Page 1

GSW-2491TXM
24Fast/1 Slide-in Slot L2 SNMP Switch
USER MANUAL
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
1. INTRODUCTION...................................... ....... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ........ ... .... ..1
Features ........................................ .............................................................. .................2
Software Features .............. .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ........ ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... ....... .... ..2
Package Contents ........................................................................................................4
Ethernet Switching Technology....................................................................................5
2. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION............................................ .... .... ... .... ....... .... .... ... .... ..6
Physical Dimension ............ .... ... .... .... ... .... ....... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ....... .... ... .... ..6
Front Panel...................................................................................................................6
LED Indicators..............................................................................................................7
Rear Panel...................... ............................................................... ...............................7
Desktop Installation ......................................................................................................8
Rack-mounted Installation............................................................................................9
3. NETWORK APPLICATION................................................... .... ... .... .... ... .... ....... ....11
Small Workgroup........................................................................................................11
Segment Bridge..........................................................................................................12
Stacking Workgroup ...................................................................................................13
Connecting to the Switch............................................................................................14
4. CONSOLE MANAGEMENT.................................................. .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ....15
Login in the Console Interface....................................................................................15
Main Menu.................................................... ..............................................................16
Status and Counters........................................................... .................................18
Port Status....................................................................................................18
Port Counters...............................................................................................19
System Information ......................................................................................20
Switch Static Configuration........................... .......................................................21
Administration Configuration........................ .... .... ....... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ....21
Device Information ................................................................................22
IP Configuration ....................................................................................22
User Name Configuration......................................................................23
Page 4

Password Configuration........................................................................24
Port Configuration ................................................ ........................................24
Trunk Configuration......................................................................................25
Port Mirroring Configuration .........................................................................26
VLAN Configuration......................................................................................28
Priority Configuration....................................................................................33
MAC Address Configuration.........................................................................34
Misc Configuration........................................................................................37
Protocol Related Configuration............................................................................40
STP..............................................................................................................40
SNMP...........................................................................................................43
LACP............................................................................................................47
IGMP/GVRP.................................................................................................50
802.1x ..........................................................................................................51
System Reset Configuration................................................................................55
Factory Default........................... .............................................................. ....55
System Reboot........................................................ .....................................56
TFTP Configuration......................................................................................56
X-modem Upgrade..............................................................................................59
5. WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT...............................................................................61
System Login....................................................... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ....... .... ... ....62
Port status ..................................................................................................................63
View the Port Information....................................................................................64
Port Statistics..............................................................................................................64
Administrator ..............................................................................................................65
IP Address...........................................................................................................66
Switch Setting............................................................................ ..........................66
Console Port Information.................................................... .................................72
Port Controls...................................... .............................................................. ....72
Trunking ..............................................................................................................73
Forwarding and Filtering .. ... ........ ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... ....... .... .... ... .... .... ... ....77
VLAN configuration..............................................................................................80
Spanning Tree.......................................... .... .... ... .... .... ... ........ ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ....86
Page 5

Port Mirroring.......................................................................................................88
SNMP Management............................................................................................90
Security Manager ..... ... .... ... .... .... ... ........ ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... ....... .... .... ... ....91
802.1X.................................................................................................................92
TFTP Update Firmware........................................... ... .... .... ... ........ ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ....94
Configuration Backup .................................................................................................95
Factory Default....................... ... .... .... ... .... .... ....... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ........ ... ....96
System Reboot............ ....... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ........ ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... ....97
Panel List....................................................................................................................97
IP Stacking .................................................................................................................97
6. TROUBLESHOOTING............................. ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... ....... .... .... ... .... .... ... ..101
7. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION ................ ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... ....... .... .... ... .... .... ... ..103
Page 6

Page 7

1. Introduction
Welcome to the World of Network Switching. In the modern business society,
communication and information sharing are fundamental to our life. And computer
networks have proven to be one of the fastest ways of communication.
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM, 24Fast/1Slide-in Slot L2 SNMP Switch, is a multi-port
Switch that can be used to build high-performance switched workgroup networks. This
switch is a store-and-forward device that offers low latency for high-speed networking.
The Switch is targeted at workgroup, department or backbone computing enviro nment.
Figure 1-1. LevelOne GSW-2491TXM, 24Fast/1Slide-in Slot L2 SNMP Switch
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM features a “store-and-forward “ switching scheme. This
allows the switch to auto-learn and store source address in a 8K-entry MAC address
table.
(Medium Dependent Interface) Port is also called an "uplink port". The MDI port
MDI
does not cross the transmit and receive lines, which is done by the regular ports
(MDI-X ports) that connect to end stations. In general,
another Hub or Switch while
Therefore,
workstation without changing non-crossover or crossover cabling.
Auto MDI/MDIX
means that you can connect to another Switch or
means connecting to a workstation or PC.
MDIX
means connecting to
MDI
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM has 24 auto-sensing 10/100Base-TX RJ-45 ports plus one
extension slot for (Optional) 1000Base-TX and miniGBIC module enables
long-distance connection or Gigabit copper module for higher connection speed.
1
Page 8
Features
Confirms to IEEE802.3u 10BASE-T, 802.3u 100BASE-TX, 802.3ab 1000BASE-T,
802.3z Gigabit fiber
24 auto-sensing 10/100Mbps Ethernet RJ-45 ports plus one expansion slot
IEEE802.3x Flow control
¾ Flow control for full duplex
Backpressure for half duplex
¾
High back-plane bandwidth 8.8Gbps
Support IEEE802.3ad Port trunk with LACP
Broadcast storm filter supported
Management via single IP address
IGMP support for Multi Media application
Support IEEE 802.1p class of service
Port security supported
Port bandwidth control supported
Support IEEE 802.1d Spanning tree protocol
Supports GVRP function
DHCP client supported
Support IEEE 802.1x user authentication
8K-entry MAC address table
3Mbits packet buffer memory
19” Standard Rack-mounted size
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Software Features
Management
Software Upgrade
RFC Standard
Telnet management, web management, Terminal console
management (RS-232)
TFTP and Console firmware upgradeable
RFC 1157 SNMP, RFC 1213 MIB II, RFC 1643 Ethernet
like, RFC 1493 Bridge MIB, RFC 1757 RMON 1, RFC 1215
2
Page 9
Trap, RFC 2674 VLAN MIB, private MIB
Support IEEE802.3ad with LACP function and provide
Port Trunk
Spanning Tree
VLAN
QOS Policy
Class of Service
Port Based Priority
7-trunk and group member up to 4 ports. The trunk port
within 24-port 10/100TX and extension module...
IEEE802.1d spanning Tree
Port based VLAN
IEEE802.1Q Tag VLAN
IEEE802.1v Protocol VLAN (IP, IPX, …etc.)
Static VLAN groups up to 256, Dynamic VLAN group up to
2048, VLAN ID from 0 to 4094.
Supports 8 priority levels ID for two priority queue
Per system supports high and low queues. The priority
service rule: first come first service, all High before Low,
WRR for High or low weight.
Support 3 settings: “Disable, Low and High priority”. When
set to “Disable”, the income packet will follow QoS policy;
Otherwise, the packet will follow port priority setting to
“High/Low” queue.
It supports IGMP snooping for Multi-Media application and
IGMP
supports 256 groups
MAC address filter for ingress and egress packet
Port Security
Static MAC address lock for source address.
Global system supports 3 mirroring types: “RX, TX and
Port Mirror
Both packet”. The maximum of port mirror entries is up to
25.
Bandwidth Control
3
Per port support Bandwidth control. Per level 100K.
Page 10
A
It can be stack and management by a single IP address.
Stacking
802.1x
DHCP
Packet filter
The master switch can manage slave switch through any
port and the stack group can be up to 8 switches.
Support IEEE802.1x UserRADIUS server.
¾ Reject
¾ Accept
¾ Authorize
¾ Disable
Support DHCP Client
Broadcast storm
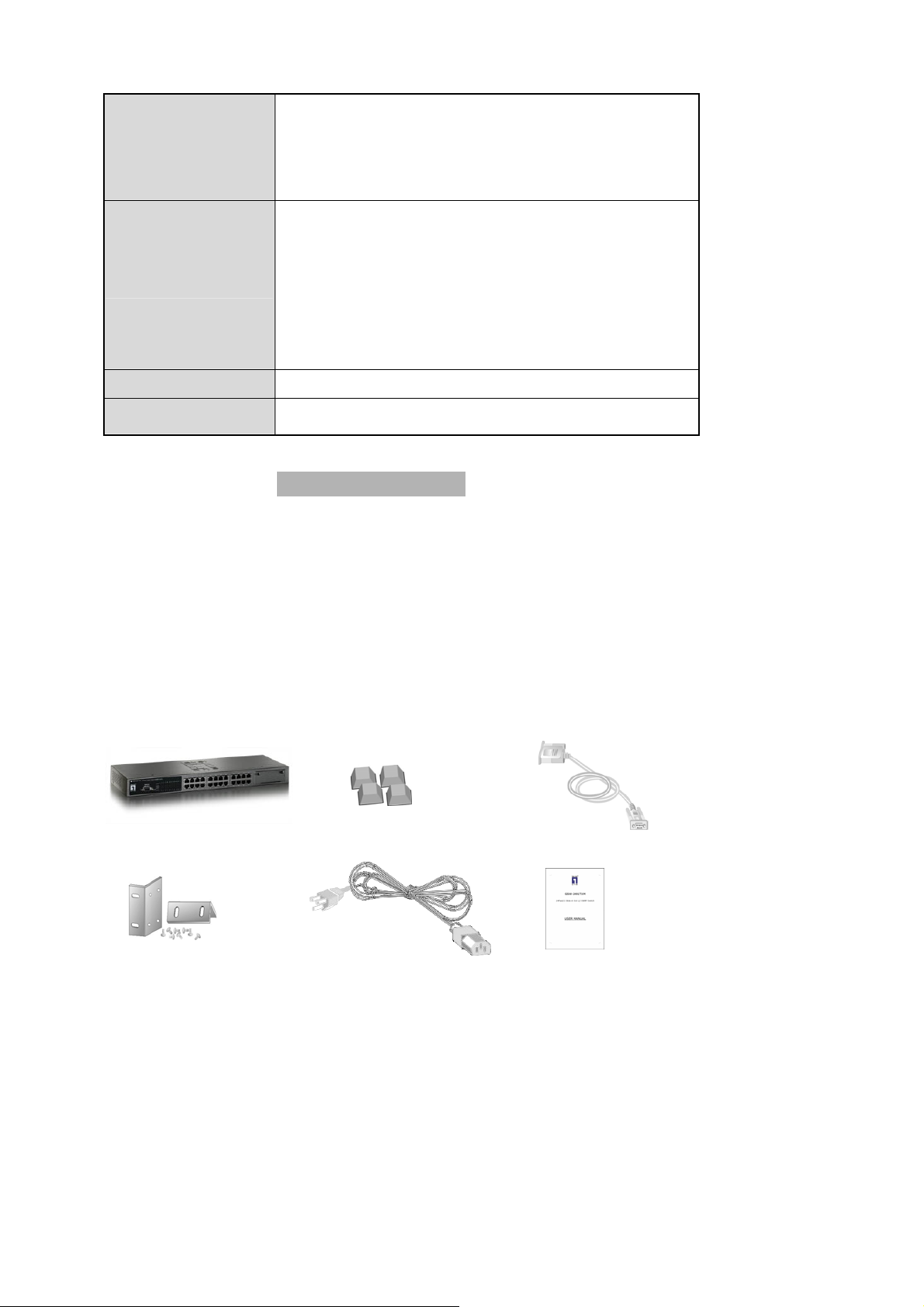
Package Contents
Unpack the contents of the
checklist below.
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM
uthentication and can report to
and verify them against the
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM
Power Cord
Four Rubber Feet
RS-232 cable
User Guide
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM
Rack-mounted Kit Power Cord User Guide
Four Rubber Feet
Figure 1-2. Package Contents
4
RS-232 Cable
Page 11

Compare the contents of your LevelOne GSW-2491TXM package with the standard
checklist above. IF any item is missing or damaged, please contact your local dealer
for service.
Ethernet Switching Technology
Ethernet Switching Technology dramatically boosted the total bandwidth of a network,
eliminated congestion problems inherent with CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense multiple
access with Collision Detection) protocol, and greatly reduced unnecessary
transmissions.
This revolutionized networking. First, by allowing two-way, simultaneous transmissions
over the same port (Full-duplex), which essentially doubled the bandwidth. Second, by
reducing the collision domain to a single switch-port, which eliminated the need for
carrier sensing. Third, by using the store-and-forward technology’s approach of
inspecting each packet to intercept corrupt or redundant data, switching eliminated
unnecessary transmission that slow the network. By employing address learning,
which replaced the inefficient receiving port.
Auto-negotiation regulates the speed and duplex of each port, based on the capability
of both devices. Flow-control allows transmission from a 100Mbps node to a 10Mbps
node without loss of data. Auto-negotiation and flow-control may require disablement
for some networking operations involves legacy equipment. Disabling the
auto-negotiation is accomplished by fixing the speed or duplex of a port.
Ethernet Switching Technology supplied higher performance at costs lower than other
solutions. Wider bandwidth, no congestion, and the reductio n in traffic is why switching
is replacing expensive routers and inefficient hubs as the ultimate networking solution.
Switching brought a whole new way of thinking to networking.
5
Page 12
2. Hardware Description
This Section mainly describes the hardware of the LevelOne GSW-2491TXM, and
gives a physical and functional overview of this Module Switch.
Physical Dimension
The LevelOne GSW-2491TXM’s physical dimension is
(W x D x H)
.
440mmx 161mm x 44.5mm
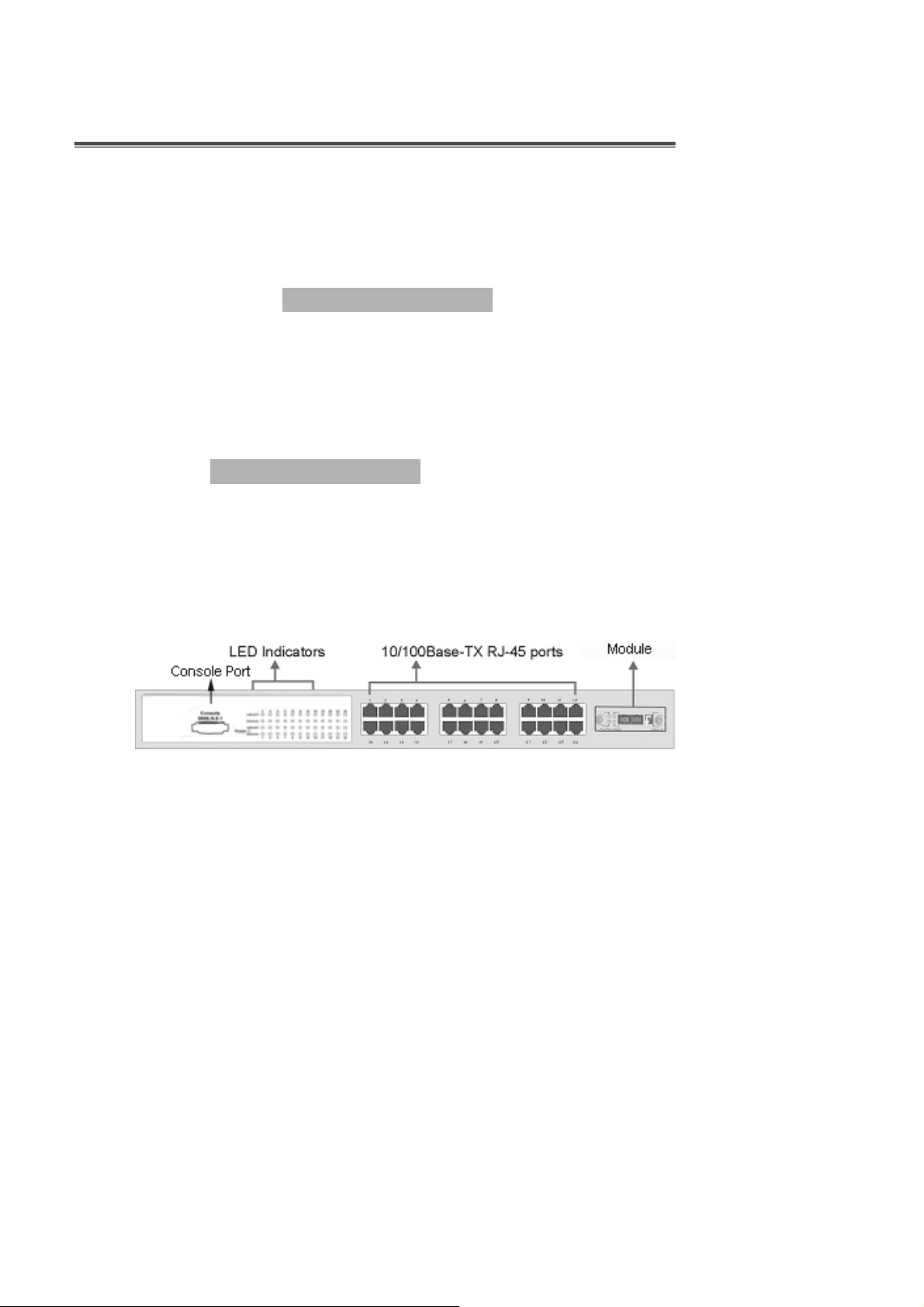
Front Panel
The Front Panel of the LevelOne GSW-2491TXM consists of 24x 10/100Base-TX
RJ-45 ports (Auto MDI/MDIX) and one Exp slot. The LED Indicators are also located
on the front panel of the Switch.
Figure 2-1. The Front panel of LevelOne GSW-2491TXM
RJ-45 Ports (Auto MDI/MDIX):
100Base-TX connections.
[In general,
connecting to a workstation or PC. Therefore,
connect to another Switch or workstation without changing non-crossover or crossover
cabling. ]
means connecting to another Hub or Switch while
MDI
24x 10/100 N-way auto-sensing for 10Base-T or
means
MDIX
Auto MDI/MDIX
means that you can
6
Page 13

Module (Optional):
There are 2 X 1000T(MDU-0140), 2 X mini GBIC(MDU-0142)
modules available for the LevelOne GSW-2491TXM.
LED Indicators
The LED Indicators gives real-time information of systematic operation status. The
following table provides descriptions of LED status and their meaning.
Figure 2-2. LED indicators
LED Status Description
Green Power On
Power
Off Power is not connected
Green The port is connecting with the device.
LNK/ACT
FDX/COL
Blinks The port is receiving or transmitting data.
Off No device attached.
Orange The port is operating in Full-duplex mode.
Blinks Collision of Packets occurs in the port.
Off In half-duplex mode
Table 2-1. The Description of LED Indicators
Rear Panel
The 3-pronged power plug and Ventilation fan are located at the rear Panel of the
7
Page 14

LevelOne GSW-2491TXM as shown in Figure 2-3. The Switch will work with AC in the
range 100-240V AC, 50-60Hz.
Figure 2-3. The Rear Panel of the LevelOne GSW-2491TXM
Desktop Installation
Set the Switch on a sufficiently large flat spa ce w ith a p ower o utlet nearby. The surface
where you put your Switch should be clean, smooth, level and sturdy. Make sure there
is enough clearance around the Switch to allow attachment of cables, power cord and
allow air circulation.
Attaching Rubber Feet
A. Make sure mounting surface on the bottom of the Switch is grease and dust free.
B. Remove adhesive backing from your Rubber Feet.
C. Apply the Rubber Feet to ea ch corner on the b ottom of the Switch. These footpads
can prevent the Switch from shock/vibration.
Figure 2-4. Attaching Rubber Feet to each corner on the bottom of the Switch
8
Page 15

Rack-mounted Installation
The LevelOne GSW-2491TXM come with a rack-mounted kid and can be mounted in
an EIA standard size, 19-inch Rack. The Switch can be placed in a wiring closet with
other equipment.
Perform the following steps to rack mount the switch:
A. Position one bracket to align with the holes on one side of the switch and secure it
with the smaller bracket screws. Then attach the remaining bracket to the other
side of the Switch.
Figure 2-4. Attach mounting brackets with screws
B. After attached both mounting brackets, position the LevelOne GSW-2491TXM
the rack by lining up the holes in the brackets with the appropriate holes on the
rack. Secure the Switch to the rack with a screwdriver and the rack-mounting
screws.
9
in
Page 16

Figure 2-5. Mount the switch in an EIA standard 19-inch Rack
For proper ventilation, allow about at least 4 inches (10 cm) of clearance on the
Note:
front and 3.4 inches (8 cm) on the back of the Switch. This is especially important for
enclosed rack installation.
Power On
Connect the power cord to the power socket on the rear panel of the Switch. The other
side of power cord connects to the power outlet. The internal power supply of the
Switch works with voltage range of AC in the 100-240VAC, frequency 5 0~60Hz. Check
the power indicator on the front panel to see if power is properly supplied.
10
Page 17

3. Network Application
This section provides you a few samples of network topology in which the Switch is
used. In general, the LevelOne GSW-2491TXM is designed as a segment switch. That
is, with its large address table (8000 MAC address) and high performance, it is ideal for
interconnecting networking segments.
PC, workstations, and servers can communicate each other by directly connecting with
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM. The switch automatically learns nodes address, which are
subsequently used to filter and forward all traffic based on the destination address.
By using Uplink port, the Switch can connect with another switch or hu b to inte rconnect
other small-switched workgroups to form a larger switched network. Meanwhile, you
can also use fiber ports to connect switches.
Small Workgroup
The LevelOne GSW-2491TXM can be used as a standalone switch to which personal
computers, server, printer server, are directly connect to form small workgroup.
11
Page 18
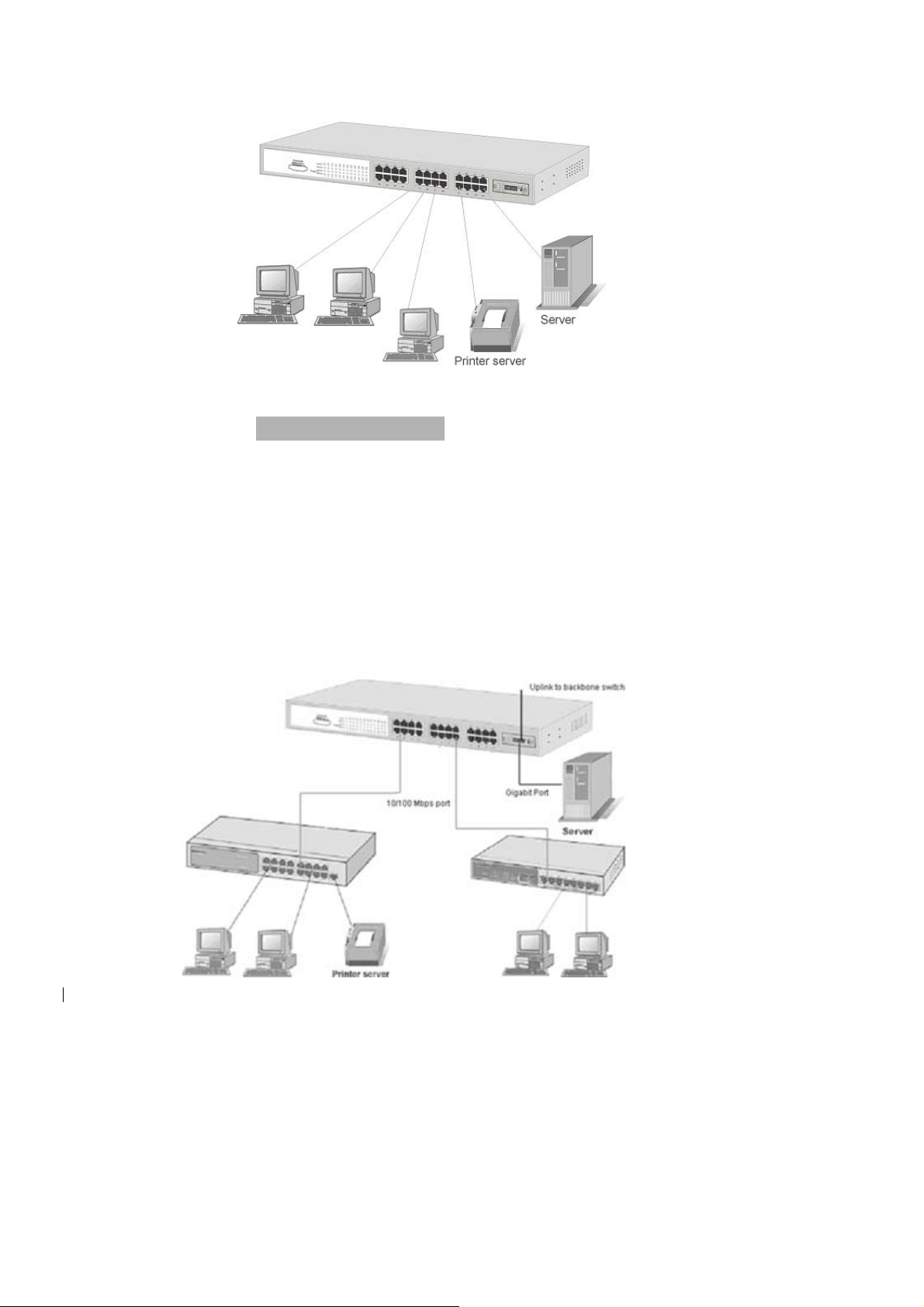
Figure 3-1. Small Workgroup Application
Segment Bridge
For enterprise networks where large data broadcasts are constantly processed, this
switch is an ideal solution for department users to connect to the corporate backbone.
In the illustration below, two Ethernet switches with PCs, print server, and local server
attached, are both connect to the Switch. All the devices in this network can
communicate with each other through the Switch. Connecting servers to the Switch
allow other users to access the data on server.
Figure 3-2 Department Bridge Application
12
Page 19

Stacking Workgroup
With stackable technology can unites up to eight individual stackable switches into a
single logical unit, using cables and with stacking software supported. The stack
behaves as a single switching unit that is managed by a master switch elected from
one of the member switches. The master switch automatically creates and updates all
the switching tables. A working stack can accept new members or delete old ones
without service interruption
Each switch in the stack has the capability to behave as a master o r subord inate in the
hierarchy. The master switch is elected and serves as the control center for the stack.
The subordinates act as forwarding processors. Each switch is assigned to a one
workgroup ID. Up to eight separate switches can be joined together as a workgroup.
The stack can have switches added and removed w ithout a ffect ing stack performance.
There are no special tools, extra software, or expensive equipment needed to form a
Stacking workgroup. It provides single image management for entire Stack (fewer
devices to manage); management applications represent the Stack as a single device,
and simple point and click management. Stackable technology allows you to increase
the resiliency and the versatility of your network edge to accommodate evolution for
speed and converged applications. Following figures are example of stacking
workgroup application.
13
Page 20
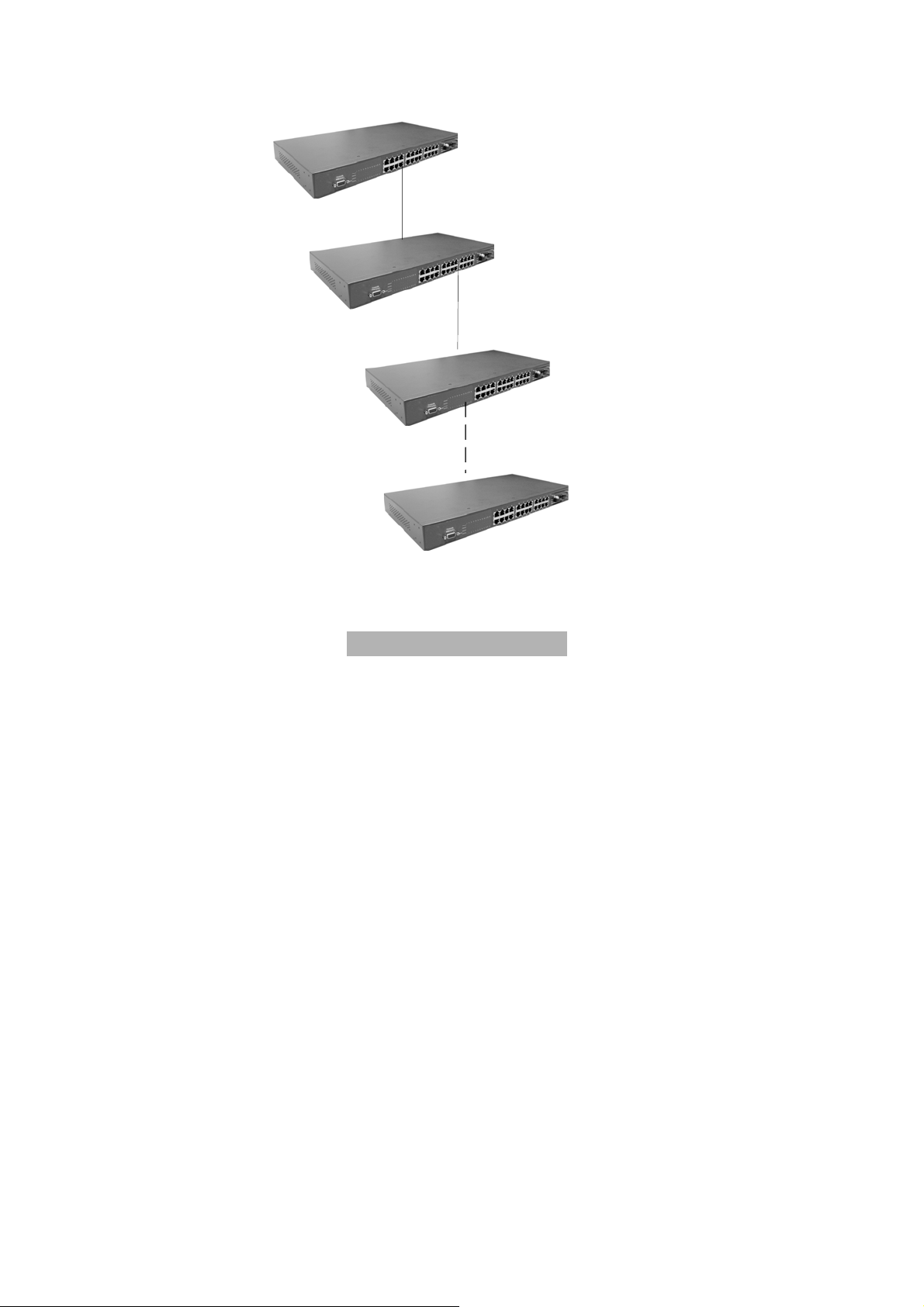
The stackable switch (Master)
Cable connection
(Cat. 5 cable)
The stackable switch
(Slave 01)
Cable connection
(Cat. 5 cable)
The stackable switch
(Slave 02)
Can units up to 8
The stackable switch
(Slave 08)
stackable switches
Figure 3-3. A stacking workgroup application
Connecting to the Switch
The Console port is a female DB-9 connector that enables a connection to a PC or
terminal for monitoring and configuring the Switch. Use the supplied RS-232 cable with
a male DB-9 connector to connect a terminal or PC to the Console port.
The Console configuration (out of band) allows you to set Switch for r emote terminal as
if the console terminal were directly connected to it.
14
Page 21
4. Console Management
Login in the Console Interface
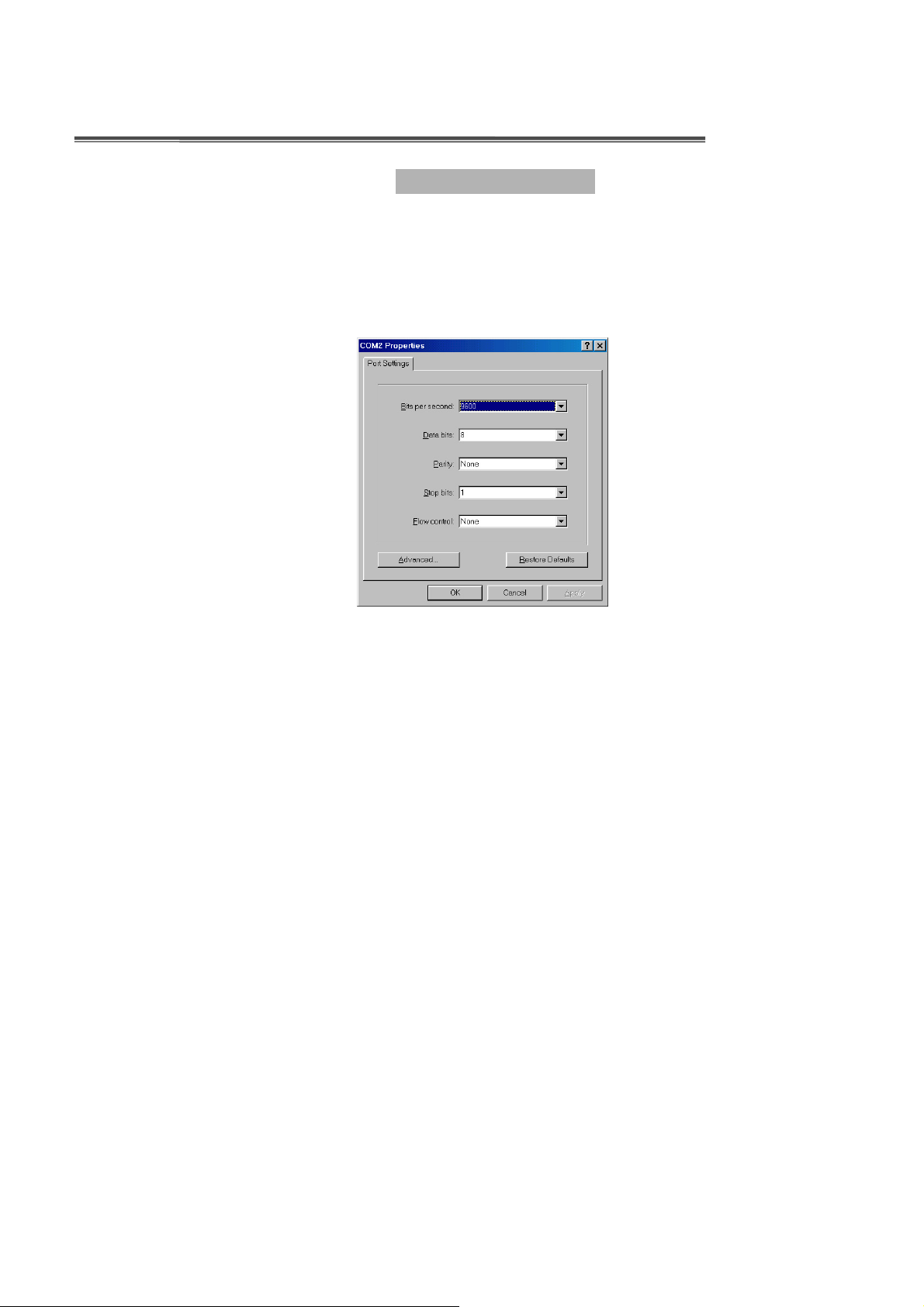
When the connection between Switch and PC is ready, turn on the PC and run a
terminal emulation program or
parameters
Baud Rate: 9600 bps
Data Bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop Bit: 1
Control flow: None
to match the following default characteristics of the console port:
Hyper Terminal
and configure its
communication
Figure 3-3. The settings of communication parameters
After finished the parameter settings, click “OK“. When the blank screen shows up,
press Enter key to bring out the login prompt. Key in the “
“(default value) for the
root
both User name and Password (use
Main Menu of console management appears. Please see below figure for login screen.
15
key to switch), then press Enter key and the
Enter
Page 22
Console login screen
Main Menu
Console – Menu Line
1. Provide a menu line interface to manage and monitor the switch. User can use
windows Hyper Terminal program through the console port to connect the switch
for configuration.
2. The default user name and password is “
root
”.
Main Menu
There are five selections as follow.
Status and Counters:
Switch Static Configuration:
Protocol Related Configuration:
System Reset Configuration:
configuration.
Logout:
Exit the menu line program.
Show the status of the switch.
Configure the switch.
Configure the protocol function.
Restart the system or reset switch to default
Formatted
16
Page 23

Main menu line interface
Control Key description:
The control keys provided in all menus:
Move the vernier to next item.
Tab:
Backspace:
Enter:
Space:
to exit the current action mode.
Esc:
Move the vernier to previous item.
Select item.
Toggle selected item to next configure or change the value.
17
Page 24

Status and Counters
In Status and Counters, you can view Port status, counters, and configure system
parameter. You can press the “
key to select item.
Status and Counters main configuration interface
Port Status
Tab
” or “
Backspace
” to choose item, and press “
Enter
”
It displays status of port. Select the
And, select the
Type:
Link:
and work normally, the link status is “UP”. Opposite is “
Speed Duplex:
State:
Negotiation:
FC:
display backpressure status.
BP:
Bandwidth In/Out:
Priority:
<Next page>
display port connection speed.
display port statuses link status. When the port is connecting with the de vice
display port duplex mode.
The port current status.
display the auto negotiation status.
display the flow control status is “enable” or “disable”.
display bandwidth In/out control status.
display the port priority status.
<Previous Page>
action to display next page.
18
action to display previous page.
”.
Down
Page 25
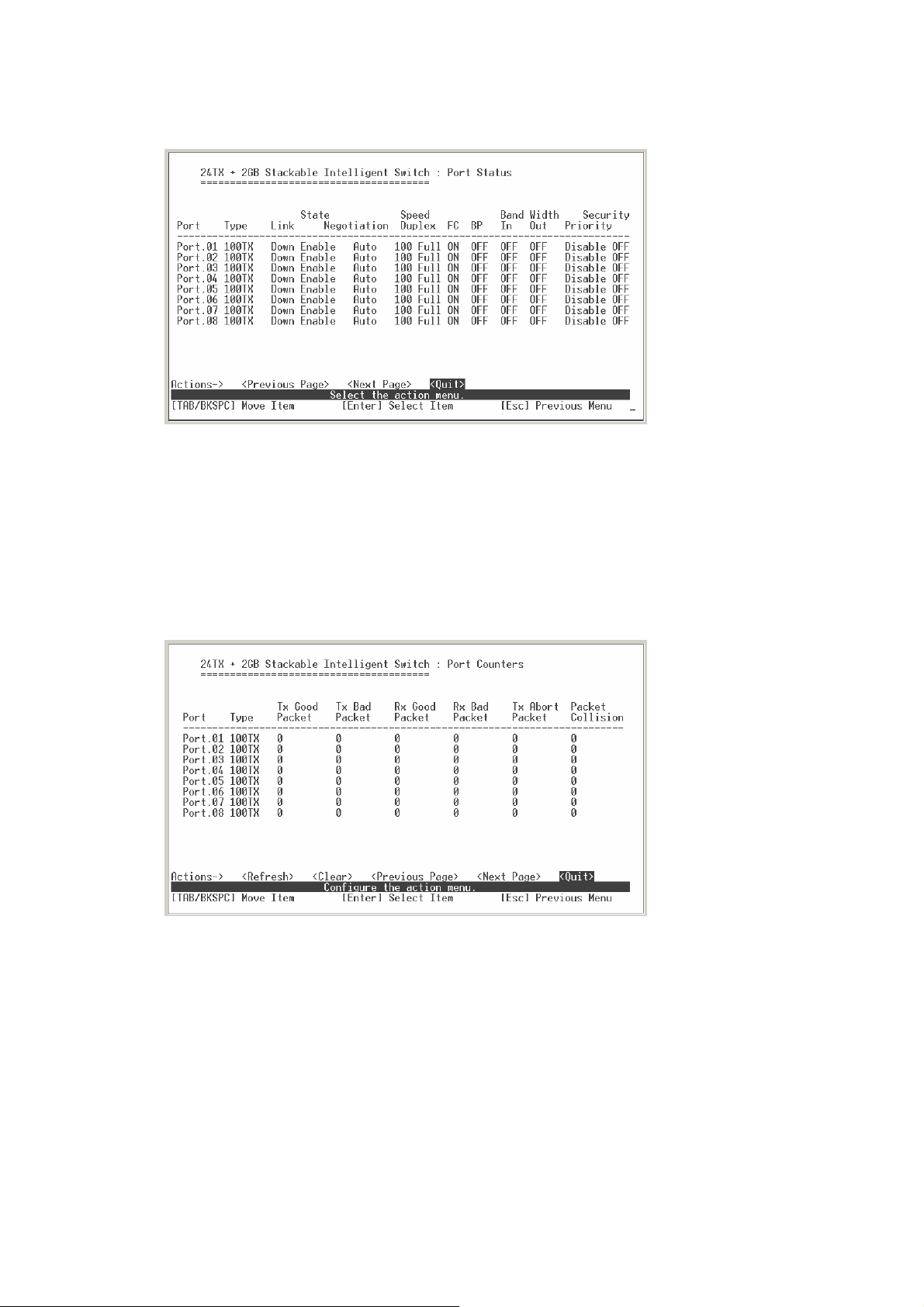
Security:
display the port security status.
Port Counters
Port status display interface
It displays the current port counter information. Select the
newest port counter information.
Port counter information interface
<Refresh>
action to get
19
Page 26

System Information
It displays the system parameter.
1.
System Name:
2.
System Location:
3.
System Description:
4.
Firmware Version:
5.
Hardware Version:
6.
Kernel Version:
7.
MAC Address:
8.
Module Information:
the name of device.
where the device is located.
the name of device type.
the switch’s firmware version.
the switch’s Hardware version.
the system kernel software version.
The unique hardware address assigned by manufacturer.
display the Module type that you have installed in switch.
System Information interface
20
Page 27

Switch Static Configuration
In Switch Static Configuration, it has 8 main functions – Administration, Port, Trunk,
Port Mirroring, VLAN, Priority, MAC Address, and Misc Configuration. Under each
function, there are more sub-functions. We will describe in following paragraph.
Switch Configur ation interface
Administration Configuration
In Administration Configuration, you can configuration system parameter, IP, login
username and password.
Administration Configuration main interface
21
Page 28

Device Information
You can configure the device information.
1. Select
2.
Name:
3.
Description:
4.
Location:
5.
Contact:
6. Select
<Edit>
assign the name for the switch.
<Save>
action to configure.
a short description for the switch.
the switch location, ex: Taipei.
the contact person or information.
action to save the configuration.
Device Information interface
IP Configuration
You can configure the IP for this switch. The system has the default IP address. You
can re-configure or use the default value.
1. Select the
2.
DHCP:
3.
IP Address:
4.
Subnet Mask:
5.
Gateway:
6. Select
Always restart the switch after finished the setup.
Note:
<Edit>
disable or enable the DHCP client function.
assign the switch IP address. The default IP is 192.168.16.1.
assign the switch IP subnet mask.
assign the switch gateway. The default value is 192.168.16.254.
<Save>
action to save the configuration.
22
Page 29

IP Configuration interface
User Name Configuration
You can change the console and web management login user name.
1. Select the
<Edit>
2. Enter the new user name
3. Select the
<Save>
User Name Configuration interface
23
Page 30

Password Configuration
You can change the console and web management login password.
1. Select the
2.
Old Password:
3.
New Password:
4.
Enter Again:
5. Select the
<Edit>
enter the old password.
enter the new password.
reenter the new password for confirmation.
<Save>
Password Configuration interface
Port Configuration
You can set up every port status.
1. Select
2. Use “
3.
State:
<Edit>
Tab
Current port status. The port can be set to disable or enable mode. If the
port setting is disable then will not receive or transmit any packet.
4.
Negotiation:
5.
Speed/Duplex:
6.
enable or disable
FC:
mode).
” key to move between items.
set auto negotiation status of port.
set the port link speed and duplex mode.
Flow control
function (Flow control for full duplex link
24
Page 31

7.
8.
9.
10.
11. Select the
enable or disable
BP:
mode).
Bandwidth In/ Out:
100Kbps. It supports individual control method of TX and RX.
Priority:
Security:
set port to high or low priority.
enable or disable port security function.
<Save>
Back Pressure
per port packet transmission rate control. Per level is
.
function (Backpressure for half duplex
Port Configuration interface
Trunk Configuration
You can configure port trunk group.
1. Select
2. Using “
3. Using “
4. Using
Static
5. Save the configuration by selecting
<Edit>
Tab
.
” key move to the port that want to be added as trunk group.
Tab
” key to mark the port.
Space
key move to
(ex. TRK1, TRK2…) to change the TRK# value to
TRK#
<Save>
25
.
Page 32

Trunk Configuration interface
Port Mirroring Configuration
The port mirroring is a method for monitor traffic of switched networks. The specific
port can monitor traffic through the mirror ports. The monitored ports in or out traffic will
be duplicated into monitoring port.
1. Select the
2.
Mirroring State:
<Edit>
select the port-mirroring mode. The default value is “
Disable
start port mirroring, you must select one of port mirroring mode.
RX packet only
RX:
TX packet only
TX:
RX and TX packet
Both:
”. To
26
Page 33

Port Mirroring interface
3.
Analysis port:
Set the destination port of mirroring packet. All of the packets of
mirroring port will be duplicated and sent to Analysis port.
4. Use “
Space
5. Select the
” key to mark the mirroring port can.
<Save>
.
Port Mirroring interface
27
Page 34

VLAN Configuration
You can configure VLAN in VLAN Configuration. There are four functions in VLAN
Configuration mode: VLAN Configuration, Create a VLAN Group, Edit/Delete VLAN
Group and Group Sorted Node. Follow the below description to configure VLAN.
VLAN Configuration Main interface
VLAN Configure
Before starting to configure VLAN, you must select the VLAN mode in VLAN Configure
function. Otherwise, user cannot create any new VLAN.
1. Select the
<Edit>
2. Select the VLAN mode by using “
PortBase mode and 802.1Q mode.
802.1Q VLAN mode:
Frame Type.
VLAN ID (Port VID: 1~255):
Ingress Filter:
.
” key. There are two VLAN modes:
Space
configuration VLAN ID, Ingress Filter, and Acceptable
Type the PVID.
It matches that Ingress Filtering Rule 1 on web. Only
forward packets with VID matching this port’s configured VID. Press
“
Space
” key to choose forward or drop the frame that VID not matching
this port’s configured VID.
Acceptable Frame type:
It matches that Ingress Filtering Rule 2 on web.
28
Page 35

3. Select
Drop untagged frame. Press “
untagged frame.
<Save>
to save the configuration.
VLAN Configure interface
Space
” key to select drop or forward the
Create VLAN Group
Create Port-Based VLAN
1. Select
2.
VLAN Name:
3.
Group ID:
4.
Member:
<Edit>.
Type a name for the new VLAN, ex: VLAN01.
Type the VLAN group ID. The group ID rang is from 1 to 4094.
Press ”
Space
” key to change the member value. There are two types to
selected:
a.
Member:
b.
NO:
5. Press
6. Select
NOTE:
the port is a member port.
it means that port is NOT a member port.
“ESC”
key to go back action menu line.
<Save>
to save the configuration.
If you had configured the trunk groups, you can see it (ex: TRK1, TRK2…)
in the port list. You also can configure the trunk group as the VLAN member.
29
Page 36

Create 802.1Q VLAN
Create VLAN Group: PortBase interface
1.
Enable security VLAN setting:
select to enable or disable security VLAN group.
When you select to enable security VLAN group, only the members in this VLAN
group can access to the switch. The steps of setting security VLAN refer to the
following step 2~ 8. After you have configured the security VLAN group, you can
continue to create other VLAN groups. When you don ’t sele ct to configure security
VLAN group, then just create VLAN group refer to following step 2 ~ 8.
There is only one security VLAN group.
Note:
Select
2.
3.
VLAN Name:
4.
VLAN ID:
<Edit>
.
Type a name for the new VLAN, ex: VLAN01.
Type a VID (between 1~4094). The default is 1. There are 256 VLAN
groups to provided configure.
5.
Protocol VLAN:
6.
Member:
Untagged:
Press “
Press “
Space
Space”
” key to change the member value.
this port is the member port of this VLAN group and outgoing
key to choose protocols type.
frames are NO VLAN-Tagged frames.
Tagged:
this port is the member port of this VLAN group and outgoing frames
are VLAN-Tagged frames.
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
NO:
Press “
7.
8. Select
it means that the port is NOT member of this VLAN group.
” key to go back action menu line.
ESC
<Save>
to save the configuration.
30
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Page 37

Create VLAN Group: 802.1Q interface
Edit / Delete VLAN Group
User can edit or delete a VLAN group.
1. Select
<Edit>
or
<Delete>
action.
2. Select the VLAN group that you want to edit or delete, then press enter.
3. In
<Edit>
action, user can modify the member port and remove some member
ports from this VLAN group.
4. After edit or delete the VLAN, select
<Save>
action to save all configures value.
NOTE:
1. The VLAN Name and VLAN ID cannot modify.
2. In 802.1Q VLAN mode, the default VLAN can’t be deleting.
3. In Port Base VLAN mode, there is no default VLAN.
31
Page 38

Group Sorted Mode
Edit/Delete a VLAN Group interface
You can select VLAN groups sorted mode: (1)
Name
(2)
VLAN ID
In the Edit/Delete a VLAN group page will display the result.
1. Select
2. Use “
3. Select
<Edit>
Space
<Save>
” key to select the sort mode.
Group Sorted Mode interface
.
32
Page 39

Priority Configuration
You can configure port priority level. There are 0~7-priority level can map to high or low
queue.
1. Select
2. Press “
3.
Qos Mode:
<Edit>
Space
.
” key to select the priority level mapping to high or low queue.
select the mode to process incoming packets.
First Come first service: the switch will process the packet that is coming first.
All High Before low: the packet priority is high will be process before the
packet priority is low.
Weight Round Ration 2:1: the switch will process 2 high priority packet first,
the process 1 low priority packet.
Weight Round Ration 3:1: the switch will process 3 high priority packet first,
the process 1 low priority packet.
Weight Round Ration 4:1: the switch will process 4 high priority packet first,
the process 1 low priority packet.
Weight Round Ration 5:1: the switch will process 5 high priority packet first,
the process 1 low priority packet.
Weight Round Ration 6:1: the switch will process 6 high priority packet first,
the process 1 low priority packet.
Weight Round Ration 7:1: the switch will process 7 high priority packet first,
the process 1 low priority packet.
4. Press “
5. Select
” goes back action menu line.
ESC
<Save>
to save all configure value.
33
Page 40

Priority Configuration interface
MAC Address Configuration
When you add a static MAC address, it remains in the switch's address table,
regardless of whether the device is physically connected to the switch. This saves the
switch from having to re-learn a device's MAC address when the disconnected or
powered-off device is active on the network again. You can add / modify / delete a
static MAC address.
MAC Address Configuration interface
34
Page 41

Static MAC Address
Add the Static MAC Address
You can add static MAC address in switch MAC table.
1. Select
2.
MAC Address:
<Add> Æ <Edit>
Enter the MAC address of the port that should permanently
key to add the static MAC address.
forward traffic, regardless of the device network activity.
3.
4.
Port No.:
VLAN ID:
press “
Space”
key to select the port number.
enter the Mac address’ s VLAD ID, if the Mac address belong to any
VLAN group.
Press “
5.
6. Select
to go back action menu line.
ESC”
<Save>
to save all configure value.
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Add Static MAC Address interface
Edit static MAC address
1. Select
<Edit>
.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to modify and then press “
3. Press
<Edit>
4. Press “
5. Select
key to modify.
” to go back action menu line.
ESC
<Save>
to save all configure value.
35
Enter
”.
Page 42

Delete static MAC address
1. Select
<Delete>
key.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to delete and then press “
3. When pressing “
” will complete deletion.
Enter
Filtering MAC Address
You can add, delete, and edit filtering MAC address.
Enter
”.
Add the Filtering MAC Address
1. Select
2.
3. Press “
4. Select
<Add> Æ <Edit>
MAC Address:
to go back action menu line.
ESC”
<Save>
Enter the MAC address that you want to filter.
to save all configure value.
Filtering MAC Address interface
key to add the static MAC address.
36
Page 43

Edit Filtering MAC address
Add Filtering MAC Address interface
1. Select
<Edit>
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to modify and then press “
3. Select
4. Press “
5. Select
<Edit>
ESC
<Save>
key to modify a static Filtering address.
key to modify.
” to go back action menu line
to save all configure value.
Enter
”.
Delete Filtering MAC address
1. Select
<Delete>
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to delete and then press “
3. After delete Filtering MAC address, you have to select
to delete a Filtering MAC address.
<Save>
”.
Enter
to complete the
deleting operation.
Misc Configuration
You can configure the switch parameters and stacking function. The stacking function
provides you can centralize the control of the switch in the network. For the manager
personal, he/she can save the time and easily on switches controlling.
MAC Address Ageing Time:
37
MAC address table refresh time setting. Type the
Page 44

number of seconds that an inactive MAC address remains in the switch’s address
table. The valid range is 0, 300~765 seconds. Default is 300 seconds.
Broadcast Storm Filter mode:
configure the broadcast storm filter mode. The
valid threshold values are 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, and N/A. The port will be
block cause of broadcast packet is over the percentage of traffic.
Max Bridge Transmit Delay Bound:
enable, the packets queued exceed will be drop. Press
Limit the packets queuing time in switch. If
key to set the time.
Space
This valid value are 1sec, 2sec, 4sec and off. Default is off.
Low Queue Delay Bound:
Limit the low priority packets queuing time in switch. If
enable, the low priority packet stays in switch exceed Low Queue Max Delay Time,
it will be sent. Press
Low Queue Max Delay Time:
Space
key to enable or disable this function.
To set the time that low priority packets queuing in
switch. Default Max Delay Time is 255ms. The valid range is 1~255 ms.
Make sure of “Max bridge transit delay bound control” is enabled before enable
NOTE:
Low Queue Delay Bound, because Low Queue Delay Bound must be work under “Max
bridge transit delay bound control” is enabled situation.
Collisions Retry Forever:
Disable – In half duplex, if happens collision, the
switch will retry 48 times and then drop frame. Enable – In half duplex, if happens
collision, the switch will retry forever
Hash Algorithm:
This Hash Algorithm is for hardware maintain on MAC table
calculation. Provide CRC or Direct Map
IFG compensation:
IP Stacking Group ID (0…65535):
Disable or Enable
assign the stacking group ID. The switches
must assigned the same stacking group ID to be stacked as a group.
IP Stacking Mode:
enabling/disabling the stacking function. There are three
stacking modes. Any port on the switch can be used to stack. To configure the
switch in stacking group, please use the Web GUI configuration interface.
¾
¾
Disable:
Master:
The stacking function is not working.
There must have a leader switch to control all other switches in
stacking group. You can only assign one switch to be the master switch in
one stacking group. When the stacking group is set up, the master switch will
control all switches in the stacking group.
¾
Slave:
besides the master switch, rest of the switches are called slave switch
in stacking group. When the stacking group is set up, you can only configure
38
Page 45

the slave switches through the master switch.
Note:
1. Before configuring the stacking function, make sure all stack switches are in
the same network.
2. Configure stacking function; you must configure the master switch first.
3. After you have configured the stacking function, use Cat. 5 cable to connect
every switch in the stacking group.
4. To remove the switch from stacking group, you must remove the salve switch
first. When all slave switches are removed, y ou can remove the master switch
from stacking group.
Misc Configuration interface
39
Page 46

Protocol Related Configuration
You can configure Spanning Tree Protocol, SNMP, LACP, IGMP/GVRP, and 802.1x in
Protocol Relate Configuration section.
Protocol Relate Configuration interface
STP
Spanning tree is a link management protocol that provides path redundancy
while preventing undesirable loops in the network.
STP Configuration interface
40
Page 47

STP Setup
You must enable Spanning Tree function before configure STP function.
1. Select
2. Use “
3. Select
<Edit>
Space
<Save>
” key to select the option.
.
STP Setup interface
System Configuration
You can configure the STP system parameter after enable the STP function.
view spanning tree information about the Root Bridge on the left.
1. Select
2.
Priority:
3.
Max Age:
4.
Hello Time:
STP current status.
5.
Forward Delay Time:
6. Select
41
<Edit>
assign path priority number.
the maximum path age
the time that controls switch sends out the BPDU packet to check
<Save>
forward delay time.
.
You can
Page 48

Per Port Setting
STP System Configuration interface
1. Select
2.
Path Cost:
<Edit>
.
specifies the path cost of the port that switch uses to determine which
port are the forwarding ports.
3.
Priority:
This is mean port priority; you can make it more or less likely to become
the root port.
4. Press “
5. Select
” goes back action menu line.
ESC
<Save>
to save all configure value.
6. On the action menu line you can press
press
<Previous Page>
return to previous page.
<Next Page>
to configure port9 ~ port26,
42
Page 49

Per Port Setting interface
SNMP
To define management stations as trap managers and to enter SNMP community
strings. You can also define a name, location, and contact person for the switch.
SNMP Configuration interface
43
Page 50

SNMP System Options
1. Press
2.
3.
4.
5. Press “
6. Press
<Edit>
System Name:
System Contact:
System Location:
ESC
<Save>
.
assign a name for the switch.
Type the name of contact person or organization.
Type the location of the switch.
” goes back action menu line.
to save configure value.
Community Strings
Add Community Strings
1. Select
2. Select
3.
Community Name:
4.
Write Access:
<Add>
<Edit>
Read only:
enable the rights is read only or read/write.
display MIB-object information.
Read/Write:
display MIB-object information and to set MIB objects.
SNMP System Options interface
type the name of community strings.
Read only, enables requests accompanied by this string to
Read write, enables requests accompanied by this string to
44
Page 51

Edit Community Name
Add Community Strings interface
1. Select
<Edit>
2. Choose the item that you want to modify and then press “
3.
Community Name:
4.
Write Access:
5. Select
<Save>
type the new name.
Press “
Space
.
” key to change the right.
Edit Community Strings interface
Delete Community Name
Enter”.
45
Page 52

1. Select
<Delete>
2. Choose the community name that you want to delete and then press “
3. When pressing “
.
” will complete deletion.
Enter
Enter
”.
Trap Managers
A trap manager is a management station that receives traps, the system alerts
generated by the switch. If no trap manager is defined, no traps will issue. Create a
trap manager by entering the IP address of the station and a community string.
Add the trap manager
1. Select
2.
IP:
3.
Community Name:
4. Press “
5. Select
<Add>
enter the IP address of trap manager.
” go back to actions menu line
ESC
<Save>
Trap Managers interface
Æ
<Edit>
to add the trap manager.
enter the community string.
to save all configure.
46
Page 53

Delete Trap Manager
Add Trap Manager interface
1. Select
<Delete>
2. Choose the trap manager that you want to delete and then press “
3. When pressing “
” will complete deletion.
Enter
Enter
”.
LACP
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for
exchanging information between Partner Systems on a link to allow their Link
Aggregation Control instances to reach agreement on the identity of the Link
Aggregation Group to which the link belongs, move the link to that Link Aggregation
Group, and enable its transmission and reception functions in an orderly manner. Link
aggregation lets you group up to eight consecutive ports into a single dedicated
connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the network.
operation requires full-duplex mode,
more detail information refers to IEEE 802.3ad.
You can configure and view all the LACP status.
LACP
47
Page 54

Working Ports Setting
LACP Configuration interface
1. Select
2.
Group:
3.
LACP:
<Edit>
Press “
Display the trunk group ID.
Space
” key to enable or disable LACP (Link Aggregation Control
Protocol) support. When LACP enable, the group is LACP static trunk group.
When LACP disable, the group is local static trunk group.
4.
Working Port Num:
The max number of ports can be aggregated at the same
time. If LACP static trunk group, the exceed ports is standby and able to
aggregate if work ports fail. If it is local static trunk group, the number must be the
same as group ports.
5. Select
NOTE:
<Save>
Before set LACP support, you have to set trunk group on the Trunk
Configuration.
48
Page 55

LACP State Activity
LACP Working Ports configuration interface
1. Select
2. Use “
<Edit>
Space
Active:
Passive:
responds only if it receives LACP protocol packets from the opposite device.
3. Select
<Save>
” key to select the Port State Activity.
The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets.
The port does not automatically send LACP protocol packets, and
.
LACP State Activity configuration interface
49
Page 56

Group Status
When you setting trunk group, you can see the relation information in here.
LACP Group State interface
IGMP/GVRP
You can enable or disable the IGMP/GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration
Protocol).
1. Select
2. Use “
3. Select
<Edit>
Space
<Save>
” key to change the value
50
Page 57

802.1x
IGMP/GVRP Configuration interface
802.1x Configuration interface
802.1x Setup
1. Select
2. Use “
3. Select
51
<Edit>
Space
<Save>
” key to Enable or Disable the 802.1x.
Page 58

802.1x Setup interface
System Configuration
After enabling the IEEE 802.1X function, you can configure the parameters of this
function.
1. Select
2.
Radius Server IP:
3.
Shared Key:
<Edit>
set the Radius Server IP address.
set an encryption key for using during authentication sessions with
the specified radius server. This key must match the encryption key used on the
Radius Server.
4.
NAS, Identifier:
5.
Server Port:
set the identifier for the radius client.
set the UDP destination port for authentication requests to the
specified Radius Server.
6.
Accounting Port:
set the UDP destination port for accounting requests to the
specified Radius Server.
7. Select
<Save>
52
Page 59

Per Port Configuration
802.1x System Configuration interface
The State provides Disable, Accept, Reject and Authorize. Use “
the state value.
802.1x Per Port Setting interface
Space”
key change
53
Page 60

Misc Configuration
1. Select
2.
Quiet period:
<Edit>
set the period during which the port doesn’t try to acquire a
supplicant.
3.
TX period:
set the period the port wait for retransmit next EAPOL PDU during an
authentication session.
4.
Supplicant timeout:
set the period of time the switch wait for a supplicant
response to an EAP request.
5.
Server timeout:
set the period of time the switch wait for a server response to an
authentication request.
6.
Reauthorize Maximum:
set the number of authentication that must time-out
before authentication fails and the authentication session ends.
7.
Reauthorize period:
set the period of time after which clients connected must be
re-authenticated.
8. Select
<Save>
802.1x Misc Configuration interface
54
Page 61

System Reset Configuration
System Reset Configuration interface
Factory Default
Reset switch to default configuration.
Press “Y”, switch will load default setting. After finished load default setting, switch will
reboot automatically.
Factory Default interface
55
Page 62

System Reboot
Reboot the switch in software reset.
TFTP Configuration
It provides user to update firmware or restore EEPROM value or upload current
EEPROM value.
TFTP Update Firmware interface
Update Firmware
It provides user uses TFTP to update firmware.
1. Start the TFTP server, and copy firmware update version image file to TFTP server.
2. Select
3.
TFTP Server IP:
4.
Firmware File Name:
5. Press “
6. Select
7. When save successfully, the image file download finished, too.
8. Restart switch.
<Edit>
<Save>
.
type the IP of TFTP server.
type the image file name.
” goes back to action line.
ESC
, it will start to download the image file.
56
Page 63

Update Firmware interface
TFTP Restore Configuration
You can restore EEPROM value, which saved in TFTP server, from TFTP server.
1. Start the TFTP server.
2. Select
3.
TFTP Server IP:
4.
Restore File Name:
5. Press “
6. Select
<Edit>
ESC
<Save>
.
type the IP of TFTP server.
type the image file name.
” back to action menu line.
, it will start to download the image file.
7. When save successfully, the image file download finished too.
8. Restart switch.
57
Page 64

TFTP Restore Configuration interface
TFTP Backup Configuration
You can save current EEPROM value to TFTP server as backup. The backup file can
be restore from TFTP server when you need.
1. Start the TFTP server.
2. Select
3.
TFTP Server IP:
4.
Backup File Name:
<Edit>
5. Press “
6. Select
<Save>
.
type the IP of TFTP server.
type the image file name.
” back to action line.
ESC
key, it will start to upload the image file.
7. When save successfully, the image file upload finished too.
8. Restart switch.
58
Page 65

X-modem Upgrade
TFTP Backup Configuration interface
Before using X-modem upgrade, disconnect terminal and modify baud rate to
57600bps, then connect again.
1. Press “X” key to start upgrading from X-modem.
2. You will see the following screen displays.
3. Select “
4. Select "
5. Select "
send file
browse
1K X-modem
" under
" button to select the path.
Transfer
" of protocol and click "
menu from menu bar.
Send
" button.
59
Page 66

6. After successfully upgraded the new firmware, please modify baud rate to
9600bps.
60
Page 67

5. Web-Based Management
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the Web-Based
management.
About Web-based Management
Inside the CPU board of the switch exists an embedded HTML web site residing in
flash memory. It offers advanced management features and allow user s to manage the
switch from anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as Microsoft
Internet Explorer.
The Web-Based Management supports Internet Explorer 5.0. It is based on Java
Applets with an aim to reduce network bandwidth consumption, enhance access
speed and present an easy viewing screen.
By default, IE5.0 or later version does not allow Java Applets to open sockets.
Note:
The user has to explicitly modify the browser setting to enable Java Applets to use
network ports.
Preparing for Web Management
Before to use web management, you can use console to login the Switch checking the
default IP of the Switch. Please refer to
login. If you need change IP address in first time, you can use console mode to modify
it. The default value is as below:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Default Gateway:
User Name:
Password:
192.168.16.1
255.255.255.0
root
root
192.168.16.254
Console Management
Chapter for console
61
Page 68

Online Help
You can click
configuring.
Help
button when you have any configuration question during the
System Login
1. Launch the Internet Explorer.
2. Type http:// and the IP address of the LevelOne GSW-2491TXM. Press “
3. The login screen appears.
4. Key in the user name and password. The default user name and password is
“
”.
root
5. Click “
appears.
” or ”OK”, then the home screen of the Web-based management
Enter
Enter
”.
LevelOne GSW-2491TXM
62
Page 69

Port status
In Port status, you can view every port status that depended on user setting and the
negotiation result.
1.
2.
3.
“Down” is “No Link”. “UP” is “Link”.
Link:
display port statuses “disable” or “enable”. “Unlink” will be treated as “off ”.
State:
Auto Negotiation:
display the auto negotiation mode: auto/force/Nway-force.
“Config” means the value that user configured. “Actual” means the current value of
the port.
4.
Speed Duplex:
display port connection speed. “Config” means the value that user
configured. “Actual” means the current value of the port.
5.
Flow Control:
Full: display the flow control status is “enable” or “disable” in full
mode. “Config” means the value that user configured. “Actual” means the current
value of the port.
6.
Back Pressure:
Display the Back Pressure status setting. “Config” means the
value that user configured. “Actual” means the current value of the port.
7.
Bandwidth:
8.
Priority:
9.
Port Security:
display the port incoming and outgoing bandwidth.
display the port static priority status is “High” or “Low” or “Disable”.
display the port security is “enable” or “disable”.
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Port Status interface
63
Page 70

View the Port Information
You can direct click the port on the Switch figure on the top of web page. Then, you will
see the port information.
Port information interface
Port Statistics
The following information provides a view of the current port statistic information.
Clear
Click
button to clean all counts.
64
Page 71

Port Statistics
Administrator
In Administrator function, it provides the following functions:
IP Configuration, Switch Settings, Console Port Information, Port Controls,
Trunking, Forwarding and Filtering, VLAN Configuration, Spanning Tree, Port
Mirroring, SNMP Management, Security Manager, and 802.1x Configuration.
65
Page 72

IP Address
Administrator interface
User can configure the IP Settings and DHCP clie nt function , than clicks
Apply
button.
After reset the IP address, you must reboot the switch.
IP configuration interface
Switch Setting
In Switch setting, it has three parts of setting – Basic, Advance, and Misc Config. We
will describe the configure detail in following.
66
Page 73

Basic Switch Settings
In Basic Switch Setting, it displays the switch basic information.
System Name:
System Location:
System Description:
Firmware Version:
Kernel Version:
Hardware version:
MAC Address:
Module:
the name of switch.
the switch physical location.
the description of switch.
the switch’s firmware version.
the kernel software version.
the switch hardware version.
the unique hardware address assigned by manufacturer (default)
the module information, if the switch doesn’t install the module, then this
column will not display any information.
Switch basic setting interface
Advanced Setting
In Advanced setting, it has two sections – MAC Table Address Entry and Priority
Queue Service. After the configuration, click
Apply
button to complete the
configuration.
MAC Address Table Entry
Age-out Time:
fill in the number of seconds that an inactive MAC address
remains in the switch's address table. The valid range is 300~765 seconds.
67
Page 74

Default is 300 seconds.
Max Bridge Transmit Delay Bound Control:
limit the packets queuing time
in switch. If enable, the packets queued exceed will be drop. This valid value
are 1sec, 2 sec, 4 sec and off.
Enable Low Queue Delay Bound:
limit the low priority packets queuing time
in switch. If the low priority packet stays in switch exceed Max Delay Time, it
will be sent. The valid range is 1~255 ms.
Make sure of “Max bridge transit delay bound control” is enabled before e nable
NOTE:
Delay Bound, because Enable Delay Bound must be work under “Max bridge transit delay
bound control is enabled” situation.
Broadcast Storm Filter:
configure broadcast storm control. Enable it an d set
the upper threshold for individual ports. The threshold is the percen tage o f the
port's total bandwidth used by broadcast traffic. When broadcast traffic for a
port rises above the threshold you set, broadcast storm control becomes
active. The valid threshold value are 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and off.
Switch Advanced setting interface
68
Page 75

Priority Queue Service settings:
First Come First Service:
order.
All High before Low:
packets.
Weighted Round Ratio:
switch's high-priority queue. These options represent the number of high
priority packets sent before one low priority packet is sent. For example, 5
High: 2 Low means that the switch sends 5 high priority packets before
sending 2 low priority packet.
Qos Policy: High Priority Levels:
queue.
Miscellaneous Setting
Collisions Retry Forever:
disable is in half duplex. If happen collision will retry 48
select the priority queue service type.
the sequence of packets sent is depend on arrive
the high priority packets sent before low priority
select the preference given to packets in the
0~7 priority level can map to high or low
times and then drop frame. Enable is in half duplex. If happen collision will retry
forever.
Hash Algorithm:
IFG Compensation:
CRC Hash or Direct Map for MAC address learning algorithm
Internal Packet Gap time compensation configure. Select to
“Enable” or “Disable”.
802.1x Protocol:
IGMP Query Mode:
enable or disable 802.1x protocol.
recognizes different queries from clients or servers to decide
which Query will be the first priority. The modes are:
a.
Auto Mode:
chooses the switch that has the smallest IP ad dre ss to be set for
the IGMP Query mode.
b.
Enable Mode:
c.
Disable Mode:
enables the switch to be the IGMP Querier.
disables all other switches from being the IGMP Querier.
69
Page 76

Switch Misc Config setting interface
IGMP Theory of Operation
The following three topologies detail how IGMP Query works and to be configured
within a network:
1. Auto mode needs to be enabled when
the router’s IP address is smaller than
other switches in the subnet.
70
Page 77

2. IGMP needs to be enabled when the
router’s IP address is not smaller than
other switches in the subnet. This
Router supports IGMP protocol, but
IGMP has to be enabled, and the
Router has to be the Querier.
3. The following topology must
be set when the IP address of
the switch is not the smallest in
the subnet. The network will
cause a multi-cast storm from th e
IGMP client report if it is in Auto
mode. All switches must be in
disable mode when the VOD
server is configured for IGMP
Querier.
It is suggested that the VOD server switch have the smallest IP address.
Note:
71
Page 78

Console Port Information
Console is a standard UART interface to communicate with Serial Port. User can use
windows HyperTerminal program to link the switch. Please refer to
Management Æ Console login
for detail steps.
Console port information shows as follow:
Bits per seconds: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop Bits: 1
Flow control: none
Console Port Information interface
Port Controls
Console
You can change the port status.
1. Select the port by scroll the list in
2.
3.
User can disable or enable this port control.
State:
Negotiation:
User can set auto negotiation mode is Auto, Nway (specify the
Port
column.
speed/duplex on this port and enable auto-negotiation), Force of the port.
4.
Speed:
5.
Duplex:
6.
Flows control:
7.
Back Pressure:
8.
Band Width:
set the speed of each port.
set full-duplex or half-duplex mode of the port.
set flow control function is ON or
set Back Pressure is ON or
OFF
in Half Duplex mode.
OFF
The port1 ~ port 24, supports port ingress and egress rate control.
in Full Duplex mode.
For example, assume port 1 is 10Mbps, users can set it’s effective egress rate is
1Mbps, ingress rate is 500Kbps. The switch will perform flow control or Back
Pressure to confine the ingress rate to meet the specified rate.
fill in the port effective ingress rate. The valid range is 0 ~ 1000. The un it is
In:
72
Page 79

100K. 0: disable rate control. 1 ~ 1000: valid rate value.
9.
Priority:
fill in the port effective egress rate. The valid range is 0~1000. The unit is
Out:
100K. 0: disable rate control. 1 ~ 1000: valid rate value.
this static priority based on port, if you set the port is high priority, income
frame from this port always high priority frame.
10.
Security:
when the port is in security mode, the port will be “locked” without
permission of address learning. Only the incoming packets with SMAC already
existing in the address table can be forwarded normally. User can disable the port
from learning any new MAC addresses, and then use the static MAC addresses
screen to define a list of MAC addresses that can use the secure port.
Apply
11. Click
button to apply all configuration.
12. When you select the port, you can see port current configure shows in below
column.
Port Control interface
Trunking
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for
exchanging information between Partner Systems on a link to allow their Link
Aggregation Control instances to reach agreement on the identity of the Link
Aggregation Group to which the link belongs, move the link to that Link Aggregation
Group, and enable its transmission and reception functions in an orderly manner. Link
aggregation lets you group up to eight consecutive ports into a single dedicated
73
Page 80

connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the network.
operation requires full-duplex mode,
more detail information refers to IEEE
802.3ad.
Aggregator setting
1.
System Priority:
lowest value has the highest priority and is selected as the active LACP.
2.
Group ID:
"
3.
LACP:
Group ID
There are seven trunk groups to provided configure. Choose the
" and click
If enable, the group is LACP static trunk group. If disable , the grou p is local
static trunk group. All ports support LACP dynamic trunking group. If connecting to
the device that also supports LACP, the LACP dynamic trunking group will be
created automatically.
4.
Work ports:
static trunk group, the exceed ports are standby and able to aggregate if work
a value used to identify the active LACP. The switch with the
Select
.
allow max four ports can be aggregated at the same time. If LACP
LACP
ports fail. If it is local static trunk group, the nu mber must be a s same as the group
member ports.
5. Select the ports to join the trunk group. Allow max four ports can be aggr egated at
Add
the same time. Click
select the port and click
button to add the port. To remove unwanted ports,
Remove
button.
6. If LACP enable, you can configure LACP Active/Passive status in each ports on
State Activity page.
Apply
7. Click
8. Use
Delete
.
button to delete Trunk Group. Select the Group ID and click
Delete
button.
74
Page 81

Trunking—Aggregator Setting interface
Aggregator Information
When you had setup the LACP aggregator, you will see relation information in here.
Trunking – Aggregator Information interface
Aggregator Information State Activity
When you had setup the LACP aggregator, you can configure port state activity. You
75
Page 82

can mark or un-mark the port. When you mark the port and click
port state activity will change to
1.
2.
Active:
Passive:
The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets.
The port does not automatically send LACP protocol packets, and
Active
. Opposite is
Passive
.
Apply
button the
responds only if it receives LACP protocol packets from the opposite device.
Note:
1. A link having either two active LACP ports or one active port can perform
dynamic LACP trunking.
2. A link has two passive LACP ports will not perform dynamic LACP trunking
because both ports are waiting for and LACP protocol packet from the op posite
device.
3. If you are active LACP’s actor, when you are select trunking port, the active
status will be created automatically.
Trunking – State Activity interface
76
Page 83

Forwarding and Filtering
A
A
IGMP Snooping
The switch support IP multicast, you can enable IGMP protocol on web management’s
switch setting advanced page, then display the IGMP snoopin g information in this page,
you can view difference multicast group VID and member port in here, IP multicast
addresses range from 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of the Internet
Protocol (IP) suite. IP manages multicast traffic by using switches, routers, and hosts
that support IGMP. Enabling IGMP allows the ports to detect IGMP queries and report
packets and manage IP multicast traffic through the switch. IGMP have three
fundamental types of message as follows:
Message Description
Query
A message sent from the querier (IGMP router or switch) asking for a
response from each host belonging to the multicast group.
message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that the host
wants to be or is a member of a give n group indicated in the report
Report
Leave
Group
When you enable the IGMP Snooping, you will see the relate information show as
following figure .
77
message.
message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that the host has
quit to be a member of a specific multicast group.
Page 84

A
IGMP Snooping interface
Static MAC Address
When you add a static MAC address, it remains in the switch's address table,
regardless of whether the device is physically connected to the switch. This saves the
switch from having to re-learn a device's MAC address when the disconnected or
powered-off device is active on the network again.
1. In
MAC Address
column, enter the MAC address to and from which the port
should permanently forward traffic, regardless of the device network activity.
2. In the
3.
Port Number
VLAN ID:
If tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLANs are set up on the switch, static
box, select a port number.
addresses are associated with individual VLANs. Type the VID (tag-based VLANs)
to associate with the MAC address.
4. Click
5. Use
dd
button.
Delete
button to delete unwanted MAC address.
78
Page 85

A
Static MAC Address interface
MAC filtering
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. Traffic is filtered
based on the destination addresses.
1. In
2.
MAC Address
VLAN ID:
If tag-based (802.1Q) VLAN are set up on the switch, in the VLAN ID
box, enter the MAC address that wants to filter.
box, type the VID to associate with the MAC address.
dd
3. Click
4. Use
button.
Delete
button to delete unwanted MAC address.
79
Page 86

VLAN configuration
MAC Filtering interface
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical network grouping that limits the broadcast domain. It
allows you to isolate network traffic so only members of the VLAN receive traffic from
the same VLAN members. Basically, creating a VLAN from a switch is logically
equivalent of reconnecting a group of network devices to another Layer 2 switch.
However, all the network devices are still plug into the same switch physically.
The switch supports port-based, 802.1Q (tagged-based) and protocol-base VLAN in
web management page. In the default configuration, VLAN support is “disable”.
80
Page 87

VLAN Configuration interface
Port-based VLAN
Packets can go among only members of the same VLAN group. Note all unselected
ports are treated as belonging to another single VLAN. If the port-based VLAN enabled,
the VLAN-tagging is ignored.
In order for an end station to send packets to different VLANs, it itself has to be either
capable of tagging packets it sends with VLAN tags or attached to a VLAN-aware
bridge that is capable of classifying and tagging the packet with different VLAN ID
based on not only default PVID but also other information about the packet, such as
the protocol.
81
Page 88

A
VLAN – PortBase interface
1. Click
dd
to create a new VLAN group.
2. Enter the VLAN name, group ID and select the members of VLAN group.
Apply
3. Click
.
VLAN—PortBase Add interface
82
Page 89

4. You will see the VLAN displays.
5. If the groups’ list is over one page, you can click
Next P age
to view other VLAN
groups.
6. Use
7. Use
Delete
Edit
button to delete unwanted VLAN.
button to modify existing VLAN group.
802.1Q VLAN
Tagged-based VLAN is an IEEE 802.1Q specification standard. Therefore, it is
possible to create a VLAN across devices from different switch venders. IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN uses a technique to insert a “tag ” into the Ethernet frame s. Tag contains a VLAN
Identifier (VID) that indicates the VLAN numbers.
You can create Tag-based VLAN, and enable or disable GVRP protocol. There are
256 VLAN groups to provide configure. Enable 802.1Q VLAN, the all ports on the
switch belong to default VLAN, VID is 1. The default VLAN can’t be deleting.
GVRP allows automatic VLAN configuration between the switch and nodes. If the
switch is connected to a device with GVRP enabled, you can send a GVRP request
using the VID of a VLAN defined on the switch; the switch will automatically add that
device to the existing VLAN.
802.1q VLAN interface
83
Page 90

A
A
Basic
1. Click
dd
button.
2.
Enable GVRP Protocol:
3.
Group Name:
4.
VLAN ID:
5.
Protocol VLAN:
assign a name for the new VLAN.
fill in a VLAN ID (between 2-4094). The default is 1.
choose the protocol type. Default is NONE.
check the check box to enable GVRP protocol.
6. From the Available ports box, select ports to add to the switch and click
dd
button. If the trunk groups exist, you can see it in here (ex: TRK1, TRK2…),
and you can configure it is the member of the VLAN or not.
7. Click
802.1q VLAN –Add interface
Next
. Then you will see the page as follow.
84
Page 91

8. To set the outgoing frames are VLAN-Tagged frames or untagged. Then click
Apply
.
Tag: outgoing frames with VLAN-Tagged.
Untag: outgoing frames without VLAN-Tagged.
Port VID:
Configure port VID settings
1.
Port VLAN ID:
2.
Ingress Filtering:
forwarded if the port belongs to that VLAN.
Enable
Disable
3.
Acceptable Frame type:
Tag Only:
enter the port VLAN ID.
Ingress filtering lets frames belonging to a specific VLAN to be
: Forward only packets with VID matching this port's configured VID.
: Disable Ingress filter function
Only packet with match VLAN ID can be permission to go through
the port.
4.
VLAN ID Range:
Acceptable all Packet
ALL:
select a range of VLAN ID. There are 16 VLAN ID range. The
ports are assigned to the same VLAN ID will be in the same VLAN group.
Apply
5. Click
6. To reset back to default value, click
.
Default
button.
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
85
Page 92

802.1q VLAN – Port VLAN ID interface
Spanning Tree
The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) is a standardized method (IEEE 802.1d) for
avoiding loops in switched networks. When STP enabled, to ensure that only one path
at a time is active between any two nodes on the network. We are recommended that
you enable STP on all switches ensures a single active path on the network.
86
Page 93

Spanning Tree – System Configuration interface
System Configuration
1. You can view spanning tree information about the Root Bridge.
2. You can view spanning tree status about the switch.
Apply
3. You can modify STP state. After modification, click
Priority:
Max Age:
Hello Time:
check STP current status.
Forward Delay Time:
assign path priority number.
the maximum path age
the time that controls switch sends out the BPDU packet to
forward delay time.
button.
Per Port Configuration
You can configure path cost and priority of every port.
1. Select the port in Port column.
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
2. Assign the Path Cost. The value range is from 1 to 65535.
87
Page 94

3. Assign the port priority value. The value range is from 0 to 255. The lowest value
has higher priority.
Apply
4. Click
button.
SPT – Per Port Configuration interface
Port Mirroring
The Port mirroring is a method for monitor traffic in switched networks. Traffic through
ports can be monitored by one specific port. That is, traffic goes in or out monitored
ports will be duplicated into mirror port.
1.
Port Mirroring State:
set mirror mode: Disable, RX, TX, and Both.
88
Page 95

2.
Analysis Port:
It’s mean mirror port can be used to see all monitor port traffic.
You can connect mirror port to LAN analyzer or Netxray.
3.
Monitor Port:
the ports you want to monitor. All monitor port traffic will be copied
to mirror port. You can select max 25 monitor ports in the switch. User can choo se
which port want to monitor in only one mirror mode.
If you want to disable the function, you must select monitor port to none.
Note:
Prot Mirroring interface
89
Page 96

SNMP Management
The SNMP is a Protocol that governs the tran sfer of in for mation between management
and agent. The switch supports SNMP V1.
You can define management stations as trap managers and to e nter SNMP commun ity
strings. You also can define a name, location, and contact person for the switch. Fill in
the system options data, and then click Apply to update the changes.
System Options
1.
2.
3.
Name:
enter a name for the switch.
Location:
Contact:
enter the switch physical location.
enter the name of contact person or organization.
SNMP Management interface
90
Page 97

A
A
Community strings
Serve as a password between trap manager and switch.
1.
2.
String:
RO:
fill the name of string.
Read only. Enables requests accompanied by this string to display
MIB-object information.
3.
Read write. Enables requests accompanied by this string to display
RW:
MIB-object information and to set MIB objects.
4. Click
dd
.
Trap Manager
A trap manager is a management station that receives traps, the system alerts
generated by the switch. If no trap manager is defined, no traps will issue. Create a
trap manager by entering the IP address of the station and a community string.
1.
IP Address:
2.
Community Strings:
3. Click
fill in the trap device IP.
the trap device community strings.
dd
.
Security Manager
You can change web management login user name and password.
1.
User name:
2.
Password:
Confirm password:
3. Click
type the new user name. The default is “root”
type the new password. The default is “root”
retype the new password.
Apply
.
Security Manager interface
91
Page 98

802.1X
When enabling the IEEE 802.1X function, you can configure the parameters of this
function.
System Configuration
1.
Radius Server IP:
2.
Server Port:
set the Radius Server IP address.
set the UDP destination port for authentication requests to the
specified Radius Server.
3.
Accounting Port:
set the UDP destination port for accounting requests to the
specified Radius Server.
4.
Shared Key:
set an encryption key for use during authentication session s wit h the
specified radius server. This key must match the encryption key used on the
Radius Server.
5.
NAS, Identifier:
6. Click
Apply
set the identifier for the radius client.
.
802.1x Configuration – System Configuration interface
Per port Configuration
1. Select the port in Port column.
2. Select the state of port. There are four states:
Reject:
the specified port is required to be held in the Unauthorized state.
92
Page 99

Accept:
Authorized:
the specified port is required to be held in the Authorized state.
the specified port is set to the Authorized or Unauthorized state
in accordance with the outcome of an authentication exchange between the
Supplicant and the authentication server.
Disable:
3. Click
Apply
The specified port is required to be held in the Authorized state.
.
4. You can see the every port Authorization information list in table.
Misc Configuration
1.
Quiet period:
supplicant.
2.
TX period:
Set the period during which the port doesn’t try to acquire a
Set the period the port waits to retransmit next EAPOL PDU during an
802.1x Configuration – Per Port Configuration
93
Page 100

authentication session.
3.
Supplicant timeout:
Set the period of time the switch waits for a supplicant
response to an EAP request.
4.
Server timeout:
Set the period of time the switch waits for a server response to
an authentication request.
5.
Max requests:
Set the number of authentication that must time-out before
authentication fails and the authentication session ends.
6.
Reauth period:
re-authenticated.
7.
Click
Apply
Set the period of time after which clients connected must be
.
802.1x Configuration – Misc Configuration interface
TFTP Update Firmware
It provides the functions to allow a user to update the switch firmware. Before updating,
make sure you have your TFTP server ready and the firmware image is on the TFTP
server.
1.
TFTP Server IP Address:
2.
Firmware File Name:
Apply
3. Click
.
fill in your TFTP server IP.
the name of firmware image.
94
 Loading...
Loading...