Page 1

MatchPort™ b/g User Guide
Part Number 900-484
Revision A March 2007
Page 2

Copyright and Trademark
© 2007, Lantronix. All rights reserved. No part of the contents of this book may be
transmitted or reproduced in any form or by any means without the written permission
of Lantronix. Printed in the United States of America.
MatchPort, with its patent-pending technology, is a trademark of Lantronix.
Ethernet is a trademark of XEROX Corporation. UNIX is a registered trademark of
The Open Group. Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows NT, and
Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft Corp. Netscape is a trademark of Netscape
Communications Corporation.
Contacts
Lantronix Corporate Headquarters
15353 Barranca Parkway
Irvine, CA 92618, USA
Phone: 949-453-3990
Fax: 949-453-3995
Technical Support
Online: www.lantronix.com/support
Sales Offices
For a current list of our domestic and international sales offices, go to the Lantronix
web site at http://www.lantronix.com/about/contact/
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 2
Page 3

Disclaimer
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
This device is intended only for OEM Integrators. The OEM integrator should be
aware of the following important issues.
Labeling of the End Product
The label of the end product integrating this module must clearly indicate that the end
product contains an FCC approved RF module. The format of such statement could
be "Contains Transmitter with FCC ID: R68MTCHDRCT" or something similar.
RSS-GEN Sections 7.1.4 and 7.1.5 Statement for Devices with Detachable
Antennas
This device has been designed to operate with the antennas listed in the Certificate,
and having a maximum gain of 5 dBi. Antennas not included in this list or having a
gain greater than 5 dBi are strictly prohibited for use with this device. The required
antenna impedance is 50 ohms.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain
should be so chosen that the equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) is not
more than that required for successful communication.
Integration Note
a) This module is authorized under limited module approval specified to mobile host
equipment. So, the antenna must be installed such that 20cm is maintained between
the antenna and users.
b) The transmitter module may not be co-located with any other transmitter or
antenna.
As long as the two conditions above are met, further transmitter testing will not be
required. However, the OEM integrator is still responsible for testing their end product
for any additional compliance requirements required with this module installed (for
example, digital device emission, PC peripheral requirements, etc.)
Note: In the event that these conditions cannot be met (for example certain
laptop configurations, general purpose PCMCIA or similar cards, or co-
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 3
Page 4

location with another transmitter), then the FCC authorization is no longer
considered valid and the FCC ID cannot be used on the final product
(including the transmitter) and obtaining a separate FCC authorization.
Note: Changes or modifications to this device not explicitly approved by Lantronix will
void the user's authority to operate this device.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 4
Page 5

Contents
Copyright and Trademark _________________________________________________2
Contacts ______________________________________________________________2
Disclaimer _____________________________________________________________3
1: Using This Guide 8
Purpose and Audience ___________________________________________________8
Chapter Summary _______________________________________________________8
Additional Documentation _________________________________________________9
2: Introduction 10
Capabilities ___________________________________________________________10
Applications ___________________________________________________________11
Protocol Support _______________________________________________________11
Configuration Methods __________________________________________________11
Addresses and Port Numbers _____________________________________________12
Hardware Address __________________________________________________________12
IP Address_________________________________________________________________12
Port Numbers ______________________________________________________________12
3: Using DeviceInstaller 13
Accessing MatchPort b/g using DeviceInstaller________________________________13
Viewing the MatchPort b/g’s Current Configuration_____________________________13
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager 16
Accessing Web-Manager using DeviceInstaller _______________________________16
Network Configuration___________________________________________________17
Network Mode Configuration __________________________________________________18
Automatic IP Address Configuration _____________________________________________18
Static IP Address Configuration ________________________________________________19
Ethernet Configuration _______________________________________________________19
Server Configuration ____________________________________________________21
Host List Configuration __________________________________________________22
Channel 1 Configuration _________________________________________________23
Serial Settings ______________________________________________________________23
Connection Settings - TCP ____________________________________________________25
Connection Settings - UDP ____________________________________________________27
Email Configuration _____________________________________________________29
Trigger Configuration ________________________________________________________29
WLAN Configuration ____________________________________________________31
Configurable Pin Settings ________________________________________________33
Updating Settings ______________________________________________________34
Applying Defaults_______________________________________________________34
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port 35
Accessing Setup Mode __________________________________________________35
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 5
Page 6

Contents
Telnet Access ______________________________________________________________35
Serial Port Access___________________________________________________________36
Server Configuration ____________________________________________________37
Network Mode ______________________________________________________________37
Set the IP Address __________________________________________________________37
Set the Gateway IP Address___________________________________________________37
Set the Netmask ____________________________________________________________38
Change Telnet Configuration Password __________________________________________38
DHCP Name _______________________________________________________________38
Channel 1 Configuration _________________________________________________39
Baudrate __________________________________________________________________39
I/F (Interface) Mode _________________________________________________________39
Flow______________________________________________________________________41
Port Number _______________________________________________________________41
Connect Mode______________________________________________________________42
Send the Escape Sequence (+++) in Modem Mode_________________________________48
Show IP addr after 'RiNG' _____________________________________________________48
Auto Increment Source Port ___________________________________________________48
Remote IP Address__________________________________________________________48
Remote Port _______________________________________________________________48
DisConnMode ______________________________________________________________48
Flush Mode ________________________________________________________________49
DisConnTime (Inactivity Timeout) _______________________________________________51
SendChar 1 and SendChar2___________________________________________________51
Telnet Terminal Type ________________________________________________________51
Channel (Port) Password _____________________________________________________51
Email Configuration _____________________________________________________52
Mail Server ________________________________________________________________52
Unit Name _________________________________________________________________52
Domain Name ______________________________________________________________53
Recipients _________________________________________________________________53
Triggers ___________________________________________________________________53
WLAN Settings ________________________________________________________54
Topology __________________________________________________________________54
Network Name (SSID) _______________________________________________________54
Adhoc Network Channel ______________________________________________________55
Security Suite ______________________________________________________________55
WEP _____________________________________________________________________55
WPA _____________________________________________________________________56
802.11i/WPA2-Personal ______________________________________________________56
Fixed or Automatic Data Rate__________________________________________________57
Transmission Data Rate ______________________________________________________57
Enable Power Management ___________________________________________________57
Expert Settings ________________________________________________________57
TCP Keepalive Time _________________________________________________________57
ARP Cache Timeout _________________________________________________________58
CPU Performance ___________________________________________________________58
HTTP Port Number __________________________________________________________58
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 6
Page 7

Contents
SMTP Port Number__________________________________________________________58
MTU Size _________________________________________________________________58
Alternate MAC Address ______________________________________________________58
Ethernet Connection Type ____________________________________________________59
Security Settings _______________________________________________________59
Disable SNMP______________________________________________________________59
SNMP Community Name _____________________________________________________59
Disable Telnet Setup_________________________________________________________59
Disable TFTP Firmware Upgrade _______________________________________________59
Disable Port 77FE (Hex) ______________________________________________________59
Disable Web Server _________________________________________________________60
Disable Web Setup __________________________________________________________60
Disable ECHO Ports _________________________________________________________60
AES Encryption _____________________________________________________________60
Enable Enhanced Password ___________________________________________________60
Disable Port 77F0 (Hex) ______________________________________________________60
Default Settings ________________________________________________________61
Channel 1 Configuration ______________________________________________________61
WLAN Settings _____________________________________________________________61
Expert Settings _____________________________________________________________61
Security Settings ____________________________________________________________62
Email Settings ______________________________________________________________62
Exit Configuration Mode _________________________________________________62
6: Configurable Pins 63
Defaults Settings ____________________________________________________________63
Features __________________________________________________________________63
Control Protocol________________________________________________________63
Guidelines _________________________________________________________________63
Commands ________________________________________________________________64
Examples_____________________________________________________________66
7: Monitor Mode 68
Entering Monitor Mode via the Serial Port____________________________________68
Entering Monitor Mode via the Network Port__________________________________68
Monitor Mode Commands ________________________________________________68
8: Updating Firmware 70
Obtaining Firmware _____________________________________________________70
Reloading Firmware ____________________________________________________70
Using TFTP: Graphical User Interface ___________________________________________70
Using TFTP: Command Line Interface ___________________________________________71
Recovering the Firmware Using the Serial Port ____________________________________71
9: Troubleshooting 72
Diagnostic LED States___________________________________________________72
Problems and Error Messages ____________________________________________73
Technical Support ______________________________________________________75
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 7
Page 8

11:: UUssiinngg TThhiiss GGuuiiddee
Purpose and Audience
This guide provides the information needed to configure, use and update the
MatchPort b/g
are embedding the unit in their designs.
Chapter Summary
The remaining chapters in this guide include:
Introduction Describes the main features of the MatchPort and the protocols it
Using DeviceInstaller Provides information for viewing the MatchPort’s configuration
Configuration Using WebManager
Configuration via Serial Mode
or Telnet Port
TM
and is intended for software developers and system integrators who
supports.
using DeviceInstaller.
Details configuration using the Web-Manager to set parameters
such as port and server properties.
Provides instructions for accessing Setup Mode (command line
interface) using a Telnet connection through the network or a
terminal or terminal emulation program through the serial port.
Details the parameters that you must configure.
Configurable Pins Provides instructions for configuring the five General Purpose I/O
pins.
Monitor Mode Provides instructions for accessing and using the command line
interface for monitoring the network and diagnosing problems.
Updating Firmware Provides instructions for obtaining the latest firmware and updating
the MatchPort.
Troubleshooting Describes common problems and error messages and provides
information about the diagnostic LEDs. Also provides Lantronix
Technical Support contact information.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 8
Page 9

Additional Documentation
The following guides are available on the product CD and the Lantronix web site
www.lantronix.com
:
1:Using This Guide
MatchPort b/g Demonstration Kit
Quick Start Guide
MatchPort b/g Integration Guide
Briefly explains the basics of getting the
MatchPort up and running.
Provides information about the MatchPort
hardware and integrating the MatchPort into
another product.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 9
Page 10

22:: IInnttrroodduuccttiioonn
MatchPort b/g is a wireless embedded device server that provides a networkenabling solution based on the IEEE 802.11b/g wireless standard. MatchPort allows
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to add wireless connectivity to their
products by incorporating it onto a circuit board.
The MatchPort functions independently of a PC, providing a fully integrated solution
that combines a processor, memory, 802.11b/g transceiver, and 230K (maximum)
baud rate serial port into a single compact module. It includes an operating system,
an embedded web server, and a full TCP/IP protocol stack. In addition, the MatchPort
sends email alerts and supports numerous other network communication protocols,
including ARP, UDP, TCP, ICMP, Telnet, AutoIP, DHCP, HTTP, SNMP, and SMTP.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wireless Protected Access (WPA ), and
802.11i/WPA2-Personal are available to guarantee the security of the wireless
communication. WEP uses an RC4 encryption algorithm with a configured 64-bit or
104-bit key to scramble the data. WPA uses TKIP, which expands upon WEP by
changing the key automatically every session, detecting intrusion and using improved
authentication.
For OEMs who wish to customize the user interface by employing common and
familiar tools, the MatchPort serves applets to a web browser, resulting in interactive
web pages. This customization of HTML web pages and configuration screens tailors
the MatchPort to fit unique requirements.
Two models of the MatchPort b/g are available: one with AES encryption and one
without.
Note: The MatchPort b/g is based on a standard release of Lantronix' s CoBos
operating system. Some CoBos products support both wired and wireless
interfaces. The MatchPort b/g currently supports only wireless. Please ignore
references and settings that deal with a wired Ethernet interface.
Capabilities
The MatchPort b/g device server has the following capabilities:
Communication between TCP and UDP to serial
Wireless interface (802.11b/g) with WEP, WPA, or 802.11i/WPA2-Personal
protection
Ethernet interface
Email notification of configurable alarms and events
Upgradeable firmware
SNMP monitoring
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 10
Page 11

Connection to devices through a TCP or UDP data channel to computers or
Web server allowing presentation of custom content and easy configuration
Contains five programmable I/O pins used to monitor or control attached
Applications
The MatchPort device server connects serial devices such as those listed below to
wireless and Ethernet networks using the IP protocol family.
Remote sensing
CNC controllers
Data collection devices
Telecommunications equipment
Data display devices
Security alarms and access control devices
Time clocks and terminals
2:Introduction
to another device server
through the browser
devices.
Protocol Support
The MatchPort device server uses the TCP/IP protocol stack for network
communications. Other supported protocols include:
ARP, UDP, TCP, ICMP, Telnet, TFTP, AutoIP, DHCP, HTTP, and SNMP for
network communications and management.
TCP, UDP, and Telnet for connections to the serial port.
TFTP for firmware and web page updates.
IP for addressing, routing, and data block handling over the network.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for typical datagram applications in which
devices interact with other devices without maintaining a point-to-point
connection.
SMTP for email transmission.
Configuration Methods
For the unit to operate correctly on a network, it must have a unique IP address on
the network. There are three basic methods for logging into the device server:
DeviceInstaller: View the current MatchPort configuration using a Graphical User
Interface (GUI) on a PC attached to a network. (See 3: Using DeviceInstaller.)
Web-Manager: Through a web interface, configure the MatchPort and its settings.
(See 4: Configuration Using Web-Manager.)
Serial & Telnet Ports: There are two approaches to accessing Serial Mode. Make a
Telnet connection to the network port (9999) or connect a terminal (or a PC running a
terminal emulation program) to the unit’s serial port. (See 5: Configuration via Serial
Mode or Telnet Port.)
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 11
Page 12

Addresses and Port Numbers
Hardware Address
The hardware address is also referred to as the Ethernet address or the MAC
address. The first three bytes of the Ethernet address are fixed and read 00-20-4A,
identifying the unit as a Lantronix product. The fourth, fifth, and sixth bytes are unique
numbers assigned to each unit.
Example: 00-20-4A-14-01-18
Note: Make note of the MAC address. It is needed to locate the MatchPort
using DeviceInstaller.
IP Address
Every device connected to an IP network must have a unique IP address. This
address is used to reference the specific unit. The MatchPort is automatically
assigned an IP address on DHCP-enabled networks, as it is DHCP-enabled by
default.
Port Numbers
Every TCP connection and every UDP datagram is defined by a destination IP
address and a port number. For example, a Telnet application commonly uses port
number 23. A port number is similar to an extension on a phone system.
2:Introduction
The unit's serial channel (port) can be associated with a specific TCP/UDP port
number. Port number 9999 is reserved for access to the unit's Setup (configuration)
Mode window. Ports 0-1024 are reserved as well. For more information on reserved
port numbers, refer to Table 5-6. Reserved Port Numbers.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 12
Page 13

33:: UUssiinngg DDeevviicceeIInnssttaalllleerr
This chapter covers the steps for viewing the MatchPort device server’s properties
and device details.
The MatchPort’s default configuration is as follows:
Network name: LTRX_IBSS
Ad hoc mode
No security
BOOTP, DHCP, and AutoIP enabled.
The computer on which DeviceInstaller will be installed needs to have access to a
wireless card with the same settings. Set the IP address to 0.0.0.0.
Note: AutoIP generates a random IP address in the range 169.254.0.1 to
169.254.255.254 if no BOOTP or DHCP server is found.
Accessing MatchPort b/g using DeviceInstaller
Note: Make note of the MAC address. You will need it to locate the
MatchPort using DeviceInstaller. For more information on the hardware
address, see Hardware Address on page 12.
Follow the instructions on the product CD to install and run DeviceInstaller.
1. Click StartÆProgramsÆLantronixÆDeviceInstallerÆDeviceInstaller.
2. Click the MatchPort folder. The list of Lantronix MatchPort devices available
displays.
3. Expand the list of MatchPort b/g units by clicking the + symbol next to the
MatchPort b/g icon. Select the MatchPort b/g unit by clicking its IP address to
view its configuration.
Viewing the MatchPort b/g’s Current Configuration
Note: The MatchPort b/g is based on a standard release of Lantronix' s CoBos
operating system. Some CoBos products support both wired and wireless
interfaces. The MatchPort b/g currently supports only wireless. Please ignore
references and settings that deal with a wired Ethernet interface.
In the right window, click the Device Details tab. The current MatchPort configuration
displays:
Name Configurable field. Enter a name to identify the MatchPort.
Double-click the field, type the value, and press Enter to
complete. This name is not visible on other PCs or laptops
using DeviceInstaller.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 13
Page 14
3: Using DeviceInstaller
Group Configurable field. Enter a group to categorize the MatchPort.
Double-click the field, type in the value, and press Enter to
complete. This group name is not visible on other PCs or
laptops using DeviceInstaller.
Comments Configurable field. Enter comments for the MatchPort. Double-
click the field, type the comment, and press Enter to
complete. This description or comment is not visible on other
PCs or laptops using DeviceInstaller.
Device Family Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort b/g’s device
family type as MatchPort.
Type
ID Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s ID embedded
Hardware Address Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s hardware
Firmware Version Non-configurable field. Displays the firmware currently
Extended Firmware
Version
Online Status Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s status as
Telnet Enabled
Telnet Port Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s port for
Web Enabled
Non-configurable field. Displays the device type as MatchPort
b/g.
within the box.
(MAC) address.
installed on the MatchPort.
Non-configurable field. Displays the
full version
nomenclature of the firmware.
online, offline, unreachable (the MatchPort is on a different
subnet), or busy (the MatchPort is currently performing a
task).
Non-configurable field. Displays True, indicating that the user
can access the MatchPort by means of a Telnet session.
Telnet sessions.
Non-configurable field. Displays True, indicating that the user
can access the MatchPort by means of a web browser.
Web Port Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s port for Web-
Manager configuration.
Maximum Baud Rate
Supported
Firmware Upgradeable
IP Address Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s current IP
Number of COB
partitions supported
Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s maximum
baud rate. Note: The MatchPort may not currently be running
at this rate.
Non-configurable field. Displays True, indicating the
MatchPort’s firmware is upgradeable as newer versions
become available.
address. To change the IP address, see
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager or 5: Configuration via
Serial Mode or Telnet Port.
Non-configurable field. Displays the number of COB partitions
supported (19).
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 14
Page 15
3: Using DeviceInstaller
Supports DynamicIP Non-configurable field. Indicates whether the current IP
address on the MatchPort was set using DHCP or other
automatic method.
Subnet Mask Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s current
subnet mask. To change the subnet mask, see
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager or 5: Configuration via
Serial Mode or Telnet Port.
Gateway Non-configurable field. Displays the MatchPort’s current
gateway. To change the gateway, see 4: Configuration Using
Web-Manager or 5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet
Port.
Number of Ports Non-configurable field. Displays the number of ports on the
MatchPort.
TCP Keepalive
Supports Configurable
Pins
Supports Email Triggers
Supports AES Data
Stream
Supports 485
Supports 920K Baud
Rate
Supports Wired Ethernet Non-configurable field. Displays True.
Supports HTTP Server Non-configurable field. Displays True.
Supports HTTP Setup Non-configurable field. Displays True.
Supports 230K Baud
Rate
Supports GPIO
Communication
Non-configurable field. Displays 1-65s, the MatchPort’s TCP
keepalive range. The default setting is 45.
Non-configurable field. Displays True, indicating configurable
pins are available on the MatchPort.
Non-configurable field. Displays True, indicating email triggers
are available on the MatchPort.
Non-configurable field. Displays True if the MatchPort unit
supports AES encryption.
Non-configurable field. Displays True, indicating the
MatchPort supports the RS-485 protocol.
Non-configurable field. Displays False. MatchPort does not
support baud rates up to 920 Kbps.
Non-configurable field. Displays True.
Non-configurable field. Displays True, indicating MatchPort
supports communication via General Purpose Input Output
(GPIO).
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 15
Page 16
44:: CCoonnffiigguurraattiioonn UUssiinngg WWeebb--MMaannaaggeerr
This chapter describes how to configure the MatchPort using Web-Manager,
Lantronix’s browser-based configuration tool. The unit’s configuration is stored in
nonvolatile memory and is retained without power. The unit performs a reset after the
configuration is changed and stored.
Note: The MatchPort b/g is based on a standard release of Lantronix' s CoBos
operating system. Some CoBos products support both wired and wireless
interfaces. The MatchPort b/g currently supports only wireless. Please ignore
references and settings that deal with a wired Ethernet interface.
Accessing Web-Manager using DeviceInstaller
Follow the instructions on the product CD to install and run DeviceInstaller.
Note: For more information on DeviceInstaller, see 3: Using DeviceInst aller.
1. Run DeviceInstaller and search for the list of available Lantronix device servers.
2. Select the MatchPort unit by clicking its IP address.
3. In the right window, click the Web Configuration tab.
4. To view the MatchPort’s Web-Manager in the current DeviceInstaller window,
click Go. To open the Web-Manager in a web browser, click Use External
Browser. The Web-Manager opens.
Note: Alternatively, if the MatchPort is connected to the network, access
Web-Manager by entering its IP address in a web browser.
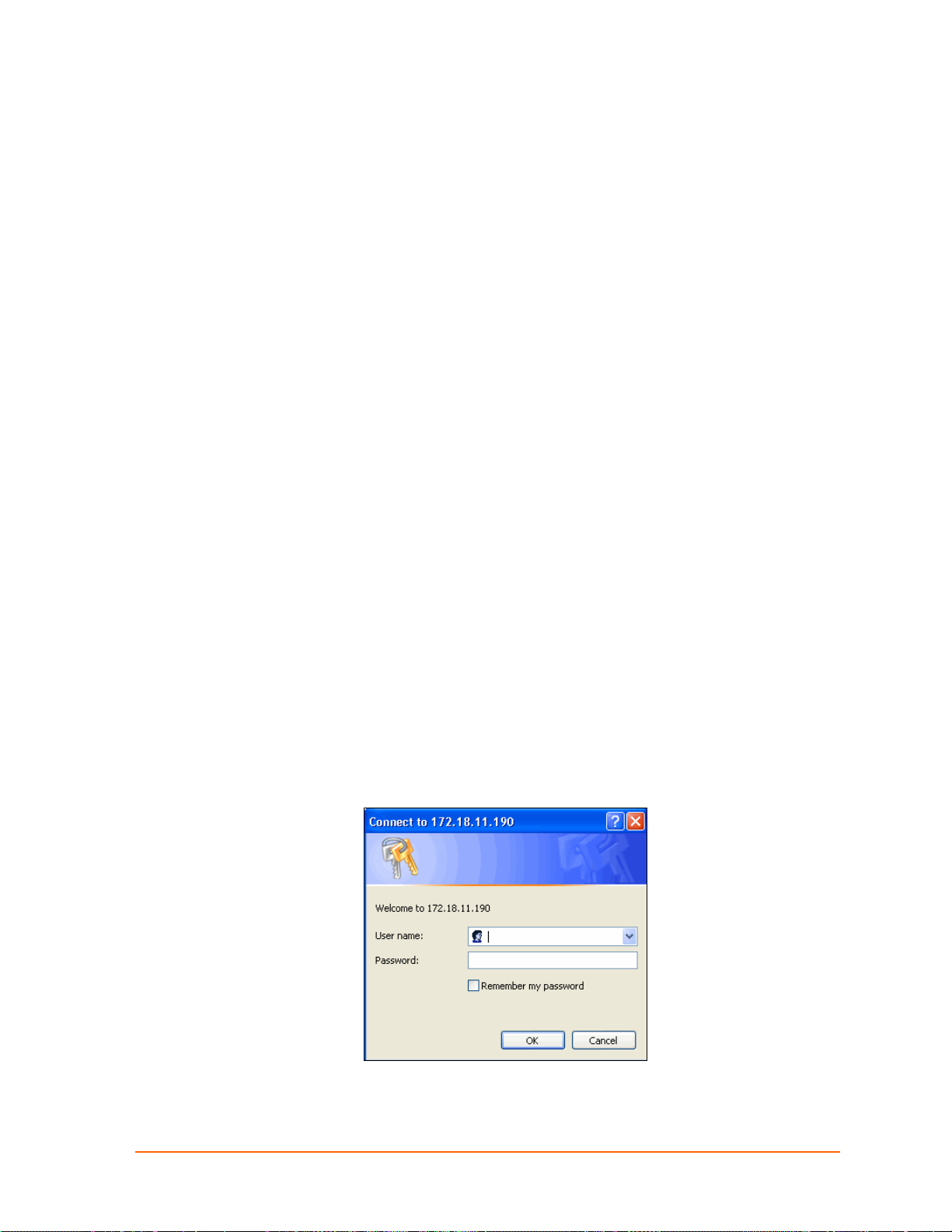
A user and password dialog box displays. By default, no username and
password are configured.
Figure 4-1. Web-Manager Login Window
5. Do one of the following:
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 16
Page 17

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
If no Telnet password has been defined (default), leave both fields blank and
click OK.
If a Telnet password has been defined, leave the username blank, type in the
password, and then click OK.
The Web-Manager displays. The main menu is in the left pane of the WebManager page.
Figure 4-2. Web-Manager
Network Configuration
The unit’s network values display when you select Network from the main menu. The
following sections describe the configurable parameters within the Network
configuration menu.
Note: The IP address is assigned via DHCP (on DHCP-enabled networks).
Assign a static IP address if preferred.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 17
Page 18
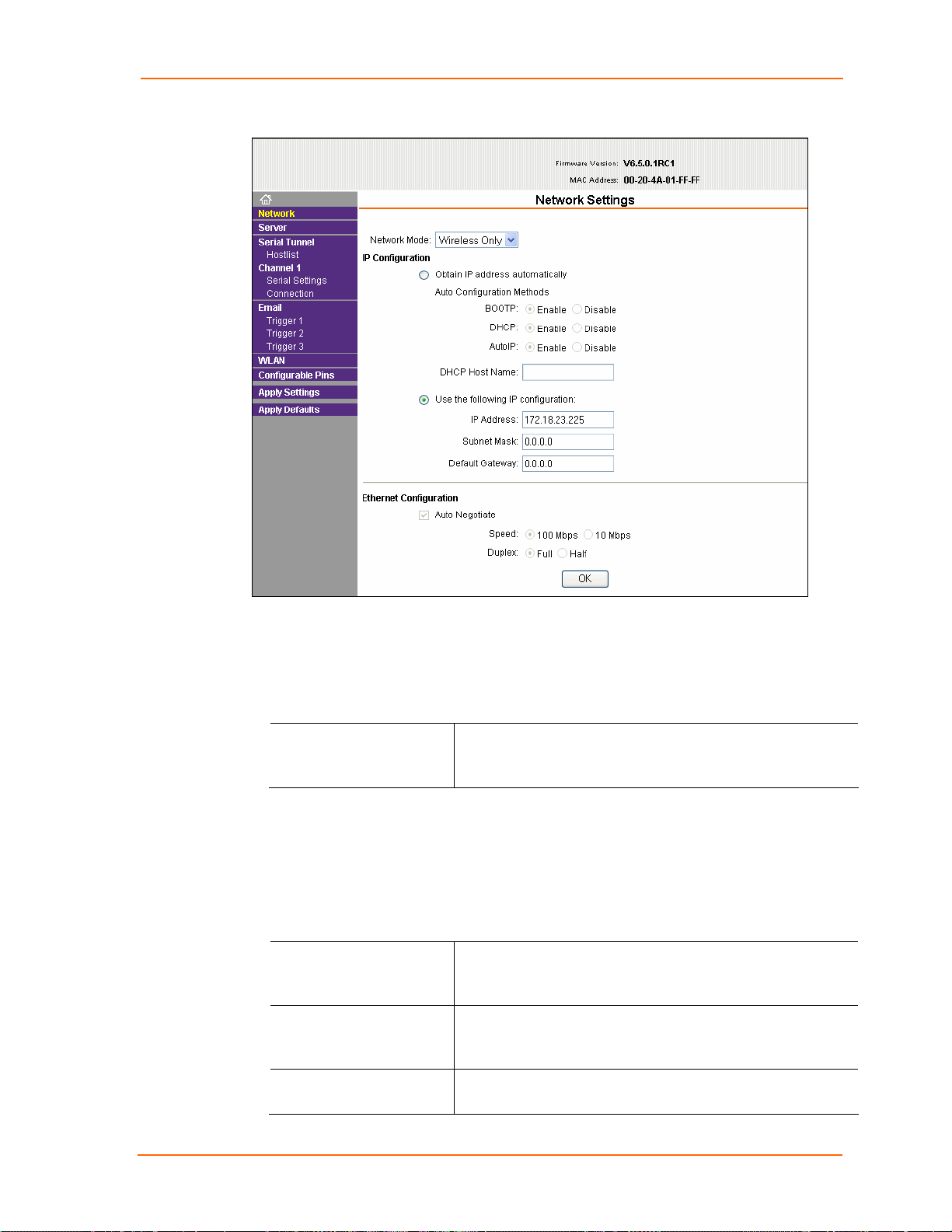
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Figure 4-3. Network Settings (Wireless Only)
Network Mode Configuration
To determine the MatchPort’s network mode:
1. Click Network from the main menu.
2. Modify the following:
Network Mode
Select Wireless Only to enable only the wireless network
connectivity for the MatchPort. Select Wired Only to enable
only the Ethernet network connectivity.
Automatic IP Address Configuration
To assign an IP address and its network configuration automatically:
1. Click Network from the main menu.
2. Select Obtain IP address automatically.
3. Enter the following (as necessary):
BOOTP
DHCP
Select Enable to permit the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP). The
BOOTP server automatically assigns the IP address from a
pool of addresses.
Select Enable to permit Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP). DHCP automatically assigns a leased IP address to
the MatchPort unit.
AutoIP The MatchPort generates an IP in the 169.254.x.x address
range with a Class B subnet. Select the Enable checkbox to
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 18
Page 19
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
enable this feature.
DHCP Host Name Enter the name of the host on the network providing the IP
address.
Note: Disabling BOOTP, DHCP, and Auto-IP (all three checkboxes) is not
advised as the only available IP assignment method will then be ARP or
serial port.
4. Click the OK button when finished.
Static IP Address Configuration
To assign an IP address and its network configuration manually:
1. Click Network from the main menu.
2. Select Use the following IP configuration.
3. Enter the following (as necessary):
IP Address If DHCP is not used to assign IP addresses, enter it manually
in standard decimal-dot notation. The IP address must be set
to a unique value in the network.
Subnet Mask A subnet mask defines the number of bits taken from the IP
address that are assigned for the host part.
Default Gateway The gateway address, or router, allows communication to
other LAN segments. The gateway address should be the IP
address of the router connected to the same LAN segment as
the unit. The gateway address must be within the local
network.
4. Click the OK button when finished.
Ethernet Configuration
If the Network Mode is Wired Only, in addition to the IP configuration, you must
specify the speed and direction of data transmission.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 19
Page 20

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Figure 4-4. Ethernet Settings (Wired Only)
To specify how data will be transmitted:
1. Enter the following (as necessary):
Auto Negotiate With this option, the Ethernet port auto-negotiates the speed
and duplex with the hardware endpoint to which it is
connected. This is the default setting.
If this option is not selected, complete the fields that become
available:
Speed: The speed of data transmission. The default setting is
100 Mbps.
Duplex: The direction of data transmission. The default
setting is Full.
2. When you are finished, click the OK button.
3. On the main menu, click Apply Settings.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 20
Page 21
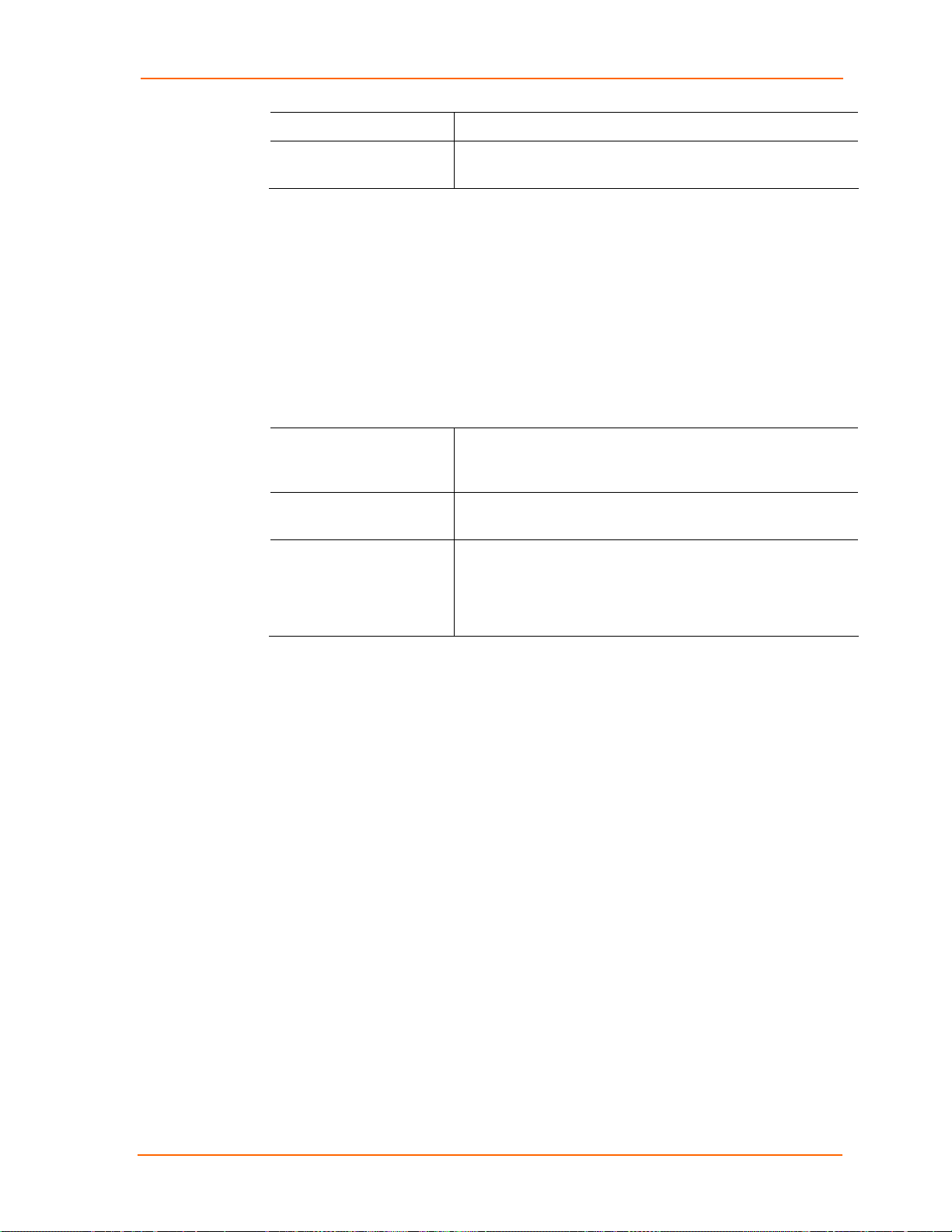
Server Configuration
The unit’s server values display when you select Server from the main menu. The
following sections describe the configurable parameters within the Server
configuration menu.
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Figure 4-5. Server Settings
To configure the MatchPort’s device server settings:
1. On the main menu, click Server to open the Server Settings page.
2. Configure or modify the following fields:
Server Configuration
Telnet Password
Retype Password
Enter the password required for Telnet access.
Re-enter the password required for Telnet access.
Advanced
ARP Cache Timeout When the unit communicates with another device on the
network, it adds an entry into its ARP table. ARP Cache
timeout defines the number of seconds (1-600) before it
refreshes this table.
TCP Keepalive TCP keepalive time defines how many seconds the unit waits
during an inactive connection before checking the connection
status. If the unit does not receive a response, it drops that
connection. Enter a value between 0 and 65 seconds. 0
disables keepalive.
Monitor Mode @ Bootup
Select Disable to disable the entry into the monitor mode via
the yyy or xx1 key sequence at startup. This command
prevents the unit from entering monitor mode by interpreting
the stream of characters that are received during the device
server's initialization at startup.
CPU Performance Mode Select the MatchPort’s performance mode. Higher
performance settings require more energy. Low is 26 Mhz,
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 21
Page 22
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
and Regular is 48 Mhz. The default is Regular.
HTTP Server Port This option allows the configuration of the web server port
number. The valid range is 1-65535. The default HTTP server
port number is 80.
0x77FE Server Port
MTU Size The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is the largest physical
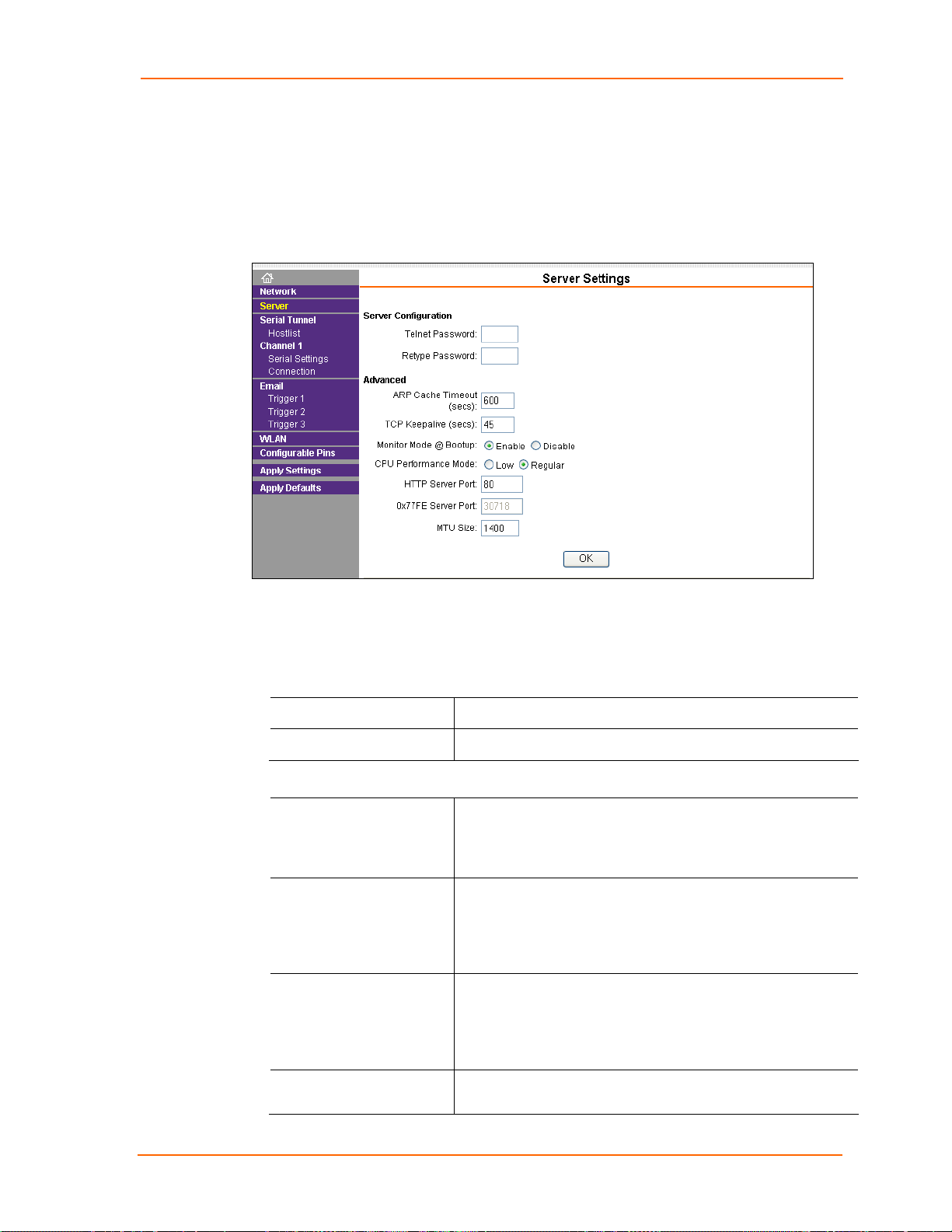
Host List Configuration
The MatchPort scrolls through the host list until it connects to a device listed in the
host list table. After a successful connection, the unit stops trying to connect to any
others. If this connection fails, the unit continues to scroll through the table until the
next successful connection.
The host list supports a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 12 entries. Each entry
contains an IP address and a port number.
Note: The host list is disabled for Manual and Modem Mode. The unit does
not accept a data connection from a remote device when the hostlist option is
enabled.
To configure the MatchPort’s host list:
1. On the main menu, click the Hostlist tab to open the Hostlist Settings page.
Figure 4-6. Hostlist Settings
Not applicable for this product.
packet size a network can transmit for TCP and UDP. Enter
between 512 and 1400 bytes. The default is 1400 bytes.
2. Enter or modify the following fields from the Hostlist Settings page:
Retry Settings
Retry Counter Enter the value for the number of times the MatchPort should
attempt to retry connecting to the host list.
Retry Timeout Enter the duration (in seconds) the MatchPort should abandon
attempting a connection to the host list.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 22
Page 23
Host Information
Host Address
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Enter or modify the host’s IP address.
Port
Channel 1 Configuration
Channel 1 configuration defines how the serial port responds to network and serial
communication.
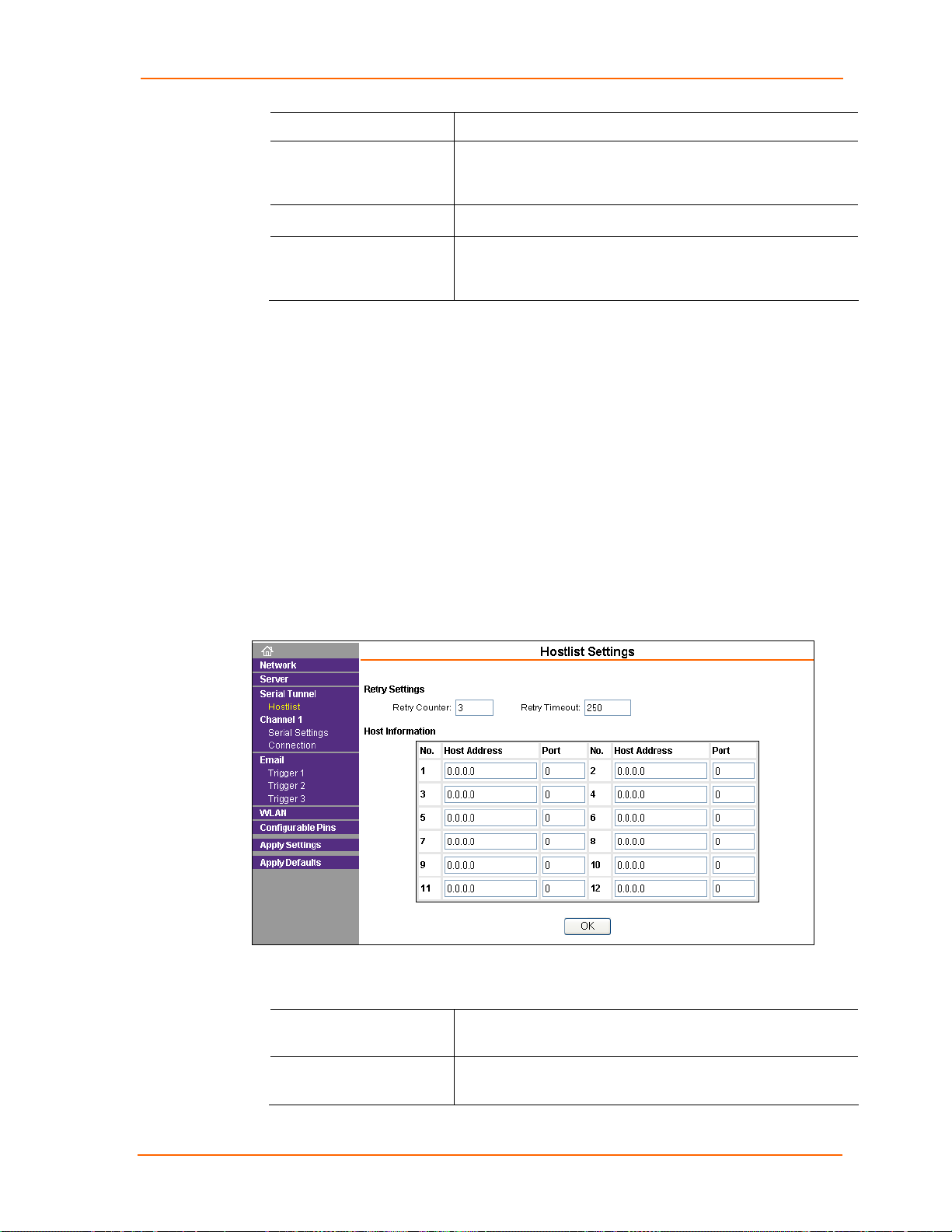
Serial Settings
To configure the channel’s serial settings:
1. On the main menu, click Serial Settings for Channel 1 to open the Serial
Settings page.
Figure 4-7. Channel Serial Settings
Enter the target port number.
2. In the available fields, enter the following information:
Channel 1
Disable Serial Port When selected, disables communication through the serial
port.
Port Settings
Protocol Select the protocol type from the drop-down list for the
selected channel. RS-422/485 4-wire and RS-485 2-wire
options are available on the MatchPort-485 only.
Flow Control Flow control manages data flow between devices in a network
to ensure it is processed efficiently. Too much data arriving
before a device is prepared to manage it causes lost or
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 23
Page 24

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
retransmitted data.
Baud Rate The unit and attached serial device, such as a modem, must
agree on a speed or baud rate to use for the serial connection.
Valid baud rates are 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600
(default), 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, and 230400.
Data Bits
Parity Checks for the parity bit. The default is None.
Stop Bits The stop bit follows the data and parity bits in serial
Indicates the number of bits in a transmitted data package.
communication. It indicates the end of transmission.
Pack Control
Enable Packing
Idle Gap Time Select the maximum time for inactivity. The default time is 12
Match 2 Byte Sequence Use to indicate the end of a series of data to be sent as one
Send Frame Immediately After the detection of the byte sequence, indicates whether to
Select the checkbox to enable packing on the MatchPort.
Two firmware-selectable packing algorithms define how and
when packets are sent to the network. The standard algorithm
is optimized for applications in which the unit is used in a local
environment, allowing for very small delays for single
characters, while keeping the packet count low. The alternate
packing algorithm minimizes the packet count on the network
and is especially useful in applications in a routed Wide Area
Network (WAN). Adjusting parameters in this mode can
economize the network data stream.
milliseconds.
group. Two bytes must occur sequentially to indicate to the
MatchPort the end of the data collection.
send the data frame or the entire buffer. Select True to send
only the data frame.
Match Bytes Use to indicate the end of a series of data to be sent as one
group. Set this value to 00 if specific functions are not needed.
Send Trailing Bytes Select the number of bytes to send after the end-of-sequence
characters.
Flush Input Buffer (Serial to Network)
With Active Connect
With Passive Connect
At Time of Disconnect
Select Yes to clear the input buffer with a connection that is
initiated from the device to the network.
Select Yes to clear the input buffer a connection
initiated from the network to the device.
Select Yes to clear the input buffer when the network
connection to or from the device is disconnected.
Flush Output Buffer (Network to Serial)
With Active Connect
Select Yes to clear the output buffer with a connection that is
initiated from the device to the network.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 24
Page 25

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
With Passive Connect
At Time of Disconnect
Select Yes to clear the output buffer with a connection initiated
from the network to the device.
Select Yes to clear the output buffer when the network
connection to or from the device is disconnected.
Connection Settings - TCP
To configure a channel’s TCP settings:
1. On the main menu, click Connection to open the Connection Settings page for
the channel.
2. In the available fields, enter the following information:
Connect Protocol
Protocol Select TCP from the drop-down list.
Figure 4-8. TCP Connection Settings
Connect Mode: Passive Connection
Accept Incoming Select Yes to accept incoming connections.
Password Required Determines whether a password is required for an incoming
passive connection. Not available when a password is set for
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 25
Page 26

Telnet mode.
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Password
If Password Required was set to Yes, enter the password for
passive connections.
Connect Mode: Active Connection
Active Connect
Start Character
Modem Mode Indicates the on-screen response type when in Modem Mode
Modem Escape
Sequence Pass Through
Select None to disable Active Connect. Otherwise, indicate
the connection type from the drop-down list:
With Any Character: Attempts to connect when any
character is received from the serial port.
With Active Mdm Ctrl In: Accepts external connection
requests only when the Modem Control In input is asserted.
With Start Character: Attempts to connect when it receives a
specific start character from the serial port. The default start
character is carriage return.
Manual Connection: Attempts to connect when directed by a
command string received from the serial port.
Auto Start: Automatically connects to the remote IP address
and port after booting up.
If Active Connect is set to With Start Character, enter the
start character in this field.
(if Modem Mode is enabled).
Disable or enable the MatchPort’s ability to send the escape
sequence. The default is Y (Yes) (send the escape
sequence).
Show IP Address After
Ring
Indicates whether to display the remote IP address upon
connection. The default setting is Yes.
Endpoint Configuration
Local Port
Auto increment for
active connect
Remote Port
Remote Host
Enter the local port number.
Select to auto-increment the local port number for new
outgoing connections. The range of auto-incremented port
numbers is 50,000 to 59,999 and loops back to the beginning
when it reaches the maximum range.
Enter the remote port number.
Enter the IP address of the remote device.
Common Options
Telnet Com Port Cntrl
Connect Response A single character is transmitted to the serial port when there
Terminal Name
Available for configuration only when Active Connect is set to
None. Select Enable to permit Telnet communication to the
MatchPort unit. The Telnet Com Port Cntrl feature is used in
conjunction with the Com Port Redirector (CPR) utility. (See
the CPR online Help for details.)
is a change in connection state. Default setting is None.
Available for configuration only when Telnet Com Port Cntrl
is set to Enable.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 26
Page 27

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Use the terminal name for the Telnet terminal type. Enter only
one name. When this option is enabled, the unit also reacts to
the end of record (EOR) and binary options, which can be
used for applications such as terminal emulation to IBM hosts.
Use Hostlist
LED
Disconnect Mode
On Mdm_Ctrl_In Drop
Hard Disconnect
Check EOT (Ctrl+D)
If this option is set to True, the device server scrolls through
the host list until it connects to a device listed in the host list
table. Once it connects, the unit stops trying to connect to any
others. If this connection fails, the unit continues to scroll
through the table until it is able to connect to another IP in the
host list.
The host list is disabled for Manual and Modem Modes. The
unit will not accept a data connection from a remote device
when the host list option is enabled.
For information on configuring the host list, see Host List
Configuration on page 22.
Select Blink for the status LEDs to blink upon connection, or
select None for no LED output.
Set to Yes for the network connection to or from the serial port
to disconnect (drop) when Modem Control In transitions from
an asserted state to not asserted state. The default setting is
No.
When set to Yes, the TCP connection closes even if the
remote site does not acknowledge the disconnect request.
Choose Yes to drop the connection when Ctrl+D or Hex 04 is
detected. Both Telnet mode and Disconnect with EOT must
be enabled for Disconnect with EOT to function properly.
Ctrl+D is only detected going from the serial port to the
network.
Inactivity Timeout Use this parameter to set an inactivity timeout. The unit drops
the connection if there is no activity on the serial line before
the set time expires. Enter time in the format mm:ss, where m
is the number of minutes, and s is the number of seconds. To
disable the inactivity timeout, enter 00:00.
Connection Settings - UDP
To configure a channel’s UDP settings:
1. On the main menu, click Connection for either Channel 1 or Channel 2 to open
the Connection Settings page for the selected channel.
2. In the available fields, enter the following information:
Connect Protocol
Protocol Select UDP from the drop-down list.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 27
Page 28

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Figure 4-9. UDP Connection Settings
Datagram Mode
Datagram Type Configures the remote IP or network broadcast address and
the remote port. Enter 01 for directed or broadcast UDP.
Accept Incoming
Select Yes to accept incoming UDP datagrams. Other options
are No and With Active Mdm Ctrl In.
Endpoint Configuration
Local Port
Remote Port
Remote Host
Use Broadcast Select to broadcast the UDP datagram. The default is not to
Enter the local port number.
Enter the port number of the remote device.
Enter the IP address of the remote device.
broadcast.
Note: Diagrams are sent as subnet-directed broadcasts.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 28
Page 29

Email Configuration
The unit sends an email to multiple recipients when a specific trigger event occurs.
There are three separate triggers, based on any combination of the configurable pins
when selected as user I/O functions. Optionally, use a two-byte serial string to initiate
a trigger. Each trigger is independent of the others. Each condition within an
individual trigger must be met before the unit will send the email.
To configure the MatchPort’s email settings:
1. On the main menu, click Email to open the Email Settings page.
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Figure 4-10. Email Settings
2. Configure the following fields:
Server IP Address
Server Port
Domain Name
Unit Name Enter the username used by the MatchPort to send email
Enter the IP address of the mail server.
Enter the port number on the email server.
Enter the email server’s domain name.
messages. Spaces are not permitted.
Recipients
Recipient 1: Email
Address
Recipient 2: Email
Address
Enter the email address designated to receive email
notifications.
Enter an additional email address designated to receive email
notifications.
Trigger Configuration
A trigger event occurs when the unit receives either one or two bytes of a specified
sequence on the serial port, or because of a specified combination of conditions on
the configurable pins.
Set the configurable pins to Active, Inactive, or None. The configurable pins are
disabled if they are all set to None. If both the serial sequence and the configurable
pins are disabled, the trigger is disabled.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 29
Page 30

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
To configure the MatchPort’s email trigger settings:
1. On the main menu, click Trigger 1, Trigger 2, or Trigger 3 to configure the
desired Trigger settings. The Email Trigger Settings page opens.
Figure 4-11. Email Trigger Settings
2. Configure the following fields:
Conditions
Configurable Pins Select the condition from the drop-down list for the
configurable pins. Repeat for each Trigger Input field.
Serial Trigger
Enable Serial Trigger
Input
Channel
Data Size
Match Data Enter the data that, when it appears in the communication
When selected, specified serial communications count as a
trigger input.
Select the channel prompting the trigger.
Select the data size prompting the trigger.
stream, prompts a trigger.
Note: All of the conditions must match to send an email notification.
Message Properties
Message The subject line of the trigger event email to the specified
recipient(s).
Priority
Min. Notification Interval The notification interval is the minimum time allowed between
The priority level for the email.
individual triggers. If a trigger event occurs within the minimum
interval since the last trigger, it is ignored.
Re-notification Interval Indicates the time interval in which a new email message is
sent to the recipient(s) when a single trigger event remains
active.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 30
Page 31

WLAN Configuration
Without adequate protection, a wireless LAN is susceptible to access by
unauthorized users.
Note: Due to regulations, the country-specific setting has been removed from the
setup menu and Web-Manager. However, we provide a separate utility for changing
the Country/Zone setting. The utility is called SetZone and is included in the
MatchPort package. It is also available for download from the Lantronix web site.
The syntax is SetZone <IP address> [<zone abbreviation>]
Leaving the zone blank causes the utility to report the current setting only. Following
are valid zone abbreviations. These settings are consistent with IEEE802.11b/g
zones:
4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
US=United States CA=Canada
FR=France
SP=Spain
To configure the MatchPort’s WLAN settings:
1. On the main menu, click WLAN to open the WLAN Settings page.
Figure 4-12. WLAN Settings
JP=Japan
OT=Others, such as Europe (excluding
France), Asia, Africa, and Australia
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 31
Page 32

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
2. Enter or modify the following fields:
Wireless Network Configuration
Network Name Enter the name of the wireless network (SSID). The
MatchPort connects to this wireless network.
Network Type
Channel
Select Infrastructure or Ad-Hoc. Infrastructure mode
communicates with Access Points. Adhoc mode
communicates only with other clients.
Configurable only when Network Type is set to Ad-Hoc.
Select from the drop-down list the radio channel for the Ad
Hoc network. The default value is 11.
Wireless Network Security
Security
As a security measure, enable WEP, WPA, or 802.11i/WPA2Personal on the MatchPort. By default, wireless security is
disabled on MatchPort.
WEP Options
Authentication
Encryption
Key Type Select the key type (Hex or Passphrase).
Key and Retype Key
Select an authentication scheme (Open/None or Shared)
from the drop-down list.
Select the encryption type (64 bits or 128 bits for WEP) from
the drop-down list. 64 bits is the default encryption for WEP.
Enter the Encrypti on Key in hexadecimal value if Hex is
selected as the key type. Enter key as a string if Passphrase
is selected as the key type. Passphrase input is not the same
as ASCII input. A passphrase of more than 20 characters is
recommended for adequate security. Spaces and punctuation
are permitted.
TX Key
Select the key to use for transmission.
WPA Options
Authentication Select Pre-Shared Keys from the drop-down list.
Encryption
Key Type Select the key type (Hex or Passphrase).
Key and Retype Key
Select the encryption type from the drop-down list. TKIP is the
default encryption for WPA.
Enter the Encrypti on Key in hexadecimal value if the key
type is Hex. Enter key as a string if the key type is
Passphrase. Passphrase input is not the same as ASCII
input. A passphrase of more than 20 characters is
recommended. Spaces and punctuation characters are
permitted.
802.11i/WPA2-Personal Options
Authentication Select Pre-Shared Keys from the drop-down list.
Encryption
Select the encryption type from the drop-down list. CCMP is
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 32
Page 33

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
the default encryption for WPA.
Key Type Select the key type (Hex or Passphrase).
Key and Retype Key
Advanced Settings
TX Data Rate MatchPort permits the control of the transmission data rate.
Radio Power
Management
Configurable Pin Settings
There are 11 configurable hardware pins on the MatchPort unit. For each pin,
configure the pin function, communication direction, and its activity level. For more
information, see Configurable Pins on page 63.
Enter the Encrypti on Key in hexadecimal value if the key
type is Hex. Enter the key as a string if the key type is
Passphrase. Passphrase input is not the same as ASCII
input. A passphrase of more than 20 characters is
recommended. Spaces and punctuation characters are
permitted.
Click the Auto fallback check box to allow the MatchPort to
set the data rate automatically (or leave unchecked to set the
transmission rate manually). The default rate is 11 Mbps.
If the Auto fallback check box is selected, choose the
maximum data rate from the drop-down list.
If the Auto fallback check box was not selected, select the
fixed data rate (in Mbps) from the drop-down list.
Power management reduces the overall power consumption
of the MatchPort unit. Selecting Enable increases the
response time. Power management is not permitted in Ad-Hoc
mode.
To configure the MatchPort’s OEM Configurable Pins:
1. On the main menu, click Configurable Pins to open the Configurable Pins page.
Figure 4-13. Configurable Pins Settings
2. Configure or modify the following fields for each pin:
Function From the drop-down list, select the purpose of the specified
pin. See Configurable Pin Functions for a description of each
available function.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 33
Page 34

4: Configuration Using Web-Manager
Direction
Trigger Input Select whether the GPIO input signal is to be used as a trigger
Active Level Select the signal active level (Low or High).
Select whether the pin inputs or outputs.
condition for email.
Configurable Pin Functions
General Purpose I/O
Modem Ctrl Channel 1 In Allows for control of the connection (and disconnection) of
Modem Ctrl Channel 1
Out
Serial Channel 1 Status
LED
Reset to Defaults
(Wireless)
RS-485 Select out
RS-485 2 Wire out Selects 2-wire line drivers. Usable as a half/full duplex
Monitors input or controls output by means of the 77F0 port.
channel 1.
Indicates a connection is established on channel 1.
Indicates channel 1 status and extended diagnostics when the
Diagnostics LED is lit.
Asserting during bootup for at least 7 seconds resets the
configuration back to factory defaults. Used when network
access is impossible because of improper configuration.
Selects between RS-232 and RS-485 line drivers.
selector.
RS-422/485 4 Wire out
Reset to Defaults
(Ethernet)
Updating Settings
Click the Apply Settings button from the main menu to save and apply the
configuration changes.
Applying Defaults
Click the Apply Defaults button from the main menu to apply the factory settings to
the MatchPort. For a list of the default settings, see Default Settings on page 61.
Selects 4-wire line drivers
Asserting during bootup for at least 7 seconds resets the
configuration back to factory default. Used when network
access is impossible because of improper configuration.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 34
Page 35

55:: CCoonnffiigguurraattiioonn vviiaa SSeerriiaall MMooddee oorr TTeellnneett PPoorrtt
As an alternative to Web-Manager, you can configure the MatchPort unit using a
terminal program to access the serial port locally. Using this terminal program to
respond to prompts is referred to as being in Setup Mode. Another way to access
Setup Mode is over the network through a Telnet connection.
The unit’s configuration is stored in nonvolatile memory and is retained without
power. You can change the configuration at any time. The unit performs a reset after
the configuration has been changed and stored.
Note: The menus in this section show a typical device. Not all devices
display information in the same manner.
Note: The MatchPort b/g is based on a standard release of Lantronix' s CoBos
operating system. Some CoBos products support both wired and wireless
interfaces. The MatchPort b/g currently supports only wireless. Please ignore
references and settings that deal with a wired Ethernet interface.
Accessing Setup Mode
Telnet Access
To configure the unit over the network, establish a Telnet connection to port 9999:
Note: Alternatively, use DeviceInstaller to access Telnet. Select the device from the
main page list, and click the Telnet Configuration tab in the right page. If using
Telnet from the DeviceInstaller toolbar, skip steps 1 through 3.
1. From the Windows Start menu, click Run.
2. From the Run dialogue box, type the following command (where x.x.x.x is the IP
address and 9999 is the unit’s fixed network configuration port number):
Windows: telnet x.x.x.x 9999
UNIX: telnet x.x.x.x:9999
3. Click OK. The following information displays:
Figure 5-1. MAC Address
4. To enter the Setup Mode, press Enter within 5 seconds.
Note: The connection fails if you do not press Enter within 5 seconds.
The configuration settings display, followed by the setup menu options:
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 35
Page 36

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Figure 5-2. Change Setup Menu Options
5. To select a menu option, enter the number of the option in the Your choice ?
field and press Enter.
View the current configuration by pressing Enter from the Change Setup menu.
To enter a value for a parameter, type the value and press Enter. To confirm a
current value, press Enter (without entering parameters).
6. When finished, save the new configurations (9 Save and exit). The unit reboots.
Serial Port Access
To configure the unit through a serial connection:
1. Connect a console terminal or PC running a terminal emulation program to your
unit's serial port. The default serial port settings are 9600 baud, 8 bits, no parity,
1 stop bit, no flow control.
2. Reset the MatchPort unit by cycling the unit's power (turning the power off and
back on). Immediately upon resetting the device, enter three lowercase x
characters (xxx).
Note: The easiest way to enter Setup Mode is to hold down the x key at
the terminal (or emulation) while resetting the unit. You must do this
within three seconds of resetting the MatchPort.
Upon connection, the following information displays:
Figure 5-3. MAC Address
3. To enter the Setup Mode, press Enter within 5 seconds.
Note: The connection fails if you do not press Enter within 5 seconds.
The configuration settings display, followed by the setup menu options:
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 36
Page 37

Figure 5-4. Change Setup Menu Options
4. Select an option on the menu by entering the number of the option in the Your
choice ? field and pressing Enter.
View the current configuration by pressing Enter from the Change Setup menu.
To enter a value for a parameter, type the value and press Enter. To confirm a
current value, press Enter (without entering parameters).
5. When finished, save the new configurations (9 Save and exit). The unit reboots.
Server Configuration
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
The unit’s basic server (network) values display when you select Server (option 0
from the Change Setup menu). The following sections describe the configurable
parameters within the Server configuration menu.
Network Mode
Select the network mode for the MatchPort. Options available are Wired Only and
Wireless Only.
Set the IP Address
If DHCP is not used to assign IP addresses, enter it manually. The IP address must
be set to a unique value in the network. Enter each octet and press Enter between
sections. The current value displays in parentheses.
IP Address : ( 0) ( 0) ( 0) ( 0) _
Set the Gateway IP Address
The gateway address, or router, allows communication to other LAN segments. The
gateway address should be the IP address of the router connected to the same LAN
segment as the unit. The gateway address must be within the local network.
The default is N (No), indicating the gateway address has not been set. To set the
gateway address, type Y. At the prompt, enter the gateway address.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 37
Page 38

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Set the Netmask
A netmask defines the number of bits taken from the IP address that are assigned for
the host part.
Netmask: Number of Bits for Host Part (0=default) (0) _
The unit prompts for the number of host bits to be entered, then calculates the
netmask, which displays in standard decimal-dot notation when the saved
parameters display (for example, 255.255.255.0).
Table 5-1. Standard IP Network Netmasks Representing Host Bits
Network Class Host Bits Netmask
A 24 255.0.0.0
B 16 255.255.0.0
C 8 255.255.255.0
Change Telnet Configuration Password
Setting the Telnet configuration password prevents unauthorized access to the setup
menu through a Telnet connection to port 9999 or by web pages. The password must
have 4 characters.
Change telnet config password (N) ? _
An enhanced password setting (for Telnet access only) of 16 characters is available
under option 6 Security from the Change Setup menu.
Note: A password is not required to access the Setup Mode window through
a serial connection.
DHCP Name
If a DHCP server has automatically assigned the IP address and network settings,
discover the unit by using the DeviceInstaller network search feature.
There are three methods for assigning DHCP names to the unit.
Default DHCP Name: If the DHCP name is not changed and the IP is
0.0.0.0, then the DHCP name defaults to CXXXXXX (XXXXXX is the last 6
digits of the MAC address shown on the label on the bottom/side of the unit).
For example, if the MAC address is 00-20-4A-12-34-56, then the default
DHCP name is C123456.
Custom DHCP Name: Create your own DHCP name. If using an IP address
of 0.0.0.0, the last option in Server configuration is Change DHCP device
name. This option allows you to change the DHCP name to an alphanumeric
name (LTX in the example).
Change DHCP device name (not set) ? (N) Y
Enter new DHCP device name : LTX
Numeric DHCP Name: You can change the DHCP name by specifying the
last octet of the IP address. When you use this method, the DHCP name is
LTXYY where YY is what you chose for the last octet of the IP address. If the
IP address you specify is 0.0.0.12, the DHCP name is LTX12. This method
only works with 2-digit numbers (0-99).
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 38
Page 39

The third octet of the IP address sets the BootP/DHCP/AutoIP options. To
disable an option, set the appropriate bit:
Table 5-2. BootP/DHCP/AutoIP Options
Options Bit
AutoIP 0
DHCP 1
BootP 2
For example, if the third octet is 0.0.5.0, the AutoIP and BootP options are
disabled; only DHCP is enabled. (The value 5 results from adding the binary
equivalents of 0 and 2.) This is the most common setting when using DHCP.
Channel 1 Configuration
Select option 1 Channel 1 or 2 Channel 2 from the Change Setup menu to define
how the serial port responds to network and serial communications. The following
sections describe the configurable parameters within the Channel configuration
menu.
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Figure 5-5. Serial and Telnet Port Parameters
Baudrate
The unit and attached serial device, such as a modem, must agree on a speed or
baud rate to use for the serial connection. Valid baud rates are 300, 600, 1200, 2400,
4800, 9600 (default), 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, or 230400. The current value
displays in parentheses.
Baudrate (9600) ? _
I/F (Interface) Mode
The Interface (I/F) Mode is a bit-coded byte entered in hexadecimal notation. The
current value displays in parentheses.
I/F Mode (4C) ? _
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 39
Page 40

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
The following table displays available I/F Mode options:
Note: All bit positions in the table that are blank represent “don’t care” bits for
that particular option, which can be set to either a 0 or 1 value.
Table 5-3. Interface Mode Options
I/F Mode Option 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RS-232
RS-422/485 4-wire 0 1
RS-485 2-wire 1 1
7 Bit 1 0
8 Bit 1 1
No Parity 0 0
Even Parity 1 1
Odd Parity 0 1
1 stop bit 0 1
2 stop bits
(1) 2 stop bits are implemented by the software. This might influence performance.
(1)
0 0
(1)
1 1
The following table demonstrates some common I/F Mode settings:
Table 5-4. Common Interface Mode Settings
Common I/F Mode Setting Binary Hex
RS-232C, 8-bit, No Parity, 1 stop bit 0100 1100 4C
RS-232C, 7-bit, Even Parity, 1 stop bit 0111 1000 78
RS-485 2-wire, 8-bit, No Parity, 1 stop
bit
RS-422, 8-bit, Odd Parity, 1 stop bit 0101 1101 5D
0100 1111 4F
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 40
Page 41

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Flow
Flow control sets the local handshaking method for stopping serial input/output. The
current value displays in parentheses.
Flow (00) ? _
Use the following table to select flow control options:
Table 5-5. Flow Control Options
Flow Control Option Hex
No flow control 00
XON/XOFF flow control 01
Hardware handshake with RTS/CTS lines 02
XON/XOFF pass characters to host 05
Port Number
The Port No setting represents the source port number in TCP connections. It is the
number that identifies the channel for remote initiating connections. The port number
functions as the TCP/UDP source port number for outgoing packets. Packets sent to
the unit with this port number are received to this channel. The port number selected
is the Incoming TCP/UDP port and Outgoing TCP/UDP source port.
Port No (10001) ? _
The current value displays in parentheses. The default setting for Port 1 is 10001.
The range is 1-65535, except for the following reserved port numbers:
Table 5-6. Reserved Port Numbers
Port Numbers Reserved for
1 – 1024 Reserved
9999 Telnet setup
14000-14009 Reserved for Redirector
30704 Reserved (77F0h)
30718 Reserved (77FEh)
Note: We recommend that you not use the reserved port numbers for this
setting as incorrect operation may result.
Use Port 0 for the outgoing local port to change with each connection. The port range
is 50,000 to 59,999. Each subsequent connection increments the number by 1 (it
wraps back around to 50,000).
Only use this automatic port increment feature to initiate a connection using TCP. Set
the port to a non-zero value when the unit is in a passive mode or when using UDP
instead of TCP.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 41
Page 42

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Connect Mode
Connect Mode defines the unit’s connection method and its reaction to incoming
connections over the network. The current value displays in parentheses.
ConnectMode (C0) ? _
Enter Connect Mode options in hexadecimal notation:
Note: All bit positions in the table that are blank represent “don’t care” bits for
that particular option, which can be set to either a 0 or 1 value.
Table 5-7. Connect Mode Options
Connect Mode Option 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
a) Incoming Connection
Never accept incoming 0 0 0
Accept with Modem Control In Active 0 1 0
Always Accept 1 1 0
b) Response
Nothing (quiet) 0
Character response (C=connect,
D=disconnect, N=unreachable)
c) Active Startup
No active startup 0 0 0 0
With any character 0 0 0 1
With Modem Control In Active 0 0 1 0
With a specific start character 0 0 1 1
Manual connection 0 1 0 0
Autostart 0 1 0 1
Hostlist 0 0 1 0
d) Datagram Type
Directed UDP 1 1 0 0
e) Modem Mode
No Echo 0 0 1 1
1
Echo & Modem Response (Numeric) 0 1 1 1 1
Echo & Modem Response (Verbose) 0 1 1 1 0
Modem Response Only (Numeric) 0 0 1 1 1 1
Modem Response Only (Verbose) 0 0 1 1 1 0
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 42
Page 43

a) Incoming Connection
Never Accept Incoming
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Rejects all external connection attempts.
Accept with Modem
Control In Active
Always Accept Accepts any incoming connection when a connection is not
b) Response
Character Response A single character is transmitted to the serial port when there is a
c) Active Startup
No Active Startup
With Any Character Attempts to connect when any character is received from the
Accept with Modem
Control In Active
With a Specific Start
Character
Accepts external connection requests only when the Modem
Control In input is asserted. Cannot be used with Modem
Mode.
already established. Default setting.
change in connection state:
C = connected, D = disconnected, N = host unreachable.
This option is overridden when the Active Start Modem Mode
or Active Start Host List is in effect. Default setting is Nothing
(quiet).
Does not attempt to initiate a connection. Default setting.
serial port.
Attempts to connect when the Modem Control In input changes
from not asserted to asserted.
Attempts to connect when it receives a specific start character
from the serial port. The default start character is carriage return.
Manual Connection Attempts to connect when directed by a command string
received from the serial port. The first character of the command
string must be a C (ASCII 0x43), and the last character must be
either a carriage return (ASCII 0x0D) or a line feed (0x0A). No
blanks or space characters may be in the command string.
Between the first and last command string characters must be a
full or partial destination IP address and can include a
destination port number.
The IP address must be in standard dot-decimal notation and
may be a partial address, representing the least significant 1, 2,
or 3 bytes of the remote IP address. The period is required
between each pair of IP address numbers.
If present, the port number must follow the IP address, must be
presented as a decimal number in the range 1-65535, and must
be preceded by a forward slash (ASCII 0x2F). The slash
separates the IP address and the port number. If you omit the
port number from a command string, the internally stored remote
port number starts a connection.
If a partial IP address is presented in a command string, it is
interpreted to be the least significant bytes of the IP address and
uses the internally stored remote IP address to provide the most
significant bytes of the IP address. If the IP address entered is
0.0.0.0/0, the device server enters Monitor Mode.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 43
Page 44

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
For example, if the remote IP address already configured in the
unit is 129.1.2.3, then an example command string would be
C3/7. (This would connect to 129.1.2.3 and port 7.) You may
also use a different ending for the connection string. For
example, C50.1/23 would connect you to 129.1.50.1 and port 23.
Table 5-8. Manual Connection Address Example
Command String Result if remote IP is 129.1.2.3 and remote port is 1234
C121.2.4.5/1 Complete override; connection is started with host 121.2.4.5, port 1
C5 Connects to 129.1.2.5, port 1234
C28.10/12 Connects to 129.1.28.10, port 12
C0.0.0.0/0 Enters Monitor Mode
Autostart (Automatic
Connection)
Hostlist If this option is set to True, the device server scrolls through the
The unit automatically attempts a connection to the remote IP
address and port after booting up.
host list until it connects to the first available device listed in the
host list table. Once it connects, the unit stops further attempts. If
this connection fails, the unit continues to scroll through the table
until it is able to connect to the next available IP address in the
host list.
The host list supports a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 12
entries. Each entry contains the IP address and the port number.
The hostlist is disabled for Manual and Modem Modes. The unit
will not accept a data connection from a remote device when the
hostlist option is enabled.
Figure 5-6. Hostlist Example
Baudrate (9600) ?
I/F Mode (4C) ?
Flow (00) ?
Port No (10001) ?
ConnectMode (C0) ?25
Hostlist :
No Entry !
Change Hostlist ? (N) Y
01. IP address : (000) 172.(000) 19.(000) 0.(000) 1 Port :
(0) ?23
02. IP address : (000) 172.(000) 19.(000) 0.(000) 2 Port :
(0) ?3001
03. IP address : (000) 172.(000) 19.(000) 0.(000) 3 Port :
(0) ?10001
04. IP address : (000) .(000) .(000) .(000)
Hostlist :
01. IP : 172.019.000.001 Port : 00023
02. IP : 172.019.000.002 Port : 03001
03. IP : 172.019.000.003 Port : 10001
Change Hostlist ? (N) N
Hostlist Retrycounter (3) ?
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 44
Page 45

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Hostlist Retrytimeout (250) ?
DisConnMode (00) ?
FlushMode (00) ?
DisConnTime (00:00) ?:
SendChar 1 (00) ?
SendChar 2 (00) ?
To enable the hostlist:
1. Enter a Connect Mode of 0x20. The menu shows a list of current entries already
defined in the product.
2. To delete, modify, or add an entry, select Yes. If you enter an IP address of
0.0.0.0, that entry and all others after it are deleted.
3. After completing the hostlist, repeat the previous step if necessary to edit the
hostlist again.
4. For Retrycounter, enter the number of times the Lantronix unit should try to
make a good network connection to a hostlist entry that it has successfully
ARPed. The range is 1-15, with the default set to 3.
5. For Retrytimeout, enter the number of seconds the unit should wait before
failing an attempted connection. The time is stored as units of milliseconds in the
range of 10-65535. The default is 250.
d) Datagram Type
Directed UDP When selecting this option, the prompt requests the Datagram type.
Enter 01 for directed or broadcast UDP.
When the UDP option is in effect, the unit uses UDP datagrams to
send and receive data.
e) Modem Mode
In Modem (Emulation) Mode, the unit presents a modem interface to the attached
serial device. It accepts AT-style modem commands and handles the modem signals
correctly.
Normally, there is a modem connected to a local PC and a modem connected to a
remote machine. A user must dial from the local PC to the remote machine,
accumulating phone charges for each connection. Modem Mode allows you to
replace modems with MatchPorts, and to use an Ethernet connection instead of a
phone call. By not having to change communications applications, you avoid
potentially expensive phone calls.
To select Modem Mode, set the Connect Mode to C6 (no echo), D6 (echo with full
verbose), or D7 (echo with numeric response).
Note: If the unit is in Modem Mode, and the serial port is idle, the unit can
still accept network TCP connections to the serial port if Connect Mode is set
to C6 (no echo), D6 (echo with full verbose), or D7 (echo with numeric
response).
Without Echo In Modem Mode, echo refers to the echo of all of the characters
entered in command mode; it does not mean to echo data that is
transferred. Quiet Mode (without echo) refers to the modem not
sending an answer to the commands received (or displaying what
was typed).
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 45
Page 46

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Echo & Modem
Response
Modem Responses
Only
Full Verbose: The unit echoes modem commands and responds
to a command with a message string shown in the table below.
Numeric Response: The unit echoes modem commands and
responds to a command with a numeric response.
Full Verbose: The unit responds to a command with a message
string shown in the table below.
Numeric Response: The unit responds to a command with a
numeric response.
Table 5-9. Modem Mode Messages
Message Meaning
Full Verbose
OK Command was executed without error.
CONNECT A network connection has been established.
NO CARRIER A network connection has been closed.
RING n.n.n.n.
A remote device, having IP address n.n.n.n, is connecting to this
device.
Numeric Response
0 OK
1 Connected
2 Ring
3 No Carrier
4 Error
Received commands must begin with the two-character sequence AT and be
terminated with a carriage return character.
The unit ignores any character sequence received not starting with AT, and only
recognizes and processes single AT-style commands. The unit treats compound AT
commands as unrecognized commands.
If the Full Verbose option is in effect, the unit responds to an unrecognized
command string that is otherwise formatted correctly (begins with AT and ends with
carriage return) with the "OK" message and takes no further action.
If the Numeric Response option is in effect, the unit responds to an unrecognized
command string that is otherwise formatted correctly with the "OK" message and
takes no further action.
When an active connection is in effect, the unit transfers data and does not process
commands received from the serial interface.
When a connection is terminated or lost, the unit reverts to command mode.
When an active connection is in effect, the unit terminates the connection if it
receives the following sequence from the attached serial device:
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 46
Page 47

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
No serial data is received for one second.
The character sequence +++ is received, with no more than one second
between each two characters.
No serial data is received for one second after the last + character. At this
time, the unit responds affirmatively according to the selected echo/response
mode.
The character string ATH is received, terminated with a carriage return. The
unit responds affirmatively according to the selected echo/response mode
and drops the network connection. The serial interface reverts to accepting
command strings.
If this sequence is not followed, the unit remains in data transfer mode.
Table 5-10. Modem Mode Commands
Modem Mode
Function
Command
ATDTx.x.x.x,pppp or
ATDTx.x.x.x/pppp
ATDTx.x.x.x
ATD0.0.0.0
ATD or ATDT
ATDx.x.x.x
ATH Hangs up the connection (Entered as +++ ATH).
ATS0=n
Makes a connection to an IP address (x.x.x.x) and a remote port
number (pppp).
Makes a connection to an IP address (x.x.x.x) and the remote port
number defined within the unit.
Forces the unit into Monitor Mode. Uses remote IP address and
port settings to initiate a connection.
Forces the unit into Monitor Mode. Uses remote IP address and
port settings to initiate a connection.
Makes a connection to an IP address (x.x.x.x) and the remote port
number defined within the unit.
Enables or disables connections from the network going to the
serial port.
n=0 disables the ability to make a connection from the network to
the serial port.
n=1-9 enables the ability to make a connection from the network
to the serial port.
n>9 is invalid.
Enables or disables character echo and responses.
ATEn
ATVn
n=0 disables character echo and responses.
n=1 enables character echo and responses.
Enables numeric response or full verbose.
n=0 enables numeric response.
n=1 enables full verbose.
Note: The unit recognizes these AT commands as single commands such as
ATE0 or ATV1; it does not recognize compound commands such as ATE0V.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 47
Page 48

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Send the Escape Sequence (+++) in Modem Mode
Send ‘+++’ in Modem Mode (Y) ? _
Disable or enable the MatchPort’s ability to send the escape sequence. The default is
Y (Yes) (send the escape sequence).
Show IP addr after 'RiNG'
Disable or enable the MatchPort's ability to show the IP address after RING in
Modem Mode. The default is Y (Yes), to show the IP address.
Auto Increment Source Port
Auto increment source port (N) ? _
Y (Yes) auto increment the source port. The MatchPort increments the port number
used with each new connection.
Remote IP Address
This is the destination IP address used with an outgoing connection.
Remote IP Address : ( 0) ( 0) ( 0) ( 0)_
Note: This option is not displayed when Hostlist is enabled from the
ConnectMode prompt (see page 42 for more information).
Remote Port
Set the remote TCP port number for the unit to make outgoing connections. This
parameter defines the port number on the target host to which a connection is
attempted.
Remote Port ( 0) ? _
To connect an ASCII terminal to a host using the unit for login purposes, use the
remote port number 23 (Internet standard port number for Telnet services).
Note: This option does not display when Hostlist is enabled from the
ConnectMode prompt (see page 42 for more information).
DisConnMode
Disconnect Mode (DisConnMode) determines the conditions under which the unit will
cause a network connection to terminate. The current value displays in parentheses.
DisConnMode ( 0) ? _
Note: All bit positions in the table that are blank represent "don't care" bits for
that particular option, which can be set to either a 0 or a 1 value.
The following table displays the available input options:
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 48
Page 49

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Table 5-11. Disconnect Mode Options
Disconnect Mode Option 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Disconnect when Modem
Control In not asserted
(6)
Ignore Modem Control In 0
1
Telnet Com Port Cntrl and
terminal type setup
Channel (port) password
Hard disconnect
(1)
(2)
(3)
0
1
1
Disable hard disconnect 1
State LED off with connection
Disconnect with EOT (^D)
(1) The MatchPort sends the "Terminal Type" upon an outgoing connection.
(2) A password is required for a connection to the serial port from the network.
(3) The TCP connection closes even if the remote site does not acknowledge the disconnection.
(4) When there is a network connection to or from the serial port, the state LED turns off instead of blinking.
(5) When Ctrl+D or Hex 04 is detected, the connection is dropped. Both Telnet Com Port Cntrl and
Disconnect with EOT must be enabled for Disconnect with EOT to function properly. Ctrl+D is only
detected going from the serial port to the network.
(6) When Modem Control In transitions from a high state to a low state, the network connection to or from the
serial port drops.
(4)
1
(5)
1
Flush Mode
The FlushMode (buffer flushing) parameter controls line handling and network buffers
with connection startup and disconnect.
FlushMode ( 0) ? _
Select between two different packing algorithms (the current configuration displays
within the parentheses).
Note: All bit positions in the table that are blank represent “don’t care” bits for
that particular option, which can be set to either a 0 or 1 value.
Available Flush Mode options are:
Table 5-12. Flush Mode Options
Function 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Input Buffer (Serial to Network)
Clear with a connection that is initiated from the
device to the network
Clear with a connection initiated from the network
to the device
Clear when the network connection to or from the
device is disconnected
1
1
1
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 49
Page 50

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Function 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Output Buffer (Network to Serial)
Clear with a connection that is initiated from the
device to the network
Clear with a connection initiated from the network
to the device
Clear when the network connection to or from the
device is disconnected
Alternate Packing Algorithm (Pack Control)
Enable 1
1
1
1
Pack Control
The packing algorithm defines how and when packets are sent to the network. The
standard algorithm is optimized for applications in which the unit is used in a local
environment. The alternate packing algorithm minimizes the packet count on the
network and is especially useful in applications in a routed Wide Area Network
(WAN). Adjusting parameters in this mode can economize the network data stream.
Pack control settings are enabled in Flush Mode. Set this value to 00 if specific
functions are not needed.
Note: All bit positions in the table that are blank represent “don’t care” bits for
that particular option, which can be set to either a 0 or 1 value.
Table 5-13. Pack Control Options
Option 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Packing Interval
Interval: 12ms 0 0
Interval: 52ms 0 1
Interval: 250ms 1 0
Interval: 5sec 1 1
Trailing Characters
None 0 0
One 0 1
Two 1 0
Send Characters
2-Byte Send Character
Sequence
Send Immediately After
Send chars
1
1
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 50
Page 51

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Packing Interval: Packing Interval defines how long the unit should wait before
sending accumulated characters. This wait period is between successive network
segments containing data. For alternate packing, the default interval is 12 ms.
Trailing Characters: In some applications, CRC, Checksum, or other trailing
characters follow the end-of-sequence character; this option helps to adapt frame
transmission to the frame boundary.
Send Characters:
If 2-Byte Send Character Sequence is enabled, the unit interprets the
sendchars as a 2-byte sequence; if this option is not enabled, the unit
interprets them independently.
If Send Immediately After Characters is not set, any characters already in
the serial buffer are included in the transmission after a "transmit" condition is
found. If this option is set, the unit sends immediately after recognizing the
transmit condition (sendchar or timeout).
Note: A transmission might occur if status information needs to be
exchanged or an acknowledgment needs to be sent.
DisConnTime (Inactivity Timeout)
Use this parameter to set an inactivity timeout. The unit drops the connection if there
is no activity on the serial line before the set time expires. Enter time in the format
mm:ss, where m is the number of minutes and s is the number of seconds.
DisConnTime (0: 0) ?:
To disable the inactivity timeout, enter 00:00. Range is 0 (disabled) to 5999 seconds
(99 minutes, 59 seconds). The default is 0.
SendChar 1 and SendChar2
Enter up to two characters in hexadecimal representation.
SendChar 1 ( 0) ? _
SendChar 2 ( 0) ? _
If the unit receives a character on the serial line that matches one of these
characters, it sends the character immediately, along with any awaiting characters, to
the TCP connection. This action minimizes the response time for specific protocol
characters on the serial line (for example, ETX, EOT). Setting the first SendChar to
00 disables the recognition of the characters. Alternatively, the unit can interpret two
characters as a sequence (see Pack Control on page 50).
Telnet Terminal Type
This parameter displays only if the terminal type option is enabled in Disconnect
Mode. If this option is enabled, use the terminal name for the Telnet terminal type.
Enter only one name.
If the terminal type option is enabled, the unit also reacts to the EOR (end of record)
and binary options, which can be used for applications such as terminal emulation to
UNIX hosts.
Channel (Port) Password
This parameter appears only if the channel (port) password option is enabled in
Disconnect Mode. If the option is enabled, set a password on the serial port.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 51
Page 52

Email Configuration
The unit sends an email to multiple recipients when a specific trigger event occurs.
There are three separate triggers, based on any combination of the configurable pins
(PIO) when selected as user I/O functions. Optionally, use a two-byte serial string to
initiate a trigger. To configure email configuration settings, select option 3 Email from
the Change Setup menu.
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Figure 5-7. Email Settings
Mail Server
Enter the IP address of the mail server. Enter each 3-digit section and press Enter
between sections. The current value displays in parentheses.
Mail Server (0.0.0.0) ? ( 0) _
Unit Name
Enter the username used by the MatchPort to send email messages. The current
value displays in parentheses. Spaces are not permitted.
Unit name () ? _
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 52
Page 53

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Domain Name
Enter the email server’s domain name. The current value displays in parentheses.
Domain name () ? _
Recipients
Enter the full email address of up to two trigger email recipients. The current value
displays in parentheses.
Recipient 1 () ? _
Recipient 2 () ? _
Triggers
A trigger event occurs when the unit receives the specified trigger input because of a
specified combination of conditions on the configurable pins.
Enable serial trigger input (N) ?
Trigger input1 [A/I/X] (X) ?
Trigger input1 [A/I/X] (X) ?
Trigger input1 [A/I/X] (X) ?
Message () ?
Priority (L) ?
Minimum notification interval (1 s) ?
Re-notification interval (0 s) ?
To change the configurable pins’ settings, send setup records to Port 77FE.
Enable serial trigger
Select (Y) Yes to enable serial trigger inputs.
input
Trigger inputs 1-3
Message
Set the configurable pins to A = Active, I = Inactive, or X
= Don’t Care. Active can mean Active Low or Active
High. If the configurable pins are all set to X (Don’t
Care), then they are disabled. If both the serial
sequence and the configurable pins are disabled, the
trigger is disabled.
Note: Each trigger is independent of the others. Each
condition within an individual trigger must be met before
the unit will send the email.
Subject line of the trigger event email to the
specified recipient(s).
Priority
Priority level for the trigger event email. Enter L
for normal priority or H for high priority.
Minimum
notification interval
Minimum time allowed between individual triggers.
If a trigger event occurs within the minimum
interval since the last trigger, it is ignored.
Re-notification
interval
Time interval in which a new email message is
sent to the recipient(s) when a single trigger event
remains active.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 53
Page 54

WLAN Settings
Without adequate protection, a wireless LAN is susceptible to access by
unauthorized users. As such, MatchPort features the WPA security standard, based
on IEEE802.11i and IEEE802.1X. WEP provides for backwards compatibility and
interaction with older devices.
When in WPA and WPA2-PERSONAL modes, the encryption setting denotes the
lowest acceptable encryption method. CCMP is higher than TKIP and TKIP is higher
than WEP. For example, if the MatchPort is configured for WEP and the access point
supports TKIP, the negotiation results the use of TKIP. If the MatchPort is configured
for TKIP and the access point supports only WEP, the association will fail since the
access point does not meet the MatchPort’s requirements.
Unicast communication occurs between the access point and a single wireless
device. It uses the pairwise encryption method. Multicast communication occurs
between the access point and multiple wireless devices. It uses the group encryption
method. The group encryption for all wireless devices communicating with the same
access point must be equal to receive broadcast and multicast messages. If any
device is WEP-only (no support for WPA), set the encryption to TKIP+WEP. To use
higher security with the MatchPort than other devices connecting to the same access
point, use a group encryption lower than the pairwise encryption.
Note: Due to regulations, the country-specific setting has been removed from the
setup menu and Web-Manager. However, we provide a separate utility for changing
the Country/Zone setting. The utility is called SetZone and is included in the
MatchPort package. It is also available for download from the Lantronix web site.
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
The syntax is SetZone <IP address> [<zone abbreviation>]
Leaving the zone blank causes the utility to report the current setting only. Following
are valid zone abbreviations. These settings are consistent with IEEE802.11b/g
zones:
US=United States
CA=Canada
FR=France
SP=Spain
To modify WLAN settings, select 4 WLAN from the Change Setup menu.
JP=Japan
OT=Others, such as Europe (excluding
France), Asia, Africa, and Australia
Topology
Select Infrastructure (ESS) mode or Adhoc (IBSS) mode. Infrastructure mode
communicates with Access Points. Adhoc mode communicates only with other
clients.
Topology 0=Infrastructure, 1=Adhoc (0) ? _
Network Name (SSID)
Enter the name of the network to which the MatchPort will connect.
Network name (LTRX_IBSS) ? _
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 54
Page 55

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Adhoc Network Channel
When Adhoc is selected in the Topology parameter, and the MatchPort cannot find
the specified network, it creates one with that name by transmitting a beacon on the
selected channel.
Channel (11) ? _
You can only select channels allowed in the country for which the MatchPort is
designated. The country displays in the settings overview.
Security Suite
The MatchPort features WEP, WPA, and 802.11i/WPA2-Personal to secure all
wireless communication. WPA and 802.11i/WPA2-Personal are not available when
Adhoc is selected as the topology.
The 802.11i/WPA2-Personal mode is compliant with the Robust Secure Network that
is specified in the IEEE standard 802.11i. It enables the AES-based strong CCMP
encryption.
Security suite 0=none, 1=WEP, 2=WPA, 3=WPA2/802.11i
(0) ? _
WEP
Authentication 0=open/none, 1=shared (0) ? _
Encryption 0=WEP64, 1=WPE128 (1) ?
Display current key (N) ?
Change key (N) ? Y
Key type 0=hex, 1=passphrase (0) ?
Enter key: **-**-**-**-**
TX Key index (1) ?
Authentication Select whether the encryption keys are matched (1 =
shared) with those of the communication partner before
passing through messages or not (2 = open/none).
Encryption Length of the encryption key and the security strength.
WEP64 uses a 40 bits/5 bytes key (option 1). WEP128 uses
a 104 bits/13 bytes key (option 2).
Display Current
Key
Change key Select (Y) Yes to modify the currently configured key.
Key type Indicate whether the new key is in hexadecimal or
Enter key Enter the new encryption key. The passphrase input is not
Select (Y) Yes to show the currently configured
key/passphrase
passphrase format.
the same as ASCII input (as used on some products). ASCII
is translated directly into hexadecimal bytes according to the
ASCII table. The MatchPort passphrase is hashed using the
Neesus Datacom algorithm (for WEP64) or MD5 (for
WEP128).
The passphrase input is safer because it is up to 63 chars
long. ASCII input is a maximum of 5 (WEP64) or 13
(WEP128) characters long and limits the number of key
combinations.
Please refer to the other equipment’s manual to determine
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 55
Page 56

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
the passphrase input style recommended.
Note: Lantronix recommends using a passphrase of 20
characters or more for maximum security.
TX Key index Select the WEP key used for transmissions. Enter a value
from 1 to 4.
WPA
This firmware version allows only Pre-Shared Keys (PSK) for authentication.
Display current key (N) ?
Change key (N) ?
Key type 0=hex, 1=passphrase (1) ?
Enter key: () ?
It is strongly recommended to use a passphrase of 20
chars or more!
Encryption: 0=TKIP, 1=TKIP+WEP (1)
Display current
key
Change key Select (Y (Yes) to modify the currently configured key.
Key type Indicate whether the new key is in hexadecimal or passphrase
Enter key
Encryption Set the type to the minimum required security level. The “+” sign
Select (Y) Yes at the prompt to show the currently configured
key/passphrase
format.
Enter the passphrase. The maximum length is 63 characters.
Note: Lantronix recommends using a passphrase of 20
characters or more for maximum security.
indicates that the group (broadcast) encryption method is
different from the pairwise (unicast) encryption (WEP and TKIP).
802.11i/WPA2-Personal
Display current key (N) ?
Change key (N) ? Y
Key type 0=hex, 1=passphrase (1) ?
Enter key: () ?
It is strongly recommended to use a passphrase of 20
chars or more!
Encryption: 0=CCMP, 1=CCMP+TKIP, 2=CCMP+WEP, 3=TKIP,
4=TKIP+WEP (4) ?
Display current
key
Change key Select (Y) Yes to modify the currently configured key.
Key type Indicate whether the new key is in hexadecimal or
Enter key Enter the passphrase. The maximum length is 63 characters.
Encryption Set the type to the minimum required security level. The “+”
Select (Y) Yes to show the currently configured
key/passphrase.
passphrase format.
Lantronix recommends using a passphrase of 20 characters
or more for maximum security.
sign indicates that the group (broadcast) encryption method
is different from the pairwise (unicast) encryption. For
example, for CCMP+TKIP, CCMP is the pairwise encryption
and TKIP is the group encryption.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 56
Page 57

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Fixed or Automatic Data Rate
MatchPort permits the control of the transmission rate. Select 0 to set a fixed data
rate or select 1 to set an automatic data rate. The default is 1 (auto fallback).
Transmission Data Rate
If the above TX Data rate is set to fixed, the selected data rate is the MatchPort’s
fixed transmission rate. If the above TX Data rate is set to auto fallback, the
selected data rate is the MatchPort’s maximum data rate. Lower data rates allow for
larger distances. It may also be required when communicating with older devices.
The default is 11 Mbps.
TX Data rate 0=1, 1=2, 2=5.5, 3=11
4=18, 5=24, 6=36, 7=54 Mbps (0) ? _
Enable Power Management
This allows the software to turn off the radio when expecting not to receive or
transmit soon. This feature reduces the power consumption by up to 140 mA.
Enabling power management increases the response time, because the radio needs
to start up again. The radio is enabled to synchronize and check for incoming
messages (every 100 ms).
Note: This option is not available when the Topology is set to Adhoc.
Enable power management (N) ? _
Expert Settings
Note: Change these settings using Telnet or a serial connection o nly.
Caution: Only an expert should change these parameters. These
changes hold serious consequences.
TCP Keepalive Time
Defines how many seconds the unit waits during a silent connection before checking
whether the currently connected network device is still on the network. If the unit
does not receive a response, it drops that connection.
TCP Keepalive time in s (1s – 65s; 0s=disable): (45)? _
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 57
Page 58

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
ARP Cache Timeout
When the unit communicates with another device on the network, it adds an entry
into its ARP table. ARP Cache timeout defines the number of seconds (1-600) the
unit waits before timing out this table.
ARP Cache timeout in s (1s – 65s; 0s=disable): (600)? _
CPU Performance
Select the MatchPort’s performance mode. Higher performance settings require more
energy. Low is 26 Mhz, and Regular is 48 Mhz. The default is Regular.
CPU performance (0=Regular, 1=Low): (0) ? _
Disable Monitor Mode
Disables entry into Monitor Mode via the yyy or xx1 key sequence at startup. This
command prevents the unit from entering Monitor Mode by interpreting the stream of
characters that are received during the device server's initialization at startup. The
default is N (No).
Disable Monitor Mode @ bootup (N) ? _
HTTP Port Number
This option allows the configuration of the web server port number. The valid range is
1-65535. The default HTTP server port number is 80.
HTTP Port Number : (80) ? _
SMTP Port Number
This option allows the configuration of the SMTP port number. The valid range is
1-65535. The default HTTP server port number is 25.
SMTP Port Number : (25) ? _
MTU Size
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is the largest physical packet size a network
can transmit for TCP and UDP. Enter between 512 and 1400 bytes. The default is
1400 bytes.
MTU Size: (1400) ? _
Alternate MAC Address
If necessary, enable the alternate MAC address (if specified in the OEM setup
record).
Enable alternate MAC (N) ? _
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 58
Page 59

Ethernet Connection Type
The MatchPort allows you to configure the Ethernet speed manually. Enter 0 for
automatic negotiation (default). To select the speed and duplex, enter one of the
following: 2 (10Mbit/half duplex), 3 (10Mbit/full duplex), 4 (100Mbit/half duplex), or 5
(100Mbit/full duplex).
Note: Manually configured speed/duplex settings only work correctly if the peer or
switch also uses a static setting. If the peer is set for auto negotiation, it will not
necessarily result in the correct mode. This is a common Ethernet problem and is not
MatchPort-specific.
Ethernet connection type: (0) ? _
Security Settings
Security settings can only be changed using the setup menu (Telnet or serial).
Caution: We recommend setting security over a dedicated network or over
the serial setup, to prevent eavesdropping.
Note: To prevent unauthorized access from the network, disable the Telnet
setup, port 77FE, and the web setup features.
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Disable SNMP
For security purposes, disable SNMP (if required) on the MatchPort unit. The current
setting displays in parentheses.
Disable SNMP (N) ? _
SNMP Community Name
The SNMP Community Name is a required field for NMS to read or write to a device.
Enter a string of 1 to 13 characters.
SNMP Community Name (public): _
The default entry is public. The current value displays in parentheses.
Disable Telnet Setup
This setting defaults to the N (No) option. The Y (Yes) option disables access
to the setup menu via Telnet to port 9999.
Disable Telnet Setup (N) ? _
Disable TFTP Firmware Upgrade
This setting defaults to the N (No) option. The Y (Yes) option disables TFTP for
network firmware upgrades.
Disable TFTP Firmware Update (N) : _
Disable Port 77FE (Hex)
Custom programs use Port 77FE to configure the unit remotely. If required,
disable this capability for security purposes.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 59
Page 60

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Disable Port 77FEh (N) ? _
The default setting is the N (No) option, which enables remote configuration.
Disable Web Server
The Y (Yes) option disables the web server. This setting defaults to the N (option).
Disable Web Server (N) ? _
Disable Web Setup
The Y (Yes) option disables configuration using the Web-Manager. This setting
defaults to the N (No) option.
Disable Web Setup (N) ? _
Disable ECHO Ports
This setting controls whether port 7 echoes characters it receives.
Disable ECHO ports (Y) ? _
AES Encryption
Enable Encryption (Y) ? _
Key length in bits (256): _
Change Key (N) ? _
Enter Key: _
Enable Encryption
Key length in bits Valid options are 128, 192 and 256 bits.
Change Key
Enter Key
This option displays only if the MatchPort model features AES
encryption. It enables AES encryption for tunneling only.
Select to modify the current AES encryption key. The default is
(N) No.
If you selected Change Key, enter the key (at the Enter Key
prompt) in hexadecimal numbers. Enter 32 characters for 128 bits
key length, 48 characters for 192 bits key length, or 64 characters
for 256 bits key length.
Enable Enhanced Password
Setting enhanced password allows an extended security password of 16-characters
for protecting Telnet access. N (No) is the default, which permits a 4-character
password protecting Setup Mode by means of Telnet and web pages.
Enable Enhanced Password (Y) ? _
Disable Port 77F0 (Hex)
Port 77F0 allows a custom application to query or set the five MatchPort configurable
pins when they are functioning as general purpose I/O (GPIO). Disable this
capability, if desired, for security purposes.
Disable Port 77F0h ? _
The default setting, the N (No) option, enables GPIO control. The Y (Yes) option
disables the GPIO control interface.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 60
Page 61

Default Settings
Select 7 Default Settings from the Change Setup menu to reset the unit’s Channel 1
configuration, Channel 2 configuration, Email settings, and Expert settings to the
factory default settings. The server configuration settings for IP address, gateway IP
address, netmask, wireless enable, infrastructure or ad hoc setting, and wireless
security settings remain unchanged. The configurable pins’ settings also remain
unchanged. The specific settings this option changes are listed below.
Note: To reset to factory defaults, use the “Reset to Defaults” Configurable
Pin. For more information on Configurable Pins, see Configurable Pins page
63.
Channel 1 Configuration
5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
Baudrate
I/F Mode 4C (1 stop bit, no parity, 8 bit, RS-232C, no flow
Port No
Connect Mode C0 (always accept incoming connection; no active
Hostlist Retry Counter
Hostlist Retry Timeout
Send Character
All other parameters
9600
control)
10001
connection startup)
3
250 (msec)
0x0D (CR)
0
WLAN Settings
Topology
Network Name
Channel
Security
1 (AdHoc)
LTRX_IBSS
11
0 (none)
TX Data Rate
TX Data Rate
Enable Power Management
0 (fixed)
11 Mbps
N (No)
Expert Settings
TCP Keepalive
ARP Cache Timeout
CPU Performance
Disable Monitor Mode
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 61
45 (seconds)
600 (seconds)
Regular
(N) No
Page 62

5: Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
HTTP Port Number
SMTP Port Number
MTU Size
Enable Alternate MAC
Ethernet Connection Type
Security Settings
Disable SNMP
SNMP Community Name
Disable Telnet Setup
Disable TFTP Firmware Update
Disable Port 77FEh
Disable Web Server
Disable Web Setup
80
25
1400
N (No) ( for OEM use only)
0 (auto negotiate)
(N) No
public
(N) No
(N) No
(N) No
(N) No
(N) No
Disable ECHO ports
Enable Encryption
Enable Enhanced password
Disable Port 77F0h
Email Settings
Trigger Priority
Min. notification interval
All other parameters
Exit Configuration Mode
To exit setup mode:
Select option 9 Save and exit from the Change Setup menu to save all
changes and reboot the device. All values are stored in nonvolatile memory.
or
Select option 8 Exit without save from the Change Setup menu to exit the
configuration mode without saving any changes or rebooting.
(Y) Yes
(N) No
(N) No
(N) No
L
1 second
0 (e.g. email notification and triggers are disabled)
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 62
Page 63

66:: CCoonnffiigguurraabbllee PPiinnss
The MatchPort has five pins configurable for General Purpose I/O (GPIO).
Use these GPIO pins to control devices such as relays, servers, lights, monitor
switches, sensors, and even processes such as data transfer.
Defaults Settings
Function: general purpose input/output
Direction: input
Active Level: low
Set the functions for the five pins independently and in any combination. The initial
directions (input/output) and active levels (low or high active) at boot up can also be
configured through 77FE.
This chapter describes how the directions, active levels, and states can be
dynamically controlled and probed through special port 77F0.
Features
TCP and UDP can be used.
The protocol supports up to 32 GPIO for future products.
Function configuration can be retrieved.
Input or output selection can be retrieved and controlled.
Active low or high selection can be retrieved and controlled.
Active or inactive selection can be retrieved and controlled.
77F0 can be disabled.
Every change of state (active/inactive) requires a command over TCP or UDP, and
thus is not very fast. If you use this port for data transfer, the throughput is low,
usually up to 1 Kbps.
Control Protocol
The GPIO control protocol, a simple, proprietary protocol, is described below.
Guidelines
The GPIO control protocol is described from the PC side. Send means from PC to
MatchPort. Response comes from MatchPort to PC.
The protocol allows for control of up to five GPIOs.
The parameters are four bytes long and represent GPIOs 0-31, with GPIO0 in bit 0 of
the first byte (Little Endian). Parameter bits for configurable pins not configured as
GPIOs are undefined for Get commands and ignored on Set commands.
Every command consists of nine bytes: one command type of one byte and two
parameters of four bytes each.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 63
Page 64

6: Configurable Pins
Command Parameter 1 Parameter 2
Byte 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Pin Number 0 7 8 15 16 23 24 31 0 7 8 15 16 23 24 31
On some commands, one or all parameters are ignored.
For UDP, command type and parameters need to be in the same datagram.
Responses to valid commands are always five bytes long, consisting of the returned
command byte and as parameters in the current or updated values. In case of an
invalid command, only one byte with value 0FFh is returned.
Command Parameter 1
Byte 0 1 2 3 4
Pin Number
0 7 8 15 16 23 24 31
When sending a command (TCP and UDP), wait for the response before sending the
next command.
Commands
Byte 0 Command Types
10h Get functions
11h Get directions (input or output)
12h Get active levels (high active or low active)
13h Get current states (active or not active)
19h Set directions
1Ah Set active levels
1Bh Set current states
There is no Set functions command. Since the pin’s function depends on the
hardware in which the MatchPort is embedded, that configuration is only allowed via
77FE. Settings changed by any of the Set commands are not stored and are lost
when the unit is powered down or rebooted.
Command 10h, Get Functions
Send:
No parameters
Response:
1 parameter
Bytes 1-4: Functions
Bit X 1 means general purpose IO available to the user.
0 means dedicated function (e.g., serial flow control, diagnostics) for
configurable pin X.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 64
Page 65

6: Configurable Pins
Command 11h, Get Directions
Send:
No parameters
Response:
1 parameter
Bytes 1-4: Directions
Bit X 1 means GPIO X is an output.
0 means it is an input.
Command 12h, Get Active Levels
Send:
No parameters
Response:
1 parameter
Bytes 1-4: Active levels
Bit X 1 means GPIO X is active low (0V when active, 3.3V when inactive).
0 means it is active high (3.3V when active, 0V when inactive).
Command 13h, Get Current States
Send:
No parameters
Response:
1 parameter
Bytes 1-4: States
Bit X 1 means GPIO X is active
0 means it is inactive.
Command 19h, Set Directions
Send:
2 parameters
Bytes 1-4: Mask
Bit X
0 means the direction for that GPIO will not change.
Bytes 5-8: New Directions
Bit X 1 means GPIO X will become an output.
0 means it will become an input.
Response:
1 parameter
Bytes 1-4: The updated directions
1 means the direction for GPIO X will be updated with the value in the
second parameter.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 65
Page 66

6: Configurable Pins
Command 1Ah, Set Active Levels
Send:
2 parameters
Bytes 1-4: Mask
Bit X
0 means the active type for that GPIO will not change.
Bytes 5-8: New Active Levels
Bit X 1 means GPIO X will become active low.
0 means it will become active high.
Response:
1 parameter
Bytes 1-4: Updated active levels
1 means the direction for GPIO X will be updated with the value in the
second parameter.
Command 1Bh, Set States
Send:
2 parameters
Bytes 1-4: Mask
Bit X
0 means the state for that GPIO will not change.
Bytes 5-8: New States
Bit X 1 means GPIO X will become active.
0 means it will become inactive.
Response:
1 parameter
Bytes 1-4: Updated states
1 means the state for GPIO X will be updated with the value in the
second parameter.
Examples
Example 1: PC sends command 10h to find out which configurable pins are
available as GPIO.
PC -> MatchPort b/g: 10h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h
MatchPort b/g -> PC: 10h, 03h, 02h, 00h, 00h
Command details:
10h = command 10h
00h, 00h, 00h, 00h = ignored
00h, 00h, 00h, 00h = ignored
Response details:
10h = response to command 10h
03h, 02h, 00h, 00h =
bits 0, 1, and 9 are 0 →CP0, CP1, and CP9 are configured as GPIOs
(GPIO0, GPIO1, GPIO9).
bits 2 to 8 and 10 are 0 → configured for a special function and are
unavailable for control or monitoring by the user.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 66
Page 67

6: Configurable Pins
Example 2: PC sends command 1Bh to change the current states of GPIO 0
and 1 (assuming they are configured as outputs).
PC -> MatchPort b/g: 1Bh, 01h, 02h, 00h, 00h, 01h, 00h, 00h, 00h
MatchPort b/g -> PC: 1Bh, 03h, 00h, 00h, 00h
Command details:
1Bh = command 1Bh
01h, 00h, 00h, 00h = the mask that determines which GPIOs will be changed.
Bit 0 and 9 are 1 → GPIO0 and GPIO9 will be changed.
bit 1 is 0 → GPIO1 will remain the same.
01h, 00h, 00h, 00h = the new states
bit 0 is 1 → GPIO0 will become 1.
bit 1 is ignored since it is masked out.
bit 0 is 0 → GPIO9 will become 0.
Response details:
1Bh = response to command 1Bh
03h, 00h, 00h, 00h =
bit 0 is 1 → GPIO0 = 1
bit 1 is 1 → GPIO1 = 1
bit 9 is 0 → GPIO9 = 0
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 67
Page 68

77:: MMoonniittoorr MMooddee
Monitor Mode is a command-line interface used for diagnostic purposes.
There are two ways to enter Monitor Mode: locally using the serial port or remotely
via the network.
Note: The MatchPort b/g is based on a standard release of Lantronix' s CoBos
operating system. Some CoBos products support both wired and wireless
interfaces. The MatchPort b/g currently supports only wireless. Please ignore
references and settings that deal with a wired Ethernet interface.
Entering Monitor Mode via the Serial Port
To enter Monitor Mode locally:
1. Follow the same steps used for setting the serial configuration parameters (see
Serial Port Access on page 36).
2. Instead of typing three x keys, however:
a) Type zzz to enter Monitor Mode with network connections.
b) Type yyy to enter Monitor Mode without network connections.
A 0> prompt indicates that you have successfully entered Monitor Mode.
Entering Monitor Mode via the Network Port
To enter Monitor Mode using a Telnet connection:
1. Establish a Telnet session to the configuration port (9999).
2. When the Press Enter to go into Setup Mode prompt displays, type M (upper
case).
A 0> prompt indicates that you have successfully entered Monitor Mode.
Monitor Mode Commands
The following commands are available in Monitor Mode.
Note: All commands must be in capital letters.
Table 7-1. Monitor Mode Commands
Command Command Name Function
VS
GC
SC
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 68
Version Queries software header record (16 bytes) of unit.
Get Configuration
Send Configuration Sets configuration of unit from hex records.
Gets configuration of unit as hex records (120
bytes).
Page 69

Command Command Name Function
PI x.x.x.x
Ping
Pings unit with IP address x.x.x.x to check device
status.
7: Monitor Mode
AT
TT TCP Connection
NC
RS
QU
G0, G1, ....,Ge, Gf Get configuration
S0, S1,...,Se, Sf Set configuration to
GM
SS
SA
ARP Table Shows the unit’s ARP table entries.
Table
Network Connection Shows the unit’s current IP address.
Reset Resets the unit.
Quit Exits diagnostics mode.
from memory page
memory page
Get MAC address Shows the unit's 6-byte MAC.
Set Security record
Scan
Shows all incoming and outgoing TCP connections.
Gets a memory page of configuration information
from the device.
Sets a memory page of configuration information
on the device.
Sets the Security record without the encryption key
and length parameters. The entire record must still
be written, but the encryption-specific bytes do not
need to be provided (they can be null since they
are not overwritten).
Initiates a wireless scan if the wireless interface is
enabled. Reports any stations found, including
BSSID, SSID, and RSSI. If SA is followed by a
string, the string is used to filter SSIDs before
reporting. If the BSS does not broadcast its SSID,
only the BSSID and RSSI are returned.
NS
Network Status
Reports the network interfaces’ statuses. Includes
potentially negotiated parameters like speed/duplex
for Ethernet or BSSID, encryption, authentication
for wireless interfaces.
Responses to some of the commands are given in Intel Hex format.
Note: Entering any of the commands listed above generates one of the
following command response codes:
Table 7-2. Command Response Codes
Response Meaning
0> OK; no error
1> No answer from remote device
2> Cannot reach remote device or no answer
8> Wrong parameter(s)
9> Invalid command
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 69
Page 70

88:: UUppddaattiinngg FFiirrmmwwaarree
This chapter explains how to obtain and update the unit’s firmware.
Obtaining Firmware
Obtain the most up-to-date firmware and release notes for the unit from the Lantronix
web site (www.lantronix.com
Reloading Firmware
There are several ways to update the unit's internal operational code (*.ROM): via
DeviceInstaller (the preferred way), via TFTP, or via the serial port. You can also
update the unit's internal web interface (*.cob) via TFTP or DeviceInstaller.
Here are typical names for those files. Check the Lantronix web site for the latest
versions and release notes.
ROM File COB (Web-Manager)
mpt_6502.rom gen_mpt_webm_1602.cob
Please refer to the DeviceInstaller online Help for information about reloading
firmware using DeviceInstaller. The other methods are discussed below.
) or by using anonymous FTP (ftp.lantronix.com/pub).
Table 8-1. Firmware Files
Using TFTP: Graphical User Interface
To download new firmware from a computer:
1. Use a TFTP client to put a binary file to the unit (*.ROM to upgrade the unit's
internal operational code and *.COB to upgrade its internal web interface).
Note: TFTP requires the .rom (binary) version of the unit's internal
operational code.
2. In the TFTP server field, enter the IP address of the unit being upgraded.
3. Select Upload operation and Binary format.
4. Enter the full path of the firmware file in the Local file name field.
5. In the Remote file name field, enter the current internal operational code or
WEB1 to WEB19 for the internal web interface.
6. Click the Upload Now button to transfer the file to the unit. The unit performs a
power reset after the firmware has been loaded and stored.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 70
Page 71

8: Updating Firmware
Using TFTP: Command Line Interface
To download new firmware from a computer, enter the following from a TFTP
command line interface:
tftp –i <ip address> put <local filename> <destination
file name>
The following examples demonstrate the TFTP command sequence to download the
.rom file, the .fwx file, and the .cob file:
tftp –i 192.168.1.111 put mpt_6502.rom W8
tftp –i 192.168.1.111 put gen_mpt_webm_1602.cob WEB1
Recovering the Firmware Using the Serial Port
If for some reason the firmware is damaged, you can recover the firmware file by
using the serial port to download the *.ROM file.
Note: See also Recovering Firmware in the DeviceInstaller User Guide.
1. Start DeviceInstaller.
2. From the Tools menu, select Advanced/Recover Firmware. The Recover
Firmware window displays.
3. Enter the com port on your PC and the location of the firmware file. The Device
Model should indicate MatchPort b/g.
4. Click OK to download the file.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 71
Page 72

99:: TTrroouubblleesshhoooottiinngg
This chapter discusses how you can diagnose and fix errors quickly without having to
contact a dealer or Lantronix. The MatchPort’s diagnostic LEDs indicate the unit’s
status. It helps to connect a terminal to the serial port while diagnosing an error to
view summary messages that may display. When troubleshooting, always ensure
that the physical connections (power cable, network cable, and serial cable) are
secure.
Note: Some unexplained errors might be caused by duplicate IP addresses on the
network. Make sure that your unit's IP address is unique.
When troubleshooting the following problems, make sure that the MatchPort is
powered up. Confirm that you are using a good network connection.
Diagnostic LED States
Condition Diagnostic LED Channel 1 Status LED
No Errors OFF N/A
Firmware storage checksum
error
RAM error ON Blink 2x/4 seconds
ON Blink 1x/4 seconds
Network controller error ON Blink 3x/4 seconds
Serial number storage
checksum error
Duplicate IP address present ON Blink 5x/4 seconds
Firmware and hardware
mismatch
Radio command failure ON Blink 7x/4 seconds
Faulty network connection Blink 2x/second Blink 4x/4 seconds
No DHCP response Blink 2x/second Blink 5x/4 seconds
Setup menu active Blink 2x/second
ON Blink 4x/4 seconds
ON Blink 6x/4 seconds
Follow Diagnostic LED for 2 seconds, off for 2
seconds
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 72
Page 73

Problems and Error Messages
Problem/Message Reason Solution
9: Troubleshooting
When you issue the ARP –S
command in Windows, The
ARP entry addition failed: 5
message displays.
When you attempt to assign an
IP address to the unit by the
ARP method and Telnet to the
device server through port 1,
the connection fails.
When you Telnet to port 9999,
the Press Enter to go into Setup
Mode message displays.
However, nothing happens
when you press Enter, or your
connection is closed.
When you Telnet to port 1 to
assign an IP address to the
device server, the Telnet
window does not respond for a
long time.
Your currently logged-in user
does not have the right to use
this command on this PC.
When you Telnet to port 1 on the
device server, you are only
assigning a temporary IP
address. When you Telnet into
port 9999 and do not press Enter
quickly, the device server
reboots, causing it to lose the IP
address.
You did not press Enter quickly
enough. You only have 5
seconds to press Enter before
the connection is closed.
You may have entered the
Ethernet address incorrectly with
the ARP command.
Have someone from your IT
department log you in with
sufficient rights.
Telnet back to Port 1. Wait for it to
fail, then Telnet to port 9999
again. Make sure you press Enter
within 5 seconds.
Telnet to port 9999 again, but
press Enter as soon as you see
the Press Enter to go into Setup
Mode message.
Confirm that the Ethernet address
that you entered with the ARP
command is correct. The Ethernet
address may only include
numbers 0-9 and letters A-F. In
Windows and usually in Unix, the
segments of the Ethernet address
are separated by dashes. In some
forms of Unix, the Ethernet
address is segmented with
colons.
When you try to assign an IP
with DeviceInstaller, you get the
following message:
No response from device!
Verify the IP, Hardware
Address and Network Class.
Please try again.
The IP address you are trying to
assign is not on your logical
subnet.
The device server may not be
plugged into the network
properly.
The cause is most likely one of
the following:
The Hardware address you
specified is incorrect.
The IP address you are trying to
assign is not a valid IP for your
Confirm that your PC has an IP
address and that it is in the same
logical subnet that you are trying
to assign to the device server.
Make sure that the Link LED is lit.
If the Link LED is not lit, then the
device server is not properly
plugged into the network.
Double-check the parameters that
you specified.
Note: You cannot assign an IP
address to a device server
through a router.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 73
Page 74

Problem/Message Reason Solution
logical subnet.
You did not choose the correct
subnet mask.
9: Troubleshooting
The device server is not
communicating with the serial
device to which it is attached.
When you try to enter the setup
mode on the device server
through the serial port, you get
no response.
You can ping the device server,
but not Telnet to the device
server on port 9999.
The most likely reason is the
wrong serial settings were
chosen.
The issue is most likely
something covered in the
previous problem, or possibly,
you have Caps Lock on.
There may be an IP address
conflict on your network
You are not Telneting to port
9999.
The Telnet configuration port
(9999) is disabled within the
device server security settings.
The serial settings for the serial
device and the device server must
match. The default serial settings
for the device server are RS-232,
9600 baud, 8 character bits, no
parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control.
Double-check everything in the
problem above. Confirm that
Caps Lock is not on.
Turn the device server off and
then issue the following
commands at the DOS prompt of
your computer:
ARP -D X.X.X.X (X.X.X.X is the IP
of the device server).
PING X.X.X.X (X.X.X.X is the IP
of the device server).
If you get a response, then there
is a duplicate IP address on the
network. If you do not get a
response, use the serial port to
verify that Telnet is not disabled.
The device server appears to
be set up correctly, but you are
not communicating with your
device attached to the device
server across the network.
If you are sure that the serial port
setting is correct, then you may
not be connecting to the correct
socket of the device server.
Another possibility is that the
device server is not set up
correctly to make a good socket
connection to the network.
You can check to see whether
there is a socket connection to or
from the device server by
checking the state of CP1, if it has
been configured for LED1
functionality.
If the state of CP1 is blinking
consistently, or is completely off,
then there is a good socket
connection.
If the state of CP1 is low, use the
Connect Mode option C0 for
making a connection to the device
server from the network. Use
Connect Mode option C1 or C5
for a connection to the network
from the device server. See the
full list of Connect Mode options
in Connect Mode on page 42.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 74
Page 75

Problem/Message Reason Solution
9: Troubleshooting
When connecting to the WebManager within the device
server, the No Connection With
The Device Server message
displays.
Technical Support
If you are experiencing an error that is not described in this chapter, or if you are
unable to fix the error, contact Lantronix Tech Support as follows:
To check our online knowledge base or send a question to Technical Support, go to
http://www.lantronix.com/support
Technical Support Europe, Middle East, and Africa
Phone: +33 (0)1 39 30 41 72
Germany: +49 (0) 180 500 13 53
Email: eu_techsupp@lantronix.com
Firmware downloads, FAQs, and the most up-to-date documentation are available at
www.lantronix.com/support
When you report a problem, please provide the following information:
Your name, and your company name, address, and phone number
Lantronix model number
Lantronix MAC number
Software version (on the first screen shown when you Telnet to port 9999)
Description of the problem
Status of the unit when the problem occurred (please try to include
information on user and network activity at the time of the problem).
Your computer is not able to
connect to port 30718 (77FEh)
on the device server.
.
or eu_support@lantronix.com
.
Make sure that port 30718
(77FEh) is not blocked with any
router that you are using on the
network. Also, make sure that port
77FEh is not disabled within the
Security settings of the device
server.
MatchPort b/g™ User Guide 75
 Loading...
Loading...