Lenovo 7X16A06ZEA User Manual

ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node
Setup Guide
Machine Type: 7X16

Note
Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure to read and understand the safety
information and the safety instructions, which are available at:
http://thinksystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/safety_documentation/pdf_files.html
In addition, be sure that you are familiar with the terms and conditions of the Lenovo warranty for your server,
which can be found at:
http://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/warrantylookup
Second Edition (September 2017)
© Copyright Lenovo 2017.
LIMITED AND RESTRICTED RIGHTS NOTICE: If data or software is delivered pursuant to a General Services
Administration “GSA” contract, use, reproduction, or disclosure is subject to restrictions set forth in Contract No.
GS-35F-05925

Contents
Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
Safety inspection checklist . . . . . . . . . . . iv
Chapter 1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . 1
Compute node package contents. . . . . . . . . 3
Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Particulate contamination . . . . . . . . . . 7
Management options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Chapter 2. Compute node
components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Power, controls, and indicators. . . . . . . . . 15
Compute node controls, connectors, and
LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Light path diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . 17
KVM cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
System-board layout. . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
System-board connectors . . . . . . . . . 19
System-board switches . . . . . . . . . . 20
Parts list. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Chapter 3. Compute node hardware
setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Compute node setup checklist . . . . . . . . . 25
Installation Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
System reliability guidelines . . . . . . . . 27
Working inside the server with the power on . . 27
Handling static-sensitive devices . . . . . . 28
Install compute node hardware options . . . . . 28
Remove the top cover . . . . . . . . . . 29
Remove the air baffle . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Remove the 2.5-inch drive backplane . . . . 31
Remove the RAID adapter . . . . . . . . . 32
Install a 2.5-inch drive backplane . . . . . . 33
Install a 2.5-inch hot-swap drive . . . . . . 34
Install a DIMM . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Install the flash power module . . . . . . . 38
Install an I/O expansion adapter. . . . . . . 39
Install the M.2 backplane . . . . . . . . . 42
Install an M.2 drive . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Install a processor-heat-sink module. . . . . 47
Install a RAID adapter. . . . . . . . . . . 49
Install the air baffle . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Install the compute node cover . . . . . . . 52
Install the compute node in the chassis . . . . . 54
Power on the compute node. . . . . . . . . . 55
Validate compute node setup . . . . . . . . . 56
Power off the compute node. . . . . . . . . . 56
Chapter 4. System configuration . . . 59
Set the network connection for the Lenovo XClarity
Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Update the firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Configure the firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
DIMM configuration . . . . . . . . . . . 63
RAID configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Install the operating system . . . . . . . . . . 67
Back up the compute node configuration. . . . . 68
Chapter 5. Resolving installation
issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Appendix A. Getting help and
technical assistance . . . . . . . . . . 73
Before you call . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Collecting service data . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Contacting Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
© Copyright Lenovo 2017 i

ii ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide

Safety
Before installing this product, read the Safety Information.
Antes de instalar este produto, leia as Informações de Segurança.
Læs sikkerhedsforskrifterne, før du installerer dette produkt.
Lees voordat u dit product installeert eerst de veiligheidsvoorschriften.
Ennen kuin asennat tämän tuotteen, lue turvaohjeet kohdasta Safety Information.
Avant d'installer ce produit, lisez les consignes de sécurité.
Vor der Installation dieses Produkts die Sicherheitshinweise lesen.
Prima di installare questo prodotto, leggere le Informazioni sulla Sicurezza.
Les sikkerhetsinformasjonen (Safety Information) før du installerer dette produktet.
Antes de instalar este produto, leia as Informações sobre Segurança.
© Copyright Lenovo 2017 iii

Antes de instalar este producto, lea la información de seguridad.
Läs säkerhetsinformationen innan du installerar den här produkten.
Safety inspection checklist
Use the information in this section to identify potentially unsafe conditions with your server. As each machine
was designed and built, required safety items were installed to protect users and service technicians from
injury.
Important: Electrical grounding of the server is required for operator safety and correct system function.
Proper grounding of the electrical outlet can be verified by a certified electrician.
Use the following checklist to verify that there are no potentially unsafe conditions:
1. Make sure that the power is off and the power cord is disconnected.
2. Check the power cord.
• Make sure that the third-wire ground connector is in good condition. Use a meter to measure thirdwire ground continuity for 0.1 ohm or less between the external ground pin and the frame ground.
• Make sure that the power cord is the correct type.
To view the power cords that are available for the server:
a. Go to:
http://lesc.lenovo.com
b. In the Customize a Model pane:
1) Click Select Options/Parts for a Model.
2) Enter the machine type and model for your server.
c. Click the Power tab to see all line cords.
• Make sure that the insulation is not frayed or worn.
3. Check for any obvious non-Lenovo alterations. Use good judgment as to the safety of any non-Lenovo
alterations.
4. Check inside the server for any obvious unsafe conditions, such as metal filings, contamination, water or
other liquid, or signs of fire or smoke damage.
5. Check for worn, frayed, or pinched cables.
iv
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide

6. Make sure that the power-supply cover fasteners (screws or rivets) have not been removed or tampered
with.
© Copyright Lenovo 2017 v

vi ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide
Chapter 1. Introduction
Each ThinkSystem SN550 compute node supports up to two 2.5-inch hot-swap Serial Attached SCSI (SAS),
Serial ATA (SATA) or Non-Volatile Memory express (NVMe) drives.
When you receive your Lenovo ThinkSystem SN550 Type 7X16 compute node, refer to the Setup Guide to
set up the compute node, install optional devices, and perform the initial configuration of the compute node.
Meanwhile, the Maintenance Manual contains information to help you solve problems that might occur in
your Lenovo ThinkSystem SN550 Type 7X16 compute node. It describes the diagnostic tools that come with
the compute node, error codes and suggested actions, and instructions for replacing failing components.
The compute node comes with a limited warranty. For details about the warranty, see:
https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/documents/ht100742
For details about your specific warranty, see:
http://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/warrantylookup
Notes:
1. The first generation Chassis Management Module (CMM1; 68Y7030) is not supported by the
ThinkSystem SN550 compute node.
2. The second generation Chassis Management Module (CMM2; 00FJ669) must be at firmware level 1.6.1
or above to support the ThinkSystem SN550 compute node. This applies to both CMMs that are
installed in the chassis.
3. The illustrations in this document might differ slightly from your model.
Identifying your compute node
When you contact Lenovo for help, the machine type, model, and serial number information helps support
technicians to identify your compute node and provide faster service.
Record information about the compute node in the following table.
Table 1. Record of the system information
Product name
Lenovo ThinkSystem
SN550 Type 7X16
Machine Type (s)
7X16
Model number Serial number
The model number and serial number are on the ID label on the front of the compute node and the chassis,
as shown in the following illustration.
Note: The illustrations in this document might differ slightly from your hardware.
© Copyright Lenovo 2017 1

Figure 1. ID label on the front of the node
1 ID label
Customer information tabs
The customer information tabs contain system-related information such as firmware level, administrator
accounts and so forth.
Figure 2. Location of customer information tabs
The system service label, which is on the cover of the compute node, provides a quick response (QR) code
for mobile access to service information. You can scan the QR code using a QR code reader and scanner
with a mobile device and get quick access to the Lenovo Service Information website. The Lenovo Service
Information website provides additional information for parts installation and replacement videos, and error
codes for server support.
The following illustration shows the QR code (https://support.lenovo.com/p/servers/sn550.)
2
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide

Figure 3. QR code
Compute node package contents
When you receive your compute node, verify that the shipment contains everything that you expected to
receive.
The compute node package includes the following items:
• Compute node
• Printed documentation
Features
Performance, ease of use, reliability, and expansion capabilities were key considerations in the design of the
compute node. These design features make it possible for you to customize the system hardware to meet
your needs today and provide flexible expansion capabilities for the future.
Your compute node implements the following features and technologies:
• Features on Demand
If a Features on Demand feature is integrated in the compute node or in an optional device that is installed
in the compute node, you can purchase an activation key to activate the feature. For information about
Features on Demand, see https://fod.lenovo.com/lkms.
• Lenovo XClarity Controller
The Lenovo XClarity Controller is the common management controller for Lenovo ThinkSystem compute
node hardware. The Lenovo XClarity Controller consolidates multiple management functions in a single
chip on the compute node system board.
Some of the features that are unique to the Lenovo XClarity Controller are enhanced performance, higherresolution remote video, and expanded security options. For additional information about the Lenovo
XClarity Controller, see http://sysmgt.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/com.lenovo.systems.management.xcc.
doc/product_page.html.
• UEFI-compliant server firmware
Lenovo ThinkSystem firmware is Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) 2.5 compliant. UEFI
replaces BIOS and defines a standard interface between the operating system, platform firmware, and
external devices.
Lenovo ThinkSystem servers are capable of booting UEFI-compliant operating systems, BIOS-based
operating systems, and BIOS-based adapters as well as UEFI-compliant adapters.
Note: The server does not support DOS (Disk Operating System).
• Large system-memory capacity
The compute node supports up to a maximum of 1.5 TB of system memory. The compute node supports
only industry-standard double-data-rate 4 DIMM (DDR4) , registered DIMM (RDIMM), or load-reduced
DIMM (LRDIMM).
• Flexible network support
Chapter 1. Introduction 3

The compute node has connectors on the system board for optional expansion adapters for adding
network communication capabilities to the compute node. You can install up to two I/O expansion
adapters for network support. This provides the flexibility to install expansion adapters that support a
variety of network communication technologies.
• Integrated Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
This integrated security chip performs cryptographic functions and stores private and public secure keys.
It provides the hardware support for the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) specification. You can
download the software to support the TCG specification, when the software is available.
Note: For customers in the People’s Republic of China, TPM is not supported. However, customers in the
People’s Republic of China can install a Trusted Cryptographic Module (TCM) adapter (sometimes called
a daughter card).
• Drive support
The compute node supports up to two hot-swap drives. You can implement RAID 0 or RAID 1 for the
drives. Additional drive types and RAID levels are supported when an optional drive backplane and RAID
adapter are installed.
• Light path diagnostics
Light path diagnostics provides light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to help you diagnose problems.
• Mobile access to Lenovo Service Information website
The compute node provides a quick response (QR) code on the system service label, which is on the
cover of the compute node, that you can scan using a QR code reader and scanner with a mobile device
to get quick access to the Lenovo Service Information website. The Lenovo Service Information website
provides additional information for parts installation and replacement videos, and error codes for compute
node support. Information about the ThinkSystem SN550 QR code can be found here: Chapter 1
“Introduction” on page 1.
• Processor technology
The compute node supports up to two multi-core Intel Xeon processors.
Note: The optional processors that Lenovo supports are limited by the capacity and capability of the
compute node. Any processor that you install must have the same specifications as the processor that
came with the compute node.
• Power throttling
By enforcing a power policy known as power-domain oversubscription, the Lenovo Flex System chassis
can share the power load between two or more power supply modules to ensure sufficient power for each
device in the Lenovo Flex System chassis. This policy is enforced when the initial power is applied to the
Lenovo Flex System chassis or when a compute node is inserted into the Lenovo Flex System chassis.
The following settings for this policy are available:
– Basic power management
– Power module redundancy
– Power module redundancy with compute node throttling allowed
You can configure and monitor the power environment by using the Chassis Management Module. For
more information, see the Flex System Chassis Management Module: Command-Line Interface Reference
Guide at http://flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/com.lenovo.acc.cmm.doc/dw1kt_cmm_cli_book.
pdf.
• Lenovo XClarity Administrator
Lenovo XClarity Administrator is a centralized resource-management solution that enables administrators
to deploy infrastructure faster and with less effort. The solution seamlessly integrates into ThinkSystem
4
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide

compute nodes, and NeXtScale compute nodes, as well as the Flex System converged infrastructure
platform.
Lenovo XClarity Administrator provides:
– Automated discovery
– Agent-free hardware management
– Monitoring
– Firmware updates and compliance
– Pattern-based configuration management
– Deployment of operating systems and hypervisors
Administrators are able to find the right information and accomplish critical tasks faster through an
uncluttered, dashboard-driven graphical user interface (GUI). Centralizing and automating foundational
infrastructure deployment and lifecycle management tasks across large pools of systems frees up
administrator time, and makes resources available to end-users faster.
Lenovo XClarity is easily extended into the leading virtualization management platforms from Microsoft
and VMware using software plug-ins, called Lenovo XClarity Integrators. The solution improves workload
uptime and service-level assurance by dynamically relocating workloads from affected hosts in the cluster
during rolling compute node reboots or firmware updates, or during predicted hardware failures.
For more information about Lenovo XClarity Administrator, see the http://shop.lenovo.com/us/en/
systems/software/systems-management/xclarity/ and the http://flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/index.
jsp.
• Systems-management support
The compute node XClarity Controller provides a web interface for remote systems-management support.
You can use the interface to view system status and to control systems-management functions and
baseboard management settings.
The XClarity Controller communicates with the Lenovo Flex System Chassis Management Module (CMM)
and the Lenovo XClarity Administrator application (if installed).
– The CMM is a hot-swap module that provides systems-management functions for all components in an
Lenovo Flex System chassis. It controls a serial port for remote connection and a 1 Gbps Ethernet
remote-management connection. For more information, see the Flex System Chassis Management
Module: Command-Line Interface Reference Guide at http://flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/
com.lenovo.acc.cmm.doc/dw1kt_cmm_cli_book.pdf.
– The Lenovo XClarity Administrator is a virtual appliance that you can use to manage Lenovo Flex
System chassis in a secure environment. The Lenovo XClarity Administrator provides a central interface
to perform the following functions for all managed endpoints:
– User management
– Hardware monitoring and management
– Configuration management
– Operating system deployment
– Firmware management
For more information, see
https://support.lenovo.com/us/en/ documents/LNVO-XCLARIT.
Specifications
The following information is a summary of the features and specifications of the compute node. Depending
on the model, some features might not be available, or some specifications might not apply.
Chapter 1. Introduction 5
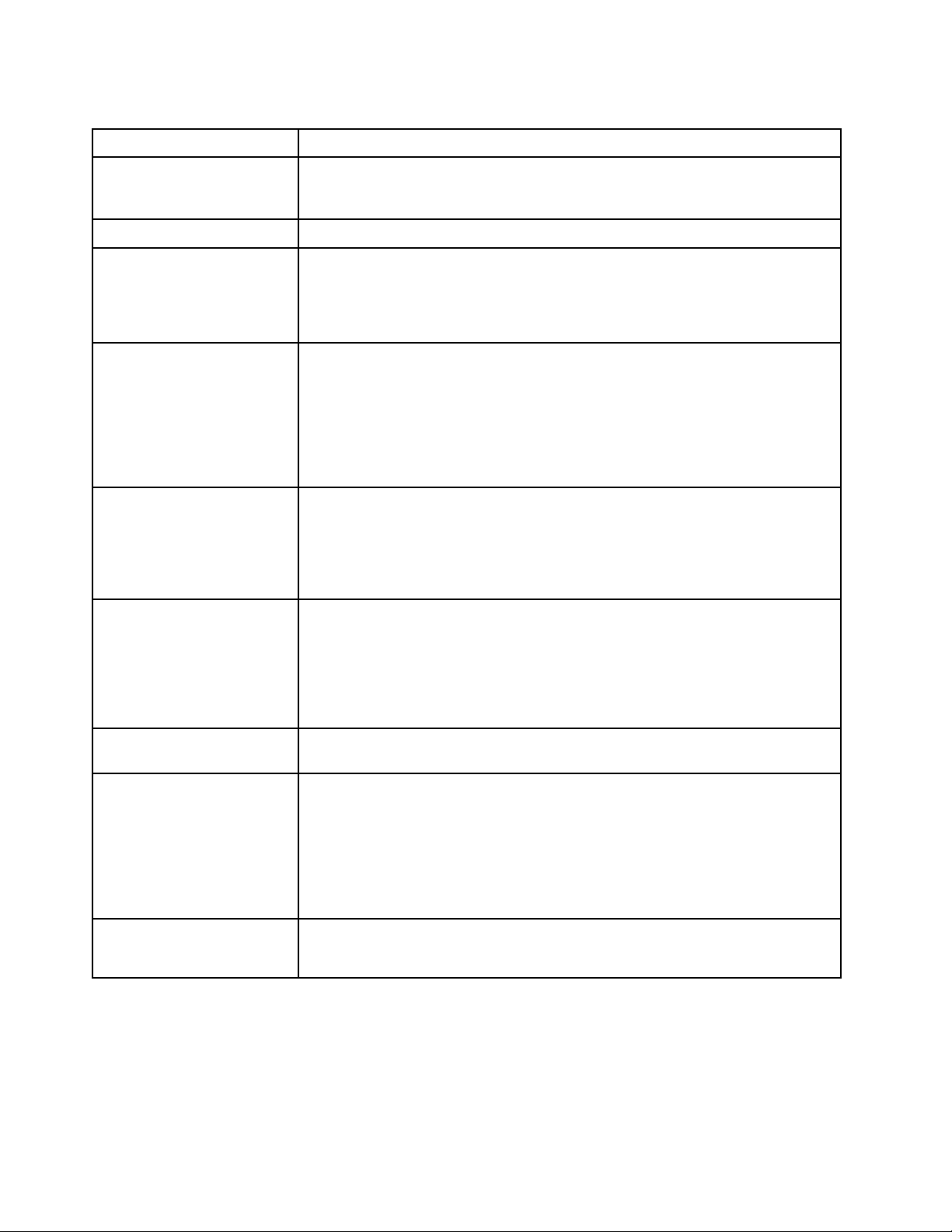
Table 2. Specifications
Specification
Size • Height: 55.5 mm (2.2 in)
Weight Approximately 4.7 kg (10.4 lb) to 7.0 kg (15.5 lb), depending on your configuration.
Processor (depending on the
model)
Memory
2.5-inch drive/backplane • Supports up to two small form factor (SFF) drive bays. Drive bay can be either
Description
• Depth: 492.7 mm (19.4 in)
• Width: 215.5 mm (8.5 in)
Processor: Up to two multi-core Intel Xeon processors.
Note: Use the Setup utility to determine the type and speed of the processors in the
compute node.
For a list of supported processors, see: http://www.lenovo.com/serverproven/
• 24 dual inline memory module (DIMM) connectors
• Type: Low-profile (LP) double-data rate (DDR4) DRAM
• Supports 8 GB, 16 GB, 32 GB and 64 GB DIMMs with up to 1.5 TB of total
memory on the system board.
Note: Future support is planned for the 128GB 3DS RDIMM. The total memory on
the system board may reach up to 3TB.
• Support for RDIMMs and LRDIMMs (combining is not supported)
SATA only, SAS/SATA, or NVMe/SATA, depending on the model.
• Supported 2.5-inch drives:
– Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)/Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
hot-swap hard disk drives/solid-state drives
– Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) solid-state drives
M.2 drive/backplane ThinkSystem M.2 with Mirroring Enablement Kit contains dual M.2 backplane
supports up to two identical M.2 drives.
Supports 3 different physical sizes of M.2 drives:
• 42 mm (2242)
• 60 mm (2260)
• 80 mm (2280)
RAID adapter • RAID 530-4i adapter
• RAID 930-4i-2GB adapter
Integrated functions • One baseboard management controller (BMC) with integrated VGA controller
(XClarity Controller or XCC)
• Light path diagnostics
• Automatic server restart (ASR)
• Additional RAID levels supported when an optional RAID controller is installed
• One external USB 3.0 port
• Serial over LAN (SOL)
• Wake on LAN (WOL) when an optional I/O adapter with WOL capability is installed.
Predictive failure analysis
(PFA) alerts
• Processors
• Memory
• Drives
6 ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide
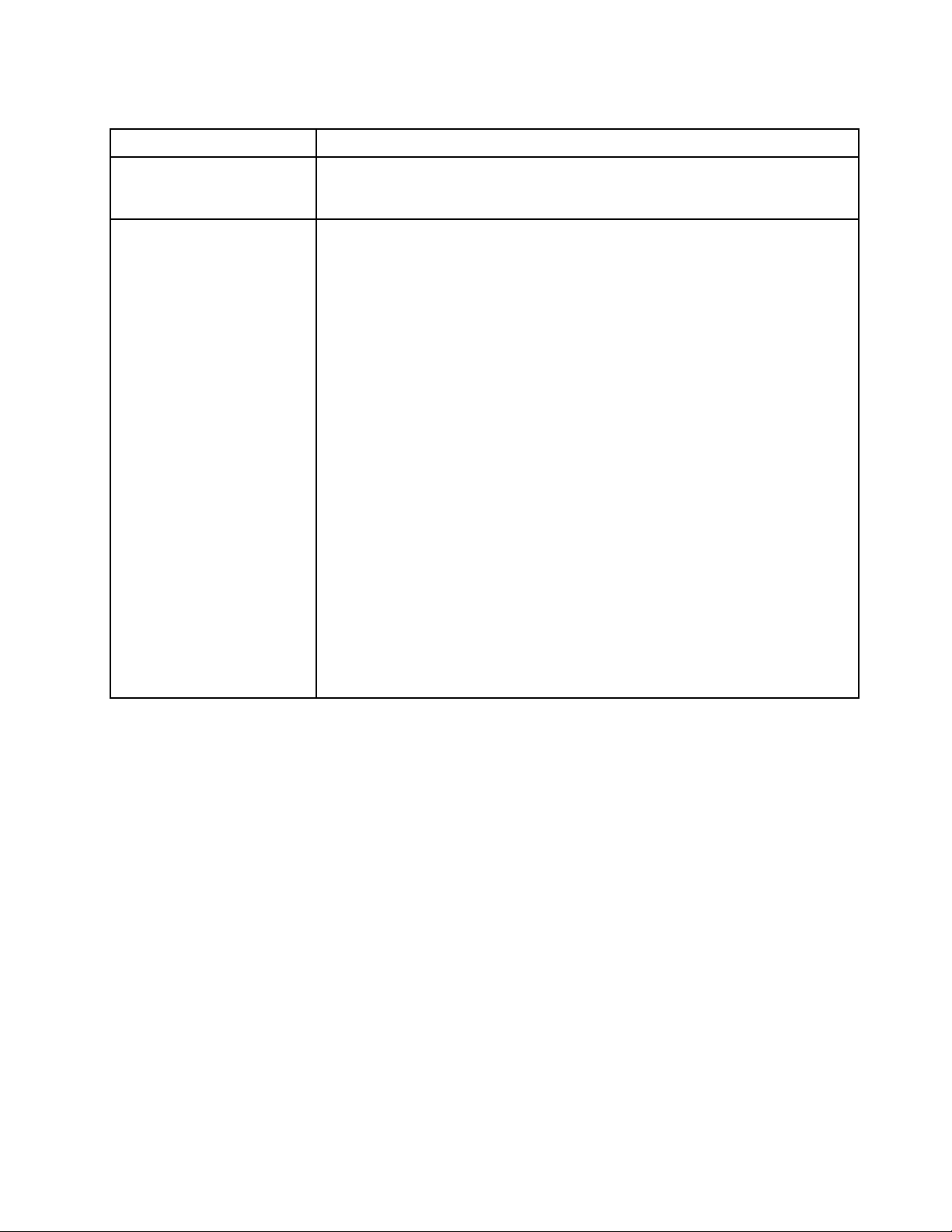
Table 2. Specifications (continued)
Specification
Security Fully compliant with NIST 800-131A. The security cryptography mode set by the
Environment The ThinkSystem SN550 compute node complies with ASHRAE Class A2
Description
managing device (CMM or Lenovo XClarity Administrator) determines the security
mode in which the compute node operates.
specifications. Depending on the hardware configuration, some models comply with
ASHRAE Class A3 specifications. System performance may be impacted when
operating temperature is outside ASHRAE A2 specification or fan failed condition.
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SN550 compute node is supported in the following
environment:
• Air temperature:
– Operating:
– ASHRAE Class A2: 10 °C - 35 °C (50 °F - 95 °F); decrease the maximum
ambient temperature by 1 °C for every 300 m (984 ft) increase in altitude
above 900 m (2,953 ft)
– ASHRAE Class A3: 5 °C - 40 °C (41 °F - 104 °F); decrease the maximum
ambient temperature by 1 °C for every 175 m (574 ft) increase in altitude
above 900 m (2,953 ft)
– Compute node off: 5°C to 45°C (41°F to 113°F)
– Shipment/Storage: -40 °C to 60 °C (-40 °F to 140 °F)
• Maximum altitude: 3,050 m (10,000 ft)
• Relative Humidity (non-condensing):
– Operating:
– ASHRAE Class A2: 8% - 80%, maximum dew point: 21°C (70°F)
– ASHRAE Class A3: 8% - 85%, maximum dew point: 24°C (75°F)
– Shipment/Storage: 8% - 90%
• Particulate contamination
Attention: Airborne particulates and reactive gases acting alone or in combination
with other environmental factors such as humidity or temperature might pose a
risk to the server. For information about the limits for particulates and gases, see
“Particulate contamination” on page 7.
Notes: Future support is planned for the single M.2 backplane function in the UEFI Setup page. Currently,
users are unable to enable this functionality. This functionality is found in the following paths in the UEFI
setup page.
• F1 Setup ➙ System Settings ➙ Device and I/O Ports ➙ Enable/Disable Onboard Device(s)
• F1 Setup ➙ System Settings ➙ Device and I/O Ports ➙ Enable/Disable Adapter Option ROM
Support
• F1 Setup ➙ System Settings ➙ Device and I/O Ports ➙ Set Option ROM Execution Order
Particulate contamination
Attention: Airborne particulates (including metal flakes or particles) and reactive gases acting alone or in
combination with other environmental factors such as humidity or temperature might pose a risk to the
device that is described in this document.
Risks that are posed by the presence of excessive particulate levels or concentrations of harmful gases
include damage that might cause the device to malfunction or cease functioning altogether. This
specification sets forth limits for particulates and gases that are intended to avoid such damage. The limits
must not be viewed or used as definitive limits, because numerous other factors, such as temperature or
moisture content of the air, can influence the impact of particulates or environmental corrosives and gaseous
contaminant transfer. In the absence of specific limits that are set forth in this document, you must
implement practices that maintain particulate and gas levels that are consistent with the protection of human
Chapter 1. Introduction 7
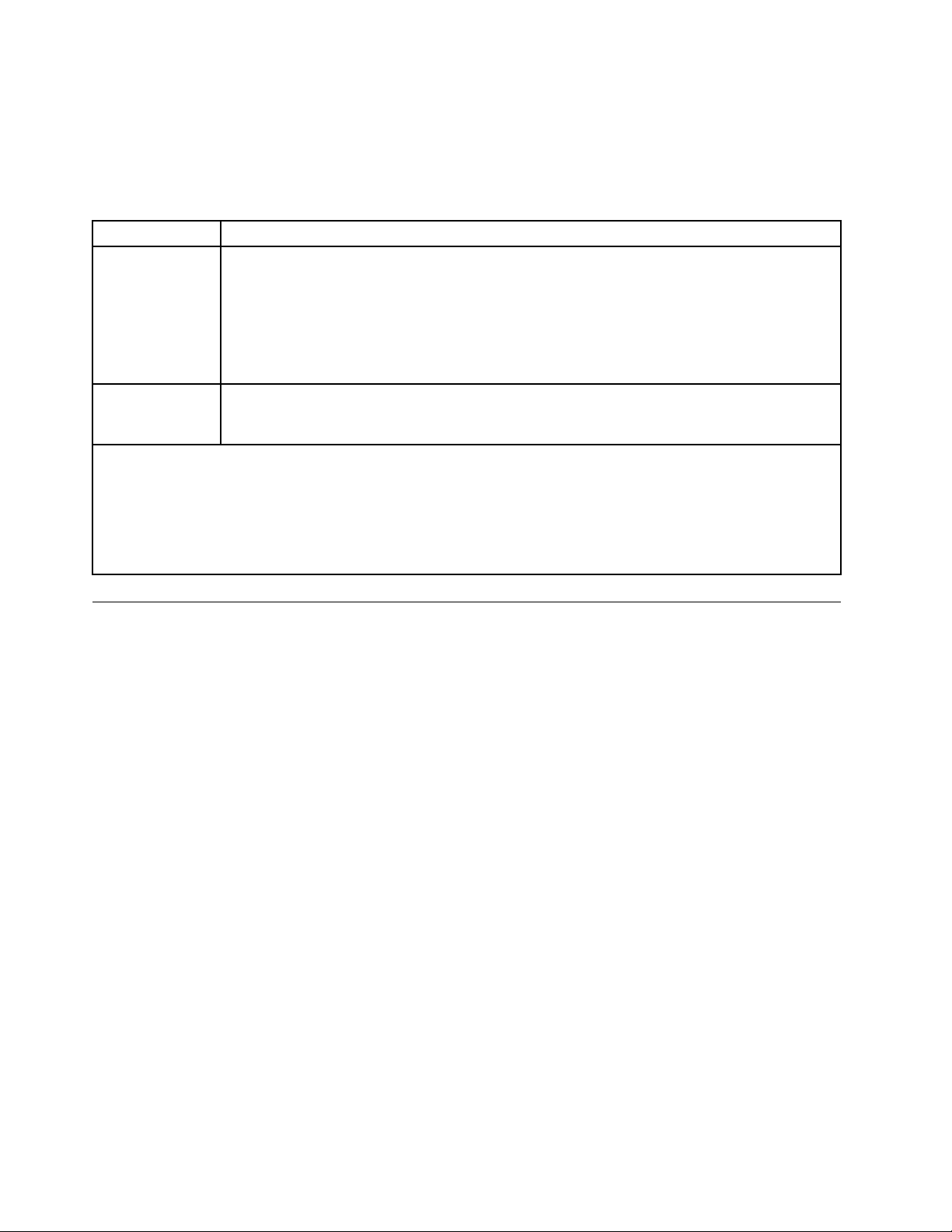
health and safety. If Lenovo determines that the levels of particulates or gases in your environment have
caused damage to the device, Lenovo may condition provision of repair or replacement of devices or parts
on implementation of appropriate remedial measures to mitigate such environmental contamination.
Implementation of such remedial measures is a customer responsibility.
Table 3. Limits for particulates and gases
Contaminant Limits
Particulate
Gaseous
1
ASHRAE 52.2-2008 - Method of Testing General Ventilation Air-Cleaning Devices for Removal Efficiency by
Particle Size. Atlanta: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.
2
The deliquescent relative humidity of particulate contamination is the relative humidity at which the dust absorbs
enough water to become wet and promote ionic conduction.
3
ANSI/ISA-71.04-1985. Environmental conditions for process measurement and control systems: Airborne
contaminants. Instrument Society of America, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, U.S.A.
• The room air must be continuously filtered with 40% atmospheric dust spot efficiency (MERV
9) according to ASHRAE Standard 52.2
• Air that enters a data center must be filtered to 99.97% efficiency or greater, using highefficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters that meet MIL-STD-282.
• The deliquescent relative humidity of the particulate contamination must be more than 60%
• The room must be free of conductive contamination such as zinc whiskers.
• Copper: Class G1 as per ANSI/ISA 71.04-1985
• Silver: Corrosion rate of less than 300 Å in 30 days
1
.
2
3
.
Management options
Several management interfaces are available for managing your server. The management options described
in this section are provided to support the direct management of Lenovo servers.
In addition to the tools described in the following table, you can use the Chassis Management Module (CMM)
to manage all devices in a Flex System chassis, including the ThinkSystem compute nodes. The CMM
provides system-management functions for all components in a Lenovo Flex System Enterprise Chassis. It
controls a serial port for connection to a local console or a serial management network and supports data
rates of 10/100 Mbps and 1 Gbps with autonegotiate. For more information about the CMM, see the
following site:
http://flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/com.lenovo.acc.cmm.doc/cmm_product_page.html
Note: The second generation Lenovo Chassis Management Module (CMM2; 00FJ669) must be at firmware
level 1.6.1 or above to support theThinkSystem SN550. This applies to both CMMs that are installed in the
chassis.
8
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide
Function
Lenovo
XClarity
Administrator
Lenovo
XClarity
Integrator
Lenovo
XClarity
Energy
Manager
Lenovo
XClarity
Provisioning
Manager
Lenovo
XClarity
Essen-
1
tials
Lenovo
XClarity
Controller
Lenovo
Capacity
Planner
Lenovo
Business
Vantage
Multiple
systems
management
Operating
system
deployment
Firmware
updates
2
System
configuration
Events /
alerts
Inventory /
Log
Power
management
Data center
planning
Security
management
√ √ √ √
√ √
√ √ √
3
√ √
√ √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √
√ √ √
5
√
√
4
√ √
√
6
√
Notes:
1. Lenovo XClarity Essentials includes Lenovo XClarity Essentials OneCLI, Lenovo XClarity Essentials
Bootable Media Creator, and Lenovo XClarity Essentials UpdateXpress.
2. Most options can be updated through the Lenovo tools. Some options, such as GPU firmware or OmniPath firmware require the use of vendor tools.
3. Firmware updates are limited to Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager, Lenovo XClarity Controller
firmware, and UEFI updates only. Firmware updates for optional devices, such as adapters, are not
supported.
4. Limited inventory.
5. Power management function is supported by Lenovo XClarity Integrator for VMware vCenter.
6. Available only in the People’s Republic of China.
Lenovo XClarity Administrator
Lenovo XClarity Administrator is a centralized, resource-management solution that simplifies infrastructure
management, speeds responses, and enhances the availability of Lenovo server systems and solutions. It
runs as a virtual appliance that automates discovery, inventory, tracking, monitoring, and provisioning for
server, network, and storage hardware in a secure environment.
Lenovo XClarity Administrator provides a central interface to perform the following functions for all managed
endpoints:
Chapter 1. Introduction 9

• Manage and monitor hardware. Lenovo XClarity Administrator provides agent-free hardware
management. It can automatically discover manageable endpoints, including server, network, and storage
hardware. Inventory data is collected for managed endpoints for an at-a-glance view of the managed
hardware inventory and status.
• Configuration management. You can quickly provision and pre-provision all of your servers using a
consistent configuration. Configuration settings (such as local storage, I/O adapters, boot settings,
firmware, ports, and Lenovo XClarity Controller and UEFI settings) are saved as a server pattern that can
be applied to one or more managed servers. When the server patterns are updated, the changes are
automatically deployed to the applied servers.
• Firmware compliance and updates. Firmware management is simplified by assigning firmware-
compliance policies to managed endpoints. When you create and assign a compliance policy to managed
endpoints, Lenovo XClarity Administrator monitors changes to the inventory for those endpoints and flags
any endpoints that are out of compliance.
When an endpoint is out of compliance, you can use Lenovo XClarity Administrator to apply and activate
firmware updates for all devices in that endpoint from a repository of firmware updates that you manage.
• Operating System deployment. You can use Lenovo XClarity Administrator to manage a repository of
operating-system images and to deploy operating-system images to up to 28 managed servers
concurrently.
• Service and support. Lenovo XClarity Administrator can be set up to collect and send diagnostic files
automatically to your preferred service provider when certain serviceable events occur in Lenovo XClarity
Administrator and the managed endpoints. You can choose to send diagnostic files to Lenovo Support
using Call Home or to another service provider using SFTP. You can also manually collect diagnostic files,
open a problem record, and send diagnostic files to the Lenovo Support Center.
Lenovo XClarity Administrator can be integrated into external, higher-level management and automation
platforms through open REST application programming interfaces (APIs). Using the REST APIs, Lenovo
XClarity Administrator can easily integrate with your existing management infrastructure. In addition, you can
automate tasks using the PowerShell toolkit or the Python toolkit.
To obtain the latest version of the Lenovo XClarity Administrator, see:
https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/documents/LNVO-LXCAUPD
Documentation for Lenovo XClarity Administrator is available at:
http://sysmgt.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/com.lenovo.lxca.doc/aug_product_page.html
Lenovo XClarity Integrator
Lenovo also provides the following integrators that you can use to manage Lenovo servers from higher-level
management tools:
• Lenovo XClarity Integrator for VMware vCenter
• Lenovo XClarity Integrator Microsoft System Center
For more information about Lenovo XClarity Integrator, see:
http://www3.lenovo.com/us/en/data-center/software/systems-management/xclarity-integrators
Lenovo XClarity Energy Manager
Lenovo XClarity Energy Manager is a web-based power and temperature management solution designed for
data center administrators. It monitors and manages the power consumption and temperature of servers,
such as Converged, NeXtScale, System x, ThinkServer, and ThinkSystem servers. Lenovo XClarity Energy
Manager models data center physical hierarchy and monitors power and temperature at the server/group
level. By analyzing monitored power and temperature data, Lenovo XClarity Energy Manager greatly
improves business continuity and energy efficiency.
10
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide

With Lenovo XClarity Energy Manager, administrators can take control of power usage through improved
data analysis and lower the TCO (total cost of ownership). The tool optimizes data center efficiency by
allowing administrators to:
• Monitor energy consumption, estimate power need, and re-allocate power to servers as needed via IPMI
or Redfish.
• Track platform power consumption, inlet temperature, CPU and memory power consumption.
• Visually check the layout of room, row and rack via 2D thermal map.
• Send notifications when certain events occur or thresholds are reached.
• Limit the consumed amount of energy of an endpoint by setting up policies.
• Optimize energy efficiency by monitoring real-time inlet temperatures, identifying low-usage servers
based on out-of-band power data, measuring power rangers for different server models, and evaluating
how servers accommodate new workloads based on the availability of resources.
• Reduce the power consumption to the minimum level to prolong service time during emergency power
event (such as a data-center power failure).
For more information about downloading, installation, and usage, see:
http://www3.lenovo.com/us/en/data-center/software/systems-management/xclarity-energy-manager/
Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager
Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager provides a graphic user interface for configuring the system. When
you start a server and press F1, the Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager interface is displayed by default.
Note: The text-based interface to system configuration (the Setup Utility) is also available. From Lenovo
XClarity Provisioning Manager, you can choose to restart the server and access the text-based interface. In
addition, you can choose to make the text-based interface the default interface that is displayed when you
press F1.
Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager provides a system summary of all installed devices and includes the
following functions:
• UEFI setup. Use this function to configure UEFI system settings, such as processor configuration, start
options, and user security. You can also view POST events and the System Event Log (SEL).
• Platform update. Use this function to update the firmware for Lenovo XClarity Controller, Lenovo XClarity
Provisioning Manager, and operating system device drivers.
• RAID setup. Use this function to configure RAID for the server. It provides an easy-to-use graphical
wizard that supports a unified process for performing RAID setup for a variety of RAID adapters. You can
also perform advanced RAID configuration from the UEFI Setup.
• OS installation. Use this function to install an operating system for the server. You can install Microsoft
Windows, Linux, and VMware ESXi.
• Diagnostics. Use this function to view the overall health of devices installed in the server and to perform
diagnostics for hard disk drives and memory. You can also collect service data that can be saved to a
USB device and sent to Lenovo Support.
Note: The service data collected by Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager does not include the operating
system logs. To collect the operating system logs and the hardware service data, use Lenovo XClarity
Essentials OneCLI.
Documentation for Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager is available at:
http://sysmgt.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/LXPM/LXPM_introduction.html
Chapter 1. Introduction 11

Lenovo XClarity Essentials
Lenovo XClarity Essentials (LXCE) is a collection of server management utilities that provides a less
complicated method to enable customers to manage Lenovo ThinkSystem, System x, and Thinkserver
servers more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lenovo XClarity Essentials includes the following utilities:
• Lenovo XClarity Essentials OneCLI is a collection of several command line applications, which can be
used to:
– Configure the server.
– Collect service data for the server. If you run Lenovo XClarity Essentials OneCLI from the server
operating system (in-band), you can collect operating system logs as well. You can also choose to view
the service data that has been collected or to send the service data to Lenovo Support.
– Update firmware and device drivers for the server. Lenovo XClarity Essentials OneCLI can help to
download UpdateXpress System Packs (UXSPs) for your server and update all the firmware and device
drivers payloads within the UXSP.
– Perform miscellaneous functions, such as rebooting the server or rebooting the BMC.
To learn more about Lenovo XClarity Essentials OneCLI, see:
https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/ documents/LNVO-CENTER
Documentation for Lenovo XClarity Essentials OneCLI is available at:
http://sysmgt.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/xclarity_essentials/overview.html
• Lenovo XClarity Essentials Bootable Media Creator (BoMC) is a software application that applies
UpdateXpress System Packs and individual updates to your system.
Using Lenovo XClarity Essentials Bootable Media Creator, you can:
– Update the server using an ISO image or CD.
– Update the server using a USB key.
– Update the server using the Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) interface.
– Update the server in unattendance mode.
– Update the server in Serial Over LAN (SOL) mode.
To learn more about Lenovo XClarity Essentials Bootable Media Creator, see:
https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/solutions/lnvo-bomc
• Lenovo XClarity Essentials UpdateXpress is a software application that applies UpdateXpress System
Packs and individual updates to your system.
Using Lenovo XClarity Essentials UpdateXpress, you can:
– Update the local server.
– Update a remove server.
– Create a repository of updates.
To learn more about Lenovo XClarity Essentials UpdateXpress, see:
https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/solutions/ht503692
Lenovo XClarity Controller
Lenovo XClarity Controller is the management processor for the server. It is the third generation of the
Integrated Management Module (IMM) service processor that consolidates the service processor
functionality, super I/O, video controller, and remote presence capabilities into a single chip on the server
system board.
12
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide

There are two ways to access the management processor:
• Web-based interface. To access the web-based interface, point your browser to the IP address for the
management processor.
• Command-line interface. To access the CLI interface, use SSH or Telnet to log in to the management
processor.
Whenever power is applied to a server, the management processor is available. From the management
processor interface, you can perform the following functions:
• Monitor all hardware devices installed in the server.
• Power the server on and off.
• View the system event log and system audit log for the server.
• Use the Remote management function to log in to the server itself.
Documentation for Lenovo XClarity Controller is available at:
http://sysmgt.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/com.lenovo.systems.management.xcc.doc/product_page.html
Lenovo Capacity Planner
Lenovo Capacity Planner is a power consumption evaluation tool that enhances data center planning by
enabling IT administrators and pre-sales to understand important parameters of different type of racks,
servers, and other devices. Lenovo Capacity Planner can dynamically calculate the power consumption,
current, British Thermal Unit (BTU), and volt-ampere (VA) rating at the rack level, and therefore improves the
efficiency of large scale deployments.
Lenovo Capacity Planner provides the following functions:
• Power/thermal evaluation in different deployments, device copying, configuration saving, and reporting.
• Customizable server configuration, selectable workload, CPU turbo model, and worst case of fans for
different evaluations in different user scenarios.
• Flex/Density servers, chassis and node level customizable configuration.
• Easy to download and run with popular web browsers, like Internet Explorer 11, Firefox, Chrome, and
Edge.
Note: Users can also access the Lenovo website to run the tool online.
More information about Lenovo Capacity Planner is available at:
http://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/products/solutions-and-software/software/lenovo-capacityplanner
Lenovo Business Vantage
Lenovo Business Vantage is a security software tool suite designed to work with the Trusted Cryptographic
Module (TCM) adapter for enhanced security, to keep user data safe, and to erase confidential data
completely from a hard disk drive.
Lenovo Business Vantage provides the following functions:
• Data Safe. Encrypt files to ensure data safety by using TCM chip , even when the disk is in “rest” status.
• Sure Erase. Erase confidential data from a hard disk. This tool follows the industry standard method to do
the erasing and allows the user to select different erasing levels.
• Smart USB Protection. Prohibit unauthorized access to the USB port of devices.
Chapter 1. Introduction 13

• USB Data Safe. Encrypt data in USB Flash on a certain device and prohibit access of data on other
devices.
Note: This tool is available in the People’s Republic of China only.
More information about Lenovo Business Vantage is available at:
http://www.lenovo.com
14
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide

Chapter 2. Compute node components
Use the information in this section to learn about each of the components associated with your compute
node.
Power, controls, and indicators
Use this information to view power features, turn on and turn off the compute node, and view the functions of
the controls and indicators.
Compute node controls, connectors, and LEDs
Use this information for details about the controls, connectors, and LEDs.
The following illustration identifies the buttons, connectors, and LEDs on the control panel.
Figure 4. Compute node control panel buttons, connectors, and LEDs
Table 4. Compute node control panel buttons, connectors, and LEDs
1 USB 3.0 connector 5 Power button/LED (green)
2 KVM connector
3 Drive activity LED (green) 7 Fault LED (yellow)
4 Drive status LED (yellow) 8 USB management button
1 USB 3.0 connector
6 Identification LED
Connect a USB device to this USB 3.0 connector.
Note: It is best practice to connect a USB device to the front of only one compute node at a time in each
Lenovo Flex System chassis.
2 KVM connector
Connect the console breakout cable to this connector (see “KVM cable” on page 19 for more
information).
Attention: Use only the console breakout cable that comes with the chassis. Attempting to connect
other console breakout cable types might damage the console breakout cable and the compute node.
Note: It is best practice to connect the console breakout cable to only one compute node at a time in
each Lenovo Flex System chassis.
3 Drive activity LED (green)
Green LEDs are on all hot swap drives. When this green LED is lit, it indicates that there is activity on the
associated hard disk drive or solid-state drive.
© Copyright Lenovo 2017 15

• When this LED is flashing, it indicates that the drive is actively reading or writing data.
• For SAS and SATA drives, this LED is off when the drive is powered but not active.
• For NVMe (PCIe) SSDs, this LED is on solid when the drive is powered but not active.
Note: The drive activity LED might be in a different location on the front of the drive, depending on the
drive type that is installed.
4 Drive status LED (yellow)
The state of this yellow LED indicates an error condition or the RAID status of the associated hard disk
drive or solid-state drive:
• When the yellow LED is lit continuously, it indicates that an error has occurred with the associated
drive. The LED turns off only after the error is corrected. You can check the CMM event log to
determine the source of the condition.
• When the yellow LED flashes slowly, it indicates that the associated drive is being rebuilt.
• When the yellow LED flashes rapidly, it indicates that the associated drive is being located.
Note: The hard disk drive status LED might be in a different location on the front of the hard disk drive,
depending on the drive type that is installed.
5 Power button/LED (green)
When the compute node is connected to power through the Lenovo Flex System chassis, press this
button to turn on or turn off the compute node.
Note: The power button works only if local power control is enabled for the compute node. Local power
control is enabled and disabled through the CMM power command and the CMM web interface.
• For more information about the CMM power command, see the Flex System Chassis Management
Module: Command-Line Interface Reference Guide at http://flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/
com.lenovo.acc.cmm.doc/cli_command_power.html.
• From the CMM web interface, select Compute Nodes from the Chassis Management menu. For
more information, see the "Flex System Chassis Management Module: User's Guide" at http://
flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/com.lenovo.acc.cmm.doc/cmm_user_guide.html. All fields
and options are described in the CMM web interface online help.
After the compute node is removed from the chassis, press and hold this button to activate the systemboard LEDs (light path diagnostics). See the Lenovo ThinkSystem SN550 Type 7X16 Maintenance
Manual for more information.
This button is also the power LED. This green LED indicates the power status of the compute node:
• Flashing rapidly (Four times per second): The LED flashes rapidly for one of the following reasons:
– The compute node has been installed in a powered chassis. When you install the compute node,
the LED flashes rapidly while the XClarity Controller in the compute node is initializing and
synchronizing with the Chassis Management Module. The time required for a compute node to
initialize varies by system configuration.
– Power permissions have not been assigned to the compute node through the Chassis
Management Module.
– The Lenovo Flex System chassis does not have enough power to turn on the compute node.
– The XClarity Controller in the compute node is not communicating with the Chassis Management
Module.
The power LED blink rate slows when the compute node is ready to be turned on.
• Flashing slowly (One time per second): The compute node is connected to power through the
Lenovo Flex System chassis and is ready to be turned on.
16
ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide
• Lit continuously: The compute node is connected to power through the Lenovo Flex System chassis
and is turned on.
When the compute node is on, pressing this button causes an orderly shutdown of the compute node so
that it can be removed safely from the chassis. This includes shutting down the operating system (if
possible) and removing power from the compute node.
Attention: If an operating system is running, you might have to press the button for approximately 4
seconds to initiate the shutdown. This forces the operating system to shut down immediately. Data loss
is possible.
6 Identification LED (blue)
The system administrator can remotely light this blue LED to aid in visually locating the compute node.
When this LED is lit, the identification LED on the Lenovo Flex System chassis is also lit. The
identification LED can be lit and turned off through the CMM led command, the CMM web interface and
the Lenovo XClarity Administrator application (if installed).
• For more information about the CMM led command, see the Flex System Chassis Management
Module: Command-Line Interface Reference Guide at http://flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/
com.lenovo.acc.cmm.doc/cli_command_led.html.
• From the CMM web interface, select Compute Nodes from the Chassis Management menu. For
more information, see the "Flex System Chassis Management Module: User's Guide" at http://
flexsystem.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/com.lenovo.acc.cmm.doc/cmm_user_guide.html. All fields
and options are described in the CMM web interface online help.
• For more information about the Lenovo XClarity Administrator application, see https://support.lenovo.
com/us/en/ documents/LNVO-XCLARIT.
7 Fault LED (yellow)
When this yellow LED is lit, it indicates that a system error has occurred in the compute node. In
addition, the fault LED on the chassis system LED panel is lit. You can check the CMM event log and the
light path diagnostics LEDs to determine the source of the condition. See “Light path diagnostics LEDs”
on page 17 for more information about the LEDs on the compute node.
The fault LED turns off only after the error is corrected.
Note: When the fault LED turns off, you should also clear the XClarity Controller event log. Use the Setup
utility to clear the XClarity Controller event log.
8 USB management button
Enables the USB port for system management.
Note: When enabling the USB port for system management, do not insert USB 3. 0 devices.
Light path diagnostics
Use this information as an overview of light path diagnostics.
Light path diagnostics is a system of LEDs above the control panel and on various internal components of
the compute node. When an error occurs, LEDs can be lit throughout the compute node to help identify the
source of the error.
Light path diagnostics LEDs
Use this information to diagnose possible errors that are indicated by the light path diagnostics LEDs.
The following table describes the LEDs on the light path diagnostics panel and the light path diagnostics
LEDs on the system board.
Chapter 2. Compute node components 17

See the Lenovo ThinkSystem SN550 Type 7X16 Maintenance Manual for information about lighting the LEDs.
Note: Additional information about error conditions is in the CMM event log.
Table 5. Light path diagnostics LEDs
Light path diagnostics LED Description
Light path diagnostics The power source for the light path diagnostics LEDs is charged.
System board The system board has failed.
NMI The system board has failed.
CPU Mismatch The processors are mismatched.
Temperature The system temperature has exceeded a threshold level.
Memory A memory error has occurred.
Storage BP 1
M.2 A M.2 backplane error has occurred.
A hard disk drive backplane error has occurred.
System-board LEDs
Use this information to locate the system-board LEDs.
The following illustration shows the locations of the LEDs on the system board.
Figure 5. System-board LEDs
18 ThinkSystem SN550 Compute Node Setup Guide
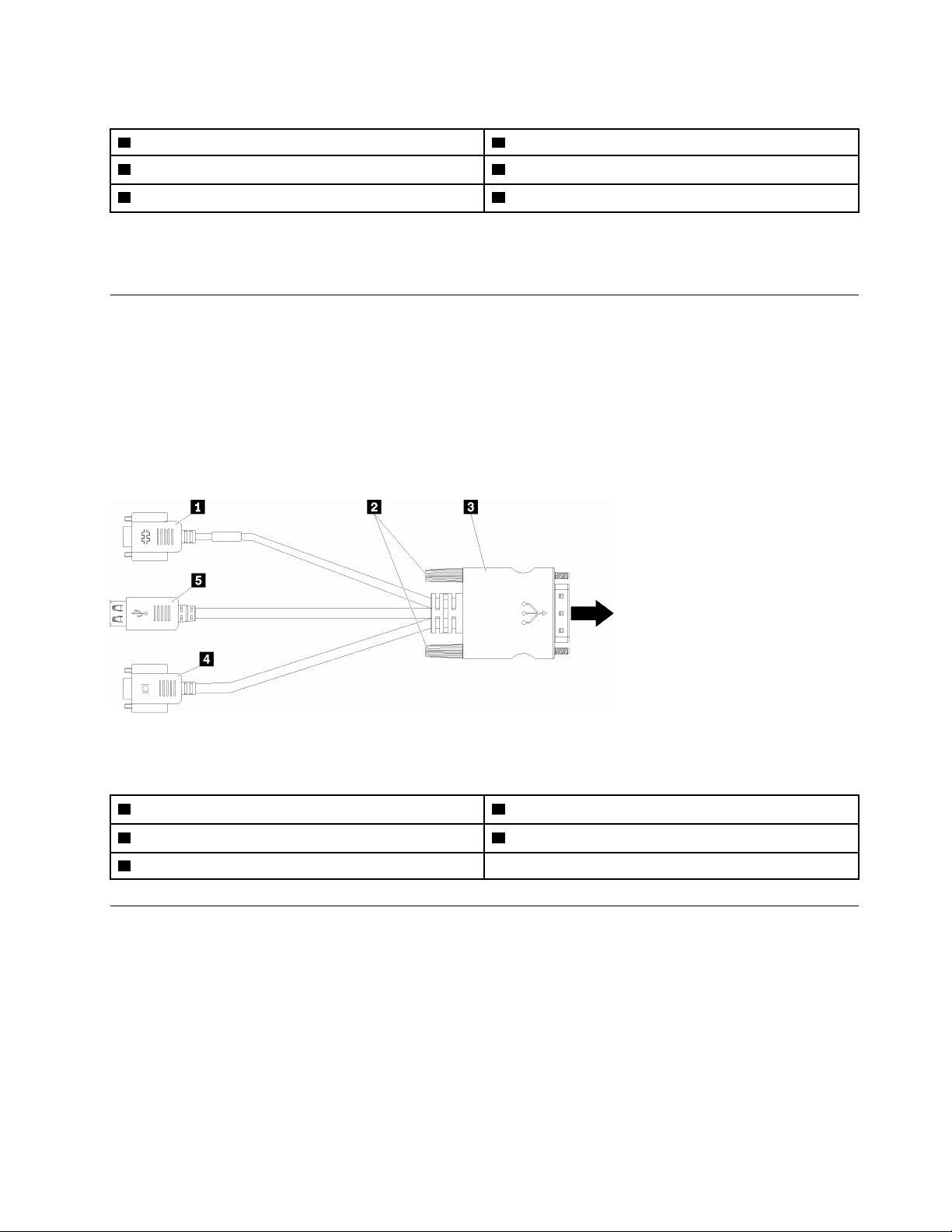
Table 6. System-board LEDs
1 DIMM error 13–18 LEDs 4 DIMM error 19–24 LEDs
2 DIMM error 1–6 LEDs 5 Battery error LEDs
3 DIMM error 7–12 LEDs 6 Light path diagnostics LEDs
See “Light path diagnostics LEDs” on page 17 for information about how to interpret the system-board
LEDs.
KVM cable
Use this information for details about the KVM cable.
Use the KVM cable to connect external I/O devices to the compute node. The KVM cable connects through
the KVM connector (see “Compute node controls, connectors, and LEDs” on page 15). The console breakout
cable has connectors for a display device (video), two USB 2.0 connectors for a USB keyboard and mouse,
and a serial interface connector.
The following illustration identifies the connectors and components on the KVM cable.
Figure 6. Connectors and components on the KVM cable
Table 7. Connectors and components on the KVM cable
1 Serial connector 4 Video connector (blue)
2 Captive screws 5 USB 2.0 ports (2)
3 to KVM connector
System-board layout
Use this information to locate the connectors, LEDs, and switches on the system board.
System-board connectors
Use this information to locate compute node system-board components and connectors for optional
devices.
The following illustration shows the system-board components, including connectors for user-installable
optional devices, in the compute node.
Chapter 2. Compute node components 19
 Loading...
Loading...