Page 1
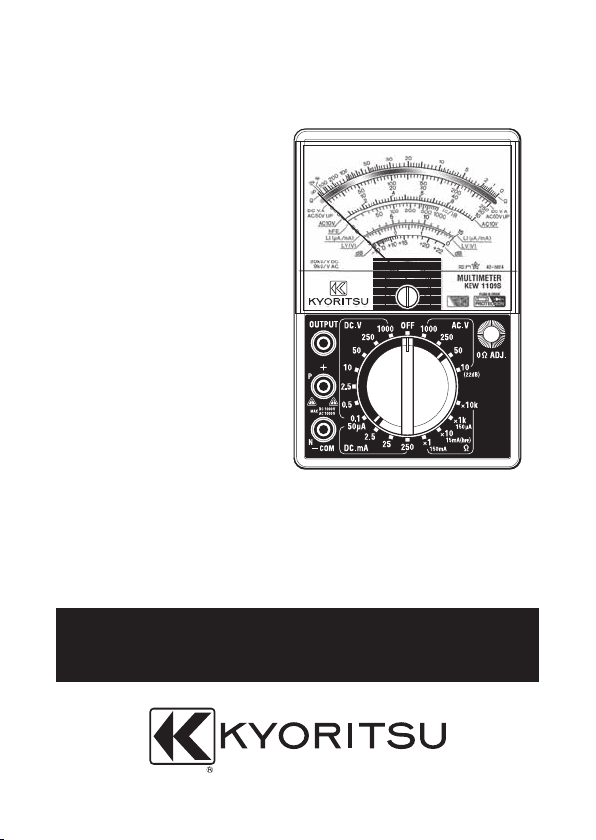
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
ANALOGUE MULTIMETER
KEW 1109S
Page 2

Table of Contents
Page
1. Safety Warnings ............................................................................... 1
• Understanding Some of the Basics in Electrical Testing
Before Using the Multimeter .......................................................... 3
2. Features ........................................................................................... 5
3. Specifications ....................................................................................6
4. Instrument Layout ............................................................................. 8
5. How to Read Scales ......................................................................... 9
6. Operating Instructions ..................................................................... 11
6-1 Preparation ................................................................................ 11
6-2 DC Voltage Measurements ...................................................... 12
6-3 AC Voltage Measurements ....................................................... 13
6-4 Low Frequency (dB) Measurements ........................................ 14
6-5 AC Output Voltage Measurements Using Output
Terminal ................................................................................... 15
6-6 DC Current Measurements ...................................................... 16
6-7 Resistance Measurements ....................................................... 17
6-8 Terminal Current LI, Terminal Voltage LV &
Diode Test ................................................................................ 20
6-9 Measuring I
6-10 Measuring h
7. Fuse & Battery Replacement .......................................................... 27
(leakage current of transistors) ......................... 22
CEO
(DC Current Amplification Factor) ................... 24
FE
Page 3

1. Safety Warnings
The instrument must be used by a competent, trained p erson and
operated in strict accordance with the instructions. Kyoritsu Electrical
Instruments Works, Ltd will not accept liability for any damage or injury
caused by misuse or non-compliance with the instructions or safety
procedures. It is essential to read and understand the safety rules
contained in the instructions. They must be observed when using the
instrument.
● This instruction manual contains warnings and safety rules
which must be observed by the user to ensure safe operation of
the instrument and retain it in safe condition for a long period.
Therefore, read these operating instructions thoroughly and
completely before using the instrument.
WARNING
#
This is a warning for the user to avoid electric shock hazard.
The symbol # on the instrument means that the user must read the
instructions in this manual for safe operation of the instrument.
CAUTION
#
This is a caution for the user to avoid damage to the instrument.
WARNING
#
● Never open the back case during measurements.
● Never use the instrument to measure voltage higher than 250V
on an industrial power line.
● When meas ur in g a high voltage greater t ha n 250V (in s ma ll
power supply circuit and not on power transmission line),
connect the test leads to the circuit under test after it is once
de-energized. Do not touch the wiring or test leads by hand
during voltage measurements. After the measurements, turn off
power to the circuit under test and disconnect the test leads.
Never test a circuit voltage higher than 250V with the rang e
selector switch erroneously set to one of the current or
resistance range positions. The fuse may not protect the circuit.
1
Page 4

● Never use the instrument in an explosive atmosphere especially
when making current measurements.
CAUTION
#
● Before makin g mea surements check that the range selec tor
switch is at a proper range position. Make sure to remove the
tips of the test leads from the circuit under test when changing
the measuring range during measurements.
● Do not apply voltage to the current or resistance ranges. It may
result in a fuse blow or instrument damage.
● Make certain to set the range selector switch to the OFF position
after every use.
● It is recommended that the range selector switch should be set
to the 250mA DC position to protect the instrument against the
possible shock or vibration in transit.
Note: Take good care not to make voltage measurements with
the range selector switch at the 250mA DC position. The
fuse may blow or instrument get damaged.
● Do not exp o se the ins t r ument to the di r e ct sun, ext r eme
temperature and humidity or dew fall for a long period. Also, care
must be taken not to give a shock to the instrument by dropping
or inadequate handling.
● Since the meter cover has been given an anti-static treatment
do not rub it strongly with a dry cloth. Where anti-static charges
are present on the meter window after it has been used for a
long period of time, causing the meter pointer to deflect in an
abnormal way, coat its surface with anti-static chemicals for
plastics or wipe it with a dilute solution of anti-static fluid as a
temporary measure.
● Understanding Some of the Basics in Electrical Testing Before
Using the Multimeter
2
Page 5
● Auxiliary Units (Prefixes)
There are a number of measurement units used for multimeters.
Vol t (V), am p e r e (A) an d ohm (Ω ) are mo s t widely us e d as
meas ure ment un its to indi cat e electri cal p otent ial , current a nd
resistance. However, it is not always straitforward to handle these
units as they sometimes too large or too small for practical use or
calculation. Prefixes are therefore used as auxiliary units to simplify
the usage of such measurement units.
The following table shows some of the examples:
Auxiliary Unit M k m μ n P
Read mega- kilo- milli- micro- nano- pico-
Multiply 10
Example
6
2MΩ
=
2000kΩ
3
10
2kΩ
=
2000Ω
-3
10
250mA
=
0.25A
-6
10
50μA
=
0.05mA
10-9 10
200nF
=
0.2μF
-12
1000pF
=
0.001μF
● Notes on Voltage & Current Measurements
It is important to understand the basic differences between current
and voltage measurements for proper use of multimeters.
Voltage measurements are designed to detect potential difference
between two points. Make certain that the multimeter is connected in
parallel with the circuit under test.
Current measurements are intended to monitor the consumption of
current in the circuit resulting from the application of voltage. Make
sure to connect the multimeter in series with the circuit under test.
Generally speaking, the internal resistance of a voltmeter should
preferably be larger, while that of an ammeter should be smaller. If
the multimeter is erroneously connected in parallel with a circuit for
current measurements, the likely result will be the flow of excessive
current and aubsequent damage to the fuses and other electronic
components. To avoid such a potential danger it is necessary to have
a good understanding of voltage and current measurements.
3
Page 6
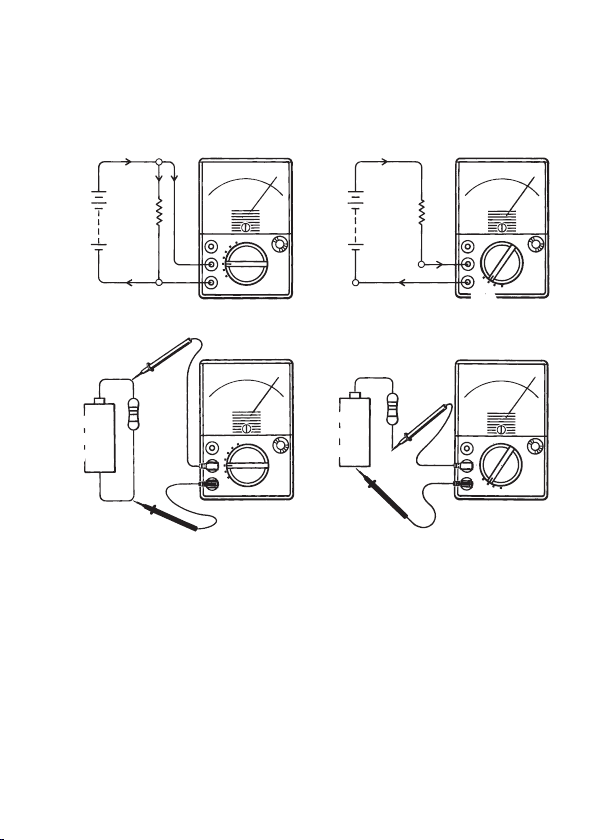
Voltage Measurements Current Measurements
IR+I
M IR
> > I
M
↓ ↓
R
M・IR
< < E
R
M・IR
I
M
I
R
I
R
Power
Source
Power
Source
E E
Load Load
R
M
= ∞
DC.V Range DC.mA Range
+
+
−COM
−COM
+
−
−
RM = 0
V
mA
mA
Battery
(Power
Source)
Battery
(Power
Source)
Battery
(Power
Source)
Battery
(Power
Source)
Resistor
(Load)
Resistor
(Load)
(Parallel Connection) (Series Connection)
Measuring voltage at both ends
of a resistor.
.......... Meter Current
I
M
I
.......... Load Current
R
E .......... Power Source Voltage
RM ........ Internal Resistance of Multimeter
M e a su r in g c u r r e n t b ei ng
consumed by a resistor.
Fig. 1
4
Page 7

2. Features
● Mirrored scale for easy and accurate reading.
● 19 measuring ranges for a wide scope of application.
● OUTPUT terminal to cut off the DC component of AC voltage being
measured.
● hFE scale for transistor checking.
● dB scale (−10 - +62dB).
● Safety designed input terminals and test leads.
5
Page 8
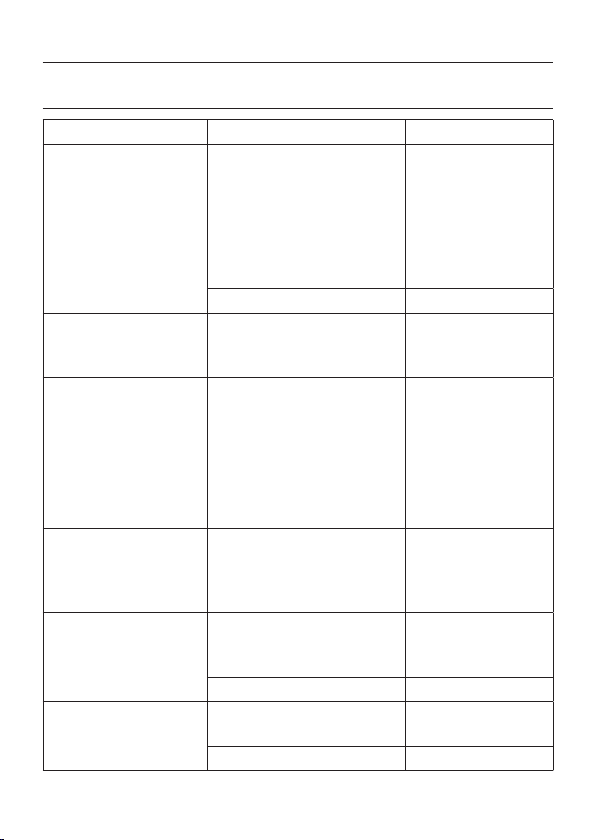
3. Specifications
Functions Measuring Ranges Accuracy
0-0.1 V
0-0.5V
0-2.5V
DC Voltage
(7 ranges)
AC Voltage
(4 ranges)
DC Current
(4 ranges)
Resistance
(4 ranges)
Current across Terminals at
Resistance Range (LI)
(4 ranges)
Voltage across Terminals at
Resistance Ranges (LV)
(4 ranges)
0-10V (20kΩ/V)
0-50V
0-250V
0-1000V
0-10V
0-50V (9kΩ/V)
0-250V
0-1000V
0-50μA
0-2.5mA
0-25mA
0-250mA
0-2kΩ (20Ω mid-scale)
0-20kΩ (200Ω mid-scale)
0-2MΩ (20kΩ mid-scale)
0-20MΩ (200kΩ mid-scale)
0-150mA (x1 range)
0-15mA (x10 range)
0-150μA (x1k range)
0-60μA (x10k range)
0-3V (x1 , x10, x1 k ranges)
0-12V (x10k)
terminal voltage
(
approx. 100mV
terminal voltage
(
approx. 100mV
terminal voltage
(
approx. 150mV
terminal voltage
(
approx. 550mV
)
)
)
)
±3% of full scale
±3% of full scale
±3%
of full scale
±3% of scale length
±5% of scale length
(Battery voltage at 3V)
(Battery voltage at 12V)
±5% of scale length
(Battery voltage at 3V)
(Battery voltage at 12 V)
6
Page 9
Low Frequency
Output Using
OUTPUT Terminal
Low Frequency
Output (dB)
(4 ranges)
0-10V
0-50V
0-250V
0-1000V
10V AC
10 - +22dB
−
50V AC +4 - +36dB
250V AC +18 - +50dB
1000V AC +30 - +62dB
(0 dB = 0.775V(1mW)
Refer to frequency
characteristic chart
Refer to frequency
characteristic chart
across a 600Ω line)
DC Current Amplication
Factor (hFE) (1 range)
hFE: 0-1000 (atΩ× 10 range)
±3% of scale length
Dimensions: 100 (W) x 150 (L) x 47 (D)mm
Weight: Approx. 330g
Accessories: Test Leads (Model 7210) - 1 set
F250V 0.5A fuse - 2 pcs. (including one spare fuse
also installed into the housing case)
1.5V Battery Type R-6P, SUM-3, AA or equivalent -
2 pcs.
(Installed into the instrument)
9V Battery Type 6F22, 006P PP3, or equivallent
- 1 pce (installed into the instrument)
Instruction Manual - 1 copy
7
Page 10
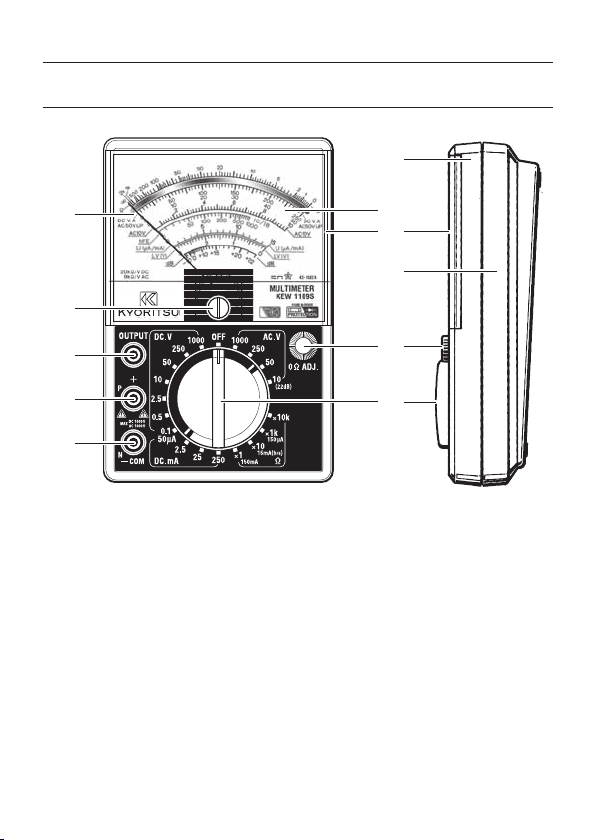
4. Instrument Layout
①
⑥
⑦
⑧
⑨
⑩
⑪
②
③
④
⑤
OUTPUT Terminal
③
-COM (N) Terminal
⑤
Mirrored Scale Plate
⑦
Housing Case
⑨
Range Selector Switch
⑪
Meter Pointer
①
Meter Zero Adjust Screw
②
+(P) Terminal
④
Front Panel
⑥
Meter Window
⑧
Ohm Zero Adjust Knob
⑩
8
Page 11
5. How to Read Scales
DC Voltage
(7 ranges)
AC Voltage
(4 ranges)
DC Current
(4 ranges)
Resistance
(4 ranges)
Current
across
Terminals
(LI)(4 ranges)
Voltage
across
Terminals
(LV)(4 ranges)
Measuring
Ranges
0.1V
0.5V
2.5V
10V
50V
250V
1000V
10V
50V
250V
1000V
50μA
2.5mA
25mA
250mA
X1Ω
x10Ω
x1kΩ
X10kΩ
X1Ω
X10Ω
X1kΩ
X10kΩ
x1Ω
X10Ω
X1kΩ
X10kΩ
Scales
B 10
B50
B 250
B 10
B50
B250
B10
C10
B50
B250
B10
B50
B250
B250
B250
A 0-2k
A0-2k
A0-2k
A0-2k
E15
E15
E15
E15
F3
F3
F3
F3
H o w t o
Read
Scales
X0.01
X0.01
X0.01
X1
X1
X1
X100
X1
X1
X1
X100
X 1
X0.01
X0.1
X1
X1
X10
X1k
X10k
X10(mA)
X1(mA)
X 10(μA)
X 4(μA)
X1(V)
X1(V)
X1(V)
X4(V)
input
Terminals
+&
COM
−
+&
COM
−
+&
COM
−
+&
COM
−
+&−COM
+&−COM
9
Page 12

Low Frequency
A
B
C
E
D
F
G
Output Using
OUTPUT Terminal
(4 ranges)
Low Frequency
Output (dB)
(4 ranges)
DC Current
Amplification
Factor (h
)
FE
(4 ranges)
10V
50V
250V
1000V
10V
50V
250V
1000V
C10
B 50
B 250
B10
G
−
G
−
G
−
G
−
10-+22dB
10-+22dB
10-+22dB
10-+22dB
X1
X1
X1
X 100
X1
X1 + 14dB
X1 + 28dB
X1 + 40dB
Output &
−
+ & −COM or
Output &
−
X10Ω D 0-1000 X1 +&
COM
COM
COM
−
10
Page 13

6. Operating Instructions
6-1. Preparation
● Make certain that the batteries are installed into the battery case with
polarity in correct position. Also, make sure that the fuses are properly
installed.
● The test leads are saf ety design ed, but make s ure that they are
securely connected to the instrument before use.
● Check that the meter pointer lines up with the "0" mark on the left end
of the scale. If it is off zero, rotate the zero adjust screw to bring the
pointer to the zero position. Accurate measurements cannot be made
without the zero adjustment.
● With the range selector switch at the x 1Ω range position and the
test leads connected to the + and
short the test leads together. If the pointer does not deflect at all, the
probable cause is the absence of batteries or the blown fuse. [Refer
to section 7]
● With the range selector switch set to the x1Ω range position, short
the tips of the test leads together. Turn the ohm zero adjust knob and
make certain that the meter pointer moves to the "0" mark on the
right end of the ohm scale. If not, the battery voltage is insufficient.
Replace all of the 1.5V batteries (R6P, SUM-3 or equivalent). Refer to
section 7 for battery replacement.
● With the range selector switch at the x10kΩ position short the tips of
the test leads together. Then, turn the zero adjust knob clock-wise
and make certain that the meter pointer moves to the "0" mark on the
right end of the ohm scale. If not, the battery voltage is insufficient.
Replace the 9V battery (6F22, 006P or equivalent).
● Select a measuring range suitable for the circuit being tested. When
in doubt as to the maximum voltage or curre'1t expected, make sure
to start with the• highest voltage or current range of the instrument.
COM terminals of the instrument,
−
11
Page 14

6-2. DC Voltage Measurements
WARNING
#
When measuring a high voltage greater than 250V, turn off power
to the circuit under test 8.nd follow the steps as described below.
Then, turn on power to the circuit being measured and proceed
with the voltage measurements. Be careful not to touch the wiring,
test leads and the instrument during voltage measurements. After
making measurements, turn off power to the circuit under test and
disconnect the test leads.
WARNING
#
Never use the instrument on a high voltage power line carrying
more than 250V.
WARNING
#
Never make voltage measurements with the range selector
switch set to the DC mA or ohm range position or the test lead
erroneously connected to the AC 15A terminal. This may not only
damage the instrument or blow the fuse, but also cause an injury
to the operator.
Applications:
Measuring voltage on batteries, electrical appliances, bias voltage of IC
of transistor circuits and any other DC voltages.
Insert the red test lead into the + terminal of the instrument and the
⑴
black test lead into the −COM Terminal.
Set the range s elector swit ch to t he desir ed DC v ol tage r an ge
⑵
position. .
Connect the red test lead to the positive (+) side of the circuit under
⑶
test and the black test lead to the negative (-) side of the circuit (in
parallel with the circuit).
If the measured voltage is less than 250V, set the range selector
⑷
switch to the lower voltage range position for more accurate reading.
12
Page 15

6-3. AC Voltage Measurements
WARNING
#
When measuring a high voltage greater than 250V, turn off power
to the circuit under test and follow the steps (1) to (3) as outlined
below. Then, turn off power to the circuit under test and proceed
with the voltage measurements. Never touch the wiring, test
leads and instrument during measurements. After the voltage
measurements, make sure to turn off power to the circuit under
test and disconnect the test leads.
WARNING
#
Never use the instrument on a high voltage power line carrying
move than 250V.
WARNING
#
Never make voltage measurements with the range selector switch
set to the DC mA or ohm range position. This may not only damage
the instrument or blow the fuse, but also cause an injury to the
operator.
Applications:
Measuring voltage on household and factory electrical installations
especially those for lighting, commercial power lines, power supply
circuits, taps of transformers, etc.
Insert the red test lead into the positive (+) terminal of the instrument
⑴
and the black test lead into the negative (-) COM terminal.
Set the range select or swi tch to the desi re d AC v oltage rang e
⑵
position.
Conn e ct the te s t lead s in para l lel wit h the cir c uit und e r test
⑶
(polarity of the circuit under test may be disregarded for AC voltage
measurements).
As described in section 6-2-(4) for DC voltage measurements, select
⑷
the desired AC voltage range switch position.
13
Page 16

6-4. Low Frequency Output (dB) Measurements
Applications:
Measuring the ratio o f output to input for amplifiers, transmission
circuits, etc.
The r atio of outp ut t o in put in ampli fi er a nd t ransmis sion c ircui ts
is expressed in l ogarithmic values as the human sense of hea ring
responds to the level of sound logarithmically. This is measured in terms
of decibels (dB). Where the load impedance of a circuit is constant two
values of power can be compared simply by indicating input to output
voltage (current) ratio in dB.
The dB readings on the scale are references to 0 (zero) dB power level
of 0.001 watt (one milliwatt) across 600 ohms, or 0.775V AC across 600
ohms. therefore, output in a 600 ohms impedance circuit can be read
directy from the dB scale. When the impedance of a measuring circuit is
not 600 ohms, however, a dB reading obtained is simply the result of
measuring an AC voltage on the corresponding dB scale.
To measure decibels, read the dB scales in accordance with the
⑴
instructions for AC voltage measurements.
For the 10V AC range read the dB scale directly (0 dB=1mW or
⑵
0.775V across 600 ohms). For other ranges including the50V range
read the dB scale and add the appropriate number of the dB to the
reading as shown on Table 2.
Table 1
AC Volt Ranges 10V 50V 250V 1000V
Add dB 0 +14dB +28dB +40dB
Max. dB +22dB +36dB +50dB +62dB
14
Page 17

6-5. Low Frequency Output Measurements Using Output Terminal
WARNING
#
When measuring a high voltage greater than 250V, turn off power
to the circuit under test onc e and then follow t he steps (1) to
(3) as described for AC voltage measuremen ts . The n, turn on
power to the circuit a nd proceed with Low Frequency Output
measurements.
Never touch the wiring, test leads or the instrument during
measurements. After taking measurements, turn off power to the
circuit under test and disconnect the test leads.
WARNING
#
Never make Low Frequency Output measurements with the range
selector switch set to the DC mA or ohm range position. This may
result in instrument damage, fuse blow or a possible injury to the
operator.
Note: The blocking capacitor connected in series with the
OUTPUT terminal may change the AC voltage response
at low frequencies. The lower the Low Frequency Output
the more apparent the change. The AC voltage response
also changes at higher frequencies due to the frequency
characteristics.
Use Table 2 for frequency characteristics to correct the
Low Frequency Output reading.
Applications:
Measuring output voltage of low frequency amplifiers.
Detecting horizontal signals in horizontal amplification circuits of TV
sets.
Detecting the presence of input signals in synchronous isolation and
amplification circuits of TV sets.
15
Page 18

The 1109S has a capacitor in series with the OUTPUT terminal. This
OUTPUT terminal is useful for measuring the AC component only of
a DC coupled Low Frequency Output in TV sets, audio equipment
circuits, etc. by blocking the DC component.
Insert the red test lead into the OUTPUT terminal and the black test
⑴
lead into the -COM terminal.
Make Low Frequency Output measurements in accordance with the
⑵
instructions given for AC voltage measurements.
Table 2 Frequency Characteristics
6-6. DC Current Measurements
WARNING
#
Make sure that the test leads are securely connected to the circuit.
If the test prods are disconnected inadvertently, a high voltage
may develope in the circuit.
WARNING
#
Never apply voltage to the current ranges. The fuse could blow or
the instrument get damaged.
Especially when a voltage higher than 250V is applied accidentally,
the fuse may not protect the circuit.
16
Page 19

Applications:
Measuring currents in DC operated electrical appliances, bias current of
transitors, IC's, etc.
Insert the red test lead into the + termin~1 and the black test lead
⑴
into the −COM terminal.
Set the range selector switch to the 250mA range position.
⑵
Turn off power to the circuit under test.
⑶
Connect the red test lead in series with the positive (+) side of the
⑷
circuit under test and the black test lead with the negative (-) side.
Turn on power to the circuit under test.
⑸
When the reading is below 25mA, set the range selector switch to
⑹
the lower range for more accurate reading and proceed with the
measurement.
6-7. Resistance Measurements
WARNING
#
Be sure to turn off power to the circuit under test before making
resistance measurements.
WARNING
#
Never apply voltage to the ohm ranges. The fuse could blow or the
instrument get damaged. Especially when a voltage higher than
250V is applied, the fuse may not protect the circuit.
CAUTION
#
A maximum voltage of 12V is present on the ×10kΩ range. It may
damage IC's for low voltage equipment.
Before making resistance measurements, carefully check t he
withstand voltage of the circuit under test.
17
Page 20

CAUTION
② Measuring Resistance
① Ohm Zero Adjustment
-COM
+
①
②
#
Make the zero ohm adjustment after every change of the
measuring range to obtain a more accurate reading.
Application:
Checking a resistance value of resistors, circuit continuity, short and
open circuits, etc.
Insert the red test lead into the +terminal and the black test lead into
⑴
COM terminal.
the
−
Set the range selector switch to the desired range position.
⑵
With the test lead tips shorted together turn the zero ohm adjust
⑶
knob so that the meter pointer lines up with the zero mark at the right
end of the ohm scale.
Turn off power to the circuit under test.
⑷
Connect the test leads to both ends of the circuit under test and take
⑸
the reading (Fig. 2).
Resistance Measurements
Fig. 2
18
Page 21

Notes: Fig . 3 sho ws the res i sta nce me asu ring circ uit . The
− +
+
−
+
LV
LI
−COMTerminal
+Terminal
ー
0Ω ADJ
positive (+) polarity of the battery is connected to the
positive (+) terminal of meter. Therefore, the polarity of
the terminals is reversed for resistance measurements,
with output voltage from the -COM terminal being
po s itiv e ( + ) and out p ut vol t age fro m the +te r mina l
negative (-). (Fig. 3).
A good knowledge of this relationship will be helpful in
testing semi-conductors such as transistors and diodes
as well as electrolytic capacitors.
Polarity of Multimeter Terminals at
Resistance Measurements
Fig. 3
19
Page 22

6-8. Terminal Current LI, Terminal Voltage LV &Diode Test
CAUTION
#
Do not measure the internal resistance of a diode with low reverse
withstand voltage using x 10kΩ range. The 12V voltage to b e
applied at this test could damage the diode. Check the rating of a
diode before testing.
Current flowing across the −COM terminal and + terminal during
⑴
resistance measurements is indicated as LI. When LI flows into the
circuit under test there occurs a voltage drop. This is defined as LV.
Use the scale marked LI and LV for reading terminal current and
voltage. Circuit impedance may change according to the current that
flows into the circuit being measured or the voltage applied to the
circuit. Also, an abnormal condition may develope in the circuit due to
its self heating. Therefore, make resistance measurements at each
range w.ith the above in full consideration
Shown below are the values of terminal current
and voltage on each resistance range: Table 3
Resistance
Range
X1 X10 X1k X10k
Multiply by 10 Direct Reading 10 4
Max. Terminal
Current LI
Max. Terminal
Voltage LV
If the connection to the c ircuit is made as shown in Fig. 4, it is
⑵
possible to measure the forward current IF or reverse current I
150mA 15mA 150μA 60μA
3V 3V 3V 12V
of a
R
diode using the LI scale. It is also possible to measure the forward
voltage VF or backward voltage VA of a diode using the LV scale (Fig.
4).
As described for the resistance measurements, make the ohm zero
⑶
adjustment after every change of the measuring range.
20
Page 23

The meter pointer deflects close to full scale when the forward
IR < < IF N(-COM)
I
RIF
P(+)
×10×1 ×1k
⑷
current I
is measured. However, it hardly deflects when the reverse
F
current IR is measured.
The forward voltage of the average germanium diode measures 0.1 V
to 0.2V and that of the silicon diode 0.5V to 0.8V.
Since the maximum open circuit voltage at the low resistance ranges
⑸
is 3V (12V at X 10k range), it is possible to light up an LED having a
forward voltage of more than 1.5V and measure forward current I
well. The reading on the LI scale indicates the forward current I
F
F
as
at
which the LED lights up. The reading on the LV scale also indicates
the forward voltage V
F
For testing a large LED use the X1 Ω range. For a smaller LED
having less than 10mA IF use the X10Ωrange.
Diode Test
Fig.4
21
Page 24

6-9. Measuring I
CAUTION
#
(leakage current of transistors)
CEO
The leakage current does not change significantly according to
voltage, but it rather exhibits constant current characteristics.
However, note that the leakage current is very sensitive to
the temperature and varies with the temperature change
(approximately twice as against 10
CAUTION
#
When measuring I
current will flow and I
CAUTION
#
, do not touch the base of a transistor. Base
CEO
increase.
CEO
If tested on the x10kΩ range, a transistor having V
temperature rise)
℃
less than
CE
12V could possi bly be damaged. Always check the rating of a
transistor before testing.
Use the resistance measuring ranges to test transistors.
⑴
In sert the red a nd blac k test leads i nt o the P(+) and N(
⑵
COM)
−
terminals respectively.
With the tips of the test leads shorted together, turn the ohm zero
⑶
adjust knob so that the meter pointer lines up with the "0" mark on
the right end of the ohm scale.
Connect the test leads to the transistors according to their polarity, as
⑷
shown in Fig. 5 Ⓐ for the NPN transistor and Fig. 5 Ⓑ for the PNP
transistor.
Fig. 5 may be represented by an electrical circuit (Fig. 6).
⑸
(Part of the circuit located on the right side of the P/N terminals
corresponds to be internal circuit of the multimeter.)
Current flowing between the P and N terminal is a reverse leakage
⑹
current I
. Take the reading on the LI scale.
CEO
22
Page 25

Measuring Leakage Current of Transistor I
(E)
EMITTER
(E)
EMITTER
(B)
BASE
(B)
BASE
(C)
COLLECTOR
(C)
COLLECTOR
P(+) P(+)
N(-COM)
N(-COM)
X10 X10
I
CEO
I
ECO
Ⓑ PNP Type TransistorⒶ NPN Type Transistor
N
(E)
(C)
(B)
NPN
TRANSISTOR
P
R
3V
+
−
I
CEO
M
CEO
Fig. 5
Th e leak age cu rre nt of
⑺
th e sil ico n tra nsis tor i s
too small to give pointer
deflection. If the pointer
s h o ul d d e f l e c t , t he
likel y ca u s e wou l d be
some fault of the silicon
transistor.
With the germanium transistor the leakage current flows even if it is
⑻
good, but the amount slightly differs with the types of the transistor.
Use Table 4 below to determine if the germanium transistors are
good or bad.
Table 4
Leakage Current I
CEO
of
Germanium Transistors
Small &Medium
Sized Transistors
Approx. 0.1 - 2mA Approx. 1 - 5mA
If the leakage current exceeds the above values
appreciably, the transistors are faulty.
23
Large Sized
Transistors
Fig. 6
Page 26

6-10. Measuring hFE (DC Current Amplification Factor)
(E) EMITTER
(C) COLLECTOR
(B) BASE
I
ECO
+(IB×hFE)=I
C
hFE=−
I
C
I
B
I
B
P(+)
R(24kΩ)
(B)
(E)
(C) N(-COM)
X10(h
FE
)
h
FE
CAUTION:
#
With the germanium transistor, the leakage current flows into
the collector side, causing that much error in leakage current
measurements. Therefore, obtain a true value of leakage current
by deducting a hFE value equivalent to the leakage current from the
measured value.
The following will explain about the principle of hFE measurements.
⑴
As s hown in Fig. 7, the collector and emitter of a transistor are
co n n ecte d to the mul t imete r. Whe n a res i stor R of a c e rtai n
resistance value (approx. 24kΩ) is connected across the N (−COM)
terminal of the instrument and the base of the transistor, baseterminal current IB, determined by R (approx. 24kΩ), flows and current
I
, multiplied by hFE, also flows into the collector of the transistor,
C
resulting in the increase of DC current and thus causing the meter
indication to change notably.
Theoretically, the hFE (=lC/lB) of a transistor (DC current amplification
factor) can be measured by plotting the amount of the current change
on a separate hFE scale.
The hFE scale for Model 1109 is marked for the 24kΩ R (approx.
100μA base current at 3V LV).
Fig. 7
24
Page 27

How to Use h
Test Lead (1)
Test Lead (2)
Test Lead (1)
Test Lead (2)
R=24kΩ
(B)
(C)
(E)
h
FE
h
FE
(B) (B)
(C)
(C)
(E)
(E)
P(+)
P(+)
N(-COM)
N(-COM)
X10 (hFE) X10 (hFE)
NPN Type Transistor PNP Type Transistor
(E) EMITTER
(C) COLLECTOR
(B) BASE
⑵
Test Leads
FE
The test lead set mainly consisting of a resistor and a clip as shown
in Fig. 8 is on the market and is recommended for use in making h
measurements.
Test Lead Set for hFE Measurements
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
25
FE
Page 28

As indicated in Fig. 9, connect the hFE test lead (1) to the multimeter,
according to the polarity of a transistor to be tested; N (-COM) terminal
for the NPN type transistor or P (+) terminal for the PNP type transistor.
Also, connect the hFE test lead (2) to the P(+) terminal for the NPN type
transistor and the N (−COM) terminal for the PNP type transistor. With
the test lead clips (E) and (C) shorted, turn the ohm zero adjust knob so
that the pointer lines up with the zero (0) mark on the right end of the
ohm scale. Then, connect the hFE test lead clips as follows:
Clip (C) and clip (B) for hFE test lead (1) to the collector and base
terminals of the transistor respectively.
Clip (E) of the hFE test lead (2) to the emitter of the transistor.
W h e n the tr a n s i s t or is good, th e in d i c a t e d val u e is sm a l l ,
⑶
representing leakage current I
only with the base terminal open
CEO
(lB=0).
If base-terminal DC current IB flows, collector-terminal DC current I
changes and meter gives a reading of the current increased by I
h
.
FE
When the transistor is faul ty, the t hree p os sible case s may be
⑷
B
X
considered.
There is no change in the current reading between the times when
the base terminal is open (lB=0) and when IB flows.
No meter pointer deflection even when IB flows.
The meter pointer moves past the hFE scale and deflects close to full
scale, even when the base terminal is open (IB=0).
C
26
Page 29

7. Fuse & Battery Replacement
WARNING
#
Never replace the fuse or batteries during measurements. Make
sure to set the range selector switch to OFF position and remove
the test leads from the instrument before replacing the fuse and
batteries.
Always use the F 2S0V 0.5A fuse as specified.
When the fuse blows remove the housing case by unscrewing the
⑴
case fixing screw to replace the fuse.
When 2 x1.5V battery (R-6P, SUM-3 or equivalent) are exhausted, it is
⑵
no longer possible to zero ohm adjust on the x 1Ω range. Remove the
housing case by unscrewing the case fixing screw to replace the batteries.
Observe correct polarity when replacing the batteries.
When the 9V battery (6F22, 006P or equivalanet) is exhausted, it is no
⑶
longer possible to zero ohm adjust on the X10kΩ range. Remove the
housing case by unscrewing the case fixing screw to replace the battery.
Fig. 10
27
Page 30

PCB Component Layout Drawing
Fig. 11
28
Page 31

PARTS LIST
No. DESCRIPTION
R1 Resistor 1/2WF, ( 15MΩ) DC 1000 V
R2 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 4MΩ) DC 250 V
R3 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 800 KΩ) DC 50 V
R4 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 150 KΩ) DC 10 V
R5 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 40KΩ) DC 2.5 V
R6 Resistor 1/2WF, ( 8KΩ) DC 0.5 V
R7 Resistor 1/2WF, ( 83.3 KΩ) AC 10 V
R8 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 360 KΩ) AC 50 V
R9 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 1.8MΩ) AC 250 V
R10 Resistor 1/2WF, ( 6.75MΩ) AC 1000 V
R11 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 40.7 Ω) DC 2.5m A
R12 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 4 Ω) DC 25m A
R13 Resistor 1/2WF, ( 0.379 Ω) DC 250m A
R14 Resistor 1/2WF, ( 18 Ω) ΩX 1
R15 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 200 Ω) ΩX 10
R16 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 34KΩ) ΩX 1K
R18 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 240 Ω)
R19 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 44KΩ)
R20 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 195 KΩ) ΩX10K
R21 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 18KΩ)
R22 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 750 Ω)
R23 Resistor 1/4WF, ( 31KΩ)
VR1 Variable Resistor, ( 10KΩ)
D1,2,3 Diode 1N4448
C1 Ceramic Capacitor, 0.047μF50V
C2 Metal Film Capacitor, 0.047μF630V(OUTPUT)
BT1 Battery 1.5V,R6P,SUM-3 or equiv. (X2)
BT2 Battery 9V, 6F22, 006P or equiv.
F1 Fuse, Fast Acting Type, F250V/0.5A,
6×30mm
φ
M Meter Movement, (44μA / 1.25KΩ)
BS1 Battery Contacts (X4)
BS2 Battery Contact (X1)
29
Page 32

30
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Page 33

MEMO
31
Page 34

MEMO
32
Page 35

Page 36

DISTRIBUTOR
Kyoritsu reserves the rights to change specifications or designs
described in this manual without notice and without obligations.
92-2025
 Loading...
Loading...