LG U8550 Service Manual

Date: November, 2005 / Issue 1.0
Service Manual
U8550
Service Manual
Model : U8550

- 3 -
1. INTRODUCTION .............................. 6
1.1 Purpose................................................... 6
1.2 Regulatory Information............................ 6
1.3 Abbreviations .......................................... 8
2. PERFORMANCE............................ 10
2.1 System Overview.................................. 10
2.2 Usable environment.............................. 11
2.3 Radio Performance............................... 11
2.4 Current Consumption............................ 19
2.5 RSSI...................................................... 19
2.6 Battery Bar............................................ 19
2.7 Sound Pressure Level........................... 20
2.8 Charging ............................................... 21
3. Technical Brief .............................. 22
3.1 Digital Baseband(DBB) & Multimedia
Processor ............................................ 22
3.1.1 General Description .........................22
3.1.2 Hardware Architecture .....................23
3.1.3 External memory interface...............27
3.1.4 RF Interface .....................................28
3.1.5 SIM Interface ...................................30
3.1.6 UART Interface ................................31
3.1.7 GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output)
map..................................................32
3.1.8 USB .................................................33
3.1.9 Folder ON/OFF Detection................35
3.1.10 Bluetooth Interface.........................36
3.1.11 TransFlash Interface......................39
3.1.12 Power On Sequence......................40
3.1.13 Keypad...........................................41
3.2 GAM Hardware Subsystem ...................43
3.2.1 General Description .........................43
3.2.2 Block Description .............................44
3.2.3 Camera & Camera FPC Interface... 46
3.2.4 Camera Regulator ...........................49
3.2.5 Display & LCD FPC Interface ..........50
3.2.6 Main&Sub LCD Backlight Illumination...52
3.2.7 Camera Flash LED Illumination ...... 52
3.2.8 Keypad Illumination .........................53
3.3 LCD Module...........................................54
3.4 Analog Baseband (ABB) Processor.......55
3.4.1 Overview of Audio path....................55
3.4.2 Audio Signal Processing
& Interface........................................56
3.4.3 Audio Mode..................................... 58
3.4.4 Voice Call.........................................59
3.4.5 MIDI (Ring Tone Play) .....................62
3.4.6 MP3 (Audio Player)..........................63
3.4.7 Video Telephony..............................64
3.4.8 Audio Part Main Components..........65
3.4.9 GPADC(General Purpose ADC) and
AUTOADC2 .....................................67
3.4.10 Charger control ..............................68
3.4.11 Fuel Gauge ....................................69
3.4.12 Battery Temperature
Measurement.................................70
3.4.13 Charging Part.................................71
3.5 Voltage Regulation.................................74
3.5.1 Internal Regulation...........................74
3.5.2 External Regulation .........................74
3.6 General Description of RF Part..............76
3.7 GSM Mode.............................................78
3.7.1 Receiver...........................................78
3.7.2 Transmitter.......................................83
3.8 WCDMA Mode.......................................85
3.8.1 Receiver.......................................... 85
3.8.2 Transmitter.......................................88
Table of Contents

Table Of Contents
- 4 -
3.8.3 Frequency Generation .....................92
4. TROUBLE SHOOTING ...................94
4.1 Power ON Trouble .................................94
4.2 USB Trouble ..........................................96
4.3 SIM Detect Trouble................................97
4.4 TransFlash Trouble................................98
4.5 Keypad Trouble......................................99
4.6 1.3M Camera Trouble..........................101
4.7 VGA Camera Trouble ..........................103
4.8 Main LCD Trouble................................105
4.9 Sub LCD Trouble .................................107
4.10 Keypad Backlight Trouble..................109
4.11 Camera Flash Trouble .......................111
4.12 Audio Trouble.....................................113
4.12.1 Receiver.......................................113
4.12.2 Speaker .......................................117
4.12.3 Microphone ..................................121
4.12.4 Headset - Receiver ......................125
4.12.5 Headset - MIC..............................126
4.12.6 Headset .......................................127
4.13 Charger Trouble.................................128
4.14 RF Component...................................130
4.15 Procedure to check............................132
4.16 Checking Common Power
Source Block......................................133
4.17 Checking VCXO Block.......................140
4.18 Checking Ant. SW Module Block .......145
4.19 Checking Antenna Switch Block input
logic....................................................146
4.19.1 Mode Logic by TP Command ......146
4.19.2 Checking Switch Block
power source ...............................148
4.20 Checking WCDMA Block ...................153
4.20.1 Checking VCXO Block.................154
4.20.2 Checking Ant. SW module...........154
4.20.3 Checking Control Signal ..............154
4.20.4 Checking RF TX Level.................156
4.20.5 Checking PAM Block ...................159
4.20.6 Checking RX I,Q ..........................162
4.21 Checking GSM Block.........................164
4.21.1 Checking Regulator Circuit ..........165
4.21.2 Checking VCXO Block.................165
4.21.3 Checking Ant. SW Module...........165
4.21.4 Checking Control Signal ..............166
4.21.5 Checking RF Tx Path...................168
4.22 Checking Bluetooth Block..................181
5. BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................185
5.1 GSM & WCDMA RF Block...................185
6. DOWNLOAD .................................187
6.1 The Purpose of Downloading
Software ............................................187
6.2 Download Environment Setup .............187
6.3 U8XXX Download ................................188
7. CALIBRATION ..............................200
7.1 General Description ............................ 200
7.2 XCALMON Environment..................... 200
7.2.1 H/W Environment.......................... 200
7.2.2 S/W Environment.......................... 200
7.2.3 Configuration Diagram of
Calibration Environment................ 200
7.3 Calibration Explanation....................... 201
7.3.1 Overview....................................... 201
7.3.2 Calibration Items........................... 201
7.3.3 EGSM 900 Calibration Items ........ 202
7.3.4 DCS 1800 Calibration Items ......... 207

Table Of Contents
- 5 -
7.3.5 WCDMA Calibration Items............ 210
7.3.6 Baseband Calibration Item ........... 218
7.4 Program Operation ............................. 219
7.4.1 XCALMON Program Overview ..... 219
7.4.2 XCALMON Icon Description ......... 220
7.4.3 Calibration Procedure ................... 223
7.4.4 Calibration Result Message.......... 225
8. Circuit Diagram ............................229
9. pcb layout .....................................239
10. EXPLODED VIEW &
REPLACEMENT PART LIST ..... 248
10.1 EXPLODED VIEW ............................ 248
10.2 Replacement Parts
<Mechanic component>.................... 251
<Main component> ........................... 255
10.3 Accessory ......................................... 282

1. INTRODUCTION
- 6 -
1.1 Purpose
This manual provides the information necessary to repair, calibration, description and download the
features of this model.
1.2 Regulatory Information
A. Security
Toll fraud, the unauthorized use of telecommunications system by an unauthorized part (for example,
persons other than your company’s employees, agents, subcontractors, or person working on your
company’s behalf) can result in substantial additional charges for your telecommunications services.
System users are responsible for the security of own system.
There are may be risks of toll fraud associated with your telecommunications system. System users
are responsible for programming and configuring the equipment to prevent unauthorized use. The
manufacturer does not warrant that this product is immune from the above case but will prevent
unauthorized use of common-carrier telecommunication service of facilities accessed through or
connected to it. The manufacturer will not be responsible for any charges that result from such
unauthorized use.
B. Incidence of Harm
If a telephone company determines that the equipment provided to customer is faulty and possibly
causing harm or interruption in service to the telephone network, it should disconnect telephone
service until repair can be done. A telephone company may temporarily disconnect service as long as
repair is not done.
C. Changes in Service
A local telephone company may make changes in its communications facilities or procedure. If these
changes could reasonably be expected to affect the use of the phones or compatibility with the
network, the telephone company is required to give advanced written notice to the user, allowing the
user to take appropriate steps to maintain telephone service.
D. Maintenance Limitations
Maintenance limitations on the phones must be performed only by the manufacturer or its authorized
agent. The user may not make any changes and/or repairs expect as specifically noted in this manual.
Therefore, note that unauthorized alternations or repair may affect the regulatory status of the system
and may void any remaining warranty.
1. INTRODUCTION

1. INTRODUCTION
- 7 -
E. Notice of Radiated Emissions
This model complies with rules regarding radiation and radio frequency emission as defined by local
regulatory agencies. In accordance with these agencies, you may be required to provide information
such as the following to the end user.
F. Pictures
The pictures in this manual are for illustrative purposes only; your actual hardware may look slightly
different.
G. Interference and Attenuation
A phone may interfere with sensitive laboratory equipment, medical equipment, etc.
Interference from unsuppressed engines or electric motors may cause problems.
H. Electrostatic Sensitive Devices
ATTENTION
Boards, which contain Electrostatic Sensitive Device (ESD), are indicated by the sign.
Following information is ESD handling:
• Service personnel should ground themselves by using a wrist strap when exchange system boards.
• When repairs are made to a system board, they should spread the floor with anti-static mat which is
also grounded.
• Use a suitable, grounded soldering iron.
• Keep sensitive parts in these protective packages until these are used.
• When returning system boards or parts like EEPROM to the factory, use the protective package as
described.
1. INTRODUCTION
- 8 -
1.3 Abbreviations
For the purpose of this manual, following abbreviations apply.
APC Automatic Power Control
BB Baseband
BER Bit Error Ratio
CC-CV Constant Current - Constant Voltage
CLA Cigar Lighter Adapter
DAC Digital to Analog Converter
DCS Digital Communication System
dBm dB relative to 1 milliwatt
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DTC DeskTop Charger
EEPROM Electrical Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
EL Electroluminescence
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
FPCB Flexible Printed Circuit Board
GMSK Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying
GPIB General Purpose Interface Bus
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GSM Global System for Mobile Communications
IPUI International Portable User Identity
IF Intermediate Frequency
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LDO Low Drop Output
LED Light Emitting Diode
OPLL Offset Phase Locked Loop
PAM Power Amplifier Module
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PGA Programmable Gain Amplifier
PLL Phase Locked Loop

1. INTRODUCTION
- 9 -
1.3 Abbreviations
For the purpose of this manual, following abbreviations apply.
I. Introduction
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
RF Radio Frequency
RLR Receiving Loudness Rating
RMS Root Mean Square
RTC Real Time Clock
SAW Surface Acoustic Wave
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
SLR Sending Loudness Rating
SRAM Static Random Access Memory
UMTS Universal Mobile Telephony System
2. PERFORMANCE
- 10 -
2.1 System Overview
2. PERFORMANCE
Item Specification
Shape GSM900/1800/1900 & WCDMA Folder- Dual Mode Handset
Size 90 x 55 x 24.7mm
Weight 134g (with Standard Battery)
Power 1400mA Li-Polymer
Talk Time
Over 180 Min (WCDMA, Tx=12 dBm, Voice)
Over 220 Min (GSM, Tx=Max, Voice)
Standby Time
Over 165 hrs (WCDMA, DRX=1.28)
Over 223 hrs (GSM, Paging period=9)
Antenna Fixed Type (Fixed Screw)
Main LCD 220 x 220 TFT LCD 262K Color
Sub LCD 128 x 160 TFT LCD 262K Color
Main/Sub LCD BL White LED Backlight
Vibrator Yes (Cylinder Type)
LED Indicator Blue
C-MIC Yes
Receiver Yes
Earphone Jack Yes
SIM Socket Yes (3.0V/1.8V)
Volume Key Push Type(+,-)
Voice Key Push Type (Memo)
External Memory T - Flash Socket
I/O Connect 24 Pin
2. PERFORMANCE
- 11 -
2.2 Usable environment
1) Environment
2) Environment(Accessory)
* CLA: 12~24V(DC)
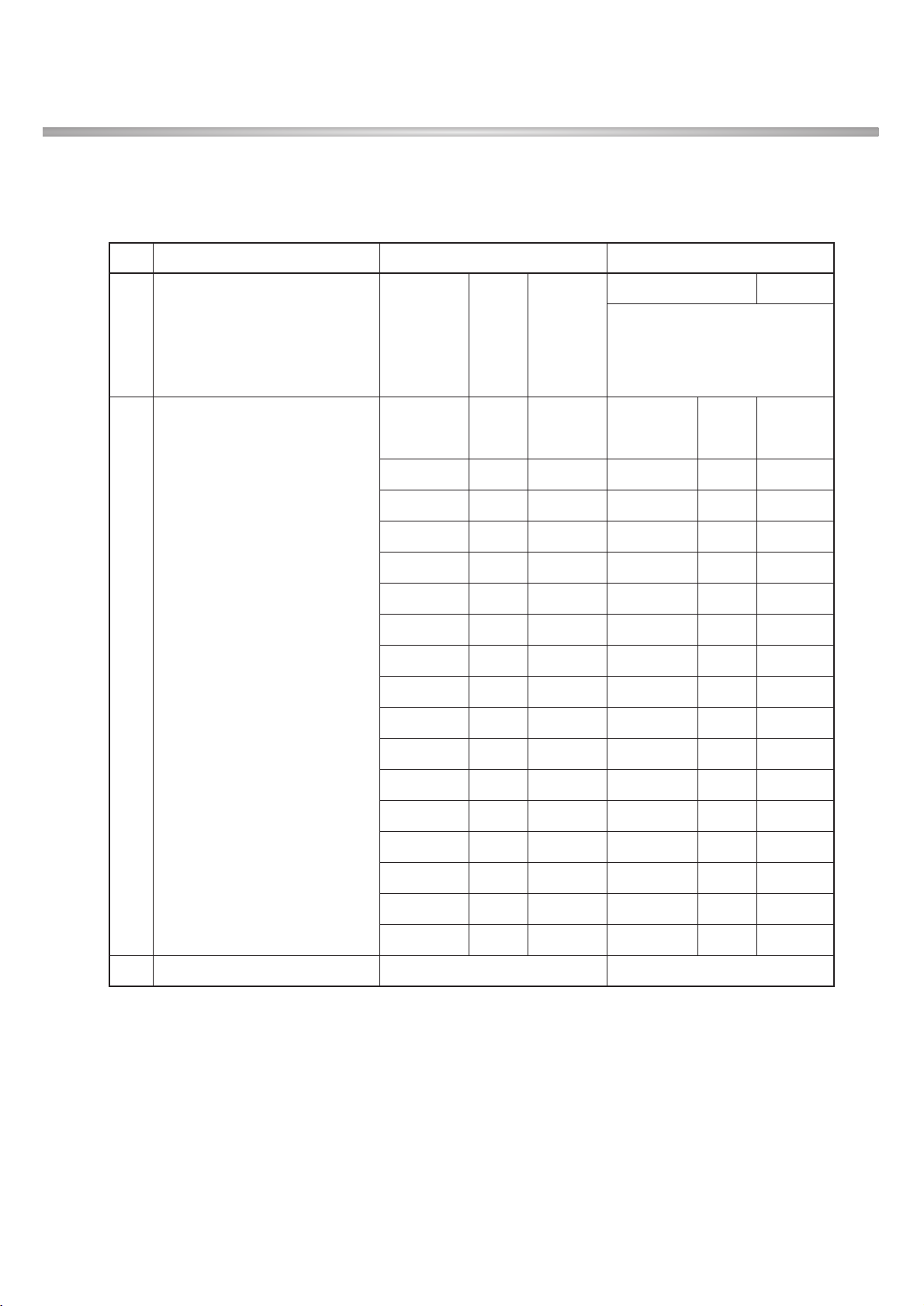
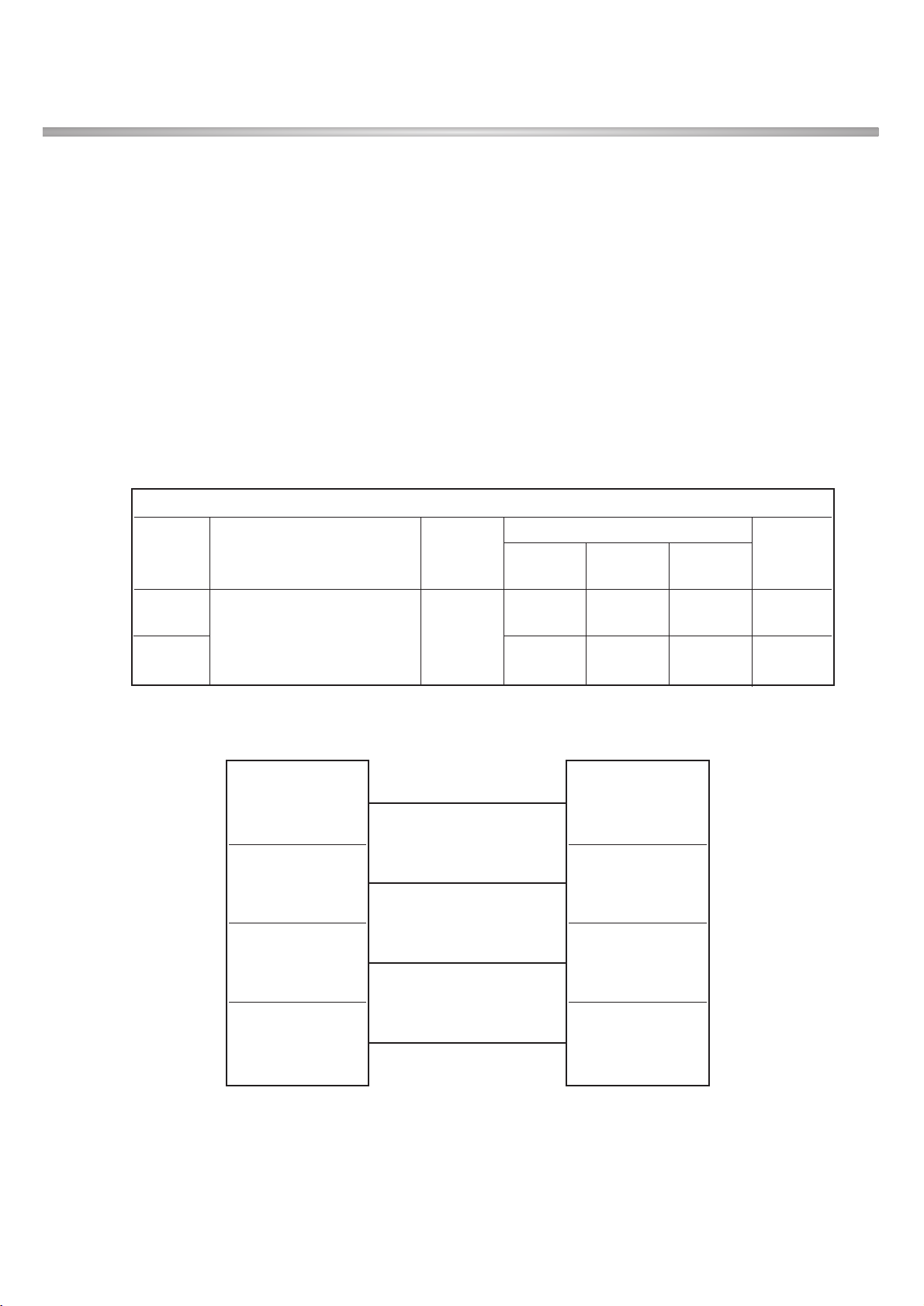
2.3 Radio Performance
1) Transmitter -GSM Mode
Item Spec. Unit
Voltage 4.0 (Typ), 3.4 (Min), (Shut Down: 3.2) V
Operating Temp. -20 ~ + 60 °C
Storage Temp. -30 ~ + 85 °C
Humidity max. 85 %
Item Spec. Min Typ. Max Unit
Power Available power 100 220 240 Vac
No Item GSM DCS/PCS
100k ~ 1GHz -39dBm
9k ~ 1GHz -39dBm
MS allocated 1G ~ 1710MHz -33dBm
Channel
1G ~ 12.75GHz -33dBm
1710M ~ 1785MHz -39dBm
Conducted 1785M ~ 12.75GHz -33dBm
1Spurious 100k ~ 880MHz -60dBm 100k ~ 880MHz -60dBm
Emission 880M ~ 915MHz -62dBm 880M ~ 915MHz -62dBm
Idle Mode
915M ~ 1000Mz -60dBm 915M ~ 1000MHz -60dBm
1G ~ 1.71GHz -50dBm 1G ~ 1.71GHz -50dBm
1.71G ~ 1.785GHz -56dBm 1.71G ~ 1.785GHz -56dBm
1.785G ~ 12.75GHz -50dBm 1.785G ~ 12.75GHz -50dBm
2. PERFORMANCE
- 12 -
No Item GSM DCS/PCS
30M ~ 1GHz -36dBm
30M ~ 1GHz -36dBm
MS allocated 1G ~ 1710MHz -30dBm
Channel
1G ~ 4GHz -30dBm
1710M ~ 1785MHz -36dBm
Radiated 1785M ~ 4GHz -30dBm
1 Spurious 30M ~ 880MHz -57dBm 30M ~ 880MHz -57dBm
Emission 880M ~ 915MHz -59dBm 880M ~ 915MHz -59dBm
Idle Mode
915M ~ 1000Mz -57dBm 915M ~ 1000MHz -57dBm
1G ~ 1.71GHz -47dBm 1G ~ 1.71GHz -47dBm
1.71G ~ 1.785GHz -53dBm 1.71G ~ 1.785GHz -53dBm
1.785G ~ 4GHz -47dBm 1.785G ~ 4GHz -47dBm
2 Frequency Error ±0.1ppm ±0.1ppm
3 Phase Error
±5(RMS) ±5(RMS)
±20(PEAK) ±20(PEAK)
3dB below reference sensitivity 3dB below reference sensitivity
Frequency Error Under RA250: ±200Hz RA250: ±250Hz
4 Multipath and Interference HT100: ±100Hz HT100: ±250Hz
Condition TU50: ±100Hz TU50: ±150Hz
TU3: ±150Hz TU1.5: ±200Hz
0 ~ 100kHz +0.5dB 0 ~ 100kHz +0.5dB
200kHz -30dB 200kHz -30dB
250kHz -33dB 250kHz -31dB
Due to 400kHz -60dB 400kHz -33dB
Output RF
modulation 600 ~ 1800kHz -66dB 600 ~ 1800kHz -60dB
5 1800 ~ 3000kHz -69dB 1800 ~ 6000kHz -60dB
Spectrum
3000 ~ 6000kHz -71dB ≥6000kHz -73dB
≥6000kHz -77dB
Due to
400kHz -19dB 400kHz -22dB
Switching
600kHz -21dB 600kHz -24dB
transient
1200kHz -21dB 1200kHz -24dB
1800kHz -24dB 1800kHz -27dB
2. PERFORMANCE
- 13 -
No Item GSM DCS/PCS
Frequency offset 800kHz
7 Intermodulation attenuation –
Intermodulation product should
be Less than 55dB below the
level of Wanted signal
Power control
Power Tolerance
Power control
Power Tolerance
Level (dBm) (dB) Level (dBm) (dB)
533±3 030±3
631±3 128±3
729±3 226±3
827±3 324±3
925±3 422±3
10 23 ±3 5 20 ±3
8 Transmitter Output Power 11 21 ±3 6 18 ±3
12 19 ±3 7 16 ±3
13 17 ±3 8 14 ±3
14 15 ±3 9 12 ±4
15 13 ±3 10 10 ±4
16 11 ±5 11 8 ±4
17 9 ±5 12 6 ±4
18 7 ±5 13 4 ±4
19 5 ±5 14 2 ±5
15 0 ±5
9 Burst timing Mask IN Mask IN
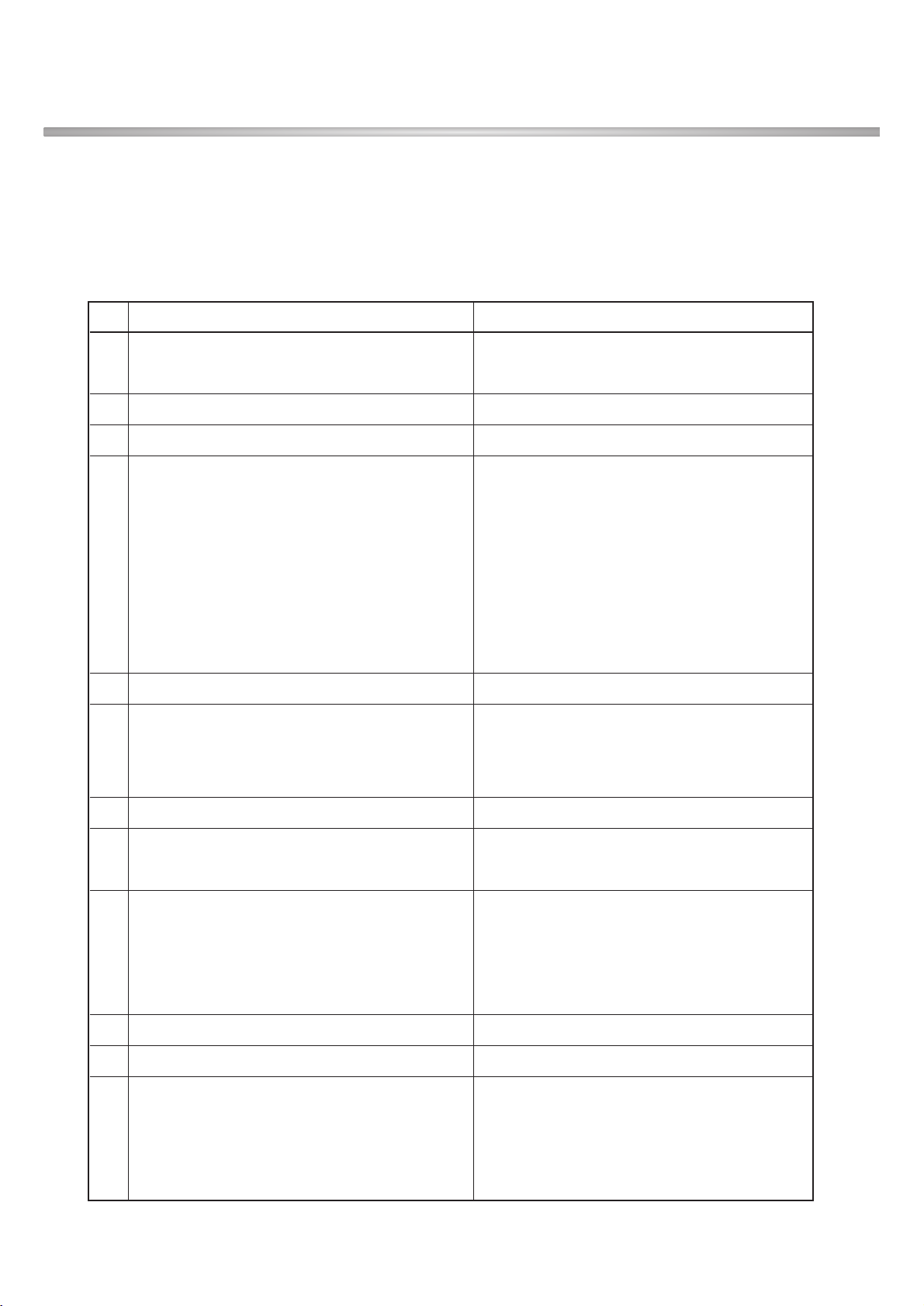
2) Transmitter-WCDMA Mode
2. PERFORMANCE
- 14 -
No Item Specification
1 Maximum Output Power
Class3: +24dBm(+1/-3dB)
Class4: +21dBm(±2dB)
2 Frequency Error ±0.1ppm
3 Open Loop Power control in uplink ±9dB@normal, ±12dB@extreme
Adjust output(TPC command)
cmd 1dB 2dB 3dB
+1 +0.5/1.5 +1/3 +1.5/4.5
4 Inner Loop Power control in uplink 0 -0.5/+0.5 -0.5/+0.5 -0.5/+0.5
-1 -0.5/-1.5 -1/-3 -1.5/-4.5
group(10equal command group)
+1 +8/+12 +16/+24
5 Minimum Output Power -50dBm(3.84MHz)
Qin/Qout:DPCCH quality levels
6 Out-of-synchronization handling of output power Toff@DPCCH/lor:-22->-28dB
Ton@DPCCH/lor:-24->-18dB
7 Transmit OFF Power -56dBm(3.84M)
8 Transmit ON/OFF Time Mask
±25us
PRACH, CPCH, uplink compressed mode
±25us
9 Change of TFC
power varies according to the data rate
DTX: DPCH off
(minimize interference between UE)
10 Power setting in uplink compressed ±3dB(after 14slots transmission gap)
11 Occupied Bandwidth(OBW) 5MHz(99%)
-35-15*(∆f-2.5)dBc@∆f=2.5~3.5MHz, 30k
12 Spectrum emission Mask
-35-1*(∆f-3.5)dBc@∆f=3.5~7.5MHz, 1M
-39-10*(∆f-7.5)dBc@∆f=7.5~8.5MHz, 1M
-49 dBc@∆f=8.5~12.5MHz, 1M
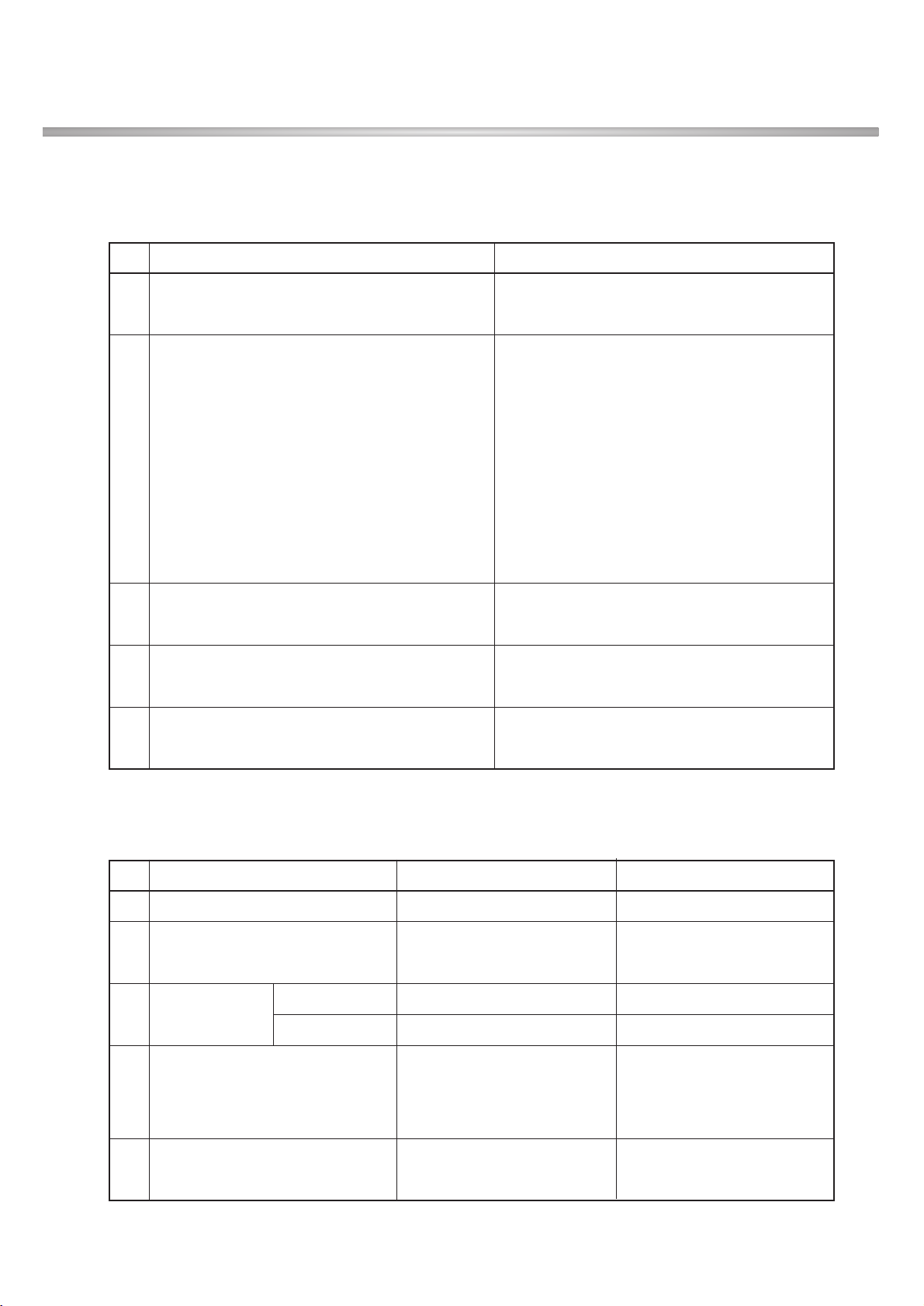
2. PERFORMANCE
- 15 -
3)Receiver - GSM Mode
No Item Specification
13 Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio(ACLR)
33dB@5MHz, ACP>-50dBm
43dB@10MHz, ACP>-50dBm
-36dBm@f=9~150KHz, 1k BW
-36dBm@f=150KHz~30MHz, 10k
-36dBm@f=30~1000MHz, 100k
14
Spurious Emissions -30dBm@f=1~12.75GHz, 1M
*: additional requirement -41dBm*@1893.5~1919.6MHz, 300k
-67dBm*@925~935MHz, 100k
-79dBm*@935~960MHz, 100k
-71dBm*@1805~1880MHz, 100k
15 Transmit Intermodulation
-31dBc@5MHz, Interferer -40dBc
-41dBc@10MHz, Interferer -40dBc
16 Error Vector Magnitude(EVM)
17.5% (>-20dBm)
(@12.2k, 1DPDCH+1DPCCH)
17 Transmit OFF Power
-15dB@SF=4, 768kbps, multi-code
transmission
No Item GSM DCS/PCS
1
Sensitivity (TCH/FS Class II) -105dBm -105dBm
2
Co-Channel Rejection
C/Ic=7dB C/Ic=7dB
(TCH/FS Class II, RBER, TUhigh/FH)
3 Adjacent Channel 200kHz C/Ia1=-12dB C/Ia1=-12dB
Rejection 400kHz C/Ia2=-44dB C/Ia2=-44dB
Wanted Signal: -98dBm Wanted Signal: -96dBm
4
Intermodulation Rejection 1’st interferer: -44dBm 1’st interferer: -44dBm
2’st interferer: -45dBm 2’st interferer: -44dBm
5
Blocking Response Wanted Signal: -101dBm Wanted Signal: -101dBm
(TCH/FS Class II, RBER) Unwanted Signal: Depend on freq. Unwanted Signal: Depend on freq.
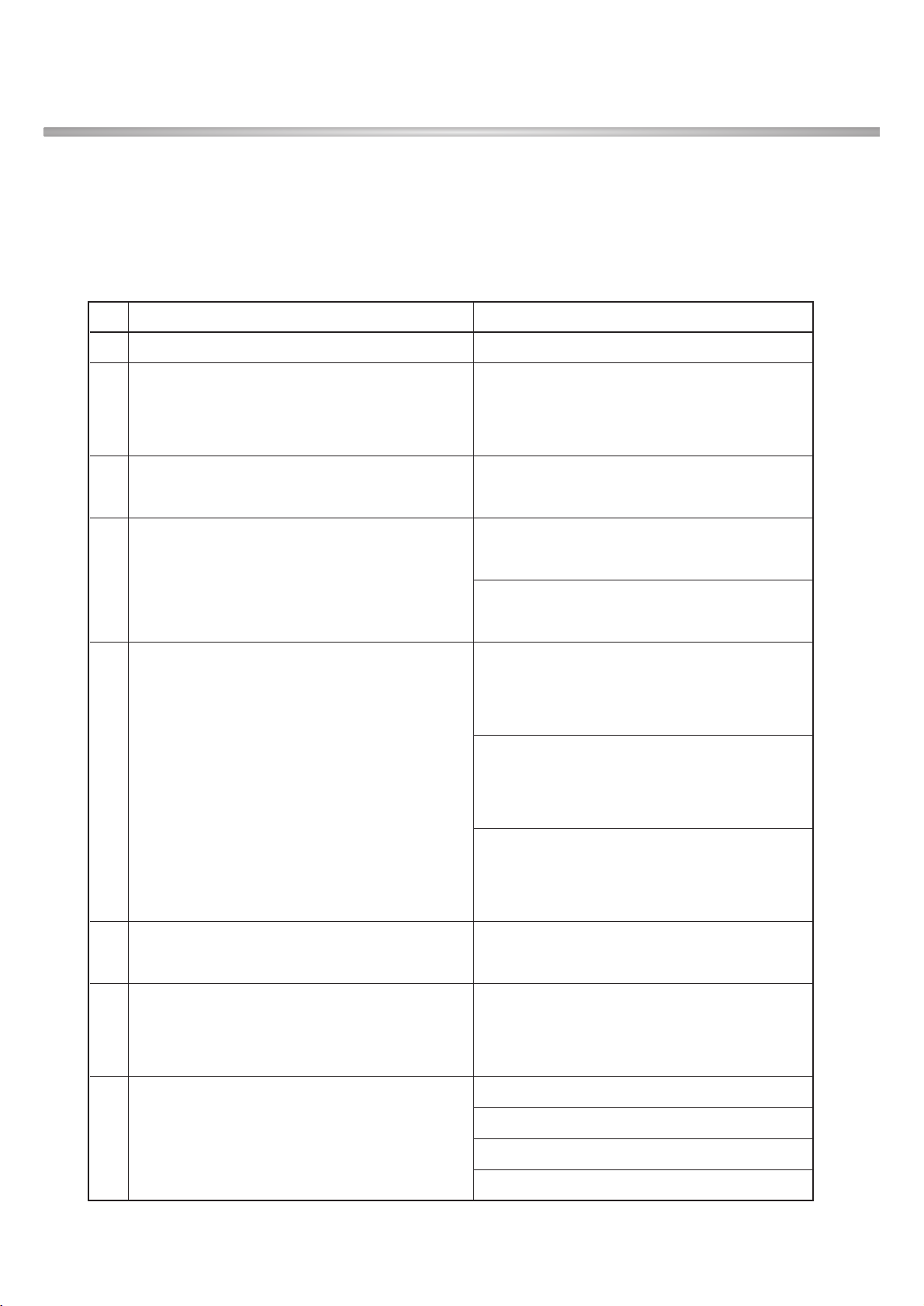
4) Receiver - WCDMA Mode
2. PERFORMANCE
- 16 -
No Item Specification
18 Reference Sensivitivity Level -106.7dBm(3.84M)
-25dBm(3.84MHz)
19 Maximum Input Level -44dBm/3.84MHz(DPCH_Ec)
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
20 Adjacent Channel Selectivity(ACS)
33dB
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
-56dBm/3.84MHz@10MHz
21 In-band Blocking UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
-44dBm/3.84MHz@15MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
-44dBm/3.84MHz@f=2050~2095 &
2185~2230MHz, band a)
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
-30dBm/3.84MHz@f=2025~2050 &
22 Out-band Blocking 2230~2255MHz, band a)
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
-15dBm/3.84MHz@f=1~2025 &
2255~12500MHz, band a)
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
23 Spurious Response
-44dBm CW
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
-46dBm CW@10MHz &
24 Intermodulation Characteristic -46dBm/3.84MHz@20MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(class3)
-57dBm@f=9KHz~1GHz, 100k BW
25 Spurious Emissions -47dBm@f=1~12.75GHz, 1M
-60dBm@f=1920~1980MHz, 3.84MHz
-60dBm@f=2110~2170MHz, 3.84MHz
2. PERFORMANCE
- 17 -
5) Bluetooth Mode
5.1) Transmitter
1 Out Power Class 2 : -6~4dBm
2 Power Density Power density < 20dBm per 100kHz EIRP
3
Power Control
Option
2dB ≤ step size ≤ 8dB
4
TX Output Spectrum fmax & fmin @ below the level of -30dBm(100khz BW)
-Frequency range within 2.4GHz~2.4835GHz
5
TX Output Spectrum
≤ 1MHz
-20dB Bandwidth
6
Tx Output Spectrum ≤ -20dBm @ C/I = 2MHz
-Adjacent channel Po ≤ -40dBm @ C/I ≥ 3MHz
140kHz ≤ delta f1 avg ≤175kHz
7 Modulation Characteristics delta f2max ≥115kHz at least 99.9% of all deltaf2max
delta f2avg/deata f1avg≥0.8
8 Init. Carrier Freq. Tolerance ≤ ±75KHz
1 slot : ≤ ± 25kHz
9 Carrier Frequency Drift
3 slot : ≤ ± 40kHz
5 slot : ≤ ± 40kHz
Maximum drift rate ≤ 20KHz/50usec
Freq.Range Operating Standby
30MHz~1GHz -36dBm -57dBm
10 Out of Band Spurious Emissions Above 1GHz~12.75GHz -30dBm -47dBm
1.8~1.9GHz -47dBm -47dBm
5.15~5.3GHz -47dBm -47dBm
2. PERFORMANCE
- 18 -
5.2) Receiver
11 Sensitivity single slot packets BER≤0.1%@-70dBm
12 Sensitivity multi slot packets BER≤0.1%@-70dBm
13 BER ≤ 0.1%@ (Low,Mid,High Frequency)
2405MHz, 2441MHz, 2477MHz
Interference Ratio
Co-Channel interference, C/I co-channel 11dB
C/I performance Adjacent(1MHz)interference, C/I 1MHz 0dB
Adjacent(2MHz)interference, C/I 2MHz -30dB
Adjacent(≥3MHz)interference, C/I ≥3MHz -40dB
Adjacent(≥3MHz)interference to in band -9dB
mirror frequency, C/I image ±1MHz -20dB
14 BER ≤ 0.1%@wanted signal -67dBm
interfering Signal Frequency Power Level
Blocking Characteristic
30MHz~2000MHz -10dBm
2000MHz~2400MHz -27dBm
2500MHz~3000MHz -27dBm
3000MHz~12.75GHz -10dBm
15 BER ≤ 0.1%@wanted signal -64dBm
Intermodluation Performance static sinwave signal at f1=-39dBm
a BT modulated signal f2=-39dBm(payload PRBS15)
16 Maximum Input Level BER ≤ 0.1%@-20dBm
2. PERFORMANCE
- 19 -
2.4 Current Consumption
(VT test : Speaker off, LCD backlight On)
2.5 RSSI
TBD
2.6 Battery Bar
Stand by Voice Call VT
WCDMA 165Hours=8.48mA 180Min=467mA 130Min=646mA
(DRX=1.28) (Tx=12dBm) (Tx=12dBm)
GSM 223Hours=6.28mA 220Min=380mA
(paging=9period) (Tx=Max)
GSM WCDMA(TBD)
BAR 4 → 3 -91 ±2dBm -87 ±2dBm
BAR 3 → 2 -96 ±2dBm -97 ±2dBm
BAR 2 → 1 -101 ±2dBm -107 ±2dBm
BAR 1 → 0 -106 ±2dBm -112 ±2dBm
Indication Voltage
BAR 4 → 3 (65%) 3.87 ± 0.05V
BAR 3 → 2 (43%) 3.77 ± 0.05V
BAR 2 → 1 (24%) 3.72 ±0.05V
BAR 1 → Icon Blinking (3%) 3.54 ±0.05V
Low voltage, warning message
3.54 ±0.03V(Talk: 1min. interval) -3%
3.50 ±0.03V(Standby: 3min. Inverval) -2%
Power OFF
3.15 ±0.03V ↓ (WCDMA Talk)
3.23 ±0.03V ↓ (else)
2. PERFORMANCE
- 20 -
2.7 Sound Pressure Level
No Test Item Specification
1 Sending Loudness Rating (SLR)
NOM
8±3dB
MAX
2 Receiving Loudness Rating (RLR)
NOM -1±3dB
MAX -15±3dB
3 Side Tone Masking Rating (STMR)
NOM
17dB over
MAX
4 Echo Loss (EL)
NOM
40dB over
MAX
5 Sending Distortion (SD) refer to TABLE 30.3
6 Receiving Distortion (RD) refer to TABLE 30.4
7 Idle Noise-Sending (INS)
NOM
-64dBm0p under
MAX
8 Idle Noise-Receiving (INR)
NOM -47dBPA under
MAX -36dBPA under
9 Sending Loudness Rating (SLR)
NOM
8±3dB
MAX
10 Receiving Loudness Rating (RLR)
NOM -1±3dB
MAX -12±3dB
11 Side Tone Masking Rating (STMR)
NOM
25dB over
MAX
12 Echo Loss (EL)
NOM
40dB over
MAX
13 Sending Distortion (SD) refer to TABLE 30.3
14 Receiving Distortion (RD) refer to TABLE 30.4
15 Idle Noise-Sending (INS)
NOM
-55dBm0p under
MAX
16 Idle Noise-Receiving (INR)
NOM -45dBPA under
MAX -40dBPA under
TDMA NOISE
GSM
SEND
–.GSM: Power Level: 5
MS
REV.
DCS: Power Level: 0
DCS
SEND
17
(Cell Power: -90 ~ -105dBm) REV.
-62dBm under
–.Acoustic(Max Vol.)
GSM
SEND
MS/HEADSET SLR: 8±3dB
Headset
REV.
MS/HEADSET RLR: -13±1dB/-15dB
DCS
SEND
(SLR/RLR: mid-Value Setting) REV.
A
C
O
U
S
T
I
C
MS
HEAD
SET

2. PERFORMANCE
- 21 -
2.8 Charging
• Normal mode: Complete Voltage: 4.2V
Charging Current: 800mA
• Await mode: In case of During a Call, should be kept 3.9V
(GSM: It should be kept 3.9V in all power level
WCDMA: It will not be kept 3.9V in some power level)
• Extend await mode: At Charging prohibited temperature(-20C under or 60C over)
(GSM: It should be kept 3.7V in all power level
WCDMA: It will not be kept 3.7V in some power level)

3. Technical Brief
- 22 -
3.1 Digital Baseband(DBB) & Multimedia Processor
3.1.1 General Description
A. Features
• CPU ARM946 running at 104 MHz
- 32 kB Instruction Cache, 16 kB Data Cache, 128 kB Instruction TCM and 128 kB Data TCM
- 8 channel DMAC
• DSP C55x (LEAD3) Megastar (MGS3_2.0B) running at 170 MHz
- 144 kWord ROM, 32 kWord DARAM, 32 kWord SARAM
- 7 channel DMAC
- Dedicated API channel to DSP memory (not locked up to other DMA channels)
• UMTS Access
- Support for WCDMA/GSM Dual Mode
- GSM/GPRS network signaling (from Layer 1 to 3)
- WCDMA Ciphering and Integrity
- High Speed Serial Link (HSSL) to the WCDMA Modem (at Layer 1)
- GSM AMR
- Multislot Class 8
- HSCSD 14.4 kb/s
• MMI
- Keypad Interface
- Tone Generator Interface
- Camera Data and Programmable Display Interfaces
- Enhanced graphics support for QCIF display
• Operation and Services
- I2 CTM‚ Interface
- SIM Interfaces
- General Purpose I/O (GPIO) Interface
- External Memory Interface that supports FLASH, SRAM and PSRAM
- JTAG
- RTC
• Data Communication
- IrDA ® (SIR)
- UARTs (ACB, EDB (RS232), Bluetooth® HCI)
- Slave USB
• Package
- 12 by 12 mm 289 pin FPBGA Production Package
3. Technical Brief
3. Technical Brief
- 23 -
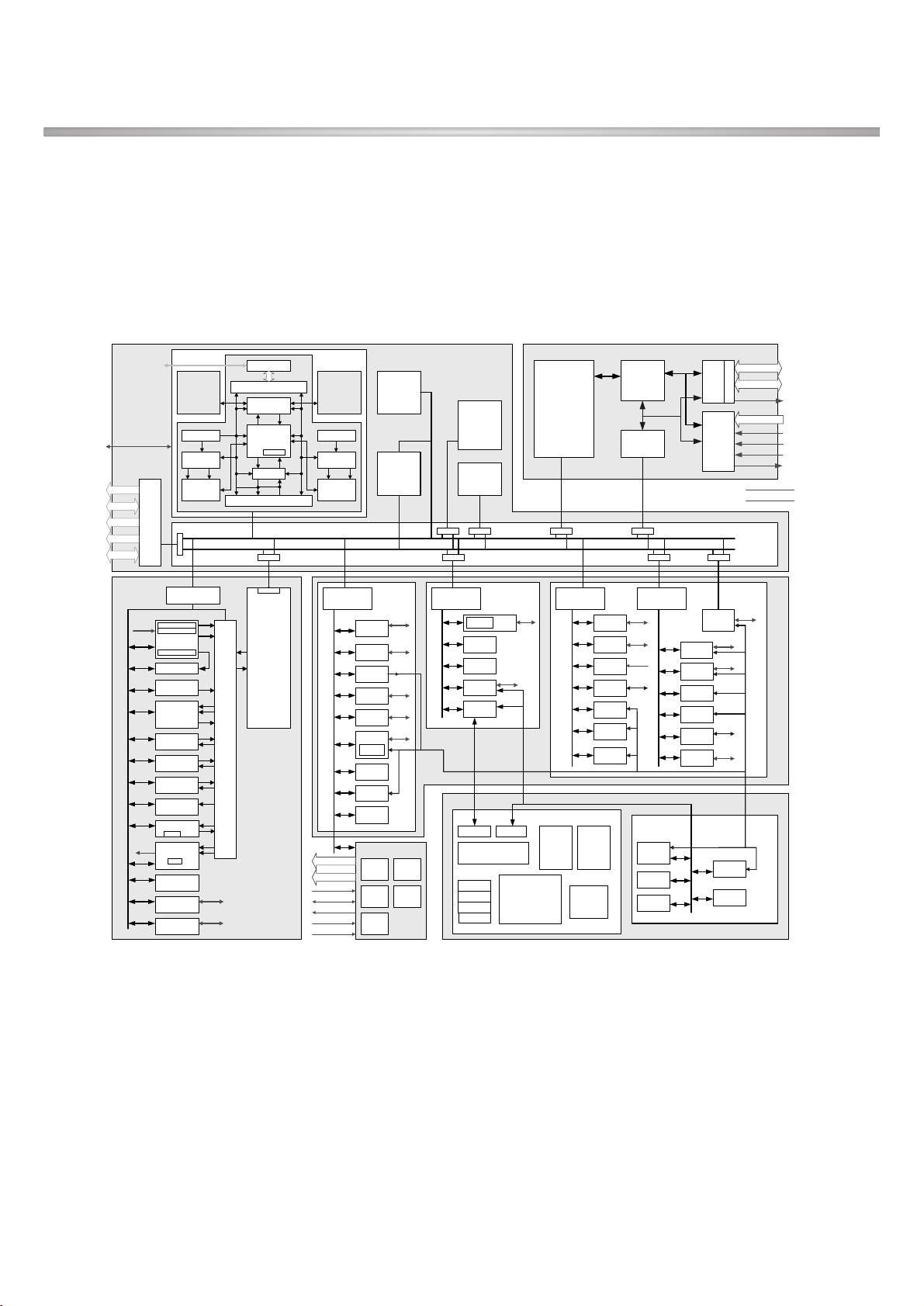
3.1.2 Hardware Architecture
The hardware structure is delivered as five separate hardware macros to the top-level design, also
depicted in Figure.
CPU Subsystem
GAM Subsystem
Peripheral Subsystem
DPS Subsystem
GSM Core
Subsystem
SYSCON
Figure 3-1-1 Simplified Block Diagram of Ericsson DB 2000
3. Technical Brief
- 24 -
A. Block Diagram
Figure 3-1-2 Detailed Block Diagram of Ericsson DB 2000
CPU Sub-Chip
Camera Module Display Module
DSP Sub-System
MGS3_2.0B
DSP_INT
MGS3
peripherals
GAM Sub-System
DL
UL
Control CPU I/O int erface
eight bit wide mul tiplexed bus,
DL
UL
DL
UL
UL
UL
UL
DL
DL
UL
DL
DL
DL
UL
DL
CHE
NODI
4 x CHD
EQU
GPRS
CRC24
GPRS
CRYPTO
SERCON
TIMGEN
FCHDET
CLKCON
RXIF
CRYPTO
DIRMOD
DMA Channels
6.5 Mbps
43x16 bit RAM
43x16 bit RAM
360x38bit RAM
144 bit
AHB1 ( CPU)
AHB2 ( DMA)
AHB
Slave
AHB
Slave
AHB Master
AHB
Master
DMA
(16Rq 8Ch)
Boot ROM
16k bytes
(4K x 32bit)
MPPCM
Ciphering
Integrity
HSSL
I2C
SYSCON
RTC
TONGEN
GPIO
UART1
EDB
UART3
BT
UART6
UART7
DSP debug
AHB
Slave
SIMIF_0
MEM
STICK
Control
SIMIF_1
AHB
Slave
AHB
Slave
Conceptual Diagram of bus
Bridge
Asynchronou s
System
BRAM
16k bytes
(4K x 32bit)
13MHz
MUX
16
16
16
16
32
32
32
16
16
16
RHEA
API (16)
IRAM
(Internal radio data RAM)
16 kB dual port SRAM
AHB
Slave
AHB
Slave
AHB
Slave
32
EMIFS
MEMSYS (DMA bus)
UART0
ACB
INTCON
KEYPAD
UART5
UART2
GPS
UART4
TS
16
16
16
16
16
32
16
13MHz
13MHz
13MHz, 26MHz
AHB
Slave
TIMER
32
IRDA
32
JOGDIAL
ETX
208
DPLL
13
APLL
48
APLL
APB Bridge
(1)
APB Bridge
(2)
MMC
APB Bridge
(Slow)
APB Bridge
(Data)
Interconnect Matrix
USB
CPU Sub-System
AHB
Slave
Peripheral Sub-System
16
16
16
32
32
16
16
32
GSM Sub-System
Default
Slave
AHB
Slave
16
26
APLL
CLK
SQR
16
16
16
16
16
ROM
144 kWords
(18 x 8 kW) BX
RHEA
DMA
DARAM
32 kWords
(8 x 4kW)
BRE
API
SARAM
32 kWords
(8 x 4kW)
BRE
HPRTD
TRACE
Timer2
DPLL
DGPIO
JTAG
Timer1
C55x CPU
AHB
Slave
AHB
Slave
AHB
Slave
CIPCLK
CID [7:0]
CIVSYNC
CIHSYNC
CIRES_N
PDIRES_N
PDIC [4:0]
PDID [7:0]
CDI
PDI
GRAPHCON
GAMCON
GRAM
160k byte
7kB RAM
4
4
4
11
3
GAM
3
3
3
5
2
3
3
CLKREQ7
BPW
MUX MUX MUX MUX
MUX MUXMUXMUX
MUX
ARM9 E
CP15
RAM Control
ETM
Data
RAM
128kB
Instruction
SRAM
128kB
IPU
I Cache
Control
I Cache
32kB
DPU
D Cache
Control
D Cache
16kB
Write Buffer & AHB IF
ETM IF
JTAG
946
11
8 JTAG
23
GAM
AHB-Lite
AHB-Lite
DAT [16]
ADD [24]
CS [4]
we/oe [2]
MEME[5]
SYSCLK [3]
MCLK
PWRREQ_N
RESOUT [5]
SERVICE
RESPOW_N
3
4
GPIO MUX
RHEA
GPIO MUX
1
External Memory
PAR/ SSI
data
data
cpu
40
28
1325
53
8
26
59
0
89
key
unused
2
4
4
4
4
4
6

3. Technical Brief
- 25 -
B. CPU Hardware Subsystem
The CPU subsystem incorporates:
• CPU Sub chip
• Backplane
• JTAG
• DMA Controller
• System Buffer RAM
• Boot ROM
• External Memory Interface (EMIF) for connection to external SRAM and Flash memories. The bus
architecture is built on the ARM AMBA standard with multi-layer AHB (Advanced High-speed Bus)
and APB (Advanced Peripheral Bus) for the peripheral buses. There are two AHB busses, the CPU
AHB and the DMA AHB.
Clocks to the CPU subsystem are distributed from the system control (SYSCON) backplane clocking.
The reset lines are all asynchronously asserted low and synchronously negated high. The CPU
subsystem has separate clocking and reset for the ARM946, AHB system, EMIF and DMAC.
C. Peripheral Hardware Subsystem
There are 29 peripherals within the peripheral hardware subsystem. With the exception of the USB, all
hardware peripheral blocks are APB slave peripherals. From an architecturehierarchy perspective, the
SYSCON block is an APB slave on the slow APB bridge, but resides at the top level of the ASIC. The
APB provides a simple interface to support low-performance peripherals. Within the peripheral
subsystem, there are four separate APB busses with AHB to APB (AHB2APB) bridges to the multilayer AHB.
D. DSP Hardware Subsystem
The DSP subsystem provides support for processor intensive activity, such as voice coding and
multimedia application support. The DSP subsystem includes the standard C55xTM Core (LEAD3)
from Texas Instruments with associated memory system and peripherals.
E. GAM Hardware Subsystem
The Graphics Accelerator Module (GAM) subsystem provides hardware support in the creation of
visual imagery and the transfer of this data to the display. GAM also provides support for the camera
module. The visual data could be graphics, still images or video.
The GAM subsystem consists of five modules:
• GRAM - graphics memory (160 kB).
• GAMCON - GAM controller.
• GRAPHCON - graphics controller.
• PDI/SSI - programmable display interface for parallel/serial displays.
• CDI - camera data interface.

3. Technical Brief
- 26 -
F. GSM Hardware Subsystem
The GSM subsystem is a stand-alone sub-chip incorporating GSM modem and interface to GSM radio
together with memory control (MEMSYS) and internal RAM (IRAM).
The hardware peripheral blocks are RXIF, FCHDET, CRYPTO, EQU, NODI, 4 x CHD, GPRS
CRYPTO, GPRS CRC24, CHE, DIRMOD, CLKCON, SERCON, TIMGEN, MEMSYS and IRAM.
The peripherals are accessible to the AHB (CPU-only) by an asynchronous I/O bridge.
The dual port IRAM is accessible to the AHB (CPU and DMA) by a synchronous AHB slave interface.
G. System Control Subsystem
The system controller subsystem (SYSCON) is primarily responsible for generating clock signals and
distributing the clock and reset signals within the ASIC and certain external devices. The GSM core,
GAM and DSP subsystems include their own system controllers that are sourced from SYSCON.
SYSCON consists of analog and digital PLL clocks and a clock squarer. The block is a slave
peripheral on the slow APB bus under control of the CPU.
The programming of SYSCON controls the fundamental modes of operation within the ASIC.
Individual blocks can also be reset and their clocks held inactive by accessing the appropriate control
registers. SYSCON also controls the requesting protocol through which different subblocks in Ericsson
DB 20000 can request clocks derived from the system clock.
The system controller also stores the chip-ID number in a read only register.
3. Technical Brief
- 27 -
3.1.3 External memory interface
There are four independent chip selects (CS0, CS1, CS2, CS3) provided for external memories
and each has an address range of 256 Mb.
RF calibration data, Audio parameters and battery calibration data etc are stored in flash memory
area.
A. U8550
• 1-MCP used (512Mb flash memory + 128Mb PSRAM)
• 4-CS (Chip Select) are used
Table 3-1-1. External Memory Interface Spec. of U8550
Figure 3-1-3. External Memory Configuration of U8550
Interface Spec.
Device Part Name Maker
Read Access Time
Write
Async Page Burst
Access
Time
Flash 85 ns 25 ns
14 ns
90 ns
RD38F4455LLYBQ1 Intel
at 54MHz
PSRAM 85 ns 25 ns
10 ns
85 ns
at 66MHz
CS0
CS1
CS2
CS3
Flash
256 Mb
(Top boot)
Flash
256 Mb
(Bottom boot)
PSRAM
64 Mb
PSRAM
64 Mb
MARITA Intel MCP
3. Technical Brief
- 28 -
3.1.4 RF Interface
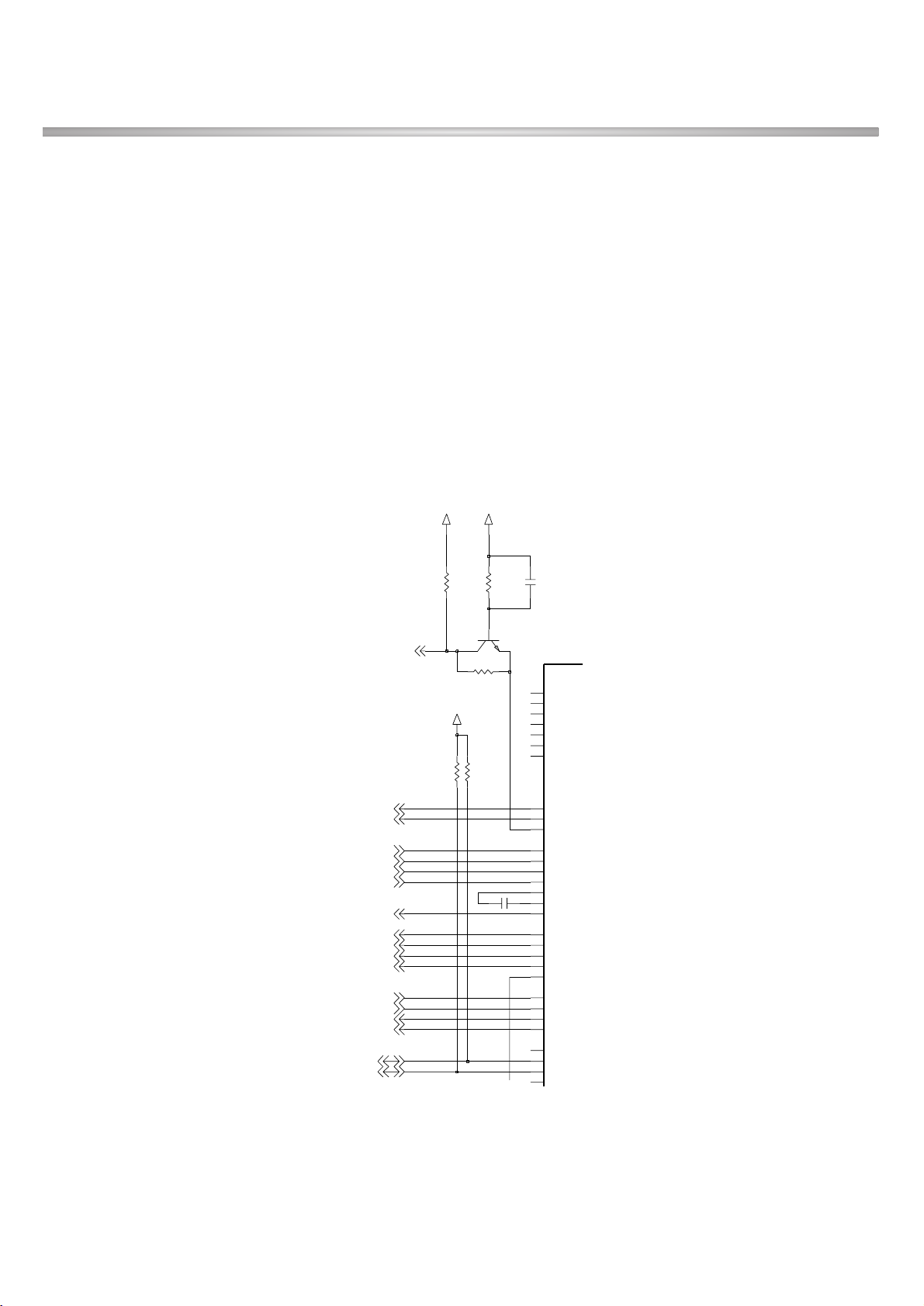
A. MARITA Interface
Marita controls GSM RF part using these signals through GSM RF chip-Ingela.
• RFCLK, RFDAT, RFSTR : Control signals for Ingela
• TXON, RXON : Control signals for TX and RX part of Ingela
• PCTL : Control signal for GSM TX PAM
• BANDSEL0 : Band selection signal for GSM or DCS
• ANTSW[0:3] : Control signals for antenna switch
• DCLK, IDATA, QDATA : GSM/DCS RX Data
• DIRMOD[A:D] : GSM/DCS TX Data
RF I/F
R631 100
0R627
TXON
G3
G2
RXON
L7
QDATA
K8
RFCLKG1RFDAT
RFSTR
H4
PCTL
L8
K3
IDATA
DIRMOD3
DCLK
K4
DIRMOD0E2DIRMOD1
J7
F3
DIRMOD2
F2
J2
ANTSW0
ANTSW1
J4
J3
ANTSW2J1ANTSW3
H3
BANDSEL0
K7
BANDSEL1
R632 NA
MODC
MODB
MODA
DCLK
BSEL0
ANTSW3
ANTSW2
ANTSW1
ANTSW0
IDATA
MODD
PCTL
RXON
RADDAT
RADCLK
QDATA
GPRFCTRL
RADSTR
TXON
Figure 3-1-4. Schematic of MARITA RF Interface
3. Technical Brief
- 29 -
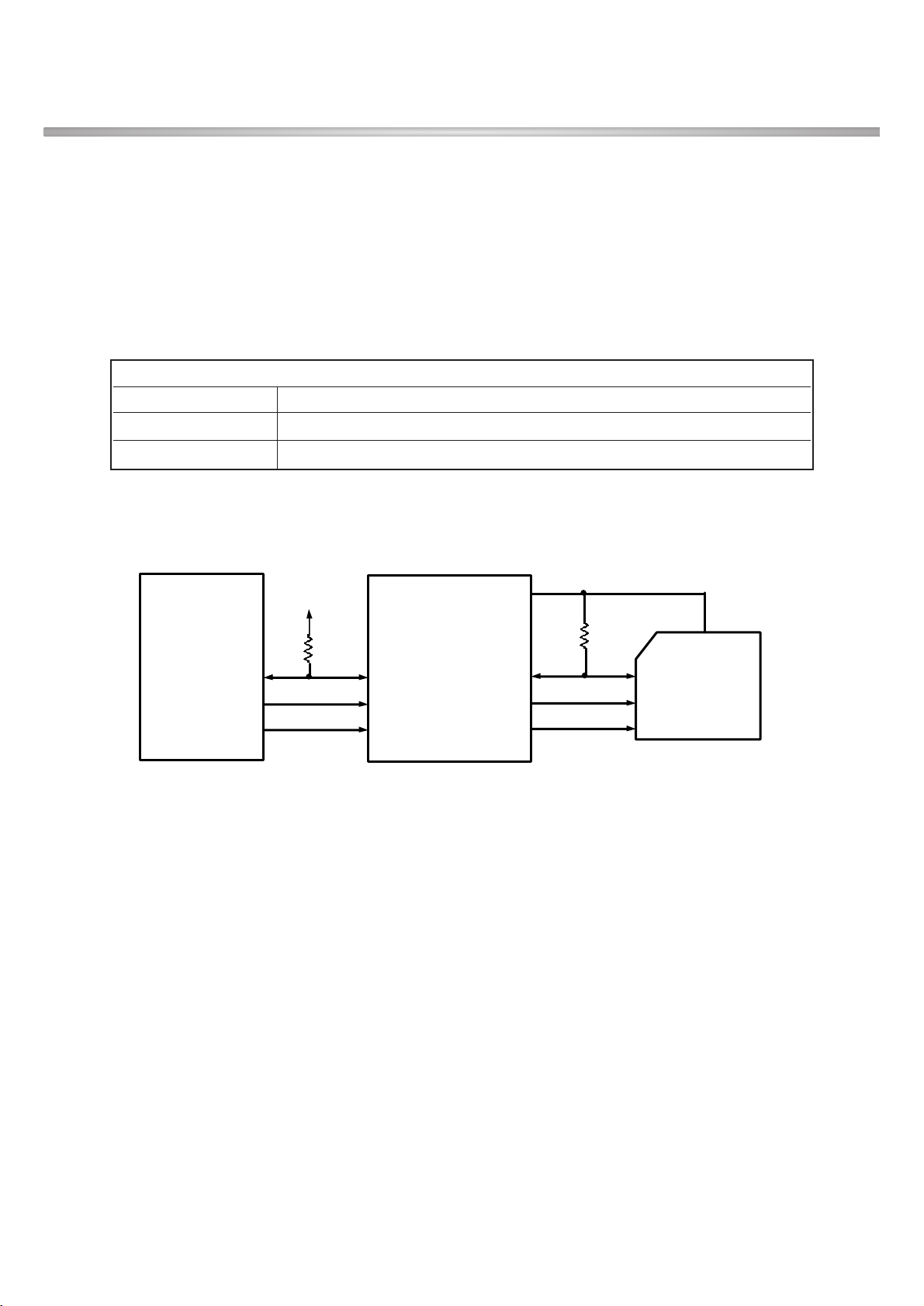
B. WANDA Interface
Wanda controls WCDMA RF part using these signals through W-CDMA RF chip-Wopy & Wivi.
• WCLK, WDAT, WSTR : Control signals for Wivi & Wopy
• RXIA, RXIB, RXQA, RXQB : WCDMA RX Data
• TXIA, TXIB, TXQA, TXQB : WCDMA TX Data
• HSSLRX_D, HSSLRX_CLK : Marita & Wanda Communication Signal
• HSSLTX_D, HSSLTX_CLK : Marita & Wanda Communication Signal
R748 100K
G13
JTAG_TMS
G15
G16
JTAG_TRSTN
R17
RADIO_CLK
RADIO_DAT
P15
M13
RADIO_STR
C14
HSSLRX_CLK
HSSLRX_D
B16
A16
HSSLTX_CLK
HSSLTX_D
A15
D4
ID_BALL
IS_EVENT_N
B12
A13
IS_SYNC_N
JTAG_TCK
G17
F16
JTAG_TDI
JTAG_TDO
EMU0
F13
E15
EMU1
N8
DAC_I_OUT
DAC_I_OUT_INV
U8
DAC_Q_OUT
U7
DAC_Q_OUT_INV
R7
T7
DAC_TXEXTRES
ADC_I_IN_INV
ADC_Q_IN
R9
T9
ADC_Q_IN_INV
N9
ADC_RXEXTREF_N
ADC_RXEXTREF_P
T10
AD_STR
M16
U12
APLL_ATEST1
ADC_I_IN
R10
N10
R749 100K
VDIG
NA
R746
VCORE
C730 0.1u
3.3K
R744
VCORE
Q702
2
3
1
PMST3904
2.7K
R745
47p
C726
TXQB
HSSLTX
HSSLRXCLK
HSSLRX
HSSLTXCLK
ISSYNCn
ISEVENTn
RXIB
RXQA
RXQB
ADCSTR
TXIA
TXIB
TXQA
WCLK
WDAT
RXIA
WSTR
Figure 3-1-5. Schematic of WANDA RF Interface
3. Technical Brief
- 30 -
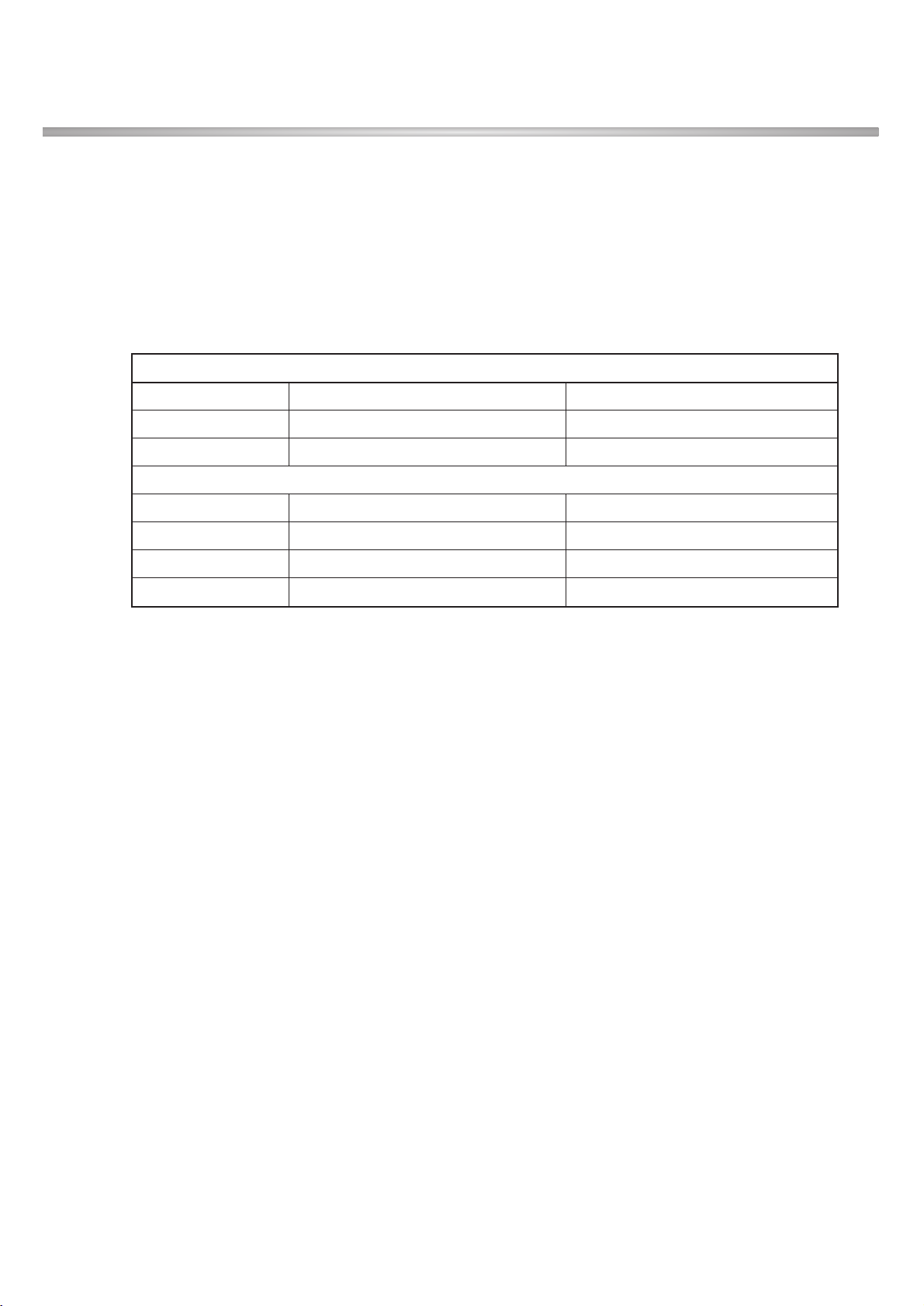
3.1.5 SIM Interface
SIM interface scheme is shown in Figure 3-1-6
SIMDAT0, SIMCLK0, SIMRST0 ports are used to communicate DBB(MARITA) with
ABB(VINCENNE) and filter.
SIM (Interface between DBB and ABB)
SIMDATO SIM card bidirectional data line
SIMCLKO SIM card reference clock
SIMRSTO SIM card async/sync reset
Table 3-1-2. SIM Interface
VDD
DAT
CLK CARD
RST
SIMVCC
VINCENNE
SDAT SIMDAT
SCLK SIMCLK
SRST SIMRST
MARITA
SIMDAT0
SIMCLK0
SIMRST0
VDIG
10K
15K
Figure 3-1-6. SIM Interface Scheme
3. Technical Brief
- 31 -
3.1.6 UART Interface
UART signals are connected to MARITA GPIO through IO connector and Bluetooth interface.
UART0
Resource Name Note
GPIO10 UARTRX0 Receive Data
GPIO11 UARTTX0 Transmit Data
UART3 for the bluetooth
GPIO24 UARTRX3 Receive Data
GPIO25 UARTTX3 Transmit Data
GPIO26 UARTCTS3 Clear To Send
GPIO27 UARTRTS3 Request To Send
Table 3-1-3. UART Interface
 Loading...
Loading...