Page 1

Model
STH
Series
Combination
Soil Outfi t
Instruction Manual
Page 2

w
Page 3

Introduction ............................................................. 4
Multiple Sample Testing
Test Methods
Available Nutrients
Soil Sampling & Preparation
Test Procedure
pH ............................................................................ 6
Extraction ................................................................ 7
Nitrate Nitrogen ....................................................... 8
Potassium ................................................................ 8
Phosphorus ............................................................. 10
Humus .................................................................... 11
Magnesium ............................................................. 12
Calcium .................................................................. 13
Sulfate .................................................................... 14
Aluminum .............................................................. 14
Chloride .................................................................. 15
Ferric Iron .............................................................. 16
Nitrite Nitrogen ...................................................... 16
Ammonia Nitrogen ................................................ 17
Manganese ............................................................. 18
Units of Measure
Fertilizer Application Rates
Green Plant Tissue Tests
Soil Test Reagents
........................................................... 5
......................................................... 6
..................................................... 19
............................................ 5
.................................................... 5
...................................... 5
....................................... 19
.......................................... 20
................................................... 22
Page 4

Introduction
This instruction manual is designed for use with the LaMotte STH Series
of professional soil testing outfi ts. The basic Model STH-4 Outfi t (Code
5029) tests soil for pH, nitrate nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Intermediate STH outfi ts combine these four tests with tests for other
important plant nutrition factors (humus, calcium and magnesium). The
Model STH-14 Outfi t (Code 5010-01) analyzes for all of the factors
listed above, along with tests for ammonia nitrogen, manganese, aluminum,
nitrate nitrogen, sulfate chloride and ferric iron. This manual also includes
special instructions for testing nitrate, phosphorus, and potassium in green
plant tissues.
*WARNING: Reagents marked with an * are considered to be potential
health hazards.
for these reagents go to www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy,
contact LaMotte by e-mail, phone or fax.
Note: Some reagents in this kit are dispensed with screw-cap pipets that
are packaged separately.
Place the screw-cap glass pipets (0341) on the following reagents:
5156 *Phosphorus Reagent #2
5101 *Aluminum T est Solution
5140 *Magnesium Test Solution #1
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
Place the screw-cap plastic pipets (0392) on the following reagents:
5146 *Nitrate Reagent #1
5108PS *Calcium T est Solution
5171 *Sulfate T est Solution
5116PS *Ferric Iron Test Solution
5103PS *Ammonia Nitrogen Test Solution
4
Page 5

Multiple Sample Testing
When extracts from two or more samples are being tested simultaneously
use separate pipets for each extract. Mixing samples will cause false test
results. Multiple test tubes, pipets, and spot plates have been provided to
facilitate proper analytical technique.
Test Methods
Color chart methods are used for all tests except for Potassium. The reaction
is performed in a tube or on a spot plate and the resulting color is compared
to a laminated color chart.
The Potassium test measures the amount of turbidity in a sample
relative to the potassium content.
Available Nutrients
All tests measure the portion of the nutrient in the soil that would
be “available” for the plant to use. Since extraction is not complete,
the amount that is measured is relative, dependent on the extraction
procedure.
Soil Sampling & Preparation
Carefully follow the soil sampling procedures discussed in detail in the
LaMotte Soil Handbook (1504). For sampling greenhouse soils, the
following specialized procedure is recommended.
Collect greenhouse samples prior to watering. Remove any mulch
covering the soil, and then use a soil sampling tube or spoon to take a
sample from the entire plant rooting space, top to bottom. A composite
sample insures representative test results. Thoroughly mix 8 to 10
individual samples, and then spread the composite sample on a sheet
of paper or plastic to dry. Allow the sample to air dry overnight. Do not
oven dry the sample. Sift the dried sample through a wire screen mesh
similar to a window screen.
5
Page 6
Test Procedures
pH
pH is a measure of acidity or basicity. Soils can have a pH from 3.5 to
11.0, but plants grow well in the range of 5.0 to 8.5. In soils with a low
pH (acidic), some nutrients can reach toxic levels and the activity of
soil microbes is greatly reduced. Soils with a high pH (alkaline) generally
have a lower micro-nutrient availability and some levels may be defi cient.
PROCEDURE
1. Fill a test tube (0204) approximately one-third full of soil. Use
the Demineralizer Bottle (1155) to add demineralized water to the
until it is fi lled to one-half inch from the top. Cap and shake
tube,
until the
soil is well dispersed.
2. Add 5 drops of Soil Flocculating Reagent (5643WT). Cap and
shake to mix. Allow contents to settle before proceeding to Step 3.
3. Use a 1 mL pipet (0354) to transfer 1 mL of the clear solution
above
the soil to one of the large depressions on a spot plate (0159).
Transfer
a second 1 mL sample to the other large depression on the
spot plate.
4. To the fi rst sample on the spot plate, add two drops of *Duplex
Indicator (2221). Compare the resulting color reaction against the
Duplex Color Chart (1313).
5. The wide range pH test result indicates which narrow range indicator
and color chart should be selected to perform a more precise pH
test. Choose the narrow range indicator and appropriate chart with
a mid-point that is as close as possible to the value obtained in the
wide range test.
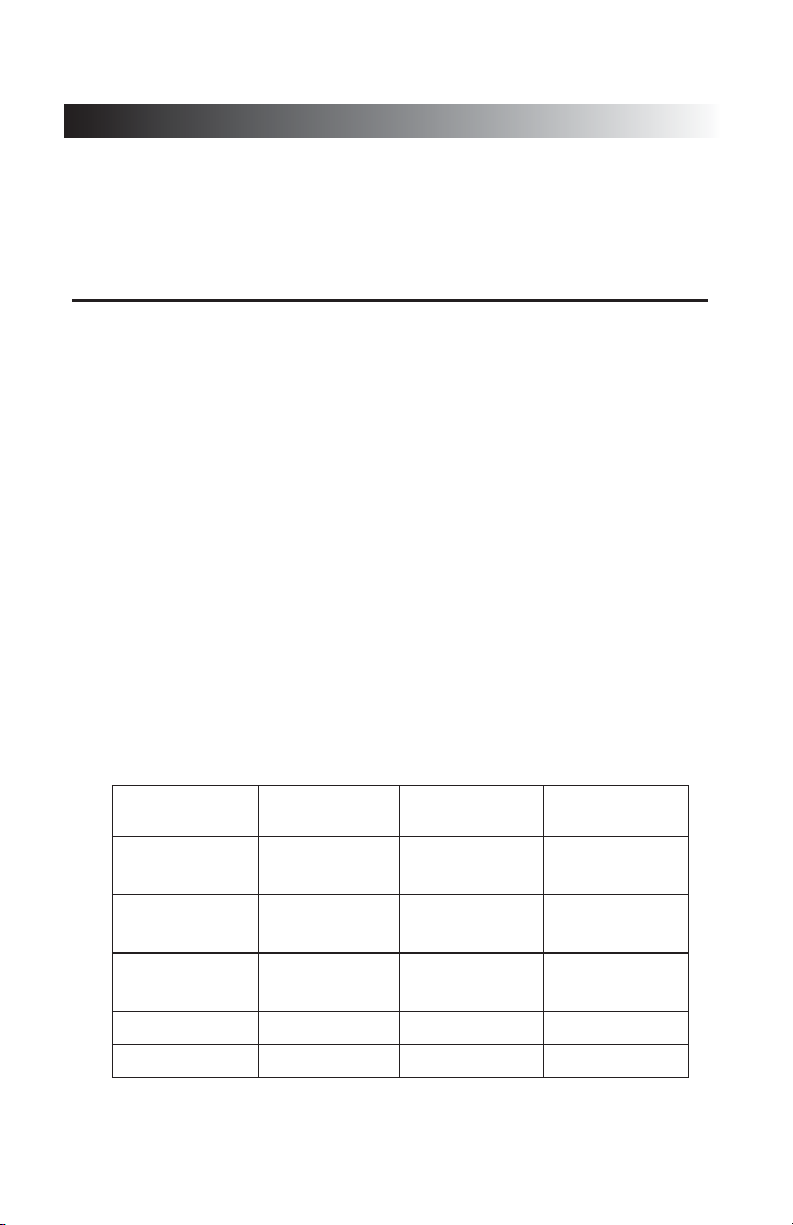
Indicator pH Range
Bromcresol
3.8-5.4 2207 1328
Indicator
Code
Color Chart
Green
Chlorphenol
5.2-6.8 2209 1329
Red
Bromthymol
6.0-7.6 2210 1331
Blue
Phenol Red 6.8-8.4 2211 1332
Thymol Blue 8.0-9.6 2213 1335
Example: If the wide range test result is pH 6.0, choose the
Chlorphenol Red Indicator (2209) & the Chlorphenol Red Color
Chart (1329) for Step 5.
6
Code
Page 7

6. Add two drops of the chosen narrow range indicator to the second
sample on the spot plate. Compare the resulting color reaction against
the appropriate color chart to obtain a precise soil pH reading.
Interpretation of pH Reading:
If the pH is Then the soil is
Below 5.5 Strongly Acid
5.5-6.0 Moderately Acid
6.1-7.0 Slightly Acid
Above 7.0 Alkaline
Extraction
The following extraction procedure uses *Universal Extracting Solution
(5173PS) to produce a single soil extract which is used in each of the
following tests: nitrate nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen,
phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfate, aluminum, iron, and
manganese. The pH, chloride, humus, and plant tissue tests use extraction
procedures described in the individual instructions for those tests.
The Extraction Tubes (0704) are marked at 7 and 14 mL. The instructions
below assume that a number of tests will be performed with the general
soil extract. Therefore 14 mL of extracting solution and eight level
measures of the soil sample are called for in Steps 1 & 2. If only a single
test is to be performed (e.g., nitrate nitrogen), fi ll the extraction tube to
the 7 mL line (Step 1) and add only four level measures of the soil
sample (Step 2).
PROCEDURE
1. Fill an Extraction Tube (0704) to the 14 mL line with *Universal
Extracting Solution (5173PS).
2. Use the 0.5 g spoon (0698) to add eight level measures of the soil
sample. Cap and shake for one minute.
Note: When adding samples with high concentrations of carbonates
to the *Universal Extracting Solution (5173), swirl tube to mix for
30 seconds before capping to allow gases to escape.
3. Use a piece of fi lter paper (0465) and a plastic funnel (0459) to fi lter
the soil suspension into a second extraction tube (0704). (Fold the
fi lter paper in half and then in half again to form a cone which is
fi tted into the funnel.) The fi ltrate in the second extraction tube is
the general soil extract for use in the 11 individual test procedures
listed previously.
7
Page 8

Nitrate Nitrogen
The role of nitrogen in plant nutrition is discussed in the LaMotte
Soil Handbook. For interpretation of test results see the LaMotte Soil
Handbook.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a 1 mL pipet (0354) to transfer 1 mL of the general soil extract
to one of the larger depressions on a spot plate (0159).
2. Add 10 drops of *Nitrate Reagent #1 (5146).
3. Use a 0.5 g spoon (0698) to add one level measure of *Nitrate
Reagent 2 Powder (5147).
4. Stir thoroughly with a clean stirring rod (0519). Allow to stand fi ve
minutes for full color development.
5. Match sample color with the Nitrate Nitrogen Color Chart (1315).
Record as pounds per acre nitrate nitrogen.
Potassium (Potash)
The role of potassium (potash) in plant nutrition is discussed in the
LaMotte Soil Handbook. For interpretation of test results, see the
LaMotte Soil Handbook.
When present in large amounts, ammonia salts will produce a precipitate
similar to that produced by potassium. If fertilizer containing ammonia
salts has recently been applied, or if the soil pH is below pH 5.0, perform
the Ammonia Nitrogen test (page 19) before performing the potassium
test. A high ammonia nitrogen test result will alert the operator to a
probable false high reading in the potassium test; actual potassium levels
will be somewhat lower.
It is important that the temperature of the test sample and the *Potassium
Reagent C (5162) be in the range of 20-27°C (68-80°F). On warm days,
prior to Step 3 below, cool both the test sample in the Potash “A” Tube
and the Reagent C container by placing them in cool water.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to fi ll a Potash “A” Tube (0245) to the
lower line with the general soil extract.
2. Add one *Potassium Reagent B Tablet (5161A). Cap and shake
until dissolved.
3. Add *Potassium Reagent C (5162) until the Potash “A” Tube is
fi lled to the upper line. Allow the *Potassium Reagent C (5162)
to run slowly down the side of the tube. Swirl the tube to mix. A
precipitate will form if potassium is present.
8
Page 9

4. Stand the empty Potash “B” Tube (0246) on the Potassium Reading
Plate (1107), a rectangular piece of white plexiglass with a solid
black line down the middle. Place the tube directly over the black
line.
5. Fill a transfer pipet (0364) with the test sample from the Potash “A”
Tube.
6. Slowly add the test sample to the Potash “B” Tube, allowing it to
run down the side of the tube. Observe the black line down through
the Potash “B” Tube. Continue to add the test sample until the black
line just disappears.
7. Record the value where the level of the liquid meets the scale
printed on the side of the Potash “B” Tube, as pounds per acre
Available Potassium.
8. If the test result is equal to or greater than 400 pounds per acre,
repeat the test on a diluted test sample as follows:
A. Fill a Potash “C” Tube (0247) to the lower mark with the
general soil extract.
B. Add *Universal Extracting Solution (5173) to the upper mark
and mix.
C. Using this diluted extract follow Steps 1 through 7 above.
Multiply the test result by 2 to obtain pounds per acre Available
Potassium.
9
Page 10

Phosphorus
The role of phosphorus in plant nutrition is discussed in the LaMotte
Soil Handbook. For interpretation of test results see the LaMotte Soil
Handbook.
The Phosphorus test is extremely sensitive. Special precautions should
be taken to prevent contamination. In particular, exposure of the test
components to fertilizer dust must be scrupulously avoided. The operator’s
hands and clothing, the work surface, and the testing area in general
must be clean and free of fertilizer residues.
LaMotte offers the Model NF Test Kit (Code 5090) for Phosphorus in
Alkaline Soils, to be used in place of the test described below when the
soils are predominantly alkaline (above pH 7.0).
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to fi ll a “Phosphorus B” Tube (0244) to
the line with the general soil extract.
2. Add 6 drops of *Phosphorus Reagent 2 (5156). Cap and shake
to mix.
3. Add one *Phosphorus Test Tablet (5706A). Cap and shake until
dissolved.
4. Immediately compare the color that develops in the test tube against
the Phosphorus Color Chart (1312). Hold the tube about one inch in
front of the white surface in the center of the color chart. View the
chart and sample under natural light for optimum color comparison.
The test result is read in pounds per acre
Available Phosphorus.
10
Page 11

Humus
Humus consists of the complex remains of fresh plant and animal residue
after extensive chemical and biological breakdown. Humus accounts for
60% to 70% of the total organic carbon in soils. It can modify the physical
properties of a soil, strongly affecting its chemical and biological properties.
PROCEDURE
1. Use the 0.5 g spoon (0698) to add eight level measures of soil to
a soil extraction tube (0704).
2. Use the Demineralizer Bottle (1155) to fi ll the tube to the 14 mL
line with demineralized water. Cap and shake to mix.
3. Use a 0.5 g spoon (0698) to add two level measures of *Humus
Screening Reagent Powder (5119). If necessary, add more
demineralized water to return the level of the liquid to the 14 mL
line. Cap and shake vigorously for one minute.
4. Add 15 drops of Soil Flocculating Reagent (5643). Cap and mix
gently. Allow to settle for several minutes.
5. Use a piece of fi lter paper (0465) and a plastic funnel (0459) to fi lter
the mixture into a second extraction tube. (Fold fi lter paper in half
and then in half again to form a cone which is fi tted into the funnel.)
6. Compare the clear fi ltrate in the second extraction tube with the
Humus Color Chart (1384).
Interpretation
The Humus color comparator is labeled with values of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
The results are interpreted as follows:
Humus or Organic Matter in Soil
Humus Reading
Agricultural Soils
Garden
Greenhouse Soils
Organic Soils
12 345
Low Medium High
Low Medium High
Low Medium High
11
Page 12

Magnesium
Magnesium is a constituent of chlorophyll, and chlorosis can result from
magnesium defi ciency. Like calcium, magnesium cations play a role in
base or cation exchange. Magnesium is subject to more leaching than
calcium. Soils giving a low test reading should receive dolomitic lime
or fertilizer which contain considerable magnesia. Soils giving high
magnesium tests and low calcium tests should receive gypsum or high
calcic lime, in order to restore the calcium-magnesium balance.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to transfer ten drops of the general soil
extract to one of the larger depressions on a spot plate (0159).
2. Add one drop of *Magnesium Test Solution 1 (5140). Stir with
a clean rod (0519). A pale yellow color will develop.
3. Add *Magnesium and Manganese Test Solution 2 (5145WT) one
drop at a time with stirring, until the pale yellow color changes to
one of the darker shades indicated on the Magnesium Color Chart
(1306). About two drops are usually required. Under some conditions,
a precipitate will form shortly after *Manganese-Magnesium Test
Solution #2 has been added. This will not effect the test reading.
The test result is expressed in relative values of Magnesium from
very low to very high. For approximate corresponding value in parts
per million or pounds per acre, see page 19.
12
Page 13

Calcium
Calcium defi ciency is seldom a direct limiting factor in plant growth,
because the lack of adequate calcium in a soil causes other growth
limiting defi ciencies to occur fi rst. Calcium is the dominant cation in
a soil’s base or cation exchange complex; it prevents excessive soil
acidity
may cause high soil acidity, diminishing the availability of some
nutrients (like nitrogen) and permitting toxic levels of other minerals
(like aluminum) to develop in the soil solution. In general, calcium
plays an essential role in maintaining the chemical equilibrium of the
soil solution.
This test measures the amount of calcium present in the base exchange
complex. Calcium test results confi rm and supplement soil acidity readings.
Sandy soils normally contain less calcium than clay or organic soils.
Sandy soils should give readings of approximately 500 ppm, clay soils
1000 ppm, and organic soils such as peats or forest loams 5000 ppm
calcium. Lower levels in clay or organic soils indicate that the active
calcium has been replaced by hydrogen or other ions, as in highly alkaline
or highly acid soils.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to transfer fi ve drops of the general soil
2. Add one drop of *Calcium Test Solution (5108PS). Swirl gently to
3. Match the milky turbidity of the test sample against the turbidity
4. If the test sample turbidity corresponds to or exceeds the lightest
and stimulates benefi cial biological activity. Low calcium levels
extract to a fl at-bottomed glass turbidity vial (0242).
mix.
standards on the Replaceable Calcium Chart (1303). Lay the chart
fl at under natural light and hold the turbidity vial one-half inch
above the black strip in the middle of the chart. View the black strip
down through the turbid sample and compare the resulting shade of
gray with the six standard shades. The test result is read in parts per
million replaceable calcium.
standard (2800 ppm), repeat the test on a diluted sample. Transfer
one drop of the general extract to a clean turbidity vial and add four
drops of demineralized water. Then follow Steps 2 and 3 as above.
Multiply the test result by 5 to obtain parts per million replaceable
calcium.
13
Page 14

Sulfate
Sulfur is essential to the formation of protein and affects various aspects
of plant metabolism. Sulfur-defi cient plants are pale green in color with
thin, reedy stems. Negatively charged sulfate ions are easily leached. The
major sources of soil sulfate are fertilizer containing sulfate compounds
and atmospheric sulfur dioxide carried into the soil by precipitation.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to transfer fi ve drops of the general soil
extract to a fl at-bottomed turbidity vial (0242).
2. Add one drop of *Sulfate T est Solution (5171). Swirl gently to mix.
3. Compare the turbidity of the sample to the turbidity standards of the
Sulfate Chart (1314). Lay the chart fl at under natural light and hold
the turbidity vial one-half inch above the black strip in the middle of
the chart. View the black strip down through the turbid
compare the resulting shade of gray with the six standard
test result is read in parts per million sulfate.
sample and
shades. The
Aluminum
All soils contain signifi cant amounts of aluminum in inorganic colloidal
material and in the form of undecomposed minerals. In neutral, slightly
alkaline, or slightly acid soils, this aluminum is in inert combinations
that do not affect plant growth. In more acidic soils, aluminum can
form soluble salts toxic to plant growth. A high test result indicates an
undesirable acid soil. Plants which normally thrive on acid soils may fail
on a soil with a high active aluminum test reading. A medium test result
is generally tolerable - especially for grasses, corn, oats, potatoes, and
tobacco. A low or negative aluminum test result is preferable.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to transfer two drops of the general soil
extract to one of the larger depressions on a spot plate (0159).
2. Add two drops of *Universal Extracting Solution (5173).
3. Add one drop of *Aluminum Test Solution (5101).
4. Stir with a clean stirring rod (0519). Allow to stand for one minute.
5. Match the resulting color with the Active Aluminum Color Chart
(1301). The test result is expressed in relative values of active
aluminum from very low to very high. For approximate corresponding
values in parts per million or pounds per acre, see page 19.
14
Page 15

Chloride
Chlorides are present in practically all soils. Application of fertilizer
may increase chloride levels. Chlorides are removed from the soil
by leaching. Excessive concentrations are toxic to plants. A high test
reading, particularly where stunted growth has been observed, may
indicate poisoning due to high chloride levels in the soil.
PROCEDURE
1. Use the Demineralizer Bottle (1155) to fi ll a tube (0970-S) to the 5
mL line with demineralized water.
2. Use the 0.5 g spoon (0698) to add four level measures of the soil
sample to the tube. Cap and shake vigorously for 2-3 minutes.
3. Use a piece of fi lter paper (0465) and a plastic funnel (0459) to fi lter
the mixture into a second tube (0970-S). (Fold fi lter paper in half
and then in half again to form a cone which is fi tted into the funnel.)
4. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to transfer fi ve drops of the fi ltrate in the
second tube to a fl at-bottomed turbidity vial (0242).
5. Add one drop of *Chloride Test Solution (5111) to the vial. Swirl
gently to mix.
6. Match the turbidity or amount of precipitation against the turbidity
standards on the Chloride Chart (1304). Lay the chart fl at under
natural light and hold the turbidity vial one-half inch above the black
strip in the middle of the chart. View the black strip down through
the turbid sample and compare the resulting shade of gray with the
six standard shades. The test result is read in parts per million chloride.
15
Page 16

Ferric Iron
The role of iron in plant nutrition is discussed in the LaMotte Soil
Handbook. Iron is essential to the formation of chlorophyll, and iron
defi ciency causes chlorosis. While most soils contain abundant iron,
only a fraction is soluble and readily available to the growing plant.
This is particularly true in neutral or alkaline soils. Acid soils contain
higher levels of available iron.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to transfer four drops of the general soil
extract to one of the larger depressions on a spot plate (0159).
2. Use the 0.05 g spoon (0696) to add one level measure of *Iron
Reagent Powder (5275). Mix with a clean stirring rod (0519).
3. Add one drop of *Ferric Iron Test Solution (5116PS). Mix again.
4. Match the resulting color to the *Ferric Iron Color Chart (1348).
The test result is read in pounds per acre ferric iron.
Nitrite Nitrogen
Nitrites are formed as an intermediate step in the production of nitrates.
Soils that are well drained and aerated contain only small amounts of
nitrite nitrogen. Excessive nitrites, which are toxic to plants, may result
from soil conditions unfavorable to the formation of nitrate, such as
inadequate aeration. High nitrite readings may also be encountered
in soils with large amounts of nitrates, where a portion of the nitrate
nitrogen decomposes to form nitrites.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to add 5 drops of soil extract to a large
depression on a spot plate (0159).
2. Add 1 drop of *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent 1 (5151WT).
3. Add 1 drop of *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent 2 (5152WT). Mix with
a clean stirring rod.
4. Add 3 drops of *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent 3 (5153WT). Mix with
a stirring rod. Wait 1 minute.
5. Match sample color to a color standard on the Nitrite Nitrogen Color
Chart (1310). Record as ppm nitrite nitrogen.
6. If sample color matches, or is deeper than, the highest standard,
repeat test on a diluted sample. Transfer one drop of soil extract to
a large depression on a spot plate. Add 4 drops of *Universal
Extracting Solution (5173). Follow Steps 2-5. Multiply fi nal result
by 5. Record as ppm Nitrite Nitrogen.
16
Page 17

Ammonia Nitrogen
A fertile soil may be expected to give a low ammonia nitrogen test reading,
unless there has been a recent application of nitrogenous fertilizer in
forms other than the nitrate. The rapid disappearance of ammonia after
fertilizer application indicates the desired transformation of the ammonia
to the more available nitrate compounds. In forest soils ammonia is the
most abundant available form of nitrogen. If there is a satisfactory rate
of nitrogen transformation, the humus layers of a forest soil will produce
very high concentrations of ammonia nitrogen.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to transfer four drops of the general soil
extract to one of the larger depressions on a spot plate (0159).
2. Add one drop of *Ammonia Nitrogen Test Solution (5103PS). Stir
with a clean stirring rod (0519). Allow to stand for one minute.
3. Compare the resulting color against the Ammonia Nitrogen Color
Chart (1302). The test result is expressed in relative values of
ammonia nitrogen from very low to very high. For approximate
corresponding values in parts per million or pounds per acre, see
page 19.
17
Page 18

Manganese
An essential element in the enzyme system of plants, manganese plays
a role in metabolic reactions affecting germination, photosynthesis, and
other vital aspects of plant development. Yellowing and stunted growth
results from manganese defi ciency. Some insoluble manganese is present
in all soils. Its solubility or availability is closely related to soil pH.
Calcareous soils or soils which have been heavily limed may be defi cient
in available manganese. Application of a soluble manganese salt, such
manganese sulfate, will correct this problem. Conversely, toxic levels
of available manganese may develop in highly acid soils; this condition
may be corrected by liming. Since available manganese may be leached
from the soil or altered to less active forms by oxidation, this test should
be conducted just prior to planting and during plant growth. Any positive
test reading, even a very low reading, generally indicates the presence
of suffi cient available manganese to meet plant requirements. A high test
reading is undesirable and indicates a need for liming.
PROCEDURE
1. Use a transfer pipet (0364) to add 10 drops of soil extract to the
large depression on a spot plate (0159).
2. Use the 0.05 g spoon (0696) to add one measure of Manganese
Buffer Reagent (6310). Mix with a clean stirring rod (0519) until
the powder dissolves.
3. Use the other 0.05 g spoon (0696) to add one measure of *Manganese
Periodate Reagent (6311). Mix with a clean stirring rod for 20 seconds.
Note: The *Manganese Periodate Reagent will not dissolve completely.
4. Match the color in the spot plate to a color standard on the Manganese
in Soil Color Chart (1307-01). Record as ppm Manganese.
Note: Immediately clean the spot plate to prevent staining.
as
18
Page 19

Units of Measure
Test results are expressed in the following terms:
Parts per Million
(ppm)
Nitrite Nitrogen Nitrate Nitrogen Ammonia Nitrogen
Calcium Phosphorus Magnesium
Sulfate Potassium Aluminum
Chloride Iron Manganese
Pounds Per Acre
(lb/acre)
Relative Amounts
from Very Low to
Very High
Pounds per acre represent the number of pounds of soil in an acre to the
plough depth of 6-7 inches, or 2,000,000 lbs. Conversion from pounds
per acre to parts per million, or vice versa, may be accomplished by
means of the following formulas:
ppm x 2 = lb/acre
lb/acre x 0.5 = ppm
In the four nutrient tests which produce relative test results, the
following approximate quantitative values may be assigned to the
relative terms:
Approximate Value Expressed in ppm
Ver y
Low
Test Factor
Ammonia Nitrogen 5 10 40 100 150
Magnesium 5 10 25 80 150
Aluminum 5 10 30 80 125
Manganese NA 5 12 25 40
(Low)
Low
(Medium
Low) Medium High
Ver y
High
Fertilizer Application Rates
When interpreting soil test results to establish a fertilizer program, a number
of variables must be considered in addition to the values obtained in the
soil tests. These variables include the composition of the soil, drainage,
climate, previous fertilizer programs and soil test results, and the type of
plant to be grown. Consult local agricultural services for guidelines to
fertilizer application rates for the specifi c soils in your area.
19
Page 20

Green Plant Tissue Tests
Testing an extract prepared from fresh plant tissue provides a means of
verifying suspected nutrient defi ciencies during plant growth. Plant
tissue testing is discussed in the LaMotte Soil Handbook. The necessary
information for testing nitrate nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in
green plant tissues is given below.
These tests are meant to be used in a comparative manner. It is important
to test tissue from healthy plants as well as those from problem plants.
Interpretations should be based on comparison of test results from plants
of the same species and same age, grown in the same general environment.
Since test reactions may vary from species to species, at different stages
of growth, or under different growing conditions, it is not possible to
accurately quantify test results. The color charts should be used in a
comparative manner. Relative values from very defi cient to abundant
have been assigned to the range of possible test reactions under each
factor below.
PREPARATION of TISSUE EXTRACT
1. Select a small lot of the leaf petioles or succulent portion of the
stem. When testing problem plants, collect tissue from those areas
where the abnormality is most observable.
2. Use a clean, sharp knife or a razor blade to cut the material into fi ne
bits not more than
1
/8” to 1/16” in length and thickness.
3. Fill an Extraction Tube (0704) to the lower line with this material.
Do not pack down.
4. Add *Universal Extracting Solution (5173PS) to the upper line. Cap
and shake vigorously for fi ve minutes.
5. Use a piece of fi lter paper (0465) and a plastic funnel (0459), fi lter
the mixture into a second Extraction Tube (0704). This fi ltrate is the
tissue extract to be used in place of the general soil extract in the
nitrate nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium test procedures.
20
Page 21

PLANT TISSUE TEST PROCEDURE
Follow the soil test procedures for nitrate nitrogen, phosphorus, and
potassium, using the tissue extract in place of the general soil extract.
Remember that the color charts should only be used in a comparative
manner, along with the relative values suggested. The most meaningful
test results will be obtained from the comparison of healthy plant and
problem plant test reactions.
Guidelines for Interpreting Plant Tissue Tests
Relative Amount of
Nutrient in Plant
Test Factor Test Reaction
Tissue
Nitrate Nitrogen Dark Pink Color Abundant
Light Pink Color Adequate
Colorless No Reserve/Probably
Defi cient
Phosphorus Deep Blue Color Abundant
Light Blue Color Adequate
Yellow to Colorless Low to Defi cient
Potassium Heavy Precipitate Adequate to Abundant
Medium Precipitate Low to Defi cient
Trace Precipitate Defi cient
No Precipitate Very Defi cient
21
Page 22

Soil Test Reagents
This information is provided to enable the soil analyst to correlate
LaMotte soil test results with results obtained using other soil test
procedures.
Soil Extraction Procedure - The *Universal Extracting Solution (5173)
is composed of sodium acetate which has been adjusted to a pH of 4.8
with acetic acid. This solution extracts the soluble nutrients, such as
phosphorus and nitrogen, as well as soluble and exchangeable potassium
and other cations, such as calcium and magnesium.
Potassium Test - The Potassium test is based on the fact that potassium
salts give a yellow crystalline precipitate with sodium cobaltinitrite,
*Potassium Reagent B Tablets (5161A). *Potassium Reagent C (5162) is
denatured ethyl alcohol which facilitates the formation of the precipitate
in more or less colloidal form.
Phosphorus Test - Phosphates react with ammonium molybdate,
*Phosphorus Reagent 2 (5156), to produce salts of a complex
ammonium phosphomolybdate, which produce the blue molybdenum
oxide color when reduced. *Phosphorus Test Tablets (5706A),
the reducing agent, are stannous chloride.
Nitrate Test - The Nitrate test is based on the so-called Denige’s test
in which two dye intermediates are coupled in the di-azo reaction to
form a color dyestuff. The nitrite required in this reaction is supplied by
reduction of the nitrate in the soil extract. *Nitrate Reagent #1 (5146) is
a solution of potassium acid sulfate. *Nitrate Reagent #2 Powder (5147)
is a mixture of the two intermediates, N(1-naphthyl)-ethylene-diamine
dihydrochloride and sulfanilamide; the reducing agent, which is zinc
dust; and the fi ller, which is barium sulfate.
Humus Test - In the humus test the disodium salt of ethylene diamine
tetraacetic acid, *Humus Screening Reagent Powder (5119), extracts
the dark colored humus fraction from the soil. This is measured against
a special color comparator which has been calibrated to give a general
relationship between this color and the content of organic matter.
Soil pH Test - Sensitive short range pH indicators are used to measure
the pH of a distilled water soil extract. Barium Sulfate is used to
accelerate settling of the soil water mixture.
Calcium Test - *Calcium Test Solution (5108PS) is sodium oxalate,
which reacts with calcium to form a precipitate of Calcium Oxalate.
Ammonia Nitrogen Test - *Ammonia Nitrogen Test Solution
(5103PS) is Nessler’s Reagent.
22
Page 23

Magnesium Test - The dye Titian Yellow, *Magnesium Test Solution 1
(5140), is absorbed on the precipitated magnesium hydroxide which
is formed when *Magnesium and Manganese Test Solution #2 (5145WT),
sodium hydroxide is added. The degree of color in the test reaction
depends on the amount of precipitate formed.
Manganese Test - Manganese is oxidized by the Manganese Periodate
Reagent (6311) to form permanganate.
Aluminum Test - *Aluminum Test Solution (5101) is an alcoholic
solution of hematein.
Nitrite Nitrogen Test - *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent 1 (5151WT) is
hydrochloric acid. *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent 2 (5152WT) is Lombard’s
Solution, which consists of sulfanilic acid, ammonium chloride, and
phenol. *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent 3 (5153WT) is sodium hydroxide.
A yellow dye is formed when nitrite is present.
Ferric Iron Test - *Ferric Iron Test Solution (5116PS) is potassium
thiocyanate, which reacts with iron to give the colored ferric thiocyanate.
Sulfate Test - *Sulfate Test Solution (5171) is barium chloride, which
reacts with sulfate to form the precipitate, barium sulfate.
Chloride Test - Deionized water is used as the extracting solution.
*Chloride Test Solution (5111) is silver nitrate, which reacts to form the
precipitate, silver chloride.
23
Page 24

LaMOTTE COMPANY
Helping People Solve Analytical Challenges
PO Box 329 • Chestertown • Maryland • 21620 • USA
800-344-3100 • 410-778-3100 (Outside USA.) • Fax 410-778-6394
Visit us on the web at www.lamotte.com
36070 • 10/14
 Loading...
Loading...