Page 1

LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
BioPaddles™ Colony Identification App
SAB/SAB
Code 5551
USE:
Selective isolation of fungi (yeasts and molds) (SAB)
Side 1 & 2: Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SAB) (colorless / slightly hazy)
APPLICATION
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SAB) is a modification of dextrose agar described by Sabouraud.1 SAB is used for cultivating
pathogenic and commensal fungi and yeasts. The high dextrose concentration and acidic pH of the formula permit
selectivity of fungi.2 Sabouraud Dextrose Agar is used for determining the microbial content of cosmetics,3 in the
mycological evaluation of food,4 and clinically to aid in the diagnosis of yeast and fungal infections.5
PADDLE AGARS
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SAB) – Enzymatic digest of casein and enzymatic digest of animal tissue provide the nitrogen
and vitamin source required for organism growth in SAB. The high concentration of dextrose is included as an energy
source. Agar and a proprietary polymer are the solidifying agents.
CULTURE CONTROLS
10-300 inoculum (CFU)
SAB Agar
Aspergillus niger GROWTH
Candida albicans GROWTH
Escherichia coli INHIBITED
Microsporum canis GROWTH
Trichophyton mentagrophytes GROWTH
1
Sabouraud, R. 1892. Ann. Dermatol. Syphilol. 3:1061.
2
Jarett, L., and A. C. Sonnenwirth (eds.). 1980. Gradwohl’s and parasitic infections, 7th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
3
Curry, A. S., J. G. Graf, and G. N. McEwen, Jr. (eds.). 1993. CTFA Microbiology Guidelines. The Cosmetic, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association, Washington, D.C.
4
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 1995. Bacteriological analytical manual, 8thed. AOAC International, Gaithersburg, MD.
5
Murray, P. R., E. J. Baron, M. A. Pfaller, F. C. Tenover, and R. H. Yolken (eds.). Manual of clinical microbiology, 6th ed. American Society for Microbiology,
Washington, D.C.
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 1
Page 2

LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
STORAGE / EXPIRATION
Store tightly sealed BioPaddles™ in a cool, dry location. Shield from direct sunlight. Store BioPaddles™ at room
temperature (65 - 77°F/18 - 25°C). Avoid sudden temperature changes. Temperature fluctuations may result in
condensation settling at the bottom of the vial. This will not affect the culture properties, but could reduce the shelf-life or
cause the agar to separate from the plastic paddle support. Do not refrigerate. Refrigeration may result in water
condensation. Avoid freezing. If freezing occurs, thaw for 3-6 hours in the refrigerator (40°F; 4.4°C). Freezing can promote
excess water loss and variation in media surface due to crystal formation.
Refer to Best Before End date (See: BBE stamped on vial). Discard if paddle agar appears oxidized and darker than the
expected color or if contaminants appear. The expiration date is based on medium in an intact container that is stored as
directed.
SAMPLING
Liquids: Twist to remove paddle from vial. Fill vial to 40 mL fill line with the liquid
to be sampled. The 40 mL volume can be used to calculate Total Viable Count
(TVC) and/or Total Colony Count (TCC). Replace paddle. Allow a contact time of
15 seconds. Remove the paddle. Empty the vial. Replace the paddle in the vial.
Surfaces: Twist to remove paddle from vial. Allow the paddle surface (10 cm2) to come into physical contact with the test
surface. Recovery rate is about 50%. To ensure an accurate recovery, gently sweep (or touch) the paddle to cover a 20 cm2
area. Replace paddle in vial.
INCUBATION
Temperature Minimum Period Optimal Period
35°C (bacteria) 72 hours 5-7 days
20-25°C (fungi) 5 days 7 days
COLONY MEASURING
Each BioPaddles™ paddle has molded media attachment points that are 4mm
in length (point-to-point). This feature provides a useful guidepost to estimating
nearby colony size.
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 2
Page 3
A
A
IDENTIFICATION
ORGANISM
ORGANISM
PHYSIOLOGY
◆
Precision Test Strip
Available
GROWTH
COLONY
LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
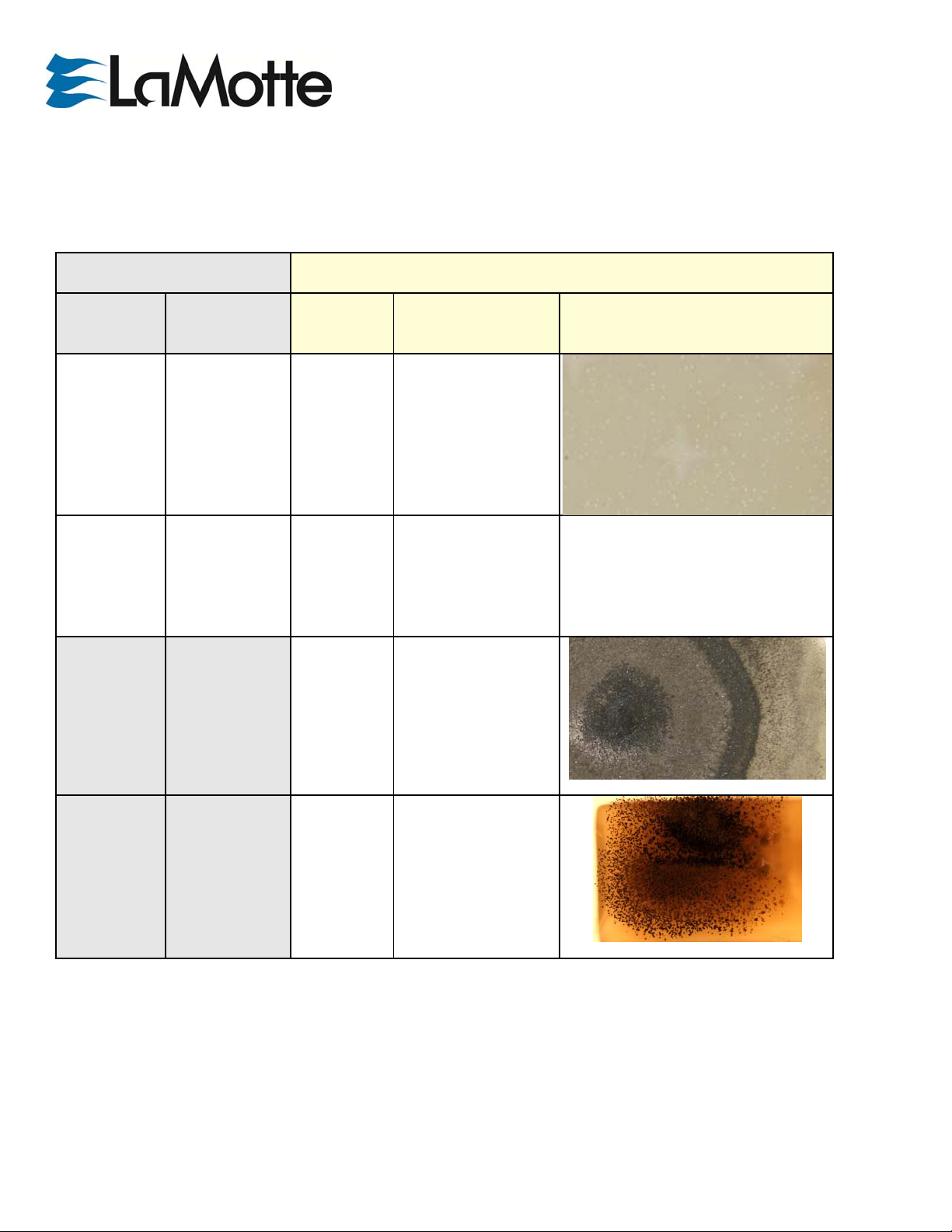
SAB
IMAGE
B. subtilis
E. coli
lternaria spp.
spergillus niger
• Lactose (-)
• Indole (-) ◆
• Oxidase (-) ◆
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Urease (+) ◆
• Gram (+) Rod
• Lactose (+)
• Indole (+) ◆
• Oxidase (-) ◆
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Urease (-) ◆
• Gram (-) Rod)
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
•
Catalase (+) ◆
•
Ascomycete
+++
PARTIAL COMPLETE
INHIBITION
++
+++
• Translucent to dull, off-white;
opaque
• Smooth to rough
• irregular / dendroid margins
to spreading
• 2-4mm
---
• Downy to woolly; flat
• Grayish, short, aerial hyphae
• later becomes greenish black
or olive brown with a light
border
• 2-5++cm
• Granular
• White, w/ jet black fruiting
bodies w/ yellow/gray hyphae
• 2-5++cm
---
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 3
Page 4

A
A
A
ORGANISM
ORGANISM
PHYSIOLOGY
◆
Precision Test Strip
Available
GROWTH
COLONY
LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
SAB
IMAGE
spergillus flavus
spergillus
fumagatus
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+++
+++
• Granular to wooly
• Yellow, yellow-green or
yellow-brown pigment
• 2-5++cm
• Granular to cottony
• Blue-green, green-gray,
green-brown pigment
• 2-5++cm
spergillus terreus
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+++
• Granular, radially rugose
(wrinkled)
• Cinnamon buff, brown
pigment
• 2-5++cm
IMAGE PENDING
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 4
Page 5

ORGANISM
ORGANISM
PHYSIOLOGY
◆
Precision Test Strip
Available
GROWTH
COLONY
LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
SAB
IMAGE
Botrytis spp.
Candida albicans
Chaetomium spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+++
+++
+++
• Wooly
• white, grey/brown pigment
• 2-5++cm
• White to cream
• Smooth /Spreading
• 2-6mm
• Wooly
• white, grey/olive pigment
• 2-5cm
Cladosporium spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+
• Granular to wooly (velvety)
• Olive-brown to blackish-brown
(sometimes gray) on a dark
base
• 2-5++cm
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 5
Page 6

ORGANISM
ORGANISM
PHYSIOLOGY
◆
Precision Test Strip
Available
GROWTH
COLONY
LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
SAB
IMAGE
Epicoccum spp.
Fusarium spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+++
+++
• Wooly / Cottony / Felty
• yellow, orange, red, brown
pigment
• 2-5++cm
• Wooly / Flat (sometimes
mucous-like)
• White, yellow, pink, purple, or
pale brown pigment
• 1-2cm
Microsporum spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+
Muccor spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Zygomycete
+++
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
• Glaborous (smooth) / Downy /
Wooly / Powdery
• White at first, later becoming
grayish yellow to blue green
with age
• 1-9+cm
• Wooly, Fluffy (like cotton
candy)
• White at first, later becoming
grayish yellow to blue green
with age
• 2-5++cm
Page | 6
Page 7

ORGANISM
ORGANISM
PHYSIOLOGY
◆
Precision Test Strip
Available
GROWTH
COLONY
LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
SAB
IMAGE
Penicillium
chrysogenum
(notatum)
Penicillium
roqueforti
Penicillium
digittum
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
++
++
+++
Granular, velvet-
like/powdery, flat
• Initially white, then various
shades of green blue-green or
yellow-green pigment
• 2-5++cm
• Granular, dull green in color
arachnoid (with many spiderweb-like fibers) colony margins)
• 2-5++cm
• Wooly, Fluffy (like cotton
candy)
• White at first, later becoming
green with age
• 2-5++cm
Rhizopus spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Zygomycete
+++
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
• Cottony
• White to blackish grey (black
fruiting bodies)
• 5++mm (rapidly spreading)
Page | 7
Page 8

ORGANISM
ORGANISM
PHYSIOLOGY
◆
Precision Test Strip
Available
GROWTH
COLONY
LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
SAB
IMAGE
Saccharomyces
cerevisiae
Stachybotrys spp.
Torula spp.
Trichoderma spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+++
++
+
++
• Creamy white to tannishcream
• Circular, entire, raised to
convex, w/ glistening surface
• 1-4mm
• Dark gray
• Powdery
• white, pink, orange, black
pigment
• 2-5++cm
•Arrowhead / Circle or Heart
shape
• Grey, white to brown pigment
with age
• 2-5++cm
•
Cottony
•
White / later scattered green
or yellow-green patches (rings)
•
2-5++cm
IMAGE PENDING
•
Trichophyton spp.
• Catalase (+) ◆
• Ascomycete
+
Wooly with indented boarders
•
White to brownish-tan pigment
•
2-5++cm
\
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 8
Page 9

ENUMERATION
SAB
Very Light Light Moderate
TVC/TCC
LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
TVC/TCC
(Total Viable Count/
Total Colony Counts)
Colony Counts <1000
Count colonies
TVC/TCC Count = Count x 2.5
Colony Counts >1000
Use chart
TVC/TCC Count = Count x 2.5
(Based on a 40 mL sample)
Example:
Inoculated NUT/TTC
paddle showing
approximately 1000
CFU/100 mL.
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 9
Page 10

LaMotte BioPaddles™ TECH DOCUMENT
Call: 800-344-3100
Email: tech@lamotte.com
DISPOSAL
Twist to remove paddle from vial. Fill vial to 40 mL fill line with 1:9 dilution of household bleach (5.25% sodium hypochlorite).
Replace paddle in vial. Allow 15 minute contact time. Remove paddle. Discard bleach solution. Replace paddle in vial and
dispose. Alternatively, loosen cap and microwave for 30 seconds, autoclave, or incinerate.
GLOSSARY:
Catalase Test Catalase enzyme will react with hydrogen peroxide to produce oxygen if the bacteria is
catalase positive.
Lactose Test Lactose positive bacteria can ferment available lactose in the agar producing an acid which
lowers the pH. Lactose negative bacteria are non-fermenting.
Indole Test Biochemical test to determine the ability of an organism to split indole from the amino acid
tryptophan. P. vulgaris is indole positive while P. mirabilis is indole negative.
Oxidase Test Oxidase positive bacteria contain cytochrome c oxidase which will turn an indicator dark blue. In
contact with oxidase negative bacteria, the indicator will remain colorless.
Urease Test Bacteria containing urease will hydrolyze urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide
causing an alkaline environment which changes the color of a pH indicator from yellow to fuchsia.
β-D-Glucoronidase The presence of E. coli is determined when both β-D-Glucoronidase and Indole
Reaction are positive, and the organism is gram negative.
Gram Staining A method for differentiating bacteria into two groups – gram positive and gram negative –
based on the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. Often the first step in identifying
bacteria.
For in vitro diagnostic use only. This product should be used only by adequately trained personnel with knowledge of microbiological techniques in the laboratory.
©LaMotte BioPaddles. All rights reserved.
LaMotte_BioPaddles_SAB_SAB 9.12
Page | 10
 Loading...
Loading...