LINKSYS WT54GV22 Yesres Manual

A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc.
®
2.4
Model No.
GHz
802.11g
WIRELESS
WRT54G
Wireless-G
Broadband Router
User Guide

Wireless-G Broadband Router
Copyright and Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco
Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Copyright © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All
rights reserved. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders.
WARNING: This product contains chemicals, including lead, known
to the State of California to cause cancer, and birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
How to Use This User Guide
This User Guide has been designed to make understanding networking with the Wireless-G Broadband Router
easier than ever. Look for the following items when reading this User Guide:
This checkmark means there is a note of interest and
is something you should pay special attention to
while using the Wireless-G Broadband Router.
This exclamation point means there is a caution or
warning and is something that could damage your
property or the Wireless-G Broadband Router.
This question mark provides you with a reminder
about something you might need to do while using
the Wireless-G Broadband Router.
In addition to these symbols, there are definitions for technical terms that are presented like this:
word: definition.
Also, each figure (diagram, screenshot, or other image) is provided with a figure number and description, like
this:
Figure 0-1: Sample Figure Description
Figure numbers and descriptions can also be found in the “List of Figures” section in the “Table of Contents”.
WRT54G_V2-UG-40901NC BW

Wireless-G Broadband Router
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Welcome 1
What’s in this Guide? 2
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network 4
Network Topology 4
Ad-Hoc versus Infrastructure Mode 4
Network Layout 4
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Broadband Router 6
The Back Panel 6
The Front Panel 7
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Broadband Router 8
Overview 8
Hardware Installation for Connection to Your Broadband Modem 8
Hardware Installation for Connection to Another Router 10
Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs 12
Overview 12
Configuring Windows 98SE and Millennium PCs 12
Configuring Windows 2000 PCs 13
Configuring Windows XP PCs 14
Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router 15
Overview 15
The Setup Tab - Basic Setup 16
The Setup Tab - DDNS 20
The Setup Tab - MAC Address Clone 21
The Setup Tab - Advanced Routing 22
The Wireless Tab - Basic Wireless Settings 23
The Wireless Tab - Wireless Security 24
The Wireless Tab - Wireless MAC Filter 26
The Wireless Tab - Advanced Wireless Settings 27
The Security Tab - Firewall 29
The Security Tab - VPN Passthrough 29
The Access Restrictions Tab - Internet Access 30

Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Applications and Gaming Tab - Port Range Forward 32
The Applications & Gaming Tab - Port Triggering 33
The Applications and Gaming Tab - DMZ 34
QoS 34
The Administration Tab - Management 36
The Administration Tab - Log 36
The Administration Tab - Diagnostics 37
The Administration Tab - Factory Defaults 38
The Administration Tab - Firmware Upgrade 38
The Administration Tab - Config Management 38
The Status Tab - Router 39
The Status Tab - Local Network 40
The Status Tab - Wireless 41
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 42
Common Problems and Solutions 42
Frequently Asked Questions 50
Appendix B: Wireless Security 56
Security Precautions 56
Security Threats Facing Wireless Networks 56
Appendix C: Upgrading Firmware 59
Appendix D: Windows Help 60
Appendix E: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter 61
Windows 98SE or Me Instructions 61
Windows 2000 or XP Instructions 61
For the Router’s Web-based Utility 62
Appendix F: Glossary 63
Appendix G: Specifications 69
Appendix H: Warranty Information 71
Appendix I: Regulatory Information 72
Appendix J: Contact Information 74

Wireless-G Broadband Router
List of Figures
Figure 3-1: The Broadband Router’s Back Panel 6
Figure 3-2: The Broadband Router’s Front Panel 7
Figure 4-1: Installing the Broadband Router Behind Another Router 8
Figure 4-2: Connecting Your Internet Connection 8
Figure 4-3: Connecting Your Network Devices 9
Figure 4-4: Connecting the Power 9
Figure 4-5: Diagram for Connection to Another Router 10
Figure 4-6: Connecting Another Router 10
Figure 4-7: Connecting Your Network Devices 11
Figure 4-8: Connecting the Power 11
Figure 5-1: Configuration Tab 12
Figure 5-2: IP Address Tab 12
Figure 5-3: Properties 13
Figure 5-4: TCP/IP 13
Figure 5-5: IP Address 13
Figure 5-6: Properties 14
Figure 5-7: TCP/IP 14
Figure 5-8: IP Address 14
Figure 6-1: Password Screen 15
Figure 6-2: Setup Tab - Basic Setup 16
Figure 6-3: DHCP Connection Type 16
Figure 6-4: Static IP Connection Type 16
Figure 6-5: PPPoE Connection Type 17
Figure 6-6: PPTP Connection Type 17
Figure 6-7: HeartBeat Signal Connection Type 18
Figure 6-8: Optional Settings 18
Figure 6-9: Router IP 19
Figure 6-10: Network Address Server Settings 19
Figure 6-11: Time Setting 19
Figure 6-12: Setup Tab - DDNS 20

Wireless-G Broadband Router
Figure 6-13: Setup Tab - MAC Address Clone 21
Figure 6-14: Setup Tab - Advanced Routing (Gateway) 22
Figure 6-15: Setup Tab - Advanced Routing (Router) 22
Figure 6-16: Wireless Tab - Basic Wireless Settings 23
Figure 6-17: Wireless Tab - Wireless Security (WPA Pre-Shared Key) 24
Figure 6-18: Wireless Tab - Wireless Security (WPA RADIUS) 24
Figure 6-19: Wireless Tab - Wireless Security (RADIUS) 25
Figure 6-20: Wireless Tab - Wireless Security (WEP) 25
Figure 6-21: Wireless Tab - Wireless MAC Filter 26
Figure 6-22: MAC Address Filter List 26
Figure 6-23: Wireless Tab - Advanced Wireless Settings 27
Figure 6-24: Security Tab - Firewall 29
Figure 6-25: Security Tab - VPN Passthrough 29
Figure 6-26: Access Restrictions Tab - Internet Access 30
Figure 6-27: Internet Policy Summary 30
Figure 6-28: List of PCs 30
Figure 6-29: Port Services 31
Figure 6-30: Access Restrictions Tab - Inbound Traffic 31
Figure 6-31: Applications and Gaming Tab - Port Range Forward 32
Figure 6-32: Applications and Gaming Tab - Port Triggering 33
Figure 6-33: Applications and Gaming Tab - DMZ 34
Figure 6-34: Applications and Gaming Tab - QOS 34
Figure 6-35: Administration Tab - Management 36
Figure 6-36: Administration Tab - Log 36
Figure 6-37: Administration Tab - Diagnostics 37
Figure 6-38: The Ping Test 37
Figure 6-39: The Traceroute Test 37
Figure 6-40: Administration Tab - Factory Defaults 38
Figure 6-41: Administration Tab - Firmware Upgrade 38
Figure 6-42: Administration Tab - Config Management 38
Figure 6-43: Status Tab - Router 39
Figure 6-44: Status Tab - Local Network 40
Figure 6-45: DHCP Clients Table 40

Wireless-G Broadband Router
Figure 6-46: Status Tab - Wireless 41
Figure C-1: Upgrade Firmware 59
Figure E-1: IP Configuration Screen 61
Figure E-2: MAC Address/Adapter Address 61
Figure E-3: MAC Address/Physical Address 61
Figure E-4: MAC Address Filter List 62
Figure E-5: MAC Address Clone 62

Wireless-G Broadband Router
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
Thank you for choosing the Linksys Wireless-G Broadband Router. The Wireless-G Broadband Router will allow
you to network wirelessly better than ever, sharing Internet access, files and fun, easily and securely.
How does the Wireless-G Broadband Router do all of this? A router is a device that allows access to an Internet
connection over a network. With the Wireless-G Broadband Router, this access can be shared over the four
switched ports or via the wireless broadcast at either 11Mbps for Wireless-B or 54Mbps for Wireless-G. In
addition, the WPA standard provides greater security opportunities while the whole network is protected through
a Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) firewall and NAT technology. All of these security features, as well as full
configurability, are accessed through the easy-to-use browser-based utility.
But what does all of this mean?
Networks are useful tools for sharing computer resources. You can access one printer from different computers
and access data located on another computer's hard drive. Networks are even used for playing multiplayer video
games. So, networks are not only useful in homes and offices, they can also be fun.
PCs on a wired network create a LAN, or Local Area Network. They are connected with Ethernet cables, which is
why the network is called “wired”.
PCs equipped with wireless cards or adapters can communicate without cumbersome cables. By sharing the
same wireless settings, within their transmission radius, they form a wireless network. This is sometimes called
a WLAN, or Wireless Local Area Network. The Wireless-G Broadband Router bridges wireless networks of both
802.11b and 802.11g standards and wired networks, allowing them to communicate with each other.
With your networks all connected, wired, wireless, and the Internet, you can now share files and Internet
access—and even play games. All the while, the Wireless-G Broadband Router protects your networks from
unauthorized and unwelcome users.
Linksys recommends using the Setup CD-ROM for first-time installation of the Router. If you do not wish to run
the Setup Wizard on the Setup CD-ROM, then use the instructions in this Guide to help you connect the
Wireless-G Broadband Router, set it up, and configure it to bridge your different networks. These instructions
should be all you need to get the most out of the Wireless-G Broadband Router.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
LAN (Local Area Network): The
computers and networking products
that make up the network in your home
or office
1

Wireless-G Broadband Router
What’s in this Guide?
This user guide covers the steps for setting up and using the Wireless-G Broadband Router.
• Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter describes the Router’s applications and this User Guide.
• Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
This chapter describes the basics of wireless networking.
• Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Broadband Router
This chapter describes the physical features of the Router.
• Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Broadband Router
This chapter instructs you on how to connect the Router to your network.
• Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs
This chapter instructs you on how to configure your PC(s) for a DHCP connection, if the network settings are
not already set to DHCP.
• Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router
This chapter explains how to use the Web-Based Utility to configure the settings on the Wireless-G Broadband
Router.
• Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix describes some problems and solutions, as well as frequently asked questions, regarding
installation and use of the Wireless-G Broadband Router.
• Appendix B: Wireless Security
This appendix explains the risks of wireless networking and some solutions to reduce the risks.
• Appendix C: Upgrading Firmware
This appendix instructs you on how to upgrade the firmware on the Router should you need to do so.
• Appendix D: Windows Help
This appendix describes how you can use Windows Help for instructions about networking, such as installing
the TCP/IP protocol.
• Appendix E: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for your Ethernet Adapter.
This appendix describes how to find the MAC address for your computer’s Ethernet adapter so you can use
the MAC filtering and/or MAC address cloning feature of the Router.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
2

Wireless-G Broadband Router
• Appendix F: Glossary
This appendix gives a brief glossary of terms frequently used in networking.
• Appendix G: Specifications
This appendix provides the technical specifications for the Router.
• Appendix H: Warranty Information
This appendix supplies the warranty information for the Router.
• Appendix I: Regulatory Information
This appendix supplies the regulatory information regarding the Router.
• Appendix J: Contact Information
This appendix provides contact information for a variety of Linksys resources, including Technical Support.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
3

Wireless-G Broadband Router
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is exactly like a regular local area network (LAN), except that each
computer in the WLAN uses a wireless device to connect to the network. Computers in a WLAN share the same
frequency channel and SSID, which is an identification name shared by the wireless devices belonging to the
same wireless network.
Ad-Hoc versus Infrastructure Mode
SSID: your wireless network’s name.
Unlike wired networks, wireless networks have two different modes in which they may be set up: infrastructure
and ad-hoc. An infrastructure configuration is a WLAN and wired LAN communicating to each other through an
access point. An ad-hoc configuration is wireless-equipped computers communicating directly with each other.
Choosing between these two modes depends on whether or not the wireless network needs to share data or
peripherals with a wired network or not.
If the computers on the wireless network need to be accessible by a wired network or need to share a peripheral,
such as a printer, with the wired network computers, the wireless network should be set up in Infrastructure
mode. The basis of Infrastructure mode centers around a wireless router or an access point, such as the
Wireless-G Broadband Router, which serves as the main point of communications in a wireless network. The
Router transmits data to PCs equipped with wireless network adapters, which can roam within a certain radial
range of the Router. You can arrange the Router and multiple access points to work in succession to extend the
roaming range, and you can set up your wireless network to communicate with your Ethernet hardware as well.
If the wireless network is relatively small and needs to share resources only with the other computers on the
wireless network, then the Ad-Hoc mode can be used. Ad-Hoc mode allows computers equipped with wireless
transmitters and receivers to communicate directly with each other, eliminating the need for a wireless router or
access point. The drawback of this mode is that in Ad-Hoc mode, wireless-equipped computers are not able to
communicate with computers on a wired network. And, of course, communication between the wirelessequipped computers is limited by the distance and interference directly between them.
Network Layout
The Wireless-G Broadband Router has been specifically designed for use with both your 802.11b and 802.11g
products. Now, products using these standards can communicate with each other.
Infrastructure: a wireless network
that is bridged to a wired network via
an access point.
Ad-hoc: a group of wireless devices
communicating directly to each other
(peer-to-peer) without the use of an
access point.
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
4

Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Wireless-G Broadband Router is compatible with all 802.11b and 802.11g adapters, such as the Notebook
Adapters (WPC54G, WPC11) for your laptop computers, PCI Adapter (WMP54G, WMP11) for your desktop PC, and
USB Adapter (WUSB54G, WUSB11) when you want to enjoy USB connectivity. The Broadband Router will also
communicate with the Wireless PrintServer (WPS54GU2, WPS11) and Wireless Ethernet Bridges (WET54G,
WET11).
When you wish to connect your wireless network with your wired network, you can use the Wireless-G
Broadband Router’s four LAN ports. To add more ports, any of the Wireless-G Broadband Router's LAN ports can
be connected to any of Linksys's switches (such as the EZXS55W or EZXS88W).
With these, and many other, Linksys products, your networking options are limitless. Go to the Linksys website at
www.linksys.com for more information about products that work with the Wireless-G Broadband Router.
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Layout
5

Wireless-G Broadband Router
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Broadband
Router
The Back Panel
The Broadband Router's ports, where the cables are connected, are located on the back panel.
Important: Resetting the Broadband Router
will erase all of your settings (WEP Encryption,
Figure 3-1: The Broadband Router’s Back Panel
Reset Button There are two ways to reset the Broadband Router's factory defaults. Either press the Reset
Button, for approximately five seconds, or restore the defaults from the Administration tab -
Factory Defaults in the Broadband Router's Web-based Utility.
Wireless and LAN settings, etc.) and replace
them with the factory defaults. Do not reset
the Broadband Router if you want to retain
these settings.
Internet The Internet port is where you will connect your broadband Internet connection.
1, 2, 3, 4 These ports (1, 2, 3, 4) connect the Broadband Router to your networked PCs and other
Ethernet network devices.
Power The Power port is where you will connect the power adapter.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Back Panel
6

Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Front Panel
The Router’s LEDs, where information about network activity is displayed, are located on the front panel.
Figure 3-2: The Broadband Router’s Front Panel
Power Green. The Power LED lights up and will stay on while the Router is powered on. When the
Router goes through its self-diagnostic mode during every boot-up, this LED will flash. When
the diagnostic is complete, the LED will be solidly lit.
DMZ Green. The DMZ LED indicates when the DMZ function is being used. This LED will remain lit
as long as DMZ is enabled.
WLAN Green. The WLAN LED lights up whenever there is a successful wireless connection. If the LED
is flashing, the Broadband Router is actively sending or receiving data over the network.
1, 2, 3, 4 Green. These numbered LEDs, corresponding with the numbered ports on the Broadband
Router’s back panel, serve two purposes. If the LED is continuously lit, the Broadband Router
is successfully connected to a device through that port. A flashing LED indicates network
activity over that port.
Internet Green. The Internet LED lights up when there is a connection made through the Internet port.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Front Panel
7
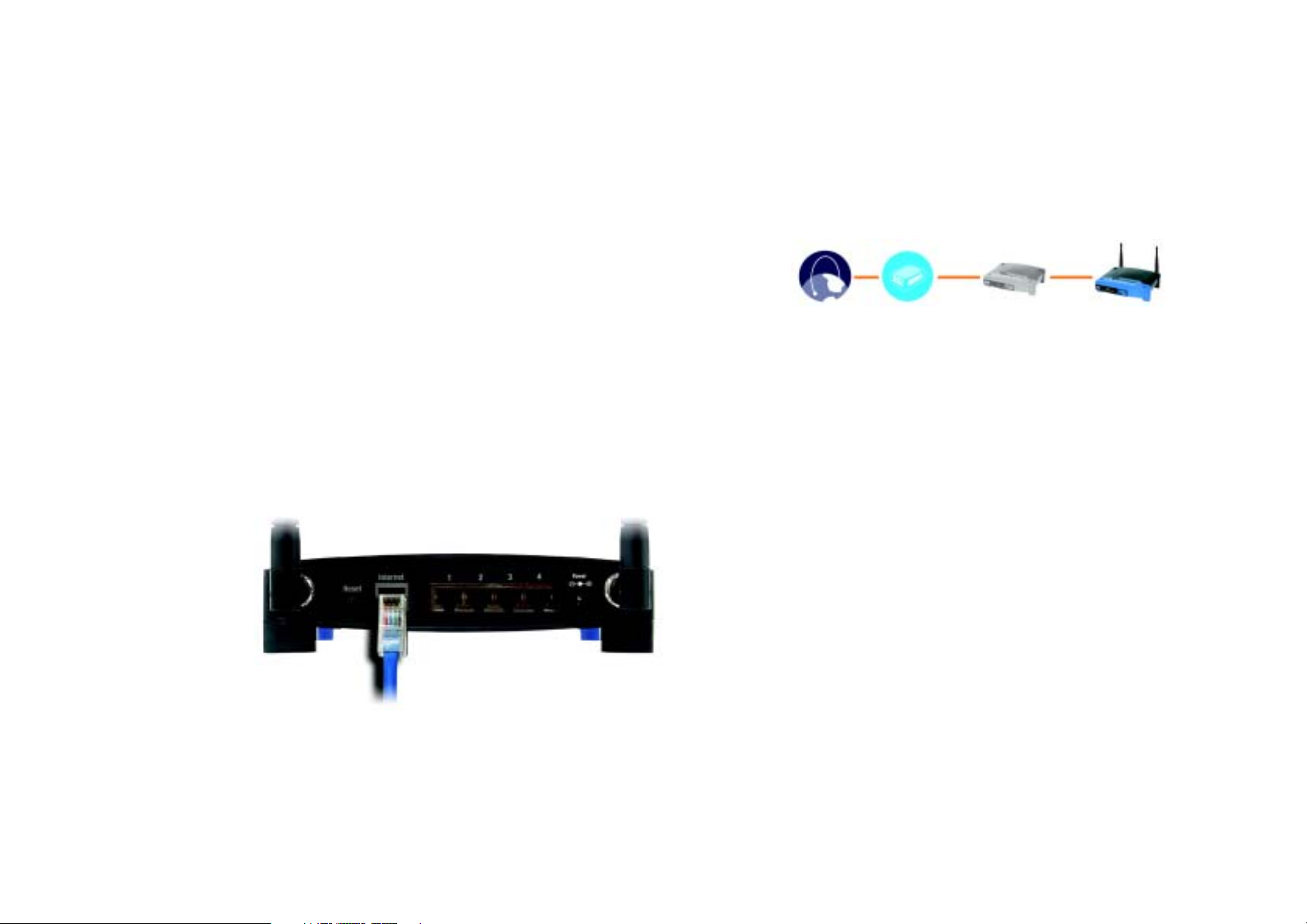
Wireless-G Broadband Router
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Broadband Router
Overview
This chapter includes two sets of instructions. If the Wireless-G Broadband Router will be the only router in your
network, follow the instructions in “Hardware Installation for Connection to Your Broadband Modem.” If you
want to install the Wireless-G Broadband Router behind another router in your network, as shown in Figure 4-1,
then follow the instructions in “Hardware Installation for Connection to Another Router.”
Hardware Installation for Connection to Your Broadband Modem
1. Power down your network devices.
2. Locate an optimum location for the Broadband Router. The best place for the Broadband Router is usually at
the center of your wireless network, with line of sight to all of your mobile stations.
3. Fix the direction of the antennas. Try to place the Router in a position that will best cover your wireless
network. Normally, the higher you place the antenna, the better the performance will be.
4. Connect a standard Ethernet network cable to the Broadband Router’s Internet port. Then, connect the other
end of the Ethernet cable to your cable or DSL broadband modem.
Figure 4-2: Connecting Your Internet Connection
Internet Broadband
Modem
Figure 4-1: Installing the Broadband Router Behind
Another Router
Router Wireless-G
Broadband
Router
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Broadband Router
Overview
8

Wireless-G Broadband Router
5. Connect your network PCs or Ethernet devices to the Broadband Router’s numbered ports using standard
Ethernet network cabling.
Figure 4-3: Connecting Your Network Devices
6. Connect the AC power adapter to the Broadband Router's Power port and the other end into an electrical
outlet. Only use the power adapter supplied with the Broadband Router. Use of a different adapter may result
in product damage.
IMPORTANT: Make sure you use the power
adapter that is supplied with the Router. Use of a
different power adapter could damage the Router.
Figure 4-4: Connecting the Power
Now that the hardware installation is complete, proceed to “Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs,” for
directions on how to configure your PCs.
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Broadband Router
Hardware Installation for Connection to Your Broadband Modem
9
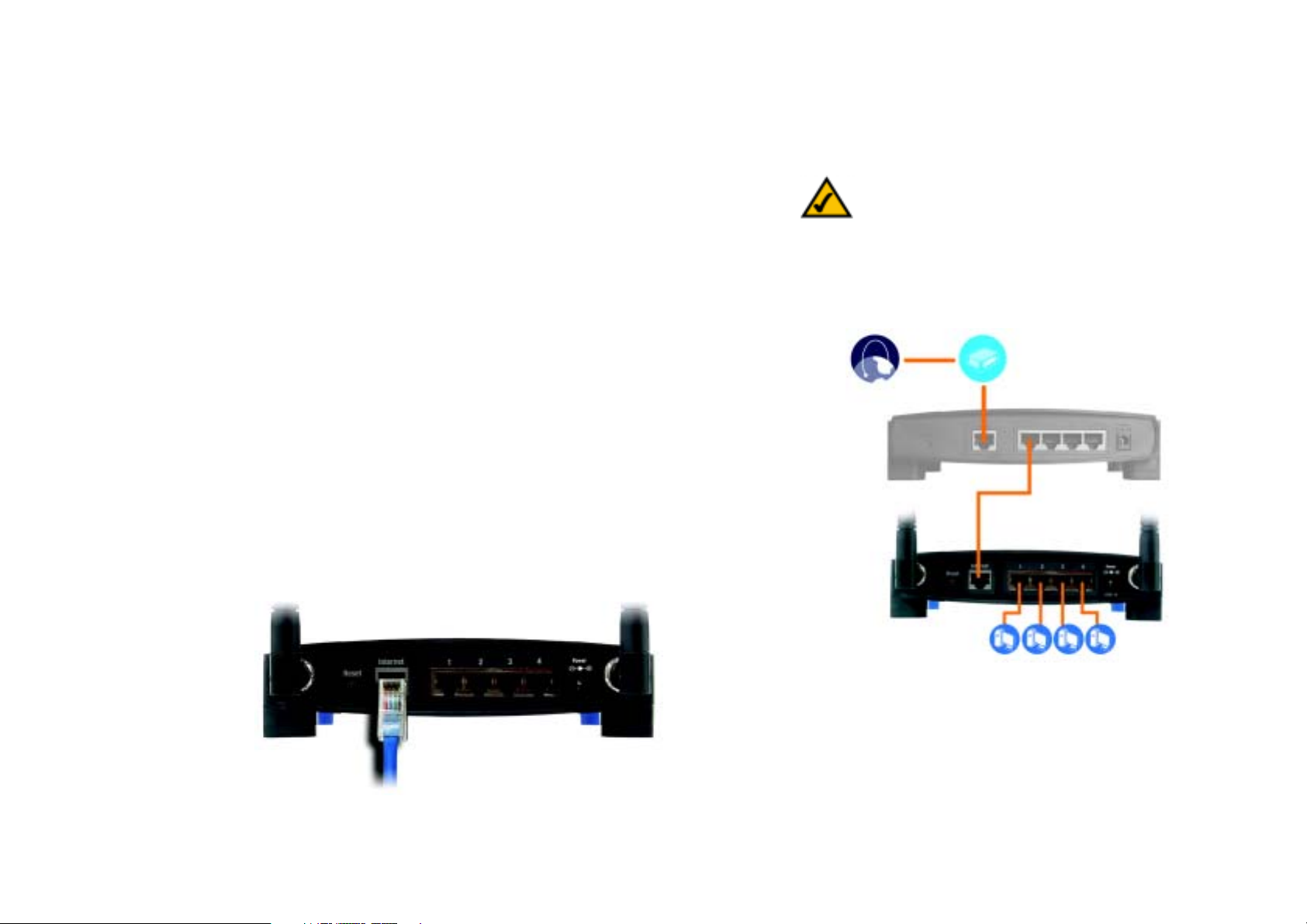
Wireless-G Broadband Router
Hardware Installation for Connection to Another Router
Before you install the Broadband Router, you must change the default IP address of the other router. This is
mandatory because both routers may be set to the same IP address by default. If you do not change the other
router’s default IP address, then you may not be able to set up the Broadband Router.
First, make sure the Broadband Router is NOT connected to your network. Then follow these instructions:
1. To access the other router’s Web-based Utility, launch Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator, and enter the
other router’s default IP address, 192.168.1.1, in the Address field. Then press Enter.
NOTE: Steps 1-4 are instructions for a typical
Linksys router; however, if you are using a nonLinksys router, refer to the other router’s
documentation for instructions on how to change its
local IP address to 192.168.2.1.
2. A password request page will appear. Leave the User Name field blank. In the Password field, enter the
password you have set (the default password is admin). Then click the OK button.
3. The first screen that appears will display the Setup tab. In the Network Setup section, there is a setting called
Local IP Address, which is set to 192.168.1.1. Change this to 192.168.2.1.
4. Click the Save Settings button to save your change, and then exit the Web-based Utility.
5. Power down your network devices. Now you will begin the hardware installation of Broadband Router.
6. Locate an optimum location for the Broadband Router. The best place for the Broadband Router is usually at
the center of your wireless network, with line of sight to all of your mobile stations.
7. Fix the direction of the antennas. Try to place the Router in a position that will best cover your wireless
network. Normally, the higher you place the antenna, the better the performance will be.
8. Connect a standard Ethernet network cable to the Broadband Router’s Internet port. Then, connect the other
end of the Ethernet cable to one of the numbered Ethernet ports on your other router.
Broadband
Internet
Modem
Router
Wireless-G
Broadband
Router
Multiple PCs
Figure 4-5: Diagram for Connection to Another Router
Figure 4-6: Connecting Another Router
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Broadband Router
Hardware Installation for Connection to Another Router
10
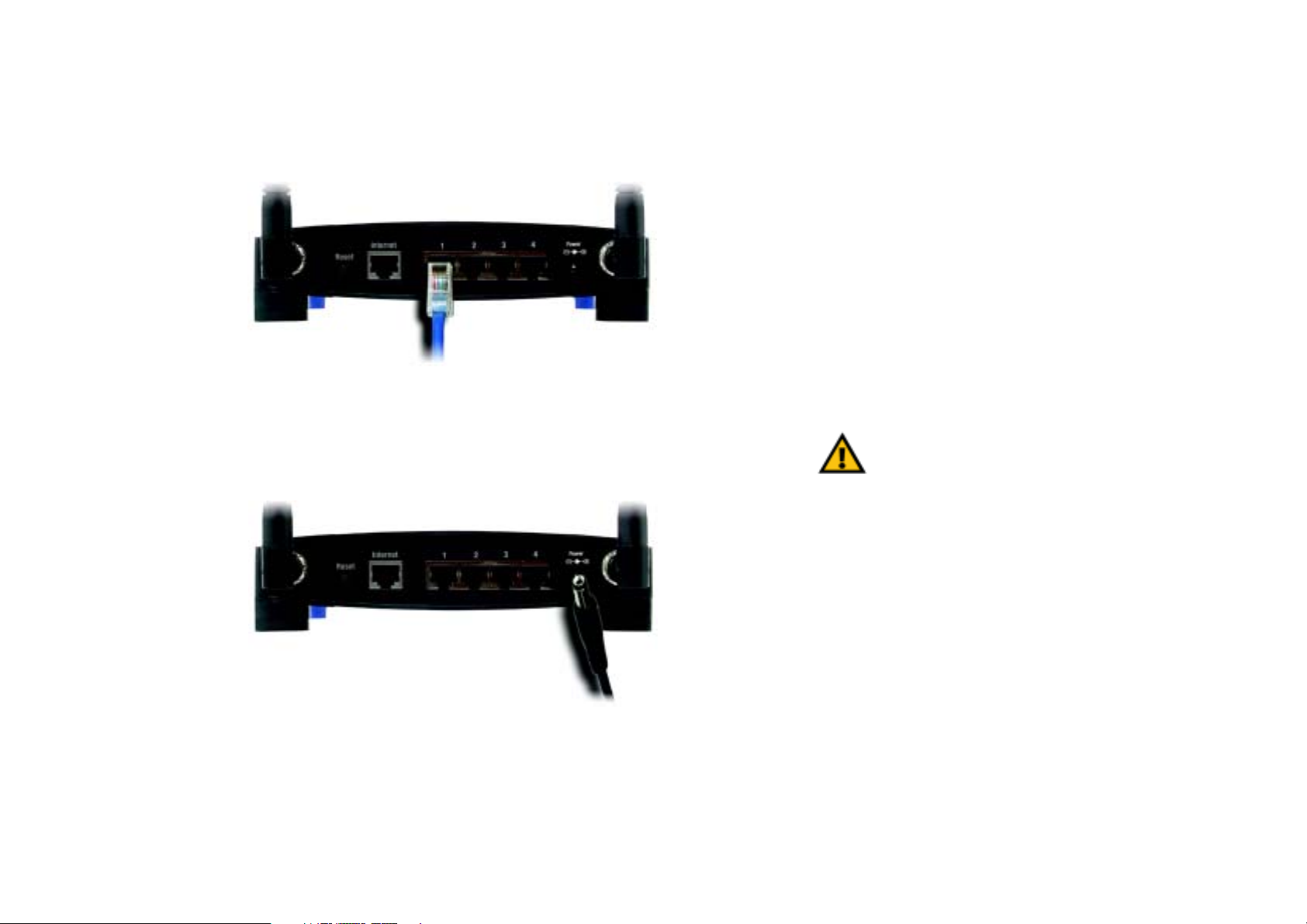
Wireless-G Broadband Router
9. Decide which network computers or Ethernet devices you want to connect to the Broadband Router.
Disconnect the selected computers or devices from the other router, and then connect them to the Broadband
Router’s numbered ports using standard Ethernet network cabling.
Figure 4-7: Connecting Your Network Devices
10. Connect the AC power adapter to the Broadband Router's Power port and the other end into an electrical
outlet. Only use the power adapter supplied with the Broadband Router. Use of a different adapter may result
in product damage.
Figure 4-8: Connecting the Power
Now that the hardware installation is complete, proceed to “Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs,” for
directions on how to configure your PCs.
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Broadband Router
Hardware Installation for Connection to Another Router
IMPORTANT: Make sure you use the power
adapter that is supplied with the Router. Use of a
different power adapter could damage the Router.
11
Wireless-G Broadband Router
Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs
Overview
The instructions in this chapter will help you configure each of your PCs, so they will be able to communicate
with the Router. To do this, you need to configure your PC’s network settings to obtain an IP (or TCP/IP) address
automatically, so your PC can function as a DHCP client. Computers use IP addresses to communicate with the
Router and each other across a network, such as the Internet.
First, find out which Windows operating system your computer is running. You can find out by clicking the Start
button. Read the side panel of the Start menu to find out which operating system your PC is running.
You may need to do this for each computer you are connecting to the Router.
The next few pages tell you, step by step, how to configure your network settings based on the type of Windows
operating system you are using. Make sure that an Ethernet or wireless adapter (also known as a network
adapter) has been successfully installed in each PC you will configure. Once you’ve configured your computers,
continue to “Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router.”
Configuring Windows 98SE and Millennium PCs
IMPORTANT: Important: By default Windows
98SE, 2000, Me, and XP has TCP/IP installed and
set to obtain an IP address automatically. If your
PC does not have TCP/IP installed, click Start and
then Help. Search for the keyword TCP/IP. Then
follow the instructions to install TCP/IP.
1. Click the Start button. Select Settings and click the Control Panel icon. Double-click the Network icon.
2. On the Configuration tab, select the TCP/IP line for the applicable Ethernet adapter, as shown in Figure 5-1.
Do not choose a TCP/IP entry whose name mentions DUN, PPPoE, VPN, or AOL. If the word TCP/IP appears by
itself, select that line. Click the Properties button.
3. Click the IP Address tab. Select Obtain an IP address automatically. (See Figure 5-2.)
4. Now click the Gateway tab, and verify that the Installed Gateway field is blank. Click the OK button.
5. Click the OK button again. Windows may ask you for the original Windows installation disk or additional files.
Check for the files at c:\windows\options\cabs, or insert your Windows CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive and
check the correct file location, e.g., D:\win98, D:\win9x, etc. (if “D” is the letter of your CD-ROM drive).
6. Windows may ask you to restart your PC. Click the Yes button. If Windows does not ask you to restart, restart
your computer anyway.
Go to “Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router.”
Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs
Overview
Figure 5-1: Configuration Tab
Figure 5-2: IP Address Tab
12
Wireless-G Broadband Router
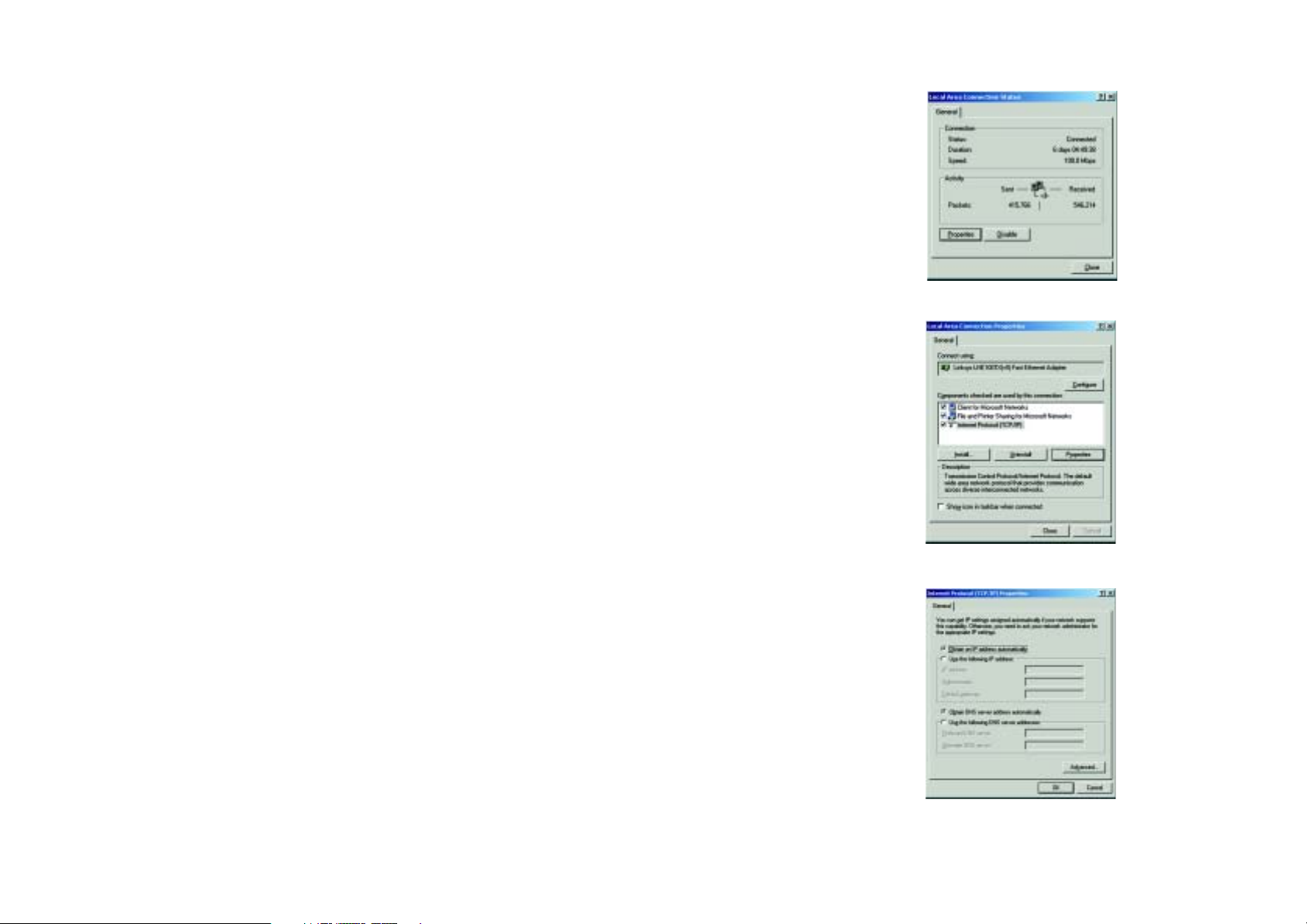
Configuring Windows 2000 PCs
1. Click the Start button. Select Settings and click the Control Panel icon. Double-click the Network and
Dial-up Connections icon.
2. Select the Local Area Connection icon for the applicable Ethernet adapter (usually it is the first Local Area
Connection listed). Double-click the Local Area Connection. Click the Properties button. (See Figure 5-3.)
3. Make sure the box next to Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is checked. Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and
click the Properties button. (See Figure 5-4.)
4. Select Obtain an IP address automatically. Once the new window appears, click the OK button. Click the
OK button again to complete the PC configuration. (See Figure 5-5.)
5. Restart your computer.
Go to “Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router.”
Figure 5-3: Properties
Figure 5-4: TCP/IP
Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs
Configuring Windows 2000 PCs
Figure 5-5: IP Address
13
Wireless-G Broadband Router
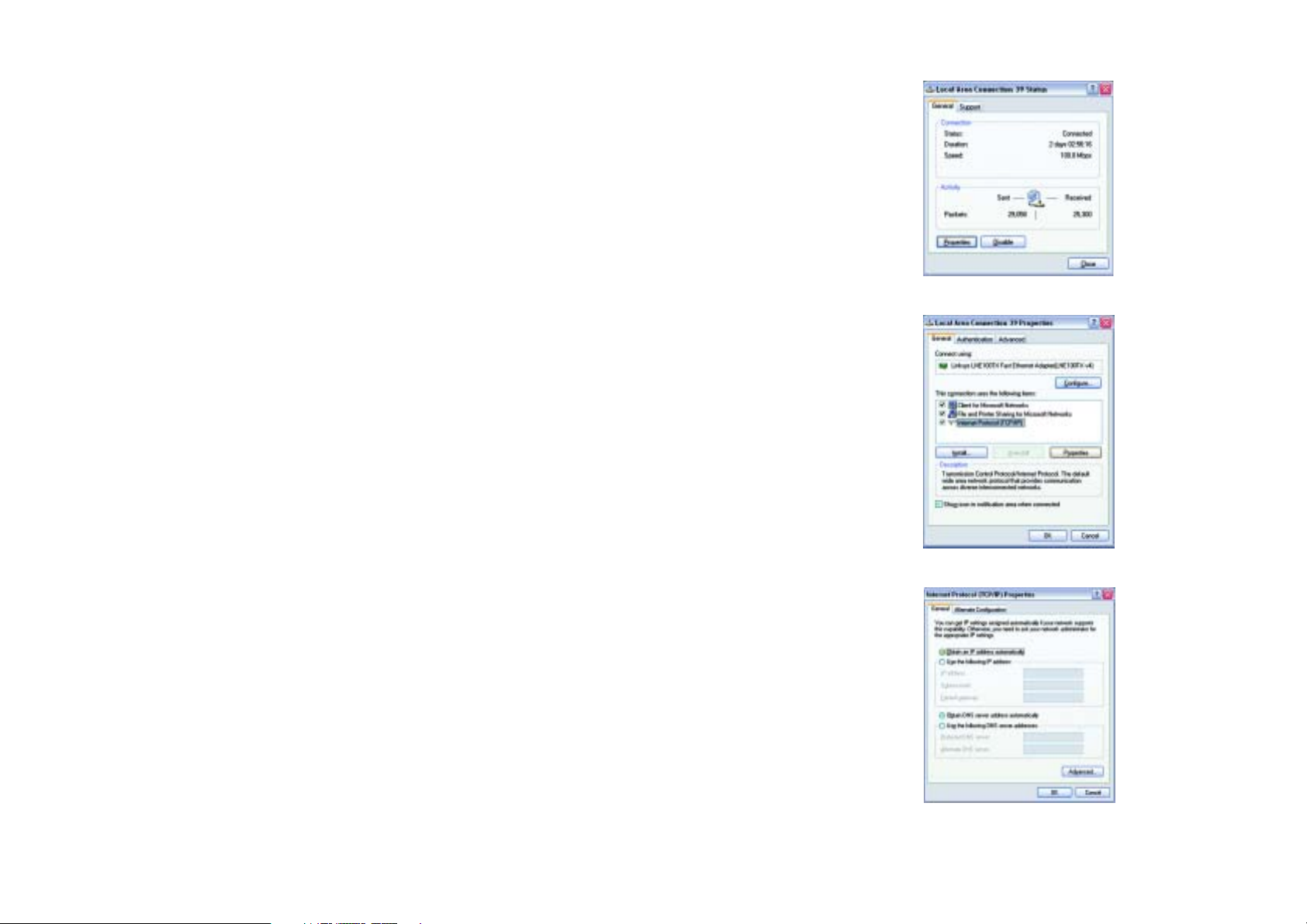
Configuring Windows XP PCs
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the default interface. If you are using the
Classic interface (where the icons and menus look like previous Windows versions), follow the instructions for
Windows 2000.
1. Click the Start button and then the Control Panel icon. Click the Network and Internet Connections icon.
Then click the Network Connections icon.
2. Select the Local Area Connection icon for the applicable Ethernet adapter (usually it is the first Local Area
Connection listed). Double-click the Local Area Connection. Click the Properties button. (See Figure 5-6.)
3. Make sure the box next to Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is checked. Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and
click the Properties button. (See Figure 5-7.)
4. Select Obtain an IP address automatically. (See Figure 5-8.) Once the new window appears, click the OK
button. Click the OK button again to complete the PC configuration.
Go to “Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router.”
Figure 5-6: Properties
Chapter 5: Configuring the PCs
Configuring Windows XP PCs
Figure 5-7: TCP/IP
Figure 5-8: IP Address
14
Wireless-G Broadband Router
Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router
Overview
Linksys recommends using the Setup CD-ROM for first-time installation of the Router. If you do not wish to run
the Setup Wizard on the Setup CD-ROM, then you can use the Web-based Utility to configure the Router. For
advanced users, you may configure the Router’s advanced settings through the Web-based Utility.
NOTE: For first-time installation, Linksys
recommends using the Setup Wizard on the Setup
CD-ROM. If you want to configure advanced settings,
use this chapter to learn about the Web-based Utility.
This chapter will describe each web page in the Utility and each page’s key functions. The utility can be accessed
via your web browser through use of a computer connected to the Router. For a basic network setup, most users
will use these two screens of the Utility:
• Basic Setup. On the Basic Setup screen, enter the settings provided by your ISP.
• Management. Click the Administration tab and then the Management tab. The Router’s default password is
admin. To secure the Router, change the Password from its default.
There are seven main tabs: Setup, Wireless, Security, Access Restrictions, Applications & Gaming,
Administration, and Status. Additional tabs will be available after you click one of the main tabs.
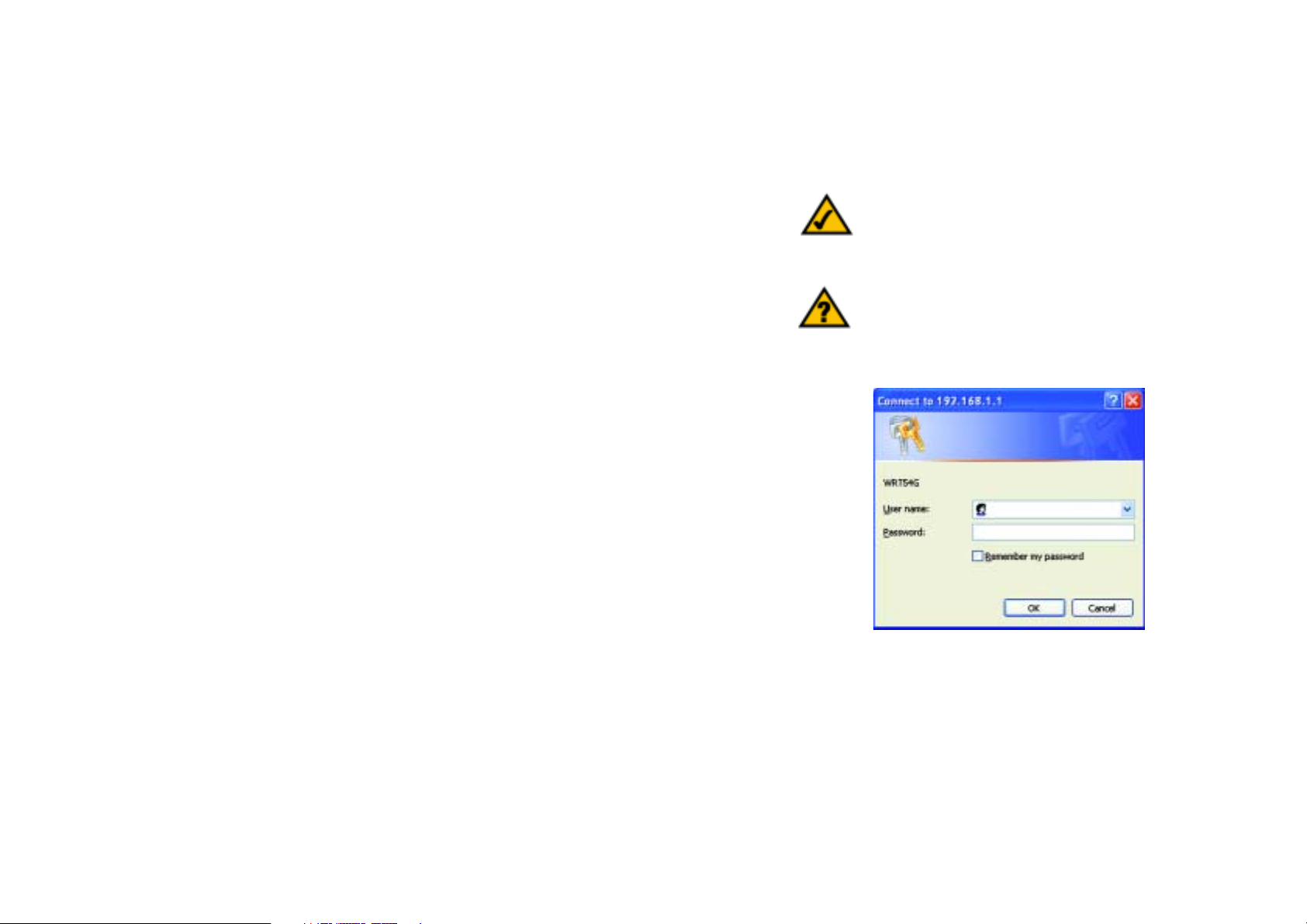
To access the Web-based Utility, launch Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator, and enter the Router’s default IP
address, 192.168.1.1, in the Address field. Then press Enter.
A password request page, shown in Figure 6-1 will appear. (Non-Windows XP users will see a similar screen.)
Leave the User Name field blank. The first time you open the Web-based Utility, use the default password admin.
(You can set a new password from the Administration tab’s Management screen.) Then click the OK button.
HAVE YOU: Enabled TCP/IP on your PCs? PCs
communicate over the network with this protocol.
Refer to “Appendix D: Windows Help” for more
information on TCP/IP.
Figure 6-1: Password Screen
Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router
Overview
15
Wireless-G Broadband Router
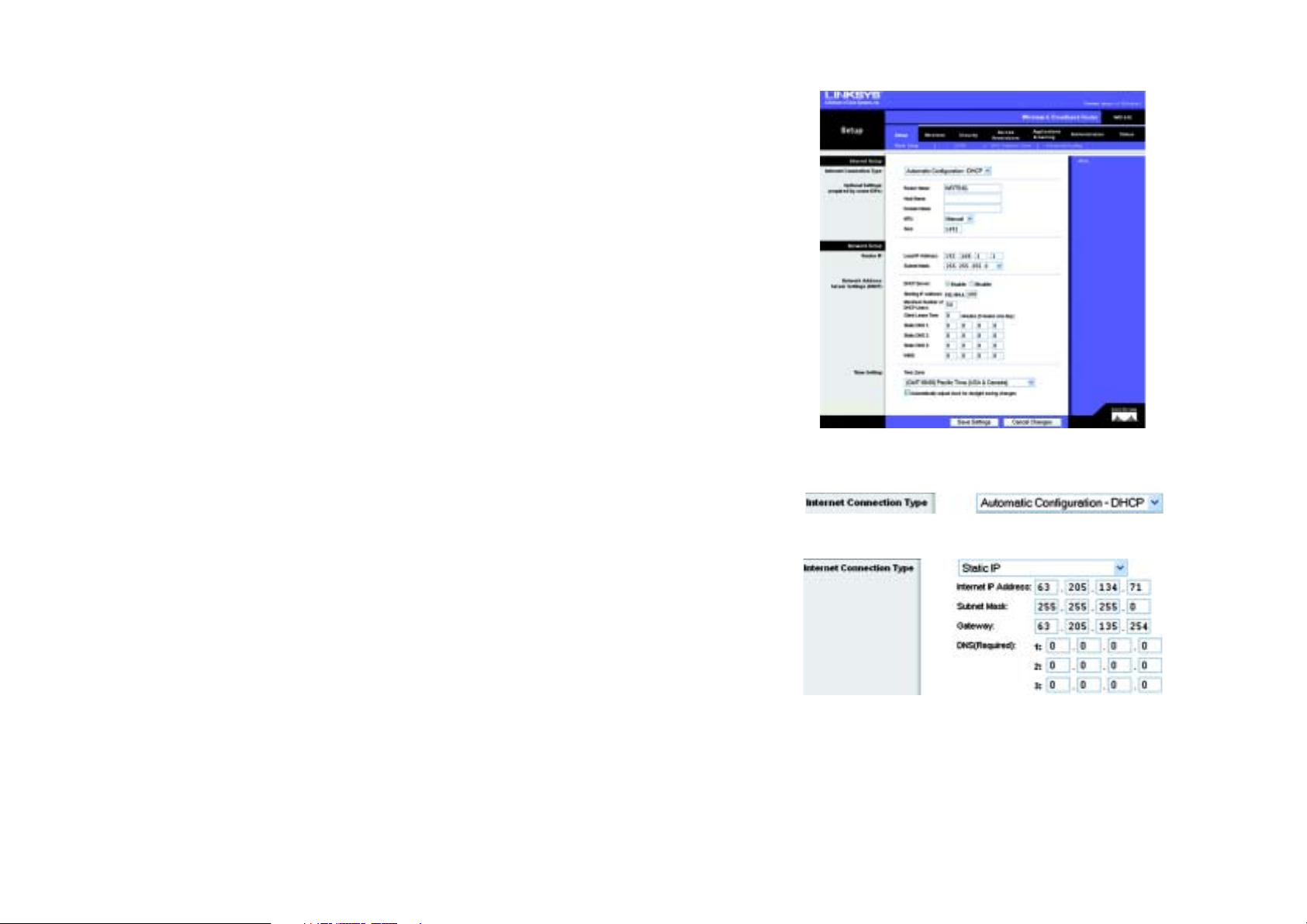
The Setup Tab - Basic Setup
The first screen that appears displays the Setup tab. This allows you to change the Broadband Router's general
settings. Change these settings as described here and click the Save Settings button to apply your changes or
Cancel Changes to cancel your changes.
Internet Setup
The Internet Setup section configures the Broadband Router to your Internet connection. Most of this information
can be obtained through your ISP.
Internet Connection Type
Choose the type of Internet connection your ISP provides from the drop down menu.
• DHCP. By default, the Router’s Internet Connection Type is set to Automatic Configuration - DHCP, which
should be kept only if your ISP supports DHCP or you are connecting through a dynamic IP address.
• Static IP. If you are required to use a permanent IP address to connect to the Internet, select Static IP.
Internet IP Address. This is the Router’s IP address, when seen from the Internet. Your ISP will provide you
with the IP Address you need to specify here.
Figure 6-2: Setup Tab - Basic Setup
Subnet Mask. This is the Router’s Subnet Mask, as seen by users on the Internet (including your ISP). Your ISP
will provide you with the Subnet Mask.
Gateway. Your ISP will provide you with the Gateway Address, which is the ISP server’s IP address.
DNS. Your ISP will provide you with at least one DNS (Domain Name System) Server IP Address.
Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Setup Tab - Basic Setup
Figure 6-3: DHCP Connection Type
Figure 6-4: Static IP Connection Type
Static IP address: a fixed address
assigned to a computer or device
connected to a network.
16

Wireless-G Broadband Router
• PPPoE. Some DSL-based ISPs use PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) to establish Internet
connections. If you are connected to the Internet through a DSL line, check with your ISP to see if they use
PPPoE. If they do, you will have to enable PPPoE.
User Name and Password. Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time. You can configure the Router to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle Time). If your Internet connection has been terminated
due to inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Router to automatically re-establish your connection as
soon as you attempt to access the Internet again. If you wish to activate Connect on Demand, click the radio
button. In the Max Idle Time field, enter the number of minutes you want to have elapsed before your Internet
connection terminates.
Keep Alive Option: Redial Period. If you select this option, the Router will periodically check your Internet
connection. If you are disconnected, then the Router will automatically re-establish your connection. To use
this option, click the radio button next to Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field, you specify how often you want
the Router to check the Internet connection. The default Redial Period is 30 seconds.
• PPTP. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a service that applies to connections in Europe only.
Specify Internet IP Address. This is the Router’s IP address, as seen from the Internet. Your ISP will provide
you with the IP Address you need to specify here.
Subnet Mask. This is the Router’s Subnet Mask, as seen by users on the Internet (including your ISP). Your ISP
will provide you with the Subnet Mask.
Gateway. Your ISP will provide you with the Gateway Address.
User Name and Password. Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time. You can configure the Router to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle Time). If your Internet connection has been terminated
due to inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Router to automatically re-establish your connection as
soon as you attempt to access the Internet again. If you wish to activate Connect on Demand, click the radio
button. In the Max Idle Time field, enter the number of minutes you want to have elapsed before your Internet
connection terminates.
Figure 6-5: PPPoE Connection Type
Figure 6-6: PPTP Connection Type
Keep Alive Option: Redial Period. If you select this option, the Router will periodically check your Internet
connection. If you are disconnected, then the Router will automatically re-establish your connection. To use
this option, click the radio button next to Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field, you specify how often you want
the Router to check the Internet connection. The default Redial Period is 30 seconds.
Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Setup Tab - Basic Setup
17

Wireless-G Broadband Router
• HeartBeat Signal. HeartBeat Signal (HBS) is a service that applies to connections in Australia only.
User Name and Password. Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
Heart Beat Server. This is the IP address that the Router has, when seen from the Internet. Your ISP will
provide you with the IP Address you need to specify here.
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time. You can configure the Router to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle Time). If your Internet connection has been terminated
due to inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Router to automatically re-establish your connection as
soon as you attempt to access the Internet again. If you wish to activate Connect on Demand, click the radio
button. In the Max Idle Time field, enter the number of minutes you want to have elapsed before your Internet
connection terminates.
Keep Alive Option: Redial Period. If you select this option, the Router will periodically check your Internet
connection. If you are disconnected, then the Router will automatically re-establish your connection. To use
this option, click the radio button next to Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field, you specify how often you want
the Router to check the Internet connection. The default Redial Period is 30 seconds.
Optional Settings
Some of these settings may be required by your ISP. Verify with your ISP before making any changes.
Router Name. In this field, you can type a name of up to 39 characters to represent the Router.
Host Name/Domain Name. These fields allow you to supply a host and domain name for the Router. Some ISPs,
usually cable ISPs, require these names as identification. You may have to check with your ISP to see if your
broadband Internet service has been configured with a host and domain name. In most cases, leaving these
fields blank will work.
MTU. MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies the largest packet size permitted for Internet
transmission. The default setting, Manual, allows you to enter the largest packet size that will be transmitted.
The recommended size, entered in the Size field, is 1492. You should leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range.
To have the Router select the best MTU for your Internet connection, select Auto.
Figure 6-7: HeartBeat Signal Connection Type
Figure 6-8: Optional Settings
Network Setup
The Network Setup section changes the settings on the network connected to the Router’s Ethernet ports.
Wireless Setup is performed through the Wireless tab.
Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Broadband Router
The Setup Tab - Basic Setup
18
 Loading...
Loading...