Page 1
____________________________________________________________
BSD SERIES
REFRIGERATORS AND FREEZERS
Installation, Operation and
Maintenance Instructions
____________________________________________________________
INSPECTION
When the equipment is received, all items should be carefully checked against the bill of
lading to insure all crates and cartons have been received. All units should be inspected
for concealed damage by uncrating the units immediately. If any damage is found, it
should be reported to the carrier at once, and a claim should be filed with the carrier. This
equipment has been inspected and tested at the manufacturing facility and has been
crated in accordance with transportation rules and guidelines. Manufacturer is not
responsible for freight loss or damage.
INSTALLATION
GENERAL
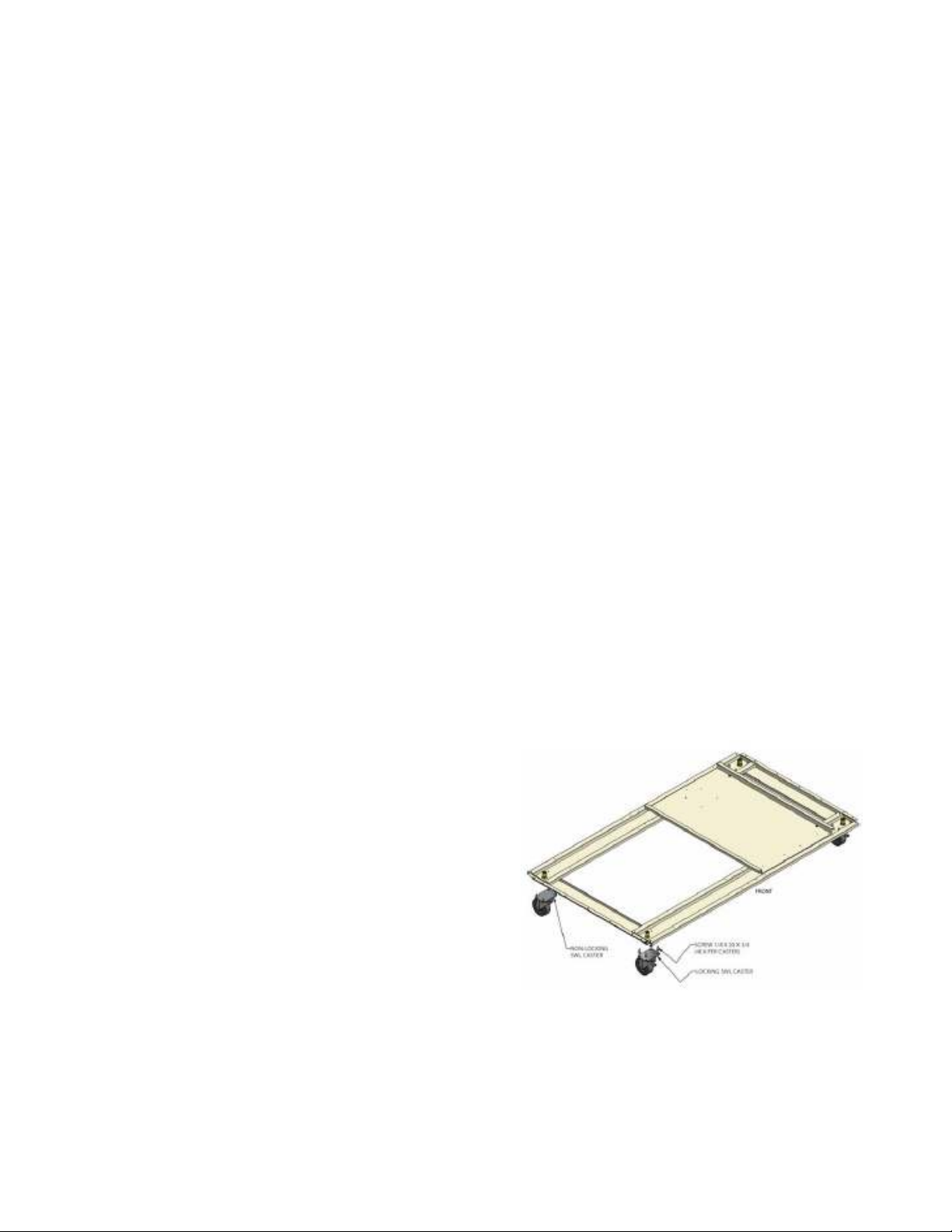
If casters are installed, care should be taken when removing the unit from the crate base.
The unit is heavy and can present a hazard if not handled with care. Remove the unit
crate and crate base. Discard hardware used to secure the cabinet to the crate base.
Ensure that at least two persons are available to install the casters. Lay the cabinet on its
back to create access to the cabinet bottom. Attach the casters to the cabinet base suing
the factory installed screws as shown below.
Remove the ¼ x 20 x ¾ screws (4 per caster)
that are factory installed. Position the caster
and reinstall. Ensure that the locking casters
are installed on the front of the cabinet. After
installation is complete, return the cabinet to its
upright position. The cabinet should set in the
upright position for at least one hour prior to
energizing. This is required to allow the
refrigeration to settle to its normal state. The
cabinet should also be leveled when it is placed
in its permanent location.
1
Page 2

If the doors are out of alignment on the cabinet, the doors can be adjusted. This can be
accomplished by opening the door(s) and loosening the screws that hold both the top and
bottom hinges to the cabinet. After adjusting the door so that it is aligned correctly,
tighten the screws to securely hold the hinges in place.
ELECTRICAL
Check the proposed outlet to be used to insure that the voltage, phase and current
carrying capacity of the circuit from the electrical panel correspond to the requirements of
the cabinet. NEVER use an extension cord to wire any unit. On permanently connected
units, those not furnished with a plug-in service cord, all inter-wiring between the
electrical panel and the unit must be done in accordance with the National Electric Code
and all state and local codes. Refer to the serial tag for all pertinent electrical information.
Observe all Warning Labels. Disconnect power supply to eliminate injury from
electrical shock or moving parts when servicing equipment.
GENERAL OPERATION
The refrigerators and freezers employ a unit cooler evaporator located outside the
cabinet as the heat removing source. Through the refrigeration process, heat is captured
in the evaporator, transferred to the condensing unit on top of the cabinet, and expelled
to the surrounding outside air. It is extremely important to allow a four (4) inch clearance
on the top, rear, and sides of the unit for the refrigeration process to function properly.
These refrigerators and freezers utilize a programmable controller to control the
temperature and defrost settings. The controller, which is located on the facade of
the unit, is factory set. Please see the default settings sheet and separate
instructions that are included on the operation of this controller.
REFRIGERATORS
During the operation of a refrigerator unit, frost will periodically form on the coil surface.
Each time the compressor cycles "off", the evaporator fans will continue to run, which will
keep the internal temperature uniform and at the same time remove any frost build up on
the coil. The water produced will collect in the unit cooler drain pan and travel down the
drain tube to the condensate vaporizer.
FREEZERS
After shutting the door on freezer models, a short amount of time must be allowed before
the door can be reopened. This is due to the tight seal maintained between the door and
the cabinet. Waiting a few moments for the pressure to equalize permits the door to be
opened easily.
A positive defrost is required to remove frost from the coil in freezer models. This is
accomplished by energizing heaters during the defrost cycle that are positioned on the
coil surface. The programmable controller is factory set to allow four defrosts per day.
2
Page 3

As the preset defrost time is reached, the controller automatically terminates the
refrigeration process by turning off the condensing unit and unit cooler fan motors, and
energizes the defrost heaters. As the coil temperature increases, the frost begins to melt
producing water which runs down the coil to the unit cooler drain pan and exits through
the drain tube to the vaporizer. After all the frost has been removed and the coil
temperature reaches approximately 50°F [10ºC], the defrost is terminated through the
action of the defrost termination control located on the unit cooler, and the refrigeration
process resumes. In order to insure that any excess water remaining on the coil is not
sprayed into the cabinet interior, and all heat generated by the defrost is removed, the
unit cooler fans will not operate until the coil temperature reaches approximately
25°F [-4ºC].
GENERAL MAINTENANCE
PERIODIC CLEANING
Beginning with the initial installation, the interior surfaces of the cabinet should be
periodically wiped down with a solution of warm water and baking soda. This solution will
remove any odors from spillage that has occurred. The exterior of the cabinet should also
be cleaned frequently with a commercial grade of glass cleaner.
Monthly cleaning of the condenser will aid the heat transfer characteristics of the
refrigeration system and increase its efficiency. To accomplish this, remove the cover
panel from the cabinet and use a wire brush to loosen any dirt particles that are attached
to the fins. Use a vacuum cleaner to remove the loosened particles. Failure to keep the
condenser coil clean and clear of obstructions could result in temperature loss
and damage to the compressor.
All moving parts have been permanently lubricated and will generally require no
maintenance.
3
Page 4

MAINTENANCE SERVICE AND ANALYSIS GUIDE
REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS - ALL MODELS
MALFUNCTION POSSIBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
Compressor will not start - 1. Service cord unplugged 1. Plug in service cord
no hum 2. Fuse blown or removed 2. Replace fuse
3. Overload tripped 3. Determine reasons and correct
4. Control stuck open 4. Repair or replace
5. Wiring incorrect 5. Check wiring against the diagram
Compressor will not start - 1. Improperly wired 1. Check wiring against the diagram
hums but trips on overload 2. Low voltage to unit 2. Determine reason and correct
protector 3. Starting capacitor defective 3. Determine reason and replace
4. Relay failing to close 4. Determine reason, correct or replace
Compressor starts and runs, 1. Low voltage to unit 1. Determine reason and correct
but short cycles on overload 2. Overload defective 2. Check current, replace overload protector
protector 3. Excessive head pressure 3. Check ventilation or restriction in
refrigeration system 4. Compressor hot-return gas hot 4. Check refrigerant charge, fix leak if necessary
Compressor operates long 1. Short of refrigerant 1. Fix leak, add charge
or continuously 2. Control contact stuck 2. Repair or replace
3. Evaporator coil iced 3. Determine cause, defrost manually
4. Restriction in refrigeration system 4. Determine location and remove restriction
5. Dirty condenser 5. Clean condenser
Compressor runs fine, but 1. Overload protector 1. Check wiring diagram
short cycles 2. Cold control 2. Differential too close - widen
3. Overcharge 3. Reduce charge
4. Air in system 4. Purge and recharge
5. Undercharge 5. Fix leak, add refrigerant
Starting capacitor open, 1. Relay contacts stuck 1. Clean contacts or replace relay
shorted or blown 2. Low voltage to unit 2. Determine reason and correct
3. Improper relay 3. Replace
Relay defective or burned out 1. Incorrect relay 1. Check and replace
2. Voltage too high or too low 2. Determine reason and correct
Refrigerated space too warm 1. Control setting too high 1. Reset control
2. Refrigerant overcharge 2. Purge refrigerant
3. Dirty condenser 3. Clean condenser
4. Evaporator coil iced 4. Determine reason and defrost
5. Not operating 5. Determine reason, replace if necessary
Standard temperature system 1. Control setting is too low 1. Reset the control
freezes the product 2. Control points stuck 2. Replace the control
Objectionable noise 1. Fan blade hitting fan shroud 1. Reform or cut away small section of shroud
2. Tubing rattle 2. Locate and reform
3. Vibrating fan blade 3. Replace fan blade
4. Condenser fan motor rattles 4. Check motor bracket mounting, tighten
5. General vibration 5. Compressor suspension bolts not loosened
on applicable models - loosen them
6. Worn fan motor bearings 6. Replace fan motor
Pan Area 1. No cooling 1. Make sure switch is in the "on" position
2. Too cold 2. Adjust temperature control - see instructions
under pan area
3. Too warm 3. Adjust temperature control - see instructions
under pan area
4
Page 5

____________________________________________________________
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVERSING
THE SWING OF SOLID DOORS
____________________________________________________________
Complete the following steps if reversing the swing of the solid door(s) is desired. These steps apply to both
refrigerators and freezers.
1. With a one, two, or three door model, first open the door and located the screws holding the hinges and door in
position.
2. Two people are recommended to make this change. One person should hold the door at a 90° angle to the cabinet
while the other person removes the screws holding the door to the cabinet. The normal installation at the factory
is to have the spring loaded door-closing mechanism located at the bottom of the cabinet. When removing the
spring tension bracket from the cabinet bottom, be careful that it does not snap back. This may result in
pinched fingers.
3. After the door(s) are removed, remove the door lock strike(s) from the cabinet by removing the two mounting
screws.
4. Find the holes, drilled through the outer skin only, located on the opposite side of the door opening from where
the hinges were previously located. Drill through the tapping plate found behind these holes using a 7/32" drill
bit.
5. Turn the door over and align it to the cabinet so it will swing in the desired direction. The spring loaded door
closing hinge will now be located at the top of the reversed door. Mount the hinges to the cabinet using the holes
that were drilled out in step 4, along with the previously removed screws. Check the door(s) to be certain that it is
mounted squarely and that the gaskets seal properly around the door opening. The door can be adjusted by
moving the top or bottom hinge slightly.
6. The original hinge holes can be filled with silicone, or with 1/4-20x3/4 pan head stainless steel screws if desired.
7. Locate the door lock strike by visually aligning it to the dead bolt lock in the door while the door is in the closed
position. While holding the strike in position, mark the top, bottom, and edge of the strike on the cabinet wall or
mullion with a pencil or fine point marker that will remain legible until completion of the task. Verify that the
strike is positioned properly by assuring that it is aligned to the marks and hold it securely; open and close the
door and extend and retract the dead bolt to make certain they clear without touching. The strike cannot be
adjusted after it is mounted.
8. Align the strike to the marks, which were made in step 7 and mark the centers of the holes for the mounting
screws. Using a #20 drill bit, drill the holes you just marked approximately one-half inch deep. Take care not to
puncture the interior side of the cabinet. Note: If a #20 bit is not available, use a 5/32" drill bit.
9. Mount the door lock strike using the screws that were removed from the original position. The screws may have
to be forced until the thread cutting tip has passed through the entire metal thickness. The original door strike
holes can be filled with silicone, or with two 10-24x1/2 stainless steel pan head screws if desired.
5
Page 6

6
Page 7

MASTER-BILT ELECTRONIC REFRIGERATION CONTROL
Display Lay-out
Compressor When power is first turned on to the control, the LED indicator for the Thermostat
output will go through the start-up delay. After a one-minute delay the compressor comes on. The
LED indicator stays on while compressor relay is energized. Display will show actual box
temperature. Picture above is the display layout. The compressor will be cycled off when the
actual box temperature reaches its set point. The Thermostat output indicator will be off.
Fan The fans will run constantly for Refrigerators application, and off during a defrost for the
Freezers application. The Evaporator fan will also cut off when the evaporator temp is above the
fan stop temperature setting.
When the Freezer is in defrost mode; the fan is off until the end of the defrost and the 2 minute
drip time has passed. There is 2 minute delay after a defrost before the fan comes on. If the
evaporator temperature is 25
indicator is on while FAN relay is energized.
o
F or below the controller will override the fan delay. FAN LED
7
Page 8

Defrost The control uses time defrost with 4 defrosts per day for the Freezers and off cycle
defrost for the Refrigerators.
The Freezers time defrost scheme can be re-set the for special applications. During defrost the
display will show dEF and the defrost LED indicator on. The control begins timing the defrost
when power is turned on. Four defrost per day means it will occur every 6 hours. To have
defrost occur at 8am, 2pm, 8pm, and 2am then power up at one of these four times.
MANUAL DEFROST
Defrosting my also be induced manually by keeping the defrost button for 5 seconds. Once
defrost has started, the defrost will go through a defrost and drip time pull down cycle.
HOW TO CHANGE THE SETPOINT
HOW TO CHANGE a parameter value
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
The controller is provided with a phoenix push terminal block to connect cables with a cross
section up to 2,5 mm2. Before connecting cables make sure the power supply complies with the
control’s requirements. Separate the probe cables from the power supply cables, the outputs and
the power connections. Do not exceed the maximum current allowed on each relay, in case of
heavier loads use a suitable external relay or contactors.
PROBE CONNECTIONS
The probes shall be mounted with the bulb upwards to prevent damage due to casual liquid
infiltration. It is recommended to place the thermostat probe at the warmest location of return air
streams to correctly measure the average room temperature. Place the defrost termination probe
among the evaporator fins in the coldest place, where most ice is formed, far from heaters or from
the warmest place during defrost, to prevent premature defrost termination.
8
Page 9

BSD-A Series Freezer
PARM* DESCRIPTION
SCL
SPL
SPH
SP
C-H
HYS
CRT
CT1
CT2
CSD
DFR
DLI
DTO
DTY
DRN
DDY
FID
FDD
FTC
FT1
FT2
FT3
ATM
ALA
AHA
ALR
AHR
ATD
ADO
ACC
IISM
IISL
IISH
IISP
IIHY
IIFT
IIDF
SB
DS
LSM
OAU
INP
OS1
T2
OS2
TLD
SIM
ADR
Temperature scale.
Minimum limit for SP setting
Maximum limit for SP setting
Setpoint (value to be maintained in the room)
Refrigerating (REF) or Heating (HEA) control mode
Thermostat differential
Compressor rest time.
Thermostat output runs when T1 is faulty.
Thermostat outputs stop when probe T1 is faulty.
Compressor stop delay after the door has been opened
Defrost frequency expressed in cycles / 24 hours.
Defrost end Temperature
Maximum defrost duration
Defrost Type: OFF, ELE, GAS
Pause after defrost (evaporator drain down time)
Display during defrost. (DEF)
Fans active during defrost.
Evaporator fan re-stat temperature after defrost.
OptimiSed fan control enabling. With FTC=NO then; FT1, FT2, FT3 = 0
Fan stop delay after compressor stop. See Fig.2.
Timed fan stop. With FT2=0 the fans remain on all the time.
Timed fan run. With FT3=0, and FT2>0, the fans remain off all the time.
Alarm threshold management: NON, ABS, REL.
Low temperature alarm threshold (ALR=0)
High temperature alarm threshold. (AHR=0)
Low temperature alarm differential. With ALR=0 the low temperature alarm is excluded.
High temperature alarm differential. With AHR=0 the high temperature alarm is excluded.
Delay before alarm temperature warning.
Delay before door open alarm warning.
Condensor periodic cleaning.
Switchover mode to second parameter set
Minimum limit for IISP setting.
Maximum limit for IISP setting.
Setpoint in mode 2.
OFF/ON differential in mode 2.
Optimised fan control enabling in mode 2.
Defrost timer set to start a defrost in mode 2.
Stand-by button enabling
Door switch input enabling (closed when door is closed)
Light control mode
AUX output operation.
Temperature sensor selection.
Probe T1 offset.
Probe T2 enabling (Evaporator).
Probe T2 offset.
Delay for minimum temperature (TLO) and maximum temperature (THI) logging
Display slowdown
AT2-5 address for PC communication.
FACTORY’S
SETTING
ºF
-10
32
-5
REF
4
1
6
4
5
4
55
30
ELE
1
4
NO
30
NO
0
0
0
ABS
-35
32
-
30
15
0
NON
-
-
-
-
-
-
NO
NO
NON
DEF
SN4
0
NO
0
5
0
1
9
Page 10

BSD-A Series Refrigerator
PARM* DESCRIPTION
SCL
SPL
SPH
SP
C-H
HYS
CRT
CT1
CT2
CSD
DFR
DLI
DTO
DTY
DRN
DDY
FID
FDD
FTC
FT1
FT2
FT3
ATM
ALA
AHA
ALR
AHR
ATD
ADO
ACC
IISM
IISL
IISH
IISP
IIHY
IIFT
IIDF
SB
DS
LSM
OAU
INP
OS1
T2
OS2
TLD
SIM
ADR
Temperature scale.
Minimum limit for SP setting
Maximum limit for SP setting
Setpoint (value to be maintained in the room)
Refrigerating (REF) or Heating (HEA) control mode
Thermostat differential
Compressor rest time.
Thermostat output runs when T1 is faulty.
Thermostat outputs stop when probe T1 is faulty.
Compressor stop delay after the door has been opened
Defrost frequency expressed in cycles / 24 hours.
Defrost end Temperature
Maximum defrost duration
Defrost Type: OFF, ELE, GAS
Pause after defrost (evaporator drain down time)
Display during defrost. (DEF)
Fans active during defrost.
Evaporator fan re-stat temperature after defrost.
OptimiSed fan control enabling. With FTC=NO then; FT1, FT2, FT3 = 0
Fan stop delay after compressor stop. See Fig.2.
Timed fan stop. With FT2=0 the fans remain on all the time.
Timed fan run. With FT3=0, and FT2>0, the fans remain off all the time.
Alarm threshold management: NON, ABS, REL.
Low temperature alarm threshold (ALR=0)
High temperature alarm threshold. (AHR=0)
Low temperature alarm differential. With ALR=0 the low temperature alarm is excluded.
High temperature alarm differential. With AHR=0 the high temperature alarm is excluded.
Delay before alarm temperature warning.
Delay before door open alarm warning.
Condensor periodic cleaning.
Switchover mode to second parameter set
Minimum limit for IISP setting.
Maximum limit for IISP setting.
Setpoint in mode 2.
OFF/ON differential in mode 2.
Optimised fan control enabling in mode 2.
Defrost timer set to start a defrost in mode 2.
Stand-by button enabling
Door switch input enabling (closed when door is closed)
Light control mode
AUX output operation.
Temperature sensor selection.
Probe T1 offset.
Probe T2 enabling (Evaporator).
Probe T2 offset.
Delay for minimum temperature (TLO) and maximum temperature (THI) logging
Display slowdown
AT2-5 address for PC communication.
FACTORY’S
SETTING
ºF
32
65
35
REF
4
1
6
4
5
2
45
20
OFF
1
3
YES
75
NO
0
0
0
ABS
0
55
-
30
15
0
NON
-
-
-
-
-
-
NO
NO
NON
DEF
SN4
0
YES
0
5
0
1
10
Page 11

11
Page 12

12
Page 13

13
 Loading...
Loading...