LINKSYS WTR54GS Users Manual

Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
Router IP
IP Address and Subnet Mask. This shows both the Router’s IP Address and Subnet Mask, as seen by your
network. The default IP Address is 192.168.16.1, and the default Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0. In most cases,
keeping the default values will work.
DHCP Server Setting
The settings allow you to configure the Router’s Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server function. The
Router can be used as a DHCP server for your network. A DHCP server automatically assigns an IP address to
each computer on your network. If you choose to enable the Router’s DHCP server option, you must make sure
there is no other DHCP server on your network.
DHCP Server. DHCP is enabled by factory default. If you already have a DHCP server on your network, or you
don’t want a DHCP server, then select Disabled (no other DHCP features will be available).
Static DHCP. Every time a PC reboots, it is assigned a new local IP address by the Router. If you want a PC to be
assigned the same IP address every time it reboots, then click the Static IP button.
On the DHCP Client List screen, enter the static local IP address in the Assign this IP field, and enter the MAC
address of the PC in the To this MAC field. Then click the Enabled checkbox. When you have finished your entries,
click the Save Settings button to save your changes. Click the Cancel Changes button to cancel your changes.
To exit this screen, click the Close button.
Figure 5-9: Static DHCP Client List
If you want to see a list of DHCP clients, click the DHCP Client Table button. On the DHCP Client Table screen, you
will see a list of DHCP clients with the following information: Client Name, Interface, IP Addresse, and MAC
Addresse. To save the information, select Static DHCP Client List. From the To S ort by drop-down menu, you can
sort the table by Client Name, Interface, IP Address, or MAC Address. To view the most up-to-date information,
click the Refresh button. To exit this screen, click the Close button.
Start IP Address. Enter a value for the DHCP server to start with when issuing IP addresses. Because the
Router’s default IP address is 192.168.16.1, the Starting IP Address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater, but smaller
than 192.168.1.254. The default Starting IP Address is 192.168.16.100.
Maximum Number of Users. Enter the maximum number of PCs that you want the DHCP server to assign IP
addresses to. This number cannot be greater than 253. The default is 50.
IP Address Range. The range of DHCP addresses is displayed here.
Client Lease Time. The Client Lease Time is the amount of time a network user will be allowed connection to the
Router with their current dynamic IP address. Enter the amount of time, in minutes, that the user will be “leased”
Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
The Setup Tab - Basic Setup
Figure 5-10: DHCP Client Table
15
Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
this dynamic IP address. After the time is up, the user will be automatically assigned a new dynamic IP address.
The default is 0 minutes, which means one day.
Static DNS (1-3). Your ISP will provide you with at least one DNS (Domain Name System) Server IP Address.
WINS. The Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) manages each PC’s interaction with the Internet. If you use
a WINS server, enter that server’s IP Address here. Otherwise, leave this blank.
Time Settings
Change the time zone in which your network functions from this pull-down menu. Click the checkbox if you want
the Router to automatically adjust for daylight savings time.
Change these settings as described here and click the Save Settings button to apply your changes or Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes. Help information is shown on the right-hand side of the screen.
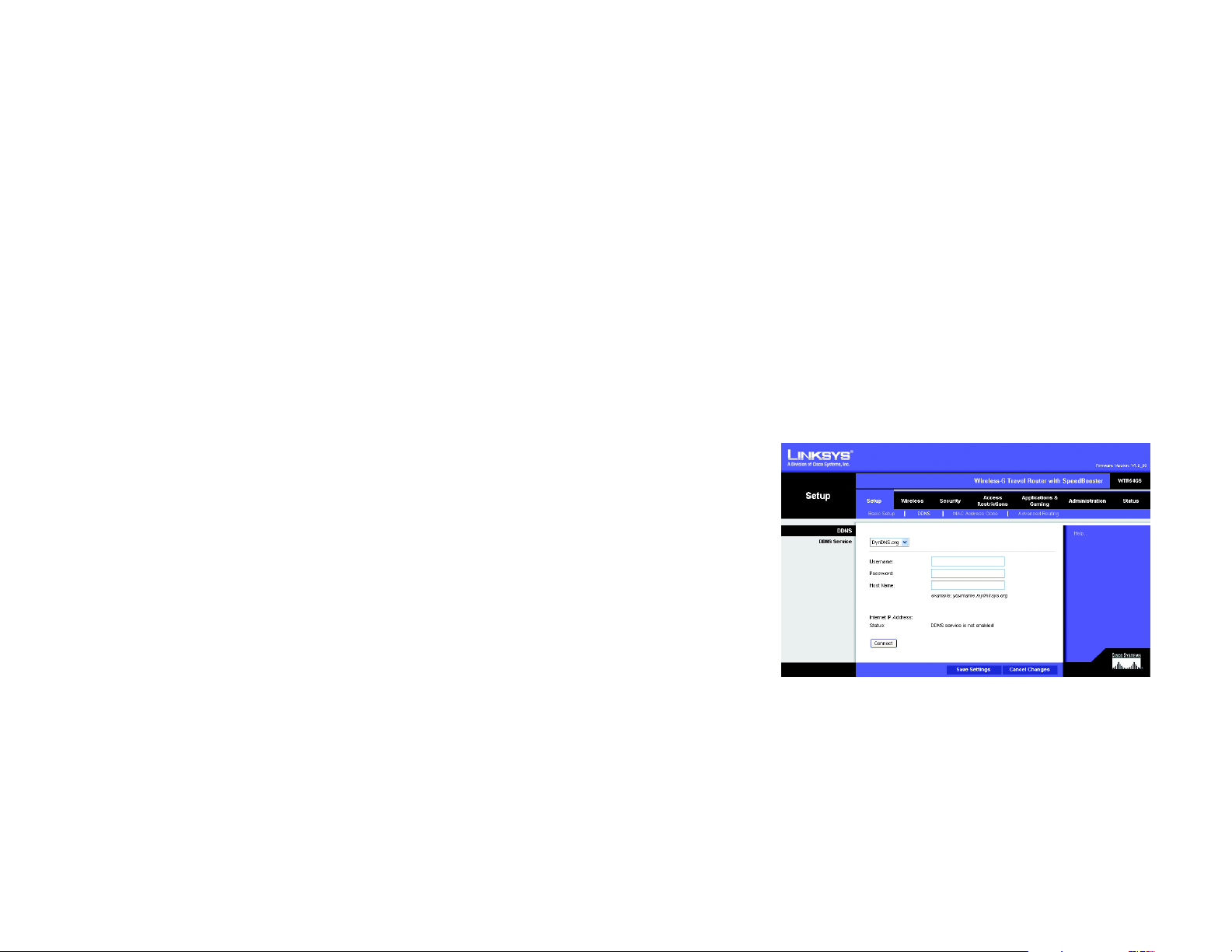
The Setup Tab - DDNS
The Router offers a Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) feature. DDNS lets you assign a fixed host and domain
name to a dynamic Internet IP address. It is useful when you are hosting your own website, FTP server, or other
server behind the Router.
Before you can use this feature, you need to sign up for DDNS service at one of two DDNS service providers, DynDNS.org or
TZO.com. If you do not want to use this feature, keep the default setting, Disabled.
dynamic ip address: a temporary IP
address assigned by a DHCP server.
DDNS
DDNS Service. If your DDNS service is provided by DynDNS.org, then select DynDNS.org from the drop-down
menu. If your DDNS service is provided by TZO, then select TZO.com. The features available on the DDNS screen
will vary, depending on which DDNS service provider you use.
DynDNS.org
User Name, Password, and Host Name. Enter the User Name, Password, and Host Name of the account you
set up with DynDNS.org.
Internet IP Address. The Router’s current Internet IP Address is displayed here. Because it is dynamic, it will
change.
Status. The status of the DDNS service connection is displayed here.
Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
The Setup Tab - DDNS
Figure 5-11: DynDNS.org
16

Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
TZO.com
E-mail Address, TZO Password, and Domain Name. Enter the Email Address, Passwor d, and Domain Name
of the service you set up with TZO.
Internet IP Address. The Router’s current Internet IP Address is displayed here. Because it is dynamic, this
will change.
Status. The status of the DDNS service connection is displayed here.
When you have finished making changes to this screen, click the Save Settings button to apply your changes or
Cancel Changes to cancel your changes. Help information is shown on the right-hand side of the screen.
The Setup Tab - MAC Address Clone
A MAC address is a 12-digit code assigned to a unique piece of hardware for identification. Some ISPs will
require you to register a MAC address in order to access the Internet. If you do not wish to re-register the MAC
address with your ISP, you may assign the MAC address you have currently registered with your ISP to the Router
with the MAC Address Clone feature.
Figure 5-12: TZO.com
MAC Address Clone
Enabled/Disabled. To have the MAC Address cloned, select Enabled from the drop-down menu.
MAC Address. Enter the MAC Address registered with your ISP here.
Clone My PC’s MAC. Clicking this button will clone the MAC address of the PC you are currently using.
Change these settings as described here and click the Save Settings button to apply your changes or Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes. Help information is shown on the right-hand side of the screen.
Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
The Setup Tab - MAC Address Clone
Figure 5-13: Setup Tab - MAC Address Clone
mac address: the unique address that a
manufacturer assigns to each networking device.
17
Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
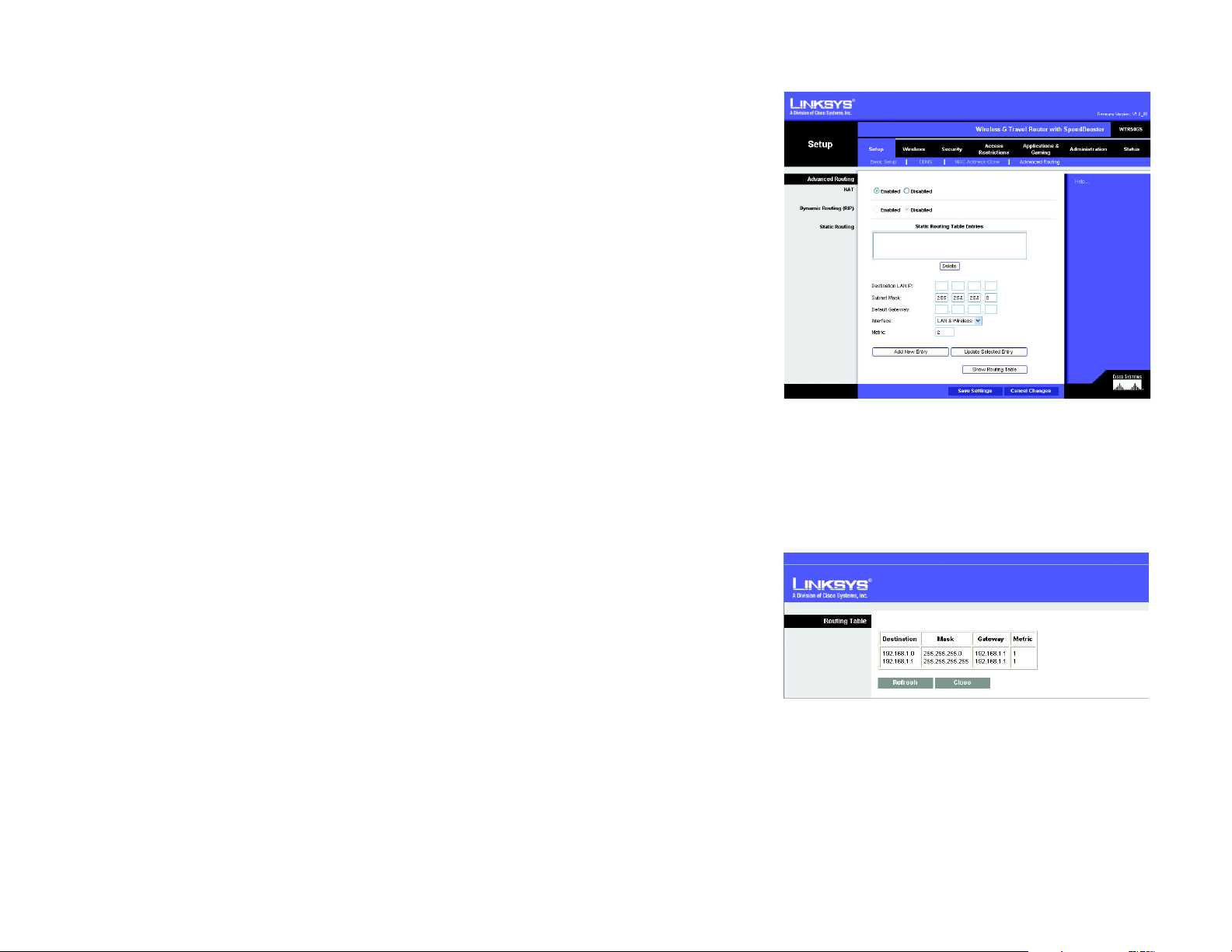
The Setup Tab - Advanced Routing
This tab is used to set up the Router’s advanced functions. Operating Mode allows you to select the type(s) of
advanced functions you use. Dynamic Routing will automatically adjust how packets travel on your network. Static
Routing sets up a fixed route to another network destination.
NAT (Network Address Translation). NAT technology translates IP addresses of a local area network to a
different IP address for the Internet. To enable NAT, click Enabled. To disable NAT, click Disabled.
Dynamic Routing (RIP)
. This feature enables the Router to automatically adjust to physical changes in the
network’s layout and exchange routing tables with the other router(s). The Router determines the network packets’
route based on the fewest number of hops between the source and the destination. This feature is
Disabled
by
default.
Static Routing
. A static route is a pre-determined pathway th at netw ork information must travel to re ach a specific
host or network. To set up a static route between the Router and another network, ente r the information described
below to set up a new static route by clicking the
Entry
button to change an existing entry. (Click the
Destination LAN IP
assign a static route.
. The Destination LAN IP is the address of the remote network or host to which you want to
Enter the IP address of the host for which you wish to create a static route. If you are
Add New Entry
Delete
button to delete a static route.)
button to add an entry. Click the
Update Selected
building a route to an entire network, be sure that the network portion of the IP address is set to 0. For
example, the Router’s standard IP address is 192.168.16.1. Based on this address, the address of the routed
network is 192.168.16, with the last digit determining the Router’s place on the network. Therefore you would
enter the IP address 192.168.16.0 if you wanted to route to the Router’s entire network, rather than just to the
Router.
Subnet Mask
portion, and which portion is the host portion.
. The Subnet Mask determines which portion of a Destination LAN IP address is the network
For example, a network may have the Subnet Mask of
255.255.255.0. This determines (by using the values 255) that the first three numbers of a network IP address
identify this particular network, while the last digit (from 1 to 254) identifies the specific host.
Default Gateway
. This is the IP address of the gateway device that allows for contact between the Router and
the remote network or host.
Interface
wireless networks) or the
performs dynamic routing over your Ethernet and wireless networks. You can also select
dynamic routing with data coming from the Internet. Finally, selecting
. This interface tells you whether the Destination IP Address is on the
Internet
(WAN). From the drop-down menu, you can also select
Both
enables dynamic routing for both
LAN & Wireless
LAN & Wireless
WAN
(Ethernet and
, which
, which performs
networks, as well as data from the Internet.
Figure 5-14: Setup Tab - Advanced Routing
Figure 5-15: Setup Tab - Advanced Routing - Routing
Table
Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
The Setup Tab - Advanced Routing
18

Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
Metric. This determines the maximum number of steps between network nodes that data packets will travel.
A node is any device on the network, such as PCs, print servers, routers, etc.
Click the
each route, the Destination (LAN IP address), (Subnet) Mask, (Default) Gateway, and Metric are displayed. Click
the Refresh button to update the information. Click the Close button to close the table.
Change these settings as described her e and click the
Changes
Show Routing Table
to cancel your changes.
button to view the Static Routes you’ve already set up.
Save Settings
button to apply your changes or
Show Routing Table. For
Cancel
The Wireless Tab - Basic Wireless Settings
The basic settings for wireless networking are set on this screen.
Basic Wireless Settings
Wireless. To use your Router’s wireless connection, click Enabled. To disable your connection, click Disabled.
Network Mode. From this drop-down menu, you can select the wireless standards running on your network. If
you have both 802.11g and 802.11b devices in your network, keep the default setting, Mixed. If you have only
802.11g devices, select Wireless-G Only. If you have only 802.11b devices, select Wireless-B Only.
Network Name (SSID). The SSID is the network name shared by all devices in a wireless network. The SSID
must be identical for all devices in the wireless network. It is case-sensitive and must not exceed 32 keyboard
characters in length. Make sure this setting is the same for all devices in your wireless network. For added
security, you should change the default SSID (linksys) to a unique name.
Channel. Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to correspond with your network settings. All
devices in your wireless network must broadcast on the same channel in order to communicate.
SSID Broadcast. When wireless clients survey the local area for wireless networks to associate with, they will
detect the SSID broadcast by the Router . To broadcast the Router's SSID, keep the default setting, Enabled. If you
do not want to broadcast the Router's SSID, then select Disabled.
Encryption. The wireless security used on your wireless network is displayed here.
Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
The Wireless Tab - Basic Wireless Settings
Figure 5-16: Wireless Tab - Basic Wireless Settings
19

Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
SecureEasySetup Button. The status of the Router’s SecureEasySetup feature is displayed here. If you want to
use the SecureEasySetup feature, click the SecureEasySetup button.
You will be asked to pr ess the SecureEasySetup button (hardw ar e or softw are) on your wireless client (computer
or other network device) within two minutes to complete the SecureEasySetup process. Click the OK button to
continue.
A new screen will be displayed while the Router is waiting for you to push the SecureEasySetup button on your
wireless client.
When the SecureEasySetup process is complete, the Basic Wireless Settings screen will appear, and the Current
Encryption and Status information will be updated.
Status. The status of your wireless security is displayed here.
Reset Security. If you already set up the network using the SecureEasySetup feature and you want to replace
your current settings with new SecureEasySetup settings, click the Reset Security button. A new screen will
appear. You will be asked to confirm that you want to reset your wireless security settings. Click the OK button to
continue.
The Router will generate a new network name (SSID) and set of keys.
Change these settings as described here and click the Save Settings button to apply your changes or Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes. Help information is shown on the right-hand side of the screen.
Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-G Travel Router with SpeedBooster
The Wireless Tab - Basic Wireless Settings
20
 Loading...
Loading...