région audio sélectionnée dans votre DAW.
Undo (Pad 15) : Ce pad permet de supprimer la dernière modification apportée au fichier dans votre DAW.
View (Pad 16) : Ce pad permet d’alterner entre différentes fenêtres (p. ex., Mix ou Edit) de votre DAW.
Important : Afin que ces raccourcis fonctionnent avec votre DAW, PC doit être réglé sur Win (Windows) ou Mac
dans le menu des réglages principaux de l'Oxygen Pro 49. Pour afficher le menu des réglages principaux, maintenez
la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur la touche Mode. Utilisez l'encodeur Select/Scroll pour ajuster le réglage
en fonction de votre type d'ordinateur (PC), puis appuyez sur la touche Back pour quitter le menu.
37
Page 38

Utilisation de mappages personnalisés
L’Oxygen Pro 49 dispose de nombreuses commandes entièrement personnalisables, et grâce à la
possibilité de créer et d'enregistrer des mappages de clavier, vous pouvez stocker différents mappages
pour différents DAW, plug-ins ou différentes prestations qui peuvent être modifiés à la volée.
En mode Preset, il y a 16 préréglages de disponibles sur le clavier (1–16). Un préréglage est un ensemble
d’assignations MIDI pour les commandes de l’Oxygen Pro 49 qui peut être sauvegardé dans la mémoire
interne du clavier pour que vous puissiez les charger ultérieurement. Les préréglages peuvent être modifiés
lorsque le clavier est en mode Preset Edit. En plus d'avoir ces 16 préréglages sur le clavier, vous pouvez
utiliser le logiciel Preset Editor fourni pour sauvegarder un nombre illimité de préréglages sur votre
ordinateur et modifier les 16 préréglages qui sont actuellement sauvegardés dans la mémoire interne du
clavier.
Lorsque le mode DAW est sélectionné, l’option User vous permet de créer un mappage personnalisé pour
le clavier qui comprend non seulement des messages MIDI, mais également des messages Mackie ou
Mackie/HUI. Cela vous permet de mapper des commandes de clavier avec des commandes pour la DAW
(comme sauvegarder ou mettre en sourdine) en plus de mapper des commandes de clavier avec des
affectations MIDI pour les paramètres d'instrument/plug-in dans le DAW. Le réglage User DAW peut être
modifié lorsque le clavier est en mode DAW Edit. En plus d'avoir le User DAW sur le clavier, vous pouvez
utiliser le logiciel Preset Editor fourni pour sauvegarder un nombre illimité de User DAW sur votre ordinateur
et modifier celui qui est actuellement sauvegardé dans la mémoire interne du clavier.
Pour accéder au mode Preset Edit, vous devez d'abord sélectionner le préréglage que vous souhaitez
modifier (comme décrit dans la section Installation > Réglage du mode de fonctionnement du clavier).
Maintenez ensuite la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur la touche Preset.
Pour accéder au mode DAW Edit, maintenez la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur la touche DAW.
Pour quitter le mode Edit et sauvegarder les modifications, appuyez sur la touche Preset (lors du
réglage des préréglages) ou la touche DAW (lors du réglage du User DAW).
Si vous avez effectué des modifications, un message s’affichera vous demandant si vous souhaitez les
sauvegarder. Utilisez l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour sélectionner Cancel (annuler), Replace (remplacer) ou
Save As (enregistrer sous). Sélectionner Cancel vous ramène au mode Edit, alors que Replace sauvegarde
le préréglage sans changer son nom. Sélectionner Save As permet de sauvegarder le préréglage sous un
autre nom et un autre numéro d’emplacement de sauvegarde. Si vous devez supprimer un caractère lors de
la modification du nom, maintenez la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur la touche Back.
Pour obtenir plus d’information sur l'utilisation du logiciel Preset Editor, veuillez consulter le guide
d'utilisation livré avec le logiciel.
38
Page 39

Utilisation des fonctions internes du clavier
Les fonctions claviers suivantes sont disponibles uniquement lorsque le clavier est en mode DAW ou en
mode Preset.
Remarque : Pour commander les fonctions de l'arpégiateur, du mode Chord ou du mode Scale décrites
dans les sections suivantes, les touches de fonction sous les curseurs doivent être réglées sur leur mode
principal. Les touches de fonction sont définies sur leur mode principal lorsqu'aucune DEL à côté de la
touche Mode n'est allumée. Si les touches de fonction ne sont pas définies sur leur mode principal,
appuyez sur la touche Mode autant de fois que nécessaire afin que toutes les DEL à droite de la touche
Mode soient éteintes.
Dans les sections suivantes, le fonctionnement des DEL décrit pour les touches de fonction suppose
qu'elles sont définies sur leur mode principal.
Répétition de la note
Lorsque cette fonction est activée, appuyer sur un des pads permet de répéter son message d’activation
des notes selon les réglages du tempo et de la division temporelle du clavier. Chaque note répétée aura la
durée sélectionnée dans le réglage de la division temporelle. Pour plus d’information sur la modification des
réglages du tempo et de la division temporelle, veuillez consulter la section Réglage du tempo et de la
division temporelle du clavier.
La touche de répétition de la note peut être définie comme momentanée ou verrouillée.
Pour utiliser momentanément la répétition de la note, maintenez la touche Note Repeat enfoncée et
appuyer sur un pad. Tant que vous maintenez la touche Note Repeat, la note jouée par le pad se répétera.
Pour verrouiller la fonction Note Repeat, maintenez la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur la touche
Note Repeat. Si vous appuyez sur un pad, la note qui lui est assignée se répétera sans que vous ayez à
maintenir la touche Note Repeat enfoncée.
Pour désactiver la fonction Note Repeat, appuyez de nouveau sur la touche Note Repeat.
Remarque : Lorsque la fonction Note Repeat est active, utilisez l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour changer le
réglage de la division temporelle de l'arpégiateur et de la fonction Note Repeat du pad.
Arpégiateur
Lorsque l'arpégiateur est activé, le clavier jouera à plusieurs reprises les touches enfoncées dans l'ordre. La
synchronisation et le rythme de l'arpégiateur sont basés sur le réglage de division temporelle du clavier et
sur le réglage de tempo du clavier ou de votre DAW. Chaque note de l'arpège a la durée telle que définie
par le réglage de la division temporelle ; p. ex., si vous sélectionnez 1/4, chaque note de l'arpège sera une
noire. Veuillez consulter la section Réglage du tempo et de la division temporelle du clavier afin d’en
savoir plus sur la modification de ces réglages.
L'arpégiateur peut être utilisé dans l'un des deux modes :
• Momentané : Avec ce mode, l'arpégiateur joue des notes que tant que les touches sont enfoncées ;
lorsque les touches sont relâchées, l'arpégiateur s'arrête.
• Verrouillé : Avec ce mode, l'arpégiateur joue des notes lorsque les touches sont enfoncées, et continue
de les jouées même après qu’elles soient relâchées.
Pour activer et désactiver l’arpégiateur, appuyez sur la touche Arp. Lorsque l’arpégiateur est activé, la
DEL de la touche est allumée.
Pour alterner entre le mode de fonctionnement momentané et verrouillé, appuyez sur la touche Latch.
Lorsque le mode verrouillé est activé, la DEL de la touche est allumée.
Pour lancer un arpège, appuyez sur n'importe quelle touche pendant que l'arpégiateur est activé.
Pour lancer un nouvel arpège verrouillé alors qu'un arpège précédemment verrouillé est toujours en
cours de lecture, appuyez sur une nouvelle combinaison de touches.
39
Page 40

Pour ajouter des notes à un arpège verrouillé en cours de lecture, maintenez enfoncées les mêmes
touches que vous avez précédemment utilisées pour l'arpège tout en appuyant sur les touches des
nouvelles notes que vous souhaitez ajouter.
Pour modifier les réglages de l'arpégiateur, maintenez la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur la
touche Arp. Le menu Arpeggiator Edit s’affichera. Utilisez l'encodeur Select/Scroll pour modifier les
réglages (comme décrit dans la section Présentation de l’écran). Lorsque vous avez terminé de modifier
les réglages, appuyez sur la touche Back pour quitter le menu Arpeggiator Edit.
Vous pouvez également maintenir Shift ou appuyer sur Shift et Bank < pour verrouiller les commandes du
bouton ARP du modificateur Shift tout en tournant les boutons 1–4 pour éditer certains paramètres mais
pas tous. L’écran actualise les réglages au fur et à mesure que vous effectuez les modifications.
Remarque : Lorsque la fonction Note Repeat est active, utilisez l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour changer le
réglage de la division temporelle de l'arpégiateur et de la fonction Note Repeat du pad.
Réglage du tempo et de la division temporelle du clavier
Les réglages du tempo et de la division temporelle de l’Oxygen Pro 49 déterminent la synchronisation et le
rythme des fonctions de répétition de la note et d'arpégiateur. Lorsque Clock est réglé sur Internal dans le
menu Tempo Edit, le tempo du clavier peut être tapé ou saisi manuellement à partir du menu Tempo Edit.
Lorsque Clock est réglé sur External, le tempo du clavier se synchronise automatiquement avec le tempo
de votre DAW.
Pour taper le tempo du clavier, tapez sur la touche Tempo deux ou trois fois au rythme (BPM) désiré.
L’écran actualise le tempo au fur et à mesure que vous tapez la touche.
Remarque : Afin de taper le tempo dans le menu du clavier, le réglage Clock du clavier dans le menu
Tempo Edit doit être sur Internal. Lorsqu’il est réglé sur External, le tempo du clavier se synchronise
automatiquement avec le tempo de votre DAW.
Pour afficher le menu Tempo Edit, maintenez la touche Tempo enfoncée. Utilisez l'encodeur
Select/Scroll pour modifier le réglage Clock ou entrer un tempo de clavier interne (20.0–240.0). Lorsque
vous avez terminé de modifier les réglages, appuyez sur la touche Back pour quitter le menu Tempo Edit.
Veuillez consulter la section Présentation de l’écran pour plus d’informations sur comment utiliser
l’encodeur Select/Scroll avec les menus Edit.
Pour définir la division temporelle du clavier, appuyez sur une des touches de division temporelle pour
modifier le réglage (comme indiqué au-dessus/en dessous des touches). Appuyez deux fois sur la touche si
vous souhaitez utiliser une division ternaire. Lorsqu'une division temporelle standard est sélectionnée, la
touche correspondante s'allume. Lorsqu'une division ternaire est sélectionnée, la touche correspondante
s'allume.
Remarque : Lorsque la fonction Note Repeat est active, utilisez l’encodeur Select/Scroll pour changer le
réglage de la division temporelle de l'arpégiateur et de la fonction Note Repeat du pad.
40
Page 41

Mode Chord
Lorsque vous activez le mode Chord, appuyer sur une seule touche ou pad permet de jouer un accord
complet plutôt qu'une seule note. La touche ou pad sur laquelle vous appuyez déterminera la note
fondamentale de l'accord et le type d'accord sélectionné dépendra des réglages actuels.
La fonction d'accord peut être utilisée dans l'un des deux modes en tournant l'encodeur Select/Scroll qui
détermine l'accord exact attribué à chaque touche :
• Mode Smart : Dans ce mode, vous assignerez d'abord une note au clavier (p. ex., ré mineur). Ensuite,
vous assignerez la disposition d’accords (voicings) souhaitée (quels intervalles seront inclus dans
l'accord, p. ex., 1-3-5). La disposition d'accord de chaque touche sera alors automatiquement
enharmonique avec la note sélectionnée.
• Mode Custom : Ce mode permet de déterminer la structure de l’accord qui sera assignée à chaque
touche en la jouant manuellement. P. ex., si vous sélectionnez ce mode et jouez un accord 1-b3-5-b7,
chaque touche sera alors assignée à jouer cette structure d'accord. La note de la touche sur laquelle
vous appuyez servira de note fondamentale de l'accord.
Pour activer ou désactiver le mode Chord, appuyez sur la touche Chord. Lorsque le mode Chord est
activé, la touche Chord est allumée.
Pour modifier les réglages du mode Chord, maintenez d'abord la touche Shift enfoncée puis appuyez
sur la touche Chord pour afficher le menu Chord Edit. Utilisez ensuite l'encodeur Select/Scroll pour
modifier les réglages (comme décrit dans la section Présentation de l’écran). Lorsque vous avez terminé
de modifier les réglages, appuyez sur la touche Back pour quitter le menu Chord Edit.
Vous pouvez également maintenir la touche Shift enfoncée tout en appuyant sur les touches C2–Bb3 en
mode Smart Chord.
Remarque : Par défaut, les touches du clavier sont réglées pour jouer des accords lorsque le mode Chord
est activé. Cependant, ce réglage peut être modifié dans le menu des réglages principaux de sorte que
lorsque le mode Chord est actif, les accords soient joués sur les touches, les pads ou les deux.
Mode Scale
Avec le mode Scale, vous pouvez définir le clavier pour que les touches en dehors des notes d'une gamme
musicale sélectionnée soient désactivées. Cela vous permet de jouer dans une gamme choisie sans risque
de jouer de « fausses » notes. Vous pouvez choisir parmi 16 options différentes lors de l'assignation d'une
gamme au clavier.
Pour activer ou désactiver le mode Scale, appuyez sur la touche Scale. Lorsque le mode Scale est
activé, la touche Scale est allumée.
Pour déterminer quelle gamme musicale est assignée au clavier, affichez le menu Scale Edit en
maintenant la touche Shift enfoncée et en appuyant sur la touche Scale. Utilisez ensuite l'encodeur
Select/Scroll pour modifier les réglages (comme décrit dans la section Présentation de l’écran). Lorsque
vous avez terminé de modifier les réglages, appuyez sur la touche Back pour quitter le menu Scale Edit.
Menu des réglages principaux
Le menu des réglages principaux permet de personnaliser certaines des commandes par défaut du clavier.
Ces paramètres s'appliquent au clavier en mode DAW et en mode Preset, et toutes les modifications
apportées à partir du menu des réglages principaux seront sauvegardées après la mise hors tension du
clavier.
Pour afficher le menu des réglages principaux, maintenez la touche Shift enfoncée et appuyez sur la
touche Mode. Utilisez l'encodeur Select/Scroll pour modifier les réglages (comme décrit dans la section
Présentation de l’écran).
Pour quitter le menu des réglages principaux, appuyez sur la touche Back.
41
Page 42

Guida per l’uso (Italiano)
Introduzione
Contenuti della confezione
Oxygen Pro 49
Cavo USB
Scheda per il download del software
Guida per l’uso
Istruzioni di sicurezza e garanzia
Assistenza
Recarsi alla pagina m-audio.com per visualizzare e scaricare la documentazione più recente,
requisiti di sistema e altre informazioni in merito a questo prodotto.
Per ulteriore assistenza sul prodotto, recarsi alla pagina m-audio.com/support.
Configurazione
Per iniziare a utilizzare l’Oxygen Pro 49, occorre collegare il dispositivo, configurare adeguatamente il
software e impostare la modalità operativa della tastiera.
Per collegare l’Oxygen Pro 49 al computer, servirsi del cavo USB in dotazione. Collegare il capo
USB-B del cavo alla tastiera e il capo USB-A al computer (o a un hub USB collegato al computer).
Nota bene: oltre a inviare i dati, il cavo USB alimenta la tastiera. Se si desidera collegare l’Oxygen
Pro 49 a un hub USB cui sono collegati altri dispositivi, si consiglia di utilizzare un hub USB
alimentato.
Per configurare il DAW in modo tale che funzioni con l’Oxygen Pro 49, abilitare l’Oxygen Pro 49
come superficie di comando MIDI nell’apposito menu impostazioni del DAW (Preferiti, Opzioni,
Configurazione dispositivo, ecc.).
Se si utilizzerà l’Oxygen Pro 49 con il software MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition in
dotazione o conl’Ableton Live Lite, si veda Installazione del software in dotazione per istruzioni
più specifiche sulla configurazione DAW with Oxygen Pro 49. Se si utilizzerà un DAW diverso,
consultare il manuale per l’uso fornito con il DAW per ulteriore aiuto con questo passaggio.
Se si utilizzerà l’Oxygen Pro 49 con un sintetizzatore hardware anziché con il computer, collegare la
porta MIDI Out dell’Oxygen Pro 49 a un sintetizzatore con un cavo MIDI standard a 5 poli. Quindi
assicurarsi che l’Oxygen Pro 49 sia impostato per operare con uno dei suoi preset personalizzati
selezionato (come indicato in Impostazione della modalità operativa della tastiera) e che l’Oxygen
Pro 49 sia configurato per inviare dati MIDI dalla porta di uscita MIDI a 5 poli sotto le Impostazioni
Globali. Per poter utilizzare un sintetizzatore hardware esterno, si dovrà collegare l’Oxygen Pro 49 a
un computer, laptop, o a un hub USB alimentato.
42
Page 43

Installazione del software in dotazione
Con l’Oxygen Pro 49 abbiamo incluso MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition e Ableton Live Lite
in modo da poter iniziare subito a fare musica con software professionale. Inoltre, abbiamo incluso un set di
Pacchetti espansione e plugin AIR per strumenti virtuali da utilizzare con il proprio DAW.
Per scaricare il software MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition o Ableton Live Lite in
dotazione, registrare il proprio Oxygen Pro 49 su m-audio.com e seguire le istruzioni per l’installazione
presenti nel proprio account utente. Se si desidera utilizzare l’Ableton Live Lite, si raccomanda di recarsi
alla pagina ableton.com per verificare l’eventuale disponibilità di aggiornamenti del software. Per ottenere
aiuto nella configurazione di un DAW con l’Oxygen Pro 49, si veda Configurazione
Audio Edition
Per scaricare i plugin AIR per strumento virtuale in dotazione, seguire le istruzioni presenti sulla scheda
di download del software contenuta nella confezione. In seguito all’installazione, la maggior parte dei DAW
non caricherà automaticamente i plugin per strumenti virtuali; potrebbe essere necessario scegliere
manualmente una cartella per i plug-in che possa essere scansionata dal software. Le cartelle dei plugin per
Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition e Ableton Live Lite dipendono dal proprio sistema operativo, come
indicato qui di seguito.
Cartelle plugin di Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition/AAX:
• Windows (32-bit): C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• Windows (64-bit): C:\Program Files\Common Files\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Application Support/Avid/Audio/Plug-Ins
Plugin Ableton/VST :
• Windows (32-bit): C:\Program Files (x86)\VSTplugins
• Windows (64-bit): C:\Program Files\VSTplugins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Plugins/VST
Per configurare la cartella dei plugin in Ableton Live Lite:
1. Recarsi al menu Preferiti.
2. Selezionare la scheda Cartella file (File Folder). Sotto Plug-In Sources, fare clic su Browse e selezionare la
giusta cartella plugin (come indicato in alto).
3. Dopo aver effettuato la scelta, il tasto Use VST Custom Plug-In Folder dovrebbe essere attivo. Se non
lo è, cliccare sul tasto per attivarlo. Si può quindi uscire dal menu Preferiti.
Setup o Configurazione Ableton Live Lite Setup qui di seguito.
Pro Tools | First M-
43
Page 44

Configurazione Ableton Live Lite
1. Innanzitutto, collegare l’Oxygen Pro 49 al computer. Quindi lanciare Ableton Live Lite.
2. Aprire la finestra Preferiti di Ableton Live Lite. Se si utilizza un Mac, recarsi su Live > Preferences. Se
si utilizza un PC, recarsi su Opzioni > Preferiti.
3. Selezionare la scheda Link / MIDI a sinistra. Sotto la sezione Porte MIDI, regolare le impostazioni
come segue:
Sotto Superfici di controllo, per Ingresso e Uscita selezionare Oxygen Pro 49.
Vicino a Ingresso: Oxygen Pro 49, selezionare On nelle colonne Track e Remote.
Vicino a Uscita: Oxygen Pro 49, selezionare On nelle colonne Track e Remote.
4. Chiudere la finestra Preferences (Preferiti).
5. Per aggiungere uno strumento o un plugin da attivare con l’Oxygen Pro 49, selezionare Instruments o
Plug-ins sotto la colonna Categorie.
6. Nella colonna Name a destra della colonna Categories, individuare lo strumento o il plugin desiderato.
Cliccare e trascinare lo strumento su una traccia MIDI in Ableton Live Lite per caricarlo.
Lo strumento può ora essere attivato con l’Oxygen Pro 49.
Configurazione di Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition
1. Collegare l’Oxygen Pro 49 al computer. Lanciare Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition.
2. Selezionare Apri o Crea progetto.
3. Selezionare il menu a discesa Setup e aprire MIDI Input Devices (dispositivi di ingresso MIDI). Abilitare
MIDI Input da Oxygen Pro 49 facendo clic sulla casella accanto all’Oxygen Pro 49.
4. Creare una nuova traccia strumentale selezionando il menu a discesa Track e facendo clic su New.
5. Nel menu a discesa New, selezionare Stereo e quindi Instrument Track.
6. Nella nuova traccia creata, aggiungere un inserto alla traccia facendo clic su Inserts A-E della traccia
stessa e selezionando Multichannel Plugin > Instrument. Selezionare lo strumento che si desidera
utilizzare come Xpand!2 (Stereo).
Il plugin può ora essere attivato con l’Oxygen Pro 49.
Preset Editor
Per scaricare il software Preset Editor in dotazione, seguire le istruzioni presenti sulla scheda di
download del software contenuta nella confezione. Questo software può essere utilizzato per creare
mappature MIDI personalizzate da caricare sull’Oxygen Pro 49. Per maggiori informazioni sull’uso della
tastiera con uno dei preset personalizzati selezionati, si veda il seguente paragrafo e Operazione > Uso
delle mappature personalizzate. Il Preset Editor è inoltre fornito con la propria Guida per l’uso specifica.
44
Page 45

Impostazione della modalità operativa della tastiera
Una volta impostato l’Oxygen Pro 49 in modo da farlo funzionare con il proprio DAW, occorre impostare la
modalità operativa della tastiera. Scegliendo la modalità operativa è possibile impostare la tastiera in modo
che si coordini automaticamente con le caratteristiche del proprio DAW o configurarla in modo che funzioni
come un controller personalizzato. Con queste due modalità, l’Oxygen Pro 49 offre l’opzione di passare
rapidamente dal controllo di un plugin al controllo del DAW con il semplice tocco di un pulsante.
Le due modalità di funzionamento determinano il funzionamento dei comandi editabili della tastiera MIDI:
• DAW: in modalità DAW i comandi della tastiera saranno
manopole e pad nel proprio DAW.
• Preset: in modalità Preset, i comandi modificabili della tastiera possono essere impostati su funzioni
progettate personalmente. Una serie di mappature di singoli preset può essere creata e salvata nella
memoria interna della tastiera per poi essere caricata in un secondo momento.
Per impostare la tastiera in modo che funzioni in modalità DAW, premere il tasto DAW. Il tasto sarà
illuminato per mostrare che la modalità DAW è stata selezionata.
Per cambiare il controllo di quale DAW la tastiera è impostata:
1. Premere e tenere premuto il tasto DAW per aprire il menu DAW Select a Display.
2. Girare il comando Select/Scroll Encoder per scorrere lungo i DAW disponibili a Display. Mentre si gira
l’encoder, il DAW selezionato correntemente si aggiornerà a Display. L’opzione Utente consente di
mappare comandi DAW personalizzati sulla tastiera, come descritto in Operazione > Uso delle
mappature personalizzate.
3. Quando il DAW desiderato compare a Display, premere il comando Select/Scroll Encoder per
confermare la scelta.
Nota bene: per uscire dalla modalità DAW senza cambiare il DAW attualmente selezionato, premere il
tasto Back.
Per impostare la tastiera in modo che funzioni in moalità Preset, premere il tasto Preset. Il tasto sarà
illuminato per mostrare che la modalità Preset è stata selezionata.
Per cambiare il preset attualmente selezionato:
1. Premere e tenere premuto il tasto Preset per aprire il menu Preset Select a Display.
2. Girare il comando Select/Scroll Encoder per scorrere lungo i Preset disponibili a Display. Mentre si
gira l’encoder, il preset selezionato correntemente si aggiornerà a Display.
3. Quando il preset desiderato compare a Display, premere il comando Select/Scroll Encoder per
confermare la scelta. Si veda Operazione > Uso delle mappature personalizzate per maggiori
informazioni sulla mappatura dei Preset.
mappati automaticamente su cursori, tasti,
45
Page 46

Caratteristiche
Pannello superiore
22
2
3
4
Nota bene: le scritte tra virgolette che accompagnano i comandi della tastiera indicano funzioni secondarie
cui è possibile accedere premendo Shift mentre si utilizza il comando.
1. Tastiera: questa tastiera sensibile alla velocità è il metodo principale per l’invio di dati MIDI Note
On/Off. Oltre a essere sensibile alla velocità, la tastiera include anche l’aftertouch di canale; ciò significa
che è possibile influire sul suono prodotto dal plugin di uno strumento virtuale variando la pressione
applicata sul tasto dopo una pressione iniziale su di esso.
Tenere premuto Shift e premere i tasti C2–Bb3 per modificare le impostazioni della modalità Accordo.
Si veda Operazione > Utilizzo delle funzioni interne della tastiera per saperne di più su questa
funzione.
2. Tasti ottava: premere questi tasti per regolare l’intervallo del pitch dei tasti di un’ottava in alto o in
basso. Tenere premuto Shift e premere questi tasti per regolare l’intervallo del pitch dei tasti di un
semitono in alto o in basso. La tastiera può essere alzata fino a quattro ottave o abbassata a tre ottave
rispetto alla sua gamma di ottave predefinita e di un totale di dodici semitoni dalla sua trasposizione
predefinita.
Per riportare l’Oxygen Pro 49 alla sua gamma di ottave e alla sua trasposizione predefinite (C2–C4 sulla
tastiera), premere contemporaneamente i tasti Octave - e Octave +.
3. Rotella di bend del pitch: alzare o abbassare questa rotella partendo dalla posizione centrale per
effettuare il bend del pitch della tastiera mentre si suona. L’intervallo predefinito di bend del pitch varia
a seconda del sintetizzatore software. La rotella è a molla e tornerà alla posizione centrale quando
rilasciata.
4. Rotella di modulazione: girare questa rotella per inviare dati controller continui—MIDI CC #01
(modulazione), in via predefinita.
25
10
18
17
11 12
14
19
15 16
13
23
20
21
5
6
7
9
8
1
46
Page 47

5. Tasto DAW: premere questo tasto per configurare l’Oxygen Pro
49 affinché operi in modalità DAW. Premere e tenere premuto il
tasto per aprire il menu DAW Select a Display.
Tenere premuto Shift e premere questo tasto per modificare e
creare il proprio preset DAW. Dopo aver modificato il DAW
Utente, premere nuovamente questo tasto per salvare le
modifiche sul DAW Utente.
Si veda Setup > Impostazione della modalità operativa della
tastiera per maggiori informazioni DAW Mode. Si veda
Operazione > Uso delle mappature personalizzate per
informazioni sulla mappatura User preset.
6. Tasto Preset: premere questo tasto per configurare l’Oxygen Pro 49 affinché operi in modalità Preset.
Premere e tenere premuto il tasto per aprire il menu Preset Select a Display.
Tenere premuto Shift e premere questo tasto per modificare un Preset. Dopo aver modificato uno dei
preset, premere nuovamente questo tasto per salvare le modifiche sul preset corrente.
Si veda Setup > Impostazione della modalità operativa della tastiera per maggiori informazioni sulla
modalità Preset. Si veda Operazione > Uso delle mappature personalizzate per informazioni sulla
mappatura di un preset.
7. Display: la schermata principale del Display mostra lo stato dell’ultimo comando utilizzato. Servirsi di
questa schermata per monitorare i livelli dei parametri mentre si regolano i comandi sulla tastiera.
Servirsi inoltre del Display con il comando Select/Scroll Encoder per visualizzare e modificare le
impostazioni della tastiera. Per maggiori informazioni, si veda Operazione > Panoramica del display
Display.
8. Select/Scroll Encoder: se ci si trova in uno dei menu di modifica (Edit) del Display, girare questo
codificatore per modificare le impostazioni/i parametri e premerlo per confermare una scelta.
Se non si visualizza alcuno dei menu di modifica (Edit), girando il codificatore e premendolo, si vedrà
ciascuna funzione sotto forma di comandi MIDI distinti. Quando si lavora con un DAW, i comandi
assegnati saranno predeterminati. Quando si lavora con un preset o con il DAW Utente selezionato, i
comandi possono essere modificati.
9. Tasto Back: se ci si trova in uno dei menu di modifica (Edit) del Display, premere questo tasto per
tornare alla schermata principale.
Se non si visualizza uno dei menu di modifica (Edit), questo tasto sarà assegnato a un comando.
Quando si lavora con un DAW, i comandi assegnati saranno predeterminati. Quando si lavora con un
preset o con il DAW Utente selezionato, i comandi possono essere modificati. Al momento di
modificare il nome di un Preset o di un DAW, premere il tasto Shift e il tasto Back per cancellare una
lettera.
10. Tasto Shift: tenere premuto il
tastiera per accedere alle rispettive funzioni secondarie.
11. Tasto <<: a seconda di quale schermo viene selezionato nel DAW, questo tasto riavvolgerà la canzone
aperta o si muoverà verso il basso nella finestra attiva.
12. Tasto >>: a seconda di quale schermo viene selezionato nel DAW, questo tasto farà avanzare
rapidamente la canzone aperta o si muoverà verso l’alto nella finestra attiva.
13. Tasto Loop: premere questo tasto per attivare/disattivare la funzione di loop nel DAW.
14. Tasto Stop: premere questo tasto per fermare la canzone aperta nel DAW. Premere due volte questo
tasto per fermare la canzone aperta e far tornare la testina di riproduzione all’inizio della canzone.
Premere Shift e questo tasto per inviare un messaggio MIDI panic per spegnere tutti i messaggi Note e
azzerare tutti i comandi.
15. Tasto di riproduzione (Play): premere questo tasto per riprodurre la canzone aperta nel DAW.
16. Tasto di registrazione (Record): premere questo tasto per attivare la registrazione nel DAW.
tasto Shift mentre si muovono o si premono i comandi o i tasti sulla
5
10
9
6
7
18
11 12
8
14
17
15 16
19
13
47
Page 48

17. Tasti Bank (banco): se si lavora in modalità DAW o su uno dei preset personalizzati, servirsi di questi
tasti per commutare il banco attualmente selezionato per cursori, manopole, pad e tasti funzione.
Sono presenti quattro banchi per questi comandi, che offrono l’equivalente di 36 cursori, 32 manopole,
e 64 pad. Premere Shift e il tasto Bank < per bloccare i comandi di modifica Shift della manopola ARP.
Questo è utile per modificare i parametri ARP durante un’esibizione dal vivo. Premere Shift e il tasto
Bank > per bloccare i comandi di modifica Shift dei Pad. Questo è utile per apportare modifiche
durante il mixaggio di una canzone. Per far tornare manopole o pad alla loro modalità normale, premere
il tasto Shift e il tasto Bank < o Bank >.
18. Tasto tempo: toccare questo tasto per impostare il tempo dell’Oxygen Pro 49 oppure tenerlo premuto
per far comparire il menu Tempo Edit a Display, dove si può utilizzare Select/Scroll Encoder per
inserire manualmente il tempo e scegliere di sincronizzare il tempo dell’Oxygen Pro 49 con il proprio
DAW. L’impostazione del tempo influisce sulle funzioni di arpeggiatore e note repeat della tastiera. Si
veda Operazione > Utilizzo delle funzioni interne della tastiera per maggiori dettagli.
Tenere premuto Shift e premere questo tasto per accendere o spegnere la funzione di metronomo del
DAW.
19. Tasto Note Repeat: premere questo tasto per attivare la funzione note repeat dei pad. Per bloccare o
sbloccare la funzione note repeat, tenere premuto Shift e premere questo tasto. Quando Note Repeat
è attivo, servirsi dello Select/Scroll Encoder per modificare le impostazioni di Time Division correnti
dell’Arpeggiatore e del pad Note Repeat. Per bloccare o sbloccare la funzione note repeat, tenere
premuto Shift e premere questo tasto. Si veda Operazione > Utilizzo delle funzioni interne della
tastiera per maggiori informazioni su Note Repeat.
20. Pad (1–16): servirsi di questi pad sensibili alla velocità per inviare messaggi MIDI Note On/Off o
eseguire altre assegnazioni MIDI (se si utilizza un preset o il DAW Utente). Tenere premuto Shift mentre
si premono i
Pad 9–11 per riassegnare la funzione delle manopole e tenere premuto shift mentre si
premono i Pad 13–16 per utilizzare le scorciatoie del DAW (si veda Operazione > Uso dei comandi
secondari in modalità DAW per saperne di più).
21. Pad Row Play: premere questo tasto per suonare gli audio clip assegnati a ciascun pad presente nella
corrispondente fila di pad. A seconda del DAW, questi tasti avranno diverse funzioni.
22. Cursori (1–9): spingere questi cursori in alto/in basso per eseguire i comandi ad essi assegnati. Quando
si lavora con un DAW, i comandi assegnati saranno predeterminati. Quando si lavora con un preset o
con il DAW Utente selezionato, i comandi possono essere modificati.
23. Manopole (1–8): girare queste manopole a destra/sinistra per eseguire i comandi ad esse assegnati.
Quando si lavora con un DAW, i comandi assegnati saranno predeterminati. Quando si lavora con un
preset o con il DAW Utente selezionato, i comandi possono essere modificati.
Si veda Operazione > Uso dei comandi secondari in modalità DAW per sapere come modificare le
assegnazioni predeterminate delle Manopole quando si lavora in modalità DAW con un DAW
selezionato.
Tenere premuto Shift mentre si girano le manopole 1–4 per modificare le impostazioni dell’arpeggiatore. Si veda
Utilizzo delle funzioni interne della tastiera per saperne di più sull’arpeggiatore.
Importante: sia i cursori che le manopole sono abilitati con un’ ”assunzione di controllo morbida”.
Ciò significa che se si cambia banco, il cursore o la manopola non funzionerà fino a quando non sarà
posizionato sul valore corrente del nuovo comando software selezionato. Ad esempio, se si muove il
Cursore 1 nel Banco 1 e poi si passa al Banco 2, il Cursore 1 fisico non influirà sul cursore software 10
fino a quando quello fisico non sarà posizionato sul valore corrente del cursore software 10. Questa
funzione consente di apportare modifiche a un banco e quindi cambiare banco senza apportare
modifiche indesiderate ai comandi del nuovo banco. Il Display mostrerà un misuratore di valore a
quadri se un Cursore o una Manopola deve essere spostato prima di poter “assumere il controllo” del
comando ad esso assegnato (si veda Panoramica del display per un’illustrazione).
Importante: in Avid Pro Tools, le tracce stereo hanno due comandi di panning: sinistro e destro.
Premere il tasto Shift per far commutare le manopole tra il canale sinistro e quello destro. Se i comandi
di panning non si muovono lungo una traccia mono, premere il tasto Shift per riportare la manopola
pan al controllo normale del comando pan.
48
Page 49

24. Tasto modalità (con LED): premere il Tasto modalità per attivare una delle modalità secondarie per i
tasti funzione. Quando la tastiera è impostata per funzionare in modalità DAW, le modalità secondarie
disponibili per i tasti funzione sono Rec, Select, Mute e Solo; in queste modalità i tasti eseguono
funzioni predeterminate DAW channel Record Arm, Track Select, Mute, e Solo (si veda Operazione >
Uso dei comandi secondari in modalità DAW per saperne di più). Quando la tastiera è impostata per
funzionare in modalità Preset, la modalità secondaria disponibile per i tasti funzione è MIDI: in questa i
tasti eseguono comandi MIDI predeterminati in uno dei preset personalizzati.
I LED a destra del tasto Mode indicano in quale modalità si trovano i tasti funzione.
Tenere premuto Shift e premere il tasto modalità per avere accesso al menu impostazioni globali della
tastiera.
25. Tasti funzione (1-8): quando i tasti funzione sono impostati sulla loro modalità principale, controllano
le funzioni interne della tastiera come descritto qui di seguito:
Tasto ARP: premere questo tasto per attivare l’arpeggiatore. Tenere premuto Shift e premere
questo tasto per modificare le impostazioni dell’Arpeggiatore.
Tasto Latch: premere questo tasto per commutare l’arpeggiatore dalla modalità momentanea a
quella di blocco.
Tasto Chord: premere questo tasto per attivare la modalità di accordo Tenere premuto Shift e
premere questo tasto per modificare le impostazioni della modalità Accordo.
Tasto Scale: premere questo tasto per attivare la modalità di scala. Tenere premuto Shift e premere
questo tasto per modificare le impostazioni della modalità scala.
1/4–1/32T (tasti Time Division): utilizzare questi tasti per selezionare l’impostazione time division
della tastiera per le funzioni note repeat e arpeggiatore. Ciascuna pressione di uno di questi tasti
alterna tra il timing standard elencato sopra il tasto e il suo timing di terzina elencato sotto il tasto.
Un LED illuminato di rosso fisso mostra che è stato selezionato un timing standard, mentre un LED
lampeggiante mostra che è stato selezionato un timing a terzine.
Si veda Operazione > Utilizzo delle funzioni interne della tastiera per saperne di più sulle funzioni
mensionate in alto.
Pannello posteriore
1. Interruttore di alimentazione: servirsi di questo
interruttore per accendere e spegnere l’Oxygen Pro 49.
2. Ingresso pedale sustain: questo ingresso accoglie un
pedale a contatto momentaneo (non in dotazione).
Quando premuto, questo pedale sostiene in via
predefinita il suono riprodotto senza dover continuare a
premere i tasti con le dita. L’ingresso del pedale sustain
può essere rimappato per eseguire un’assegnazione MIDI
personalizzata.
Nota bene: la polarità del pedale sustain è determinata dalla tastiera all'avviamento. Quando una
tastiera Oxygen Pro 49 si sta accendendo, si suppone che il pedale sustain sia in posizione "sollevata"
(Off). È importante che il pedale sustain non sia in posizione abbassata prima di avviare la tastiera, in
quanto il pedale in quel caso funzionerà al contrario e le note saranno sostenute quando il pedale non
viene premuto.
3. Porta USB: quando collegata a un computer, la porta USB fornisce alimentazione alla tastiera e
trasmette dati MIDI.
4. Uscita MIDI: servirsi di un cavo MIDI standard a 5 poli per collegare questa porta a un sintetizzatore
hardware o ad un altro dispositivo MIDI.
Nota bene: la porta di uscita MIDI può inviare MIDI dall’Oxygen Pro 49, dal computer connesso o da
entrambi. Recarsi su Impostazioni Globali per stabilire cosa viene inviato all’uscita MIDI.
5. Connettore per lucchetto Kensington
Kensington standard per computer per la protezione contro i furti.
®
: questo connettore è compatibile con cavi di sicurezza
2
345
1
49
Page 50

Uso
Panoramica del display
Schermata principale
Mentre si utilizzano cursori, manopole, pad e tasti funzione della
tastiera durante l'esibizione, il Display si aggiorna con il banco corrente
per l’ultimo comando utilizzato, il nome/numero del comando, il livello
corrente applicato dal comando (00–127, se applicabile), e un misuratore
grafico che illustra il livello (se applicabile). Durante l’esibizione, la
schermata del Display avrà uno sfondo nero con scritte bianche.
Nota bene: il Display mostra il numero del comando software, che non corrisponde sempre al numero del
comando hardware sulla tastiera. Ad esempio, se la tastiera è impostata sul Banco 3 e si gira la Manopola
1 sulla tastiera, a Display comparirà la Manopola 20, in quanto la Manopola 1 hardware controlla la
Manopola software 20 quando la tastiera si trova sul Banco 3.
Come descritto in Caratteristiche > Pannello superiore, i Cursori e le
Manopole sono abilitati con un’assunzione di controllo morbida. Se i
banchi interruttori e un Cursore o una Manopola devono essere spostati
prima che possano assumere il controllo assegnatogli, il Display illustra la
situazione mostrando un misuratore grigio a scacchi sotto il livello del
comando. Come illustrato nell’esempio a destra, il banco è appena
passato al Banco 2 e il Cursore 1 deve essere alzato fino in cima per
poter iniziare a controllare il Cursore software 10.
Menu di modifica (Edit)
Oltre a mostrare gli ultimi comandi utilizzati durante l'esibizione, il Display (insieme allo Select/Scroll
Encoder) è lo strumento principale a disposizione dell’utente per modificare diverse impostazioni della
tastiera, incluse le assegnazioni MIDI per i comandi modificabili, le impostazioni per le funzioni interne della
tastiera (come l'arpeggiatore) e le impostazioni hardware globali.
Quando si entra in un menu Edit per qualsiasi funzione della tastiera, il
Display mostrerà il nome del menu Edit, un campo impostazioni
evidenziato per la modifica, un campo parametri che mostra lo stato
corrente delle impostazioni e blocchi grafici in fondo allo schermo per
indicare quante altre impostazioni sono disponibili nel menu Edit. Quando
entra in un menu Edit, il Display avrà uno sfondo bianco e scritte nere.
Per scorrere lungo le impostazioni in un menu Edit, girare Select/Scroll Encoder quando il campo
impostazioni è evidenziato.
Per selezionare un’impostazione da modificare, premere Select/Scroll Encoder quando il campo
impostazioni è evidenziato. Il campo del parametro sarà evidenziato.
Per modificare il parametro delle impostazioni, selezionare l’impostazione da modificare come descritto
in alto. Quindi girare Select/Scroll Encoder mentre il campo del parametro è evidenziato. Una volta
evidenziato il parametro desiderato, premere Select/Scroll Encoder per confermare la modifica. Il Display
tornerà a evidenziare il campo impostazioni.
Per uscire dal menu Edit senza salvare le modifiche, premere il tasto Back. Per uscire dal menu Edit e
salvare le modifiche, premere il tasto DAW (se si modifica il DAW Utente) o il tasto Preset (se si modifica
un Preset).
Nota bene: le impostazioni disponibili nel menu Edit possono cambiare a seconda di quali parametri
vengono selezionati. Ad esempio, il menu Modifica Arpeggiatore varia a seconda del parametro selezionato
per l’impostazione Tipo di arpeggiatore.
50
Page 51

Uso dei comandi secondari in modalità DAW
Laddove la modalità DAW è concepita in modo tale che non sia necessario utilizzare una mappatura complessa per
usare Oxygen Pro 49 con il proprio DAW, alcuni dei comandi della tastiera hanno diverse funzioni tra cui passare in
modalità DAW.
Modalità per i tasti funzioni
Quando la tastiera è configurata per funzionare in modalità DAW ed è selezionato un DAW, i tasti funzione possono
commutare tra cinque modalità diverse.
Per commutare la modalità per i tasti funzione, premere il tasto Mode a destra dei tasti funzione. A ciascuna
pressione, il LED del tasto mode cambierà a indicare quale modalità è attualmente selezionata. Sono disponibili le
seguenti modalità:
Primary (nessun LED): quando non ci sono LED accesi, i tasti funzione sono impostati sulle rispettive assegnazioni
primarie (stampate sopra/sotto ciascun tasto). Queste assegnazioni si riferiscono alle funzioni interne della tastiera:
arpeggiatore, note repeat, modalità accordo e modalità scala. Per maggiori informazioni sull’uso dei tasti funzione
con queste caratteristiche, si veda Utilizzo delle funzioni interne della tastiera.
Rec (LED rosso): quando impostato sulla modalità Record, ciascun tasto attiverà/disattiverà la registrazione della
traccia corrispondente nel DAW (tracce 1–32, a seconda di quale tasto viene premuto e di quale banco viene
selezionato).
Select (LED verde): in questa modalità, ciascuna manopola porterà in evidenza la traccia software corrispondente
(tracce 1–32, a seconda di quale manopola viene girata e di quale banco viene selezionato).
Mute (LED blu): in questa modalità, ciascun tasto silenzierà/annullerà il silenziamento della traccia software
corrispondente (tracce 1–32, a seconda di quale tasto viene premuto e di quale banco viene selezionato).
Solo (LED giallo): in questa modalità, ciascun tasto effettuerà un assolo della traccia software corrispondente (tracce
1–32, a seconda di quale tasto viene premuto e di quale banco viene selezionato).
Nota bene: la modalità MIDI è intesa per la mappatura MIDI personalizzata. Questa modalità è disponibile
unicamente quando la tastiera viene impostata per funzionare in modalità Preset.
Modifica della funzione delle manopole in modalità DAW
Nota bene: non tutti i parametri sono disponibili in tutti i DAW.
Durante il funzionamento in modalità DAW, le manopole possono svolgere una di tre funzioni.
Per modificare la modalità di funzionamento delle manopole, tenere premuto il tasto Shift e premere i Pad 9, 10
o 11. Sono disponibili le seguenti funzioni:
Pan (Pad 9): ciascuna manopola eseguirà il panning della traccia software corrispondente (tracce 1–32, a seconda
di quale manopola viene girata e di quale banco viene selezionato).
Dispositivo (Pad 10): ciascuna manopola controllerà i comandi del dispositivo della traccia software corrispondente
(tracce 1–32, a seconda di quale manopola viene girata e di quale banco viene selezionato).
Sends (Pad 11): Ciascuna manopola controllerà il livello degli aux send per la traccia software corrispondente
(tracce 1–32, a seconda di quale manopola viene girata e di quale banco viene selezionato).
Accesso alle scorciatoie del DAW con i Pad
Nota bene: non tutti i parametri sono disponibili in tutti i DAW.
In modalità DAW, la pressione di un pad invierà un messaggio Note On per poter attivare un sintetizzatore o un
campione nel proprio software. Tuttavia, è possibile tenere premuto Shift e premere i Pad 13, 14, 15 o 16 per
eseguire i seguenti comandi:
Save (Pad 13): salva le modifiche apportate al file attualmente aperto nel DAW.
Quantize (Pad 14): quantizza la regione audio attualmente selezionata nel DAW.
Undo (Pad 15): annulla l’ultima modifica apportata al file nel DAW.
View (Pad 16): commuta tra diverse finestre (ad es. Mix o Edit) per il DAW.
Importante: affinché queste scorciatoie funzionino con il DAW, il PC deve essere impostato su Win (Windows) o
Mac nel menu impostazioni globali dell’Oxygen Pro 49. Per entrare nel Menu impostazioni globali a Display, tenere
premuto Shift e premere il tasto Mode. Servirsi di Select/Scroll Encoder per regolare l’impostazione in base al
proprio tipo di PC, quindi premere il tasto Back per uscire dal menu.
51
Page 52

Uso delle mappature personalizzate
L’Oxygen Pro 49 ha numerosi comandi interamente personalizzabili e con la possibilità di creare e salvare
mappature della tastiera, è possibile memorizzare diverse mappature per DAW diversi, plugin o scenari che
possono essere modificati al volo.
Quando si lavora in modalità Preset, sulla tastiera sono disponibili 16 preset (1–16). Un preset è un gruppo
di assegnazioni MIDI per i comandi dell’Oxygen Pro 49 che possono essere salvate nella memoria interna e
caricate in un secondo momento. I preset possono essere modificati quando la tastiera si trova in modalità
Preset Edit. Oltre ad avere questi 16 preset sulla tastiera, è possibile utilizzare il software Editor in dotazione
per memorizzare un numero illimitato di preset sul computer e modificare i 16 che sono attualmente salvati
nella memoria interna della tastiera.
Quando si lavora in modalità DAW, l’impostazione Utente consente di creare una mappatura personalizzata
della tastiera che include non solo i messaggi MIDI, ma anche i messaggi Mackie o Mackie/HUI. Ciò
consente di mappare i comandi della tastiera con i comandi per il DAW stesso (come “Save” o “Mute”), oltre
a mappare i comandi della tastiera con assegnazioni MIDI per i parametri strumento/plug-in nell’ambito del
DAW. L’impostazione DAW Utente può essere modificata quando la tastiera si trova in Modalità Edit del
DAW. Oltre ad avere il DAW Utente sulla tastiera, è possibile utilizzare il software Editor in dotazione per
memorizzare un numero illimitato di DAW Utente sul computer e modificare quello attualmente salvato nella
memoria interna della tastiera.
Per entrare in modalità Preset Edit, selezionare innanzitutto il preset che si desidera modificare (così
come descritto in Setup > Impostazione della modalità operativa della tastiera). Quindi tenere premuto
Shift e premere il tasto Preset.
Per entrare in modalità di modifica del DAW, tenere premuto Shift e premere il tasto DAW.
Per uscire dalla modalità Edit e salvare le modifiche, premere il tasto Preset (se si stavano modificando
i preset) o il tasto DAW (se si stavano modificando le impostazioni DAW Utente).
Se sono state apportate modifiche, la schermata a Display chiederà se si desidera salvarle. Servirsi di
Select/Scroll Encoder per scegliere tra Cancel, Replace e Save As (annulla, sostituisci e salva con nome).
Selezionando Cancel si torna alla modalità Edit, mentre selezionando Replace il preset verrà salvato senza
cambiarne il nome. Selezionare Save As per salvare potendo rinominare e cambiando il numero di
ubicazione del preset utilizzando Select/Scroll Encoder. Per cancellare un carattere mentre si modifica il
nome, tenere premuto il tasto Shift e Back Button.
Per indicazioni nell’uso del Preset Editor, si veda la Guida per l’uso dell’editor fornita con il software.
52
Page 53

Utilizzo delle funzioni interne della tastiera
Le seguenti funzioni della tastiera possono essere utilizzate quando la tastiera è impostata per funzionare in
modalità DAW o Preset.
Nota bene: per poter controllare l’arpeggiatore, la modalità accordo o la modalità Scala descritte nei
seguenti paragrafi, i tasti funzione sotto i cursori sono stati impostati sulla loro modalità principale. I tasti
funzione sono impostati sulla loro modalità principale quando nessun LED a destra del tasto modalità è
acceso. Se i tasti funzione non sono impostati sulla loro modalità principale, premere il tasto modalità
tutte le volte necessarie, fino a quando nessun LED a destra del tasto modalità è acceso.
Nei seguenti paragrafi, il funzionamento del LED descritto per i tasti funzione presuppone che questi siano
impostati sulla loro modalità principale.
Note Repeat
Quando questa funzione è attivata, qualsiasi Performance Pad premuto ripeterà il suo messaggio Note On
a ritmo con il tempo corrente della tastiera e con le impostazioni di time division. Ciascuna nota ripetuta
sarà della lunghezza selezionata per l’impostazione di time division. Per maggiori indicazioni sulla modifica
del tempo e della time division, si veda Tempo e time division della tastiera.
La funzione note repeat può essere attivata momentaneamente o può essere bloccata.
Per utilizzare la funzione note repeat momentaneamente, tenere premuto il tasto Note Repeat, quindi
premere un pad. Finché si tiene premuto il tasto Note Repeat, la nota suonata dal pad verrà ripetuta.
Per bloccare la funzione note repeat, tenere premuto Shift e premere il tasto Note Repeat. La pressione
di qualsiasi pad farà sì che la nota ad esso assegnata venga ripetuta senza dover tenere premuto il tasto
Note Repeat.
Per spegnere la funzione Toggle/Latch, premere nuovamente il tasto Note Repeat.
Nota bene: Quando Note Repeat è attivo, servirsi dello Select/Scroll Encoder per modificare le
impostazioni di Time Division correnti dell’Arpeggiatore e del pad Note Repeat.
Arpeggiatore
Quando l’arpeggiatore viene attivato, la tastiera suonerà ripetutamente i tasti premuti in sequenza. Il timing e
il ritmo dell’arpeggiatore sono basati sull’impostazione della time division della tastiera e dall’impostazione
del tempo della tastiera o del DAW. Ciascuna nota dell’arpeggio sarà della lunghezza selezionata per
l’impostazione del time division; ad esempio, se si seleziona 1/4, ciascuna nota nell’arpeggio sarà una
semiminima. Si veda Tempo e time division della tastiera per indicazioni circa la modifica di queste
impostazioni.
L’arpeggiatore può essere utilizzato in una di due modalità:
• Momentary: l’arpeggiatore suona note solo per il tempo in cui i tasti vengono premuti; quando si
rilasciano i tasti, l'arpeggiatore si ferma.
• Latch: l’arpeggiatore suona note quando vengono premuti i tasti e continua a suonare anche quando si
staccano le dita dai tasti.
Per attivare o disattivare l’arpeggiatore, premere il tasto Arp. Quando l’arpeggiatore è attivo, il LED del
tasto sarà illuminato.
Per commutare tra le modalità momentary e latch, premere il tasto Latch. Quando la funzione di blocco
latch è attiva, il LED del tasto sarà illuminato.
Per avviare un arpeggio, premere qualsiasi tasto mentre l’arpeggiatore è attivato.
Per avviare un nuovo arpeggio bloccato mentre un arpeggio precedentemente bloccato sta
suonando, premere una nuova combinazione di tasti.
Per aggiungere note a un arpeggio bloccato mentre sta ancora suonando, tenere premuti gli stessi tasti
premuti in precedenza per l'arpeggio mentre si premono i tasti delle nuove note che si desiderano
aggiungere.
53
Page 54

Per modificare le impostazioni dell’arpeggiatore, tenere premuto Shift e premere il tasto Arp. Il Display
entrerà nel menu per la modifica dell’Arpeggiatore. Servirsi di Select/Scroll Encoder per regolare le
impostazioni (come descritto in Panoramica del display). Una volta conclusa la modifica delle
impostazioni, premere il tasto Back per uscire dal menu Modifica Arpeggiatore.
Alternativamente, è possibile tenere premuto Shift o premere Shift e Bank < per bloccare i controlli della
manopola ARP del modificatore Shift mentre si ruotano le manopole 1–4 per modificare alcune ma non
tutte le impostazioni. A Display compariranno le nuove impostazioni man mano che vengono modificate.
Nota bene: Quando Note Repeat è attivo, servirsi dello Select/Scroll Encoder per modificare le
impostazioni di Time Division correnti dell’Arpeggiatore e del pad Note Repeat.
Tempo e time division della tastiera
Le impostazioni di tempo e di time division dell’Oxygen Pro 49 determinano il timing e il ritmo per le funzioni
note repeat e arpeggiatore. Quando l’Orologio è impostato su Interno nella schermata Tempo Edit a
Display, il tempo della tastiera può essere battuto o inserito direttamente dalla schermata di Modifica del
Tempo. Quando l’Orologio è impostato su Esterno, il tempo della tastiera si sincronizzerà
automaticamente con il tempo del proprio DAW.
Per battere il tempo sulla tastiera, toccare il tasto Tempo due o più volte al BPM desiderato. Quando si
batte il tasto, il Display si aggiornerà mostrando il nuovo tempo.
Nota bene: per toccare nel menu della tastiera, l’impostazione dell’Orologio nel menu Modifica Tempo
deve essere su Interno. Se è impostato su Esterno, il tempo della tastiera si sincronizzerà con il proprio
DAW.
Per entrare nel menu Modifica Tempo a Display, premere e tenere premuto il tasto Tempo. Servirsi di
Select/Scroll Encoder per modificare l’impostazione dell’Orologio o per inserire un tempo interno della
tastiera (20.0–240.0). Una volta conclusa la modifica delle impostazioni, premere il tasto Back per uscire dal
menu Modifica Tempo. Si veda Panoramica del display per ulteriori indicazioni sull’uso di Select/Scroll
Encoder con i menu di modifica del Display.
Per impostare la time division della tastiera, premere il tasto Time Division per l’impostazione desiderata
(come stampato sopra/sotto il tasto). Premere due volte il tasto se si desidera utilizzare un’impostazione per
terzine. Quando una time division standard è stata selezionata, il tasto corrispondente sarà illuminato.
Quando una time division a terzine è stata selezionata, il tasto corrispondente lampeggerà.
Nota bene: Quando Note Repeat è attivo, servirsi dello Select/Scroll Encoder per modificare le
impostazioni di Time Division correnti dell’Arpeggiatore e del pad Note Repeat.
54
Page 55

Modalità accordo
Quando si attiva la modalità accordo, la pressione di un singolo tasto o pad suonerà un intero accordo
anziché una singola nota. Il tasto o pad premuto determinerà la nota radice dell’accordo e il tipo di accordo
selezionato dipenderà dalle impostazioni correnti.
La funzione di accordo può essere utilizzata in due modi ruotando l'encoder Select/Scroll che determinerà
l'accordo preciso assegnato a ciascun tasto:
• Modalità Smart: in questa modalità si assegna innanzitutto la tastiera a una nota musicale (ad es. D
minor). Quindi si assegna la voce desiderata per gli accordi (quali intervalli saranno inclusi nell'accordo,
ad es. 1-3-5). La voce dell'accordo di ciascun tasto sarà quindi automaticamente enarmonica rispetto
al tasto selezionato.
• Custom (personalizzata): in questa modalità è possibile determinare la struttura degli accordi che sarà
assegnata a ciascun tasto suonandolo manualmente. Ad esempio, se si seleziona questa modalità e si
suona un accordo 1-b3-5-b7 ogni tasto sarà assegnato per suonare la struttura di questo accordo. La
nota del tasto premuto servirà da radice dell'accordo.
Per attivare o disattivare la Modalità accordo, premere il tasto Accordo. Quando la modalità Accordo è
attivata, il tasto Accordo sarà acceso.
Per modificare le impostazioni della modalità Accordo, tenere premuto Shift premendo il tasto Accordo
per entrare nel menu Modifica accordo a Display. Quindi, servirsi di Select/Scroll Encoder per regolare le
impostazioni (come descritto in Panoramica del display). Una volta conclusa la modifica delle
impostazioni, premere il tasto Back per uscire dal Menu modifica accordo.
Alternativamente, è possibile tenere premuto Shift premendo i tasti C2–Bb3 se si utilizza la modalità di
accordo Smart.
Nota bene: in via predefinita, i tasti sono configurati per suonare gli accordi quando la modalità accordo è
attiva. Ciò può tuttavia essere modificato nel menu impostazioni globali in modo tale che quando la
modalità accordo è attiva gli accordi suonino sui tasti o sui pad o su entrambi.
Modalità Scala
Con la modalità Scala, è possibile impostare la tastiera in modo che i tasti al di fuori delle note di una scala
musicale prescelta siano disattivati. Ciò consente di suonare all’interno di una scala prescelta senza il
rischio di suonare note “sbagliate”. Al momento di assegnare una scala alla tastiera è possibile scegliere tra
16 opzioni diverse.
Per attivare o disattivare la Modalità Scala, premere il tasto Scala. Quando la modalità Scala è attivata, il
tasto Scala sarà acceso.
Per stabilire su quale scala musicale è impostata la tastiera, entrare nel menu Modifica Scala a Display
tenendo premuto Shift e premendo il tasto Scala. Quindi, servirsi di Select/Scroll Encoder per regolare le
impostazioni (come descritto in Panoramica del display). Una volta conclusa la modifica delle
impostazioni, premere il tasto Back per uscire dal Menu modifica Scala.
Menu impostazioni globali
Servirsi del Menu impostazioni globali a Display per personalizzare alcuni dei comandi predefiniti della
tastiera. Queste impostazioni si applicano alla tastiera in modalità DAW e Preset e qualsiasi modifica
apportata dal Menu impostazioni globali sarà salvata al momento dello spegnimento della tastiera.
Per entrare nel Menu impostazioni globali, tenere premuto Shift e premere il tasto Mode. Servirsi di
Select/Scroll Encoder per regolare le impostazioni (come descritto in Panoramica del display).
Per uscire dal Menu impostazioni globali, premere il tasto Back (indietro).
55
Page 56

Benutzerhandbuch (Deutsch)
Einführung
Lieferumfang
Oxygen Pro 49
USB-Kabel
Software-Download-Karte
Benutzerhandbuch
Sicherheitshinweise und Garantieinformationen
Kundendienst
Besuchen Sie m-audio.com, um die neueste Dokumentation, Systemanforderungen und andere
Informationen über Ihr Produkt aufzurufen und herunterzuladen.
Für zusätzlichen Produkt-Support besuchen Sie m-audio.com/support.
Setup
Um Ihren Oxygen Pro 49 verwenden zu können, müssen Sie Ihr Gerät anschließen, Ihre Software
richtig konfigurieren und dann den Betriebsmodus des Keyboards einstellen.
Um Ihren Oxygen Pro 49 an Ihren Computer anzuschließen, verwenden Sie das mitgelieferte
USB-Kabel. Verbinden Sie das USB-B-Kabelende mit Ihrem Keyboard und das USB-A-Kabelende
mit Ihrem Computer (oder mit einem an Ihren Computer angeschlossenen USB-Hub).
Hinweis: Zusätzlich zum Senden von Daten versorgt das USB-Kabel das Keyboard mit Strom. Wenn
Sie das Oxygen Pro 49 an einen USB-Hub anschließen, an den andere Geräte angeschlossen sind,
empfehlen wir die Verwendung eines USB-Hubs mit Stromversorgung.
Um Ihre DAW für die Arbeit mit Oxygen Pro 49 zu konfigurieren, aktivieren Sie Oxygen Pro 49
als MIDI-Bedienoberfläche im entsprechenden Einstellungsmenü der DAW (Einstellungen,
Optionen, Geräte-Setup usw.).
Wenn Sie Oxygen Pro 49 mit den enthaltenen MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition, oder
Ableton Live Lite-Software verwenden, klicken Sie auf Installieren der mitgelieferten Software,
um genauere Anweisungen zum Konfigurieren Ihrer DAW mit Oxygen Pro 49 zu erhalten. Wenn Sie
eine andere DAW verwenden, lesen Sie das Benutzerhandbuch der DAW für weitere Hilfe bei diesem
Schritt.
Wenn Sie Oxygen Pro 49 nicht mit Ihrem Computer, sondern mit einem Hardware-Synthesizer
verwenden, verbinden Sie den MIDI Out Port des Oxygen Pro 49 über ein standardmäßiges, 5poliges MIDI-Kabel mit einem Synthesizer. Stellen Sie dann sicher, dass Oxygen Pro 49 so
eingestellt ist, dass es mit einer seiner benutzerdefinierten Voreinstellungen arbeitet (wie unter
Einstellen des Keyboard-Betriebsmodus beschrieben), und dass Oxygen Pro 49 so eingestellt ist,
dass es MIDI-Daten vom 5-poligen MIDI-Ausgang in den Globale Einstellungen sendet. Um einen
externen Hardware-Synthesizer verwenden zu können, müssen Sie Oxygen Pro 49 an einen
Computer, einen Laptop oder einen USB-Hub mit Stromversorgung anschließen.
56
Page 57

Installieren der mitgelieferten Software
Im Lieferumfang enthalten sind MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition und Ableton Live Lite mit
Oxygen Pro 49, damit Sie Ihre Musikproduktion sofort mit professioneller Software beginnen können.
Darüber hinaus haben wir eine Reihe von Erweiterungspaketen und AIR-Plugins für virtuelle Instrumente zur
Verwendung mit Ihrer DAW hinzugefügt.
Um die mitgelieferten MPC Beats, Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition, oder Ableton Live Lite Software
herunterzuladen, registrieren Sie Ihren Oxygen Pro 49 auf m-audio.com und befolgen Sie die
Installationsanweisungen in Ihrem Benutzerkonto. Wenn Sie Ableton Live Lite verwenden, empfehlen wir,
ableton.com zu besuchen, um nach verfügbaren Software-Updates zu suchen. Hilfe zum Konfigurieren
einer DAW mit Oxygen Pro 49 finden Sie unter Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition
Lite Setup unten.
Befolgen Sie zum Herunterladen der enthaltenen Plugins für virtuelle AIR-Instrumente die
Anweisungen auf der Software-Download-Karte in der Verpackung. Nach der Installation laden die meisten
DAWs Plugins für virtuelle Instrumente nicht automatisch. Möglicherweise müssen Sie manuell einen PlugIn-Ordner auswählen, den Ihre Software scannen soll. Die Plugin-Ordner für Pro Tools | First M-Audio
Edition und Ableton Live Lite hängen von Ihrem Betriebssystem ab, wie unten angegeben.
Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition/AAX-Plugin-Ordner:
• Windows (32-bit): C:\Programme (x86)\Gemeinsame Dateien\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• Windows (64-bit): C:\Programme\Gemeinsame Dateien\Avid\Audio\Plug-Ins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Application Support/Avid/Audio/Plug-Ins
Ableton/VST Plugins:
• Windows (32-bit): C:\Program Files (x86)\VSTplugins
• Windows (64-bit): C:\Program Files\VSTplugins
• MacOS: Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Plugins/VST
So legen Sie Ihren Plugin-Ordner in Ableton Live Lite fest:
1. Navigieren Sie in das Menü Einstellungen.
2. Wählen Sie die Registerkarte Dateiordner. Klicken Sie unter Plug-In-Quellen auf Durchsuchen
und wählen Sie den entsprechenden Plugin-Ordner aus (wie oben angegeben).
3. Nach der Auswahl muss die Schaltfläche Verwenden der VST Custom Plug-In Folder AKTIVIERT
sein. Wenn dies nicht der Fall ist, klicken Sie zur Aktivierung auf die Schaltfläche. Sie können dann das
Menü Einstellungen verlassen.
Setup oder Ableton Live
57
Page 58

Ableton Live Lite Setup
1. Schließen Sie zuerst Oxygen Pro 49 an Ihren Computer an. Starten Sie dann Ableton Live Lite.
2. Öffnen Sie danach das Einstellungen-Fenster in Ableton Live Lite. Wenn Sie einen Mac verwenden,
gehen Sie zu Live > Einstellungen. Wenn Sie einen PC verwenden, gehen Sie zu Optionen >
Einstellungen.
3. Wählen Sie links die Registerkarte Link / MIDI. Passen Sie die Einstellungen im Abschnitt MIDI Ports
wie folgt an:
Wählen Sie unter Steuerflächen für Eingabe und Ausgabe Oxygen Pro 49 aus.
Neben Eingang: Oxygen Pro 49, wählen Sie Ein in den Kolumnen Track und Remote.
Neben Ausgang: Oxygen Pro 49, wählen Sie Ein in den Kolumnen Track und Remote.
4. Schließen Sie das Eigenschaften-Fenster.
5. Um ein Instrument oder Plugin zum Triggern mit dem Oxygen Pro 49 hinzuzufügen, wählen Sie in der
Spalte Kategorien die Option Instrumente oder Plug-Ins.
6. Suchen Sie in der Spalte Name rechts neben der Spalte Kategorien das Instrument oder das Plug-In
Ihrer Wahl. Klicken und ziehen Sie das Instrument auf eine MIDI-Spur in Ableton Live Lite, um das
Instrument zu laden.
Das Instrument kann jetzt mit Oxygen Pro 49 getriggert werden.
Pro Tools | First M-Audio Edition Setup
1. Schließen Sie zuerst Oxygen Pro 49 an Ihren Computer an. Starten Sie dann Pro Tools | First M-Audio
Edition.
2. Öffnen oder erstellen Sie ein Projekt.
3. Wählen Sie das Setup-Pulldown-Menü und öffnen Sie MIDI-Eingabegeräte. Aktivieren Sie den MIDI
Eingang vom Oxygen Pro 49, indem Sie auf das Feld neben Oxygen Pro 49 klicken.
4. Um eine neue Instrumentenspur zu erstellen, wählen Sie das Pulldown-Menü Track und wählen Sie
Neu.
5. Wählen Sie im Pulldown-Menü Neu die Option Stereo und dann Instrument-Track.
6. Fügen Sie Ihrem neu erstellten Track ein Insert hinzu, indem Sie in die Inserts A-E Ihres Tracks klicken
und Mehrkanal-Plugin > Instrument auswählen. Wählen Sie das Instrument aus, das Sie verwenden
möchten, z. B. Xpand! 2 (Stereo).
Das Plugin kann jetzt mit Oxygen Pro 49 getriggert werden.
Preset-Editor
Befolgen Sie zum Herunterladen der mitgelieferten Preset Editor-Software, die Anweisungen auf der
Software-Download-Karte in der Box. Mit dieser Software können Sie benutzerdefinierte MIDI-Zuordnungen
erstellen, die Sie auf Oxygen Pro 49 laden können. Weitere Informationen zum Bedienen des Keyboards mit
einer der ausgewählten benutzerdefinierten Presets finden Sie im folgenden Abschnitt und unter
Bedienung > Benutzerdefinierte Zuordnungen verwenden. Der Preset-Editor verfügt außerdem über ein
eigenes Editor-Benutzerhandbuch.
58
Page 59

Einstellen des Keyboard-Betriebsmodus
Sobald Sie Oxygen Pro 49 für die Arbeit mit Ihrer DAW eingerichtet haben, müssen Sie den Betriebsmodus
des Keyboards einstellen. Durch die Auswahl des Betriebsmodus können Sie das Keyboard so einstellen,
dass es automatisch mit den Funktionen Ihrer DAW koordiniert wird oder als individuell angepasster
Controller fungiert. Mit diesen beiden Modi bietet Ihnen Oxygen Pro 49 die Möglichkeit, schnell zwischen
der Steuerung eines Plugins und der Steuerung Ihrer DAW per Knopfdruck zu wechseln.
Die beiden Betriebsmodi bestimmen die Funktion der bearbeitbaren Steuerelemente des MIDI-Keyboards:
• DAW: Im DAW-Modus werden die Steuerelemente der Tastatur automatisch Schiebereglern, Tasten,
Reglern und Pads in Ihrer DAW zugeordnet.
• Preset: Im Preset-Modus können die bearbeitbaren Steuerelemente des Keyboards auf Funktionen
eingestellt werden, die Sie selbst entwerfen. Eine Reihe von einzelnen Preset-Zuordnungen können
erstellt und dann im internen Speicher des Keyboards gespeichert werden, damit Sie sie zu einem
späteren Zeitpunkt laden können.
Um das Keyboard in den DAW-Modus zu bringen, drücken Sie die DAW-Taste. Die Taste leuchtet, um
anzuzeigen, dass der DAW-Modus ausgewählt ist.
So ändern Sie, welche DAW Ihr Keyboard steuern soll:
1. Halten Sie die DAW-Taste gedrückt, um das DAW-Auswahlmenü auf dem Display zu öffnen.
2. Drehen Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder, um durch die verfügbaren DAWs auf dem Display zu blättern.
Wenn Sie den Encoder drehen, wird die aktuell ausgewählte DAW auf dem Display aktualisiert. Mit der
User-Option können Sie dem Keyboard benutzerdefinierte DAW-Steuerelemente zuordnen, wie unter
Betrieb > Benutzerdefinierte Zuordnungen verwenden beschrieben.
3. Wenn die gewünschte DAW auf dem Display angezeigt wird, drücken Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder,
um Ihre Auswahl zu bestätigen.
Hinweis: Um den DAW-Modus zu verlassen, ohne die aktuell ausgewählte DAW zu ändern, drücken Sie
die Back-Taste.
Drücken Sie die Preset-Taste, um das Keyboard auf den Preset-Modus einzustellen. Die Taste leuchtet,
um anzuzeigen, dass der Preset-Modus ausgewählt ist.
So ändern Sie das aktuell ausgewählte Preset:
1. Halten Sie die Preset-Taste gedrückt, um das Preset-Auswahlmenü auf dem Display zu öffnen.
2. Drehen Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder, um durch die verfügbaren Presets auf dem Display zu blättern.
Wenn Sie den Encoder drehen, wird der aktuell ausgewählte Preset auf dem Display aktualisiert.
3. Wenn das gewünschte Preset auf dem Display angezeigt wird, drücken Sie den Select/Scroll
Encoder, um Ihre Auswahl zu bestätigen. Siehe Betrieb > Benutzerdefinierte Zuordnungen
verwenden für weitere Informationen zum Zuordnen von Presets.
59
Page 60

Funktionen
Oberseite
18
17
11 12
14
1
19
15 16
13
23
20
21
5
10
6
7
9
8
22
2
3
4
Hinweis: Der in Klammern gesetzte Text neben den Keyboard-Steuerelementen zeigt sekundäre Funktionen
an, auf die durch Drücken der Shift-Taste während der Verwendung des Steuerelements zugegriffen
werden kann.
1. Klaviatur: Diese anschlagdynamische Klaviatur ist die primäre Methode zum Senden von Note On/OffMIDI-Daten. Die Klaviatur ist nicht nur anschlagdynamisch, sondern besitzt auch einen KanalAftertouch. Dies bedeutet, dass Sie den Klang eines Plugins für virtuelle Instrumente beeinflussen
können, indem Sie variieren, wie viel Druck Sie nach dem ersten Anschlagen der Taste auf die Taste
ausüben.
Halten Sie die Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie die Tasten C2–Bb3, um die Einstellungen für den
Akkordmodus zu bearbeiten. Weitere Informationen zu dieser Funktion finden Sie unter Bedienung >
Verwenden der internen Keyboard-Funktionen.
2. Oktaventasten: Drücken Sie diese Tasten, um den Pitch-Bereich der Tasten um eine Oktave nach
oben oder unten anzupassen. Halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Tasten, um den PitchBereich der Tasten um einen Halbton nach oben oder unten anzupassen. Das Keyboard kann von
seinem Standardoktavbereich bis zu vier Oktaven angehoben und bis zu drei Oktaven abgesenkt und
von seiner Standardtransposition insgesamt zwölf Halbtöne transponiert werden.
Um Oxygen Pro 49 auf den Standard-Oktavbereich und die Transposition zurückzusetzen (C2–C4 auf
der Klaviatur), drücken Sie gleichzeitig die Tasten Octave - und Octave +.
3. Pitch-Bend-Rad: Bewegen Sie dieses Rad von der Mittelposition auf und ab, um die Tonhöhe des
Keyboards während des Spielens zu verändern. Der Standardbereich des Pitch-Bend variiert zwischen
den Software-Synthesizern. Dieses Rad ist federmontiert und kehrt in die mittlere Raststellung zurück,
wenn es losgelassen wird.
4. Modulationsrad: Wenn dieses Rad bewegt wird, werden standardmäßig Continuous Controller Daten,
MIDI CC #01 (Modulation), gesendet.
60
25
Page 61

5. DAW-Taste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um Oxygen Pro 49 für den
DAW-Modus einzustellen. Halten Sie die Taste gedrückt, um das
DAW-Auswahlmenü auf dem Display zu öffnen.
Halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Taste, um Ihr
eigenes DAW -Preset zu bearbeiten und zu erstellen. Drücken Sie
nach dem Bearbeiten der Benutzer- DAW die Taste erneut, um
Ihre Änderungen in der Benutzer-DAW zu speichern.
Unter Setup > Einstellen des Keyboard-Betriebsmodus finden
Sie weitere Informationen zum DAW-Modus. Unter Betrieb >
Benutzerdefinierte Zuordnungen verwenden finden Sie
Informationen zum Zuordnen der Benutzer-Presets.
6. Preset-Taste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um Oxygen Pro 49 für den Preset-Modus einzustellen. Halten
Sie die Taste gedrückt, um das Preset-Auswahlmenü auf dem Display zu öffnen.
Halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Taste, um ein Preset zu bearbeiten. Drücken Sie nach
dem Bearbeiten eines Presets die Taste erneut, um Ihre Änderungen am aktuellen Preset zu speichern.
Unter Setup > Einstellen des Keyboard-Betriebsmodus finden Sie weitere Informationen zum PresetModus. Unter Betrieb > Benutzerdefinierte Zuordnungen verwenden finden Sie Informationen zum
Zuordnen der Presets.
7. Display: Das Haupt-Display zeigt den Status des zuletzt verwendeten Steuerelements an. Verwenden
Sie diesen Bildschirm, um die Parameterebenen zu überwachen, während Sie die Steuerelemente am
Keyboard anpassen. Verwenden Sie außerdem das Display zusammen mit dem Select/Scroll
Encoder, um die Keyboard-Einstellungen anzuzeigen und zu bearbeiten. Unter Betrieb > Überblick
über das Display finden Sie weitere Informationen zum Display.
8. Select/Scroll Encoder: Wenn Sie sich in einem der Display-Bearbeitungsmenüs befinden, drehen Sie
diesen Encoder, um Einstellungen / Parameter zu ändern, und drücken Sie den Encoder, um eine
Auswahl zu bestätigen.
Wenn Sie keines der Bearbeitungsmenüs anzeigen, fungieren Drehen/Drücken des Encoders jeweils als
separate MIDI-Regler. Beim Betrieb mit einer DAW werden die zugewiesenen Steuerelemente
vorgegeben. Wenn Sie mit einem Preset oder der ausgewählten Benutzer-DAW arbeiten, können die
Steuerelemente bearbeitet werden.
9. Taste Zurück: Wenn Sie sich in einem der Display-Bearbeitungsmenüs befinden, drücken Sie diese
Taste, um zum Haupt-Display zurückzukehren.
Wenn Sie keines der Bearbeitungsmenüs anzeigen, wird diese Taste einem Steuerelement zugewiesen.
Beim Betrieb mit einer DAW werden die zugewiesenen Steuerelemente vorgegeben. Wenn Sie mit
einem Preset oder der ausgewählten Benutzer-DAW arbeiten, können die Steuerelemente bearbeitet
werden. Drücken Sie beim Bearbeiten eines Preset- oder DAW-Namens die Umschalttaste und die
Zurück-Taste, um einen Buchstaben zu löschen.
10. Shift-Taste: Halten Sie die Shift-Taste gedrückt, während Sie Steuerelemente oder Tasten am
Keyboard bewegen oder drücken, um auf deren sekundäre Funktionen zuzugreifen.
11. << Taste: Je nachdem, welcher Bildschirm in Ihrer DAW ausgewählt ist, spult diese Taste entweder den
geöffneten Song zurück oder bewegt sich im aktiven Fenster nach unten.
12. >> Taste: Je nachdem, welcher Bildschirm in Ihrer DAW ausgewählt ist, spult diese Taste entweder den
geöffneten Song vorwärts oder bewegt sich im aktiven Fenster nach oben.
13. Loop-Taste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Loop-Funktion in Ihrer DAW zu aktivieren/deaktivieren.
14. Stopp-Taste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um den geöffneten Song in Ihrer DAW zu stoppen. Drücken Sie
diese Taste zweimal, um den geöffneten Song anzuhalten und den Abspielkopf an den Anfang des
Songs zurückzusetzen. Drücken Sie Shift und diese Taste, um eine MIDI-Panikmeldung zu senden, um
alle Note-Meldungen auszuschalten und alle Steuerelemente auf Null zurückzusetzen.
15. Wiedergabe-Taste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um den Song in Ihrer DAW abzuspielen.
16. Aufnahmetaste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Aufnahme in Ihrer DAW zu aktivieren.
5
10
9
6
7
18
11 12
8
14
17
15 16
19
13
61
Page 62

17. Bank-Tasten: Wenn Sie im DAW-Modus oder in einer der benutzerdefinierten Presets arbeiten, können
Sie mit diesen Tasten die aktuell ausgewählte Bank für die Schieberegler, Regler, Pads und
Funktionstasten wechseln. Es gibt vier Bänke für diese Steuerelemente, sodass Sie 36 Schieberegler,
32 Regler, und 64 Pads.
Drücken Sie die Umschalttaste und die Taste Bank <, um die ARP-Regler des Umschalt-Modifikators
zu sperren. Dies ist nützlich, um ARP-Parameter während einer Live-Performance zu ändern. Drücken
Sie die Umschalttaste und die Taste Bank >, um die Umschalt-Modifikator Pad-Controllen zu
sperren. Dies ist nützlich, um Änderungen beim Mischen eines Songs vorzunehmen. Um die Regler
oder Pads in den normalen Modus zurückzusetzen, drücken Sie die Umschalttaste und die Bank <Taste oder Bank >.
18. Tempo-Taste: Tippen Sie auf diese Taste, um das Tempo von Oxygen Pro 49 einzustellen, oder halten Sie sie
gedrückt, um das Tempo- Bearbeitungsmenü auf dem Display aufzurufen. Dort können Sie das Tempo mit dem
Select/Scroll Encoder manuell eingeben und Oxygen Pro 49 mit dem Tempo Ihrer DAW synchronisieren. Die
Tempoeinstellung wirkt sich auf die Arpeggiator- und Notenwiederholungsfunktionen des Keyboards aus. Weitere
Informationen finden Sie unter Bedienung > Verwenden der internen Keyboard-Funktionen.
Halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Taste, um das Metronom Ihrer DAW ein- oder
auszuschalten.
19. Notenwiederholungstaste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Notenwiederholungsfunktion für die Pads zu
aktivieren. Halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Notenwiederholungsfunktion zu halten
oder aufzuheben. Verwenden Sie bei aktivierter Notenwiederholung den Select/Scroll-Encoder, um die
aktuelle Zeitteilungseinstellung des Arpeggiators und der Notenwiederholung zu ändern. Halten Sie
Umschalten gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Notenwiederholungsfunktion zu halten oder
aufzuheben. Weitere Informationen zur Notenwiederholung finden Sie unter Bedienung > Verwenden der
internen Keyboard-Funktionen.
20. Pads (1–16): Verwenden Sie diese geschwindigkeitsabhängigen Pads, um MIDI Note On/OffNachrichten zu senden oder andere MIDI -Zuweisungen durchzuführen (wenn Sie ein Preset oder die
Benutzer-DAW verwenden). Halten Sie Shift gedrückt, während Sie die Pads 9–11 drücken, um die
Funktion der Regler neu zuzuweisen, und halten Sie die Umschalttaste gedrückt, während Sie die Pads
13–16 drücken, um die DAW-Verknüpfungen zu verwenden (weitere Informationen finden Sie unter
Betrieb > Verwenden von Sekundärsteuerelementen im DAW-Modus ).
21. Pad-Reihenwiedergabe: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Audioclips abzuspielen, die jedem Pad in
der entsprechenden Pad-Reihe zugewiesen sind. Abhängig von der DAW haben diese Tasten
unterschiedliche Funktionen.
22. Schieberegler (1–9): Schieben Sie diese Schieberegler nach oben/unten, um die zugewiesenen
Steuerfunktionen auszuführen. Beim Einsatz mit einer DAW sind die zugewiesenen Steuerelemente
vorgegeben. Wenn Sie mit einem Preset oder der ausgewählten Benutzer-DAW arbeiten, können die
Steuerelemente bearbeitet werden.
23. Regler (1–8): Drehen Sie diese Regler nach links/rechts, um die zugewiesenen Steuerfunktionen
auszuführen. Beim Betrieb mit einer DAW sind die zugewiesenen Steuerfunktionen vorgegeben. Wenn
Sie mit einem Preset oder der ausgewählten Benutzer-DAW arbeiten, können die Steuerelemente
bearbeitet werden.
Unter Betrieb > Verwenden von Sekundärsteuerelementen im DAW-Modus erfahren Sie, wie Sie
die vorgegebenen Zuordnungen der Regler ändern, wenn Sie im DAW-Modus mit einer ausgewählten
DAW arbeiten.
Halten Sie Shift gedrückt, während Sie die Regler 1–4 drehen, um die Arpeggiator-Einstellungen zu
bearbeiten. Weitere Informationen zum Arpeggiator finden Sie unter Verwenden der internen
Keyboard-Funktionen.
Wichtig: Sowohl die Schieberegler als auch die Regler werden mit "Soft Takeover" aktiviert. Dies
bedeutet, dass beim Wechseln der Bank ein Schieberegler oder Regler erst dann funktioniert, wenn er
auf dem aktuellen Wert des neu ausgewählten Softwaresteuerelements positioniert ist. Wenn Sie
beispielsweise Schieberegler 1 in der Bank 1 verschieben und dann zu Bank 2 wechseln, wirkt sich der
physische Schieberegler 1 nicht auf den Software-Schieberegler 10 aus, bis der physische
Schieberegler auf dem aktuellen Wert von Software-Schieberegler 10 positioniert ist. Mit dieser
Funktion können Sie Änderungen an einer Bank vornehmen und dann die Bank wechseln, ohne
unerwünschte Änderungen an den Kontrollen der neuen Bank vorzunehmen. Das Display zeigt eine
karierte Anzeige an, wenn ein Schieberegler oder Regler bewegt werden muss, bevor er die ihm
zugewiesene Steuerung „übernehmen“ kann (Abbildung siehe Überblick über das Display).
62
Page 63

Wichtig: In Avid Pro Tools verfügen Stereospuren über zwei Panning-Steuerelemente: links und rechts.
Drücken Sie die Umschalttaste, um die Regler zwischen dem linken und dem rechten Kanal
umzuschalten. Wenn sich die Pan-Regler nicht auf einem Monotrack bewegen, drücken Sie die
Umschalttaste, um den Pan-Regler wieder auf die normale Steuerung des Pan-Reglers umzustellen.
24. Modus-Taste (mit LEDs): Drücken Sie die Modustaste, um einen der sekundären Modi für die
Funktionstasten zu aktivieren. Wenn das Keyboard so eingestellt ist, dass es im DAW-Modus arbeitet,
sind die verfügbaren sekundären Modi für die Funktionstasten Rec, Select, Mute und Solo. In diesen
Modi führen die Tasten vorgegebene DAW-Kanal-Funktionen für Scharfstellen, Trackauswahl,
Stummschaltung und Solo aus (weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Betrieb > Verwenden von
Sekundärsteuerelementen im DAW-Modus). Wenn das Keyboard so eingestellt ist, dass es im
Preset-Modus arbeitet, ist der verfügbare sekundäre Modus für die Funktionstasten MIDI, in dem die
Tasten MIDI-Controls ausführen, die in einem der benutzerdefinierten Presets vorgegeben sind.
Die LEDs rechts neben der Modustaste zeigen an, in welchem Modus sich die Funktionstasten
befinden.
Halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie die Modustaste, um auf das Menü "Globale Einstellungen"
zuzugreifen.
25. Funktionstasten (1–8): Wenn die Funktionstasten auf ihren primären Modus eingestellt sind, steuern
sie die internen Funktionen des Keyboards wie folgt:
ARP-Taste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um den Arpeggiator zu aktivieren. Drücken Sie Shift und diese
Taste, um die Einstellungen des Arpeggiators zu konfigurieren.
Latch-Taste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um zwischen den Arpeggiator-Modi Temporär und Halten zu
wechseln.
Akkordtaste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um den Akkordmodus zu aktivieren. Halten Sie Shift
gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Einstellungen für den Akkordmodus zu bearbeiten.
Tonleitertaste: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um den Tonleiter-Modus zu aktivieren. Halten Sie Shift
gedrückt und drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Einstellungen für den Tonleiter-Modus zu bearbeiten.
1/4–1/32T (Zeitteilungstasten): Verwenden Sie diese Tasten, um die Zeitteilung der Tastatur für die
Notenwiederholungs- und Arpeggiatorfunktionen auszuwählen. Jeder Druck auf eine dieser Tasten
wechselt zwischen dem über der Taste aufgeführten Standard-Timing und dem unter der Taste
aufgeführten Triolen-Timing. Eine durchgehend rote LED zeigt an, dass ein Standard-Timing
ausgewählt ist, während eine blinkende LED anzeigt, dass ein Triolen-Timing ausgewählt ist.
Weitere Informationen zu dieser Funktion finden Sie unter Bedienung > Verwenden der internen
Keyboard-Funktionen.
63
Page 64

Rückseite
1. Netzschalter: Verwenden Sie diesen Schalter, um
Oxygen Pro 49 ein- oder auszuschalten.
2. Sustain Pedal-Eingang: Sie können an diese Eingänge
ein Tast-Fußpedal anschließen (nicht im Lieferumfang
enthalten). Wird das Pedal betätigt, so wird es den von
Ihnen gespielten Ton halten, ohne dass Sie die Tasten
gedrückt halten müssen. Der Sustain-Pedal-Eingang
kann neu zugeordnet werden, um eine benutzerdefinierte
MIDI-Zuweisung durchzuführen.
Hinweis: Die Polarität des Sustain-Pedals wird bei der Inbetriebnahme durch das Keyboard bestimmt.
Wenn ein Oxygen Pro 49-Keyboard eingeschaltet wird, wird angenommen, dass sich das Sustain-Pedal
in der Position "up" (Aus) befindet. Es ist wichtig, dass sich das Sustain-Pedal vor dem Einschalten des
Keyboards nicht in der unteren Position befindet, da das Pedal dann "verkehrt" funktioniert und die
Noten gehalten werden, wenn das Pedal nicht gedrückt wird.
3. USB-Anschluss: Der USB-Port versorgt das Keyboard mit Strom und überträgt MIDI-Daten, wenn es
an einen Computer angeschlossen ist.
4. MIDI Out: Verwenden Sie ein 5-poliges Standard-MIDI-Kabel, um diesen Port mit einem HardwareSynthesizer oder einem anderen MIDI-Gerät zu verbinden.
Hinweis: Der MIDI-Ausgangsport kann MIDI-Daten vom Oxygen Pro 49, Ihrem angeschlossenen
Computer oder von beiden Quellen senden. Gehen Sie in die globalen Einstellungen, um festzulegen,
was an den MIDI-Ausgang gesendet wird.
5. Kensington
Laptops kompatibel, um Diebstähle zu vermeiden.
®
Lock Anschluss: Dieser Anschluss ist mit einem Kensington -Sicherheitskabel für
2
345
1
64
Page 65

Betrieb
Überblick über das Display
Haupt-Display
Wenn Sie während der Performance die Schieberegler, Regler, Pads und
Funktionstasten des Keyboards verwenden, zeigt das Display die
aktuelle Bank für das zuletzt verwendete Steuerelement, Namen/Nummer
des Steuerelements, den aktuellen Wert, der auf das Steuerelement
angewendet wird (00–127) und eine grafische Darstellung, die den Wert
anzeigt (falls zutreffend). Während der Performance hat das Display einen
schwarzen Hintergrund mit weißem Text.
Hinweis: Auf dem Display wird die Nummer des Softwaresteuerelements angezeigt, die nicht immer mit der
Nummer des Hardwaresteuerelements auf Ihrem Keyboard übereinstimmt. Wenn das Keyboard
beispielsweise auf Bank 3 eingestellt ist und Sie Regler 1 am Keyboard drehen, zeigt das Display Regler
20 an, da der Hardware-Regler 1 den Software-Regler 20 steuert, wenn das Keyboard auf Bank 3
eingestellt ist.
Wie unter Funktionen > Oberseite beschrieben, werden die Schieberegler
und Regler mit einem "Soft Takeover" aktiviert. Wenn Sie die Bank
wechseln und ein Schieberegler oder Regler bewegt werden muss,
bevor er die ihm zugewiesene Steuerung übernehmen kann, zeigt das
Display dies an, indem eine karierte, graue Anzeige unter der
Steuerungsebene dargestellt wird. Wie im Beispiel rechts dargestellt,
wurde die Bank gerade auf Bank 2 umgestellt, und Schieberegler 1 muss
ganz nach oben geschoben werden, damit der Software-Schieberegler 10
gesteuert werden kann.
Bearbeitungsmenüs
Neben der Anzeige der zuletzt verwendeten Steuerelemente während der Performance ist das Display
(zusammen mit dem Select/Scroll Encoder) Ihr Hauptwerkzeug zum Bearbeiten verschiedener KeyboardEinstellungen, einschließlich der MIDI-Zuweisungen für bearbeitbare Steuerelemente und der Einstellungen
für die internen Funktionen des Keyboards (z.B. Arpeggiator) sowie globale Hardwareeinstellungen.
Wenn Sie ein Bearbeitungsmenü für eine Keyboard-Funktion aufrufen, zeigt das
Display den Namen des Bearbeitungsmenüs, ein zum Bearbeiten
hervorgehobenes Einstellungsfeld, ein Parameterfeld mit dem aktuellen Status der
Einstellung und grafische Blöcke am unteren Bildschirmrand an, um anzuzeigen,
wie viele andere Einstellungen im Bearbeitungsmenü verfügbar sind. Während der
Eingabe im Bearbeitungsmenü hat das Display einen weißen Hintergrund mit
schwarzem Text.
Um durch die Einstellungen in einem Bearbeitungsmenü zu scrollen, drehen Sie den Select/Scroll
Encoder während das Einstellungsfeld markiert ist.
Um eine zu bearbeitende Einstellung auszuwählen, drücken Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder, während
das Einstellungsfeld markiert ist. Das Parameterfeld wird dann hervorgehoben.
Um den Einstellungsparameter zu bearbeiten, wählen Sie die zu bearbeitende Einstellung wie oben
beschrieben aus. Drehen Sie dann den Select/Scroll Encoder, während das Parameterfeld markiert ist.
Sobald der gewünschte Parameter markiert ist, drücken Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder, um die
Bearbeitung zu bestätigen. Das Display kehrt dann zur Hervorhebung des Einstellungsfelds zurück.
Um das Menü Bearbeiten zu verlassen, ohne die Änderungen zu speichern, drücken Sie die ZurückTaste. Um das Bearbeitungsmenü zu verlassen und Änderungen zu speichern, drücken Sie die DAW-Taste
(wenn Sie die Benutzer-DAW bearbeiten) oder die Preset-Taste (wenn Sie ein Preset bearbeiten).
Hinweis: Die im Bearbeitungsmenü verfügbaren Einstellungen können sich je nach den von Ihnen
ausgewählten Parametern ändern. Das Arpeggiator-Bearbeitungsmenü hängt beispielsweise vom
ausgewählten Parameter für die Einstellung Arpeggiator-Typ ab.
65
Page 66

Verwenden von Sekundärsteuerelementen im DAW-Modus
Während der DAW-Modus so konzipiert ist, dass für die Verwendung des Oxygen Pro 49 mit Ihrer DAW keine
komplexe Zuordnung erforderlich ist, verfügen einige Steuerelemente des Keyboards noch über mehrere
Funktionen, zwischen denen Sie im DAW-Modus wechseln können.
Modi für die Funktionstasten
Wenn das Keyboard auf DAW-Modus eingestellt ist und eine DAW ausgewählt ist, können die Funktionstasten
zwischen fünf verschiedenen Modi umgeschaltet werden.
Um den Modus für die Funktionstasten umzuschalten, drücken Sie die Modustaste rechts neben den
Funktionstasten. Bei jedem Drücken ändert sich die Modustasten-LED, um anzuzeigen, welcher Modus gerade
ausgewählt ist. Folgende Modi stehen zur Verfügung:
Primär (Keine LED): Wenn keine LED leuchtet, werden die Funktionstasten auf ihre primären Zuordnungen
eingestellt (über/unter jeder Taste gedruckt). Diese Zuweisungen beziehen sich auf die internen Funktionen der
Tastatur: Arpeggiator, Notenwiederholung, Akkordmodus und Tonleiter-Modus. Weitere Informationen zur
Verwendung der Funktionstasten mit diesen Funktionen finden Sie unter Verwenden der internen Keyboard-
Funktionen.
Rec (Rote LED): Wenn der Aufnahmemodus eingestellt ist, aktiviert/deaktiviert jede Taste die Aufnahme für den
entsprechenden Track in Ihrer DAW (Track 1–32, abhängig davon, welche Taste gedrückt und welche Bank
ausgewählt wurde).
Auswahl (Grüne LED): In diesem Modus fokussiert jede Taste den entsprechenden Software-Track (Track 1–32, je
nachdem, welche Taste gedrückt und welche Bank ausgewählt wurde).
Stummschalten (Blau LED): In diesem Modus schaltet jede Taste den entsprechenden Software-Track stumm bzw.
hebt die Stummschaltung auf (Track 1–32, je nachdem, welche Taste gedrückt und welche Bank ausgewählt wurde).
Solo (Gelbe LED): In diesem Modus schaltet jede Taste den entsprechenden Software-Track solo bzw. hebt die
Solo-Schaltung auf (Track 1–32, je nachdem, welche Taste gedrückt und welche Bank ausgewählt wurde).
Hinweis: Der MIDI-Modus ist entweder für die benutzerdefinierte MIDI-Zuordnung vorgesehen. Dieser Modus ist nur
verfügbar, wenn sich das Keyboard im Preset-Modus befindet.
Ändern der Regler-Funktion im DAW-Modus
Hinweis: Nicht alle Parameter sind in jeder DAW verfügbar.
Im DAW-Modus können die Regler eine von drei Funktionen ausführen.
Um die Funktionsweise der Regler zu ändern, halten Sie Shift-Taste gedrückt und drücken Sie Pad 9, 10 oder
11. Die folgenden Funktionen stehen zur Verfügung:
Pan (Pad 9): Jeder Regler schwenkt den entsprechenden Software-Track (Track 1–32, je nachdem, welcher Regler
gedreht und welche Bank ausgewählt ist).
Gerät (Pad 10): Jeder Regler steuert Geräte des entsprechenden Software-Tracks (Track 1–32, je nachdem, welcher
Regler gedreht und welche Bank ausgewählt ist).
Sends (Pad 11): Jeder Regler steuert den Pegel der Aux-Sends für den entsprechenden Software-Track (Track 1–
32, je nachdem, welcher Regler gedreht und welche Bank ausgewählt ist).
Zugriff auf DAW-Verknüpfungen mit den Pads
Hinweis: Nicht alle Parameter sind in jeder DAW verfügbar.
Wenn Sie im DAW-Modus ein Pad drücken, wird eine Note On-Nachricht gesendet, damit Sie einen Synth oder ein
Sample in Ihrer Software triggern können. Sie können jedoch Shift gedrückt halten und die Pads 13, 14, 15 oder 16
drücken, um die folgenden Befehle auszuführen:
Speichern (Pad 13): Speichern Sie die Änderungen an der aktuell geöffneten Datei in Ihrer DAW.
Quantisieren (Pad 14): Quantisieren Sie den aktuell ausgewählten Audiobereich in Ihrer DAW.
Rückgängig machen (Pad 15): Machen Sie die letzte Änderung rückgängig, die an der Datei in Ihrer DAW
vorgenommen wurde.
Ansicht (Pad 16): Wechseln Sie für Ihre DAW zwischen verschiedenen Fenstern (z. B. Mixen oder Bearbeiten).
Wichtig: Damit diese Verknüpfungen mit Ihrer DAW funktionieren, muss Ihr PC auf Win (Windows) oder Mac in den
Globalen Einstellungen Ihres Oxygen Pro 49 eingestellt sein. Um auf das Menü Globale Einstellungen im Display
zuzugreifen, halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie die Modustaste. Verwenden Sie den Select/Scroll
Encoder, um die Einstellung an Ihren PC-Typ anzupassen, und drücken Sie dann die Zurück-Taste, um das Menü
zu verlassen.
66
Page 67

Benutzerdefinierte Zuordnungen verwenden
Oxygen Pro 49 verfügt über viele vollständig anpassbare Steuerelemente mit der Möglichkeit,
Tastaturzuordnungen zu erstellen und zu speichern. Auf diese Weise können Sie verschiedene Zuordnungen
für verschiedene DAWs, Plugins oder Performance-Szenarien speichern, die spontan geändert werden
können.
Im Preset-Modus stehen 16 Presets am Keyboard zur Verfügung (1–16). Ein Preset ist eine Gruppe von
MIDI-Zuweisungen für Oxygen Pro 49-Steuerelemente, die im internen Speicher des Keyboards gespeichert
und zu einem späteren Zeitpunkt geladen werden können. Presets können bearbeitet werden, wenn sich
das Keyboard im Preset-Bearbeitungsmodus befindet. Zusätzlich zu diesen 16 Presets am Keyboard
können Sie mit der mitgelieferten Editor-Software eine unbegrenzte Anzahl von Presets auf Ihrem Computer
speichern und die 16 im internen Speicher ändern.
Wenn Sie im DAW-Modus arbeiten, können Sie mit der Benutzereinstellung eine benutzerdefinierte
Zuordnung für das Keyboard erstellen, die nicht nur MIDI-Nachrichten, sondern auch Mackie- oder
Mackie/HUI-Nachrichten enthält. Auf diese Weise können Sie Keyboard-Steuerelemente mit Befehlen für die
DAW selbst zuordnen (z. B. „Speichern“ oder „Stummschalten“) und Keyboard-Steuerelemente mit MIDIZuweisungen für Instrumenten-/Plug-In-Parameter innerhalb der DAW zuordnen. Die Benutzer-DAW-
Einstellung kann bearbeitet werden, wenn sich das Keyboard im DAW-Bearbeitungsmodus befindet.
Zusätzlich zur Benutzer-DAW am Keyboard können Sie mit der mitgelieferten Editor-Software eine
unbegrenzte Anzahl von Benutzer-DAWs auf Ihrem Computer speichern und können jene DAW ändern, die
aktuell im internen Speicher Ihres Keyboards gespeichert ist.
Um in den Preset-Bearbeitungsmodus zu gelangen, wählen Sie zunächst das Preset aus, das Sie
bearbeiten möchten (wie unter Setup > Einstellen des Keyboard-Betriebsmodus beschrieben). Halten
Sie dann Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie die Preset-Taste.
Um den DAW-Bearbeitungsmodus aufzurufen, halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie die DAW-
Taste.
Um den Bearbeitungsmodus zu verlassen und Ihre Änderungen zu speichern, drücken Sie die PresetTaste (wenn Sie Presets bearbeitet haben) oder die DAW-Taste (wenn Sie die Benutzer-DAW-Einstellung
bearbeitet haben).
Wenn Sie Änderungen vorgenommen haben, werden Sie am Display gefragt, ob Sie sie speichern
möchten. Verwenden Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder, um zwischen Abbrechen, Ersetzen und Speichern
als zu wählen. Wenn Sie Abbrechen auswählen, kehren Sie zum Bearbeitungsmodus zurück. Wenn Sie
Ersetzen auswählen, wird das Preset gespeichert, ohne den Namen zu ändern. Wählen Sie Speichern als,
um zu speichern und die Preset-Speicherortnummer des Presets mit dem Select/Scroll Encoder
umzubenennen und zu ändern. Wenn Sie während der Bearbeitung des Namens ein Zeichen löschen
müssen, halten Sie die Shift-Taste und die Zurück-Taste gedrückt.
Hilfe zur Verwendung des Preset-Editors finden Sie im Editor-Benutzerhandbuch, das mit der Software
geliefert wird.
67
Page 68

Verwenden der internen Keyboard-Funktionen
Die folgenden Keyboard-Funktionen können verwendet werden, wenn das Keyboard so eingestellt ist, dass
es entweder im DAW- oder im Preset-Modus arbeitet.
Hinweis: Um die in den folgenden Abschnitten beschriebenen Funktionen Arpeggiator, Akkordmodus oder
Tonleiter-Modus zu steuern, müssen die Funktionstasten unter den Schiebereglern auf ihren primären
Modus eingestellt werden. Die Funktionstasten werden auf ihren primären Modus eingestellt, wenn keine
LED rechts neben der Modustaste leuchtet. Wenn die Funktionstasten nicht auf ihren primären Modus
eingestellt sind, drücken Sie die Modustaste so oft wie nötig, bis keine LED rechts neben der Modustaste
leuchtet.
In den folgenden Abschnitten wird bei der beschriebenen LED-Bedienung für die Funktionstasten davon
ausgegangen, dass sie auf ihren primären Modus eingestellt sind.
Notenwiederholung
Wenn diese Funktion aktiviert ist, wiederholt jedes gedrückte Performance-Pad seine Note On-Meldung im
Rhythmus der aktuellen Tempo- und Zeiteinteilungseinstellungen des Keyboards. Jede wiederholte Note
entspricht der Länge, die für die Einstellung der Zeitteilung ausgewählt wurde. Weitere Hilfe zum Ändern der
Einstellungen für Tempo und Zeitteilung finden Sie unter Tempo und Zeitteilung des Keyboards.
Die Notenwiederholungsfunktion kann vorübergehend aktiviert oder gehalten werden.
Um die Notenwiederholung kurz zu verwenden, halten Sie die Notenwiederholungstaste gedrückt und
drücken Sie dann auf ein Pad. Solange Sie die Notenwiederholungstaste gedrückt halten, wird die vom
Pad gespielte Note wiederholt.
Um die Notenwiederholungsfunktion zu halten, halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie die Taste
Notenwiederholung. Durch Drücken eines beliebigen Pads wird die zugewiesene Note wiederholt, ohne
dass Sie die Notenwiederholungstaste gedrückt halten müssen.
Um die Umschalt-/Verriegelungsfunktion zu deaktivieren, drücken Sie die Notenwiederholungstaste
erneut.
Hinweis: Verwenden Sie bei aktivierter Notenwiederholung den Select/Scroll-Encoder, um die aktuelle
Zeitteilungseinstellung des Arpeggiators und der Notenwiederholung zu ändern.
Arpeggiator
Wenn der Arpeggiator aktiviert ist, spielt das Keyboard wiederholt nacheinander gedrückte Tasten. Das
Timing und der Rhythmus des Arpeggiators basieren auf der Zeitteilungseinstellung des Keyboards und
entweder auf der Tempoeinstellung des Keyboards oder Ihrer DAW. Jede Note im Arpeggio entspricht der
Länge, die Sie für die Einstellung der Zeitteilung ausgewählt haben. Wenn Sie beispielsweise 1/4
auswählen, ist jede Note im Arpeggio eine Viertelnote. Informationen zum Bearbeiten dieser Einstellungen
finden Sie unter Tempo und Zeitteilung des Keyboards.
Der Arpeggiator kann in einem von zwei Modi betrieben werden:
• Momentan: Der Arpeggiator spielt Noten nur so lange, wie die Tasten gedrückt werden. Wenn Sie die
Tasten loslassen, stoppt der Arpeggiator.
• Halten: Der Arpeggiator spielt Noten, wenn Sie die Tasten drücken und spielt die Noten weiterhin, auch
wenn Sie die Tasten loslassen.
Um den Arpeggiator zu aktivieren oder zu deaktivieren, drücken Sie die Arp-Taste. Wenn der
Arpeggiator aktiviert ist, leuchtet die Tasten-LED.
Um zwischen dem Momentan- und dem Halten-Modus umzuschalten, drücken Sie die Halten-Taste.
Wenn die Taste aktiv ist, leuchtet ihre LED.
Um ein Arpeggio zu starten, drücken Sie eine beliebige Taste, während der Arpeggiator aktiviert ist.
Um ein neues Arpeggio zu starten, während ein zuvor gehaltenes Arpeggio abgespielt wird, drücken
Sie eine neue Tastenkombination.
68
Page 69

Um einem gehaltenen Arpeggio Noten hinzuzufügen, während es noch abgespielt wird, halten Sie die
gleichen Tasten gedrückt, die Sie zuvor für das Arpeggio gedrückt haben, während Sie die Tasten für die
neuen Noten drücken, die Sie hinzufügen möchten.
Um die Einstellungen des Arpeggiators zu konfigurieren, halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken die
Arp-Taste. Das Display ruft dann das Menü zum Bearbeiten des Arpeggiators auf. Verwenden Sie den
Select/Scroll Encoder, um die Einstellungen anzupassen (wie in Überblick über das Display beschrieben).
Wenn Sie mit dem Bearbeiten der Einstellungen fertig sind, drücken Sie die Zurück-Taste, um das
Arpeggiator-Bearbeitungsmenü zu verlassen.
Alternativ können Sie die Shift gedrückt halten oder Shift und Bank < drücken, um die ARP-Regler des
Shift-Modifikators zu sperren, während Sie die Regler 1–4 drehen, um einige, aber nicht alle Einstellungen
zu bearbeiten. Das Display zeigt die neuen Einstellungen an, wenn Sie sie ändern.
Hinweis: Verwenden Sie bei aktivierter Notenwiederholung den Select/Scroll-Encoder, um die aktuelle
Zeitteilungseinstellung des Arpeggiators und der Notenwiederholung zu ändern.
Tempo und Zeitteilung des Keyboards
Die Tempo- und Zeitteilungseinstellungen von Oxygen Pro 49 bestimmen das Timing und den Rhythmus für
die Notenwiederholungs- und Arpeggiatorfunktionen. Wenn die Uhr im Tempo-Bearbeitungsbildschirm des
Displays auf Intern eingestellt ist, kann das Tempo des Keyboards eingetippt oder genau im TempoBearbeitungsbildschirm eingegeben werden. Wenn die Uhr auf Extern eingestellt ist, wird das Tempo der
Tastatur automatisch mit dem Tempo Ihrer DAW synchronisiert.
Um das Tempo der Tastatur einzugeben, tippen Sie zweimal oder mehrmals auf die Tempo-Taste im
gewünschten BPM-Tempo. Das Display wird mit dem neuen Tempo aktualisiert, wenn Sie auf die Taste
tippen.
Hinweis: Um auf das Keyboard-Menü zu tippen, muss die Uhreinstellung des Keyboards im Menü "Tempo
bearbeiten" auf Intern gestellt sein. Bei der Einstellung Extern wird das Tempo des Keyboards mit Ihrer
DAW synchronisiert.
Um das Tempo-Bearbeitungsmenü auf dem Display aufzurufen, halten Sie die Tempo-Taste gedrückt.
Verwenden Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder, um die Uhr-Einstellung zu ändern oder ein internes
Keyboardtempo (20,0–240,0) einzugeben. Wenn Sie mit dem Bearbeiten der Einstellungen fertig sind,
drücken Sie die Zurück-Taste, um das Tempo-Bearbeitungsmenü zu verlassen. Siehe Überblick über das
Display für weitere Hilfe zur Verwendung des Select/Scroll Encoder mit den Bearbeitungsmenüs des
Displays.
Um die Zeitteilung des Keyboards einzustellen, drücken Sie die Zeitteilungstaste für die gewünschte
Einstellung (wie über bzw. unter der Taste gedruckt). Drücken Sie die Taste zweimal, wenn Sie eine TriolenEinstellung verwenden möchten. Wenn eine Standardzeitteilung ausgewählt ist, leuchtet die entsprechende
Taste. Wenn eine Triolen-Zeitteilung ausgewählt ist, blinkt die entsprechende Taste.
Scroll-Encoder und Notenwiederholung auswählen: 1/4–1/32T (Zeitteilung): Halten Sie die
Notenwiederholung gedrückt und drehen Sie den Scroll/Auswahl-Encoder, um die Zeitteilung des
Keyboards für die Notenwiederholungs- und Arpeggiator-Funktionen auszuwählen.
Hinweis: Verwenden Sie bei aktivierter Notenwiederholung den Select/Scroll-Encoder, um die aktuelle
Zeitteilungseinstellung des Arpeggiators und der Notenwiederholung zu ändern.
69
Page 70

Akkord-Modus
Wenn Sie den Akkord-Modus aktivieren, wird durch Drücken einer einzelnen Taste oder Pad ein
vollständiger Akkord und nicht nur eine Note gespielt. Die Taste oder Pad, die Sie drücken, bestimmt den
Grundton im Akkord, und die Art des ausgewählten Akkords hängt von den aktuellen Einstellungen ab.
Die Akkordfunktion kann in einem von zwei Modi betrieben werden, indem der Select/Scroll-Encoder
gedreht wird, der den genauen Akkord bestimmt, der jeder Taste zugewiesen ist:
• Smart-Modus: In diesem Modus weisen Sie dem Keyboard zunächst eine Tonart (z. B. D-Moll) zu.
Dann weisen Sie den Akkorden die gewünschte Stimme zu (welche Intervalle im Akkord enthalten sein
werden, z. B. 1-3-5). Die Akkordstimme jeder Note ist mit der ausgewählte Note automatisch
enharmonisch.
• Benutzerdefiniert: In diesem Modus können Sie die Akkordstruktur bestimmen, die jeder Taste
zugewiesen wird, indem Sie sie manuell spielen. Wenn Sie diesen Modus auswählen und beispielsweise
einen 1-b3-5-b7-Akkord spielen, wird jeder Taste diese Akkordstruktur zugewiesen. Die Note der
Taste, die Sie drücken, dient als Grundton des Akkords.
Um den Akkordmodus zu aktivieren oder zu deaktivieren, drücken Sie die Akkordtaste. Während der
Akkordmodus aktiviert ist, leuchtet die Akkordtaste.
Um die Einstellungen für den Akkordmodus zu bearbeiten, halten Sie zuerst die Umschalttaste
gedrückt, während Sie die Akkordtaste drücken, um das Menü für die Akkordbearbeitung im Display
aufzurufen. Verwenden Sie dann den Select/Scroll Encoder, um die Einstellungen anzupassen (wie in
Überblick über das Display beschrieben). Wenn Sie mit dem Bearbeiten der Einstellungen fertig sind,
drücken Sie die Zurück-Taste, um das Akkord-Bearbeitungsmenü zu verlassen.
Alternativ können Sie Shift gedrückt halten, während Sie die Tasten C2 - Bb3 drücken, wenn Sie den
Smart-Akkord-Modus verwenden.
Hinweis: Standardmäßig sind die Tasten so eingestellt, dass sie Akkorde spielen, wenn der Akkordmodus
aktiviert ist. Im Menü "Globale Einstellungen" kann dies jedoch so geändert werden, dass bei aktivem
Akkordmodus Akkorde auf den Tasten oder Pads oder auf beiden gespielt werden.
Tonleiter-Modus
Im Tonleiter-Modus können Sie die Klaviatur so einstellen, dass Noten außerhalb der Noten einer
ausgewählten Tonleiter deaktiviert sind. Auf diese Weise können Sie innerhalb einer ausgewählten Tonleiter
spielen, ohne das Risiko, eine „falsche“ Note zu spielen. Sie können aus 16 verschiedenen Optionen
auswählen, wenn Sie dem Keyboard eine Tonleiter zuweisen.
Um den Tonleiter-Modus zu aktivieren oder zu deaktivieren, drücken die Tonleiter-Taste. Während der
Tonleiter-Modus aktiviert ist, leuchtet die Tonleiter-Taste.
Um festzustellen, auf welche Tonleiter die Klaviatur eingestellt ist, rufen Sie das Menü Tonleiter
Bearbeiten auf dem Display auf, indem Sie Shift gedrückt halten und die Tonleiter-Taste drücken.
Verwenden Sie dann den Select/Scroll Encoder, um die Einstellungen anzupassen (wie in Überblick über
das Display beschrieben). Wenn Sie mit dem Bearbeiten der Einstellungen fertig sind, drücken Sie die
Zurück-Taste, um das Tonleiter-Bearbeitungsmenü zu verlassen.
Menü Globale Einstellungen
Verwenden Sie das Menü Globale Einstellungen auf dem Display, um einige der Standardsteuerelemente
des Keyboards anzupassen. Diese Einstellungen gelten für das Keyboard sowohl im DAW- als auch im
Preset-Modus. Alle im Menü Globale Einstellungen vorgenommenen Änderungen werden nach dem
Ausschalten des Keyboards gespeichert.
Um das Menü Globale Einstellungen aufzurufen, halten Sie Shift gedrückt und drücken Sie die
Modustaste. Verwenden Sie den Select/Scroll Encoder, um die Einstellungen anzupassen (wie in
Überblick über das Display beschrieben).
Um das Menü Globale Einstellungen zu verlassen, drücken Sie die Zurück-Taste.
70
Page 71

Appendix (English)
Preset List
1. MPC Pl (MPC Plugin) 9. Preset
2. Hybrid (Hybrid 3) 10. Preset
3. MiniGrd (MiniGrand) 11. Preset
4. Velvet 12. Preset
5. Xpand (Xpand!2) 13. Preset
6. Vacuum 14. Preset
7. Boom 15. Preset
8. DB33 16. Preset
DAW List
1. Pro Tools 7. Logic
2. MPC (MPC Beats) 8. Bitwig
3. Ableton 9. Garage (Garage Band)
4. Studio One 10. Reaper
5. Reason 11. FL St. (FL Studio)
6. Cubase 12. User DAW
Technical Specifications
Power
Dimensions (Length x Width x Height)
Weight
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Trademarks and Licenses
M-Audio is a trademark of inMusic Brands, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
AAX, Avid, and Pro Tools are registered trademarks of Avid Technology, Inc. in the U.S. and
other countries.
Ableton is a trademark of Ableton AG.
Apple Store, macOS, Macintosh, and iPad are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S.
and other countries.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other
countries.
Kensington is a registered trademark of ACCO Brands.
All other product or company names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective owners.
USB bus-powered
10.4” x 31.5” x 3.3”
264.2 x 800.1 x 83.8 mm
9.3 lbs.
4.2 kg
71
Page 72

m-audio.com
Manual Version 1.3
 Loading...
Loading...