LaMotte SL-P70 User Manual


Table of Contents
Introduction.........................................1
MultipleSampleTesting................................2
TestMethods ........................................2
AvailableNutrients ...................................2
SoilSampling&Preparation............................2
pH.................................................3
ExtractionProcedure..................................5
NitrateNitrogen......................................6
Potassium...........................................7
Phosphorus..........................................9
Humus ............................................10
Magnesium.........................................11
Calcium ...........................................12
Sulfate.............................................14
Aluminum .........................................15
Chlorides ..........................................16
FerricIron..........................................17
NitriteNitrogen.....................................18
Ammonia Nitrogen ..................................19
Manganese.........................................20
UnitsofMeasure.....................................21
Fertilizer Application Rates ............................22
GreenPlantTissueTests...............................23
Soil Test Reagents....................................25
LaMOTTE COMPANY
Helping People Solve Analytical Challenges
PO Box 329 • Chestertown • Maryland • 21620 • USA
800-344-3100 • 410-778-3100 (Outside U.S.A.)
Visit us on the web at www.lamotte.com
© 2001 LaMotte Company • Printed in U.S.A. • 04.01 • Code 36070
i
®

Introduction
This instruction manual is designed for use with the LaMotte
STH Series of professional soil testing outfits. The basic Model
STH-4 Outfit (Code 5029) tests soil for pH, nitrate nitrogen,
phosphorus, and potassium. Intermediate STH outfits combine
these four tests with tests for other important plant nutrition
factors. The Model STH-14 Outfit (Code 5010-01) analyzes for
all of the factors listed above. This manual also includes special
instructions for testing nitrate, phosphorus, and potassium in
green plant tissues.
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered
hazardous substances. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are
supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label and
accompanying MSDS before using.
Note: Some reagents in this kit are dispensed with screw-cap
pipets that are packaged separately .
Place the screw-cap glass pipets (0341) on the following reagents:
5156 *Phosphorus Reagent #2
5101 *Aluminum Test Solution
5140 *Magnesium Test Solution #1
Place the screw-cap plastic pipets (0392) on the following
reagents:
5146 *Nitrate Reagent #1
5108PS *Calcium Test Solution
5151PS *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent #1
5152PS *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent #2
5153PS *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent #3
5171 *Sulfate Test Solution
5116PS *Ferric Iron Test Solution
5103PS *Ammonia Nitrogen Test Solution
5145PS *Magnesium and Manganese Solution #2
1

Multiple Sample Testing
When extracts from two or more samples are being tested
simultaneously use separate pipets for each extract. Mixing
samples will cause false test results. Multiple test tubes, pipets, and
spot plates have been provided to facilitate proper analytical
technique.
Test Methods
Color chart methods are used for all tests except for Potassium.
The reaction is performed in a tube or on a spot plate and the
resulting color is compared to a laminated color chart.
The Potassium test measures the amount of turbidity in a sample
relative to the potassium content.
Available Nutrients
All tests measure the portion of the nutrient in the soil that would
be “available” for the plant to use. Since extraction is not
complete, the amount that is measured is relative, dependent on
the extraction procedure.
Soil Sampling & Preparation
Carefully follow the soil sampling procedures discussed in detail in
the LaMotte Soil Handbook. For sampling greenhouse soils, the
following specialized procedure is recommended.
Collect greenhouse samples prior to watering. Remove any mulch
covering the soil, and then use a soil sampling tube or spoon to
take a sample from the entire plant rooting space, top to bottom.
A composite sample insures representative test results.
Thoroughly mix 8 to 10 individual samples, and then spread the
composite sample on a sheet of paper or plastic to dry. Allow the
sample to air dry overnight. Do not oven dry the sample. Sift the
dried sample through a wire screen mesh similar to as a window
screen.
2

Test Procedures
pH
pH is a measure of acidity or basicity. Soils can have a pH from 3.5
to 11.0, but plants grow well in the range of 5.0 to 8.5. In soils
with a low pH (acidic), some nutrients can reach toxic levels and
the activity of soil microbes is greatly reduced. Soils with a high
pH (alkaline) generally have a lower micro-nutrient availability
and some levels may be deficient.
Procedure:
1. Fill a test tube (0204) approximately one-third full of soil. Use
the Demineralizer Bottle (1155) to add demineralized water
to the tube, until it is one-half inch from the top. Cap and
shake until the soil is well dispersed.
2. Add 5 drops of Soil Flocculating Reagent (5643WT). Cap
and shake to mix. Allow contents to settle before proceeding
to Step 3.
3. Use a 1 mL pipet (0354) to transfer 1 mL of the clear solution
above the soil to one of the large depressions on a spot plate
(0159). T ransfer a second 1 mL sample to the other large
depression on the spot plate.
4. To the first sample on the spot plate, add two drops of
*Duplex Indicator (2221). Compare the resulting color
reaction against the Duplex Color Chart (1313).
3
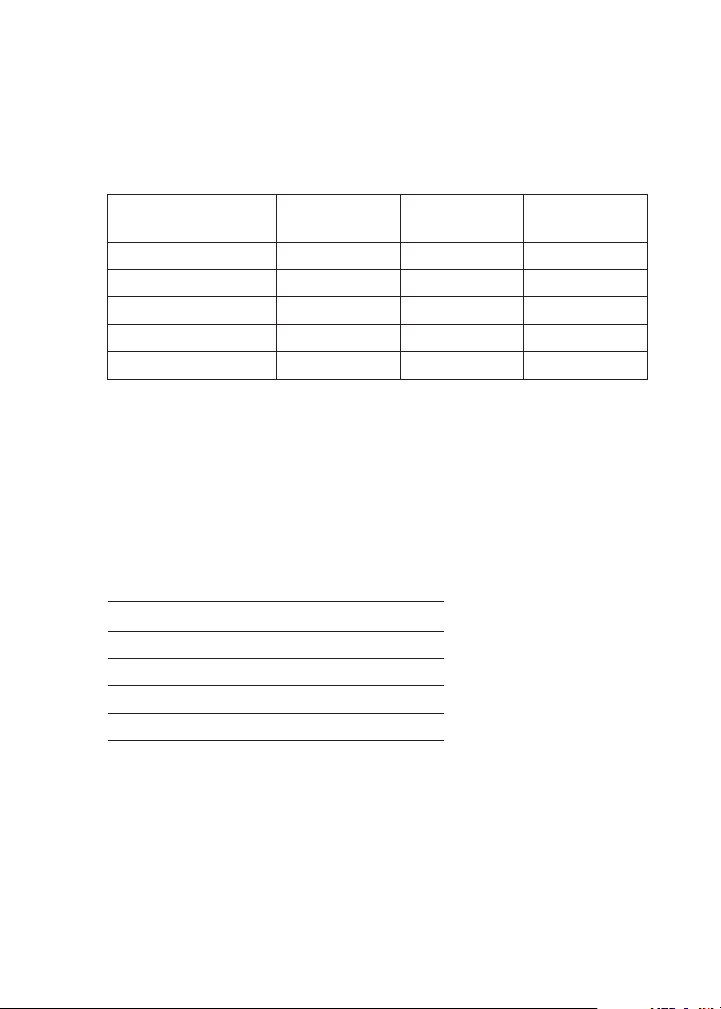
Note: The wide range pH test result indicates which narrow
range indicator and color chart should be selected to perform
a more precise pH test. Choose the narrow range indicator
and appropriate chart with a mid-point that is as close as
possible to the value obtained in the wide range test.
Indicator pH Range
Bromcresol Green 3.8-5.4 2207 1328
Chlorphenol Red 5.2-6.8 2209 1329
Bromthymol Blue 6.0-7.6 2210 1331
Phenol Red 6.8-8.4 2211 1332
Thymol Blue 8.0-9.6 2213 1335
Indicator
Code
Color
Chart Code
Example: If the wide range test result is pH 6.0, choose the
Chlorphenol Red Indicator (2209) & the Chlorphenol Red
Color Chart (1329) for Step 5.
5. Add two drops of the chosen narrow range indicator to the
second sample on the spot plate. Compare the resulting color
reaction against the appropriate color chart to obtain a precise
soil pH reading.
Interpretation of pH Reading:
If the pH is Then the soil is
Below 5.5 Strongly Acid
5.5-6.0 Moderately Acid
6.1-7.0 Slightly Acid
Above 7.0 Alkaline
4

Extraction Procedure
The following extraction procedure uses *Universal Extracting
Solution (5173PS) to produce a single soil extract which is used
in all of the following tests: nitrate nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen,
nitrite nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium,
sulfate, aluminum, iron, and manganese. The pH, chloride,
humus, and plant tissue tests use extraction procedures described
in the individual instructions for those tests.
The Extraction Tubes (0704) are marked at 7 and 14 mL. The
instructions below assume that a number of tests will be performed
with the general soil extract. Therefore 14 mL of extracting
solution and two level measures of the soil sample are called for in
Steps 1 & 2. If only a single test is to be performed (e.g., nitrate
nitrogen), fill the extraction tube to the 7 mL line (Step 1) and
add only one level measure of the soil sample (Step 2).
Procedure:
1. Fill an Extraction Tube (0704) to the 14 mL line with
*Universal Extracting Solution (5173PS).
2. Use the plastic soil measure (0819) to add two level measures
of the soil sample. Cap and shake for one minute.
3. Use a piece of filter paper (0465) and a plastic funnel (0459)
to filter the soil suspension into a second extraction tube
(0704). (Fold the filter paper in half and then in half again to
form a cone which is fitted into the funnel.) The filtrate in
the second extraction tube is the general soil extract for use in
the 11 individual test procedures listed previously.
5

Nitrate Nitrogen
The role of nitrogen in plant nutrition is discussed in the LaMotte
Soil Handbook. For interpretation of test results see the LaMotte
Soil Handbook and page 22 of this manual.
Procedure:
1. Use a 1 mL pipet (0354) to transfer 1 mL of the general soil
extract to one of the larger depressions on a spot plate (0159).
2. Add 10 drops of *Nitrate Reagent #1 (5146).
3. Use a 0.5 g spoon (0698) to add one level measure of *Nitrate
Reagent 2 Powder (5147).
4. Stir thoroughly with a clean stirring rod (0519). Allow to
stand five minutes for full color development.
5. Match sample color with the Nitrate Nitrogen Color Chart
(1315). Record as pounds per acre nitrate nitrogen.
6

Potassium (Potash)
The role of potassium (potash) in plant nutrition is discussed in
the LaMotte Soil Handbook. For interpretation of test results, see
the LaMotte Soil Handbook and page 22 of this manual.
When present in large amounts, ammonia salts will produce a
precipitate similar to that produced by the potassium. If fertilizer
containing ammonia salts has recently been applied, or if the soil
pH is below pH 5.0, perform the Ammonia Nitrogen test (page
19) before performing the potassium test. A high ammonia
nitrogen test result will alert the operator to a probable false high
reading in the potassium test; actual potassium levels will be
somewhat lower.
It is important that the temperature of the test sample and the
*Potassium Reagent C (5162) be in the range of 20-27°C
(68-80°F). On warm days, prior to Step 3 below, cool both the
test sample in the Potash “A” Tube and the Reagent C contained
by placing them in cool water .
7
 Loading...
Loading...