Page 1
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
MULTI-FUNCTION TESTER
KEW 6016
Page 2

Fig.55
Fig.56
Fig.54
CONTENTS
1. Safe Testing ............................................................................................................. 1
2. Instruments Layout ....
3. Accessories ............................................................................................................. 5
4. Features .................................................................................................................. 6
5. Specification ..............................
5.1 Measurement Specification .............................................................................. 8
5.2 Operating error ............................................................................................... 11
5.3 General Specification .........................................................
5.4 Applied standards ........................................................................................... 14
5.5 List of Display Message ................................................................................. 15
6. Configuration ......................................................................................................... 16
7. Continu
7.1 Test procedure ............................................................................................... 17
7.2 2Ω Buzzer ..................................................................................................... 19
8. Insulation tests .............................
8.1.1 The nature of insulation resistance ............................................................. 20
8.1.2 Capacitive current ....................................................................................... 20
8.1.3 Conduction current .....................................................................
8.1.4 Surface leakage current .............................................................................. 21
8.1.5 Total leakage current ................................................................................... 21
8.2 Damage to voltage sensitive equipment ........................................................ 22
8.3 Preparation for measurement ..........
8.4 Insulation resistance measurement ............................................................... 23
9. LOOP/PSC/PFC test ............................................................................................. 26
9.1 Principles of measurement of fault loop impedance and PFC ....................... 26
9.2 Principles of
9.3 Operating instructions for LOOP and PSC/PFC ............................................ 32
9.3.1 Initial Checks ............................................................................................... 32
9.3.2 Measurement of LOOP and PSC/PFC ........................................................ 34
10. R
10.1 Principles of RCD Measurement .................................................................. 37
10.2 Principles of Uc Measurement ..................................................................... 39
10.3 Operating Instructions for RCD ......................
10.3.1 Initial Checks ............................................................................................. 39
10.3.2 RCD Measurement ................................................................................... 41
ity(resistance) tests ................................................................................... 17
CD tests .............................................................................................................. 37
.............................................................................................. 3
.............................................................................. 8
............................ 13
......................................................................... 20
................. 21
.............................................................. 23
measurement of line impedance and PSC ................................ 31
.............................................. 39
Page 3

11. Earth tests ............................................................................................................. 43
11.1 Principles of Earth Measurement ................................................................. 43
11.2 Earth resistance Measurement .................................................................... 43
12. Phase Rotation tests .............................
13. Volts ....................................................................................................................... 46
14. Touch Pad ............................................................................................................. 46
15. Back Light ..........................................................
16. Memory Function .................................................................................................. 47
16.1 How to save the data ................................................................................... 47
16.2 Recall the saved data ................................................................................
16.3 Delete the saved data .................................................................................. 50
16.4 Transfer the stored data to PC ..................................................................... 52
17. General ................................................................................................................. 53
18. Battery replacement ..............
19. Fuse replacement ................................................................................................. 54
20. Servicing ............................................................................................................... 55
21. Case and strap assembly ......................................
The KEW6016 incorporates Anti Trip Technology (ATT) which electronically bypasses
RCDs when performing loop impedance tests. This saves time and money by not having
to take the RCD out of the circuit during testing and is a safer procedure to follow.
With the ATT function enabled , a test of 15mA or less is applied between line & earth.
It enables
above.
Please read this instruction manual carefully before using this equipment.
loop impedance measurements without tripping RCDs rated at 30mA and
................................................................................ 54
................................................................ 45
................................................... 46
... 49
................................................ 56
Page 4

1
1. SAFE TESTING
Electricity is dangerous and can cause injury and death. Always treat it with the
greatest of respect and care. If you are not quite sure how to proceed, stop and
take advice from a qualified person.
1 This instrument must only be used by a competent and trained person and operated
in strict accordance with the instructions. KYORITSU will not accept liability for any
damage or inj
the safety procedures.
2 It is essential to read and to understand the safety rules contained in these
instructions. They must always be observed when using the instrument.
3 This instrument is designed to work in distribution systems where the line to earth
has a maximum voltage of 300V 50/60Hz and for some ranges where line to
has a maximum voltage of 500V 50/60Hz.
Be sure to use it within this rated voltage.
For use in the continuity testing and insulation testing modes this instrument must
be used ONLY on circuits which are de-energized.
4 When conducting tests do not touch any exposed metalwork associated with the
installation. Such metalwork may become live for the duration of the test.
5 Never open the instru
this case disconnect all leads first) because dangerous voltages are present. Only
fully trained and competent electrical engineers should open the case. If a fault
develops, return the instrument to your distributor for inspection and repair.
6 If the overheat symbol appears in the display disconnect the instrument from the
mains supply an
7 If abnormal conditions of any sort are noted (such as a faulty display, unexpected
readings, broken case, cracked test leads, etc) do not use the tester and return it to
your distributor for repair.
8 For safety reasons only use accessories (test leads, probes, fuses, cases, etc)
designed to be used with this instrument and recommended by KYORITSU. The
use of other accessor
features.
9 When testing, always be sure to keep your fingers behind the finger guards on the
test leads.
10 During testing it is possible that there may be a momentary degradation of the
reading due to the presence of excessive transients or discharges on the electrical
system under test. Should this be observed, the test must be r
correct reading. If in doubt, contact your distributor.
ury caused by misuse or non-compliance with the instructions or with
line
ment case (except for fuse and battery replacement and in
d allow to cool down.
ies is prohibited as they are unlikely to have the correct safety
epeated to obtain a
Page 5

2
11 Do not operate the function selector while the instrument is connected to a circuit.
If, for example, the instrument has just completed a continuity test and an insulation
test is to follow, disconnect the test leads from the circuit before moving the selector
switch.
12 Do not rotate rotary switch when test button is depressed. If the function switch is
inadvertently moved to a new function w
down position the test in progress will be halted.
13 Always check the test lead resistance before carrying out tests. This ensures the
leads are ok before taking measurements. The resistance of leads and/or crocodile
clips may be significant when measuring low resistances. If crocodile clips can be
avoided for low resistance measurements, this will redu
accessories
14 When carrying out Insulation Resistance tests, always release the test button and
wait for charged capacitances to totally discharge before removing the test leads
from the test circuit.
hen the test button is depressed or in lock-
ce the error due to lead
Page 6

3
2. INSTRUMENT LAYOUT
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
Name Operation
Fig.1
(1) Back Light Button Switches on/off the Backlight of the Display(LCD)
(2) Test Button Starts measurements. (press and rotate for lock
down feature)
(3) Touch Pad Checks the electrical potential at the PE terminal
(4) Power Switch Power Switch
(5) Function Switch Function setting (F1 ~ F4)
(6) Display (LCD) Dot Matrix LCD 160(W)X240(H)
(7) Insulation resistance LED Alerts that the test voltage is
(8) Rotary Switch Selects measurement functions.
(9) MEM (ESC) Button Activates Memory Function, or ESC Key
being output
Page 7
4
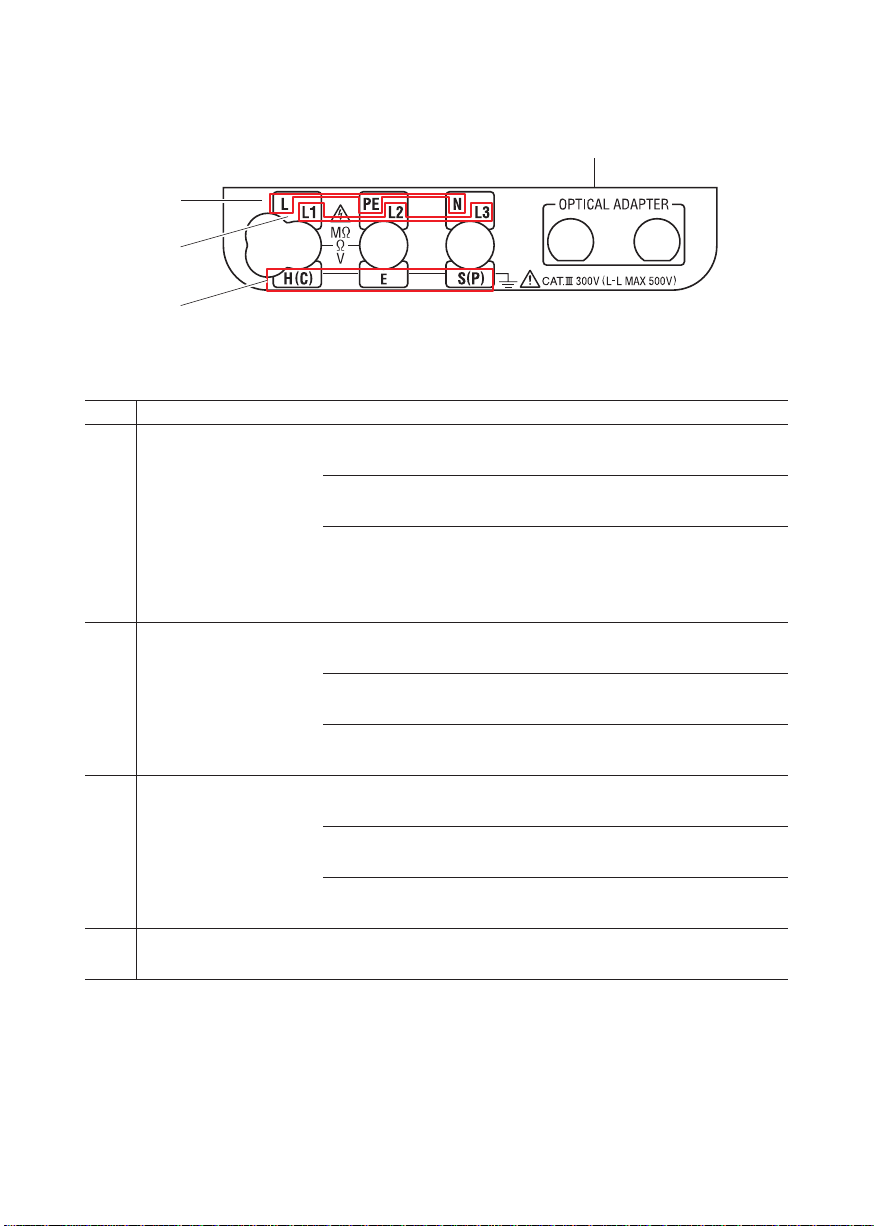
Input Terminal
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Function Terminal
Terminal Names for :
INSULATION,
CONTINUITY
LOOP,
(1)
PFC/PSC,
RCD,
VOLTS
Fig.2
L : Line
PE : Protective Earth
N : Neutral (for LOOP,PSC/PFC, RCD)
L1 : Line1
Terminal Name for
(2)
PHASE ROTATION
Terminal Name for
(3)
EARTH
(4) Optical Adapter Com
L2 : Line2
L3 : Line3
H(C) : Terminal for auxiliary earth spike (current)
E : Terminal for the earth under test
S(P) : Terminal for auxiliary earth spike (potential)
munication port for Model8212USB
Page 8
5
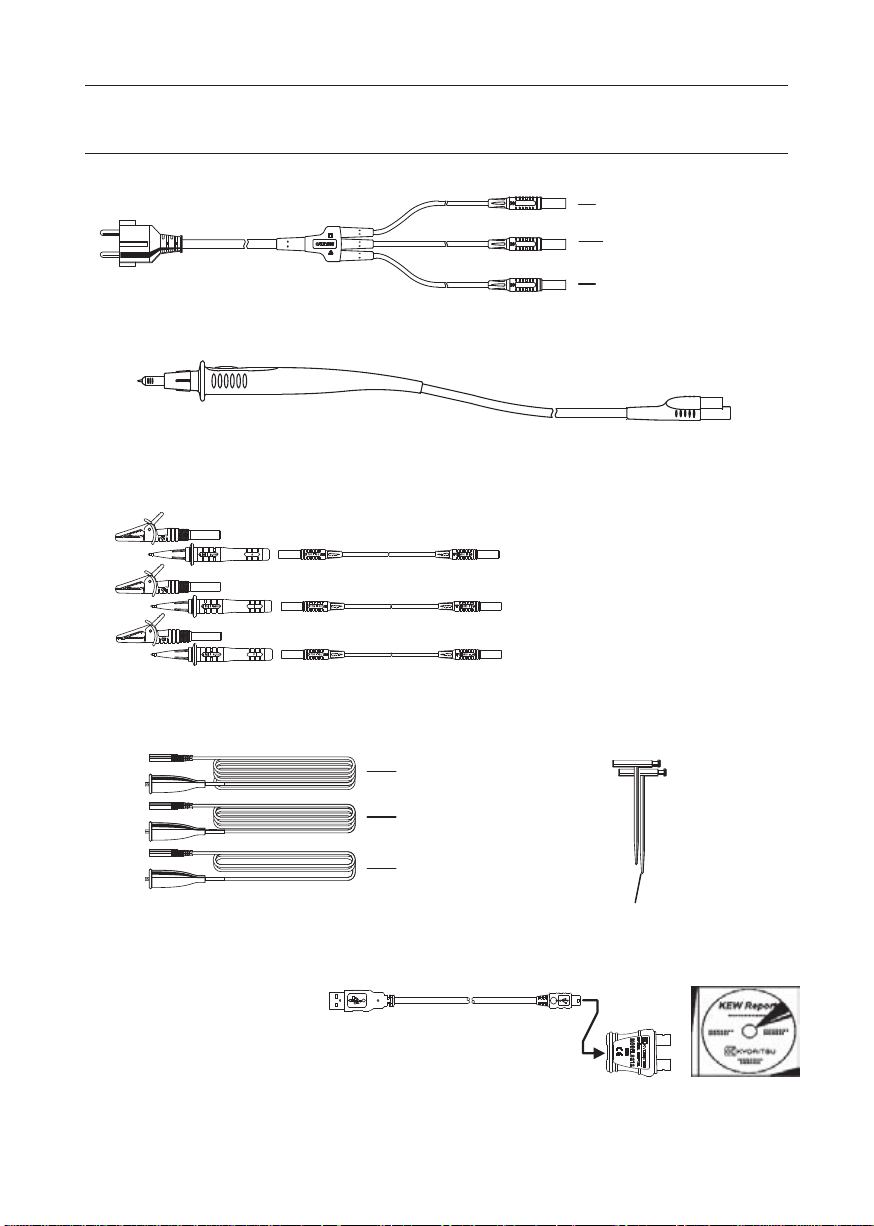
3. Accessories
Blue(Neutral)
Red(Line)
Green(Protective Earth)
Blue(Neutral or L3)
Green(Protective Earth or L2)
Red(Line or L1)
Yellow S(P)10m
Green E 5m
Red H(C) 20m
Auxiliary Earth Spikes x2
1.Main Test Lead (Model7218)
2.Remote Test Lead (Model 7196)
Fig.3
Fig.4
3.Distribution Board fused test lead (Model7188)
(Fuse: 10A/600V fast acting ceramic)
Fig.5
4. Earth Tests Lead(Model7228) and Auxiliary Earth Spikes
Fig.7
Fig.6
5.Test Lead Carry pouch・・・x1
6.Carrying Bag・・・x1
7.Instruction Manual・・・x1
8.Shoulder Strap・・・x1
9.Buckle・・・x2
10.Battery・・・x8
11.Model8212USB with PC Software KEW Report.
Fig.8 Model8212 USB
Page 9

6
4. FEATURES
The KEW6016 Multi-Function tester performs eight functions in one instrument.
1 Continuity tester
2 Insulation resistance tester
3 Loop impedance tester
4 Prospective short circuit current tester
5 RCD tester
6 Voltage tester
7 Phase rotation tester
8 Earth tester
Continuity function has the following features:
Live circuit warning Live Circuit warning on the display.
Fuse Protection Continui
prevent a fuse blow at live working. With this function,
a fuse rarely blow while measuring continuity on live
conductors.
Continuity Null Allows automatic subtraction of test lead resistance from
continuity measurements.
Continuity 2Ω Buzzer Buzzer sounds at 2Ω or less at Continuity function.
(Switchable on or off)
ty Function has a fuse protection function to
Insulation function has the following
Live circuit warning Live Circuit warning on the display.
Auto discharge Electric charges stored in capacitive circuits are
Insulation Resistance LED
LED lights up while making measurements at Insulation
features:
discharged automatically after testing by releasing the test
button.
function and alerts that test voltage is being output.
Page 10

7
Loop impedance, PSC/PFC and RCD testing functions have the following features:
Wiring check Three Wiring symbols indicate if the wiring of the circuit
under test is correct.
Over temperature protection
Phase angle selector The test can be selected from either the positive (0° )
UL value selector Select UL (limit of contact voltage) 25V or 50V. Where Uc
ALL testing functions have the following
Touch Pad Gives an alert, when touching the Touch Pad, while the
Memory Function Save the measured data in the internal memory.
The data can be edited on a PC by using Communication
Auto power off Automatically switches the instrum
Detects overheating of the internal resistor (used for
LOOP and PSC/PFC tests) and of the current control
MOS FET (used for RCD tests) displaying a warning
symbol and automatically halting further m
or from the negative (180° ) half cycle of voltage. This
selector is used in the RCD mode to obtain the maximum
trip time of an RCD for the test selected.
(contact voltage) exceeds UL value at RCD testing, Uc >
UL will be displayed wi
PE terminal is connected to Line by mistake.
Adapter Model8212USB and PC Software KEW Report.
approximately 10 minutes. The Auto power off mode can
only be cancelled by switching the instrument on again.
thout starting the measurement.
easurements.
ent off after a period of
Page 11
8
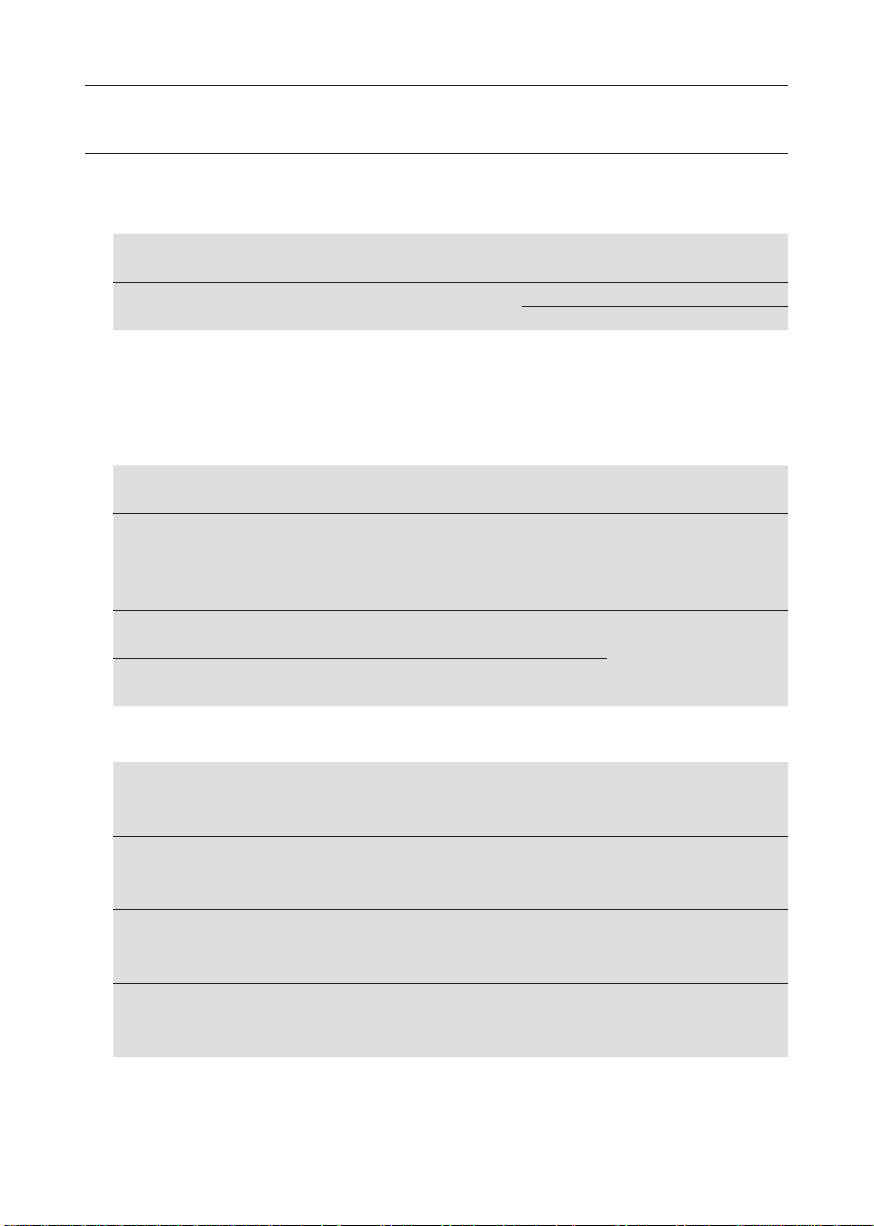
5. Specification
5.1 Measurement Specification
Continuity
Open Circuit
Voltage (DC)
5V±20%(*1)
2Ω Buzzer : Buzzer sounds when measured resistance is 2Ω or less.
2Ω Buzzer Accuracy : 2Ω±0.4Ω
(*1) Voltages are output when measurement resistance is under 2100 ohm.
Insulation Resistance
Open Circuit
Voltage (DC)
250V+25% -0%
500V+25% -0%
1000V+20% -0%
Short Circuit
Current
Greater than
200mA
Rated Current Range Accuracy
1mA or greater
@ 250kΩ
1mA or greater
@ 500kΩ
1mA or greater
@ 1MΩ
Range Accuracy
20/200/2000Ω
Auto-Ranging
20/200MΩ
Auto-Ranging
20/200/2000MΩ
Auto-Ranging
20/200/2000MΩ
Auto-Ranging
0~0.19Ω ±0.1Ω
0.2~2000Ω ±(2%rdg+8dgt)
0~19.99MΩ:
20~200MΩ:
0~199.9MΩ:
200~2000MΩ:
±(2%rdg+6dgt)
±(5%rdg+6dgt)
±(2%rdg+6dgt)
±(5%rdg+6dgt)
Loop Impedance
Function
L-PE
L-PE
(ATT)
L-N / L-L
*2: at 230V
*3: 230V+10%-15%
*4: voltages except for *3
Rated
Voltage
100~260V
50/60Hz
100~260V
50/60Hz
50/60Hz
L-N:100~300V
L-L:300~500V
Nominal Test Current
at 0Ω External Loop:
Magnitude/Duration(*2)
20Ω: 6A/20ms
200Ω: 2A/20ms
2000Ω: 15mA/500ms
L-N: 6A/60ms
N-PE: 10mA/approx. 5s
20Ω: 6A/20ms 20Ω
Range Accuracy
20/200/2000Ω
Auto-Ranging
20/200/2000Ω
Auto-Ranging
(L-N < 20Ω)
±(3%rdg+4dgt) *3
±(3%rdg+8dgt) *4
±(3%rdg+6dgt) *3
±(3%rdg+8dgt) *4
±(3%rdg
±(3%rdg+8dgt) *4
+4dgt) *3
Page 12

9
PSC (L-N/L-L) / PFC (L-PE)
Function
Rated
Voltage
Nominal Test Current
at 0Ω External Loop:
Magnitude/Duration(*5)
Range Accuracy
*5: at 230V
RCD
PSC
PFC
PFC
(ATT)
Function Rated Voltage
Ramp(◢) ±4% ± 10%
100~500V
50/60Hz
100~260V
50/60Hz
100~260V
50/60Hz
X1/2
X1 +2%~+8% 0%~+10%
X5 +2%~+8% 0%~+10%
Auto
230V+10%-15%
50/60Hz
Depending on the accuracy at each function.
Measurement sequence:
X1/2 0°→X1/2 180°→X1 0°→X1 180°→X5 0°→X5 180°
Measurements with x5 are not carried out for RCDs with nominal
current of 100mA or more.
6A/20ms
6A/20ms
2A/20ms
15mA/500ms
L-N: 6A/60ms
N-PE: 10mA/approx. 5s
Trip Current
AC Type A Type
-8%~-2% -10%~0%
2000A/20kA
Auto-Ranging
Accuracy
PSC/PFC
accuracy is
derived from
measured loop
impedance
specification and
measured voltage
specification
Trip Time
±(1%rdg+3dgt)
RCD(Uc)
Function Rated Voltage Range Test Current Accuracy
UC
230V+10%-15%
50/60Hz
100.0V
≦ 1/2I⊿n
(max150mA)
+5% ~ +15%rdg
±8dgt
Page 13

10
RCD Trip Current Duration
Function Type
X1/2
Trip
Current
Duration
(ms)
Earth
Measuring
Frequency
X1
X5
Ramp
(◢)
825Hz
RCD Trip Current Duration
10 30 100 300 500 1000
AC 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000
G
A 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 n.a
AC 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 n.a
S
A 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 n.a
AC 550 550 550 550 550 550
G
A 550 550 550 550 550 n.a
AC 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 n.a
S
A 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 n.a
AC 410 410 410 n.a n.a n.a
G
A 410 410 410 n.a n.a n.a
AC 410 410 410 n.a n.a n.a
S
A 410 410 410 n.a n.a n.a
AC
G
A n.a
AC
S
A n.a
Range Accuracy
20/200/2000Ω
Auto-Ranging
Goes up by 10% from 20% to 110%
00ms×10 times
3
Goes up by 10% from 20% to 110%
500ms×10 times
20Ω range : ±(3%rdg+0.1Ω)
200/2000Ω range : ±(3%rdg+3dgt)
(Auxiliary earth resistance 100±5%)
n.a
n.a
PHASE ROTATION
Rated Voltage Remarks
50-500V
50/60Hz
Volts
Function Rated voltage Measuring Range Accuracy
Volts
Frequency
Correct phase sequence: are displayed 1.2.3 and
Reversed phase sequence: are displayed 3.2.1 and
25~500V
45~65Hz
25~500V
45~65Hz
mark
mark
25~500V ±(2%rdg+4dgt)
45~65Hz ±(0.5%rdg+2dgt)
Page 14
11
Possible number of tests with fresh batteries.
Continuity :Approx. 2000 times min. at load 1Ω
Insulation Resistance :Approx. 1000 times min. at load 1MΩ (1000V)
LOOP/PFC/PSC :Approx. 1000 times min. (ATT)
RCD :Approx. 2000 times min. (G-AC X1 30mA)
EARTH :Approx. 1000 times min. at load 10Ω
VOLT/PHASE ROTATION :Approx. 50H
Reference Conditions
Ambient temperature 23±5℃
Relative humidity 45% to 75%
Nominal system voltage and frequency 230V, 50Hz
Altitude Less than 2000m
5.2 Operating error
Continuity (EN61557-4)
Operating range compliant with
EN61557-4 operating error
0.20~1999MΩ ±30%
The influencing variations used for calculating the operating error are denoted as
follows;
Temperature : 0 ℃ and 35 ℃
Supply voltage : 8V to 13.8V
Maximum percentage
operating error
Insulation Resistance(EN61557-2)
Volt
250V 0.25~199.9MΩ
1000V 1.00~1999MΩ
The influencing variations used for calculating the operating error are denoted as
follows;
Temperature : 0 ℃ and 35 ℃
Supply voltage : 8V to 13.8V
Operating range compliant with
EN61557-2 operating error
Maximum percentage
operating error
±30%500V 0.50~1999MΩ
Page 15
12
Loop Impedance(EN61557-3)
Volt
L-PE 0.50~1999Ω
L-N 0.50~19.99Ω
The influencing variations used for calculating the operating error are denoted as
follows;
Temperature : 0 ℃ and 35 ℃
Phase angle : At a phase angle 0°to 18°
System frequency : 49.5Hz to 50.5Hz
System voltage : 230V+10%-15%
Supply voltage : 8V to 13.8V
Harmonics : 5% of 3rd harmo
5% of 5th harmonic at 180°phase angle
5% of 7th harmonic at 0°phase angle
D.C quantity : 0.5% of the nominal voltage
RCD(EN61557-6)
The influencing variations used for calculating the operating error are denoted as follows
Temperature : 0 ℃ and 35 ℃
Operating range compliant with
EN61557-3 operating error
nic at 0° phase angle
Function Operating error of trip current
X1/2 -10%~0%
X1, X5 0%~+10%
Ramp -10%~+10%
Maximum percentage
operating error
±30%
Earth electrode Resistance (shall not exceed below) :
IΔn (mA)
10 2000 2000
30 600 600
100 200 200
300 130 65
500 80 40
1000 40 20
System voltage: 230V+10%-15%
Supply voltage : 8V to 13.8V
Earth electrode resistance (Ω max.)
UL50V UL25V
Table.1
Page 16

13
Earth Resistance (EN61557-5)
Operating range compliant with
EN61557-5 operating error
5.00~1999Ω ±30%
The influencing variations used for calculating the operating error are denoted as
follows;
Temperature : 0 ℃ and 35 ℃
Series interference voltage : 3V
Resistance of the probes and auxiliary
earth electrode resistance : 100 x RA, 50kΩ or less
Supply voltage : 8V to 13.8V
5.3 General specification In
strument dimensions 235 X 136 X 114mm
Instrument weight:- 1350g (including batteries.)
Reference conditions Specifications are based on the following
conditions except where otherwise stated:-
1. Ambient temperature: 23±5°C:
2. Relative humidity 45% to 75%
3. Position: horizontal
4. AC power source 230V, 50Hz
5. DC power source: 12.0 V, ripple content 1% or less
6. Altitude up to 2000m, Indoor use
Battery typ
Operating temperature
and humidity.
Storage temperature
and humidity
Display Dot Matrix LCD 160(W) X 240(H) pixels.
Overload protection The continuity test circuit is protected by a 0.5A/600V
e Eight LR6 or R6 batteries.
0 to +40℃ , relative humidity 80% or less, no condensation
-20 to +60 ℃ , relative humidity 75% or less, no condensation.
fast acting (HRC) ceramic fuse mounted in the battery
compartment, wh
The insulation resistance test circuit is protected by a
resistor against 1000 V AC for 10 seconds.
Maximum percentage operating error
ere a spare fuse is also stored.
Page 17

14
5.4 Applied standards
Instrument operating Standard IEC/EN61557-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,10
Safety standard IEC/EN 61010-1(2001),
CATIII (300V) -Instrument
IEC/EN 61010-031(2001),
CATII (250V)-Test Lead Model7218
CATIII (600V)-Test Lead Model7188
CATIII (1000V)-Test Lead Model7196
CATIII (300V)-Test Lead Model7228
Protection degree IEC 60529 (1989 + A1) IP40
EMC EN 61326
EN55022/24
This manual and product may use the follow
Safety Standards;
CAT.III
Measurement category CAT III applies to;
Primary electrical circuits of the equipment connected directly to the
distribution panel, and feeders from the distribution panel to outlets.
Equipment protected throughout by DOUBLE INSULATION or
REINFORCED INSULATION;
Caution (refer to accompanying documents)
Caution, risk of electric shock
Protection against wrong connection is up to 500V
Earth Ground
ing symbols adopted from International
Page 18

15
5.5 List of Display Message
Low battery warning
Temperature monitor for internal resistance, available at
Loop, PSC/PFC & RCD function. Further measurements are
suspended until the
symbol disappears.
Measuring Measurements in progress
Live Circuit Live circuit warning (Continuity / Insulation Function)
PE Hi V
L-N >20Ω
Noise
N - PE Hi V
Uc > UL
no
OK
Caution : Presence of 100V or more at PE terminal, appears
when touching the Touch Pad
Alert : Presence of 20Ω or more between Line - Neutral at ATT
measurement
Caution : Presence of noise in the circuit under test during ATT
measurement. ATT function should be
disabled to continue
measurements.
Caution: Presence of high voltage between NEUTRAL - EARTH
during ATT measurement. ATT function should be disabled to
continue measurements.
Caution : Uc at RCD measurement is exceeding the preset UL
value (25 or 50V).
Error message : When on the RCD function, RCD tripped before
measuring RCD trip time. Selected IΔn value may not be
correct.
When o
n the LOOP, PSC/PFC function, supply may have been
interrupted.
Wiring check for LOOP, PSC/PFC function
Appears when all results passed during the RCD Auto Test
function.
× NO
R
Hi, RS Hi
H
Appears when any results failed during the RCD Auto Test
function.
Appears when a Probe resistance of H terminal (R
terminal (R
) at Earth measurement is exceeded the measurable
S
) or of S
H
range.
No 3-phase system Appears to indicate wrong connection at Phase Rotation check.
Page 19

16
6. Configuration
Fig.9
1. Press the Config Button
(F4) when powering on
KEW6016. (Fig.9)
2. Then, Configuration
Screen (Fig.10) is
displayed.
Fig.10
Push
KEW
TESTER
MULTI FUNCTION
6016
Config
Touch Pad :
UL :
OFF
Configuration
Back Light :
ON
50V
Language :
(EN)
Setting for following three parameters
● UL value・・・・・・・・Selects a UL value for RCD function
● Touch Pad・・・・・・Enables / disables Touch Pad function
● Back Light・・・・・・ Selects Backlight ON / OFF. When ON is selected, the Backlight
automatically turns on at powering on the instrument.
● Language・・・・・・ Select and change the languages to be displayed.
Setting method
3. Press the F1 – F4 Bu
F1 UL value 25V, 50V 50V
F2 Touch Pad ON, OFF ON
F3 Back Light ON, OFF OFF
F4 Language
4. Press the ESC Button (
normal screen.
tton to change following setting.
Parameter Selection Initial value
EN, FR, PL,
IT, ES, RU
) when setting change is completed, and return to the
EN
EN: English
FR: French
IT : Italian
ES: Spanish
RU: Russian
PL: Polish
Page 20

17
7. CONTINUITY (RESISTANCE) TESTS
NULL OFF
ON
Ω
Fig.11
Fig.12
Red
Green
WARNING
Ensure that circuits to be tested are not live.
Disconnect the instrument from the circuit under test before operating the
function switch.
To select the low resistance range select CONTINUITY.
7.1 Test Procedure
The object of continuity testing is to measure only the resistance of the parts of the
wiring system under test. This measurement should not inclu
test leads used. The resistance of the test leads needs to be subtracted from any
continuity measurement. The KEW6016 is provided with a continuity null feature which
allows automatic compensation for any test lead resistance.
You should only use the test leads supplied with the instrument.
Operation of Function Switch
F1 Switches on / off NULL function
F2 Switches on / off 2Ω buzzer
F3 N/A
de the resistance of any
F4 N/A
Proceed as follows:1 Select the continuity test by rotating the Rotary switch.
2 Insert the Test Leads to the L and PE terminal on KEW6016 respectively as shown in
Fig.12.
L terminal
Red cord of Model7188, or
Model7196 Remote Test Lead
PE terminal
Green cord of Model7188
3 Connect the ends of the test leads firmly together (see Fig.13) and press and lock
down the test button. The value of the lead resistance will be displayed.
Page 21

18
4 Operate the Continuity Null (F1) button, this will null out the lead resistance and the
NULL
ON
Ω
Measuring
NULL
ON
Ω
Measuring
Fig.13
indicated reading should go to zero.
5 Release the test button. Press the test button and ensure the display reads zero
before proceeding. While using the Continuity null function, NULL
is displayed
on the LCD as indicated in Fig.13. The null value will be stored even if the instrument
is powered off. This memorized null value can be cancelled by disconnecting the
test leads and pushing the Continuity Null button (F1) with the test button pressed or
locked. When this is cancelled you will know because NULL OFF is displayed on the
LCD.
CAUTION - before taking any measurements
always check the leads have been
zeroed.
6 Connect the test leads to the circuit whose resistance is required (see Fig.14 for a
typical connection arrangement), having first made sure that the circuit is not live.
Note that Live Circuit warning will be displayed on the LCD if the circuit is live - but
check first anyway!
7 Press the test button and read the circuit resistance from the display.
The reading
will have the test lead resistance already subtracted if the Continuity null function has
been used.
8 Note that if the circuit resistance is greater than 20Ω the instrument will autorange to
the 200Ω, if it is greater than 200Ω it will autorange to the 2000Ω range.
Note: If the reading is greater than 2000Ω the overange symbol > will remain
displayed.
WARNING
The results of measureme
additional operating circuits connected in parallel or by transient currents.
nts can be adversely affected by impedances of
Page 22

19
7.2 2Ω Buzzer ( ) function
Use F2 Button to enable / disable the 2Ω Buzzer. The buzzer sounds when measured
resistance is 2Ω or less while this function is enabled. The buzzer does not sound if it is
disabled.
PE
PE
MAIN EQUIPOTENTIAL BONDING
GAS
WATER
NULL
ON
Ω
Fig.14 Example of continuity test for main equipotential bonding.
Page 23

20
8. INSULATION TESTS
Fig.15
WARNING
Ensure that circuits to be tested are not live.
Disconnect the instrument from the circuit under test before operating the
function switch.
To select the insulation resistance range select INSULATION.
8.1.1 The nature of insulation resistance
Live conductors are separated from each other and from earth metal by insulation,
which has a resistance which is high enough to
conductors and to earth is kept at an acceptably low level. Ideally insulation resistance
is infinite and no current should be able to flow through it. In practice, there will normally
be a current between live conductors and to earth, and this is known as leakage current.
This current is made up of three components, which are:-
1. capacitive current
2. conduction cu
3. surface leakage current.
8.1.2 Capacitive Current
The insulation between conductors which have a potential difference between them
behaves as the dielectric of a capacitor, the conductors acting as the capacitor plates.
When a direct voltage is applied to the conductors, a charging current will flow to the
system which will die away to zero (usually in less than a second) when the effec
capacitor becomes charged. This charge must be removed from the system at the
end of the test, a function which is automatically performed by the KEW6016. If
an alternating voltage is applied between the conductors, the system continuously
charges and discharges as the applied voltage alternates, so that there is a continuous
alternating leakage current flowing to the system.
rrent, and
ensure that the current between
tive
Page 24

21
8.1.3 Conduction Current
Fig.16
Fig.17
Since the insulation resistance is not infinite, a small leakage current flows through the
insulation between conductors. Since Ohm's Law applies, the leakage current can be
calculated from
8.1.4 Surface Leakage Current
Where insulation is removed, for the connection of conductors and so on, current will
flow across the surfaces of the insulation between the bare conductors.
leakage current depends on the condition of the surfaces of the insulation between the
conductors.
If the surfaces are clean and dry, the value of the leakage current will be very small.
Where the surfaces are wet and/or dirty, the surface leakage current may be significant.
If it becomes large enough, it may constitute a flashover between the conductors.
Whether this happens depends
applied voltage; this is why insulation tests are carried out at higher voltages than those
normally applying to the circuit concerned.
on the condition of the insulation surfaces and on the
The amount of
8.1.5 Total Leakage Current
The total leakage current is the sum of the capacitive, conduction and surface leakage
current described above. Each of the currents, and hence the total leakage current, is
affected
the applied voltage.
by factors such as ambient temperature, conductor temperature, humidity and
Page 25

22
If the circuit has alternating voltage applied, the capacitive current (8.1.2) will always be
present and can never be eliminated. This is why a direct voltage is used for insulation
resistance measurement, the leakage current in this case quickly falling to zero so that it
has no effect on the measurement. A high voltage is used because this will often break
down poor insulation and cause flashov
showing up potential faults which would not be present at lower levels.
The insulation tester measures the applied voltage level and the leakage current
through the insulation. These values are internally calculated to give the insulation
resistance using the expression:-
er due to surface leakage (see 8.1.4), thus
As the capacitance of the system charges up, so the charging current falls to zero an
steady insulation resistance reading indicates that the capacitance of the system is fully
charged. The system is charged to the full test voltage, and will be dangerous if left with
this charge. The KEW6016 provides an automatic path for discharging current as soon
as the test button is released to ensure that the circuit under test is safely discharged.
If the wiring system is wet and/or dirt
current will be high, resulting in low insulation resistance reading. In the case of a very
large electrical installation, all the individual circuit insulation resistances are effectively
in parallel and the overall resistance reading will be low. The greater the number of
circuits connected in parallel the lower will be the overall insulation resis
8.2 Damage to Voltage-Sensitive Equipment
An increasing number of electronic-based items of equipment are being connected
to electrical installations. The solid state circuits in such equipment are likely to be
damaged by the application of the levels of voltage used to test insulation resistance. To
prevent such damage, it is important that voltage-sensitive equipment is disconnected
e installation before the test is carried out and reconnected again immediately
from th
afterwards. The devices which may need to be disconnected before the test include:-
● Electronic fluorescent starter switches
● Passive infra-red detectors (PIRs)
● Dimmer switches
● Touch switches
● Delay timers
● Power controllers
● Emergency lighting units
● Electronic RCDs
● Computers and printers
● Electronic point-of-sale
● Any other device which includes electronic components.
terminals (cash registers)
y, the surface leakage component of the leakage
tance.
d a
Page 26

23
8.3 Preparation for measurement
Fig.18
Fig.19
Before testing, always check the following:1 The low battery Indication is not displayed
2 There is no visually obvious damage to the tester or to the test leads
3 Test the continuity of the test leads by switching to continuity test and shorting out
the lead ends. A high reading will indicate that there is a faulty lead or that the fuse is
blown.
4 Make sure the
the instrument is connected to a live circuit but test the circuit as well!
Operation of Function Switch
8.4 Insulation resistance measurement
The KEW6016 has three selectable test voltages of 250V, 500V and 1000V DC.
1 Select INSULATION function with the Rotary switch.
2. Press the VOLT Switch (F4) and select desirable voltage range.
3. Insert the Test Leads to the L and PE terminal on KEW6016 respectively as shown in
Fig.19.
circuit to be tested is not live. Live Circuit warning is displayed if
F1 N/A
F2 N/A
F3 N/A
F4 Voltage setting
L terminal
Red cord of Model7188, or
Model7196 Remote Test Lead
PE terminal
Green cord of Model7188
Page 27

24
4 Attach the test leads to the circuit or the appliance under test (see Figs 20 & 21)
1000V
MΩ
Fig.20 Example of Insulation resistance test on 4 wire-3 phase system.
1000V
MΩ
Fig.21
5 If the Live Circuit warning is displayed on the LCD and/or the buzzer sounds, do
not press the test button but disconnect the instrument from the circuit. Make the
circuit dead before proceeding.
6 Press the test button, the display will show the insulation resistance of the circuit or
the appliance to which
the instrument is connected.
7 Note that if the circuit resistance is greater than 20MΩ, the instrument will autorange
to the 200MΩ range. If it is greater than 200MΩ at the 500V or 1000V range, it will
autorange to the 2000MΩ range.
8 When testing is complete release the test button before disconnecting the test leads
from the circuit or from the appliance. This will ensure that the charge built
circuit or the appliance during insulation test is dissipated in the discharge circuit. In
the discharging process, Live Circuit warning will be displayed on the LCD and the
live circuit warning buzzer will sound.
up by the
Page 28

25
WARNING
● Never touch the circuit, test lead tips or the appliance under test during insulation
testing because high voltages exist.
CAUTION
● Never turn the Rotary switch while the test button is depressed as this may damage
the instrument.
● Always release the test button first after testing before removing the test leads from
the circuit. This is to ensure that charges stored in the circuit
totally discharged.
Note: If the reading measured greater than 2000MΩ (200MΩ at 250V) the over range
reading > will be displayed.
capacitance have been
Page 29

26
9. LOOP/ PSC/PFC
Fig.22
9.1 Principles of measurement of fault loop impedance and PFC
If an electrical installation is protected by over-current protective devices including circuit
breakers or fuses, the earth loop impedance should be measured.
In the event of a fault the earth fault loop impedance should be low enough (and the
prospective fault current high enough) to allow automatic disconnection of th
supply by the circuit protection device within a prescribed time interval. Every circuit
must be tested to ensure that the earth fault loop impedance value does not exceed that
specified or appropriate for the over-current protective device installed in the circuit. The
KEW6016 takes a current from the supply and measures the difference between the
unloaded and loaded supply voltages.
loop resistance.
TT System
For a TT system the earth fault loop impedance is the sum of the following impedances;
● Impedance of the power transformer secondary winding.
● Impedance of the phase conductor resistance from the power transformer to the
location of the fault.
● The impedance of the protective conductor from the fault location to the
system.
● Resistance of the local earth system (R).
● Resistance of the power transformer earth system (Ro).
From this difference it is possible to calculate the
e electrical
earth
The figure below shows (dotted line) the Fault loop impedance for TT systems.
Page 30

27
According to the International Standard IEC 60364, for TT systems the characteristics of
the protective device and the circuit resistance shall fulfill the following requirements:
Ra x Ia ≤ 50V Where:
Ra is the sum of the resistances in Ω of the local earth system and the protective
conductor for the exposed conductive parts.
50 is the maximum safety touch voltage limit (it can be 25V in particul
construction sites, agricultural premises, etc.).
Ia is the current causing the automatic disconnection of the protective device within the
maximum disconnecting times required by IEC 60364-41:
- 200 ms for final circuits not exceeding 32A (at 230 / 400V AC)
- 1000 ms for distribution circuits and circuits over 32A (at 230 / 400V AC)
ar cases like
The compliance with the above rules shall be verif
1) Measurement of the resistance Ra of the local earth system by Loop tester or Earth
tester.
2) Verification of the characteristics and/or the effectiveness of the RCD associated
protective device.
Generally in TT systems, RCDs shall be used as protective device and in this case, Ia
is the rated residual operating current I△n. For instance in a TT system protected by a
RCD the max Ra value
Rated residual operating current I△n 30 100 300 500 1000 (mA)
RA (with touch voltage of 50V) 1667 500 167 100 50 (Ω)
RA (with touch voltage of 25V) 833 250 83 50 25 (Ω)
Shown below is a practical example of verification of the protection by RCD in a TT
system according to the international Standard IEC 60364.
s are:
ied by:
Page 31

28
For this example the max permissible value is 1667 Ω (RCD =30mA and contact
Ω
L - PE
L-PE
L-N
230
V
50.0Hz
ATT
:ON
!
F
ig.23
Fig.24
voltage limit of 50 V). The instruments reads 12.74 Ω, thus the condition RA ≤ 50/Ia
is respected. However, considering that the RCD is essential for protection, it must be
tested (Please refer to RCD TESTS section).
TN System
For TN systems the earth fault loop impedance is the sum of the following impedances.
● Impedance of
the power transformer secondary winding.
● Impedance of the phase conductor from the power transformer to the location of the
fault.
● Impedance of the protective conductor from the fault location to the power
transformer.
The figure below shows (dotted line) the Fault loop impedance for TN systems.
Page 32

29
According to the International Standard IEC 60364, for TN system the characteristics of
the protective device and the circuit impedance shall fulfill the following requirement:
Zs x Ia ≤ Uo Where:
Zs is the Fault loop impedance in ohm.
Uo is the nominal voltage between phase to earth (typically 230V AC for both single
phase and three phase circuits).
Ia is the current causing the automatic disconne
maximum disconnecting times required by IEC 60364-41 that are:
- 400 ms for final circuits not exceeding 32A (at 230 / 400V AC)
- 5 s for distribution circuits and circuits over 32A (at 230 / 400V AC)
The compliance with the above rules shall be verified by:
1) Measurement of the fault loop impedance Zs by Loop tester.
2) Verification of the characteristic
device. This verification shall be made:
- for circuit-breakers and fuses, by visual inspection (i.e. short time or instantaneous
tripping setting for circuit-breakers, current rating and type for fuses);
- for RCDs, by visual inspection and test using RCD testers recommending that the
disconnecting times mentioned above are met (Please see
s and/or the effectiveness of the associated protective
ction of the protective device within the
RCD TEST section).
For instance in a TN system with nominal mains voltage Uo = 230 V protected by
General purpose gG fuses or MCBs (Miniature Current Breakers) required by IEC 898 /
EN 60898, the Ia and max Zs values could be:
Page 33

30
Rating
Ω
L-PE
230
V
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
ATT
:ON
Fig.25
(A)
Protection by gG fuses
with Uo of 230V
Disconnection
Disconnection
time 5s
Ia
(A)
Zs
(Ω)
time 0.4s
Ia
(A)
Zs
(Ω)
Protection by MCBs with Uo of 230V
(Disconnection time 0.4 and 5s)
CharacteristicBCharacteristicCCharacteristic
D
Ia
(A)
Zs
(Ω)
Ia
(A)Zs (Ω)
Ia
(A)
Zs
(Ω)
6 17 13.5 38 8.52 30 7.67 60 3.83 120 1.92
10 31 7.42 45 5.11 50 4.6 100 2.3 200 1.15
16 55 4.18 85 2.7 80 2.87 160 1.44 320 0.72
20 79 2.91 130 1.77 100 2.3 200 1.15 400 0.57
25 100 2.
3 160 1.44 125 1.84 250 0.92 500 0.46
32 125 1.84 221 1.04 160 1.44 320 0.72 640 0.36
40 170 1.35 -- -- 200 1.15 400 0.57 800 0.29
50 221 1.04 -- -- 250 0.92 500 0.46 1000 0.23
63 280 0.82 -- -- 315 0.73 630 0.36 1260 0.18
80 403 0.57 -- --
100 548 0.42 -- --
The most complete loop testers or Multifunction testers also have the Prospective Fault
current measurement. In this case, Prospective Fault current measured with instruments
must be higher than the tabu
lated Ia of the protective device concerned.
Below is a practical example of verification of the protection by MCB in a TN system
according to the international Standard IEC 60364.
Page 34

31
Max value of Zs for this example is 1.44 Ω (MCB 16A, characteristic C), the instrument
PSC
A
230
V
L-N
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.26
reads 1.14 Ω (or 202 A on Fault current range) it means that the condition
Zs x Ia ≤ Uo is respected.
In fact the Zs of 1.14 Ω is less than 1.44 Ω (or the Fault current of 202 A is more than Ia
of 160A).
In other words, in case of fault between phase and earth, the wall socket tested in this
example is protected b
ecause the MCB will trip within the disconnection time required.
9.2 Principles of the measurement of line impedance and PSC
The method for measuring Line – neutral impedance and line-line impedance is exactly
the same as for earth fault loop impedance measurement with the exception that the
measurement is carried out between line and neutral or line and line.
Prospective short circuit or fault curre
nt at any point within an electrical installation
is the current that would flow in the circuit if no circuit protection operated and a
complete (very low impedance) short circuit occurred. The value of this fault current
is determined by the supply voltage and the impedance of the path taken by the fault
current. Measurement of prospective short circuit current can be used to check that the
prote
ctive devices within the system will operate within safety limits and in accordance
with the safe design of the installation. The breaking current capacity of any installed
protective device should be always higher than the prospective short circuit current.
Page 35

32
9.3. Operating instructions for LOOP and PSC/PFC
L-PE
Ω
ATT : ON
230V
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.27
PFC
A
230V
50.0Hz
L-PE
ATT
:ON
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.28
Fig.29
9.3.1 Initial Checks: to be carried out before any testing
1. Preparation
Always inspect your test instrument and lead accessories for abnormality or damage:
If abnormal conditions exist DO NOT PROCEED WITH TESTING. Have the instrument
checked by your distributor.
Operation of Function Switch
LOOP
Switches measurement mode:
F1
L-PE or L-N/L-L
F2 ATT setting (on or off)
F3 N/A
F4 N/A
PSC/PFC
Switches measurement mode:
F1
PFC or PSC
F2 ATT setting (on or off)
F3 N/A
F4 N/A
(1) Operate the Power button and turn on the instrument. Turn the Function switch and
set it to either the LOOP or PSC/PFC position.
(2) Insert the Test Lead into the instrument. (Fig.29)
Page 36

33
(3) Press the MODE switch(F1) and select L-N to measure Loop(L-N/L-L) or PSC
Fig.30
or select L-PE to measure earth loop impedance or PFC. Display changes
automatically as follows depending on the applied voltages while LOOP(L-N/L-L) or
PSC is selected.
(4) Pressing the ATT switch (F2) disables ATT mode. Then ATT OFF is displayed on
the LCD.
● ATT(Anti Trip Technology) is to measure LOOP resistan
RCDs rated at 30mA or more. ATT ON is displayed while it is activated.
2. Wiring Check
After the connection, ensure that the symbols for Wiring check on the LCD are in the
status indicated in Fig.29 before pressing the test button.
If the status of the symbols for Wiring check differ from Fig.29 or
indicated on the LCD, DO NOT PROCEED AS THERE IS INCORRECT WIRING. The
cause of the fault must be investigated and rectified.
3. Voltage Measurement
When the instrument is first connected to the system, it will display the line-earth voltage
(MODE L-PE) or line-neutral voltage (MODE L-N/L-L) which is updated every 1s. If this
voltage is not normal or as expected, DO NOT PROCEED.
ces without tripping the
symbol is
Page 37

34
9.3.2 Measurement of LOOP and PSC/PFC a. Measurement at Mains Socket Outlet
Connect the mains test lead to the instrument. Insert the moulded plug of mains test
lead into the socket to be tested. (see Fig.31)
Press MODE Switch (F1) and select L-N or PSC to measure between Line – Neutral,
or L-PE or PFC to measure between Line-PE.
Carry out the initial checks
Press the test button. A
impedance will be displayed.
b. Measurement at the distribution board
Connect the distribution board lead Model7188 to the instrument.
Measurement of Line – Earth Loop Impedance and PFC
Press the Mode Switch (F1) and select L-PE or PFC.
Connect the green PE lead of the Model7188 to the earth, the blue N lead to the
neutr
al of the distribution board and the brown L lead to one line of the distribution
board. (See Fig.32)
Measurement of Line – Neutral Loop Impedance and PSC
Press the Mode Switch (F1) and select L-N/L-L or PSC.
Connect the blue N lead of the Model7188 to the neutral of the distribution board, the
brown L lead to one line of the distribution board. (See Fig.33)
Carry out the initial ch
Press the test button. A beep will sound as the test is conducted and the value of loop
impedance will be displayed. When disconnecting from the distribution board, it is
good practice to disconnect the line first.
beep will sound as the test is conducted and the value of loop
ecks
c. Measurement between LINE-LINE
Connect the distribution board lead Model7188 to the instrument.
Press the Mode Switch(F1) and select L-N/L-L or PSC.
Connect the bl
brown L lead to another line of the distribution board. (See Fig.34)
Carry out the initial checks
Press the test button. A beep will sound as the test is conducted and the value of loop
impedance will be displayed.
● If the display shows '>' then this usually means the value measured exceeds the
range.
● ATT mode enables
current of 30mA or more.
ue N lead of the Model7188 to the line of the distribution board, the
a measurement without tripping the RCDs with the rated residual
Page 38

35
● Measurement in ATT mode requires longer time than that is required for the other
Ω
L-PE
230
V
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
ATT
:ON
Fig.31 Connection for using Outlet
measurements (approx. 7 sec). When measuring a circuit with a large electrical
noise, the 'Noise' Message is displayed on the LCD and the measurement time
will be extended to 20 sec. If the 'NOISE' symbol is displayed on the LCD, it is
recommended to disable the ATT mode and take a measurement (RCDs may trip).
● If
an impedance of 20Ω or more is measured between L-N during measurements
with ATT enabled, L-N>20Ωis displayed on the LCD and no measurement can be
made. In this case, disable the ATT function and make measurement. When a large
contact voltage exists in the circuit under test,N-PE HiVis displayed on the LCD
and no measurement can be made. In this case, disable the ATT function and make
measure
ment. Be aware that if the ATT mode is disabled, RCDs may trip.
● Measured result may be influenced depending on the phase angle of the distribution
system when making measurement near a transformer and the result may lower than
the actual impedance value. Errors in measured result are as follows.
System Phase
Difference
Error
(approx.)
10° -1.5%
20° -6%
30° -13%
● ATT mode is automatically enabled after one measurement when making a
measurement with ATT mode disabled.
Page 39

36
PE
Ω
L-PE
230
V
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
ATT
:ON
PSC
A
230
V
L-N
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.33 Connection for Line – Neutral measurement
Fig.34 Connection for Line – Line measurement
Fig.32 Connection for distribution
PSC
A
400
V
L-L
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Page 40

37
10. RCD TESTS
10.1 Principles of RCD Measurement
The RCD tester is connected between phase and protective conductor on the load side
of the RCD after disconnecting the load.
A precisely measured current for a carefully timed period is drawn from the phase and
returns via the earth, thus tripping the device. The instrument measures and displays
the exact time taken for the circuit to be opened.
An RCD is a switching device designed for breaking currents when the residual current
attains a specific value. It works on the basis of the current difference between phase
currents flowing to different loads and returning current flowing through the neutral
conductor (for a single-phase installation). In the case where the current difference is higher
than the RCD tripping current, the device will tr
There are two parameters for RCDs; the first due to the shape of the residual current wave
form (types AC and A) and the second due to the tripping time (types G and S).
●
RCD type AC will trip when presented with residual sinusoidal alternating currents
whether applied suddenly or slowly rising. This type is the most frequently used on
electrical installations.
●
RCD type A will trip when presented with residual sinusoidal alternating currents
(similar to type AC) and residual pulsating direct currents (DC) whether suddenly
applied or slowly rising. This type of RCD is not commonly used at present, however,
it is increasing in popularity and is required by the local regulations in some countries.
Making measurement with setting uses pulsating direct currents for test.
● RCD type G. In this case G stands for general type (without tripping time delay) and
is for general use and applications.
●
RCD type S where S stands for selective type (with tripping time delay).This type of RCD
is specifically designed for installations where the time delay characteristic is required.
ip and disconnect the supply from the load.
Given that when the protective device is an RCD, Ia is typically 5 times the rated
residual operating current I△n, then the RCD must be tested recommending the
tripping time, measured by RCD testers or Multifunction tes
maximum disconnecting times required in IEC 60364-41 (see also LOOP/PSC/PFC
section) that are:
TT system
(at 230V / 400V AC)
TN system
(at 230V / 400V AC)
200 ms for final circuits not exceeding 32A
1000 ms for distribution circuits and circuits over 32A
400 ms for final circuits not exceeding 32A
5 s for distribution circuits and circuits over 32A
ters, shall be lower than the
Page 41

38
However it is also good practice to consider even more stringent trip time limits, by following
×1
ms
30 mA
230V
L-PE
UL50
V
PHASE : 0
°
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.35
×1
ms
30 mA
230V
L-PE
UL50
V
PHASE : 0°
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.36
the standard values of trip times at I△n defined by IEC 61009 (EN 61009) and IEC 61008
(EN 61008). These trip time limits are listed in the table below for IΔn and 5I△n:
Type of RCD IΔn 5IΔn
General(G)
Selective(S)
300ms
max allowed value
500ms
max allowed value
130ms
min allowed value
40ms
max allowed value
150ms
max allowed value
50ms
min allowed value
Examples of instrument connections
Practical example of 3-phase + neutral RCD test in a TT system.
Practical example of single phase RCD test in a TN system.
Page 42

39
Practical example of RCD test with distribution leads.
PE
×1
ms
30 mA
230V
L-PE
UL50
V
PHASE : 0°
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.37
×1 / 2
ms
30 mA
L-PE
UL50
V
PHASE : 0
°
230V
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.38
10.2 Principles of Uc Measurement
Ground being imperfect in the Fig35, when R exists, when a fault current flows to R,
electric potential occurs. There is a possibility the person contacting in this imperfect
ground, it calls the voltage, which it occurs in the human body of this time, called Uc.
When with the Uc Test letting flow IΔN to the RCD
, the Uc is calculated.
Uc voltage is calculated based on the Rated Residual Current (I△N) with the
impedance measured.
10.3 Operating Instructions for RCD
10.3.1 Initial Checks: to be carried out before any testing;
1. Preparation
Always inspect your test instrument and lead accessories for abnormality or damage:
If abnormal conditions exist DO NOT PROCEED WITH TESTING. Have the instrument
checked by y
Operation of Function Switch
our distributor.
F1 Measurement mode setting
(X1/2, X1, X5, Ramp, Auto, Uc)
F2 IΔn setting
F3 RCD Type setting (
F4 PHASE setting (0° ,180° )
, , , )
Page 43

40
1. Operate the Power button and turn on the instrument.
L
PE
N
Fig.39
Turn the rotary switch and select the RCD function.
2. Press the MODE switch(F1) and select any desirable measurement mode.
X1/2 For testing RCD's to verify that they are not too sensitive.
X1 For measuring the trip time.
X5 For testing at IΔn X5
RAMP(◢) For measuring the tripping level in mA.
AUTO
For automatic measurement in following sequence:
X1/2(0° ), X1/2(180° ), X1(0° ),X1 (180° ), X5(0° ), X5(180° )
Uc For measuring Uc
3. Press the IΔn switch (F2) to set Rated Tripping Current (IΔn) to the rated trip current
of the RCD.
4. Pre
ss (F3) to select the RCD type.
Refer to "10.1 Principles of RCD measurement" for the details of RCD type. (*6)
5. Press (F4) to select phase at which the test current should start. (*7)
(*6),(*7) except for Uc measurement
*UL value change
As a UL value, 25V or 50V is selectable. Refer to 6. Configuration in this manual and
select either of them.
2. Wiring Check
1. Insert the Test Lead into th
e instrument. (Fig.39)
2. Connect the test leads to the circuit to be tested. (Fig.35, 36, 37)
3. After the connection, ensure that the symbols for Wiring check on the LCD are in the
status indicated in Fig.39 before pressing the test button.
If the status of the symbols for Wiring check differ from Fig.39 or
indicated on the LCD, DO NOT PROCEED AS THERE IS INCORRECT WIRING. The
cause of the fault must be investigated and rectified.
symbol is
Page 44

41
3. Voltage Measurement
When the instrument is first connected to the system, it will display the line-earth
voltage which is updated every 1s. If this voltage is not normal or as expected, DO NOT
PROCEED.
NOTE: This is a single phase (230V AC) instrument and under no circumstances should
it be connected to 2- phases or a voltage exceeding 230VAC+10%.
If the input voltage is greater than 260V the disp
measurements can not be made even if the Test button is pressed.
10.3.2 RCD Measurement
a) Single Tests
1. Press the Test button
Operating time of RCD is displayed on LCD. (At Ramp test, operating current value of
RCD will be displayed. Uc values are displayed at Uc Function.)
● ×1/2...................The Breaker should not trip.
● ×1......................The Breaker sh
● ×5......................The Breaker should trip.
● Auto Ramp(◢)..The Breaker should trip. The tripping current should be displayed.
● Uc......................Uc values are displayed.
2. Press the 0° /180° switch to change the phase and repeat step (1).
3. Change the phase again and repeat step (1).
ould trip.
lay will indicate '>260V' and RCD
b) Auto Test
Measurements are automatically performed under the Auto Test function in the follow
sequence: X1/2(0° ), X1/2(180° ), X1(0° ),X1 (180° ), X5(0° ), X5(180° ).
1. Press F1 to select Auto
2. Press F2 & F3 to select IΔn & RCD type
3. Press the Test button. The KEW6016 will automatically conduct the sequence as
above. When the RCD trips each time reset it.
4. Return to the tester and the results will be displayed
● Be sure to return the tested RCD to the original condition after the test.
●
When the Uc voltage rises to UL value or greater, the measurement is automatically
suspended and "Uc > UL" is displayed on the LCD.
● If " IΔn" setting is greater than the rated residual current of the RCD, the RCD will
trip and "no" may be displayed on LCD.
● If a voltage exists between the protective conductor and earth, it may influence the
measurements.
● If a voltage exists between neutral
and earth, it may influence the measurements,
ing
Page 45

42
therefore, the connection between neutral point of the distribution system and earth
should be checked before testing.
● If leakage currents flow in the circuit following the RCD, it may influence the
measurements.
● The potential fields of other earthing installations may influence the measurement.
● Special conditions of RCDs of a particular design, for example S- type, should be
taken into consi
● The earth electrode resistance of a measuring circuit with a probe shall not exceed
table1.
● Equipment following the RCD, e.g. capacitors or rotating machinery, may cause a
significant lengthening of the measured trip time.
deration.
Page 46

43
11. EARTH TESTS
Fig.40
Fig.41
Red Green
Yellow
11.1 Principles of Earth Measurement
This Earth function is to test power distribution lines, in-house wiring system, electrical
appliances etc.
This instrument makes earth resistance measurement with fall-of-potential method,
which is a method to obtain earth resistance
value Rx by applying AC constant current I
between the measurement object E (earth
electrode) and H(C) (current
and finding out the potential difference V
between E and S(P) (potential electrode).
Rx = V / I
11.2 Earth resistance Measurement
WARNING
● The instrument will produce a maximum voltage of about 50V between
terminals E-H(C) in earth resistance function. Take enough caution to avoid
electric shock hazard.
CAUTION
● When measuring earth resistance, do not apply voltage between measuring
terminals.
electrode),
1.Select Earth function with the Rotary Switch
2.Insert the Test Leads (MODEL7228) into the instrument. (Fig.41)
3.Test Lead connection
Stick the auxiliary earth spikes S(P) and H(C) into the ground deeply. They should be
aligned at an interval of 5-10m from the earthed equipment under test. Connect the
green wire to the earthed equipment under test, the yellow wire to the auxiliary earth
s
pike S(P) and the red wire to the auxiliary earth spike H(C) from terminals E, S(P) and
H(C) of the instrument in order.
Page 47

44
Note :
H(C)
S(P)
Ω
E
Fig.42
● Make sure to stick the auxiliary earth spikes in the moist part of the soil. Give enough
water where the spikes have to be stuck into the dry, stony or sandy part of the earth
so that it may become moist.
● In case of concrete, lay the auxiliary earth spike down and water it, or put a wet dust
cloth etc. on the spike when making measurement.
4.Press the test button, the display will show t
he earth resistance of the circuit.
● If measurement is made with the probes twisted or in touch with each other, the
reading of the instrument may be affected by induction. When connecting the probes,
make sure that they are separated.
● If earth resistance of auxiliary earth spikes is too large, it may result in inaccurate
measurement. Make sure to stick the auxiliary earth spike and H(C) into t
he moist
part of the earth carefully, and ensure sufficient connections between the respective
connections. High auxiliary earth resistance may exist if R
Hi or RH Hi is
S
displayed during measurements.
● Great errors may included in the measured earth resistance when earth voltage of
10V or more exist. In this case, power off the devices which is using earth resistance
under test to reduce the
earth voltages.
Page 48

45
12. PHASE ROTATION TESTS
Fig.43
L1
L3
L2
Fig.44
Correct phase sequence
Reversed phase sequence
64.giF 54.giF
1. Operate the Power button and turn on the instrument. Turn the rotary switch and
select the PHASE ROTAION function.
2. Insert the Test Leads into the instrument. (Fig.43)
3. Connect each test leads to a circuit. (Fig.44)
4. Results are displayed as follows.
● When a message No 3-phase system or --- is displayed, the circuit may not be a
3-phase system or a wrong conn
the connection.
● Presence of Harmonics in measurement voltages, such as an inverter power supply,
may influence the measured results.
ection may have been made. Check the circuit and
Page 49

46
13. VOLTS
Fig.47
1. Operate the Power button and turn on the instrument. Turn the rotary switch and
select the VOLTS function.
2. Insert the Test Leads into the instrument. (Fig.47)
3. Voltage value and frequency will be displayed on the LCD when applying AC voltage.
Note : A message DC V may be displayed when measuring AC voltages with
frequencies out of the range 45Hz - 65Hz.
14. TOUCH PAD
1. The touch pad measures the potential between the operator and the tester's PE
terminal.
A message PE HiV is displayed on the LCD with the audible buzzer if a potential
difference of 100V or more is present between the operator and the PE terminal at
touching the Touch pad.
2. Touch Pad function can be enabled and disabled (ON / OFF); refer to 6.
Configuration in this manual and select ON or OFF
warning for PE HiV does not appear and the buzzer does not sound.
* Initial value: ON
Note :
A message PE HI V may be displayed when testing inverters or measuring
voltages containing high frequencies even if a user isn't touching with the Touch Pad.
. In case that OFF is selected, a
15. BACK LIGHT
Pressing the Back Light Button selects Backlight ON / OFF. Backlight automatically
turns off
either ON or OFF. Refer to 6. Configuration in this manual how to select ON / OFF.
in 60 sec after it turns on. Backlight at powering on the instrument can be set
Page 50

47
16. MEMORY FUNCTION
250V
MΩ
18.52
Fig.48-1
Fig.48-2
Fig.48-3
ALL DELETE
MEMORY MODE
ESC:MEM BUTTON
DELETE
RECALL
SAVE
OK
SAVE MODE
DOWN
UP
SITE:
01
DATA No.001
BOARD:
CIRCUIT:
01
01
SELECT
Measured result at each function can be saved in the memory of the instrument.
(MAX : 1000)
16.1 How to save the data
Save the result according to following sequence.
(1) Measured result.
(2) Press
(3) Press
to enter into MEMORY MODE.
to enter into SAVE MODE.
(4) Make setting for following items.
1. CIRCUIT No
2. BOARD No
3. SITE No
4. DATA No
Press the SELECT Button to choose the parameter to change.
CIRCUIT No → BOARD No → SITE No → DATA No
Use the UP or DOWN Button and change settings.
Keep the UP/DOWN Key
pressed down to alter the
number quickly.
Page 51

48
(5) Press OK( ). (Confirmed)
Normal mode
Saving
250V
MΩ
18.52
Fig.48-4
Fig.48-5
Fig.48-6
SAVE
INSULATION
18.52M
Ω
SITE : 01
250V
BOARD : 01
CIRCUIT : 01
SAVE MODE
DATA No.001
BACK
(6) Press SAVE(
). (Confirmed)
(7) SAVING is displayed for about 2 sec on the
LCD, and then returns to the start screen. Saving
completes.
Returns to Normal mode once data save
completes. (Measurement mode)
Page 52

49
16.2 Recall the saved data
Fig.49-1
Fig.49-2
Fig.49-3
ALL DELETE
MEMORY MODE
ESC:MEM BUTTON
DELETE
RECALL
SAVE
RECALL MODE
INSULATION
18.52M
Ω
SITE : 01
250V
BOARD : 01
CIRCUIT : 01
DOWN
UP
DATA No.
000
BACK
250V
MΩ
Save data can be displayed on LCD according to following sequence.
(1) Press
(2) Press
(3) Press Up(
Data No.
Keep the UP/DOWN Key
pre s s e d dow n until a
buzzer sounds to skip the
number containing no data
and display the next data.
to enter into MEMORY MODE.
to enter into RECALL MODE.
)or DOWN( )and select
Page 53

50
ALL DELETE
DELETE
Fig.50-1
Fig.50-2
Fig.50-3
Fig.50-4
ALL DELETE
MEMORY MODE
ESC:MEM BUTTON
DELETE
RECALL
SAVE
DELETE MODE
DATA No.
000
INSULATION
18.52M
Ω
250V
SITE : 01
BOARD : 01
CIRCUIT : 01
DELETE
DOWN
UP
BACK
ALL DELETE
Delete All?
ESC:MEM BUTTON
BACK
250V
MΩ
16.3 Delete the saved data
Save data can be deleted according to following sequence.
(1) Press
MEMORY MODE.
(2) Press
into DELETE MODE
(3) Press Up(
or DOWN(
and select Data
No.
to enter into
to enter
)
)
(2) Press to
enter into ALL
DELETE MODE
(4) Press DELETE
(
(Confirmed)
).
(3) Press ALL
DELETE (
(Confirmed)
).
Page 54

51
ALL DELETEDELETE
Deleting
Fig.50-5
Fig.50-6
Fig.50-7
Fig.50-8
Fig.50-9
DELETE MODE
DATA No.001?
DELETE
INSULATION
18.52M
Ω
250V
SITE : 01
BOARD : 01
CIRCUIT : 01
BACK
All Deleting
250V
MΩ
250V
MΩ
(5) Press
DELETE (
(Confirmed)
).
(6) Returns to
Normal mode
when selected
data deleted.
(Measurement
mode)
(4) Returns to
Normal mode
when selected
data is deleted.
(Measurement
mode)
Page 55

52
16.4 Transfer the stored data to PC
F
ig.51
Fig.52
250V
MΩ
The stored data can be transferred to PC via Optical Adapter Model8212USB (Optional
Accessory).
●How to transfer the data:
(1) Connect Model8212USB to the USB Port of a
PC.(Special driver for Model8212USB should
be installed. See the instruction manual for
Model8212USB for further details.)
(2) Insert Model8212USB into the KEW6016 as
shown in Fig 52. Test Leads sh
ould be removed
from the KEW6016 at this time.
(3) Power on the KEW6016. (Any function is OK.)
(4) Start special software "KEW Report" on your PC and set the communication port.
Then click "Down load" command, and the data in the KEW6016 will be transferred
to your PC. Please refer to the instruction manual of Model8212USB and HELP of
KEW Report for further details.
Note: Use "KEW Report" with
version 2.00 or more.
The latest "KEW Report" can be downloaded from KYORITSU's web site.
http://www.kew-ltd.co.jp/en/
Page 56

53
17. GENERAL
17.1 If the symbol ( )appears, this means that the test resistor is too hot and the
automatic cut out circuits have operated. Allow the instrument to cool down before
proceeding. The overheat circuits protect the test resistor against heat damage.
17.2 The test button may be turned clockwise to lock it down. In this auto mode,
when using distribution board lead Model7188, tests are conducted by simply
disconnecting an
need to physically press the test button i.e. 'hands free'.
17.3 When the display shows the low battery indication, ( ), disconnect the test leads
from the instrument. Remove the battery cover and the batteries.
d reconnecting the red phase prod of the Model7188 avoiding the
Page 57

54
18. BATTERY REPLACEMENT
Screw
Spare Fuse
Fuse
Fig.53
When the display shows the low battery indication , , disconnect the test leads from
the instrument. Remove the battery cover and the batteries. Replace with eight (8) new
1.5V AA batteries, taking care to observe correct polarity. Replace the battery cover.
19. FUSE REPLACEMENT
The continuity test circuit is protected by a 600V 0.5A HRC ceramic type fuse situated in
the battery compartment, together with a spare. If the instrument fails to operate
continuity test mode, first disconnect the test leads from the instrument. Next remove
the battery cover, take out the fuse and test its continuity with another continuity tester.
If it has failed, replace it with a spare, before refitting the battery cover. Do not forget to
obtain a new fuse and place it in the spare position. If the instrument will not operate
in the loop impedance, PSC/
fitted on the printed circuit board have blown. If you suspect that the fuses have failed,
return the instrument to your distributor for service - do not attempt to replace the fuses
yourself.
PFC and RCD modes, it may be that the protective fuses
in the
Page 58

20. SERVICING
If this tester should fail to operate correctly, return it to your distributor stating the exact
nature of the fault. Before returning the instrument ensure that:-
1.The leads have been checked for continuity and signs of damage.
2.The continuity mode fuse (situated in the battery compartment) has been checked.
3.The batteries are in good condition.
Please remember to give all the inf
fault, as this will mean that the instrument will be serviced and returned to you
more quickly.
ormation possible concerning the nature of the
55
Page 59

Fig.55
Fig.56
Fig.54
21. CASE AND STRAP ASSEMBLY
Correct assembly is shown in Fig 54, 55 and 56. By hanging the instrument round the
neck,
both hands will be left free for testing.
1. Attach the Buckle to the KEW6016 as shown in Fig.54.
Match the hole of the Buckle and
the protrusion at the side face of
KEW6016, and slide it upwards.
2. How to install the Strap belt
Pass the strap belt down through
the buckle from the top, and up.
3. How to fasten the Strap belt
Pass the strap through the
buckle, adjust the strap for length
and secure.
56
Page 60

DISTRIBUTOR
Kyoritsu reserves the rights to change specifications or designs described in this
manual without notice and without obligations.
08-09 92-1959B
 Loading...
Loading...