Page 1

Instant Wireless™ Series
Wireless Access Point
Router with 4-Port Switch
Use this Guide to install: BEFW11S4 ver. 2
User Guide
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Copyright © 2002 Linksys, All Rights Reserved. Instant Wireless is a trademark of
Linksys. Microsoft, Windows, and the Windows logo are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation. All other trademarks and brand names are the property of their
respective proprietors.
LIMITED WARRANTY
Linksys guarantees that every Instant Wireless™ Wi reless Access Point Router with 4-Port
Switch is free from physical defects in material and workmanship for one year from the
date of purchase, when used within the limits set forth in the Specifications section of this
User Guide. If the product proves defective during this warranty period, call Linksys
Technical Support in order to obtain a Return Authorization number. BE SURE TO HAVE
YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE ON HAND WHEN CALLING. When returning a product,
mark the Return Authorization number clearly on the outside of the package and include
a copy of your original proof of purchase. RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE
PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. All customers located outside of the
United States of America and Canada shall be held responsible for shipping and handling charges.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS OFFERS NO REFUNDS FOR ITS PRODUCTS. Linksys makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory,
with respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or
fitness for any particular purpose. Linksys reserves the right to revise or update its products, software, or documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity.
Please direct all inquiries to:
Linksys P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623.
FCC STATEMENT
The Instant Wireless™ Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch has been tested
and complies with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used according to the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, ther e is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
UG-BEFW11S4 ver. 2-080702F JL
Page 3

Instant WirelessTMSeries
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
The Linksys Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch 1
Features 1
Package Contents 2
Minimum Requirements 2
An Introduction to LANs and WANs 2
IP Addresses 3
The Wireless Access Point Router’s Ports 5
The Wireless Access Point Router’s LEDs 6
Chapter 2: Connecting the Router 8
Before You Start 8
Connecting Your Hardware Together & Booting Up 8
Chapter 3: Configuring the PCs 11
Overview 11
Configuring Windows 95, 98, and Millennium PCs 11
Configuring Windows 2000 PCs 13
Configuring Windows XP PCs 15
Chapter 4: Configuring the Router 17
Chapter 5: Using the Router’s Web-Based Utility 22
Setup 23
Password 27
Status 28
DHCP 30
Log 31
Security 33
Help 35
Advanced Tab: Filters 37
Advanced Tab: Port Range Forwarding 41
Advanced Tab: Dynamic Routing 46
Advanced Tab: Static Routing 47
Advanced Tab: DMZ Host 49
Advanced Tab: MAC Address Cloning 50
Advanced Tab: Wireless 51
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 54
Common Problems and Solutions 54
Frequently Asked Questions 67
Appendix B: How to Ping Your
ISP’s E-mail and Web Addresses 73
Appendix C: Configuring Wireless Security 76
Configuring Wireless Security in Windows XP 79
Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address
and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter 84
Appendix E: Glossary 88
Appendix F: Specifications 102
Environmental 103
Appendix G: Warranty Information 104
Appendix H: Contact Information 105
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 4
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Chapter 1: Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of a Wireless Access Point Router with 4Port Switch. The W ireless Access Point Router with 4-P ort Switch pro vides the
ideal solution for connecting your wireless network to a high-speed broadband
Internet connection and a 10/100 Fast Ethernet backbone. Configurable as a
DHCP server for your existing network, the Wireless Access Point Router with
4-Port Switch acts as the only externally recognized Internet gateway on your
local area network (LAN) and serves as an Internet NAT firewall against
unwanted outside intruders. The Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port
Switch can also be configured to filter internal users’ access to the Inter net.
A typical router relies on a hub or a switch to share its Internet connection, but
the Linksys Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch channels this
connection through the blazing, full duplex speed of its built-in EtherFast
®
10/100 4-Port Switch. This cutting-edge combination of wireless router and
switch technology eliminates the need to buy an additional hub or switch and
extends the range of your wireless network. Now your entire wireless network
can enjoy blazing broadband Internet connections supported by its robust
switched backbone. With the dual-function speed and power of the Wireless
Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch, your network will take off at speeds
faster than you ever imagined possible.
• Supports Universal Plug-and-Play for easy configuration
• Capable of up to 128-bit WEP Encryption
• Supports enhanced security using NAT firewall, ZoneAlarm Pro and PCcillin Software
• Access your network remotely over the Internet through Virtual Private
Networking (VPN)
• Supports IPSec and PPTP Pass-Through
• Administer and upgrade the Router remotely over the Internet
• Configurable as a DHCP Server on your network
• Advanced security management functions for Port Filtering, MAC Address
Filtering, and DMZ Hosting
• Includes one Ethernet Cable to Connect to a Cable or DSL modem
2
Features
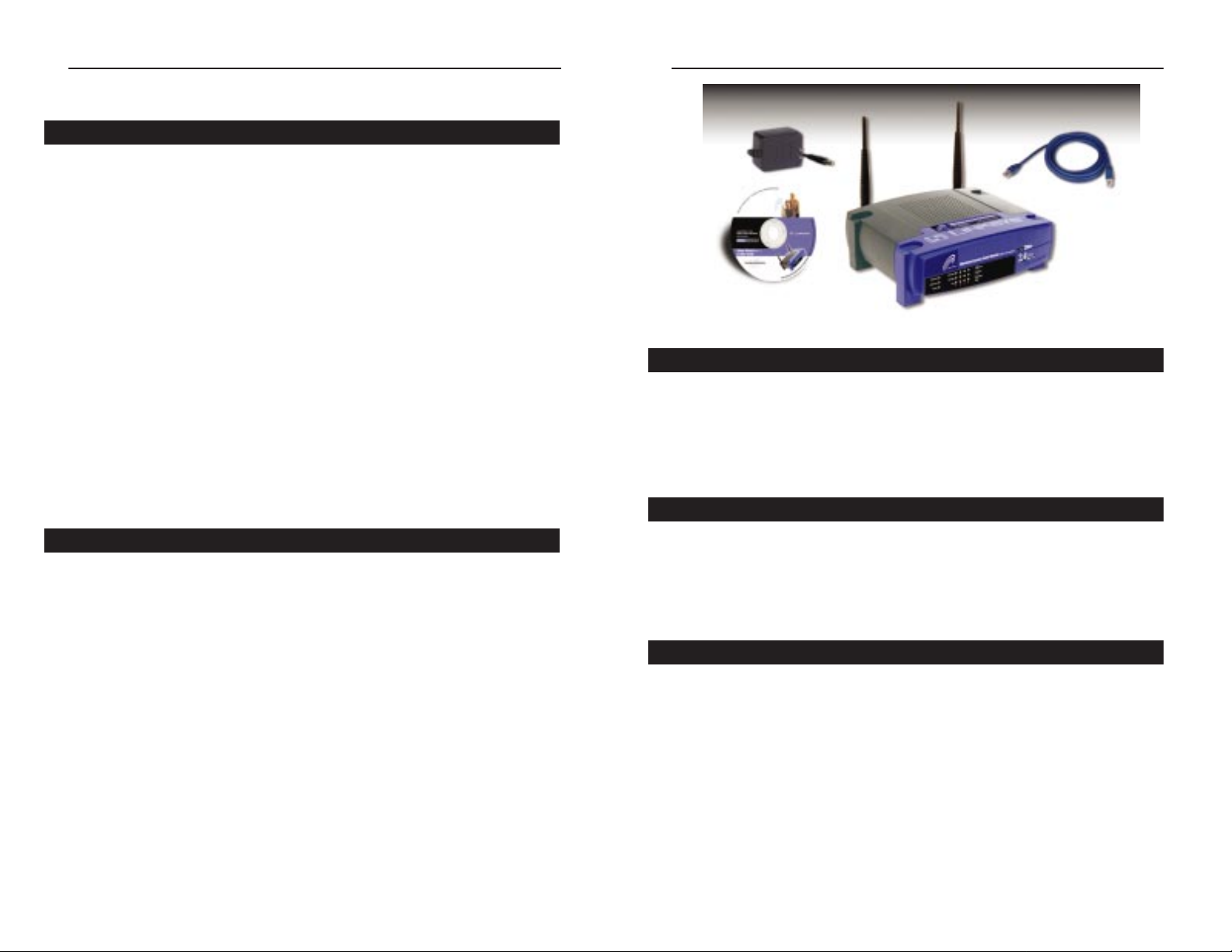
• One Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
• Two detachable Antennas
• One Setup Wizard CD-ROM with User Guide included
• One Power Adapter
• One CAT 5 UTP Cable
• One Fast Start Guide and One Registration Card (not shown)
• One Windows 98 SE, Millennium, 2000, or XP PC equipped with TCP/IP
Protocol, Internet Explorer 4.0 or Netscape Navigator 4.7 for web-based
configuration, a CD-ROM Drive and an Ethernet Adapter with a UTP CAT
5 Network Cable
• Cable or DSL Modem with Ethernet Connection and Internet Access
Simply put, a router is a network device that connects two networks together.
In this instance, the Router connects your Local Area Network (LAN), or the
group of PCs in your home or office, to the Wide Area Network (WAN) that is
the Internet. The Router processes and regulates the data that travels between
these two networks.
1
The Linksys Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Package Contents
Minimum Requirements
Figure 1-1
An Introduction to LANs and WANs
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Page 5
Think of the Router as a network device with two sides. The f irst side is made
up of your private Local Area Network (LAN) of PCs. The other, public side
is the Internet, or the Wide Area Network (WAN), outside of your home or
office.
The Router’s firew all (NAT) protects your network of PCs so users on the public, Internet side cannot “see” your PCs. This is how your LAN, or network,
remains private. The Router protects your network by inspecting the first packet coming in from the WAN port before delivery to the final destination on the
LAN port. The Router inspects Internet port services like the web server, ftp
server, or other Internet applications, and, if allowed, it will forward the packet to the appropriate PC on the LAN side.
What’s an IP Address?
IP stands for Internet Protocol. Every device on an IP-based network, including PCs, print servers, and routers, requires an IP address to identify its “location, ” or address, on the network. This applies to both the WAN and LAN connections.
There are two ways of assigning an IP address to your network devices.
Static IP Addresses
A static IP address is a fixed IP address that you assign manually to a PC or
other device on the network. Since a static IP address remains valid until you
disable it, static IP addressing insures that the device assigned it will have that
same IP address until you change it. Static IP addresses are commonly used
with network devices such as server PCs or print servers.
If you use the Router to share your cable or DSL Internet connection, contact
your ISP to find out if they have assigned a static IP address to your account.
If so, you will need that static IP address when configuring the Router. You can
get the information from your ISP.
3
Dynamic IP Addresses
A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned to a device on the network,
such as PCs and print servers. These IP addresses are called “dynamic”
because they are only temporarily assigned to the PC or device. After a certain
time period, they expire and may change. If a PC logs on to the network (or the
Internet) and its dynamic IP address has expired, the DHCP server will assign
it a new dynamic IP address.
For DSL users, many ISPs may require you to log on with a user name and
password to gain access to the Internet. This is called “Point to Point Protocol
over Ethernet” or PPP oE. PPPoE is similar to a dial-up connection but does not
have a phone number to dial into, and PPPoE is a dedicated high-speed connection. PPPoE also will provide the Router with a dynamic IP address to
establish a connection to the Internet.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Servers
DHCP frees you from having to assign IP addresses manuall y every time a new
user is added to your network. PCs and other network devices using dynamic
IP addressing are assigned a new IP address by a DHCP server. The PC or network device obtaining an IP address is called the DHCP client. The Router’s
WAN port is, by default, set as a DHCP client.
DHCP servers can either be a designated PC on the network or another netw ork
device, such as the Router. By default, a DHCP server is enabled on your
Router’s LAN ports. If you already have a DHCP server running on your network, you mustdisable one of the two DHCP servers. If you run more than one
DHCP server on your network, you will experience network errors, such as
conflicting IP addresses. To disable the Router’s DHCP function, see the
DHCP section in Chapter 3: Configuring the Router.
IP Addresses
NNoottee::
Since the Router is a device that connects two networks, it needs two
IP addresses—one for the LAN side, and one for the WAN side. In this User
Guide, you’ll see references to the “WAN IP address” and the “LAN IP
address.”
Since the Router has firewall security (NAT), only the Router’s WAN IP address
can be seen from the Internet.
However, even the WAN IP address can be blocked, so that the Router and
network seem invisible to the Internet—This is shown in the Filters section in
“Chapter 5: Using the Routers Web-Based Utility”.
NNoottee::
Even if you assign a static IP address to a PC, other PCs can still use
DHCP’s dynamic IP addressing, as long as the static IP is not within the
DHCP range of the LAN IP Address.
If the Router’s DHCPfunction fails to provide a dynamic IP address for any
reason, please refer to Appendix A: Troubleshooting.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
4
Page 6

The LAN Indicators
WLAN Act Green. This LED indicates wireless activity.
WLAN Link Green. This LED indicates that the Router’s wireless func-
tions have been enabled through the Web-based utility.
Power Green. This LED indicates that the Router’s power is on.
Link/Act Green. This LED serves two purposes. When this LED is lit
continuously, this indicates that the Router is connected to a
device through the corresponding port (1, 2, 3, or 4). A blinking LED indicates that the Router is actively sending or
receiving data over that port. When the Uplink Port is in use,
the LED for Port 4 will be lit continuously.
6
The Wireless Access Point Router’s LEDs
TThhee RReesseett BBuuttttoonn
Pressing the Reset Button and holding it in for a few seconds will clear all
of the Router’s data and restore the factory defaults. This should be done
only if you are experiencing heavy routing problems, and only after you
have exhausted all of the other troubleshooting options. By resetting the
Router, you run the risk of creating conflicts between your PCs’ actual IP
Addresses and what the Router thinks their IP Addresses should be. You
may be forced to reboot each network PC.
If the Router locks up, simply press the reset button or power it down for
three to five seconds by removing the power cable from the Router’s
Power Port. Leaving the power off for too long could result in the loss of
network connections.
Figure 1-3
The
Router’s rear panel (as shown in Figure 1-2) is where all of its connections are
made.
WAN The WAN (Wide Area Network) Port is where you will con-
nect your cable or DSL modem with an Ethernet cable. Your
modem connection will not work from any other port.
Ports 1-4 These four LAN (Local Area Network) ports are where you
will connect networked devices, such as PCs, print servers,
and any other Ethernet devices you want to put on your network. If Port 4 is being used, the Uplink Port will not work.
Uplink The Uplink Port is where you can expand your network by
connecting to another switch or hub. Uplinking to another
switch or a hub is done by simply running a cable from the
Uplink Port to the other device. The Uplink Port is shared
with Port 4. If the Uplink port is being used, Por t 4 will not
work.
Power The Power Port is where you will connect the included AC
Power adapter.
Antenna Jacks The Antenna Jacks are where the included antennas are con-
nected.
Figure 1-2
The Wireless Access Point Router’s Ports
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
5
Page 7
Chapter 2: Connecting the Router
Before plugging everything together, it’s always a good idea to have everything
you’ll need to get the Router up and running. Depending upon how you configure the Router in Chapter 4: Configuring the Router, you may need some of the
following values from your ISP:
When connecting through a Static IP connection, be sure to have 1) Your
broadband-configured PC’s f ixed Internet IP Address, 2) Your broadbandconfigured PC’s Computer Name and Workgroup Name, 3) Your Subnet
Mask, 4) Your Default Gateway, and 5) Your Primary DNS IP address.
When connecting through a PPPoE connection, be sure to have 1) Your
PPPoE User Name and 2) Your PPPoE Password.
The installation technician from your ISP should hav e left this information with
you after installing your broadband connection. If not, you can call your ISP to
request the data.
Once you have the above values, you can begin the Router’s installation and
setup.
Once you are sure that you have the above values on hand, you can begin the
Installation and Setup of the Router.
1. Power everything down, including your PCs, your cable or DSL modem and
the Router.
2. Connect an Ethernet cable from one of
your PC’s Ethernet ports to one of the
Router’s LAN ports (as shown in Figure 2-
1). Do the same with all the PCs you wish
to connect to the Router. (LAN Port 4 will
become inactive if you use the Uplink
port.)
In addition to accessing the Router through
Before You Star t
Full/Col Green. This LED also serves two purposes. When this LED
is lit continuously, the connection made through the cor responding port is running in Full Duplex mode. A blinking
LED indicates that the connection is experiencing collisions.
Infrequent collisions are normal. If this LED blinks too
often, there may be a problem with y our connection. Refer to
the Troubleshooting Appendix if you think there is a problem.
100 Orange. This LED indicates when a successful 100Mbps
connection is made through the corresponding port.
The WANIndicators
Link Green. This LED indicates a connection between the Router
and your broadband device or network.
Act Green. This LED blinks when the Router is sending or
receiving data over the broadband (WAN) por t.
Diag Red. This LED indicates the Router’s self-diagnosis mode
during boot-up and restart. It will turn off upon completing
the diagnosis. If this LED stays on for an abnormally long
period of time, refer to the Troubleshooting Appendix.
7
Connecting Your Hardware Together and Booting Up
Figure 2-1
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
8
Page 8

For Wireless Connections: In addition to accessing the Router through an
Ethernet connection, a wireless connection can be used to access the Router.
After powering on the Router and connecting it to your modem, enter the
Router’s IP Address in the Address f ield of your wireless PC’s web-browser as
follows: http://192.168.1.1 and press Enter.
IImmppoorrttaanntt::
The Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch is
configured by default to work out of the box with all Linksys Wireless
Adapters. If you have changed the defaults on your Linksys Wireless
Adapters, or are using other wireless adapters, you must temporarily change your wireless adapter settings to: (SSID = linksys) in
order to initially access the Router wirelessly. After you have
accessed the Router with the default settings, you can change the
router settings to coincide with your Network settings and reset your
adapters.
IImmppoorrttaanntt::
Some ISPs—most notably some cable providers—configure their networks so that you do not have to enter a full Internet
address into your web browser or e-mail application to reach your
home page or receive your e-mail. If your Internet home page
address is something very simple, such as “www”, rather than
“www.linksys.com”, or your e-mail server’s address is something similar to “e-mail” or “pop3”, rather than “pop.mail.linksys.com”, you
won’t be able to properly configure the Router until you determine the
actual Internet addresses of your Web and e-mail connections.
You
mmuusstt
obtain this information prior to connecting the Router to
your network. You can obtain this information by contacting your ISP .
10
an Ethernet connection, a wireless connection can be used to access the
Router. See the “For Wireless Connections” section that follows these connection instructions.
3. Connect another Ether net cable from your
cable or DSL modem to the Router’s WAN
port (as shown in Figure 2-2).
4. Connect the Power Adapter (included) to
the Router’s Power port (as shown in Figure
2-3) and plug the other end into a power
outlet.
• The Power LED will illuminate green
as soon as the power adapter is connected.
• The Diag LED will illuminate red for a
few seconds while the Router goes
through its internal diagnostic test. The
LED will tur n off when the self-test is
complete.
5. Power on the cable or DSL modem. Verify that the power is on by checking
the LinkLED in the WAN column on the front of the Router. The Link LED
will be illuminated if the power is on and the modem is ready.
6. Press the Reset button on the back of the Router. Hold the button in for three
seconds, or until the Diag LED illuminates red. This restores the Router’s
default settings.
7. Power on your PC.
The Router is now connected. Continue to the next chapter to configure
your PCs.
Figure 2-2
Figure 2-3
Instant WirelessTMSeries Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
9
Page 9
2. Select the Configuration tab
and highlight the TCP/IP
line for the applicable
Ethernet adapter (as shown
in Figure 3-1). If the word
TCP/IP appears by itself,
select that line. (Note: If
there is no TCP/IP line listed, refer to your Ethernet
adapter’s documentation to
install TCP/IP now.) Then,
click the Properties button.
3. Click the IP Address tab
and select Obtain an IP
address automatically (as
shown in figure 3-2).
4. Click the Gateway tab and verify that the Installed Gateway field is blank.
Click the OK button.
Chapter 3: Configuring the PCs
These instructions will help you configure each of your computers to communicate with the Router.
To do this, you will need to configure your PC’s network settings to obtain an
IP (or TCP/IP) address automatically. Computers use IP addresses to communicate with each other across a network or the Internet.
You will need to know which operating system your computer is running, such
as Windows 95, 98, Millennium, 2000, or XP. You can find out by clicking the
Start button and then selecting the Settings option. (If your Start menu does-
n’t have a Settings option, you’re running Windows XP. You can select the
Control Panel directly from the Start Menu.) Then, click Control Panel and
double-click the System icon. Click the Cancel button when done.
Once you know which Windows operating system you are running, follow the
directions in this step for your computer’s operating system. If you PC is not
configured with the TCP/IP protocol, you will need to do this for each computer you are connecting to the Router.
The next few pages tell you, step by step, how to configure your TCP/IP settings based on the type of Windows operating system you are using. Once
you've configured your computers, continue to Chapter 4: Configuring the
Router.
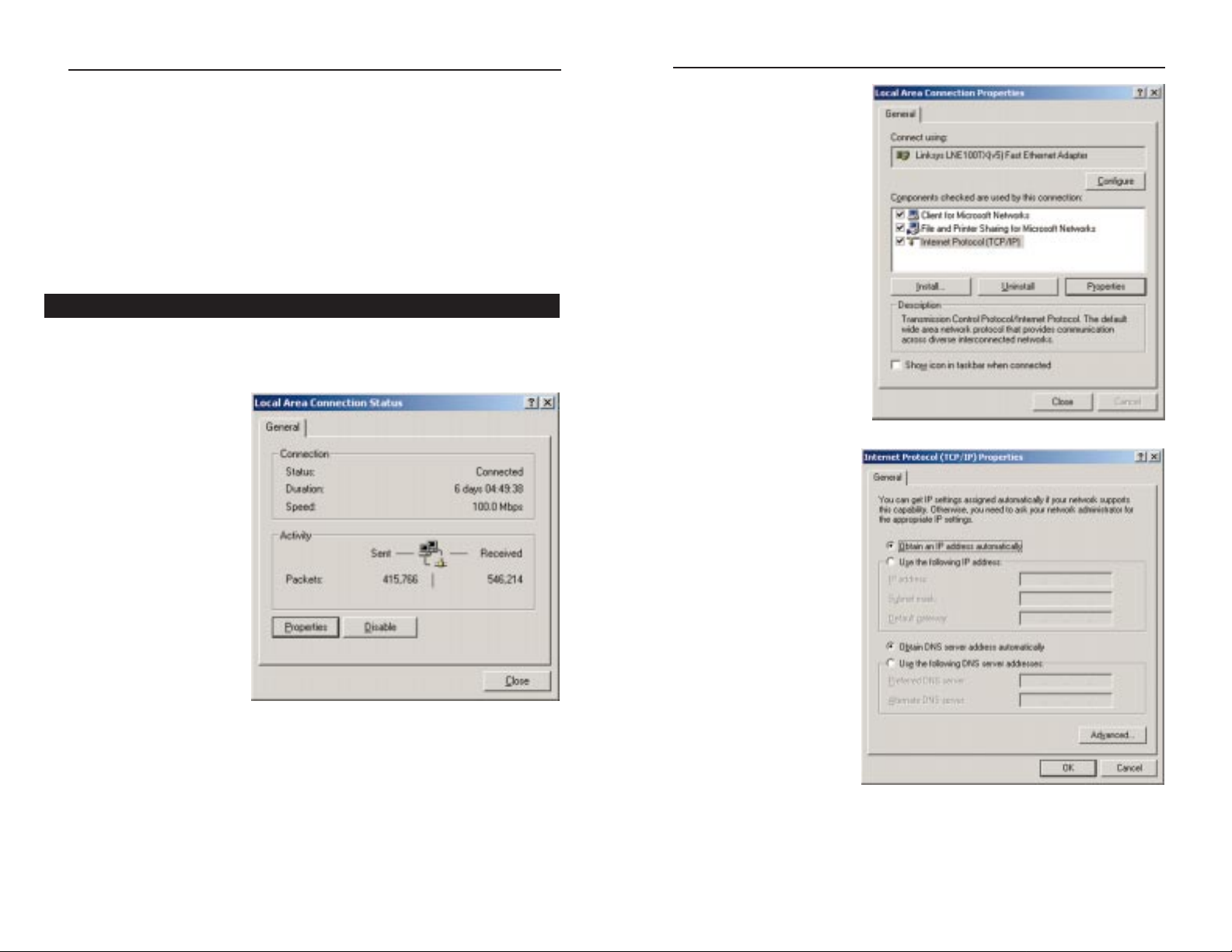
1. Click the Start button, click Settings and open the Control Panel. From
there, double-click the Network icon to open the Network screen.
12
Overview
Configuring Windows 95, 98, and Millennium PCs
Figure 3-1
Figure 3-2
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
11
Page 10
5. Click the OK button again. Windows may ask you for the original
Windows installation disk or additional f iles. Supply them by pointing to
the correct file location, e.g., D:\win98, D:\win9x,
c:\windows\options\cabs, etc. (This assumes that “D” is the letter of your
CD-ROM drive).
6. If Windows asks you to restart your PC, click the Yes button. If Windows
does not ask you to restart, restart your computer anyway.
Repeat steps 1-6 for each PC on your network. When all of your PCs are
configured, proceed to Chapter 4: Configuring the Router.
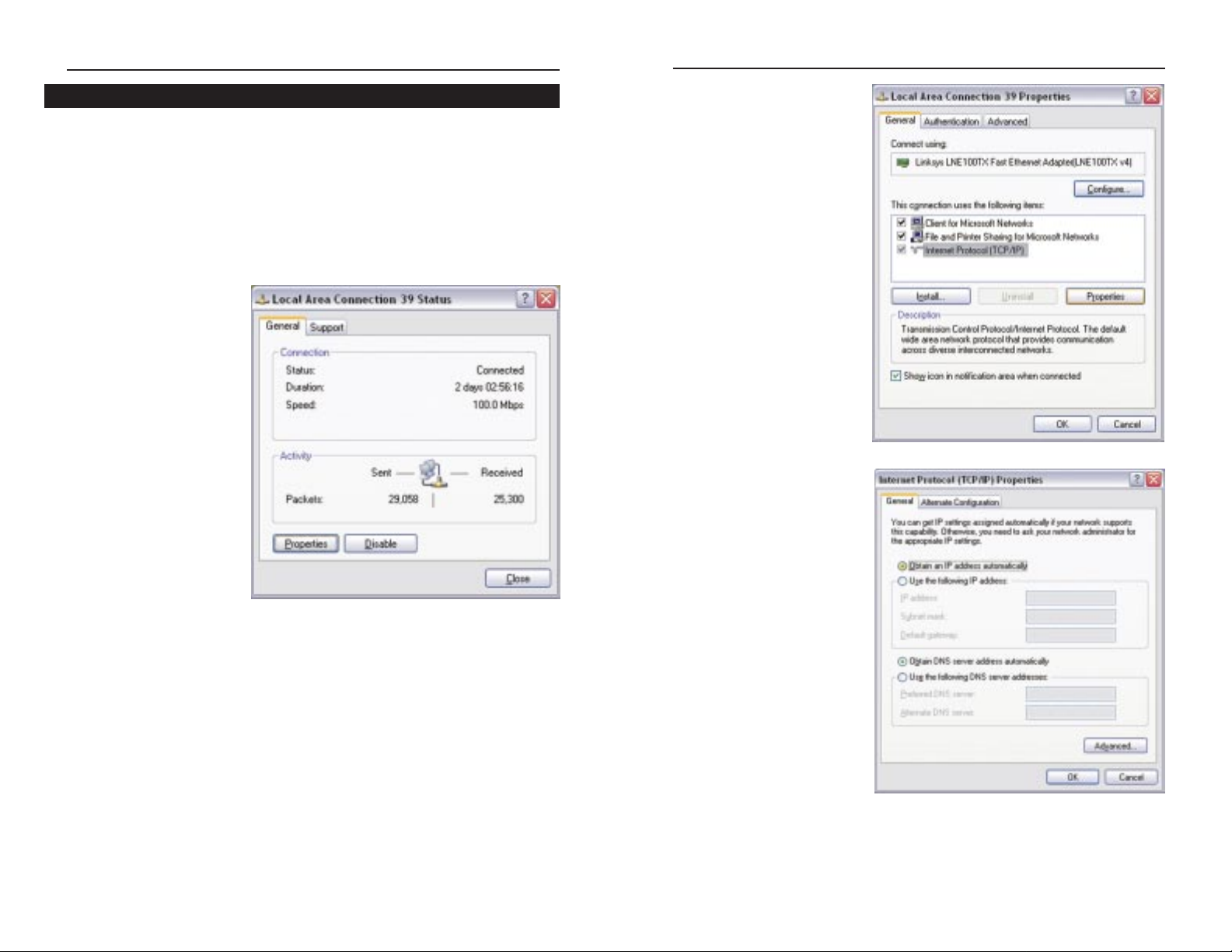
1. Click the Start button, click Settings and open the Control Panel. From
there, double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon. This will
display the Network screen.
2. Select the Local Area
Connection icon for the
applicable Ethernet
adapter (usually it is the
first Local Area
Connection listed).
Double-click Local
Area Connection and
click the Properties
button. (See Figure 3-
3.)
3. When the Local Area Connection Status screen appears, click the
Properties button.
4. Select Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) (as shown in
Figure 3-4) and click the
Properties button.
5. Select Obtain an IP
address automatically
and verify that Obtain
DNS server address
automatically is select-
ed (as shown in Figure
3-5). Then, click the OK
button and click the OK
button on the subsequent screens to complete the PC’s configuration.
Repeat steps 1-5 for each PC on your network. When all of your PCs are
configured, proceed to Chapter 4: Configuring the Router.
Configuring Windows 2000 PCs
Figure 3-3
Figure 3-4
Figure 3-5
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
13 14
Page 11
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP’s default
interface. If you are using the Classic interface (where the icons and menus
look like previous Windows versions), please follow the instructions for
Windows 2000.
1. Click the Start button, open the Control Panel. and click the Network and
Internet Connections icon. Then, click the Network Connections icon to
display the Network screen.
2. Select the Local Area
Connection icon for
the applicable Ethernet
adapter (usually it is
the first Local Area
Connection listed).
Double-click Local
Area Connection and
click the Properties
button. (See Figure 3-
6.)
3. When the Local Area Connection Status screen appears, click the
Properties button.
4. Select Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) (as shown in
Figure 3-7) and click the
Properties button.
5. Select Obtain an IP
address automatically
and verify that Obtain
DNS server address automatically is selected (as
shown in Figure 3-8).
Then, click the OK button
and click the OK button on
the subsequent screens to
complete the PC’s configuration.
Repeat steps 1-5 for each PC on your network. When all of your PCs are
configured, proceed to Chapter 4: Configuring the Router.
Configuring Windows XP PCs
Figure 3-6
Figure 3-7
Figure 3-8
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
15 16
Page 12
3. If required by your ISP, enter the Router’s Host Name and Domain Name
in the appropriate fields on the Setup tab. (This is usually required by cable
ISPs.)
4. To configure the
Router for your wireless network, verify
that the Setup tab’s
Wireless fields (shown
in Figure 4-3) are completed as follows:
Enable/Disable:
Selecting the Enable
radio button will
enable the Router’s
wireless feature.
Wireless functions will
not be available unless
enabled.
SSID: The SSID is a unique name for y our wireless network. It is case sensitive and must not exceed 32 characters. The default SSID is "linksys " but
you should change this to a personal wireless network name. All wireless
points in your network must use the same SSID.
Allow “Broadcast” SSID to associate?: To increase network security, the
Router’s Utility prevents the SSID from being seen on networked PCs.
Without this enabled, someone could easily obtain this information with site
survey software of any software and gain access to your network. To enable
this function, click the Yes radio button beside this question.
Channel: Select the appropriate channel for your network from the list provided. All wireless points in your network must use the same channel in
order to function properly.
Do not change the WEP setting from the default, “Disabled”, without first
referring to the Wireless Security sections of the User Guide or Setup
Wizard CD-ROM for advanced features and settings.
17 18
Chapter 4: Configuring the Router
This chapter will show you how to configure the Router to function in your network and gain access to the Internet through your Internet Service Provider
(ISP). Detailed description of the Router’s Web-based Utility can be found in
the Chapter 5: Using the Router’s Web-Based Utility. Your ISP may require the
use of a Host Name and Domain Name. Further, you will set the WAN
Configuration Type on the Router’s Setup tab from the information given by
your ISP. You will need this setup information from your ISP. If you do not have
this information, please contact your ISP before proceeding.
The instructions from your ISP tell you how to set up your PC for Internet
access. Since you are now using the Router to share Internet access among several computers, you will use this setup information for Router configuration.
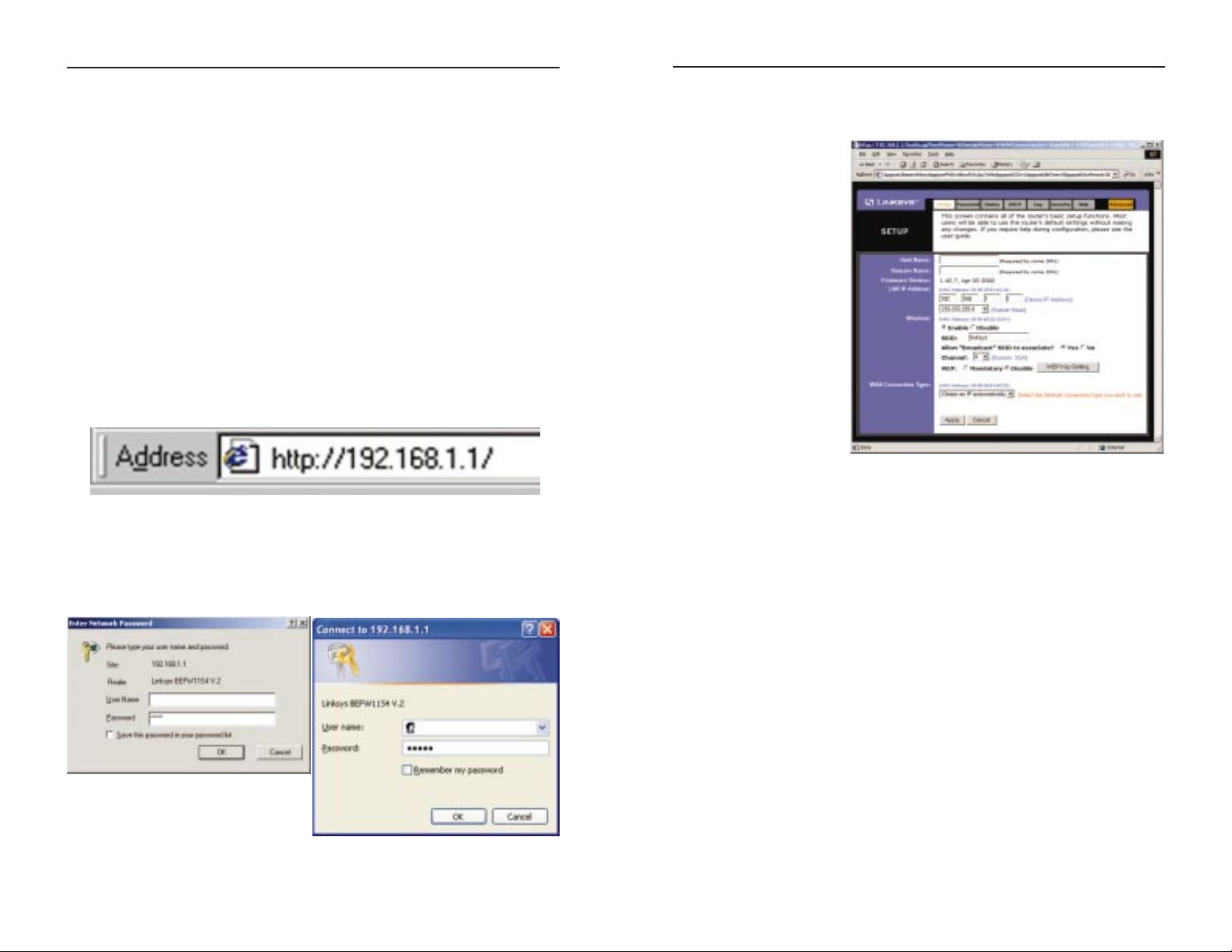
1. Open your web browser, and enter 192.168.1.1 into the web browser’s
Address field, as shown in Figure 4-1. Then, press the Enter key.
2. An Enter Network Password window, shown in Figure 4-2a, will appear.
(Windows XP users will see a Connect to 192.168.1.1 window, shown in
Figure 4-2b.) Leave the User Name field empty, and enter admin (the
default password) in lowercase letters in the Password field. Then, click the
OK button.
Figure 4-1
Figure 4-2a
Figure 4-2b
Figure 4-3
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 13

PPPoE
If your DSL provider
says that you are connecting through PPPoE or if
you normally enter a user
name and password to
access the Internet, perform these steps (shown
in Figure 4-5):
a. Select PPPoE as the
WAN Connection
Type.
b. Enter the User Name.
c. Enter the Password.
d. Click the Apply button followed by the Continue button to save the set-
tings.
RAS (for SingTel Users)
RAS is a service used in
Singapore only. If you are
using a RAS connection
(as shown in Figure 4-6),
check with your ISP for the
necessary setup information.
19 20
5. The Router supports f ive connection types: DHCP (obtain an IP automatically), PPPoE, Static IP Address, RAS, and PPTP. These types are selected
from the drop-down menu beside WAN Connection Type. The Setup tab
and availab le features will dif fer depending on what kind of connection type
you select, the instructions for which are included here:
Obtain an IP Automatically
If your ISP says that you are connecting through a dynamic IP address (or
DHCP), perform these steps:
a. Select Obtain an IP automatically as the WAN Connection Type (as
previously shown in Figure 4-3).
b. Click the Apply button followed by the Continue button to save the set-
tings.
Static IP
If your ISP says that you are connecting through a static (or fixed) IP
address, perform these steps (as shown in Figure 4-4):
a. Select Static IP as the
WAN Connection Type.
b. In the fields beside
“Specify WAN IP
Address”, enter the IP
Address.
c. Enter the Subnet Mask.
d. Enter the Default
Gatewa y Addr ess.
e. Enter the DNS in the 1, 2,
and/or 3 fields. You must
enter at least one DNS
address.
f. Click the Apply button
followed by the Continue
button to save the settings.
Figure 4-4
Figure 4-5
Figure 4-6
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 14
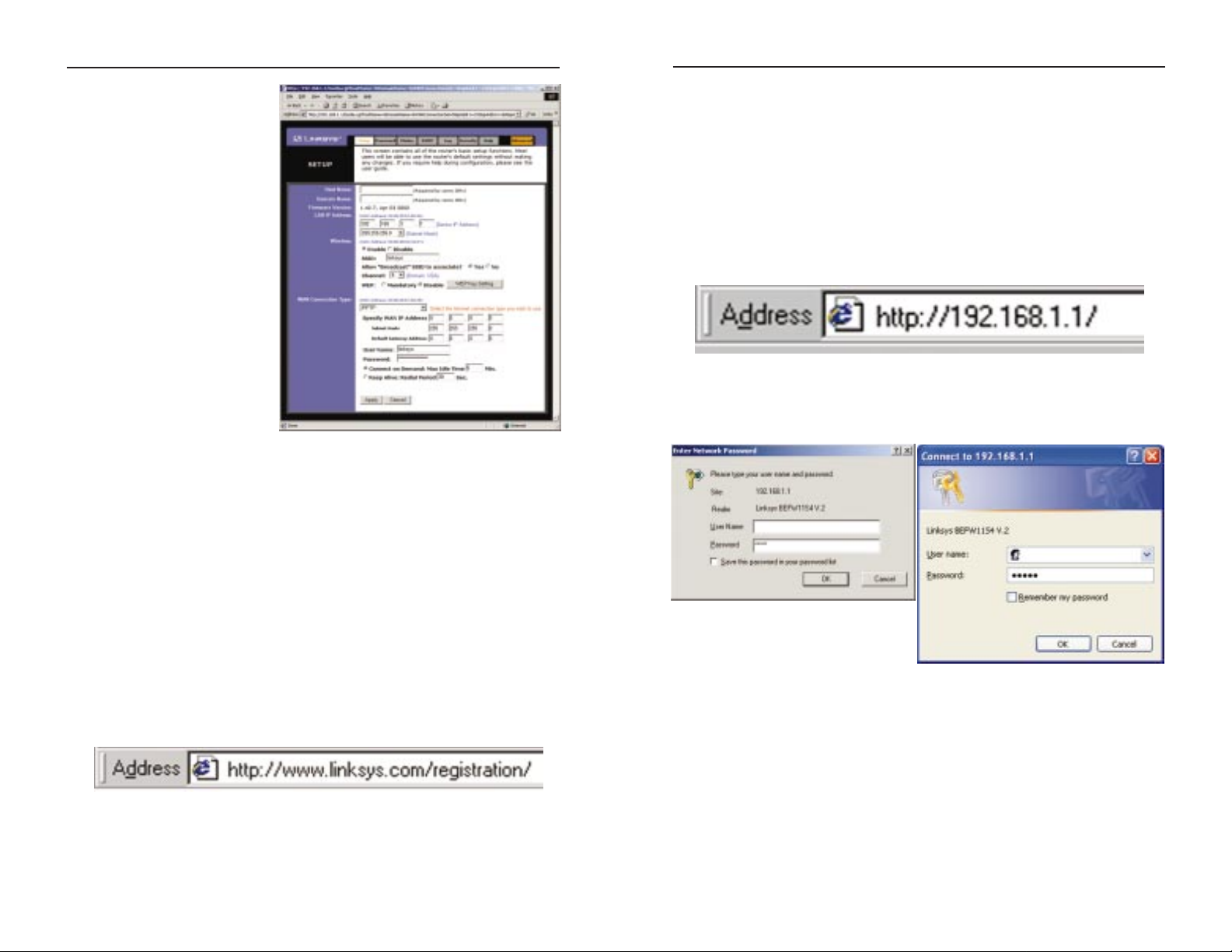
Chapter 5: Using the Router’s
Web-Based Utility
For your convenience, an administrative utility has been programmed into the
Router. This chapter will explain all of the functions in this utility. All routerbased administrative tasks are performed through this web utility. The web utility can be accessed by any PC on the network by typing “http://192.168.1.1” in
the PC’s web browser address window, as shown in Figure 5-1.
Upon entering the address into the web browser, a password request page will
pop up, as shown in Figure 5-2a. (Windows XP users will see a “Connect to
192.168.1.1” window, shown in Figure 5-2b.)
Leave the User Name field empty, and enter admin (the default password) in
lowercase letters in the Password field. Then, click the OK button.
In this chapter, you will find brief descriptions of each of the utility’s tabs and
its more important functions. More detailed explanations and instructions can
be found by clicking each page’s Help button or on Linksys’s website at
www.linksys.com. To clear any values you’ve entered on any page, click the
Cancel button. To apply any settings you’ve altered on any page, click the
Apply button. Once all settings are cor rect, click Continue.
21
PPTP
PPTP is a service used in
Europe only. If you are using
a PPTP connection (as
shown in Figure 4-7), check
with your ISP for the necessary setup information.
6. If you haven’t already done so, click the Apply button followed by the
Continue button to save the settings.
7. Reset the power on your cable or DSL modem and restart your computers.
They will now obtain the Router's new settings.
Note: You only need to configure the Router from one computer. If you
need advanced setting information, please refer to the Linksys support website at support.linksys.com or the User Guide on the Setup Wizard CDROM.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully configured the Router. You can test
the setup by opening your web browser from any computer and entering
www.linksys.com/registration (as shown in Figure 4-8).
If you are unable to reach our website, you may want to review what you
did in this section or refer to the Troubleshooting Appendix.
Figure 4-7
Figure 4-8
Figure 5-1
Figure 5-2a
Figure 5-2b
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
22
Page 15
• SSID: The SSID is a unique name for y our wireless network. It is case sen-
sitive and must not exceed 32 characters. The default SSID is "linksys " but
you should change this to a personal wireless network name. All wireless
points in your network must use the same SSID. Verify that you are using
the correct SSID and click the Apply button to set it.
• Allow “Broadcast” SSID to associate?: To increase network security, the
Router’s Utility prevents the SSID from being seen on networked PCs.
Without this enabled, someone could easily obtain this information with site
survey software of any software and gain access to your network. To enable
this function, click the Yes radio button beside this question.
• Channel Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to corre-
spond with your network settings, between 1 and 11. (Higher channels can
only be used outside of the United States and Canada.) All points in your
wireless network must use the same channel in order to function correctly.
Verify that the correct channel is selected and click the Apply button to set
it.
• WEP (Mandatory/Disable). In order to utilize WEP encryption, select
Enable. If you do not wish to utilize WEP encryption, make sure Disable
is selected.
• WEP Key Setting When WEP Encryption is Enabled, press this button to
modify the WEP Key Settings.
For further details on configuring Wireless Security, using WEP, refer to
Appendix C: Configuring Wireless Security.
• WAN Connection Type The Router supports five connection types: DHCP
(obtain an IP automatically), PPPoE, Static IP Address, RAS, and PPTP.
These types are selected from the drop-down menu beside WAN
Connection T ype. The Setup tab and available features will differ depending on what kind of connection type you select. Each option is described on
the following pages.
Obtain an IP Automatically
If your ISP says that you are connecting through a dynamic IP address (or
DHCP), select this option from the drop-down menu (as shown in Figure 5-
3). Now, the Router will accept the dynamic IP addresses assigned by your
ISP when connecting to the Internet.
23 24
The utility’s tabs: Setup, Password, Status, DHCP, Log, Security and Help are
used for Basic Setup of the Router. When the Advanced Tab is clicked, further
options will be displayed for Filters, Forwarding, Dynamic Routing, Static
Routing DMZ Host, MAC Address Cloning, and Wireless configuration.
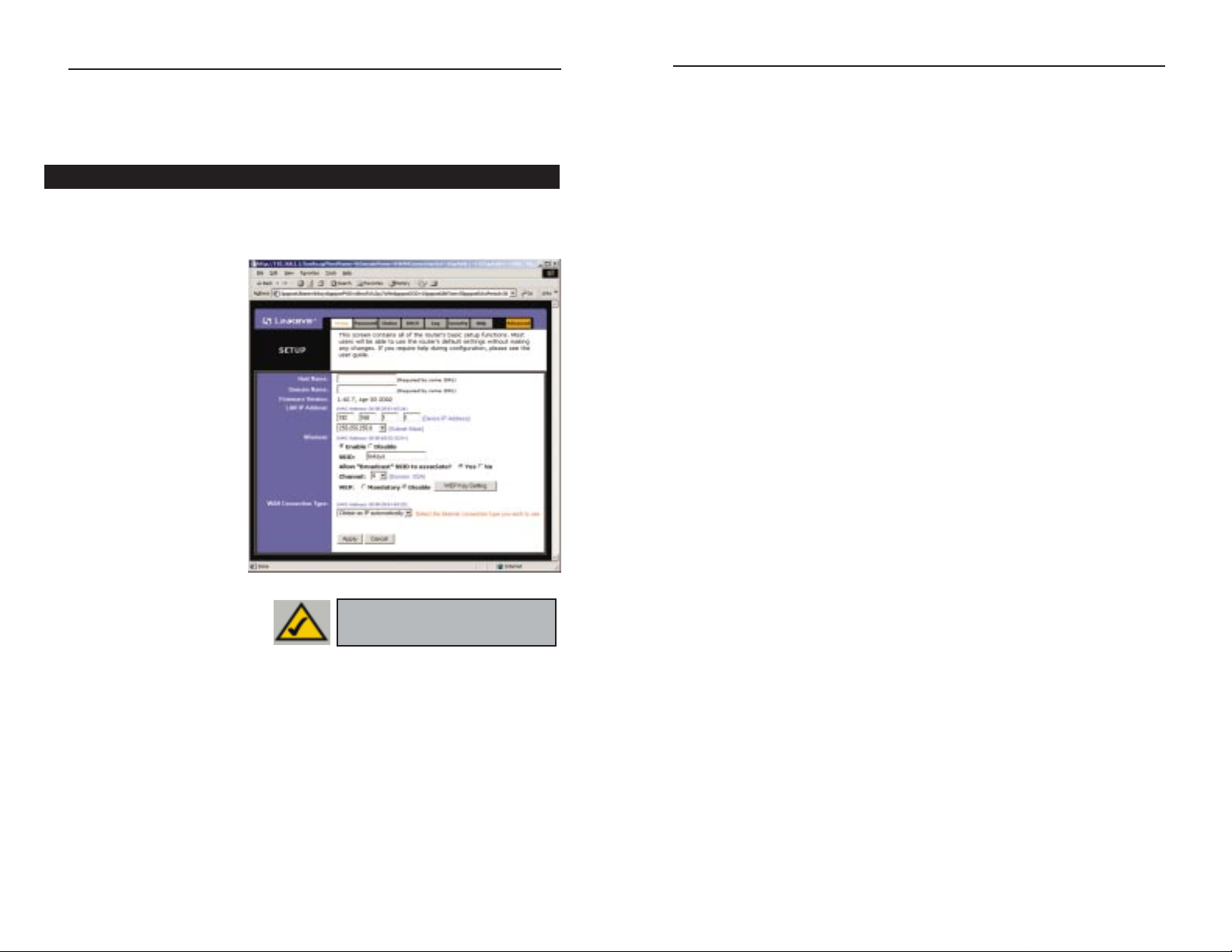
The Setup tab is the first tab you will see when you access the Utility. If you
have already installed and set up the Router, you have already seen this tab and
have already properly conf igured all of the values.
• Host Name This entry
is necessary for some
ISPs and can be provided by them.
• Domain Name This
entry is necessary for
some ISPs and can be
provided by them.
• Firmware Version
This displays the
firmware version the
Router is currently
using. As future versions of the Router’s
fir mware become available, they can be downloaded from the Linksys
website at www.linksys.com.
• LAN IP Address and Subnet Mask This is the Router’s IP Address and
Subnet Mask as seen on the internal LAN. The default value is 192.168.1.1
for IP Address and 255.255.255.0 for Subnet Mask.
• Wireless (Enable/Disable). In order to utilize the Router’s wireless func-
tions, select Enable. If you do not wish to utilize any wireless functions,
make sure Disable is selected. (Note: No other wireless functions will be
available unless you enable this setting.)
Setup
Figure 5-3
NNoottee::
Due to differences in web
browsers, some screen shots may differ.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 16

25
PPPoE
Some DSL-based
ISPs use PPPoE
(Point-to-Point
Protocol over
Ethernet) to establish communications with an enduser. If you are
using a DSL line,
check with your
ISP to see if they
use PPPoE. If they
do use PPPoE,
select this from the
drop-down menu
(as shown in Figure
5-5).
If you do enable PPPoE, remember to remove any existing PPPoE applications already on any of your PCs.
• User Name and Password Enter the User Name and Password you use
when logging onto your ISP connection.
• Connect on Demand and Max Idle Time You can conf igure the Router
to disconnect your ISP connection after a specified period of time (Max
Idle Time). If you have been disconnected due to inactivity, Connect on
Demand enables the Router to automatically re-establish y our connection as
soon as you attempt to access the Internet again. If you wish to activate
Connect on Demand, click the radio button. If you want your Internet connection to remain on at all times, enter 0 in the Max Idle Time field.
Otherwise, enter the number of minutes you want to have elapsed before
your Internet access disconnects.
• Keep Alive Option and Redial PeriodThis option keeps you connected to
your ISP indefinitely, even when your connection sits idle. To use this
option, click the radio button next to Keep Aliv e. The default Redial P eriod
is 30 seconds.
26
Static IP
If your ISP says that you are connecting through a static (or fixed) IP
address, select this option from the drop-down menu (as shown in Figure 5-
4). The Router will utilize that static IP Address when the following information is entered into the appropriate field:
• W AN IP Address and Subnet Mask This is the Router’ s IP Address and
Subnet Mask as seen by external users on the Internet (including your
ISP).
• Default Gateway AddressYour ISP will provide you with the Gateway
IP Address.
• DNS (Domain Name Server) IP Address Your ISP will provide you
with at least one DNS IP Address.
Figure 5-4
Figure 5-5
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 17
28
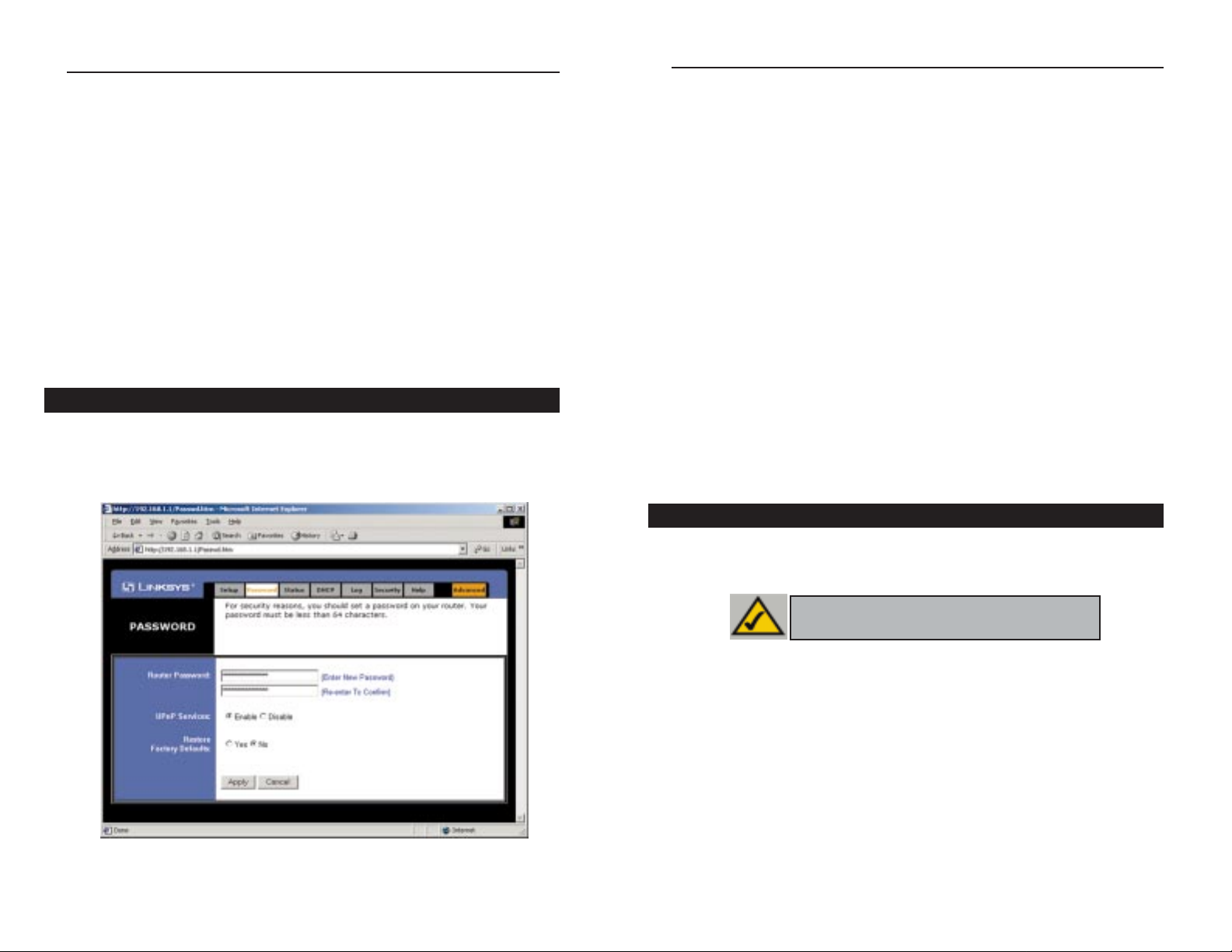
• Router Password For greater security, you should set a password for the
Router. If you don’t set the password, all users on your network will be able
to access the Router using the default password admin. We recommend that
you change your password often.
• UPnP Services Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) allows systems, such as
Windows XP PCs to automatically configure the Router for various Internet
applications, such as gaming and videoconferencing. Click the radio button
next to Enable to enable UPnP Services, or Disable to disable UPnP
Services.
• Restore Factory Defaults If you select the Restore Factory Default option
and click the Apply button, you will clear all of the Router’s settings and
restore the default settings.
Do not restore the factory defaults unless you are having difficulties with the
Router and have exhausted all other troubleshooting measures. Once the Router
is reset, you will have to re-enter all of your configuration data.
To clear any values you’ve entered on any page, click the Cancel button. To
apply any settings you’ve altered on any page, click the Apply button. Once all
settings are correct, click Continue.
The Status tab, shown in Figure 5-8, displays the Router’s current status; it
reflects the data and selections you’ve entered using the Setup tab and provides
options for DHCP users.
All of the information provided on the Status tab is read-only and can be
changed using the Setup tab.
• Host Name This f ield shows the name of the Router. This entry is necessary for some ISPs.
• Firmware Version This field shows the installed version and date of the
fir mware. Version dates are slightly more accurate than version numbers.
• Login This indicates if you are using a dial-up style connection like PPPoE,
RAS, or PPTP. For PPPoE, RAS, or PPTP only, there is a Connect button to
click if you are disconnected and want to re-establish a connection.
RAS (for SingTel Users)
RAS is a service used in Singapore only. If you are using a RAS connection
(as shown in Figure 4-6), check with y our ISP for the necessary setup information.
PPTP
PPTP is a service used in Europe only. If you are using a PPTP connection
(as shown in Figure 4-7), check with y our ISP for the necessary setup information.
You can confirm that the above settings are correct by successfully connecting
to the Internet.
To clear any values you’ve entered on any page, click the Cancel button. To
apply any settings you’ve altered on any page, click the Apply button. Once
all settings are correct, click Continue.
From the Password tab, shown in Figure 5-7, you can change the Router’s
Password, enable Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Services for systems such as
Windows XP PCs, and restore the Router’s factor y default settings.
Password
Figure 5-7
Status
Note: The information provided on the Status
tab may vary depending on the Router’s settings.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
27
Page 18
29
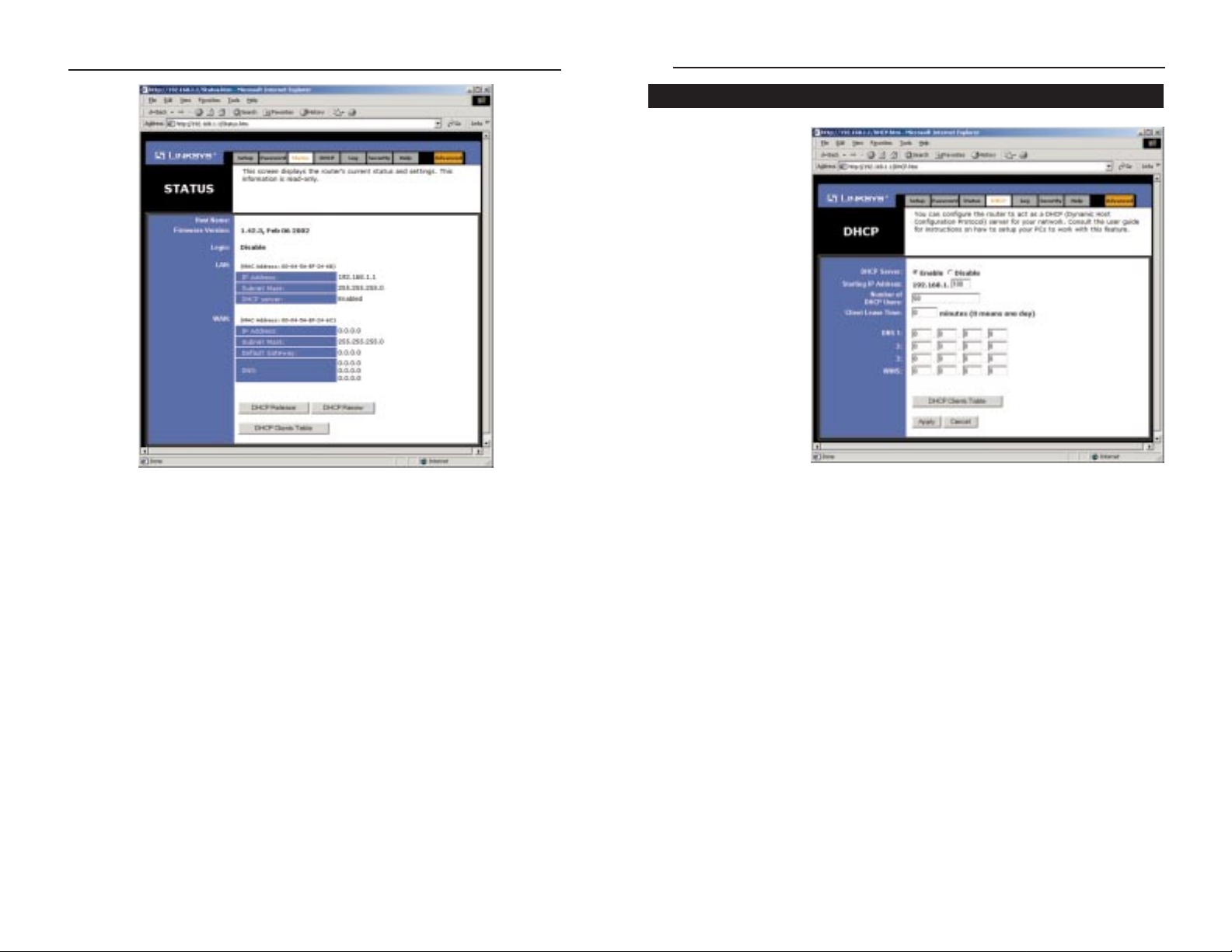
A DHCP (Dynamic
Host Configuration
Protocol) Server
automatically
assigns IP addresses
to each computer on
its network. Unless
you already have
one, you should set
the Router up as a
DHCP server. This
is done on the DHCP
tab, shown in Figure
5-9.
• DHCP Server Click the Enable option to enable the Router’s DHCP serv-
er function If you already have a DHCP server on your network, set the
Router’s DHCP option to Disable.
• Starting IP Address Enter a numerical value for the DHCP server to start
with when issuing IP addresses.
• Number of DHCP users Enter the maximum number of PCs that will
require IP addresses assigned by the Router. No more than 253 computers
can be used. In order to determine the DHCP IP Address range, add the
starting IP address (e.g., 100) to the number of DHCP users. By default, as
shown in Figure 5-9, if you add 50 users, the range or IP Addresses will be
192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.149.
• Client Lease Time The Client Lease Time is the amount of time a network
user will be allow ed connection to the Router with their current dynamic IP
address. Enter the amount of time, in minutes, that the user will be “leased”
this dynamic IP address.
DHCP
30
• LAN These f ields display the current IP Address and Subnet Mask of the
Router, as seen by users on your local area network. The DHCP Server f ield
shows the status of the Router’s DHCP server function, which is either
enabled or disabled.
•WANThese fields display the WAN IP Address, WAN Subnet Mask, and
WAN Default Gateway IP Address of the Router, as seen by external users on
the Internet. The DNS (Domain Name System) IP Address fields show the IP
address(es) of the DNS currently used by the Router. Multiple DNS IP settings are common. In most cases, the first available DNS entry is used.
• DHCP Release Click the DHCP Release button to delete the current IP
address of the device connected to the Router’s WAN port.
• DHCP Renew Click the DHCP Renew button to replace the current IP
address—of the device connected to the Router’s WAN port—with a new IP
address.
• DHCP Clients Tab le This table lists the PCs that were given IPaddresses by
the Router.
Figure 5-9
Figure 5-8
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 19

For a permanent record of these logs, Logviewer software must be used. This
software is downloadable from the Linksys website at www.linksys.com. The
Logview er sa v es all incoming and outgoing acti vity as a permanent file on your
PC’s hard drive. Next to “Send Log to”, enter the fixed IP address of the PC
running the Logviewer software. The Router will now send updated logs to that
PC.
To clear any values you’ve entered on any page, click the Cancel button. To
apply any settings you’ve altered on any page, click the Apply button. Once
all settings are correct, click Continue.
32
• DNS The Domain Name System (DNS) is how the Internet translates
domain or website names into Internet addresses or URLs. Your ISP will
provide you with at least one DNS Server IP Address. If you wish to use
another, type that IP Address in one of these f ields. You can type up to
three DNS Ser ver IP Addresses here. The Router will use these for quicker
access to functioning DNS ser vers.
• WINS The Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) manages each PC’s
interaction with the Internet. If you use a WINS server, enter that server’s
IP Address here. Otherwise, left this blank.
• DHCP Clients Table When this button is clicked, a table similar to that
shown in Figure 5-10 appears, displaying a list of PCs assigned IP addresses by the Router. Click the Refresh button to display the most current
information. If you
wish to delete a
client’s IP address,
select that client by
clicking the box to
the right and click
the Delete button.
To clear any values you’ve entered on any page, click the Cancel button. To
apply any settings you’ve altered on any page, click the Apply button. Once
all settings are correct, click Continue.
The Log tab, shown in F igure 5-11, provides you with a log of all incoming and
outgoing URLs or IP addresses for your Internet connection.
To access activity logs, select the Enable option next to “Access Log”. This
function can be disabled by clicking the Disable radio button.
With logging Enabled, you can choose to view temporary logs or have a permanent record, using the Logviewer software. Temporary logs can be accessed
from the Log tab by clicking either the Incoming Access Log or Outgoing
Access Log buttons. The Incoming Access Log gives you a log of all the
incoming Internet traffic while the Outgoing Access Log lists all the URLs and
IP addresses of Internet sites that users on your network have accessed.
Figure 5-10
Log
Figure 5-11
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
31
Page 20

The Security tab, as shown in Figure 5-12, enables configuration of the Router
to provide enhanced network security using ZoneAlarm Pro and PC-cillin
(each sold separately). While the Router provides a built-in Inter net NAT f irewall, ZoneAlarm Pro enhances the Router’s security capabilities for increased
protection against hackers and other threats from the Internet and PC-cillin protects against viruses. ZoneAlarm Pro and PC-cillin work independently of each
other. For more infor mation on ZoneAlarm Pro, PC-cillin, and DSL or cable
network security, please click the on-screen link to the Internet Security Center.
Software Download
Click this button to purchase and download ZoneAlarm Pro and/or PC-cillin at
the Internet Security Center. Print the summary page, which contains the
license key needed for installation, or write down the license key if you are
unable to print the page. You will also be e-mailed a confirmation invoice with
the key included. When adding security enhancements to your other networked
computers, you can either copy the downloaded files to the other PCs or redownload the software on each indi vidual PC without incurring any more costs.
ZoneAlarm Pro Settings
If you have downloaded ZoneAlarm Pro, complete this section.
License Key Enter the License Key for ZoneAlarm Pro. The License Key
will be e-mailed to you after you purchase ZoneAlarm Pro.
Enforce ZoneAlarm Pro Security Check this box to enable ZoneAlarm
Pro on the Router. This will require every PC to have ZoneAlarm Pro
installed before being allowed to access the Internet (except for exempt
computers).
Enforcement Level This sets how often ZoneAlarm Pro will check for
unauthorized intrusions. More Secure(default setting) enables ZoneAlarm
Pro to check frequently. Conserve Bandwidth enables ZoneAlarm Pro to
check less frequently; this uses less bandwidth. It is recommended to set
the Enforcement Level at the More Secure setting unless there is a decrease
in the Router’s performance.
PC-cillin Settings
If you have downloaded PC-cillin, complete this section.
Enforce PC-cillin Anti-Virus Check this box to enable PC-cillin AntiVirus on the Router.
Exempt Computers
If you wish to exempt any computers from enforcement of ZoneAlarm Pro
and/or PC-cillin, complete this section.
Enable/Disable To enable or disable computer exemptions, click Enable
or Disable.
From IP Address/To IP Address Enter the range of IP addresses for the
computers you want to exempt from enforcement of ZoneAlarm Pro and/or
PC-cillin.
Security
Note:Your license key will be e-mailed to you.
Figure 5-12
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
33 34
Page 21

2. Click the Browse button and find the f ir mware upgrade file that you
downloaded from the Linksys website. Double-click the upgrade file.
This will place the file into the “File Path:” f ield.
3. When the correct file is in the “File Path:” field, click the Upgrade button and follow the instructions there. This will complete your fir mware
upgrade.
Filters
35
Important: Do not interrupt the firmware upgrade process in
any way or power down the Router while the upgrade is in
progress as this could damage the Router.
The Help tab, as shown in Figure 5-13, contains links to all of the Utility’s internal support documentation, a link to Linksys’s website, and the application that
upgrades the Router’s firmware. To utility these links, you must have an active
Internet connection.
Click the Linksys Website link to connect to the Linksys homepage for
Knowledgebase help files and information about other Linksys products.
For an Online Man ual in PDFformat, click that text link. The manual will appear
in Adobe PDF format. If you do not have the Adobe PDF Reader installed on your
computer, click the Adobe Website link to download this software.
Firmware can be upgraded by clicking the Upgrade Firmw arelink. Do not upgrade
your firmware unless you are experiencing problems with the Access Point.
To upgrade the Router’s firmware:
1. Access the Help tab and click Upgrade Firmware. A new page, shown in
Figure 5-14, will appear.
36
Important: In order to upgrade the Router’s f irmware, you
must use Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher, or Netscape
Navigator 4.7 or higher. Upgrading the f irmware may cause
the Router to be reset to the factory defaults. Make a record of
all settings before attempting the upgrade.
Help
Figure 5-13
Figure 5-14
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 22

• Editing MACFilter Setting
This feature filters the Ethernet adapter’s specific MAC address from going
out to the Internet.
To check your Ethernet adapter’s MAC address, r un winipcfg or ipconf ig
in the command prompt, depending on which Windows operating system
you are using. To set the MAC f ilter, click the Edit MAC Filter Setting
button. When a second window appears, select the range in the drop-down
menu, and in a MAC number field, enter the 12-digit MAC address you
want to filter. Click the Apply button and the Continue button, before
closing the window. For information on obtaining a MAC address, go to
Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet
Adapter.
• SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection)
This feature checks the state of a packet to verify that the destination IP
address matches the source IP of the original request. To use the f irewall,
click the Enable button; otherwise select Disable to use the NAT firewall.
• Blocking WAN Requests
By enabling the Block WAN Request feature, you can prevent your network
from being “pinged,” or detected, by other Internet users. The Block WAN
Request feature also reinforces your network security by hiding your network ports. Both functions of the Block WAN Request feature make it more
difficult for outside users to work their way into your network.
Click the Apply button and then the Continue button to save your changes.
• Using Multicast Pass Through
This feature allows for multiple transmissions to specific recipients at the
same time. Select Enable to support the feature, or Disable to keep the
Router from multicasting.
37
Filters block specific
internal users from
accessing the Internet.
From the Filters tab, as
shown in Figure 5-15,
you can set up a filter
through an IP address
or a network port number.
• Setting Up Filters
To set up a filter
using IP addresses,
enter the range of
IP addresses you
wish to filter in the
IP address fields.
Users who hav e filtered IP addresses
will not be able to
access the Internet
at all. If you only
want to filter one
IP address instead
of a range of IP
addresses, enter the same value into both fields. For instance, if you wish to
filter the PC with the IP address of 192.168.1.5, enter 5 into both f ields on
one line: 192.168.1.5 ~ 192.168.1.5. Click the Apply button when you’re
done.
To f ilter users by network port number, enter a network port number or a
range of network ports. Enter the port numbers you want to filter in the port
numbers fields. Users connected to the Router will no longer be able to
access any port number listed there.
38
Advanced Tab: Filters
Important: Filtering is an Advanced Function. No changes
should be made to this tab without a thorough understanding
of networking concepts.
Figure 5-15
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 23

• Using Multicast Pass Through
This feature allows for multiple transmissions to specific recipients at the
same time. Select Enable to support the feature, or Disable to keep the
Router from multicasting.
• Using IPSec Pass Through
This feature lets you use IPSec Pass Through. To use this feature, click the
Enable button next to IPSec Pass Through, and then the Apply button.
Click the Continue button.
IPSec Pass Through is enabled by default. To disable IPSec Pass Through,
click on Disable and then the Apply button. Click the Continue button.
• Using PPTP Pass Through
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is the method used to enable VPN
sessions. To enable this feature, click the Enable button next to PPTP Pass
Through, and click the Apply button. Then click the Continue button.
PPTP Pass Through is enabled by default. To disable this feature, click on
Disable next to PPTP Pass Through, and then the Apply button. Click the
Continue button.
• Using Remote Management
This feature allows you to manage the Router from a remote location, such
as over the Internet. To enable this feature, click on Enable, and click the
Apply button. Then click the Continue button. Remote Management must
be activated before you can manage the Router from a remote location.
T o disab le Remote Management, click on Disa ble, and click the A pplybutton. Then click the Continue button. If you wish to use this feature, enter
http:\\<W AN IP Address>:8080 into your web bro wser’s address field and
press the Enter key. (Enter your specific WAN IP Address in place of
<WAN IP Address>.)
To disable this feature, click on Disable, and click the Apply button. Then
click the Continue button.
• Using Remote Upgrade
This feature allows you to upgrade the Router’s f irmware from a remote
location. To enable Remote Upgrade, click on Enable, and then click the
Apply button. Then click the Continue button. Remote Management must
be activated before you can manage the Router from a remote location.
• Using MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit)
This feature specifies the largest packet size permitted for network transmission. Select Enable and enter the value desired. It is recommended that
you leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. For most DSL users, it is
recommended to use the value 1492. By default, MTU is set at 1500 when
disabled.
IImmppoorrttaanntt::
Upgrading may cause the
Router to be reset to the factory
defaults. Make a record of all settings before attempting the upgrade.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
39 40
Page 24

2. Next to the name of the application, enter the number or range of the
external port(s) used by the server or Internet application in the Ext. Port
column. Check with the Internet application software documentation for
more information.
3. On the same line, select the protocol TCP or UDP, or select both protocols.
4. Enter the IP address of the ser ver that you want the Internet users to be
able to access. To find the IP address, go to Appendix D: Finding the MAC
Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter.
5. Check the Enable box to enable the services you have defined. Port Range
Forw arding will not function if the Ena ble button is left unchecked. This is
disabled (unchecked) by default.
6. Configure as many entries as needed—the Router supports up to 10 ranges
of ports. Click the Apply button and Continue button when you are done.
UPnP Forwarding
Clicking the UPnP
Forwarding button on
the Port Range
Forwarding tab will
display the UPnP
Forwarding tab. The
UPnP Forwarding tab,
shown in Figure 5-17,
displays preset application settings as well
as options for customization of port
services for other
applications.
This table is similar to
the Port Forwarding
table, but the items on
this table will automatically synchronize with
other UPnP devices
and operating systems,
such as Windows XP.
Figure 5-17
Port Range F orw arding
from this tab, as shown
in Figure 5-16, sets up
public services on your
network, such as web
servers, ftp servers, email servers, or other
specialized Internet
applications.
(Specialized Internet
applications are any
applications that use
Internet access to perform functions such as
videoconferencing or
online gaming. Some
Internet applications
may not require any
forwarding.) When
users send this type of request to your network via the Internet, the Router will
forward those requests to the appropriate PC. Before using Forwarding, the
DHCP function on the PC whose port is being forwarded must be disabled and
have a new static IP address assigned because its IP address may change when
using the DHCP function.
If you need to forward all ports to one PC, see the “DMZ” section.
To add a server using Port Range Forwarding:
1. Enter the name of the application in the appropriate Customized
Applications field.
42
Advanced Tab: Port Range Forwarding
Important: Port Range Forwarding is an Advanced
Function. No changes should be made to this tab without a
thorough understanding of networking concepts.
Figure 5-16
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
41
Page 25

• POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) A standard mail server commonly used on
the Internet. It provides a message store that holds incoming e-mail until
users log on and download it. POP3 is a simple system with little selectivity.
All pending messages and attachments are downloaded at the same time.
POP3 uses the SMTP messaging protocol.
• NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) The protocol used to connect to
Usenet groups on the Internet. Usenet newsreaders support the NNTP protocol.
• SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) A widely used network
monitoring and control protocol. Data is passed from SNMP agents, which
are hardware and/or software processes reporting activity in each network
device (hub, router, etc.) to the workstation console used to oversee the network. The agents return information contained in a MIB (Management
Information Base), which is a data structure that def ines what is obtainable
from the device and what can be controlled (turned off, on, etc.).
You must check the Enable box to enable the applications you have defined.
To add a server using UPnP Forwarding:
1. Enter the name of the application in the appropriate Application Name
field.
2. Next to the name of the application, enter the number of the external port
used by the server in the Ext. Port column. Check with the Internet application software documentation for more information.
3. On the same line, select the protocol UDP or TCP.
4. Enter the numberof the internal port used by the server in the Int. Port column. Check with the Internet application software documentation for more
information.
5. Enter the IP address of the server that you want the Internet users to be able
to access. To find the IP address, go to Appendix D: Finding the MAC
Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter.
6. Check the Enable box to enable the services you have defined. UPnP
Forw arding will not function if the Ena ble button is left unchecked. This is
disabled (unchecked) by default.
The Preset Applications are among the most widely used Internet applications
that may require forwarding. They include the following:
• FTP (File Transfer Protocol) A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP
network (Internet, UNIX, etc.). For example, after developing the HTML
pages for a website on a local machine, they are typically uploaded to the
web server using FTP. FTP includes functions to log onto the network, list
directories, and copy files. It can also convert between the ASCII and
EBCDIC character codes. FTP operations can be performed by typing commands at a command prompt or via an FTP utility running under a graphical
interface such as Windows. FTP transfers can also be initiated from within a
web browser by entering the URL preceded by ftp://.
• Telnet A terminal emulation protocol commonly used on Internet and
TCP/IP-based networks. It allo ws a user at a terminal or computer to log onto
a remote device and run a program.
• SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) The standard e-mail protocol on the
Internet. It is a TCP/IP protocol that defines the message format and the
message transfer agent (MTA), which stores and forwards the mail.
• DNS (Domain Name System) The way that Internet domain names are
located and translated into IP addresses. A domain name is a meaningful and
easy-to-remember “handle” for an Internet address.
• TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) A version of the TCP/IP FTP proto-
col that has no directory or password capability.
• Finger A UNIX command widely used on the Internet to f ind out infor ma-
tion about a particular user, such as a telephone number, whether the user is
currently logged on, and the last time the user was logged on. The person
being “fingered” must have placed his or her prof ile on the system in order
for the information to be available. Fingering requires entering the full
user@domain address.
• HTTP (HyperText Transpor t Protocol) The communications protocol used
to connect to servers on the World Wide Web. Its primary function is to
establish a connection with a web server and transmit HTML pages to the
client web browser.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
43 44
Page 26

From the Dynamic
Routing tab, shown
in Figure 5-19, you
can automatically
adjust to physical
changes in the network’s layout. The
Router, using the
RIP protocol,
determines the network packets’
route based on the
fewest number of
hops between the
source and the destination. The RIP
protocol regularly
broadcasts routing information to other routers on the network. To set up
Dynamic Routing:
1. Choose the cor rect Working Mode. Gateway Mode should be used if the
Router is hosting your network’s connection to the Internet. Router Mode
should be selected if the Router exists on a network with other routers.
2. In the TX field, choose the protocol by which you transmit data on the net-
work.
3. In the RX f ield, choose the protocol by which the Router receives network
data.
4. Click the Apply button to save your changes.
To view the Routing Table, which shows the network layout, click the Show
Routing T a ble button.
To clear any values you’ve entered on any page, click the Cancel button. To
apply any settings you’ve altered on any page, click the Apply button. Once
all settings are correct, click Continue.
45
Advanced Tab: Dynamic Routing
Important: Dynamic Routing is an Advanced Function. No
changes should be made to this tab without a thorough understanding of networking concepts.
Figure 5-19
Port Triggering
From the Port Range
Forw arding tab, shown
in Figure 5-18, click
the Port Triggering
button to allow the
Router to watch outgoing data for specific
port numbers. The IP
address of the computer that sends the
matching data is
remembered by the
Router, so that when
the requested data
returns through the Router, the data is pulled back to the proper computer by
way of IP address and port mapping rules.
1. Enter the Application Name of the trigger.
2. Enter the Trigger Port Range used by the application. Check with the
Internet application for the port number needed.
3. Enter the Incoming Por t Range used by the application. Check with the
Internet application for the port number needed.
4. Click the Apply button and then click the Continue button.
Figure 5-18
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
46
Page 27

2. Enter the following data to create a new static route:
Destination LAN IP. The Destination LAN IP is the address of the remote
network or host to which you want to assign a static route. Enter the IP
address of the host for which you wish to create a static route here. If you
are building a route to an entire network, be sure that the host portion of the
IP address is set to zero. For example, the Router’s standard IP address is
192.168.1.1. Based on this address, the address of the network to which the
Router is connected is 192.168.1. You would enter the IP address
192.168.1.0 if you wanted to route to the entire network, rather than just to
the Router.
Subnet Mask. The Subnet Mask indicates which portion of an IP address
is the network portion and which portion is the host portion. If, for instance,
you use a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0 with the example sho wn abo v e for
Destination LAN IP, then this would indicate that the first three numbers of
an network IP address identifies this particular network, while the last
number in the network address (from 1 to 254) would identify the specif ic
host.
Gateway IP. This IP address should be the IP address of the gateway
device that allows for contact between the Router and the remote network
or host.
Hop Count. This value gives the number of nodes that a data packet passes through before reaching its destination. A node is any device
on the network, such as switches, PCs, etc.
Interface. This interf ace tells you whether your network is on the internal
LAN or the WAN, or the external Internet. If you’re connecting to a subnetwork, select LAN. If you’re connecting to another network through the
Internet, select WAN.
T o delete a Static Routing entry, select an entry, and click the Delete this entry
button.
To clear any values you’ve entered on any page, click the Cancel button. To
apply any settings you’ve altered on any page, click the Apply button. Once
all settings are correct, click Continue.
If the Router is connected to more than one network, it may be necessary to set
up a static route between them. This is set on the Static Routing tab, as shown
in Figure 5-20. A static route is a pre-determined pathway that network information must travel to reach a specific host or network. Click the Show
Routing T a ble button to view the current static routing configuration.
To create a static route entry:
1. Select Static Route Entry from the drop-down list. The Router supports
up to 20 static route entries.
48
Advanced Tab: Static Routing
Important: Static Routing is an Advanced Function. No
changes should be made to this tab without a thorough understanding of networking concepts.
Figure 5-20
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
47
Page 28

From the MAC
Address Cloning tab,
shown in Figure 5-22,
you can assign the
Router a MAC
address, which is a 12digit code assigned to
a unique piece of
hardware for identification, like a social
security number.
Some ISPs require
that you register the
MAC address of your
network card/adapter, which was connected to your cable or DSL modem during
installation. Therefore, in order to connect the Router to your cable or DSL
modem in place of the PC (network card or adapter), you must change the Router
MAC to duplicate (or clone) your network card/adapter MAC. You can find your
adapter's MAC address by doing the following:
• If you are running Windows 95, 98 or Millennium:
Go to Start, Run, type in command, and press Enter. At the DOS prompt,
type winipcfg.
• If you are running Windows NT 4.0 or 2000:
Go to Start, Run, type in command, and press Enter. At the DOS prompt,
type ipconfig /all.
The Physical Address with 12 digits is your adapter’s MAC address. Enter
those 12 digits into the MAC Address f ields, and click Apply. This “clones”
your network adapter’s MAC address onto the Router, and prevents you from
having to call your ISP to change the registered MAC address to the adapter’s
MAC address.
Advanced Tab: MAC Address Cloning
50
Important: MAC Address Cloning is an Advanced
Function. No changes should be made to this tab without a
thorough understanding of networking concepts.
Figure 5-22
The DMZ Hosting feature, accessed from the DMZ Host tab as shown in
Figure 5-21, allows one local user to be e xposed to the Internet for use of a special-purpose service such as Inter net gaming and videoconferencing.
Whereas Port Range Forwarding can only forward a maximum of ten port
ranges, DMZ hosting forwards all the ports at the same time to one PC.
Before using this feature, the DHCP function on the PC whose port is being
exposed must be disabled and ha v e a new static IP address assigned because its
IP address may change when using the DMZ function.
To expose one PC, enter the computer’s IP address. To get the IP address of a
computer, refer to Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for
Your Ethernet Adapter.
Deactivate DMZ by entering a zero in the f ield.
When finished, click the Apply button and click the Continue button to save
the settings. Otherwise, click the Cancel button to undo changes made on this
screen.
Advanced Tab: DMZ Host
49
Important: DMZ Hosting is an Advanced Function. No
changes should be made to this tab without a thorough understanding of networking concepts.
Figure 5-21
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 29

• Fragmentation Thr eshold. This value indicates how much of the Router’s
resources are devoted to recovering packet errors. The value should remain
at its default setting of 2,346. If you have decreased this value and experience high packet error rates, you can increase it again, but it will likely
decrease overall network perfor mance. Only minor modif ications of this
value are recommended.
• DTIM Interval. This value indicates the interval of the Delivery Traffic
Indication Message (DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing
clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the Router has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for
associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value.
Clients for the Router hear the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast
and multicast messages.
• Basic Rates. The basic transfer rates should be set depending on the speed
of your wireless network. You must select 1-2 (Mbps) if you have older
802.11 compliant equipment on your network, such as wireless adapters
that support only 1 or 2 Mbps. Selecting 1-2 (Mbps), however, does not
limit the basic transfer rates of faster adapters.
• TX Rates. Select all the supported rates at which an access point will com-
municate with a client.
• Preamble Type. The preamble def ines the length of the CRC block for
communication between the Router and the roaming Network Card. (High
network traffic areas should use the shorter preamble type.) Select the
appropriate preamble type and click the Apply button to set it.
• Authentication Type. You may choose between Open System, Shared
Key, and Both. The Authentication Type default is set to Open System, in
which the sender and the recipient do NOT share a secret key. Each party
generates its own key-pair and asks the receiver to accept the randomlygenerated key. Once accepted, this key is used for a short time only. Then
a new key is generated and agreed upon. Shared Key is when both the
sender and the recipient share a secret key.
• Antenna Selection. This selection is for choosing which antenna transmits
data. By default, the Diversity Antenna selection, used to increase reception, is chosen.
52
Before making any
changes to the
Wireless tab, shown
in Figure 5-23,
please check the
wireless settings for
all your wireless
PCs, as these
changes will alter the
Router’s effectiveness. In most cases,
these settings do not
need to be changed.
• Firmware Version. This indicates the Router’s firmware version.
• Beacon Interval. This value indicates the frequency interval of the beacon.
A beacon is a packet broadcast by the Router to keep the network synchronized. A beacon includes the wireless LAN service area, the IP address, the
Broadcast destination addresses, a time stamp, Delivery Traffic Indicator
Maps, and the Traffic Indicator Message (TIM).
• RTS Threshold. This value should remain at its default setting of 2,346.
Should you encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor modifications are
recommended.
Advanced Tab: Wireless
51
Important: Wireless is an Advanced Function. No changes
should be made to this tab without a thorough understanding
of networking concepts.
Figure 5-23
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 30

Appendix A:Troubleshooting
This appendix consists of two parts: “Common Problems and Solutions” and
“Frequently Asked Questions.” Provided are possible solutions to problems
regarding the installation and operation of the Router . If your situation is described
here, the problem should be solved by appl ying the corresponding solution. If you
can’t find an answer here, check the Linksys website at www.linksys.com.
1. I need to set a static IP address on a PC.
The Router, by default, assigns an IP address range of 192.168.1.100 to
192.168.1.150 using the DHCP server on the Router. To set a static IP address, you
can only use the ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.151 to
192.168.1.254. Each PC or network device that uses TCP/IP must have a unique
address to identify itself in a network. If the IP address is not unique to a netw ork,
Windows will generate an IP conflict error message. You can assign a static IP
address to a PC by performing the following steps:
For Windows 95, 98, and Me:
A. Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click Network.
B. In The following network components are installed box, select the TCP/IP->
associated with your Ethernet adapter. If you only have one Ethernet adapter
installed, you will only see one TCP/IP line with no association to an Ethernet
adapter. Highlight it and click the Properties button.
C. In the TCP/IP properties window, select the IP address tab, and select Specify
an IP address. Enter a unique IP address that is not used by any other computer on the network connected to the Router. You can only use an IP address
in the ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.151 to
192.168.1.254. Make sure that each IP address is unique for each PC or network device.
D. Click the Gateway tab, and in the New Gateway prompt, enter 192.168.1.1,
which is the default IP address of the Router. Click the Add button to accept
the entry.
E. Click the DNS tab, and make sure the DNS Enabled option is selected. Enter
the Host and Domain names (e.g., John for Host and home for Domain).
Enter the DNS entry provided by your ISP. If your ISP has not provided the
DNS IP address, contact your ISP to get that information or go to its website
for the information.
F. Click the OKbutton in the TCP/IP properties window, and click Close or the
OK button for the Network window.
G. Restar t the computer when asked.
53
Common Problems and Solutions
• Station MACFilter. This option will allow you to prevent wireless users
on your network from accessing the Router’s functions.
Clicking the Active MAC Table button will display all MAC Addresses
filtered on your network.
To filter users, click the Edit MAC Filter Setting button. The window
shown in Figure 5-24 will appear.
Click the Wireless MAC Entry drop-down menu to select a range of users
on your network. From within this range, select the user you wish to filter.
Verify that the appropriate MA C Address is entered into the MAC Address
field. Click the Filter field beside that MAC Address. Now, this user will
be prevented from accessing the Router.
Click the Apply button to set these changes or Undo if you do not wish
these changes to go into effect.
When finished with the Wireless Tab, click the Apply button and click the
Continue button to save the settings. Otherwise, click the Cancel button to
undo changes made on this screen.
Figure 5-23
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
54
Page 31

For W indows XP:
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the default
interface. If you are using the Classic interface (where the icons and menus look
like previous Windows versions), please follow the instructions for W indows 2000.
A. Click Start and Control Panel.
B. Click the Network and Internet Connections icon and then the Network
Connections icon.
C. Right-click the Local Area Connection that is associated with the Ether net
adapter you are using, and select the Properties option.
D. In the This connection uses the following items box, highlight Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP). Click the Properties button.
E. Enter a unique IP address that is not used by any other computer on the net-
work connected to the Router. You can only use an IP address in the ranges
192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.151 to 192.168.1.254.
F. Enter the Subnet Mask, 255.255.255.0.
G. Enter the Default Gateway, 192.168.1.1 (Router’s default IP address).
H. Toward the bottom of the window, select Use the following DNS server
addresses, and enter the Preferred DNS server and Alternative DNS server
(provided b y y our ISP). Contact your ISP or go on its website to find the information.
I. Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
Click the OK button in the Local Area Connection Properties window.
2. I want to test my Internet connection.
A. Check your TCP/IP settings.
For Windows 95, 98, and Me:
Refer to your Ethernet adapter’s documentation for details. Make sure Obtain
IP address automatically is selected in the settings.
For W indows 2000:
• Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Doub le-click Network and DialUp Connections.
• Right-click the Local Area Connection that is associated with the Ethernet
adapter you are using, and select the Properties option.
• In the Components checked are used by this connection box, highlight
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties button. Make sure
that Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server addr ess
automatically are selected.
55
For W indo ws 2000:
A. Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click Network and
Dial-Up Connections.
B. Right-click the Local Area Connection that is associated with the Ethernet
adapter you are using, and select the Properties option.
C. In the Components checked are used by this connection box, highlight
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties button. Select Use
the following IP address option.
D. Enter a unique IP address that is not used by any other computer on the
network connected to the Router. You can only use an IP address in the
ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.151 to 192.168.1.254.
E. Enter the Subnet Mask, 255.255.255.0.
F. Enter the Default Gateway, 192.168.1.1 (Router’s default IP address).
G. Toward the bottom of the window, select Use the following DNS server
addresses, and enter the Preferred DNS server and Alternative DNS
server (provided b y y our ISP). Contact y our ISP or go on its w ebsite to find
the information.
H. Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window,
and click the OK button in the Local Area Connection Properties window.
I. Restar t the computer if asked.
For Windows NT 4.0:
A. Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click the Network icon.
B. Click the Protocol tab, and double-click TCP/IP Protocol.
C. When the window appears, make sure you have selected the correct
Adapter for your Ethernet adapter.
D. Select Specify an IP address, and enter a unique IP address that is not
used by any other computer on the network connected to the Router. You
can only use an IP address in the ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and
192.168.1.151 to 192.168.1.254.
E. Enter the Subnet Mask, 255.255.255.0.
F. Enter the Default Gateway, 192.168.1.1 (Router’s default IP address).
G. Click the DNS tab, and enter the Host and Domain names (e.g., John for
Host and home for Domain). Under DNS Service Search Order, click the
Add button. Enter the DNS IP address in the DNS Server field, and click
the Add button. Repeat this action for all DNS IP addresses given by your
ISP.
H. Click the OK button in the TCP/IP Protocol Properties window, and click
the Close button in the Network window.
I. Restar t the computer if asked.
56
Instant WirelessTMSeries Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 32

C. In the command prompt, type ping 192.168.1.1 and press the Enter key.
• If you get a reply, the computer is communicating with the Router.
• If you do NOT get a reply , please check the cable, and make sure Obtain
an IP address automatically is selected in the TCP/IP settings for your
Ethernet adapter.
D. In the command prompt, type ping followed by your WAN IP address and
press the Enter key. The WAN IP Address can be found in the web interface of the Router. For example, if your WAN IP address is 1.2.3.4, you
would enter ping 1.2.3.4 and press the Enter key.
• If you get a reply, the computer is connected to the Router.
• If you do NOT get a reply, try the ping command from a different computer to verify that your original computer is not the cause of the problem.
E. In the command prompt, type ping www.yahoo.com and press the Enter
key.
• If you get a reply, the computer is connected to the Internet. If you cannot open a webpage, try the ping command from a different computer to
verify that your original computer is not the cause of the problem.
• If you do NOT get a reply, there may be a problem with the connection.
Try the ping command from a different computer to verify that y our original computer is not the cause of the problem.
3. I am not getting an IP address on the WAN with my Internet connection.
A. Refer to “Problem #2, I want to test my Internet connection” to verify that
you have connectivity.
B. If you need to register the MA C address of your Ethernet adapter with your
ISP, please see “Appendix F: Finding the MAC address and IP Address for
Your Ethernet Adapter.” If you need to clone the MAC address of your
Ethernet adapter onto the Router, see the MAC Address Clone section of
“Chapter 5: Using the Router’s Web-based Utility” for details.
C. Make sure you are using the right WAN settings. Contact your ISP to see if
your WAN connection type is DHCP, Static IP Address, or PPPoE (commonly used by DSL consumers). Please refer to the Setup section of
“Chapter 5: Using the Router’s Web-based Utility” for details on WAN settings.
D. Make sure you have the right cable. Check to see if the WAN column has a
solidly lit Link LED.
E. Make sure the cable connecting from your cable or DSL modem is con-
nected to the Router’s WAN port. Verify that the Status page of the Router’s
web interface shows a valid IP address from your ISP.
57
• Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties win-
dow, and click the OK button in the Local Area Connection Properties
window.
• Restart the computer if asked.
For Windows XP:
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the
default interface. If you are using the Classic interface (where the icons and
menus look like previous Windows versions), please follow the instructions
for Windows 2000.
• Click Start and Control Panel.
• Click the Network and Internet Connections icon and then the
Network Connections icon.• Right-click the Local Area Connection
that is associated with the Ethernet adapter you are using, and select the
Properties option.
• In the This connection uses the following items box, highlight Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties button. Make sure that
Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address
automatically are selected.
• Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties win-
dow, and click the OK button in the Local Area Connection Properties
window.
• Restart the computer if asked.
For Windows NT 4.0:
• Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click the Network
icon.
• Click the Protocol tab, and double-click on TCP/IP Protocol.
• When the window appears, make sure you have selected the correct
Adapter for your Ethernet adapter and set it for Obtain an IP address
from a DHCP server.
• Click the OK button in the TCP/IP Protocol Properties window, and
click the Close button in the Network window.
• Restart the computer if asked.
B. Open a command prompt.
• For Windows 95, 98, and Me, please click Start and Run. In the Open
field, type in command. Press the Enter key or click the OK button.
• For Windows NT, 2000, and XP, please click Start and Run. In the
Open field, type cmd. Press the Enter key or click the OK button.
58
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 33

F. Turn off the computer, Router, and cable/DSL modem. Wait 30 seconds,
and then turn on the Router, cable/DSL modem, and computer. Check the
Status tab of the Router’s web-based utility to see if you get an IP address.
4. I am not able to access the Router’s web interface Setup page.
A. Refer to “Problem #2, I want to test my Internet connection” to verify that
your computer is properly connected to the Router.
B. Refer to “Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and IP address for Your
Ethernet Adapter” to verify that your computer has an IP Address, Subnet
Mask, Gateway, and DNS.
C. Set a static IP address on your system; refer to “Problem #1: I need to set a
static IP address.”
D. Refer to “Problem #10: I need to remove the proxy settings or the dial-up
pop-up window (for PPPoE users).”
5. I can’t get my Virtual Private Network (VPN) working through the Router.
Access the Router’s web interface by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP
address of the Router, and go to the Advanced => Filter tab. Make sure you
have IPsec pass-through and/or PPTP pass-through enabled.
VPNs that use IPSec with the ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload known as
protocol 50) authentication will work fine. At least one IPSec session will w ork
through the Router; however, simultaneous IPSec sessions may be possible,
depending on the specifics of your VPNs.
VPNs that use IPSec and AH (Authentication Header known as protocol 51)
are incompatible with the Router . AH has limitations due to occasional incompatibility with the NAT standard.
Change the IP address for the Router to another subnet to avoid a conflict
between the VPN IP address and your local IP address. For example, if your
VPN server assigns an IP address 192.168.1.X (X is a number from 1 to 254)
and your local LAN IP address is 192.168.1.X (X is the same number used in
the VPN IP address), the Router will have difficulties routing information to
the right location. If you change the Router’s IP address to 192.168.2.1, that
should solve the problem. Change the Router’s IP address through the Setup tab
of the web interface. If you assigned a static IP address to an y computer or network device on the network, you need to change its IP address accordingly to
192.168.2.Y (Y being any number from 1 to 254). Note that each IP address
must be unique within the network.
60
Your VPN ma y require port 500/UDP packets to be passed to the computer that
is connecting to the IPSec server. Refer to “Problem #7, I need to set up online
game hosting or use other Internet applications” for details.
Check the Linksys website for more information at www.linksys.com.
6. I need to set up a server behind my Router.
To use a server like a web, ftp, or mail server, you need to know the respective
port numbers they are using. For example, port 80 (HTTP) is used for web;
port 21 (FTP) is used for FTP, and port 25 (SMTP outgoing) and port 110
(POP3 incoming) are used for the mail server. You can get more information
by viewing the documentation provided with the server you installed. Follow
these steps to set up port forwarding through the Router’s web-based utility. We
will be setting up web, ftp, and mail servers.
A. Access the Router’s web-based utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the
IP address of the Router. Go to the Advanced => Forwarding tab.
B. Enter any name you want to use for the Customized Application.
C. Enter the Ext. Port range of the service you are using. For example, if you
have a web server, you would enter the range 80 to 80.
D. Check the protocol you will be using, TCP and/or UDP.
E. Enter the IP address of the PC or network device that you want the port
server to go to. For example, if the web server’s Ethernet adapter IP address
is 192.168.1.100, you would enter 100 in the field provided. Check
“Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet
Adapter” for details on getting an IP address.
F. Check the Enable option for the port services you want to use. Consider the
example below:
Customized Ext. Port TCP UDP IP Address Enable
Application
Web server 80 to 80 X X 192.168.1.100 X
FTP server 21 to 21 X 192.168.1.101 X
SMTP (outgoing) 25 to 25 X X 192.168.1.102 X
POP3 (incoming) 110 to 110 X X 192.168.1.102 X
When you have completed the conf iguration, click the Apply button and then
the Continue button.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
59
Page 34

7. I need to set up online game hosting or use other Internet applications.
If you want to play online games or use Internet applications, most will work
without doing any port forwarding or DMZ hosting. There may be cases when
you want to host an online game or Internet application. This would require
you to set up the Router to deliver incoming packets or data to a specific computer. This also applies to the Internet applications you are using. The best way
to get the information on what port services to use is to go to the website of the
online game or application you want to use. Follow these steps to set up online
game hosting or use a certain Internet application:
A. Access the Router’s web interface by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP
address of the Router. Go to the Advanced => Forwarding tab.
B. Enter any name you want to use for the Customized Application.
C. Enter the Ext. Port range of the service you are using. For example, if you
want to host Unreal Tournament (UT), you would enter the range 7777 to
27900.
D. Check the protocol you will be using, TCP and/or UDP.
E. Enter the IP address of the PC or network device that you want the port
server to go to. For example, if the web server’s Ethernet adapter IP address
is 192.168.1.100, you would enter 100 in the field provided. Check
“Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet
Adapter” for details on getting an IP address.
F. Check the Enable option for the port services you want to use. Consider the
example below:
Customized Ext. Port TCP UDP IP Address Enable
Application
UT 7777 to 27900 X X 192.168.1.100 X
Halflife 27015 to 27015 X X 192.168.1.105 X
PC Anywhere 5631 to 5631 X 192.168.1.102 X
VPN IPSEC 500 to 500 X 192.168.1.100 X
When you have completed the conf iguration, click the Apply button and then
the Continue button.
8. I can’t get the Internet game,server,or application to work.
If you are having diff iculties getting any Internet game, server, or application
to function properly, consider exposing one PC to the Internet using
DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) hosting. This option is available when an application requires too many ports or when you are not sure which port services to
use. Make sure you disable all the forwarding entries if you want to successfully use DMZ hosting, since forwarding has priority over DMZ hosting. (In
other words, data that enters the Router will be checked first by the forwarding
settings. If the port number that the data enters from does not have port forwarding, then the Router will send the data to whichever PC or network device
you set for DMZ hosting.) Follow these steps to set DMZ hosting:
A. Access the Router’s web-based utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the
IP address of the Router. Go to the Advanced => Forwarding tab.
B. Disable or remove the entries you have entered for forwarding. Keep this
information in case you want to use it at a later time.
C. Click the DMZ Host tab.
D. Enter the Ethernet adapter’s IP address of the computer you want exposed
to the Internet. This will bypass the NAT firewall for that computer. Please
refer to “Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your
Ethernet Adapter” for details on getting an IP address.
Once completed with the configuration, click the Apply button and then the
Continue button.
9. I forgot my password,or the password prompt always appears when saving settings to the Router.
Reset the Router to factory default by pressing the Reset button for 30 seconds
and then releasing it. If you are still getting prompted for a password when saving settings, then perform the following steps:
A. Access the Router’s web interface by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP
address of the Router. Enter the default password admin, and click the
Password tab.
B. Enter a different password in the Router Password field, and enter the
same password in the second field to confir m the password.
C. Click the Apply and Continue buttons.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
61 62
Page 35

13. The firmware upgrade failed,and/or the Diag LED is flashing.
The upgrade could have failed for a number of reasons. Follow these steps to
upgrade the f ir mware and/or make the Diag LED stop flashing:
A. If the f ir mware upgrade f ailed, use the TFTP program (it was downloaded
along with the firmware). Open the pdf that w as do wnloaded along with the
fir mware and TFTP program, and follow the pdf’s instr uctions.
B. Set a static IP address on the PC; refer to “Problem #1, I need to set a stat-
ic IP address.” Use the following IP address settings for the computer you
are using:
IP Address: 192.168.1.50
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.1
C. Perform the upgrade using the TFTP program or the Router’s web-based
utility through its Help tab.
14. My DSL service’s PPPoE is always disconnecting.
PPPoE is not actually a dedicated or always-on connection. The DSL ISP can
disconnect the service after a period of inactivity, just like a normal phone dialup connection to the Internet. There is a setup option to “keep alive” the connection. This may not always work, so you may need to re-establish connection periodically.
A. To connect to the Router, go to the web browser, and enter
http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router.
B. Enter the password, if asked. (The default password is admin.)
C. In the Setup tab, select the option Keep Alive, and set the Redial Period
option at 20 (seconds).
D. Click the Apply and Continue buttons.
E. Click the Status tab, and click the Connect button.
F. You may see the login status display as Connecting. Press the F5 key to
refresh the screen, until you see the login status display as Connected.
G. Click the Apply and Continue buttons to continue.
If the connection is lost again, follow steps E to G to re-establish connection.
10. I am a PPPoE user, and I need to remove the proxy settings or the dial-up popup window.
If you have proxy settings, you need to disable these on your computer.
Because the Router is the gateway for the Internet connection, the computer
does not need any proxy settings to gain access. Please follow these directions
to verify that you do not have any proxy settings and that the browser you use
is set to connect directly to the LAN.
For Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher:
A. Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click Internet Options.
B. Click the Connections tab.
C. Click the LAN settings button and remove anything that is checked.
D. Click the OK button to go back to the previous screen.
E. Click the option Never dial a connection. This will remove any dial-up
pop-ups for PPPoE users.
For Netscape 4.7 or higher:
A. Start Netscape Navigator, and click Edit, Preferences, Advanced, and
Proxies.
B. Make sure you have Direct connection to the Internet selected on this
screen.
C. Close all the windows to finish.
11. To start over,I need to set the Router to factory default.
Hold the Reset button for up to 30 seconds and then release it. This will return
the password, forwarding, and other settings on the Router to the factory
default settings. In other words, the Router will revert to its original factor y
configuration.
12. I need to upgrade the firmware.
In order to upgrade the firmware with the latest features, you need to go to the
Linksys website and download the latest firmware at www.linksys.com. Follow
these steps:
A. Go to the Linksys website at http://www.linksys.com and download the
latest fir mware.
B. To upgrade the f irmware, follow the steps in the Help section found in
“Chapter 5: Using the Router’s Web-based Utility.”
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
63 64
Page 36

17. The Diag LED stays lit continuously.
• The Diag LED lights up when the device is first powered up. Meantime,
the system will boot up itself and check for proper operation. After finishing the checking procedure, the LED turns off to show that the system
is working fine. If the LED remains lit after this time, the device is not
working properly. Try to flash the firmware by assigning a static IP
address to the computer, and then upgrade the firmware. Try using the
following settings, IP Address: 192.168.1.50 and Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.0.
18. When I enter a URL or IP address,I get a time-out error or am prompted to retry.
• Check if other PCs work. If they do, ensure that y our w orkstation’s IP settings are correct (IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and DNS).
Restart the computer that is having a problem.
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, check the
Router. Ensure that it is connected and ON. Connect to it and check its
settings. (If you cannot connect to it, check the LAN and power connections.)
• If the Router is configured correctly, check your Internet connection
(DSL/cable modem, etc.) to see if it is working correctly. You can remove
the Router to verify a direct connection.
• Manually configure the TCP/IP with a DNS address provided by your
ISP.
• Make sure that your browser is set to connect directly and that any dialup is disabled. For Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options, and
then the Connection tab. Make sure that Internet Explorer is set to Nev er
dial a connection. For Netscape Navigator, click Edit, Preferences,
Advanced, and Proxy. Make sure that Netscape Navigator is set to
Direct connection to the Internet.
19. The Full/Col LED keeps flickering continuously.
• Check the Category 5 Ethernet cable and its RJ-45 connectors.
• There may be interference with other network devices. Try removing
other PCs or network devices to see if the problem persists. Eliminate
each network device one at a time to determine the cause.
15. I can't access my email, web, or VPN, or I am getting corrupted data from the
Internet.
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) setting may need to be adjusted. By
default, the MTU is set at 1500. For most DSL users, it is strongly recommended to use MTU 1492. If you are having some dif ficulties, perform the following steps:
A. To connect to the Router, go to the web browser, and enter
http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router.
B. Enter the password, if asked. (The default password is admin.)
C. Click the Advanced => Filter tab.
D. Look for the MTU option, and select Enable. In the Size field, enter 1492.
E. Click the Apply and Continue buttons to continue.
If your difficulties continue, change the Size to different values. Try this list of
values, one value at a time, in this order, until your problem is solved:
1462
1400
1362
1300
16. I need to use port triggering.
Port triggering looks at the outgoing port services used and will trigger the
Router to open a specific port, depending on which port an Internet application
uses. Follow these steps:
A. To connect to the Router, go to the web browser, and enter
http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router.
B. Enter the password, if asked. (The default password is admin.)
C. Click theAdvanced => F orw ar dingtab, and click the Port T riggerbutton.
D. Enter any name you want to use for the Application Name.
E. Enter the Triggered Port Range. Check with your Internet application
provider for more information on which outgoing port services it is using.
F. Enter the Incoming Port Range. Check with your Internet Application
provider for more information on which incoming port services are
required by the Internet application.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
65 66
Page 37

What is the maximum number of IP addresses that the Router will support? The
Router will support up to 253 IP addresses.
Is IPSec Pass-Through supported by the Router?Yes, it is a built-in feature that
the Router automatically enables.
Where is the Router installed on the network? In a typical environment, the
Router is installed between the cable/DSL modem and the LAN. Plug the
Router into the cable/DSL modem’s Ethernet port.
Does the Router support IPX or AppleTalk? No. TCP/IP is the only protocol stan-
dard for the Internet and has become the global standard for communications.
IPX, a NetWare communications protocol used only to route messages from
one node to another, and AppleTalk, a communications protocol used on
Apple and Macintosh networks, can be used for LAN to LAN connections,
but those protocols cannot connect from WAN to LAN.
Does the WAN connection of the Router support 100 Mbps Ethernet? Because of
the speed limitations of broadband Internet connections, the Router’s cur rent
hardware design supports 10 Mbps Ethernet on its WAN port. It does, of
course, support 100 Mbps over the auto-sensing Fast Ether net 10/100 switch
on the LAN side of the Router.
What is Network Address Translation and what is it used for? Network Address
Translation (N AT) translates multiple IP addresses on the private LAN to one
public address that is sent out to the Internet. This adds a level of security
since the address of a PC connected to the private LAN is never transmitted
on the Internet. Furthermore, NAT allows the Router to be used with lo w cost
Internet accounts, such as DSL or cable modems, when only one TCP/IP
address is provided by the ISP. The user may have many private addresses
behind this single address provided by the ISP.
Does the Router support any operating system other than Windows 95,Windows
98,Windows 2000,Windows NT, or Windows XP? Yes, but Linksys does not, at
this time, provide technical support for setup, configuration or troubleshooting of any non-Windows operating systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does the Router support ICQ send file? Yes, with the following fix: click ICQ
menu -> preference -> connections tab->, and check I am behind a firewall or proxy. Then set the firew all time-out to 80seconds in the firewall set-
ting. The Internet user can then send a file to a user behind the Router.
I set up an Unreal Tournament Ser ver,but others on the LAN cannot join. What do
I need to do? If you have a dedicated Unreal Tournament server running, you
need to create a static IP for each of the LAN computers and forward ports
7777, 7778, 7779, 7780, 7781, and 27900 to the IP address of the server. You
can also use a port forwarding range of 7777 ~ 27900. If you want to use the
UT Server Admin, forward another port (8080 usually works well but is used
for remote admin. You may have to disable this.), and then in the
[UWeb.W ebServer] section of the server .ini file, set the ListenPort to 8080 (to
match the mapped port above) and ServerName to the IP assigned to the
Router from your ISP.
Can multiple gamers on the LAN get on one game server and play simultaneously
with just one public IP address? It depends on which network game or what
kind of game server you are using. For e xample, Unreal Tournament supports
multi-login with one public IP.
How do I get
Half-Life:Team Fortress
to work with the Router? The default client
port for Half-Life is 27005. The computers on your LAN need to have
“+clientport 2700x” added to the HL shortcut command line; the x would be
6, 7, 8, and on up. This lets multiple computers connect to the same server.
One prob lem:Version 1.0.1.6 won’ t let multiple computers with the same CD
key connect at the same time, even if on the same LAN (not a problem with
1.0.1.3). As far as hosting games, the HL server does not need to be in the
DMZ. Just forward port 27015 to the local IP address of the server computer.
How can I block corrupted FTP downloads? If you are experiencing corrupted
files when you download a file with your FTP client, try using another FTP
program.
The web page hangs; downloads are corrupt, or nothing but junk characters are
being displayed on the screen. What do I need to do? Force your Ethernet
adapter to 10Mbps or half duplex mode, and turn off the “Auto-negotiate”
feature of your Ethernet adapter as a temporary measure. (Please look at the
Network Control Panel in your Ethernet adapter’s Advanced Properties tab.)
Make sure that your proxy setting is disabled in the browser. Check our website at www.linksys.com for more information.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
67 68
Page 38

If all else fails in the installation, what can I do? Reset the Router by holding
down the reset button until the Diag LED fully turns on and off. Reset your
cable or DSL modem by powering the unit off and then on. Obtain and flash
the latest fir mware release that is readily available on the Linksys website,
www.linksys.com.
How will I be notified of new Router firmware upgrades? All Linksys f irmware
upgrades are posted on the Linksys website at www.linksys.com, where they
can be downloaded for free. The Router’s f irmware can be upgraded with
TFTP programs. If the Router’s Internet connection is working well, there is
no need to download a newer firmware version, unless that version contains
new features that you would like to use. Downloading a more current version
of Router firmware will not enhance the quality or speed of y our Internet connection, and may disrupt your current connection stability.
Will the Router function in a Macintosh environment? Yes, but the Router’s setup
pages are accessible only through Internet Explorer 4.0 or Netscape
Navigator 4.0 or higher for Macintosh.
I am not able to get the web configuration screen for the Router. What can I do?
You may have to remove the proxy settings on your Internet browser, e.g.,
Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer. Or remove the dial-up settings on
your browser. Check with your browser documentation, and make sure that
your browser is set to connect directly and that any dial-up is disabled. Make
sure that your browser is set to connect directly and that any dial-up is disabled. For Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options, and then the
Connection tab. Make sure that Internet Explorer is set to Never dial a connection. For Netscape Navigator, click Edit, Preferences, Advanced, and
Proxy. Make sure that Netscape Navigator is set to Direct connection to the
Internet.
What is DMZ Hosting? Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) allows one IP address (com-
puter) to be exposed to the Internet. Some applications require multiple
TCP/IP ports to be open. It is recommended that you set your computer with
a static IP if you want to use DMZ Hosting. To get the LAN IP address, see
“Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet
Adapter.”
If DMZ Hosting is used,does the exposed user share the public IP with the Router?
No.
Does the Router pass PPTP packets or actively route PPTP sessions? The Router
allows PPTP packets to pass through.
Is the Router cross-platform compatible? Any platform that supports Ethernet
and TCP/IP is compatible with the Router.
How many ports can be simultaneously forwarded? Theoretically, the Router can
establish 520 sessions at the same time, but you can only forward 10 ranges
of ports.
Does the Router replace a modem? Is there a cable or DSL modem in the Router?
No, this version of the Router must work in conjunction with a cable or DSL
modem.
Which modems are compatible with the Router? The Router is compatible with
virtually any cable or DSL modem that supports Ethernet.
What are the advanced features of the Router? The Router’s advanced features
include IP Filtering, Port Range Forwarding, Dynamic Routing, Static
Routing, DMZ hosting, and MAC Address Cloning.
What is the maximum number of VPN sessions allowed by the Router?
The maximum number depends on many factors. At least one IPSec session
will work through the Router; however, simultaneous IPSec sessions may be
possible, depending on the specifics of your VPNs.
How big is the memory buffer on the Router? 1MB buffer and 512KB flash.
How can I check whether I have static or DHCP IP Addresses? Consult your ISP
to obtain this information.
How do I get mIRC to work with the Router? Under the Port Range Forwarding
tab, set port forwarding to 113 for the PC on which you are using mIRC.
Can the Router act as my DHCP Server? Yes. The Router has DHCP Server soft-
ware built-in.
Can I run an application from a remote computer over the wireless network? This
will depend on whether or not the application is designed to be used over a
network. Consult the application’s documentation to deter mine if it supports
operation over a network.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
69 70
Page 39

What is the IEEE 802.11b standard? The IEEE 802.11b Wireless LAN standards
subcommittee formulates the standard for the industry. The objective is to
enable wireless LAN hardware from dif ferent manufacturers to communicate.
What IEEE 802.11 features are supported? The product suppor ts the following
IEEE 802.11 functions:
• CSMA/CA plus Acknowledge protocol
• Multi-Channel Roaming
• Automatic Rate Selection
• RTS/CTS feature
• Fragmentation
• Power Management
What is BSS ID? A specif ic Ad-hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS).
Computers in a BSS must be configured with the same BSS ID.
What is SSID? An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming
capability for mobile workers. More than one BSS can be configured as an
Extended Service Set (ESS). Users within an ESS could roam freely between
BSSs while maintaining a continuous connection to the wireless network stations and Access Points.
What is ISM band? The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set
aside bandwidth for unlicensed use in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific and
Medical) band. This presents a truly revolutionary opportunity to place convenient high speed wireless capabilities in the hands of users around the
globe.
What is Spread Spectrum? Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio
frequency technique developed b y the military for use in reliable, secure, mission-critical communications systems. It is designed to trade off bandwidth
efficiency for reliability, integrity, and security. In other words, more bandwidth is consumed than in the case of narrowband transmission, but the tradeoff produces a signal that is, in effect, louder and thus easier to detect, provided that the receiver knows the parameters of the spread-spectrum signal
being broadcast. If a receiver is not tuned to the right frequency, a spreadspectrum signal looks like background noise. There are two main alternativ es,
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency Hopping Spread
Spectrum (FHSS).
What is DSSS? What is FHSS? And what are their differences? Frequency
Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) uses a narrowband carrier that changes
frequency in a pattern that is known to both transmitter and receiv er. Properly
synchronized, the net effect is to maintain a single logical channel. To an
unintended receiver , FHSS appears to be short-duration impulse noise. Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) generates a redundant bit pattern for each
bit to be transmitted. This bit pattern is called a chip (or chipping code). The
longer the chip, the greater the probability that the original data can be recovered. Even if one or more bits in the chip are damaged during transmission,
statistical techniques embedded in the radio can recover the original data
without the need for retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears
as low power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband
receivers.
Would the information be intercepted while transmitting on air? WLAN features
two-fold protection in security. On the hardware side, as with Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum technology, it has the inherent security feature of
scrambling. On the software side, the WLAN series offers the encryption
function (WEP) to enhance security and access control. Users can set it up
depending upon their needs.
What is WEP? WEP is Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism
based on a 40/64 bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11
standard.
What is a MAC Address? The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique
number assigned by the manufacturer to any Ethernet networking device,
such as a network adapter, that allows the network to identify it at the hardware level. For all practical purposes, this number is usually permanent.
Unlike IP addresses, which can change every time a computer logs on to the
network, the MAC address of a device stays the same, making it a valuable
identifier for the network.
If your questions are not addressed here, refer to the Linksys website,
www.linksys.com.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
71 72
Page 40

3. At the DOS command prompt, type “ping mail” (assuming that the loca-
tion for which you’re trying to find an IP address is configured as “mail”).
Press Enter. Information such as the following data, taken from a ping of
Microsoft Network’s e-mail ser ver, will be displayed.
4. Write down the IP address returned by the ping command. (In the
example above: 24.53.32.4.) This IP address is the actual IP address of the
server “mail,” or any other word or value you have pinged.
Step T w o:Pinging for a Web Address
While the IP address returned above would work as your e-mail server address,
it may not be permanent. IP addresses change all the time. W eb addresses, ho wever, usually don’t. Because of this, you’re likely to have fewer problems by
configuring your system with web addresses rather than IP addresses. Follow
the instructions below to find the web address assigned to the IP address you
just pinged.
1. At the DOS command prompt, type “ping -a 24.53.32.4,” where
24.53.32.4 is the IP address you just pinged. Information such as the following data will be displayed.
C:\>ping mail
Pinging mail [24.53.32.4] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
74
Appendix B: How to Ping You r
ISP’s E-mail and Web Addresses
Virtually all Internet addresses are configured with words or characters (i.e.,
www.linksys.com, www.yahoo.com, etc.) In actuality, however, these Internet
addresses are assigned to IP addresses, which are the true addresses on the
Internet. For example, www.linksys.com is actually 216.23.162.142. Entering
that into your web browser will bring up at the Linksys home page every time.
IP and web addresses, however, can sometimes be long and hard to remember.
Because of this, certain ISPs will shorten their server addresses to single words
or codes on their users’ web browser or e-mail configurations. If your ISP’s email and web server addresses are configured with single words (“www,” “email,” “home,” “pop3,” etc.) rather than whole Internet Addresses or IP
Addresses, the Router may have problems sending or receiving mail and
accessing the Internet. This happens because the Router has not been configured by your ISP to accept their abbreviated server addresses.
The solution is to determine the true web addresses behind your ISP’s code
words. You can determine the IP and web addresses of your ISP’s ser vers by
“pinging” them.
Step One: Pinging an IP Address
The first step to deter mining your ISP’s web and e-mail server address is to
ping its IP address.
1. Power on the computer and the cable or DSL modem, and restore the
network configuration set by your ISP if you have since changed it.
2. Click Start, then Run, and type “command.” This will bring up the DOS
window.
73
NNoottee::
If you don’t have your ISP’s web and e-mail IP addresses, you must
either get them from your ISP or follow these steps prior to connecting the
Router to your network.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 41

Appendix C:Configuring
Wireless Security
An acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy, WEP is an encryption method used
to protect your wireless data communications. WEP uses a combination of 64bit or 128-bit keys to provide access control to your network and encryption
security for every data transmission. To decode a data transmission, each point
in a network must use an identical 64-bit or 128-bit key. Higher encryption levels mean higher levels of security, but due to the complexity of the encryption,
they may mean decreased network performance.
You may also have heard the term “40-bit” used in conjunction with WEP
encryption. This is simply another term for 64-bit WEP encryption. This level
of WEP encryption has been called 40-bit because it uses a 40-bit secret key
along with a 24-bit Initialization Vector (40 + 24 = 64). Wireless vendors may
use either name. Linksys uses the term “64-bit” when referring to this level of
encryption.
Make sure your wireless netw ork is functioning before attempting to configure
WEP encryption.
A 128-bit WEP encrypted wireless network will NOT communicate with a 64bit WEP encrypted wireless network. Therefore, make sure that all of your
wireless devices are using the same encryption level. All wireless de vices complying with the 802.11b standard will support 64-bit WEP.
In addition to enabling WEP, Linksys also recommends the following security
implementations:
• Changing the SSID from the default “linksys”
• Changing the WEP key regularly
Note: WEP encryption is an additional data securi-
ty measure and not essential for router operation.
Note: In order for WEP Encryption to be enabled, wireless functions must
first be enabled. Select Enable under the Wireless section before proceeding.
2. Write down the web address returned by the ping command (in the
example above: mail.msnv3.occa.home.com.). This web address is the web
address assigned to the IP address you just pinged. While the IP address of
“mail” could conceivably change, it is likely that this web address will not.
3. Replace your ISP’s abbreviated server address with this extended web
address in the corresponding Internet application (web browser, e-mail
application, etc.).
Once you have replaced the brief server address with the true ser ver address,
the Router should have no problem accessing the Internet through that Internet
application.
C:\>ping -a 24.53.32.4
Pinging mail.msnv3.occa.home.com [24.53.32.4] with
32 bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
75
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
76
Page 42

• WEP (64Bit or 128B) Select the level of encryption from the drop-down
box. 128-bit WEP encryption is unique to Linksys and may conflict with
other vendors’WEP encr yption.
The WEP Encryption key is generated in one of two ways:
1. You may create an encryption key by using a Passphrase.
a. Enter a Passphrase, a user-defined password, into the Passphrase field.
The Passphrase can be a maximum of 31 letters, symbols, and numbers.
No spaces can be used.
b. Click the Generate button to create a key. The key will be 10 digits if
you chose 64-bit encryption, or 26 digits if you chose 128-bit encryption.
This key will be used to encrypt and decrypt the data being sent between
the Router and your network’s wireless PCs.
The Key field may not display all digits. Using the mouse, click anywhere within the Key field. Move the cursor to the right to view the rest
of the Key. Make sure your write down the entire Key EXACTLY the
way it is displayed.
2. You may enter the encryption key manually.
Make a note of the Passphrase or Manual Key. You will need it for the other
wireless devices on the network, as the same WEP encryption key must be
entered in all wireless devices on the network.
Once you have chosen your key encryption method and entered either the
Passphrase or manual key, click the Apply button, and the encryption portion
of the setup is complete.
Note: In order to utilize WEP encryption, all points in your wireless
network must have WEP enabled and be set to the same Key Setting.
Note: In Windows XP, a 128-bit Key generated by the Router
will be called a "104 bits (26 digits)" key, and a 64-bit Key generated by the Router will be called a “40 bits (10 digits)” key.
The following steps will show you how to utilize WEP encryption
1. From the Web-based Utility’s Setup tab, select Mandatory under the WEP
section.
2. Press the WEP Key Setting button to set the WEP Encryption type and
level.
3. The screen displayed in Figure
C-1 may appear,
verifying that you
are enabling WEP
Encryption. Press
the OK button to
continue.
4. This will display the screen sho wn in F igure C-2. F rom this screen, y ou will
choose your WEP Encryption settings.
Figure C-2
Figure C-1
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
77 78
Page 43

2. In the “Control Panel” window, click the Network and Internet
Connections icon, shown in Figure C-4.
3. Click the Network Connections icon, shown in Figure C-5.
4. The “Network Connections” window will appear, as shown in Figure C-6.
Under LAN or High-Speed Internet you will see all Network cards that are
installed and operating in your computer. Double-click the Wireless
Network Connection icon associated with your wireless adapter.
If the “Wireless Network Connection Status” window appears, continue to
the next step
Figure C-4
Figure C-5
As Windows XP does not allow for the use of the Linksys Passphrase feature
with the wireless PC adapters, you will need to manually enter the key generated in the previous section.
The following steps will help you enable WEP and enter the encryption key
manually for your wireless PC cards, in order to enable your Windows XP system to communicate with the Router wirelessly.
These steps assume that your CD-ROM drive is letter D and that you are running Windows XP in the default mode.
Be sure you have the WEP Key generated by the Router.
1. As shown in Figure C-3, click the Start button and go to the Control Panel.
Figure C-3
Configuring Wireless Security in Windows XP
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
79 80
Page 44

6. When the “Wireless
Network Connection
Properties” window
appears, as in Figure C8, click the Wireless
NetworksTab.
7. If the appropriate wireless network, specified
by the Router’s SSID, is
displayed in the
“Preferred networks”
section, as shown in
Figure C-9, doubleclick it and continue to
the next step.
Otherwise, click on the
appropriate wireless
network, specified by
the Router’s SSID, in
the “Available networks” section. Then,
click the Configure
button
Figure C-8
Figure C-9
If a “Connect to Wireless Network” window appears, in the Available
Networks section, click the desired wireless network, specified by the
Router’s SSID. Then, doub le-click the W ir eless Netw ork Connectionicon.
5. When the “Wireless Network Connection Status” window appears, as in
Figure C-7, click the Properties button.
Figure C-6
Figure C-7
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
81 82
Page 45

Appendix D:Finding the MAC
Address and IPAddress for Yo u r
Ethernet Adapter
This section describes how to find the MAC address for your Ethernet adapter
to do either MAC Filtering or MAC Address Cloning for the Router and ISP.
You can also find the IP address of your computer’s Ethernet adapter. The IP
address is used for filtering, forwarding, and DMZ. Follow these steps to find
the MAC address or IP address for your adapter in Windows 95, 98, ME, NT,
2000, and XP.
For Windows 95, 98, and ME:
1. Click on Start and Run. In the Open f ield, enter winipcfg, as shown in
Figure D-1. Then press the Enter key or the OK button.
2. When the IP Configuration window appears, as shown in Figure D-2, select
the Ethernet adapter you are using to connect to the Router via a CAT 5
Ethernet cable.
Figure D-1
Figure D-2
8. The “Wireless Network Properties” window (shown in Figure C-10) will
appear.
Click the check box for the Data encryption (WEP enabled) option.
Remove the check from the Network Authentication (Shared mode) and
The key is provided for me automatically fields.
In the "Network key" field, enter the exact Key (all 10 or 26 digits, depending on the level of encryption) generated by the Router.
Verify that the “Key format” f ield displays “Hexadecimal digits” and that
the “Key length” field displays either “40 bits (10 digits)” or “104 bits (26
digits)”. If this is not displayed, you have entered the key incorrectly.
Click the OK button to save the settings. Click on OK buttons until you
get back to the “Wireless Network Connection Status” window. Close any
open windows to get back to the Windows XP desktop.
Close any applications and reboot your PC. After reboot, WEP conf iguration
is complete and you should be able to connect wirelessly to the Router.
Figure C-10
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
83 84
Page 46

2. In the command prompt, enter ipconfig /all. Then press the Enter key.
3. Write down the Physical Address as shown on your computer screen; it is
the MAC address for your Ethernet adapter. This will appear as a series of
letters and numbers.
The MAC address/Physical Address is what you will use for MAC Address
Cloning or MAC Filtering.
The example in Figure D-5 shows the IP address of your Ethernet adapter
as 192.168.1.100. Your computer may show something different.
Figure D-5
Note: The MAC address is also called the Physical
Address.
3. Write down the Adapter Address as shown on your computer screen (see
Figure D-3). This is the MAC address for your Ethernet adapter and will
be shown as a series of numbers and letters.
The MAC address/Adapter Address is what you will use for MAC Address
Cloning or MAC Filtering.
The example in Figure F-3 shows the IP address of your Ethernet adapter
as 192.168.1.100. Your computer may show something different.
For Windows NT, 2000, and XP:
The following steps sho w an alternativ e w ay of obtaining the MAC address and
IP address for your Ethernet adapter.
1. Click on Start and Run. In the Open field, enter cmd, as shown in Figure
D-4. Press the Enter key or click the OK button.
Figure D-3
Figure D-4
Note: The MAC address is also called the Adapter
Address.
Instant WirelessTMSeries Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
85 86
Page 47

Appendix E: Glossary
10BaseT - An Ethernet standard that uses twisted wire pairs.
100BaseTX - IEEE physical layer specification for 100 Mbps over tw o pairs of
Category 5 wire.
Adapter - Printed circuit board that plugs into a PC to add to capabilities or
connectivity to a PC. In a networked environment, a network interface card is
the typical adapter that allows the PC or server to connect to the intranet and/or
Internet.
Ad-hoc Network - An ad-hoc network is a group of computers, each with a
wireless adapter, connected as an independent 802.11 wireless LAN. Ad-hoc
wireless computers operate on a peer-to-peer basis, communicating directly
with each other without the use of an access point. Ad-hoc mode is also
referred to as an Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) or as peer-to-peer
mode.
AppleTalk - An Apple Computer networking system that support Apple's proprietary local talk.
Auto-negotiate - To automatically determine the correct settings. The term is
often used with communications and networking. For example, Ethernet
10/100 cards, hubs and switches can determine the highest speed of the node
they are connected to and adjust their transmission rate accordingly.
Backbone - The part of a network that connects most of the systems and networks together and handles the most data.
Bandwidth - The transmission capacity of a given facility, in terms of how
much data the facility can transmit in a fixed amount of time; expressed in bits
per second (bps).
Beacon Interval - A beacon is a packet broadcast by the Access Point to keep
the network synchronized. A beacon includes the wireless LAN service area,
the AP address, the Broadcast destination addresses, a time stamp, Delivery
Traffic Indicator Maps, and the Traffic Indicator Message (TIM).
88
When entering the information using the Router’s web-based utility, you will
type the 12-digit MAC address in this format, XXXXXXXXXXXX without
the hyphens for MAC Filtering. See Figure D-6.
When entering information for MAC Address Cloning, type the 12-digit MAC
address (see Figure D-7).
Figure D-6
Figure D-7
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
87
Page 48

cabling systems (wires, junctions, and connectors) in terms of the data rates
that they can sustain. CAT 5 cable has a maximum throughput of 100 Mbps and
is usually utilized for 100BaseTX networks.
CA T 5e- The additional cabling performance parameters of return loss and farend crosstalk (FEXT) specified for 1000BASE-T and not specified for
10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX are related to differences in the signaling implementation. 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX signaling is unidirectional-signals
are transmitted in one direction on a single wire pair. In contrast, Gigabit
Ethernet is bi-directional-signals are transmitted simultaneously in both directions on the same wire pair; that is, both the transmit and receive pair occupy
the same wire pair.
CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance) - In local
area networking, this is the CSMA technique that combines slotted time-division multiplexing with carrier sense multiple access/collision detection
(CSMA/CD) to avoid having collisions occur a second time. This works best if
the time allocated is short compared to packet length and if the number of situations is small.
Data Packet - One frame in a packet-switched message. Most data communications is based on dividing the transmitted message into packets. F or e xample,
an Ethernet packet can be from 64 to 1518 bytes in length.
Default Gateway - The routing device used to forward all traff ic that is not
addressed to a station within the local subnet.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A protocol that lets network
administrators manage centrally and automate the assignment of Internet
Protocol (IP) addresses in an organization's network. Using the Internet's set of
protocol (TCP/IP), each machine that can connect to the Internet needs a
unique IP address. When an organization sets up its computer users with a connection to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each machine.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer and,
if computers move to another location in another part of the network, a new IP
address must be entered. DHCP lets a network administrator supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point and automatically sends a new IP
address when a computer is plugged into a different place in the network.
DHCP uses the concept of a "lease" or amount of time that a given IP address
will be valid for a computer. The lease time can vary depending on how long a
user is likely to require the Internet connection at a particular location. It's espe-
90
Bit - A binary digit. The value - 0 or 1-used in the binary numbering system.
Also, the smallest form of data.
Boot - To cause the computer to start executing instructions. Personal computers contain built-in instructions in a ROM chip that are automatically executed
on startup. These instructions search for the operating system, load it and pass
control to it.
Broadband - A data-transmission scheme in which multiple signals share the
bandwidth of a medium. This allows the transmission of voice, data and video
signals over a single medium. Cable television uses broadband techniques to
deliver dozens of channels over one cable.
Browser - A browser is an application program that provides a way to look at
and interact with all the information on the World Wide Web or PC. The word
"browser" seems to have originated prior to the Web as a generic term for user
interfaces that let you browse text files online.
BSS (Basic Service Set) - An infrastructure network connecting wireless
devices to a wired network using a single access point.
Buffer - A buffer is a shared or assigned memory area used by hardware
devices or program processes that operate at different speeds or with different
sets of priorities. The buffer allows each device or process to operate without
being held up by the other. In order for a buffer to be effective, the size of the
buffer and the algorithms for moving data into and out of the buffer need to be
considered by the buffer designer. Like a cache, a buffer is a "midpoint holding
place" but exists not so much to accelerate the speed of an activity as to support the coordination of separate activities.
Cable Modem - A device that connects a computer to the cable television network, which in turn connects to the Internet. Once connected, cable modem
users have a continuous connection to the Internet. Cable modems feature
asymmetric transfer rates: around 36 Mbps downstream (from the Internet to
the computer), and from 200 Kbps to 2 Mbps upstream (from the computer to
the Internet).
CAT 5 - ANSI/EIA (American National Standards Institute/Electronic
Industries Association) Standard 568 is one of several standards that specify
"categories" (the singular is commonly referred to as "CAT") of twisted pair
89
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 49

associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. AP
Clients hear the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast
messages.
Dynamic IP Address - An IP address that is automatically assigned to a client
station in a TCP/IP network, typically by a DHCP server. Network devices that
serve multiple users, such as servers and printers, are usually assigned static IP
addresses.
Dynamic Routing - The ability for a router to forward data via a dif ferent route
based on the current conditions of the communications circuits. For example,
it can adjust for overloaded traff ic or failing lines and is much more flexible
than static routing, which uses a fixed forwarding path.
Encryption - A security method that applies a specific algorithm to data in
order to alter the data's appearance and prevent other devices from reading the
information.
ESS (Extended Service Set) - A set of more than two or more BSSs (multiple
access points) forming a single network.
Ethernet - IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed
on and retrieved from a common transmission medium. Has a transfer rate of
10 Mbps. Forms the underlying transport vehicle used by several upper-level
protocols, including TCP/IP and XNS.
Fast Ethernet - A 100 Mbps technology based on the 10Base-T Ethernet
CSMA/CD network access method.
FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) - FHSS continuously changes
(hops) the carrier frequency of a conventional carrier several times per second
according to a pseudo-random set of channels. Because a fixed frequency is not
used, and only the transmitter and receiver know the hop patterns, interception
of FHSS is extremely difficult.
Finger - A UNIX command widely used on the Internet to f ind out information about a particular user, such as telephone number, whether currently
logged on or the last time logged on. The person being "f ingered" must have
placed his or her profile on the system. Fingering requires entering the full
user@domain address.
92
cially useful in education and other environments where users change frequently. Using very short leases, DHCP can dynamically reconfigure networks
in which there are more computers than there are available IP addresses.
DHCP supports static addresses for computers containing Web servers that
need a permanent IP address.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) - Allows one IP address (or computer) to be
exposed to the Internet. Some applications require multiple TCP/IP ports to be
open. It is recommended that you set your computer with a static IP address if
you want to use DMZ Hosting.
DNS - The domain name system (DNS) is the way that Internet domain name
are located and translated into Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. A domain name
is a meaningful and easy-to-remember "handle" for an Internet address.
Domain - A subnetwork comprised of a group of clients and servers under the
control of one security database. Dividing LANs into domains improves performance and security.
Download - To receive a f ile transmitted over a network. In a communications
session, download means receive, upload means transmit.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) - A technology that dramatically increases the
digital capacity of ordinary telephone lines into the home or office and, by
employing unused bandwidth, still allows for normal phone usage. DSL provides "always-on" operation, eliminating the need to dial in to the service.
DSSS (Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum) - DSSS generates a redundant bit
pattern for all data transmitted. This bit pattern is called a chip (or chipping
code). Even if one or more bits in the chip are damaged during transmission,
statistical techniques embedded in the receiver can recover the original data
without the need for retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears
as low power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband
receivers. However, to an intended receiver (i.e. another wireless LAN endpoint), the DSSS signal is recognized as the only valid signal, and interference
is inherently rejected (ignored).
DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) - A DTIM field is a countdown
field infor ming clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the AP has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for
91
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 50

Firewall - A firewall is a set of related programs, located at a network gateway
server, that protects the resources of a netw ork from users from other networks.
(The term also implies the security policy that is used with the programs.) An
enterprise with an intranet that allows its workers access to the wider Internet
installs a firewall to prevent outsiders from accessing its own private data
resources and for controlling what outside resources to which its own users
have access.
Basically, a f irewall, working closely with a router, examines each network
packet to determine whether to forward it toward its destination.
Firmware - Code that is written onto read-only memory (ROM) or programmable read-only memory (PROM). Once firmware has been written onto the
ROM or PROM, it is retained even when the device is turned off.
Fragmentation - Breaking a packet into smaller units when transmitting over
a network medium that cannot support the original size of the packet.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP
network (Internet, UNIX, etc.). F or example, after de v eloping the HTML pages
for a Web site on a local machine, they are typically uploaded to the Web server using FTP.
FTP includes functions to log onto the network, list directories and copy files.
It can also convert betw een the ASCII and EBCDIC character codes. FTP operations can be performed by typing commands at a command prompt or via an
FTP utility running under a graphical interface such as Windows. FTP transfers
can also be initiated from within a Web browser by entering the URL preceded
with ftp://.
Unlike e-mail programs in which graphics and program files have to be
"attached," FTP is designed to handle binary files directly and does not add the
overhead of encoding and decoding the data.
Full Duplex - The ability of a device or line to transmit data simultaneously in
both directions.
Gateway - A device that interconnects networks with different, incompatible
communications protocols.
Half Duplex - Data transmission that can occur in two directions over a single
line, but only one direction at a time.
93
Hardware - Hardware is the physical aspect of computers, telecommunications, and other information technology devices. The term arose as a wa y to distinguish the "box" and the electronic circuitry and components of a computer
from the program you put in it to make it do things. The program came to be
known as the software.
Hop - The link between two network nodes.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) - The communications protocol used
to connect to servers on the World Wide Web. Its primary function is to establish a connection with a Web server and transmit HTML pages to the client
browser.
Hub - The device that serves as the central location for attaching wires from
workstations. Can be passive, where there is no amplification of the signals; or
active, where the hubs are used like repeaters to provide an extension of the
cable that connects to a workstation.
ICQ - A conferencing program for the Internet that provides interactive chat,
e-mail and file transfer and can alert you when someone on y our predefined list
has also come online.
IEEE (The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) - The IEEE
describes itself as "the world's largest technical professional society, promoting
the development and application of electrotechnology and allied sciences for
the benefit of humanity, the advancement of the profession, and the well-being
of our members."
The IEEE fosters the development of standards that often become national and
international standards. The organization publishes a number of journals, has
many local chapters, and several large societies in special areas, such as the
IEEE Computer Society.
Infrastructure Network - An infrastructure network is a group of computers
or other devices, each with a wireless adapter, connected as an 802.11 wireless
LAN. In infrastructure mode, the wireless devices communicate with each
other and to a wired network by first going through an access point. An infrastructure wireless network connected to a wired network is referred to as a
Basic Service Set (BSS). A set of two or more BSS in a single network is
referred to as an Extended Service Set (ESS). Infrastr ucture mode is useful at
a corporation scale, or when it is necessary to connect the wired and wireless
networks.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
94
Page 51

IP Address - In the most widely installed level of the Internet Protocol
(Internet Protocol) today, an IP address is a 32-binary digit number that identifies each sender or receiver of information that is sent in packet across the
Internet. When you request an HTML page or send e-mail, the Internet
Protocol part of TCP/IP includes your IP address in the message (actually, in
each of the packets if more than one is required) and sends it to the IP address
that is obtained by looking up the domain name in the Uniform Resource
Locator you requested or in the e-mail address you're sending a note to. At the
other end, the recipient can see the IP address of the Web page requestor or the
e-mail sender and can respond by sending another message using the IP address
it received.
IPCONFIG - A W indows NT or 2000 utility that provides for querying, defining and managing IP addresses within a network. A commonly used utility for
configuring networks with static IP addresses.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) - A suite of protocols used to implement
secure exchange of packets at the IP layer. IPSec supports two basic modes:
Transport and Tunnel. Transport encrypts the payload of each packet, leaving
the header untouched, w hile Tunnel mode encrypts both the header and the payload and is therefore more secure. IPSec must be supported on both transmitter and receiver and must share a public key. Tunnel mode is widely deployed
in VPNs (Virtual Private Networks).
IPX (Internetwork Packet EXchange) - A NetWare communications protocol
used to route messages from one node to another. IPX packets include network
addresses and can be routed from one network to another.
ISM band - The FCC and their counterpar ts outside of the U.S. have set aside
bandwidth for unlicensed use in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical)
band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made available worldwide. This presents a tr uly revolutionary opportunity to place convenient high-speed wireless capabilities in the hands of users around the globe.
ISP - An ISP (Internet service provider) is a company that provides individuals
and companies access to the Internet and other related services such as W eb site
building and virtual hosting.
LAN - A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and associated
devices that share a common communications line and typically share the
resources of a single processor or server within a small geographic area (for
example, within an office building).
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - A unique number assigned by the
manufacturer to any Ethernet networking device, such as a network adapter,
that allows the network to identify it at the hardware level.
Mbps (MegaBits Per Second) - One million bits per second; unit of measure-
ment for data transmission.
MIB (Management Information Base) - A set of database objects. This set con-
tains information about a specif ic device for utilizing SNMP.
mIRC - mIRC runs under Windows and provides a graphical interface for logging onto IRC servers and listing, joining and leaving channels.
Multicasting - Sending data to a group of nodes instead of a single destination.
NAT (Network Address Translation) - The translation of an Internet Protocol
address (IP address) used within one network to a different IP address known
within another network. One network is designated the inside network and the
other is the outside.
Network- A system that transmits an y combination of v oice, video and/or data
between users.
NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) - The protocol used to connect to
Usenet groups on the Internet. Usenet newsreaders support the NNTP protocol.
Node - A network junction or connection point, typically a computer or work
station.
Packet- A unit of data routed between an origin and a destination in a network.
Passphrase - Used much like a password, a passphrase simplifies the WEP
encryption process by automatically generating the WEP encryption keys for
Linksys products.
PC Card - A credit-card sized removable module that contains memory, I/O,
or a hard disk.
Ping (Packet INternet Groper) - An Internet utility used to determine whether
a particular IP address is online. It is used to test and debug a network by sending out a packet and waiting for a response.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
95 96
Page 52

Plug-and-Play - The ability of a computer system to configure expansion
boards and other devices automatically without requiring the user to turn off
the system during installation.
Port - A pathway into and out of the computer or a network device such as a
switch or router. For example, the serial and parallel ports on a personal computer are external sockets for plugging in communications lines, modems and
printers.
PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) - PPPoE is a method for the
encapsulation of PPP packets over Ethernet frames from the user to the ISP
over the Internet. One reason PPP oE is preferred by ISPs is because it provides
authentication (username and password) in addition to data transport. A PPP oE
session can be initiated by either a client application residing on a PC, or by
client fir mware residing on a modem or router.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) - A protocol (set of communication
rules) that allows corporations to extend their own corporate network through
private "tunnels" over the public Internet. Effectively, a corporation uses a
wide-area network as a single large local area network. A company no longer
needs to lease its own lines for wide-area communication but can securely use
the public networks. This kind of interconnection is known as a virtual private
network.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) - A simple routing protocol that is part of
the TCP/IP protocol suite. It determines a route based on the smallest hop count
between source and destination. RIP is a distance vector protocol that routinely broadcasts routing information to its neighboring routers.
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) - A connector similar to a telephone connector that
holds up to eight wires, used for connecting Ethernet devices.
Roaming - In an infrastructure mode wireless network, this refers to the ability to move out of one access point's range and into another and transparently
reassociate and reauthenticate to the new access point. This reassociation and
reauthentication should occur without user intervention and ideally without
interruption to network connectivity. A typical scenario would be a location
with multiple access points, where users can physically relocate from one area
to another and easily maintain connectivity.
Router - Protocol-dependent device that connects subnetworks together.
Routers are useful in breaking down a very large network into smaller subnetworks; they introduce longer delays and typically have much lower throughput
rates than bridges.
RTS (Request To Send) - An RS-232 signal sent from the transmitting station
to the receiving station requesting permission to transmit.
Server - Any computer whose function in a network is to provide user access
to files, printing, communications, and other ser vices.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - The standard e-mail protocol on the
Internet. It is a TCP/IP protocol that defines the message format and the message transfer agent (MTA), which stores and forwards the mail.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - A widely used network
monitoring and control protocol. Data is passed from SNMP agents, which are
hardware and/or software processes reporting activity in each network device
(hub, router, bridge, etc.) to the workstation console used to oversee the network. The agents return information contained in a MIB (Management
Information Base), which is a data structure that def ines what is obtainable
from the device and what can be controlled (turned off, on, etc.).
Software- Instructions for the computer. A series of instructions that performs
a particular task is called a "program." The tw o major categories of softw are are
"system software" and "application software." System software is made up of
control programs such as the operating system and database management system (DBMS). Application software is any program that processes data for the
user.
A common misconception is that software is data. It is not. Software tells the
hardware how to process the data.
Spread Spectrum - Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio frequency technique developed by the military for use in reliable, secure, mission-critical communications systems. It is designed to trade off bandwidth efficiency
for reliability, integrity, and security. In other words, more bandwidth is consumed than in the case of narrowband transmission, but the trade off produces
a signal that is, in effect, louder and thus easier to detect, provided that the
receiver knows the parameters of the spread-spectrum signal being broadcast.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
97 98
Page 53

If a receiver is not tuned to the right frequency, a spread-spectrum signal looks
like background noise. There are two main alternatives, Direct Sequence
Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS).
SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) - A firewall technolo gy that monitors the state
of the transaction so that it can verify that the destination of an inbound packet matches the source of a previous outbound request. It examines not just the
headers of the packet, but also the contents, to determine more about the packet than just its source and destination information. It is called "stateful" because
verifies that the stated destination computer has previously requested the current communication. In this way, it verifies that all communications are initiated by the recipient computer and are taking place only with sources that are
known and trusted from previous interactions. In addition to being a more rigorous inspection, stateful packet inspection closes off ports until connection to
the specific port is requested. This allows an added layer of protection from the
threat of port scanning.
SSID (Service Set IDentif ier) - A unique name shared among all points in a
wireless network. The SSID must be identical for each point in the wireless network and is case-sensitive.
Static IP Address - A permanent IP address that is assigned to a node in an IP
or a TCP/IP network.
Static Routing - Forwarding data in a network via a fixed path. Static routing
cannot adjust to changing line conditions as can dynamic routing.
Subnet Mask - The method used for splitting IP networks into a series of subgroups, or subnets. The mask is a binary pattern that is matched up with the IP
address to turn part of the host ID address field into a field for subnets.
Switch - 1. A data switch connects computing devices to host computers,
allowing a large number of devices to share a limited number of ports. 2. A
device for making, breaking, or changing the connections in an electrical circuit.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A method (protocol) used along with
the IP (Internet Protocol) to send data in the form of message units (datagram)
between netw ork devices over a LAN or WAN. While IP takes care of handling
the actual delivery of the data (routing), TCP takes care of keeping track of the
individual units of data (called packets) that a message is divided into for eff i-
cient delivery over the network. TCP is known as a "connection oriented" protocol due to requiring the receiver of a packet to return an acknowledgment of
receipt to the sender of the packet resulting in transmission control.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - The basic com-
munication language or set of protocols for communications over a network
(developed specifically for the Internet). TCP/IP defines a suite or group of
protocols and not only TCP and IP.
Telnet - A terminal emulation protocol commonly used on the Internet and
TCP/IP-based networks. It allows a user at a terminal or computer to log onto
a remote device and run a program.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) - A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol
that has no directory or password capability.
Throughput - The amount of data moved successfully from one place to
another in a given time period.
TX Rate - Transmission Rate.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - A method (protocol) used along with the IP
(Internet Protocol) to send data in the form of message units (datagram)
between netw ork devices over a LAN or WAN. While IP takes care of handling
the actual delivery of the data (routing), UDP takes care of keeping track of the
individual units of data (called packets) that a message is divided into for eff icient delivery over the network. UDP is known as a "connection-less" protocol
due to NOT requiring the receiver of a packet to return an acknowledgment of
receipt to the sender of the packet (as opposed to TCP).
Upgrade - To replace existing software or fir mware with a newer version.
Upload - To transmit a file over a network. In a communications session,
upload means transmit, download means receive.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - The address that defines the route to a file
on the Web or any other Internet facility. URLs are typed into the browser to
access Web pages, and URLs are embedded within the pages themselves to provide the hypertext links to other pages.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
99 100
Page 54

Appendix F: Specifications
Standards IEEE 802.3 (10BaseT), IEEE 802.3u
(100BaseTX), IEEE 802.11b (Wireless)
Protocol CSMA/CD
Ports
WAN: One 10Base-T RJ-45 Port for cable or DSL Modem
LAN: Four 10/100 RJ-45 Switched Ports,
One Shared Uplink Port
Speed WAN - 10Mbps, Switch - 10/100Mbps (Half
Duplex) 20/200 (Full Duplex), Wireless (See
Below)
Cabling Type UTP Category 5 or better
Button Reset
Operating Range: (Wireless)
Indoors: Up to 30m (100 ft.) @ 11 Mbps
Up to 50m (165 ft.) @ 5.5 Mbps
Up to 70m (230 ft.) @ 2 Mbps
Up to 91m (300 ft.) @ 1 Mbps
Outdoors: Up to 152m (500 ft.) @ 11 Mbps
Up to 270m (885 ft.) @ 5.5 Mbps
Up to 396m (1300 ft.) @ 2 Mbps
Up to 457m (1500 ft.) @ 1 Mbps
Topology Star (Ethernet)
LED Indicators Power, WLAN Activity, WLAN Link
WAN Link/Activity, Diag for WAN
LAN Full Duplex/Collision, Link/Activity 100
Connectors 2 Antenna Connectors
102
UTP - Unshielded twisted pair is the most common kind of copper telephone
wiring. Twisted pair is the ordinar y copper wire that connects home and many
business computers to the telephone company. To reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires, two insulated copper wires are
twisted around each other. Each signal on twisted pair requires both wires.
Since some telephone sets or desktop locations require multiple connections,
twisted pair is sometimes installed in two or more pairs, all within a single
cable.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) - A technique that allows two or more LANs to
be extended over public communication channels by creating private communication subchannels (tunnels). Effectively, these LANs can use a WAN as a
single large "virtually private" LAN. This removes the need to use leased lines
for WAN communications through secure use of a publicly available WAN
(such as the Internet). Examples of VPN technology are: PPTP (Point to Point
Tunneling Protocol), L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol), and IPSec (Internet
Protocol Security).
WAN (Wide Area Network)- A communications network that covers a rela-
tively large geographic area, consisting of two or more LANs. Broadband
communication over the WAN is often through public networks such as the
telephone (DSL) or cable systems, or through leased lines or satellites. In its
most basic definition, the Inter net could be considered a WAN.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A data privacy mechanism based on a 64-
bit or 128-bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
WINIPCFG - Conf iguration utility based on the Win32 API for querying,
defining and managing IP addresses within a network. A commonly used utility for configuring networks with static IP addresses.
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
101
Page 55

104
Appendix G: Warranty
Information
BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE AND A BARCODE
FROM THE PRODUCT’S PACKAGING ON HAND WHEN CALLING.
RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF
PURCHASE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’S LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE
PAID FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE
USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS
DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS DOES NOT OFFER REFUNDS FOR ANY
PRODUCT.
LINKSYS OFFERS CROSS SHIPMENTS, A FASTER PROCESS FOR PROCESSING AND RECEIVING YOUR REPLACEMENT. LINKSYS PAYS
FOR UPS GROUND ONLY. ALL CUSTOMERS LOCATED OUTSIDE OF
THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AND CANADA SHALL BE HELD
RESPONSIBLE FOR SHIPPING AND HANDLING CHARGES. PLEASE
CALL LINKSYS FOR MORE DETAILS.
103
Dimensions 7.31" x 6.06" x 2.44" (186mm x 154mm x 62mm)
Unit Weight 19.2 oz. (0.56 kg.)
Power Input External, 5V DC, 2.1A
Certif ications FCC Class B, CE Mark
Operating Temperature 0ºC to 40ºC (32ºF to 104ºF)
Storage Temperature -20ºC to 70ºC (-4ºF to 158ºF)
Operating Humidity 10% to 85%, Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity 5% to 90%, Non-Condensing
Environmental
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Wireless Access Point Router with 4-Port Switch
Page 56

Appendix H: Contact
Information
For help with the installation or operation of this product, contact Linksys
Technical Suppor t at one of the phone numbers or Inter net addresses below.
Sales Information 800-546-5797 (LINKSYS)
Technical Support 800-326-7114
RMA Issues 949-271-5461
Fax 949-265-6655
E-mail support@linksys.com
Web http://www.linksys.com
FTP Site ftp.linksys.com
105
Instant WirelessTMSeries
Page 57

© Copyright 2002 Linksys,All Rights Reserved.
Printed in the USA.
http://www.linksys.com
 Loading...
Loading...