LG 21FG3RG-T9 Schematic

COLOR TV
SERVICE MANUAL
CHASSIS: CP-079A
Model : 21FG3RG-T9
CAUTION
BEFORE SERVICING THE CHASSIS,
READ THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS IN THIS MANUAL.

CONTENTS
Contents
Location & Function of control
Safety Precautions
Specifications
Adjustment
Block Diagram
R,G,B Section / Deflection Section
Audio AMP. Section
Exploded View
2
3
4
7
9
15
16
17
18
Exploded View Parts List
Replacement Parts List
Schematic Diagram
19
20
2
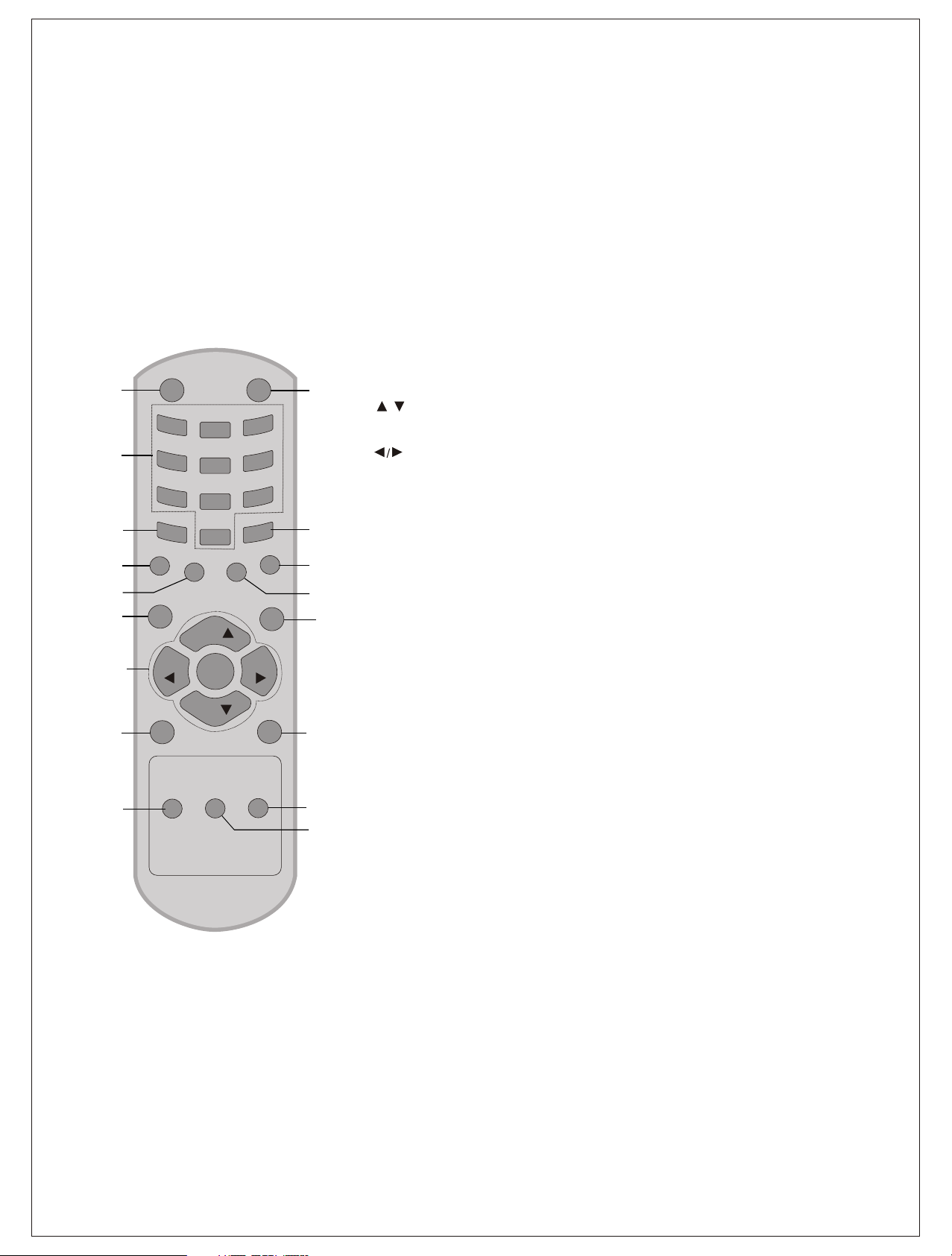
Location and function of controls
All the functions can be controlled with the remote control handset. Some functions
can also be adjusted with the buttons on the front panel of the set.
Remote control handset
Before you use the remote control handset, please install the batteries. See the
previous page.
1. POWER
switches the set from On to standby or standby to On.
2. NUMBER BUTTONS
switches the set On from standby or directly select a Programme number.
3. MENU
selects a menu.
POWER
MUTE
1
1
2
4
7
PSM
7 14
EYE/*
4
ARC/*
2
5
8
0
Q.VIEW
3
6
9
SSM
LIST
15
13
VOL
PR
OK
PR
MENU
VOL
SLEEP
5
10
TV/AV
FAVOURITE
I/II/*
MM/*
XDP/*
16
9
12
17
11
4. EYE/ (option)
*
switches the eye function On or Off.
5. / (Programme Up/Down)
selects a programme or a menu item.
switches the set on from standby.
(Volume Up/Down)
adjusts the volume.
adjusts menu settings.
OK
accepts your selection or displays the current mode.
6. Q. VIEW
returns to the previously viewed programme.
6
7. PSM (Picture Status Memory)
recalls your preferred picture setting.
3
8. XDP/*
Select excellent Digital picture.
9. MUTE
switches the sound On or Off.
10. TV/AV
selects TV or AV mode.
clears the menu / text from the screen switches the set On from Standby.
11. I/II/* (option)
8
output.
selects the language during dual language broadcast selects the sound
(option)
12. LIST
displays the programme table.
press LIST key again to clear the LIST table from the screen.
13. SLEEP
sets the sleep timer.
14. SSM/* (option) (Sound Status Memory)
recalls your preferred sound setting.
15. ARC/* (option)
change picture format (Normal/zoom).
16.FAVOURITE
pressing each time this button will select a stored favourite programme.
17.MM/*(Option)
select Music Mode
Remarks :
1. Some keys in remote can be non-functional, these keys are use in other models.
2. Keys marked * are non functional.
3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special safety-related characteristics. These parts are identified by in the
Schematic Diagram and Replacement Parts List.
It is essential that these special safety parts should be replaced with the same components as recommended in this manual to prevent XRADIATION, Shock, Fire, or other Hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
General Guidance
An Isolation Transformer should always be used during the
servicing of a receiver whose chassis is not isolated from the AC
power line. Use a transformer of adequate power rating as this
protects the technician from accidents resulting in personal injury
from electrical shocks.
It will also protect the receiver and it's components from being
damaged by accidental shorts of the circuitary that may be
inadvertently introduced during the service operation.
If any fuse (or Fusible Resistor) in this TV receiver is blown, replace it
with the specified.
When replacing a high wattage resistor (Oxide Metal Film
Resistor, over 1W), keep the resistor l0mm away from PCB.
Keep wires away from high voltage or high temperature parts.
Due to high vacuum and large surface area of picture tube, extreme
care should be used in handling the Picture Tube. Do not lift the
Picture tube by it's Neck.
X-RAY Radiation
Warning:
The source of X-RAY RADIATION in this TV receiver is the
High Voltage Section and the Picture Tube.
For c ontinued X-RAY RADIATION protection, the
replacement tube must be the same type tube as specified
in the Replacement Parts List.
Before returning the receiver to the customer,
always perform an AC leakage current check on the exposed metallic
parts of the cabinet, such as antennas, terminals, etc., to be sure the
set is safe to operate without damage of electrical shock.
Leakage Current Cold Check (Antenna Cold Check)
With the instrument AC plug removed from AC source connect an
electrical jumper across the two AC plug prongs. Place the AC switch
in the on position, connect one lead of ohm-meter to the AC plug
prongs tied together and touch other ohm-meter lead in turn to each
exposed metallic parts such as antenna terminals, phone jacks, etc.
If the exposed metallic part has a return path to the chassis, the
measured resistance should be between 1MW and 5.2MW.
When the exposed metal has no return path to the chassis the
reading must be infinite.
An other abnormality exists that must be corrected before the
receiver is returned to the customer.
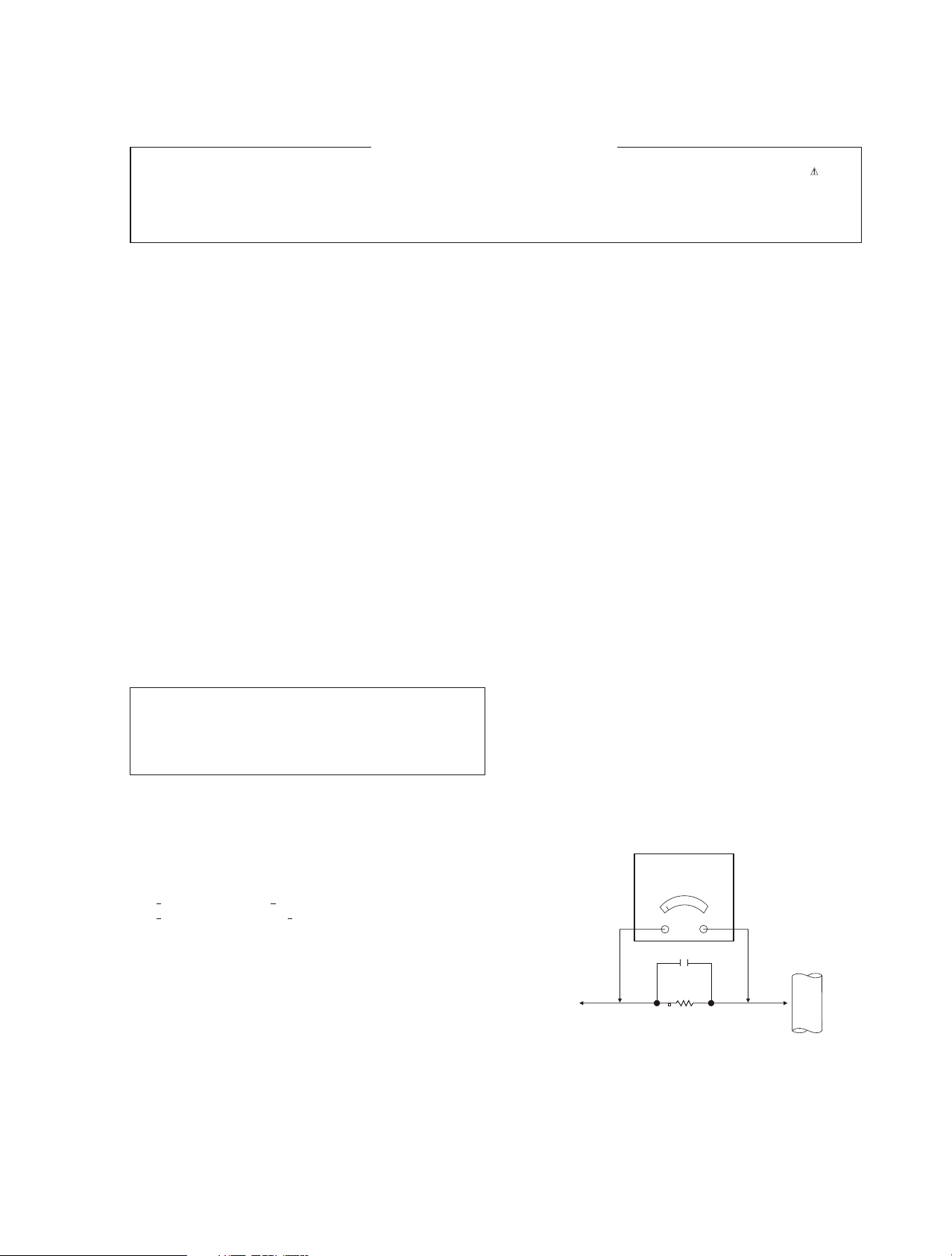
Leakage Current Hot Check (See below Figure)
Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet.
Do not use a line Isolation Transformer during this check.
Connect 1.5K/10watt resistor in parallel with a 0.15uF capacitor
between a known good earth ground (Water Pipe, Conduit, etc.) and
the exposed metallic parts.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor using AC voltmeter with
1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity.
Reverse plug the AC cord into the AC outlet and repeat AC voltage
measurements for each esposed metallic part. Any voltage
measured must not exceed 0.75 volt RMS which is corresponds to
0.5mA.
In case any measurement is out of the limits sepcified, there is
possibility of shock hazard and the set must be checked and repaired
before it is returned to the customer.
To determine the presence of high voltage, use an accurate high
impedance HV meter.
Adjust brightness, color, contrast controls to minimum. Measure the
high voltage.
The meter reading should indicate
+ +
23.5 .5KV: 14-19 inch, 26 1.5KV: 19- 21 inch,
+ +
29.0 1.5KV: 25-29 inch, 30.0 1.5KV: 32 inch,
If the meter indication is out of tolerance, immediate service and
correction is required to prevent the possibility of premature
component failure.
Leakage Current Hot Check circuit
AC Volt - meter
To Instrument's
exposed
METALLIC PARTS
1.5 Kohm10W
4
0.15uF
Good Earth Ground
such as WATER PIPE,
CONDUIT etc.

SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION: Before servicing receivers covered by this service manual
and its supplements and addenda, read and follow the SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS on page 3 of this publication.
NOTE: If unforeseen circumstances create conflict between the
following servicing precautions and any of the safety precautions on
page 3 of this publication, always follow the safety precautions.
Remember: Safety First.
General Servicing Precautions
1. Always unplug the receiver AC power cord from the AC power
source before;
a. Removing or reinstalling any component, circuit board module
or any other receiver assembly.
b. Disconnecting or reconnecting any receiver electrical plug or
other electrical connection.
c. Connecting a test substitute in parallel with an electrolytic
capacitor in the receiver.
CAUTION: A wrong part substitution or incorrect polarity
installation of electrolytic capacitors may result in an explosion
hazard.
d. Discharging the picture tube anode.
2. Test high voltage only by measuring it with an appropriate high
voltage meter or other voltage measuring device (DVM, FETVOM,
etc) equipped with a suitable high voltage probe. Do not test high
voltage by "drawing an arc".
3. Discharge the picture tube anode only by (a) first connecting one
end of an insulated clip lead to the degaussing or kine aquadag
grounding system shield at the point where the picture tube socket
ground lead is connected, and then (b) touch the other end of the
insulated clip lead to the picture tube anode button, using an
insulating handle to avoid personal contact with high voltage.
4. Do not spray chemicals on or near this receiver or any of its
assemblies.
5. Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, clean electrical
contacts only by applying the following mixture to the contacts with
a pipe cleaner, cotton-tipped stick or comparable nonabrasive
applicator; 10% (by volume) Acetone and 90% (by volume)
isopropyl alcohol (90%-99% strength)
CAUTION: This is a flammable mixture.
Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, lubrication of
contacts in not required.
6. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage interlocks with which
receivers covered by this service manual might be equipped.
7. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any of its
electrical assemblies unless all solid-state device heat sinks are
correctly installed.
8. Always connect the test receiver ground lead to the receiver
chassis ground before connecting the test receiver positive lead.
Always remove the test receiver ground lead last.
9. Use with this receiver only the test fixtures specified in this service
manual.
CAUTION: Do not connect the test fixture ground strap to any
heatsink in this receiver.
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily
by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES
devices are integrated circuits and some fieldeffect
transistors and semicounductor "chip" components. The following
techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of
component damage caused by static by static electricity.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or
semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any electostatic
charge on your body by touching a known earth ground.
Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available
discharging wrist strap device, which should be removed to
prevent potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit
under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices,
place the assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminum foil,
to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the
assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES
devices.
4. Use only an anti-static type solder removal device. Some solder
removal devices not classified as "anti-static" can generate
electrical charges sufficent to demage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon - propelled chemicals. These can generate
electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a repalcement ES device from its protective
package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically
shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or comparable
conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the
ieads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material to
the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit,
and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement
ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the bruching
together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a
carpeted floor can generate static electricity sufficient to damage
an ES device.)
General Soldering Guidelines
1. Use a grounded-tip, low-wattage soldering iron and appropriate tip
size and shape that will maintan tip temperature within the range or
500º F to 600º F.
2. Use an appropriate gauge of RMA resin-core solder composed of
60 parts tin/40 parts lead.
3. Keep the soldering iron tip clean and well tinned.
4. Thorohly clean the surfaces to be soldered. Use a mall wirebristle
(0.5 inch, or 1.25cm) brush with a metal handle.
Do not use freon- propelled spray-on cleaners.
5.Use the following unsoldering technique
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach normal temperature. (500º F
to 600º F)
b.Heat the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly draw the melted solder with an anti-static, suction-type
solder removal device or with solder braid.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuiboard
printed foil.
6. Use the following soldering technique.
a.Allow the soldering iron tip to reach a normal temperature (500º F
to 600º F)
b.First, hold the soldering iron tip and solder the strand against the
component lead the solder melts.
5

c. OuIckly move the soldering iron tip to the junction of the
component lead and the printed circuit foil, and hold it t her e
only until the solder flows onto and around both the
component lead and the foil.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit board
printed foil.
d. Closely inspect the solder area and remove any excess or
splashed solder with a small wire-bristle brush.
IC Remove/Replacement
Some chassis circuit boards have slotted holes (oblong) through
which the IC leads are inserted and then bent flat against the circuit
foil. When holes are the slotted type, the following technique should
be used to remove and replace the IC. When working with boards
using the familiar round hole, use the standard technique as outlined
in parapraphs 5 and 6 above.
Removal
1. Desolder and straighten each IC lead in one operation by gently
prying up on the lead with the soldering iron tip as the solder melts.
2. Draw away the melted solder with an anti-static suction type
solder removal device (or with solder braid) before removing the
IC.
Replacement
1. Carefully insert the replacement IC in the circuit boare.
2. Carefully bend each IC lead against the circuit foil pad and solder
it.
3. Clean the soldered areas with a small wire-bristle brush. (It is not
necessary to reapply acrylic coating to the areas).
"Small-Signal" Discrete Transistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Remove the defective transistor by clipping its leads as close as
possible to the component body.
2. Bend into a "U" shape the end of each of three leads remaining on
the circuit board.
3. Bend into a "U" shape the replacement transistor leads.
4. Connect the replacement transistor leads to the corresponding
leads extending from the circuit board and crimp the "U" with long
nose pliers to insure metal to metal contact then solder each
connection.
Power Output, Transistor Device
Removal/Replacement
1. Heat and remove all solder from around the transistor leads.
2. Remove the heatsink mounting screw (if so equipped).
3. Carefully remove the transistor from the heat sink of the circuit
board.
4. Insert new transistor in the circuit board.
5. Solder each transistor lead, and clip off excess lead.
6. Replace heatsink.
Diode Removal/Replacement
1. Remove defective diode by clipping its leads as close as possible
to diode body.
2. Bend the two remaining leads perpendicula y to the circuit board.
3. Observing diode polarity, wrap each lead of the new diode around
the corresponding lead on the circuit board.
4. Securely crimp each connection and solder it.
5. Inspect (on the circuit board copper side) the solder joints of the
two "original" leads. If they are not shiny, reheat them and if
necessary, apply additional solder.
Fuse and Conventional Resistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Clip each fuse or resistor lead at top of the circuit board hollow
stake.
2. Securely crimp the leads of replacement component around notch
at stake top.
3. Solder the connections.
CAUTION: Maintain original spacing between the replaced
component and adjacent components and the circuit board to
prevent excessive component temperatures.
Circuit Board Foil Repair
Excessive heat applied to the copper foil of any printed circuit board
will weaken the adhesive that bonds the foil to the circuit board
causing the foil to separate from or "lift-off" the board. The following
guidelines and procedures should be followed whenever this
condition is encountered.
At IC Connections
To repair a defective copper pattern at IC connections use the
following procedure to install a jumper wire on the copper pattern side
of the circuit board. (Use this technique only on IC connections).
1. Carefully remove the damaged copper pattern with a sharp knife.
(Remove only as much copper as absolutely necessary).
2. carefully scratch away the solder resist and acrylic coating (if
used) from the end of the remaining copper pattern.
3. Bend a small "U" in one end of a small gauge jumper wire and
carefully crimp it around the IC pin. Solder the IC connection.
4. Route the jumper wire along the path of the out-away
copper pattern and let it overlap the previously scraped end of the
good copper pattern. Solder the overlapped area and clip off any
excess jumper wire.
At Other Connections
Use the following technique to repair the defective copper pattern at
connections other than IC Pins. This technique involoves the
installation of a jumper wire on the component side of the circuit
board.
1. Remove the defective copper pattern with a sharp knife. Remove
at least 1/4 inch of copper, to ensure that a hazardous condition will
not exist if the jumper wire opens.
2. Trace along the copper pattern from both sides of the pattern break
and locate the nearest component that is directly connected to the
affected copper pattern.
3. Connect insulated 20-gauge jumper wire from the lead of the
nearest component on one side of the pattern break to the lead of
the nearest component on the other side. Carefully crimp and
solder the connections.
CAUTION: Be sure the insulated jumper wire is dressed so the it
does not touch components or sharp edges.
6

SPECIFICATIONS
Note : Specification and others are subject to change without notice for improvement.
< Video input system:
PAL-B/G, D/K, I/I
SECAM -B/G, D/K,L/L**
NTSC M **
NTSC 4.43**
< Intermediate Frequency (Unit : Mhz)
VISION IF : 38.9MHz
35.32MHz(3.58) : NTSC-M
COLOR IF : 34.47MHz(4.43)
VIF-4.25000 MHz
( )
V I F-4.40625MHz**
: SECAM**
< Tuning range
SOUND IF : 33.4MHz (B/G)
< Power requirement : 110 240V, 50/60Hz
< Power consumption :
< STAND-BY : <6W
32.9MHz (I/I)
32.4MHz (D/K)
34.4MHz (M)
~
*
Band
B/G
D/K
VHF-Low Ch2-4 Ch1-5
For TV
I/I
NTSC
For CATV
S1'-S3', S1
S2-S10,
VHF-High
Ch5-12
Ch6-12
Ch2-13
Hyper
UHF
< Tuning system : <Feature : Auto programme /Manual programme
FVS Auto Sleep
100 Programme memory (option) PSM (Picture Status Memory)
200 Programme memory(W/0 TXT) Programme Editing
< Antenna input impedance : VHF/UHF 75 ohm, unbalanced SSM (Sound Status Memory)
< OSD (On Screen Display) : EASY_MENU XDP*
< Voice coil impedance : 8 ohm
< Sound output :
Dual/Stereo : A2/NICAM(Option)
*
Ch4-13
Chl4-69 Ch21-69
Auto Volume Level
Favourite Program
S11-S20
S21-S41
< External connection : Head Phone Jack
A/V in : 2
PERI Connector(Full Scart) :1 (option)
DVD in (option)
< External In/Output
Audio-In:O.5Vrms±3dB, over 10Kohm
Audio-Out:0.5Vrms±3dBb,below 1Kohm
Video-In/Out:1Vp-p±3d8, 75ohm
DVD In Y: 1Vp-p±3dB
Pb,Pr : 0.7Vp-p±3dB
*Depend on model.
** For Export model.
7
DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
Important note
This set is disconnected from the power supply through the converter.
transformer. An isolating transformer is necessary for service
operations on the primary side of the converter transformer.
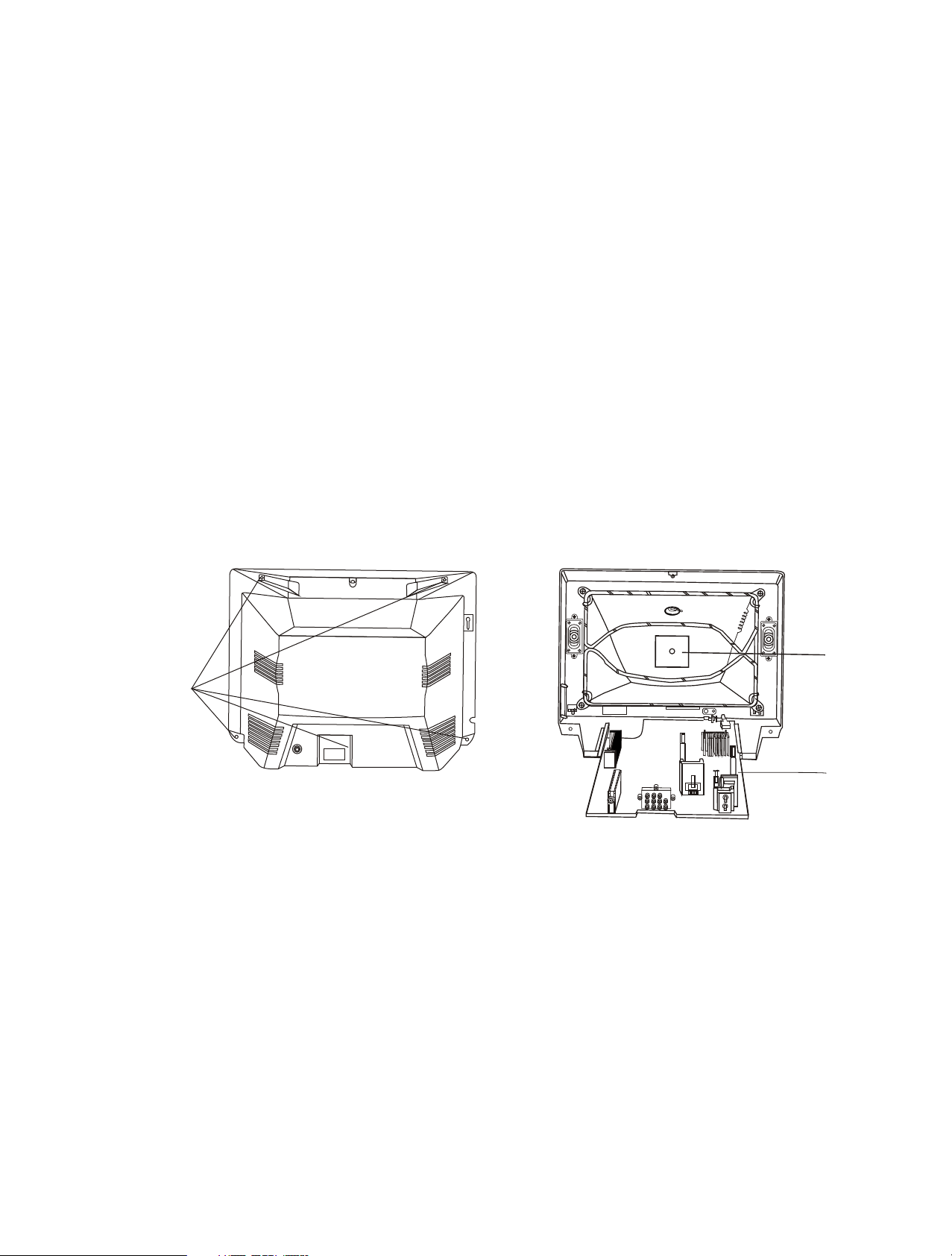
Back Cabinet Removal
Removal the screws residing on the back cabinet and carefully
separate the back cabinet from the front cabinet cabinet. (Fig. 2-1).
CPT Removal
1. Pull out the CPT board from the CPT neck.
2. Place the front cabinet on soft material not to mar the front surface
or damage control knobs.
3. Remove 5 screws securing the picture tube mounting brackets to
the front cabinet.
4. Carefully separate CPT from the front cabinet.
Chassis Assy Removal
Grasp both side of Frame and pull it backward smoothly.
PICTURE TUBE HANDLING CAUTION
Due to high vacuum and large surface area of picture tube, great care
must be exercised when handling picture tube. Always lift picture tube
by grasping it firmly around faceplate.
NEVER LIFT TUBE BY ITS NECK! The picture tube must not be
scratched or subjected to excessive pressure as fracture of glass may
result in an implosion of considerable violence which can cause
personal injury or property damage.
Remove
Screws
CPT
board
Main
PCB
8
 Loading...
Loading...