Page 1
User Guide
Wireless Access Point
With Cloud Manager
LAPAC1200C / LAPAC1750C
1
Page 2

Contents
Package Contents .................................................................................................. 4
Device Features ....................................................................................................................................... 4
Mounting Guide ........................................................................................................................................ 5
Access Point Setup Guide ................................................................................... 6
Setup to manage your access point with Linksys cloud server .............................................. 6
Setup to manage your access point locally with browser-based admin tool ..................... 7
Cloud Management Interface ............................................................................. 8
Networks .................................................................................................................................................... 8
Overview .................................................................................................................................................. 10
Access Points ........................................................................................................................................ 11
Wireless .................................................................................................................................................... 16
Clients ....................................................................................................................................................... 21
Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 23
Account settings................................................................................................................................... 24
Inventory .................................................................................................................................................. 27
Local Management Interface ........................................................................... 28
Setup Wizard (Local Administration) ............................................................................................. 28
Administration ....................................................................................................................................... 32
LAN ............................................................................................................................................................ 41
Wireless .................................................................................................................................................... 47
Captive Portal ........................................................................................................................................ 80
Cluster ...................................................................................................................................................... 89
System Status ....................................................................................................................................... 96
Maintenance ........................................................................................................................................ 106
Appendix A - Troubleshooting ...................................................................... 112
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 112
General Problems .............................................................................................................................. 112
Appendix B - About Wireless LANs ............................................................. 114
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 114
Wireless LAN Terminology ............................................................................................................. 114
2
Page 3

Appendix C - PC and Server Configuration ............................................. 118
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 118
Using WEP ............................................................................................................................................ 118
Using WPA2-PSK .............................................................................................................................. 119
Using WPA2-Enterprise .................................................................................................................. 119
802.1x Server Setup (Windows 2000 Server) ....................................................................... 120
802.1x Client Setup on Windows XP ......................................................................................... 129
Using 802.1x Mode (without WPA) ............................................................................................. 135
Regulatory Approvals ...................................................................................................................... 136
3
Page 4
Package Contents
•
Linksys Wireless Access Point
•
Quick Start Guide
•
Ethernet Cable
•
AC Power Adapter
•
CD with Documentation
•
Mounting Bracket
•
Mounting Kit
•
Ceiling Mount Back Plate
•
Drilling Layout Template
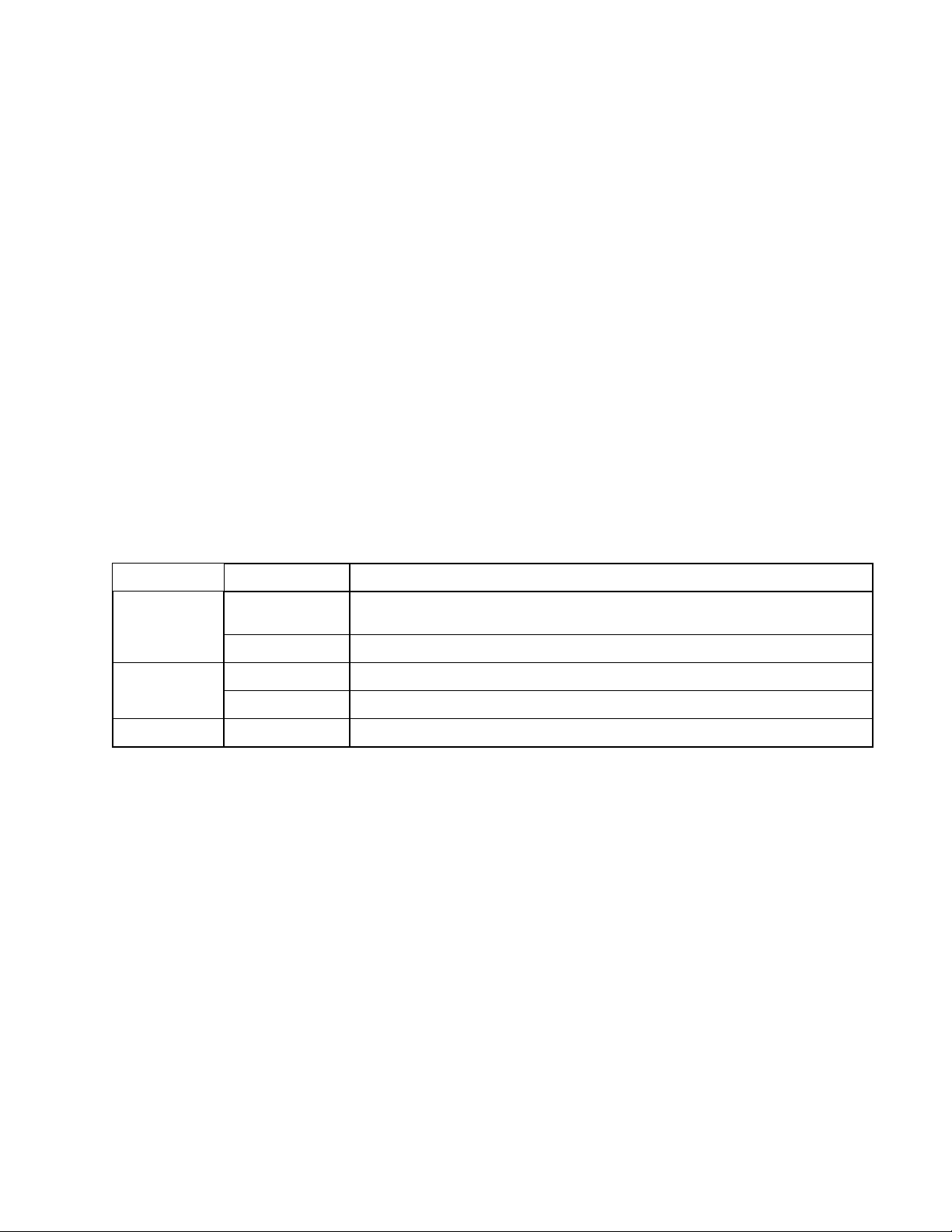
Device Features
There is one indicator light on the front/top of the access point.
Light Color Activity Status
Green
Blue
Red Solid Startup process or update failed; hard reset or service required.
Blinking System is starting.
Solid System is normal; no wireless devices connected.
Blinking Software upgrade in process.
Solid System is normal; at least one wireless device connected.
Ports and Button
Power Port—Connect the AC power adapter to this port.
Note—Use only the adapter that came with your access point.
Ethernet Port—Connect a wired network device to this port. This port supports PoE (Power
over Ethernet) with a PoE switch or PoE injector. LAPAC1200C and LAPAC1750C can be
powered on from an 802.3 af/at (PoE+) compliance source. Using CAT5e or better cable is high
recommended. The maximum power consumption of LAPAC1200C is 13W and LAPAC1750C is
15W.
Note—When both PoE and AC power adapter are connected to access point, device will
get power from PoE as higher precedence.
Reset Button—Press and hold this button for less than 15 seconds to power cycle device. Press
and hold for longer than 15 seconds to reset the device to factory default settings.
4
Page 5

Mounting Guide
To avoid overheating, do not install your access point if ambient temperatures exceed 104°F
(40°C). Install on a flat, stable surface, near the center of your wireless coverage area making
sure not to block vents on the sides of the device enclosure.
Wall Installation
1. Position drilling layout template at the desired location.
2. Drill four screw holes on the mounting surface. If your ethernet cable is routed behind the
wall, mark ethernet cable hole as well.
3. Secure the mounting bracket on the wall with anchors and screws.
4. If your ethernet cable is routed behind the wall, cut or drill the ethernet cable hole you
marked in Step 2. Feed the ethernet cable through the hole.
5. Connect the ethernet cable and/or AC power adapter to your device.
6. Slide the device into the bracket. Turn clockwise until it locks into place.
Ceiling Installation
1. Select ceiling tile for mounting and remove tile.
2. Position drilling layout template at the desired location.
3. Drill four screw holes and ethernet cable hole on the surface of ceiling tile.
4. Place back plate on the opposite side of ceiling tile. Secure mounting bracket to the ceiling
tile with flathead screw and nut. Route the ethernet cable through the ethernet cable hole.
5. Replace tile in ceiling.
6. Connect the ethernet cable and/or AC power adapter to your device
7. Slide the device into the bracket. Turn access point clockwise until it locks.
IMPORTANT—Improper or insecure mounting could result in damage to the device or personal
injury. Linksys is not responsible for damages caused by improper mounting.
5
Page 6
Access Point Setup Guide
Once your Linksys access point is installed, choose which way you will manage it:
•
Remotely, using the Linksys cloud server, or
•
Locally, through a browser-based user interface
Setup to manage your access point with Linksys cloud server
Step 1
Make sure the access point is powered on and connected with an ethernet cable to your network
with internet access. By factory default, the IP address is assigned by a DHCP server. If there is
no DHCP server in your network, the default IP address is 192.168.1.252/255.255.255.0.
Log in to the access point’s browser-based admin tool locally and click the Configure LAN Settings link. Change the IP address or VLAN so the access point can access the internet.
If the indicator light is off, check that the AC power adapter, or PoE cable, is properly connected on both ends.
Step 2
Enter http://Business.Linksys.com in a web browser to access the cloud dashboard. If you already
have a Linksys Small Business Cloud server account, log in.
6
Page 7

If not, create an account by completing the on-screen forms. Then, register the access point at
the new account.
We'll send you a confirmation email. Click on the link and finish setting up your access point.
Setup to manage your access point locally with browserbased admin tool
Step1
Make sure the access point is powered on and connected with an ethernet cable to your network.
If the indicator light is off, check that the AC power adapter, or PoE cable, is properly connected
on both ends.
Step 2
Enter the IP address of your access point. By default, the IP address will be assigned by a DHCP
server (usually the network router). If there is no DHCP server on your network, the default IP
address is 192.168.1.252/255.255.255.0.
Step 3
Type in default username: admin, and password: admin.
Step 4
Click Login and disable the cloud management capability by clicking the Disable Cloud Manager
button in the upper right corner of the screen.
7
Page 8

Cloud Management Interface
Once you are logged in to Business.Linksys.com you can create and manage your networks.
Networks
Create network
To create a new network, go to Networks and click
New Network
8
Page 9
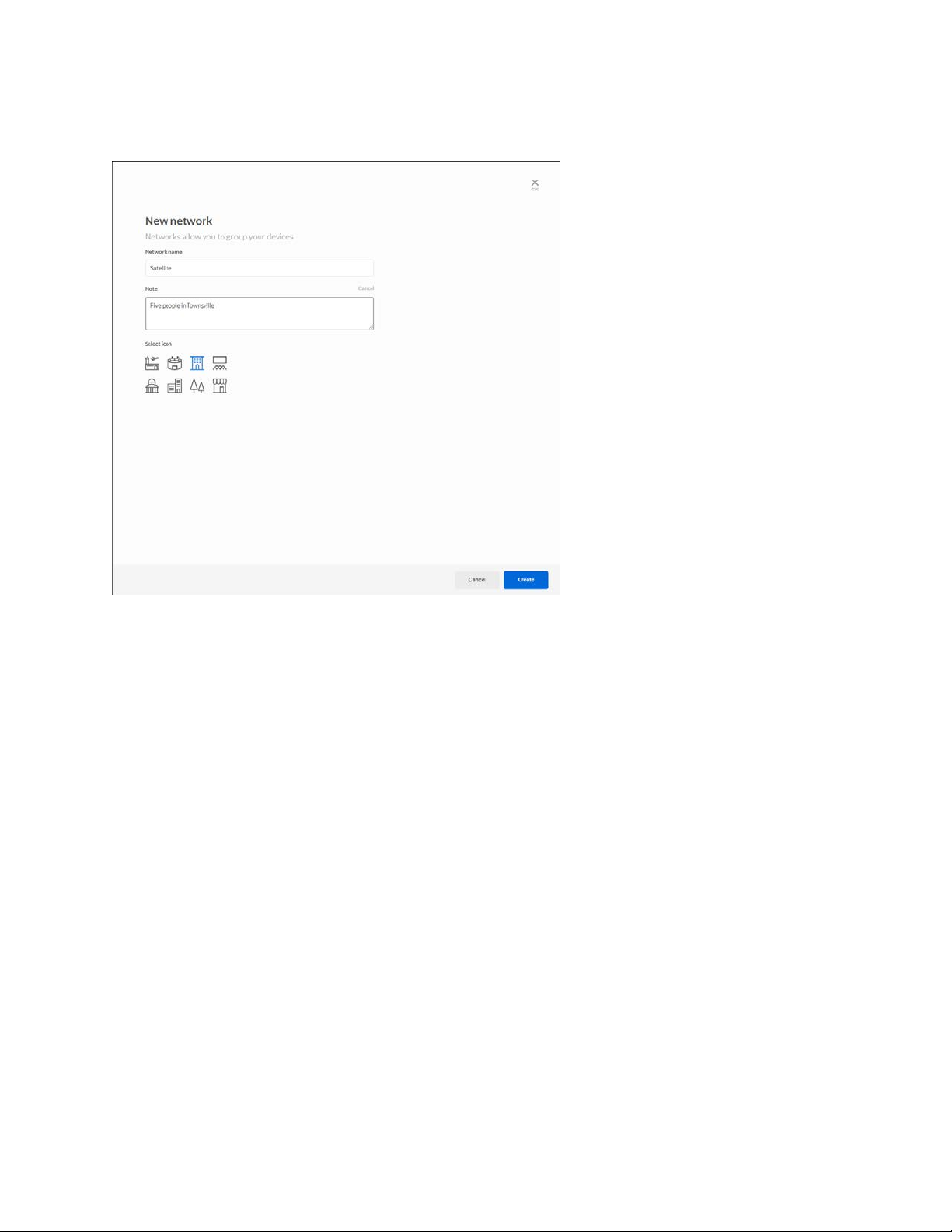
Choose a name for your network and add any descriptive notes about the network. Choose an
icon to represent your network.
9
Page 10
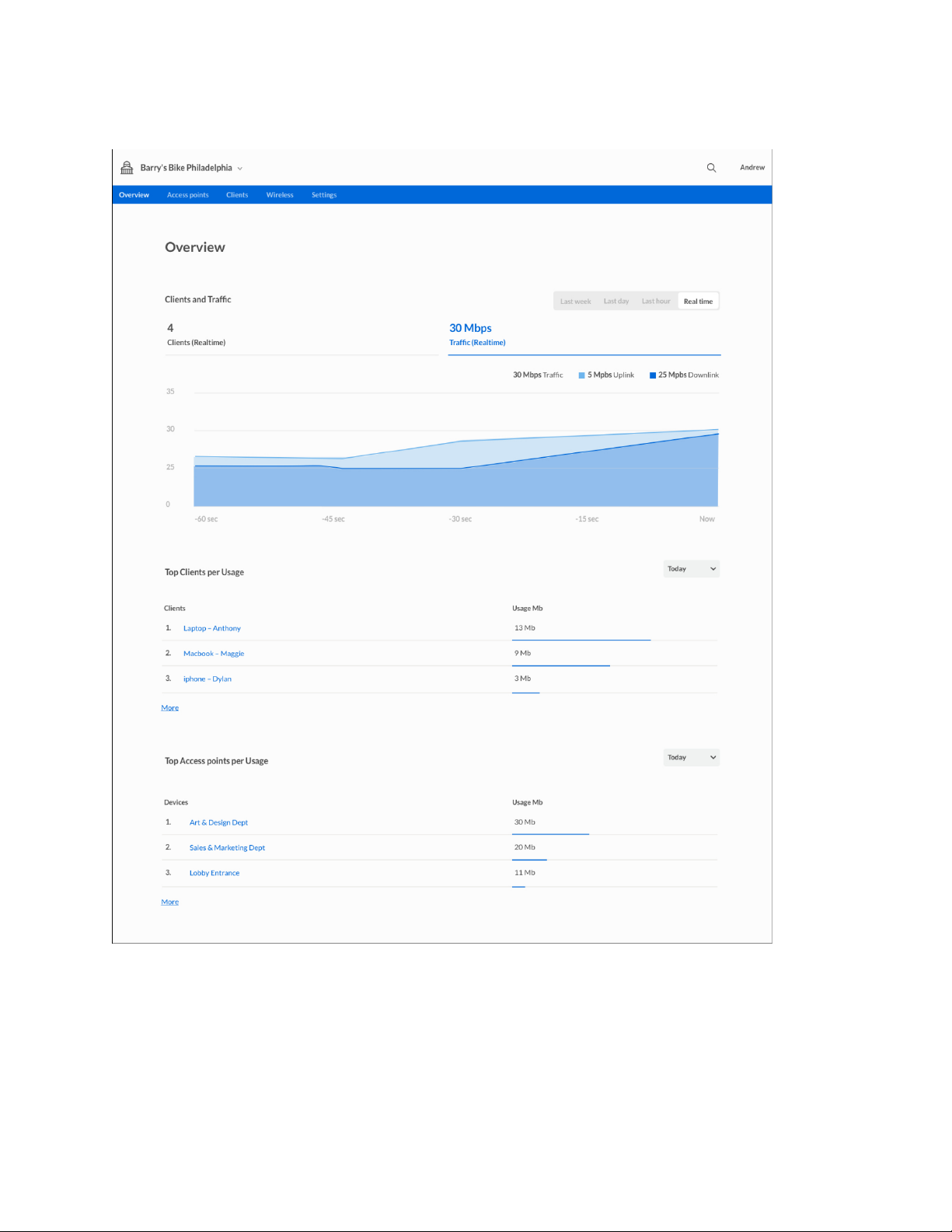
Overview
Overview provides information on a network, its access points and client devices:
•
Clients and usage
•
Top clients per usage
•
Top devices per usage
•
Channel
•
Devices on map
10
Page 11

Access Points
Go to Networks and click on a network name. Click on
access points on your network.
To add a new access point to the network, click Add access point.
Access Points
in the menu bar to manage
1. Connect your access point to internet.
2. Enter the MAC address and serial number of the access point you want to add, then click
Next.
11
Page 12

Once the access point has been found, you can rename it and click the Add device button.
Monitor
Load—Shows the access point’s consumption of CPU load.
Memory—Shows the access point’s consumption of memory.
Status—Shows the access point’s status for the last seven days
Clients and usage—Shows data about clients and traffic for the last seven days.
Connected clients—Shows the list of connected clients.
12
Page 13

Details
View whether the access point is connected to the cloud. See the current firmware version and
check for updates. You can also see the MAC address, model number, the name you gave it and
any device notes or description.
Wireless slot
To add a new wireless name to the device, click Add wireless name and select one from the list.
Authentication—Shows whether the wireless name is open or requires a password.
Broadcast—Shows how many access points in the network are broadcasting the wireless name.
Splash page—Shows whether a splash page is enabled or disabled.
Bandwidth limit—Shows the bandwidth limit set by the administrator.
13
Page 14

TCP/IP
Configure IP—Select Automatic Configuration or Static IP Address.
Server IP—Enter an unused IP address from the address range used on your LAN.
Gateway—Enter the gateway for IP Server.
Subnet mask—Enter the subnet mask for the IP address.
Primary DNS server—Enter the DNS Address.
Secondary DNS server—Optional.
VLAN Tagging—Enter tag of your VLAN.
Radio
Radio mode—Choose a radio mode
Channel width --Choose 20 MHz, 40 MHz or 80 MHz
Channel—Choose Auto or a channel from 1-5
TX Power—Choose the strength of signal when access point is transmitting
14
Page 15
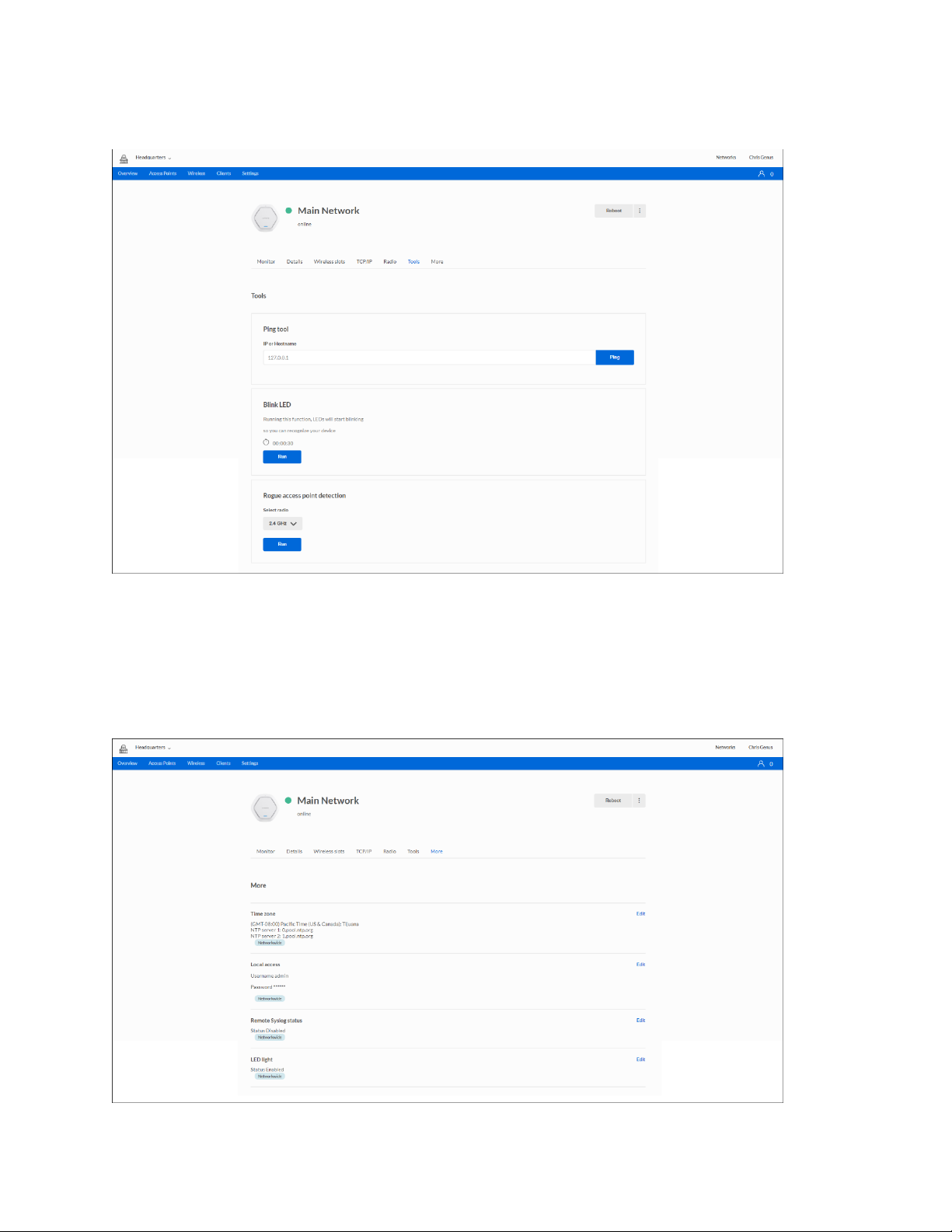
Tools
Ping tool—Determine the accessibility of a host on the network.
Blink LED—Make your device LED blink so you can identify it.
Rogue access point detection—Detect an unexpected or unauthorized access point installed in a
secure network environment.
More
15
Page 16

Time zone—View and edit the device time zone.
Local access—The username and password for local access to device. Default is “admin”.
Remote syslog status --Decide whether to send logs to a Syslog server and enter the server’s IP
address.
LED Light—Device LED status.
Wireless
Create, view and edit names for the wireless names on your networks.
To create a new wireless name, choose a network, click Wireless and then + New wireless
name
.
Wireless Settings
To edit a wireless name’s settings, click settings to the right of a wireless name.
16
Page 17
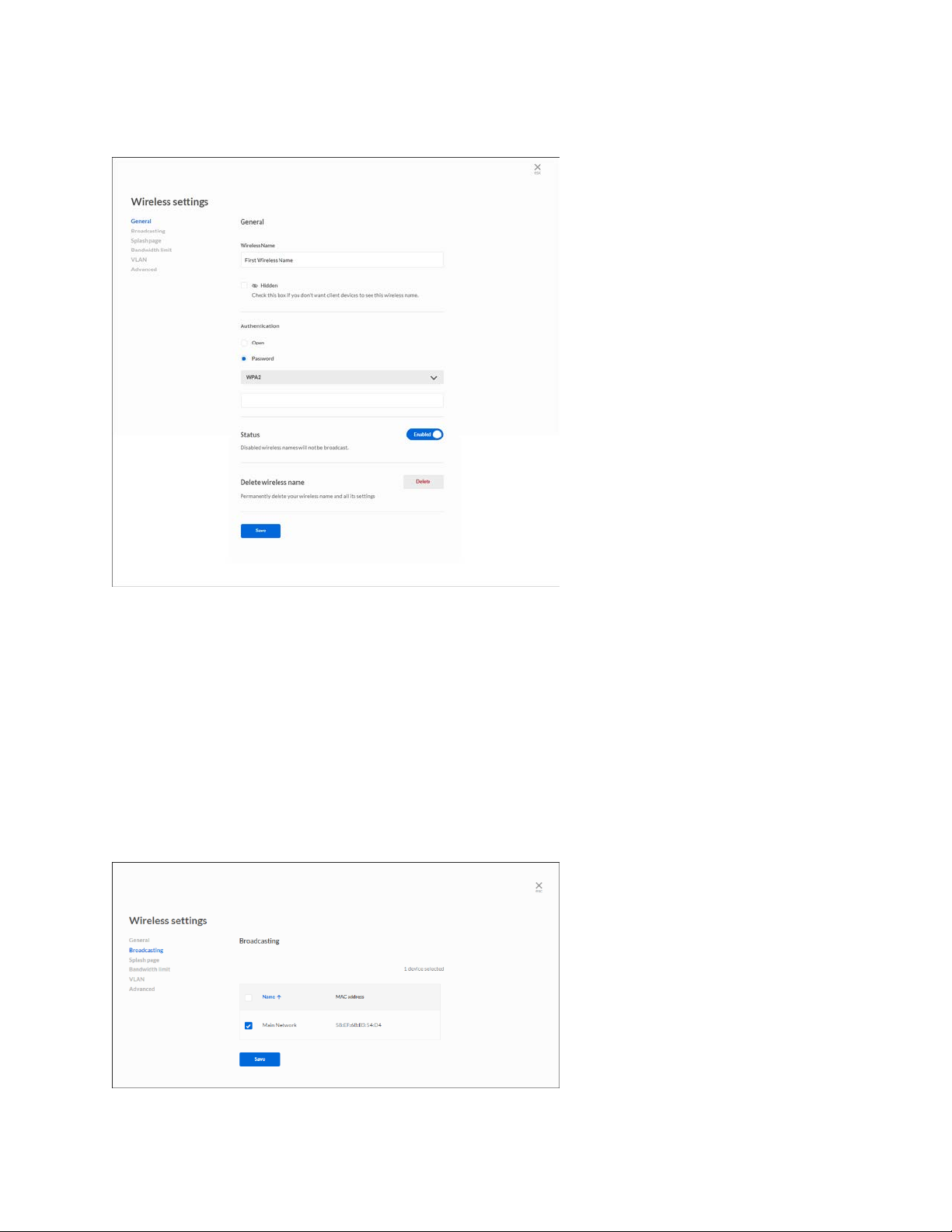
General
Wireless Name—Choose a name and decide whether to broadcast or hide that name.
Authentication—Choose whether to protect the wireless name with a password or allow all
devices to connect. If using a password, choose a security type - either WEP or WPA2.
Status—Enable or disable the wireless name. Disabled wireless names will not be broadcast.
Delete wireless name—Remove the wireless name and all settings from the cloud.
Be sure to click the Save button when you are finished making changes.
Broadcasting
Choose whether to broadcast the wireless names available on an access point.
17
Page 18
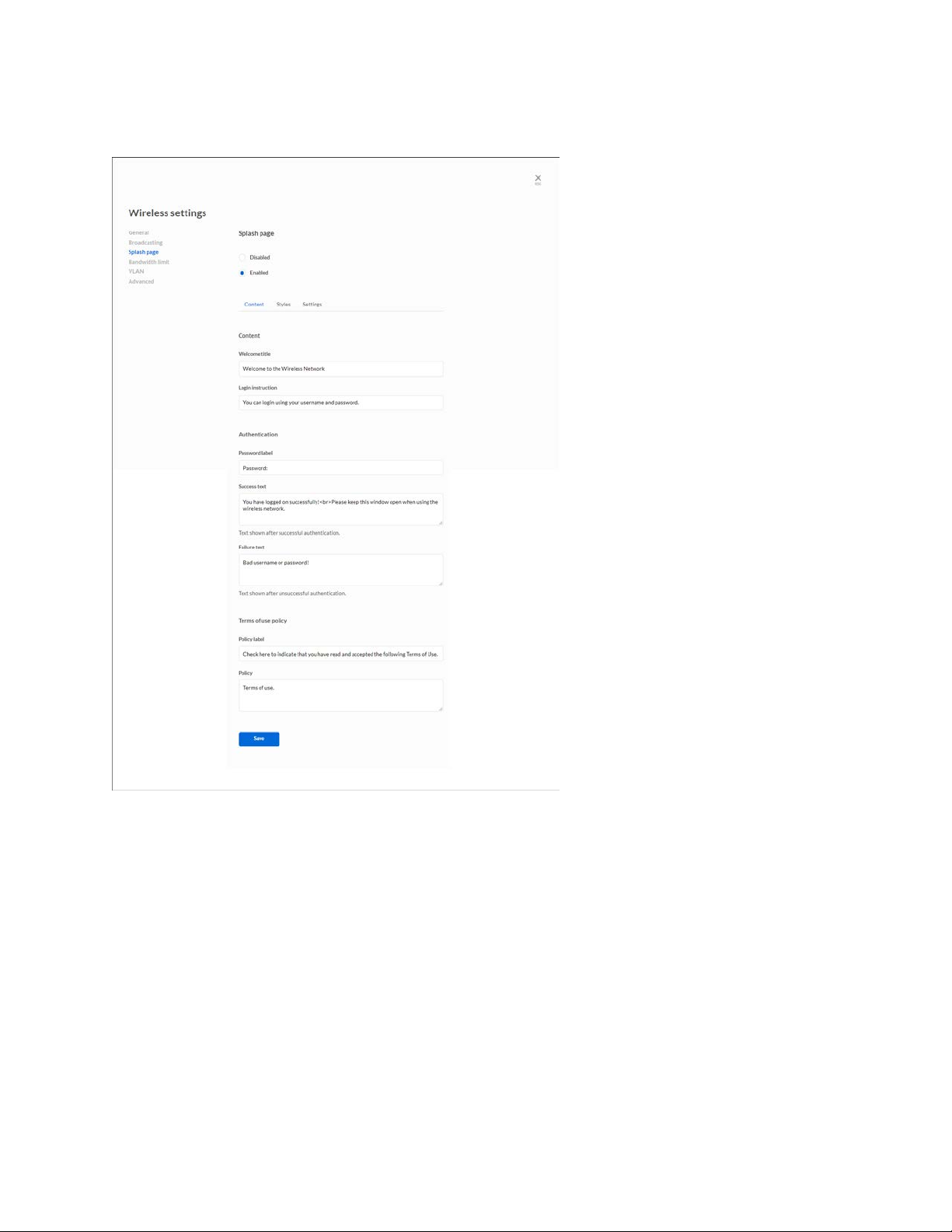
Splash page
Enabled/Disabled—Choose whether to send users to a splash page when connecting to the
wireless name.
Content
• Content
o Welcome title—Create a greeting.
o Login Instruction—Tell users how to log in.
• Authentication
o Password label—Label the password field.
o Success text—Create a message for users who log in successfully.
o Failure text—Create a message for users who are unsuccessful logging in.
18
Page 19

• Term of use policy
o Policy label—Create message to instruct users to confirm they have read your
terms of use.
o Policy—Create terms of use.
Be sure to click the Save button when you are finished making changes.
Styles
• Style
o Logo—Upload a file as a logo for your wireless name.
o Colors—Choose colors for background, text and buttons.
Be sure to click the Save button when you are finished making changes.
Settings
• Client session time out—Set the amount of time (in minutes) that clients can remain
connected to the wireless name. Allowed range is 0-1440 minutes.
• Authentication type—Choose whether to require users to enter a password to move
beyond the splash page.
• Set password—Choose a password for users to enter.
• Custom landing page (Promotional URL)—Turn on to redirect users to a specific website
after authentication.
• URL—Enter the URL of the website users will be redirected to after authentication.
Bandwidth limit
Per wireless bandwidth limit—Turn on bandwidth limit and use the slider to set the
maximum bandwidth (in Mbps) for devices on the wireless band.
19
Page 20

VLAN
VLAN tagging—Turn on to enable tags on traffic related to this wireless name.
VLAN ID—Choose a VLAN ID.
Advanced
Client isolation—When turned on, prevents wireless clients from connecting to each other.
Maximum concurrent clients—When turned on, limits the number of clients that can be
connected at the same time.
20
Page 21
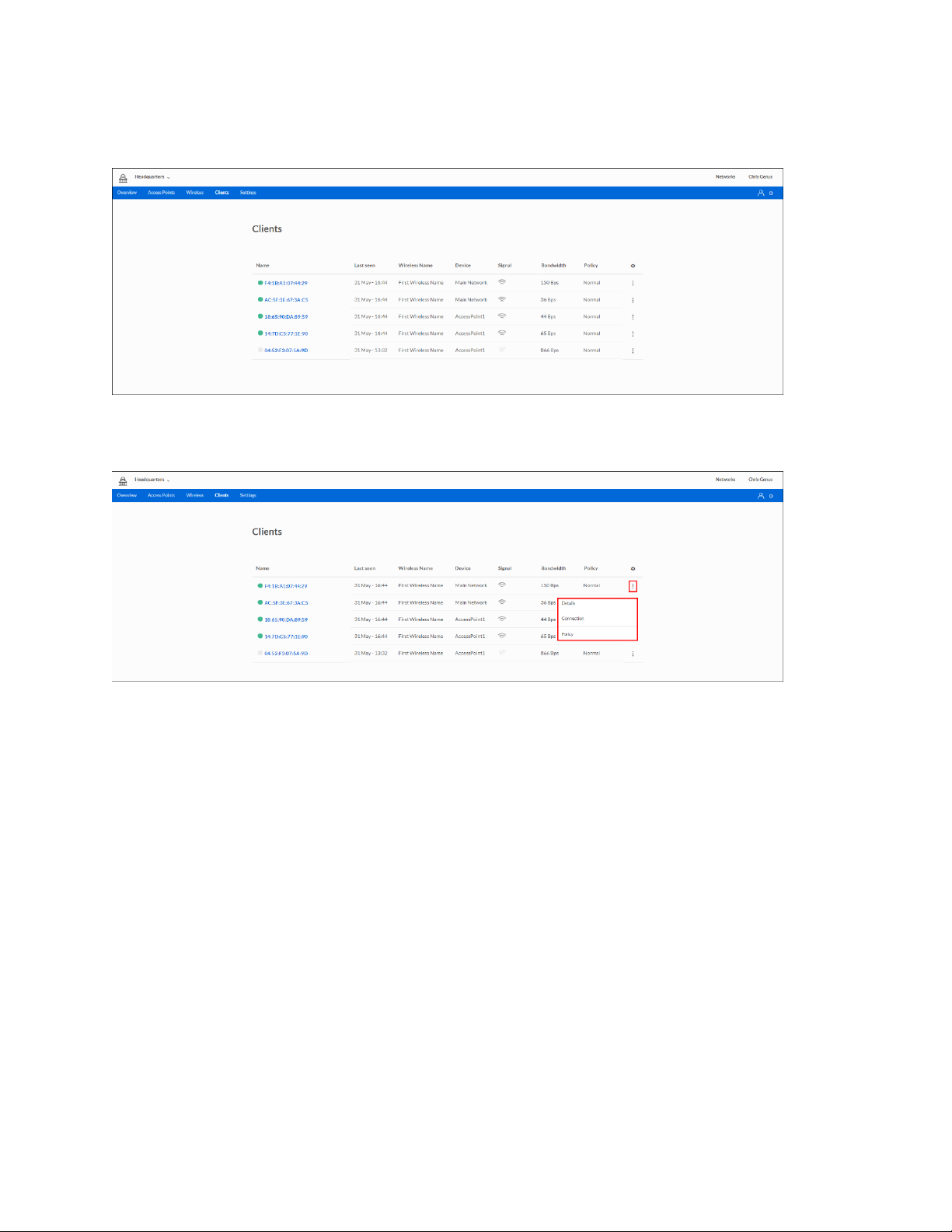
Clients
Click the settings icon in the far column to view information about a specific client. You also can
change the client’s name.
21
Page 22

Details
MAC address—Client MAC address
Name—Custom client label
Notes—Client note or description
First seen—The first time the client connected
Last seen—Last seen client date
Connection
Duration—How long the client has been connected
Traffic—The speed of the connection
Signal—The strength of the connection
Last seen—The last time the client was connected
Wireless Name—The Wi-Fi SSID the client connected to
Device IP address—The client’s IP address
22
Page 23

Settings
Select a network and click on the Settings tab. Choose a setting to view or edit.
General
View or edit a network’s icon, name and any notes. You can also delete a network from cloud
management.
Access point configuration
View or edit a network’s time zone, local login information, remote syslog status and turn the
access point’s light on or off.
Notifications
Decide whether to send email notifications to network members when an access point goes
offline.
23
Page 24
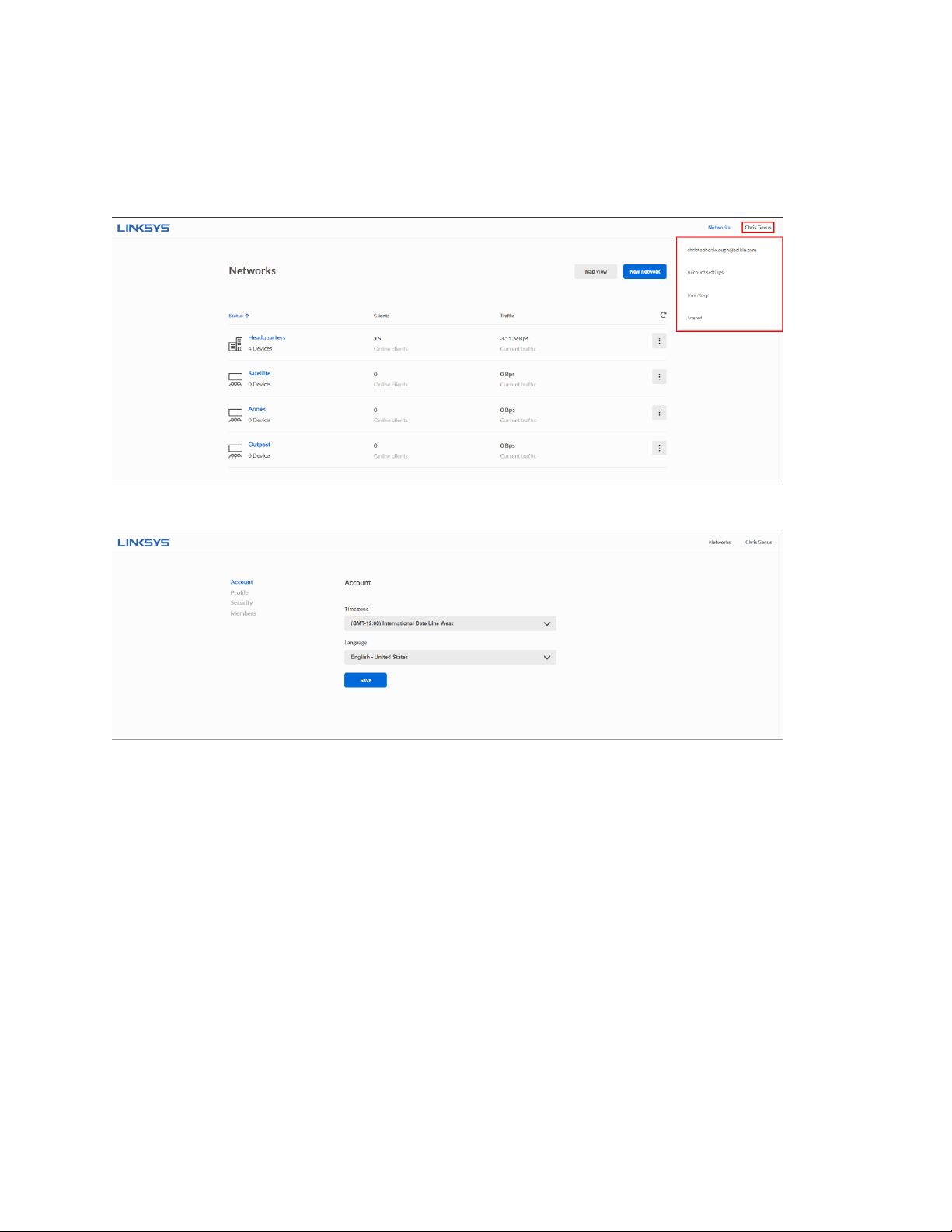
Account settings
To view or edit your account settings, click on your account name and choose Account settings
from the drop-down menu.
Account
Time zone—Set the time zone for your account.
Language—Set the language for the user interface.
24
Page 25

Profile
The profile screen shows your personal data:
•
Name
•
Last name
•
Email
•
Phone number
•
Time zone
•
Language
Security
Change your account password and view information about users logged in to the cloud
management account.
25
Page 26
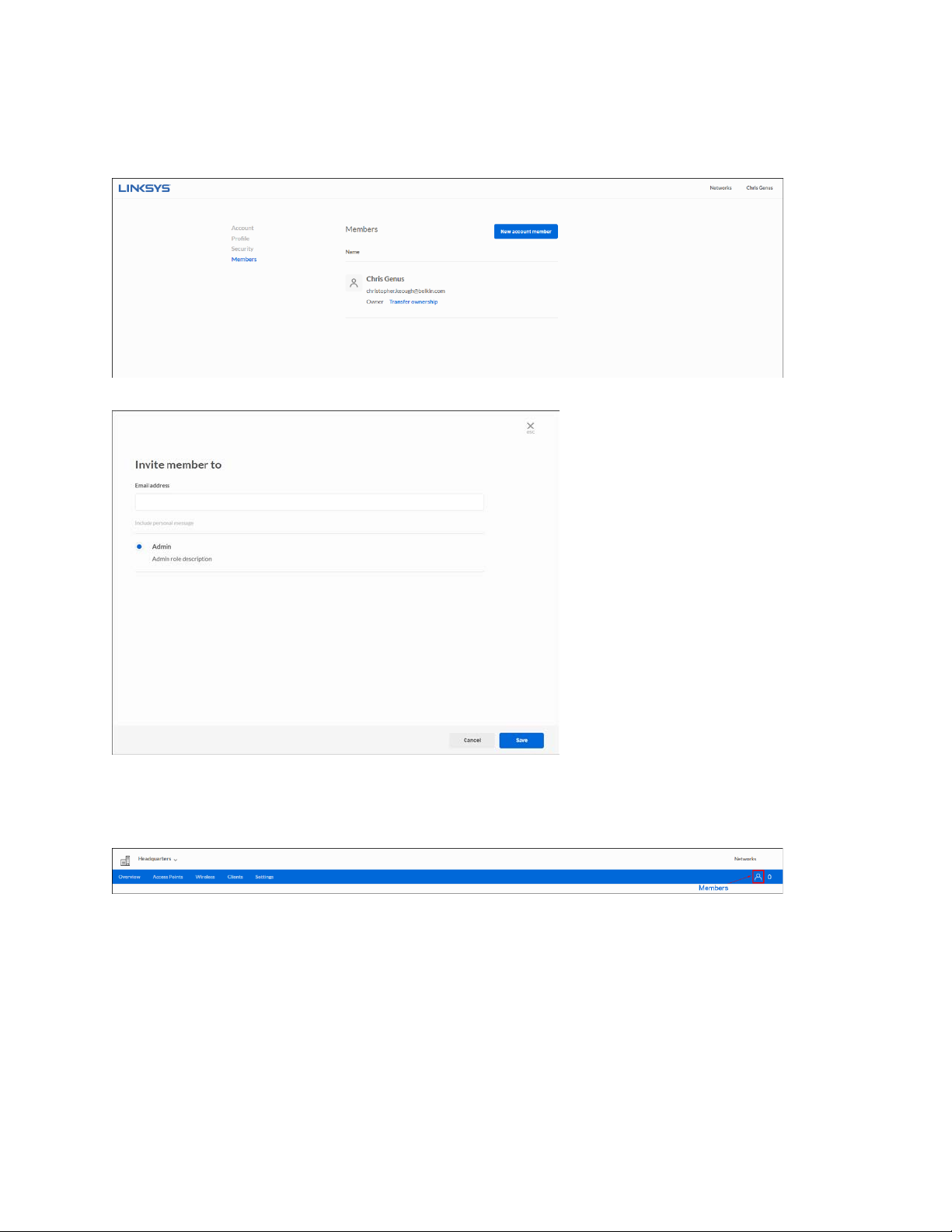
Members
Lists all the members of the account.
To add a new member to an account, click on New account member.
You can also add a new member to your network by clicking the person icon on the far right of the
menu bar. Click Invite
Viewer).
Member
and enter and email address and assign permissions (Manager or
To transfer ownership of your account, click Transfer ownership and enter the email address of
the member you would like to give ownership.
26
Page 27

Inventory
Inventory is the virtual deposit for the devices you're not using.
To add a device, click the Add new access point button.
Connect your device to the internet
Enter the MAC address and serial number of the device you want to add. Click the Next button.
Once the device has been found, rename it and click the Add access point button.
27
Page 28

Local Management Interface
Setup Wizard (Local Administration)
If you are setting up the access point as a standalone device, run the Setup Wizard. If the access
point will be part of a cluster – master or slave - go to Configuration > Cluster > Settings & Status
page instead.
1. Click the Quick Start tab on the main menu.
2. On the first screen, click Launch...
3. Set the password on the Device Password screen, if desired.
28
Page 29

4. Configure the time zone, date and time for the device on System Settings screen.
5. On the IPv4 Address screen configure the IP address of the device (
then click Next.
Static
or
Automatic
)
29
Page 30
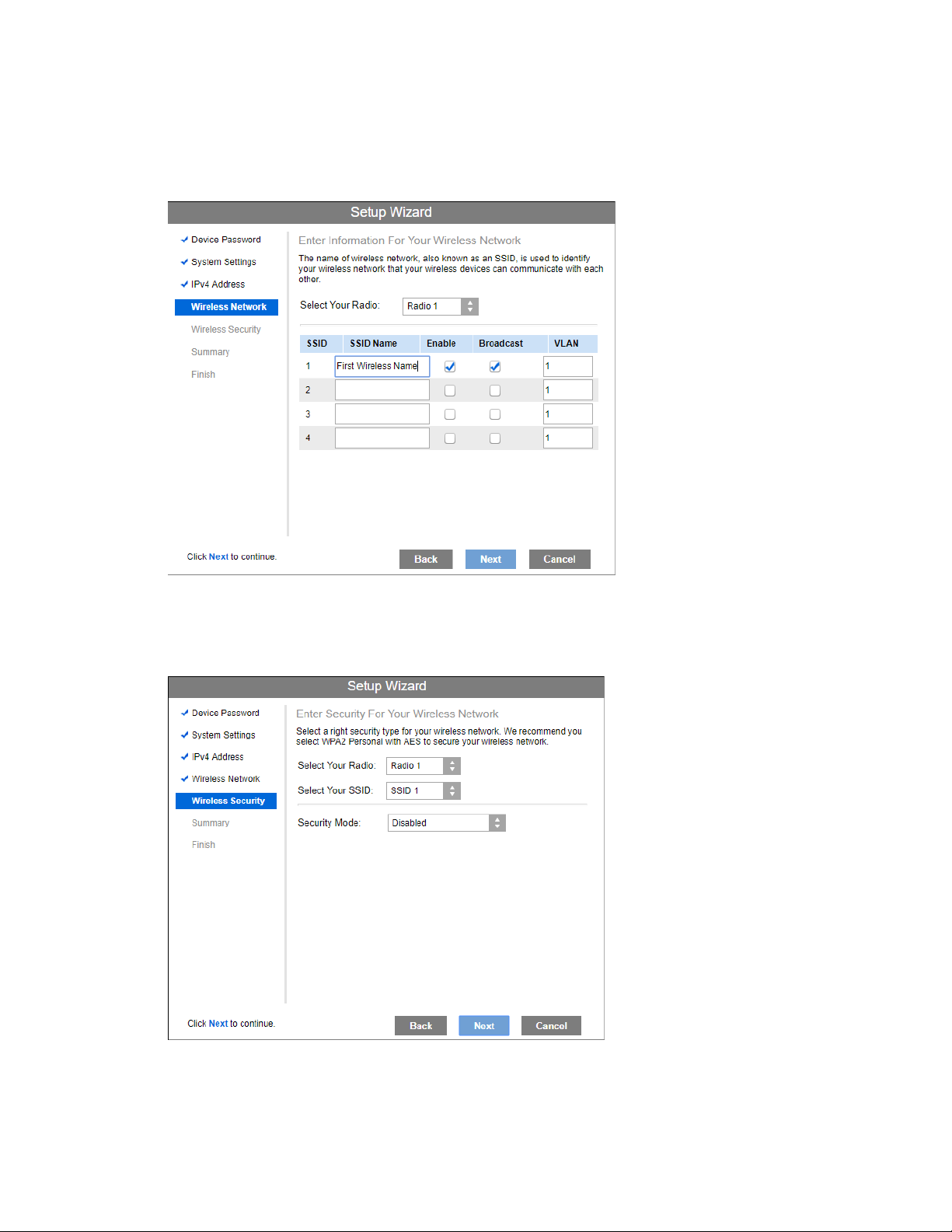
6. Set the SSID information on the Wireless Network screen. Click Next. If you want to
configure more than four SSIDs, go to Configuration > Wireless > Basic Settings. The
access point supports up to eight SSIDs per radio.
7. On the Wireless Security screen, configure the wireless security settings for the device.
Click Next. If you are looking for security options that are not available in the wizard, go to
Configuration > Wireless Security page. The access point supports more sophisticated
security options there.
30
Page 31

8. On the Summary screen, check the data to make sure they are correct and then click
Submit to save the changes.
9. Click Finish to leave the wizard.
31
Page 32

Administration
User Accounts
Go to Configuration > Administration and select User Accounts to manage user accounts. The
access point supports up to five users: one administrator and four normal users.
User Account Table
User Name
Enter the User Name to connect to the
access point’s admin interface. User Name is
effective once you save settings.
User Name can include up to 63 characters.
Special characters are allowed.
User Level
Only administrator account has Read/Write
permission to the access point’s admin
interface. All other accounts have Read Only
permission.
32
Page 33

New Password
Confirm New Password
Enter the Password to connect to the access
point’s admin interface.
Password must be between 4 and 63
characters. Special characters are allowed.
Re-enter password.
Time
Go to Configuration > Administration and select Time to configure system time of the device.
Time
Current Time
Manually
Automatically
Display current date and time of the system.
Set date and time manually.
When enabled (default setting) the access point will get the
current time from a public time server.
33
Page 34

Time Zone
Start Time
End Time
Offset
NTP
NTP Server 1
NTP Server 2
Choose the time zone for your location from the drop-down
list. If your location observes daylight saving time, enable
“Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving changes.”
Specify the start time of daylight saving.
Specify the end time of daylight saving.
Select the adjusted time of daylight saving.
Enter the primary NTP server. It can be an IPv4 address or a
domain name.
Valid characters include alphanumeric characters, "_", "-"
and ".". Maximum length is 64 characters.
Enter the secondary NTP server. It can be an IPv4 address
or a domain name.
Valid characters include alphanumeric characters, "_", "-"
and ".". Maximum length is 64 characters.
34
Page 35

Log Settings
Go to Configuration > Administration and select Log Settings to configure logs. Logs record
various types of activity on the access point. This data is useful for troubleshooting, but enabling
all logs will generate a large amount of data and adversely affect performance.
Log Types
Log Types
Email Alert
Email Alert
SMTP Server
Data Encryption
Port
Select events to log. Checking all options increase the size of the log,
so enable only events you believe are required.
Enable email alert function.
Enter the e-mail server that is used to send logs. It can be an IPv4
address or a domain name.
Valid characters include alphanumeric characters, "_", "-" and ".".
Maximum length is 64 characters.
Enable if you want to use data encryption.
Enter the port for the SMTP server. The port is a value from 1 to
65535 and default is 25.
35
Page 36

Username
Password
Email Address for
Logs
Log Queue Length
Log Time
Threshold
Syslog
Syslog Notification
Enter the Username to login to your SMTP server.
The Username can include up to 32 characters. Special characters
are allowed.
Enter the Password to login to your SMTP server.
The Password can include up to 32 characters. Special characters
are allowed.
Enter the email address the log messages are to be sent to.
Valid characters include alphanumeric characters, "_", "-", "." and "@".
Maximum length is 64 characters.
Enter the length of the queue: up to 500 log messages. The default is
20 messages. When messages reach the set length the queue will be
sent to the specified email address.
Enter the time threshold (in seconds) used to check if the queue is
full. It’s a value from 1 to 600 and default is 600 seconds.
Enable Syslog notification.
IP Type
Server IP Address
Select the IP type of the syslog server: IPv4 or IPv6.
Enter the IPv4 or IPv6 address of syslog server here.
36
Page 37

Management Access
Go to Configuration > Administration and select
management methods of the access point.
Management Access
page to configure the
37
Page 38

Web Access
HTTP
HTTP Port
HTTP to HTTPS
Redirect
HTTPS
HTTPS Port
From Wireless
HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) is the standard for
transferring files (text, graphic images and other
multimedia files) on the World Wide Web.
Enable to allow Web access by HTTP protocol.
Specify the port for HTTP. It can be 80 (default) or from
1024 to 65535.
Enable to redirect Web access of HTTP to HTTPS
automatically.
This field is available only when HTTP access is disabled.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) can provide
more secure communication with the SSL/TLS protocol,
which support data encryption to HTTP clients and
servers.
Enable to allow Web access by HTTPS protocol.
Specify the port for HTTPS. It can be 443 (default) or
from 1024 to 65535.
Enable wireless devices to connect to access point’s
admin page. Disabled by default.
Access Control
SNMP Settings
SNMP
Contact
Location
By default, no IP addresses are prohibited from
accessing the device’s admin page. You can enable
access control and enter specified IP addresses for
access. Four IPv4 and four IPv6 addresses can be
specified.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a
network monitoring and management protocol.
Enable or disable SNMP function here. Disabled by
default.
Enter contact information for the access point.
The contact includes 1 to 32 characters. Special
characters are allowed.
Enter the area or location where the access point
resides.
The location includes 1 to 32 characters. Special
characters are allowed.
38
Page 39

SNMP v1/v2 Settings
Get Community
Set Community
SNMP v3 Settings
SNMP v3 Settings
Enter the name of Get Community. Get Community is
used to read data from the access point and not for
writing data into the access point.
Get Community includes 1 to 32 characters. Special
characters are allowed.
Enter the name of Set Community. Set Community is
used to write data into the access point.
The Set Community includes 1 to 32 characters. Special
characters are allowed.
Configure the SNMPv3 settings if you want to use
SNMPv3.
Username: Enter the username. It includes 0 to 32
characters. Special characters are allowed.
Authentication Protocol: None or HMAC-MD5.
Authentication Key: 8 to 32 characters. Special
characters are allowed.
Access Control
Access Control
SNMP Trap
Trap Community
Trap Destination
Privacy Protocol: None or CBC-DES.
Privacy Key: 8 to 32 characters. Special characters are
allowed.
When SNMP is enabled, any IP address can connect to
the access point MIB database through SNMP. You can
enable access control to allow specified IP addresses.
Two IPv4 and two IPv6 addresses can be specified.
Enter the Trap Community server. It includes 1 to 32
characters. Special characters are allowed.
Two Trap Community servers are supported: can be IPv4
or IPv6.
39
Page 40

SSL Certificate
Go to Configuration > Administration and select SSL Certificate to manage the SSL certificate
used by HTTPS.
Export/Restore to/from Local PC
Export SSL
Certificate
Install Certificate
Export to TFTP Server
Destination File
TFTP Server
Export
Click to export the SSL certificate.
Browse to choose the certificate file. Click
Enter the name of the destination file.
Enter the IP address for the TFTP server. Only support IPv4
address here.
Click to export the SSL certificate to the TFTP server.
Install Certificate.
40
Page 41

Restore from TFTP Server
Source File
TFTP Server
Install
Enter the name of the source file.
Enter the IP address for the TFTP server. Only support IPv4
address here.
Click to install the file to the device.
LED Lighting
Go to Configuration > Administration and select LED Lighting to turn off/on the LED on the front/top of the access point.
41
Page 42

LAN
Network Setup
Go to Configuration > LAN > Network Setup to configure basic device settings, VLAN settings
and settings for the LAN interface, including static or dynamic IPv4/IPv6 address assignment.
TCP/IP
Host Name
VLAN
Assign a host name to this access point. Host name consists of 1 to
15 characters. Valid characters include A-Z, a-z, 0-9 and -. Character
cannot be first and last character of hostname and hostname cannot
be composed of all digits.
Enables or disables VLAN function.
42
Page 43

Untagged
VLAN
Untagged
VLAN ID
Management
VLAN
Enables or disables VLAN tagging. If enabled (default), traffic from the
LAN port is untagged when the following conditions are met: 1) VLAN
ID is equal to Untagged VLAN ID and 2) untagged traffic can be
accepted by LAN port. If disabled, traffic from the LAN port is always
tagged and only tagged traffic can be accepted from LAN port.
By default all traffic on the access point uses VLAN 1, the default
untagged VLAN. All traffic will be untagged until you disable the
untagged VLAN, change the untagged traffic VLAN ID, or change the
VLAN ID for a SSID.
Specifies a number between 1 and 4094 for the untagged VLAN ID.
The default is 1. Traffic on the VLAN that you specify in this field is
not be tagged with a VLAN ID when forwarded to the network.
Untagged VLAN ID field is active only when untagged VLAN is
enabled.
VLAN 1 is the default for both untagged VLAN and management
VLAN.
The VLAN associated with the IP address you use to connect to the
access point. Provide a number between 1 and 4094 for the
Management VLAN ID. The default is 1.
IPv4/v6
IP Settings
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default
Gateway
Primary DNS
Secondary
DNS
Select Automatic Configuration or Static IP Address.
Enter an unused IP address from the address range used on your LAN.
Enter the subnet mask for the IP address above.
Enter the gateway for the IP address above.
Enter the DNS address.
Optional. If entered, this DNS will be used if the Primary DNS does not
respond.
43
Page 44
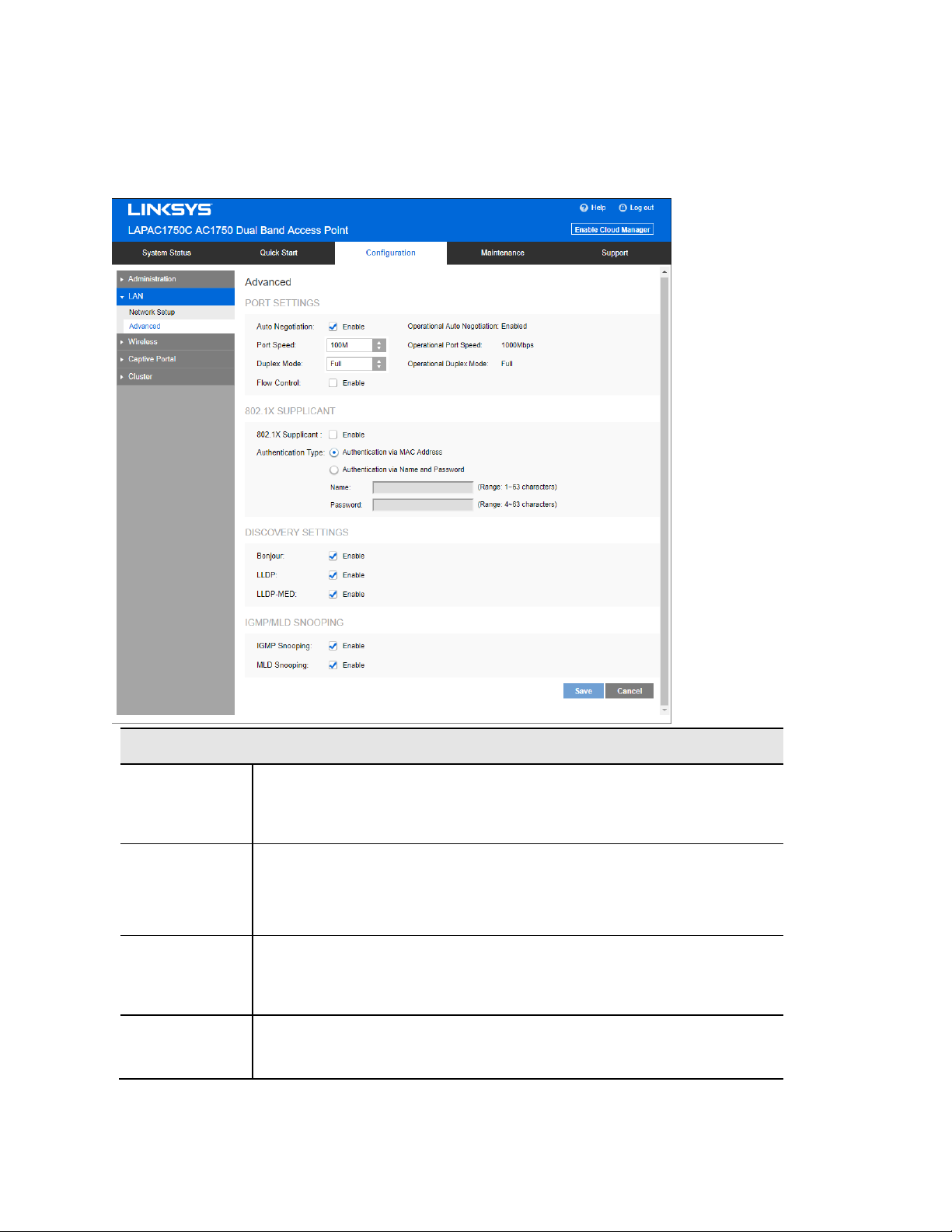
Advanced
Go to Configuration > LAN > Advanced this screen to configure advanced network settings of the
access point.
Port Settings
Auto
Negotiation
Operational
Auto
Negotiation
Port Speed
Operational
Port Speed
If enabled, Port Speed and Duplex Mode will become grey and cannot
be configured. If disabled, Port Speed and Duplex Mode can be
configured.
Current Auto Negotiation mode of the ethernet port.
Select the speed of the ethernet port. Available only when Auto
Negotiation is disabled. The option can be 10M, 100M or 1000M
(default).
Displays the current port speed of the ethernet port.
44
Page 45

Duplex Mode
Operational
Duplex Mode
Flow Control
802.1x Supplicant
802.1x
Supplicant
Authentication
Select the duplex mode of the ethernet port. Available only when
Auto Negotiation is disabled. The option can be Half or Full (default).
Displays the current duplex mode of the ethernet port.
Enable or disable flow control of the ethernet port.
Enable if your network requires this access point to use 802.1X
authentication in order to operate.
This feature supports following two kinds of authentication:
•
•
Authentication via MAC Address
Select this if you want to use MAC Address for authentication.
The access point uses lowercase MAC address for Name and
Password, like xxxxxxxxxxxx.
Authentication via Name and Password
Select this if you want to use name and password for
authentication.
Discovery Settings
Bonjour
LLDP
LLDP-MED
Enable if administrator wants the access point to be discovered by
Bonjour enabled devices automatically. If VLAN is enabled, the
discovery packets will be sent out via management VLAN only. The
access point supports http and https services.
Enable if administrator wants the access point to be discovered by
switch by LLDP protocol. Information such as product name, device
name, firmware version, IP address, MAC address and so on will be
advertised.
Enable if administrator wants the access point to be discovered by
switch by LLDP-MED protocol. Information such as product name,
device name, firmware version, IP address, MAC address and so on
will be advertised.
Name - Enter the login name. The name includes 1 to 63
characters. Special characters are allowed.
Password - Enter the desired login password. The password
includes 4 to 63 characters. Special characters are allowed.
45
Page 46

IGMP/MLD Snooping
IGMP
Snooping
MLD Snooping
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a communications
protocol used by hosts and adjacent routers on IP networks to
establish multicast group memberships. IGMP is an integral part of IP
multicast.
IGMP snooping streamlines multicast traffic handling by examining
(snooping) IGMP membership report messages from interested
hosts, multicast traffic is limited to the subset of ports on which the
hosts reside.
IGMP snooping is enabled by default in the access point
The access point supports IGMPv1, IGMPv2 and IGMPv3 in IGMP
Snooping.
MLD (Multicast Listener Discovery) is a component of the Internet
Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) suite. MLD is used by IPv6 routers for
discovering multicast listeners on a directly attached link, much like
IGMP is used in IPv4.
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping provides multicast
containment by forwarding traffic only to those clients that have
MLD receivers for a specific multicast group (destination address).
The access point maintains the MLD group membership information
by processing MLD reports and generating messages so traffic can
be forwarded to ports receiving MLD reports.
MLD snooping is enabled by default in the access point
The access point supports MLDv1 and MLDv2 in MLD Snooping.
46
Page 47

Wireless
Basic Settings
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Basic Settings to configure your wireless radio and SSIDs.
Advanced wireless settings such as Band Steering, Channel Bandwidth, are on the Advanced
Settings screen.
Basic Wireless Settings
Wireless
Radio
Enable Radio
Select the wireless radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
Enable or disable the wireless radio.
47
Page 48

Wireless
Mode
Wireless
Channel
Select the desired option for radio 1:
G only - allow connection by 802.11G wireless stations only.
N only - allow connection by 802.11N wireless stations only.
B/G-Mixed - allow connection by 802.11B and G wireless
stations only.
B/G/N-Mixed (Default) - allow connections by 802.11N,
802.11B and 802.11G wireless stations.
Select the desired option for radio 2:
N/A-Mixed - allow connection by 802.11A and N wireless
stations only.
N only - allow connection by 802.11N wireless stations only.
AC only - allow connection by 802.11AC wireless stations
only.
A/N/AC-Mixed - allow connection by 802.11A, 802.11N and
802.11AC wireless stations.
Select wireless channel of the radio.
If Auto is selected, the access point will select the best
available channel when device boots up.
SSID Settings
SSID Name
Broadcast
Isolation
If you experience lost connections and/or slow data
transfers,
experiment with manually setting different channels to see
which is the best.
Enter the desired SSID Name. Each SSID must have a unique
name. The name includes 1 to 32 characters
Enable or disable the broadcast of the SSID.
When the access point does not broadcast its SSID, the
network name is not shown in the list of available networks on
a client station. Instead, you must enter the exact network
name manually into the wireless connection utility on the
client so that it can connect.
Enable or disable isolation among clients of the SSID. If
enabled, wireless clients cannot communicate with others in
the same SSID.
It’s disabled by default.
48
Page 49

VLAN ID
Max Clients
Enter the VLAN ID of the SSID.
Used to tag packets which are received from the wireless
clients of the SSID and sent from Ethernet or WDS
interfaces.
Applicable only when VLAN function is enabled. VLAN
function can be configured in Configuration -> LAN ->
Network Setup screen.
Enter the number of clients that can connect to the SSID. The
range is from 0 to 32 and 0 means no limit.
Security
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Security to configure security settings of SSIDs to provide data
protection over the wireless network.
Security
Select SSID
Security Mode
Security Mode
•
Disabled - No security. Anyone using the correct SSID can connect to your network.
•
WEP - The 802.11b standard. Data is encrypted before transmission, but the
encryption system is not very strong.
Select the desired SSID from the drop-down list.
Select the desired security method from the list.
49
Page 50

•
WPA2-Personal - This is a further development of WPA-PSK, and offers even greater
security, using the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) method.
•
WPA/WPA2-Personal - This method, sometimes called Mixed Mode, allows clients to
use either WPA-Personal (with TKIP) or WPA2-Personal (with AES).
•
WPA2-Enterprise - Requires a RADIUS Server on your LAN to provide the client
authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are encrypted
using the WPA2 standard.
If this option is selected:
-
This access point must have a client login on the RADIUS Server.
-
Each user must authenticate on the RADIUS Server. This is usually done using
digital certificates.
-
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the RADIUS
authentication data when required.
-
All data transmission is encrypted using the WPA2 AES standard. Keys are
automatically generated, so no key input is required.
•
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise – This method, sometimes called Mixed Mode, allows clients to
use either WPA-Enterprise (with TKIP) or WPA2-Enterprise (with AES).
•
RADIUS - RADIUS mode utilizes RADIUS server for authentication and dynamic WEP
key generation for data encryption.
50
Page 51

WEP
This is the 802.11b standard. Data is encrypted before transmission, but the encryption system
is not very strong.
WEP
Authentication
Default Transmit Key
WEP Encryption
Passphrase
Key Value
Select Open System or Shared Key. All wireless stations must use the
same method.
Select a transmit key.
Select an encryption option, and ensure your wireless stations have
the same setting:
64-Bit Encryption - Keys are 10 Hex characters.
128-Bit Encryption - Keys are 26 Hex characters.
Generate a key or keys, instead of entering them directly. Enter a word
or group of printable characters in the Passphrase box and click the
Generate button. It consists of 1 to 30 characters.
Enter a key in hexadecimal format.
Note--Due to hardware limitation, one set of WEP key is supported per
radio.
51
Page 52

also use AES.
the same key.
must cope with an ever-changing secret key.
WPA2-Personal
This is a further development of WPA-Personal and offers even greater security.
WPA2-Personal
WPA Algorithm The encryption method is AES. Wireless stations must
Pre-shared Key Enter the key value. It is 8 to 63 ASCII characters or
64 HEX characters. Other wireless stations must use
Key Renewal Specify the value of Group Key Renewal. It’s a value
from 600 to 36000 and default is 3600.
WPA automatically changes secret keys after a certain
period of time. The group key interval is the period of
time in between automatic changes of the group key,
which all devices on the network share.
Constantly keying the group key protects your
network against intrusion, as the would-be intruder
52
Page 53

WPA/WPA2-Personal
This method, sometimes called Mixed Mode, allows clients to use either WPA-Personal or WPA2Personal.
WPA/WPA2-Personal
WPA Algorithm
Pre-shared Key
Key Renewal
The encryption method is TKIP or AES.
Enter the key value. It is 8 to 63 ASCII characters or
64 HEX characters. Other wireless stations must use
the same key.
Specify the value of Group Key Renewal. It’s a value
from 600 to 36000, and default is 3600.
WPA automatically changes secret keys after a certain
period of time. The group key interval is the period of
time in between automatic changes of the group key,
which all devices on the network share.
Constantly keying the group key protects your
network against intrusion, as the would-be intruder
must cope with an ever-changing secret key.
53
Page 54

WPA2-Enterprise
This version of WPA2-Enterprise requires a RADIUS Server on your LAN to provide the client
authentication. Data transmissions are encrypted using the WPA2 AES standard.
WPA2-Enterprise
Primary Server
Primary Server Port
Primary Shared
Secret
Backup Server
Backup Server Port
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Server on your
network.
Enter the port number used for connections to the
RADIUS Server. It is a value from 1 to 65534, and
default is 1812.
Enter the key value to match the RADIUS Server. It
consists of 1 to 64 characters.
The Backup Authentication Server will be used when
the Primary Authentication Server is not available.
Enter the port number used for connections to the
Backup RADIUS Server. It’s a value from 1 to 65534,
and default is 1812.
54
Page 55

Backup Shared
Secret
WPA Algorithm
Key Renewal
Timeout
Enter the key value to match the Backup RADIUS
Server. It consists of 1 to 64 characters.
The encryption method is AES.
Specify the value of Group Key Renewal. It is a value
from 600 to 36000, and default is 3600.
WPA automatically changes secret keys after a
certain period of time. The group key interval is the
period of time in between automatic changes of the
group key, which all devices on the network share.
Constantly keying the group key protects your
network against intrusion, as the would-be intruder
must cope with an ever-changing secret key.
55
Page 56

WPA/WPA2-Enterprise
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise requires a RADIUS Server on your LAN to provide the client
authentication. Data transmissions are encrypted using WPA/WPA2 standard.
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise
Primary Server
Primary Server Port
Primary Shared
Secret
Backup Server
Backup Server Port
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Server on your
network.
Enter the port number used for connections to the
RADIUS Server. It is a value from 1 to 65534, and
default is 1812.
Enter the key value to match the RADIUS Server. It
consists of 1 to 64 characters.
The Backup Authentication Server will be used when
the Primary Authentication Server is not available.
Enter the port number used for connections to the
Backup RADIUS Server. It is a value from 1 to 65534,
and default is 1812.
56
Page 57

Backup Shared
Secret
WPA Algorithm
Key Renewal
Timeout
Enter the key value to match the Backup RADIUS
Server. It consists of 1 to 64 characters.
The encryption method is TKIP or AES.
Specify the value of Group Key Renewal. It is a value
from 600 to 36000, and default is 3600 second.
WPA automatically changes secret keys after a
certain period of time. The group key interval is the
period of time between automatic changes of the
group key, which all devices on the network share.
Constantly keying the group key protects your
network against intrusion, as the would-be intruder
must cope with an ever-changing secret key.
57
Page 58

RADIUS
Use RADIUS server for authentication and dynamic WEP key generation for data encryption.
Authentication Server
Primary Server
Primary Server Port
Primary Shared
Secret
Backup Server
Backup Server Port
Backup Shared
Secret
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Server on your
network.
Enter the port number used for connections to the RADIUS
Server. It is a value from 1 to 65534, and default is 1812.
Enter the key value to match the RADIUS Server. It
consists of 1 to 64 characters.
The Backup Authentication Server will be used when the
Primary Authentication Server is not available.
Enter the port number used for connections to the Backup
RADIUS Server. It is a value from 1 to 65534, and default
is 1812.
Enter the key value to match the Backup RADIUS Server. It
consists of 1 to 64 characters.
58
Page 59

Rogue AP Detection
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP Detection to detect an unexpected or unauthorized
access point installed in a secure network environment.
Radio
Wireless Radio
Rogue AP
Detected Rogue AP List
Action
MAC Address
SSID
Channel
Security
Signal
Select the desired radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
Enable or disable Rogue AP Detection on the selected radio.
Click Trust to move the AP to the Trusted AP List.
The MAC address of the Rogue AP.
The SSID of the Rogue AP.
The channel of the Rogue AP.
The security method of the Rogue AP.
The signal level of the Rogue AP.
59
Page 60
Trusted AP List
Action
MAC Address
SSID
Channel
Security
Signal
New MAC
Address
Click Untrust to move the AP to the Rogue AP List.
The MAC address of the Trusted AP.
The SSID of the Trusted AP.
The channel of the Trusted AP.
The security method of the Trusted AP.
The signal level of the Trusted AP.
Add one trusted AP by MAC address.
60
Page 61

Scheduler
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Scheduler to configure a rule with a specific time interval for
SSIDs to be operational. Automate enabling or disabling SSIDs based on the profile definition.
Support up to 16 profiles and each profile can include four time rules.
Scheduler
Wireless
Scheduler
Enable or disable wireless scheduler on the radio. It is
disabled by default.
If disabled, even if some SSIDs are associated with
profiles, they will be always active.
61
Page 62

Scheduler Operational Status
Status
Reason
Scheduler Profile configuration
New Profile Name
Profile Name
Day of the Week
The operational status of the scheduler.
The detailed reason for the scheduler operational status.
It includes the following situations.
•
System time is outdated.
Scheduler is inactive because system time is
outdated.
•
Administrative Mode is disabled.
Scheduler is disabled by administrator.
•
Active
Scheduler is active.
Enter the name for new profile.
Select the desired profile from the list to configure.
Select the desired day from the list.
Option “None” means this time rule is disabled.
Start Time
Finish Time
Choose the start time.
Choose the finish time.
62
Page 63

Scheduler Association
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Scheduler Association to associate defined scheduler profiles
with SSIDs.
Radio
Wireless Radio
Scheduler Association
SSID
SSID Name
Profile Name
Interface Status
Select the desired radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
The index of SSID.
The name of the SSID.
Choose the profile that is associated with the SSID.
If the profile associated with the SSID is deleted, then
the association will be removed.
Option ”None” means no scheduler profile is associated.
The status of the SSID. It can be Enabled or Disabled.
Scheduler only works when the SSID is enabled.
63
Page 64

Connection Control
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Connection Control to define whether listed client stations may
authenticate with the access point.
64
Page 65

SSID
Control Type
Select the desired SSID from the list.
Select the option from the drop-down list as desired.
•
Local: Choose either “Allow only following MAC
addresses to connect to wireless network” or
“Prevent following MAC addresses from connection
to wireless network.” You can enter up to 20 MAC
addresses of wireless stations or choose the MAC
address.
•
RADIUS
Primary/Backup RADIUS Server - Enter the IP
address of the RADIUS Server.
Primary/Backup RADIUS Server Port – Enter the
Port
number of the RADIUS Server.
Primary/Backup Shared Secret - This is shared
between the wireless access point and the RADIUS
Server while
authenticating the device attempting to connect.
•
Disabled
65
Page 66

Rate Limit
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Rate Limit to limit downstream and upstream rate of SSIDs.
Radio
Wireless Radio
Rate Limit
SSID
SSID Name
Upstream
Rate
Downstream
Rate
Select the desired radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
The index of SSID.
The name of the SSID.
Enter a maximum upstream rate for the SSID. The range is
from 0 to 200 Mbps for Radio 1 and from 0 to 600 Mbps
for Radio 2; 0 means no limitation.
Enter a maximum downstream rate for the SSID. The range
is from 0 to 200 Mbps for Radio 1 and from 0 to 600 Mbps
for Radio 2; 0 means no limitation.
66
Page 67

QoS
Go to Configuration > Wireless > QoS (Quality of Service) to specify priorities for different traffic
coming from your wireless client. Lower priority traffic will be slowed down to allow greater
throughput or less delay for high priority traffic.
QoS Setting
Wireless Radio
QoS Settings
SSID
SSID Name
VLAN ID
Select the desired radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
The index of SSID.
The name of the SSID.
The VLAN ID of the SSID.
67
Page 68

Priority
WMM
Select the priority level from the list. VLAN must be enabled
in order to set priority.
The 802.1p will be included in the VLAN header of the
packets which are received from the SSID and sent from
Ethernet or WDS interface.
Enable or disable WMM.
WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) is a component of the IEEE
802.11e wireless LAN standard for QoS.
WMM provides prioritization of wireless data packets from
different applications based on four access categories:
voice, video, best effort, and background. For an application
to receive the benefits of WMM QoS, both it and the client
running that application have to have WMM enabled.
Legacy applications that do not support WMM and
applications that do not require QoS, are assigned to the
best effort category, which receives a lower priority than
voice and video.
WMM is enabled by default.
68
Page 69

WDS
Go to Configuration > Wireless > WDS (Wireless Distribution System) to expand a wireless
network through multiple access points instead of linking them with a wired backbone.
The access point can act as WDS Root or WDS Station:
•
WDS Root - Receives WDS connections from remote WDS Stations.
•
WDS Station - Connects to remote WDS Root. Supports up to 4 WDS Stations on each
wireless radio.
69
Page 70

Spanning Tree (recommended if you configure WDS connections)
Spanning Tree
WDS Settings
Radio
WDS Root
Interface
Status
When enabled, STP helps prevent switching loops.
Select the desired radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
Enable or Disable the WDS Root.
Be sure the following settings on WDS Root device are
determined and configured. The WDS Station must use the
same settings as Root afterwards.
•
Radio
•
IEEE 802.11 Mode
•
Channel Bandwidth
•
Channel
Note-It is highly recommended that static channel is
configured on both APs. Do not use Auto channel option
Local SSID
Local MAC
Address
Local Channel
when you enable WDS, as both APs in a WDS link must be
on the same radio channel. If Auto option is configured,
there is chance two access points run on different channels
and WDS link cannot establish.
Workgroup Bridge and WDS will not work at the same time
on one wireless radio. When Workgroup Bridge is enabled,
WDS will be disabled automatically on the same radio.
Enter name of the WDS Root SSID (used when connected
by WDS Stations).
MAC address of the WDS Root SSID.
The channel used by WDS Root SSID. WDS stations must
use same channel as the WDS Root.
Channel can be changed in "Basic Settings" page.
70
Page 71

Allowed VLAN
List
Security
Settings
WDS Station
Interface
Status
Enter the list of VLANs accepted by the WDS Root.
When VLAN is enabled, WDS Root receives from WDS
Stations only packets in the VLAN list. Packets not in the
list will be dropped.
The VLAN list is only applicable when VLAN is enabled.
The VLAN list includes 1 to 16 VLAN IDs separated by ","
such as "100,200,300,400,500,600,700,800".
Setting can be Disabled, WPA-Personal, WPA2-Personal,
WPA2-Enterprise or WPA/WPA2-Enterprise.
Enable or disable the WDS Station.
Before configuring a WDS Station, be sure the following
settings of the device are identical to the WDS Root that
will be connected.
•
Radio
•
IEEE 802.11 Mode
•
Channel Bandwidth
•
Channel
Remote SSID
Note-It is highly recommended that static channel is
configured on both APs. Do not use Auto channel option
when you enable WDS, as both APs in a WDS link must be
on the same radio channel. If Auto option is configured,
there is chance two access points run on different channels
and WDS link cannot establish.
Workgroup Bridge and WDS will not work at the same time
on one wireless radio. When Workgroup Bridge is enabled,
WDS will be disabled automatically on the same radio.
Enter the name of the Root’s SSID. Click Site Survey
button and choose from the list. You must do this for WDS
Station to connect to a remote WDS Root.
71
Page 72

Remote MAC
Address
VLAN List
Security Mode
MAC address of the access point on the other end of the
WDS link. Optional
WDS Station connects to remote WDS Root by matching
SSIDs. When there is more than one remote WDS Root with
the same SSID, the WDS Station can differentiate them by
MAC address.
The format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
Enter the list of VLANs that are accepted by the WDS
Station.
When VLAN is enabled, the WDS Station forwards to the
remote WDS Root only packets in the VLAN list. Packets
not in the VLAN list cannot be forwarded to the remote
WDS Root.
The VLAN List is only applicable when VLAN is enabled.
The VLAN list includes 1 to 8 VLAN IDs separated by ","
such as "100,200,300,400,500,600,700,800".
The type of encryption to use on the WDS link. It must be
unique to the access point on the other end of the WDS link.
Status
The options are Disabled, WPA Personal, WPA2 Personal,
WPA Enterprise or WPA2 Enterprise.
Status of the WDS interface. It can be Disabled, Connected
or Not Connected.
72
Page 73

Workgroup Bridge
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Workgroup Bridge to extend the accessibility of a remote
network. In Workgroup Bridge mode, the access point acts as a wireless station (STA) on the
wireless LAN. It can bridge traffic between a remote wired network and a wireless LAN.
When Workgroup Bridge is enabled, SSID configuration still works to provide wireless services to
clients.
All access points participating in Workgroup Bridge must have the identical settings for Radio
interface, IEEE 802.11 mode, Channel Bandwidth, Channel (Auto is not recommended).
73
Page 74

Workgroup Bridge
Radio
Workgroup Bridge Status
Status
Select the desired radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
Enable or disable Workgroup Bridge function.
Before configuring Workgroup Bridge, make sure all devices
in Workgroup Bridge have the following identical settings.
•
Radio
•
IEEE 802.11 Mode
•
Channel Bandwidth
•
Channel
Note-It is highly recommended that static channel is
configured on both APs. Do not use Auto channel option
when you enable Workgroup Bridge, as both APs in a
Workgroup Bridge link must be on the same radio channel. If
Auto option is configured, there is chance two access
points run on different channels and Worgroup Bridge link
cannot establish.
Remote AP Settings
SSID
Remote MAC
Address
Enter the name of the SSID to which Workgroup Bridge will
connect. Click Site Survey button to choose from the list.
You must do this for Workgroup Bridge to connect to a
remote access point.
Normally, Workgroup Bridge connects to a remote access
point by matching SSID. When more than one remote
access point has the same SSID, Workgroup Bridge can
connect to different remote access points.
Optional: You can specify the MAC address of the remote
access point to limit Workgroup Bridge’s connection to a
specific remote access point.
The format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
74
Page 75

Security Mode
Select the desired mode from the list.
•
Disabled
•
WPA-Personal
•
WPA2-Personal
•
WPA-Enterprise
•
WPA2-Enterprise
75
Page 76

communicate with each other. Enabled by default.
Advanced Settings
Go to Configuration > Wireless > Workgroup Bridge to configure advanced parameters of
wireless radios.
Band Steering
Band Steering
Isolation
Isolation between
SSIDs
Advanced Parameters
Enable or disable Band Steering function.
Band Steering is a technology that detects whether
the wireless client is dual-band capable. If it is, band
steering pushes the client to connect to the lesscongested 5 GHz network. It does this by actively
blocking the client’s attempts to connect with the
2.4GHz network.
Define whether to isolate traffic between SSIDs. If
enabled, wireless clients in different SSIDs cannot
76
Page 77

Wireless Radio
Worldwide Mode
(802.11d)
Channel Bandwidth
Guard Interval
Select the desired radio from the list.
Radio 1 is for 2.4 GHz, and Radio 2 is for 5 GHz.
Worldwide Mode (802.11d) enables the access point
to direct connected wireless devices to radio settings
specific to where in the world the devices are in use.
Select the designed channel bandwidth for the
wireless radio.
20MHz - Select if you are not using any 802.11n
wireless devices.
20/40MHz - Select if you are using both 802.11n and
non-802.11n wireless devices.
20/40/80MHz - Select if you are using 802.11ac,
802.11n and non-802.11n wireless devices.
Select the guard interval manually for Wireless-N
connections. The two options are Short (400
nanoseconds) and Long (800 nanoseconds). The
default is Auto.
CTS Protection
Mode
Beacon Interval
CTS (Clear-To-Send) Protection Mode boosts the
access point's ability to catch all Wireless-G
transmissions, but it severely decreases
performance. By default, CTS Protection Mode is
disabled, but the access point will automatically
enable this feature when Wireless-G devices are not
able to transmit to the access point in an environment
with heavy 802.11b traffic.
The access point transmits beacon frames at regular
intervals to announce the existence of the wireless
network. Enter the interval between the
transmissions of beacon frames. The value range is
between 40 and 1000 milliseconds and default is
100 milliseconds.
77
Page 78
DTIM Interval
RTS Threshold
Enter the Delivery Traffic Information Map (DTIM)
period, an integer from 1 to 255 beacons. The default
is 1 beacon.
The DTIM message is an element included in some
beacon frames. It indicates which client stations,
currently sleeping in low-power mode, have data
buffered on the access point awaiting pickup.
The DTIM period that you specify indicates how often
the clients served by this WAP device should check
for buffered data still on the access point awaiting
pickup.
For example, if you enter 1, clients check for buffered
data on the access point at every beacon. If you enter
10, clients check on every 10th beacon.
Enter the Request to Send (RTS) Threshold value, an
integer from 1 to 2347. The default is 2347 octets.
The RTS threshold indicates the number of octets in a
Medium Access Control Protocol Data Unit (MPDU)
below which an RTS/CTS handshake is not performed.
Changing the RTS threshold can help control traffic
flow through the access point, especially one with a
lot of clients. If you specify a low threshold value, RTS
packets are sent more frequently, which consumes
more bandwidth and reduces the throughput of the
packet. However, sending more RTS packets can help
the network recover from interference or collisions
that might occur on a busy network, or on a network
experiencing electromagnetic interference.
78
Page 79

Fragmentation
Threshold
Output Power
Enter the fragmentation threshold, an integer from
256 to 2346. The default is 2346.
The fragmentation threshold is a way of limiting the
size of packets (frames) transmitted over the
network. If a packet exceeds the fragmentation
threshold you set, the fragmentation function is
activated and the packet is sent as multiple 802.11
frames.
If the packet being transmitted is equal to or less than
the threshold, fragmentation is not used. Setting the
threshold to the largest value (2,346 bytes, which is
the default) effectively disables fragmentation.
Fragmentation involves more overhead because of
the extra work of dividing up and reassembling of
frames it requires, and because it increases message
traffic on the network. However, fragmentation can
help improve network performance and reliability if
properly configured.
Select the output power of the access point. If many
access points exist, lower power can reduce the
signal interference among them.
79
Page 80

Captive Portal
Captive Portal is a method of securing access to the Internet from within a wireless network.
Users must enter authentication credentials before their wireless client devices can access the
Internet.
Global Configuration
Go to Configuration > Captive Portal > Global Configuration to change settings and modify
captive portal authentication access port number if needed.
Captive Portal
Authentication
Timeout
Additional HTTP
Port
Enable or Disable Captive Portal function globally.
Captive Portal is disabled by default.
The number of seconds the access point keeps an
authentication session open with a wireless client. If
the client fails to enter authentication credentials
within the timeout period, the client may need to
refresh the web authentication page.
The range is from 60 to 600 seconds. Default is 300.
HTTP portal authentication uses the HTTP
management port by default. You can configure an
additional port for that process.
80
Page 81

HTTP Port
Additional HTTPS
Port
HTTPS Port
Once Additional HTTP Port is enabled, define an
additional port for HTTP protocol. The value can be
80 or 1024 to 65535 and is 80 by default. The HTTP
Port must be different from the HTTP port in
Administration > Management Access
HTTPS portal authentication uses the HTTPS
management port by default. You can configure an
additional port for that process.
Once Additional HTTPS Port is enabled, define an
additional port for HTTPS protocol. The value can be
443 or 1024 to 65535 and is 443 by default. The
additional HTTPS Port must be different from the
HTTPS port in
page.
Administration > Management Access
page.
Portal Profiles
Go to Configuration > Captive Portal > Portal Profiles to define detailed settings for Captive
Portal profile. Create up to two profiles.
81
Page 82

Portal Profiles
Captive Portal
Profile
Protocol
Authentication
Landing Page
Select a profile to configure.
Select the protocol used to access the Portal
Authentication web server. It can be HTTP or HTTPS.
Select an authentication method for clients.
Local - The access point uses a local database to
authenticated wireless clients.
Radius - The access point uses a database on a
remote RADIUS server to authenticate wireless
clients. The RADIUS server must support EAP-MD5.
Password Only - Wireless clients only need a
password. Username is unnecessary.
No Password - Wireless clients accept defined terms
to access the wireless network. Password and
username both are unnecessary.
Enable Landing Page to determine where
authenticated wireless clients will be directed after
logging in at Captive Portal. Choose
Promotion URL
.
Original URL
or
Redirect to Original
URL
Promotion URL
Session Timeout
Local Authentication
Group Name
If Landing Page is enabled, this setting redirects
authenticated wireless clients from the Captive
Portal login screen to the URL the user typed in.
Enter a URL to which authenticated clients will be
redirected from the Captive Portal login page.
Landing Page must be enabled and Redirect to
Original URL must be disabled.
Set the session time in minutes. The access point will
disconnect authenticated clients when the session
time expires. Session time can range from 0 to 1440
minutes. The default is 0 minutes, which means no
timeout.
Assigns an existing group to the profile. All users who
belong to the group are permitted to access the
network through this portal. The option 'Default'
means a group which includes all users.
82
Page 83

Radius Authentication
Primary Server
Primary Server Port
Primary Shared
Secret
Backup Server
Backup Server Port
Backup Shared
Secret
Password Only Authentication
Password
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Server on your
network.
Enter the port number used for connections to the
RADIUS Server.
Enter the key value to match the RADIUS Server.
The Backup Authentication Server will be used when
the Primary Authentication Server is not available.
Enter the port number used for connections to the
Backup RADIUS Server.
Enter the key value to match the Backup RADIUS
Server.
The password for the profile. Wireless clients only
need one password to access the wireless network.
Local User
Go to Configuration > Captive Portal > Local User to configure user settings for Captive Portal.
Up to 128 users are supported.
83
Page 84

User Name
Password
Confirm Password
Enter the name of the user account.
The user name includes 1 to 32 characters. Special
characters except ':' and ';' are allowed.
Enter the password of the user account.
The password must be between 4 and 32 characters
in length. Special characters except ':' and ';' are
allowed.
Re-enter the password to confirm it.
Local Group
Go to Configuration > Captive Portal > Local Group to configure group settings. Groups include
multiple local users and are mapped to Captive Portal profiles. Up to two groups are supported.
84
Page 85

Group Name
Group Selection
Members
Other Users
Enter the name of the new group.
The group name includes 1 to 32 characters. Special
characters except ':' and ';' are allowed.
Click Add.
Select one group to delete or configure its user
members.
User members of the selected group. You can select
one user and click ">>" button to remove it.
Other users which don't belong to the selected group.
You can select one user and click "<<" button to add it
into the group.
Web Customization
Go to Configuration > Captive Portal > Web Customization to customize the authentication web
page of Captive Portal.
85
Page 86

Profile
New Logo Upload
Logo Selection
Background Color
Font Color
Welcome Title
Login Instruction
Select a profile to configure.
Logos display in the web page. Select an image file
from your local PC and click Upload.
Formats .gif, .png and .jpg are supported. File size
cannot exceed 5KB.
One profile can support one default and one new logo
image. If a second new logo is uploaded, it will replace
the first new logo.
Select a logo image from the list.
The HTML code for the background color in 6-digit
hexadecimal format. The default is #0073BA.
The HTML code for the font color in 6-digit
hexadecimal format. The default is #FFFFFF.
Customize text to go with your logo. The default is
Welcome to the Wireless Network.
Customize text to go with the login box. Default text
for different authentication options:
User Label
Password Label
Button Name
Button Color
Terms of Use Label
Local Authentication/Radius Authentication
You can log in using your username and password.”
Password Only Authentication
You can log in using your password.
Local Authentication
Click Connect to log in.
Customize the username text box. Enter up to 16
characters. The default is "Username".
Customize the user password text box. Enter up to
16 characters. The default is "Password".
Customize the text that appears in the log in button.
Enter up to 12 characters. The default is "Connect".
The HTML code for the background color of the
button in 6-digit hexadecimal format. The default is
#70A0D4.
Customize the text to go with the checkbox. Enter up
to 128 characters. The default is "Check here to
indicate that you have read and accepted the
following Terms of Use."
86
Page 87

Terms of Use
Success Text
Failure Text
Customize the text to go with Terms of Use. Enter up
to 512 characters. The default is "Terms of Use".
Customize the text that shows when the client has
been authenticated. The default is "You have logged
on successfully! Please keep this window open when
using the wireless network."
Customize the text that shows when authentication
fails. Enter up to 128 characters. The default is "Bad
username or password"
Profile Association
Go to Configuration > Captive Portal > Profile Association to associate defined Captive Portal
profiles with SSIDs.
87
Page 88

SSID
SSID Name
Profile Name
A list of available SSIDs.
The name of the SSID.
Choose the profile that is associated with the SSID.
If the profile associated with the SSID is deleted, then
the association will be removed.
If
None
is selected, it means no profile is associated.
Client Information
Go to Configuration > Captive Portal > Client Information to view the status of wireless clients
that are authenticated by Captive Portal.
MAC Address
IP Address
User Name
SSID Name
Online Time
MAC address of the client.
IP address of the client.
User name used by the client to log in.
Name of the SSID to which the client is connected.
How long the client has been online. Measured in
seconds.
88
Page 89

Away Timeout
Session Timeout
An authenticated client that has been disconnected
from the access point has a specific amount of time
within which it may reconnect without reauthentication. The timer starts when the client
disconnects from the SSID. After the time reaches
zero, the client is de-authenticated. If the timeout is
set to 0, the client is not de-authenticated. Measured
in seconds.
The remaining time of the authenticated session. The
timer starts when the client is authenticated. After
the time reaches zero, the client is de-authenticated.
If the value is fixed to 0, the session won't time out.
Measured in seconds.
Cluster
The cluster function provides a centralized method to administer and control wireless services
across multiple devices. When access points are clustered, you can view, deploy, configure, and
secure the wireless network as a single entity.
Note-Firmware version 1.1.0 or above support cluster feature. If your device has legacy
firmware installed, download the latest one from www.linksys.com/support
The access points within a cluster must have the same management VLAN configured. A cluster
can support 16 LAPAC1200C/LAPAC1750C access points, as long as they are same model
number.
In each cluster, one access point must be manually configured as the master access point. There
can only be one master in a cluster. This master will propagate configuration information, such as
wireless settings, time settings etc. to the other team members within a cluster. Log in to the
master access point to change sharable parameter settings instead of slaves.
When firmware is upgraded on the master, all slaves within the same cluster will receive the
upgrade.
.
89
Page 90

Clustered access points share these configurations:
•
User Accounts
•
Time Settings
•
Log Settings
•
Management Access
•
Discovery Settings
•
IGMP/MLD Snooping
•
Wireless Network Mode
These configurations and not shared by clustered access points:
•
IP Settings
•
WDS
•
Output Power
•
SSID Settings
•
Wireless Security
•
Rogue AP Detection
•
Wireless Scheduler
•
Wireless Scheduler
Association
•
Wireless Connection
Control
•
Hostname
•
Workgroup Bridge
Settings & Status
Go to
Configuration > Cluster > Settings & Status
to manage the AP cluster function.
•
Rate Limit
•
QoS
•
Advanced Wireless
Settings
•
Captive Portal
Settings
•
Ethernet Port
Settings
•
VLAN Settings
•
Wireless Channel
•
802.1x Supplicant
Choose a member type.
90
Page 91

Type
Master
Disabled—Disable the cluster function.
Master—Enable the cluster function and assign the
access point to be the master.
Note— If system detects there is one Master
already existed in the same cluster, the new
access point that likes to become master will be
assigned to slave automatically.
Slave—Enable the cluster function and assign the
access point to be the slave.
Note—When the cluster function is enabled, WDS
and workgroup bridge will be disabled
automatically.
91
Page 92

Status
Member Number
Location (Optional)
Cluster Name
Backup Master
Disabled—Cluster function is disabled.
Active—Cluster function is enabled and master is active.
Active (Backup Master)—Cluster function is enabled and backup master
is active.
Inactive (Cannot reach the master)—Cluster function is enabled but it's
inactive because device cannot reach the master.
Number of the members active in the cluster. If an access point joins the
cluster but is powered off or cannot reach the master, it is not counted.
Where the access point is physically located; for example, Reception.
Length is from 0 to 32 bytes.
Name of the cluster for the LAP device to join; for example, “lab cluster”.
All access points with the same cluster name belong to the same
cluster. Length of this value is from 4 to 32 bytes and special
characters are allowed. This is a mandatory field if the cluster function
is turned on.
When an access point works as a cluster slave, it can be enabled as a
backup master. When master gets offline, it will take the role of master.
When the backup master begins to work, it will send advertisements
and slaves will send keep-alive and report sessions to it. When
shareable settings are modified in it, it will share them to all slaves.
When master gets online again, this backup master AP will stop the
master function and let original master AP take over master role.
92
Page 93

Client Sessions
Go to Configuration > Cluster > Client Sessions to see the status of wireless clients within the
cluster.
The session is the period of time in which a user on a client device (station) with a unique MAC
address maintains a connection with the wireless network. The session begins when the WLAN
client logs on to the network, and the session ends when the WLAN client either logs off
intentionally or loses the connection for some other reason.
When one wireless client of Captive Portal roams from one access point to another in the same
cluster, it need not re-authenticate.
IP Address
Location
SSID
User MAC
Online Time
Link Rate
Signal
IP address of the access point to which the client
connects.
Location of the access point to which the client
connects.
SSID name of the access point to which the client
connects.
MAC address of the client.
Displays how long this client has been online since it is
authenticated. Unit is second.
Indicates the link rate of the client. Unit is Mbps.
The signal strength of the client is displayed. Unit is
dBm.
Rx Total
The total bytes which are received from the client by
the access point. Unit is Byte.
93
Page 94

Tx Total
Rx Rate
Tx Rate
The total bytes which are sent to the client by the
access point. Unit is Byte.
Current transfer rate of the data which are received
from the client by the access point. Unit is Kbps.
Current transfer rate of the data which are sent to
the client by the access point. Unit is Kbps.
Channel Management
Go to Configuration > Cluster > Channel Management to manage the channel assignments for
access points within a cluster.
When channel management is enabled, the access point automatically assigns radio channels
within a cluster. Auto channel assignment reduces mutual interference (or interference with other
access points outside of its cluster) and maximizes Wi-Fi bandwidth to help maintain efficient
communication over the wireless network.
94
Page 95

Auto Channel
Auto Channel
Scan Day
Scan Time
Scan Trigger
Access point scans available Wi-Fi channels and
changes the channel if better network performance is
possible. Disabled by default.
Choose the day of the week when Auto Channel scans
Wi-Fi channels. You may choose specific days or have
the access point scan and select the best channel
daily.
Choose the time of day when Auto Channel performs
scan.
Because Auto Channel will change the channel if it
finds a better one, you can choose when to allow a
scan.
•
Immediately – Scan according to the day/time
specified.
•
No Clients – Scan only if no clients are
connected to the wireless radio. If there are
clients connected, the access point will
complete the Auto Channel operation the next
scheduled time when no clients are
connected.
Current Channels
Type
Location
IP Address
Wireless Radio
Status
Channel
Locked
Member type of the access point. It can be Master,
Slave or Backup Master.
Where the access point is physically located
IP address of the access point.
1 stands for 2.4Ghz radio, and 2 stands for 5Ghz
radio.
Status of the wireless radio. It can be Active or
Inactive.
Current channel number of the wireless radio.
Select if you feel the current channel is the best for
that radio.
95
Page 96

System Status
Status
System Summary
Go to System Status > Status > System Summary for status of the access point.
System Summary
Device SKU
Firmware Version
Firmware
Checksum
The SKU is often used to identify device model number
and region.
The version of the firmware currently installed.
The checksum of the firmware running in the access
point.
Hardware Version
Local MAC
Address
Serial Number
The version of the hardware.
The MAC (physical) address of the wireless access
point.
The serial number of the device.
96
Page 97

Host Name
System Up Time
System Time
Power Source
Cloud Status
LAN Status
Go to System Status > Status > LAN Status to see settings and status of LAN interface.
The host name assigned to the access point.
How long the system has been running since the last
restart or reboot.
The current date and time.
The power source of the access point. It can be Power
over Ethernet (PoE) or Power Adapter. When two power
sources are plugged in, Power Adaptor will be
displayed.
Whether cloud management is enabled or disabled.
97
Page 98

VLAN
VLAN
Untagged VLAN
Untagged VLAN
ID
Management
VLAN
Enabled or disabled (default).
Enabled (default) or disabled.
When enabled, and if its VLAN ID is equal to Untagged
VLAN ID, all traffic is untagged when sent from LAN
ports. Untagged traffic can be accepted by LAN ports. If
disabled, traffic is always tagged when sent from LAN
port and only tagged traffic can be accepted from LAN
port.
By default all traffic on the access point uses VLAN 1,
the default untagged VLAN. This means that all traffic is
untagged until you disable the untagged VLAN, change
the untagged traffic VLAN ID, or change the VLAN ID for
a SSID.
Displays the untagged VLAN ID. Traffic on the VLAN
that you specify in this field is not be tagged with a VLAN
ID when forwarded to the network. VLAN 1 is the default
ID for untagged VLAN and management VLAN.
Displays the Management VLAN ID. The VLAN
associated with the IP address you use to connect to the
access point. Provide a number between 1 and 4094 for
the Management VLAN ID. The default is 1.
IPv4
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Primary DNS
Secondary DNS
This VLAN is also the default untagged VLAN. If you
already have a management VLAN configured on your
network with a different VLAN ID, you must change the
VLAN ID of the management VLAN on the access point.
The IP address of the wireless access point.
The Network Mask (Subnet Mask) for the IP address
above.
Enter the gateway for the LAN segment to which the
wireless access point is attached (the same value as the
PCs on that LAN segment).
The primary DNS address provided by the DHCP server
or configured manually.
The secondary DNS address provided by the DHCP
server or configured manually.
98
Page 99

IPv6
IP Address
Default Gateway
Primary DNS
Secondary DNS
Wireless Status
Go to System Status > Status > Wireless Status to see settings and status of wireless radios and
SSIDs.
The IP address of the wireless access point.
Enter the gateway for the LAN segment to which the
wireless access point is attached (the same value as the
PCs on that LAN segment).
The primary DNS address provided by the DHCP server
or configured manually.
The secondary DNS address provided by the DHCP
server or configured manually.
99
Page 100

Radio Status
Mode
Current Channel
Channel
Bandwidth
SSID Status
Interface
SSID Name
Status
MAC Address
VLAN ID
Priority
Scheduler State
Current 802.11mode (a/b/g/n/ac) of the radio.
The channel currently in use.
Current channel bandwidth of the radio.
When set to 20 MHz, only the 20 MHz channel is in use.
When set to 20/40 MHz, Wireless-N connections will use
40 MHz channel, but Wireless-B and Wireless-G will still
use 20 MHz channel.
SSID index.
Name of the SSID.
Status of the SSID: Enabled or Disabled.
MAC Address of the SSID.
VLAN ID of the SSID.
The 802.1p priority of the SSID.
•
N/A—No scheduler is enabled on the SSID, or the
SSID is disabled by administrator.
•
Active—The SSID is enabled.
•
Inactive—The SSID is disabled.
100
 Loading...
Loading...