Page 1

IES-1081
8 FE + 2 GE SFP Managed Switch -40 to 75C, DIN-rail
User Manual
v1.00 - 1206
Page 2

Preface
This manual describes how to install and use the Hardened Managed Ethernet Switch. This
switch introduced here is designed to deliver full scalability with SNMP/RMON web-based
management functions by providing:
To get the most out of this manual, you should have an understanding of Ethernet
networking concepts.
In this manual, you will find:
Features on the Hardened Managed Ethernet Switch
Illustrative LED functions
Installation instructions
Management Configuration
Specifications
IES-1081 User Manual Page 2
Page 3

Table of Contents
PREFACE .................................................................................................................................................. 2
QUICK START GUIDE ..................................................................................................................................... 5
PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................................ 5
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................................................................... 7
CONSOLE CONFIGURATION ....................................................................................................................................... 7
WEB CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................................................................. 9
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................................. 10
HARDENED MANAGED ETHERNET SWITCH ................................................................................................................. 10
PACKAGE CONTENTS .............................................................................................................................................. 10
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS ........................................................................................................................................... 11
FRONT PANEL DISPLAY ........................................................................................................................................... 13
PHYSICAL PORTS ................................................................................................................................................... 14
SWITCH MANAGEMENT ......................................................................................................................................... 15
INSTALLATION ....................................................................................................................................... 16
SELECTING A SITE FOR THE SWITCH ........................................................................................................................... 16
CONNECTING TO POWER ........................................................................................................................................ 17
CONNECTING TO YOUR NETWORK ............................................................................................................................ 19
SWITCH MANAGEMENT ....................................................................................................................... 20
MANAGEMENT ACCESS OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................... 20
ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE (CLI) ............................................................................................................................ 21
WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................................................. 22
SNMP-BASED NETWORK MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................................. 22
PROTOCOLS ......................................................................................................................................................... 22
MANAGEMENT ARCHITECTURE ................................................................................................................................ 23
SNMP & RMON MANAGEMENT ........................................................................................................... 24
OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................................................... 24
SNMP AGENT AND MIB-2 (RFC 1213) .................................................................................................................. 24
RMON MIB (RFC 2819) AND BRIDGE MIB (RFC 1493) ........................................................................................... 25
WEB-BASED BROWSER MANAGEMENT ........................................................................................... 27
LOGGING ON TO THE SWITCH ................................................................................................................................... 27
UNDERSTANDING THE BROWSER INTERFACE ............................................................................................................... 28
SYSTEM ............................................................................................................................................................... 30
PORT .................................................................................................................................................................. 37
SWITCHING .......................................................................................................................................................... 40
TRUNKING ........................................................................................................................................................... 43
STP / RING ......................................................................................................................................................... 44
VLAN ................................................................................................................................................................ 51
QOS ................................................................................................................................................................... 55
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................................... 57
802.1X .............................................................................................................................................................. 61
OTHER PROTOCOLS ............................................................................................................................................... 64
COMMAND LINE CONSOLE MANAGEMENT ..................................................................................... 68
ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE .................................................................................................................................... 68
SYSTEM ............................................................................................................................................................... 77
PORT .................................................................................................................................................................. 86
IES-1081 User Manual Page 3
Page 4

SWITCHING .......................................................................................................................................................... 91
TRUNKING ........................................................................................................................................................... 96
STP / RING ......................................................................................................................................................... 97
VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................. 110
QOS ................................................................................................................................................................. 116
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................................. 119
802.1X ............................................................................................................................................................ 126
OTHER PROTOCOLS ............................................................................................................................................. 131
SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................................................. 142
APPENDIX A .......................................................................................................................................... 143
APPENDIX B .......................................................................................................................................... 144
IES-1081 User Manual Page 4
Page 5
Quick Start Guide
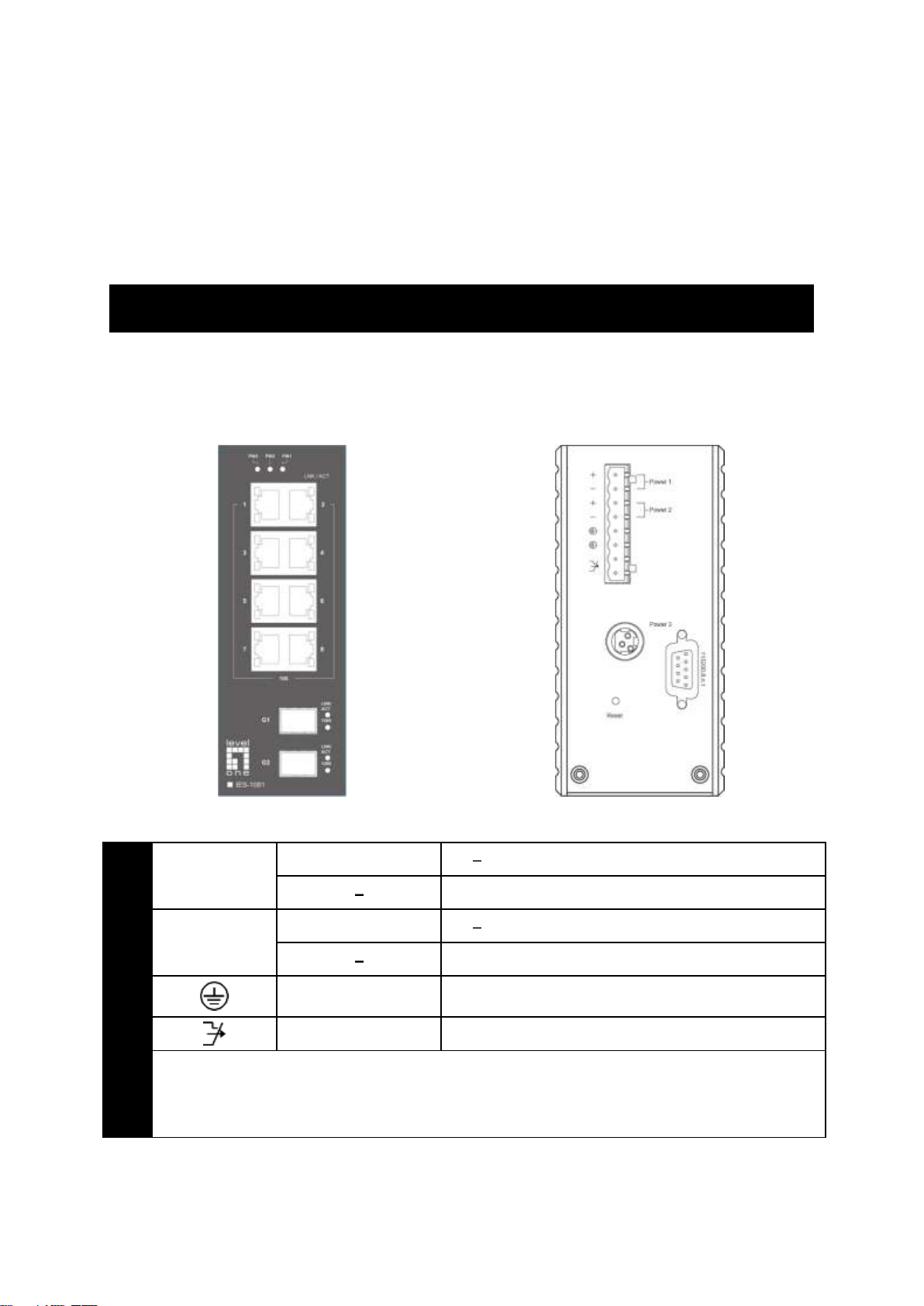
Front Panel
Rear Panel
Terminal Block
PW1
+
12 48VDC
Power Ground
PW2
+
12 48VDC
Power Ground
Earth Ground
Relay Output
1A @ 24VDC
Relay Alarm warning signal disable for following:
1. The relay contact closes if Power1 and Power2 are both failed but Power3 on
2. The relay contact closes if Power3 is failed but Power1 and Power2 are both on
This quick start guide describes how to install and use the Hardened Managed Ethernet
Switch. This is the switch of choice for harsh environments constrained by space.
Physical Description
The Port Status LEDs and Power Inputs
IES-1081 User Manual Page 5
Page 6
The relay output is normal open position when there is no power to the switch. Please do
LED
Status
Description
PW 1,2,3
Steady
Power On
Off
Power Off
10/100Base-TX & 100Base-FX
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
100
Steady
Connection at 100Mbps
10/100/1000Base-TX & 1000Base-FX & SFP
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
1000
Steady
Connection at 1000Mbps
not connect any power source to this terminal to prevent shorting your power supply.
There are three power inputs can be used. Redundant power function is supported
PW3 is DC Jack type with 12VDC input
IES-1081 User Manual Page 6
Page 7

Functional Description
Complies with EN50121-4 environmental requirements for railway applications.
Meets NEMA TS1/TS2 Environmental requirements such as temperature, shock, and
vibration for traffic control equipment.
Meets EN61000-6-2 & EN61000-6-4 EMC Generic Standard Immunity for industrial
environment.
Manageable via SNMP, Web-based, Telnet, and RS-232 console port.
Supports IEEE802.3/802.3u/802.3ab/802.3z/802.3x. Auto-negotiation:
1000Mbps-full-duplex; 10/100Mbps-full/half-duplex; Auto MDI/MDIX.
100Base-FX: Multi mode SC or ST type, Single mode SC or ST type. 100Base-BX: WDM
Single mode SC type.
1000Base-SX/LX: Multi mode SC type, Single mode SC type. 1000Base-BX: WDM Single
mode SC type.
Supports 8192 MAC addresses. Provides 2M bits memory buffer.
Store-and-forward mechanism.
Full wire-speed forwarding rate.
Alarms for power and port link failure by relay output.
Power Supply: Redundant DC Terminal Block power inputs and 12VDC DC JACK with
100-240VAC external power supply.
Operating voltage and Max. current consumption: 0.92A @ 12VDC, 0.46A @ 24VDC,
0.23A @ 48VDC. Power consumption: 11W Max.
-40℃ to 75℃ (-40℉ to 167℉) operating temperature range. Tested for functional
operation @ -40℃ to 85℃ (-40℉ to 185℉).
Supports DIN-Rail and Panel Mounting installation.
Console Configuration
Connect to the switch console:
Connect the DB9 straight cable to the RS-232 serial port of the device and the RS-232
serial port of the terminal or computer running the terminal emulation application.
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a
terminal or a PC equipped with a terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal)
to the switch console port.
Configuration settings of the terminal-emulation program:
- Baud rate: 115,200bps
- Data bits: 8
- Parity: none
- Stop bit: 1
- Flow control: none
Press the Enter key. The Command Line Interface (CLI) screen should appear as below:
Logon to Exec Mode (View Mode):
Mode (or View Mode). > reen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 7
Page 8
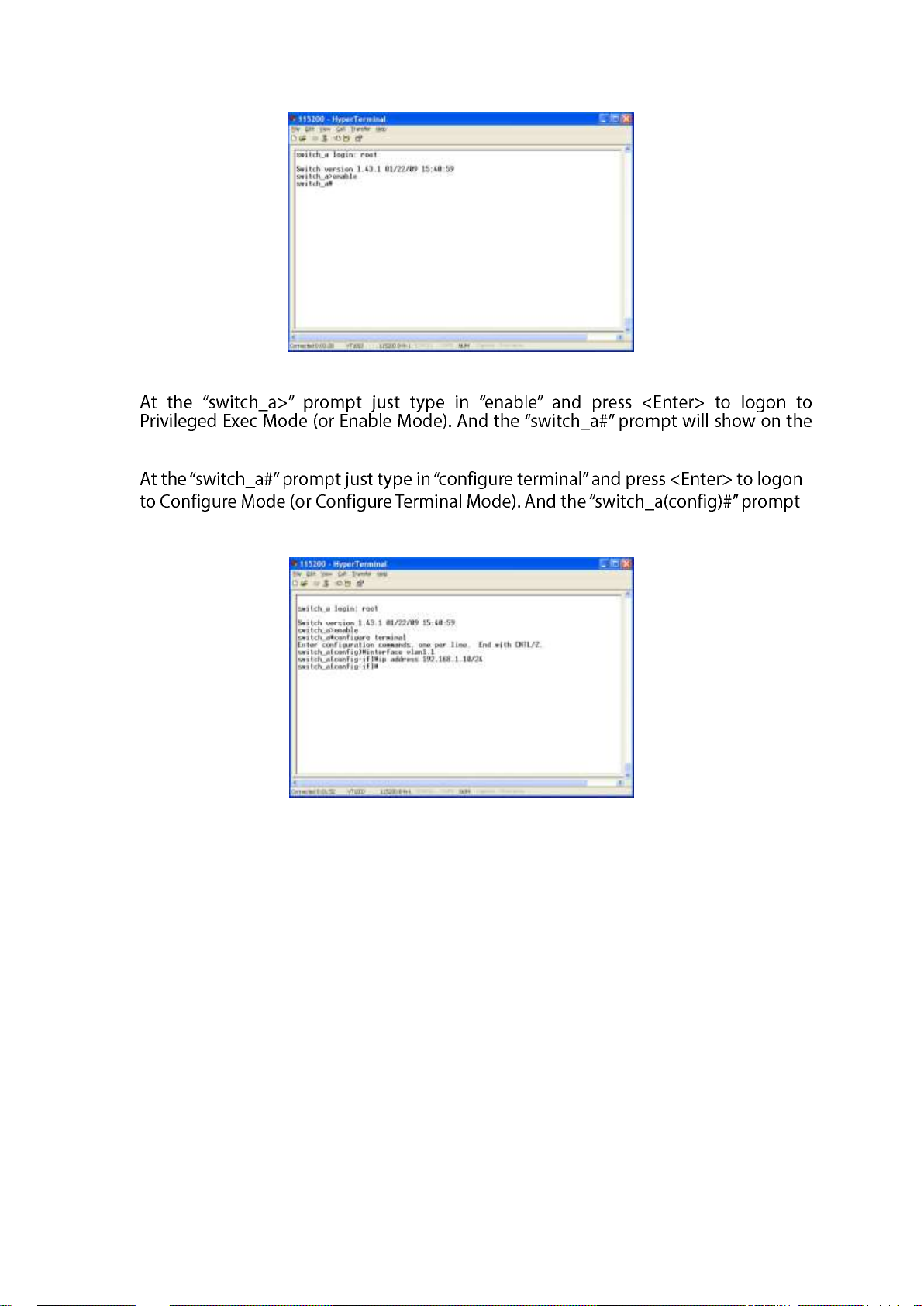
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode):
screen.
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode):
will show on the screen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 8
Page 9
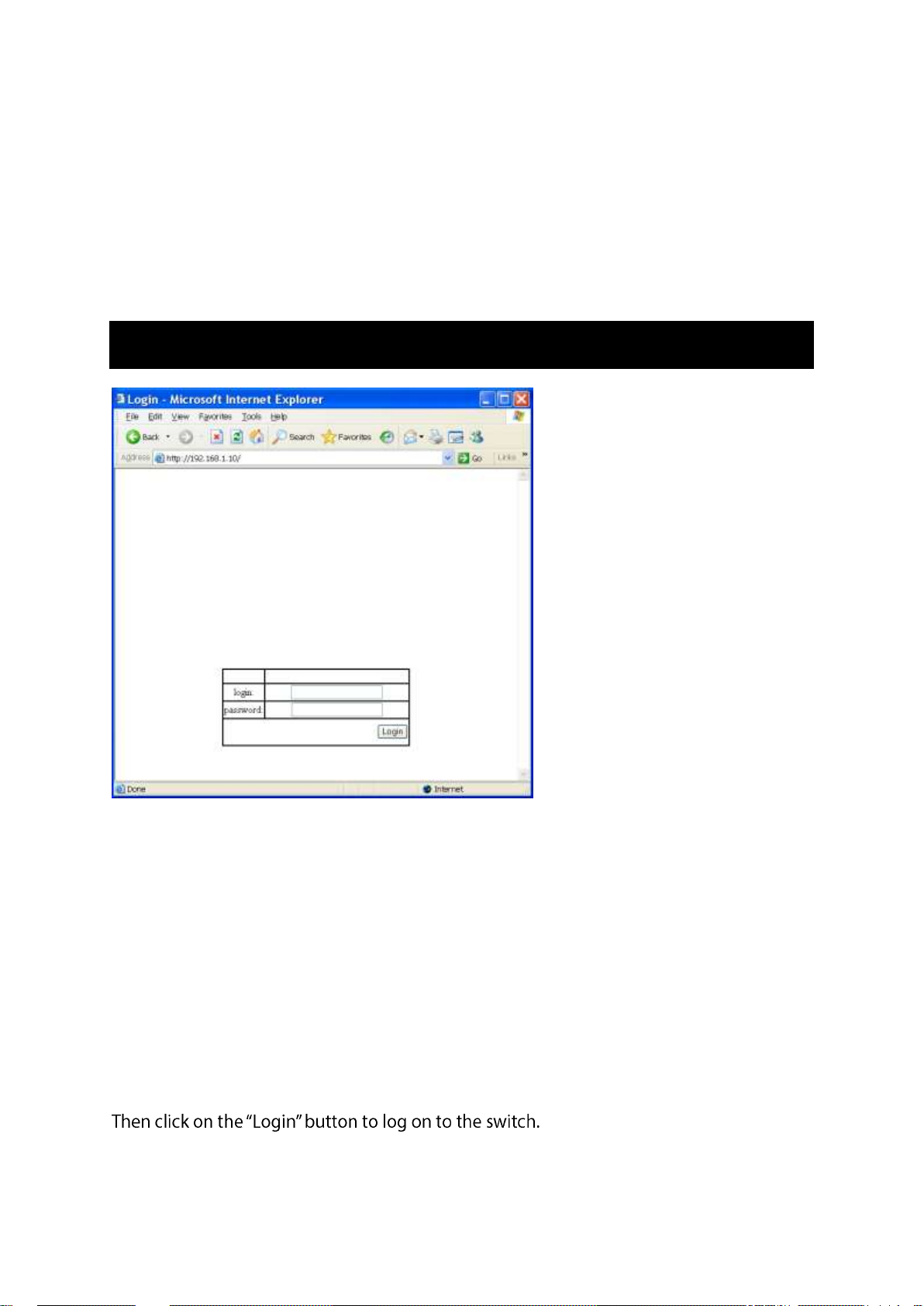
Web Configuration
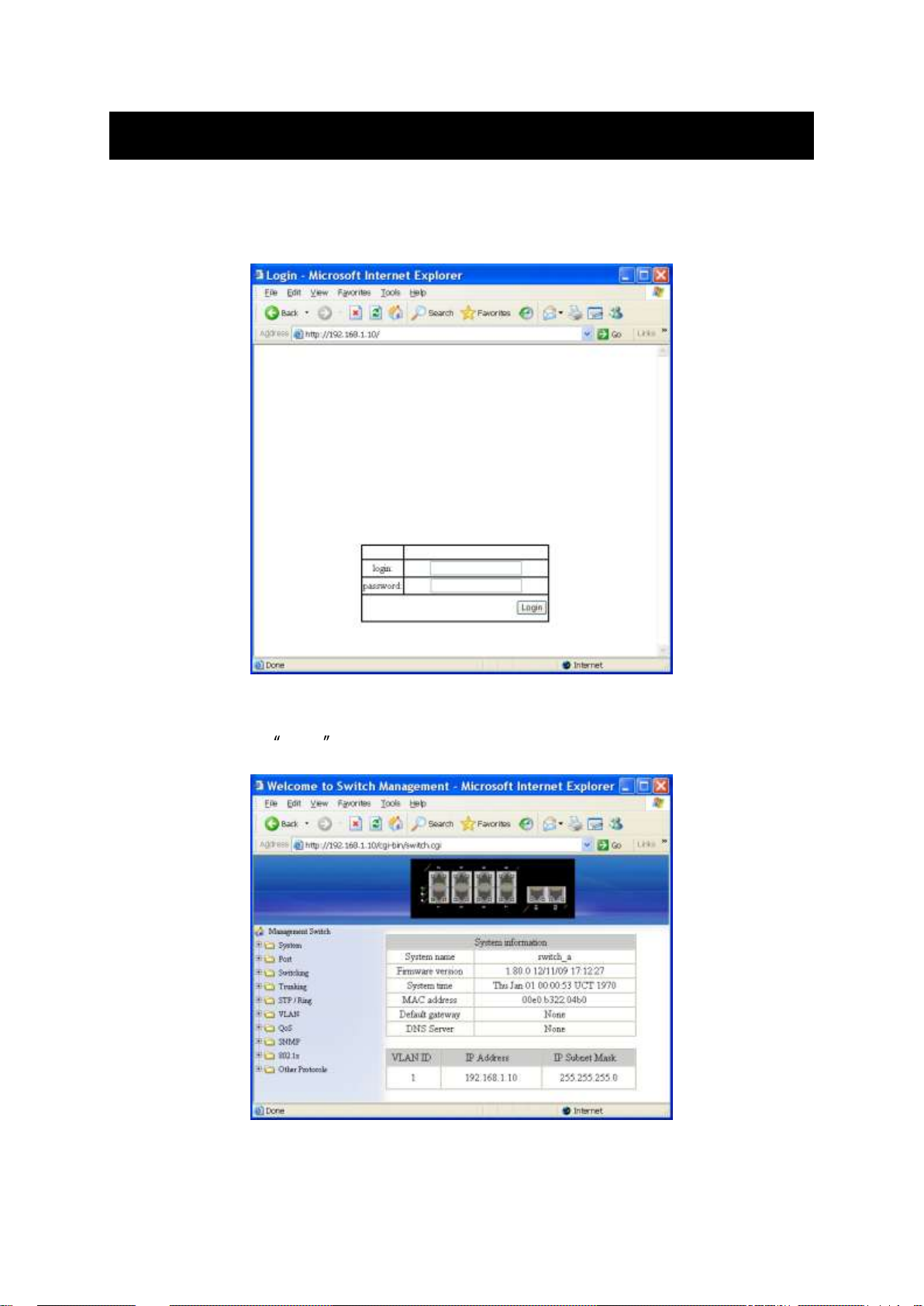
Login the switch:
Specify the default IP address (192.168.1.10) of the switch in the web browser. A login
window will be shown as below:
Enter the factory default login ID: root.
Enter the factory default password (no password).
Then click on the Login button to log on to the switch.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 9
Page 10
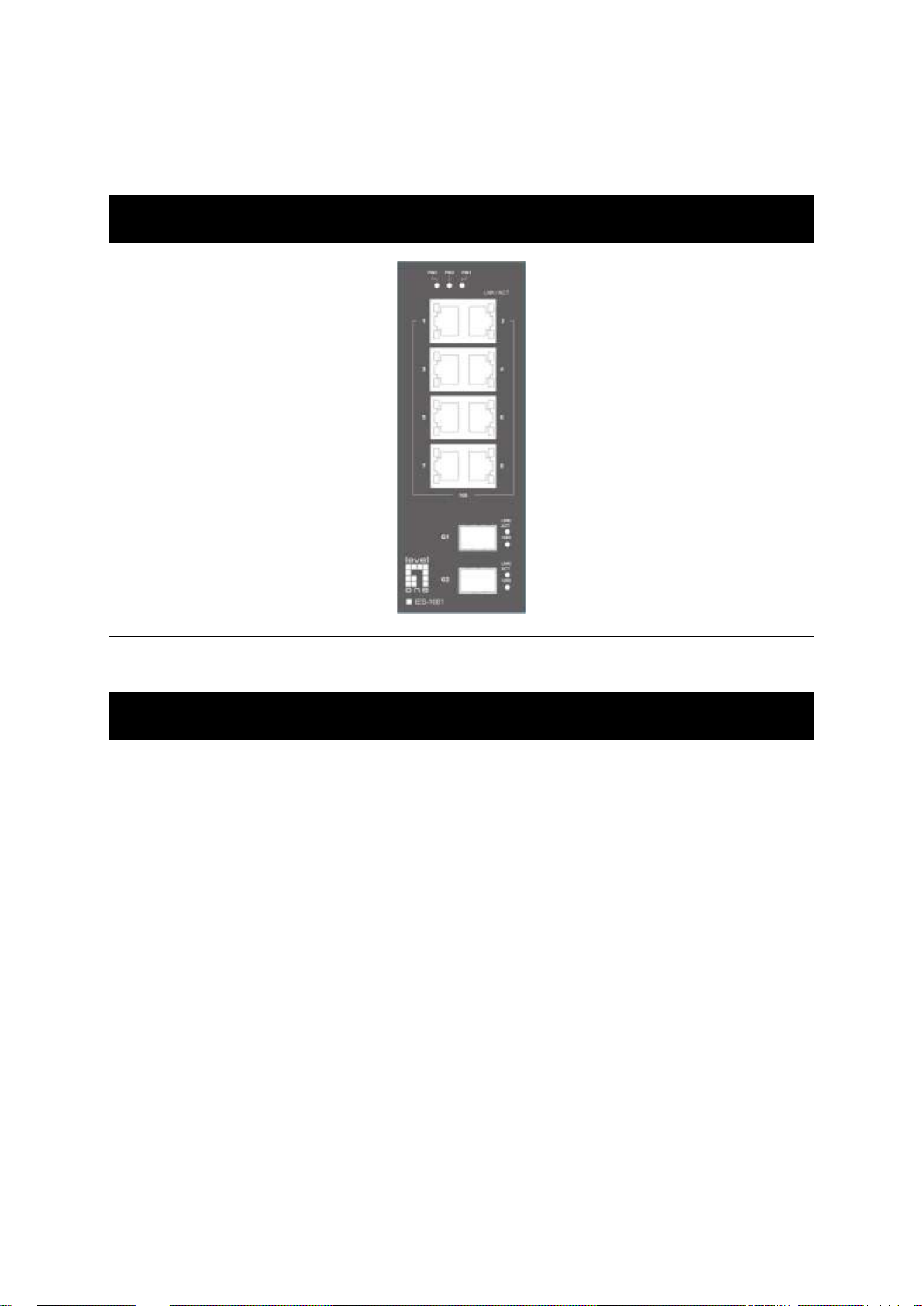
Overview
Hardened Managed Ethernet Switch
Front View
Package Contents
When you unpack the product package, you shall find the items listed below. Please
inspect the contents, and report any apparent damage or missing items immediately to
your authorized reseller.
IES-1081
Quick Installation Guide
CD User Manual
RS232 cable
IES-1081 User Manual Page 10
Page 11

Product Highlights
Basic Features
Complies with EN50121-4 environmental requirements for railway applications.
Meets NEMA TS1/TS2 Environmental requirements such as temperature, shock, and
vibration for traffic control equipment.
Meets EN61000-6-2 & EN61000-6-4 EMC Generic Standard Immunity for industrial
environment.
Manageable via SNMP, Web-based, Telnet, and RS-232 console port.
Supports IEEE802.3/802.3u/802.3ab/802.3z/802.3x. Auto-negotiation:
1000Mbps-full-duplex; 10/100Mbps-full/half-duplex; Auto MDI/MDIX.
100Base-FX: Multi mode SC or ST type, Single mode SC or ST type. 100Base-BX: WDM
Single mode SC type.
1000Base-SX/LX: Multi mode SC type, Single mode SC type. 1000Base-BX: WDM Single
mode SC type.
Supports 8192 MAC addresses. Provides 2M bits memory buffer.
Store-and-forward mechanism.
Full wire-speed forwarding rate.
Alarms for power and port link failure by relay output.
Power Supply: Redundant DC Terminal Block power inputs and 12VDC DC JACK with
100-240VAC external power supply.
Operating voltage and Max. current consumption: 0.92A @ 12VDC, 0.46A @ 24VDC,
0.23A @ 48VDC. Power consumption: 11W Max.
-40℃ to 75℃ (-40℉ to 167℉) operating temperature range. Tested for functional
operation @ -40℃ to 85℃ (-40℉ to 185℉).
Supports DIN-Rail and Panel Mounting installation.
Management Support
VLAN
Port-based VLAN
IEEE802.1Q tagged VLAN
TRUNKING
MAC-based Trunking with automatic link fail-over
PORT-SECURITY
Per-port programmable MAC address locking
Up to 24 Static Secure MAC addresses per port
IEEE802.1x Port-based Network Access Control
IES-1081 User Manual Page 11
Page 12

PORT-MIRRORING
Port-mirroring
QOS (IEEE802.1p Quality of Service)
4 priority queues
INTERNETWORKING PROTOCOLS
Bridging:
IEEE802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree
IEEE802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree compatible
IEEE802.1Q GVRP
Ring
IP Multicast:
IGMP Snooping
Rate Control
NTP
NETWORK MANAGEMENT METHODS
Console port access via RS-232 cable (CLI, Command Line Interface)
Telnet remote access
SNMP agent:
MIB-2 (RFC1213)
Bridge MIB (RFC1493)
RMON MIB (RFC2819) statistics, history, alarm and events
VLAN MIB (IEEE802.1Q/RFC2674)
Private MIB
Web browser
TFTP software-upgrade capability
IES-1081 User Manual Page 12
Page 13
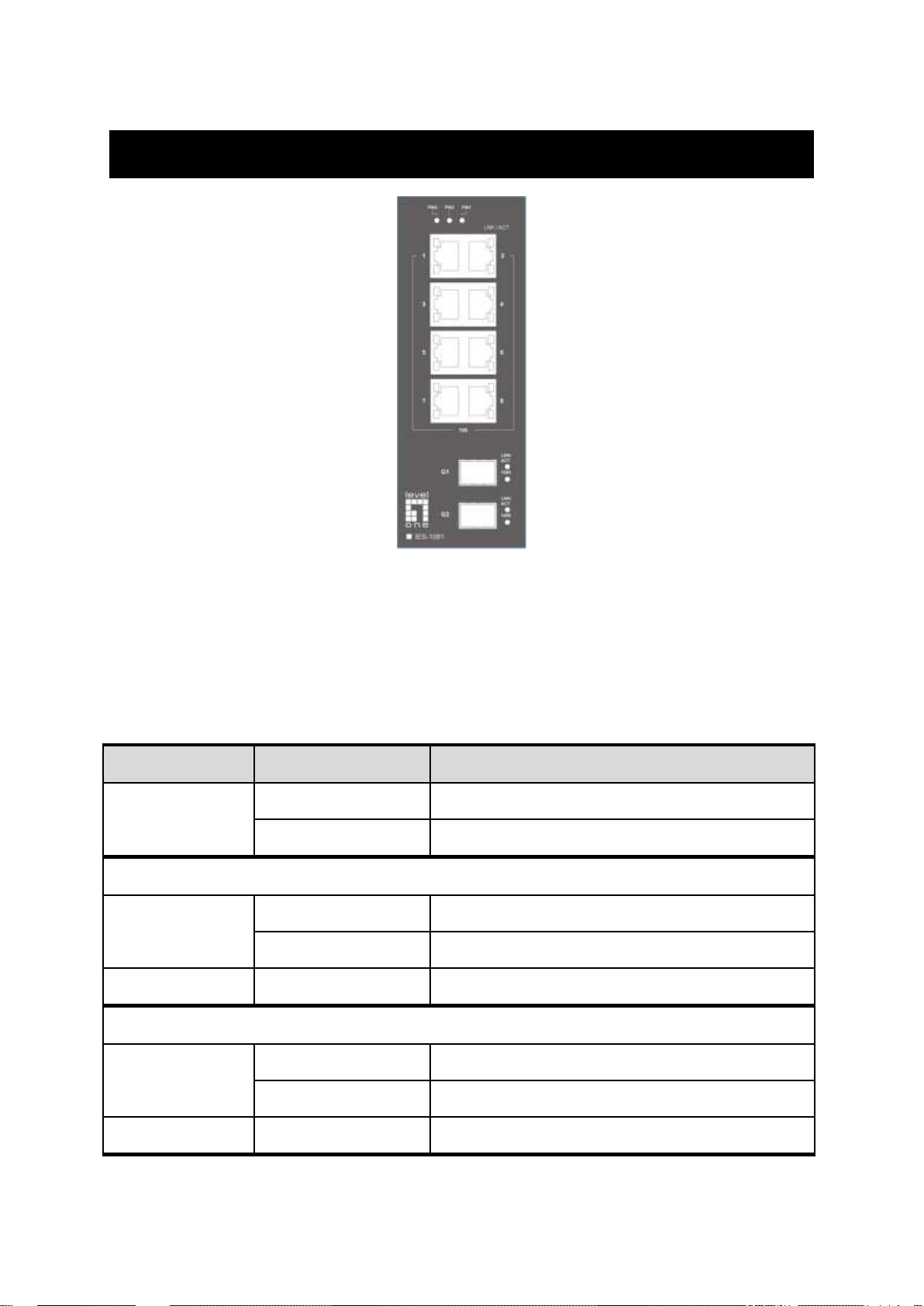
Front Panel Display
LED
Status
Description
PW 1,2,3
Steady
Power On
Off
Power Off
10/100Base-TX & 100Base-FX
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
100
Steady
Connection at 100Mbps
10/100/1000Base-TX & 1000Base-FX & SFP
LNK/ACT
Steady
Network connection established
Flashing
Transmitting or Receiving data
1000
Steady
Connection at 1000Mbps
POWER
This LED comes on when the switch is properly connected to power and
turned on.
Port Status LEDs
The LEDs are located on the front panel, displaying status for each respective
port. Please refer to the following table for more details.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 13
Page 14
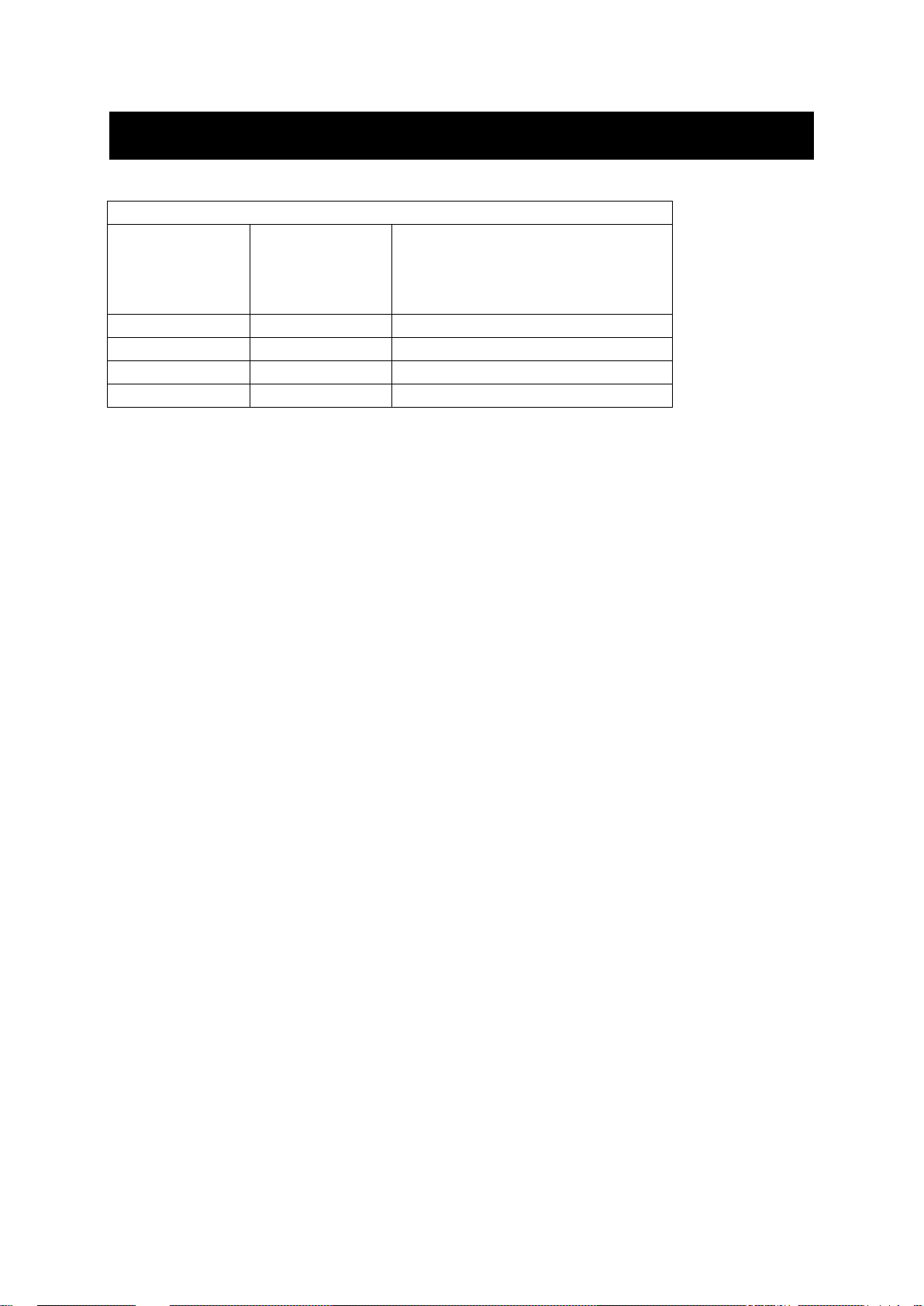
Physical Ports
Number of ports
10/100Base-TX
100Base-FX/BX
100Base SFP
Gigabit:
10/100/1000Base-TX
1000Base-SX/LX/BX
1000Base SFP
8 0 0, 1, 2
6 2 0, 1, 2
4 2 0, 1, 2
4 4 0
The Hardened Managed Ethernet Switch provides:
CONNECTIVITY
RJ-45 connectors on TX ports
ST or SC connector on 100Base-FX fiber port
SC connector on 100Base-BX fiber port
Duplex LC connector on SFP 100Base-FX/BX fiber transceiver
SC connector on 1000Base-SX/LX/BX fiber port
Duplex LC connector on SFP 1000Base-SX/LX/BX fiber transceiver
MODE SELECTION
10Base-T full-duplex mode
10Base-T half-duplex mode
100Base-TX full-duplex mode
100Base-TX half-duplex mode
100Base-FX full-duplex mode
1000Base-T/SX/LX full-duplex mode
Auto-negotiating mode
IES-1081 User Manual Page 14
Page 15

Switch Management
Web-based browser interface
The switch also boasts a point-and-click browser-based interface that lets user access full
switch configuration and functionality from a Netscape or Internet Explorer browser.
Administration console via RS-232 serial port (CLI)
The switch provides an onboard serial port, which allows the switch to be configured via a
directly connected terminal.
External SNMP-based network management
application
The switch can also be configured via SNMP.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 15
Page 16

Installation
This chapter gives step-by-step instructions about how to install the switch:
Selecting a Site for the Switch
As with any electric device, you should place the switch where it will not be subjected to
extreme temperatures, humidity, or electromagnetic interference. Specifically, the site you
select should meet the following requirements:
-The ambient temperature should be between -40°C to 75℃ (-40℉ to 167℉).
-The relative humidity should be less than 95 percent, non-condensing.
-Surrounding electrical devices should not exceed the electromagnetic field (RFC)
standards.
-Make sure that the switch receives adequate ventilation. Do not block the ventilation
holes on each side of the switch.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 16
Page 17
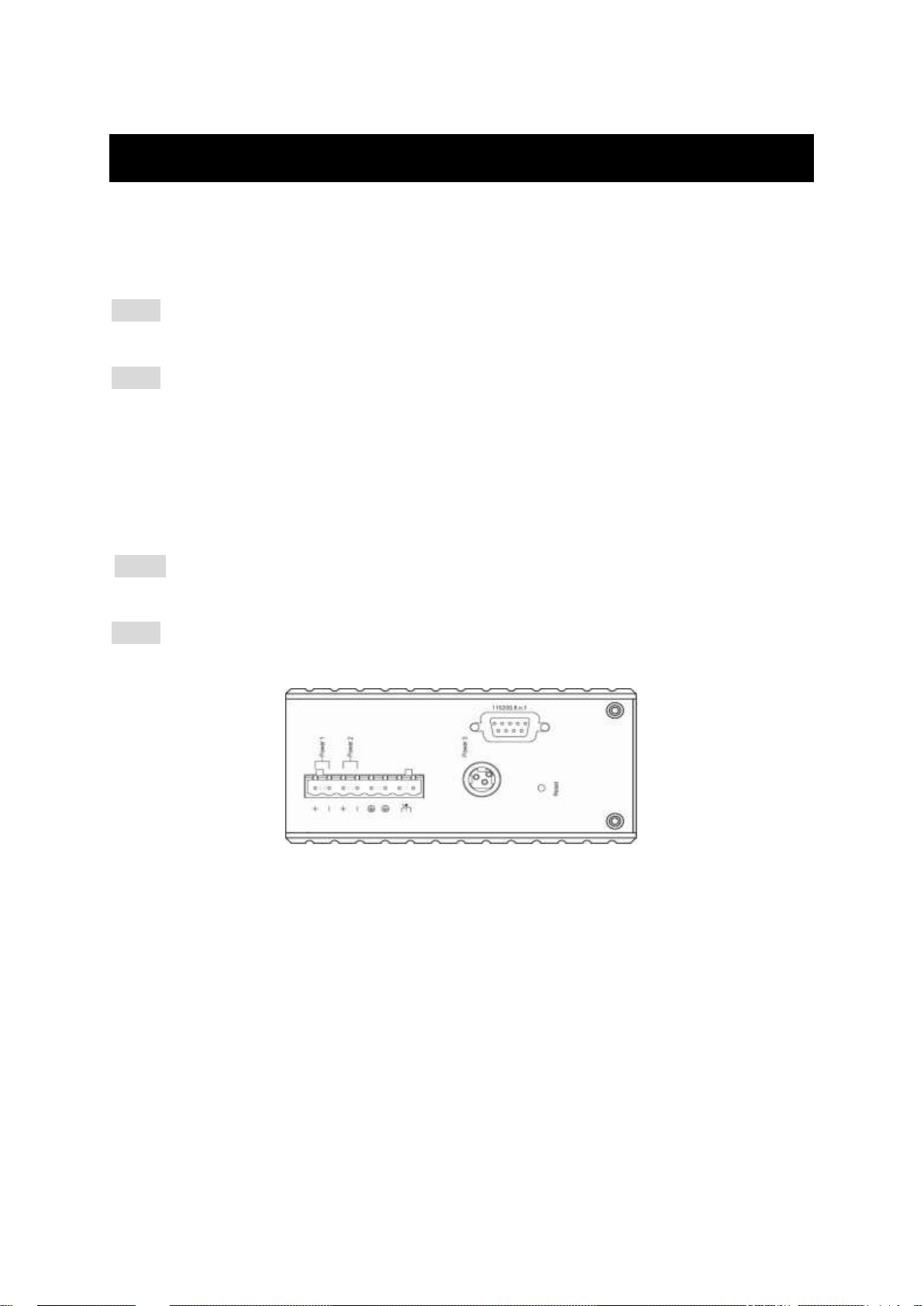
Connecting to Power
Redundant DC Terminal Block Power Inputs or 12VDC DC Jack:
12VDC DC Jack
Step 1: Connect the supplied AC to DC power adapter to the receptacle on the topside of
the switch.
Step 2: Connect the power cord to the AC to DC power adapter and attach the plug into a
standard AC outlet with the appropriate AC voltage.
Redundant DC Terminal Block Power Inputs
There are two pairs of power inputs for use with redundant power sources. You only need
to have one power input connected to run the switch.
Step 1: Connect the DC power cord to the plug-able terminal block on the switch, and
then plug it into a standard DC outlet.
Step 2: Disconnect the power cord if you want to shut down the switch.
Top View
IES-1081 User Manual Page 17
Page 18
Alarms for Power Failure
Terminal Block
PW1
+
12 48VDC
Power Ground
PW2
+
12 48VDC
Power Ground
Earth Ground
Relay Output
1A @ 24VDC
Relay Alarm warning signal disable for following:
3. The relay contact closes if Power1 and Power2 are both failed but Power3 on
4. The relay contact closes if Power3 is failed but Power1 and Power2 are both on
DC Jack
PW3
DC Jack
12VDC
Step 1: There are two pins on the terminal block used for power failure detection. It
provides the normally closed output when the power source is active. Use this as a
dry contact application to send a signal for power failure detection.
Special note:
The relay output is normal open position when there is no power to the switch.
Please do not connect any power source to this terminal to prevent shorting your
power supply.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 18
Page 19
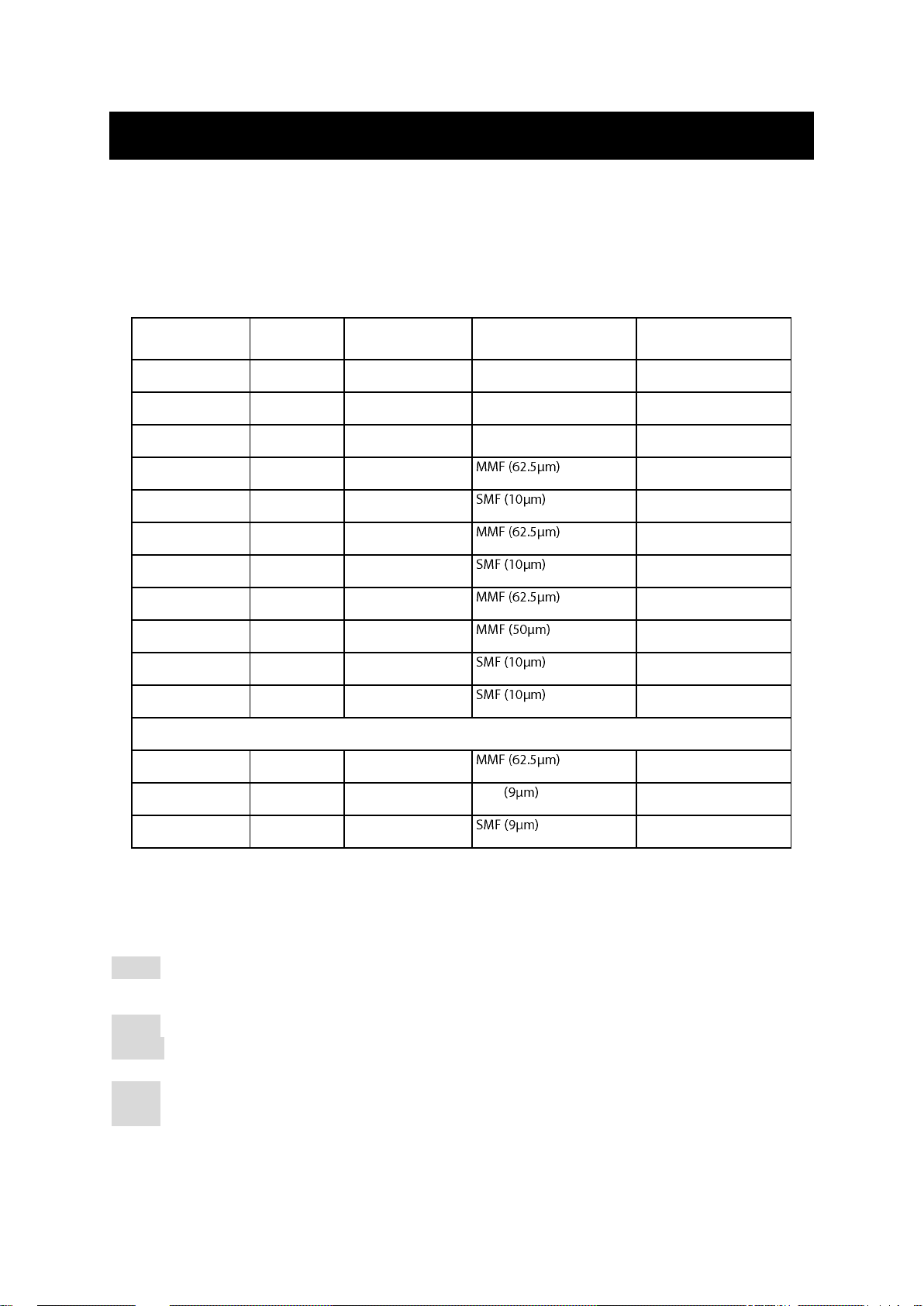
Connecting to Your Network
Speed
Connector
Port Speed
Half/Full Duplex
Cable
Max. Distance
10Base-T
RJ-45
10/20 Mbps
2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 3, 4, 5
100 m
100Base-TX
RJ-45
100/200 Mbps
2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5
100 m
1000Base-T
RJ-45
2000 Mbps
4-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5
100 m
100Base-FX
ST, SC
200 Mbps
2 km
100Base-FX
ST, SC
200 Mbps
20, 40, 75, 100 km
100Base-BX
SC
200 Mbps
2, 5 km
100Base-BX
SC
200 Mbps
20, 40 km
1000Base-SX
SC
2000 Mbps
220 m, 2 km
1000Base-SX
SC
2000 Mbps
550 m
1000Base-LX
SC
2000 Mbps
10, 20, 50 km
1000Base-BX
SC
2000 Mbps
20, 40 km
SFP
1000Base-SX
Duplex LC
2000 Mbps
550 m, 2 km
1000Base-LX
Duplex LC
2000 Mbps
SMF
10, 40, 60 km
1000Base-BX
Duplex LC
2000 Mbps
70 km
Cable Type & Length
It is necessary to follow the cable specifications below when connecting the switch to your
network. Use appropriate cables that meet your speed and cabling requirements.
Cable Specifications
Cabling
Step 1: First, ensure the power of the switch and end devices are turned off.
<Note> Always ensure that the power is off before any installation.
Step 2: Prepare cable with corresponding connectors for each type of port in use.
Step 3: Consult Cable Specifications Table on previous page for cabling requirements
Step 4: Connect one end of the cable to the switch and the other end to a desired device.
Step 5: Once the connections between two end devices are made successfully, turn on the
IES-1081 User Manual Page 19
based on connectors and speed.
power and the switch is operational.
Page 20
Switch Management
This chapter explains the methods that you can use to configure management access to
the switch. It describes the types of management applications and the communication
and management protocols that deliver data between your management device
(workstation or personal computer) and the system. It also contains information about
port connection options.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Management Access Overview
Key Concepts
Key Guidelines for Implementation
Web Management Access
Administration Console Access
SNMP Access
Standards, Protocols, and Related Reading
Management Access Overview
The switch gives you the flexibility to access and manage the switch using any or all of the
following methods.
The web browser interface and administration console (CLI) support are embedded in the
switch software and are available for immediate use.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 20
Page 21

Administration Console (CLI)
The administration console is an internal, character-oriented, Command Line Interface (CLI)
for performing system administration such as displaying statistics or changing option
settings.
Using this method, you can view the administration console from a terminal, personal
computer, Apple Macintosh, or workstation
There are two ways to use this management method: direct access or modem access. The
following sections describe these methods.
Direct Access
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a terminal
or a PC equipped with a terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal) to the
switch console port.
When using the management method, configure the terminal-emulation program to use
the following parameters (you can change these settings after login):
[DEFAULT PARAMETERS]
115,200bps
8 data bits
No parity
1 stop bit
This management method is often preferred because you can remain connected and
monitor the system during system reboots. Also, certain error messages are sent to the
serial port, regardless of the interface through which the associated action was initiated. A
Macintosh or PC attachment can use any terminal-emulation program for connecting to
the terminal serial port. A workstation attachment under UNIX can use an emulator such
as TIP.
Modem Access
external modem attached to the console port. The switch management program provides
Console Port screen, accessible from the Basic Management screen that lets you
configure parameters for modem access.
When you have configured the external modem from the administration console, the
switch transmits characters that you have entered as output on the modem port. The
switch echoes characters that it receives as input on the modem port to the current
administration console session. The console appears to be directly connected to the
external modem.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 21
Page 22

Web Management
The switch provides a browser interface that lets you configure and manage the switch
remotely.
applications directly in your web browser by entering the IP address of the switch. You can
then use your web browser to list and manage switch configuration parameters from one
SNMP-Based Network Management
You can use an external SNMP-based application to configure and manage the switch. This
management method requires the SNMP agent on the switch and the SNMP Network
Management Station to use the same community string. This management method, in fact,
uses two community strings: the get community string and the set community string. If
the SNMP Network management station only knows the set community string, it can read
and write to the MIBs. However, if it only knows the get community string, it can only read
MIBs. The default get and set community strings for the switch are public.
Protocols
The switch supports the following protocols:
VIRTUAL TERMINAL PROTOCOLS, SUCH AS TELNET
A virtual terminal protocol is a software program, such as Telnet, that allows
you to establish a management session from a Macintosh, a PC, or a UNIX
workstation. Because Telnet runs over TCP/IP, you must have at least one IP
address configured on the switch before you can establish access to it with a
virtual terminal protocol.
<Note> Terminal emulation is different from a virtual terminal protocol in that you must
connect a terminal directly to the console port.
SIMPLE NETWORK MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL (SNMP)
SNMP is the standard management protocol for multivendor IP networks.
SNMP supports transaction-based queries that allow the protocol to format
messages and to transmit information between reporting devices and
data-collection programs. SNMP runs on top of the User Datagram Protocol
(UDP), offering a connectionless-mode service.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 22
Page 23

Management Architecture
All of the management application modules use the same Messaging Application
Programming Interface (MAPI). By unifying management methods with a single MAPI,
configuration parameters set using one method (e.g. console port) are immediately
displayed the other management methods (e.g. SNMP agent of web browser).
The management architecture of the switch adheres to the IEEE open standard. This
compliance assures customers that the switch is compatible with, and will interoperate
with other solutions that adhere to the same open standard.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 23
Page 24

SNMP & RMON Management
Thi
Remote Monitoring (RMON) capabilities.
Overview
RMON is an abbreviation for the Remote Monitoring MIB (Management Information Base).
RMON is a system defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) document RFC
2819, which defines how networks can be monitored remotely.
RMONs typically consist of two components: an RMON probe and a management
workstation:
- The RMON probe is an intelligent device or software agent that continually
collects statistics about a LAN segment or VLAN. The RMON probe transfers
the collected data to a management workstation on request or when a
pre-defined threshold is reached.
- The management workstation collects the statistics that the RMON probe
gathers. The workstation can reside on the same network as the probe, or it
can have an in-band or out-of-band connection to the probe.
The switch provides RMON capabilities that allow network administrators to set
parameters and view statistical counters defined in MIB-II, Bridge MIB, and RMON MIB.
RMON activities are performed at a Network Management Station running an SNMP
network management application with graphical user interface.
SNMP Agent and MIB-2 (RFC 1213)
The SNMP Agent running on the switch manager CPU is responsible for:
- Retrieving MIB counters from various layers of software modules according
to the SNMP GET/GET NEXT frame messages.
- Setting MIB variables according to the SNMP SET frame message.
- Generating an SNMP TRAP frame message to the Network Management
Station if the threshold of a certain MIB counter is reached or if other trap
conditions (such as the following) are met:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 24
Page 25
WARM START
COLD START
LINK UP
LINK DOWN
AUTHENTICATION FAILURE
RISING ALARM
FALLING ALARM
TOPOLOGY ALARM
MIB-II defines a set of manageable objects in various layers of the TCP/IP protocol suites.
MIB-II covers all manageable objects from layer 1 to layer 4, and, as a result, is the major
SNMP MIB supported by all vendors in the networking industry. The switch supports a
complete implementation of SNMP Agent and MIB-II.
RMON MIB (RFC 2819) and Bridge MIB (RFC 1493)
The switch provides hardware-based RMON counters in the switch chipset. The switch
manager CPU polls these counters periodically to collect the statistics in a format that
complies with the RMON MIB definition.
RMON Groups Supported
The switch supports the following RMON MIB groups defined in RFC 2819:
- RMON Statistics Group maintains utilization and error statistics for the
switch port being monitored.
- RMON History Group gathers and stores periodic statistical samples from
the previous Statistics Group.
- RMON Alarm Group allows a network administrator to define alarm
thresholds for any MIB variable. An alarm can be associated with Low
Threshold, High Threshold, or both. A trigger can trigger an alarm when the
value of a specific MIB variable exceeds a threshold, falls below a threshold,
or exceeds or falls below a threshold.
- RMON Event Group allows a network administrator to define actions
based on alarms. SNMP Traps are generated when RMON Alarms are
triggered. The action taken in the Network Management Station depends on
the specific network management application.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 25
Page 26

Bridge Groups Supported
The switch supports the following four groups of Bridge MIB (RFC 1493):
- The dot1dBase Group a mandatory group that contains the objects
applicable to all types of bridges.
- The dot1dStp Group contains objects
respect to the Spanning Tree Protocol. If a node does not implement the
Spanning Tree Protocol, this group will not be implemented. This group is
applicable to any transparent only, source route, or SRT bridge that
implements the Spanning Tree Protocol.
- The dot1dTp Group
bridging status. This group is applicable to transparent operation only and
SRT bridges.
- The dot1dStatic Group contains objects that describe
destination-address filtering status. This group is applicable to any type of
bridge which performs destination-address filtering.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 26
Page 27
Web-Based Browser Management
The switch provides a web-based browser interface for configuring and managing the
switch. This interface allows you to access the switch using a preferred web browser.
This chapter describes how to configure the switch using its web-based browser interface.
Logging on to the switch
SWITCH IP ADDRESS
In your web browser, specify the IP address of the switch. Default IP address is
192.168.1.10.
LOGIN
Enter the factory default login ID: root.
PASSWORD
Enter the factory default password (no password).
Or enter a user-defined password if you followed the instructions later and changed the
factory default password.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 27
Page 28
Understanding the Browser Interface
The web browser interface provides groups of point-and-click buttons at the left field of the screen for
configuring and managing the switch.
SYSTEM
System Information, System Name/Password, IP Address, Save Configuration,
Firmware Upgrade, Alarm Setting, Reboot, Logout
PORT
Configuration, Port Status, Rate Control, RMON Statistics, Per Port Vlan
Activities
SWITCHING
Bridging, Static MAC Entry, Port Mirroring
TRUNKING
Port Trunking
STP / RING
Global Configuration, RSTP Port Setting, MSTP Properties, MSTP Instance Setting, MSTP
Port Setting, Ring Setting
VLAN
VLAN Mode Setting, 802.1Q VLAN Setting, 802.1Q Port Setting, Port Based
VLAN
IES-1081 User Manual Page 28
Page 29

QOS
Global Configuration, 802.1p Priority, DSCP
SNMP
SNMP General Setting, SNMP v1/v2c, SNMP v3
802.1X
Radius Configuration, Port-Based Authentication
OTHER PROTOCOLS
GVRP, IGMP Snooping, NTP
IES-1081 User Manual Page 29
Page 30
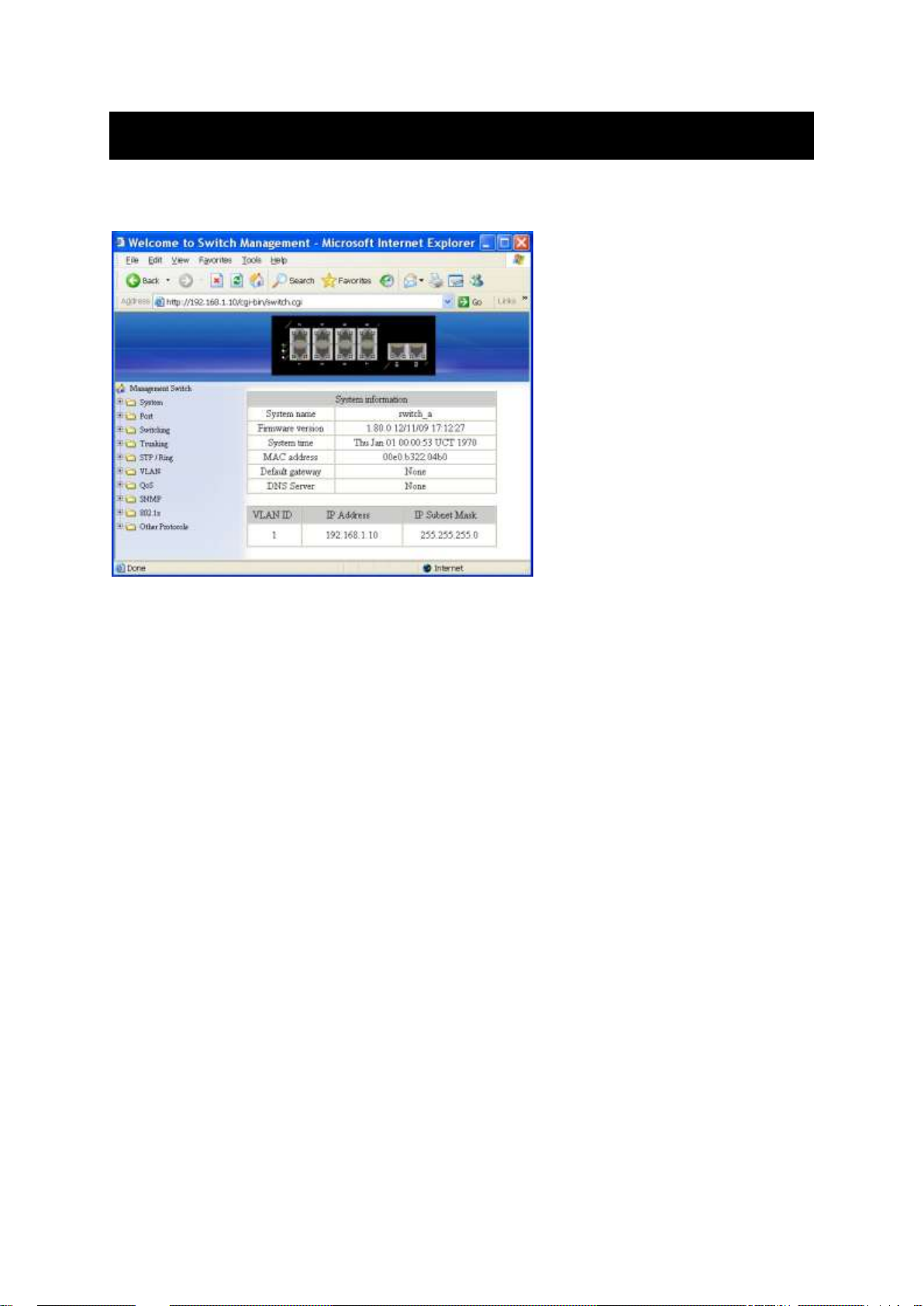
System
System Information
View System information, VLAN ID, IP Address, and IP Subnet Mask of the Switch.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 30
Page 31

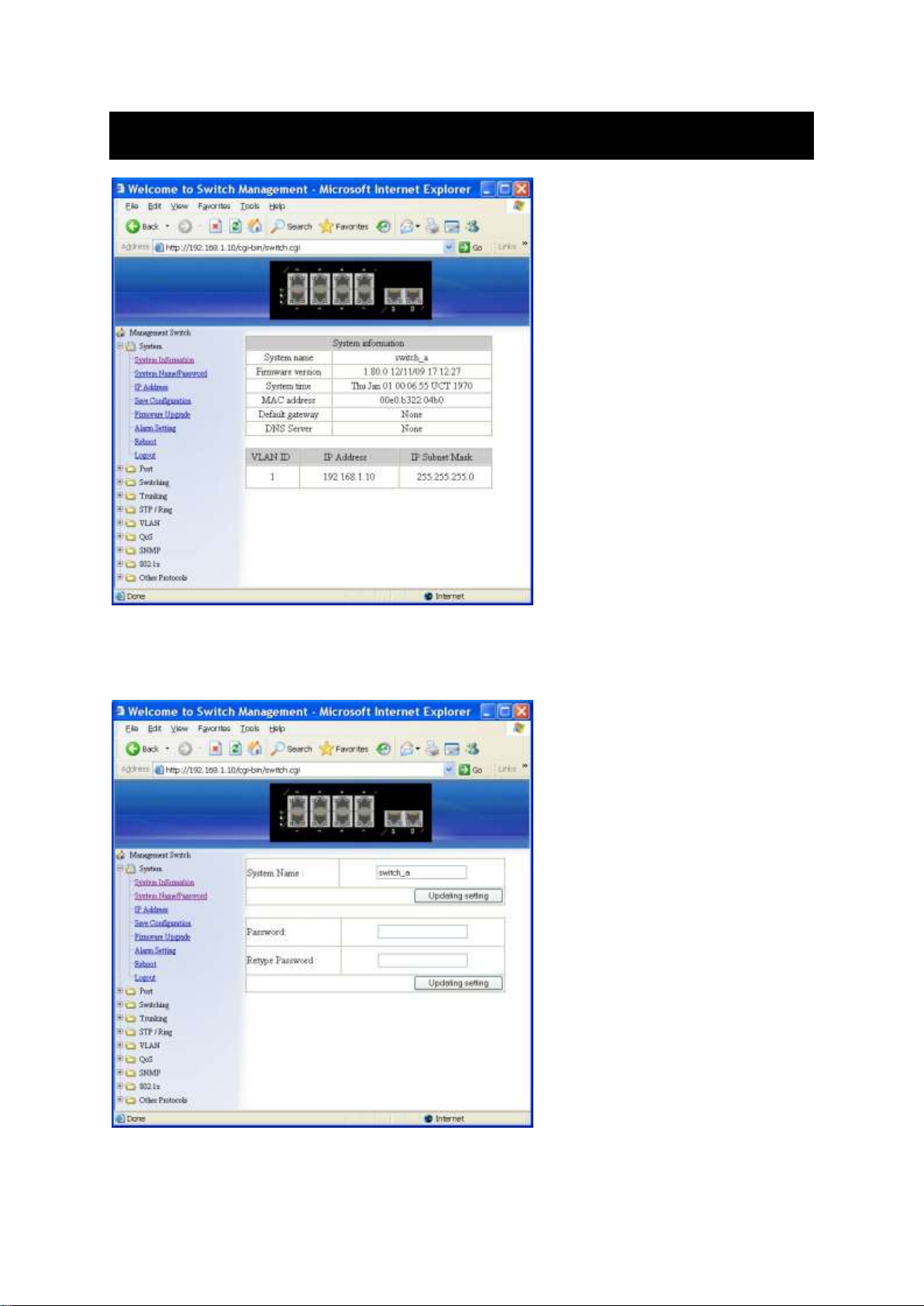
System Name/Password
1. System Name: System Name . Type a system name if it is blank, or
replace the current system name with a new one.
2. Updating setting: C Updating setting button to update your settings.
3. Password: Password . Type a password.
4. Retype Password: Retype Password . Type the same password in
Password again to verify it.
5. Updating setting: Click Updating setting button to update your settings.
IP Address
1. IP Address: C IP Address text box and type a new address to change the IP
Address.
2. IP Subnet Mask: C IP Subnet Mask text box and type a new address to change
the IP Subnet Mask.
3. Submit: C Submit button when you finished these selections.
4. You need to enter the new IP address on the browser and reconnect to the switch after
IP or subnet mask are changed.
5. Default Gateway: C Default Gateway drop-down menu to choose Disable or
Enable Default Gateway drop-down list to disable or enable Default
Gateway Setting for the switch.
Click the text box and type a new address to change the Default Gateway. (Need to
choose Enable Default Gateway drop-down menu.)
6. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Default Gateway.
7. DNS Server: C DNS Server drop-down menu to choose Disable or Enable
DNS Server drop-down list to disable or enable DNS Server Setting for the switch.
Click the text box and type a new address to change the DNS Server. (Need to choose
Enable DNS Server drop-down menu.)
IES-1081 User Manual Page 31
Page 32

8. Submit: C Submit button when you finished DNS Server.
Save Configuration
1. Load config from TFTP server:
C TFTP Server text box and type the TFTP server IP address from where the
file will be obtained.
C FILE text box and type the name of the file that will be obtained.
Load button to load the file from the TFTP server.
2. Backup config to TFTP server:
C TFTP Server text box and type the TFTP server IP address to where the file
will be back upped.
C FILE text box and type the name of the file that will be back upped.
Backup button to backup the file to the TFTP server.
3. Save Configuration: Save Configuration button to save your configuration
settings.
4. Restore Default: Restore Default button to restore the default settings of the
switch.
5. Auto save: C Auto save drop-down menu to choose Disable or Enable
Auto save drop-down list to disable or enable Auto save for the switch.
6. Auto save interval (5~65536 sec): C Auto save interval
decimal number between 5 and 65536.
7. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Auto save configuration.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 32
Page 33

Firmware Upgrade
1. Filename: C Filename text box and type the name of the file that you intend to
upgrade it to the switch.
2. TFTP server IP: C TFTP server IP text box and type the TFTP server IP address
from where the file will be obtained.
3. Upgrade: C upgrade button to upgrade firmware to the switch. Please follow the
message on the screen during the firmware upgrade process. Do not turn off the
power or perform other functions during this period of time. Reboot the switch after
completing the upgrade process.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 33
Page 34

Please follow the message on the screen during the firmware upgrade process. Do not
turn off the power or perform other functions during this period of time.
Firmware has been upgraded successfully to the switch. Reboot the switch after
completing the upgrade process.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 34
Page 35

Alarm Setting
1. Name: C Name drop-down menu to choose fe1~fe8, ge1~ge2 , or
Power1~Power3 Name drop-down list.
2. Trigger Enabled: C Trigger Enabled drop-down menu to choose YES or NO
Trigger Enabled drop-down list to enable or disable Trigger.
3. Update Setting: C Update Setting button to update settings to the switch.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 35
Page 36

Reboot
Reboot: Reboot button to restart the switch.
Logout
Logout: Logout button to logout of the switch.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 36
Page 37

Port
Configuration
1. Admin Setting: C Admin Setting drop-down menu to choose Link down or Link
up Admin Setting drop-down list to disable or enable Admin Setting for the
port.
2. Speed: C Speed drop-down menu to change the line speed and duplex settings
Speed drop-down list for the port.
3. Flow control: C Flow control drop-down menu to choose Disable or Enable
Flow control drop-down list to disable or enable Flow control for the port.
4. Submit: C Submit button when you finished configurations.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 37
Page 38

Port Status
View the Link Status, Speed, Duplex, and Flow control status for all ports.
Rate Control
1. Ingress: C Ingress text box and type a new Rate to change the Ingress Rate
Control for the port.
Rate Values: 64kbps, 128kbps, 192kbps, , 1792kbps.
2Mbps, 3Mbps, 4Mbps, , 100Mbps.
104Mbps, 112Mbps, 120Mbps, , 1000Mbps.
<Note>: M = 1024k.
2. Egress: C Egress text box and type a new Rate to change the Egress Rate Control
for the port.
Rate Values: 64kbps, 128kbps, 192kbps, , 1792kbps.
2Mbps, 3Mbps, 4Mbps, , 100Mbps.
104Mbps, 112Mbps, 120Mbps, , 1000Mbps.
<Note>: M = 1024k.
3. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished these Rate Control
settings.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 38
Page 39

RMON Statistics
Click Port 1 ~ Port 10 to view corresponding RMON Statistics.
Per port vlan activities
Click Port 1 ~ Port 10 to view corresponding vlan activities.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 39
Page 40

Switching
Bridging
1. Aging Time (seconds): Click the text box and type a decimal number as Bridging Aging
Time in seconds.
2. Update setting: C update setting button when you finished Aging Time settings.
3. Threshold level (0-100): Click Level for the port.
Need to choose Broadcast and/or DFL-Multicast from Storm-control enabled type
for the port. DLF (Destination Lookup Failure).
4. Storm-control enabled type: Choose Broadcast and/or DLF-Multicast from
Storm-control enabled type for the port.
5. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished Threshold level and
Storm-control enabled type settings.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 40
Page 41

Static MAC Entry
Static-MAC-Entry Forward:
1. Add MAC address: Click in Add MAC address locked forwarding
MAC address for the port.
2. VLAN ID: C VLAN ID drop-down menu and choose a VLAN ID VLAN ID
drop-down list.
3. Delete MAC address: C Delete MAC address drop-down menu and choose a
locked forwarding MAC address Delete MAC address drop-down list to be
deleted from the port.
4. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Static-MAC-Entry Forward settings.
Static-MAC-Entry Discard:
1. Add MAC address: Add MAC address MAC address to be
discarded for the VLAN.
2. VLAN ID: VLAN ID: C VLAN ID drop-down menu and choose a VLAN ID from the
VLAN ID drop-down list.
3. Delete MAC address: C Delete MAC address drop-down menu and choose a MAC
address Delete MAC address drop-down list to be discarded from the VLAN.
4. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Static-MAC-Entry Discard settings.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 41
Page 42

Port Mirroring
1. Mirror From: Choose Mirror From port from Port 1 ~ Port 10.
2. Mirror To: Click Mirror To drop-down menu to Choose Mirror To port (Port 1 ~ Port 10)
from Mirror To drop-down list.
3. Mirror Mode: C Mirror Mode drop-down menu to Choose Tx/Rx , Tx , or Rx from
Mirror Mode drop-down list.
4. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Port Mirroring settings.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 42
Page 43

Trunking
Port Trunking
Static Channel Group:
1. Trunk 1: Click Port 1 ~ Port 8 to assign ports to Trunk 1. (Maximum 4 ports in Trunk 1.)
GE Trunking:
1. Trunk 3: Click Static or Disable for Trunk 3.
2. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Port Trunking settings.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 43
Page 44

STP / Ring
Global Configuration
1. Spanning Tree Protocol: C Spanning Tree Protocol drop-down menu to Choose
Enable or Disable from Spanning Tree Protocol drop-down list to enable or disable
Spanning Tree Protocol.
2. Bridge Priority (0..61440): C Bridge Priority
between 0 and 61440.
3. Hello Time (sec) (1..9): C Hello Time
between 1 and 9.
4. Max Age (sec) (6..28): C Max Age
6 and 28.
5. Forward Delay (sec) (4..30): C Forward Delay
number between 4 and 30.
6. STP Version: C STP Version drop-down menu to choose MSTP , RSTP , or STP
compatible from STP Version drop-down list.
7. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished Global Configuration.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 44
Page 45

RSTP Port Setting
1. STP Version: C STP Version drop-down menu to choose RSTP from STP Version
drop-down list.
2. Port: C Port drop-down menu to Choose Port 1 ~ Port 10 from Port drop-down
list.
3. Priority(Granularity 16): C Priority enter a value between 0 and 240
to set the priority for the port. A higher priority will designate the port to forward
packets first. A lower number denotes a higher priority. This entry must be divisible by
16. The default priority setting is 128.
4. Admin. Path Cost: C Admin. Path Cost enter a value between 0 and
2000000 to set the Admin. Path Cost for the port. 0 (auto) - Setting 0 for the Admin.
Path Cost will automatically set the speed for forwarding packets to the port for
optimal efficiency. Default port cost: 100Mbps port = 200000. Gigabit port = 20000.
5. Point to Point Link: C Point to Point Link drop-down menu to Choose Enable or
Disable from Point to Point Link drop-down list to enable or disable Point to Point
Link for the port.
6. Edge Port: C Edge Port drop-down menu to Choose Enable, Disable, or Auto
from Edge Port drop-down list to set Enable, Disable, or Auto Edge Port for the port.
7. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished RSTP Port Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 45
Page 46

MSTP Properties
1. STP Version: C STP Version drop-down menu to choose MSTP from STP Version
drop-down list.
2. Region Name: C Region Name to create an MST region and specify a
name to it. MST bridges of a region form different spanning trees for different VLANs.
By default, each MST bridge starts with the region name as its bridge address. This
means each MST bridge is a region by itself, unless specifically added to one.
3. Revision Level: C Revision Level to specify the number for configuration
information. The default value of revision number is 0.
4. Max Hops: C Max Hops to specify the maximum allowed hops for BPDU
in an MST region. This parameter is used by all the instances of the MST. Specifying the
IES-1081 User Manual Page 46
Page 47

max hops for a BPDU prevents the messages from looping indefinitely in the network.
When a bridge receives a MST BPDU that has exceeded the allowed max-hops, it
discards the BPDU.
5. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished MSTP Properties
setting.
MSTP Instance Setting
VLAN Instance Configuration
1. VLAN Instance Configuration: C VLAN Instance Configuration button. The VLAN
Instance Configuration window appears.
2. VLAN ID: C VLAN ID drop-down menu to choose VLAN from VLAN ID drop-down
list to simultaneously add multiple VLANs for the corresponding instance of a bridge.
3. Instance ID (1..15): C Instance ID to specify the instance ID.
4. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished VLAN Instance
IES-1081 User Manual Page 47
Page 48

Configuration.
Included VLANs
1. Instance ID: C Instance ID drop-down menu to choose instance ID from Instance
ID drop-down list.
2. Included VLAN: C Included VLAN drop-down menu to choose VLAN from
Included VLAN drop-down list.
Instance Setting
1. Bridge Priority (0..61440): C Bridge Priority to set the bridge priority for
an MST instance to the value specified. The lower the priority of the bridge, the better
the chances are the bridge becoming a root bridge or a designated bridge for the LAN.
2. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished VLAN Instance
Configuration.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 48
Page 49

MSTP Port Setting
Port Instance Configuration
1. Instance ID: C Instance ID drop-down menu to choose instance ID from Instance
ID drop-down list.
2. Click Port 1 ~ Port 10 to assign ports to the corresponding instance ID.
3. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished Port Instance
Configuration.
Instance ID
1. Instance ID: C Instance ID drop-down menu to choose instance ID from Instance
ID drop-down list.
MSTP Port Configuration
1. Port: C Port drop-down menu to choose port from Port drop-down list.
2. Priority(Granularity 16): C Priority to set the port priority for a bridge
group. The Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol uses port priority as a tiebreaker to
determine which port should forward frames for a particular instance on a LAN, or
which port should be the root port for an instance. A lower value implies a better
priority. In the case of the same priority, the interface index will serve as the tiebreaker,
with the lower-numbered interface being preferred over others. The permitted range
is 0-240. The priority values can only be set in increments of 16.
3. Admin. Path Cost: C Admin. Path Cost to set the cost of a path
associated with an interface.
4. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished MSTP Port Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 49
Page 50

Ring Setting
Ring state
1. C Ring state drop-down menu from Ring state drop-down list to choose Enable
or Disable to enable or disable Ring state.
2. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished Ring state setting.
Set ring port
1. Ring port 1: C Ring port 1 drop-down menu to choose Ring port 1 from Ring port
1 drop-down list.
2. Ring port 2: C Ring port 2 drop-down menu to choose Ring port 2 from Ring port
2 drop-down list.
3. Update setting: C Update setting button when you finished Set ring port.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 50
Page 51

VLAN
VLAN Mode Setting
1. VLAN Mode Setting: C VLAN Mode Setting drop-down menu to choose
Tag-based VLAN or Port-based VLAN from VLAN Mode Setting drop-down list.
2. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished VLAN Mode Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 51
Page 52

802.1Q VLAN setting
Add VLAN:
1. VLAN setting: Click VLAN setting. The VLAN Setting window appears.
2. Add VLAN: C Add VLAN button to create a new VLAN from VLAN Setting window.
3. VLAN ID(2-4094): VLAN ID textbox and specify a new VLAN ID number
from 2 ~ 4094.
4. VLAN Name: VLAN Name textbox and type a name for this newly created
VLAN.
Add port to or delete port from VLAN:
1. VLAN Member: Choose the port to be added to or deleted from the VLAN.
2. Tag or Untag: C Tag or Untag drop-down menu to Choose Tag or Untag from
Tag or Untag drop-down list for a Hybrid port.
3. Submit: C Submit button when you finished VLAN setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 52
Page 53

Delete VLAN:
1. VLAN setting: Click VLAN setting. The VLAN Setting window appears.
2. Delete VLAN: C Delete VLAN button.
3. Select a VLAN ID: C Select a VLAN ID drop-down menu from Select a VLAN ID
drop-down list to choose the VLAN to be deleted.
4. Submit: C Submit button when you finished VLAN setting.
802.1Q Port Setting
1. VLAN Port Setting: Click VLAN Port Setting. The VLAN Port Setting window appears.
2. Mode: C Mode drop-down menu to choose Access , Trunk, or Hybrid from
Mode drop-down list for the port. The port will be Tag port if you choose Trunk
Mode for the port. And the port will be Tag or Untag port if you choose Hybrid Mode
for the port.
3. PVID: PVID textbox and specify a new PVID number for the port.
4. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished VLAN Port Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 53
Page 54

Port Based VLAN
1. VLAN: Choose the port to be added to or deleted from the VLAN.
2. Select all: C select all button to choose Port 1 ~ Port 10 all to be added to the
VLAN.
3. Delete all: C delete all button to choose Port 1 ~ Port 10 all to be deleted from the
VLAN.
4. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Port Based VLAN setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 54
Page 55

QoS
Global Configuration
1. QoS: C QoS drop-down menu from QoS drop-down list to choose Enable or
Disable to enable or disable QoS.
2. Trust: Enable or disable the switch port to trust the CoS (Class of Service) labels of all
traffic received on that port. Enable or disable a routed port to trust the DSCP
(Differentiated Service Code Point) labels of all traffic received on that port.
3. Policy: Choose Strict Priority(Queue3) + WRR(Queue0-2) or WRR(Queue0-3) . A strict
priority queue is always emptied first. The queues that are used in the WRR (Weighted
Round Robin) fashion, and you can configure the weight
for each queue.
4. Weighted Round Robin: Weight(1~55) textbox and specify a new number
from 1 ~ 55 for Queue 0 ~ 3.
5. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Global Configuration.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 55
Page 56

802.1p Priority
1. Priority: C Priority drop-down menu from Priority drop-down list to choose 0 ~ 3
for VLAN Priority 0 ~ 7.
2. Submit: C Submit button when you finished 802.1p priority.
DSCP
1. Priority: C Priority drop-down menu from Priority drop-down list to choose 0 ~ 3
for DSCP Priority 0 ~ 63.
2. Submit: C Submit button when you finished DSCP.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 56
Page 57

SNMP
SNMP General Setting
1. SNMP Status: C SNMP Status drop-down menu from SNMP Status drop-down list
to choose Enable or Disable to enable or disable SNMP.
2. Description: Click in Description textbox and specify a new description for SNMP.
3. Location: Location textbox and specify a new location for SNMP.
4. Contact: Contact textbox and specify a new contact for SNMP.
5. Trap Community Name: For each Trap Community Name, Trap
Community Name textbox and specify a trap community name.
6. Trap Host IP Address: For each Trap Host IP Address, Trap Host IP Address
textbox and specify a trap host IP address.
7. Link Down Trap: C Link Down Trap drop-down menu from Link Down Trap
drop-down list to choose Enable or Disable to enable or disable link down trap.
8. Link Up Trap: C Link Up Trap drop-down menu from Link Up Trap drop-down list
to choose Enable or Disable to enable or disable link up trap.
9. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished SNMP General
Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 57
Page 58

SNMP v1/v2c
1. Get Community Name: Get Community Name textbox and specify a get
community name.
2. Set Community Name: Cl Set Community Name textbox and specify a set
community name.
3. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished SNMP V1/V2c Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 58
Page 59

SNMP v3
Add User:
1. Add User: C Add User button. The SNMP V3 Setting window appears.
2. SNMP Version: C SNMP Version drop-down menu from SNMP Version drop-down
list to choose SNMPv3 No-Auth, SNMPv3 Auth-MD5, SNMPv3 Auth-SHA, SNMPv3
Priv Auth-MD5, or SNMPv3 Priv Auth-SHA.
SNMPv3 No-Auth: Add a user using SNMP v3 without authentication.
SNMPv3 Auth-MD5: Add a user using SNMP v3 with authentication. Auth.
Password textbox and specify an authentication password.
SNMPv3 Auth-SHA: Add a user using SNMP v3 with authentication. Auth.
Password textbox and specify an authentication password.
SNMPv3 Priv Auth-MD5: Add a user using SNMP v3 with authentication and privacy.
Auth. Password textbox and specify an authentication password. Click in
Privacy PassPhrase textbox and specify a privacy pass phrase.
SNMPv3 Priv Auth-SHA: Add a user using SNMP v3 with authentication and privacy.
Auth. Password textbox and specify an authentication password. Click in
Privacy PassPhrase textbox and specify a privacy pass phrase.
3. User Name: User Name textbox and specify a user name for user using
SNMP v3.
4. Access Mode: C Access Mode drop-down menu from Access Mode drop-down list
to choose Read Only or Read/Write.
Read Only: Add a user using SNMP v3 with read-only access mode.
Read/Write: Add an user using SNMP v3 with read-write access mode
5. Submit: C Submit button when you finished SNMP V3 Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 59
Page 60

Delete User:
1. Delete User: C Delete User button. The Select User Name window appears.
2. Select User Name: C Select User Name drop-down menu from Select User Name
drop-down list to choose the user to be deleted from using SNMP v3.
3. Submit: C Submit button when you finished user deletion.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 60
Page 61

802.1x
Radius Configuration
1. Radius Status: C Radius Status drop-down menu from Radius Status drop-down
list to choose Enable or Disable to globally enable or disable authentication.
2. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished Radius Status Setting.
Add Radius:
1. Add Radius: C Add Radius button. The Radius Server Setting window appears.
2. Radius Server IP: Radius Server IP textbox and specify the IP address of the
remote radius server host.
3. Radius Server Port: Radius Server Port textbox and specify the UDP
destination port for authentication requests. The host is not used for authentication if
set to 0.
4. Secret Key: Secret Key textbox and specify the authentication and
encryption key for all radius communications between the Switch and radius server.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 61
Page 62

This key must match the encryption used on the radius daemon. All leading spaces are
ignored, but spaces within and at the end of the key are used. If spaces are used in the
key, do not enclose the key in quotation marks unless the quotation marks themselves
are part of the key.
5. Timeout <1-1000>: Timeout textbox and specify the time interval (in
seconds) that the Switch waits for the radius server to reply before retransmitting.
Enter a value in the range 1 to 1000.
6. Retransmit <1-100>: Click Retransmit textbox and specify the number of times
a radius request is resent to a server if that server is not responding or responding
slowly. Enter a value in the range 1 to 100.
7. Submit: C Submit button when you finished Radius Server Setting.
Delete Radius:
1. Delete Radius: C Delete Radius button. The Select Radius Server IP window
appears.
2. Select Radius Server IP: C Select Radius Server IP drop-down menu from Select
Radius Server IP drop-down list to choose the IP address of the remote radius server
host to be deleted.
3. Submit: C Submit button when you finished radius server deletion.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 62
Page 63

Port Authentication
1. Interface: C Interface drop-down menu from Interface drop-down list to choose
the port to be set port-based authentication.
2. Authentication State: C Authentication State drop-down menu from
Authentication State drop-down list to choose Enable or Disable to enable or
disable authentication state.
3. Port Control: C Port Control drop-down menu from Port Control drop-down list
to choose Auto, Force Authorized, or Force Unauthorized to force a port state. Auto
specifies to enable authentication on port. Force Authorized specifies to force a port
to always be in an authorized state. Force Unauthorized specifies to force a port to
always be in an unauthorized state.
4. Periodic Reauthentication: C Periodic Reauthentication drop-down menu from
Periodic Reauthentication drop-down list to choose Enable or Disable to enable or
disable periodic reauthentication.
5. Reauthentication Period <1-4294967295>: Reauthentication Period
textbox and specify the seconds between reauthorization attempts. The default time is
3600 seconds.
6. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished port-based
authentication setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 63
Page 64

Other Protocols
GVRP
GVRP Global Setting:
1. GVRP: C GVRP drop-down menu from GVRP drop-down list to choose Enable or
Disable to enable or disable GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol).
2. Dynamic VLAN creation: C Dynamic VLAN creation drop-down menu from
Dynamic VLAN creation drop-down list to choose Enable or Disable to enable or
disable Dynamic VLAN creation. GARP (Generic Attribute Registration Protocol)
provides IEEE802.1Q compliant VLAN pruning and dynamic VLAN creation on
IEEE802.1Q trunk ports.
3. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished GVRP Global Setting.
Per port setting (include LAG):
1. GVRP: C GVRP drop-down menu from GVRP drop-down list to choose Enable or
Disable to enable or disable GVRP for the port.
2. GVRP applicant: C GVRP applicant drop-down menu from GVRP applicant
drop-down list to choose Active or Normal to the port. Ports in the GVRP active
applicant state send GVRP VLAN declarations when they are in the STP (Spanning Tree
Protocol) blocking state, which prevents the STP bridge protocol data units (BPDUs)
from being pruned from the other port. Ports in the GVRP normal applicant state do
not declare GVRP VLANs when in the STP blocking state.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 64
Page 65

3. GVRP registration: C GVRP registration drop-down menu from GVRP registration
drop-down list to choose Enable or Disable to enable or disable GVRP registration to
the port. Configuring an IEEE802.1Q trunk port in registration mode allows dynamic
creation (if dynamic VLAN creation is enabled), registration, and deregistration of
VLANs on the trunk port.
4. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished Per port setting.
IGMP Snooping
1. - -down list to
for the switch. Disable: Disable IGMP on the
switch. Passive: The switch with only multicast-data-forwarding capability. Querier: The
switch acts as the querier for the network. There is only one querier on a network at
any time.
2. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished IGMP mode settings.
3. VLAN ID: VLAN ID - VLAN ID -down list to choose
the VLAN under configuration for the switch.
4. IGMP version: version - version -down
1 2 3 for the switch.
5. Fast-leave: fast-leave - fast-leave -down list to
Enable Disable for the switch. Enable this function will allow members of a
multicast group to leave the group immediately when an IGMP Leave Report Packet is
received by the Switch.
IGMP querier:
1. Query-interval: query-interval textbox and specify a new number from 1 ~
18000. The query-interval field is used to set the time (in seconds) between
transmitting IGMP queries. Entries between 1 and 18000 seconds are allowed. Default
= 125.
2. Max-response-time: max-response-time textbox and specify a new
number from 1 ~ 124. This determines the maximum amount of time in seconds
allowed before sending an IGMP response report. The max-response-time field allows
IES-1081 User Manual Page 65
Page 66

an entry between 1 and 124 (seconds). Default = 10.
IGMP passive snooping:
1. Report suppression: report suppression - report
suppression - Enable Disable for the switch. Use this
command to enable report suppression for IGMP version 1 and version 2. Report
suppression does not apply to IGMP version 3, and is turned off by default for IGMP
version 1 and IGMP version 2 reports. The switch uses IGMP report suppression to
forward only one IGMP report per multicast router query to multicast devices. When
IGMP router suppression is enabled, the switch sends the first IGMP report from all
hosts for a group to all the multicast routers. The switch does not send the remaining
IGMP reports for the group to the multicast routers. This feature prevents duplicate
reports from being sent to the multicast devices.
2. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished IGMP Snooping.
NTP
NTP Setting:
1. NTP Status: NTP Status - NTP Status -down list to
Enable Disable to enable or disable NTP for the Switch.
2. NTP Server (IP Address or Domain name): NTP Server textbox and specify
the IP address or Domain name of NTP server.
3. Sync Time: C Sync Time button to synchronize time with NTP server.
4. Time Zone: Time Zone - Time Zone -down list to set
time zone.
5. Polling Interval (1-10080 min): Polling Interval textbox and specify the
polling interval.
6. Update Setting: C Update Setting button when you finished NTP Setting.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 66
Page 67

Daylight Saving Setting:
1. Daylight Saving Mode: Click "Daylight Saving Mode" drop-down menu from "Daylight
Saving Mode" drop-down list to choose "Disable", "Weekday", or "Date" to choose
disable, weekday, or date daylight saving for the Switch.
2. Time Set Offset (1-1440 min): Click in the "Time Set Offset" textbox and specify the
offset time of daylight saving. For example enter 60 for one hour offset.
3. Daylight Saving Timezone: Click in the "Daylight Saving Timezone" textbox and specify
the daylight saving timezone. This can be any given name in 14-character
alpha-numerical. Enter the Daylight-Saving time zone using the following example:
EDT - East Daylight Saving Time Zone.
CDT - Central Daylight-Saving Time Zone.
MDT - Mountain Daylight-Saving Time Zone.
PDT - Pacific Daylight-Saving Time Zone.
ADT - Alaska Daylight-Saving Time Zone.
4. Weekday: Click in the textboxes and specify the daylight saving period.
Month: Click "Month" drop-down menu from "Month" drop-down list to choose
from January to December.
Week: <1-5> Specifies weekdays from Monday to Friday.
Day: Click "Day" drop-down menu from "Day" drop-down list to choose from
Sunday to Saturday.
Hour: <0-23> Specifies from 0 to 23.
Minute: <0-59> Specifies from 0 to 59.
5. Date: Click in the textboxes and specify the daylight saving period.
Month: Click "Month" drop-down menu from "Month" drop-down list to choose
from January to December.
Day: <1-31> Specifies from 1 to 31.
Hour: <0-23> Specifies from 0 to 23.
Minute: <0-59> Specifies from 0 to 59.
6. Update Setting: Click "Update Setting" button when you finished Daylight Saving
Setting.
<Note> T W , Hour , Minute , Day s would not accept the
alphabetic characters (Like Jan, Feb, sun, mon). They only accept the two digit
numbers (0 through 9).
IES-1081 User Manual Page 67
Page 68

Command Line Console Management
The switch provides a command line console interface for configuration purposes. The switch can be
configured either locally through its RS-232 port or remotely via a Telnet session. For the later, you
must specify an IP address for the switch first.
This chapter describes how to configure the switch using its console by Commend Line.
Administration Console
Connect the DB9 straight cable to the RS-232 serial port of the device to the RS-232 serial
port of the terminal or computer running the terminal emulation application.
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a terminal
or a PC equipped with a terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal) to the
switch console port.
When using the management method, configure the terminal-emulation program to use
the following parameters (you can change these settings after login):
[Default parameters]
115,200bps
8 data bits
No parity
1 stop bit
Exec Mode (View Mode)
Logon to Exec Mode (View Mode)
At the switch_a login:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 68
Page 69

(or View Mode).
switch_a login: root
switch_a>?
switch_a>show ?
Basic commands
Exec Mode (or View Mode) is the base mode from where users can perform basic
commands like:
clear, debug, disable, enable, exit, help, logout, no, quit, show, terminal
The CLI contains a text-based help facility. Access this help by typing in the full or partial
command string then
or parameters along with a short description.
At the switch_a> prompt just press <?> to list the above basic commands.
At the switch_a> prompt just type in the full or partial command string then typing a
to display the command keywords or parameters along with a short
description.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 69
Page 70

switch_a login: root
Login timed out
The login session to Exec Mode (or View Mode) has timed out due to an extended period
of inactivity (60 seconds) to indicate authentication attempt timed out. And the switch_a
login: prompt will show on the screen.
Logon back to Exec Mode (View Mode)
At the switch_a login: ter> to logon back to Exec
Mode (or View Mode).
IES-1081 User Manual Page 70
Page 71

switch_a>exit
switch_a>enable
Exit from Exec Mode (View Mode)
At the switch_a>
View Mode).
Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode)
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode)
At the switch_a>
Exec Mode (or Enable Mode). And the switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 71
Page 72

switch_a#?
Commands
Privileged Exec Mode (or Enable Mode) allows users to run commands as following.
At the switch_a# prompt just press <?> to list the commands.
At the switch_a# prompt just type in the full or partial command string then typing a
IES-1081 User Manual Page 72
Page 73

question to display the command keywords or parameters along with a short
switch_a#show ?
switch_a login: root
description.
Login timed out
The login session to Privileged Exec Mode (or Enable Mode) has timed out due to an
extended period of inactivity (60 seconds) to indicate authentication attempt timed out.
And the switch_a login: prompt will show on the screen.
Logon back to Exec Mode (View Mode)
At the switch_a login: ter> to logon back to Exec
Mode (or View Mode).
IES-1081 User Manual Page 73
Page 74

switch_a#exit
switch_a#configure terminal
Exit from Privileged Exec Mode (or Enable Mode)
At the switch_a#
Mode (or Enable Mode).
Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode)
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode)
At the switch_a#
Configure Mode (or Configure Terminal Mode). And the switch_a(config)# prompt will
show on the screen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 74
Page 75

switch_a(config)#?
Commands
Configure Mode (or Configure Terminal Mode) serves as a gateway into the modes as
following.
At the switch_a(config)# prompt just press <?> to list the commands.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 75
Page 76

At the switch_a(config)# prompt just type in the full or partial command string then
switch_a(config)#show ?
switch_a login: root
switch_a(config)#exit
to display the command keywords or parameters along with a
short description.
Login timed out
The login session to Configure Mode (or Configure Terminal Mode) has timed out due to
an extended period of inactivity (60 seconds) to indicate authentication attempt timed out.
And the switch_a login: prompt will show on the screen.
Logon back to Exec Mode (View Mode)
At the switch_a login:
Mode (or View Mode).
Exit from Configure Mode (or Configure Terminal Mode)
At the switch_a(config)#
Configure Mode (or Configure Terminal Mode).
IES-1081 User Manual Page 76
Page 77

switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#hostname switch
switch(config)#
System
System Information, System Name/Password, IP Address, Save Configuration,
Firmware Upgrade, Alarm Setting, Reboot, Logout
System Name/Password
System Name:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use hostname command to set or change the network server name.
Use the no hostname command to disable this function.
3. Command Syntax:
(no) hostname HOSTNAME
HOSTNAME specifies the network name of the system.
4. Example:
The following example sets the hostname to switch, and shows the change in the prompt:
Password:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 77
Page 78

switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#enable password mypasswd
switch_a(config)#
2. Usage:
Use enable password command to modify or create a password to be used when
entering the Enable mode.
3. Command Syntax:
enable password PASSWORD
PASSWORD specifies the new password of the system.
4. Example:
The following example sets the new password mypasswd to switch:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 78
Page 79

IP Address
switch_a(config)#interface vlan1.1
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface vlan1.1
switch_a(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.10/24
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#
IP Address/IP Subnet Mask:
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
vlan1.1 means vlan 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use ip address command to set the IP address of an interface.
Use the no ip address command to remove the IP address from an interface.
3. Command Syntax:
ip address IP-ADDRESS
no ip address IP-ADDRESS
no ip address
IP-ADDRESS A.B.C.D/M specifies the IP address and prefix length of an interface.
M specifies IP subnet mask, 8: 255.0.0.0, 16:255.255.0.0, 24: 255.255.255.0.
4. Example:
The following example sets the new IP address 192.168.1.10 and new IP subnet mask
255.255.255.0 to switch:
Default Gateway:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use ip default-gateway command to set the IP address of the default gateway.
Use the no ip default-gateway command to remove the IP address of the default
gateway.
3. Command Syntax:
ip default-gateway IP-ADDRESS
no ip default-gateway
IP-ADDRESS A.B.C.D specifies the IP address of the default gateway.
4. Example:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 79
Page 80

The following example sets the default gateway 192.168.1.254 to switch:
switch_a(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.1.254
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#ip dns 192.168.1.100
switch_a(config)#
switch_a#
switch_a#install image 192.168.1.100 flash.tgz
DNS Server:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use ip dns command to set the IP address of the DNS server.
Use the no ip dns command to remove the IP address of the DNS server.
3. Command Syntax:
ip dns IP-ADDRESS
no ip dns
IP-ADDRESS A.B.C.D specifies the IP address of the DNS server.
4. Example:
The following example sets the DNS server 192.168.1.100 to switch:
Save Configuration
Load config from TFTP server:
1. Command Mode: Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use install image command to load configuration file from tftp server to switch.
3. Command Syntax:
install image IP-ADDRESS WORD
IP-ADDRESS specifies the IP address of tftp server.
WORD specifies the file name to be loaded to switch.
4. Example:
The following example specifies upgrading firmware (file name: flash.tgz) from tftp server
(IP address: 192.168.1.100) to switch:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 80
Page 81

switch_a#
switch_a#
switch_a#write config-file 192.168.1.100
switch_a#
switch_a#
switch_a#copy running-config startup-config
switch_a#
Load config to TFTP server:
1. Command Mode: Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use write config-file command to backup configuration file to tftp server.
3. Command Syntax:
write config-file IP-ADDRESS
IP-ADDRESS specifies the IP address of tftp server.
4. Example:
The following example backups configuration file to tftp server (IP address:
192.168.1.100):
Save Configuration:
1. Command Mode: Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use copy running-config startup-config command to write configurations to the file to
be used at startup. This is the same as the write memory command.
3. Command Syntax:
copy running-config startup-config
4. Example:
The following example specifies writing configurations to the file to be used at startup to
switch:
Restore Default:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 81
Page 82

1. Command Mode: Privileged Exec mode
switch_a#
switch_a#restore default
switch_a#
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#service auto-config enable
switch_a(config)#no service auto-config enable
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use restore default command to restore default setting of the switch.
3. Command Syntax:
restore default
4. Example:
The following example restores default setting of the switch:
Auto Save:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to enable auto save configuration function. The configuration will be
automatically saved at every configured interval while this command is enabled. Use the
no form of this command to disable this feature.
3. Command Syntax:
service auto-config enable
no service auto-config enable
4. Example:
The following example enables or disables auto save configuration to switch:
Auto Save Interval (5~65536 sec):
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 82
Page 83

2. Usage:
switch_a(config)#service auto-config interval 10
switch_a(config)#
switch_a#
switch_a#install image 192.168.1.100 flash.tgz
switch_a#
Use this command to set the interval when the configuration would be automatically
saved. The range of interval value is from 5 to 65535. And the default value is 30 seconds.
3. Command Syntax:
service auto-config interval WORD
WORD specifies the interval value.
4. Example:
The following example sets the interval WORD (10) when the configuration would be
automatically saved to switch:
Firmware Upgrade
1. Command Mode: Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use install image command to upgrade firmware from tftp server to switch.
3. Command Syntax:
install image IP-ADDRESS WORD
IP-ADDRESS specifies the IP address of tftp server.
WORD specifies the file name to be upgraded to switch.
4. Example:
The following example specifies upgrading firmware (file name: flash.tgz) from tftp server
(IP address: 192.168.1.100) to switch:
Please follow the message on the screen during the firmware upgrade process. Do not
turn off the power or perform other functions during this period of time.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 83
Page 84

switch_a(config)#
# eload reboot the switch
after completing the upgrade process.
Alarm Setting
Alarm-trigger if:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to enable or disable alarm trigger on interface.
3. Command Syntax:
(no) alarm-trigger if INTERFACE
INTERFACE specifies the interface.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 84
Page 85

4. Example:
switch_a(config)#alarm-trigger if fe1
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#alarm-trigger power 1
switch_a(config)#
switch_a#
switch_a#reload
switch_a login:
The following example enables alarm trigger on interface fe1 to switch:
Alarm-trigger power:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to enable or disable alarm trigger of power source.
3. Command Syntax:
(no) alarm-trigger power POWER
POWER specifies the power source.
4. Example:
The following example enables alarm trigger of power 1 to switch:
Reboot
1. Command Mode: Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use reload command to restart switch.
3. Command Syntax:
reload
4. Example:
The following example specifies restarting switch:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 85
Page 86

Logout
switch_a>
switch_a#
switch_a>logout
switch_a login:
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
1. Command Mode: Exec mode or Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Exec Mode (View Mode) or Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a> or switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use logout command to exit from the Exec mode or Privileged Exec mode.
3. Command Syntax:
logout
4. Example:
The following example specifies to exit from the Exec mode or Privileged Exec mode.
Port
Configuration, Port Status, Rate Control, RMON Statistics, Per Port Vlan
Activities
Configuration
Admin Setting:
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use the shutdown command to shut down the selected interface.
Use the no shutdown to disable this function.
3. Command Syntax:
(no) shutdown
4. Example:
The following example shows the use of the shutdown command to shut down the
interface fe1 (port 1):
IES-1081 User Manual Page 86
Page 87

switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#shutdown
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#duplex full
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
Duplex:
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use duplex command to specify the duplex mode to be used for each interface.
Use the no duplex to disable this function.
3. Command Syntax:
(no) duplex MODE
MODE specifies the duplex mode: auto, full, half.
4. Example:
The following example shows the use of duplex MODE (full) to the interface fe1 (port 1):
Flow control:
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use flowcontrol on command to enable flow control, and configure the flow control
mode for the port.
Use the no flowcontrol to disable this function.
3. Command Syntax:
flowcontrol on
IES-1081 User Manual Page 87
Page 88

no flowcontrol
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#flowcontrol on
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a>
switch_a#
switch_a>show interface fe1
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
4. Example:
The following example shows the use of flowcontrol on to the interface fe1 (port 1):
Port Status
1. Command Mode: Exec mode or Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Exec Mode (View Mode) or Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a> or switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use the show interface command to display interface configuration and status.
3. Command Syntax:
show interface IFNAME
IFNAME specifies the name of the interface for which status and configuration
information is desired.
4. Example:
The following example shows the use of show interface to display interface configuration
and status of the interface fe1 (port 1):
Rate Control
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to specify the ingress/egress rate to be used for each interface. The
bandwidth value is in bits.
Use the no parameter with this command to remove the ingress/egress rate to be used for
each interface.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 88
Page 89

switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#rate-control ingress 10m
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a>
switch_a#
switch_a>show interface statistics fe1
switch_a>
switch_a#
3. Command Syntax:
(no) rate-control ingress/egress VALUE
VALUE
<1-10000000000 bits> (usable units: k, m, g)
<1-999>k|m for 1 to 999 kilo bits or mega bits.
1g for 1 giga bits.
4. Example:
The following example shows the use of rate-control ingress VALUE (10 mega bits) to the
interface fe1 (port 1):
RMON Statistics
1. Command Mode: Exec mode or Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Exec Mode (View Mode) or Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a> or switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use the show interface statistics command to display RMON statistics of interface.
3. Command Syntax:
show interface statistics IFNAME
IFNAME specifies the name of the interface for which RMON statistics is desired.
4. Example:
The following example shows the use of show interface statistics to display RMON
statistics of the interface fe1 (port 1):
Per Port Vlan Activities
1. Command Mode: Exec mode or Privileged Exec mode
Logon to Exec Mode (View Mode) or Privileged Exec Mode (Enable Mode).
The switch_a> or switch_a# prompt will show on the screen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 89
Page 90

2. Usage:
switch_a>show vlan 2
Use show vlan command to display information about a particular VLAN by specifying the
VLAN ID.
3. Command Syntax:
show vlan <2-4094>
<2-4094> VLAN ID.
4. Example:
The following is an output of show vlan command displaying information about VLAN 2:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 90
Page 91

Switching
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 ageing-time 1000
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
Bridging, Static MAC Entry, Port Mirroring
Bridging
Aging Time (seconds):
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to specify an ageing-out time for a learned MAC address. The learned
MAC address will persist till this specified time.
3. Command Syntax:
Bridge GROUP ageing-time AGEINGTIME
no bridge GROUP ageing-time
Group = <1-1> The ID of the bridge-group that this ageing time is for.
AGEINGTIME = <10-1000000> The number of seconds of persistence.
4. Example:
The following example sets the new AGEINGTIME (1000) to bridge GROUP (1):
Threshold level (0-100):
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use storm-control level command to specify the rising threshold level for broadcasting,
multicast, or destination lookup failure traffic. The storm control action occurs when traffic
utilization reaches this level.
3. Command Syntax:
storm-control level LEVEL
LEVEL <0-100> specifies the percentage of the threshold; percentage of the maximum
speed (pps) of the interface.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 91
Page 92

switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#storm-control level 30
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#storm-control broadcast enable
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
4. Example:
The following example shows setting storm-control level LEVEL (30) to the interface fe1
(port 1):
Broadcast:
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use storm-control broadcast enable command to enable broadcast traffic.
Use no storm-control broadcast command to disable broadcast traffic.
3. Command Syntax:
storm-control broadcast enable
no storm-control broadcast
4. Example:
The following example shows setting storm-control broadcast enable to the interface
fe1 (port 1):
Multicast:
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use storm-control multicast enable command to enable multicast traffic.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 92
Page 93

Use no storm-control multicast command to disable multicast traffic.
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#storm-control multicast enable
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#storm-control dlf enable
switch_a(config-if)#
3. Command Syntax:
storm-control multicast enable
no storm-control multicast
4. Example:
The following example shows setting storm-control multicast enable to the interface fe1
(port 1):
DLF:
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use storm-control dlf enable command to enable destination lookup failure traffic.
Use no storm-control dlf command to disable destination lookup failure traffic.
3. Command Syntax:
storm-control dlf enable
no storm-control dlf
dlf destination lookup failure
4. Example:
The following example shows setting storm-control dlf enable to the interface fe1 (port
1):
Static MAC Entry
Static-MAC-Entry Forward:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 93
Page 94

switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 address 2222.2222.2222 forward fe1 vlan 2
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 address 2222.2222.2222 discard vlan 1
switch_a(config)#
2. Usage:
Use this command to statically configure a bridge entry to forward matching frames.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP address MAC forward IFNAME VLANID
no bridge GROUP address MAC forward IFNAME VLANID
GROUP <1-1> Bridge-group ID used for bridging.
MAC the Media Access Control (MAC) address in the HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format.
IFNAME the interface on which the frame comes in.
VLANID The VID of the VLAN that will be enabled or disabled on the bridge <2-4094>.
4. Example:
The following example configures a bridge GROUP (1) to forward matching frames (MAC
address 2222.2222.2222) to the interface fe1 (port 1) in vlan VLANID (2):
Static-MAC-Entry Discard:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to statically configure a bridge entry to discard matching frames in a
particular VLAN.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP address MAC discard vlan VLANID
no bridge GROUP address MAC discard vlan VLANID
GROUP <1-1> Bridge-group ID used for bridging.
MAC the Media Access Control (MAC) address in the HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format.
VLANID The VID of the VLAN on the bridge <1-4094>.
4. Example:
The following example configures a bridge GROUP (1) to discard matching frames (MAC
address 2222.2222.2222) in vlan VLANID (1):
IES-1081 User Manual Page 94
Page 95

switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#mirror interface fe2 direction both
switch_a(config-if)#
Port Mirroring
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to define a mirror source port and its direction.
Use the no parameter with this command to disable port mirroring by the destination port
on the specified source port.
3. Command Syntax:
mirror interface SOURCEPORT direction SNOOPDIRECTION
no mirror interface SOURCEPORT
SOURCEPORT Name of the Source interface to be used.
SNOOPDIRECTION [both|receive|transmit]
both Specifies mirroring of traffic in both directions.
receive Specifies mirroring of received traffic.
transmit Specifies mirroring of transmitted traffic.
4. Example:
The following example enables port mirroring by the destination port fe1 (port 1) on the
specified source port fe2 (port 2):
IES-1081 User Manual Page 95
Page 96

Trunking
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#static-channel-group 1
switch_a(config-if)#
Port Trunking
Port Trunking
1. Command Mode: Interface mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
Then logon to Interface mode.
fe1 means port 1.
The switch_a(config-if)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use static-channel-group command to create a static aggregator, or add a member port
to an already-existing static aggregator.
Use the no static-channel-group command to detach the port from the static
aggregator.
3. Command Syntax:
static-channel-group <1-3>
no static-channel-group
<1-3> Channel group number.
Maximum 4 ports in static-channel-group 1 and static-channel-group 2.
Maximum 2 ports in static-channel-group 3
4. Example:
The following example adding the interface fe1 (port 1) to static-channel-group 1:
IES-1081 User Manual Page 96
Page 97

STP / Ring
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 protocol rstp vlan-bridge
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
Global Configuration, RSTP Port Setting, MSTP Properties, MSTP Instance
Setting, MSTP Port Setting, Ring Setting
Global Configuration
STP Version:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to choose the Spanning Tree protocol, Rapid Spanning Tree protocol,
or Multiple Spanning Tree protocol on a bridge.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP protocol PROTOCOL vlan-bridge
GROUP <1-1> Bridge group name used for bridging.
PROTOCOL
ieee IEEE 802.1Q spanning-tree protocol.
mstp IEEE 802.1s multiple spanning-tree protocol.
rstp IEEE 802.1w rapid spanning-tree protocol.
4. Example:
The following example chooses the PROTOCOL (rstp) on bridge GROUP (1):
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to enable the Multiple Spanning Tree protocol on a bridge.
Use the no form of the command to disable the Multiple Spanning Tree protocol on a
bridge.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP multiple-spanning-tree enable
no bridge GROUP multiple-spanning-tree enable BRIDGE-FORWARD
GROUP <1-1> Bridge group name used for bridging.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 97
Page 98

BRIDGE-FORWARD Puts all ports of the specified bridge into the forwarding state.
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 multiple-spanning-tree enable
switch_a(config)#no bridge 1 multiple-spanning-tree enable bridge-forward
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 rapid-spanning-tree enable
switch_a(config)#no bridge 1 rapid-spanning-tree enable bridge-forward
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
4. Example:
The following example enables or disables the multiple-spanning-tree on bridge GROUP
(1):
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol:
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to enable the Rapid Spanning Tree protocol on a bridge.
Use the no form of the command to disable the Rapid Spanning Tree protocol on a bridge.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP rapid-spanning-tree enable
no bridge GROUP rapid-spanning-tree enable BRIDGE-FORWARD
GROUP <1-1> Bridge group name used for bridging.
BRIDGE-FORWARD Puts all ports of the specified bridge into the forwarding state.
4. Example:
The following example enables or disables the rapid-spanning-tree on bridge GROUP (1):
Spanning Tree Protocol:
5. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
6. Usage:
Use this command to enable the Spanning Tree protocol on a bridge.
Use the no form of the command to disable the Spanning Tree protocol on a bridge.
7. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP spanning-tree enable
no bridge GROUP spanning-tree enable BRIDGE-FORWARD
GROUP <1-1> Bridge group name used for bridging.
IES-1081 User Manual Page 98
Page 99

BRIDGE-FORWARD Puts all ports of the specified bridge into the forwarding state.
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 spanning-tree enable
switch_a(config)#no bridge 1 spanning-tree enable bridge-forward
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 priority 4096
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
8. Example:
The following example enables or disables the spanning-tree on bridge GROUP (1):
Bridge Priority (0..61440):
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to set bridge priority for the common instance. Using a lower priority
indicates a greater likelihood of the bridge becoming root.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP priority PRIORITY
no bridge GROUP priority
GROUP <1-1> The ID of the bridge group for which the priority is set.
PRIORITY <0-61440> The bridge priority.
4. Example:
The following example sets the priority PRIORITY (4096) of bridge GROUP (1):
Hello Time (sec) (1..9):
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to set the hello-time, the time in seconds after which (if this bridge is
the root bridge) all the bridges in a bridged LAN exchange Bridge Protocol Data Units
(BPDUs).
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP hello-time HELLOTIME
no bridge GROUP hello-time
IES-1081 User Manual Page 99
Page 100

GROUP <1-1> The ID of the bridge group to which this hello time is assigned.
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 hello-time 9
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 max-age 28
switch_a(config)#
switch_a(config)#
HELLOTIME <1-9> The hello BPDU interval in seconds.
4. Example:
The following example sets the hello-time HELLOTIME (9) of bridge GROUP (1):
Max Age (sec) (6..28):
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to set the max-age for a bridge.
Use the no parameter with this command to restore the default value of max-age.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP max-age MAXAGE
no bridge GROUP max-age
GROUP <1-1> The ID of the bridge group to which this maximum age time is assigned.
MAXAGE <6-28> The maximum time, in seconds, to listen for the root bridge.
4. Example:
The following example sets the max-age MAXAGE (28) of bridge GROUP (1):
Forward Delay (sec) (4..30):
1. Command Mode: Configure mode
Logon to Configure Mode (Configure Terminal Mode).
The switch_a(config)# prompt will show on the screen.
2. Usage:
Use this command to set the time (in seconds) after which (if this bridge is the root bridge)
each port changes states to learning and forwarding.
Use the no parameter with this command to restore the default value.
3. Command Syntax:
bridge GROUP forward-time FORWARD_DELAY
no bridge GROUP forward-time
IES-1081 User Manual Page 100
 Loading...
Loading...