Page 1

LevelOne
FBR-1430
VPN Broadband Router, 1W 4L
User Manual
V1.0.0-0702
Page 2

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ...................................................................................................................................................... 1
VPN BROADBAND ROUTER FEATURES............................................................................................................................................ 1
Internet Access Features............................................................................................................................................................. 1
Advanced Internet Functions ...................................................................................................................................................... 1
LAN Features .............................................................................................................................................................................. 2
Configuration & Management.................................................................................................................................................... 2
Security Features......................................................................................................................................................................... 2
IPSec VPN Gateway Features..................................................................................................................................................... 2
Microsoft VPN Gateway Support................................................................................................................................................2
PACKAGE CONTENTS ....................................................................................................................................................................... 3
PHYSICAL DETAILS .......................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Front-mounted LEDs .................................................................................................................................................................. 4
Rear Panel................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION........................................................................................................................................................6
REQUIREMENTS................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
PROCEDURE .....................................................................................................................................................................................6
CHAPTER 3 SETUP........................................................................................................................................................................ 8
OVERVIEW ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
CONFIGURATION PROGRAM ............................................................................................................................................................. 9
Preparation................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
SETUP WIZARD ..............................................................................................................................................................................11
Common Connection Types....................................................................................................................................................... 11
Home Screen .............................................................................................................................................................................13
LAN SCREEN ................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
DHCP........................................................................................................................................................................................15
PASSWORD.....................................................................................................................................................................................15
CHAPTER 4 PC CONFIGURATION........................................................................................................................................... 17
OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
WINDOWS CLIENTS........................................................................................................................................................................17
TCP/IP Settings - Overview ...................................................................................................................................................... 17
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 9x/ME:.......................................................................................................................... 18
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 2000:............................................................................................................................. 20
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows XP................................................................................................................................. 22
Internet Access .......................................................................................................................................................................... 24
MACINTOSH CLIENTS.....................................................................................................................................................................25
LINUX CLIENTS.............................................................................................................................................................................. 25
OTHER UNIX SYSTEMS................................................................................................................................................................... 25
CHAPTER 5 OPERATION AND STATUS................................................................................................................................. 26
OPERATION .................................................................................................................................................................................... 26
STATUS SCREEN.............................................................................................................................................................................26
CONNECTION STATUS - PPPOE...................................................................................................................................................... 27
CONNECTION STATUS - PPTP ........................................................................................................................................................ 30
CONNECTION STATUS - TELSTRA BIG POND .................................................................................................................................. 31
CONNECTION DETAILS - SINGTEL RAS ......................................................................................................................................... 32
CONNECTION DETAILS - FIXED/DYNAMIC IP ADDRESS ................................................................................................................. 34
CHAPTER 6 INTERNET FEATURES......................................................................................................................................... 36
OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 36
WAN PORT CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................................................................................ 37
ADVANCED SETUP ......................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Communication Applications....................................................................................................................................................40
Special Applications.................................................................................................................................................................. 40
Multi-DMZ ................................................................................................................................................................................ 41
URL Filter................................................................................................................................................................................. 42
Page 3

URL Filter Screen .....................................................................................................................................................................42
DYNAMIC DNS (DOMAIN NAME SERVER)..................................................................................................................................... 43
Dynamic DNS Screen................................................................................................................................................................43
VIRTUAL SERVERS......................................................................................................................................................................... 45
IP Address seen by Internet Users ............................................................................................................................................45
Virtual Servers Screen............................................................................................................................................................... 45
Defining your own Virtual Servers............................................................................................................................................ 46
Connecting to the Virtual Servers............................................................................................................................................. 46
OPTIONS......................................................................................................................................................................................... 47
CHAPTER 7 SECURITY CONFIGURATION............................................................................................................................ 48
OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
ACCESS CONTROL..........................................................................................................................................................................49
Access Control Screen............................................................................................................................................................... 49
Group Members Screen............................................................................................................................................................. 51
Access Control Log ................................................................................................................................................................... 51
FIREWALL RULES...........................................................................................................................................................................52
Firewall Rules Screen ............................................................................................................................................................... 52
Define Firewall Rule................................................................................................................................................................. 54
LOGS..............................................................................................................................................................................................56
E-MAIL...........................................................................................................................................................................................58
SECURITY OPTIONS........................................................................................................................................................................ 60
SCHEDULING.................................................................................................................................................................................. 62
Define Schedule Screen.............................................................................................................................................................62
SERVICES ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 63
CHAPTER 8 VPN (IPSEC)........................................................................................................................................................... 64
OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
IPSec ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
IKE ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 64
Policies......................................................................................................................................................................................64
VPN Configuration.................................................................................................................................................................... 65
COMMON VPN SITUATIONS...........................................................................................................................................................65
VPN Pass-through..................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Client PC to VPN Gateway....................................................................................................................................................... 66
Connecting 2 LANs via VPN..................................................................................................................................................... 66
VPN CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................................................................................67
VPN Policies Screen.................................................................................................................................................................. 67
Adding a New Policy.................................................................................................................................................................68
VPN EXAMPLES............................................................................................................................................................................. 77
Example 1: Connecting 2 VPN Broadband Routers................................................................................................................. 77
Example 2: Windows 2000/XP Client to LAN.......................................................................................................................... 79
Example 3: Windows 2000 Server to VPN Gateway................................................................................................................. 92
CERTIFICATES ................................................................................................................................................................................ 95
Trusted Certificates................................................................................................................................................................... 95
Requesting a Trusted Certificate............................................................................................................................................... 95
Self Certificates ......................................................................................................................................................................... 96
Requesting a Self Certificate ..................................................................................................................................................... 97
CRLS ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 99
STATUS ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 100
CHAPTER 9 MICROSOFT VPN................................................................................................................................................102
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................................................................... 102
SERVER SETUP ............................................................................................................................................................................. 102
CLIENT DATABASE....................................................................................................................................................................... 103
STATUS SCREEN...........................................................................................................................................................................105
WINDOWS CLIENT SETUP............................................................................................................................................................. 106
Windows 98/ME...................................................................................................................................................................... 106
Windows 2000......................................................................................................................................................................... 108
Windows XP............................................................................................................................................................................ 111
CHAPTER 10 OTHER FEATURES & SETTINGS .................................................................................................................114
ii
Page 4

OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................................................................... 114
CONFIG FILE ................................................................................................................................................................................ 115
NETWORK DIAGNOSTICS.............................................................................................................................................................. 116
PC DATABASE.............................................................................................................................................................................. 117
PC Database Screen................................................................................................................................................................ 117
PC Database (Admin) ............................................................................................................................................................. 119
REMOTE ADMINISTRATION ..........................................................................................................................................................121
ROUTING...................................................................................................................................................................................... 123
Overview ................................................................................................................................................................................. 123
Routing Screen........................................................................................................................................................................ 123
Configuring Other Routers on your LAN................................................................................................................................ 125
Static Routing - Example......................................................................................................................................................... 126
UPGRADE FIRMWARE................................................................................................................................................................... 128
UPNP........................................................................................................................................................................................... 129
APPENDIX A TROUBLESHOOTING....................................................................................................................................... 130
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................................................................... 130
GENERAL PROBLEMS ...................................................................................................................................................................130
INTERNET ACCESS........................................................................................................................................................................ 130
APPENDIX B SPECIFICATIONS.............................................................................................................................................. 132
VPN BROADBAND ROUTER ......................................................................................................................................................... 132
FCC STATEMENT ......................................................................................................................................................................... 132
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement........................................................................................................................................132
CE MARKING WARNING .............................................................................................................................................................. 133
iii
Page 5

Page 6
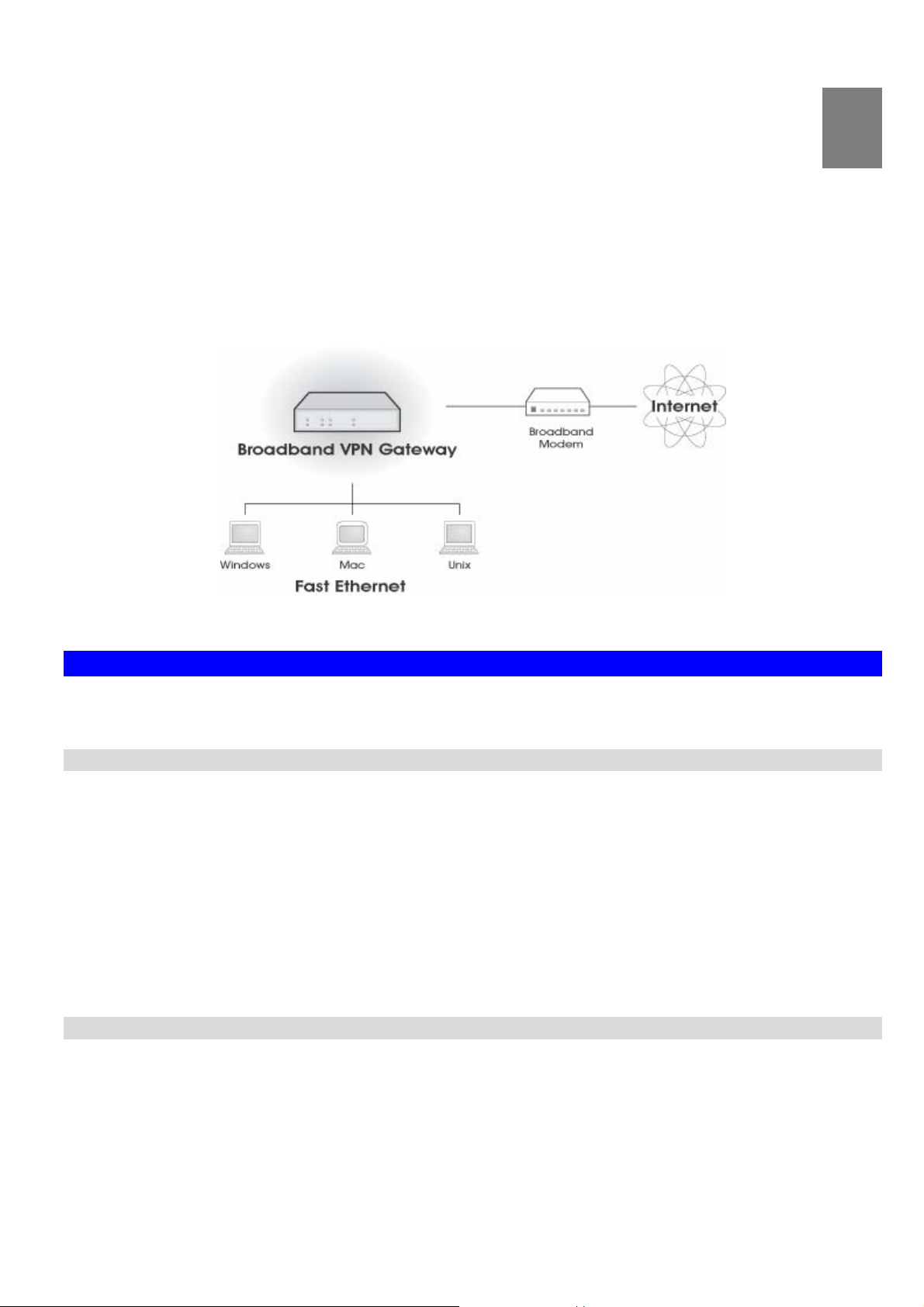
Chapter 1
Introduction
Introduction
This Chapter provides an overview of the VPN Broadband Router's features and capabilities.
Congratulations on the purchase of your new VPN Broadband Router. The VPN Broadband Router is a multi-function
device providing the following services:
Shared Broadband Internet Access for all LAN users.
•
VPN Gateway for IPSec, PPTP VPN connections to remote PCs or sites.
•
4-Port Switching Hub for 10BaseT or 100BaseT connections.
•
Figure 1: VPN Broadband Router
1
VPN Broadband Router Features
The VPN Broadband Router incorporates many advanced features, carefully designed to provide sophisticated functions while being easy to use.
Internet Access Features
• Shared Internet Access. All users on the LAN can access the Internet through the VPN Broadband Router,
using only a single external IP Address. The local (invalid) IP Addresses are hidden from external sources. This
process is called NAT (Network Address Translation).
DSL & Cable Modem Support. The VPN Broadband Router has a 100BaseT Ethernet port for connecting a
•
DSL or Cable Modem. All popular DSL and Cable Modems are supported. SingTel RAS and Big Pond (Australia)
login support is also included.
PPPoE, PPTP, SingTel RAS and Telstra Big Pond Support. The Internet (WAN port) connection sup-
•
ports PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet), PPTP (Peer-to-Peer Tunneling Protocol), SingTel RAS and Telstra Big Pond
(Australia), as well as "Direct Connection" type services.
Fixed or Dynamic IP Address. On the Internet (WAN port) connection, the VPN Broadband Router supports
•
both Dynamic IP Address (IP Address is allocated on connection) and Fixed IP Address.
Advanced Internet Functions
• Communication Applications. Support for Internet communication applications, such as interactive Games,
Telephony, and Conferencing applications, which are often difficult to use when behind a Firewall, is included.
Special Internet Applications. Applications which use non-standard connections or port numbers are nor-
•
mally blocked by the Firewall. The ability to define and allow such applications is provided, to enable such
applications to be used normally.
Virtual Servers. This feature allows Internet users to access Internet servers on your LAN. The required setup
•
is quick and easy.
1
Page 7

VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Multi-DMZ. For each WAN (Internet) IP address allocated to you, one (1) PC on your local LAN can be config-
•
ured to allow unrestricted 2-way communication with Servers or individual users on the Internet. This provides the
ability to run programs which are incompatible with Firewalls.
URL Filter. Use the URL Filter to block access to undesirable Web sites by LAN users.
•
Internet Access Log. See which Internet connections have been made.
•
VPN Pass through Support. PCs with VPN (Virtual Private Networking) software using PPTP, L2TP and
•
IPSec are transparently supported - no configuration is required.
LAN Features
• 4-Port Switching Hub. The VPN Broadband Router incorporates a 4-port 10/100BaseT switching hub, making
it easy to create or extend your LAN.
DHCP Server Support. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol provides a dynamic IP address to PCs and other
•
devices upon request. The VPN Broadband Router can act as a DHCP Server for devices on your local LAN and
WLAN.
Multi Segment LAN Support. LANs containing one or more segments are supported; via the VPN Broadband
•
Router's RIP (Routing Information Protocol) support and built-in static routing table.
Configuration & Management
• Easy Setup. Use your WEB browser from anywhere on the LAN or WLAN for configuration.
Remote Management. The VPN Broadband Router can be managed from any PC on your LAN. And, if the
•
Internet connection exists, it can also (optionally) be configured via the Internet.
UPnP Support. UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) allows automatic discovery and configuration of the VPN
•
Broadband Router. UPnP is by supported by Windows ME, XP, or later.
Configuration File Backup & Restore. You can backup (download) the VPN Broadband Router's configura-
•
tion file to your PC, and restore (upload) a previously-saved configuration file to the VPN Broadband Router.
Security Features
• Password - protected Configuration. Optional password protection is provided to prevent unauthorized
users from modifying the configuration data and settings.
NAT Protection. An intrinsic side effect of NAT (Network Address Translation) technology is that by allowing all
•
LAN users to share a single IP address, the location and even the existence of each PC is hidden. From the external viewpoint, there is no network, only a single device - the VPN Broadband Router.
Stateful Inspection Firewall. All incoming data packets are monitored and all incoming server requests are
•
filtered, thus protecting your network from malicious attacks from external sources.
Protection against DoS attacks. DoS (Denial of Service) attacks can flood your Internet connection with
•
invalid packets and connection requests, using so much bandwidth and so many resources that Internet access
becomes unavailable. The VPN Broadband Router incorporates protection against DoS attacks.
Rule-based Policy Firewall. To provide additional protection against malicious packets, you can define your
•
own firewall rules. This can also be used to control the Internet services available to LAN users.
IPSec VPN Gateway Features
• IPSec. Support for IPSec standards, including IKE and certificates.
10 Tunnels. Up to 10 VPN tunnels can be created.
•
High performance. High performance encryption engine maintains high throughput even when using 3DES.
•
Microsoft VPN Gateway Support
• PPTP Server. The VPN Broadband Router emulates a Microsoft PPTP VPN Server, allowing clients to use the
Microsoft VPN client provided in Windows.
Windows Client Support. Remote users can use the Microsoft VPN client (VPN Adapter) provided in recent
•
versions of Windows.
Easy Setup. For both the Administrator and remote users, the Microsoft VPN is much easier to configure than
•
IPSec VPN.
2
Page 8

Package Contents
The following items should be included:
• FBR-1430
• Power Adapter
• Quick Installation Guide
• CD Manual
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
Introduction
3
Page 9

VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Physical Details
Front-mounted LEDs
Power On - Power on.
Status (Red) On - Error condition.
Figure 2: Front Panel
Off - No power.
Off - Normal operation.
Blinking - This LED blinks during start up.
LAN
WAN On - Connection to the modem attached to the WAN (Internet) port
Each port has 2 LEDs
• Link/Act
• On - Corresponding LAN (hub) port is active.
• Off - No active connection on the corresponding LAN (hub)
port.
• Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the
corresponding LAN (hub) port.
• 100
• On - Corresponding LAN (hub) port is using 100BaseT.
• Off - Corresponding LAN (hub) port connection is using
10BaseT, or no active connection.
is established.
Off - No connection to a modem on the WAN (Internet) port.
Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the WAN port.
4
Page 10
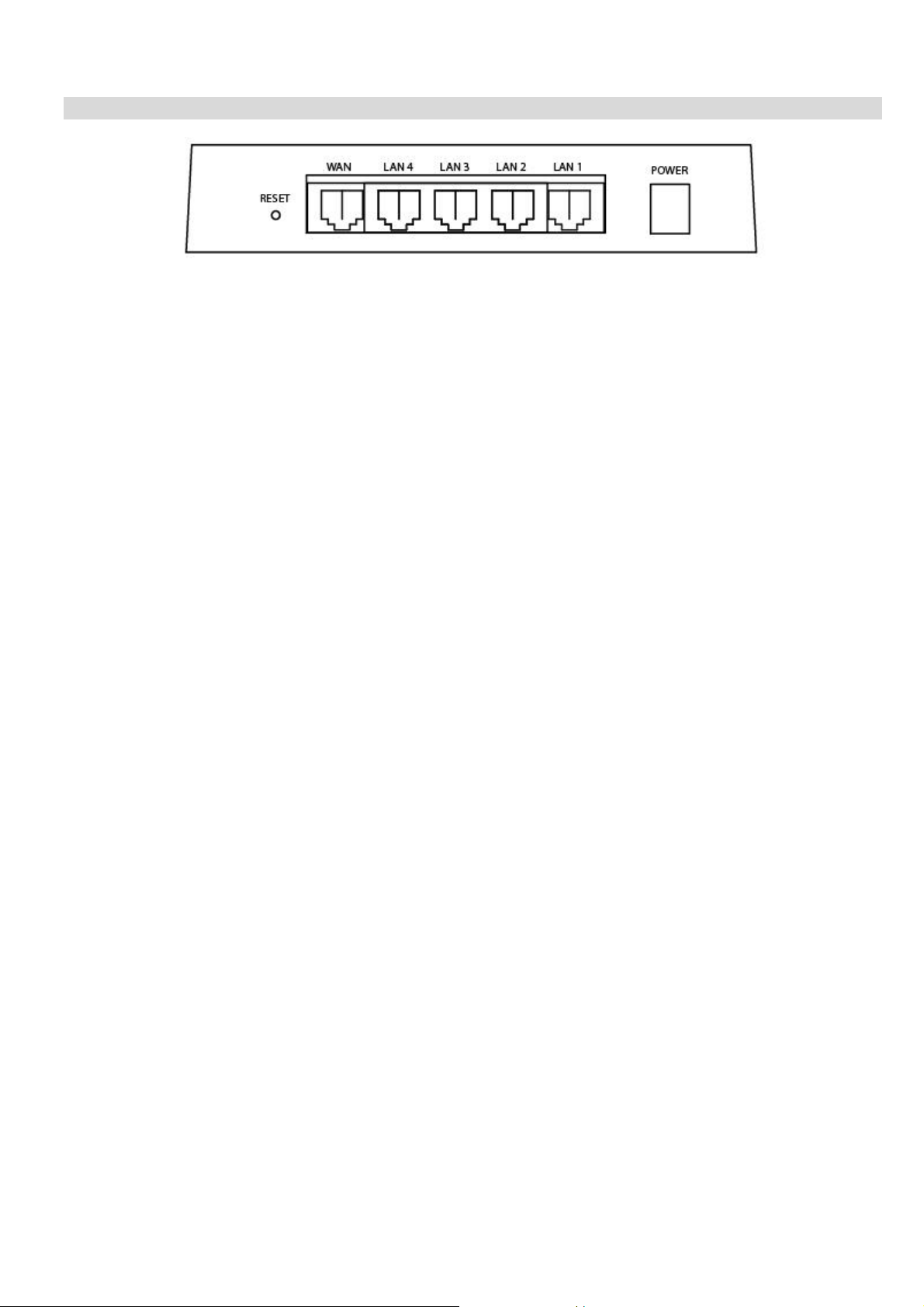
Rear Panel
Introduction
Figure 3: Rear Panel
Reset Button
WAN port
(10/100BaseT)
10/100BaseT
LAN connections
This button has two (2) functions:
• Reboot. When pressed and released, the VPN Broad-
band Router will reboot (restart).
• Clear All Data. This button can also be used to clear ALL
data and restore ALL settings to the factory default values.
To Clear All Data and restore the factory default values:
1. Power Off.
2. Hold the Reset Button down while you Power On.
3. Keep holding the Reset Button for a few seconds, until the
RED LED has flashed TWICE.
4. Release the Reset Button. The VPN Broadband Router is
now using the factory default values.
Connect the DSL or Cable Modem here. If your modem came
with a cable, use the supplied cable. Otherwise, use a standard LAN cable.
Use standard LAN cables (RJ45 connectors) to connect your
PCs to these ports.
Note:
Any LAN port on the VPN Broadband Router will automatically
function as an "Uplink" port when required. Just connect any
port to a normal port on the other hub, using a standard LAN
cable.
Power port
Connect the supplied power adapter here.
5
Page 11
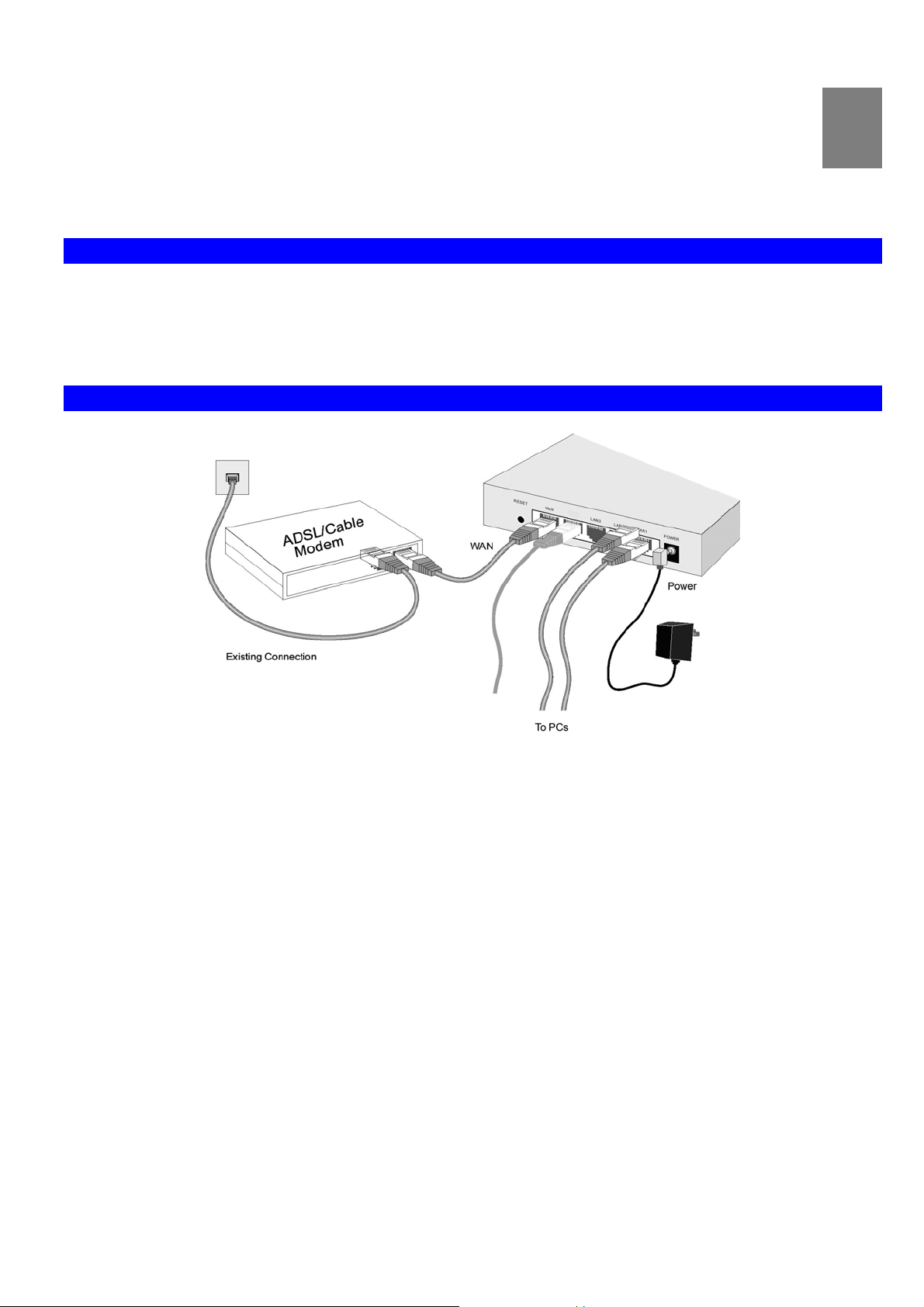
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Chapter 2
Installation
This Chapter covers the physical installation of the VPN Broadband Router.
2
Requirements
• Network cables. Use standard 10/100BaseT network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
• TCP/IP protocol must be installed on all PCs.
• For Internet Access, an Internet Access account with an ISP, and a Broadband modem (usually, DSL or Cable
modem).
Procedure
Figure 4: Installation Diagram
1. Choose an Installation Site
Select a suitable place on the network to install the VPN Broadband Router.
Ensure the VPN Broadband Router and the DSL/Cable modem are powered OFF.
2. Connect LAN Cables
• Use standard LAN cables to connect PCs to the Switching Hub ports on the VPN Broadband Router. Both
10BaseT and 100BaseT connections can be used simultaneously.
• If required, you can connect any LAN port to another Hub. Any LAN port on the VPN Broadband Router will auto-
matically function as an "Uplink" port when required. Just connect any LAN port to a normal port on the other hub,
using a standard LAN cable.
3. Connect WAN Cable
Connect the Broadband modem to the WAN port on the VPN Broadband Router. Use the cable supplied with your
Broadband modem. If no cable was supplied, use a standard LAN cable.
4. Power Up
• Power on the Broadband modem.
• Connect the supplied power adapter to the VPN Broadband Router and power up.
Use only the power adapter provided. Using a different one may cause hardware damage
6
Page 12

5. Check the LEDs
• The Power LED should be ON.
• The Status LED should blink during start up, then turn Off. If it stays on, there is a hardware error.
• For each LAN (PC) connection, the LAN Link/Act LED should be ON (provided the PC is also ON.)
• The WAN LED should be ON.
For more information, refer to Front-mounted LEDs in Chapter 1.
Installation
7
Page 13
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Chapter 3
Setup
This Chapter provides Setup details of the VPN Broadband Router.
3
Overview
This chapter describes the setup procedure for:
• Internet Access
• LAN configuration
PCs on your local LAN may also require configuration. For details, see Chapter 4 - PC Configuration.
Other configuration may also be required, depending on which features and functions of the VPN Broadband Router
you wish to use. Use the table below to locate detailed instructions for the required functions.
To Do this: Refer to:
Configure PCs on your LAN. Chapter 4:
PC Configuration
Check VPN Broadband Router operation and Status. Chapter 5:
Operation and Status
Use any of the following Internet features:
• WAN Port
• Advanced Setup
• Dynamic DNS
• Virtual Servers
• Options
Chapter 6:
Internet Features
Change any of the following Security-related
settings:
• Admin Login
• Access Control
• Firewall Rules
• Logs
• E-mail
• Security Options
• Scheduling
• Services
Use the IPSec VPN features:
• VPN Policies
• Certificates
• CRLs
• VPN Status
Use the Microsoft VPN feature:
• PPTP Server in the VPN Broadband Router.
• User and Client setup.
• Checking VPN connection Status.
Chapter 7:
Security Configuration
Chapter 8:
VPN (IPSec)
Chapter 9:
Microsoft VPN
8
Page 14
Setup
Configure or use any of the following:
• Configuration File backup and restore.
• Network Diagnostic
• PC Database
• Remote Administration
• Routing
• Upgrade Firmware
• UPnP
Where use of a certain feature requires that
PCs or other LAN devices be configured, this
is also explained in the relevant chapter.
Chapter 9:
Other Features and Settings
Configuration Program
The VPN Broadband Router contains an HTTP server. This enables you to connect to it, and configure it, using your
Web Browser. Your Browser must support JavaScript. The configuration program has been tested on the following
browsers:
• Netscape V4.08 or later
• Internet Explorer V4 or later
Preparation
Before attempting to configure the VPN Broadband Router, please ensure that:
• Your PC can establish a physical connection to the VPN Broadband Router. The PC and the VPN Broadband
Router must be directly connected (using the Hub ports on the VPN Broadband Router) or on the same LAN segment.
• The VPN Broadband Router must be installed and powered ON.
• If the VPN Broadband Router's default IP Address (192.168.0.1) is already used by another device, the other
device must be turned OFF until the VPN Broadband Router is allocated a new IP Address during configuration.
Using UPnP
If your Windows system supports UPnP, an icon for the VPN Broadband Router will appear in the system tray, notifying you that a new network device has been found, and offering to create a new desktop shortcut to the newlydiscovered device.
• Unless you intend to change the IP Address of the VPN Broadband Router, you can accept the desktop shortcut.
• Whether you accept the desktop shortcut or not, you can always find UPnP devices in My Network Places (previ-
ously called Network Neighborhood).
• Double - click the icon for the VPN Broadband Router (either on the Desktop, or in My Network Places) to start the
configuration. Refer to the following section Setup Wizard for details of the initial configuration process.
Using your Web Browser
To establish a connection from your PC to the VPN Broadband Router:
1. After installing the VPN Broadband Router in your LAN, start your PC. If your PC is already running, restart it.
2. Start your WEB browser.
3. In the Address box, enter "HTTP://" and the IP Address of the VPN Broadband Router, as in this example, which
uses the VPN Broadband Router 's default IP Address:
HTTP://192.168.0.1
9
Page 15
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
If you can't connect
If the VPN Broadband Router does not respond, check the following:
• The VPN Broadband Router is properly installed, LAN connection is
OK, and it is powered ON. You can test the connection by using the
"Ping" command:
• Open the MS-DOS window or command prompt window.
• Enter the command:
ping 192.168.0.1
If no response is received, either the connection is not working, or
your PC's IP address is not compatible with the VPN Broadband
Router s IP Address. (See next item.)
• If your PC is using a fixed IP Address, its IP Address must be within the
range 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.254 to be compatible with the VPN
Broadband Router's default IP Address of 192.168.0.1. Also, the Net-
work Mask must be set to 255.255.255.0. See Chapter 4 - PC
Configuration for details on checking your PC's TCP/IP settings.
• Ensure that your PC and the VPN Broadband Router are on the same
network segment. (If you don't have a router, this must be the case.)
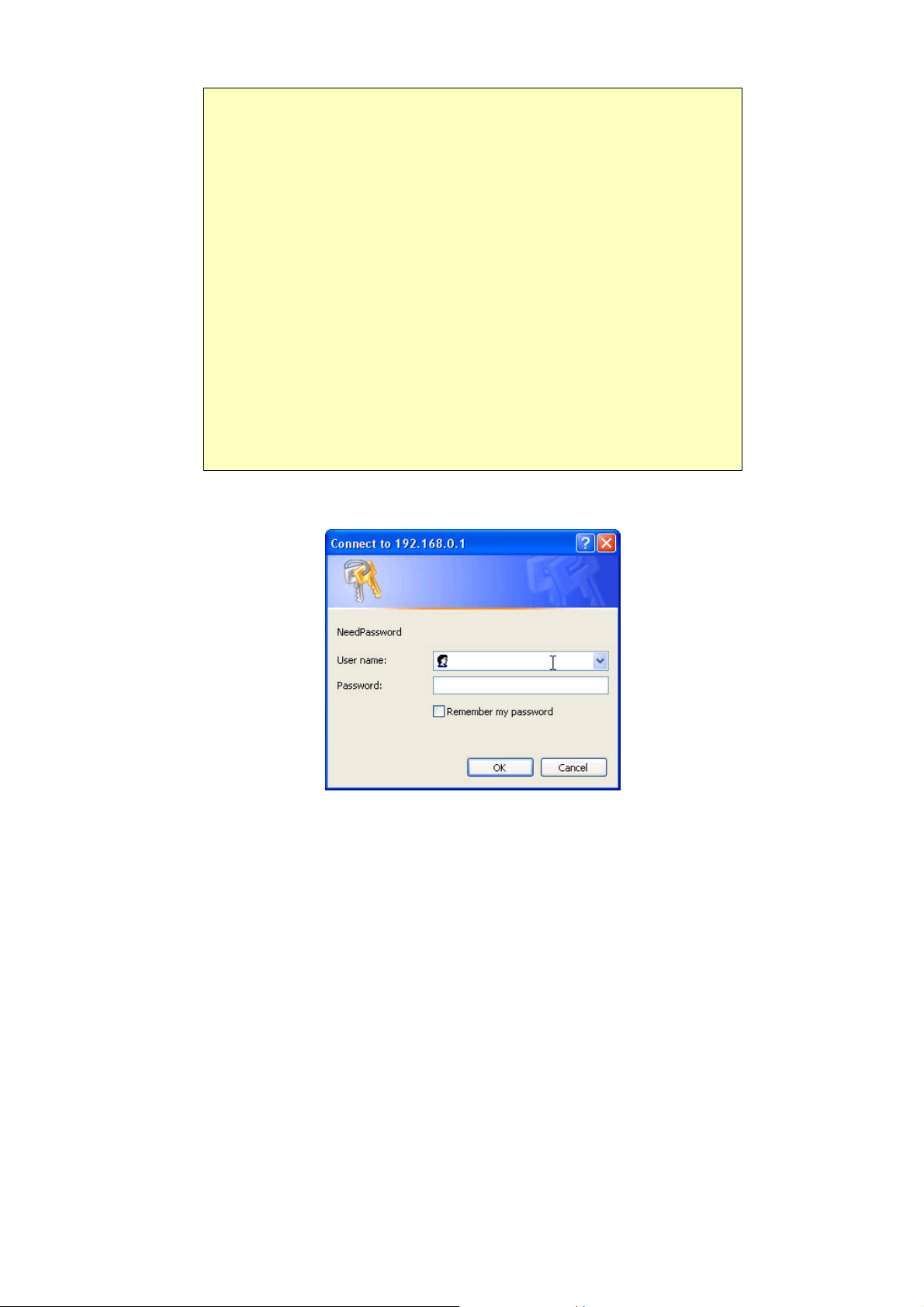
4. You will be prompted for a username and password, as shown below.
Figure 5: Password Dialog
• Enter admin for the User Name, and password for Password
• These are the default values. Both the name and password can (and should) be changed, using the Admin Login
screen. Once you have changed either the name or the password, you must use the current values.
10
Page 16
Setup Wizard
The first time you connect to the VPN Broadband Router, you should click the WAN Wizard to begin initial setup.
1. Step through the Wizard until finished.
• You need to know the type of Internet connection service used by your ISP. Check the data supplied by your
ISP.
• The common connection types are explained in the tables below.
2. On the final screen of the Wizard, run the test and check that an Internet connection can be established.
3. If the connection test fails:
• Check your data, the Cable/DSL modem, and all connections.
• Check that you have entered all data correctly.
• If using a Cable modem, your ISP may have recorded the MAC (physical) address of your PC. Run the Wiz-
ard, and on the Cable Modem screen, use the "Clone MAC address" button to copy the MAC address from
your PC to the VPN Broadband Router.
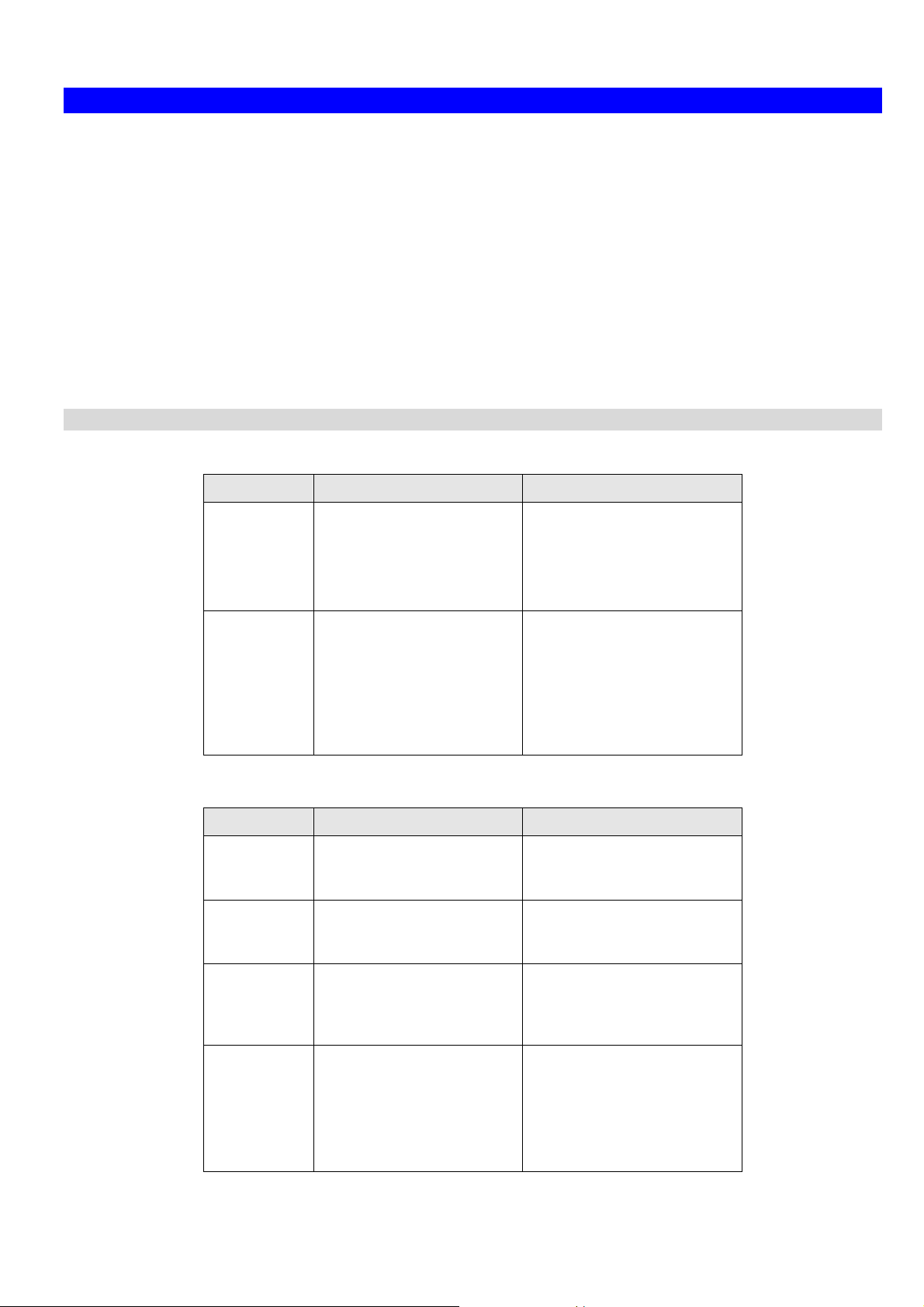
Common Connection Types
Cable Modems
Type Details ISP Data required
Setup
DSL Modems
Dynamic
IP Address
Static (Fixed)
IP Address
Type Details ISP Data required
Dynamic
IP Address
Static (Fixed)
IP Address
Your IP Address is allocated automatically, when
you connect to you ISP.
Your ISP allocates a permanent IP Address to you.
Your IP Address is allocated automatically, when
you connect to you ISP.
Your ISP allocates a permanent IP Address to you.
Usually, none.
However, some ISP's may
require you to use a particular Hostname, Domain name,
or MAC (physical) address.
IP Address allocated to you,
mask and gateway (if provided), and DNS address.
Some ISP's may also require
you to use a particular Hostname, Domain name, or
MAC (physical) address.
None.
IP Address allocated to you,
mask and gateway (if provided), and DNS address.
PPPoE You connect to the ISP only
when required. The IP
address is usually allocated
automatically.
PPTP Mainly used in Europe.
You connect to the ISP only
when required. The IP
address is usually allocated
automatically, but may be
Static (Fixed).
11
User name and password.
• PPTP Server IP Address.
• User name and pass-
word.
• IP Address allocated to
you, if Static (Fixed).
Page 17
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Other Modems (e.g. Broadband Wireless)
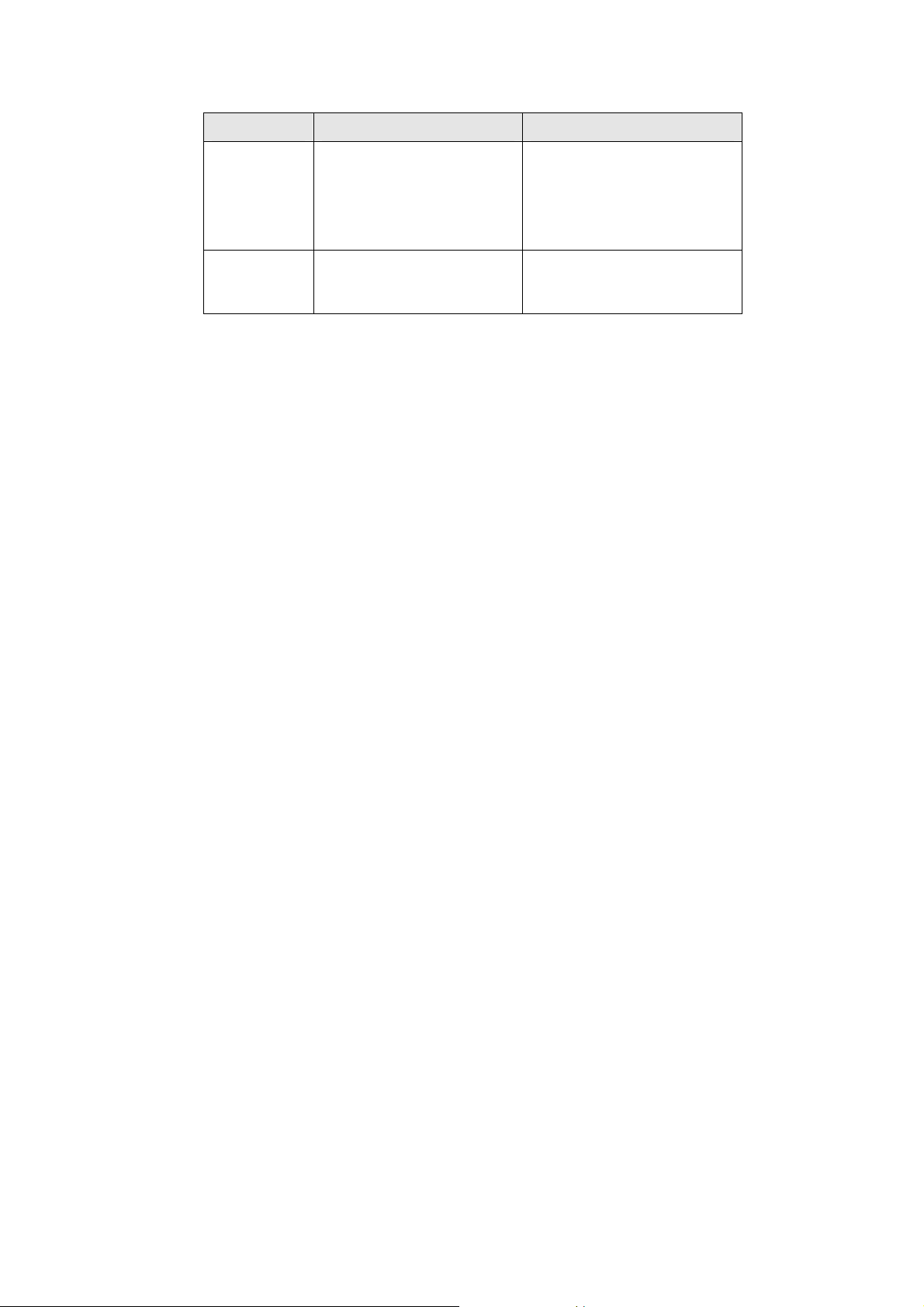
Type Details ISP Data required
Dynamic
IP Address
Static (Fixed)
IP Address
Your IP Address is allocated automatically, when
you connect to you ISP.
Your ISP allocates a permanent IP Address to you.
Big Pond Cable (Australia)
For this connection method, the following data is required:
• User Name
• Password
• Big Pond Server IP address
SingTel RAS
For this connection method, the following data is required:
• User Name
• Password
• RAS Plan
Usually, none.
However, some ISP's may
require you to use a particular Hostname, Domain name,
or MAC (physical) address.
IP Address allocated to you,
mask and gateway (if provided), and DNS address.
12
Page 18

Setup
Home Screen
After finishing or exiting the WAN Wizard setup, you will see the Home screen. When you connect in future, you will
see this screen when you connect. An example screen is shown below.
Figure 6: Home Screen
Navigation & Data Input
• Use the menu bar on the top of the screen, and the "Back" button on your Browser, for navigation.
• Changing to another screen without clicking "Save" does NOT save any changes you may have made. You must
"Save" before changing screens or your data will be ignored.
On each screen, clicking the "Help" button will
display help for that screen.
From any help screen, you can access the list of all
help files (help index).
13
Page 19

VPN Broadband Router User Manual
LAN Screen
Use the LAN link on the main menu to reach the LAN screen an example screen is shown below.
Figure 7: LAN Screen
Data - LAN Screen
TCP/IP
IP Address
Subnet Mask
DHCP Server
IP address for the VPN Broadband Router, as seen from the
local LAN. Use the default value unless the address is already in
use or your LAN is using a different IP address range. In the
latter case, enter an unused IP Address from within the range
used by your LAN.
The default value 255.255.255.0 is standard for small (class "C")
networks. For other networks, use the Subnet Mask for the LAN
segment to which the VPN Broadband Router is attached (the
same value as the PCs on that LAN segment).
• If Enabled, the VPN Broadband Router will allocate IP
Addresses to PCs (DHCP clients) on your LAN when they
start up. The default (and recommended) value is Enabled.
• If you are already using a DHCP Server, this setting must be
Disabled, and the existing DHCP server must be reconfigured to treat the VPN Broadband Router as the default
Gateway. See the following section for further details.
• The Start IP Address and Finish IP Address fields set the
values used by the DHCP server when allocating IP Addresses to DHCP clients. This range also determines the
number of DHCP clients supported.
See the following section for further details on using DHCP.
Buttons
Save
Cancel
Save the data on screen.
The "Cancel" button will discard any data you have entered and
reload the file from the VPN Broadband Router.
14
Page 20

Setup
DHCP
What DHCP Does
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server allocates a valid IP address to a DHCP Client (PC or device)
upon request.
• The client request is made when the client device starts up (boots).
• The DHCP Server provides the Gateway and DNS addresses to the client, as well as allocating an IP Address.
• The VPN Broadband Router can act as a DHCP server.
• Windows 98SE/ME and other non-Server versions of Windows will act as a DHCP client. This is the default
Windows setting for the TCP/IP network protocol. However, Windows uses the term Obtain an IP Address automatically instead of "DHCP Client".
• You must NOT have two (2) or more DHCP Servers on the same LAN segment. (If your LAN does not have other
Routers, this means there must only be one (1) DHCP Server on your LAN.)
Using the VPN Broadband Router's DHCP Server
This is the default setting. The DHCP Server settings are on the LAN screen. On this screen, you can:
• Enable or Disable the VPN Broadband Router's DHCP Server function.
• Set the range of IP Addresses allocated to PCs by the DHCP Server function.
You can assign Fixed IP Addresses to some devices
while using DHCP, provided that the Fixed IP Addresses
are NOT within the range used by the DHCP Server.
Using another DHCP Server
You can only use one (1) DHCP Server per LAN segment. If you wish to use another DHCP Server, rather than the
VPN Broadband Router's, the following procedure is required.
1. Disable the DHCP Server feature in the VPN Broadband Router. This setting is on the LAN screen.
2. Configure the DHCP Server to provide the VPN Broadband Router's IP Address as the Default Gateway.
To Configure your PCs to use DHCP
This is the default setting for TCP/IP under Windows 98SE/ME.
See Chapter 4 - Client Configuration for the procedure to check these settings.
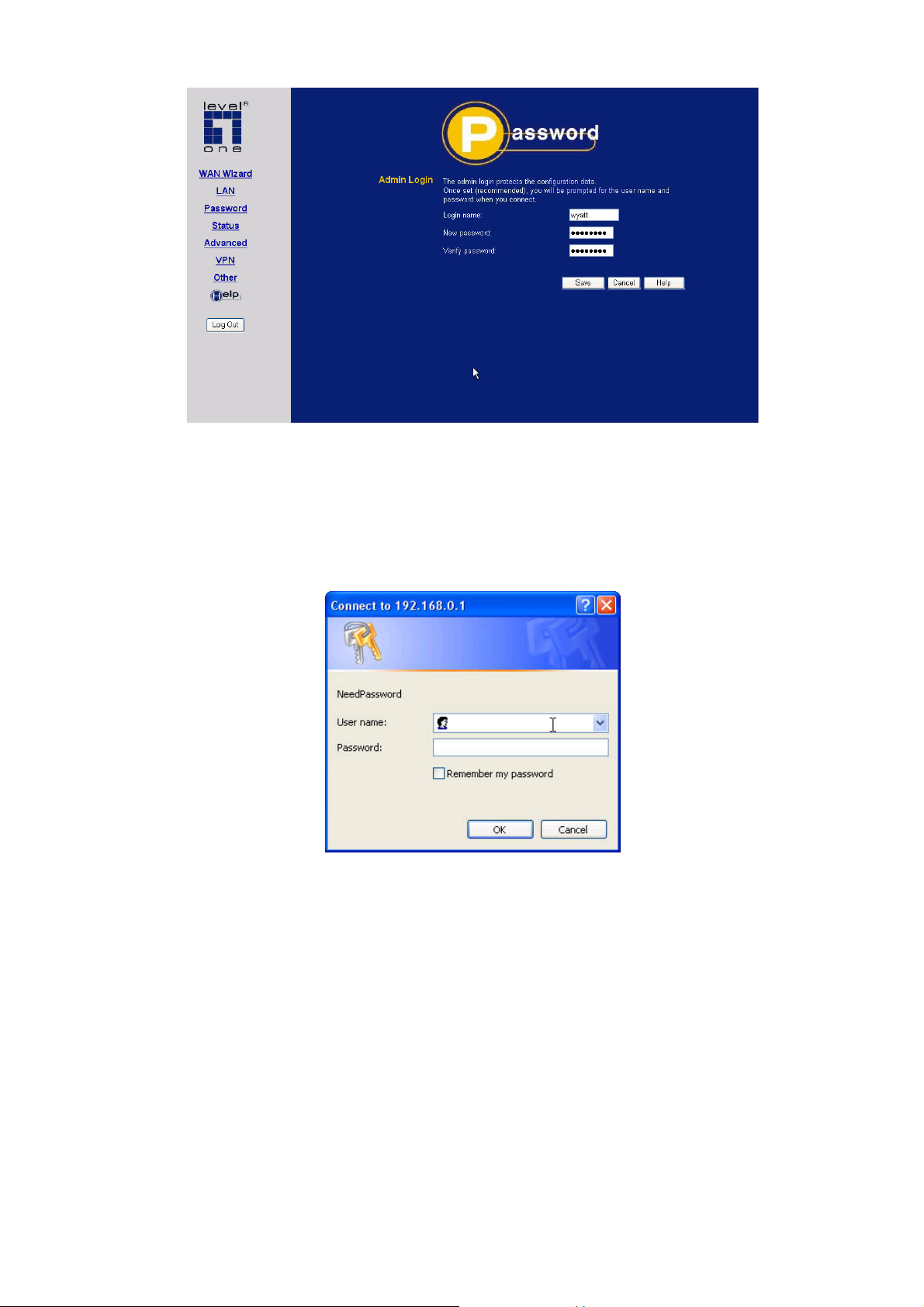
Password
From the menu, select Password. This screen allows you to assign a user name and password to the VPN Broadband
Router.
15
Page 21
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Figure 8: Password Screen
1. The default login name is "admin". Change this to the desired value.
2. The default password is “password”. Enter the desired password in the New Password and Verify Password fields.
3. Save your changes.
You will see a login prompt when you connect to the VPN Broadband Router, as shown below.
Figure 9: Password Dialog
Enter the "User Name" and "Password" you set on the Admin Login screen above.
16
Page 22

Chapter 4
PC Configuration
PC Configuration
This Chapter details the PC Configuration required on the local ("Internal") LAN.
4
Overview
For each PC, the following may need to be configured:
• TCP/IP network settings
• Internet Access configuration
Windows Clients
This section describes how to configure Windows clients for Internet access via the VPN Broadband Router.
The first step is to check the PC's TCP/IP settings.
The VPN Broadband Router uses the TCP/IP network protocol for all functions, so it is essential that the TCP/IP
protocol be installed and configured on each PC.
TCP/IP Settings - Overview
If using the default VPN Broadband Router settings and the default Windows TCP/IP settings, no
changes need to be made.
• By default, the VPN Broadband Router will act as a DHCP Server, automatically providing a suitable IP Address
(and related information) to each PC when the PC boots.
• For all non-Server versions of Windows, the default TCP/IP setting is to act as a DHCP client.
If using a Fixed (specified) IP address, the following changes are required:
• The Gateway must be set to the IP address of the VPN Broadband Router
• The DNS should be set to the address provided by your ISP.
If your LAN has a Router, the LAN Administrator must reconfigure the Router itself. Refer to Chapter 8 - Other
Features and Operations for details.
17
Page 23
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 9x/ME:
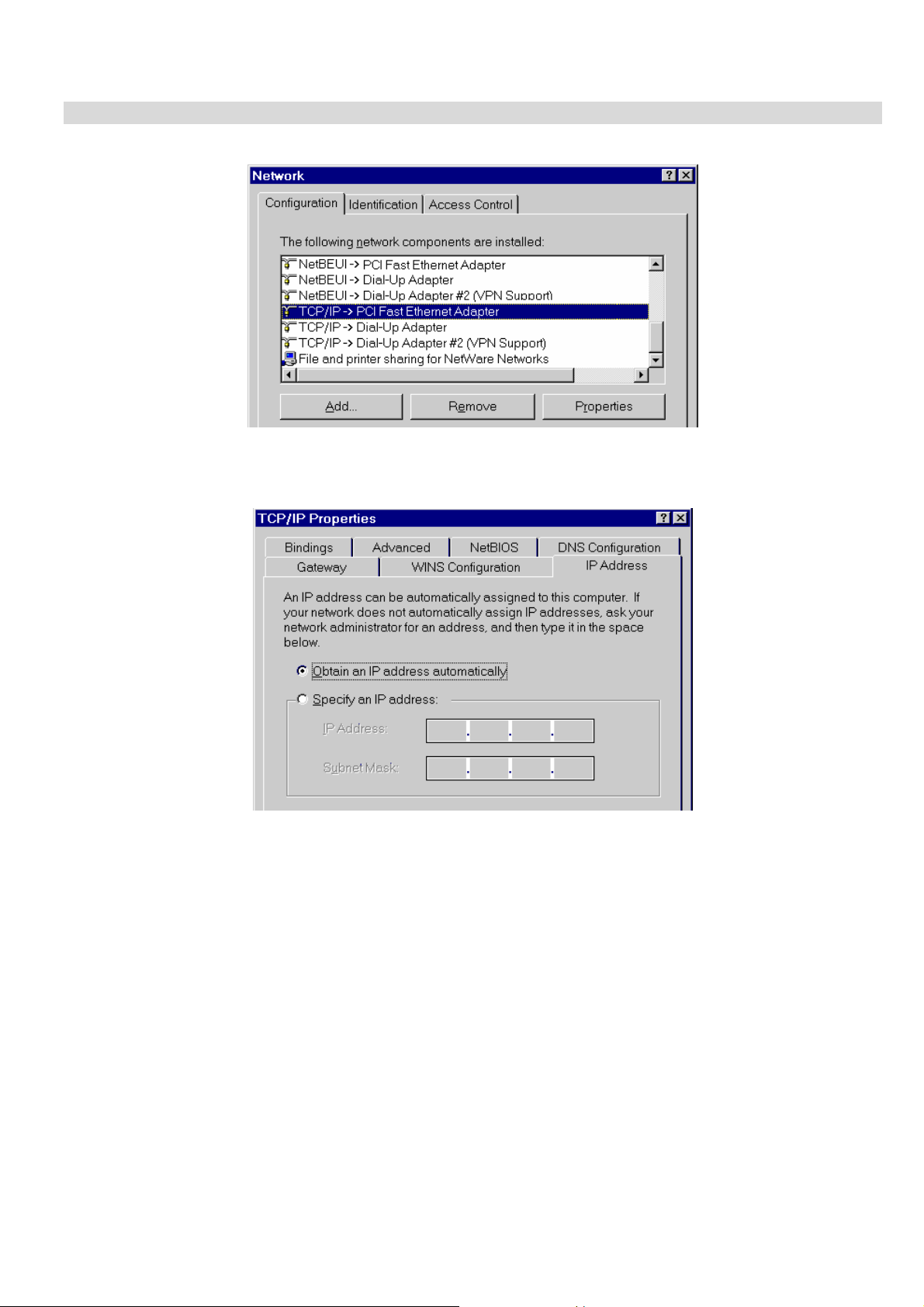
1. Select Control Panel - Network. You should see a screen like the following:
Figure 10: Network Configuration
2. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
3. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Figure 11: IP Address (Win 95)
Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct, as follows:
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default Windows setting. Using
this is recommended. By default, the VPN Broadband Router will act as a DHCP Server.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the VPN Broadband Router.
Using "Specify an IP Address"
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making the following changes:
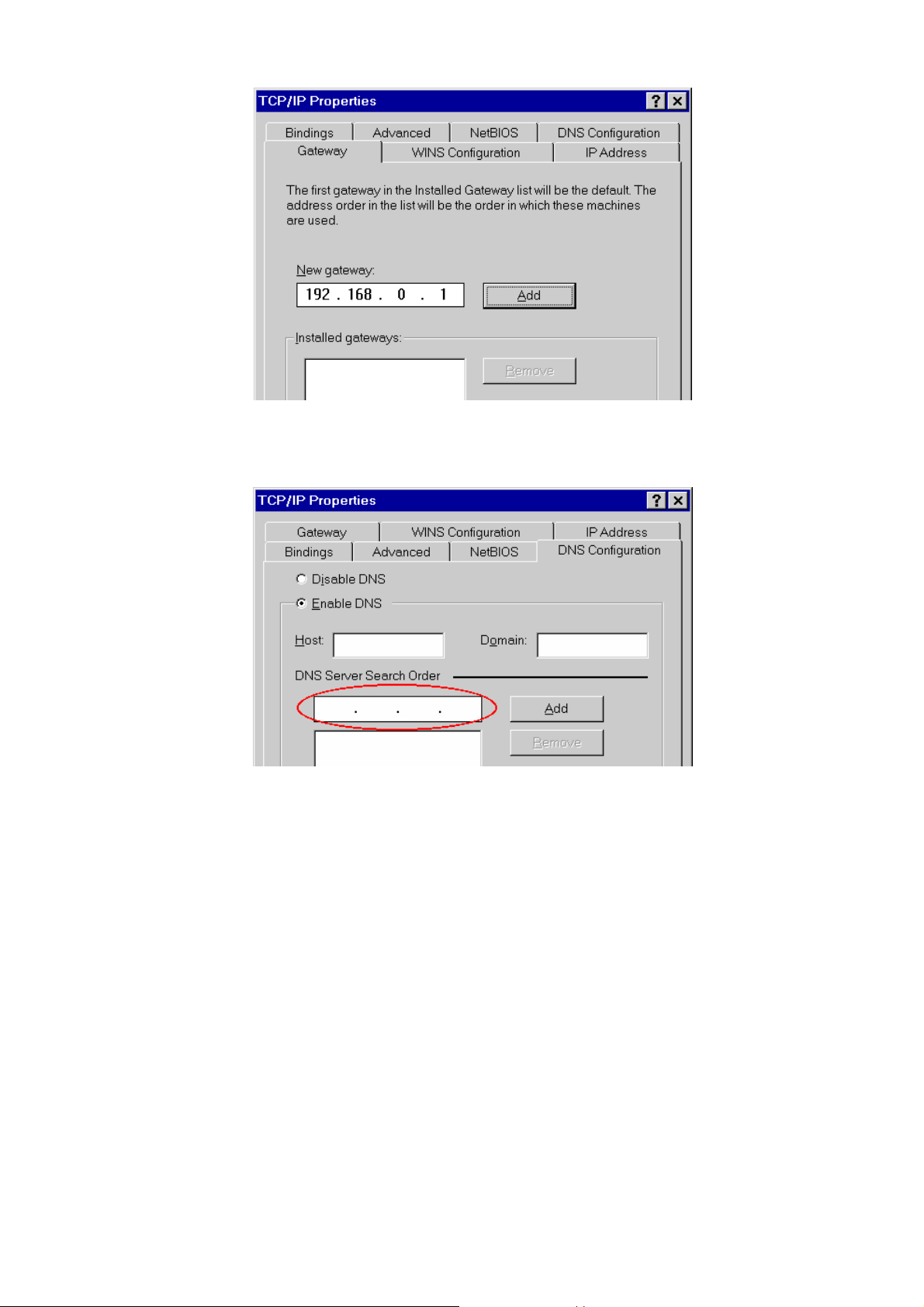
• On the Gateway tab, enter the VPN Broadband Router's IP address in the New Gateway field and click Add, as
shown below. Your LAN administrator can advise you of the IP Address they assigned to the VPN Broadband
Router.
18
Page 24
PC Configuration
Figure 12: Gateway Tab (Win 95/98)
• On the DNS Configuration tab, ensure Enable DNS is selected. If the DNS Server Search Order list is empty,
enter the DNS address provided by your ISP in the fields beside the Add button, then click Add.
Figure 13: DNS Tab (Win 95/98)
19
Page 25
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 2000:
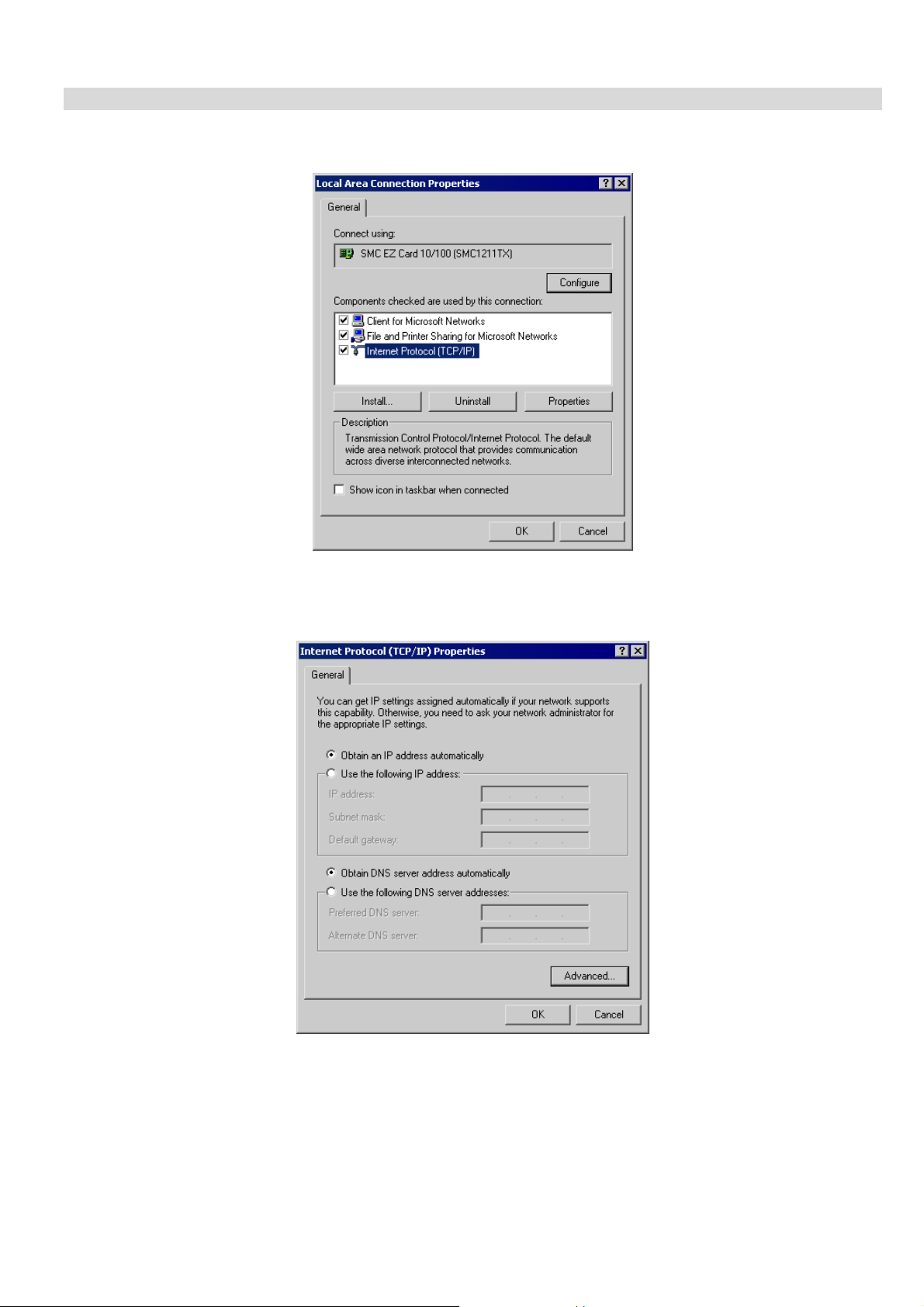
1. Select Control Panel - Network and Dial-up Connection.
2. Right - click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties. You should see a screen like the following:
Figure 14: Network Configuration (Win 2000)
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Figure 15: TCP/IP Properties (Win 2000)
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct, as described below.
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default Windows setting. Using
this is recommended. By default, the VPN Broadband Router will act as a DHCP Server.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the VPN Broadband Router.
20
Page 26

PC Configuration
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making the following changes.
• Enter the VPN Broadband Router 's IP address in the Default gateway field and click OK. (Your LAN administrator
can advise you of the IP Address they assigned to the VPN Broadband Router.)
• If the DNS Server fields are empty, select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the DNS address or
addresses provided by your ISP, then click OK.
21
Page 27
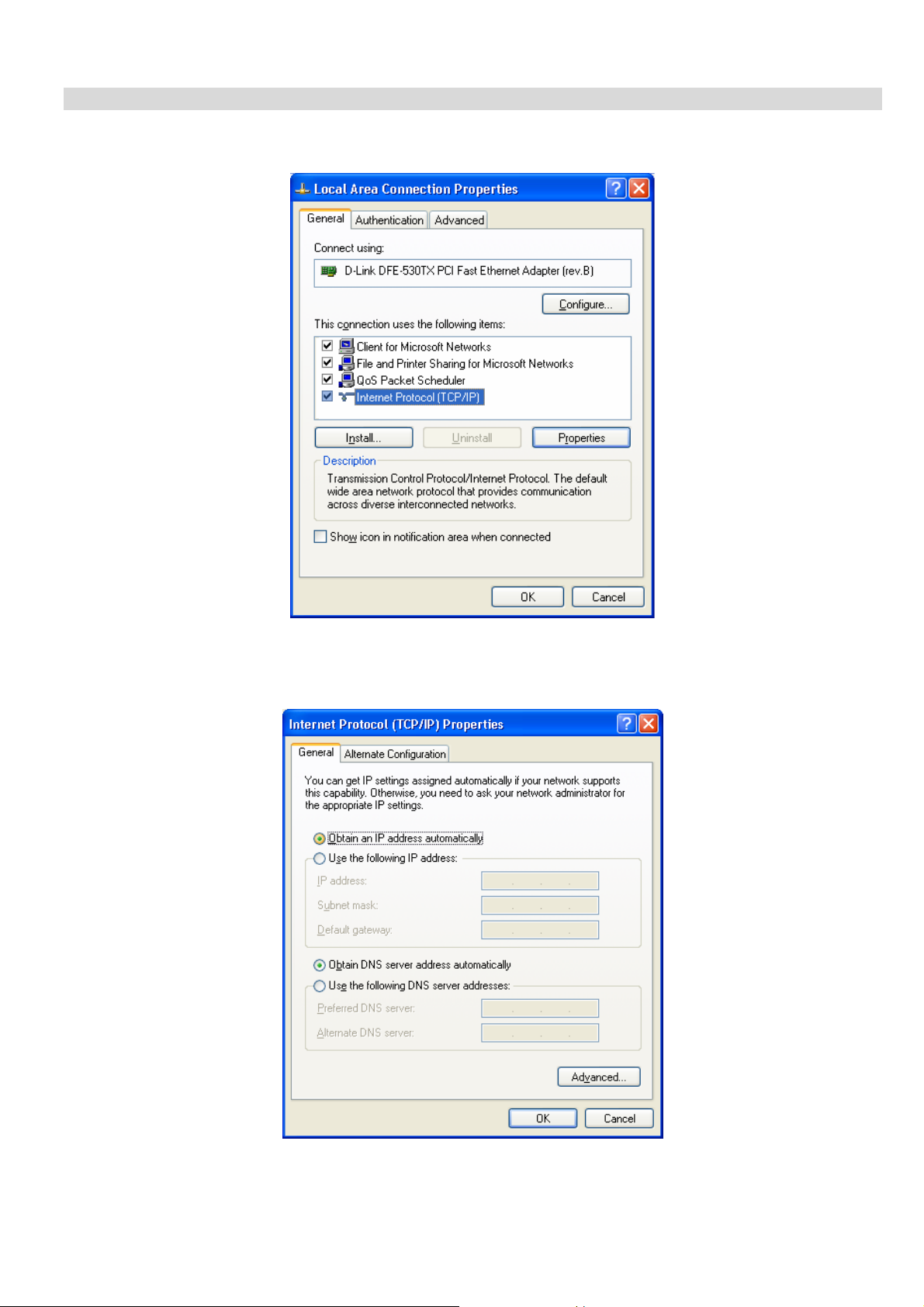
VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows XP
1. Select Control Panel - Network Connection.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection and choose Properties. You should see a screen like the following:
Figure 16: Network Configuration (Windows XP)
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Figure 17: TCP/IP Properties (Windows XP)
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct.
22
Page 28

PC Configuration
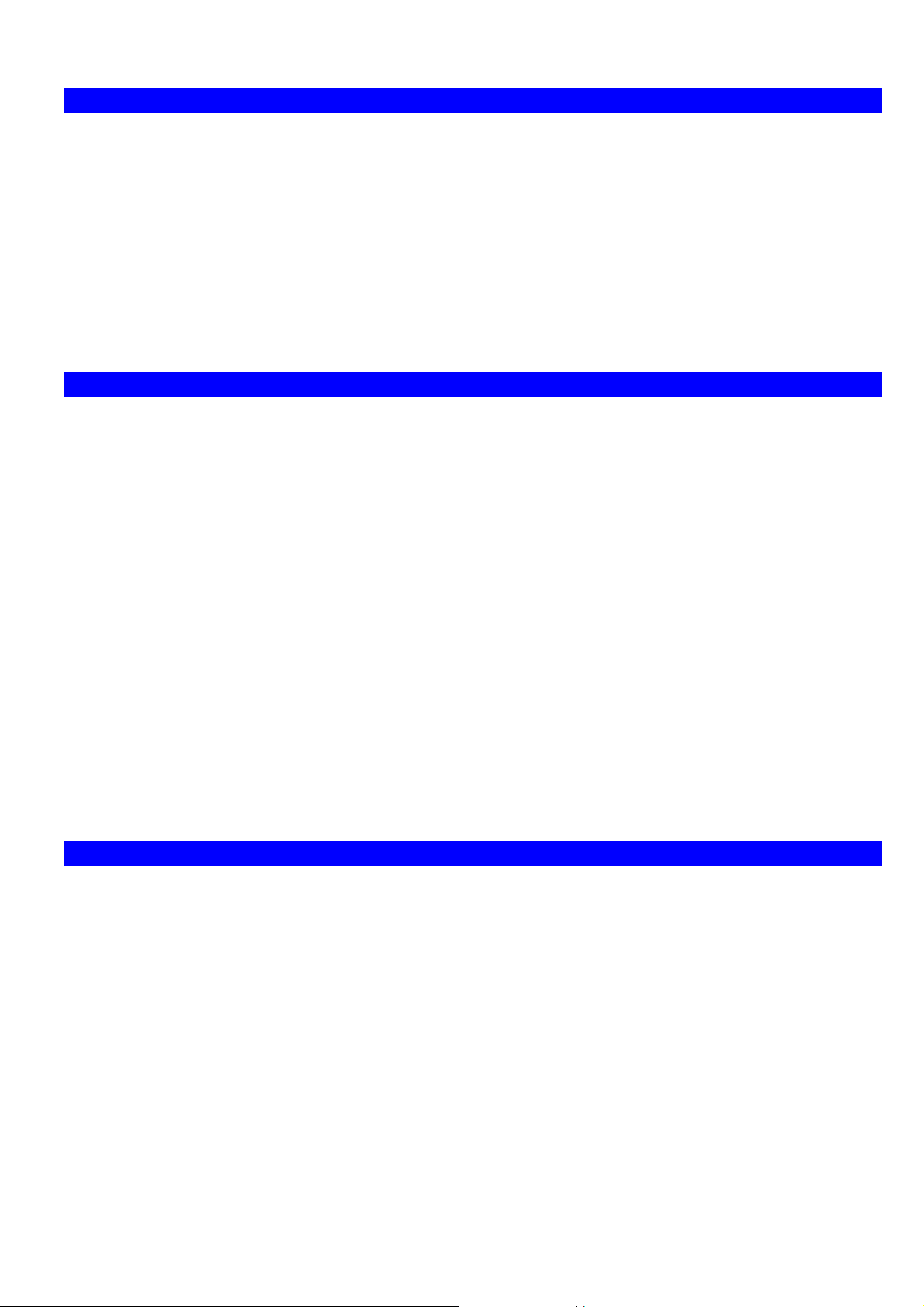
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default Windows setting. Using
this is recommended. By default, the VPN Broadband Router will act as a DHCP Server.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the VPN Broadband Router.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making the following changes.
• In the Default gateway field, enter the VPN Broadband Router 's IP address and click OK. Your LAN administrator
can advise you of the IP Address they assigned to the VPN Broadband Router.
• If the DNS Server fields are empty, select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the DNS address or
addresses provided by your ISP, then click OK.
23
Page 29

VPN Broadband Router User Manual
Internet Access
To configure your PCs to use the VPN Broadband Router for Internet access:
• Ensure that the DSL modem, Cable modem, or other permanent connection is functional.
• Use the following procedure to configure your Browser to access the Internet via the LAN, rather than by a Dial-up
connection.
For Windows 9x/ME/2000
1. Select Start Menu - Settings - Control Panel - Internet Options.
2. Select the Connection tab, and click the Setup button.
3. Select "I want to set up my Internet connection manually, or I want to connect through a local area network (LAN)"
and click Next.
4. Select "I connect through a local area network (LAN)" and click Next.
5. Ensure all of the boxes on the following Local area network Internet Configuration screen are unchecked.
6. Check the "No" option when prompted "Do you want to set up an Internet mail account now?".
7. Click Finish to close the Internet Connection Wizard.
Setup is now completed.
For Windows XP
1. Select Start Menu - Control Panel - Network and Internet Connections.
2. Select Set up or change your Internet Connection.
3. Select the Connection tab, and click the Setup button.
4. Cancel the pop-up "Location Information" screen.
5. Click Next on the "New Connection Wizard" screen.
6. Select "Connect to the Internet" and click Next.
7. Select "Set up my connection manually" and click Next.
8. Check "Connect using a broadband connection that is always on" and click Next.
9. Click Finish to close the New Connection Wizard.
Setup is now completed.
Accessing AOL
To access AOL (America On Line) through the VPN Broadband Router, the AOL for Windows software must be
configured to use TCP/IP network access, rather than a dial-up connection. The configuration process is as follows:
• Start the AOL for Windows communication software. Ensure that it is Version 2.5, 3.0 or later. This procedure will
not work with earlier versions.
• Click the Setup button.
• Select Create Location, and change the location name from "New Locality" to "VPN Broadband Router ".
• Click Edit Location. Select TCP/IP for the Network field. (Leave the Phone Number blank.)
• Click Save, then OK.
Configuration is now complete.
• Before clicking "Sign On", always ensure that you are using the "VPN Broadband Router " location.
24
Page 30
PC Configuration
Macintosh Clients
From your Macintosh, you can access the Internet via the VPN Broadband Router. The procedure is as follows.
1. Open the TCP/IP Control Panel.
2. Select Ethernet from the Connect via pop-up menu.
3. Select Using DHCP Server from the Configure pop-up menu. The DHCP Client ID field can be left blank.
4. Close the TCP/IP panel, saving your settings.
Note:
If using manually assigned IP addresses instead of DHCP, the required changes are:
• Set the Router Address field to the VPN Broadband Router 's IP Address.
• Ensure your DNS settings are correct.
Linux Clients
To access the Internet via the VPN Broadband Router, it is only necessary to set the VPN Broadband Router as the
"Gateway".
Ensure you are logged in as "root" before attempting any changes.
Fixed IP Address
By default, most Unix installations use a fixed IP Address. If you wish to continue using a fixed IP Address, make the
following changes to your configuration.
• Set your "Default Gateway" to the IP Address of the VPN Broadband Router.
• Ensure your DNS (Name server) settings are correct.
To act as a DHCP Client (recommended)
The procedure below may vary according to your version of Linux and X -windows shell.
1. Start your X Windows client.
2. Select Control Panel - Network
3. Select the "Interface" entry for your Network card. Normally, this will be called "eth0".
4. Click the Edit button, set the "protocol" to "DHCP", and save this data.
5. To apply your changes
• Use the "Deactivate" and "Activate" buttons, if available.
• OR, restart your system.
Other Unix Systems
To access the Internet via the VPN Broadband Router:
• Ensure the "Gateway" field for your network card is set to the IP Address of the VPN Broadband Router.
• Ensure your DNS (Name Server) settings are correct.
25
Page 31

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Chapter 5
Operation and Status
This Chapter details the operation of the VPN Broadband Router and the status screens.
5
Operation
Once both the VPN Broadband Router and the PCs are configured, operation is automatic.
However, there are some situations where additional Internet configuration may be required:
• If using Internet-based Communication Applications, it may be necessary to specify which PC receives an
incoming connection. Refer to Chapter 6 - Internet Features for further details.
• Applications which use non-standard connections or port numbers may be blocked by the VPN Broadband
Router's built-in firewall. You can define such applications as Special Applications to allow them to function normally. Refer to Chapter 6 - Internet Features for further details.
• Some non-standard applications may require use of the DMZ feature. Refer to Chapter 6 - Internet Features for
further details.
Status Screen
Use the Status link on the main menu to view this screen.
Data - Status Screen
Internet
Connection Method
Broadband Modem
Internet Connection
Figure 18: Status Screen
This indicates the current connection method, as set in the
WAN Wizard setup.
This shows the connection status of the modem.
Current connection status:
• Active
• Idle
• Unknown
26
Page 32

• Failed
If there is an error, you can click the "Connection Details"
button to find out more information.
Operation and Status
Internet IP Address
"Connection Details" Button
LAN
IP Address
Network Mask
DHCP Server
System
Device Name
Firmware Version
"System Data"
Button
This IP Address is allocated by the ISP (Internet Service
Provider).
Click this button to open a sub-window and view a detailed
description of the current connection. Depending on the
type of connection, a "log" may also be available.
The IP Address of the VPN Broadband Router.
The Network Mask (Subnet Mask) for the IP Address
above.
This shows the status of the DHCP Server function - either
"Enabled" or "Disabled".
For additional information about the PCs on your LAN, and
the IP addresses allocated to them, use the PC Database
option on the Other menu.
This displays the current name of the VPN Broadband
Router.
The current version of the firmware installed in the VPN
Broadband Router.
Clicking this button will open a Window which lists all system details and settings.
Buttons
Connection Details
System Data
Restart Router
Refresh Screen
View the details of the current Internet connection. The subscreen displayed will depend on the connection method
used. See the following sections for details of each subscreen.
Display all system information in a sub-window.
Restart (reboot) the Router. You will have to wait for the
restart to be completed before continuing.
Update the data displayed on screen.
Connection Status - PPPoE
If using PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet), a screen like the following example will be displayed when the "Connection
Details" button is clicked.
27
Page 33

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 19: PPPoE Status Screen
Data - PPPoE Screen
Connection
Physical Address
IP Address
Network Mask
PPPoE Link Status
Connection Log
Connection Log
The hardware address of this device, as seen by remote
devices on the Internet. (This is different to the hardware
address seen by devices on the local LAN.)
The IP Address of this device, as seen by Internet users.
This address is allocated by your ISP (Internet Service
Provider).
The Network Mask associated with the IP Address above.
This indicates whether or not the connection is currently
established.
• If the connection does not exist, the "Connect" button
can be used to establish a connection.
• If the connection currently exists, the "Disconnect"
button can be used to break the connection.
• The Connection Log shows status messages relating to
the existing connection.
• The most common messages are listed in the table
below.
• The "Clear Log" button will restart the Log, while the
Refresh button will update the messages shown on
screen.
Buttons
Connect
Disconnect
Clear Log
If not connected, establish a connection to your ISP.
If connected to your ISP, hang up the connection.
Delete all data currently in the Log. This will make it easier
to read new messages.
Refresh
Update the data on screen.
28
Page 34

Connection Log Messages
Message Description
Connect on Demand Connection attempt has been triggered by the "Connect
Manual connection Connection attempt started by the "Connect" button.
Operation and Status
automatically, as required" setting.
Reset physical connec-
Preparing line for connection attempt.
tion
Connecting to remote
Attempting to connect to the ISP's server.
server
Remote Server located ISP's Server has responded to connection attempt.
Start PPP Attempting to login to ISP's Server and establish a PPP
connection.
PPP up successfully Able to login to ISP's Server and establish a PPP con-
nection.
Idle time-out reached The connection has been idle for the time period speci-
fied in the "Idle Time-out" field. The connection will now
be terminated.
Disconnecting The current connection is being terminated, due to either
the "Idle Time-out" above, or "Disconnect" button being
clicked.
Error: Remote Server
not found
Error: PPP Connection
failed
ISP's Server did not respond. This could be a Server
problem, or a problem with the link to the Server.
Unable to establish a PPP connection with the ISP's
Server. This could be a login problem (name or password) or a Server problem.
Error: Connection to
Server lost
The existing connection has been lost. This could be
caused by a power failure, a link failure, or Server failure.
Error: Invalid or unknown packet type
The data received from the ISP's Server could not be
processed. This could be caused by data corruption
(from a bad link), or the Server using a protocol which is
not supported by this device.
29
Page 35

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Connection Status - PPTP
If using PPTP (Peer-to-Peer Tunneling Protocol), a screen like the following example will be displayed when the
"Connection Details" button is clicked.
Data - PPTP Screen
Connection
Physical Ad-
dress
IP Address
PPTP Status
Connection Log
Connection Log
Figure 20: PPTP Status Screen
The hardware address of this device, as seen by remote
devices on the Internet. (This is different to the hardware
address seen by devices on the local LAN.)
The IP Address of this device, as seen by Internet users. This
address is allocated by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
This indicates whether or not the connection is currently established.
• If the connection does not exist, the "Connect" button can
be used to establish a connection.
• If the connection currently exists, the "Disconnect" button
can be used to break the connection.
• The Connection Log shows status messages relating to
the existing connection.
• The "Clear Log" button will restart the Log, while the Re-
fresh button will update the messages shown on screen.
Buttons
Connect
Disconnect
Clear Log
Refresh
If not connected, establish a connection to your ISP.
If connected to your ISP, hang up the connection.
Delete all data currently in the Log. This will make it easier to
read new messages.
Update the data on screen.
30
Page 36

Connection Status - Telstra Big Pond
An example screen is shown below.
Figure 21: Telstra Big Pond Status Screen
Operation and Status
Data - Telstra Big Pond Screen
Connection
Physical Address
IP Address
Connection
Status
Connection Log
Connection Log
The hardware address of this device, as seen by remote
devices. (This is different to the hardware address seen by
devices on the local LAN.)
The IP Address of this device, as seen by Internet users.
This address is allocated by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
This indicates whether or not the connection is currently
established.
• If the connection does not exist, the "Connect" button can
be used to establish a connection.
• If the connection currently exists, the "Disconnect" button
can be used to break the connection.
• Normally, it is not necessary to use the Connect and
Disconnect buttons unless the setting "Connect automatically, as required" is disabled.
• The Connection Log shows status messages relating to
the existing connection.
• The Clear Log button will restart the Log, while the Re-
fresh button will update the messages shown on screen.
Buttons
Connect
Disconnect
Clear Log
Refresh
If not connected, establish a connection to Telstra Big Pond.
If connected to Telstra Big Pond, terminate the connection.
Delete all data currently in the Log. This will make it easier to
read new messages.
Update the data on screen.
31
Page 37

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Connection Details - SingTel RAS
If using the SingTel RAS access method, a screen like the following example will be displayed when the "Connection
Details" button is clicked.
Data - SingTel RAS Screen
Internet
RAS Plan
Physical Ad-
dress
IP Address
Network Mask
Default Gateway
DNS IP Address
DHCP Client
Figure 22: Connection Details - SingTel RAS
The RAS Plan which is currently used.
The hardware address of this device, as seen by remote
devices on the Internet. (This is different to the hardware
address seen by devices on the local LAN.)
The IP Address of this device, as seen by Internet users. This
address is allocated by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
The Network Mask associated with the IP Address above.
The IP Address of the remote Gateway or Router associated
with the IP Address above.
The IP Address of the Domain Name Server which is currently
used.
This will show "Enabled" or "Disabled", depending on whether
or not this device is functioning as a DHCP client.
If "Enabled" the "Remaining lease time" field indicates when
the IP Address allocated by the DHCP Server will expire. The
lease is automatically renewed on expiry; use the "Renew"
button if you wish to manually renew the lease immediately.
Buttons
Release/Renew
Button will
display EITHER
"Release"
OR
"Renew"
This button is only useful if the IP address shown above is
allocated automatically on connection. (Dynamic IP address). If
you have a Fixed (Static) IP address, this button has no effect.
• If the ISP's DHCP Server has NOT allocated an IP Ad-
dress for the VPN Broadband Router, this button will say
"Renew". Clicking the "Renew" button will attempt to reestablish the connection and obtain an IP Address from
the ISP's DHCP Server.
• If an IP Address has been allocated to the VPN Broadband
32
Page 38

Router (by the ISP's DHCP Server), this button will say
"Release". Clicking the "Release" button will break the
connection and release the IP Address.
Operation and Status
Refresh
Update the data shown on screen.
33
Page 39

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Connection Details - Fixed/Dynamic IP Address
If your access method is "Direct" (no login), a screen like the following example will be displayed when the "Connection Details" button is clicked.
Figure 23: Connection Details - Fixed/Dynamic IP Address
Data - Fixed/Dynamic IP address Screen
Internet
Physical Ad-
dress
IP Address
Network Mask
Default Gateway
DNS IP Address
DHCP Client
Buttons
The hardware address of this device, as seen by remote
devices on the Internet. (This is different to the hardware
address seen by devices on the local LAN.)
The IP Address of this device, as seen by Internet users. This
address is allocated by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
The Network Mask associated with the IP Address above.
The IP Address of the remote Gateway or Router associated
with the IP Address above.
The IP Address of the Domain Name Server which is currently
used.
This will show "Enabled" or "Disabled", depending on whether
or not this device is functioning as a DHCP client.
If "Enabled" the "Remaining lease time" field indicates when
the IP Address allocated by the DHCP Server will expire. The
lease is automatically renewed on expiry; use the "Renew"
button if you wish to manually renew the lease immediately.
Release/Renew
Button will
display EITHER
"Release"
OR
"Renew"
This button is only useful if the IP address shown above is
allocated automatically on connection. (Dynamic IP address). If
you have a Fixed (Static) IP address, this button has no effect.
• If the ISP's DHCP Server has NOT allocated an IP Ad-
dress for the VPN Broadband Router, this button will say
"Renew". Clicking the "Renew" button will attempt to reestablish the connection and obtain an IP Address from
the ISP's DHCP Server.
• If an IP Address has been allocated to the VPN Broadband
Router (by the ISP's DHCP Server), this button will say
"Release". Clicking the "Release" button will break the
connection and release the IP Address.
34
Page 40

Operation and Status
Refresh
Update the data shown on screen.
35
Page 41

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Chapter 6
Internet Features
This Chapter explains when and how to use the VPN Broadband Router's "Internet" Features.
Overview
The following advanced features are provided.
• WAN Port Configuration
• Advanced Internet
• Communication Applications
• Special Applications
• Multi-DMZ
• URL filter
• Dynamic DNS
• Virtual Servers
• Options
6
36
Page 42

Internet Features
WAN Port Configuration
The WAN Port Configuration screen provides an alternative to using the Wizard. It can be accessed from the Internet
menu under Advanced section. An example screen is shown below.
Figure 24: WAN Port Configuration Screen
Data – WAN Port Configuration Screen
Identification
Hostname
Domain name
MAC Address
IP Address
IP Address
is assigned
automatically
Normally, there is no need to change the default name, but if
your ISP requests that you use a particular “Hostname”, enter
it here.
If your ISP provided a domain name, enter it here. Otherwise,
this may be left blank.
Also called Network Adapter Address or Physical Address.
This is a low-level identifier, as seen from the WAN port.
Normally there is no need to change this, but some ISPs
require a particular value, often that of the PC initially used for
Internet access.
You can use the Copy from PC button to copy your PC's
address into this field, the Default button to insert the default
value, or enter a value directly.
Also called Dynamic IP Address. This is the default, and the
most common.
Leave this selected if your ISP allocates an IP Address to the
VPN Broadband Router upon connection.
37
Page 43

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Specified
IP Address
Also called Static IP Address. Select this if your ISP has
allocated you a fixed IP Address. If this option is selected, the
following data must be entered.
• IP Address.
The IP Address allocated by the ISP.
• Network Mask (Not required for PPPoE)
This is also supplied by your ISP. It must be compatible
with the IP Address above.
• Gateway IP Address (Not required for PPPoE)
The address of the router or gateway, as supplied by your
ISP.
NAT
Enable NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation) is the technology which
allows all PCs on your LAN to share the Internet IP address
allocated to the WAN port on this Router. From the Internet, all
PCs appear to have the same IP address.
For normal operation, this setting must be ENABLED.
Disable NAT Disabling NAT will disable Internet access, unless all PCs
have valid Internet IP addresses.
If you wish to use this device for Routing ONLY (and NOT for
Internet access), then NAT should be disabled.
DNS
Automatically
obtain from
Server
Use this DNS
Login
Login Method
The DNS (Domain Name Server) address will be obtained
automatically from your ISP's server. Note that if using a fixed
IP address, with no login (login is set to "None"), then no
Server is used, and this option cannot be used.
If this option is selected, you must enter the IP address of the
DNS (Domain Name Server) you wish to use.
Note: If the DNS is unavailable, the "Backup DNS", entered on
the Internet - Options screen, will be used.
If your ISP does not use a login method (username, password)
for Internet access, leave this at the default value "None (Direct connection)"
Otherwise, check the documentation from your ISP, select the
login method used, and enter the required data.
• PPPoE - this is the most common login method, widely
used with DSL modems. Normally, your ISP will have provided some software to connect and login. This software is
no longer required, and should not be used.
• PPTP - this is mainly used in Europe. You need to know
the PPTP Server address as well as your name and password.
• Big Pond Cable - for Australia only.
• SingTel RAS - for Singapore only.
Login User
Name
Login Password
RAS Plan
The User Name (or account name) provided by your ISP.
Enter the password for the login name above.
For SingTel customers only, select the RAS plan you are on.
38
Page 44

Internet Features
Server Address
Connection
behavior
Auto-disconnect
Idle Time-out
If using PPTP or Big Pond Cable, enter the address of your
ISP's server.
For PPPoE or SingTel RAS, the Server address in not required.
Select the desired option:
• Automatic Connect/Disconnect
An Internet connection is automatically made when required, and disconnected when idle for the time period
specified by the "Auto-disconnect Idle Time-out".
• Manual Connect/Disconnect
You must manually establish and terminate the connection.
• Keep alive (maintain connection)
The connection will never be disconnected by this device.
If disconnected by your ISP, the connection will be reestablished immediately. (However, this does not ensure
that your Internet IP address will remain unchanged.)
This field has no effect unless the setting above is Automatic
Connect/Disconnect.
If Auto-disconnect is being used, enter the desired idle timeout period (in minutes). After the connection to your ISP has
been idle for this time period, the connection will be terminated.
Advanced Setup
Figure 25: Internet Screen
This screen allows configuration of all advanced features relating to Internet access.
• Communication Applications
• Special Applications
39
Page 45

VPN Broadband Router User manual
• Multi-DMZ
• URL filter
Communication Applications
Most applications are supported transparently by the VPN Broadband Router. But sometimes it is not clear which PC
should receive an incoming connection. This problem could arise with the Communication Applications listed on
this screen.
If this problem arises, you can use this screen to set which PC should receive an incoming connection, as described
below.
Communication Applications
Select an Applica-
tion
Send incoming
calls to
This lists applications which may generate incoming connections, where the destination PC (on your local LAN) is
unknown.
This lists the PCs on your LAN.
• If necessary, you can add PCs manually, using the PC
Database option on the Other menu.
• For each application listed above, you can choose a
destination PC.
• There is no need to "Save" after each change; you can
set the destination PC for each application, then click
"Save".
Special Applications
If you use Internet applications which use non-standard connections or port numbers, you may find that they do not
function correctly because they are blocked by the VPN Broadband Router's firewall. In this case, you can define the
application as a "Special Application".
Special Applications Screen
This screen can be reached by clicking the Special Applications button on the Advanced Internet screen. Click Advanced, Advanced Setup then Special Applications
You can then define your Special Applications. You will need detailed information about the application; this is normally available from the supplier of the application.
Also, note that the terms "Incoming" and "Outgoing" on this screen refer to traffic from the client (PC) viewpoint
Figure 26: Special Applications Screen
40
Page 46

Data - Special Applications Screen
Internet Features
Checkbox
Name
Incoming
Ports
Outgoing
Ports
Use this to Enable or Disable this Special Application as required.
Enter a descriptive name to identify this Special Application.
• Type - Select the protocol (TCP or UDP) used when you receive
data from the special application or service. (Note: Some applications use different protocols for outgoing and incoming data).
• Start - Enter the beginning of the range of port numbers used by
the application server, for data you receive. If the application
uses a single port number, enter it in both the "Start" and "Finish"
fields.
• Finish - Enter the end of the range of port numbers used by the
application server, for data you receive.
• Type - Select the protocol (TCP or UDP) used when you send
data to the remote system or service.
• Start - Enter the beginning of the range of port numbers used by
the application server, for data you send to it. If the application
uses a single port number, enter it in both the "Start" and "Finish"
fields.
• Finish - Enter the end of the range of port numbers used by the
application server, for data you send to it. If the application uses
a single port number, enter it in both the "Start" and "Finish"
fields.
Using a Special Application
• Configure the Special Applications screen as required.
• On your PC, use the application normally. Remember that only one (1) PC can use each Special application at
any time. Also, when 1 PC is finished using a particular Special Application, there may need to be a "Time-out" before another PC can use the same Special Application. The "Time-out" period may be up to 3 minutes.
If an application still cannot function correctly,
try using the "DMZ" feature.
Multi-DMZ
This feature, if enabled, allows one (1) or more computers on your LAN to be exposed to all users on the Internet. You
can set a DMZ PC for each WAN IP address. If you only have 1 WAN IP addresses, only 1 DMZ PC can be used.
This allows unrestricted 2-way communication between the "DMZ PC" and other Internet users or Servers.
• This allows almost any application to be used on the "DMZ PC".
• The "DMZ PC" will receive all "Unknown" connections and data.
• If the DMZ feature is enabled, you must select the PC to be used as the "DMZ PC".
• To use more than one (1) DMZ, your ISP must assign multiple fixed IP addresses to you. You must enter each IP
address; you can then assign a DMZ PC for each IP address.
The "DMZ PC" is effectively outside the Firewall, making it more vulnerable to attacks. For this reason, you
should only enable the DMZ feature when required.
41
Page 47

VPN Broadband Router User manual
URL Filter
The URL Filter allows you to block access to undesirable Web site
• To use this feature, you must define "filter strings". If the "filter string" appears in a requested URL, the request is
blocked.
• Enabling the URL Filter also affects the Internet Access Log. If Enabled, the "Destination" field in the log will
display the URL. Otherwise, it will display the IP Address.
• The URL Filter can be Enabled or Disabled on the Advanced Internet screen.
URL Filter Screen
Click the "Configure URL Filter" button on the Advanced Internet screen to access the URL Filter screen. An example
screen is shown below.
Data - URL Filter Screen
Filter Strings
Current Entries
Add Filter
String
Buttons
Delete/Delete
All
Add
Figure 27: URL Filter Screen
This lists any existing entries. If you have not entered any values, this list will be empty.
To add an entry to the list, enter it here, and click the "Add"
button.
An entry may be a Domain name (e.g. www.trash.com) or simply
a string. (e.g. ads/ )
Any URL which contains ANY entry ANYWHERE in the URL will
be blocked.
Use these buttons to delete the selected entry or all entries, as
required. Multiple entries can be selected by holding down the
CTRL key while selecting. (On the Macintosh, hold the SHIFT
key while selecting.)
Use this to add the current Filter String to the site list.
42
Page 48

Internet Features
Dynamic DNS (Domain Name Server)
This free service is very useful when combined with the Virtual Server feature. It allows Internet users to connect to
your Virtual Servers using a URL, rather than an IP Address.
This also solves the problem of having a dynamic IP address. With a dynamic IP address, your IP address may
change whenever you connect, which makes it difficult to connect to you.
The Service works as follows:
1. You must register for the service at one of the listed DDNS Service providers.
2. After registration, follow the Service Provider's procedure to request a Domain Name, and have it allocated to you.
3. Enter your DDNS data on the VPN Broadband Router's DDNS screen (shown below).
4. The VPN Broadband Router will then automatically ensure that your current IP Address is recorded and updated
at the DDNS server.
If the DDNS Service provides software to perform this "IP address update"; you should disable the "Update" function, or not use the software at all.
5. From the Internet, users will be able to connect to your Virtual Servers (or DMZ PC) using your Domain name, as
shown on this screen.
Dynamic DNS Screen
Select Advancedt on the main menu, then Dynamic DNS, to see a screen like the following:
Figure 28: DDNS Screen
Data - Dynamic DNS Screen
DDNS Service
DDNS Service
• You must register for the service at one of the listed Ser-
vice Providers. You can reach the Service provider's Web
Site by selecting them in the list and clicking the "Web
Site" button.
• Apply for a Domain Name, and ensure it is allocated to
you.
• Details of your DDNS account (Name, password, Domain
name) must then be entered and saved on this screen.
• This device will then automatically ensure that your current
IP Address is recorded by the DDNS Service Provider.
43
Page 49

VPN Broadband Router User manual
DDNS Data
(You do NOT need to use the "Client" program provided by
some DDNS Service providers.)
• From the Internet, users will now be able to connect to
your Virtual Servers (or DMZ PC) using your Domain
name.
DDNS Service
User Name
Password/Key
Domain Name
Select the desired DDNS Service provider.
Enter your Username for the DDNS Service.
Enter your current password for the DDNS Service.
Enter the domain name allocated to you by the DDNS Service.
If you have more than one name, enter the name you wish to
use.
DDNS Status
• This message is returned by the DDNS Server
• Normally, this message should be something like "Update
successful" or "IP address updated".
• If the message indicates some problem, you need to
connect to the DDNS Service provider and correct this
problem.
44
Page 50

Internet Features
Virtual Servers
This feature allows you to make Servers on your LAN accessible to Internet users. Normally, Internet users would not
be able to access a server on your LAN because:
• Your Server does not have a valid external IP Address.
• Attempts to connect to devices on your LAN are blocked by the firewall in this device.
The "Virtual Server" feature solves these problems and allows Internet users to connect to your servers, as illustrated
below.
Figure 29: Virtual Servers
IP Address seen by Internet Users
Note that, in this illustration, both Internet users are connecting to the same IP Address, but using different protocols.
To Internet users, all virtual Servers on your LAN have the same IP Address. This IP Address is allocated by
your ISP.
This address should be static, rather than dynamic, to make it easier for Internet users to connect to your Servers.
However, you can use the DDNS (Dynamic DNS) feature to allow users to connect to your Virtual Servers using a
URL, instead of an IP Address.
Virtual Servers Screen
The Virtual Servers screen is reached by the Virtual Servers link on the Advancedmenu. An example screen is shown
below.
45
Page 51

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 30: Virtual Servers Screen
This screen lists a number of pre-defined Servers, providing a quick and convenient method to set up the common
server types.
Data - Virtual Servers Screen
Servers
Servers
Properties
Enable
PC (Server)
This lists a number of pre-defined Servers, plus any Servers
you have defined. Details of the selected Server are shown in
the "Properties" area.
Use this to Enable or Disable support for this Server, as
required.
• If Enabled, any incoming connections will be forwarded
to the selected PC.
• If Disabled, any incoming connection attempts will be
blocked.
Select the PC for this Server. The PC must be running the
appropriate Server software.
Defining your own Virtual Servers
If the type of Server you wish to use is not listed on the Virtual Servers screen, you can use the Firewall Rules to allow
particular incoming traffic and forward it to a specified PC (Server).
Connecting to the Virtual Servers
Once configured, anyone on the Internet can connect to your Virtual Servers. They must use the Internet IP Address
(the IP Address allocated to you by your ISP).
e.g.
http://203.70.212.52
ftp://203.70.212.52
It is more convenient if you are using a Fixed IP Address from your ISP, rather than Dynamic. However, you can use
the Dynamic DNS feature, described in the following section, to allow users to connect to your Virtual Servers using a
URL, rather than an IP Address.
46
Page 52

Internet Features
Options
This screen allows advanced users to enter or change a number of settings. For normal operation, there is no need to
use this screen or change any settings.
Figure 31: Options Screen
Data - Options Screen
Backup DNS
IP Address
MTU
MTU size
Enter the IP Address of the DNS (Domain Name Servers) here.
These DNS will be used only if the primary DNS is unavailable.
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value should only be
changed if advised to do so by Technical Support.
• Enter a value between 1 and 1500.
• This device will still auto-negotiate with the remote server, to
set the MTU size. The smaller of the 2 values (autonegotiated, or entered here) will be used.
• For direct connections (not PPPoE or PPTP), the MTU used
is always 1500.
47
Page 53

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Chapter 7
Security Configuration
This Chapter explains the settings available via the “Advanced” configuration section of the "Security"
menu.
Overview
The following advanced configurations are provided.
• Access Control
• Firewall Rules
• Logs
• E-mail
• Security Options
• Scheduling
• Services
7
48
Page 54

Security Configuration
Access Control
This feature is accessed by the Access Control link on the Advanced, Security menu.
The Access Control feature allows administrators to restrict the level of Internet Access available to PCs on your LAN.
With the default settings, everyone has unrestricted Internet access.
To use this feature:
1. Set the desired restrictions on the "Default" group. All PCs are in the "Default" group unless explicitly moved to
another group.
2. Set the desired restrictions on the other groups ("Group 1", "Group 2", "Group 3" and "Group 4") as needed.
3. Assign PC to the groups as required.
Restrictions are imposed by blocking "Services", or types of
connections. All common Services are pre-defined.
If required, you can also define your own Services.
Access Control Screen
To view this screen, select the Access Control link on the Security menu.
Figure 32: Access Control Screen
Data - Access Control Screen
Group
Group
Select the desired Group. The screen will update to display
the settings for the selected Group. Groups are named
"Default", "Group 1", "Group 2", "Group 3" and "Group 4",
and cannot be re-named.
49
Page 55

VPN Broadband Router User manual
"Members" Button
Internet Access
Restrictions
Block by Schedule
Click this button to add or remove members from the current
Group.
• If the current group is "Default", then members can not
be added or deleted. This group contains PCs not allocated to any other group.
• To remove PCs from the Default Group, assign them to
another Group.
• To assign PCs to the Default Group, delete them from
the Group they are currently in.
See the following section for details of the Group Members
screen.
Select the desired options for the current group:
• None - Nothing is blocked. Use this to create the least
restrictive group.
• Block all Internet access - All traffic via the WAN port is
blocked. Use this to create the most restrictive group.
• Block selected Services - You can select which Services
are to block. Use this to gain fine control over the Internet
access for a group.
If Internet access is being blocked, you can choose to apply
the blocking only during scheduled times. (If access is not
blocked, no Scheduling is possible, and this setting has no
effect.)
Services
Buttons
Members
Save
Cancel
View Log
Clear Log
To define the schedule, use the Schedule option on the
menu.
This lists all defined Services. Select the Services you wish
to block. To select multiple services, hold the CTRL key while
selecting. (On the Macintosh, hold the SHIFT key rather than
CTRL.)
Click this button to add or remove members from the current
Group.
If the current group is "Default", then members can not be
added or deleted. This group contains PCs not allocated to
any other group.
See the following section for details of the Group Members
screen.
Save the data on screen.
Reverse any changes made since the last "Save".
Click this to open a sub-window where you can view the
"Access Control" log. This log shows attempted Internet
accesses which have been blocked by the Access Control
feature.
Click this to clear and restart the "Access Control" log, making new entries easier to read.
50
Page 56

Group Members Screen
This screen is displayed when the Members button on the Access Control screen is clicked.
Figure 33: Group Members
Security Configuration
Use this screen to add or remove members (PCs) from the current group.
• The "Del >>" button will remove the selected PC (in the Members list) from the current group.
• The "<< Add" button will add the selected PC (in the Other PCs list) to the current group.
PCs not assigned to any group will be in the
"Default" group.
PCs deleted from any other Group will be added
to the "Default" group.
Access Control Log
To check the operation of the Access Control feature, an Access Control Log is provided. Click the View Log button on
the Access Control screen to view this log.
This log shows attempted Internet accesses which have been blocked by the Access Control function.
Data shown in this log is as follows:
Date/Time
Name
Date and Time of the attempted access.
If known, the name of the PC whose access was blocked.
This name is taken from the Network Clients database
Source IP address
MAC address
Destination
The IP Address of the PC or device whose access request
was blocked
The hardware or physical address of the PC or device whose
access request was blocked
The destination URL or IP address
51
Page 57

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Firewall Rules
For normal operation and LAN protection, it is not necessary to use this screen.
The Firewall will always block DoS (Denial of Service) attacks. A DoS attack does not attempt to steal data or damage
your PCs, but overloads your Internet connection so you can not use it - the service is unavailable.
As well, you can use this screen to create Firewall rules to block or allow specific traffic. But incorrect configuration
may cause serious problems.
This feature is for advanced administrators only!
Firewall Rules Screen
Click the Firewall Rules option on the Security menu to see a screen like the following example. This example contains two (2) rules for outgoing traffic.
Since the default rule for outgoing (LAN => WAN) traffic is
"Allow", having an "Allow" rule for LAN => WAN only makes
sense in combination with another rule.
Data - Firewall Rules Screen
Rule List
View Rules
for..
Figure 34: Firewall Rules Screen
Select the desired option; the screen will update and list any
current rules. If you have not defined any rules, the list will be
empty.
52
Page 58

Security Configuration
Data
Add
Edit
Move
For each rule, the following data is shown:
• Name - The name you assigned to the rule.
• Source - The traffic covered by this rule, defined by the
source IP address. If the IP address is followed by ... this indicates there is range of IP addresses, rather than a single
address.
• Destination - The traffic covered by this rule, defined by
destination IP address. If the IP address is followed by ...
this indicates there is range of IP addresses, rather than a
single address.
• Action - Action will be "Forward" or "Block"
To add a new rule, click the "Add" button, and complete the
resulting screen. See the following section for more details.
To Edit or modify an existing rule, select it and click the "Edit"
button.
There are 2 ways to change the order of rules
• Use the up and down indicators on the right to move the
selected rule. You must confirm your changes by clicking
"OK". If you change your mind before clicking "OK", click
"Cancel" to reverse your changes.
• Click "Move" to directly specify a new location for the se-
lected rule.
Delete
View Log
To delete an existing rule, select it and click the "Delete" button.
Clicking the "View Log" button will open a new window and
display the Firewall log.
System Rules
Clicking the "System Rules" button will open a new window and
display the default firewall rules currently applied by the system.
These rules cannot be edited, but any rules you create will take
precedence over the default rules.
53
Page 59

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Define Firewall Rule
Clicking the "Add" button in the Firewall Rules screen will display a screen like the example below.
Data - Define Firewall Rule Screen
Name
Type
Source IP
Figure 35: Define Firewall Rule
Enter a suitable name for this rule.
This determines the source and destination ports for traffic
covered by this rule. Select the desired option.
These settings determine which traffic, based on their
source IP address, is covered by this rule.
Select the desired option:
• Any - All traffic from the source port is covered by this
rule.
• Single address - Enter the required IP address in the
"Start IP address" field". You can ignore the "Subnet
Mask" field.
• Range address - If this option is selected, you must
complete both the "Start IP address" and "Finish IP address" fields. You can ignore the "Subnet Mask" field.
• Subnet address - If this option is selected, enter the
required mask in the "Subnet Mask" field.
54
Page 60

Security Configuration
Dest. IP
These settings determine which traffic, based on their
destination IP address, is covered by this rule.
Select the desired option:
• Any - All traffic from the source port is covered by this
rule.
• Single address - Enter the required IP address in the
"Start IP address" field". You can ignore the "Subnet
Mask" field.
• Range address - If this option is selected, you must
complete both the "Start IP address" and "Finish IP address" fields. You can ignore the "Subnet Mask" field.
• Subnet address - If this option is selected, enter the
required mask in the "Subnet Mask" field.
Services
Select the desired Service or Services. This determines
which packets are covered by this rule, based on the protocol (TPC or UDP) and port number. If necessary, you can
define a new Service on the "Services" screen, by defining
the protocols and port numbers used by the Service.
Action
Log
Select the desired action for packets covered by this rule:
This determines whether packets covered by this rule are
logged. Select the desired option.
55
Page 61

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Logs
The Logs record various types of activity on the VPN Broadband Router. This data is useful for troubleshooting, but
enabling all logs will generate a large amount of data and adversely affect performance.
Since only a limited amount of log data can be stored in the VPN Broadband Router, log data can also be E-mailed to
your PC or sent to a Syslog Server.
Data - Logs Screen
Enable Logs
Incoming
Traffic
Figure 36: Logs Screen
Select the desired option:
• All IP traffic - this will log all incoming TCP/IP connections,
of any type. This will generate the largest logs, and fill the internal log buffer more quickly.
• All TCP/UDP/ICMP traffic - These 3 protocols are used by
most internet traffic. TCP is used by HTTP, FTP, Telnet, Email and other common Internet protocols and applications.
UDP is used by Video streams and other communications
where speed is more important than guaranteed delivery.
ICMP is used by the "ping" and "trace route" applications,
and other network diagnostics.
56
Page 62

Security Configuration
Outgoing
Traffic
System Log
Select the desired option:
• All IP traffic - - this will log all outgoing TCP/IP connections,
of any type. This will generate the largest logs, and fill the internal log buffer more quickly.
• All TCP/UDP/ICMP traffic - These 3 protocols are used by
most internet traffic. TCP is used by HTTP, FTP, Telnet, Email and other common Internet protocols and applications.
UDP is used by Video streams and other communications
where speed is more important than guaranteed delivery.
ICMP is used by the "ping" and "trace route" applications,
and other network diagnostics.
Because most connections are logged, the logs will still be
large.
• Selected Traffic only - This selection will reduce the size of
the log considerably. Only HTTP connections are logged.
Select the traffic you wish to include:
• Attempted access to blocked sites - This will only log
Web connections which are blocked by the URL filter.
• Websites and news groups - This logs successful (al-
lowed) connections to Web Sites and newsgroup
servers.
Select the desired option:
• Router operations (start up, get time etc) - This option will
log normal Router operations.
• Connections to the Web - based interface of this Router
- This option will log each connection to the Router itself,
whenever the Web-based management interface is used.
• Other connections and traffic to this Router - This option
will log other traffic sent to the Router itself, such as "pings"
or RIP (Router Information Protocol) packets.
• Known DoS attacks and Port Scans - This will log details
of DoS (Denial of Service) attacks which have been blocked
by the built-in Firewall. This Firewall uses "Stateful Inspection" technology to block packets which are individually valid,
but collectively form an attack. Port scans, where a series of
ports are checked to see if they are open (available) are also
logged.
VPN
View Log
Button
Clear Log
Button
Timezone
Timezone
Syslog Server
Enable Syslog
Syslog Server
Include
If enabled, the VPN log will record incoming and outgoing VPN
connections.
Use this to view each log, as required.
Use this to restart the required log. This makes it easier to read
the latest entries.
Select the correct Timezone for your location. This is required
for the date/time shown on the logs to be correct.
If enabled, log data will be sent to your Syslog Server.
Enter the IP address of your Syslog Server.
Select the logs you wish to be included in the data sent to the
Syslog Server.
57
Page 63

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Data – E-Mail Screen
E-Mail Alerts
Send E-Mail alert
E-Mail Logs
Send Logs by E-
Mail
Include
Send
Figure 37: E-Mail Screen
If enabled, an E-mail will be sent immediately if a DoS
(Denial of Service) attack is detected. If enabled, the E-mail
address information must be provided.
If enabled, logs will be logs to the specified E-mail address.
You need to select the Logs to be E-mailed, and complete
the E-mail address settings on this screen.
Select the log items to be included in the E-mail.
Select the desired option for sending the log by E-mail.
• When log is full - The time is not fixed. The log will be
sent when the log is full, which will depend on the volume of traffic.
• Every day, Every Monday... - The log is sent on the
interval specified.
• If "Every day" is selected, the log is sent at the time
specified.
• If the day is specified, the log is sent once per
week, on the specified day.
• Select the time of day you wish the E-mail to be
sent.
• If the log is full before the time specified to send it,
it will be sent regardless.
58
Page 64

Security Configuration
E-mail address
Enter the E-mail address the Log is to be sent to. The Email will also show this address as the Sender's address.
Subject
Enter the text string to be shown in the "Subject" field for
the E-mail.
SMTP Server
Enter the address or address or IP address of the SMTP
(Simple Mail Transport Protocol) Server you use for outgoing E-mail.
Port No.
Enter the port number used to connect to the SMTP Server.
The default value is 25.
59
Page 65

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Security Options
This screen allows you to set Firewall and other security-related options.
Figure 38: Security Options Screen
Data - Security Options Screen
Firewall
Enable DoS
Firewall
Threshold
If enabled, DoS (Denial of Service) attacks will be detected and
blocked. The default is enabled. It is strongly recommended that
this setting be left enabled.
Note:
• A DoS attack does not attempt to steal data or damage your
PCs, but overloads your Internet connection so you can not
use it - the service is unavailable.
• This device uses "Stateful Inspection" technology. This
system can detect situations where individual TCP/IP packets are valid, but collectively they become a DoS attack.
This setting affects the number of "half-open" connections
allowed.
• A "half-open" connection arises when a remote client con-
tacts the Server with a connection request, but then does
not reply to the Server's response.
• While the optimum number of "half-open" connections
allowed (the "Threshold") depends on many factors, the
most important factor is the available bandwidth of your
Internet connection.
• Select the setting to match the bandwidth of your Internet
connection.
60
Page 66

Options
Security Configuration
Respond to
ICMP (ping)
Allow VPN passthrough
Drop fragmented
IP packets
The ICMP protocol is used by the "ping" and "trace route"
programs, and by network monitoring and diagnostic programs.
• If checked, the VPN Broadband Router will respond to
ICMP packets received from the Internet.
• If not checked, ICMP packets from the Internet will be
ignored. Disabling this option provides a slight increase in
security.
If enabled, PCs on the LAN can use VPN software to connect
to remote clients via the Internet connection. The protocols
supported are:
• IPSec
IPSec protocol is used to establish a secure connection,
and is widely used by VPN (Virtual Private Networking)
programs.
• PPTP
PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol) is widely used by
VPN (Virtual Private Networking) programs.
• L2TP
L2TP is a protocol developed by Cisco for VPNs (Virtual
Private Networks).
If enabled, fragmented IP packets are discarded, forcing retransmission of these packets. In some situations, this could
prevent successful communication.
Normally, this setting should be disabled.
Block TCP Flood
A TCP flood is excessively large number of TCP connection
requests. This is usually a DoS (Denial of Service) attack.
This setting should normally be enabled.
Block UDP Flood
A UDP flood is excessively large number of UDP packets. This
is usually a DoS (Denial of Service) attack.
This setting should normally be enabled.
Block nonstandard packets
Abnormal packets are often used by hackers and in DoS
attacks, but may also be generated by incorrectly configured
network devices. (PCs will normally not generate non-standard
packets.)
This setting should normally be enabled.
61
Page 67

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Scheduling
• This schedule can be (optionally) applied to any Access Control Group.
• Blocking will be performed during the scheduled time (between the "Start" and "Finish" times.)
• Two (2) separate sessions or periods can be defined.
• Times must be entered using a 24 hr clock.
• If the time for a particular day is blank, no action will be performed.
Define Schedule Screen
This screen is accessed by the Scheduling link on the Security menu.
Data - Define Schedule Screen
Day
Session 1
Session 2
Start Time
Finish Time
Figure 39: Define Schedule Screen
Each day of the week can scheduled independently.
Two (2) separate sessions or periods can be defined. Session
2 can be left blank if not required.
Enter the start using a 24 hr clock.
Enter the finish time using a 24 hr clock.
62
Page 68

Security Configuration
Services
Services are used in defining traffic to be blocked or allowed by the Access Control or Firewall Rules features. Many
common Services are pre-defined, but you can also define your own services if required.
To view the Services screen, select the Services link on the Security menu.
Data - Services Screen
Available Services
Available Ser-
vices
Delete Button
Add New Service
Name
Type
Start Port
Finish Port
Figure 40: Services Screen
This lists all defined Services.
Use this to delete the selected Service from the list.
Note that you can only delete Services you have added; the
pre-defined services can not be deleted.
Enter a suitable name for this Service.
Select the correct type for this Service.
If the "Type" (above) is TCP, UDP, or TCP/UDP, enter the port
number for this Service. If a port range is required, enter the
beginning of the range here, and the end of the range in the
"Finish Port" field.
If the "Type" (above) is TCP, UDP, or TCP/UDP, this field can
be used to enter the end of range of port numbers. This can be
left blank if not required.
ICMP Type
If the "Type" (above) is ICMP, enter the ICMP type here.
Otherwise, this field should be left blank.
63
Page 69

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Chapter 8
VPN (IPSec)
This Chapter describes the VPN capabilities and configuration required for common situations.
8
Overview
This section describes the VPN (Virtual Private Network) support provided by your VPN Broadband Router.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) provides a secure connection between 2 points, over an insecure network - typically
the Internet. This secure connection is called a VPN Tunnel.
There are many standards and protocols for VPNs. The standard implemented in the VPN Broadband Router is IPSec.
IPSec
IPSec is a near-ubiquitous VPN security standard, designed for use with TCP/IP networks. It works at the packet level,
and authenticates and encrypts all packets traveling over the VPN Tunnel. Thus, it does not matter what applications
are used on your PC. Any application can use the VPN like any other network connection.
IPsec VPNs exchange information through logical connections called SAs (Security Associations). An SA is simply a
definition of the protocols, algorithms and keys used between the two VPN devices (endpoints).
Each IPsec VPN has two SAs - one in each direction. If IKE (Internet Key Exchange) is used to generate and exchange keys, there are also SAs for the IKE connection as well as the IPsec connection.
There are two security modes possible with IPSec:
• Transport Mode - the payload (data) part of the packet is encapsulated through encryption but the IP header
remains in the clear (unchanged).
The VPN Broadband Router does NOT support Transport Mode.
• Tunnel Mode - everything is encapsulated, including the original IP header, and a new IP header is generated.
Only the new header in the clear (i.e. not protected). This system provides enhanced security.
The VPN Broadband Router always uses Tunnel Mode.
IKE
IKE (Internet Key Exchange) is an optional, but widely used, component of IPsec. IKE provides a method of negotiating and generating the keys and IDs required by IPSec. If using IKE, only a single key is required to be provided
during configuration. Also, IKE supports using Certificates (provided by CAs - Certification Authorities) to authenticate
the identify of the remote user or gateway.
If IKE is NOT used, then all keys and IDs (SPIs) must be entered manually, and Certificates can NOT be used. This is
called a "Manual Key Exchange".
When using IKE, there are 2 phases to establishing the VPN tunnel:
• Phase I is the negotiation and establishment up of the IKE connection.
• Phase II is the negotiation and establishment up of the IPsec connection.
Because the IKE and IPsec connections are separate, they have different SAs (security associations).
Policies
VPN configuration settings are stored in Policies.
Note that different vendors use different terms. Generally, the terms "VPN Policy", "IPSec Policy", and "IPSec Pro-
posal" have the same meaning. However, some vendors separate IKE Policies (Phase 1 parameters) from IPSec
Policies (Phase 2 parameters).
For the VPN Broadband Router; each VPN policy contains both Phase 1 and Phase 2 parameters (if IKE is used).
Each policy defines:
64
Page 70

Microsoft VPN
• The address of the remote VPN endpoint
• The traffic which is allowed to use the VPN connection.
• The parameters (settings) for the IPsec SA (Security Association)
• If IKE is used, the parameters (settings) for the IKE SA (Security Association)
Generally, you will need at least one (1) VPN Policy for each remote site for which you wish to establish VPN connections.
It is possible, and sometimes necessary, to have multiple Policies for the same remote site. However, you should only
Enable one (1) policy at a time. If multiple policies for the same remote site are enabled, the policies are examined in
the order in which they are listed, and the first matching policy will be used. While it is possible to change the order of
the policies, it may not be easy to get the desired action from multiple policies.
VPN Configuration
The general rule is that each endpoint must have matching Policies, as follows:
VPN Endpoint
address
Traffic Selector
IKE parameters
IPsec parameters
Common VPN Situations
Each VPN endpoint must be configured to initiate or accept
connections to the remote VPN client or Gateway.
Usually, this requires having a fixed Internet IP address. However, it is possible for a VPN Gateway to accept incoming
connections from a remote client where the client's IP address
is not known in advance.
This determines which outgoing traffic will cause a VPN connection to be established, and which incoming traffic will be
accepted. Each endpoint must be configured to pass and accept the desired traffic from the remote endpoint.
If connecting 2 LANs, this requires that:
• Each endpoint must be aware of the IP addresses used on
the other endpoint.
• The 2 LANs MUST use different IP address ranges.
If using IKE (recommended), the IKE parameters must match
(except for the SA lifetime, which can be different).
The IPsec parameters at each endpoint must match.
VPN Pass-through
Figure 41: VPN Pass-through
Here, a PC on the LAN behind the Router/Gateway is using VPN software, but the Router/Gateway is NOT acting as a
VPN endpoint. It is only allowing the VPN connection.
• The PC software can use any VPN protocol supported by the remote VPN.
65
Page 71

VPN Broadband Router User manual
• The remote VPN Server must support client PCs which are behind a NAT router, and so have an IP address
which is not valid on the Internet.
• The Router/Gateway requires no VPN configuration, since it is not acting as a VPN endpoint.
Client PC to VPN Gateway
Figure 42: Client PC to VPN Server
In this situation, the PC must run appropriate VPN client software in order to connect, via the Internet, to the VPN
Broadband Router. Once connected, the client PC has the same access to LAN resources as PCs on the local LAN
(unless restricted by the network administrator).
• IPsec is not the only protocol which can be used in this situation, but the VPN Broadband Router supports IPsec
ONLY.
• Windows 2000 and Windows XP include a suitable IPsec VPN client program. Configuration of this client program
for use with the VPN Broadband Router is covered later in this document.
Connecting 2 LANs via VPN
Figure 43: Connecting 2 VPN Gateways
This allows two (2) LANs to be connected. PCs on each endpoint gain secure access to the remote LAN.
• The 2 LANs MUST use different IP address ranges.
• The VPN Policies at each end determine when a VPN tunnel will be established, and what systems on the remote
LAN can be accessed once the VPN connection is established.
• It is possible to have simultaneous VPN connections to many remote sites.
66
Page 72

Microsoft VPN
VPN Configuration
This section covers the configuration required on the VPN Broadband Router when using Manual Key Exchange
(Manual Policies) or IKE (Automatic Policies).
Details of using Certificates are covered in a later section.
VPN Policies Screen
To view this screen, select VPN Policies from the VPN menu. This screen lists all existing VPN policies. If no policies
exist, the list will be empty.
Figure 44: VPN Policies Screen
Note that the order of policies is important if you have more than one policy for a particular site. In that case, the first
matching policy (for the traffic under consideration) will be used.
Data - VPN Policies Screen
VPN List
Policy Name
Enable
Remote VPN
Endpoint
Key Type
Operations
Add
Edit
The name of the policy. When creating a policy, you should select
a suitable name.
This indicates whether or not the policy is currently enabled. Use
the "Enable/Disable" button to toggle the state of the selected
policy.
The IP address of the remote VPN endpoint (Gateway or client).
This will indicate "Manual" (manual key exchange) or "IKE" (Internet Key Exchange)
To add a new policy, click the "Add" button. See the following
section for details.
To Edit or modify an existing policy, select it and click the "Edit"
button.
67
Page 73

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Move
The order in which policies are listed is only important if you have
multiple polices for the same remote site. In that case, the first
matching policy is used. There are 2 ways to change the order of
policies:
• Use the up and down indicators on the right to move the
selected row. You must confirm your changes by clicking
"OK". If you change your mind before clicking "OK", click
"Cancel" to reverse your changes.
• Click "Move" to directly specify a new location for the selected
policy.
En-
Use this to toggle the On/Off state of the selected policy.
able/Disable
Copy
If you wish to create a policy which is similar to an existing policy,
select the policy and click the "Copy" button.
Remember that the new policy must have a different name, and
there can only be one active (enabled) policy for each remote
VPN endpoint.
Delete
View Log
To delete an exiting policy, select it and click the "Delete" button.
Clicking the "View Log" button will open a new window and dis-
play the VPN log.
Adding a New Policy
1. To create a new VPN Policy, click the Add New Policy button on the VPN Policies screen. This will start the VPN
Wizard, as shown below.
Figure 45: VPN Wizard – Start Screen
• If you prefer to use a single setup screen instead of a Wizard, click the Setup Screen button. This is recom-
mended for experienced users only.
• Otherwise, click Next to continue. You will see a screen like the following.
68
Page 74

Figure 46: VPN Wizard – General Screen
Microsoft VPN
General Settings
Policy Name
Enable Policy
Allow NetBIOS traffic
Remote VPN
Endpoint
Keys
Enter a suitable name. This name is not supplied to the remote
VPN. It is used only to help you manage the policies.
Enable or disable the policy as required. For each remote VPN,
only 1 policy can be enabled at any time.
Enable this if you require NetBIOS traffic to be transferred through
the VPN tunnel. NetBIOS is used by Microsoft (Windows) networking. This setting should not be enabled unless necessary,
because it increases traffic volume.
The Internet IP address of the remote VPN endpoint (Gateway or
client).
• Dynamic. Select this if the Internet IP address is unknown. In
this case, only incoming connections are possible.
• Fixed. Select this if the remote endpoint has a fixed Internet
IP address. If selected, enter the Internet IP address of the
remote endpoint.
• Domain Name. Select this if the remote endpoint has a
Domain Name associated with it. If selected, enter the Domain Name of the remote endpoint.
Select Manually assigned or IKE (Internet Key Exchange) as
required.
If you are setting up both endpoints, using IKE is recommended.
2. Click Next to continue. You will see a screen like the following:
69
Page 75

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 47: VPN Wizard - Traffic Selector Screen
• For outgoing VPN connections, these settings determine which traffic will cause a VPN tunnel to be created, and
which traffic will be sent through the tunnel.
• For incoming VPN connections, these settings determine which systems on your local LAN will be available to the
remote endpoint.
• The 2 VPN endpoints MUST use different address ranges.
If the addresses were in the same range, traffic intended for the remote VPN would be considered local LAN traffic.
So it would not be forwarded to the Gateway.
Local IP addresses
Type
• Any - no additional data is required. Any IP address is
acceptable.
• For outgoing connections, this allows any PC on the
LAN to use the VPN tunnel.
• For incoming connections, this allows any PC using
the remote endpoint to access any PC on your LAN.
• Single address - enter an IP address in the "Start IP
address" field.
• Range address - enter the starting IP address in the "Start
IP address" field, and the finish IP address in the "Finish IP
address" field.
• Subnet address - enter the desired IP address in the
"Start IP address" field, and the network mask in the "Subnet Mask" field.
The remote VPN must have these IP addresses entered as it's
"Remote" addresses.
70
Page 76

Microsoft VPN
Remote IP addresses
Type
• Single address - enter an IP address in the "Start IP
address" field.
• Range address - enter the starting IP address in the "Start
IP address" field, and the finish IP address in the "Finish IP
address" field.
• Subnet address - enter the desired IP address in the
"Start IP address" field, and the network mask in the "Subnet Mask" field.
The remote VPN should have these IP addresses entered as
it's "Local" addresses.
3. Click Next to continue. The screen you will see depends on whether you previously selected "Manual Key Ex-
change" or "IKE".
Manual Key Exchange
Figure 48: VPN Wizard - Manual Key Exchange Screen
These settings must match the remote VPN. Note that you cannot use both AH and ESP.
Manually assigned Keys
AH Authentication
AH (Authentication Header) specifies the authentication
protocol for the VPN header, if used. (AH is often NOT used)
If AH is not enabled, the following settings can be ignored.
Keys
• The "in" key here must match the "out" key on the remote
VPN, and the "out" key here must match the "in" key on
the remote VPN.
• Keys can be in ASCII or Hex (0..9 A..F)
• For MD5, the keys should be 32 hex/16 ASCII charac-
ters.
• For SHA-1, the keys should be 40 hex/20 ASCII charac-
ters.
SPI
71
Page 77

VPN Broadband Router User manual
• Each SPI (Security Parameter Index) must be unique.
• The "in" SPI here must match the "out" SPI on the re-
mote VPN, and the "out" SPI here must match the "in"
SPI on the remote VPN.
• Each SPI should be at least 3 characters.
ESP Encryption
ESP Authentication
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) provides security for
the payload (data) sent through the VPN tunnel. Generally,
you will want to enable both Encryption and Authentication.
Encryption Algorithm
• The 3DES algorithm provides greater security than DES,
but is slower.
• If using AES, you must select the Key Size. If using DES
or 3DES, this field is ignored.
Key - In / Key - Out
• The "In" key here must match the "Out" key on the re-
mote VPN, and the "Out" key here must match the "In"
key on the remote VPN.
• For DES, keys should be 8 ASCII characters (16 HEX
chars).
• For 3DES, keys should be 24 ASCII characters (48 HEX
chars).
• If using AES encryption, the key input size must match
the Key Size selected above.
Generally, you should enable ESP Authentication. There is
little difference between the available algorithms. Just ensure
each endpoint use the same setting.
• The "In" key here must match the "Out" key on the re-
mote VPN, and the "Out" key here must match the "In"
key on the remote VPN.
• Keys can be in ASCII or Hex (0 ~ 9 and A ~ F)
• For MD5, the keys should be 32 hex/16 ASCII charac-
ters.
• For SHA-1, the keys should be 40 hex/20 ASCII charac-
ters.
ESP SPI This is required if either ESP Encryption or ESP Authen-
tication is enabled.
• Each SPI (Security Parameter Index) must be unique.
• The "in" SPI here must match the "out" SPI on the re-
mote VPN, and the "out" SPI here must match the "in"
SPI on the remote VPN.
• Each SPI should be at least 3 characters.
For Manual Key Exchange, configuration is now complete.
• Click "Next" to view the final screen.
• On the final screen, click "Finish" to save your settings, then "Close" to exit the Wizard.
IKE Phase 1
If you selected IKE, the following screen is displayed after the Traffic Selector screen. This screen sets the parameters
for the IKE SA.
72
Page 78

Figure 49: VPN Wizard - IKE Phase 1 Screen
Microsoft VPN
IKE Phase 1 (IKE SA)
Local Identity
This setting must match the "Remote Identity" on the remote
VPN. Select the desired option, and enter the required data in
the "Local Identity Data" field.
• WAN IP Address - This is the most common method. If
• Fully Qualified Domain Name - enter the Domain Name
• Fully Qualified User name - This name does not have to
• DER ANS.1 DN - This must be a DER ANS.1 Domain
Remote Identity
This setting must match the "Local Identity" on the remote
VPN. Select the desired option, and enter the required data in
the "Remote Identity Data" field.
• IP Address - This is the most common method. If se-
• Fully Qualified Domain Name - enter the Domain Name
• Fully Qualified User name - This name does not have to
• DER ANS.1 DN - This must be a DER ANS.1 Domain
Authentication
• RSA Signature requires that both VPN endpoints have
• For Pre-shared key, enter the same key value in both
selected, no input is required.
assigned to this device.
a valid Internet Domain Name. E-mail addresses are often
used for this entry.
Name.
lected, no input is required.
assigned to this device.
a valid Internet Domain Name. E-mail addresses are often
used for this entry.
Name.
valid Certificates issued by a CA (Certification Authority).
endpoints. The key should be at least 8 characters (maximum is 128 characters). Note that this key is used for the
IKE SA only. The keys used for the IPsec SA are automatically generated.
73
Page 79

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Authentication
Algorithm
Encryption
Algorithm
IKE Exchange
Mode
Direction
Select the desired option, and ensure that both endpoints have
the same settings.
Select the desired method, and ensure the remote VPN endpoint uses the same method.
• The 3DES algorithm provides greater security than DES,
but is slower.
• If using AES, you must select the Key Size. If using DES
or 3DES, this field is ignored.
Select the desired option, and ensure the remote VPN endpoint uses the same mode.
• Main Mode provides identity protection for the hosts initiat-
ing the IPSec session, but takes slightly longer to
complete.
• Aggressive Mode provides no identity protection, but is
quicker.
Select the desired option:
• Initiator - Only outgoing connections will be created.
Incoming connection attempts will be rejected.
• Responder - Only incoming connections will be accepted.
Outgoing traffic which would otherwise result in a connection will be ignored.
• Both Directions - Both incoming and outgoing connec-
tions are allowed.
IKE SA Life Time
This setting does not have to match the remote VPN endpoint;
the shorter time will be used. Although measured in seconds, it
is common to use time periods of several hours, such 28,800
seconds.
DH Group
Select the desired method, and ensure the remote VPN endpoint uses the same method. The smaller bit size is slightly
faster.
IKE PFS
If enabled, PFS (Perfect Forward Security) enhances security
by changing the IPsec key at regular intervals, and ensuring
that each key has no relationship to the previous key. Thus,
breaking 1 key will not assist in breaking the next key.
This setting should match the remote endpoint.
IKE Keep Alive
Click Next to see the following IKE Phase 2 screen.
74
Page 80

Microsoft VPN
IKE Phase 2 Screen
This screen sets the parameters for the IPSec SA. When using IKE, there are separate connections (SAs) for IKE and
IPSec.
Figure 50: VPN Wizard - IKE Phase 2 Screen
IKE Phase 2 (IPsec SA)
IPsec SA Life
Time
This setting does not have to match the remote VPN endpoint; the shorter time will be used. Although measured in
seconds, it is common to use time periods of several hours,
such 28,800 seconds.
IPSec PFS
If enabled, PFS (Perfect Forward Security) enhances security
by changing the IPsec key at regular intervals, and ensuring
that each key has no relationship to the previous key. Thus,
breaking 1 key will not assist in breaking the next key.
AH Authentication
AH (Authentication Header) specifies the authentication
protocol for the VPN header, if used.
AH is often NOT used. If you do enable it, ensure the algorithm selected matches the other VPN endpoint.
ESP Encryption
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) provides security for
the payload (data) sent through the VPN tunnel. Generally,
you will want to enable both ESP Encryption and ESP Authentication.
Select the desired method, and ensure the remote VPN
endpoint uses the same method.
• The 3DES algorithm provides greater security than DES,
• If using AES, you must select the Key Size. If using DES
but is slower.
or 3DES, this field is ignored.
ESP Authentication
Generally, you should enable ESP Authentication. There is
little difference between the available algorithms. Just ensure
each endpoint use the same setting.
75
Page 81

VPN Broadband Router User manual
For IKE, configuration is now complete.
Click "Next" to view the final screen.
Figure 51: VPN Wizard - Final Screen
On the final screen, click "Finish" to save your settings, then "Close" to exit the Wizard.
76
Page 82

VPN Examples
This section describes some examples of using the VPN Broadband Router in common VPN situations.
Example 1: Connecting 2 VPN Broadband Routers
In this example, 2 LANs are connected via VPN.
Figure 52: Connecting 2 VPN Broadband Routers
Note
• The LANs MUST use different IP address ranges.
• Both endpoints have fixed WAN (Internet) IP addresses.
Microsoft VPN
Configuration Settings
Setting LAN A Gate-
Name Policy 1 Policy 1 Name does not affect
Remote Endpoint 205.17.11.43 202.11.13.211 Other endpoint's WAN
Local
IP addresses
Remote
IP addresses
Key Exchange IKE IKE Must match
IKE SA Parameters
IKE Direction Both ways Both ways Does not have to match.
Local Identity IP address IP address IP address is the most
LAN B Gate-
way
Any Any Use a more restrictive
192.168.1.1 to
192.168.1.254
way
192.168.0.1 to
192.168.0.254
Notes
operation. Select a
meaningful name.
(Internet) IP address.
definition if possible.
Address range on other
endpoint.
Use a more restrictive
definition if possible.
Either endpoint can
block 1 direction.
common ID method
Remote Identity IP address IP address IP address is the most
common ID method
IKE Authentication method
Pre-shared Key Xxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxx Must match
IKE Authentica-
tion algorithm
IKE Encryption DES DES Must match
Pre-shared Key Pre-shared Key Certificates are not
widely used.
MD5 MD5 Must match
77
Page 83

VPN Broadband Router User manual
IKE Exchange
Main Mode Main Mode Must match
mode
DH Group Group 1 (768
bit)
Group 1 (768
bit)
Must match
IKE SA Life time 28800 28800 Does not have to match.
Shorter period will be
used.
IKE PFS Disable Disable Must match
IPSec SA Parameters
IPSec SA Life
time
28800 28800 Does not have to match.
Shorter period will be
used.
IPSec PFS Disabled Disabled Must match
AH authentication Disabled Disabled AH is rarely used
ESP authentica-
Enable/MD5 Enable/MD5 Must match
tion
ESP encryption Enable/DES Enable/DES Must match
78
Page 84

Microsoft VPN
Example 2: Windows 2000/XP Client to LAN
In this example, a Windows 2000/XP client connects to the VPN Broadband Router and gains access to the local LAN.
Figure 53: Windows 2000/XP Client to VPN Broadband Router
To use 3DES encryption on Windows 2000, you
need Service Pack 3 or later installed.
VPN Broadband Router Configuration
Setting Value Notes
Name Win Client Name does not affect operation. Select a
Remote Endpoint 172.16.9.10 Other endpoint's WAN (Internet) IP ad-
Local
IP addresses
Remote
IP addresses
Key Exchange IKE Must match client PC
IKE SA Parameters
IKE Direction Both ways Using "Responder only" is not possible.
Local Identity IP address Required.
Remote Identity IP address Required
IKE Authentica-
tion method
Pre-shared Key Xxxxxxxxxx Must match client PC
Subnet address:
192.168.0.0
255.255.255.0
172.16.9.10 For a single client, this address is the
Pre-shared Key Certificates are not widely used.
meaningful name.
dress.
Allows access to entire LAN. Use a more
restrictive definition if possible.
same as the endpoint address.
IKE Authentication algorithm
IKE Encryption 3DES Must match client PC
IKE Exchange
mode
DH Group Group 1 (768 bit) Must match client PC
IKE SA Life time 28800 Does not have to match client PC. Shorter
IKE PFS Disable Must match client PC
IPSec SA Parameters
SHA-1 Must match client PC
Main Mode Windows 2000 only supports Main Mode.
period will be used.
79
Page 85

VPN Broadband Router User manual
IPSec SA Life
time
28800 Do not have to match. Shorter period will
be used.
IPSec PFS Disable Must match client PC
AH authentication Disabled AH is rarely used
ESP authentica-
Enable/MD5 Must match client PC
tion
ESP encryption Enable/DES Must match client PC
Windows Client Configuration
1. Select Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Local Security Policy.
2. Right click IP Security Policy on Local Machine and select Create IP Security Policy
Figure 54: Windows 2000/XP - Local Security Settings
3. Click "Next", then enter a policy name, for example "DUT To Win2K", then click "Next".
4. Step through the Wizard:
• Deselect Activate the default response rule. Click "Next",
• Leave Edit Properties checked. Click "Finish".
5. The following "Properties - Rules" screen will be displayed.
80
Page 86

Figure 55: Windows 2000/XP - Policy Properties
• Note that no rules are in use. Two (2) rules are required - incoming and outgoing.
• The outgoing rule will be added first.
Microsoft VPN
6. Deselect the "Use Add Wizard" checkbox, then click "Add" to view the screen below.
Figure 56: IP Filter List
7. Type "To DUT" for the name, then click "Add" to see a screen like the following.
81
Page 87

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 57: Filter Properties: Addressing
8. Enter the Source IP address and the Destination IP address.
• Since this is the outgoing filter, the Source IP address is "My IP address" and the Destination IP address is the
address range used on the remote LAN.
• Ensure the Mirrored option is checked.
9. Click "OK" to save your settings and close this dialog.
Figure 58: New Rule Properties: IP Filter List
10. On the resulting screen (above), ensure the "To DUT" filter is selected, then click the Filter Action tab to see a
screen like the following
82
Page 88

Figure 59: New Rule Properties: Filter Action
11. Select Require Security, then click the "Edit" button, to view the Require Security Properties screen.
Microsoft VPN
Figure 60: Require Security Properties
12. Select Negotiate security (this selects IKE), then click "Add".
83
Page 89

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 61: Modify Security Method
13. On the resulting screen (above), select High [ESP] then click "OK" to save your changes and return to the Require
Security Properties screen.
Figure 62: Require Security Properties
14. Ensure the following settings are correct, then click "OK" to return to the Filter Action tab of the Edit Rule Properties screen.
VPN Setting Windows Setting
IKE enabled Negotiate security
AH disabled AH Integrity: <None>
ESP encryption: Enable/DES ESP Confidentially: DES
ESP authentication: Enable/MD5 ESP Integrity: MD5
84
Page 90

Microsoft VPN
15. Click the Tunnel Setting tab, then select The tunnel endpoint is specified by this IP address. Enter the WAN (Inter-
net) IP address of the VPN Broadband Router, as shown below.
Figure 63: Tunnel Setting
16. Click the Authentication Methods tab, then click the "Edit" to see the screen like the example below.
Figure 64: Authentication Method
17. Select Use this string to protect the key exchange (preshared key), then enter your preshared key in the field
provided.
18. Click "OK" to save your changes and return to the Authentication Methods tab of the Edit Rule Properties screen.
19. Click "Close" to return to the DUT to Win2K properties screen. The "To DUT" filter should now be listed, as shown
below.
85
Page 91

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 65: Windows 2000/XP Client to VPN Broadband Router
20. To add the second (incoming) rule, click "Add". For the name, enter "To Win2K", then click "Add".
Figure 66: Windows 2000/XP Client to VPN Broadband Router
21. Enter the Source IP address and the Destination IP address as shown below.
• Since this is the incoming filter, the Source IP address is the address range used on the remote LAN and the
Destination IP address is "My IP address".
• Ensure the Mirrored option is checked.
86
Page 92

Figure 67: Filter Properties: Addressing
22. Click "OK" to save your changes, then "Close".
Microsoft VPN
Figure 68: Filter List
23. Ensure the "To Win2K" filter is selected, then click the Filter Action tab.
87
Page 93

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 69: Filter Action
24. Select Require Security, then click "Edit". On the Require Security Methods screen below, select Negotiate secu-
rity.
Figure 70: Security Methods
25. Click the "Add" button. On the resulting Modify Security Method screen below, select High [ESP].
88
Page 94

Microsoft VPN
Figure 71: Modify Security Method
26. Click "OK" to save your changes, then click "OK" again to return to the Filter Action screen.
27. Select the Tunnel Setting tab, and enter the WAN (Internet) IP address of this PC (172.16.9.10 in this example).
Figure 72: Tunnel Setting
28. Select the Authentication Methods tab, and click the "Edit" button to see the screen below.
89
Page 95

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Figure 73: Authentication Method
29. Select Use this string to protect the key exchange (preshared key), then enter your preshared key in the field
provided.
30. Click "OK" to save your settings, then "Close" to return to the DUT to Win2K Properties screen. There should now
be 2 IP Filers listed, as shown below.
31. Select the General tab.
Figure 74: DUT to Win2K Properties
90
Page 96

Figure 75: Properties - General Tab
32. Click the "Advanced" button to see the screen below.
Microsoft VPN
Figure 76: Key Exchange Settings
33. Click the "Methods" button to see the screen below.
Figure 77: Key Exchange Security Methods
91
Page 97

VPN Broadband Router User manual
34. Select the first entry, and click the "Edit" button to see the following screen.
Figure 78: IKE Security Algorithms
35. Select "SHA1" for Integrity Algorithm, "3DES" for Encryption algorithm, and "Low(1)" for the Diffie-Hellman Group.
36. Click "OK" to save, then "OK" again, and then "Close" to return to the Local Security Settings screen.
37. Right click the DUT to Win2K Policy and select "Assign" to make your policy active.
Figure 79: Windows 2000/XP Client to VPN Broadband Router
Configuration is now complete.
Example 3: Windows 2000 Server to VPN Gateway
In this example, a Windows 2000 Server connects to the VPN Broadband Router. Users on each LAN can then gain
access to the remote LAN.
Figure 80: VPN Broadband Router to Windows 2000 Server
92
Page 98

Microsoft VPN
VPN Broadband Router Configuration
This is the same as for the client setup earlier, with the exception of the IP address range for the remote endpoint.
Setting Single Client Server/Gateway
Remote
IP addresses
172.16.9.10
For a single client, this is
the same as the Gateway
address
Subnet address:
11.5.0.0
255.255.0.0
Address range used on the remote
LAN.
93
Page 99

VPN Broadband Router User manual
Windows 2000 Server Configuration
Configuration is the same as for Example 2: Windows 2000/XP Client to except for specifying the Source and Destination addresses for the "Filter Properties". Instead, for both IP Filters, the Filter Properties- Addressing should be
completed as follows.
Figure 81: Windows 2000 Server – Addressing
• The Source Address should be set to "A specific IP Subnet", and the IP address and Subnet mask set to the
address range used on the VPN Broadband Router's LAN.
• The Destination Address should be set to "A specific IP Subnet", and the IP address and Subnet mask set to the
address range used on the Windows 2000 LAN.
94
Page 100

Microsoft VPN
Certificates
Certificates are used to authenticate users. Certificates are issued to you by various CAs (Certification Authorities).
These Certificates are called "Self Certificates".
Each CA also issues a certificate to itself. This Certificate is required in order to validate communication with the CA.
These certificates are called "Trusted Certificates."
The Certificates screen lists either the Trusted Certificates - the certificates of each CA itself - or Self Certificates the certificates issued to you.
Use the radio button in the Type section of the screen to choose which type of Certificate you wish to view.
Trusted Certificates
Figure 82: Trusted Certificates Screen
Data – Trusted Certificates Screen
Trusted Certificates
Subject Name
(CA)
Issuer Name
Expiry Time
Delete button
Add Trusted
Certificate button
The "Subject Name" is always the company or person to whom
the Certificate is issued. For trusted certificates, this will be a
CA.
The CA (Certification Authority) which issued the Certificate.
The date on which the Certificate expires. You should renew
the Certificate before it expires.
Use this button to delete a Trusted Certificate. Select the
checkbox in the Delete column for any Certificates you wish to
delete, then click the "Delete" button.
Use this to add a new Trusted Certificate to the table. See
below for details.
Requesting a Trusted Certificate
1. After obtaining a new Certificate from the CA, you need to upload it to the VPN Broadband Router.
2. On the "Certificates" screen, click the "Add Trusted Certificate" button to view the Add Trusted Certificate screen,
shown below.
95
 Loading...
Loading...