Lennox GSB8-112E, GSB8-112S, GSB8-150E, GSB8-150S, GSB8187E Installation Instructions Manual
...Page 1

PRODUCT LITERATURE
affi xed on or adjacent to the boiler.
GAS-FIRED HOT WATER BOILERS
These Gas-Fired Water Boilers are low
Association) for use with Natural and
for cast iron heating boilers.
Lennox Industries Inc.
Dallas, Texas
INSTALLATION
INSTRUCTIONS
GSB8-E
GAS-FIRED STEAM BOILER
GSB8-S
GAS-FIRED STEAM BOILER
RETAIN THESE INSTRUCTIONS FOR
FUTURE REFERENCE
These instructions must be
affi xed on or adjacent to the boiler.
GAS-FIRED HOT WATER BOILERS
These Gas-Fired Water Boilers are low
pressure, sectional cast iron boilers Design
Certified by CSA (Canadian Standards
Association) for use with Natural and
Propane Gases. They are constructed and
hydrostatically tested for a maximum working
pressure of 50 psi (pounds per square inch)
in accordance with A.S.M.E. (American
Society of Mechanical Engineers) Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Code Section IV Standards
for cast iron heating boilers.
WARNING
Impr oper insta l lat i on, ad just ment ,
alteration, service, or maintenance can
cause injury or property damage. Refer
to this manual. For assistance or additional
information consult a qualified installer,
service agency, or the gas supplier.
P/N# 14683453, Rev. 2.2 [11/07]
Page 2

Page 3
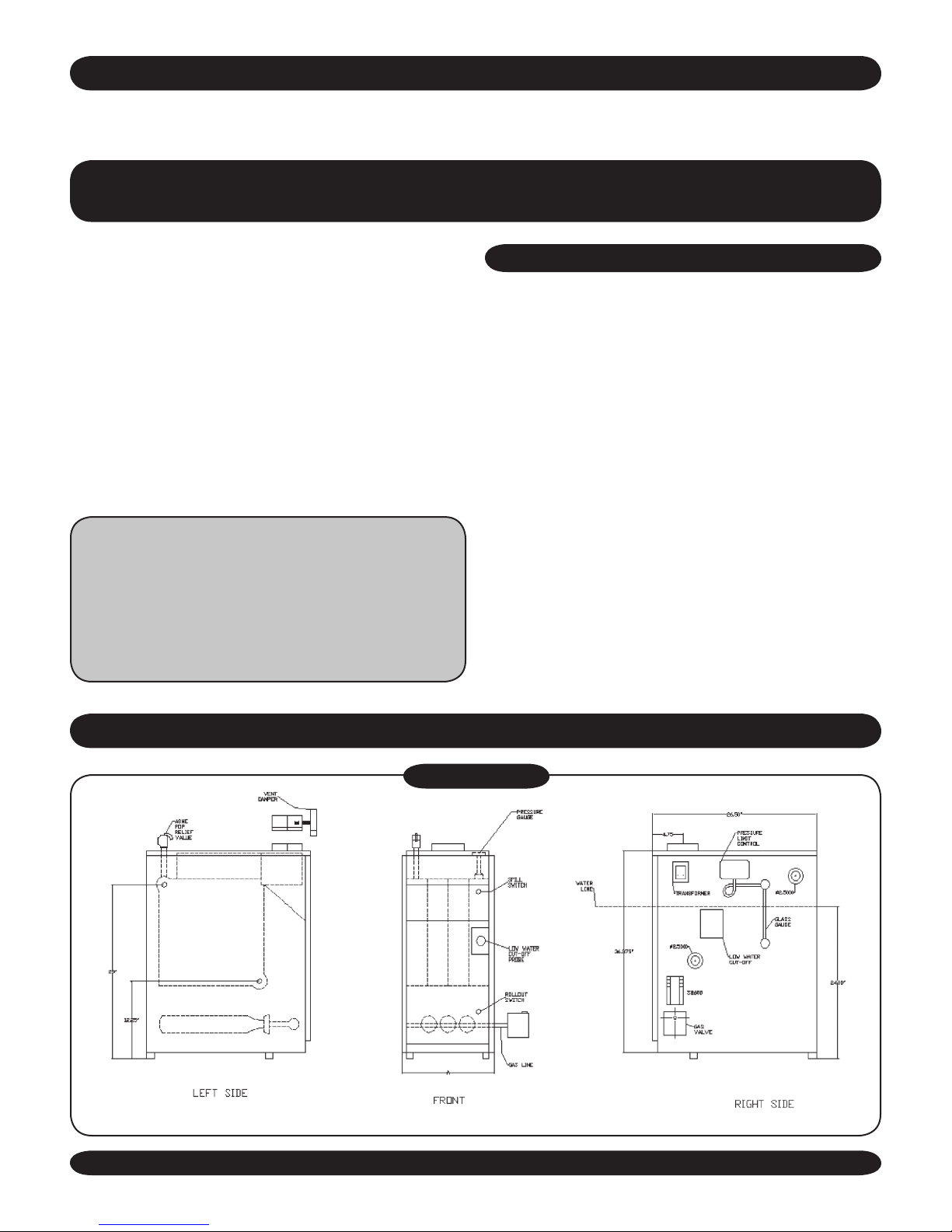
GSB8-E GAS-FIRED STEAM BOILER & GSB8-S GAS-FIRED STEAM BOILER
INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL
P/N# 14683453, Rev.2.2 [11/07]
RETAIN THESE INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
These instructions must be afxed on or adjacent to the boiler
GAS-FIRED HOT STEAM BOILERS
These Gas-Fired Steam Boilers are low pres-
sure, sectional cast iron boilers Design Certied
by AGA (American Gas Association) for use with
Natural and Propane Gases. They are constructed and hydrostatically tested for a maximum
working pressure of 15 psi (pounds per square
inch) in accordance with A.S.M.E. (American
Society of Mechanical Engineers) Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Code Section IV Standards for
cast iron heating boilers.
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, or maintenance can cause
injury or property damage. Refer to this
manual. For assistance or additional
information consult a qualied installer,
service agency or the gas supplier.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Boiler Ratings and Capacities ................3, 4
Before You Start .........................................4
Locating the Boiler ......................................5
Fresh Air for Combustion .......................6, 7
Installation – System Piping ..................7-10
Chimney and Vent Pipe Connection ....10-12
Vent Damper Operation ............................13
Gas Supply Piping ....................................14
Electrical Wiring ........................................15
Controls & Accessories – What They Do .....21, 22
For Your Safety – Read Before Operating .....22
Gas Valve Operating Instructions .......23, 24
Operating Your Boiler .........................24, 25
Checking and Adjusting .......................25-26
Cleaning Your Boiler ............................26,27
Maintaining Your Boiler ........................27-30
Service Hints ............................................30
Troubleshooting ........................................31
Repair Parts.........................................32-35
BOILER RATINGS AND CAPACITIES
Figure #1
DESIGN CERTIFIED FOR NATURAL AND PROPANE GAS
3
Page 4
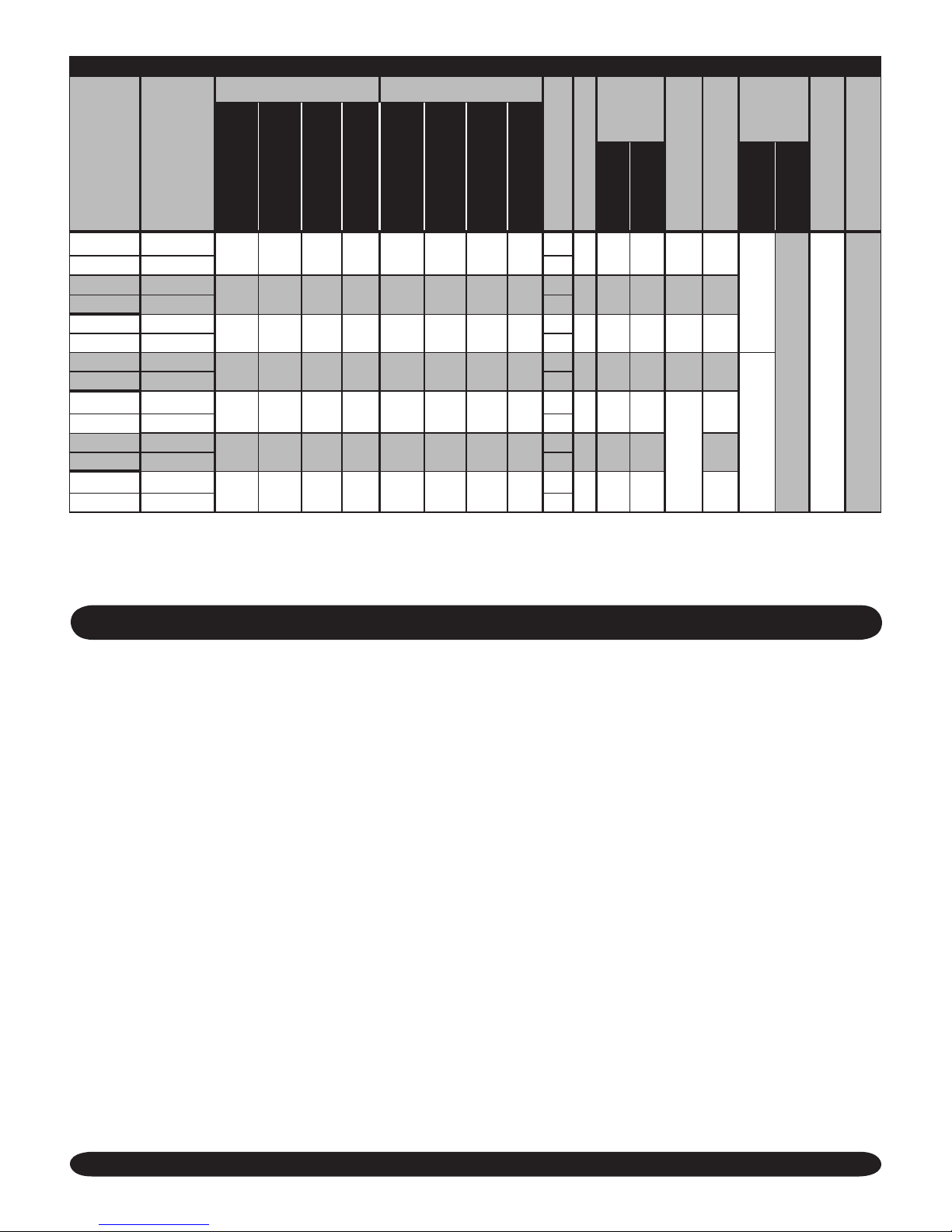
BOILER SPECIFICATIONS
Natural gas Propane
Capacity US
Gallons (L)
Size IPS
Gas Piping
in. (mm)
Model No.
GSB8-075E Electronic
GSB8-075S Standing Pilot 81.1
GSB8-112E Electronic
GSB8-112S Standing Pilot 78.8
GSB8-150E Electronic
GSB8-150S Standing Pilot 79.2
GSB8187E Electronic
GSB8187S Standing Pilot 79.6
GSB8-225E Electronic
GSB8-225S Standing Pilot 80.1
GSB8-262E Electronic
GSB8-262S Standing Pilot 80.5
GSB8-299E Electronic
GSB8-299S Standing Pilot 80.9
1) The Ratings marked “Net I=B=R Ratings” indicate the amount of equivalent direct cast iron radiation each boiler will take care of under normal conditions and
thermostatic control. The Net I=B=R Steam Ratings shown are based on an allowance of 1.333 in accordance with the factors shown in the I=B=R Code as
published by the Hydronics Institute. Selection of boiler size should be based upon “Net I=B=R Rating” Being equal to or greater than installed radiation in
square feet. Consult manufacturer before selecting a boiler for installations having unusual piping and pickup requirements. Specications and dimensions are
subject to change without notice.
2) Annual Flue Utilization Efciency based on U.S. DOE test procedures and FTC labeling regulations.
Type of Ignition
Input Btuh (KW)
75,000
(22.0)
112,500
(33.0)
105,000
(44.0)
187,000
(54.8)
225,000
(65.9)
262,000
(76.9)
299,000
(87.6)
(KW
Heating Capacity Btuh
62,000
47,000
(18.5)
(14.7)
91,000
68,000
(26.7)
(19.9)
122,000
92,000
(35.7)
(27.0)
153,000
115,000
(44.8)
(33.7)
183,000
137,000
(53.6)
(40.1)
214,000
161,000
(62.7)
(47.2)
245,000
184,000
(71.8)
(53.9)
sq.ft. Radiation
1) Net I=B=R Rating
1) Net I=B=R Btuh (KW)
196
(18.2)
283
(26.3)
383
(35.6)
479
(44.5)
571
(53.0)
671
(62.3)
767
(71.3)
Input Btuh (KW)
70,000
(20.0)
105,000
(30.8)
140,000
(41.0)
175,000
(51.3)
210,000
(61.5)
245,000
(71.8)
280,000
(82.0)
(KW
Heating Capacity Btuh
58,000
44,000
(16.1)
(13.0)
85,000
64,000
(24.9)
(18.6)
114,000
86,000
(33.4)
(25.2)
143,000
107,000
(41.9)
(31.4)
171,000
128,000
(50.1)
(37.5)
200,000
150,000
(58.6)
(44.0)
229,000
172,000
(67.1)
(50.4)
sq.ft. Radiation
1) Net I=B=R Rating
1) Net I=B=R Btuh (KW)
183
(17.0)
267
(24.8)
358
(33.3)
446
(41.4)
553
(51.4)
625
(58.1)
717
(66.7)
82.7
80.4
80.6
80.9
81.1
81.3
81.5
2) AFUE %
Number of Sections
4.20
3
(16.1)
5.90
4
(22.3)
7.60
5
(28.8)
9.30
6
(35.2)
11.00
7
(41.6)
12.70
8
(48.1)
14.40
9
(54.5)
Full
Water Level
2.60
(9.84)5(12.7)
3.80
(14.4)6(15.2)
5.00
(18.9)6 (15.2)
6.20
(23.5)7(17.8)
7.40
(28.0)
8.60
(32.6)
9.80
(37.1)
Flue Size Connection
7
(17.8)
Package
Natural
Sipping Weight Lbs. (kg)
Diameter in. (mm) round
325
(147)
1/2
404
(12.7)
(183)
483
(219)
564
(256)
649
3/4
(294)
(19.0)
719
(326)
800
(363)
Propane
3/4
(19.0)
Supply & Return Connection
2-1/2
(64.0)
NPT in. (mm)
(19.0)
(mm)
Drain Connection NPT in.
3/4
BEFORE YOU START
Check to be sure you have the right size boiler before
starting the installation. See rating and capacity table on
previous page. Also be sure the new boiler is for the type
of gas you are using. Check the rating plate on the right
side of the boiler.
You must see that the boiler is supplied with the correct type of gas, fresh air for combustion, and a suitable
electrical supply. Also, the boiler must be connected to a
suitable venting system and an adequate piping system.
Finally, a thermostat, properly located, is needed for control
of the heating system. If you have any doubts as to the
various requirements, check with local authorities and
obtain professional help where needed. Take the time to
complete all of the steps for SAFE and PROPER operation of the heating system.
If this boiler is installed in a building under construction,
special care must be taken to insure a clean combustion air supply during the construction process. Airborne
particulates such as from drywall dust and from berglass
insulation can clog the burner ports and cause incomplete
combustion and sooting.
These boilers are designed for use in closed heating
systems where all of the steam is returned to the boiler as
condensate and the amount of make-up water required is
minimal. These boilers are not designed for or intended
for use in open systems of process applications using
100% make-up water. Damage to the boiler resulting
from such use shall not be covered under the warranty.
Where required by the authority having jurisdiction,
the installation must conform to American Society of Mechanical Engineers Safety Code for Controls and Safety
Devices for Automatically Fired Boilers, No. CSD-1.
The installation must conform to the requirements
of the authority having jurisdiction or, in the absence
of such requirements, to the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1-latest revision.
The following steps are all necessary for proper
installation and safe operation of your boiler.
1. LOCATING THE BOILER
2. FRESH AIR FOR COMBUSTION
3. INSTALLATION – SYSTEM PIPING
4. CHIMNEY & VENT PIPE CONNECTION
5. GAS SUPLY PIPING
6. ELECTRICAL WIRING
7. CHECKING & ADJUSTING
KEEP BOILER AREA CLEAN AND FREE FROM
COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS, GASOLINE AND
OTHER FLAMMABLE VAPORS AND LIQUIDS
4
Page 5
LOCATING THE BOILER
1. Select level location as centralized with piping
system, and as near chimney, as possible.
2. Place crated boiler at selected location, remove
crate by pulling crate sides from top and bottom
boards. Combustible oors: When boiler is to be
installed on a combustible oor, a Special Base
Plate must be used – 146-14-031 (3-6 Section)
or 146-14-032 (7-9 Section). This boiler must
not be installed on carpeting.
3. Boiler is to be level. Metal shims may be used
under base legs for nal leveling.
4. Additional clearances for service may exceed
clearances for re protection. Always comply
with the minimum re protection clearances
shown on the boiler. An 18 inch clearance
should be maintained on any side where passage is required to access another side for
cleaning, servicing, inspection or replacement
of any part that may need attention. An 18 inch
clearance is recommended on the control side
for servicing.
Where the actual ceiling height of a room is
greater than 8’, the volume of a room shall be
gures on the basis of a ceiling height of 8’.
Determination of room size should be based
on the total volume of all gas red equipment
installed in the room. Consult section 6.3.1 of
the National Fuel Gas Code for further information, including approved methods for reducing
clearances in large rooms.
5. Equipment shall be installed in a location in
which the facilities for ventilation permit satisfactory combustion of gas, proper venting, and
maintenance of ambient temperature at safe
limits under normal conditions of use. Equipment shall be located so as not to interfere
with proper circulation of air. When normal
inltration does not provide the necessary air,
outside air shall be introduced (See - “Fresh
Air for Combustion” following page).
6. Advise owner to keep air passages free of
obstructions. Ventilating and combustion air
must enter boiler room without restrictions.
Figure 2 shows minimum clearances to com-
bustible construction. Rooms that are large
in comparison with the size of the boiler are
dened as rooms having a volume equal to or
greater than 16 times the volume of the boiler.
Figure #2
BOILER CLEARANCES
Alcove*, or Room
Unit
To p 6” 6”
Rear 6” 6”
Control Side 7” 6”
Opposite Side 6” 6”
Front 18” 18”
Flue/Vent Connector 6” 6”
Near Boiler Piping 1” 1”
* Alcove - boiler may be installed in an area inclosed on 3 sides (U shped) with
the front open.
Not Large in
Comparison
With Boiler
Room Large In
Comparison
With Boiler
7. The boiler shall be installed such that the automatic gas ignition system components are
protected from water (dripping, spraying, rain,
etc.) during appliance operation and service
(condensate trap, control replacement, etc.).
BOILER VOLUME SPECIFICATIONS
Boiler
Size
3 sect. 6.3 100.4
4 sect. 8.1 129.4
5 sect. 9.9 158.4
6 sect. 11.7 187.4
7 sect. 13.5 216.4
8 sect. 15.3 245.4
9 sect. 17.2 274.5
* For room with single boiler only.
Boiler
Volume
(Cu. Ft.)
Minimum Room
Volume Required
To Be Large (Cu.Ft.)*
This unit must be set on a concrete or other noncombustible material base or oor.
IT MUST NOT BE INSTALLED ON CARPETING.
5
Page 6

FRESH AIR FOR COMBUSTION
Provision for combustion and ventilation air must be in accordance with Section 5.3,
Air for Combustion and Ventilation, of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI A223.1 – latest
revision, or applicable provisions of the local building codes.
WARNING
!
!
Be sure to provide enough fresh air for
combustion. Enough air insures proper combustion and assures that no hazard will
develop due to the lack of oxygen.
You must provide for enough fresh air to assure
proper combustion. The re in the boiler uses
oxygen. It must have a continuous supply. The
air in a house contains only enough oxygen to
supply the burner for a short time. Outside air
must enter the house to replace that used by
the burner. Study following examples 1 and 2 to
determine your fresh air requirements.
EXAMPLE 1:
Boiler Located in Unconned Space
An unconned space is dened as a space
whose volume is not less than 50 cubic feet per
1,000 Btu per hour of the total input rating of all
appliances installed in that space.
If your boiler is in an open area (un-partitioned
basement) in a conventional house, the air that
leaks through the cracks around doors and windows will usually be adequate to provide air for
combustion. The doors should not t tightly. Do
not caulk the cracks around the windows.
Equipment located in buildings of unusually
tight construction shall be provided with air for
combustion, ventilation, and dilution of ue gases
using the methods described in example 2B
or shall be specially engineered. The authority
having jurisdiction must approve specially engineered installations.
EXAMPLE 2:
Boiler Located in Unconned Space
A. All Air from Inside the Building: The conned
space shall be provided with two permanent
openings communicating directly with an ad-
ditional room(s) of sufcient volume so that
the combined volume of all spaces meets the
criteria for an unconned space. The total input
of all gas utilization equipment installed in the
combined space shall be considered in making
this determination. Each opening shall have a
minimum free area of one square inch per 1,000
Btu per hour of the total input rating of all gas
utilization equipment in the conned space, but
not less than 100 square inches. One opening
shall be within 12 inches of the top and one
within 12 inches of the bottom of the enclosure.
The minimum dimension of air openings shall
not be less than 3 inches.
B. All Air from Outdoors: The conned space
shall communicate with the outdoors in accordance with methods 1 or 2. The minimum
dimension of air openings shall not be less than
3 in. Where ducts are used, they shall be of the
same cross-sectional area as the free area of
the openings to which they connect.
1. Two permanent openings, one commencing
within 12 inches of the top, and one commencing within 12 inches of the bottom, of
the enclosure shall be provided. The openings shall communicate directly, or by the
ducts, with the outdoors or spaces (crawl
or attic) that freely communicate with the
outdoors.
a) Where directly communicating with the
outdoors or where communicating to the
outdoors through vertical ducts, each
opening shall have a minimum free area
of 1 sq. in. per 4000 Btu per hour or total
input rating of all equipment in the enclosure. (See Figure 3A.)
b) Where communicating with the outdoors
through horizontal ducts, each opening
shall have a minimum free area of 1 sq.
in. per 2000 Btu per hour or total input
rating of all equipment in the enclosure.
(See Figure 3B.)
6
Page 7
FRESH AIR FOR COMBUSTION
2. One permanent opening commencing with
12 inches of the top of the enclosure, shall
be permitted where the equipment has clearance of at least 1 inch from the sides and back
and 6 inches from the front of the appliance.
The opening shall directly communicate with
the outdoors or shall communicate through
a vertical or horizontal duct to the outdoors
or spaces (crawl or attic) that freely communicate with the outdoors, and shall have a
minimum free area of:
a) 1 sq. inch per 3000 Btu per hour of the
total input of all equipment located in the
enclosure (See Figure 4), and
b) Not less than the sum of the areas of all
vent connectors in the conned space.
Figure #3A
FRESH AIR DUCT CAPACITIES (Btuh)
1 Square Inch per 4,000 Btuh
100% Free
Area
Fresh Air
Duct Size
3” x 12” 144,000 108,000 36,000
8” x 8” 256,000 192,000 64,000
8” x 12” 384,000 288,000 96,000
8½” x 16” 512,000 384,000 128,000
¼” Wire
Mesh
75% Free
Area
Metal
Louvers
25% Free
Area
Wood
Louvers
Figure #3B
FRESH AIR DUCT CAPACITIES (Btuh)
1 Square Inch per 2,000 Btuh
100% Free
Area
Fresh Air
Duct Size
3” x 12” 72,000 54,000 18,000
8” x 8” 128,000 96,000 32,000
8” x 12” 192,000 144,000 48,000
8½” x 16” 256,000 192,000 64,000
¼” Wire
Mesh
75% Free
Area
Metal
Louvers
25% Free
Area
Wood
Louvers
Figure #4
FRESH AIR DUCT CAPACITIES (Btuh)
1 Square Inch per 3,000 Btuh
100% Free
Area
Fresh Air
Duct Size
3” x 12” 108,000 81,000 27,000
8” x 8” 192,000 144,000 48,000
8” x 12” 288,000 216,000 72,000
8½” x 16” 384,000 288,000 96,000
¼” Wire
Mesh
75% Free
Area
Metal
Louvers
25% Free
Area
Wood
Louvers
INSTALLATION — SYSTEM PIPING
The near boiler piping, that is the piping around
the boiler must be considered as part of the boiler
for proper water level control, and to produce dry
steam. Correct near boiler piping is crucial to the
proper operation of the boiler and the heating system. Follow these recommendations carefully.
1. Place boiler in selected location, as near chimney
as possible.
2. Install the pop safety valve, using the furnished
¾” coupling, into the ¾” pipe nipple on the top
of the boiler. Make a discharge pipe, using ¾”
pipe (not furnished) to carry the water or steam
to a nearby drain. Do not connect the discharge
pipe directly to a drain but leave an air gap. The
downstream end of the discharge pipe must be
unthreaded. No shutoff of any description shall
be placed between the pop safety valve and
the boiler, or on discharge pipes between such
safety valves and the atmosphere. Installation
of the pop valve shall conform to the requirements of the ANSI/ASME Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Code, Section IV. The manufacturer is
not responsible for any water damage.
3. This boiler is equipped with two 2 ½” supply
connections and two 2 ½” return connections,
one each on both the left and right sides of the
boiler. Unused connections must be plugged
with the 2 ½” plugs (furnished).
4. Recommended near boiler piping for gravity
return systems is shown in Figure 5. This
7
Page 8
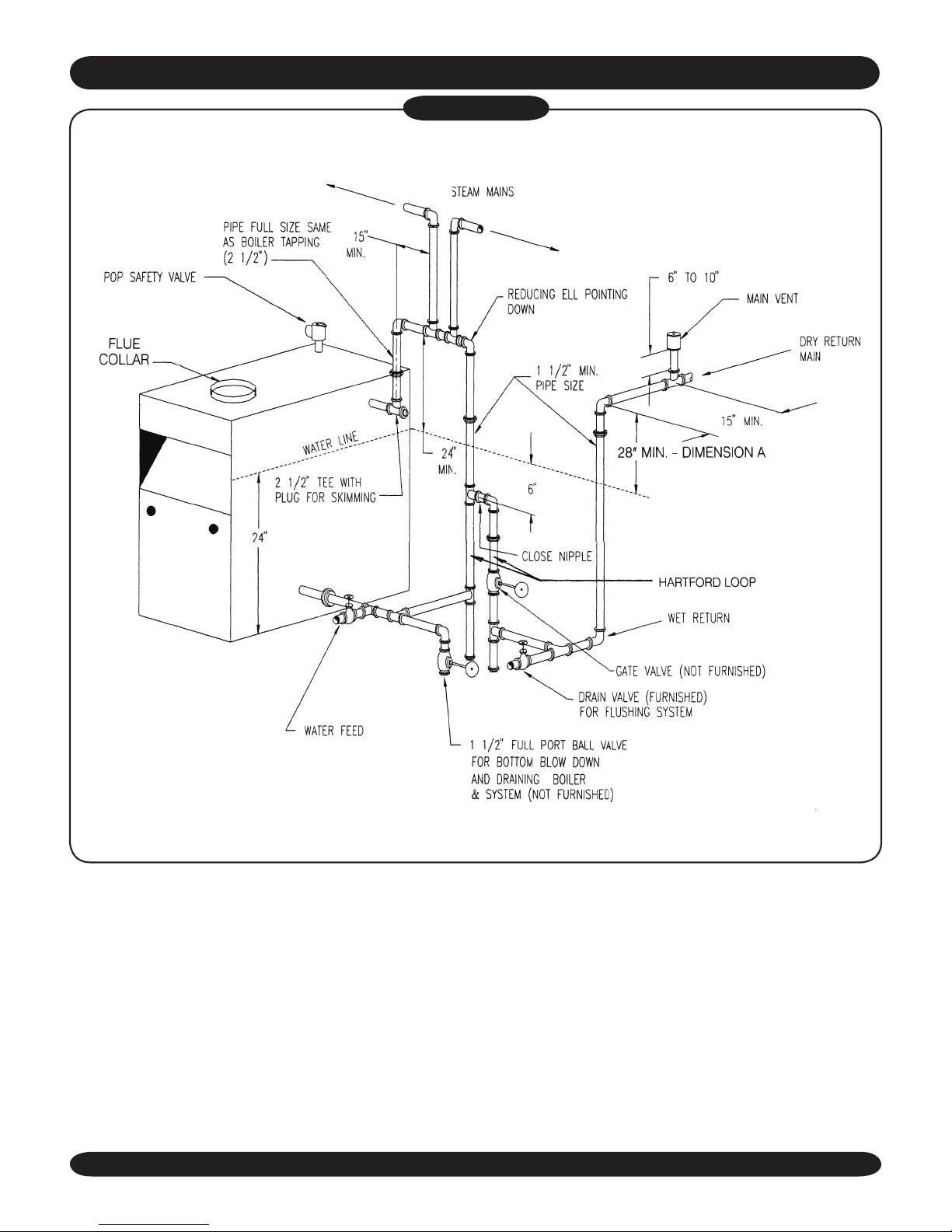
INSTALLATION — SYSTEM PIPING
Figure #5
RECOMMENDED NEAR BOILER PIPING USING ONE SUPPLY TAPPING
con guration uses one supply and one return
tapping. This setup can be used on any size
boiler in this series. The supply and return
connections may be piped both into the same
side (either left or right) or one into each side
of the boiler.
5. For installers choosing to use both supply tappings, Figure 6A shows the correct way to
pipe this system. Figure 6B shows the wrong
way to pipe a header with two risers.
• Headers must be tted with header offsets or
swing joints, or be equipped with expansion
joints, so that thermal expansion and contraction of the header will not damage the boiler.
Headers shall not be welded.
• System takeoffs from the header must be
between the equalizer and the riser to the
header nearest the equalizer. System takeoffs must never be between two risers.
6. System takeoffs from the header must never
be bullheaded. If the steam main goes in two
directions, there must be two takeoffs from the
header, one for each main.
8
Page 9
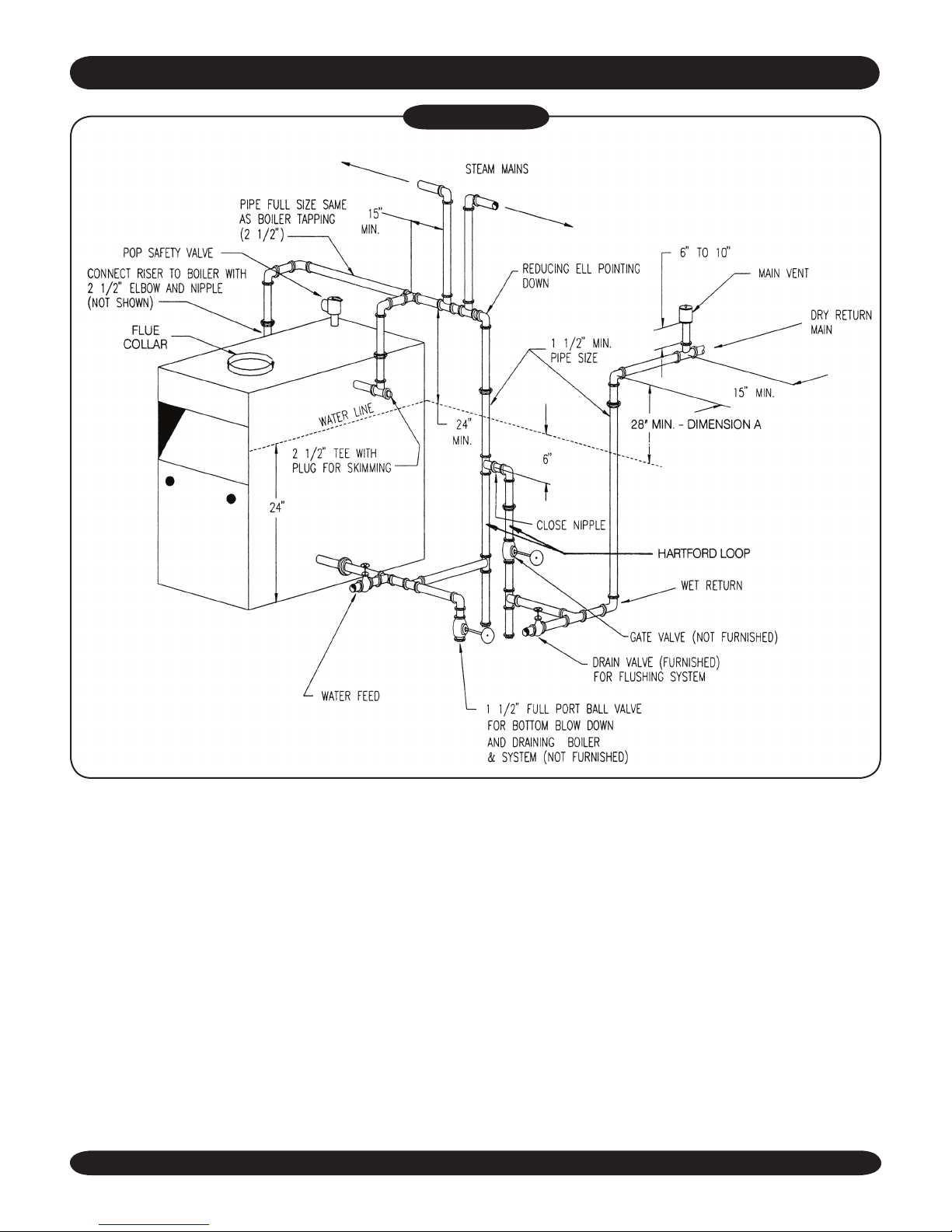
INSTALLATION — SYSTEM PIPING
Figure #6A
RECOMMENDED NEAR BOILER PIPING USING TWO SUPPLY TAPPINGS
7. All boilers in gravity return systems must be
equipped with a Hartford Loop as shown in
Figures 5 and 6A.
8. When piping the vertical risers from the boiler
to the header, the bottom of the header must
be a minimum of 24 inches above the water
level line on the right side of the boiler.
9. Steam riser(s) and header shall be 2 ½” pipe size.
10. Equalizer line shall be minimum 1 ½” size.
11. The near boiler piping shall include a 2 ½” tee
with a plug located on the supply line as shown
for skimming (i.e. surface blowdown).
12. The near boiler piping shall include a 1 ½” ball
valve in the return piping as shown for bottom
blowdown and draining.
13. For gravity return systems, the bottom of the
lowest steam carrying pipe, be it a dry return,
or the end of the steam main, must be at least
28” above the normal water level line on the
right side of the boiler. This is known as “Dimension A.”
14. For pumped return systems, follow the condensate pump or boiler feed pump manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation and
hookup.
15. In connecting the cold water supply to the
water inlet valve, make sure that a clean water
supply is available. When the water supply is
from a well or pump, a sand strainer should be
installed at the pump.
9
Page 10

INSTALLATION — SYSTEM PIPING
Figure #6B
COMMON NEAR BOILER PIPING MISTAKES
FOR USE WITH COOLING UNITS
A. This boiler, when used in connection with
chilled water systems, must be installed so
that the chilled water is piped in parallel with
the heating boiler. Appropriate valves must be
used to prevent the chilled water from entering
the heating boiler (Figure 7).
B. When this boiler is connected to heating coils
located in air handling units where they may be
exposed to refrigerated air circulation, the pip-
ing system shall be equipped with ow control
valves or other automatic means to prevent
gravity circulation of the boiler water during the
cooling cycle.
Figure #7
CHILLED WATER PIPING
10
Page 11
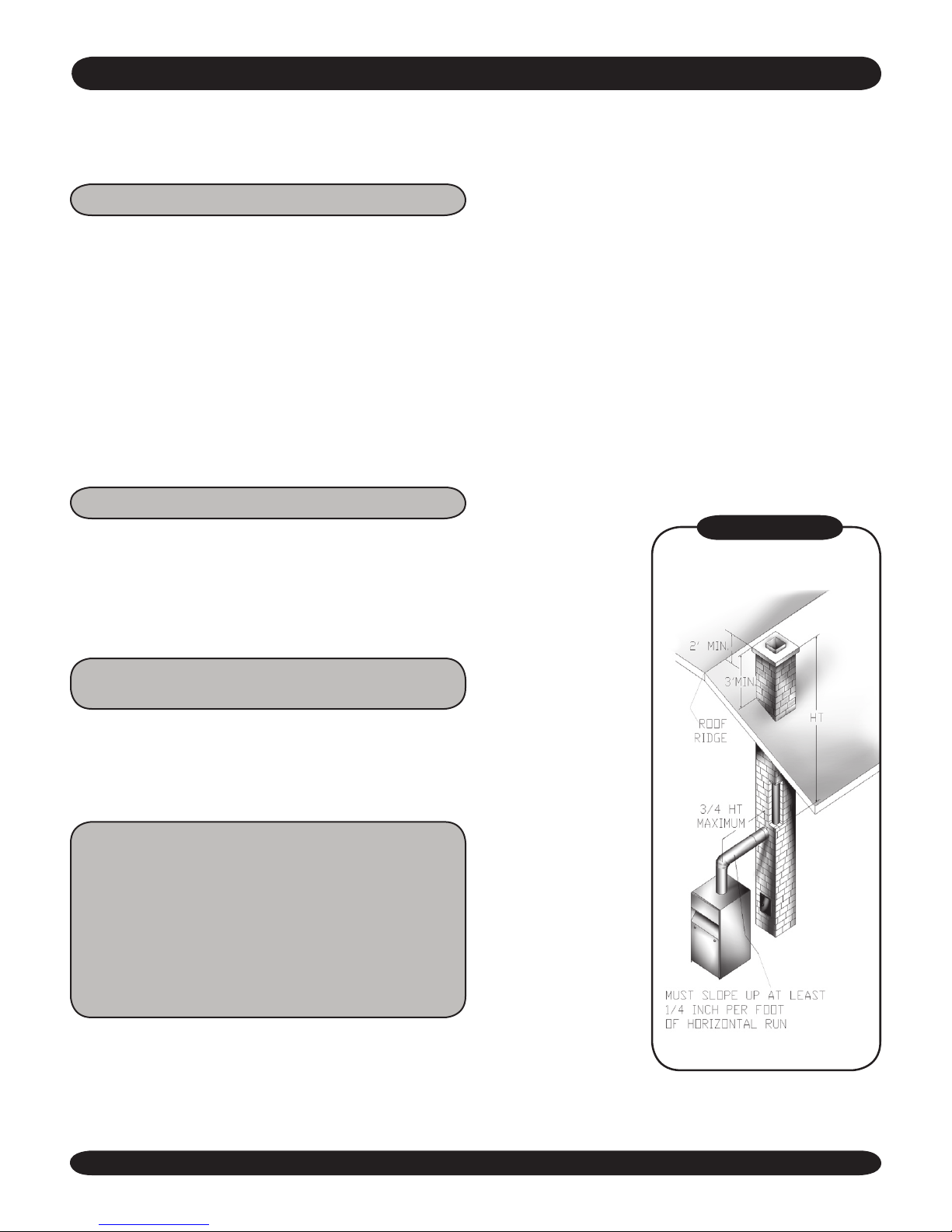
CHIMNEY AND VENT PIPE CONNECTION
For boilers for connection to gas vents or chimneys, vent installations shall be
in accordance with Part 7, Venting of Equipment, of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1-latest revision and applicable provisions of the local building codes.
CHECK YOUR CHIMNEY
This is a very important pat of your heating system. It must be clean, the right size, properly
constructed and in GOOD CONDITION. No boiler
can function properly with a bad chimney. Inspect
the chimney and verify that the construction and
size of the chimney meets all applicable provisions of the National Fuel Gas Code and local
building codes. Figure 8 gives you an idea how
a boiler might be vented to a chimney. Note that
the height (HT) is measured from the vent pipe
to the top.
CHIMNEY SIZING
Chimney sizing and all other aspects of the vent
installation must be in accordance with Part 7 of
the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1-latest
revision, and applicable provisions of the local
building codes.
CONNECTING THE VENT DAMPER AND
VENT CONNECTOR
Refer to Figure 1 ue diagram for the size and
location of the vent (ue opening). Use a 28
gauge (minimum) galvanized pipe to connect to
the chimney.
IMPORTANT: The damper blade on the
furnished vent damper has a ½ square inch
hold (approximately ¾” diameter). On boilers equipped with standing pilot, the hole
must be left open. On boilers equipped
with intermittent ignition, the hole should be
plugged by using the plug supplied with the
vent damper.
1. Position furnished vent damper on top of ue
outlet collar. Fasten damper securely to ue
outlet collar with sheet metal screws. Make
sure damper blade has clearance to operate
inside of diverter.
AS AN OPTION:
The damper may be installed in any horizontal or ver-
tical position, closer to the ue outlet collar preferred.
Follow the diagrams – Figures 9, 10, and 11.
2. Install the vent damper to service only the single boiler for which it is intended. The damper
position indicator shall be in a visible location
following installation. Locate the damper so
that it is accessible for servicing.
3. The damper must be in the open position when
appliance main burners are operating.
4. The boiler is equipped with a factory wired harness that plugs into the vent damper. The thermostat must be connected to the black wires
marked 24 Volt
thermostat on
the boiler.
5. Vent pipe must be
CHIMNEY REQUIREMENTS
Figure #8
TYPICAL MASONRY
same size as the
ue outlet collar.
6. Slope pipe up
from boiler to
chimney not less
than ¼” per foot.
7. Run pipe as
directly as possible with as
few elbows as
possible.
8. Do not connect to
replace ue.
9. End of vent pipe
must be flush
with inside face
of chimney ue.
Use a sealed-in
thimble for the
chimney connection.
10. Horizontal run should not be longer than ¾
the chimney height (HT) (Figure 8).
11
Page 12

CHIMNEY AND VENT PIPE CONNECTION
The sections of vent pipe should be fastened
with sheet metal screws to make the piping rigid.
Horizontal portions of the vent system must be
supported to prevent sagging. Use stovepipe
wires every 5’ to support the pipe from above.
If the vent pipe must go through a crawl space,
double wall vent pipe should be used. Where vent
pipe passes through a combustible wall or partition, use a ventilated metal thimble. The thimble
should be 4 inches larger in diameter than the
vent pipe.
MINIMUM VENT PIPE CLEARANCE
Wood and other combustible materials must not
be closer than 6” from any surface of single wall
metal vent pipe. Listed Type B vent pipe or other
listed venting systems shall be installed in accordance with their listing.
REMOVING EXISTING BOILER FROM
COMMON VENTING SYSTEM
When an existing boiler is removed from a common venting system, the common venting system
is likely to be too large for proper venting of the
appliances remaining connected to it.
At the time of removal of an existing boiler, the
following steps shall be followed with each appliance remaining connected to the common venting system placed in operation, while the other
appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are not in operation.
1. Seal any unused openings in the common
venting system.
2. Visually inspect the venting system for proper
size and horizontal pitch and determine there
is no blockage or restriction, leakage, corrosion
and other deciencies which could cause an
unsafe condition.
3. Insofar as is practical, close all building doors
and windows and all doors between the space
in which the appliances remaining connected
to the common venting system are located and
other spaces of the building. Turn on clothes
dryers and any appliance not connected to the
common venting system. Turn on any exhaust
fans, such as range hoods and bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at maximum speed.
Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. Close
replace dampers.
4. Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow the lighting instructions. Adjust thermostat so appliance will operate continuously.
5. Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening
after 5 minutes of main burner operation. Use
the ame of a match or candle, or smoke from
a cigarette, cigar, or pipe.
6. After it has been determined that each appliance remaining connected to the common
venting system properly vents when tested as
outlined above, return doors, windows, exhaust
fans, replace dampers, and any other gas-
burning appliance to their previous conditions
of use.
7. Any improper operation of the common venting
system should be corrected so that the installation conforms with the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1-latest revision. When resizing
any portion of the common venting system,
the common venting system should be resized
to approach the minimum size as determined
using the appropriate tables in Part 11 in the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1-latest
revision.
For boilers for connection to gas vents or
chimneys, vent installations shall be in accordance with Part 7, Venting of Equipment,
of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1latest revision and applicable provisions of
the local building codes.
Vent connectors serving appliances vented by
natural draft shall not be connected into any
portion of mechanical draft systems operating
under positive pressure.
12
Page 13

VENT DAMPER OPERATION
ROTATION
ROTATION
OPEN
CLOSED
FLUE GAS FLOW
FLUE GAS FLOW
CLOSED
OPEN
DAMPER CLOSED DAMPER OPEN
SHOWING OPEN AND CLOSED POSITION
Figure #9
Figure #10
For safe, efcient operation, the vent damper and
all ue product carrying areas of the appliance must
be checked annually by you, with particular attention
given to deterioration from corrosion or other sources.
If you see corrosion or other deterioration, contact your
heating contractor for repairs. Check vent damper
operation as follows:
1. When the boiler is off, check that the vent damper
positions indicator points to the closed position,
Figure 11.
2. Turn the thermostat or controller up to call for heat
and check the vent damper indicator points to the
open position, Figure 11.
3. Turn the thermostat or controller down again and
check that the damper position indicator returns to
the closed position.
4. If you have central air conditioning, set the thermostat to COOL and turn it down to call for cooling.
Cooling system should operate.
5. Return thermostat to desired position.
The vent damper must be inspected at least once a
year by a trained, experienced service technician.
The name of the person who originally installed your
vent damper is shown on the installation label.
TYPICAL INSTALLATION FOR VENT DAMPER
NOTE CAUTION AND FOOTNOTES
1. Install the vent damper to service only the single appliance for which it is intended. If improperly installed, a
hazardous condition, such as an explosion or carbon
monoxide poisoning, could result.
2. Do not install the vent damper on vent pipe curve.
MANUAL OPERATION OF THE VENT DAMPER
The vent damper may be placed in the open position to permit burner operation by using the “HOLD
DAMPER OPEN” switch, located on the damper con-
troller. The thermostat will control the burner ring as
before, while the damper will remain open.
DO NOT turn damper open manually or motor damage will result. Set switch to “AUTOMATIC OPERATION” to close vent damper during burner off cycle.
For further information, and for a vent camper trouble
shooting guide, refer to the manual that was packaged
with the vent damper.
Figure #11
VENT DAMPER POSITION INDICATOR
3. Do not run wires near high temperature surfaces. Use
stand-off brackets if necessary.
13
Page 14

GAS SUPPLY PIPING
CHECK GAS SUPPLY
The gas pipe to your boiler must be the correct
size for the length of the run and for the Btu per
hour input of all gas utilization equipment connected to it. See Figure 12 for the proper size.
Be sure your gas line complies with local codes
and gas company requirements.
The boiler and its individual shut-off valve must
be disconnected from the gas supply piping system during any pressure testing of that system at
test pressures in excess of ½ psig (3.5 kPa).
This boiler must be isolated from the gas supply piping system by closing its individual manual
shut-off valve during any pressure testing of the
gas supply piping system at test pressures equal
to or less than ½ psig (3.5 kPa).
CONNECTING THE GAS PIPING
Refer to
Figure 13 for the general layout at the
boiler. It shows the basic ttings you will need. The
gas line enters the boiler from the right side.
The following rules apply:
1. Use only those piping materials and joining
methods listed as acceptable by the authority
having jurisdiction or in the absence of such
requirements, by the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1-latest revision.
2. Use pipe joint compound suitable for LP gas
on male threads only.
3. Use ground joint unions.
4. Install a sediment trap upstream of gas con-
trols.
5. Use two pipe wrenches when making the
connection to the gas valve to keep it from
turning.
6. Install a manual shut-off valve in vertical pipe
about 5 feet above oor.
7. Tighten all joints securely.
8. Propane – gas connections should only be
made by a licensed propane installer.
9. Two-stage regulation should be used by the
propane installer.
10. Propane – gas piping should be checked out
by the propane installer.
CHECKING THE GAS PIPING
Upon completion of piping, check immediately for
gas leaks. Open the manual shut-off valve. Test for
leaks by applying soap suds (or a liquid detergent) to
each joint. Bubbles forming indicate a leak. CORRECT EVEN THE SMALLEST LEAK AT ONCE.
WARNING
!
!
Never use a match or open fl ame to test for leaks
Figure #12
GAS PIPE SIZES
NATURAL GAS
Length
of Pipe
– Ft.
20 92,000 190,000 350,000 625,000
40 63,000 130,000 245,000 445,000
60 50,000 105,000 195,000 365,000
Length
of Pipe
– Ft.
20 131,000 216,000 189,000 393,000
40 90,000 145,000 129,000 267,000
60 72,000 121,000 103,000 217,000
*Outside diameter
The length of pipe or tubing should be measured from the gas meter
or propane second stage regulator.
Pipe Capacity – Btu Per Hour Input
Includes Fittings
1
/2”
PROPANE GAS
Pipe Capacity – Btu Per Hour Input
Copper Tubing* Iron Pipe
5
/8”
3
/4” 1” 1 1/4”
Includes Fittings
3
/4”
1
/2”
Figure #13
GAS PIPING AT BOILER
3
/4”
14
Page 15

ELECTRICAL WIRING
ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY
All electrical work must conform to local codes,
as well as the National Electrical Code, ANSI/
NFPA-70, latest revision.
Run a separate 120 Volt circuit from a separate
over-current protective device in your electrical service entrance panel. This should be a 15 ampere
circuit. Locate a shut-off switch at the boiler. It must
be turned off during any maintenance. Connect 120
Volt electrical supply to the primary leads on the
24 Volt transformer. Solder and tape or securely
fasten these connections with wire nuts.
The boiler, when installed, must be electrically
grounded in accordance with the requirements of
the authority having jurisdiction or, in the absence of
such requirements, with the National Electrical Code,
ANSI/NFPA No. 70-latest revision. Run a 14 gauge
or heavier copper wire from the boiler to a grounded
connection in the service panel or a properly driven
and electrically grounded ground rod.
WARNING
!
Turn off electric power at fuse box before making any line
Voltage connections. Follow local electrical codes.
!
INSTALL YOUR THERMOSTAT
The thermostat location has an important effect
on the operation of your boiler system. BE SURE
TO FOLLOW THE INSTRUCTIONS INCLUDED
WITH YOUR THERMOSTAT.
Locate the thermostat about ve feet above
the oor on an
inside wall. It
may be mounte d d i r e c t l y
on th e w al l
or on a vertically mounted
o u t l e t b o x .
It should be
sensing aver a ge ro o m
temperature,
so avoid the
THERMOSTAT LOCATIONS TO AVOID
DEAD SPOTS:
Comers and
alcoves
COLD SPOTS: HOT SPOTS:
Concealed pipes
or ducts
Stairwells - drafts
Unheated rooms
on
other side of wall
Behind doors
Concealed pipes
Fireplace
TV sets
Radios
Lamps
Direct sunlight
Kitchens
following:
Set heat anticipator at 0.4 amps for boilers
equipped with standing pilot, and at 0.6 amps for
boilers equipped with intermittent ignition. The
24 Volt thermostat leads shall be connected to
the two wires tagged “24 Volt thermostat” on the
boiler. For boilers with 67D-1 oat type low water
cut-off, the two wires are black. One wire is located on the secondary of the 24 Volt transformer,
the second wire is located on the pressure limit
control. For boilers with PS-802 probe type low
water cut-off, one wire is green and is located on
terminal B or the PS-802, the second wire is black
and located on the pressure limit control.
ELECTRONIC THERMOSTATS
Certain types of electronic thermostats may lose
their memory or shut down. With 67D-1 oat type
low water cut-offs, this may occur each time the
thermostat calls for heat, due to the internal circuit
in the vent damper. With PS-802 probe type low
water cut-offs, this may occur each time the low
water cut-off detects a low water condition. If this
is the case, an isolation relay is required for the
thermostat circuit. A 24 bolt single pole single
throw (SPST) normally open (N.O.) relay is required, such as the Honeywell R8222A or equivalent. Wire as shown in Figures 14A or 14B.
VENT DAMPER
The boiler is equipped with a factory wired
harness with 4 pin molex plug, that plugs into the
4 pin molex receptacle inside the vent damper
operator.
The vent damper must be connected for the
boiler to operate. Wiring diagrams follow for the
various different models.
CAUTION
!
!
Label all wires prior to disconnection when
servicing controls. Wiring errors can cause
improper and dangerous operation. Verify
proper operation after servicing.
15
Page 16

Figure #14A
ISOLATION RELAY WIRING FOR STEAM BOILERS WITH FLOAT TYPE
LOW WATER CUT OFF AND USING AN ELECTRONIC THERMOSTAT
Figure #14B
ISOLATION RELAY WRITING FOR STEAM BOILERS WITH PROBE TYPE
LOW WATER CUT OFF AND USING AN ELECTRONIC THERMOSTAT
16
Page 17

WIRING DIAGRAMS FOR BOILERS WITH PS-802 PROBE TYPE LOW WATER CUT-OFF
INTERMITTENT IGNITION
IF ANY OF THE ORIGINAL WIRE AS SUPPLIED WITH THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE REPLACED,
IT MUST BE REPLACED WITH TYPE 105°C THERMOPLASTIC WIRE OR ITS EQUIVALENT.
17
Page 18

WIRING DIAGRAMS FOR BOILERS WITH PS-802 PROBE TYPE LOW WATER CUT-OFF
STANDING PILOT
IF ANY OF THE ORIGINAL WIRE AS SUPPLIED WITH THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE REPLACED,
IT MUST BE REPLACED WITH TYPE 105°C THERMOPLASTIC WIRE OR ITS EQUIVALENT.
18
Page 19

WIRING DIAGRAMS FOR BOILERS WITH 67D-1FLOAT TYPE LOW WATER CUT-OFF
INTERMITTENT IGNITION
IF ANY OF THE ORIGINAL WIRE AS SUPPLIED WITH THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE REPLACED,
IT MUST BE REPLACED WITH TYPE 105°C THERMOPLASTIC WIRE OR ITS EQUIVALENT.
19
Page 20

WIRING DIAGRAMS FOR BOILERS WITH 67D-1FLOAT TYPE LOW WATER CUT-OFF
STANDING PILOT
IF ANY OF THE ORIGINAL WIRE AS SUPPLIED WITH THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE REPLACED,
IT MUST BE REPLACED WITH TYPE 105°C THERMOPLASTIC WIRE OR ITS EQUIVALENT.
20
Page 21

CONTROLS AND ACCESSORIES — WHAT THEY DO
POP SAFETY VALVE
The pop safety valve should open automatically
if the boiler steam pressure exceeds the pressure
rating of the valve (15 psig). Should it ever fail to
open under this condition, shut down your boiler.
If valve discharge occurs, or valve fails to open as
described above, contact an authorized contrac-
tor or qualied service technician to replace the
pop safety valve and inspect the heating system
to determine the cause, as this may indicate an
equipment malfunction.
Run a pipe from the safety valve outlet (pipe
must be same size as outlet and open end must
not be threaded) to an open drain, tub or sink, or
other suitable drainage point not subject to freezing. Failure to do so may cause water damage or
injury should relief valve release. Do not cap off
the drain line from this valve!
STEAM PRESSURE GAUGE
Every system should have a pressure gauge
installed in the boiler. This gauge enables you to
monitor the pressure in the system. If the safety
devices fail to shut off your boiler at the proper
settings, notify your serviceman immediately.
WATER LEVEL GAUGE
The water level in the boiler can be seen through
the glass tube in the water level gauge at side of
boiler. Correct cold boiler water level is stamped
on side jacket panel. The water level should be
checked regularly for the proper level.
On the right side jacket panel of the boiler, there
are three hoes for the glass water level gauge.
The top hole is common for both types of low
water cut off, and is used for the upper gauge
glass tting. The middle hole, 9” down from the
top hole, is used for the bottom gauge glass tting for the Model 67D-1 and 47-2 oat type low
water cut off. The lowest hole, 12 ¼” down from
the top hole, is used for the bottom gauge glass
tting for the Model PS-802 probe type low water
cut off. The hole that is not being used is covered
with a sheet of metal knockout.
STEAM PRESSURE CONTROL
The steam pressure limit control (pressuretrol)
shuts off the gas to the main burners when the
steam pressure in the boiler reaches the cut-off
set-point (i.e. the sum of the cut-in and the differ-
ential set-points). Burners rere when the steam
pressure drops to the cut-in set-point. System
pressure requirements are based on the size and
condition of the pipes, and the load.
LOW WATER CUT-OFF
1. Model 67D-1
This is a oat operated switch which shuts down
the gas burner if water falls below the visible
bottom of the gauge glass.
2. Model PS-802
This is an electronic probe type LWCO. The
probe is located inside the boiler. The LWCO will
shut down the burners if the water loses contact
with the probe for a period of 10 seconds.
Refer to manufacturer’s instructions (enclosed)
for more information.
WATER FEEDER (Optional)
The Model WF-2U-24 water feeder may be
used with either of the available low water cutoffs. The water feeder’s job is to maintain a safe
minimum water level. It’s used to keep the boiler
running by compensating for minor evaporative
steam leaks, and to prevent freeze-ups if the
homeowners are away and a return line should
spring a leak.
McDonnell and Miller Model 101 water feeders
may be used, however, the water feed rates are
too high ad need to be regulated or throttled, and
wiring will have to be revised. Consult the boiler
manufacturer before using these or any other
non-standard types of controls.
The automatic water feeder is a safety device,
not a convenience item. It is not designed to
maintain a “normal” water line. The water feeder
does not take the place of a responsible person
monitoring and maintaining the normal water line.
Steam boilers require personal attention.
21
Page 22
CONTROLS AND ACCESSORIES — WHAT THEY DO
VENT DAMPER
This is an automatic, motorized stack damper
that has been developed to increase the efciency
of heating systems by reducing standby losses
from the boiler and the conditioned air space.
The damper closes the chimney vent when the
burner is off and fully opens it when combustion
is required.
ROLLOUT SWITCH
(FLAME ROLLOUT SAFETY SHUTOFF)
The rollout switch is a temperature-sensitive
fuse link device. It is located on the boiler base
just outside the re box. In the event of the heat
exchanger ueway blockage causing ame to roll
out of the re box, the fuse will blow, shutting down
the ow of gas to the main burners. The fuse does
not change in appearance when blown.
If the rollout switch blows, it must be replaced
with an exact replacement. Check heat exchanger
ueways for blockage when restoring system to
operating condition. Do not operate system without a rollout switch.
SPILL SWITCH
(BLOCKED VENT SAFETY SHUTOFF)
The spill switch is a manual reset disc thermo-
stat with a xed setpoint (280˚ F), and normally
closed contacts. It is located at the relief opening of the draft diverter. In the event of chimney
or venting system blockage causing products
of combustion to spill out of the relief opening,
the spill switch disc heats up and the spill switch
contacts will open, shutting down the ow of gas
to the main burners by removing power to the gas
valve.
In the event that the spill switch contacts open,
the reset button on the back of the switch will
pop up. The spill switch must be reset manually,
after the switch has cooled off, by pushing the
reset button down. Check the venting system and
chimney for blockage when restoring the system
to operating condition. DO NOT operate the boiler
without a spill switch.
FOR YOUR SAFETY READ BEFORE OPERATING
WARNING
!
If you do not follow these instructions exactly,
a re or explosion may result causing prop-
erty damage, personal injury of loss of life.
A. Some boilers are equipped with an intermittent
ignition device which automatically lights the
pilot. Do not try to light the pilot by hand.
Some boilers are equipped with a continuous
pilot and must be manually lighted. (See lighting
instructions on page 18-19.) A match holder is
included in the parts bag.
B. BEFORE OPERATING smell all around the ap-
pliance area for gas. Be sure to smell next to the
oor because some gas is heavier than air and
will settle on the oor.
!
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electric switch; do not use
any phone in you building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a neighbor’s
phone. Follow the gas supplier’s instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the
re department.
C. Use only your hand to push in or turn the gas
control knob. Never use tools. If the knob will not
push in or turn by hand, don’t try to repair it, call a
qualied service technician. Force or attempted
repair may result in a re or explosion.
D. Do not use this appliance if any part has been
under water. Immediately call a qualied service technician to inspect the appliance and to
replace any part of the control system and nay
gas control which has been under water.
22
Page 23

/&&
/.
).,%4
'!3#/.42/,+./"
3(/7.)./.0/3)4)/.
GAS VALVE OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
INTERMITTENT IGNITION BOILER –
VR8204A/VR8304M
1. STOP! Read the safety information on this page.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. This appliance is equipped with an ignition
device which automatically lights the pilot. Do
not try to light the pilot by hand.
5. Remove lower front panel.
6. Rotate the gas control knob clockwise to
“OFF”.
CONTINUOUS PILOT BOILER –
VR8200A/VR8300A
1. STOP! Read the safety information on page 21.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. Remove lower front panel.
5. Rotate gas control knob slightly and turn clockwise to “OFF”.
7. Wait ve (5) minutes to clear out any gas.
Then smell for gas, including near the oor. If
you smell gas, STOP! Follow “B” in the safety
information on this page. If you don’t smell gas,
go to next step.
8. Rotate the gas control knob counterclockwise
to
“ON”.
9. Replace lower front panel.
10. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
11. Set thermostat to desired setting.
12. If the appliance will not operate, follow the instructions “To Turn Off Gas To Appliance” and
call your service technician or gas supplier.
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if
service is to be performed.
3. Push in gas control knob lightly and turn clockwise
to “OFF”. Do not force.
6. Wait ve (5) minutes to clear out any gas.
Then smell for gas, including near the oor. If
you smell gas, STOP! Follow “B” in the safety
information on page 22. If you don’t smell gas,
go to next step.
7. Find pilot – follow metal tube from gas control. The pilot is between two burner tubes as
shown in Figure 15.
8. Turn knob on gas control counterclockwise
to PILOT”.
9. Rotate the gas control knob counterclockwise
to “PILOT”. Push down and hold the red reset
button while you light pilot burner with a match.
After about one minute, release reset button.
Pilot should remain lit. If it goes out, turn gas
control knob clockwise to OFF. To relight,
repeat steps 5 – 9.
• If button does not pop up when released, stop
and immediately call your service technician
or gas supplier.
• If pilot will not stay lit after several tries, turn
the gas control knob to “OFF” and call your
service technician or gas supplier.
23
Page 24

10. After pilot remains lit when red reset button is
released, turn as control knob counterclockwise to “ON”.
11. Replace lower front panel.
12. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
13. Set thermostat to desired setting.
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if
service is to be performed.
3. Push in gas control knob slightly and turn
clockwise
to “OFF”. Do not force.
Figure #15
LIGHTING PILOT
Figure #16
VR8200A VR8300A AUTOMATIC GAS VALVE
Figure #17
VR8204A VR8304A AUTOMATIC GAS VALVE
OPERATING YOUR BOILER
HOW A STEAM SYSTEM OPERATES
The water in the boiler is heated until it reaches the
boiling point. As the water boils it turns into steam.
The steam rises from the top of the water through
the supply main to the radiation units. As it passes
through the radiators it releases its heat and condenses into water. The water returns to the boiler
through the return main. Most residential systems
operate at less than 1 pound steam pressure.
FILLING SYSTEM WITH WATER
On steam heating systems the boiler is partially
lled with water. If is very important to the proper
operation of the entire system that your boiler be
lled to the proper level. The correct water level
is about halfway up the glass water level gauge
as marked on the boiler jacket. To ll:
1. Close the boiler drain valve.
WARNING
!
Never run water into a hot empty boiler.
!
2. Open the valves at the top and bottom of the
glass water level gauge. Also open the drain
valve at the bottom of the gauge.
3. Open the ll valve and allow water to run into
the boiler.
4. Allow boiler to ll until water runs out the gauge
drain valve. Then close the gauge drain valve.
5. Continue to ll boiler until water reaches the
indicated water line. This is about halfway up
the glass tube.
WATER LEVEL
The normal water level is shown on the right
side of the boiler and is 24” above the oor. The
normal water level is determined when the boiler
is off and cold, i.e. when all of the water in the
system is inside the boiler and the return piping
below the water line, and everything above the
water line is air, no steam. When the boiler is
making steam, the water level will drop two to
three inches below the normal water line.
24
Page 25

AUTOMATIC GAS VALVE
NOTE
The Automatic Gas Valve opens or closes according to the heat requirements of the thermostat and temperature limit control. It closes if the
pilot goes out. Each individual control must be
operating correctly before any gas can pass to
the burners. Any one control can hold the gas
supply from burner regardless of the demand of
any other control.
THERMOSTAT
Keep it set at a desired room temperature. If
windows are to be opened or heat is not needed,
move thermostat pointer to a lower setting.
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
ADJUST PILOT BURNER
Pilot ame should surround 3/8” to ½” of the pilot
sensor. Refer to Figure 19. If ame needs adjusting,
do it as follows:
1. Remove screw
cover over pilot
adjusting screw.
2. I n s e r t s m a l l
screwdriver and
adjust flame a
ne e de d. Tu rn
screw counterclockwise to increas e fl ame,
clockwise to decrease.
3. Replace screw
cover over pilot
adjusting screw.
MAIN BURNER(S)
The main burners do not require primary air
adjustment and are not equipped with primary air
shutters. Main burner ames should form sharp
blue inner cones in a softer blue outer mantel, with
no yellow. Puffs of air from blowing on the ame
or stamping on the oor will cause the ames
to turn orange momentarily. This is not unusual.
Remain still when observing the main burner
Figure #19
In the event of failure of any component, the
system will not operate or will go into safety
lockout. The system is completely self-checking.
On every call for heat, each component must
be functioning properly to permit operation. On
safety lockout the system has to be reset by
turning the thermostat to the lowest setting for
one minute, the back to the normal setting.
Safe lighting and other performance criteria
were met with the gas manifold and control assembly provided on the boiler when the boiler
underwent tests specied in ANSI Z21.13 – latest
revision.
ames. If the ame appearance is not correct,
check main burner orices and the burner throat
and ame ports for dust and lint obstruction. It
may be necessary to remove the rollout shield to
observe the main burner ames. Replace rollout
shield after observation. Refer to Figure 18.
Figure #18
GAS VALVE SAFETY SHUTDOWN TEST
1. For boilers equipped with continuous pilot,
with main burners ring, disconnect the thermocouple from the gas valve. The gas valve
should immediately shut off the main burners
and the pilot.
2. For boilers equipped with intermittent ignition,
with main burners ring, disconnect the ignition
cable from the intermittent pilot control box.
The gas valve should shut off the main burners. TURN OFF ELECTRIC POWER to boiler
before reconnecting ignition cable, to prevent
electric shock.
25
Page 26

CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
ADJUST STEAM PRESSURE CONTROL
The steam pressure limit control (pressuretrol)
shuts off the gas to the main burners when the
steam pressure in the boiler reaches the cut-off
setpoint (i.e. the sum of the cut-in and the differ-
ential setpoints). Burners rere when the steam
pressure drops to the cut-in setpoint. System
pressure requirements are based on the size and
condition of the pipes, and the load.
For good system operation, the cut-in setting
of the pressuretrol should never be less than twice
the system pressure drop. In a typical single family
residence with a clean one pipe heating system and
case iron radiation, this means that the cut-in will
usually be set at the minimum setting, i.e. ½ psi.
Steam radiation is usually sized based on
square feet of equivalent direct radiation (EDR).
This is based on a steam pressure in the radiator
of just less than 1 psi. Therefore, in our example
system from above, we would set the differential
adjustment at 1 psi, i.e. the steam pressure required in the radiators. This will give us a cut-off
setpoint of 1½ psi.
The above is an example of a typical one
pipe system. For larger systems or other types of
systems such as two pipe systems, or systems
with convectors or fan coil units the pressuretrol
settings will need to be determined on a systemby-system basis.
The cut-in setpoint is determined by the system
pressure drop to the furthest radiator or terminal
unit. Double the system pressure drop as a safety
factor, resulting in the rule that the cut-in setting
should never be less than twice the system pressure drop.
The differential setpoint is the steam pressure
required at the terminal heating units.
Now your boiler will operate in the correct pressure range. It will maintain enough steam pressure to send the steam out to the furthest radiator,
and not go over the optimum steam pressure that
is required at the radiators.
CHECKING CONTROLS
To check the Low Water Cut-Off, turn off power
to the boiler or turn the thermostat down to the
lowest setting. Drain water to below the visible
bottom of the water gauge glass. Turn power on
the turn the thermostat to call for heat. When the
boiler is equipped with the oat type LWCO, the
gas valve should not open on a call for heat when
the water is low. When the boiler is equipped with
a probe type LWCO, the gas control should be
powered for approximately 10 seconds (the time
delay on the probe type LWCO), then the gas
valve will close and the red indicator will illuminate
on the LWCO.
If your boiler is equipped with the optional
WF-2U-24 water feeder, continue to keep the
thermostat calling for heat after the low water cut
off recognizes the low water condition. After a one
minute time delay, the water feeder should start
feeding water to the boiler. The feeder should
feed for one minute and then go into another one
minute waiting period. This cycle of alternately
waiting and feeding should repeat until:
1. For Model 67D-1 oat type low water cut-offs
– as the water level raises the oat above the
burner cut off switch level, the burners should
ignite. The water feeder remains powered until
the water level raises the oat to the water feeder switch level, satisfying the water feeder.
2. For Model PS-802 probe type low water cut
offs – the water level will rise until water in the
boiler makes contact with the probe, satisfying
the water feeder, and igniting the burners.
In either case, there should be between one
and two inches of water visible in the gauge glass
when both the water feeder is satised, and the
burners are allowed to ignite.
The time delays in the feed cycles are de-
signed to prevent the boiler from ooding due to
slow return lines.
To check the pressure limit, run the boiler until
the pressure reaches system demand. Then turn
the pressure screw and drop the pressure setting
until the boiler shuts down. This will show that the
pressure limit is operating properly.
26
Page 27

CLEANING YOUR BOILER
Refer to control manufacturer’s instructions
(enclosed) for more information.
Check thermostat operation. When set above
temperature indicated on the thermometer, boiler
should ignite. Make certain the thermostat turns
off the boiler when room temperature reaches the
selected setting and starts the boiler operating
when room temperature falls a few degrees.
Finally, set the thermostat for the desired temperature. Special conditions in your home and the
location of the thermostat will govern this setting.
It is very important to clean a new steam boiler
after it has been installed and put into continuous
operation. This must be done to remove any accumulation of oil, grease, sludge, etc., that may have
been present in the system. These substances
may cause the boiler water to foam and surge, thus
producing a very unsteady water line, throwing water into the steam header, and possibly preventing
steam generation. Follow these steps in order to
remove these contaminants.
SKIMMING AND BLOWDOWN
and at least once a week thereafter. Follow the
instructions on the tag attached to the control.
Probe type low water cut-offs require no
maintenance at this time.
7. After blowing down the low water cut-off and
before blowing down the boiler, ll the boiler
to the water line. Fire the burners and allow
normal steam pressure to build up. Run a connection from the blowdown valve to a nearby
sewer or oor rain or to a safe discharge point
outside. Shut off the gas burners, open the
blowdown valve, and allow all of the water I
the boiler to drain out. Close the blowdown
valve. Allow the boiler to cool thoroughly, and
then slowly rell the boiler to the water line.
Repeat this step as many times as necessary
until the blowdown water is clear.
8. Following the nal blowdown, allow the boiler
to thoroughly cool, and then add fresh water
slowly up to the normal water line. Start the
burners and maintain at least 180 degrees for
15 minutes to remove dissolved gasses from
the fresh water. Shut off burners.
New boilers must be skimmed at the time of installation to remove threading oil and other impurities
that oat on the surface of the water.
1. Remove the plug from the skimmer tapping
and pipe to a oor drain or bucket.
2. Raise the water level to the skimmer tapping.
3. Fire the boiler to maintain a water temperature
of 180-200 degrees.
4. Feed water to the boiler to maintain the water
level. Adjust the water feed rate to keep water
continuously owing out of the skimmer tapping without the water level going above or
falling below the tapping. Cycle the burners
to prevent boiling.
5. Continue skimming until the water runs clear.
This may take several hours.
6. Float type low water cut-offs must be blown
down after skimming. The oat chamber of
the low water cut-off must be ushed clean
and maintained clear or sediment to allow
free movement of the oat. This must be done
frequently during initial operation of the boiler,
Now, let the boiler steam for a few days, to give
the majority of the system dirt a chance to work
its way back to the boiler. Then check the water
in the gauge glass. The gauge glass should be
dry above the water line. The water line should
not bounce more than one inch when the boiler
is steaming. If you see water droplets carrying
over from the top of the gauge glass, or excessive bounding of the water line, the boiler needs
further cleaning. Take a water sample and boil it
on the stove, to see if it foams. If it does, this also
indicates the boiler needs to be cleaned.
If cleaning is necessary, repeat the skimming
and blow down procedure from above. Usually, a
long skim will be all you need to clean the boiler.
In more troublesome cases, it may be desirable to ush the system as well. This is accomplished by closing the gate valve in the Hartford
Loop, and opening the drain(s) at the end of the
wet return(s). Run a hose from the drain valve on
the wet return to a nearby oor drain or bucket. Run
the boiler at two pounds of steam pressure. Feed
27
Page 28

CLEANING AND MAINTAINING YOUR BOILER
just enough water to compensate for the waste
condensate going down the drain, and to keep the
boiler from going off on low water cut off. Run the
boiler until all waste condensate runs clear.
NOTE:
Boiler cleaners and chemical cleaning additives are not recommended. If used and not
rinsed properly, they will do more harm then
good. The cleaning procedures laid out above
will clean out the typical oils and impurities
found in new boilers and in residential heating systems. The best thing for your boiler
and heating system is clean water with no
additives.
In very extreme cases it may be necessary to
chemically clean and ush the heating system.
Consult the boiler manufacturer before introducing
any chemicals into the boiler.
Check the water level every day or two. Verify
the water line shown by operating the drain valve
on the gauge. BE SURE TOP AND BOTTOM
VALVES ON GAUGE ARE ALWAYS OPEN SO
THAT ACTUAL WATER LEVEL WILL BE SHOWN
AT ALL TIMES.
The gauge glass should be dry above the water
line. The water line should not bounce more than
about one inch when the boiler is steaming. If you
see water droplets carrying over through the top
of the gauge glass, or excessive bouncing of the
water line, the boiler needs to be cleaned. Follow
the instructions under “Cleaning Your Boiler”.
POPS SAFETY VALVE
Before testing, make certain discharge pipe is
properly connected to valve outlet and arranged
to contain and safely dispose of boiler discharge.
Under normal operating conditions a “try lever
test” must be performed every month. A “try lever
test” must also be performed at the end of any
non-service period. Test at normal system operating pressure by holding the test lever fully open
for at least ve seconds to ush the valve seat
free of sediment and debris. Then release lever
and permit the valve to snap shut. If lift lever does
not activate, or there is no evidence of discharge,
turn off boiler immediately and contact a licensed
contractor or qualied service personnel.
LOW WATER CUT-OFF
The Low Water Cut-Off will interrupt the electrical current to the burner when the water line in
the boiler drops to a low level.
On oat type low water cut-offs, it is very
important to keep the oat chamber free from
sediment, a condition essential to dependability.
To keep any accumulation from interfering with
oat action is to “BLOW DOWN” or ush out the
control regularly. This must be done two to three
times during the rst week after installation and
once a week thereafter during the heating season.
Do it while the boiler is in operation. First note
water level in gauge glass. Open blow-off valve
at bottom of control; water will pour out, ushing
away sediment. Drain until water is clear, about
a pailful, then close valve. If water level in gauge
glass has dropped, add water to boiler to restore
level. Consult low water cut-off manufacturer’s
instructions included with boiler.
NOTE:
Opening blow-off valve checks cut-off opera-
tion too. As oat drops with falling water level,
burners will shut off. After valve is closed and
normal operating conditions are restored,
burners will resume ring. For probe type
Low Water Cut-Offs, check action of the Low
Water Cut-Off monthly to make sure it is
providing the proper protection. See “Checking and Adjusting” on page 24. Low Water
Cut-Off remote probes must be removed for
periodic inspection and cleaning, preferably at
the beginning of each heating season. More
frequent cleaning may be required on boilers
requiring constant or very frequent additions
of make up water.
28
Page 29

MAINTAINING YOUR BOILER
BURNERS
A visual check of the pilot and main burner
ames should be made at least once each year,
preferably at the beginning of the heating season.
See page 23.
BOILER FLUE PASSAGES
Under normal operating conditions, with the
burners properly adjusted, it should not be nec-
essary to clean the boiler ue gas passages.
However, to assure trouble-free operation, we
recommend that you have the ue passages,
burner adjustment, and operation of the controls
checked once each year by a competent Service
Technician.
Before the start of each season (or whenever
system has been shut down for some time) recheck the whole system for leaks . . . and recheck
the boiler and vent pipe for leaks.
VENT PIPE
The venting of this unit is very important and
the piping should be checked at least once a season. If the vent piping shows any sign of leaking,
replace it immediately.
CLEANING YOUR BOILER FUEL
PASSAGES AND BURNERS
Flue Passages between sections should be
examined yearly and cleaned, if necessary. To
clean, remove burners, pilot, and vent pipe. Remove top and front jacket panels. Remove the
two screws attaching the intermediate front panel
to the left and right side jacket panels. Remove
the draft diverter and intermediate front panel as
a unit. Carefully remove the gasket strips. Clean
passageways between sections with a exible
handle wire brush. Remove dirt from bottom of
boiler and from between sections by vacuuming.
Make sure all ame ports in burners are open and
clear. Shake out or blow out all loose dirt in burners. Reseal seams between adjacent sections as
necessary with 400F RTV silicone sealant. Reas-
semble all parts. Be sure to check tightness of pilot
connections and condition of burner ames after
reassembly (see Figures 18 and 19). Be sure vent
pipe connections to chimney are secure and no
obstructions are present.
FOAMING, PRIMING OR SURGING
These terms are used to describe a uctuating water
line – when water leaves the boiler with the steam.
It is caused by any combination of the following:
1. Threading oil and organic matter in the boiler
water. (Mineral oil, or core sand does not cause
surging.) Follow instructions under “Cleaning
Your Boiler”.
2. Faulty quick vents that do not release air until
a sizeable pressure is built up – if old style,
replace – if dirty, clean so you can easily blow
through valve.
3. Improper header design – when steam ows in
opposite direction or equalizer line on “Hartford
Loop”. Generally a 15” horizontal run between
riser and main takeoff will allow entrained water
to fall out of the steam vapor so it can return to
boiler. (See Figures 5, 6A, and 6B on pages
5 and 6).
4. Adjustment of steam limit control to a wide dif-
ferential increases difculty if quick vents are
old style, slow-releasing type or dirty. Always
set steam limit control differential as low as
possible.
5. Soap and detergents in the boiler water cause
extreme surging. Boiler cleaners and chemical
cleaning additives are not recommended. If used
and not rinsed properly, they will do more harm
than good. The cleaning procedures laid out in
these instructions will clean out the typical oils
and impurities found in new boilers and in residential heating systems. The best thing for your
boiler and eating system is clean water with no
additives.
CAUTION
!
!
Never rell a hot boiler with cold water – the
danger of thermal shock may crack a section.
29
Page 30

MAINTAINING YOUR BOILER
BOILER WATER TREATMENT
(Other Than Cleaners)
In steam systems where the system is tight,
free from leaks, and all the steam is returned to
the boiler as condensate, the amount of make up
water is small. Water treatment is generally not
required.
In steam systems with less than 90% of the
steam being returned as condensate, or with very
hard or corrosive make up water, treatment may
be desirable. Follow the recommendations of your
local boiler water treatment specialist.
SERVICE HINTS
You may avoid inconvenience and service calls by checking these points
before you call for service.
BETWEEN HEATING SEASONS
Boilers should not be drained between heating
seasons. Steam boilers should be entirely lled with
water during the summer months to exclude air.
FOR YOUR SAFETY
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
1. Do Not try to light any appliance.
2. Do not touch any electric switch, do not use the phone.
3. Leave the building immediately, then call your gas supplier.
4. If you cannot reach the gas supplier, call the re department.
30
Page 31

TROUBLESHOOTING
IF YOUR SYSTEM IS NOT HEATING OR NOT GIVING ENOUGH HEAT . . .
POSSIBLE CAUSE WHAT TO DO
Thermostat is not set correctly Reset thermostat above room temperature
Burner is not operating properly Check ame. If it is yellow, the burner is not getting enough air.
Or, if ame is blue and noisy and seems to lift off the burner, the
burner is getting too much air. Contact your service technician.
No electric power to boiler Check overcurrent protection. Check to be sure electric power
supply circuit is “ON”.
Controls out of adjustment Reset according to instructions.
Radiators not heating Steam air vents are not operating properly.
Check ow control valve (if used). It may be in closed position.
Poor electrical contact Check all control terminals and wire joints.
Rollout switch blown Have your service technician check heat exchanger for blockage.
Replace rollout switch with exact replacement.
Chimney ue is blocked Spill switch contacts open, requiring manual reset of spill switch.
Have your service technician check and correct chimney problem.
Vent damper not operating Consult troubleshooting guide in Efkal manual, packaged with vent
damper.
IF BURNER IS NOISY . . .
POSSIBLE CAUSE WHAT TO DO
Gas input amount is incorrect Contact your service technician.
IF WALLS OR WINDOWS SWEAT . . .
POSSIBLE CAUSE WHAT TO DO
Not enough ventilation Contact your service technician.
Chimney ue is blocked Have your service technician check and correct, if necessar
y.
IF RADIATORS ARE NOISY . . .
POSSIBLE CAUSE WHAT TO DO
Air in system Refer to “Radiators Not Heating Properly” above.
POP SAFETY VALVE LEAKING . . .
POSSIBLE CAUSE WHAT TO DO
Dirt on seat Open valve manually. Allow steam to blow and clear valve seat.
HAVE YOUR SERVICE TECHNICIAN CHECK ANY PROBLEM YOU ARE UNABLE TO CORRECT
31
Page 32
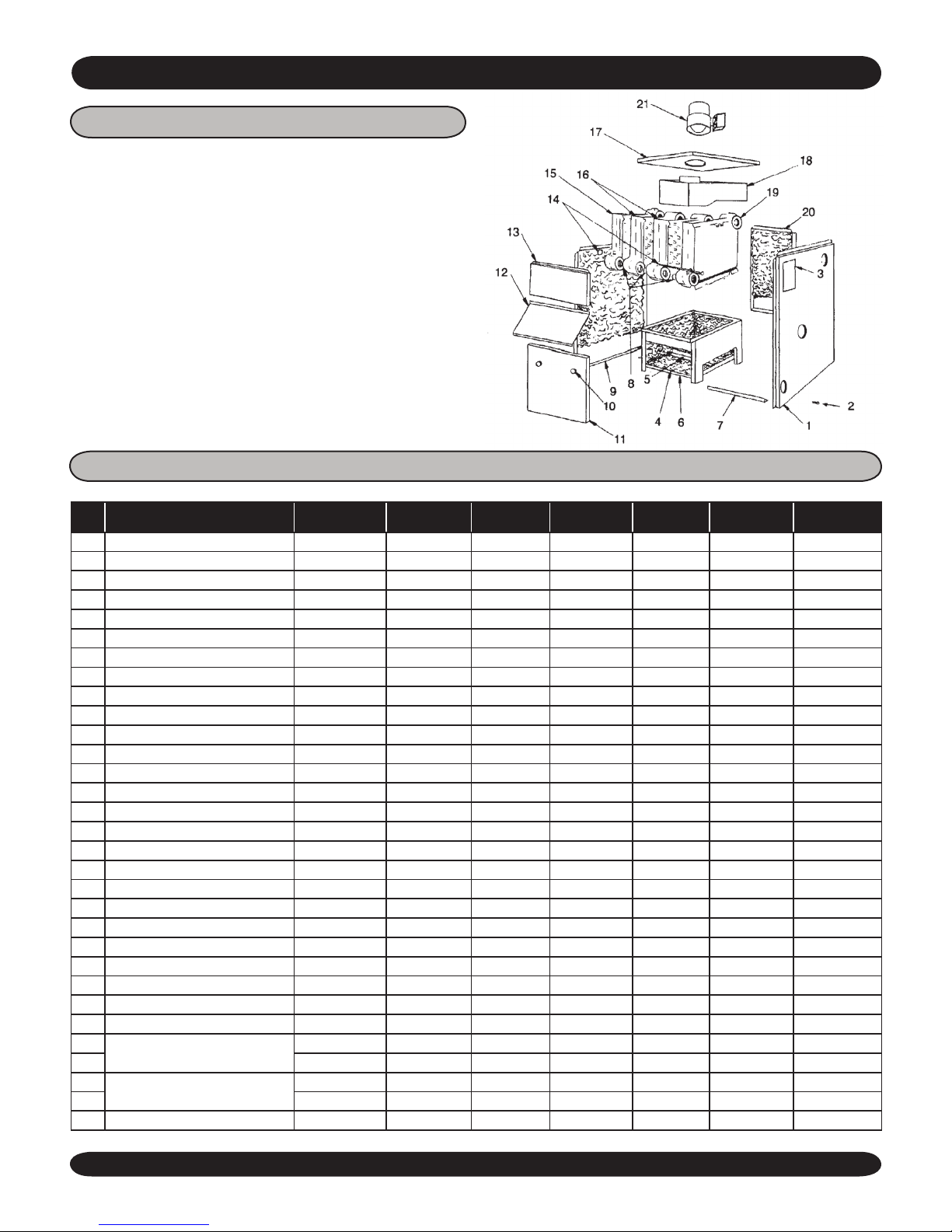
REPAIR PARTS
GAS – FIRED HOT WATER BOILERS
- IMPORTANT -
READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS
BEFORE ORDERING
All parts are listed in the following Parts List
may be ordered through your nearest supplier.
When ordering parts, rst obtain the Model
Number fro the data plate on your boiler, then
determine the part No. (not the Key No.) and
the Description of each part from the following
illustrations and list. Be sure to give us all this
information: The Part No. – The Part Description
– The Boiler Model No.
JACKET - SECTION AND BASE PARTS
THIS IS A REPAIR PARTS LIST – NOT A PACKAGING LIST
KEY
NO.
1 Jacket, Right Side Panel 425-00-801AF 425-00-801AF 425-00-801AF 425-00-801AF 425-00-801AF 425-00-801AF 425-00-801AF
2 #10 x 1/2 Sheet Metal Screw 146-95-074 146-95-074 146-95-074 146-95-074 146-95-074 146-95-074 146-95-074
3 Rating Plate 146-80-901 146-80-901 146-80-901 146-80-901 146-80-901 146-80-901 146-80-901
4 Base Insulation - Base Sides (2) 146-14-130 146-14-130 146-14-130 146-14-130 146-14-130 146-14-130 146-14-130
5 Base Bafe 425-00-643 425-00-644 425-00-645 425-00-646 425-00-647 425-00-648 425-00-649
6 Base 425-00-663 425-00-664 425-00-665 425-00-666 425-00-667 425-00-668 425-00-669
7 Jacket Tie Bar 425-00-653 425-00-654 425-00-655 425-00-656 425-00-657 425-00-658 425-00-659
8 Push Nipple 433-00-976 433-00-976 433-00-976 433-00-976 433-00-976 433-00-976 433-00-976
9 Jacket, Left Side Panel 425-00-800AF 425-00-800AF 425-00-800AF 425-00-800AF 425-00-800AF 425-00-800AF 425-00-800AF
10 Knob, Service Door (Pair) 137-02-153 137-02-153 137-02-153 137-02-153 137-02-153 137-02-153 137-02-153
11 Jacket, Service Door 425-00-823AF 425-00-824AF 425-00-825AF 425-00-826AF 425-00-827AF 425-00-828AF 425-00-829AF
12 Jacket, Int’d. Panel 425-00-813AF 425-00-814AF 425-00-815AF 425-00-816AF 425-00-817AF 425-00-818AF 425-00-819AF
13 Jacket, Front Panel 425-00-811AF 425-00-804AF 425-00-805AF 425-00-806AF 425-00-807AF 425-00-808AF 425-00-809AF
14 1/4” Tie Rod, Nut 146-05-001 146-05-002 146-05-051 146-05-053 146-05-005 146-05-007 146-05-009
15 Boiler Section, Left 410-00-013 410-00-013 410-00-013 410-00-013 410-00-013 410-00-013 410-00-013
16 Boiler Section, Middle 410-00-015 410-00-015 410-00-015 410-00-015 410-00-015 410-00-015 410-00-015
17 Jacket, Top Panel 109006276AF 109006277AF 109006278AF 109006279AF 109006280AF 109006281AF 109006282AF
18 Draft Diverter 425-00-673 425-00-674 425-00-675 425-00-676 425-00-677 425-00-678 425-00-679
19 Boiler Section, Right 410-00-014 410-00-014 410-00-014 410-00-014 410-00-014 410-00-014 410-00-014
20 Jacket, Back Panel 425-00-833AF 425-00-834AF 425-00-835AF 425-00-836AF 425-00-837AF 425-00-838AF 425-00-839AF
‡ Jacket Complete 109006332AF 109006333AF 109006334AF 109006335AF 109006336AF 109006337AF 109006338AF
‡ Block Assembly (19, 16, 15, 14, 8) 410-00-330 410-00-430 410-00-530 410-00-630 410-00-730 410-00-830 410-00-930
‡ Combustable Floor Plate 146-14-031 146-14-031 146-14-031 146-14-031 146-14-032 146-14-032 146-14-032
‡
21
‡ Base Assembly (6, 5, 4) 433-00-663 433-00-664 433-00-665 433-00-666 433-00-667 433-00-668 433-00-669
‡ Not illustrated
DESCRIPTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 SECTION 6 SECTION 7 SECTION 8 SECTION 9 SECTION
Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No.
- Base Front 146-14-113 146-14-114 146-14-115 146-14-116 146-14-117 146-14-118 146-14-119
- Base Rear 146-14-123 146-14-124 146-14-125 146-14-126 146-14-127 146-14-128 146-14-129
Gasket
Vent Damper
146-14-018 146-14-018 146-14-018 146-14-018 146-14-018 146-14-018 146-14-018
CAT#99X92 CAT#99X92 CAT#99X92 CAT#99X92 CAT#99X92 CAT#99X92 CAT#99X92
118-20-05 118-20-06 118-20-06 118-20-07 118-20-07 118-20-07 118-20-07
CAT#75Y12 CAT#75Y13 CAT#75Y13 CAT#75Y14 CAT#75Y14 CAT#75Y14 CAT#75Y14
32
Page 33

FOR USE WITH
NATURAL GAS ONLY
NOTE: Actual gas valve may look
different than gas valve shown
NATURAL GAS BURNERS AND MANIFOLD PARTS
THIS IS A REPAIR PARTS LIST - NOT A PACKING LIST
ELECTRONIC INTERMITTENT IGNITION (Shown)
REPAIR PARTS
NO.” DESCRIPTION
24 Volt Gas Valve, Elect.
1
2 Pilot Tube
3
4 Gas Manifold 14616033 14616034 14616035 14616013 14616014 14616015 14616016
5 Main Burner Orice* 14615031 14615031 14615031 14615035 14615035 14615035 14615035
6 Main Burner, Regular**
6A
7 Pilot Burner
‡ Rollout Shield 42500933 42500934 42500935 42500936 42500937 42500938 42500939
1
3
7 Pilot Burner 14662098 14662098 14662098 14662098 14662098 14662098 14662098
‡ Thermocouple 1520001 14662039 14662039 14662039 14662039 14662036 14662036
Quantity is 1 unless otherwise noted.
* Requires 1 less than the number of sections.
** Requires 2 less than the number of sections
‡ Not Illustrated
Inter. Ignition
10-32 3/16 Hex Hd.
Screw
Main Burner,
Pilot Mount
24 Volt Gas Valve,
Continuous Pilot
10-32 3/16 Hex Hd.
Screw (2 req’d)
3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 SECTION 6 SECTION 7 SECTION 8 SECTION 9 SECTION
Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No.
14662052 14662052 14662052 14662058 14662058 14662058 14662058
CAT#74P70 CAT#74P70 CAT#74P70 CAT#74P71 CAT#74P71 CAT#74P71 CAT#74P71
43300201 43300201 43300201 43300201 43300201 43300200 43300200
CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72 CAT#74P74 CAT#74P74
14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301
14615532 14615532 14615532 14615532 14615532 14615532 14615532
CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96
14615531 14615531 14615531 14615531 14615531 14615531 14615531
CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849
14662092 14662092 14662092 14662092 14662092 14662092 14662092
CAT#70N68 CAT#70N68 CAT#70N68 CAT#70N68 CAT#70N68 CAT#70N68 CAT#70N68
14662051 14662051 14662051 14662060 14662060 14662060 14662060
CAT#74P80 CAT#74P80 CAT#74P80 CAT#74P29 CAT#74P29 CAT#74P29 CAT#74P29
14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301 14695301
33
Page 34

FOR USE WITH
PROPANE GAS ONLY
NOTE: Actual gas valve may look
different than gas valve shown
REPAIR PARTS
PROPANE GAS BURNERS AND MANIFOLD PARTS
THIS IS A REPAIR PARTS LIST - NOT A PACKING LIST
ELECTRONIC INTERMITTENT IGNITION (Shown)
“KEY
NO.”
1 24 Volt Gas Valve, Elect. Inter. Ignition
2 Pilot Tube
3 10-32 3/16 Hex Hd. Screw 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301
4 Gas Manifold 146-16-010 146-16-011 146-16-012 146-16-013 146-16-014 146-16-015 146-16-016
5 Main Burner Orice* 146-15-036 146-15-036 146-15-036 146-15-036 146-15-036 146-15-036 146-15-036
6 Main Burner, Regular**
6A Main Burner, Pilot Mount
7 Pilot Burner
‡ Rollout Shield 425-00-933 425-00-934 425-00-935 425-00-936 425-00-937 425-00-938 425-00-939
DESCRIPTION
ALTERNATE PARTS FOR CONTINUOUS PILOT - 24 VOLT
1 24 Volt Gas Valve, Continuous Pilot
3 10-32 3/16 Hex Hd. Screw (2 req’d) 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301 146-95-301
7 Pilot Burner 146-62-098 146-62-098 146-62-098 146-62-098 146-62-098 146-62-098 146-62-098
‡ Thermocouple 152-00-01 146-62-039 146-62-039 146-62-039 146-62-039 146-62-036 146-62-036
Quantity is 1 unless otherwise noted.
* Requires 1 less than the number of sections.
** Requires 2 less than the number of sections
‡ Not Illustrated
3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 SECTION 6 SECTION 7 SECTION 8 SECTION 9 SECTION
Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No. Part No.
146-62-062 146-62-062 146-62-062 146-62-059 146-62-059 146-62-059 146-62-059
CAT#74P94 CAT#74P94 CAT#74P94 CAT#74P97 CAT#74P97 CAT#74P97 CAT#74P97
433-00-201 433-00-201 433-00-201 433-00-201 433-00-201 433-00-200 433-00-200
CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72 CAT#74P72
146-15-532 146-15-532 146-15-532 146-15-532 146-15-532 146-15-532 146-15-532
CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96 CAT#99X96
146-15-531 146-15-531 146-15-531 146-15-531 146-15-531 146-15-531 146-15-531
CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849 CAT#X1849
146-62-094 146-62-094 146-62-094 146-62-094 146-62-094 146-62-094 146-62-094
CAT#71N72 CAT#71N72 CAT#71N72 CAT#71N72 CAT#71N72 CAT#71N72 CAT#71N72
146-62-061 146-62-061 146-62-061 146-62-060 146-62-060 146-62-060 146-62-060
CAT#74P95 CAT#74P95 CAT#74P95 CAT#75P29 CAT#75P29 CAT#75P29 CAT#75P29
- - - - - - - -
34
Page 35

BOILER CONTROLS
AND PIPING
REPAIR PARTS
KEY
NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
‡
10
‡
11
‡
12
13
14
15
16
‡
‡
‡
‡
‡
‡
‡
‡
‡
‡
Not Illustrated
DESCRIPTION
3
∕4” Pop Safety Valve
3
∕4” Coupling
3
∕4” x 61∕2” Nipple
Steam Pressure Gauge
1
∕4” Coupling
1
∕4” x 3” Nipple
AT-150D Transformer
PA-404A Pressretrol
Glass Water Gauge Set (used with PS-802 LWCO)
Glass Water Gauge Set (used with 67D-1 LWCO)
90˚ Pigtail (used with PS-802 LWCO)
180˚ Pigtail (used with 67D-1 LWCO)
PS-802 Low Water Cut-Off Kit
67D-1 Low Water Cut Off
Intermittent Pilot Control
1
∕2” x 3” Brass Nipple (PS-802 only)
1
∕2” x 1∕2” x 1∕4” Brass Tee (PS-802 only)
1
∕2” Brass Coupling (PS-802 only)
1
∕2” x 31∕2” Brass Nipple (PS-802 only)
3
∕4” Drain Valve
WF-2U-24 Water Feeder (Optional)
Rollout Switch
Spill Switch (36TX16-6282) 280˚F
5” Vent Damper (3 Section Boilers)
6” Vent Damper (4, 5 Section Boilers)
7” Vent Damper (6, 7, 8, 9 Section Boilers)
Vent Damper Operator (Motor)
400˚F Black Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant (10.3 oz. Cartridge)
PART
NO.
C AT.
NO.
157-00-01 75Y25
155-00-01
146-07-002
146-23-005
146-93-054
146-07-001
146-62-305
146-62-015
146-22-005
146-22-101
146-43-004
146-43-005
433-00-522
146-26-042
146-62-070
131-00-03
146-93-051
146-93-052
146-07-024
146-22-000
163-00-01
146-29-002
150-00-009
118-20-05
118-20-06
118-20-07
114-00-02
146-06-020
- - - -
- - - -
75P98
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
98E80
51X59
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
75P04
75P05
92X30
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
74P50
98E36
75P10
99P37
75Y12
75Y13
75Y14
75P12
- - - -
35
Page 36

 Loading...
Loading...