Page 1

MSL-3S79
3-Slot Gigabit Modular L2 Managed Switch
User Manual
V1.0
I
Page 2

FCC Warning
This Equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class-A
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class-A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
II
Page 3

Content
0BChapter 1 Introduction ............................................................................................... 1
8B1.1 Hardware Features ................................................................................................. 2
9B1.2 Software Feature .................................................................................................... 4
10B1.3 Package Contents .................................................................................................. 6
1BChapter 2 Hardware Description ...................................................................................... 8
11B2.1 Physical Dimension ................................................................................................ 8
12B2.2 LED Indicators ........................................................................................................ 8
13B2.3 Rear Panel ............................................................................................................ 10
2BChapter 3 Hardware Installation ..................................................................................... 11
14B3.1 Desktop Installation .............................................................................................. 11
15B3.2 Rack-mounted Installation .................................................................................... 11
16B3.3 Power On .............................................................................................................. 12
3BChapter 4 Network Application ....................................................................................... 13
17B4.1 Desktop Application .............................................................................................. 13
18B4.2 Segment Application ............................................................................................. 13
4BChapter 5 Console Management .................................................................................... 15
19B5.1 Connecting to the Console Port ............................................................................ 15
20B5.2 Login in the Console Interface .............................................................................. 15
21B5.3 CLI Management .................................................................................................. 16
5BChapter 6 Web-Based Management ............................................................................... 17
22B6.1 About Web-based Management ........................................................................... 17
23B6.2 Preparing for Web Management ........................................................................... 17
24B6.3 System Login ........................................................................................................ 18
25B6.4 System .................................................................................................................. 18
51B6.4.1 System Information ..................................................................................... 18
52B6.4.2 Switch Information ...................................................................................... 19
75B6.4.2.1 Main Board ....................................................................................... 19
76B6.4.2.2 Management Software ..................................................................... 19
53B6.4.3 IP Configuration .......................................................................................... 20
54B6.4.4 DHCP Configuration ................................................................................... 20
55B6.4.5 Firmware Update ........................................................................................ 22
77B6.4.5.1 TFTP Download Firmware ................................................................ 22
78B6.4.5.2 TFTP Backup Configuration ............................................................. 22
III
Page 4

79B6.4.5.3 TFTP Restore Configuration ............................................................. 23
56B6.4.6 System Event Log ...................................................................................... 23
80B6.4.6.1 LOG Configuration ............................................................................ 23
81B6.4.6.2 Logging Events Level ....................................................................... 25
82B6.4.6.3 Logging RAM Table .......................................................................... 26
83B6.4.6.4 Logging Flash Table ......................................................................... 27
57B6.4.7 Security Manager ....................................................................................... 27
26B6.5 Port ....................................................................................................................... 28
58B6.5.1 Port Statistics .............................................................................................. 28
59B6.5.2 Port Information .......................................................................................... 28
60B6.5.3 Port Control ................................................................................................ 29
61B6.5.4 Port Trunk ................................................................................................... 30
84B6.5.4.1 Trunk Configuration .......................................................................... 30
85B6.5.4.2 Trunk Information ............................................................................. 31
86B6.5.4.3 Port Activity ...................................................................................... 31
62B6.5.5 Port Mirror ................................................................................................... 32
63B6.5.6 Rate Limiting ............................................................................................... 34
27B6.6 Protocol ................................................................................................................ 34
64B6.6.1 VLAN .......................................................................................................... 34
87B6.6.1.1 VLAN Mode Configuration ................................................................ 35
88B6.6.1.2 Port VLAN Id Configuration .............................................................. 35
89B6.6.1.3 VLAN Entry ....................................................................................... 36
65B6.6.2 Rapid Spanning Tree .................................................................................. 37
90B6.6.2.1 STP System Configuration ............................................................... 37
91B6.6.2.2 STP Port Configuration ..................................................................... 39
66B6.6.3 SNMP ......................................................................................................... 40
67B6.6.4 QoS ............................................................................................................ 41
92B6.6.4.1 QoS Configuration ............................................................................ 42
93B6.6.4.2 Port-bace Configuration .................................................................... 42
94B6.6.4.3 COS Configuration ........................................................................... 43
95B6.6.4.4 DSCP Configuration ......................................................................... 43
68B6.6.5 SNTP .......................................................................................................... 44
69B6.6.6 IGMP .......................................................................................................... 45
96B6.6.6.1 IGMP Configuration .......................................................................... 45
IV
Page 5

97B6.6.6.2 IGMP Static Configuration ................................................................ 46
70B6.6.7 LLDP........................................................................................................... 47
98B6.6.7.1 LLDP Configuration .......................................................................... 47
99B6.6.7.2 LLDP Neighbor Table ....................................................................... 48
28B6.7 Security ................................................................................................................. 48
71B6.7.1 802.1x/ RADIAS ......................................................................................... 48
100B6.7.1.1Misc Configuration ............................................................................. 48
101B6.7.1.2 Port Configuration ............................................................................. 50
102B6.7.1.3Radius Client Configuration ............................................................... 50
72B6.7.2 Port Security ............................................................................................... 51
103B6.7.2.1 Static MAC Address Table ............................................................... 51
104B6.7.2.2 Filter MAC Address Table ................................................................ 52
105B6.7.2.3 MAC Address Table Aging ............................................................... 53
73B6.7.3 IP Security .................................................................................................. 53
74B6.7.4 ACL ............................................................................................................ 54
29B6.8 Factory Default ..................................................................................................... 55
30B6.9 Save Configuration ............................................................................................... 55
31B6.10 System Reboot ................................................................................................... 56
6BTroubleshooting .............................................................................................................. 57
7BAppendix A- Command Sets ........................................................................................... 59
32BCommands Set List .................................................................................................... 59
33BSystem Commands Set .............................................................................................. 60
34BPort Commands Set ................................................................................................... 61
35BMac / Filter Table Commands Set .............................................................................. 63
36BPort Mirroring Commands Set .................................................................................... 65
37BTFTP Commands Set ................................................................................................. 65
38BQOS Commands Set .................................................................................................. 66
39BSpanning Tree Commands Set .................................................................................. 67
40BVLAN Commands Set ................................................................................................. 69
41BSystem log Commands Set ........................................................................................ 71
42BSNTP Commands Set ................................................................................................ 73
43BIGMP Commands Set ................................................................................................. 74
44BTRUNK Commands Set .............................................................................................. 75
45BSNMP Commands Set ................................................................................................ 76
V
Page 6

46BDHCP Server Commands Set .................................................................................... 77
47BSecurity IP Commands Set ......................................................................................... 78
48B802.1X Commands Set ............................................................................................... 78
49BLLDP Commands Set ................................................................................................. 79
50BACL Commands Set ................................................................................................... 80
VI
Page 7

0B
Chapter 1 Introduction
The MSL-3S79 is a modular switch that can be used to build high-performance
switched workgroup networks. This switch is a store-and-forward device that offers low
latency for high-speed networking. The Switch is targeted at workgroup, department or
backbone computing environment.
The MSL-3S79 features a “store-and-forward” switching scheme. This allows the
switch to auto-learn and store source address in an 16K-entry MAC address table.
MDI (Medium Dependent Interface) Port is also called an "uplink port". The MDI port
does not cross transmit and receive lines, which is done by the regular ports (MDI-X
ports) that connect to end stations. In general, MDI means connecting to another Hub
or Switch while MDIX means connecting to a workstation or PC. Therefore, Auto
MDI/MDIX means that you can connect to another Switch or workstation without
changing non-crossover or crossover cabling.
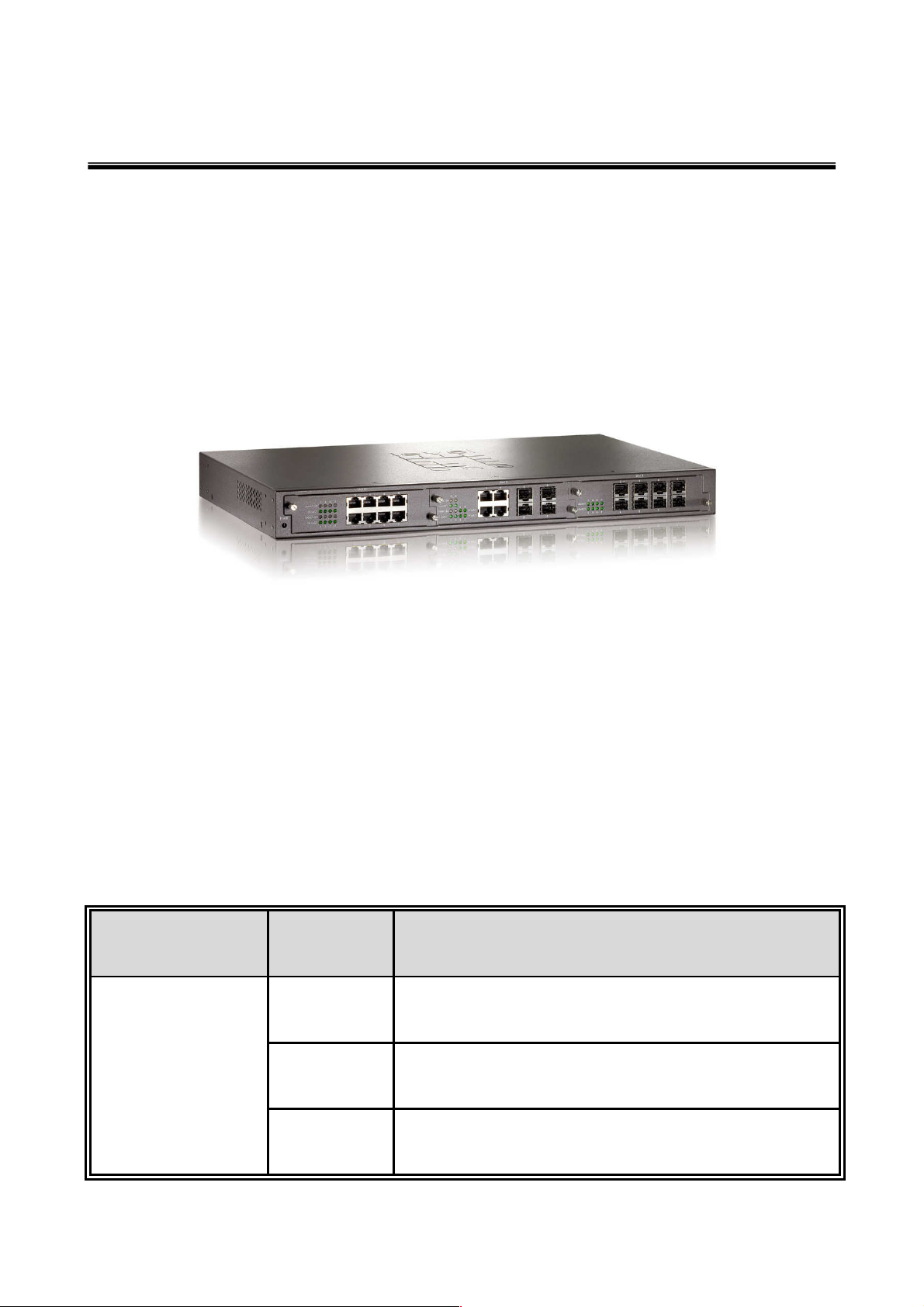
The MSL-3S79 has 3-module slot. User can purchase the modules in accordance with
their needs as well as giving elasticity on network application.
1
Page 8
8 Port Gigabit Fiber module: Link/Activity
8B
1.1 Hardware Features
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit fiber
IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T
IEEE 802.3x Flow control and Back pressure
IEEE 802.3ad Port trunk with LACP
Standards
IEEE 802.1d Spanning tree protocol
IEEE 802.1w Rapid spanning tree
IEEE 802.1p Class of service
LED Indicators
IEEE 802.1q VLAN Tagging
IEEE 802.1x User authentication
IEEE 802.1ab LLDP
System Power
10/100/1000TX module: Link/Activity, 1000/100/10Mbps
speed
8 Port MINI GBIC: Link/Activity
4 Port Gigabit copper + 4 Port MINI GBIC module: RJ-45
(Link/Activity, 1000/100/10Mbps speed), MINI GBIC
(Link/Activity)
RS-232 console: Female DB-9
Gigabit copper module: 8 x RJ-45
MINI GBIC module: 8 x MINI GBIC socket
Connector
Gigabit Fiber module: 8 x SC for Gigabit SX or LX
4 Gigabit Copper & 4 MINI GBIC module: 4 x RJ-45 + 4 x
3.3v MINI GBIC Socket
Switch architecture
2
Store and forward switch architecture with Back-plane up to
Page 9
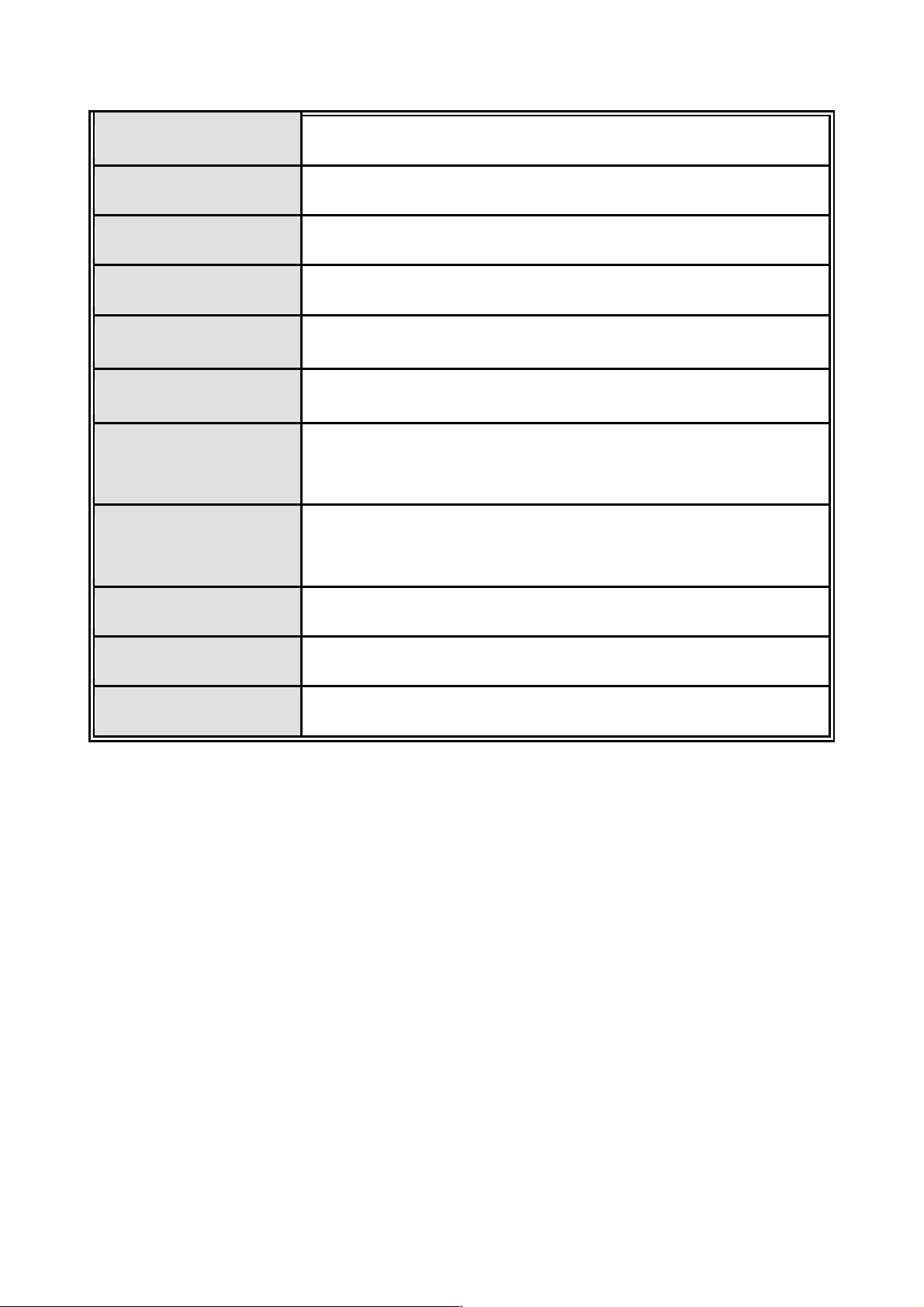
48Gbps.
Packet buffer 6Mbits
Dimensions 440mm(W) x 280mm(D) x 44mm(H)
MAC Address 16K
Storage Temp.
Operational Temp.
-40℃~70℃, 5%~95%RH
0℃~45℃, 5%~95%RH
AC 100~240V 50/60Hz,
Power Supply
Redundant Power: DC 12~48V
Power
35 Watts
Consumption
Ventilation 2 fan at the rear
EMI Compliance with FCC Class A, CE
Safety Compliance with UL, cUL, CE/EN60950-1
3
Page 10
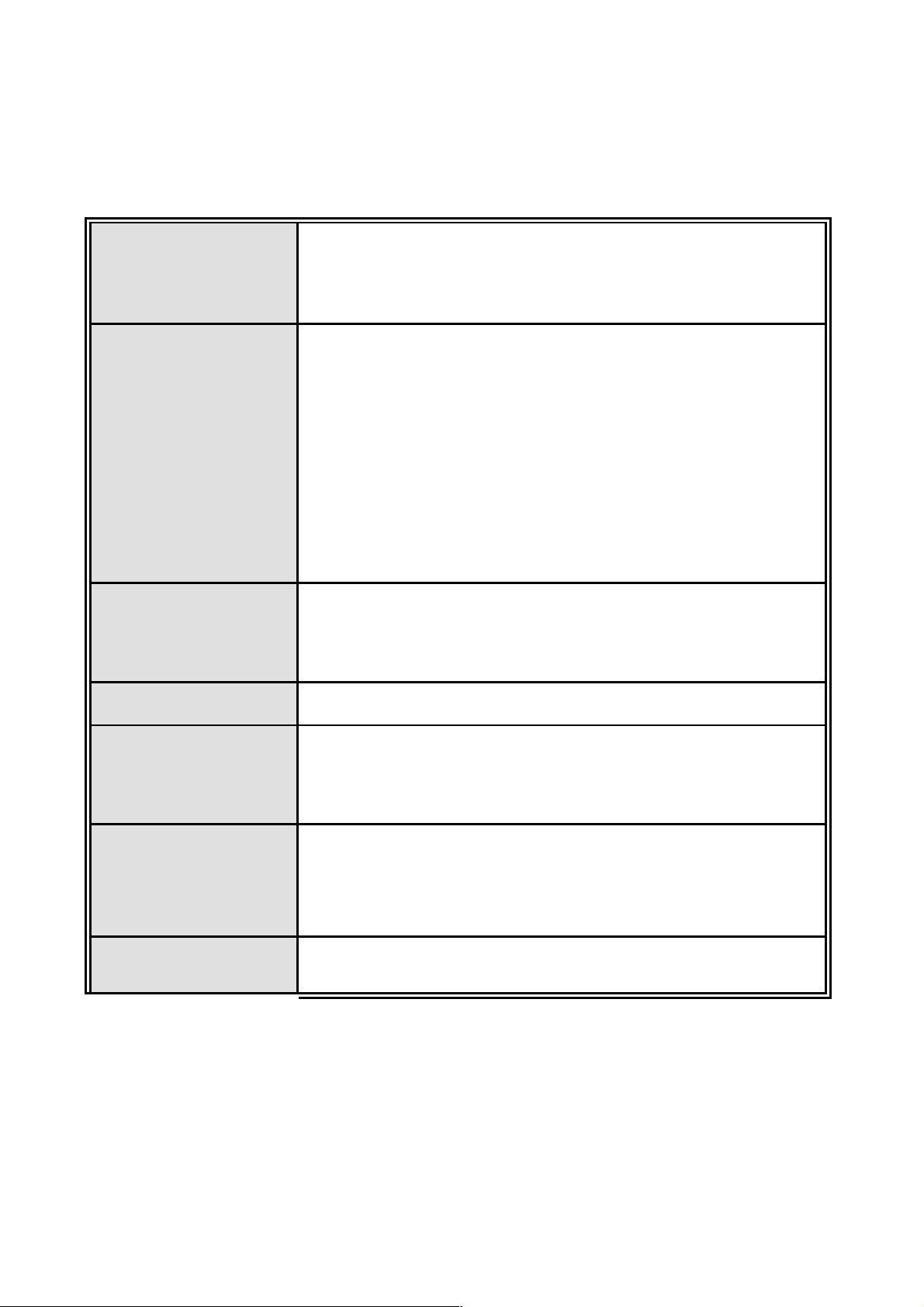
RFC 2863 Interface Group MIB,
RFC 1213 MIBII,
RFC 1493 Bridge MIB,
RFC 2674 VLAN MIB,
Ethernet Like MIB,
IB,
RMON MIB,
9B
1.2 Software Feature
Management SNMP v1/v2c, Telnet, RMON1, CLI and Web management.
MIB
RFC 1643
RFC 1215 Trap M
RFC 1757
Private MIB
Cold start/Warm start trap,
SNMP Trap
Link down/Link up trap,
Authentication fail trap,
Firmware Upgrade TFTP
Configuration
upload and
System quick installation and backup by TFTP
download
Support IEEE802.3ad with LACP function.
Port Trunk
Up to 7 trunk groups with failover feature and the member
up to 8 ports.
Spanning Tree IEEE802.1w Rapid spanning tree (Compatible with STP)
4
Page 11
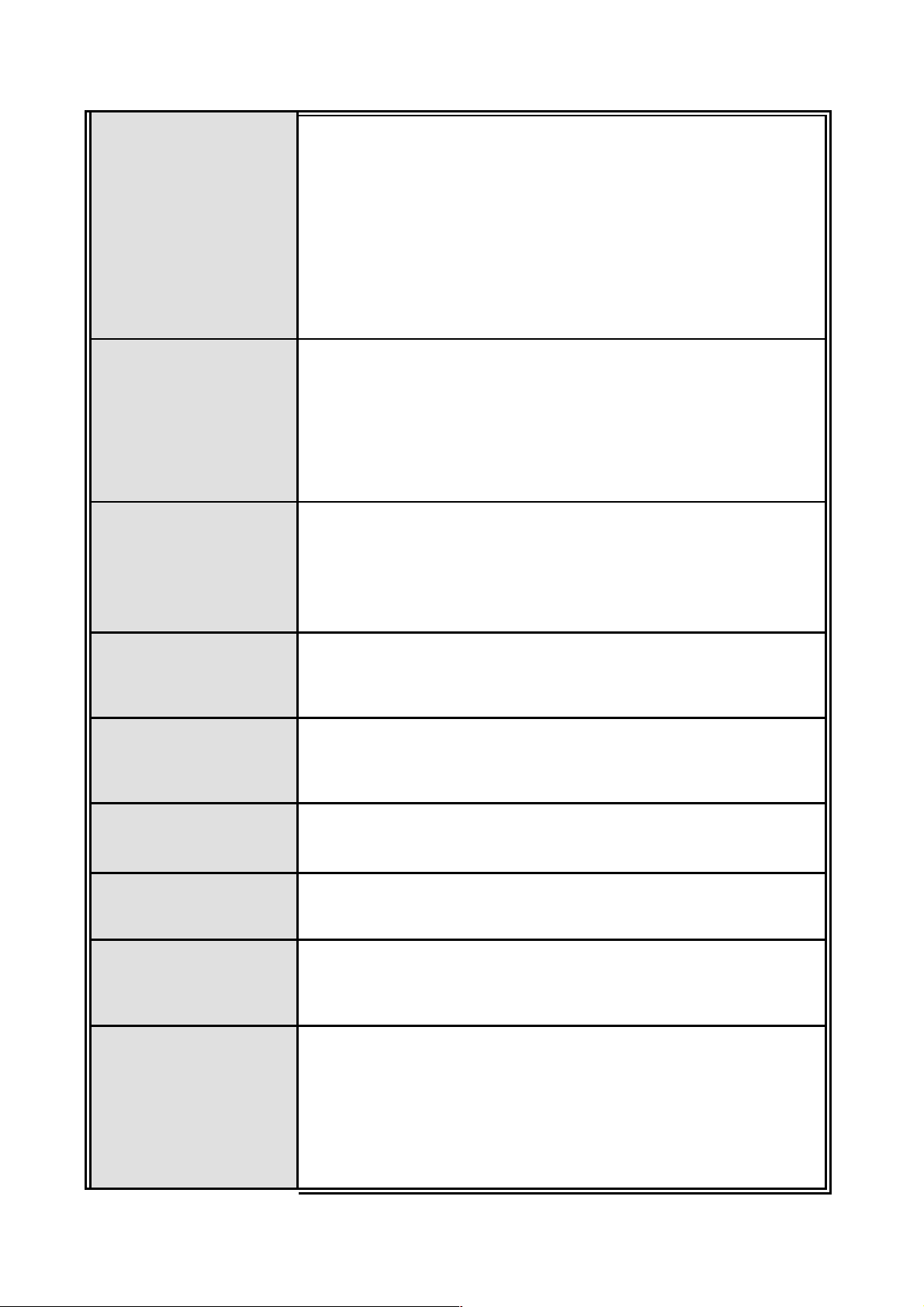
VLAN
Port based VLAN, up to 24 groups
IEEE802.1Q Tag VLAN
Static VLAN groups up to 256 entries and dynamic VLAN
groups up to 2048, the VLAN ID can be assigned from 1 to
4094.
GVRP
Per port 8 priority queues and support strict and WRR
priority rule.
Class of Service
Weight round ratio (WRR):1:2:3:4:5:6:7:8
Weight round ratio (WRR):1:1:2:2:3:3:4:4
Weight round ratio (WRR):1:1:2:2:4:4:8:8
Port based,
Tag based,
Quality of service
IPv4 Type of service,
IPv4 Different service.
IGMP v1, v2
IGMP
Supports 256 multicast groups and IGMP query
Support 128 entries of MAC address for static MAC and
Port Security
another 128 for MAC filter
Port Mirror Supports 3 mirroring types: “RX, TX and Both packet”.
Per port support ingress rate limiting and egress rate
Bandwidth Control
shaping control.
IP Management Security: Support IP addresses security to
Access security
prevent unauthorized intruder.
Support IEEE802.1x User-Authentication and can report to
RADIUS server.
802.1x
Reject
Authentication
Accept
Authorize
5
Page 12
Disable
The system provides control list on Source IP & Destination
Access Control List
IP.
DHCP DHCP Client and DHCP Server
Provide DNS client feature and support Primary and
DNS
Secondary DNS server.
1000 records (Maximum)
System log
Provide remote storage ability and also can view the log by
Web/Telnet/SNMP interface.
SNTP Support RFC 2030 SNTP client.
System supports 5 mail accounts and 2 Mail servers for
Primary and Secondary.
SMTP
The SMTP will auto send event message to supervisor
whom is pre-defined in the SMTP system through the
pre-defined mail server.
Packet filter Broadcast storm control
LLDP Support IEEE 802.1ab Link Layer Discovery Protocol
10B
1.3 Package Contents
Unpack the contents of the
below.
One MSL-3S79
Four Rubber Feet
6
MSL-3S79
and verify them against the checklist
Page 13

Power Cord
Rack-mounted kit
RS-232 Cable
CD Manual
Compare the contents of your MSL-3S79 package with the standard checklist above.
IF any item is missing or damaged, please contact your local dealer for service.
7
Page 14
1B
Chapter 2 Hardware Description
This section mainly describes the hardware of the MSL-3S79.
11B
2.1 Physical Dimension
The physical dimensions of the MSL-3S79 is 440mm(W) x 280mm(D) x 44mm(H)
12B
2.2 LED Indicators
The LED Indicators gives real-time information of systematic operation status. The
LED indicators are located in every module. The LED indicators will be different for
different module. The following table provides descriptions of LED status and their
meaning.
8-port 1000Base-T module
106B
LED
107B
Status
Meaning
Green Link on 1000Mbps speed mode
1000/100
Amber Link on 100Mbps speed mode
Off Link on 10Mbps speed mode or No device attached
8
Page 15
Green Ethernet Link connected
LK/ACT
Blink The port is receiving or transmitting data.
Off No device attached or Link is disconnected
4-port 1000Base-T + 4-port Mini GBIC module
108B
LED
109B
Status
Meaning
Gigabit Copper
Green Link on 1000Mbps mode
1000/100
Amber Link on 100Mbps speed mode
LK/ACT
LK/ACT
Off Link on 10Mbps speed mode or No device attached
Green Ethernet Link is connected
Blink The port is receiving or transmitting data.
Off No device attached or Link is disconnected
Mini GBIC
Green Link is connected
Blink The port is receiving or transmitting data.
Off No device attached or Link is disconnected
9
Page 16
8-port Mini GBIC module
LED
112B
Status
Meaning
Green Link connected
LNK/ACT
Blink The port is receiving or transmitting data.
Off No device attached or Link is disconnected
13B
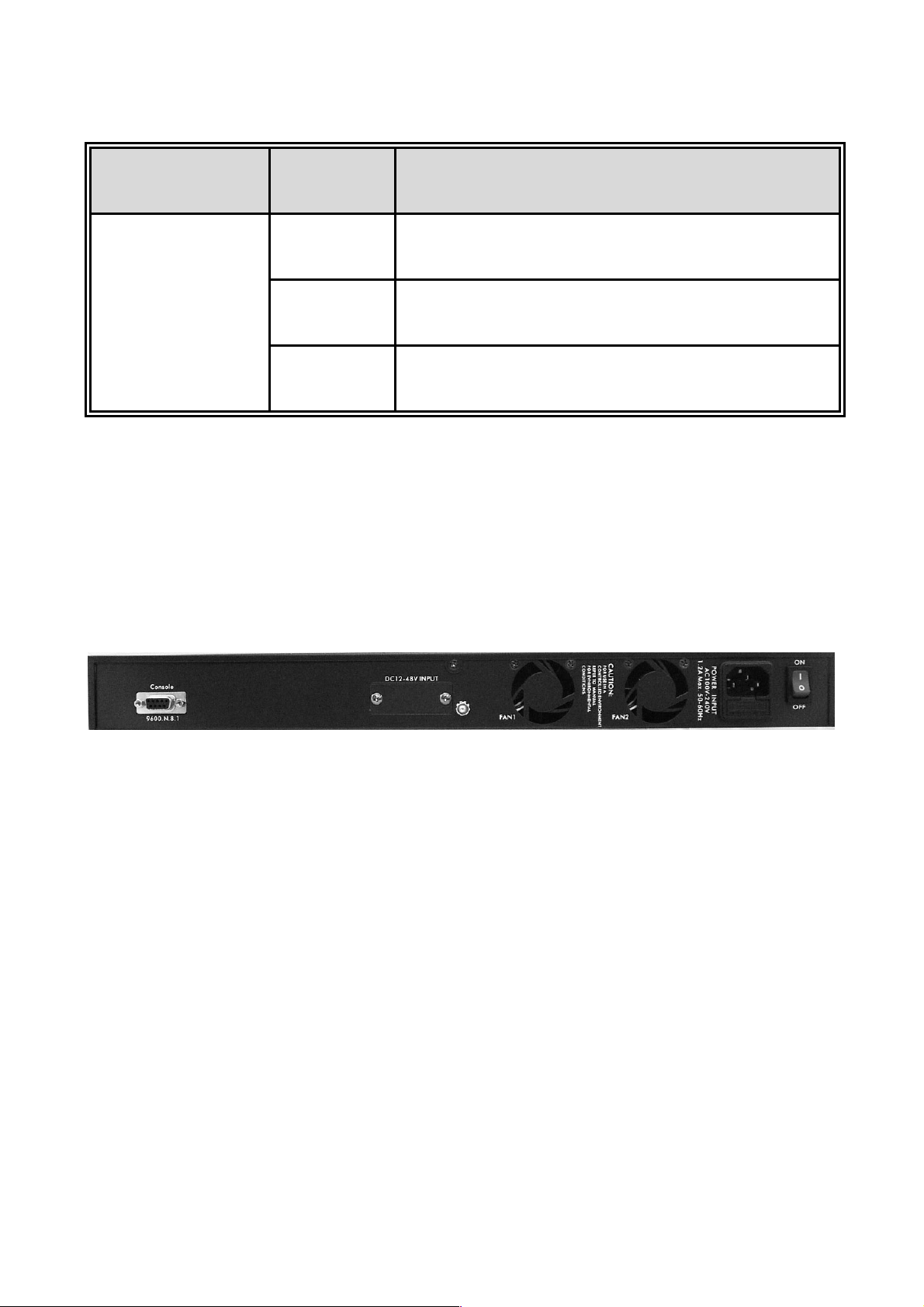
2.3 Rear Panel
The 3-pronged power plug is located at the Rear Panel of the MSL-3S79 as shown in
figure. The Switches will work with AC in the range 100-240V AC, 50-60Hz. The DC
redundant power jack is optional.
Rear Panel of the MSL-3S79
10
Page 17

2B
Chapter 3 Hardware Installation
14B
3.1 Desktop Installation
Set the switch on a sufficiently large flat space with a power outlet nearby. The surface
where you put your Switch should be clean, smooth, level, and sturdy. Make sure
there is enough clearance around the Switch to allow attachment of cables, power
cord and air circulation.
Attaching Rubber Feet
1. Make sure mounting surface on the bottom of the Switch is grease and dust free.
2. Remove adhesive backing from your Rubber Feet.
3. Apply the Rubber Feet to each corner on the bottom of the Switch. These
footpads can prevent the Switch from shock/vibration.
15B
3.2 Rack-mounted Installation
The switch come with a rack-mounted kid and can be mounted in an EIA standard size,
19-inch Rack. The Switch can be placed in a wiring closet with other equipment.
Perform the following steps to rack mount the switch:
A. Position one bracket to align with the holes on one side of the switch and secure it
with the smaller bracket screws. Then attach the remaining bracket to the other
side of the Switch.
B. After attaching both mounting brackets, position the switch in the rack by lining up
the holes in the brackets with the appropriate holes on the rack. Secure the
Switch to the rack with a screwdriver and the rack-mounting screws.
Note: For proper ventilation, allow about at least 4 inches (10 cm) of clearance on
the front and 3.4 inches (8 cm) on the back of the Switch. This is especially
important for enclosed rack installation.
11
Page 18

16B
3.3 Power On
Connect the power cord to the power socket at the rear panel of the Switch. The other
side of power cord connects to the power outlet. The internal power can work with AC
in the voltage range of 100-240VAC/ frequency 50~60Hz or 12-48VDC (It’s optional).
Besides, The AC and DC input can be used for redundant power supply. When one
fails, another one is able to keep providing power to the switch. Check the power
indicator on the front panel to see if power is properly supplied.
12
Page 19

3B
Chapter 4 Network Application
This section provides you a few samples of network topology in which the switch is
used. In general, the MSL-3S79 is designed as a segment switch. That is, with its
large address table (16K MAC address) and high performance, it is ideal for
interconnecting networking segments.
PC, workstations, and servers can communicate each other by directly connecting
with MSL-3S79. The switch automatically learns nodes address, which are
subsequently used to filter and forward all traffic based on the destination address.
.
By using Gigabit or Gigabit Fiber, the switch can connect with another switch or hub to
interconnect other small-switched workgroups to form a larger switched network.
Meanwhile, you can also use Ethernet or Gigabit fiber ports to connect switches.
17B
4.1 Desktop Application
The MSL-3S79 is designed to be a switch that is an ideal solution for small
workgroup. The Switch can be used as a standalone switch to which personal
computers, server, printer server are directly connected to form small
workgroup.
18B
4.2 Segment Application
For enterprise networks where large data broadcast are constantly processed, this
switch is suitable for department user to connect to the corporate backbone.
You can use the MSL-3S79 to connect PCs, workstations, and servers to each other.
All the devices in this network can communicate with each other by connecting directly
to the Switch. Connecting servers to the backbone switch allow other users to access
the server’s data.
13
Page 20

The switch automatically learns node address, which are subsequently used to filter
and forward all traffic based on the destination address. You can use any of the RJ-45
port of the MSL-3S79 to connect with another Switch or Hub to interconnect each of
your small-switched workgroups to form a larger switched network.
14
Page 21

4B
Chapter 5 Console Management
19B
5.1 Connecting to the Console Port
The Console port is a female DB-9 connector that enables a connection to a PC or
terminal for monitoring and configuring the Switch. Use the supplied RS-232 cable
with a male DB-9 connector to connect a terminal or PC to the Console port.
Connecting the switch to a terminal via RS-232 cable
20B
5.2 Login in the Console Interface
When the connection between Switch and PC is ready, turn on the PC and run a
terminal emulation program or Hyper Terminal and configure its communication
parameters to match the following default characteristics of the console port:
Baud Rate: 9600 bps
Data Bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop Bit: 1
Flow control: None
15
Page 22
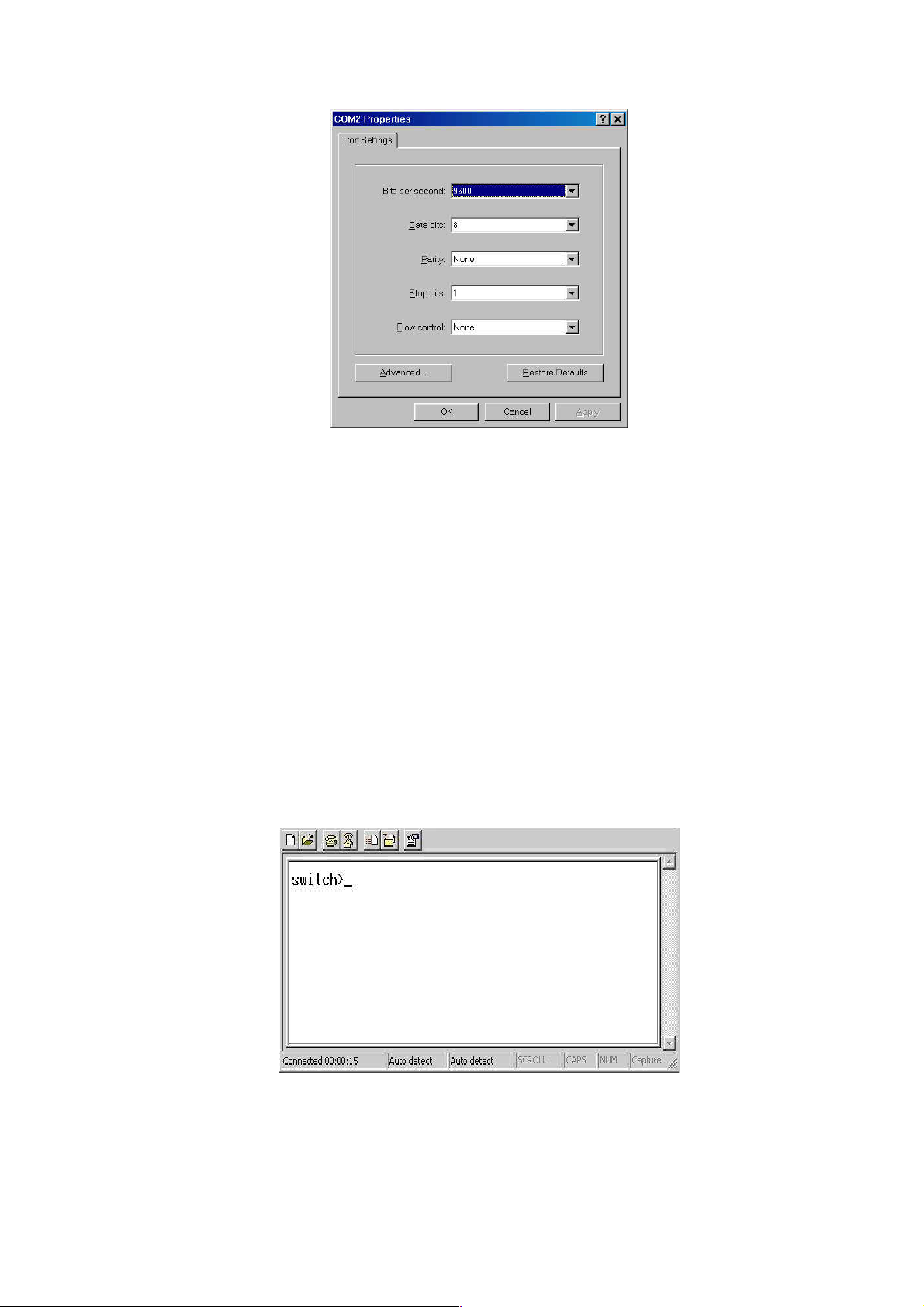
The settings of communication parameters
After finishing the parameter settings, click “OK“. When the blank screen shows up,
press Enter key to get into command line mode. Please see below figure for login
screen.
21B
5.3 CLI Management
The system supports console management (CLI command). After you login to the
system, you will see a command prompt. To enter CLI management interface, enter
“enable” or “e” command.
CLI command interface
16
Page 23
5B
Chapter 6 Web-Based Management
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the Web-Based
management.
22B
6.1 About Web-based Management
On CPU board of the switch there is an embedded HTML web site residing in flash
memory, which offers advanced management features and allow users to manage the
switch from anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as Microsoft
Internet Explorer.
The Web-Based Management supports Internet Explorer 5.0 or later. And, it is applied
for Java Applets for reducing network bandwidth consumption, enhance access speed
and present an easy viewing screen.
[NOTE] By default, IE5.0 or later version does not allow Java Applets to activate
sockets. In fact, the user has to explicitly modify the browser setting to enable Java
Applets to operate network ports.
23B
6.2 Preparing for Web Management
Before using web management, install the industrial switch on the network and make
sure that any one of PC on the network can connect with the industrial switch through
the web browser. The switch default value of IP, subnet mask, username and
password is as below:
IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.1.254
User Name: admin
Password: admin
17
Page 24

24B
6.3 System Login
1. Launch the Internet Explorer on the PC
2. Key in “http:// “+” the IP address of the switch”, and then Press “Enter”.
3. The login screen will appear right after
4. Key in the user name and password. The default user name and password are
the same as “admin”
5. Press “Enter” or ”OK”, and then the home screen of the Web-based management
appears
25B
6.4 System
51B
6.4.1 System Information
Assigning the system name, location and view the system information
System Name: Assign the name of switch. The maximum length is 31 bytes
Description: Display the description of switch. The maximum length is 31 bytes
Location: Assign the switch physical location. The maximum length is 31 bytes
Contact: Enter the name of contact person or organization
Object ID: object ID. The most common OIDs seen "in the wild" usually belong to
the private enterprise numbers allocated by IANA under the 1.3.6.1.4.1
(iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise) arc. In computer networking, an OID, in
the context of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), consists of the
object identifier for an object in a Management Information Base (MIB).
18
Page 25

System information interface
52B
6.4.2 Switch Information
75B
6.4.2.1 Main Board
Hardware Version: display the hardware version
Fan 1 Status: display the status of Fan 1
Fan 2 Status: display the status of Fan 2
76B
6.4.2.2 Management Software
Firmware Version: display the firmware version
Configure Data version: display the configure data version
Command Line Version: display the command line version
Web UI Version: display the Web UI version
Switch information interface
19
Page 26

53B
6.4.3 IP Configuration
User can configure the IP Settings.
IP Address Mode:
Static:
DHCP:
It means the IP address of this switch will be assigned by user.
It means the IP address of this switch will be assigned by the network
DHCP server.
IP Address:
Assign the IP address that the network is using. If
IP Address Mode
function is set in DHCP mode, user needn’t assign the IP address manually. And,
the network DHCP server will assign the IP address which is going to be
displayed in this column for the switch. The default IP is 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask:
Assign the subnet mask of the IP address. If
IP Address Mode
function is in DHCP mode, user need not assign the subnet mask manually.
Gateway IP Address:
Assign the network gateway for the switch. The default
gateway is 192.168.1.254
DNS1:
DNS2:
MAC Address:
Assign the IP address of DNS server1 that the network is using.
Assign the IP address of DNS server2 that the network is using.
Display the unique hardware address assigned by manufacturer
(default)
And then, click
Apply
54B
6.4.4 DHCP Configuration
IP configuration interface
The system provides the DHCP server function. Enable the DHCP server function, the
20
Page 27

switch system will be a DHCP server.
DHCP Server Settings
1. DHCP Server: Enable or disable the DHCP Server function. Enable – the switch
will be a DHCP server on your local network.
2. DHCP IP Address Pool: User has to set a range of IP addresses for the DHCP
server assigning an IP address to the DHCP client by giving the starting IP
address and how many IP addresses within this address pool. For instance, user
can set 192.168.1.100 to be the beginning IP address and 50 (can’t be greater
than 253) to be the maximum number. The range of the address pool should be
from 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.49.
3. Netmask: the dynamic IP assign range subnet mask.
4. Default Gateway: the gateway in your network.
5. DNS Servers: Domain Name Server IP Address in your network.
6. Lease Duration(hours): Assign the lease duration time in hours
7. And then, click
Apply
21
Page 28

DHCP Server Configuration interface
DHCP Client Information
Display the DHCP Client information which has gotten an IP address from the DHCP
server.
55B
6.4.5 Firmware Update
77B
6.4.5.1 TFTP Download Firmware
It provides the functions to allow a user to update the switch firmware. Before updating,
make sure you have your TFTP server ready and the firmware image is on the TFTP
server.
1. TFTP Server IP Address: Fill in your TFTP server IP.
2. Firmware File Name: The name of firmware image.
3. Click
Apply
.
TFTP-Update Firmware interface
78B
6.4.5.2 TFTP Backup Configuration
User can save current EEPROM value from the switch to TFTP server, then go to the
TFTP restore configuration page to restore the EEPROM value.
1. TFTP Server IP Address: Fill in the TFTP server IP
2. Backup File Name: Fill in the file name
3. Click
Apply
.
22
Page 29
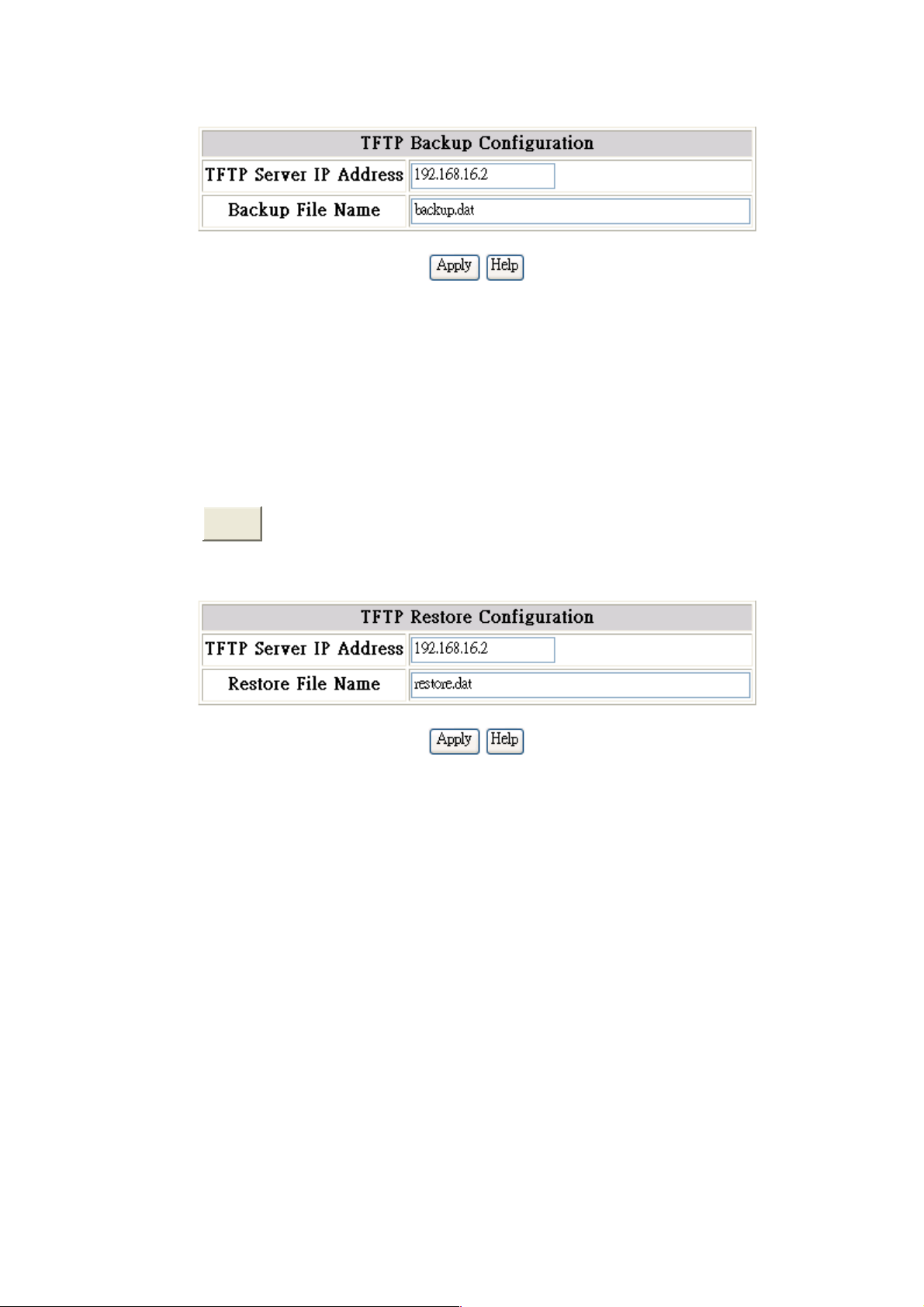
TFTP-Configuration Backup interface
79B
6.4.5.3 TFTP Restore Configuration
User can restore EEPROM value from TFTP server, but user must put back the
backup file in TFTP server, switch will download it back.
1. TFTP Server IP Address: Fill in the TFTP server IP.
2. Restore File Name: Fill in the correct restore file name.
3. Click
Apply
.
TFTP-Configuration Restore interface
56B
6.4.6 System Event Log
80B
6.4.6.1 LOG Configuration
You can mark the check box of Local Logging, Remote Logging, and SMTP Logging to
enable the functions of LOG Configuration.
Local Logging: Mark this check box for enabling to set Flash Level and RAM
Level. Set Flash Level to send event log to flash ROM or RAM by assigning the
level.
Flash Level: Set the level range of 0 to 7.
RAM Level: Set the level range of 0 to 7.
23
Page 30

Remote Logging: Mark this check box for enabling to set Facility Level, Trap
Level, Log Server IP 1, and Log Server IP 2.
Facility Level: Set the level range of 16 to 23.
Trap Level: Set the level range of 0 to 7.
Log Server IP 1: Assign a remote log server IP address.
Log Server IP 2: Assign a remote log server IP address.
24
Page 31
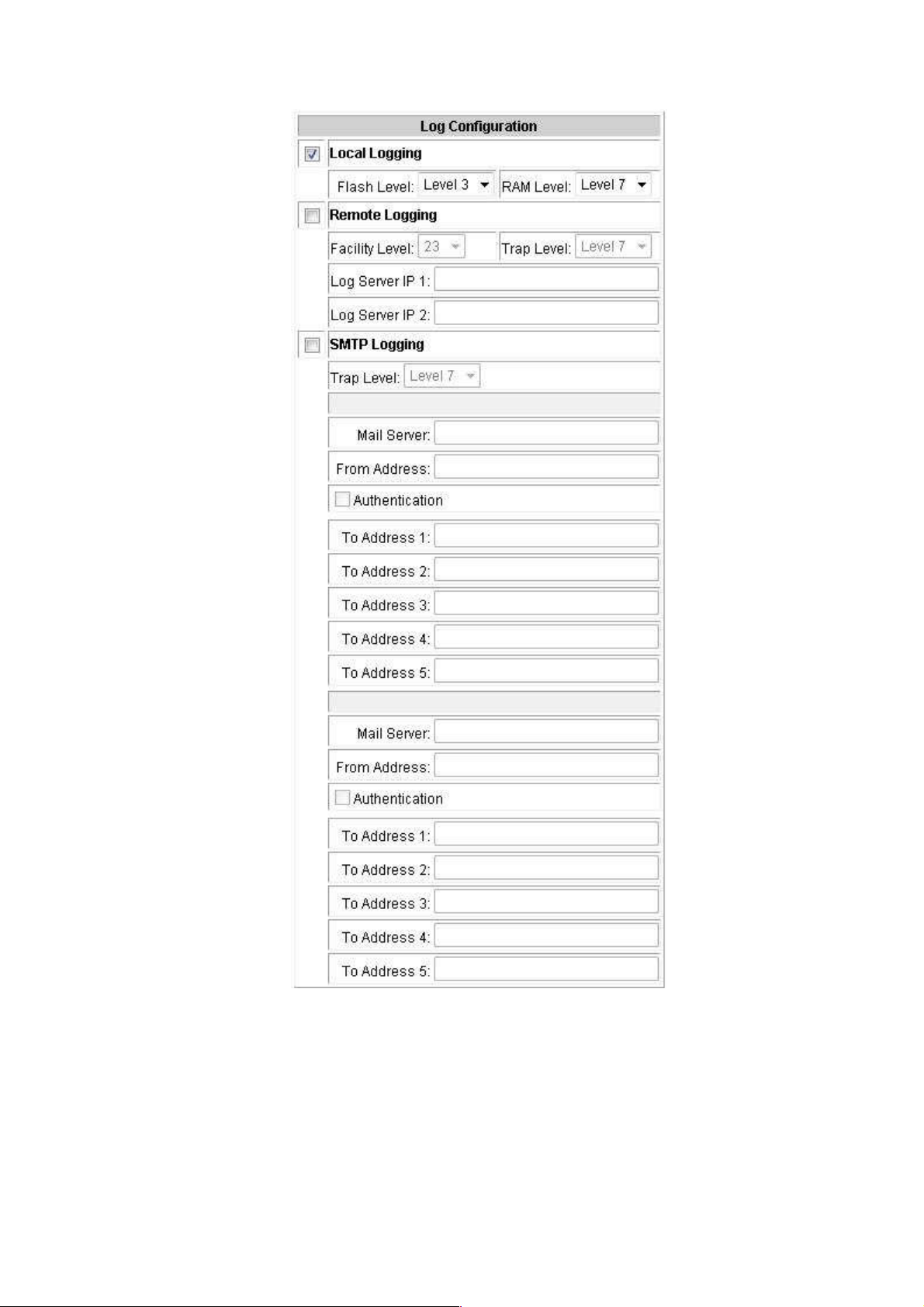
LOG Configuration interface
81B
6.4.6.2 Logging Events Level
User can select the system log events and SMTP events. When selected events occur,
the system will send out the log information. The range of Logging Event Level is from
level 0 to level 7. When the level value is the same as the one among Local Logging,
25
Page 32

Remote Logging, and SMTP Logging, the system will issue a log record to location
where user has designated. After configuring, click
Apply
.
Logging Event Level: 4 events – Cold Start Event, Warm Start Event, Auth
Failure Event, and Port Link Change Event. Pull down the right side item menu to
select the event level. When selected events occur, the system will issue the logs.
Cold Start Event: when the device executes cold start action, the system will
issue a log event.
Warm Start Event: when the device executes warm start, the system will
issue a log event.
Auth Failure Event: You get this trap if a network management system
(NMS) polls the device with the wrong community string.
Port Link Change Event: when the port link has changed, the system will
issue a log event.
Logging Events Level interface
82B
6.4.6.3 Logging RAM Table
Logging RAM Table displays the logs which have been sent to RAM.
26
Page 33

83B
6.4.6.4 Logging Flash Table
Logging RAM Table interface.
Logging Flash Table displays the logs which have been sent to Flash ROM.
Logging ROM Table interface
57B
6.4.7 Security Manager
Change login user name and password for the management security issue
User Name: Key in the new user name (The default is “admin”)
New Password: Key in the new password (The default is “admin”)
Confirm Password: Re-type the new password
And then, click
Apply
27
Page 34

26B
6.5 Port
58B
6.5.1 Port Statistics
Display the port statistic information.
Port Statistic interface
59B
6.5.2 Port Information
The following information provides the current port statistic information
28
Page 35

Port Information interface
60B
6.5.3 Port Control
In Port configuration, user can view every port status that depended on user setting
and the negotiation result.
1. Port: select the port that user wants to configure.
2. State: Current port status. The port can be set to disable or enable mode. If the
port setting is disabled, it will not receive or transmit any packet.
3. Auto Negotiation: enable or disable auto negotiation
4. Speed: when Auto Negotiation is disabled, user can select the port link speed.
5. Duplex: set full-duplex or half-duplex mode of the port.
6. Flow Control: set flow control function is Enable or Disable. The default value is
Enable.
7. Jumbo: Assign the Jumbo frame size. The maximum is 10K bytes.
8. Click
Apply
.
29
Page 36

Port Configuration interface
61B
6.5.4 Port Trunk
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for
exchanging information between Partner Systems on a link to allow their Link
Aggregation Control instances to reach agreement on the identity of the Link
Aggregation Group to which the link belongs, move the link to that Link Aggregation
Group, and enable its transmission and reception functions in an orderly manner. Link
aggregation lets you group up to eight ports into two dedicated connections. This
feature can expand bandwidth between 2 (or more) devices. LACP operation requires
full-duplex mode, more detail information refers to IEEE 802.3ad.
84B
6.5.4.1 Trunk Configuration
1. Group ID: list the Trunk group ID.
2. Type: Static and LACP for selecting
3. select the port number from the right column list and then click
add the port into a trunk group
30
Add
button to
Page 37

4. Click
Remove
button to remove the port from a trunk group
5. To delete Trunk Group, select the Group Id and click
Trunk Configuration interface
Delete
button.
85B
6.5.4.2 Trunk Information
After setting up the trunk group, user will see the related information as below.
Trunk Information interface
86B
6.5.4.3 Port Activity
User will see the related information of LACP Port Activity State as below.
31
Page 38

Port Activity interface
62B
6.5.5 Port Mirror
The port mirror is a method for monitor traffic in switched networks. Traffic through
ports can be monitored by specific port. That means traffic goes in or out monitored
ports will be duplicated into analysis port.
32
Page 39

Port Mirror Configuration interface
1. Port Mirroring State: enable or disable the port mirror function
2. Analysis Port: Select a port for analyzing all monitor port traffic. User can
connect mirror port to LAN analyzer or Netxray.
3. Monitor Port: The ports which user wants to monitor. All monitored port traffic will
be copied to analysis port. (UP to 8 ports)
4. State: User can choose the monitored port packet in RX, TX or Both state by
pulling down the pull-down menu.
33
Page 40

5. Click
Apply
.
63B
6.5.6 Rate Limiting
User can set up the bandwidth rate and packet limitation type of each port.
Input
State: There are 4 check boxes of Bc, Mc, UnkUc, KnownUc for selecting.
Rate (1~1526)(Rate*655Kbps): Type in the input rate limit in number
between 1~1526.
Output
State: Enable or disable the output rate limit.
Rate (Rate*312Kbps): Type in the output rate limit which is a multiple of 312.
Port Configuration interface
27B
6.6 Protocol
64B
6.6.1 VLAN
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical network grouping that limits the broadcast domain,
which would allow you to isolate network traffic, so only the members of the VLAN will
receive traffic from the same members of VLAN. Basically, creating a VLAN from a
switch is logically equivalent of reconnecting a group of network devices to another
Layer 2 switch. However, all the network devices are still plugged into the same switch
34
Page 41

physically.
87B
6.6.1.1 VLAN Mode Configuration
The switch supports port-based and 802.1Q (tagged-based) VLAN. The default
configuration of VLAN operation mode is “802.1Q”.
VLAN Mode Configuration interface
88B
6.6.1.2 Port VLAN Id Configuration
1. Port: Select the port number in the table list.
2. VLAN ID: Key in the VLAN ID.
3. Ingress Filter: Enable or Disable the ingress filter.
4. Acceptable Frame Type: Choose Tag only or All type.
5. Click
Apply
Port VLAN Id Configuration interface
35
Page 42

89B
6.6.1.3 VLAN Entry
Edit the existing VLAN Group.
1. Select the VLAN group in the table list.
2. Click
Edit
VLAN Table Configuration interface
3. User can add/ remove the ports from a VLAN group.
4. Click
Next
.
VLAN Table Configuration - Edit interface
5. Mark the check box to tag the ports of a VLAN group.
36
Page 43

6. Click
Apply
.
VLAN Table Configuration - Edit interface
65B
6.6.2 Rapid Spanning Tree
The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an evolution of the Spanning Tree
Protocol and provides for faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change.
The system also supports STP and the system will auto detect the connected device
that is running STP or RSTP protocol.
90B
6.6.2.1 STP System Configuration
User can view spanning tree information about the Root Bridge
User can modify RSTP state. After modification, click
Apply
button
Mode: user must enable or disable RSTP function before configure the
related parameters
Priority (0-61440): a value used to identify the root bridge. The bridge with
the lowest value has the highest priority and is selected as the root.
Max Age (6-40): the number of seconds a bridge waits without receiving
37
Page 44

Spanning-tree Protocol configuration messages before attempting a
reconfiguration. Enter a value between 6 through 40
Hello Time (1-10): the time that controls switch sends out the BPDU packet
to check RSTP current status. Enter a value between 1 through 10
Forward Delay Time (4-30): the number of seconds a port waits before
changing from its Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol learning and listening states
to the forwarding state. Enter a value between 4 through 30
[NOTE] Follow the rule to configure the MAX Age, Hello Time, and Forward
Delay Time.
2 x (Forward Delay Time value –1) > = Max Age value >= 2 x (Hello Time
value +1)
RSTP System Configuration interface
38
Page 45

91B
6.6.2.2 STP Port Configuration
User can configure path cost and priority of every port.
1. Select the port in Port column.
1. Priority: Decide which port should be blocked by priority in LAN. Enter a number 0
through 240.
2. Path Cost: The cost of the path to the other bridge from this transmitting bridge at
the specified port. Enter a number 1 through 200000000.
3. AdmP2P: Some of the rapid state transactions that are possible within RSTP are
dependent upon whether the port concerned can only be connected to exactly one
other bridge (i.e. it is served by a point-to-point LAN segment), or can be
connected to two or more bridges (i.e. it is served by a shared medium LAN
segment). This function allows the P2P status of the link to be manipulated
administratively. Enable is P2P enabled; disable is P2P disabled; and auto means
auto-sense.
4. AdmEdge: The port directly connected to end stations which cannot create
bridging loop in the network. To configure the port as an edge port, set the port to
“Enable” status.
5. AdmStp: The port includes the STP mathematic calculation. Enable is including
STP mathematic calculation. Disable is not including the STP mathematic
calculation.
6. Click
Apply
.
39
Page 46

66B
6.6.3 SNMP
RSTP Port Configuration interface
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the protocol developed to manage
nodes (servers, workstations, routers, switches and hubs etc.) on an IP network.
SNMP enables network administrators to manage network performance, find and
solve network problems, and plan for network growth. Network management systems
learn of problems by receiving traps or change notices from network devices
implementing SNMP.
SNMP Information
Enter the system name, contact and location information.
Name: Assign a name for the switch.
Location: Type the location of the switch.
Contact: Type the name of contact person or organization.
SNMP Community String
User can define new community string set and remove unwanted community string.
RO: Read only. Enable requests accompanied by this string to display MIB-object
information.
RW: Read write. Enable requests accompanied by this string to display
MIB-object information and to set MIB objects.
40
Page 47

Add
SNMP Trap managers
A trap manager is a management station that receives traps, the system alerts
generated by the switch. If no trap manager is defined, no traps will issue. Create a
trap manager by entering the IP address of the station and a community string. To
define management stations as trap manager and enter SNMP community strings and
selects the SNMP version.
IP Address: enter the IP address of trap manager.
Community: enter the community string.
Click
.
SNMP Configuration interface
67B
6.6.4 QoS
User can configure QoS policy and priority setting, per port priority setting, COS and
DSCP setting.
41
Page 48

Adpply
Adpply
92B
6.6.4.1 QoS Configuration
Queue Profile: Select the queue profile from the column list.
Priority Precedence: There are 4 priority precedence selections available.
Click
.
QoS Configuration interface
93B
6.6.4.2 Port-bace Configuration
Port: Select the number port from the column list.
Default Port Priority (0-7): Assign the priority level.
Click
.
Port-base Configuration interface
42
Page 49

94B
6.6.4.3 COS Configuration
Set up the COS priority level.
COS priority: Set up the COS priority level 0~7, 7 is the highest priority.
Click
Apply
.
COS Configuration interface
95B
6.6.4.4 DSCP Configuration
Set up the DSCP priority.
Mapping DSCP priority: The system provides 0~63 DSCP priority level. Each
level has 8 types of priority – 0~7, 7 is the highest priority. When the IP packet is
received, the system will check the DSCP level value in the IP packet that has been
received. For example: user set the DSCP level 25 as high. When the packet received,
the system will check the DSCP value of the received IP packet. If the DSCP value of
received IP packet is 25(priority = high), and then the packet priority will have highest
priority.
Click
Apply
.
43
Page 50

DSCP Configuration interface
68B
6.6.5 SNTP
User can configure the SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) settings. The SNTP
allows user to synchronize switch clocks in the Internet.
1. SNTP Server Link Status: Display the link status of SNTP server.
2. Switch Current Time: Display the current time of the switch.
3. SNTP Client: Enable or disable SNTP function. When it is enabled, user can
assign the domain name or IP address of SNTP server for getting the time from
SNTP server.
4. UTC Timezone: Set the switch location time zone.
5. SNTP Period: The SNTP period is used for sending synchronizing packets
periodically.
6. SNTP Sever IP Address: Assign the SNTP server IP address.
7. Click
44
Apply
.
Page 51

SNTP Configuration interface
69B
6.6.6 IGMP
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of the Internet
Protocol (IP) suite. IP manages multicast traffic by using switches, routers, and hosts
that support IGMP. Enabling IGMP allows the ports to detect IGMP queries and report
packets and manage IP multicast traffic through the switch. IGMP have three
fundamental types of message as follows:
Message Description
A message sent from the querier (IGMP router or switch)
Query
asking for a response from each host belonging to the
multicast group.
A message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that the
Join Group
host wants to be or is a member of a given group indicated in
the report message.
A message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that the
Leave Group
host has quit being a member of a specific multicast group.
96B
6.6.6.1 IGMP Configuration
The switch support IP multicast, user can enable IGMP protocol on web
management’s switch setting advanced page, then display the IGMP snooping
45
Page 52

information. IP multicast addresses range from 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255.
IGMP Snoop: Enable or disable the IGMP snoop.
IGMP Query: The IGMP query function has 3 modes - Enable, Disable or Auto -
for selection. The IGMP query information will be displayed in IGMP status
section.
IGMP interval: The interval of General Query being sent. (Read Only)
Click
Apply
.
IGMP Configuration interface
97B
6.6.6.2 IGMP Static Configuration
Multicasts are similar to broadcasts, they are sent to all end stations on a LAN or
VLAN. Multicast filtering is the system by which end stations only receive multicast
traffic if they register to join specific multicast groups. With multicast filtering, network
devices only forward multicast traffic to the end stations that are connected to
registered ports.
This function action when IGMP Configuration disable.
46
Page 53

Port ID: Select the port number in the specific multicast group IP address.
VLAN ID: Input the value of VLAN ID.
IP Address: Assign a multicast group IP address in the range of 224.0.0.0 ~
239.255.255.255.
Click "Add".
If you want to delete an entry from table, select the entry and click "Delete".
IGMP Static Configuration interface
70B
6.6.7 LLDP
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) specified in this standard allows stations
attached to an IEEE 802 LAN to advertise, to other stations attached to the same IEEE
802 LAN, the major capabilities provided by the system incorporating that station, the
management address or addresses of the entity or entities that provide management
of those capabilities, and the identification of the station’s point of attachment to the
IEEE 802 LAN required by those management entity or entities.
98B
6.6.7.1 LLDP Configuration
Mode Configuration: Enable or disable the LLDP function.
Port Configuration: Enable or disable the LLDP state of the number port.
47
Page 54

LLDP Configuration interface
99B
6.6.7.2 LLDP Neighbor Table
User will see all information of port by LLDP enable.
LLDP Neighbor Table interface
28B
6.7 Security
71B
6.7.1 802.1x/ RADIAS
802.1x is an IEEE authentication specification that allows a client to connect to a
wireless access point or wired switch but prevents the client from gaining access to the
port until it provides authority, like a user name and password that are verified by a
separate server.
100B
6.7.1.1Misc Configuration
1. Mode: Enable or disable 802.1 x protocols.
2. Quiet Period: Set the period during which the port doesn’t try to acquire a
supplicant.
3. TX Period: Set the period the port waits for retransmit next EAPOL PDU during
an authentication session.
48
Page 55

4. Supplicant Timeout: Set the period of time the switch waits for a supplicant
response to an EAP request.
5. Server Timeout: Set the period of time the switch waits for a server response to
an authentication request.
6. ReAuthMax: Set the number of authentication that must time-out before
authentication fails and the authentication session ends.
7. Reauth period: set the period of time after which clients connected must be
re-authenticated.
8. Click
Apply
.
MISC Configuration interface
49
Page 56

101B
6.7.1.2 Port Configuration
Port Configuration interface
You can configure 802.1x authentication state for each port. The State provides
Disable, Authorize, Accept and Reject.
Disable: This function is disabled.
Authorize: The specified port is set to the Authorized or Unauthorized state in
accordance with the outcome of an authentication exchange between the
supplicant and the authenticator.
Accept: The specified port will allow the client accessing in any case.
Reject: The specified port rejects the client accessing regardless of whether the
authentication passed or not.
Click
Apply
.
102B
6.7.1.3Radius Client Configuration
After having enabled the IEEE 802.1X function, user can configure the parameters of
this function.
1. Radius Server IP: Set the Radius Server IP address.
2. Server Port: Set the UDP destination port for authentication requests to the
specified Radius Server.
3. Accounting Port: Set the UDP destination port for accounting requests to the
50
Page 57

specified Radius Server.
4. Shared Key: Set an encryption key for using during authentication sessions with
the specified radius server. This key must match the encryption key used on the
Radius Server.
5. NAS Identifier: A string used to identify this switch.
6. Click
Apply
.
72B
6.7.2 Port Security
Use the MAC address table to ensure the port security.
103B
6.7.2.1 Static MAC Address Table
User can add a static MAC address; it remains in the switch's address table,
regardless of whether the device is physically connected to the switch. This saves the
switch from having to re-learn a device's MAC address when the disconnected or
powered-off device is active on the network again. User can add / modify / delete a
static MAC address.
Packets with the specified destination address received in the specified VLAN are
forwarded to the specified interface.
Static MAC Addresses interface
Add the Static MAC Address
51
Page 58
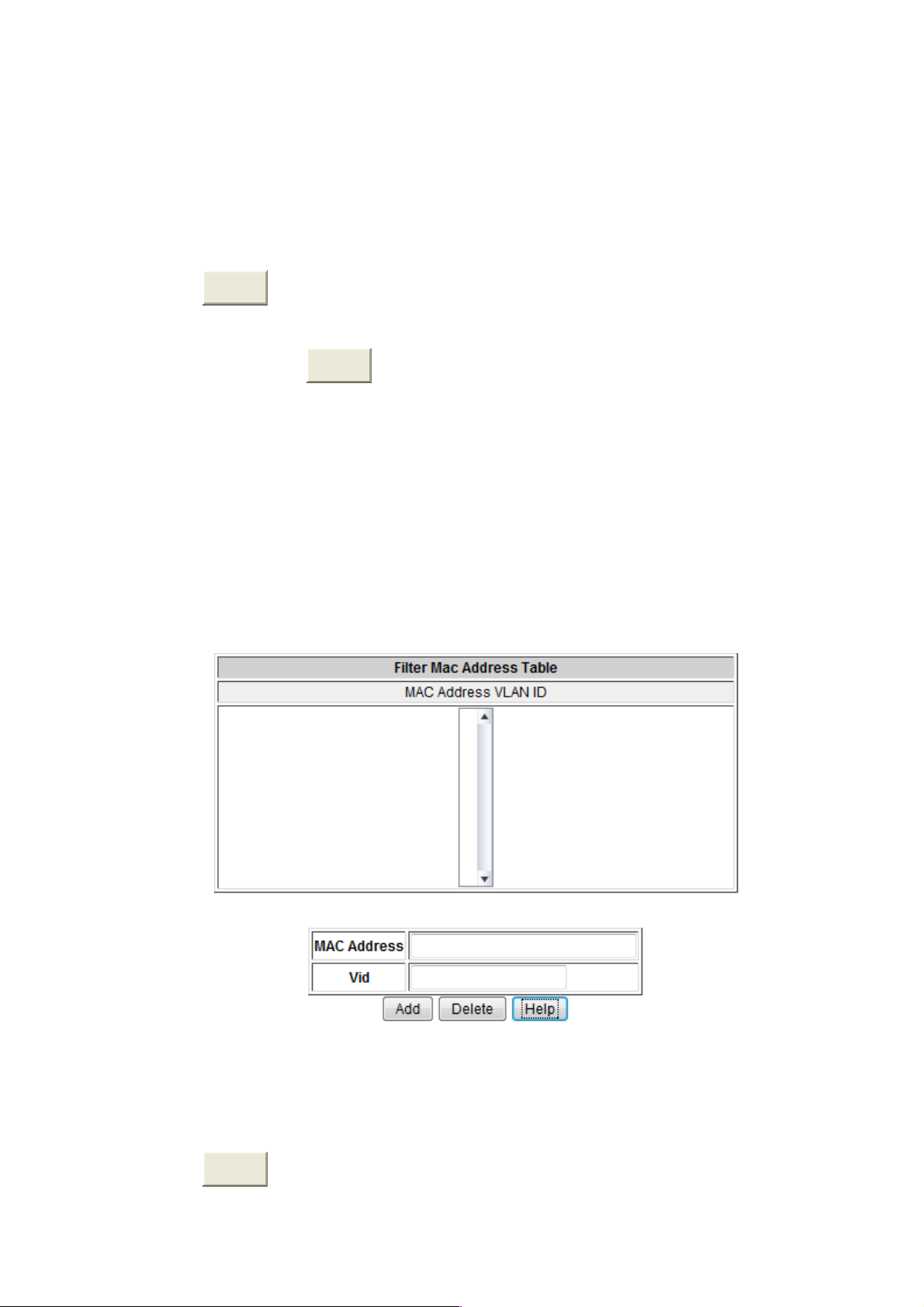
User can add static MAC address in switch MAC table.
1. MAC Address Port VLAN ID: list the MAC Address Port. VLAN ID
2. MAC Address: Specify the destination MAC address to add to the address table.
3. Port.No: pull down the selection menu to select the port number.
4. Vid: enter the Vid of the MAC address, it has to be between 1 to 4094.
5. Click
Add
.
6. If user wants to delete the MAC address from filtering table, select the MAC
address and click
Delete
.
104B
6.7.2.2 Filter MAC Address Table
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. Traffic is filtered
based on the destination addresses. For example, if your network is congested
because of high utilization from one MAC address, you can filter all traffic transmitted
to that MAC address, restoring network flow while you troubleshoot the problem.
MAC Filtering interface
1. MAC Address: Enter the MAC address that user wants to filter.
2.
3. Click
52
enter the Vid of the MAC address, it has to be between 1 to 4094.
Vid:
Add
.
Page 59

4. If user wants to delete the MAC address from filtering table, select the MAC
address and click
Delete
.
105B
6.7.2.3 MAC Address Table Aging
Aging Status: Pull-down menu to enable MAC address table aging function.
Aging Time (20~620): Assign the aging time in second.
Address Aging interface
73B
6.7.3 IP Security
User can assign up to 10 security IP addresses for accessing the switch via HTTP,
TELNET or both, any other IPs which are not included will be restricted.
IP Security interface
1. Mode: When mode is set at ON, user can assign up to 10 Security IP addresses.
53
Page 60

2. HTTP: mark the check box to enable the access via HTTP for the assigned IP
3. TELNET: mark the check box to enable the access via TELNET for the assigned
IP.
4. Click
5. And then, click
Clear
button to clear IP address and all the check box.
Apply
74B
6.7.4 ACL
An ACL is a sequential list of permit or deny conditions that apply to IP addresses.
This switch tests ingress or egress packets against the conditions in an ACL one by
one. A packet will be accepted as soon as it matches a permit rule, or dropped as soon
as it matches a deny rule. If no rules match for a list of all permit rules, the packet is
dropped; and if no rules matches for a list of all deny rules, the packet is accepted.
The following restrictions apply to ACLs:
The ACL only support single port and not support trunk group.
The maximum number of ACLs is also 5 for each port.
Command Attributes
Enable: An ACL can be enable per port.
Default Action: The action if no rules matched.
Action: An ACL can be permit or deny rule.
IP Address and Prefix Length: Include destination and source IP address.
Ex: source 192.168.16.1/24 means all frames that source IP address is 192.168.16.x
matched.
54
Page 61

Save Flash
29B
6.8 Factory Default
Access Control Configuration Interface
Reset switch to default configuration. Click
default value or
PART
to reset all configuration except reserved IP, user name and
password.
Factory Default interface
30B
6.9 Save Configuration
ALL
to reset all configurations to the
Save all configurations that user has made in the system. To ensure the all
configuration will be saved. Click
to save the all configuration to the flash
memory.
Please be noted, it is recommend to do the “save configuration” once changes has
been made on system.
Save Configuration interface
55
Page 62

31B
6.10 System Reboot
Reboot the switch in software reset. Click
System Reboot interface
Reboot
to reboot the system.
56
Page 63

6B
Troubleshooting
This section is intended to help you solve the most common problems on MSL-3S79.
Incorrect connections
The switch port can automatically detect straight or crossover cable when you link
switch with other Ethernet device. As for RJ-45 connection, you should use correct
UTP or STP cable that 10/100/1000Mbps port uses 2-pairs twisted cable and Gigabit
1000T port uses 4 pairs twisted cable. If the RJ-45 connector is not correctly pinned on
right position then the link will fail. As for fiber connection, please notice the fiber cable
mode and fiber module should match.
Faulty or loose cables
Look for loose or obviously faulty connections. If they appear to be OK, make sure the
connections are snug. If that does not correct the problem, try a different cable.
Non-standard cables
Non-standard and miss-wired cables may cause numerous network collisions and
other network problem, and can seriously impair network performance. A category
5-cable tester is a recommended tool for every 100Base-T network installation.
RJ-45 ports: Use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shield twisted-pair ( STP ) cable for
RJ-45 connections: 100Ω Category 3, 4 or 5 cable for 10Mbps connections, 100Ω
Category 5 cable for 100Mbps connections or Category-5e / Category-6 for above
1000Mbps connections. Also be sure that the length of any twisted-pair connection
does not exceed 100 meters (328 feet). Gigabit port should use Cat-5 or cat-5e cable
for 1000Mbps connections. The length does not exceed 100 meters.
Improper Network Topologies
It is important to make sure that you have a valid network topology. Common topology
faults include excessive cable length and too many repeaters (hubs) between end
57
Page 64

nodes. In addition, you should make sure that your network topology contains no data
path loops. Between any two ends nodes, there should be only one active cabling path
at any time. Data path loops will cause broadcast storms that will severely impact your
network performance.
Diagnosing LED Indicators
The Switch can be easily monitored through panel indicators, which describes
common problems you may encounter and where you can find possible solutions to
assist in identifying problems.
If the power indicator is not lighted when the power cord is plugged in, you may have a
problem with power outlet, or power cord. However, if the switch powers off after
running for a while check for loose power connections, power losses or surges at
power outlet. If you still cannot resolve the problem, contact your local dealer for
assistance.
58
Page 65
7B
Appendix A- Command Sets
32B
Commands Set List
Modes Access Method Prompt Exit Method About This Model
The user commands
available at the user level
are a subset of those
User EXEC
Privileged
EXEC
Global
configuration
Begin a session with
your switch.
Enter the enable
command while in
user EXEC mode.
Enter the configure
command while in
privileged EXEC mode.
switch>
switch#
switch(config)#
Enter logout or
quit.
Enter disable to
exit.
To exit to
privileged
EXEC mode,
enter exit or end
available at the privileged
level.
Use this mode to
• Perform basic tests.
• Display system
information.
The privileged command
is advance mode
Privileged this mode to
• Display advance
function status
• save configures
Use this mode to
configure
Parameters that apply to
your switch as a whole.
VLAN
database
Interface
configuration
Enter the vlan database
command while in
privileged EXEC mode.
Enter the interface
command (with a
specific interface) while
in global configuration
mode
switch(vlan)#
switch(config-if)#
To exit to user
EXEC mode,
enter
Exit.
To exit to global
Configuration
mode, enter exit.
To exist to
privileged
EXEC mode or
end.
Use this mode to
configure
VLAN-specific
parameters.
Use this mode to
configure
Parameters for the switch
and Ethernet ports.
59
Page 66

system name
system location
system
system contact
ip address
ip address
an IP address for a switch. Use
write memory
Privileged
write memory
r
eload
default
default
admin username
admin
admin password
Global
admin
33B
System Commands Set
Commands Command
[system name]
[system Location]
description
[description]
[contact]
[ip-address]
[subnet-mask]
[gateway]
configuration
configuration
configuration
configuration
configuration
Level
Global
mode
Global
mode
Global
mode
Global
mode
Global
mode
Description Defaults
Set switch system name string
Set switch system location
string
Set switch system description
string
Set switch system contact
window string
Use the
configuration command to set
the no form
interface
Example
switch(config)#
system name xxx
switch(config)#
system location xxx
switch(config)#
system description xxx
switch(config)#
system contact xxx
switch(config)#
ip address 192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0 192.168.1.254
[Username]
[Username]
EXEC
Global
configuration
mode
Global
configuration
mode
Global
configuration
mode
configuration
of this command to remove an
IP address or to disable IP
processing.
Save user configuration into
permanent memory(flash rom)
Halt and perform a cold restart
Restore to default
no: restore all to default.
yes: reserved ip, username
and password.
Changes a login username.
(maximum 32 words)
Specifies a password
(maximum 32 words)
switch#
switch(config)#
reload
switch(config)#
switch(config)#
username xxxxxx
switch(config)#
password xxxxxx
60
Page 67

mode
conso
le-timeout
Global
Set console timeout. The range
console
-
timeout
show system
-
info Privileged
show system
-
info
show ip
Privilege
d
show ip
show admin
Privileged
show admin
show version
Privileged
show version
show version
show
terminal
Privileged
show terminal
show
terminal
show
fan-status
Privileged
interface
[port ID]
Interface
E
thernet
switch(config)#
interface
gigaethernet 1
duplex
[
Interface
Use the duplex
command to specify the duplex
switch(conf
interface
gigae
switch(config
or
switch(config
speed
[10|100|1000|auto]
Interface
Use the
switch(conf
interface
gigae
switch(config
or
[time(sec)]
180 sec
configuration
mode
EXEC
EXEC
EXEC
EXEC
EXEC
of timeout is 30 sec ~ 600 sec.
Show system information
Show ip information of switch
Show username & password
Use the
EXEC command to display
version information for the
hardware and firmware.
Use the
command to display console
information for the switch
user
switch(config)#
30
switch#
switch#
switch#
switch#
switch#
EXEC
34B
Port Commands Set
Commands
gigaethernet
full | half]
Command
Level
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
Use the show fan-status
command to display fan status
Description Default
Use the
configuration command
Use the module Ethernet
interface configuration
command
mode of operation for Fast
Ethernet.
interface
configuration
switch(config)#
show fan-status
Example
Auto
switch(config)#interface
gigaethernet 1
ig)#
thernet 1
-if)#duplex full
-if)#duplex half
configuration
mode
speed configuration
command to specify the speed
mode of operation for Fast
Ethernet.
61
ig)#
thernet 1
-if)#speed 1000
Page 68

switch(config
speed 10
0
or
switch(config
or
switch(config
flowcontrol
[enable|disable]
Interface
Use the flowcontrol
Use the no form of this
command to disable security on
Configure flow control
Disable flow control of interface
switch(config)#
interface
switch(config
enable
or
switch(config
disable
jumbo [size]
Interface
Set jumbo frame size.
Use the
[Jumbo size must be even and
s
interface
gigaetherne
s
or
s
rate-limit
or
no rate
Interface
Set
rate-limit input
You can enable rate
Use the
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
s
rate
or
s
no
or
s
rate
or
s
no rate
rate-limit
Interface
Set
rate-limit input
rate value.
Input rate limit must be
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
switch(config
rate
rate-limit
or
no rate
Interface
Set
rate-limit output
You can enable output
Use the
command to disable output rate
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
s
rate
s
-if)#
-if)#speed 10
-if)#speed auto
Off
configuration
mode
configuration command on
Ethernet ports to control traffic
rates during congestion.
gigaethernet 1
-if)#flowcontrol
input-mode
{bc|mc|unkuc|kno
wnuc}
-limit
input-mode
{bc|mc|unkuc|kno
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
the port.
no form of this
command to default value.
between 1522~10240]
mode.
-limit for
specific packets such as
broadcast, multicast, unknown
unicast and known unicast.
no form of this
command to disable for that
packets
1522
Disable
-if)#flowcontrol
witch(config)#
t 1
witch(config-if)# jumbo 1524
witch(config-if)# jumbo 10240
witch(config)#
witch(config-if)#
-limit input-mode bc
witch(config-if)#
rate-limit input-mode bc
wnuc}
input-rate [value]
output-mode
-limit
output-mode
62
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
between 1~1526
rate-limit.
no form of this
mode.
Disable
Disable
witch(config-if)#
-limit input-mode mc
witch(config-if)#
-limit input-mode mc
witch(config)#
-if)#
-limit input-rate 1000
witch(config)#
witch (config-if)#
-limit output-mode
witch (config-if)#
Page 69

no rate
-
limit output
-
mode
rate-limit
Interface
Set
rate-limit output
Range is
Output rate limit must be
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
s
rate
shutdown
or
no shutdown
Interface
Use the
shutdown
Interface configuration
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
s
shutdown
s
no shutdown
show
interfaces
Privileged
Show
s
show interfaces status
gigaethernet 1
or
s
show interfaces status port
channel 1
or
s
show interfa
show interfaces
Privileged
Show
s
show interfaces counters
gigaethernet 1
or
s
show interfaces counters
port
mac-address
-
table
Global
mac
tbl aging
-
time
output-rate
[value]
status
limit.
rate
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
EXEC
value.
1~3130 for 312Kbps
unit on the port.
between 1~3130
command to disable the port.
Use the no shutdown form of
this command to enable the
port.
interface configuration
status and configuration.
Disable
Enable
witch (config)#
witch (config-if)#
-limit output-rate 1000
witch (config)#
witch(config-if)#
witch(config-if)#
witch #
[gigaethernet|portchannel|vlan]
[if-num]
interface statistic
counters
[gigaethernet|portchannel] [if-num]
EXEC
counter.
35B
Mac / Filter Table Commands Set
Commands
Command
Description
Level
Use the
witch #
-
witch #
ces status vlan 1
witch #
witch #
-channel 1
Default
Example
300 secs (Enable)
aging-time [sec.]
or
configuration
mode
global configuration command
to set the length of time that a
63
switch(config)#
mac-address-table aging-time
Page 70

no
150
mac-address
-
table
table
Interface
interface
mac-address
-
table
ble
Global
mac
-
address
-
ta
show
table
table
Privileged
show
dynamic entry remains in the
mac-address-table
aging-time
static hwaddr
[MAC] vlan
[VLAN-ID]
or
configuration
mode
MAC address table after the
entry is used or updated.
Range: 0-300 seconds; 0 to
disable aging)
Use the no form of this
command to use the default
aging-time interval. The aging
time applies to all VLANs.
time must be 20~620 and in
steps of 20 seconds
Configure MAC address table
of interface (static)
Remove an entry of MAC
address table of interface
(Disable)
switch(config)#
mac-address-table aging-time
0
(Default)
switch(config)#
no mac-address-table
aging-time
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#mac-address-t
able static hwaddr
000012345678 vlan 1
no
mac-addressstatic hwaddr
[MAC] vlan
[VLAN-ID]
filter hwaddr
[MAC] vlan
[VLAN-ID]
or
no
mac-address-ta
filter hwaddr
[MAC] vlan
[VLAN-ID]
mac-address[static|filter|all]
or
show
mac-addressstatic
or
show
configuration
mode
EXEC mode
(static)
Configure MAC address
table(filter)
Remove an entry of MAC
address table (filter)
Show static MAC address table
Show filter MAC address table.
Show all MAC address table
or
interface
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#no
mac-address-table static
hwaddr 000012345678 vlan 1
switch(config)#
ble filter hwaddr 000012348678
vlan 1
or
switch(config)#no
mac-address-table filter
hwaddr 000012348678 vlan 1
switch#
mac-address-table static
or
switch#show
mac-address-table filter
or
64
Page 71

mac-address
-
table
table
show
show
table
Privileged
show
monitor
Interface
show monitor
Privileged
backup
Global
backup
restore
Global
restore
filter
or
show
mac-addressall
S
how current aging time setup
mac-addressaging-time
EXEC mode
36B
Port Mirroring Commands Set
Commands
[port number]
[rx | tx | both]
Command
Level
configuration
mode
Description Default
Use the port monitor interface
configuration command to
enable Switch Port Analyzer
switch#
mac-address-table all
switch(config)#interface
switch#
mac-address-table aging-time
Example
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#monitor 3 both
or
no monitor [port
number| all]
EXEC
37B
TFTP Commands Set
Commands
flash:backup_cfg
flash:restore_cfg
Command
Level
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
(SPAN) port
monitoring on a port. Use the
no form of this command to
return the port to its default
value.
Show port monitor information switch#show monitor
Description Default
Save configuration to TFTP
server and need to specify the
IP of TFTP server and the file
name of image.
Get configuration from TFTP
server and need to specify the
IP of TFTP server and the file
or
switch(config-if)#no monitor 3
or
(Disable)
switch(config-if)#
no monitor all
Example
switch(config)#
flash:backup_cfg
switch(config)#
flash:restore_cfg
TFTP server ip address
name of image.
[192.168.16.2]:
Restore file name [restore.dat]:
*config success.*
65
Page 72

upgrade
Global
and
upgrade
show qos
Privileged
show qos
qos priority c
os
Global
qos priority cos
qos priority dscp
Global
qos priority
qos priority profile
Global
qos pr
iority
Interface
interface
q
os priority
Global
qos priority
flash:upgrade_fw
configuration
mode
38B
QOS Commands Set
Commands
[Cos] [Qid]
or
no qos priority cos
Command
Level
EXEC
configuration
mode
Upgrade firmware by TFTP
need to specify the IP of TFTP
server and the file name of
image.
Description Default
Show QoS settings
Configure COS Priority Qid =
Set DSCP Map
Traffic
Class
switch(config)#
lash:upgrade_fw
Example
switch#
switch(config)#
0 2
or
(Default)
switch(config)# no qos priority
cos
switch(config)#
[dscp] [Qid]
or
no qos priority
dscp
[profile]
portbased[Qid]
or
no qos priority
portbased
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
dscp 61 5
or
(Default)
switch(config)# no qos priority
dscp
Set Qos Port Profile [0~3] 0 switch(config)#
qos priority profile 3
Set Qos Port Priority [0~7] 0
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
qos priority portbased 3
or
(Default)
switch(config-if)# no qos
priority portbased
Set Priority Precedence Port-base
switch(config)#
precedence
[port-base|
cos-only|
dscp-only|
dscp-first]
66
configuration
mode
precedence port-base
or
switch(config)# qos priority
precedence cos-only
or
Page 73

qos priority
sho
w
Privileged
Display a summary of the
switch#
show spanning
-
tree
spanning
-
tree
or
no
Global
Enable
switch(config)#
spanning
-
tree
enable
or
swi
spanning
spanning
-
tree
Global
Use the
Priority must be a multiple of
switch(config)#
spanning
-
tree
priority
spanning
-
tree
Global
Use the spanning
age
switch(config)#
spanning
-
tree
max
spanning
-
tree
Global
Use the span
command to specify the interval
switch(config)#
spanning
-
tree
hello
or
no qos priority
precedence
39B
Spanning Tree Commands Set
Commands
spanning-tree
enable
Command
Level
EXEC
configuration
Description Default
spanning-tree states.
/disable spanning tree Disable
switch(config)#
precedence dscp-only
or
switch(config)# qos priority
precedence dscp-first
or
(Default)
switch(config)# no qos priority
precedence
Example
spanning-tree
priority [0~61440]
max-age
[6~40seconds]
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
spanning-tree priority
global configuration command
to change the priority.
4096
-tree maxglobal configuration command
to change the interval between
messages the spanning tree
receives from the root switch. If
a switch does not receive a
bridge protocol data unit
(BPDU) message from the root
switch within this interval, it
recomputed the Spanning Tree
tch(config)#no
-tree
32768
4096
20 sec
-age 15
hello-time
[1~10seconds]
configuration
mode
Protocol (STP) topology.
ning-tree
hello-time global configuration
between hello bridge protocol
67
2 sec.
-time 3
Page 74

spanning
-
tree
Global
Use the spanni
the listening and learning states
switch
spanning
-
tree
forward
stp-port priority
Interface
Use the
stp-port
path cost that is used when two
128 s
interface
gigaethernet 1
switch(config
stp
200000
stp-admin
-
p2p
[disable|enable|aut
Interface
Use the stp
Enable
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
s
p2p
auto
or
s
p2p
enable
or
s
p2p
disable
stp-admin
-
edge
[disable|enable]
Interface
Use the stp
Enable
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
s
stp
or
s
stp
data units (BPDUs).
forward-time
[4~30seconds]
[port priority]
pathcost [path
cost]
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
ng-tree
forward-time global
configuration command to set
the forwarding-time for the
specified spanning-tree
instances. The forwarding time
determines how long each of
last before the port begins
forwarding.
interface
configuration command to
configure a port priority and
switches tie for position as the
root switch.
-admp2p interface
15 sec.
(config)#
-time 20
witch(config)#
-if)#
-port priority 16 pathcost
witch (config)#
o]
configuration
configuration
mode
mode
configuration command to
configure a port AdmP2P
variable.
-admedge interface
configuration command to
configure a port AdmEdge
variable.
witch(config-if)# stp-admin-
witch(config-if)# stp-admin-
witch(config-if)# stp-admin-
witch (config)#
witch(config-if)#
-admin-edge enable
witch(config-if)#
-admin-edge disable
68
Page 75
stp-admin
- stp
[disabl
Interface
Use the stp
Enable
s
interface
gigaethernet 1
s
enable
vlan database
Privileged
vlan database
vlanmode
VLAN database
8021q
vlanmode
VLAN database
show vlan
VLAN dat
abase
no vlan
group 2
vlan port
-
based
VLAN database
vlan port
-
based
vlan 8021q name
VLAN database
e|enable]
configuration
mode
40B
VLAN Commands Set
Commands
[portbase| 802.1q|
gvrp ]
show vlan
or
show vlan
[GroupName|
VLAN ID]
Port Base VLAN mode
no vlan group
[VLAN ID]
Command
Level
EXEC
mode
mode
mode
-admstp interface
configuration command to
configure a port controlled by
stp protocol.
Description Default
Enter VLAN configure mode
To set switch VLAN mode.
Show VLAN information
Delete port base group ID
witch (config)#
witch(config-if)# stp-admin stp
Example
switch#
switch(vlan)#
switch(vlan)#
portbase
or
switch(vlan)#vlanmode 802.1q
or
switch(vlan)#vlanmode gvrp
switch(vlan)#
or
switch(vlan)#show vlan 2
switch(vlan)#
grpname
[Group Name]
grpid
[VLAN ID]
port
[PortNumbers]
802.1Q | 802.1Q with GVRP VLAN mode*
[GroupName] vid
[VLAN ID] media
Add new port based VALN
mode
Change the name of VLAN
mode
group, if the group didn’t exist,
this command can’t be applied.
switch(vlan)#
grpname test grpid 2 port 2-4
or
switch(vlan)#vlan port-based
grpname test grpid 2 port 2,3,4
switch(vlan)#
vlan 8021q name RD vid 2
media gigaethernet state
69
Page 76

gigaethernet state
active
switchport
Interface
interface
switchport native
Interface
1
switchport
Interface
all
switchport
Interface
disable
or
active
or
no vlan 8021q
[VLAN ID]
allowed vlan
8021q add [VLAN
ID]
[tagged|untagged]
or
switchport
allowed vlan
8021q remove
[VLAN ID]
or
no switchport
allowed vlan8021q
configuration
mode
Delete port base group ID
Add port to the VLAN
Remove port to the VLAN
Remove port from all VLAN
except default VLAN
or
switch(vlan)#no vlan 8021q 2
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
switchport allowed vlan 8021q
add 2 tagged
or
switch(config-if)#
switchport allowed vlan 8021q
remove 2
or
switch(config-if)#
no switchport allowed vlan
8021q
vlan [PVID]
or
no switchport
native vlan
acceptable-frame-t
ypes [all|tagged]
or
no switchport
acceptable-frame-t
ypes
ingress-filtering
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
Set Port PVID
Set accept frame type
Set ingress filter
switch(config)#
interface gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
switchport native vlan 2
or
switch(config-if)#
no switchport native vlan
switch(config)#
interface gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
switchport
acceptable-frame-types all
or
switch(config-if)#
no switchport
acceptable-frame-types
switch(config)#
interface gigaethernet 1
or
no switchport
ingress-filtering
70
mode
switch(config-if)#
switchport ingress-filtering
or
switch(config-if)#
no switchport ingress-filtering
Page 77

show vlan
Privileged
show vlan id
show interfaces
Privileged
Command
show logging
Privileged
show logging flash
logging
-
mode
Global
logging
-local
Global
Show VLAN of Group Name or
[id|name]
[VLAN ID | Name]
switchport
[gigaethernet|portchannel] [port]
EXEC
EXEC
VLAN ID information
vlanid: 1 ~ 4094
show Port PVID and ingress
filter & accept frame type
*Future Release
41B
System log Commands Set
Commands
[flash | ram |
Level
Show system log information
EXEC
switch#
Description Default
switch#
show interfaces switchport
gigaethernet 1
Example
switch#
sendmail | trap|
map]
{local|remote|smt
p}
or
no logging-mode
{local|remote|smt
p}
history [flash |
ram] [level]
or
no logging-local
history [flash |
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
Enable logging mode for local,
remote and smtp
Set system log level Flash:3(le
Switch(config)#
vel 3-0)
RAM:7(lev
el 7-0)
logging-mode local
Switch(config)#
no logging-mode local
Switch(config)#
logging-mode remote
Switch(config)#
logging-local history flash 3
ram]
71
Page 78

logging
-
events
Global
Logging
-
host
Global
Add or delete the remote server
logging facility
Global
logging trap
Global
clear logging
-
local
Global
logging sendmail
Global
[coldstart |
warmstart |
authfailure |
portlinkchange]
[level]
or
no logging-events
[coldstart |
warmstart |
authfailure |
portlinkchange]
[server]
or
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
Set the level of each logging
events.
address
Level 7 Switch(config)#
logging-events coldstart 3
Switch(config)#
no logging-events coldstart
Switch(config)#
logging-host 192.168.16.5
no logging-host
[server]
[value]
or
no logging facility
[value]
or
no logging trap
[flash | ram]
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
Switch(config)# no
logging-host 192.168.16.5
Set system log facility 23 Switch(config)#
logging facility 19
Switch(config)# no logging
facility
Set system log trap 7 Switch(config)#
logging trap 4
Switch(config)# no logging trap
4
Clear system log buffer Switch(config)#
clear logging-local flash
{host-0|host-1}
[server]
or
no logging
72
configuration
mode
Set the SMTP server address Switch(config)#
logging sendmail host-0
192.168.16.5
Switch(config)# no logging
Page 79

sendmail
sendmail host
-
0 192.168.16.5
logging sendmail
Global
logging sendmail
Global
logging sendmail
Global
system log SMTP
logging sendmail
Gl
obal
{host-0|host-1}
Set system log SMTP level 7 Switch(config)#
level [value]
or
no logging
sendmail level
{src-0|src-1}
[email addr]
or
no logging
sendmail
{src-0|src-1}
{dst-0|dst-1}
[email addr]
or
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
Set system log SMTP
source-email address
Add or delete
destination-email address
logging sendmail level 4
Switch(config)# no logging
sendmail level 4
Switch(config)#
logging sendmail src-0
bill@this-company.com
Switch(config)# no logging
sendmail src-0
bill@this-company.com
Switch(config)#
logging sendmail dst-0
bill@this-company.com
no logging
sendmail
{dst-0|dst-1}
[email addr]
service
or
no logging
sendmail service
configuration
mode
42B
SNTP Commands Set
Commands
Command
Level
Enable or disable system log
SMTP
Description Default
Switch(config)# no logging
sendmail dst-0
bill@this-company.com
Disable Switch(config)#
logging sendmail service
Switch(config)#
No logging sendmail service
Example
73
Page 80

calendar set
Global
calendar set 15
sntp timezone
Global
sntp timezone
show sntp
Privileged
show sntp timezone
no sntp timezone
Global
no
sntp
show sntp
Privileged
show sntp
sntp server
Global
no sntp server
Global
sntp enable
Global
sntp enable
no sntp
Global
no sntp
sntp poll [sec]
Global
no sntp poll
Global
igmp enable
Global
igmp
enable
[hour] [min] [sec]
[day] [mon] [year]
hours [hours]
minute [min]
[after-UTC|beforeUTC]
timezone
[ipaddr]
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
EXEC
configuration
mode
EXEC
configuration
Set system time
Set timezone index, use “show
sntp timezone” command to
get more information of index
number
Show index number of time
zone list
Set system time zone to default (GMT+08:
Show system time
configuration.
Set SNTP server IP address. switch(config)# sntp server
00)
switch(config)#
03 30 29 4 2006
switch(config)#
hours 9 minute 0 after-UTC
switch#
switch(config)#
timezone
switch#
192.168.16.5
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
Set SNTP server IP address to
default.
Enable SNTP Client.
Disable SNTP Client.
Set SNTP client polling interval
seconds.
Set SNTP client polling interval
seconds to default.
NULL switch(config)# no sntp server
switch(config)#
switch(config)#
16 switch(config)# sntp poll 60
switch(config)# no sntp poll
43B
IGMP Commands Set
Commands
74
Command
Level
Description Default
Enable IP IGMP Snooping disable
Example
switch(config)#
Page 81

configuration
no igmp
Global
no igmp
igmp
-
query
Global
i
gmp
-
query auto
igmp vlan [vid]
Globa
l
igmp vlan 1
thernet
no igmp vlan [vid]
Global
no igmp vlan 1
ethernet
show igmp
Privileged
Displays the details of an IGMP
show igmp
show mactbl
Privileg
ed
show mactbl
Privileged
interface
Global
interface
no interface
Global
no
interface
service.
mode
{enable |disable
|auto}
static [ipaddr]
[gigaethernet|portchannel] [port]
static [ipaddr]
[gigaethernet|portchannel] [port]
configuration
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
EXEC
Disable IP IGMP Snooping
service to default disable.
Set IP IGMP query mode. disable
Adds a static multicast group
and its member port.
Remove a static multicast
group and its member port.
configuration
Shows known multicast
switch#show mactbl multicast
switch(config)#
switch(config)#
switch(config)#
static 224.0.0.251 gigae
1
switch(config)#
static 224.0.0.251 giga
1
switch#
configuration
multicast vlan
[vid]
multicast [user |
igmp-snooping]
EXEC
EXEC
44B
TRUNK Commands Set
Commands
port-channel
[group id]
Command
Level
configuration
mode
addresses for specific VLAN Id.
Shows known multicast
addresses only the
user-configured multicast
entries or only entries learned
through IGMP snooping.
Description
Configures a trunk and enters
interface configuration mode
for the trunk.
If the trunk group isn’t exist,
you should create it by add a
vlan 1
switch#show mactbl multicast
user
switch(config)#
port-channel 1
Example
port-channel
configuration
member port
Delete the trucking group.
75
switch(config)#
port-channel 1
Page 82

[group id]
mode
trunk mode
Interface
interface
channel
-
group
Interface
interface
no channel
-
group
Interface
interface
show interfaces
Privileged
show interfaces status
show port activity
Privileged
show port activity
port
Interface
interface
snmp name
Global
snmp name
snmp location
G
lobal
snmp location
snmp contact
Global
snmp
[lacp|static]
or
no trunk mode
[group id]
status
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
EXEC
Configure the mode of the
trunk group.
Adds a port to a trunk.
If the trunk group doesn’t exist,
it will create the group.
Remove a port from a trunk.
Shows trunk information
static
switch(config)#
port-channel 1
switch(config-if)#
trunk mode static
or
switch(config-if)#
no trunk mode
switch(config)#
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
channel-group 1
switch(config)#
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
no channel-group 1
switch#
port-channel 1
port-channel
[group id]
EXEC
{active|passive}
configuration
mode
45B
SNMP Commands Set
Commands
[station name]
[station location]
Command
Level
configuration
mode
configuration
Show lacp port activity
information
Set port active|passive
Description Default
Configure station name.
Configure station location.
active
switch#
switch(config)#
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)# port passive
Example
switch(config)#
station1
switch(config)#
Taiwan
mode
Configure station contact.
[station contact]
76
configuration
mode
switch(config)#
contact HUsupport@level1.com
UH
Page 83

snmp
Global
public,
snmp
no snmp
Global
no snmp
snmp
-
server host
Global
snmp
-
serve
r
no snmp
-
server
Global
no snmp
-
server
show snmp
Privileged
show snmp
dhcpserver [ip
Global
dhcpserver
no dhcpserver
Global
no dhcpserver
show dhcpserver
Privileged
show dhcpserver
community-string
s [Community]
right [RO/RW]
community-string
s [Community]
[IP address]
community
[Community-strin
g]
host
[Host-address]
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
Add SNMP community string.
Remove the specified
community.
Configure SNMP trap manager
information and community
string
Remove the SNMP server
host.
Show snmp configuration
private
switch(config)#
community-strings public
right rw
switch(config)#
community-strings public
switch(config)#
host 192.168.1.50 community
public
switch(config)#
host 192.168.1.50
switch#
EXEC
46B
DHCP Server Commands Set
Commands
start] [ip number]
Command
Level
configuration
mode
Enable dhcp server and add
lease entry.
Disable dhcp server.
Description
switch(config)#
192.168.1.5 5
Netmask [255.255.255.0]:
255.255.255.0
Gateway [192.168.16.254]:
192.168.16.254
DNS [192.168.16.254]:
192.168.16.254
Lease Duration [24](hours)
24
switch(config)#
Example
configuration
mode
Show configuration of dhcp
EXEC
server and client status.
77
switch#
Page 84

security [entry id]
ip [ip address] http
Global
security 1 ip
no security
Global
no security
show security
Privileged
show securi
ty
8021x enable
Global
8021x
enable
8021x misc
G
lobal
8021x misc
8021x misc
Global
8021x misc
8021x misc
Global
8021x misc
8021x misc
Global
8021x misc
8021x misc
Global
8021x misc
47B
Security IP Commands Set
Commands
[on/off] telnet
[on/off]
Command
Level
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
EXEC
48B
802.1X Commands Set
Commands
Command
Level
Description Default
Enable and add security ip.
Entry id: 1 - 10
Disable IP security function
Show the information of IP
security
Description
Use the 802.1x global
Disable
Example
switch(config)#
192.168.16.5 http on telnet on
switch(config)#
switch#
Example
switch(config)#
quietperiod
[sec.]
txperiod
[sec.]
supportimeout
[sec.]
servertimeout
[sec.]
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
configuration command to
enable 802.1x protocols.
Use the 802.1x misc quiet
period global configuration
command to specify the quiet
period value of the switch.
Use the 802.1x misc TX period
global configuration command
to set the TX period.
Use the 802.1x misc supp
timeout global configuration
command to set the supplicant
timeout.
Use the 802.1x misc server
timeout global configuration
command to set the server
timeout.
60
30
30
30
switch(config)#
quietperiod 10
switch(config)#
txperiod 5
switch(config)#
supportimeout 20
switch(config)#
servertimeout 20
maxrequest
[number]
78
configuration
mode
Use the 802.1x misc max
request global configuration
command to set the MAX
switch(config)#
2
maxrequest 3
Page 85

8021x misc
Global
8021x misc
8021x portstate
Interface
mand to set the state of the
interface
show 8021x
Privileged
show
8021x
802
1x system
Global
8021x system
8021x system
Global
8021x system
8021x
system
Global
802.1x system account
8021x system
8021x system
Global
8021x system
lldp [enable]
Global
lldp enable
show lldp status
Privileged
show lldp status
requests.
reauthperiod
[sec.]
[disable | reject |
accept | authorize]
radiusip
[IP address]
serverport
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
EXEC
configuration
mode
configuration
Use the 802.1x misc reauth
period global configuration
command to set the reauth
period.
Use the 802.1x port state
interface configuration
com
selected port.
Displays a summary of the
802.1x properties and also the
port status.
Use the 802.1x system radius
IP global configuration
command to change the radius
server IP.
Use the 802.1x system server
port global configuration
3600
Disable
switch(config)#
reauthperiod 3000
switch(config)#
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#8021x
portstate accept
switch#
switch(config)#
radiusip 192.168.1.1
switch(config)#
serverport 1815
[port ID]
accountport
[port ID]
sharekey
[ID]
mode
configuration
mode
configuration
mode
49B
LLDP Commands Set
Commands
or
Command
Level
configuration
command to change the radius
server port
Use the
port global configuration
command to change the
accounting port
Use the 802.1x system share
key global configuration
command to change the
shared key value.
Description Default
Enable or disable LLDP
protocol.
Disable
switch(config)#
accountport 816
switch(config)#
sharekey 123456
Example
switch(config)#
or
no lldp
mode
EXEC
Show LLDP status.
79
switch(config)# no lldp
switch#
Page 86

show lldp remote
Privileged
show lldp remote
lldp-port
[
disable
Interface
interface
acl-port
Interface
interface
acl-rule [index] dst
Interface
or
N/A
interface
show
acl
Privileged
N/A
show
acl gigaethernet
EXEC
|rx|tx|both]
configuration
mode
50B
ACL Commands Set
Commands
[deny|permit]
or
no acl-port
Command
Level
configuration
mode
Show LLDP remote table.
Use those commands to set
lldp port tx and rx mode.
Description Defaults
Use the acl-port interface
configuration command to
enable Access Control on a
port. The default action can be
Disable
Disable
switch#
switch(config)#
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)# lldp-port
disable
or
switch(config-if)# lldp-port rx
Example
switch(config)#
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
acl-port deny
[dstIp/prefix] src
[srcIp/prefix]
{deny|permit}
or
no acl-rule [index]
[gigaethernet|portchannel][port]
configuration
mode
EXEC
Deny or Permit. Use the no
form of this command to return
the port to its default value
(disable).
Use those commands to add
delete the acl rules of the port.
[index] range= 0~4
Show acl configuration of the
port.
or
switch(config-if)#
no acl-port
switch(config)#
gigaethernet 1
switch(config-if)#
acl-rule 0 dst 192.168.16.1/32
src 192.168.16.2/32 permit
or
switch(config-if)#
no acl-rule 0
switch#
1
80
 Loading...
Loading...