Page 1

Instant Broadband™ Series
EtherFast
®
Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL Router
with PrintServ er
User Guide
Use this guide to install: BEFW11P1
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Copyright © 2001 Linksys, All Rights Reserved. Instant Broadband is a registered
trademark of Linksys. Microsoft, Windows, and the Windows logo are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other trademarks and brand names are the property of their respective proprietors.
LIMITED WARRANTY
Linksys guarantees that every Instant Broadband EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router with PrintServer is free from physical defects in material and workmanship under
normal use for one year from the date of purchase. If the product proves defective during this warranty period, call Linksys Customer Support in order to obtain a Return
Authorization Number. BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE AND A BARCODE FROM THE PRODUCT'S PACKAGING ON HAND WHEN CALLING. RETURN
REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. When returning a product, mark the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside of the package and include your original proof of purchase. All customers located outside of the
United States of America and Canada shall be held responsible for shipping and handling charges.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS DOES NOT OFFER REFUNDS FOR ANY
PRODUCT. Linksys makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all
accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose. Linksys reserves the right to revise or
update its products, software, or documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity. Please direct all inquiries to:
Linksys P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623.
FCC STATEMENT
This Instant Broadband EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer has
been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used according to the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment
does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or device
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
UG-BEFW11P1-10110A KL
Page 3

Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
DMZ 36
Routing 38
WAN Port MAC Address 40
The EtherFast Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router’s PrintServer 41
Connecting the PrintServer to Your Network 41
Installing the PrintServer’s Drivers 41
Adding a Printer under Windows 95, 98, and Millennium 44
Adding a Printer under Windows NT 51
Adding a Printer under Windows 2000 57
Troubleshooting 61
Common Problems and Solutions 61
Frequently Asked Questions 63
Appendix 70
How to Ping Your ISP’s E-mail & Web Addresses 70
Installing the TCP/IP Protocol 72
How to Determine Your PCs MAC Address 74
Twisted-Pair Cabling 75
Crimping Your Own Network Cables 76
Glossary 77
Specifications 83
Environmental 84
Warranty Information 85
Contact Information 86
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Table of Contents
Introduction 1
The Linksys EtherFast Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer 1
Features 1
Package Contents 2
System Requirements 2
Getting to Know the EtherFast
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router 3
The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s Rear Panel 3
The Reset Button 4
The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s Front Panel LEDs 4
Planning Your Wireless Network 6
Network Topology 6
Roaming 7
Connecting The EtherFast Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router to Your Network 8
Overview 8
About Static & Dynamic IP Addresses 8
Connecting the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router & Booting Up 9
The EtherFast Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router’s Web-based Utility 11
Setting Up 11
Basic Setup 12
DHCP Server 15
Device Options 17
Wireless 19
Status 22
Advanced Options 24
Special Applications 24
Access Control: Groups 26
Access Control: PCs 29
Access Control: Filters 32
Virtual Servers 34
Page 4
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Introduction
The EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer provides the
ideal solution for connecting your wireless network to a high-speed broadband
Internet connection and a 10/100 Fast Ethernet backbone. Configurable as a
DHCP server for your existing network, the EtherFast Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer acts as the only externally recognized
Internet gateway on your local area network (LAN) and serves as an Internet
firewall against unwanted outside intruders. The Router can also be configured
to filter inter nal users' access to the Inter net.
The EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Routers provide an operating range of
up to 500 meters (1640 feet), providing seamless roaming throughout your
wireless LAN infrastructure, and its advanced user authentication feature
ensures a high level of network security. The EtherFast Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s easy to install and easy to use-Windows-based diagnostics
and statistic tools put you in control of your network.
• Fully Compatible with IEEE 802.11b Standard and Supports a High Data
Rate Up to 11 Mbps
• Build a Wireless Broadband Network in Your Home or Small Office with
Just One IP Address
• Create a Natural Firewall to Protect Your PCs From Outside Intruders
• Auto Fallback Data Rate for Long-Distance Communication and Noisy
Environments
• Provides Roaming, Best Access Point Selection, Load Balancing, and
Network T raf fic Filtering
• Long Operating Range Supports 150m (Indoors) and 500m (Outdoors)
• Capable of up to 128-Bit WEP Encryption
• Supports IPSec Pass-Thru and PPTP
• Acts as a DHCP Server and a Print Server for Your Existing Network
• Administrators Can Block Specific Internal Users’ Internet Access with
Filtering
• Free Technical Support—24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week for North
America Only
• 1-Year Limited Warranty
1
Features
The Linksys EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router
with PrintServer
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
• One EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
• One Instant Wireless
TM
Network PC Card
• One Setup CD-ROM (for PrintServer Setup)
• One AC Pow er Adapter
• One User Guide and Registration Card
• One RJ-45 Broadband Internet connection, with a cable or DSL modem
• One PC with an installed 10Mbps, 100Mbps, or 10/100 Mbps Ethernet card
(optional)
• TCP/IP network adapter protocol for each PC
• UTP network cable with RJ-45 connector
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 or later, or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or later.
(5.0 and 4.7, respectively, are strongly recommended.)
• Windows 95, 98, Millennium, NT 4.0, or 2000
2
Package Contents
System Requirements
Page 5

Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
43
The Reset Button
Briefly pressing the Reset Button will refresh the Wireless AP+
Cable/DSL Router’s connections, potentially clearing any jammed links.
To Reset the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s factory default settings, pow er
off the Router and then press the Reset button. Then, power on the Router and
press the Reset button again. This should be done only if you are experiencing
heavy routing problems, and onl y after y ou ha v e exhausted all of the other troubleshooting options. By resetting the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router, you
run the risk of creating conflicts between your PCs’ actual IP Addresses and
what the W ireless AP + Cable/DSL Router thinks their IP Addresses should be.
You may be forced to reboot the entire system(s).
If the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router locks up, simply power it down for 3
to 5 seconds by removing the power cable from the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router’s Power Port. Leaving the power off for too long could result in the
loss of network connections.
The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s Front Panel LEDs
The LAN Indicators
Power Green. The Power LED illuminates when the Router is pow-
ered on.
Diag Red. The Diag LED illuminates when the Router goes
through its self-diagnosis mode during boot-up. It will turn
off upon successful completion of the diagnosis. If this LED
stays on for an abnormally long period of time, refer to the
Troubleshooting section.
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Getting to Know the EtherFast
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router
The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s Rear Panel
The rear panel of the W ireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is w here all of the connections are made.
The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s Ports
WAN The WAN (Wide Area Netw ork) P ort is where you will
connect your cable or DSL modem.
PC/Uplink The PC and Uplink ports are shared, which means that
if one is used the other cannot be used. The PCport is
used for connecting the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router to a single PC. The Uplink port is used for connecting the W ireless AP+ Cab le/DSL Router to a network device and will automatically determine the
speed of that device.
PCMCIA The Instant Wireless
TM
Network PC Card is inserted
into the PCMCIA slot to enable the wireless features
of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router. This slot is
not hot swappable.
Printer Connect a printer to the Printer port to use the Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL Router’s PrintServer function.
Power The Po wer Port is where you will connect the included
AC Power adapter.
Page 6

Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Planning Your Wireless Network
A wireless LAN is a group of computers, each equipped with one Instant
WirelessTMNetwork PC Card. Computers in a wireless LAN must be configured to share the same radio channel.
Wireless LAN configurations are appropriate for branch level departments or
SOHO operations.
The Instant WirelessTMNetwork PC Card provides access to a wired LAN for
wireless workstations. An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an
Infrastructure conf iguration. A group of Instant WirelessTMNetwork PC Card
users and a Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router compose a Basic Service Set
(BSS). Each PC utilizing an Instant W irelessTMNetwork PC Card in a BSS can
talk to any computer in a wired LAN infrastructure via the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router.
An infrastructure configuration extends the accessibility of an Instant
WirelessTMNetwork PC Card PC to a wired LAN, and doubles the effective
wireless transmission range for two Instant WirelessTMNetwork PC Card PCs.
Since the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is able to forward data within its
BSS, the effective transmission range in an infrastructure LAN is doubled.
The use of a unique ID in a BSS is essential. All PCs using an Instant
WirelessTMNetwork PC Card configured without roaming options in an independent BSS must be configured with a BSS ID used in the BSS.
The Wireless LAN Infrastructure conf iguration is appropriate for enterprisescale wireless access to a central database, or as a wireless application for
mobile users.
65
Network Topology
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
WAN Green. This LED illuminates when a successful connection
is made between the Router and your Broadband device
(such as a modem) or network.
LAN (10/100) Green. The Uplink or PC port will automatically determine
your network’s speed and run accordingly. The 10 and 100
LEDs display the connection speed determined by either
port.
WLAN Green. This LED illuminates when a successful connection
to a wireless network is made.
Printer/Err Red. The Error LED illuminates when there is an error with
the PrintServer. To correct this, clear your print queue. If that
does not work, reset your printer. If that does not work, power
off the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
Printer/Act Green. The Act LED flickers when the PrintServer is sending
or receiving data.
Page 7

Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
8
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users. More
than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Ser vice Set (ESS). This continuous network allows users to roam freely within an ESS. All PCs using an
Instant WirelessTMNetwork PC Card within one ESS must be configured with
the same ESS ID and use the same radio channel.
Before enabling an ESS with roaming capability, choosing a feasible radio
channel and optimum position of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Routers is recommended. Proper Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router positioning combined
with a clear radio signal will greatly enhance performance.
7
Connecting the EtherFast
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Routerto
Your Network
Unlike a simple hub or switch, the setup of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router consists of more than simply plugging everything together. Because the
Router acts as a DHCP server for your Network, you will have to set some values within the Router, and also configure your networked PCs to accept the IP
Addresses the Router chooses to assign them.
You will need the following values from your ISP in order to install the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router:
• Your broadband-configured
PC’s fixed Internet IP Address
(if applicable)
• Your broadband-configured
PC’s Computer Name and Workgroup Name
• Your Subnet Mask
• Your Default Gateway
• Your Primary DNS IP address
Whoever installed your broadband access should have left this information
with you. If not, call your ISP and they will be able to supply you with it.
Static IP Addresses A Static IP address is an IP address permanently assigned
to a computer in a TCP/IP network. Static IP addresses are usually assigned to
networked devices, which are consistently accessed by multiple users, such as
Server PCs, or printers. If you are using the Router to share your cable or DSL
Internet connection, contact your ISP to see if they have assigned your home or
business a Static IP address. You will need that address during the Router’s configuration.
}
Only if applicable
Overview
About Static & Dynamic IP Addresses
Roaming
Page 8
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
3. Connect an RJ-45 (network) cable to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router in either the PC or Uplink port. The PC port is used when con-
necting the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router to a single PC and the Uplink
port is used when connecting to a 10/100 Network. Then, connect the other
end of the Ethernet cable to either a PC or a network device. The Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL Router will then be connected to your 10/100 Network.
4. Connect another RJ-45 (netw ork) cable to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router in the WAN port. The other end of the cable is used to connect the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router to your Cable/DSL modem. Connect to
your Cable/DSL modem at this time.
5. Connect the AC Power Adapter to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router’s Power Socket. Only use the power adapter supplied with the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router. Use of a different adapter may result in
product damage.
6. Verify that the LEDs are functioning. The Power LED should remain on,
while the Diag LED will flash and turn off right away. If the Diag LED
remains on, there is a hardware error. Refer to the Troubleshooting section
for resolution.
The Hardware Installation is complete.
For directions on connecting your printer to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router’s PrintServer, see the EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router
section in this user guide.
109
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Dynamic IP Addresses A dynamic IP address is an IP address that is automati-
cally assigned to a client station (computer, printer, etc.) in a TCP/IP network.
Dynamic IP addresses are typically assigned by a DHCP server on your
Network, which can be a computer on the network or another piece of hardware, such as the Router. A dynamic IP address may change every time your
computer connects to the network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) DHCP automatically assigns IP
addresses to client stations logging onto a TCP/IP network. DHCP eliminates
having to manually assign permanent IP addresses to every device on your network. DHCP typically runs in servers and is also found in netw ork de vices such
as Routers.
1. Locate an optimum location for the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
The best place for your Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is usually at the
center of your wireless network, with line of sight to all of your mobile stations.
2. Insert the Instant WirelessTMNetwork PC Card into the slot. With the
Network PC Card’s 68-pin connector facing the slot in the rear and the
“Network PC Card” label facing up, slide the Network PC Card completely
into the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
NNoottee::
Some ISPs—most notably some cable providers—
configure their networks so that you do not have to enter a
full Internet address into your web browser or e-mail application to reach your home page or receive your e-mail. If
your Internet home page address is something very simple,
such as “www”, rather than “www.linksys.com”, or your e-mail server’s
address is something similar to “e-mail” or “pop3”, rather than
“pop.mail.linksys.com”, you
wwoonn’’tt
be able to properly configure the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router until you determine the actual Internet
addresses of your Web and e-mail connections.
You
mmuusstt
obtain this information prior to connecting the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router to your network. You can obtain this information by contacting your ISP, or turn to the Appendix to learn how to
ping
for an IP
address.
Connecting the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router & Booting Up
Page 9
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
1211
This is the first screen that will appear when you start up the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s web-based utility. You can return to this screen at any
time by clicking the Setup button.
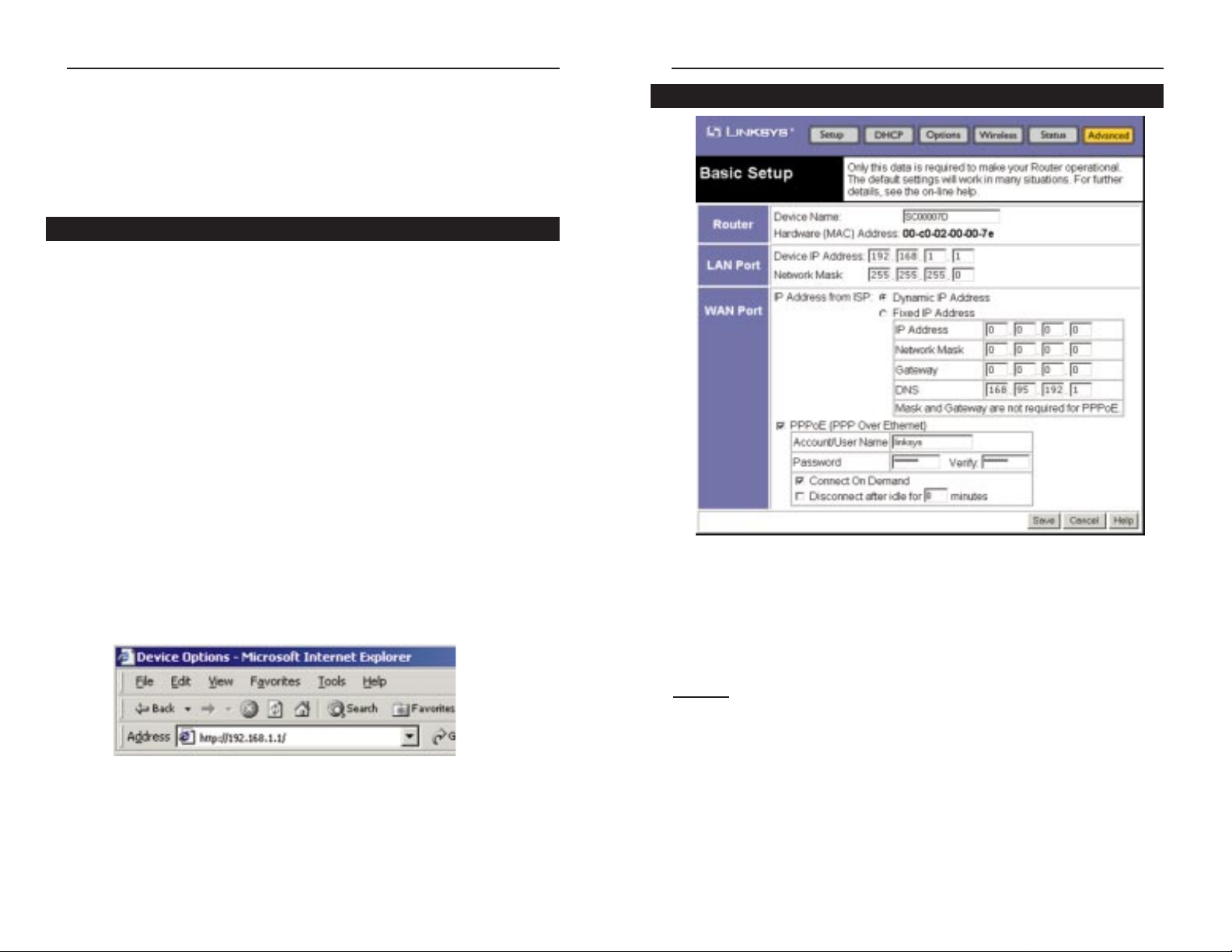
Router
This is general information used to identify the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router.
Device Name. This name identifies the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router to
your ISP. This is also called the "Hostname". Some ISPs require that you use
the "Hostname" they provide. If so, enter the "Hostname" provided by your ISP.
Basic Setup
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
The EtherFast Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s Web-based
Utility
To establish a connection from your PC to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router:
1. After installing the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router to your network, start
your PC. If your PC is already running, restart it.
2. Make sure that the TCP/IP protocol has been installed. See the Installing
the TCP/IP Protocol section in the Appendix if you have any questions on
how to do this.
3. Start your WEB browser.
4. In the Address box, enter "HTTP://" and the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router’s IP Address, as in the following example, which uses the default IP
Address: HTTP://192.168.1.1.
The PC accessing the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router must have its IP
address set within the range applicable for the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router (192.168.1.2 through 192.168.1.51) and be set at the same Subnet
Mask (255.255.255.0).
5. This will then bring up the Basic Setup screen.
Setting Up
Page 10

Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
DNS IP Address. This is the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s Domain
Name System address.
• PPPoE (PPP Over Ethernet)
Only enable this checkbox if your ISP uses PPPoE. If your ISP's data does not
mention PPPoE, do NOT enable this checkbox.
Account/User Name. This is the name of the Inter net account provided by
your ISP.
Password. Enter the password for the ISP account. Re-enter this password in
the V erify field.
Connect On Demand. Normally, this should be Enabled. If disabled, you
must use the Reconnect button on the Status screen to connect to your ISP.
Disconnect after Idle. After a connection if inactive for longer than the
time period put in this field, the connection will be terminated. If set at
zero, the connection will never be terminated.
When you are ready to save any changes you have made, click the Save button. To undo any changes before saving, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
14
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Hardware (MAC) Address. That address which specifically identifies the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router on the WAN port. Some ISPs may require
you to register this address with them.
LAN Port
For most users, the default values for these fields should be satisfactory and
won’t require changing.
• Device IP Address. This is the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s IP
Address in your Network. Use the default value unless that address is already
used by your Network or your Network is using a different IP Address range.
If the IP Address is already in use, change this value to reflect an unused
address. If your Network is using a different IP Address range, change this
value to fit within the range utilized.
• Network Mask. The default value is set for standard, small networks. For
other networks, use the Network Mask for the segment to which the Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL Router is attached, i.e. the same value as the PCs on that segment.
WAN Port
• IP Address from ISP - Dynamic IPAddress. Leave this enabled if your ISP
allocates an IP Address to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router upon connecting to the Internet.
• IP Address from ISP - Fixed IPAddr ess.Select this if using a fixed (Static)
IP Address. If this option is selected, the following data must be entered:
IP Address. If connecting to an ISP, this is the address allocated by the ISP.
If connecting to another Network, this must be a valid address on that
Network.
Network Mask.This must be compatible with the IP address, as above.
Gateway IP Address. If you are conf iguring the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router for another network, this would be the default gateway for the other
network. However, if you are configuring the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router to share Internet access, this is your ISP’s IP Address as provided by
your ISP.
13
Page 11

Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Allocated
This field will show the IP Addresses presently allocated to the other clients on
your Network.
When you are ready to save any changes you have made, click the Save button. To undo any changes, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
1615
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
You can access this screen at any time by clicking the DHCP button.
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Ser ver allocates a valid IP
Address to the DHCP Clients that it serves, when the client device boots. The
DHCP Server also provides the Gateway and DNS addresses to the client.
Operation
The DHCP Server function is enabled by default. Select Disable DHCP Server
to disable this function.
You will want to disable the DHCP Server when your Network is already using
another DHCP Server. You can only use one DHCP Server.
IP Address Range
This range represents the range of IP addresses available in the DHCP pool that
can be assigned to the PCs on your Network.
DHCP Server
Page 12

18
You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Options button.
Password
Once a password is entered, it is required in order to change the device configuration. Passw ords are case sensitive and can be up to eight alphanumeric char-
acters in length.
To create or change a password, enter the password in both the New password
and Verify password fields.
17
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Additional DNS
The fields for secondary and tertiary DNS IP Addresses are optional and
should only be completed if provided by your ISP.
NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation) allows PCs on your Network to share a
single external (Internet) IP Address. This IP Address is supplied by your ISP.
Use the following to determine if you need NAT:
• For Internet access, NAT must be enabled unless all of the PCs on your
Network have valid external (or public) IP Addresses.
• If the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is not being used to provide shared
Internet access, NAT is not normally necessary. With NAT disabled, the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router will act as a static router.
• If NAT is disabled, the Firewall protection provided by the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router is lost and the Advanced Features (Special Applications,
Access Control, Virtual Servers, DMZ, and Routing) are no longer available.
When you are ready to save any changes you have made, click the Save button. To undo any changes before saving, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Device Options
NOTE: When prompted for the password,
leave the “User Name” field blank.
Page 13

2019
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
• SSID (Service Set Identifier). All Wireless devices in your Network must
use the same SSID. Make sure that this field reflects the correct SSID for your
network.
• Channel No: All Wireless devices in your Network must use the same SSID.
Make sure that this field reflects the cor rect channel for your network. Should
you experience any interference, you may need to experiment with different
channels to establish a better connection.
WEP Data Privacy
WEP is Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism based on a 64-bit
or 128-bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11b standard.
Using a 128-bit shared key algorithm will increase network security. However,
you may experience decreased network performance when using a 128-bit
shared key algorithm.
• Off - no data encryption. When WEP is turned off, data will not be encrypt-
ed before being transmitted, compromising security.
• 64 Bit Encryption using this key table. For your wireless Network to utilize
WEP encryption, an encryption key must be entered fields. All wireless
devices on your Network must utilize the same encryption key and all keys
must be set identically.
• Default Key. Select the algorithm key to be used in y our 64-bit WEP-enabled
wireless Network.
• 128 Bit Encryption using this key.For your wireless Netw ork to utilize WEP
encryption, an encryption key must be entered f ields. All wireless devices on
your Network must utilize the same encryption key and all keys must be set
identically.
The WEP keys (1 - 4) are five two-digit numerals in length and can be any
numeric combination. However, these keys must be used identically for each
point on your wireless Network.
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Wireless button.
Any changes made to the Wireless settings must match those of the other wireless devices in your Network.
Configuration
• Regulatory Domain. It is illegal to use this device in any location outside of
the Regulatory Domain.
• Station Name. This is the same as the Device Name that w as set on the Basic
Setup screen.
Wireless
Page 14

22
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Status button.
The Status screen will display current data on your Wireless Access Point
Router. This screen will change if you do not enable PPPoE.
Hardware
• Firmware Version. Displays the current program code installed on the hard-
ware.
• Hardware ID.This is utilized by Linksys to identify this device.
• NAT (Network Address Translation). This will display your current NAT
selection.
Status
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Wireless Stations
• Access Permission.
When Allow everyone access, the default selection, is utilized, no check is
performed on the station’s address before allowing it to use the Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router.
If you chose Only allow access if on this list, then a station must have an
address that appears on the address list.
• Existing Stations. This lists the IP Addresses of those wireless stations in
your Network with access to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
• New Station.To add a new station to the list above, enter its address here and
click the Add button.
When you are ready to save any changes you have made, click the Save button. To undo any changes, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this page, click the Help button to
bring up the Help window for this screen.
21
Page 15

2423
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
The Advanced Options screens gives you the opportunity for further customization of the W ireless AP + Cable/DSL Router. While the previous screens
allow ed you to setup the W ireless AP + Cable/DSL Router to use, the Adv anced
Options screens are optional and should not be modified without consulting
either your Network Administrator or reading this user guide. Help buttons are
provided on each screen. If you make a mistake, return to one of the previous
screens and click the Cancel button.
You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Advanced button and
then clicking the Special Apps button.
This feature is only required if you wish to use Internet applications that require
2-way communication, multiple connections, or combined TCP/UDP connections. Some examples of such applications are Internet Video-conferencing, IP
Telephony, Games Servers, and other special-purpose Servers.
Advanced Options
Special Applications
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
LAN Port
• Physical Address. This is the physical address (Hardware MAC Address) of
the LAN Port to which an IP address has been allocated.
• IP Address. This is the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s IP Address, as
seen by the other devices on your Network.
• Network Mask.This is the Network Mask for the above IP Address.
• DHCP Server. This is the status of the DHCP Server function, as selected on
the DHCP Server screen.
WAN Port
• Physical Address. This is the ph ysical address that identifies the Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router to your ISP and should be used if your ISP requires you
to register this with them.
• IP Address. This is the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s IP Address, as
seen by the other devices outside your Network.
• Network Mask.This is the Network Mask for the above IP Address.
• PPPoE Link Status. This shows the status of the PPPoE link, as specified
on the Basic Setup screen. (If PPPoE has not been enabled, this selection will
not appear.)
• Connection Log. This log will only be enabled when PPPoE (PPP Over
Ethernet) is selected on the Basic Setup Screen and will display your connec-
tion activity. (If PPPoE has not been enabled, this selection will not appear.)
Click the Connect button to connect your PPPoE link.
Click the Disconnect button to disconnect your PPPoE link.
To reload your Connection Log data, click the Clear Log button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
Page 16

You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Advanced button, fol-
lowed by the Access Control button, and then the Groups button.
The Access Control feature allows administrators to restrict Internet access
through the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s by individual PCs on the network. The feature utilizes Packet Filtering to block or discard data packets.
Selected Entry
• Group. By default, this pull-down menu will always be set to Everyone,
which means that all the Access Right for all PCs in the Network will be
restricted uniformly according to the settings under Access Rights (below).
2625
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Access Control: Groups
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
To Add a New Application
Click the Clear Form button and enter the Application’s details in the f ields
provided. (This information is available in your application’s documentation.)
Select either a UDP or TCP protocol from the drop-down box as shown. Click
the Create button when completed. Ignore the drop-do wn menu next to Special
Application.
To Delete an Existing Application
Selected the Application from the drop-down menu next to Selected Entry.
Click the Get Data button to view the information, if it is not brought up automatically, and confirm that this is the correct Application. Then, click the
Delete button.
To Change an Existing Application’s Details
Select the Application from the drop-down menu next to Selected Entry. Click
the Get Data button if the information on that particular Application is not
brought up automatically. Make any necessary changes and click the Update
button when completed.
To List All of the Special Applications
Click the List All button to generate a list of all applications.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
Page 17

When you are ready to sav e any changes you have made, click the Savebutton.
To undo any changes before saving, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
28
To choose another Selected Entry, simply select the Group from the pull-down
menu. Then, click the Get Data button to bring up the information specif ic to
that Selected Entry, if it does not come up automatically.
Access Rights
Changing the option in these fields will affect the group selected under
Selected Entry. Access Rights may be modified as follows:
• No restrictions. No packets are blocked. Use this to create an “Unlimited
Access” Group, or to temporarily remove restrictions from a group.
• Block all Internet Access. Group members cannot access the Inter net at all.
Use this to create the most restrictive group.
• Use Packet Filter Table below. Use this to define intermediate levels of
access. Using the Packet Filter table gi v es y ou fine control over Internet access.
Packet Filter Table
Simply select the items you wish to block. You can choose from the pre-defined
filters in the Applications column or use your own pre-defined filters (as shown
in the Access Control:F ilters section) in the TCP Packet Filters and UDP Packet
Filters fields.
• Applications. Any items checked will be blocked. Users will not be able to
use the application.
• TCP Packet Filters. This lists any TCP filters you hav e defined at the Access
Control:Filters screen. If no filters have been defined, this will appear empty.
Multiple filters can be selected (or deselected) by holding down the Ctrl key
while selecting filters. Any filters selected will not be accessible by members
of this group.
• UDP Packet Filters. This lists any UDP filters you have defined at the
Access Control:Filters screen. If no filters have been defined, this will appear
empty . Multiple filters can be selected (or deselected) by holding down the Ctr l
key while selecting filters. Any filters selected will not be accessible by members of this group.
27
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 18

• Reserve entry in DHCP Table. Check this if you wish to reserve an IP
Address for this PC. This is useful if you have to provide the IP Address for
other programs or users. If this is left unchecked , the Reser ve IP Address field
will not be active.
• Reserved IP Address. When the Reserve entry in DHCP Table box is
checked, this f ield will be active. Enter the reserve address here. This must be
within the range used by the DHCP server.
• Security Group.Use this field to identify the security group for this PC. The
security group selected will be one of the Groups that was set on the Access
Control:Groups screen.
To Add a New Workstation
Click the Clear Formbutton and enter the Workstation details in the fields provided. Click the Create button when completed. Ignore the drop-down menu
next to Existing PCs.
To Delete an Existing Workstation
Selected the Workstation from the drop-down menu next to Existing PCs.
Click the Get Data button to view the information, if it is not brought up automatically, and confirm that this is the correct Workstation. Then, click the
Delete button.
To Change an Existing Workstation’s Details
Select the Workstation from the drop-down menu next to Existing PCs. Click
the Get Data button, which will call up the information on that particular
Workstation if it is not brought up automatically. Make any necessary changes
and click the Update button when completed.
30
You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Advanced button, fol-
lowed by the Access Control button, and then the PCs button.
Selected Entry
• Existing PCs. When this pull-down menu is active, it will show the names of
the PCs currently connected to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
To choose another Selected Entry, simply select the PC from the pull-down
menu. Then, click the Get Data button to bring up the information specif ic to
that Selected Entry, if it is not brought up automatically.
Properties
• W or kstation Name. Use this field to identify the PC within the Network.
• Hardware (MAC) Address. Enter the Hardware Address of the PC into this
field. This is also called the "Physical Address" or "Network Adapter Address".
For information on how to determine your PC’s MAC address, refer to the
“How to Determine Your PC’s MAC Address” section in the Appendix.
29
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Access Control: PCs
Page 19

You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Advanced button, fol-
lowed by the Access Control button, and then the Filters button.
The Access Control:F ilters screen allows you to define packet filters for use on
the Access Control:Groups screen. When you define security groups on the
Access Control:Groups screen, you can select from any filters def ined here,
along with those pre-set filters.
TCP Packets
• Name. Enter a name describing this filter.
• Port No. Enter an integer representing the Port Number for this type of pack-
et. This information can normally be provided by the service provider.
Otherwise, refer to the documentation for the application you are looking to filter, to find the specif ied por t
UDP Packets
• Name. Enter a name describing this filter.
32
To List All of the Workstations
Click the List All button to generate a list of all workstations.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
31
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Access Control: Filters
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 20

You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Advanced button and
then clicking the Virtual Servers button.
The Virtual Servers screen allows you to create virtual servers within your
Network. In this way, you can make various resources accessible via your web
browser and other applications.
The Virtual Servers feature allows access to Servers on your network from the
Internet. Without this feature, such access would be blocked by the Firewall.
All of your Virtual Servers have the IP Address allocated by your ISP. This IP
Address is shown on the Status screen. It is preferable to have your ISP allocate you a Fixed IP Address if you wish to use the Virtual Servers feature.
Otherwise, this Address will change often, making if diff icult to connect to
your Servers. This option should not be used if your ISP provides you with a
Dynamic IP Address.
34
• Port No.Enter an integer representing the Port Number for this type of packet. This information can normally be provided by the service provider.
Otherwise a Network Analyzer or Packet Sniffer can be used to determine the
correct port number.
When you are ready to sav e any changes you have made, click the Savebutton.
To undo any changes before saving, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
33
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Virtual Servers
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 21

You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Advanced button and
then clicking the DMZ button.
The DMZ feature, when enabled, drops firewall protection from a device on
your Network, allow in one computer on your Network to be exposed to the
Internet. This enables unrestricted 2-way communication between the “DMZ”
and other Internet users or servers. Without this feature, such access would be
blocked by the Firewall. Any Internet user who knows the DMZ computer’s IP
Address can connect to the DMZ.
This allows connection to special-purpose servers that require proprietary
client software as well as two-way user connections such as Video-conferencing, which requires both users to run special software.
36
When configuring the Virtual Servers screen, the PCs entered in the "LAN IP
Address" field must be r unning the appropriate Server software. Again, it is
preferable for the "Server" PCs to use a fixed IP Address. If acting as DHCP
clients, their IP Address could change, making this entry invalid.
Only one PC can use each Special Application at any time.
To create a virtual server, select the type of server desired from the list provided. Click the Enable box to set-up the server. Then, type in the LAN IP
Address of the device on your Network being used as the Virtual Server.
When you are ready to sav e any changes you have made, click the Savebutton.
To undo any changes before saving, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
35
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
DMZ
NOTE: Only one PC can be setup to utilize the DMZ feature.
Using the DMZ feature allows unrestricted access and disables
the firewall to the DMZ device, creating a security risk.
You should only use this feature if the Special Applications fea-
ture is insufficient to allow an application to function correctly.
This feature should be turned ON only when necessary and
turned OFF the remainder of the time.
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 22

You can access this screen at any time by clicking the Advanced button and
then clicking the Routing button.
If you have a router already attached to your network and are connecting the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router, you will need to utilize the Routing feature
to prevent conflicts.
Any existing entries are listed. To view and edit the details of an existing entry,
select it from the “Routing Table” drop-down menu and click the Get Data button. After making any changes in the “Properties” fields, click the Update button to save your changes.
Selected Entry
• Routing Table. This pull-down menu will show the Destination IP Addresses
created on this screen.
To add a new entry, click the Clear Form button, enter your data in the
“Properties” f ields and click the Create button to save your new entry.
38
The DMZ computer should have the IP Address allocated by your Router. This
IP Address is shown on the Status screen. It is preferable to hav e your ISP allocate you a Fix ed IP Address if y ou wish to use the DMZ feature. Otherwise, this
Address will change often, making if difficult to make 2-way connections.
When configuring the DMZ screen, the PC entered in the "LAN IP Address"
field must be r unning the appropriate software. Again, it is preferable for the
DMZ PCs to use a fixed IP Address. If acting as DHCP client, its IP Address
could change, making this entry invalid.
When using the DMZ feature, the Special Application feature should not be
used.
To use this feature, check the box next to Enable DMZ feature. Then, type in
the appropriate LAN IP Address for the chosen device in the empty IP Address
fields. Click the Save button to use this feature. To undo any selections before
saving, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
37
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Routing
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
USING DMZ:
Since DMZ enables 2-way communication through the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router, you can utilize the DMZ function for:
(1) Playing games over the Internet
(2) Video-conferencing
(3) IP Telephony
(4) or whenever the software you are trying to run over the Internet
is burdened by the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s natural
firewall.
Page 23

Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
You can access this screen at any time by entering the following IP Address into
your web browser: http://192.168.1.1/MAC_addr.htm
You should see the following screen displayed within your browser:
The MAC address specifically identifies the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router
on the WAN port. Some ISPs may require you to register this address with
them. When necessary , y ou can set the MA C Address from this screen and click
the Save button to set the address. To restore the default address, click the
Retrieve Defaults button. To exit without saving, click the Cancel button.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen. For further help, enter the following IP Address into your web browser: http://192.168.1.1/MAC_hlp.htm
40
Properties
• Destination IP Address. The Destination LAN IP is the Address of the
remote network or host to which you want to assign a static route. Enter the IP
address of the host for which you wish to create a static route here. If you are
building a route to an entire network, be sure that the network portion of the IP
address is set to zero.
• Network Mask. The Network Mask (also known as the Subnet Mask) determines which portion of an IP address is the network portion, and which portion
is the host portion. For class “C” networks, the standard Network Mask is
255.255.255.0
• Gateway IP Address. This IP address should be the IP address of the router
on the Network segment to which this device is attached.
• Interface. Select the appropriate interface - LAN (internal Network) or WAN
(external Network) - from the drop-down menu.
• Metric. This is the number of routers which must be traversed to reach the
remote LAN segment. The default Metric value is 1.
To List All of the Routing Tables
Click the List All button to generate a list of all routing tables.
If you have any questions about anything on this screen, click the Help button
to bring up the Help window for this screen.
39
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
NOTE: Linksys does not provide technical support for the
Routing feature
WAN Port MAC Address
Page 24

1. When you see the Welcome screen, click the Next button to continue. This
will bring up the Select Components screen. “User Manual” and “Print Port
Driver” will be selected by default. If either of these is deselected, the
PrintServer drivers will not be installed completely. Click the Next button
to continue.
2. The next screen will ask you to choose a destination location. A default
installation path will appear but you may click the Browse button to choose
a different location. Then, click the Next button to continue.
42
The EtherFast Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s PrintServ er
Connecting the Power
The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s PrintServer does not have an ON/OFF
power switch. Whenever its AC power adapter is plugged into a power supply,
the PrintServer’s power is on. Make sure that the power adapter is plugged into
the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s Power Port (on the back panel) and that
the power adapter is plugged into an electrical outlet. The Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s Powe r LED should light up g reen.
Follow the directions for Connecting Everything Together and Booting Up in
the “Connecting the EtherFast Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router to Your
Network” section.
Connecting the Printer
1. Connect your printer to the Printer port with your printer cable. Some printers, especially bidirectional models, may require special shielded cabling.
Consult your printer’s user guide for cabling specif ications.
2. Power on your printer.
You are now ready to install the PrintServer software.
To install the PrintServer drivers, put the Setup CD in your CD-ROM drive. A
window will come up asking you to make sure that your printer and the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router are both connected and powered on.
Verify that this has been done and click the OK button. This will begin the
installation process.
41
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Installing the PrintServer’s Drivers
Connecting the PrintServer to Your Network
Page 25

Adding a printer under Windows 95, 98, or Millennium is done in two parts.
First, you’ll identify the printer for the PrintServer and then the printer will be
configured. In the example given below, our printer may vary from yours and
it is assumed that no printer has yet been added. Screens, therefore, will vary
depending on the printer you add and if a printer was previously added.
1. After you finish installing your PrintServer drivers, the following screen
will appear, asking for you to verify that the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router and the printer that connects to it are both connected properly and
powered on. Make sure you have done this and click the OK button.
2. The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router will now scan the printer port for
your printer. As no printer has previously been added, the Print Port Setup
screen will show the printer port (Port 1) OFF-Line. This port should be
selected. If it is not, click on it to select it. Then, click the Add button to
begin adding the printer.
44
3. You will now be asked to select a Program Folder from which you can run
the PrintServer software. The PrintServer Program Folder will be created
after the PrintServer software has been installed. If you wish to keep the
default folder, click the Next button to continue. Otherwise, select or type
in a Program
Folder and
click the Next
button to continue.
4. Driver installation is now ready to begin. The “Run Print Port Setup now”
selection will
be selected by
default. This
will assign
your printer to
the Wireless
A P + Cable/DSL
Router’s printer port. Click
the Finish
button to Add
your Printer.
43
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Adding a Printer under Windows 95, 98, and Millennium
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
NOTE: If you are using Windows NT or 2000, you
must NOT select “Run Print Port Setup now”. Make
sure the box next to this selection is NOT selected
before clicking the Finish button.
Page 26

For the next part, you will need to configure your printer to function through
the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s
Printer port.
1. Go to “Add Printer” by clicking the
Start button, selecting Settings, and
clicking Printers.
Then, to begin the configuration
process, click the Next button.
2. The next screen will ask how your printer is attached to your computer.
Since your printer is being connected to a network, rather than a single
computer, you will still want to select Local Printer. Do not select
Network Printer, even though your printer is being connected to a
Network, since it is being connected directly to the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router. Make sure Local Printer is selected, as in the screen
below, and click the Next button to continue.
46
3. Is the printer connected to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s printer
port? Verify that it is connect and powered on and click the Yes button to
continue.
4. When you reach the “Add Printer Wizard” screen, you must click the
Cancel button. The remainder of the process for adding a printer under
Windows 95, 98, and Millennium will be performed through Windows.
45
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 27

5. The “Print Port Configuration” screen will now assign the printer drivers
that you installed to
the printer connected to the Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL
Router. Click the
Browse Device
button to select the
driver.
6. The driver for the device that you
selected in step 4 will automatically
appear with the device number and IP
Address, as shown in this screen as
“SC00007D 192.168.0.1”. (Your port
number may be different.) Make sure
the device is selected and click the
OK button to continue.
7. The “Print Port
Configuration”
screen will now
appear with the
printer selected.
Click the OK button to continue.
48
3. You will now be asked to select your printer’s manufacturer and model
name in order to install the appropriate driver.
If you have a driver disk that came with your printer, click the Have Disk
button and select the driver’s correct location.
Once the correct printer has been selected or the driver’s location has been
specified on your driver disk, click the Next button.
4. The next screen shows all of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s available ports. The port you will want to configure is the printer port, shown in
this screen as “SC00007D P1 Shared Port”. (Your port number may be different.) Make sure this port is selected and click the Configure Port button
to continue.
47
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 28

9. Your printer has now been added. To verify that it is functioning properly
through the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router, you will want to print a test
page. Click the button beside “Yes (recommended)” to print the test page
and then click the Finish button to complete adding your printer.
If you opt to print a test page, a window will appear asking if the test page
printed correctly. If it did, click the Yes button to close the window . If it did not
print correctly, click the No button and you will be given Windows
Troubleshooting for your printer.
50
8. The next screen will ask for your printer name. For best performance, make
sure your printer name is less than 31 characters long. Enter this name in
the blank field under “Printer Name”. Then, click the Next button to continue.
Windows 95 will automatically use this printer as the default printer.
Windows 98 and Millennium will ask if you want to use this printer as the
default printer. Make the appropriate selection before clicking the Ne xtbutton.
49
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 29

3. The next screen shows all of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s available ports. The port you will want to configure is the printer port, shown in
this screen as “LPT1:SC00007D Shared Port”. (Your port number may be
different.) Make sure this port is selected and click the Configure Portbutton to continue.
4. The “Print Port Configuration” screen will now assign the printer drivers
that you installed to the printer connected to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router. Click the OK button to continue.
52
When adding a printer under Windows NT, make sure that the final window in
the Installing the PrintServer’s Drivers section does NOT have the “Run
Print Port Setup now” box checked. Selecting this box will lead to an error in
the installation process. Make sure that this box is NOT selected before con-
tinuing to this section.
1. Go to “Add Printer” by clicking the
Start button, selecting Settings, and
clicking Printers.
2. The next screen will ask you how you want to manage your printer.
Windo ws NT will not manage the printer as through a Netw ork printer server so you will need to click the button next to the My Computer selection.
Then, click the Next button to continue.
51
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Adding a Printer under Windows NT
Page 30

Once the correct printer has been selected or the driver’s location has been
specified on your driver disk, click the Next button.
7. At this stage, Windows NT will notify you that a driver has already been
installed for this printer. This is due to an idiosyncrasy in Windows NT.
Though you have not already installed printer drivers, you will want to
select Keep Existing Driver (recommended). DO NOT choose Replace
existing driver. Click the Next button to continue.
54
5. Now that the port has been configured, click the Next button to continue.
6. The “Add Printer Wizard” will ask you to select the Printer’s Manufacturer
and Model Name in order to select the appropriate driver.
If you have a driver disk that came with your printer, click the Have Disk
button and select the driver’s correct location.
53
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 31

11. Your printer has now been added. To verify that it is functioning properly
through the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router, you will want to print a test
page. Click the button beside “Yes (recommended)” to print the test page
and then click the Finish button to complete adding your printer.
If you opt to print a test page, a window will appear asking if the test page printed correctly . If it did, click the Yes button to close the window. If it did not print
correctly, click the No button and you will be given Windows Troubleshooting
for your printer.
56
9. The Add Printer Wizard will now ask you to enter a “Printer Name”. For
best performance, make sure your printer name is less than 31 characters
long. Enter this name in the blank field under “Printer Name”. Then, click
the Next button to continue.
10. Will this printer be shared over the network? If so, select Shared on the following screen and enter a “Shared Name” for the printer. Then, select the
operating systems under which this printer will be shared. In the example
below, the printer is being shared. If you choose not to share this over the
network, select Not shared. Then, click the Next button to continue.
55
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 32

3. The next screen shows all of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s available ports. The port you will want to conf igure is the printer por t, shown in
this screen as “SC0D8B45_P1 Shared Port”. (Your port number may be different.)Make sure this port is selected and click the Next button to continue.
4. At this stage, Windows 2000 will notify you that a driver has already been
installed for this printer. This is due to an idiosyncrasy in Windows 2000.
Though you hav e not already installed printer dri vers, y ou will w ant to select
Keep Existing Driver (recommended). DO NOT choose Replace existing
driver. Click the Next button to continue.
58
When adding a printer under Windows 2000, make sure that the final window
in the Installing the PrintServer’s Drivers section does NOT have the “Run
Print Port Setup now” box checked. Selecting this box will lead to an error in
the installation process. Make sure that this box is NOT selected before con-
tinuing to this section.
1. Go to “Add Printer” by clicking the Start button, selecting Settings, and
clicking Printers.
Then, to begin the configuration process, click the Next button.
2. The next screen will ask how your printer is attached to your computer.
Since your printer is being connected to a network, rather than a single
computer, you will still want to select Local Printer. Do not select
Network Printer, even though your printer is being connected to a
Network, since it is being connected directly to the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router. Nor should you select Automatically Detect and Install;
this is only done when the printer is connected to the PC. Make sure Local
Printer is selected, as in the screen below, and click the Next button to con-
tinue.
57
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Adding a Printer under Windows 2000
Page 33

7. Your printer has now been added. To print the test page, click the Finish
button. This will complete adding your printer.
If you opt to print a test page, a window will appear asking if the test page printed correctly . If it did, click the OK button to close the window . If it did not print
correctly, click the Troubleshoot button and you will be given Windows
Troubleshooting for your printer.
60
5. The Add Printer Wizard will now ask you to enter a “Printer Name”. For
best performance, make sure your printer name is less than 31 characters
long. Enter this name in the blank field under “Printer Name”. Then, click
the Next button to continue.
6. To verify that it is functioning properly through the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router, you will want to print a test page. Click the button
beside Yes to print the text page and then click the Finish button to com-
plete adding your printer.
59
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 34

6261
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
• Make sure that the same values are in the Basic Setup screen of the Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL Router web-based utility.
4. When I enter a URL or IP address,I get a time out error.
• Make sure that the other PCs work. If they do, ensure that your workstations IP settings are correct (IP address, Network Mask, Gateway and
DNS).
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, check the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router to make sure that it is connected and
ON. Once this is the case, check its settings. (If you cannot connect to the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router, check the LAN and power connections.)
• If the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is configured correctly, check
your Internet connection (the Cable/DSL modem) to see that it is working correctly.
5. I can’t obtain an IP address from my cable or DSL modem.
• Make sure that all of your cabling is properly connected and that all of
the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s LEDs are correctly illuminated.
• Power down your cable or DSL modem for a few seconds. Tur n it back
on. After the modem goes through its self-test, check to see that y ou now
have an IP address.
• Make sure that your cable or DSL modem is DHCP-capable.
• You may have to enter the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router or Device
Name in the Basic Setup page of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s
web-based utility.
• Your ISP may require Mac Addresses. Check with your ISP. This address
can be obtained in the Basic Setup screen of the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s Web-based Utility.
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
This section provides possible solutions to problems regarding the installation and
operation of the Cable/DSL Router. Read the description below to solve your problems. If you can’ t find an answer here, check the Frequentl y Ask ed Questions section
or the Linksys website at www.linksys.com.
1. I can’t connect to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
• Verify that the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is properly installed, LAN
connections are OK, and it is powered ON.
• Make sure that your PC and the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router are on the
same network segment. If y ou are not sure, initiate the DHCP function and let
the PC get the IP address automatically.
• Make sure that your PC is using an IP address within the default range of
192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254 and thus compatible with the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s default IP Address of 192.168.1.1.
• The Network Mask should be set to 255.255.255.0 to match the Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router. In the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router , you can check
these settings by going to the Basic Setup screen.
2. The Diag LED stays lit when it shouldn’t.
• The Diag LED lights up when the device is first powered up. Meantime, the
system will boot up itself and check for proper operation. After finishing the
checking procedure, the LED turns off to show the system is working f ine. If
the LED remains lit after this time, the device is not working properl y. First, try
restoring the W ireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’to it’s default settings by holding down the Reset button for more than five seconds. If the LED remains on
after restoring the default settings, try to re-flash the f ir mware by assigning a
static IP address to the computer, then upgrade the firmware again. If that doesn’t help, contact y our dealer for further information.
3. I can’t browse through the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
• Make sure that both ends of the network cable and power adapter are
properly connected and that the status LEDs on the front panel are functioning properly.
• If using Windows 95 or 98, check the TCP/IP setup on the client side. Run
"winipcfg" by clicking on the Startbutton, then selecting Run. The PC should
have an IP address of 192.168.1.xxx ("xxx" is from 2 to 254.) Network Mask
is 255.255.255.0, the default gateway IP should be the Router’s IP Address.
Page 35

6463
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Does the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router support any operating system other than
Windows 95, 98, Millennium, NT, or 2000? The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router’s Web Utility is configured via the Internet web browser on your
Linux system. The PrintServer, though, is conf igured through Windows and
will not function under Linux. Linksys does not, at this time, provide technical support for setup, conf iguration or troubleshooting of any non-Windows
operating systems.
Does the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Routersupport ICQ send file? Yes, with the fol-
lowing fix: ICQ menu-> preference -> connections tab-> check "I am behind
a firewall or proxy", and set the firewall time-out to 80 seconds in firewall
setting. The Internet user can then send a file to a user behind the Wireless AP
+ Cable/DSL Router.
I setup an Unreal Tournament Server, but others on the LAN cannot join. What do I
need to do? If you have a dedicated Unreal Tournament server running, you
need to create a static IP for each of the LAN computers and forward ports
7777, 7778, 7779, 7780, 7781, and 27900 to the IP address of the server. If
you want to use the UT Server Admin, forward another port (8080 usually
works well), then in the [UWeb.WebServer] section of the server.ini f ile, set
the ListenPort to 8080 (to match the mapped port above) and ServerName to
the IP assigned to the Router from your ISP.
How do I get
Half-Life: Team Fortress
to Work with the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router? The def ault client port for Half-Life is 27005. The computers on
your LAN need to have "+clientport 2700x" to the HL shortcut command
line; the x would be 6, 7, 8, and on up. This lets multiple computers connect
to the same server. One problem: version 1.0.1.6 won't let multiple comput-
ers with the same CD key connect at the same time, even if on the same LAN
(not a problem with 1.0.1.3). As far as hosting games, the HL server does not
need to be in the DMZ. Just forward port 27015 or 27016 to the local IP of
the server computer. There remains, however, a problem with people being
booted after a few minutes with an "illegible server message."
Can multiple gamers on the LAN get on one game server and play simultaneously
with just one public IP address? It depends on which network game or what
kind of game server you are using. For e xample, Unreal T ournament supports
multi-login with one public IP.
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Can I use firmware for other routers with my Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router? No.
If you attempt to use other router's firmware, you could damage your router.
Only use firmware specifically written for the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router as posted on the Linksys web site: www.linksys.com.
What is the maximum number of IP addresses and users supported by the Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL Router? The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router supports up to
253 IP addresses and users.
Where is the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router installed on the network? In a typi-
cal environment, the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is installed between
the Cable/DSL Modem and the LAN. Plug the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router into the Cable/DSL Modem's Ethernet port.
Does the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router support IPX or AppleTalk? No. TCP/IP
is the only protocol standard for the Internet and has become the global standard for communications. IPX, a NetWare communications protocol used
only to route messages from one node to another, and AppleTalk, a communications protocol used on Apple and Macintosh networks, can be used from
LAN to LAN connections, but those protocols cannot connect from WAN to
LAN.
Does the WAN connection of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router support 100Mb
Ethernet? Because of the speed limitations of broadband Internet connections,
the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s current hardware design supports
10Mb Ethernet on its WAN port. It does, of course, support 100Mbps over in
the auto-sensing Fast Ethernet 10/100 switch on the LAN side of the Wireless
AP + Cable/DSL Router.
What is Network Address Translation and what is it used for? Network Address
Translation (N AT) translates multiple IP addresses on the private LAN to one
public address that is sent out to the Internet. This adds a level of security
since the address of a PC connected to the private LAN is never transmitted
on the Internet. Furthermore, NAT allows the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router to be used with low cost Internet accounts, such as cable or DSL
modems, where only one TCP/IP address is provided by the ISP. The user ma y
have many private addresses behind this single address provided by the ISP.
Frequently Asked Questions
Page 36

What is DMZ? Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) allows one IP Address (computer) to
be exposed to the Internet. Some applications require multiple TCP/IP ports
to be open. It is recommended that you set your computer with a static IP if
you want to use DMZ.
If DMZ is used, does the exposed user share the public IP with the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router? No.
Does the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router pass PPTP packets or actively route
PPTP sessions? The Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router allows PPTP packets
to pass through.
Is the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router cross-platform compatible? Any platform
that supports Ethernet and TCP/IP is compatible with the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router.
Will the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router allow me to use my own public IPs and
Domain, or do I have to use the IPs provided by the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router? The router mode allows for customization of your public IPs and
Domain.
Does the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router replace a modem? Is there a cable or
DSL modem in the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router? No, this version of the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router must work in conjunction with a cable or
DSL modem.
Which modems are compatible with the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router? The
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router is compatible with virtually any cable or
DSL modem that supports Ethernet.
What are the advanced features of the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router? The
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s advanced features include Filters,
Forwarding, Dynamic Routing, Static Routing, and DMZ host.
Does Linksys provided syslog support? No, Linksys does not currently provide
syslog support.
How can I check whether I have static or DHCP IP Addresses? Consult your ISP
to confir m the infor mation.
66
How can I receive uncorrupted FTP downloads? If you are experiencing cor-
rupted f iles when you download a file with your FTP client, try using another FTP program.
Web page hangs,corrupt downloads, or nothing but junk characters are being dis-
played on the screen. What do I need to do? Force your NIC to 10Mbps or half
duplex mode, and turn off the "Auto-negotiate" feature of your NIC as a temporary measure. (Please look at the Network Control Panel, in your Ethernet
Adapter's Advanced Properties tab.). Check our website at www.linksys.com
for more information.
If all else fails in the installation, what can I do? Reset the Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router by holding down the reset button for at least three seconds
and reset your cable or DSL modem by powering the unit off and then on.
Obtain and flash the latest firmware release that is readily available on
Linksys website, www.linksys.com.
How can I find upgrades to the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s firmware? All
Linksys firmware upgrades are posted on the Linksys website at
www.linksys.com, where they can downloaded for free. The Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router’s firmware can be upgraded with TFTP programs.
Will the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router function in a Macintosh environment?
Yes, but the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router’s web-based utility is accessible only through Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator, versions 4.0 or
higher for Macintosh. (Linksys does not provide technical support for the
Macintosh platform.)
With which type of firewall is the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router equipped? The
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router uses NAT and TCP/IP port inspections.
Does the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router do stateful packet inspection? No
I am not able to get the web configuration screen for the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router. What can I do? You may have to remove the proxy settings on your
Internet browser, e.g., Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer. You may also
need to remove any Firewall software you may be running or remove the dialup settings on your browser. Check with your browser documentation.
65
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 37

To achieve true seamless connectivity, the wireless LAN must incorporate a
number of different functions. Each node and Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router, for example, must always acknowledge receipt of each message. Each
node must maintain contact with the wireless network even when not actually
transmitting data. Achieving these functions simultaneously requires a dynamic RF networking technology that links Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Routers and
nodes. In such a system, the user’s end node under takes a search for the best
possible access to the system. First, it evaluates such factors as signal strength
and quality, as well as the message load currently being carried by each
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router and the distance of each Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router to the wired backbone. Based on that information, the node
next selects the right W ireless AP + Cab le/DSL Router and registers its address.
Communications between end node and host computer can then be transmitted
up and down the backbone.
As the user moves on, the end nodes RF transmitter regularly checks the system to determine whether it is in touch with the original Wireless AP +
Cable/DSL Router or whether it should seek a new one. When a node no longer
receives acknowledgment from its original Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router,
it undertakes a new search. Upon finding a new Wireless AP + Cable/DSL
Router, it then re-registers, and the communication process continues.
What is BSS ID? A specific Ad hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS).
Computers in a BSS must be configured with the same BSS ID.
What is ESS ID? An Infrastr ucture configuration could also support roaming
capability for mobile workers. More than one BSS can be configured as an
Extended Service Set (ESS). Users within an ESS could roam freely between
BSSs while served as a continuous connection to the network wireless stations
and W ireless AP + Cable/DSL Routers within an ESS must be configured with
the same ESS ID and the same radio channel.
What is ISM band? The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set
aside bandwidth for unlicensed use in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific and
Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being
made available worldwide. This presents a truly revolutionary opportunity to
place convenient high-speed wireless capabilities in the hands of users around
the globe.
What is Spread Spectrum? Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio
frequency technique developed by the military for use in reliable, secure, mission-critical communications systems. It is designed to trade off bandwidth
68
How do I get mIRC to work with the Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router? Set port for-
warding to 113 for the computer on which you are using mIRC.
Can I run an application from a remote computer over the wireless network? This
will depend on whether or not the application is designed to be used over a network. Consult the application's user guide to determine if it supports operation
over a network.
Can I play computer games with other members of the cordless network? Yes, as
long as the game supports multiple players over a LAN (local area network).
Refer to the game's user guide for more information.
What is the IEEE 802.11b standard? The IEEE 802.11b Wireless LAN standards
subcommittee, which is formulating a standard for the industry. The objective
is to enable wireless LAN hardware from dif ferent manufacturers to communicate.
What IEEE 802.11 features are supported? The Wireless AP + Cab le/DSL Router
supports the following IEEE 802.11 functions:
• CSMA/CA plus Acknowledge protocol
• Multi-Channel Roaming
• Automatic Rate Selection
• RTS/CTS feature
• Fragmentation
• Power Management
What is Ad-hoc? An Ad-hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with
a WLAN adapter , connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad-hoc wireless
LAN is applicable at a departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operation.
What is Infrastructure? An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an
Infrastructure conf iguration. Infrastr ucture is applicable to enterprise scale for
wireless access to central database, or wireless application for mobile workers.
What is Roaming? Roaming is the ability of a portable computer user to communicate continuously while mo ving freel y throughout an area greater than that
covered by a single Wireless Network Access Point. Before using the roaming
function, the PC must make sure that it is the same channel number with the
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router of dedicated coverage area.
67
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 38

Appendix
Virtually all Internet addresses are configured with words or characters (i.e.,
www.linksys.com, www.yahoo.com, etc.) In actuality, however, these Internet
addresses are assigned to IP addresses, which are the true addresses on the
Internet.
IP and web addresses, however, can sometimes be long and hard to remember.
Because of this, certain ISPs will shorten their server addresses to single words
or codes on their users’ web browser or e-mail configurations. If your ISP’s Email and Web server addresses are configured with single words (“www”, “email”, “home”, “pop3”, etc.) rather than whole Internet Addresses or IP
Addresses, the Router may have problems sending or receiving mail and
accessing the Internet. This happens because the Router has not been configured by your ISP to accept their abbreviated server addresses.
The solution is to determine the true web addresses behind your ISPs code
words. You can determine the IP and web addresses of your ISP’s servers by
“pinging” them.
Step One: Pinging for an IP Address
The first step to deter mining your ISP’s web and e-mail server address is to
ping its IP Address.
1. Power on the computer and the cable or DSL modem, and restore the
network configuration set by your ISP if you have since changed it.
2. Click Start, then Run, and type "command". This will bring up the DOS
Window.
70
efficiency for reliability, integrity, and security. In other words, more bandwidth is consumed than in the case of narrowband transmission, but the trade
off produces a signal that is, in effect, louder and thus easier to detect, provided that the receiver knows the parameters of the spread-spectrum signal being
broadcast. If a receiver is not tuned to the right frequency, a spread-spectr um
signal looks like background noise. There are two main alternatives, Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum
(FHSS).
What is DSSS? What is FHSS? And what are their differences? Frequency-hopping spread-spectrum (FHSS) uses a narrowband carrier that changes frequency in a pattern that is known to both transmitter and receiver. Properly synchronized, the net effect is to maintain a single logical channel. To an unintended receiver, FHSS appears to be short-duration impulse noise. Directsequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) generates a redundant bit pattern for each
bit to be transmitted. This bit pattern is called a chip (or chipping code). The
longer the chip, the greater the probability that the original data can be recovered. Even if one or more bits in the chip are damaged during transmission, statistical techniques embedded in the radio can recover the original data without
-the need for retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears as low
power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband receivers.
Would the information be intercepted while transmitting on air? WLAN features
two-fold protection in security. On the hardware side, as with Direct Sequence
Spread Spectrum technology, it has the inherent security feature of scrambling.
On the software side, WLAN series offer the encryption function (WEP) to
enhance security and Access Control. Users can set it up depending upon their
needs.
What is WEP? WEP is Wired Equivalent Privacy; a data privacy mechanism
based on a 40 bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
69
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
How to Ping Your ISP’s E-mail & Web Addresses
NOTE: If you don’t have your ISP’s web and email IP Addresses, you must either get them from
your ISP or follow these steps prior to connecting
the Cable/DSL Router to your network.
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 39

7271
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
1. At the DOS command prompt, type “ping -a 24.53.32.4”, where
24.53.32.4 is the IP address you just pinged. Information such as the following data will be displayed.
(Please note that the screen displayed below is only an example and may
appear differently on your system.)
C:\>ping -a 24.53.32.4
Pinging mail.msnv3.occa.home.com [24.53.32.4] with 32
bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
2. Write down the web address returned by the ping command. (In the
example above: mail.msnv3.occa.home.com.) This web address is the web
address assigned to the IP address you just pinged. While the IP address of
“mail” could conceivably change, it is likely that this web address will not.
3. Replace your ISP’s abbreviated server address with this extended web
address in the corresponding Internet application (web browser, e-mail
application, etc.).
Once you have replaced the brief server address with the true ser ver address,
the Router should have no problem accessing the Internet through that Internet
application.
Follo w these instructions to install the TCP/IP Protocol on one of your PCs only
after a network card has been successfully installed inside the PC. These
instructions are for Windows 95, 98, and Millennium. For TCP/IP setup under
Windows NT or 2000, please refer to your Windows manual.
Installing the TCP/IP Protocol
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
3. At the DOS command prompt, type "ping mail" (assuming that the loca-
tion for which you’re trying to find an IP address is configured as “mail”).
Press Enter. Information such as the following data, taken from a ping of
Microsoft Network’s e-mail server, will be displayed.
(Please note that the screen displayed below is only an example and may
appear differently on your system.)
C:\>ping mail
Pinging mail [24.53.32.4] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
4. Write down the IP address returned by the ping command. (In the
example above: 24.53.32.4.) This IP address is the actual IP address of the
server “mail”, or any other word or value you have pinged.
Step Two: Pinging for a Web Address
While the IP address returned above would work as your e-mail server address,
it may not be permanent. IP Addresses change all the time. Web addresses,
however, usually don’t. Because of this, you’re likely to have less problems by
configuring your system with web addresses rather than IP addresses. Follow
the instructions below to find the web address assigned to the IP address you
just pinged.
Page 40

7473
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
7. After a few seconds you will be brought back to the main Network window.
The TCP/IP Protocol should now be listed.
8. Click the OK button. Windows may ask for original Windows installation
files. Supply them as needed (i.e.: D:\win98, D:\win95,
c:\windows\options\cabs.)
9. Windows will ask you to restart the PC. Click the Yes button to restart.
The TCP/IPInstallation is complete.
In Windows 95, 98, and Millennium, you can use the Winipcfg program to
determine the MAC Address:
1. Open the "Run" dialog by clicking the Start button and selecting Run.
2. Type in “winipcfg” and click the OK button.
3. In Winipcfg, select your network adapter from the drop-down list. The hardware address will be shown on screen.
In Windows NT or 2000, you can use the cmd program to determine the MAC
Address:
1. Open the "Run" dialog by clicking the Start button and selecting Run.
2. Type in “cmd” and click the OK button.
3. In the cmd window, type “ipconf ig /all”. Your MAC Address will be displayed as the “Physical Address”.
How to Determine Your PC’s MAC Address
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
1. Click the Start button. Choose Settings, then Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon. Your Network window should pop up.
Select the Configuration tab.
3. Click the Add button.
4. Double-click Protocol.
5. Highlight Microsoft under the list of manufactures.
6. Find and double-click TCP/IP in the list to the right (below).
Page 41

7675
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
• Straight-Through Cabling
•Cross-Over Cabling
Crimping Your Own Network Cables
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Twisted-Pair Cabling
There are different grades, or categories, of twisted-pair cabling. Category 5 is
the most reliable and is highly recommended. Category 3 is a good second
choice. Straight-through cables are used for connecting computers to a hub.
Crossover cables are used for connecting a hub to another hub (there is an
exception: some hubs have a built-in uplink port that is crossed internally,
which allows y ou to link or connect hubs together with a straight-through cable
instead).
You can buy pre-made Category 5
cabling, or cut and crimp your own.
Category 5 cables can be purchased or
crimped as either straight-through or
crossover. Inside a Category 5 cable are
8 thin, color-coded wires inside that run
from one end of the cable to the other.
All 8 wires are used. In a straightthrough cable, wires 1, 2, 3, and 6 at one
end of the cable are also wires 1, 2, 3,
and 6 at the other end. In a crossover
cable, the order of the wires change from
one end to the other: wire 1 becomes 3,
and 2 becomes 6. See the diagrams on
the next page for more detailed informa-
tion on straight-through
and crossover cabling.
To determine which wire is wire number 1, hold the cable so that the end of the
plastic RJ-45 tip (the part that goes into a wall jack first) is facing away from
you. Face the clip down so that the copper side faces up (the springy clip will
now be parallel to the floor).When looking do wn on the copper side, wire 1 will
be on the far left.
Page 42

DNS - The domain name system (DNS) is the way that Internet domain name
are located and translated into Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. A domain name
is a meaningful and easy-to-remember "handle" for an Internet address.
DSSS - Also known as “Direct Sequence Spred Spectrum”, this is a variety of
radio transmission methods that continuously change frequencies or signal patterns. Direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS), which is used in CDMA, multiplies the data bits by a very fast pseudo-random bit pattern (PN sequence) that
"spreads" the data into a large coded stream that takes the full bandwidth of the
channel
Dynamic IP Address - An IP address that is automatically assigned to a client
station in a TCP/IP network, typically by a DHCP server. Network devices that
serve multiple users, such as servers and printers, are usually assigned static IP
addresses.
ESS - More than one BSS in a network.
FHSS - Also known as “Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum”. Frequency
hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) continuously changes the center frequency of
a conventional carrier several times per second according to a pseudo-random
set of channels, while chirp spread spectrum changes the carrier frequency.
Because a fixed frequency is not used, illegal monitoring of spread spectrum
signals is extremely difficult, if not downright impossible depending on the
particular method.
Firewall - A firewall is a set of related programs, located at a network gateway
server, that protects the resources of a netw ork from users from other networks.
(The term also implies the security policy that is used with the programs.) An
enterprise with an intranet that allows its workers access to the wider Internet
installs a firewall to prevent outsiders from accessing its own private data
resources and for controlling what outside resources to which its own users
have access.
Basically, a firewall, working closely with a router program, examines each
network packet to determine whether to forward it toward its destination.
Firmware - Programming that is inserted into programmable read-only memory (programmable read-only memory), thus becoming a permanent part of a
computing device.
78
Glossary
Ad-hoc Network - An ad-hoc network is a wireless network or other small network in which some of the network devices are part of the network only for the
duration of a communications session while in some close proximity to the rest
of the network.
BSS (Basic Service Set) - A group of Instant WirelessTMNetwork PC Card
users and a Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router.
Default Gateway - The router used to forward all traffic that is not addressed
to a station within the local subnet.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - Aprotocol that lets network
administrators manage centrally and automate the assignment of Internet
Protocol (IP) addresses in an organization's network. Using the Internet's set of
protocol (TCP/IP), each machine that can connect to the Internet needs a
unique IP address. When an organization sets up its computer users with a connection to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each machine.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer and,
if computers move to another location in another part of the network, a new IP
address must be entered. DHCP lets a network administrator supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point and automatically sends a new IP
address when a computer is plugged into a different place in the network.
DHCP uses the concept of a "lease" or amount of time that a given IP address
will be valid for a computer. The lease time can vary depending on how long a
user is likely to require the Internet connection at a particular location. It's especially useful in education and other environments where users change frequently. Using very short leases, DHCP can dynamically reconfigure networks
in which there are more computers than there are available IP addresses.
DHCP supports static addresses for computers containing Web servers that
need a permanent IP address.
DMZ - A DMZ (demilitarized zone) is a computer host or small network
inserted as a "neutral zone" between a company's private network and the outside public network. It prevents outside users from getting direct access to a
server that has company data.
77
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 43

LAN - A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and associated
devices that share a common communications line and typically share the
resources of a single processor or server within a small geographic area (for
example, within an office building).
MAC Address - The MAC (Media Access Control) address is your computer's
unique hardware number.
mIRC - mIRC runs under Windows and provides a graphical interface for logging onto IRC servers and listing, joining and leaving channels.
NAT - NAT (Network Address Translation) is the translation of an Internet
Protocol address (IP address) used within one network to a different IP address
known within another network. One network is designated the inside network
and the other is the outside.
Network Mask - also known as the “Subnet Mask”.
Packet Filtering - Discarding unwanted network traff ic based on its originat-
ing address or range of addresses or its type (e-mail, file transfer, etc.).
PCMCIA - The PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Card International
Association) is an industry group organized in 1989 to promote standards for a
credit card-size memory or I/O device that would fit into a personal computer,
usually a notebook or laptop computer.
Ping - (Packet INternet Groper) An Internet utility used to determine whether
a particular IP address is online. It is used to test and debug a network by sending out a packet and waiting for a response.
PPPoE(Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) - A method used mostl y b y DSL
providers for connecting personal computers to a broadband modem for
Internet access. It is similar to how a dial-up connection works but at higher
speeds and quicker access.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) - A protocol (set of communication
rules) that allows corporations to extend their own corporate network through
private "tunnels" over the public Internet. Effectively, a corporation uses a
wide-area network as a single large local area network. A company no longer
needs to lease its own lines for wide-area communication but can securely use
the public networks. This kind of interconnection is known as a virtual private
network.
80
IEEE - The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The IEEE
describes itself as "the world's largest technical professional society -- promoting the development and application of electrotechnology and allied sciences
for the benefit of humanity, the advancement of the profession, and the wellbeing of our members."
The IEEE fosters the development of standards that often become national and
international standards. The organization publishes a number of journals, has
many local chapters, and several large societies in special areas, such as the
IEEE Computer Society.
Infrastructure- An infrastructure network is a wireless netw ork or other small
network in which the wireless network devices are made a part of the network
through the Access Point which connects them to the rest of the network.
IP Address - In the most widely installed level of the Internet Protocol
(Internet Protocol) today, an IP address is a 32-binary digit number that identifies each sender or receiver of information that is sent in packet across the
Internet. When you request an HTML page or send e-mail, the Internet
Protocol part of TCP/IP includes your IP address in the message (actually, in
each of the packets if more than one is required) and sends it to the IP address
that is obtained by looking up the domain name in the Uniform Resource
Locator you requested or in the e-mail address you're sending a note to. At the
other end, the recipient can see the IP address of the Web page requestor or the
e-mail sender and can respond by sending another message using the IP address
it received.
IPCONIFG - A utility that provides for querying, defining and managing IP
addresses within a network. A commonly used utility, under Windows NT and
2000, for configuring networks with static IP addresses.
IPSec - IPSec (Inter net Protocol Security) is a developing standard for security at the network or packet processing layer of network communication. A big
advantage of IPSec is that security arrangements can be handled without
requiring changes to individual user computers.
ISP - An ISP (Internet service provider) is a compan y that provides individuals
and companies access to the Internet and other related services such as W eb site
building and virtual hosting.
79
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 44

Network applications that want to save processing time because they have very
small data units to exchange (and therefore very little message reassembling to
do) may prefer UDP to TCP.
UTP - Unshielded twisted pair is the most common kind of copper telephone
wiring. Twisted pair is the ordinary copper wire that connects home and many
business computers to the telephone company. To reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires, two insulated copper wires are
twisted around each other. Each signal on twisted pair requires both wires.
Since some telephone sets or desktop locations require multiple connections,
twisted pair is sometimes installed in two or more pairs, all within a single
cable.
Virtual Server - Multiple servers that appear as one server, or one system
image, to the operating system or for network administration
WAN - A communications network that co vers a wide geographic area, such as
state or country.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A data privacy mechanism based on a 64bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
WINIPCFG - Configuration utility based on the Win32 API for querying,
defining and managing IP addresses within a network. A commonly used utility, under Windows 95, 98, and Millennium, for configuring networks with
static IP addresses.
82
PrintServer - A hardware device that enables a printer to be located anywhere
in the network.
RJ-45 - A connector similar to a telephone connector that holds up to eight
wires, used for connecting Ethernet devices.
Roaming - The ability to use a wireless device and be able to move from one
access point’s range to another without losing the connection.
Static IP Address - A permanent IP address that is assigned to a node in a
TCP/IP network.
Subnet Mask - The method used for splitting IP networks into a series of subgroups, or subnets. The mask is a binary pattern that is matched up with the IP
address to turn part of the host ID address field into a f ield for subnets.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A method (protocol) used along with
the Internet Protocol (Internet Protocol) to send data in the form of message
units between computers over the Internet. While IP takes care of handling the
actual delivery of the data, TCP takes care of keeping track of the individual
units of data (called packet) that a message is divided into for efficient routing
through the Internet.
TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the
basic communication language or protocol of the Internet. It can also be used
as a communications protocol in a private network (either an intranet or an
extranet). When you are set up with direct access to the Internet, your computer is provided with a copy of the TCP/IP program just as every other computer
that you may send messages to or get information from also has a copy of
TCP/IP.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - A communications method (protocol) that
offers a limited amount of service when messages are exchanged betw een computers in a network that uses the Internet Protocol (IP). UDP is an alternative
to the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and, together with IP, is sometimes
referred to as UDP/IP. Like the Transmission Control Protocol, UDP uses the
Internet Protocol to actually get a data unit (called a datagram) from one computer to another. Unlike TCP, however, UDP does not provide the service of
dividing a message into packets (datagrams) and reassembling it at the other
end. Specifically, UDP doesn't provide sequencing of the packets that the data
arrives in. This means that the application program that uses UDP must be able
to make sure that the entire message has arrived and is in the right order.
81
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 45

8483
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
Dimensions: 7.44” x 6.16” X 2.64” (186mm x 154mm x 48mm)
Unit W eight: 17.5 oz. (0.5 Kg)
Power: External, 5V DC, 3A
Certifications: FCC Class B Part 15, CE Mark Commercial
Operating Temp: 0ºC to 40ºC (32ºF to 104ºF)
Storage Temp: -20ºC to 70ºC (-4ºF to 158ºF)
Operating Humidity: 10% to 85%, Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity: 5% to 90%, Non-Condensing
Environmental
Instant BroadbandTMSeries
Specifications
Standards: IEEE 802.3 (10BaseT), IEEE 802.3u
(100BaseTX), IEEE 802.11b (Wireless), IEEE1284
Protocol: CSMA/CD
Ports: WAN: One 10Base-T RJ-45 Port for
Cable/DSL Modem
LAN: One Shared Uplink Port
Wireless: PCMCIA slot
Printer: One DMA-Equipped, Bi-Directional
Parallel Port
Cabling Type: 10BaseT: UTP Category 3 or better
100BaseTX: UTP Category 5 or better
Printer: Standard Printer Cable
Speed (Mbps): WAN: Up to 10
LAN: 10/100 (Half or Full Duplex)
Wireless: Up to 11
Operating Range Indoor: up to 60M (205ft.) @ up to 11 Mbps
(Wireless): up to 80M (275 ft.) @ up to 5.5 Mbps
up to 130M (425ft.) @ up to 2 Mbps
up to 150M (492 ft.) @ up to 1 Mpbs
Outdoor: up to 250M (820 ft.) up to @ 11 Mbps
up to 350M (1148 ft.) up to @ 5.5 Mbps
up to 400M (1312 ft.) up to @ 2 Mbps
up to 500M (1640 ft.) up to @ 1 Mbps
LEDs: Power, Diag, WAN, WLAN
LAN: 10, 100
Printer: Err, Act
Page 46

Contact Information
For help with the installation or operation of this product, contact Linksys
Customer Support at one of the phone numbers or Internet addresses below.
Information 800-546-5797 (LINKSYS)
Tech Support 800-326-7114
RMA Issues 949-261-1288
Fax 949-261-8868
Email support@linksys.com
Web http://www.linksys.com
FTP Site ftp.linksys.com
86
Warranty Information
BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE AND A BARCODE
FROM THE PRODUCT'S PACKAGING ON HAND WHEN CALLING.
RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF
PURCHASE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID
FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE
OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS DOES NOT OFFER REFUNDS FOR ANY PRODUCT.
LINKSYS OFFERS CROSS SHIPMENTS, A FASTER PROCESS FOR PROCESSING AND RECEIVING YOUR REPLACEMENT. LINKSYS PAYS
FOR UPS GROUND ONLY. ALL CUSTOMERS LOCATED OUTSIDE OF
THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AND CANADA SHALL BE HELD
RESPONSIBLE FOR SHIPPING AND HANDLING CHARGES. PLEASE
CALL LINKSYS FOR MORE DETAILS.
85
Etherfast®Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServerInstant BroadbandTMSeries
Page 47

© Copyright 2001 Linksys,All Rights Reserved.
http://www.linksys.com
 Loading...
Loading...