LevelOne IES-1085 User Manual

IES-1085
4 x 802.3af + 4 x 802.3at + 2 GE SFP Managed Switch -40 to 75C, DIN-rail
User Manual
v1.00 - 1206

Preface
This manual describes how to install and use the Industrial Managed PoE (Power over
Ethernet) Ethernet Switch. This switch introduced here is designed to deliver full scalability
with SNMP/RMON web-based management functions by providing:
To get the most out of this manual, you should have an understanding of Ethernet
networking concepts.
In this manual, you will find:
Features on the Industrial Managed PoE Ethernet Switch
Illustrative LED functions
Installation instructions
Management Configuration
Specifications
User Manual Page 2

Table of Contents
PREFACE .................................................................................................................................................. 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS .................................................................................................................................... 3
QUICK START GUIDE .............................................................................................................................. 5
PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................................ 5
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................................................................... 7
CONSOLE CONFIGURATION ....................................................................................................................................... 8
WEB CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................................................................. 9
PRODUCT OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................... 10
INDUSTRIAL MANAGED ETHERNET SWITCH ................................................................................................................ 10
PACKAGE CONTENTS .............................................................................................................................................. 10
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS ........................................................................................................................................... 11
FRONT PANEL DISPLAY ........................................................................................................................................... 13
PHYSICAL PORTS ................................................................................................................................................... 14
SWITCH MANAGEMENT ......................................................................................................................................... 15
INSTALLATION ....................................................................................................................................... 16
SELECTING A SITE FOR THE SWITCH ........................................................................................................................... 16
WIRING DIAGRAM ................................................................................................................................................ 16
DIN RAIL MOUNTING ............................................................................................................................................ 17
CONNECTING TO POWER ........................................................................................................................................ 17
CONNECTING TO YOUR NETWORK ............................................................................................................................ 19
SWITCH MANAGEMENT ....................................................................................................................... 20
MANAGEMENT ACCESS OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................... 20
ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE (CLI) ............................................................................................................................ 21
WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................................................. 22
SNMP-BASED NETWORK MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................................. 22
PROTOCOLS ......................................................................................................................................................... 22
MANAGEMENT ARCHITECTURE ................................................................................................................................ 23
SNMP & RMON MANAGEMENT ........................................................................................................... 24
OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................................................... 24
SNMP AGENT AND MIB-2 (RFC 1213) .................................................................................................................. 24
RMON MIB (RFC 2819) AND BRIDGE MIB (RFC 1493) ........................................................................................... 25
WEB-BASED BROWSER MANAGEMENT ........................................................................................... 27
LOGGING ON TO THE SWITCH ................................................................................................................................... 27
UNDERSTANDING THE BROWSER INTERFACE ............................................................................................................... 28
SYSTEM ............................................................................................................................................................... 30
PORT .................................................................................................................................................................. 40
SWITCHING .......................................................................................................................................................... 44
TRUNKING ........................................................................................................................................................... 48
STP / RING ......................................................................................................................................................... 49
VLAN ................................................................................................................................................................ 56
QOS ................................................................................................................................................................... 60
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................................... 62
802.1X .............................................................................................................................................................. 66
OTHER PROTOCOLS ............................................................................................................................................... 69
COMMAND LINE CONSOLE MANAGEMENT ..................................................................................... 73
User Manual Page 3

ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE .................................................................................................................................... 73
SYSTEM ............................................................................................................................................................... 82
PORT .................................................................................................................................................................. 92
SWITCHING .......................................................................................................................................................... 99
TRUNKING ......................................................................................................................................................... 108
STP ................................................................................................................................................................. 109
VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................. 122
QOS ................................................................................................................................................................. 128
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................................. 131
802.1X ............................................................................................................................................................ 138
OTHER PROTOCOLS ............................................................................................................................................. 143
SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................................................. 154
APPENDIX A .......................................................................................................................................... 155
APPENDIX B .......................................................................................................................................... 156
User Manual Page 4
Quick Start Guide
This quick start guide describes how to install and use the Industrial Managed PoE (Power
over Ethernet) Ethernet Switch. This is the switch of choice for harsh environments
constrained by space.
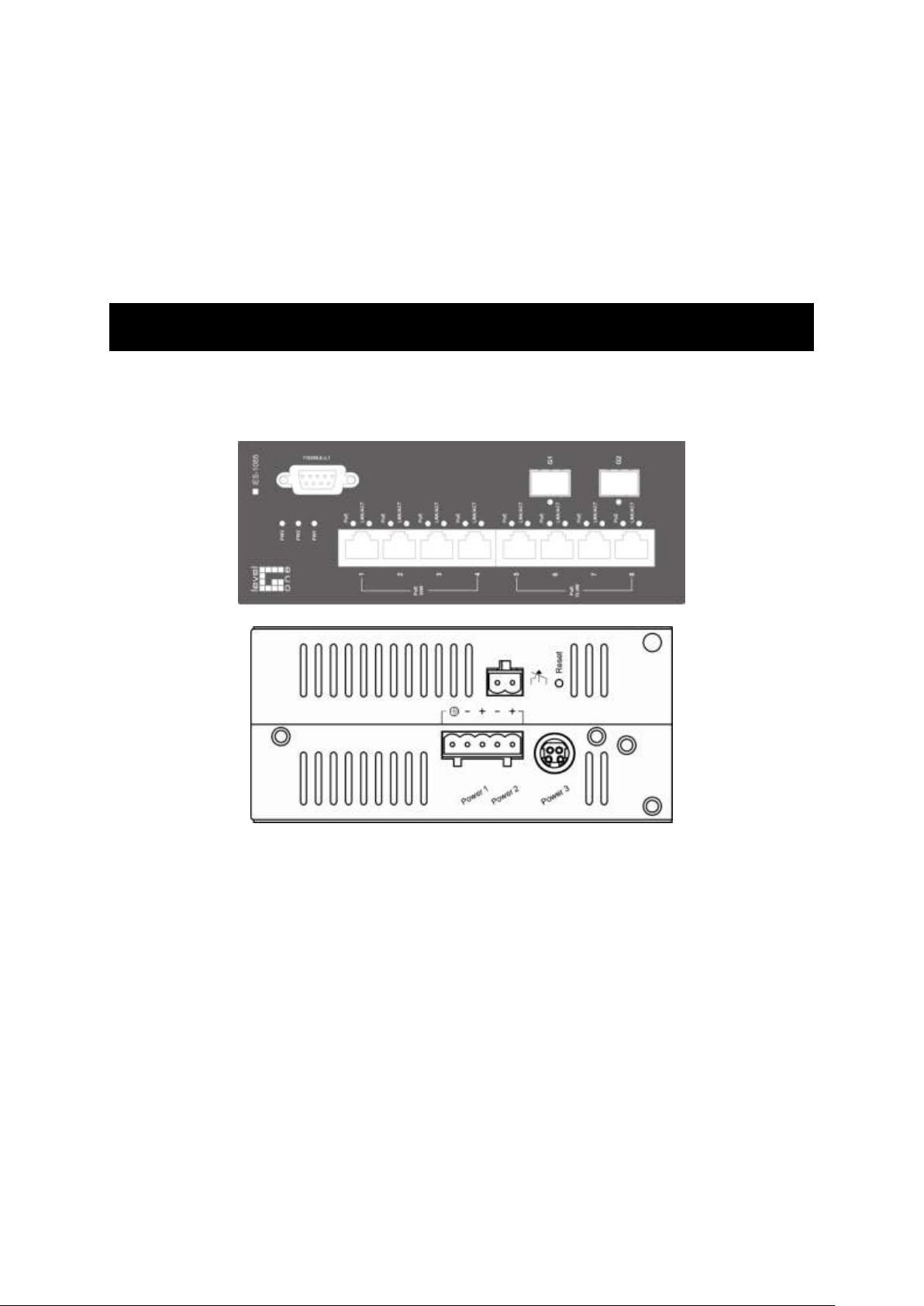
Physical Description
The Port Status LEDs and Power Inputs
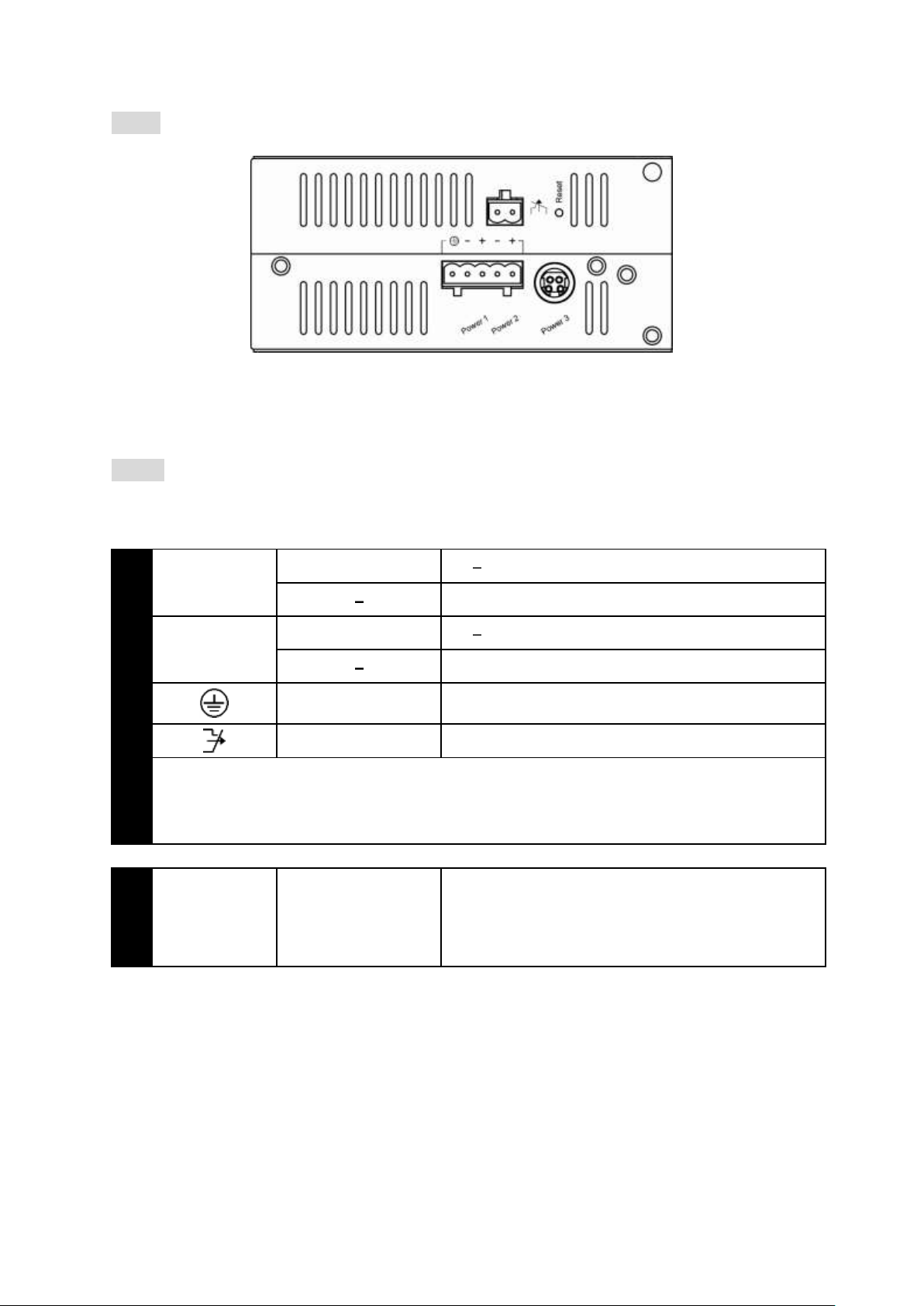
User Manual Page 5
Power Input
Terminal Block
PW1
+
47 57VDC
Power Ground
PW2
+
47 57VDC
Power Ground
Earth Ground
Relay Output
1A @ 250VAC
Relay Alarm warning signal disable for following:
1. The relay contact closes if Power1 and Power2 are both failed but Power3 on
2. The relay contact closes if Power3 is failed but Power1 and Power2 are both on
LED
Status
Description
PW 1,2,3
Steady
Power On
Off
Power Off
10/100Base-TX
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
PoE
Steady
Power Device (PD) is connected
Off
Power Device (PD) is disconnected
100Base-FX
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
10/100/1000Base-TX & 1000Base-FX & SFP
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
There are three power inputs can be used. Redundant power function is supported
PW3 is DC Jack type with 47 57VDC input
LED Status
User Manual Page 6

Functional Description
Meets NEMA TS1/TS2 Environmental requirements such as temperature, shock, and
vibration for traffic control equipment.
Meets EN61000-6-2 & EN61000-6-4 EMC Generic Standard Immunity for industrial
environment.
RS-232 console, Telnet, SNMP v1 & v2c & v3, RMON, Web Browser, and TFTP
management.
Supports Command Line Interface in RS-232 console.
Supports 8192 MAC addresses. Provides 2M bits memory buffer.
Port 1 ~ Port 4 support IEEE802.3at Power over Ethernet (PoE) Power Sourcing
Equipment (PSE) and/or Port 5 ~ Port 8 support IEEE802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE).
Supports IEEE802.3/802.3u/802.3ab/802.3z/802.3x. Auto-negotiation,
1000Mbps-full-duplex, 10/100Mbps-full/half-duplex, Auto MDI/MDIX.
100Base-FX: Multi mode or Single mode duplex LC type. 100Base-BX: WDM Multi mode
or Single mode single LC type.
1000Base-SX/LX: Multi mode or Single mode duplex LC type. 1000Base-BX: WDM Multi
mode or Single mode single LC type.
Store-and-forward mechanism. Full wire-speed forwarding rate.
Alarms for power and port link failure by relay output.
Power Supply: Redundant 47-57VDC Terminal Block power inputs or 47-57VDC DC Jack
power input.
Field Wiring Terminal: Use Copper Conductors Only, 60/75℃, 12-24 AWG torque value 7
lb-in.
Operating voltage and Max. current consumption: 0.31A @ 48VDC. Power
consumption: Power consumption: 230W Max. (Full load with PoE), 15W Max. (Without
PoE).
-40℃ to 75℃ (-40℉ to 167℉) operating temperature range. Tested for functional
operation @ -40℃ to 85℃ (-40℉ to 185℉). UL508 Industrial Control Equipment
certified Maximum Surrounding Air Temperature @ 75℃ (167℉).
For use in Pollution Degree 2 Environment.
Industrial metal case.
Supports Din-Rail or Panel Mounting installation.
User Manual Page 7
Console Configuration
Connect to the switch console:
Connect the DB9 straight cable to the RS-232 serial port of the device and the RS-232
serial port of the terminal or computer running the terminal emulation application.
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a
terminal or a PC equipped with a terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal)
to the switch console port.
Configuration settings of the terminal-emulation program:
Baud rate: 115,200bps
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop bit: 1
Flow control: none
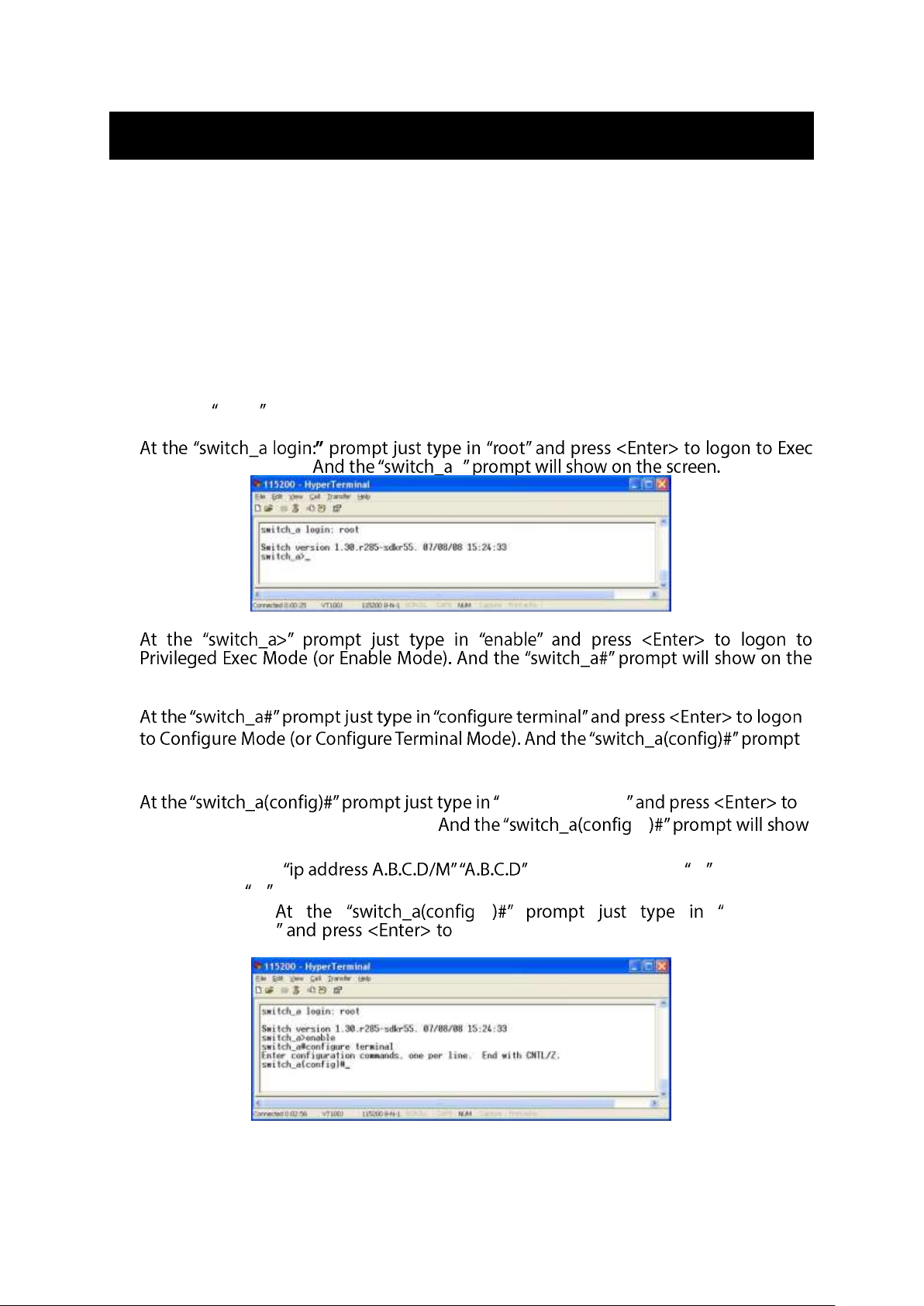
Press the Enter key. The Command Line Interface (CLI) screen should appear as below:
Logon to Exec Mode (View Mode):
Mode (or View Mode). >
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode):
screen.
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode):
will show on the screen.
Set new IP address and subnet mask for Switch:
interface vlan1.1
logon to vlan 1 (vlan1.1 means vlan 1). -if
on the screen.
Command Syntax: . specifies IP address. M specifies IP
subnet mask. M = 8: 255.0.0.0, 16:255.255.0.0, or 24: 255.255.255.0.
For example, -if ip address
192.168.1.10/24 set new IP address (192.168.1.10) and new IP
subnet mask (255.255.255.0) for Switch.
User Manual Page 8
Web Configuration
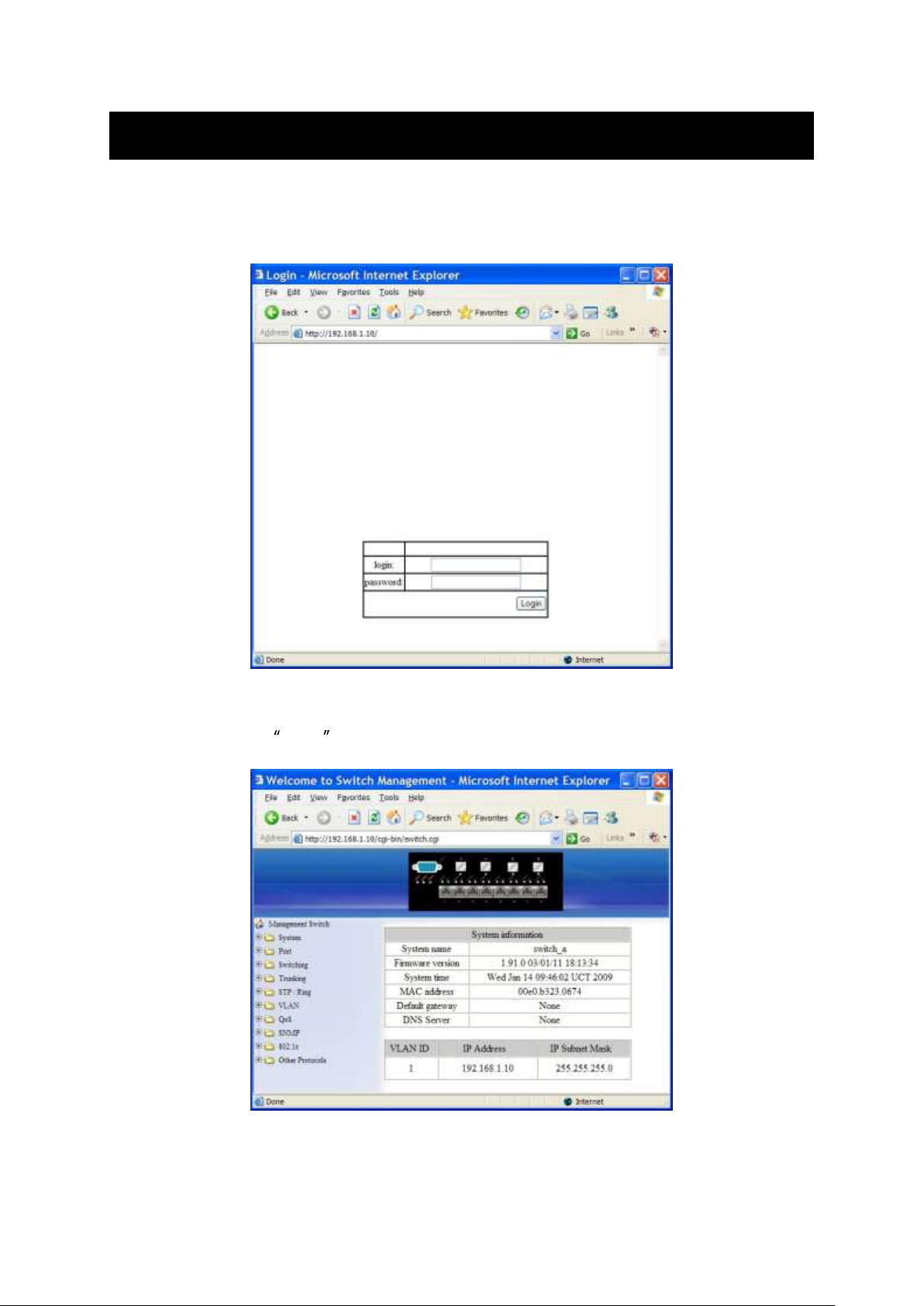
Login the switch:
Specify the default IP address (192.168.1.10) of the switch in the web browser. A login
window will be shown as below:
Enter the factory default login ID: root.
Enter the factory default password (no password).
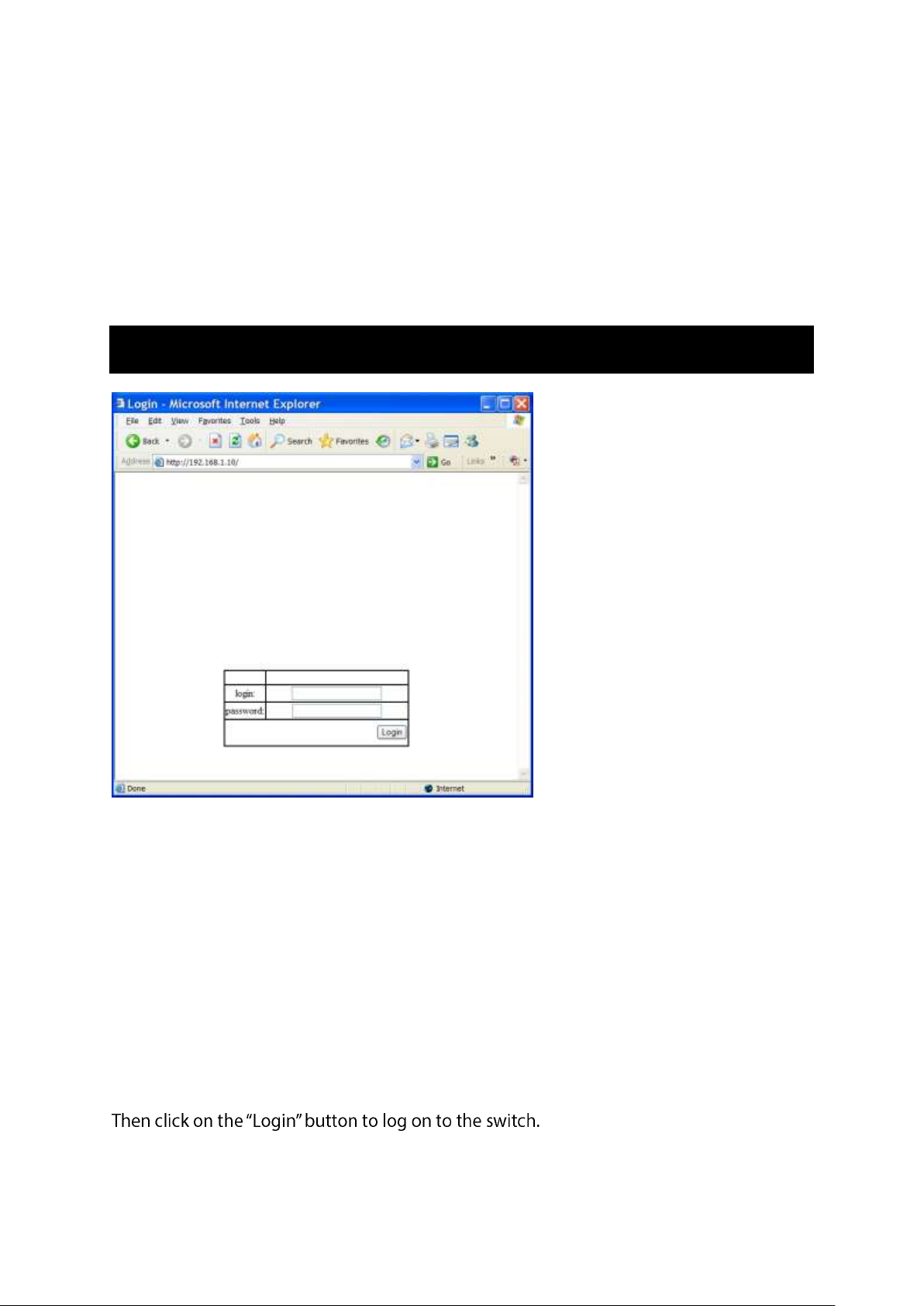
Then click on the Login button to log on to the switch.
User Manual Page 9
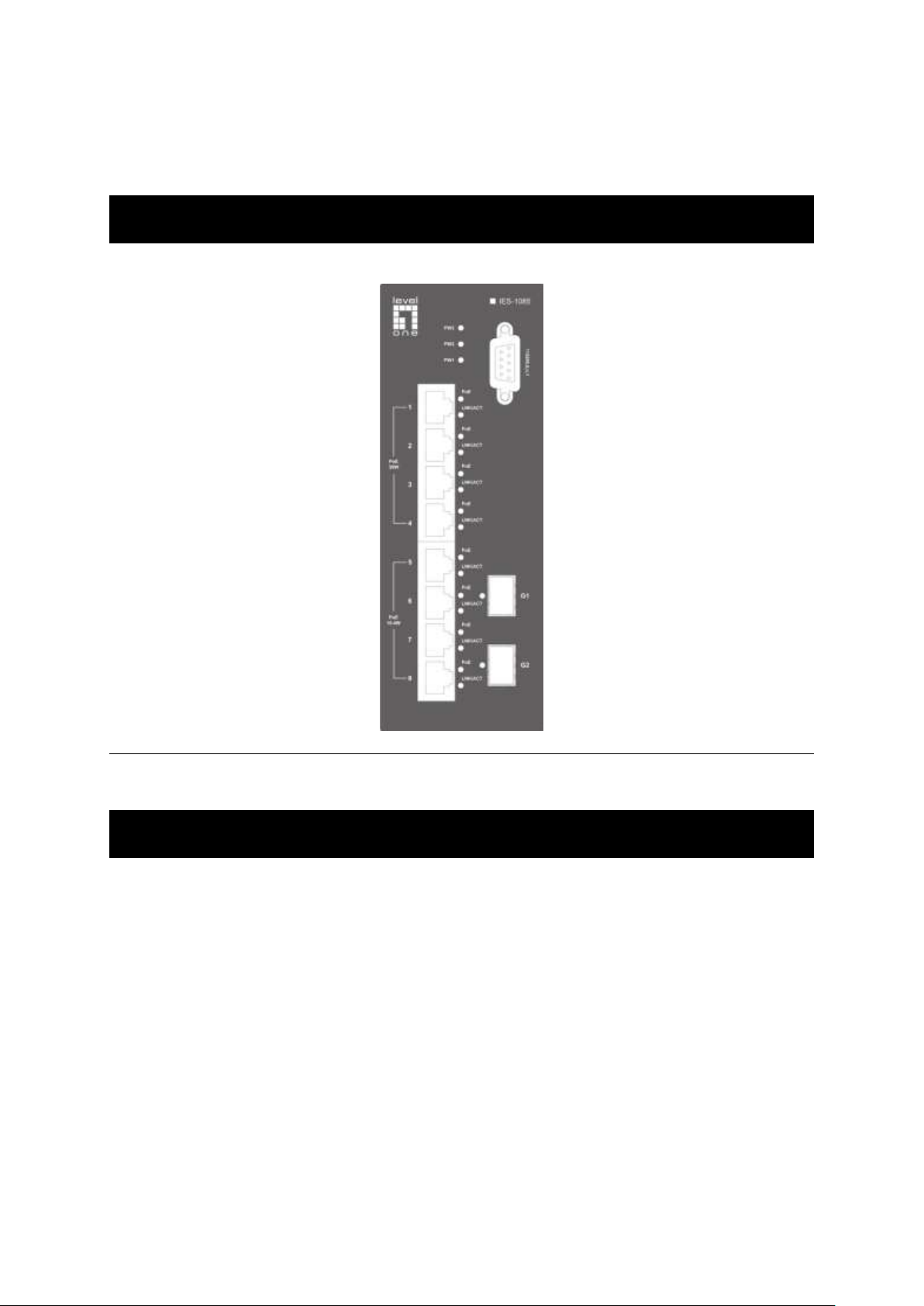
Product Overview
Industrial Managed Ethernet Switch
Front View
Package Contents
When you unpack the product package, you shall find the items listed below. Please
inspect the contents, and report any apparent damage or missing items immediately to
your authorized reseller.
IES-1085
Quick Installation Guide
CD User Manual
RS-232 cable
User Manual Page 10

Product Highlights
Basic Features
Meets NEMA TS1/TS2 Environmental requirements such as temperature, shock, and
vibration for traffic control equipment.
Meets EN61000-6-2 & EN61000-6-4 EMC Generic Standard Immunity for industrial
environment.
RS-232 console, Telnet, SNMP v1 & v2c & v3, RMON, Web Browser, and TFTP
management.
Supports Command Line Interface in RS-232 console.
Supports 8192 MAC addresses. Provides 2M bits memory buffer.
Port 1 ~ Port 4 support IEEE802.3at Power over Ethernet (PoE) Power Sourcing
Equipment (PSE) and/or Port 5 ~ Port 8 support IEEE802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE).
Supports IEEE802.3/802.3u/802.3ab/802.3z/802.3x. Auto-negotiation,
1000Mbps-full-duplex, 10/100Mbps-full/half-duplex, Auto MDI/MDIX.
100Base-FX: Multi mode or Single mode duplex LC type. 100Base-BX: WDM Multi mode
or Single mode single LC type.
1000Base-SX/LX: Multi mode or Single mode duplex LC type. 1000Base-BX: WDM Multi
mode or Single mode single LC type.
Store-and-forward mechanism. Full wire-speed forwarding rate.
Alarms for power and port link failure by relay output.
Power Supply: Redundant 47-57VDC Terminal Block power inputs or 47-57VDC DC Jack
power input.
Field Wiring Terminal: Use Copper Conductors Only, 60/75℃, 12-24 AWG torque value 7
lb-in.
Operating voltage and Max. current consumption: 0.31A @ 48VDC. Power
consumption: Power consumption: 230W Max. (Full load with PoE), 15W Max. (Without
PoE).
-40℃ to 75℃ (-40℉ to 167℉) operating temperature range. Tested for functional
operation @ -40℃ to 85℃ (-40℉ to 185℉). UL508 Industrial Control Equipment
certified Maximum Surrounding Air Temperature @ 75℃ (167℉).
For use in Pollution Degree 2 Environment.
Industrial metal case.
Supports Din-Rail or Panel Mounting installation.
Management Support
VLAN
Port-based VLAN
IEEE802.1Q tagged VLAN
User Manual Page 11

TRUNKING
Port Trunking
PORT-SECURITY
Per-port programmable MAC address locking
Up to 24 Static Secure MAC addresses per port
PORT-MIRRORING
Port-mirroring
QOS (IEEE802.1p Quality of Service)
4 priority queues
INTERNETWORKING PROTOCOLS
Bridging:
IEEE802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree
IEEE802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree compatible
IEEE802.1Q GVRP
Ring
IP Multicast:
IGMP Snooping
Rate Control
NTP
NETWORK MANAGEMENT METHODS
Console port access via RS-232 cable (CLI, Command Line Interface)
Telnet remote access
SNMP agent:
MIB-2 (RFC1213)
Bridge MIB (RFC1493)
RMON MIB (RFC2819) statistics, history, alarm and events
VLAN MIB (IEEE802.1Q/RFC2674)
Private MIB
Web browser
TFTP software-upgrade capability
User Manual Page 12
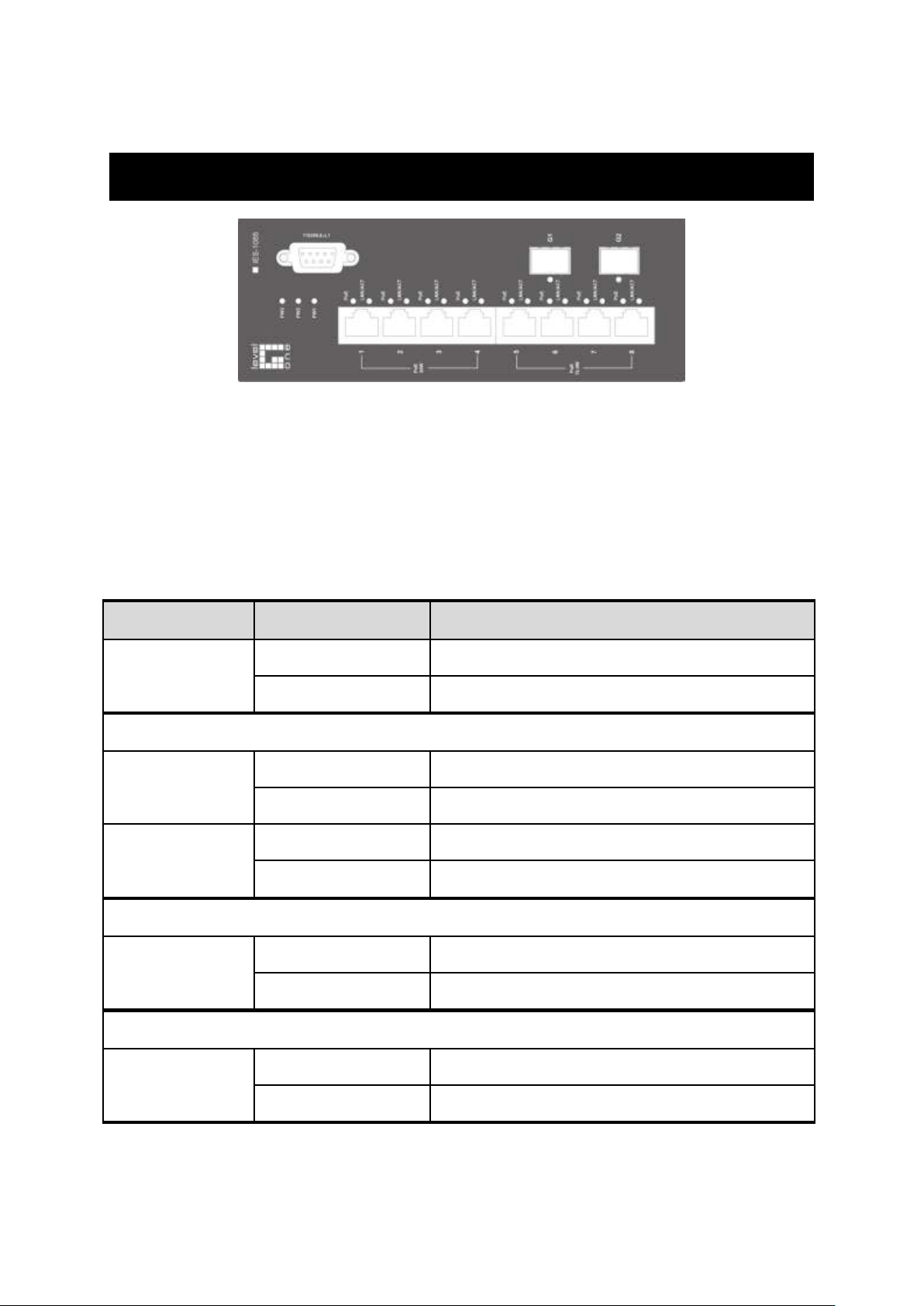
LED
Status
Description
PW 1,2,3
Steady
Power On
Off
Power Off
10/100Base-TX
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
PoE
Steady
Power Device (PD) is connected
Off
Power Device (PD) is disconnected
100Base-FX
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
10/100/1000Base-TX & 1000Base-FX & SFP
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
Front Panel Display
POWER
This LED comes on when the switch is properly connected to power and
turned on.
Port Status LEDs
The LEDs are located on the front panel, displaying status for each respective
port. Please refer to the following table for more details.
User Manual Page 13
Physical Ports
Number of ports
10/100Base-TX (802.3at)
4
10/100Base-TX (802.3af)
4
100Base SFP:
10/100Base-TX
100Base-FX/BX
0
1000Base SFP:
10/100/1000Base-TX
1000Base-SX/LX/BX
2
The Industrial Managed Ethernet Switch provides:
CONNECTIVITY
RJ-45 connectors on TX ports
Single or Duplex LC connectors on SFP 100Base-FX/BX fiber transceiver
Single or Duplex LC connectors on SFP 1000Base-SX/LX/BX fiber transceiver
MODE SELECTION
10Base-T full-duplex mode
10Base-T half-duplex mode
100Base-TX full-duplex mode
100Base-TX half-duplex mode
100Base-FX full-duplex mode
1000Base-T/SX/LX full-duplex mode
Auto-negotiating mode
User Manual Page 14

Switch Management
Web-based browser interface
The switch also boasts a point-and-click browser-based interface that lets user access full
switch configuration and functionality from a Netscape or Internet Explorer browser.
Administration console via RS-232 serial port (CLI)
The switch provides an onboard serial port, which allows the switch to be configured via a
directly connected terminal.
External SNMP-based network management
application
The switch can also be configured via SNMP.
User Manual Page 15

Installation
This chapter gives step-by-step instructions about how to install the switch:
Selecting a Site for the Switch
As with any electric device, you should place the switch where it will not be subjected to
extreme temperatures, humidity, or electromagnetic interference. Specifically, the site you
select should meet the following requirements:
-The ambient temperature should be between -40℃ to 75℃ (-40℉ to 167℉).
-The relative humidity should be less than 95 percent, non-condensing.
-Surrounding electrical devices should not exceed the electromagnetic field (RFC)
standards.
-Make sure that the switch receives adequate ventilation. Do not block the ventilation
holes on each side of the switch.
Wiring Diagram
Field Wiring Terminal Markings: Use Copper Conductors Only, 60/75℃, wire range 12-24
AWG, torque value 7 lb-in.
User Manual Page 16
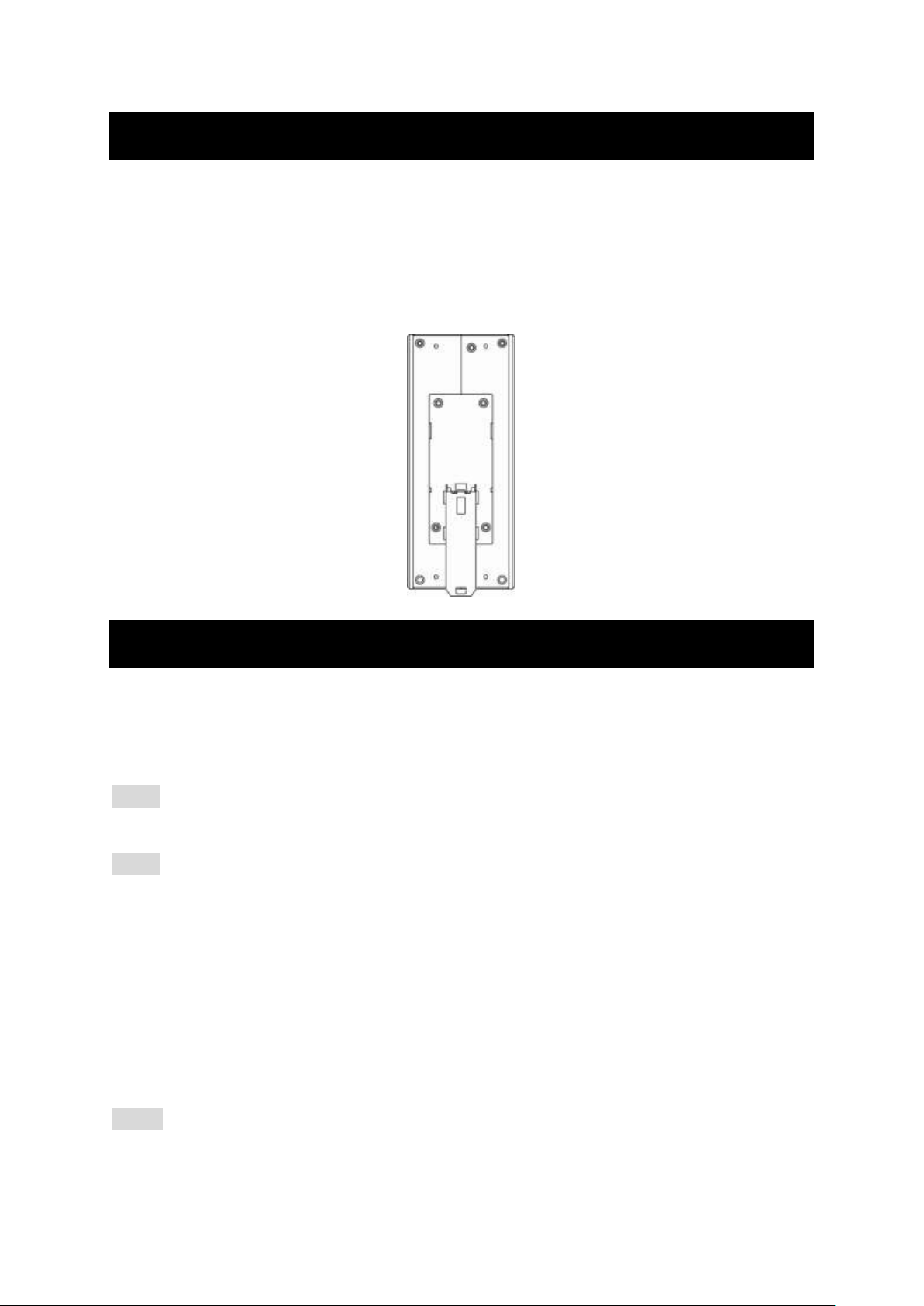
DIN Rail Mounting
Fix the DIN rail attachment plate to the back panel of the Media Converter.
Installation: Place the Media Converter on the DIN rail from above using the slot. Push the
front of the Media Converter toward the mounting surface until it audibly snaps into place.
Removal: Pull out the lower edge and then remove the Media Converter from the DIN rail.
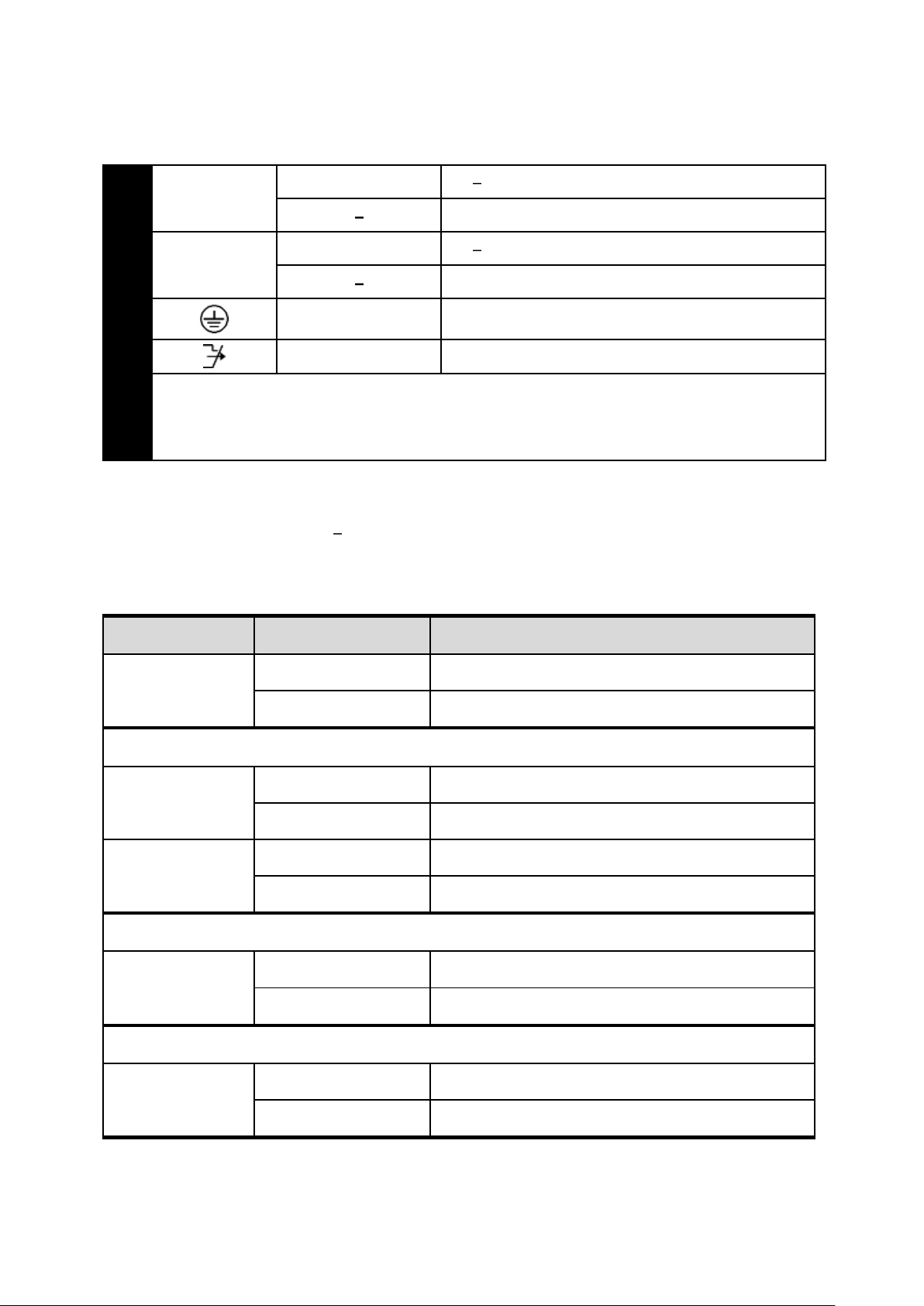
Connecting to Power
Redundant DC Terminal Block Power Inputs or DC Jack Power Input:
47-57VDC Jack
Step 1: Connect the supplied AC to DC power adapter to the receptacle on the topside of
the switch.
Step 2: Connect the power cord to the AC to DC power adapter and attach the plug into a
standard AC outlet with the appropriate AC voltage.
Redundant 47-57VDC DC Terminal Block Power
Inputs
There are two pairs of power inputs for use with redundant power sources. You only need
to have one power input connected to run the switch.
Step 1: Connect the DC power cord to the plug-able terminal block on the switch, and
then plug it into a standard DC outlet.
User Manual Page 17
Step 2: Disconnect the power cord if you want to shut down the switch.
Terminal Block
PW1
+
47 57VDC
Power Ground
PW2
+
47 57VDC
Power Ground
Earth Ground
Relay Output
1A @ 250VAC
Relay Alarm warning signal disable for following:
3. The relay contact closes if Power1 and Power2 are both failed but Power3 on
4. The relay contact closes if Power3 is failed but Power1 and Power2 are both on
DC Jack
PW3
DC Jack
47 to 57VDC
Back View
Alarms for Power Failure
Step 1: There are two pins on the terminal block used for power failure detection. It
provides the normally closed output when the power source is active. Use this as a
dry contact application to send a signal for power failure detection.
Special note:
The relay output is normal open position when there is no power to the switch.
Please do not connect any power source to this terminal to prevent shorting your
power supply.
User Manual Page 18
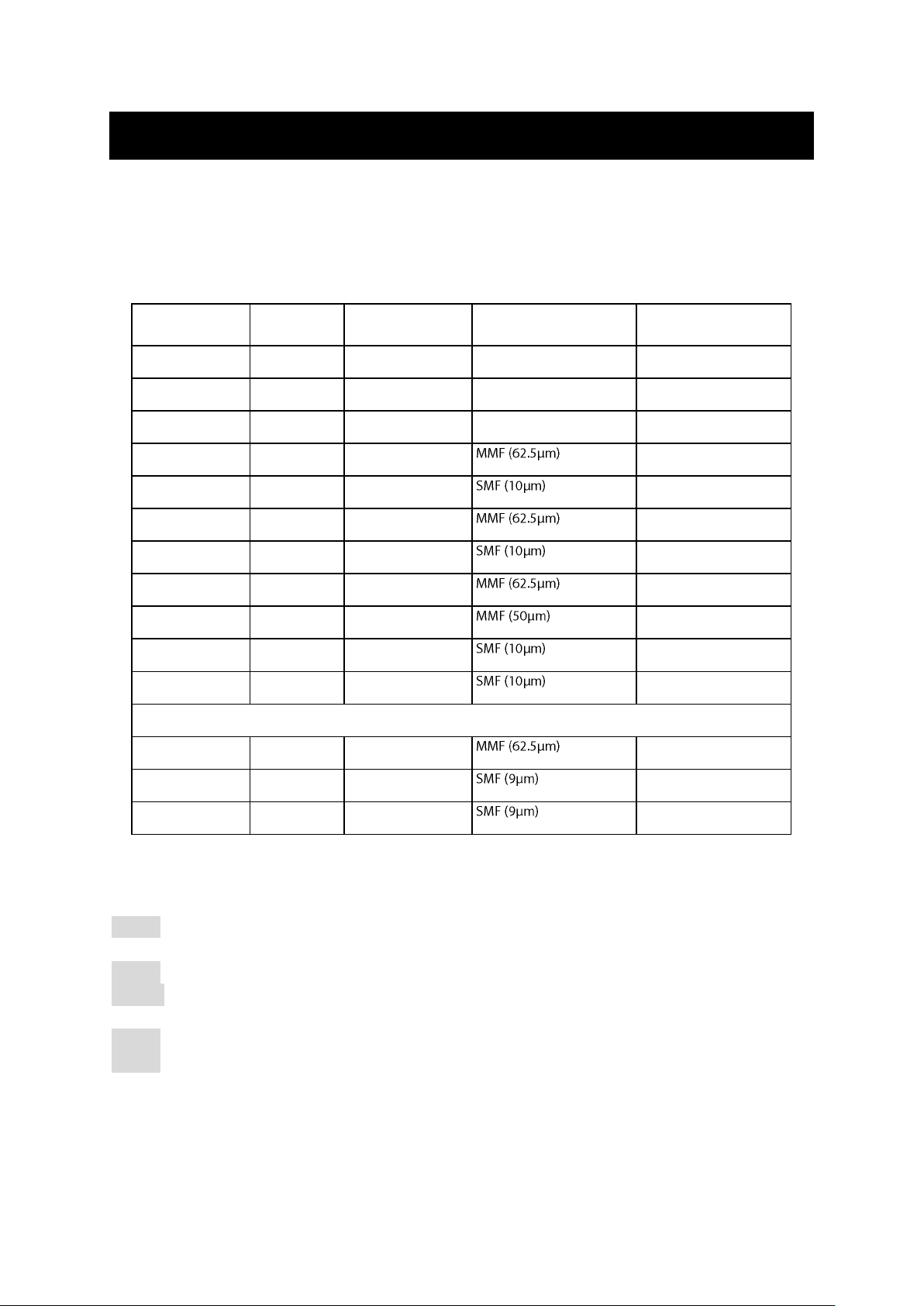
Connecting to Your Network
Speed
Connector
Port Speed
Half/Full Duplex
Cable
Max. Distance
10Base-T
RJ-45
10/20 Mbps
2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 3, 4, 5
100 m
100Base-TX
RJ-45
100/200 Mbps
2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5
100 m
1000Base-T
RJ-45
2000 Mbps
4-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5
100 m
100Base-FX
ST, SC
200 Mbps
2 km
100Base-FX
ST, SC
200 Mbps
20, 40, 75, 100 km
100Base-BX
SC
200 Mbps
2, 5 km
100Base-BX
SC
200 Mbps
20, 40 km
1000Base-SX
SC
2000 Mbps
220 m, 2 km
1000Base-SX
SC
2000 Mbps
550 m
1000Base-LX
SC
2000 Mbps
10, 20, 50 km
1000Base-BX
SC
2000 Mbps
20, 40 km
SFP
1000Base-SX
Duplex LC
2000 Mbps
550 m, 2 km
1000Base-LX
Duplex LC
2000 Mbps
10, 40, 60 km
1000Base-BX
Duplex LC
2000 Mbps
70 km
Cable Type & Length
It is necessary to follow the cable specifications below when connecting the switch to your network. Use appropriate
cables that meet your speed and cabling requirements.
Cable Specifications
Cabling
Step 1: First, ensure the power of the switch and end devices are turned off.
<Note> Always ensure that the power is off before any installation.
Step 2: Prepare cable with corresponding connectors for each type of port in use.
Step 3: Consult Cable Specifications Table on previous page for cabling requirements
Step 4: Connect one end of the cable to the switch and the other end to a desired device.
Step 5: Once the connections between two end devices are made successfully, turn on the
User Manual Page 19
based on connectors and speed.
power and the switch is operational.
Switch Management
This chapter explains the methods that you can use to configure management access to
the switch. It describes the types of management applications and the communication
and management protocols that deliver data between your management device
(workstation or personal computer) and the system. It also contains information about
port connection options.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Management Access Overview
Key Concepts
Key Guidelines for Implementation
Web Management Access
Administration Console Access
SNMP Access
Standards, Protocols, and Related Reading
Management Access Overview
The switch gives you the flexibility to access and manage the switch using any or all of the
following methods.
The web browser interface and administration console (CLI) support are embedded in the
switch software and are available for immediate use.
User Manual Page 20

Administration Console (CLI)
The administration console is an internal, character-oriented, Command Line Interface (CLI)
for performing system administration such as displaying statistics or changing option
settings. Using this method, you can view the administration console from a terminal,
personal computer, Apple Macintosh, or workstation co
port. There are two ways to use this management method: direct access or modem access.
The following sections describe these methods.
Direct Access
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a terminal
or a PC equipped with a terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal) to the
switch console port.
When using the management method, configure the terminal-emulation program to use
the following parameters (you can change these settings after login):
[DEFAULT PARAMETERS]
115,200bps
8 data bits
No parity
1 stop bit
This management method is often preferred because you can remain connected and
monitor the system during system reboots. Also, certain error messages are sent to the
serial port, regardless of the interface through which the associated action was initiated. A
Macintosh or PC attachment can use any terminal-emulation program for connecting to
the terminal serial port. A workstation attachment under UNIX can use an emulator such
as TIP.
Modem Access
external modem attached to the console port. The switch management program provides
Console Port screen, accessible from the Basic Management screen that lets you
configure parameters for modem access.
When you have configured the external modem from the administration console, the
switch transmits characters that you have entered as output on the modem port. The
switch echoes characters that it receives as input on the modem port to the current
administration console session. The console appears to be directly connected to the
external modem.
User Manual Page 21

Web Management
The switch provides a browser interface that lets you configure and manage the switch
remotely.
applications directly in your web browser by entering the IP address of the switch. You can
then use your web browser to list and manage switch configuration parameters from one
SNMP-Based Network Management
You can use an external SNMP-based application to configure and manage the switch. This
management method requires the SNMP agent on the switch and the SNMP Network
Management Station to use the same community string. This management method, in fact,
uses two community strings: the get community string and the set community string. If
the SNMP Network management station only knows the set community string, it can read
and write to the MIBs. However, if it only knows the get community string, it can only read
MIBs. The default get and set community strings for the switch are public.
Protocols
The switch supports the following protocols:
VIRTUAL TERMINAL PROTOCOLS, SUCH AS TELNET
A virtual terminal protocol is a software program, such as Telnet, that allows
you to establish a management session from a Macintosh, a PC, or a UNIX
workstation. Because Telnet runs over TCP/IP, you must have at least one IP
address configured on the switch before you can establish access to it with a
virtual terminal protocol.
<Note> Terminal emulation is different from a virtual terminal protocol in that you must
connect a terminal directly to the console port.
SIMPLE NETWORK MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL (SNMP)
SNMP is the standard management protocol for multivendor IP networks.
SNMP supports transaction-based queries that allow the protocol to format
messages and to transmit information between reporting devices and
data-collection programs. SNMP runs on top of the User Datagram Protocol
(UDP), offering a connectionless-mode service.
User Manual Page 22

Management Architecture
All of the management application modules use the same Messaging Application
Programming Interface (MAPI). By unifying management methods with a single MAPI,
configuration parameters set using one method (e.g. console port) are immediately
displayed the other management methods (e.g. SNMP agent of web browser).
The management architecture of the switch adheres to the IEEE open standard. This
compliance assures customers that the switch is compatible with, and will interoperate
with other solutions that adhere to the same open standard.
User Manual Page 23

SNMP & RMON Management
Remote Monitoring (RMON) capabilities.
Overview
RMON is an abbreviation for the Remote Monitoring MIB (Management Information Base).
RMON is a system defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) document RFC
2819, which defines how networks can be monitored remotely.
RMONs typically consist of two components: an RMON probe and a management
workstation:
- The RMON probe is an intelligent device or software agent that continually
collects statistics about a LAN segment or VLAN. The RMON probe transfers
the collected data to a management workstation on request or when a
pre-defined threshold is reached.
- The management workstation collects the statistics that the RMON probe
gathers. The workstation can reside on the same network as the probe, or it
can have an in-band or out-of-band connection to the probe.
The switch provides RMON capabilities that allow network administrators to set
parameters and view statistical counters defined in MIB-II, Bridge MIB, and RMON MIB.
RMON activities are performed at a Network Management Station running an SNMP
network management application with graphical user interface.
SNMP Agent and MIB-2 (RFC 1213)
The SNMP Agent running on the switch manager CPU is responsible for:
- Retrieving MIB counters from various layers of software modules according
to the SNMP GET/GET NEXT frame messages.
- Setting MIB variables according to the SNMP SET frame message.
- Generating an SNMP TRAP frame message to the Network Management
Station if the threshold of a certain MIB counter is reached or if other trap
conditions (such as the following) are met:
User Manual Page 24

WARM START
COLD START
LINK UP
LINK DOWN
AUTHENTICATION FAILURE
RISING ALARM
FALLING ALARM
TOPOLOGY ALARM
MIB-II defines a set of manageable objects in various layers of the TCP/IP protocol suites.
MIB-II covers all manageable objects from layer 1 to layer 4, and, as a result, is the major
SNMP MIB supported by all vendors in the networking industry. The switch supports a
complete implementation of SNMP Agent and MIB-II.
RMON MIB (RFC 2819) and Bridge MIB (RFC 1493)
The switch provides hardware-based RMON counters in the switch chipset. The switch
manager CPU polls these counters periodically to collect the statistics in a format that
complies with the RMON MIB definition.
RMON Groups Supported
The switch supports the following RMON MIB groups defined in RFC 2819:
- RMON Statistics Group maintains utilization and error statistics for the
switch port being monitored.
- RMON History Group gathers and stores periodic statistical samples from
the previous Statistics Group.
- RMON Alarm Group allows a network administrator to define alarm
thresholds for any MIB variable. An alarm can be associated with Low
Threshold, High Threshold, or both. A trigger can trigger an alarm when the
value of a specific MIB variable exceeds a threshold, falls below a threshold,
or exceeds or falls below a threshold.
- RMON Event Group allows a network administrator to define actions
based on alarms. SNMP Traps are generated when RMON Alarms are
triggered. The action taken in the Network Management Station depends on
the specific network management application.
User Manual Page 25

Bridge Groups Supported
The switch supports the following four groups of Bridge MIB (RFC 1493):
- The dot1dBase Group a mandatory group that contains the objects
applicable to all types of bridges.
- The dot1dStp Group
respect to the Spanning Tree Protocol. If a node does not implement the
Spanning Tree Protocol, this group will not be implemented. This group is
applicable to any transparent only, source route, or SRT bridge that
implements the Spanning Tree Protocol.
- The dot1dTp Group
bridging status. This group is applicable to transparent operation only and
SRT bridges.
- The dot1dStatic Group
destination-address filtering status. This group is applicable to any type of
bridge which performs destination-address filtering.
Web-Based Browser Management
The switch provides a web-based browser interface for configuring and managing the
switch. This interface allows you to access the switch using a preferred web browser.
This chapter describes how to configure the switch using its web-based browser interface.
Logging on to the switch
SWITCH IP ADDRESS
In your web browser, specify the IP address of the switch. Default IP address is
192.168.1.10.
LOGIN
Enter the factory default login ID: root.
PASSWORD
Enter the factory default password (no password).
Or enter a user-defined password if you followed the instructions later and changed the
factory default password.
User Manual Page 27
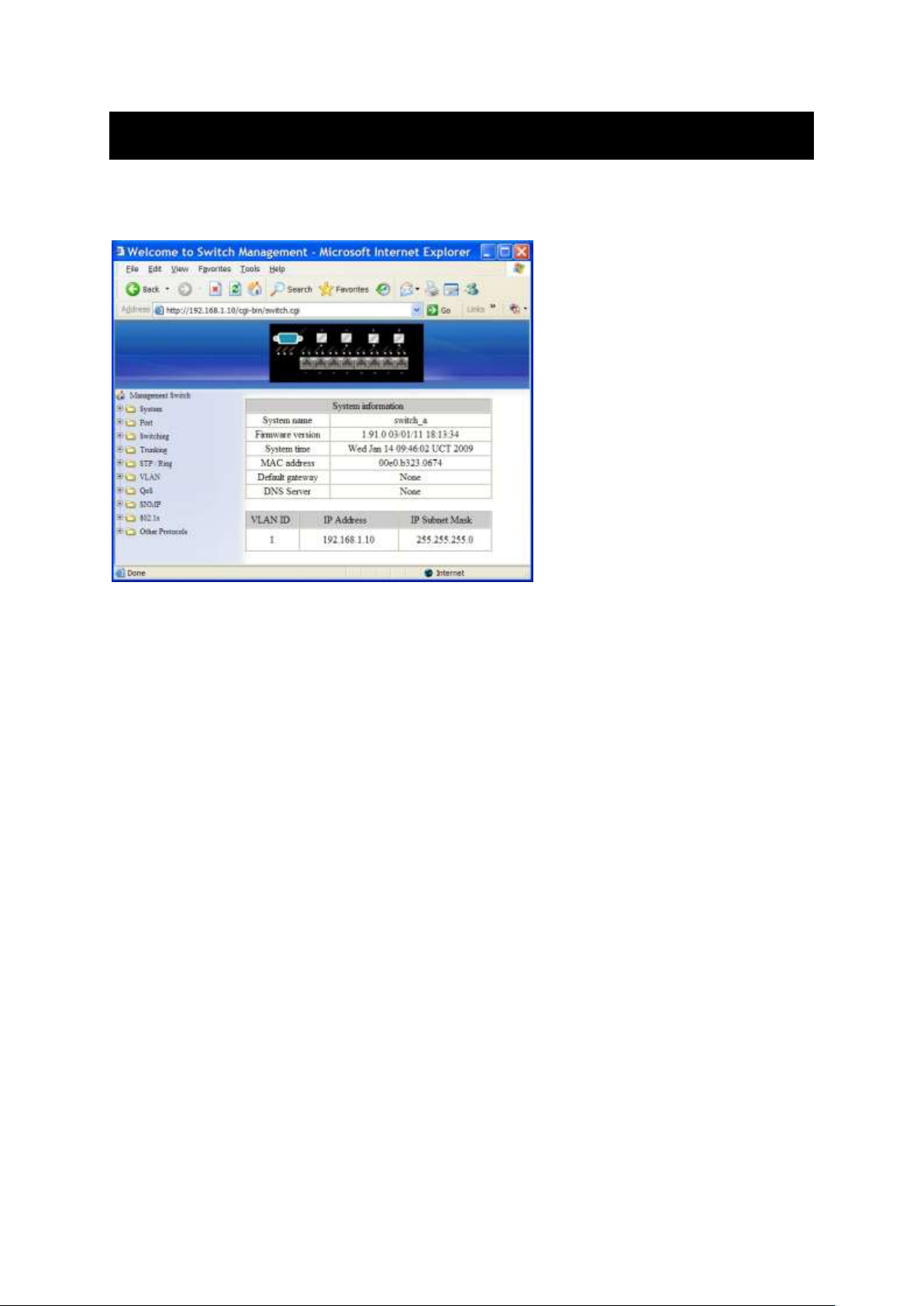
Understanding the Browser Interface
The web browser interface provides groups of point-and-click buttons at the left field of
the screen for configuring and managing the switch.
SYSTEM
System Information, System Name/Password, IP Address, ARP Table, Route
Table, Save Configuration, Firmware Upgrade, Alarm Setting, Reboot, Logout
PORT
Configuration, Port Status, Rate Control, RMON Statistics, Per Port Vlan
Activities
SWITCHING
Bridging, Static MAC Entry, Port Mirroring, PoE, PoE Scheduling
TRUNKING
Port Trunking
STP / RING
Global Configuration, RSTP Port Setting, MSTP Properties, MSTP Instance Setting, MSTP
Port Setting, Ring Setting
VLAN
VLAN Mode Setting, 802.1Q VLAN Setting, 802.1Q Port Setting, Port Based
VLAN
User Manual Page 28

QOS
Global Configuration, 802.1p Priority, DSCP
SNMP
SNMP General Setting, SNMP v1/v2c, SNMP v3
802.1X
Radius Configuration, Port Authentication
OTHER PROTOCOLS
GVRP, IGMP Snooping, NTP
User Manual Page 29
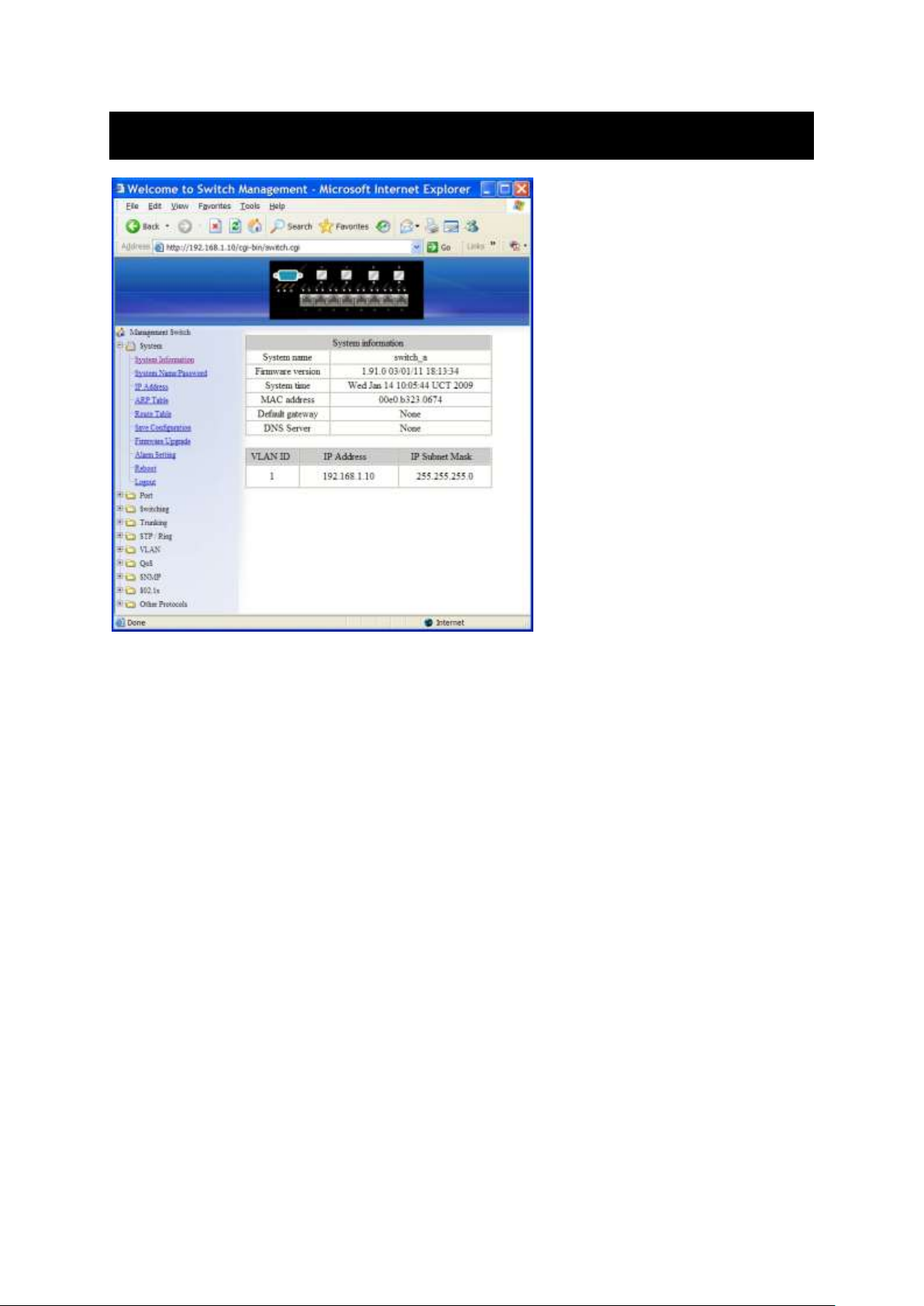
System
System Information
The System name, Firmware version, System time, MAC address, Default gateway, DNS
Server, VLAN ID, IP Address, and IP Subnet Mask of Switch.
User Manual Page 30
 Loading...
Loading...