Kyocera KD135SX-UPU, KD140SX-UPU User Manual

35SX
U
,
0SX
INSTALLATION MANUAL
FOR THE
KD1
-UP
KD14
-UPU
OF
SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER MODULES
Please read this manual carefully before installing the modules.
KYOCERA
6C-209365
1. INTRODUCTION
As the world leader in development and application of high technology
ceramic/silica materials, Kyocera offers a wide range of highly efficient
and reliable crystalline silicon solar photovoltaic (PV) power modules.
Kyocera began to extensively research PV technology in 1975 and
commenced manufacturing operations in 1978. Since then, Kyocera
has supplied millions of cells and modules throughout the world. With
years of experience and state-of-the-art technology, Kyocera provides
the highest quality PV power modules in a range of sizes designed to
meet the requirements of the most demanding energy and power users
worldwide.
2. POWER MODULES
Kyocera PV power modules consist of a series of electrically
interconnected crystalline silicon solar cells, which are permanently
laminated within a pottant and encapsulated between a tempered glass
cover plate and a back sheet. The entire laminate is secured within an
anodized aluminum frame for structural strength, ease of installation,
and to protect the cells from the most severe environmental conditions.
3. APPLICATIONS
Kyocera PV modules are a reliable, virtually maintenance-free direct
current (DC) power source, designed to operate at the highest level of
efficiency. Kyocera PV modules are ideal to remote homes,
recreational vehicles, water pumps, telecommunication systems and
many other applications either with or without using storage batteries.
4. WARNINGS & SAFETY
PV modules generate electricity when exposed to light. Arrays of many
modules can cause lethal shock and burn hazards. Only authorized
and trained personnel should have access to these modules. To
reduce the risk of electrical shock or burns, PV modules may be
covered with an opaque material during installation. Do not touch live
terminals with bare hands. Use insulated tools for electrical
connections. Do not use these PV modules for solar concentration.
WARNING
“SUITABLE FOR USE IN CLASS I, DIVISION 2, GROUPS A, B, C
AND D HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS, OR NONHAZARDOUS
LOCATIONS ONLY.”
“WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT DISCONNECT
EQUIPMENT WHILE THE CIRCUIT IS LIVE OR UNLESS THE AREA
IS KNOWN TO BE FREE OF IGNITABLE CONCENTRATIONS.”
“WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - SUBSTITUTION OF ANY
COMPONENT MAY IMPAIR SUITABILITY FOR CLASS I, DIVISION
2.”
PERMIT
・ Before installing your PV system, contact local authorities to
determine the necessary permitting, installation and inspection
requirements.
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION
・ Systems should be installed by qualified personnel only. The
system involves electricity, and can be dangerous if the
personnel are not familiar with the appropriate safety procedures.
・ Do not step on a PV module.
・ Although Kyocera PV modules are quite durable, the glass can
be broken (and PV module will no longer work properly) if it is
dropped or hit by tools or other objects.
・ PV module frame is made of anodized aluminum, and therefore
corrosion can occur if PV module is subject to a salt-water
environment and is in contact with another type of metal
(electrolytic corrosion), If required, PVC or stainless steel
washers can be placed between PV module frame and support
structure to prevent this type of corrosion.
・ KD series module frames must be attached to a support structure
by one of the methods described in Section 7, Installing KD series
modules.
・ Module support structures to be used to support PV modules
should be wind rated and approved by the appropriate local and
civil codes prior to installation.
・ Do not expose the back of PV module to direct sunlight.
・ In Canada installation shall be in accordance with CSA C22.1,
Safety Standard for Electrical Installations, Canadian Electrical
Code, Part 1.
FIRE RATING
・In case of roof installation, PV module assembly shall be mounted
on a fire resistant roof covering rated for the application. KD series
modules are comprised of a glass front surface, polyethylene
terephthalate (PET) back sheet with a Class C fire rating.
GROUNDING
・ Refer to “Grounding” section.
BATTERY
・ When PV modules are used to charge batteries, the battery must
be installed in a manner which will ensure the performance of the
system and the safety of its users. Follow the battery
manufacturer’s safety guidelines concerning installation,
operation and maintenance recommendations. In general,
the battery (or battery bank) should be kept away from people
and animals. Select a battery site that is protected from sunlight,
rain, snow, debris, and is well ventilated. Most batteries generate
hydrogen gas when charging, which can be explosive. Do not
light matches or create sparks near the battery bank. When a
battery is installed outdoors, it should be placed in an insulated
and ventilated battery case specifically designed for this purpose.
5. SITE SELECTION
In most applications, Kyocera modules should be installed in a location
where they will receive maximum sunlight throughout the year. In the
Northern Hemisphere, the modules should typically face south, and in
the Southern Hemisphere, the modules should typically face north.
Modules facing 30 degrees away from true South (or North) will lose
approximately 10 to 15 percent of their power output. If the module
faces 60 degrees away from true South (or North), the power loss will
be 20 to 30 percent. When choosing a site, avoid trees, buildings or
obstructions which could cast shadows on PV modules especially
during winter season when the arc of the sun is lowest over the horizon.
6. MODULE TILT ANGLE
Kyocera modules produce bigger power when they are pointed directly
at the sun. For stand alone installations PV modules should be tilted for
optimum winter performance. As a general rule, if the system power
production is adequate in the winter, it will be satisfactory during the
rest of the year. PV module tilt angle is measured between PV
modules and the ground. Refer to the recommended module tilt angle
table for your site.
MODULE
SUNLIGHT
TILT ANGLE
GROUND(HORIZONTAL)
Figure 1. Module Tilt Angle
1
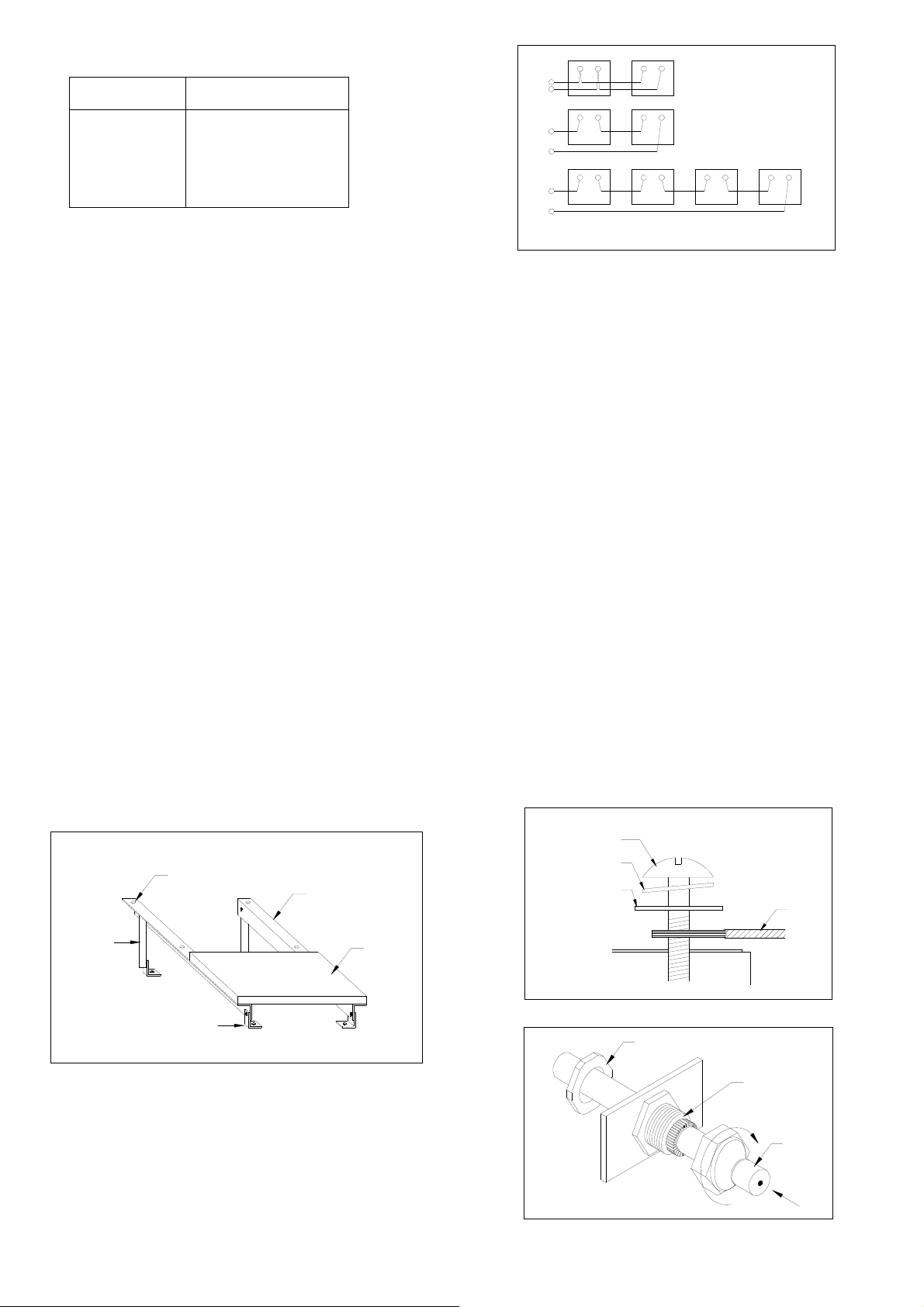
Table 1. Recommended Tilt Angles for Stand Alone
Fixed Systems - Based on Winter Performance
SITE LATITUDE
IN DEGREES
0°TO 15
15°TO 25°
25°TO 30°
30°TO 35°
35°TO 40°
40°+
FIXED TILT ANGLE
15°
SAME AS LATITUDE
LATITUDE + 5°
LATITUDE + 10°
LATITUDE + 15°
LATITUDE + 20°
For grid tie installations where the solar modules are attached to a
permanent structure, PV modules should be tilted at an angle equal to
the site's latitude. This will typically result in the highest annual energy
output.
7. INSTALLING KD SERIES MODULES
The minimum spacing of 50mm (2”) is required between PV module
and the mounting surface around the perimeter of PV module. The
frame of each PV module has 9mm (0.35”) diameter mounting holes
(Refer to Module Mounting Specifications). These are used for fixing
PV modules to the supporting structure. PV module frames must be
attached to a support structure using M8 (5/16”) stainless steel screw in
a minimum of four (4) places symmetrical on PV module. The stainless
steel screw used for fixing the module frame should secure with an
adequate torque. (usually, 19 N-m (14 ft-lb).) An example of a ground
mounted structure is shown in Figure 2. The four holes close to the
corners of the module are most often used for installation. Refer to the
Mounting Specifications for the position of these holes. Clearance
between PV module frame and the mounting surface may be required
to prevent the junction box from touching the surface, and to circulate
cooling air around the back of PV module. Spacing between PV
modules must be a minimum of 1/8" (3.2 mm) to allow for thermal
expansion. If the modules are to be installed on the roof or wall of a
building, the stand-off method or the rack method is recommended.
STAND-OFF METHOD: PV modules are supported parallel to the
surface of the building wall or roof. Clearance between PV module
frames and surface of the wall or roof is required to prevent PV module
and / or wiring from damage.
The recommended stand-off height is 4.5” (about 115 mm). If other
mounting means are employed, this may affect the Listing For Fire
Class Ratings.
RACK METHOD: The supporting frame is used to mount PV modules
at correct tilt angles. PV modules specified in this installation manual
are not designed for Building Integrated Photovoltaic (B.I.P.V)
application as part of a roof or wall. The mounting design may have an
impact on the fire resistance.
OTHER: Other method(s) certified by a registered professional
engineer, and in compliance with local codes.
MOUNTING HOLE
ARRAY FRAME
21
1 2
+--+
+
-
+
-
+
BLACK
RED
12
- ++-
BLACK
RED
12 212121
+- - + +- -
BLACK BLACK BLACK
EXAMPLE OF 'IM' TYPE J-BOX WIRING
12 VOLT (2 PARALLEL)
2
1
24 VOLT (2 SERIES)
48 VOLT (4 SERIES)
RED
+
Figure 3. Standard Wiring Examples
To wire Kyocera PV modules:
A. Determine the nominal system array voltage of your system.
Each panel is equivalent to a 12 VDC nominal block. Standard
array voltages 12, 24 and 48 volt are shown as examples in
Figure 3.
B. Open the "IM" box cover by loosening the screws in the cover.
C. The wire used to interconnect PV modules may be single or two
conductors, from 14AWG (2.08 mm
2
) up to 10AWG (5.26 mm2)
gauge stranded copper wire, in a “SUNLIGHT RESISTANT” and
insulated for 90℃ minimum jacket cable. This cable is suitable for
applications where wiring is exposed to the direct rays of the sun.
The maximum and minimum outer diameters of the cable that may
be used with the cable connector are 8 mm and 6 mm respectively
(Figure 4).
D. Using a flat blade screw driver, remove only the appropriate
"KNOCK-OUTS" from the sides of the "IM" box.
E. Route wires through the knock-outs and clamps refer to
installation example (see Figure 5).
F. Gentl y hand tighten the terminal screws with cross slot (Phillips
-head) screwdriver. Do not over tighten, as the terminal can be
damaged.
(Recommendation Torque : 1.5N-m (13.3 in-lb)
G. The output wiring from the final module is generally run to a
separate array junction box. In commercial system, this wiring
from the array box to the next component (i.e. fuse box. or charge
regulator, etc.) is generally run in conduit. The maximum electrical
rating of an acceptable series fuse is 15 amperes.
H. After checking that PV module wiring is correct, close all the
junction boxes. Use a Phillips head screw driver to secure all
screws on the junction box cover to ensure a waterproof seal.
I. Refer to the cable clamp specifications for KD135SX-UPU and
KD140SX-UPU.
Refer to below for a cable clamp of our designation.
(Manufacturer / Part Number)
Cable Gland : LAPP / S2212 (NPT-1/2")
Nut : LAPP / 911371K (NPT-1/2")
TERMINAL SCREW
SPRING WASHER
SQUARE WASHER
CABLE
SUPPORT
LEGS
FOOT ANGLE
MODULE
Figure 2. Basic Rack or Stand-off Mounting Structure
8. MODULE WIRING
As shown in Figure 3 Standard Wiring Examples, Kyocera PV modules
utilize the Type "IM" junction box (see J-box details). This junction box,
located on the back side of the module, is weatherproof and is
designed to be used with standard wiring or conduit connections.
A cable clamp with a minimum rating of IP65 must be used to maintain
the weatherproof integrity of the junction box. Bypass diodes are
preinstalled at factory.
Figure 4. Ring or Spade Terminal Connectors
NUT
CABLE CLAMP
CABLE
2
 Loading...
Loading...