Linksys HU200 Owner's Manual

2,4
GHz
802.11g
WIRELESS
Home Wireless-G
USB Adaptor
User Guide
Model No.
HU200
Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Copyright and Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco
Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S . and certain other countries. Copyright © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All
rights reserved. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders.
This User Guide
The User Guide to the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor has been designed to make understanding networking
easier than ever. Look for the following items when reading this guide:
This checkmark means there is a note of interest and
is something you should pay special attention to while
using the Adaptor.
This exclamation point means there is a caution or
warning and is something that could damage your
property or the Adaptor.
This question mark provides you with a reminder about
something you might need to do while using the Adaptor.
In addition to these symbols, there are definitions for technical terms that are presented like this:
word: definition.
Also, each figure (diagram, screenshot, or other image) is provided with a figure number and description, like
this:
Figure numbers and descriptions can also be found in the “List of Figures” section in the “Table of Contents”.
HU200-UG-50308NC JL
Figure 0-1: Sample Figure Description

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Welcome 1
What’s in this Guide? 2
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network 4
Network Topology 4
Roaming 4
Network Layout 5
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor 6
The USB Port 6
The LED Indicators 6
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor 7
Using the Setup Wizard 7
Chapter 5: Connecting the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor 14
Connecting the Adaptor 14
Using the Adaptor’s Wall Mount 15
Chapter 6: Using the Wireless Network Monitor 16
Using the Wireless Network Monitor Icon 16
Accessing the Wireless Network Monitor 17
Link Information 17
Site Survey 20
Profiles 21
Creating a New Profile 22
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 29
Common Problems and Solutions 29
Frequently Asked Questions 30
Appendix B: Using Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration 33
Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration 33
Appendix C: Wireless Security 36
Security Precautions 36
Security Threats Facing Wireless Networks 36
Appendix D: Windows Help 39

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Appendix E: Glossary 40
Appendix F: Specifications 47
Appendix G: Warranty Information 49
Appendix H: Regulatory Information 50
Appendix I: Contact Information 56

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
List of Figures
Figure 3-1: USB Port 6
Figure 3-2: Front Panel 6
Figure 4-1: Setup Wizard’s Welcome Screen 7
Figure 4-2: Setup Wizard’s License Agreement 7
Figure 4-3: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Mode Screen 8
Figure 4-4: Setup Wizard’s Ad-Hoc Mode Settings Screen 8
Figure 4-5: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security Screen 9
Figure 4-6: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security - WEP Screen 9
Figure 4-7: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security - PSK Using TKIP Screen 10
Figure 4-8: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security - PSK + RADIUS Using EAP-TLS Screen 11
Figure 4-9: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security - PSK + RADIUS Using PEAP Screen 11
Figure 4-10: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security - RADIUS Using EAP-TLS Screen 12
Figure 4-11: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security - RADIUS Using PEAP Screen 12
Figure 4-12: Setup Wizard’s Check Settings Screen 13
Figure 4-13: Setup Wizard’s Congratulations Screen 13
Figure 5-1: How the Adaptor Connects to Your PC 14
Figure 5-2: Adaptor’s USB Port 14
Figure 5-3: PC’s USB Ports 14
Figure 5-4: Using the Wall Mount - Step A 15
Figure 5-5: Using the Wall Mount - Step B 15
Figure 5-6: Using the Wall Mount - Step C 15
Figure 6-1: Wireless Network Monitor Icon 16
Figure 6-2: Windows XP - Use Windows XP Wireless Configuration 16
Figure 6-3: Windows XP - Use Linksys Wireless Network Monitor 16
Figure 6-4: Link Information 17
Figure 6-5: More Information - Wireless Network Status 18
Figure 6-6: More Information-Network Statistics 19
Figure 6-7: Site Survey 20
Figure 6-8: WEP Key Needed for Connection 20
Figure 6-9: PSK (Pre-Shared Key) Needed for Connection 20

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Figure 6-10: Profiles 21
Figure 6-11: Import a Profile 21
Figure 6-12: Export a Profile 21
Figure 6-13: Create a New Profile 22
Figure 6-14: Enter Profile Name 22
Figure 6-15: Network Settings for New Profile 22
Figure 6-16: Wireless Mode for New Profile 23
Figure 6-17: Ad-Hoc Mode Settings for New Profile 23
Figure 6-18: Wireless Security for New Profile 24
Figure 6-19: Wireless Security - WEP for New Profile 24
Figure 6-20: Wireless Security - PSK for New Profile 25
Figure 6-21: Wireless Security - PSK + RADIUS Using EAP-TLS for New Profile 26
Figure 6-22: Wireless Security - PSK + RADIUS Using PEAP for New Profile 26
Figure 6-23: Wireless Security - RADIUS Using EAP-TLS for New Profile 27
Figure 6-24: Wireless Security - RADIUS Using PEAP for New Profile 27
Figure 6-25: Confirm New Settings for New Profile 28
Figure 6-26: Congratulations for New Profile 28
Figure B-1: Wireless Network Monitor Icon 33
Figure B-2: Windows XP - Use Windows XP Wireless Configuration 33
Figure B-3: Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration Icon 33
Figure B-4: Available Wireless Network 34
Figure B-5: Network Connection - No Wireless Security 34
Figure B-6: Network Connection - Wireless Security 35
Figure B-7: Wireless Network Connection 35

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
Thank you for choosing the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor. With this Adaptor, your wireless networking
experience will be faster and easier than ever.
How does the Adaptor do this? Like all wireless products, the Adaptor allows for greater range and mobility
within your wireless network, whether it’s using the Wireless-G (802.11g) or Wireless-B (802.11b) standard.
But what does all of this mean?
Networks are useful tools for sharing computer resources. You can access one printer from different computers
and access data located on another computer's hard drive. Networks are even used for playing multiplayer video
games. So, networks are not only useful in homes and offices, they can also be fun.
PCs equipped with wireless cards and adapters can communicate without cumbersome cables. By sharing the
same wireless settings, within their transmission radius, they form a wireless network.
network: a series of computers or devices
connected for the purpose of data sharing,
storage, and/or transmission between users.
adaptor: a device that adds network functionality
to your PC.
802.11g: an IEEE wireless networking standard
that specifies a maximum data transfer rate of
54Mbps and an operating frequency of 2.4GHz.
By incorporating two fast technologies—USB 2.0 and Wireless-G (802.11g)—the Adaptor delivers data rates up
to 54Mbps. And since the 802.11g and 802.11b standards share the same 2,4GHz radio band, the Adaptor can
still communicate with devices using the popular 802.11b standard.
The included Setup Wizard will walk you through configuring the Adaptor to your network's settings, step by step.
Then just connect the Adaptor to your computer’s USB port, so you can enjoy Internet connectivity with your
computer, while retaining true mobility.
Use the instructions in this Guide to help you install and use the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor. These
instructions should be all you need to get the most out of the Adaptor.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
802.11b: an IEEE wireless networking standard
that specifies a maximum data transfer rate of
11Mbps and an operating frequency of 2.4GHz.
1

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
What’s in this Guide?
This user guide covers the steps for setting up and using the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor.
• Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter describes the Adaptor’s applications and this User Guide.
• Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
This chapter discusses a few of the basics about wireless networking.
• Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
This chapter describes the physical features of the Adaptor.
• Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
This chapter instructs you on how to run the Adaptor’s Setup Wizard and configure the Adaptor.
• Chapter 5: Connecting the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
This chapter shows you how to connect the Adaptor to your PC.
• Chapter 6: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
This chapter explains how to use the Adaptor’s Wireless Network Monitor.
• Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix describes some potential problems and solutions, as well as frequently asked questions,
regarding installation and use of the Adaptor.
• Appendix B: Using Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration
This appendix explains how you can use Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration to control the Adaptor.
• Appendix C: Wireless Security
This appendix discusses security issues regarding wireless networking and measures you can take to help
protect your wireless network.
• Appendix D: Windows Help
This appendix describes how you can use Windows Help for instructions about networking, such as installing
the TCP/IP protocol.
• Appendix E: Glossary
This appendix gives a brief glossary of terms frequently used in networking.
• Appendix F: Specifications
This appendix provides the Adaptor’s technical specifications.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
2

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
• Appendix G: Warranty Information
This appendix supplies the Adaptor’s warranty information.
• Appendix H: Regulatory Information
This appendix supplies the Adaptor’s regulatory information.
• Appendix I: Contact Information
This appendix provides contact information for a variety of Linksys resources, including Technical Support.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
3

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
A wireless network is a group of computers, each equipped with one wireless adaptor. Computers in a wireless
network must be configured to share the same radio channel. Several PCs equipped with wireless cards or
adaptors can communicate with one another to form an ad-hoc network.
Linksys wireless adaptors also provide users access to a wired network when using an access point or wireless
router. An integrated wireless and wired network is called an infrastructure network. Each wireless PC in an
infrastructure network can talk to any computer in a wired network infrastructure via the access point or wireless
router.
An infrastructure configuration extends the accessibility of a wireless PC to a wired network, and can double the
effective wireless transmission range for two wireless adaptor PCs. Since an access point is able to forward data
within a network, the effective transmission range in an infrastructure network can be doubled.
Roaming
Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users. Roaming means that you can move your
wireless PC within your network and the access points will pick up the wireless PC's signal, provided that they
both share the same channel and SSID.
topology: the physical layout of a network.
ad-hoc: a group of wireless devices
communicating directly with each other (peerto-peer) without the use of an access point.
infrastructure: a wireless network that is
bridged to a wired network via an access point.
roaming: the ability to take a wireless device
from one access point's range to another without
losing the connection.
Choose a feasible radio channel and optimum access point position. Proper access point positioning combined
with a clear radio signal will greatly enhance performance.
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
ssid: your wireless network's name.
4

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Network Layout
Linksys wireless access points and wireless routers have been designed for use with 802.11b and 802.11g
products. Products using the 802.11g and 802.11b standards can communicate with each other.
Access points and wireless routers are compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g adaptors, such as the notebook
adaptors for your laptop computers, PCI adaptors for your desktop PCs, and USB adaptors for when you want to
enjoy USB connectivity. Wireless products will also communicate with a wireless print server.
When you wish to connect your wireless network to your wired network, network ports on access points and
wireless routers can be connected to any of Linksys's switches or routers.
With these, and many other, Linksys products, your networking options are limitless. Go to the Linksys website at
www.linksys.com/international for more information about wireless products.
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Layout
5

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
The USB Port
The Adaptor’s USB port is located on the side of the Adaptor. You will connect the included USB cable to this port
and your PC’s USB port. All power is provided through the USB connection, so a power adaptor is not needed.
The LED Indicators
The Adaptor's LEDs indicate the status of the Adaptor’s power and wireless connection.
Figure 3-1: USB Port
Figure 3-2: Front Panel
Power Green. The Power LED lights up when the Adaptor is adequately powered by the USB connection.
Link Green. The Link LED lights up when the Adaptor has an active wireless connection. It will flash when
data is transmitted.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
The USB Port
6
Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
The Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor Setup Wizard will guide you through the installation procedure. The Setup
Wizard will install the driver and Wireless Network Monitor, as well as configure the Adaptor.
NOTE: You must run the Setup Wizard before connecting the Adaptor
to your computer.
Using the Setup Wizard
Insert the Setup Wizard CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive. The Setup Wizard should run automatically, and the
Welcome screen should appear. If it does not, click the Start button and choose Run. In the field that appears,
enter D:\setup.exe (if “D” is the letter of your CD-ROM drive).
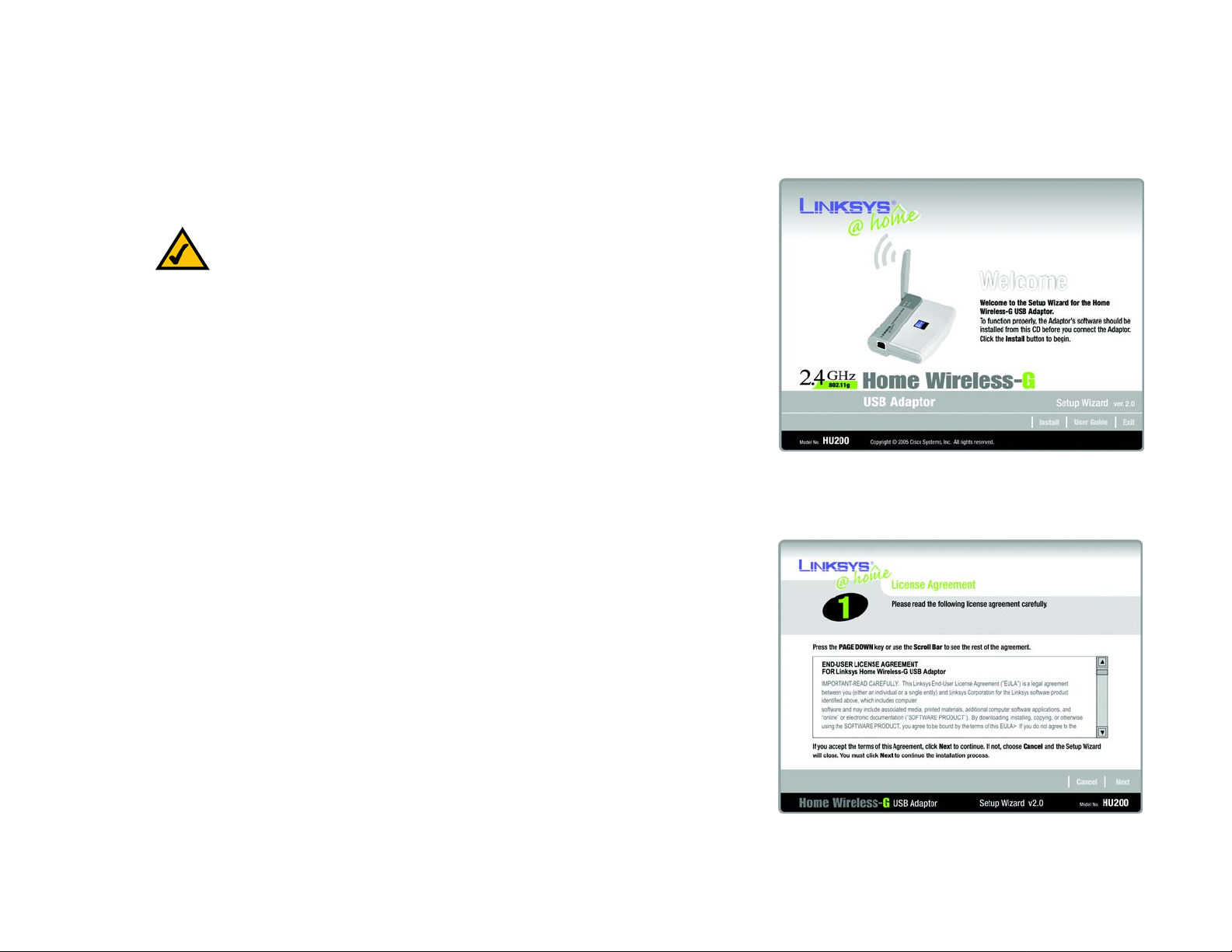
On the Welcome screen, you have the following choices:
Install - Click the Install button to begin the software installation process.
Figure 4-1: Setup Wizard’s Welcome Screen
User Guide - Click the User Guide button to open the PDF file of this User Guide.
Exit - Click the Exit button to exit the Setup Wizard.
1. To install the Adaptor, click the Install button on the Welcome screen.
2. After reading the License Agreement, click the Next button if you agree, or click the Cancel button to end the
installation.
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Using the Setup Wizard
Figure 4-2: Setup Wizard’s License Agreement
7

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
3. The Setup Wizard will ask you to choose a network mode. Click the Infrastructure Mode radio button if you
want to connect to a wireless router or access point. Click the Ad-Hoc Mode radio button if you want to
connect directly to another wireless device without using a wireless router or access point.
In the SSID field, enter the SSID of your wireless network. The SSID must be identical for all devices in the
network. The default setting is linksys (all lowercase). Click the Next button.
NOTE: Network SSIDs should be unique to your network and identical for all
devices within the network.
4. If you chose Infrastructure Mode, go to Step 5 now. If you chose Ad-H oc Mode , select the correct operating
channel for your network. Then, select the Network Mode from the drop-down menu. Click the Next button,
and go to Step 5. Click the Back button to change any settings.
Figure 4-3: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Mode Screen
Channel - The channel you choose should match the channel set on the other devices in your wireless
network. If you are unsure about which channel to use, keep the default channel.
Network Mode - Select Mixed Mode if you want to allow Wireless-G and Wireless-B computers on the
network, even though network speeds will be reduced. For maximum speed, select G-Only Mode; however,
no Wireless-B users will be allowed on the network.
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Using the Setup Wizard
Figure 4-4: Setup Wizard’s Ad-Hoc Mode Settings Screen
8

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
5. If you don’t want to use encryption, select Disabled and then click the Next button to continue. Proceed to
Step 7.
Select the method of security you want to use: WEP, PSK, PSK + RADIUS, or RADIUS. WEP stands for Wired
Equivalent Privacy, and PSK stands for Pre-Shared Key. RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User
Service.
NOTE: If your network is using WPA-Personal or WPA-PSK security, then
select PSK. If your network is using WPA-Enterprise or WPA-RADIUS security,
then select PSK + RADIUS.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
6. Proceed to the appropriate section for your security method: WEP, PSK, PSK-RADIUS, or RADIUS.
WEP
WEP - Select 64-bit or 128-bit encryption from the drop-down menu, and enter a passphrase or WEP key.
Passphrase - Enter a passphrase in the Passphrase field, so a WEP key is automatically generated. It is case-
sensitive and should not be longer than 16 alphanumeric characters. This passphrase must match the
passphrase of your other wireless network devices and is compatible with Linksys wireless products only. (If
you have any non-Linksys wireless products, enter the WEP key manually on those products.)
WEP Key - The WEP key you enter must match the WEP key of your wireless network. For 64-bit encryption,
enter exactly 10 hexadecimal characters. For 128-bit encryption, enter exactly 26 hexadecimal characters.
Valid hexadecimal characters are “0” to “9” and “A” to “F”.
Advanced Users
TX Key - The default transmit key number is 1. If your network’s access point or wireless router uses transmit
key number 2, 3, or 4, select the appropriate number from the TX Key drop-down box.
Authentication -The default is set to Auto, so it will auto-detect for Shared Key or Open System
authentication. For Shared Key authentication, both the sender and the recipient share a WEP key for
authentication. For Open System authentication, the sender and the recipient do not share a WEP key for
authentication. If you are not sure which authentication method to select, keep the default, Auto.
Click the Next button to continue. Click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-5: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security Screen
Figure 4-6: Setup Wizard’ s Wireless Security -
WEP Screen
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Using the Setup Wizard
9
Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
PSK
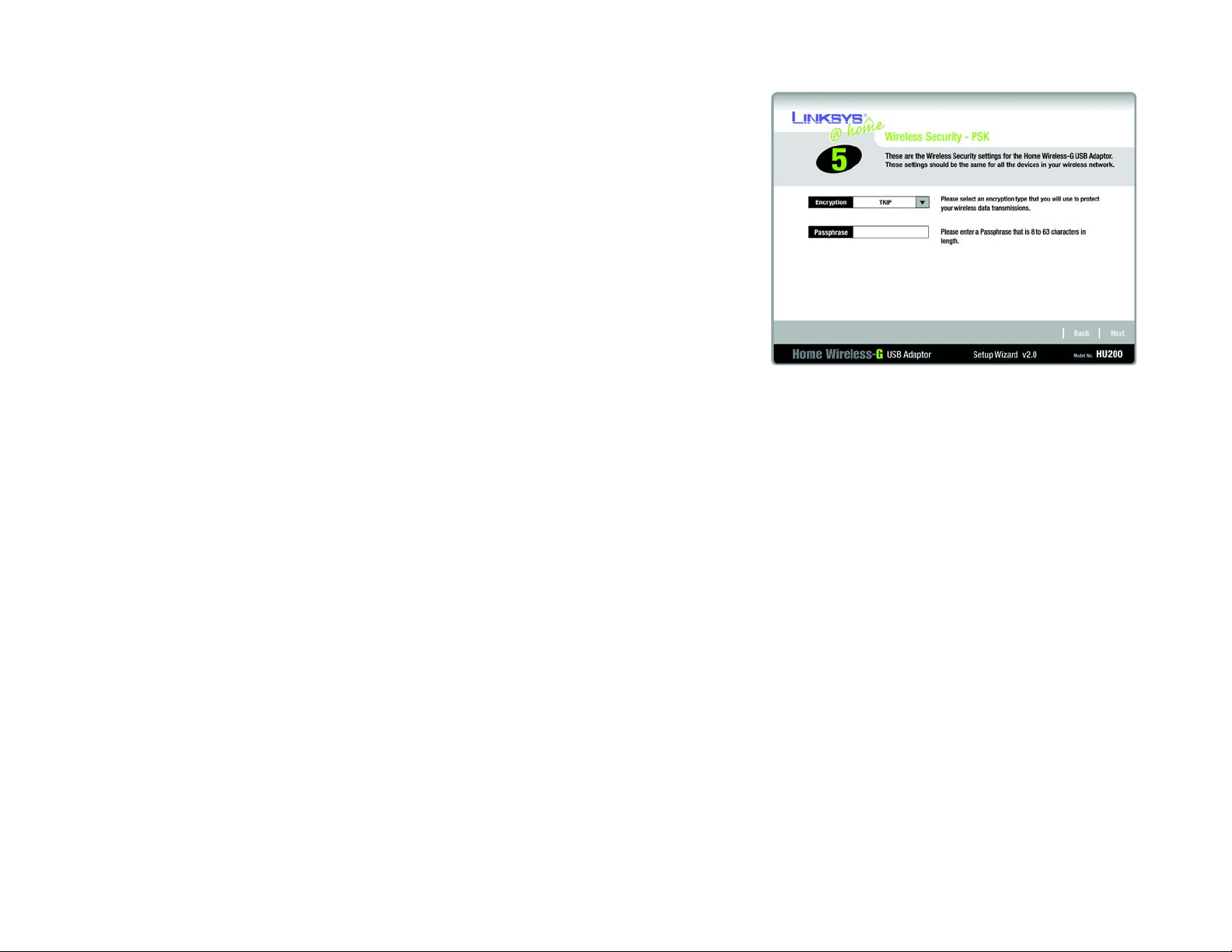
PSK offers two encryption methods, TKIP and AES, with dynamic encryption keys. Select the type of
algorithm, TKIP or AES, for the Encryption Type. Then enter a P assphrase that is 8-63 characters in length.
Encryption - Select the type of algorithm you want to use, TKIP or AES, for the Encryption setting.
Passphrase - Enter a Passphrase, also called a Pre-Shared Key, of 8-63 characters in the Passphrase field.
The longer and more complex your Passphrase is, the more secure your network will be.
Click the Next button to continue. Click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-7: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security -
PSK Using TKIP Screen
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Using the Setup Wizard
10

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
PSK + RADIUS
PSK + RADIUS features a Pre-Shared Key used in coordination with a RADIUS server. (This should only be
used when a RADIUS server is connected to the Router.) PSK + RADIUS offers two encryption methods, TKIP
and AES, with dynamic encryption keys, as well as two authentication methods, EAP-TLS and PEAP.
Authentication - Select the authentication method your network is using, EAP-TLS or PEAP.
EAP-TLS
If you selected EAP-TLS, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
name of the authentication server in the Server Name field. From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the
certificate you have installed to authenticate you on your wireless network. Select the type of encryption,
TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down menu.
Click the Next button to continue. Click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
PEAP
If you selected PEAP, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
password of your wireless network in the Password field. Enter the name of the authentication server in the
Server Name field. From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the certificate you have installed to
authenticate you on your wireless network. Select the type of encryption, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption
drop-down menu.
Click the Next button to continue. Click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-8: Setup Wizar d’s Wireless Security -
PSK + RADIUS Using EAP-TLS Screen
Figure 4-9: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security -
PSK + RADIUS Using PEAP Screen
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Using the Setup Wizard
11

Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
RADIUS
RADIUS features use of a RADIUS server. (This should only be used when a RADIUS server is connected to the
Router.) RADIUS offers two authentication types: EAP-TLS and PEAP.
Authentication - Select the authentication method your network is using, EAP-TLS or PEAP.
EAP-TLS
If you selected EAP-TLS, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
name of the authentication server in the Server Name field. From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the
certificate you have installed to authenticate you on your wireless network.
Click the Next button to continue. Click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
PEAP
If you selected PEAP, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
password of your wireless network in the Password field. Enter the name of the authentication server in the
Server Name field. From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the certificate you have installed to
authenticate you on your wireless network.
Click the Next button to continue. Click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-10: Setup Wizard’s Wireless Security -
RADIUS Using EAP-TLS Screen
Figure 4-11: Setup Wizard’s Wire less Security -
RADIUS Using PEAP Screen
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Using the Setup Wizard
12
Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
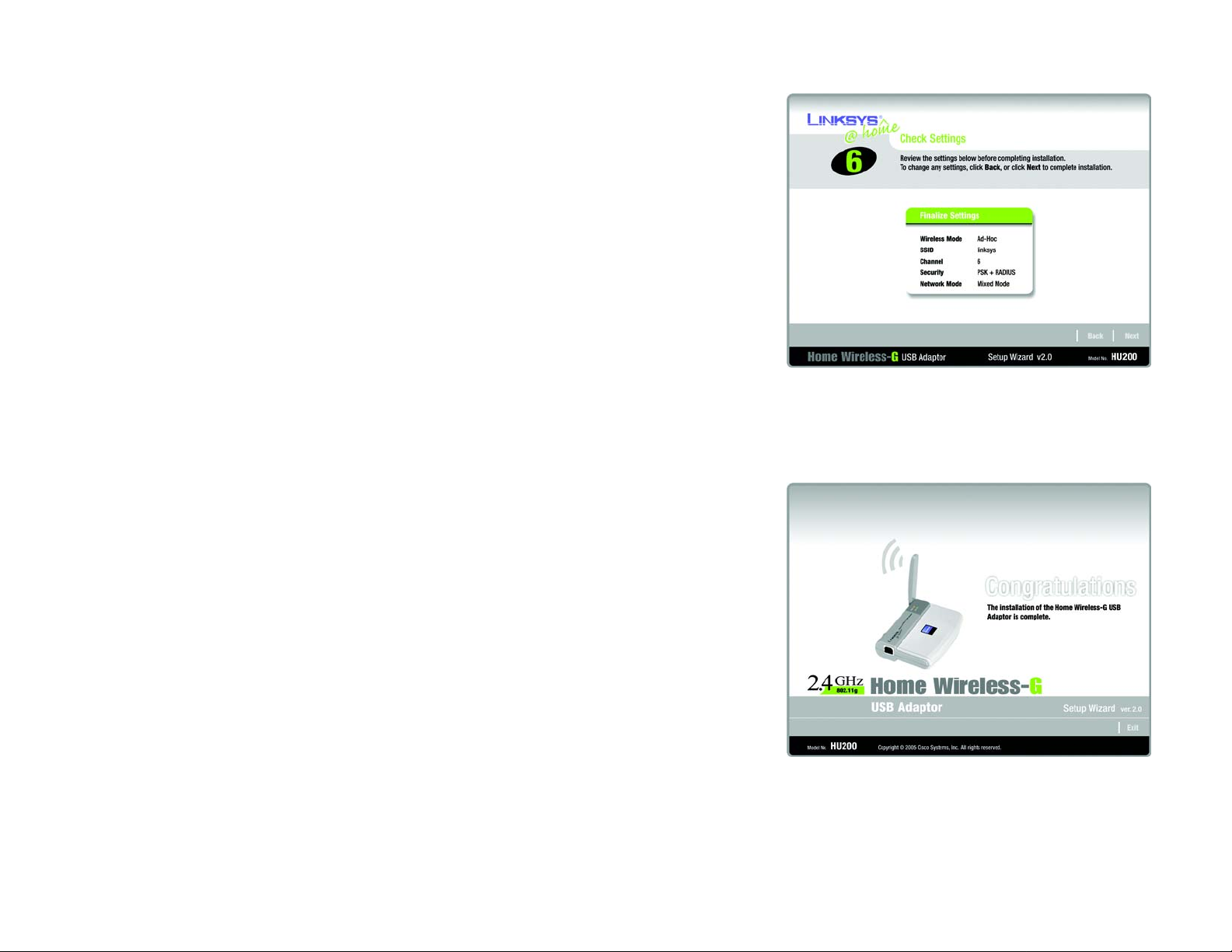
7. The Setup Wizard will ask you to review your settings before it starts to install files. Click Next if you are
satisfied with your settings, or click Back to change any settings.
8. After the software has been successfully installed, the Congratulations screen will appear. Click the Exit
button.
Figure 4-12: Setup Wizard’s Check Settings Screen
Proceed to “Chapter 5: Connecting the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor.”
Chapter 4: Setting up the Home Wireless-G USB Adaptor
Using the Setup Wizard
Figure 4-13: Setup Wizard’s Congratulations Screen
13
 Loading...
Loading...