Page 1

user’s guide
A Guide to the TracPhone F33
Satellite Communications
KVH TracPhone
®
F33
Page 2

Congratulations!
You have selected one of the most advanced and convenient marine communications
systems available today. The KVH
®
Industries’ TracPhone®F33/F55/F77 system,
manufactured by Thrane & Thrane, is designed to provide high-quality voice, fax,
data, and high-speed Internet access.
Technical Support
Please direct any technical questions to:
North America Europe/Middle East/Africa
KVH Industries, Inc. KVH Europe A/S
50 Enterprise Center Kokkedal Industripark 2B
Middletown, RI 02842 USA 2980 Kokkedal, Denmark
Tel: +1 401 847-3327 Tel: +45 45 160 180
Fax: +1 401 849-0045 Fax: +45 45 160 181
E-mail: techs@kvh.com E-mail: customersupport@kvh.dk
Internet: www.kvh.com Internet: www.kvh.com
Product Registration
Don’t forget to register your TracPhone
system for KVH’s free customer support
subscription service. When you register,
you will receive technical and service
updates specific to your system along with
customer support and product news. In
addition, with your information on file,
KVH will be able to offer you even faster,
more convenient product, customer, and
warranty support. KVH will NOT sell or
share your data with other companies or
organziations.
To register your system, simply fill out the
enclosed Product Registration Form or
visit www.kvh.com/register.
TracPhone F33/F55/F77 Customer Service Information
34-0003 Rev. D
Product Information
Before installing the TracPhone, be sure
to write down the following
information:
ISN: _________________________
Above Decks Unit (ADU)
S/N: _________________________
Below Decks Unit (BDU)
S/N: _________________________
BDU Build Date: ____ /____ / _____
YY MM DD
This information will be required for
all troubleshooting or service calls
made regarding this product.
11
Page 3

PLEASE READ!
Important Notice About Your Data Connection
To prevent inadvertent airtime usage, the user must disconnect the
data connection when not in use. If the data connection is not
properly disconnected, your computer may dial out on its own,
which could result in an unintended airtime charge.
KVH accepts no responsibility if this occurs. It is the vessel
owner’s responsibility to ensure that the TracPhone is correctly
interfaced with the vessel’s computer.
If you have any questions about data connections, please contact
KVH Technical Support.
TracPhone F33/F55/F77 Customer Service Information
33
34-0003 Rev. D
Page 4

Thrane & Thrane A/S
SAILOR Fleet33
TT-3088A
User Manual
Copyright© Thrane & Thrane A/S
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Page 5

Information in this document is subject to change without
notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
Thrane & Thrane A/S. It is recommended to download the
latest version of the manual from the Thrane Extra net or
request this from the distributor.
© 2005 Thrane & Thrane A/S. All rights reserved. Printed
in Denmark.
Trademark Acknowledgements:
WinPoET is a trademark of iVasion, a RouterWare Company.
Document No: TT98—116874-F.
Release date: 26 May 2005.
Page 6
Safety Summary
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases
of operation, service and repair of this equipment. Failure to comply with
these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual violates
safety standards of design, manufacture and intended use of the equipment.
Thrane & Thrane A/S assumes no liability for the customer's failure to comply
During transmission the antenna in this system radiates Microwave Power.
This radiation may be hazardous if exposed directly to humans, close to the
antenna. During transmission, make sure that nobody gets closer than the
recommended minimum safety distance. The minimum safety distance to the
with these requirements.
Microwave Radiation Hazards
antenna on the focal line is 1.3 m.
MICROWAVE RADIATION
NO PERSONNEL WITHIN 1.3 m
1.3m
25°
GROUND THE EQUIPMENT
To minimize shock hazard, the equipment chassis and cabinet must be
connected to an electrical ground.
Page 7
DO NOT OPERATE IN AN EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERE
Do not operate the equipment in the presence of flammable gases or
fumes. Operation of any electrical equipment in such an environment
constitutes a definite safety hazard.
KEEP AWAY FROM LIVE CIRCUITS
Operating personnel must not remove equipment covers. Component
replacement and internal adjustment must be made by qualified
maintenance personnel. Do not replace components with the power cable
connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even
with the power cable removed. To avoid injuries, always disconnect power
and discharge circuits before touching them.
DO NOT SERVICE OR ADJUST ALONE
Do not attempt internal service or adjustments unless another person,
capable of rendering first aid resuscitation, is present.
Page 8

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
About the Manual...................................................... 1
1
1.1 Abbreviations..................................................... 1
2 Introduction ............................................................. 3
2.1 The Inmarsat Fleet Service .................................. 3
2.2 The SAILOR Fleet33 System................................. 6
2.3 Hardware Interfaces............................................ 9
2.4 The Handset .................................................... 11
2.4.1 LCD/LED................................................ 12
2.4.2 Function Buttons..................................... 16
2.4.3 Alpha-Numeric Section ............................ 18
3 Getting Started....................................................... 23
3.1 Get Ready to Make a Call................................... 23
3.1.1 How to Power-Up the System. .................. 23
3.1.2 How to Shut Down the System. ................ 25
3.2 Use of PIN Codes.............................................. 26
3.3 Normal Calls .................................................... 27
3.3.1 Calling From the TT-3088A....................... 27
3.3.2 Calling To the TT-3088A........................... 28
3.4 Data Calls........................................................ 29
3.4.1 MPDS Connection.................................... 29
3.4.2 Call waiting............................................ 30
3.4.3 9600 Data Connection ............................. 31
4 Operation............................................................... 33
4.1 Call Functions .................................................. 33
4.1.1 Calls Using the Phone Book ...................... 33
4.1.2 Call From Handset Connected to RJ11........ 33
4.1.3 Fax Calls................................................ 34
4.1.4 Internal Calls.......................................... 35
4.2 Using the Menu System ..................................... 35
4.3 Menu System – All Users ................................... 36
May 2005 i
Page 9

Table of Contents
4.3.1 Phonebook..............................................36
4.3.2 Area.......................................................38
4.3.3 LES........................................................39
4.3.4 Mailbox ..................................................40
4.3.5 Help Desk...............................................41
4.3.6 Alarm Log...............................................42
4.3.7 Status....................................................43
4.4 Menu System - Super User .................................46
4.4.1 Call Logs ................................................46
4.4.2 Routing ..................................................47
4.4.3 Data Setup .............................................49
4.4.4 Contrast .................................................49
4.4.5 Ring Setup..............................................50
4.4.6 Key Beep................................................50
4.4.7 Set UTC Time..........................................51
4.4.8 Set UTC Date ..........................................51
4.4.9 Disclose Pos............................................52
4.4.10 Allowed Dial............................................52
4.4.11 Ph.Book Dial ...........................................53
4.4.12 Auto Prefix..............................................54
4.4.13 BarServiceIn...........................................54
4.4.14 BarServiceOut.........................................55
4.4.15 LED Dimm ..............................................55
4.4.16 Ant.Setup...............................................56
4.4.17 Alarm log................................................57
4.4.18 Warning Log............................................58
4.4.19 Help Desk...............................................58
4.4.20 PIN codes...............................................59
4.4.21 Mail Box .................................................59
4.4.22 RJ11 Setup .............................................60
4.4.23 LES Config..............................................61
4.4.24 Additional Features ..................................62
4.4.25 Data Limits.............................................63
4.4.26 Call Waiting Notification............................64
5 PC Programs ...........................................................67
5.1 System Set-up using FleetCP ..............................67
ii May 2005
Page 10

Table of Contents
5.1.1 The Map ................................................ 68
5.1.2 Pin Codes .............................................. 69
5.1.3 Phonebook............................................. 70
5.1.4 Satellite Setup........................................ 71
5.1.5 Routing ................................................. 72
5.1.6 Setting up Time and Date......................... 73
5.1.7 Barring Services ..................................... 74
5.1.8 Settings................................................. 75
5.1.9 Antenna ................................................ 76
5.2 Set-up Using RS-232......................................... 77
5.2.1 Set-up for MPDS..................................... 77
5.2.2 Set-up for 9600 Data............................... 81
5.3 Set-up using Ethernet/PPPoE.............................. 84
5.3.1 Windows XP with Built-in PPPoE Client ....... 84
5.3.2 Windows 2000 WinPoET PPPoE Client......... 85
6 Troubleshooting...................................................... 89
6.1 List of Error messages....................................... 89
6.1.1 Satellite Network Messages ...................... 89
6.1.2 TT-3088A Messages ...............................103
7 Index ...................................................................107
Appendix A - Menu Tree.................................................109
May 2005 iii
Page 11

Table of Contents
Blank page
iv May 2005
Page 12

Abbreviations About the Manual
1 About the Manual
Congratulations on purchasing your TT-3088A SAILOR
Fleet33 product. This system makes it possible for you to
communicate from virtually any ocean region in the world
using the Inmarsat Fleet service established by Inmarsat.
The system supports inexpensive voice services as well as
data and fax (Spot beam only). This manual has the
following chapters:
Chapter 2 Introduction - an overview of the Inmarsat
Fleet system and its services. Also a brief description of the
systems.
Chapter 3 Getting Started - a description of how to make
and receive calls and the use of PIN codes.
Chapter 4 Operation - a detailed description of the menu
system in the terminal.
1
Chapter 5 PC Programs - a description on how to use the
accompanying configuration PC software (FleetCP).
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting – a description of the most
common errors, how to deal with them and how to get
further help if necessary.
Chapter 7 Index - a subject index
Appendix A - Menu Tree
1.1 Abbreviations
ACU Antenna Control Unit
ADU Above Deck Unit
AORE Atlantic Ocean Region East
May 2005 1
Page 13

1
About the Manual Abbreviations
AORW Atlantic Ocean Region West
BDU Below Deck Unit
FEU Front End Unit
GPS Global Positioning System
IMN Inmarsat Mobile Number
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network
ISN Inmarsat Serial Number
IOR Indian Ocean Region
ISP Inmarsat Service Provider
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
LES Land Earth Stations
MES Mobile Earth Station
MMI Man Machine Interface
MPDS Mobile Packet Data Service
MSN Multiple Subscriber Number
NCS Network Co-ordination Station
NSR Network Status Record
PIN Personal Identification Number
PUK Personal Unblocking Key
POR Pacific Ocean Region
PSTN Public Services Telephone Network
RCC Rescue Co-ordination Center
STE Secure Telephone Equipment
T&T Thrane & Thrane A/S
TNID Terrestrial Network ID
UDI Unrestricted Digital Information
2 May 2005
Page 14
The Inmarsat Fleet Service Introduction
2 Introduction
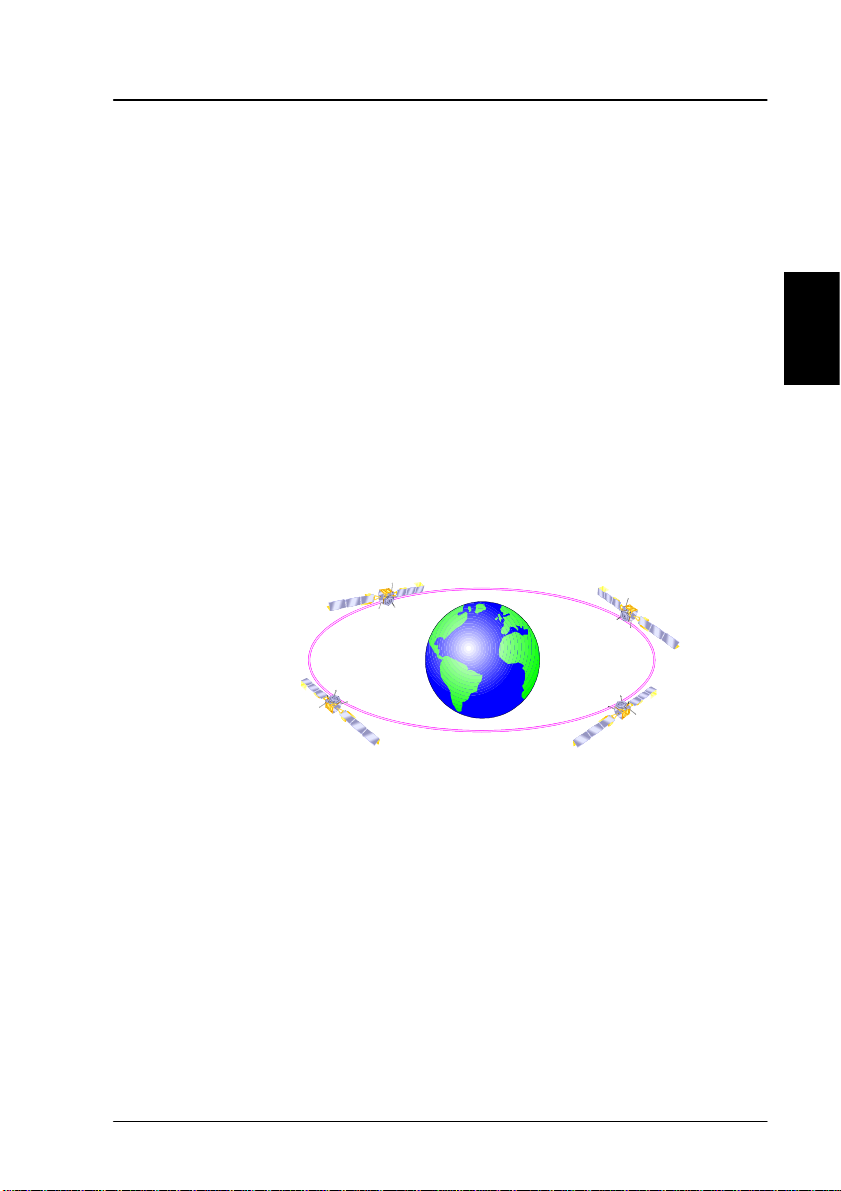
2.1 The Inmarsat Fleet Service
The Inmarsat Fleet service is based on 4 Geo-stationary 3rd
generation satellites situated above the equator. Geostationary means that the satellites are always located in
the same position, i.e. they rotate at the same speed as
that of the earth. Each satellite covers a certain area
(footprint) and supports a number of powerful spot-beams
making the service available in virtually all ocean regions
on the earth between approximately 76°N and 76°S.
The 4 Geo-Stationary Inmarsat Satellites
The satellites are your connection to the worldwide
networks, and they are managed by the Network Coordination Stations (NCSs), run by Inmarsat. The primary
functions of the NCSs are to constantly keep track of which
terminals are logged on to the system, and assign a free
channel whenever a call is made.
2
A Land Earth Station (LES) is a gateway between the public
network and the satellites. Different operators around the
world run the various LES’s.
May 2005 3
Page 15
2
Introduction The Inmarsat Fleet Service
The Fleet services are prepared for operation with the next
generation of Inmarsat satellites (Inm-IV) expected in
2005. The services, which allow for a wide range of
applications, supported by the Inmarsat Fleet encompass:
• Circuit switched services:
• Mini M voice call (Global)
• 9.6 kbps data (Spot beam only)
• 9.6 kbps fax (Spot beam only)
• Packet switched services
• 64/28 kbps MPDS (Spot beam only)
(cf. Appendix B for a map on global and spot beam
coverage).
Service explanation:
The mini-M voice service is only for voice transmission.
The voice transmitted over the satellite is subject to a
compression process down to 4.8 kbit/s, which reduces the
bandwidth use and subsequently the cost.
The 9.6 kbps fax service is a service that enables G3 fax
machines employing one of the modem standards: V.27 or
V.29.
The 9.6 kbps data service allows you to establish a 9.6
kbps circuit switched data connection employing the
modem standard: V.24.
The MPDS service is a packet data service where the tariff
depends on the amount of data transmitted. This service is
a more cost-effective solution for web browsing, and other
applications where there is no need for constant
transmission of data in both directions. It is also suitable
for applications where a constant connection is required,
because the user is no longer charged the “per minute
rate”. The channel is a shared channel i.e. the transmission
4 May 2005
Page 16

The Inmarsat Fleet Service Introduction
speed may be reduced when other users are using the
same channel. The channel to be shared among the users
has a capacity of 64 kbps in the direction to the terminal,
and from the terminal the channel to be shared among the
users has a capacity of 28 kbps.
Important notice: Before a terminal can be used on the
network, it has to be commissioned by one of the Inmarsat
Service Providers (ISP’s). In order to use the different
Inmarsat Fleet services it is necessary to have at least one
Inmarsat Mobile Number (IMN) for each of the above
mentioned services. In case all 3 circuit switched services
are commissioned on your terminal, you will have 3 IMN
numbers.
Calling an Inmarsat Fleet terminal is equal to making
international calls. If the satellite region/area is not known
for the terminal the “country” code for a terminal is 870.
When you dial an Inmarsat Fleet terminal through the
public network, you have to dial the IMN number in
addition to the international access code for Inmarsat, e.g.:
2
+870 600 555 555
Making calls from an Inmarsat Fleet terminal is equal to
making international calls, as the country code always has
to be dialed.
May 2005 5
Page 17

2
Introduction The SAILOR Fleet33 System
2.2 The SAILOR Fleet33 System
The SAILOR Fleet33 System includes the following system
components:
• TT-3008G SAILOR Fleet33 Antenna (ADU)
• TT-3038G SAILOR Fleet33 Transceiver Unit (BDU)
• TT-3622E SAILOR Fleet33 Handset Cradle
• TT-3620G SAILOR Fleet33 Control Handset (4 wire)
• Accessories (manual, software, etc.)
Instructions on how to assemble the system, wiring and
specification, can be found in the Installation Manual.
TT-3008G SAILOR Fleet33 Antenna
The TT-3008G antenna or ADU (
stabilized high-gain antenna. The antenna has built-in all
functions for satellite tracking including a GPS system.
6 May 2005
Above Deck Unit) is a
Page 18

The SAILOR Fleet33 System Introduction
2
TT-3038G SAILOR Fleet33 Transceiver Unit (BDU)
All the interface connectors are located on the rear of the
Transceiver Unit or BDU (
May 2005 7
Below Deck Unit).
Page 19

2
Introduction The SAILOR Fleet33 System
TT-3622E SAILOR Fleet33 Handset Cradle /
TT-3620G SAILOR Fleet33 Control Handset (4 wire)
The Handset is used to configure the system and to make
calls. See section 2.4 for a description of buttons, LED's
and display of the handset.
8 May 2005
Page 20

Hardware Interfaces Introduction
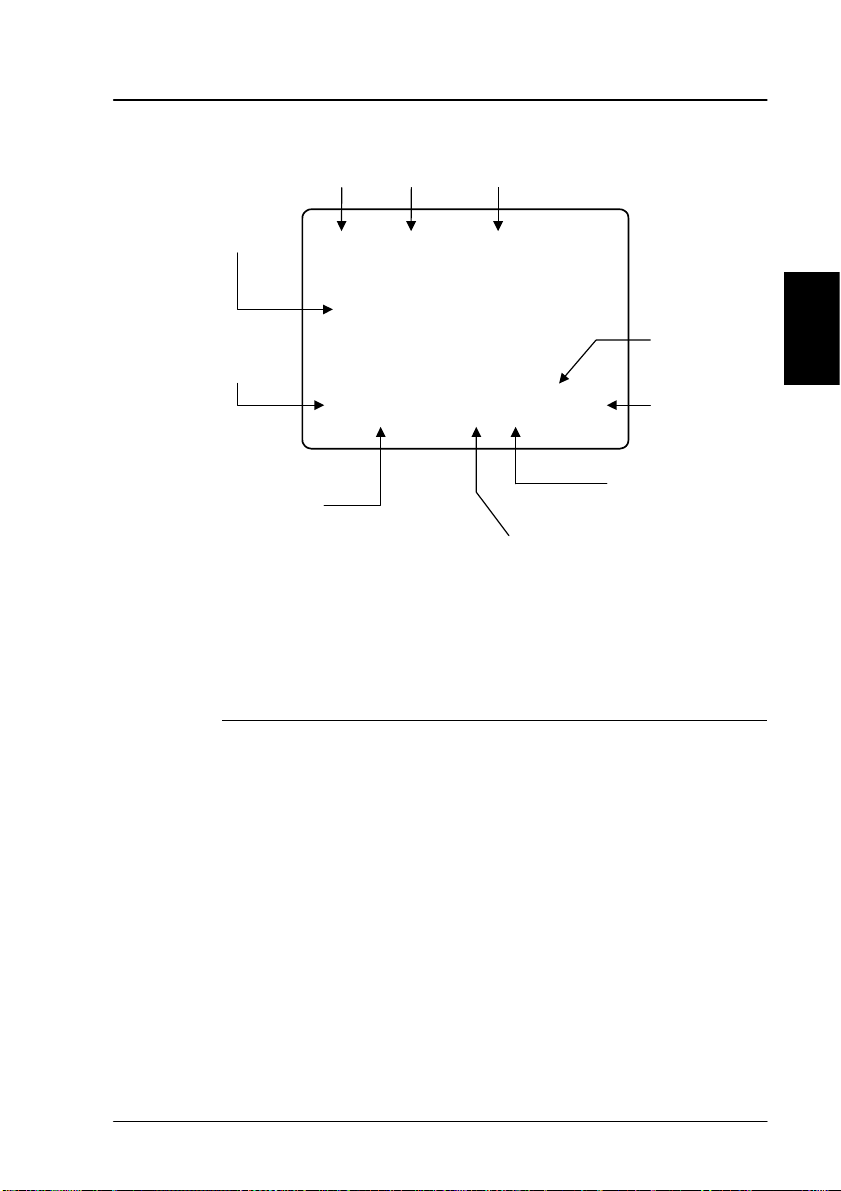
2.3 Hardware Interfaces
The Transceiver Unit of the SAILOR Fleet33 has the
following hardware interfaces:
• Analogue RJ11 number 1
• Analogue RJ11 number 2
• Handset (4 wire)
• Ethernet
• RS-232
• 4 Discrete I/O
• Power Connector
All connectors for these interfaces are found on the rear of
the Transceiver Unit.
Two Analogue RJ11 interfaces:
2
The RJ11 ports as shown above can be used for connection
of analogue phones and G3 fax machines.
Selection of service for the interfaces is independent of
each other. If the mini-M voice is selected, a phone must
be connected as only voice connections can be established.
Cradle/Handset interface:
May 2005 9
Page 21

Introduction Hardware Interfaces
The transceiver has one 4-wire handset port with RS-485
data control. The Handset can be used to set-up the
terminal and it can be used to make or receive phone calls.
Ethernet interface:
2
The Ethernet interface is a RJ45 connector. It can be used
for the following service types:
• MPDS service
• Connection of an IP Router
RS-232 interface:
The RS-232 interface is a standard 9-pin serial port, with a
maximum port speed of 115.2 kbps. It can be used for the
following service types:
• MPDS service
• 9.6 kbps data
• Configuration of the terminal via FleetCP software
• Connection of a IP Router
When using the FleetCP program, the PC must be
connected to the RS-232 interface (see section 5.1).
10 May 2005
Page 22

The Handset Introduction
Discrete I/O interface:
The transceiver also has a discrete I/O interface, containing
4 configurable input/output.
Power Connector:
For connection of power, see Installation Manual.
2
2.4 The Handset
The Handset is the primary interface for the SAILOR Fleet
33 system. It enables the user to dial numbers, it di splays
error and status messages, and it is used to configure the
transceiver.
The Handset is divided into 3 distinct and inter-working
sections.
1. The first is the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) and Light
Emitting Diodes (LED) section. This section gives the
user visual indications about the operation and status
of the system.
May 2005 11
Page 23

Introduction The Handset
2. The second is the Function buttons section. This section
enables the user to interact with the software menu
system of the transceiver.
3. The third is the Alpha-Numeric section. This section
enables the user to dial and perform data entry
functions into the transceiver.
2
In the following these sections are described in details.
2.4.1 LCD/LED
As shown in the picture above, the top of the handset
contains the LCD for displaying information to the user. It
can be adjusted for contrast and is backlit for viewing in
dimly lit areas or night operations. The LCD display is
graphically shown below:
12 May 2005
Page 24
The Handset Introduction
Scroll Up Mailbox Signal Strength
Text
a
Are
Speaker
Enabled
Handset
Off hook
Scro
Dow
IOR:LESNAME
ll
n
Ready
2
condary
Se
Func
Enabled
The display contains a set of symbols, which together with
the 4 indicators situated below the display gives continuous
indication of current status.
Symbol Meaning
tions
More menu entries above.
More menu entries below
Turned on when the key has been
pressed.
Turned on when the keypad is in alpha mode.
Alpha mode is used to enter letters (for
example names in the phone book).
The value in a menu must be selected
Alphabetic
Entry Enabled
Locked
More Options
Available
May 2005 13
Page 25
2
Introduction The Handset
Symbol Meaning
between certain predefined values by means
of the
The speaker. The user can turn the external
speaker on and off by pressing
symbol is displayed in the LCD when on.
Short message stored at a LES – see section
4.3.4 and 4.4.21 Mail Box for further
information.
The number of bars () following this antenna
symbol indicates received signal strength. Up
to 5 bars. The number of displayed bars may
fluctuate during a call. This is due to a power
reduction, negotiated between the terminal
and the LES.
The handset is off hook The handset is off hook
and keys.
. The
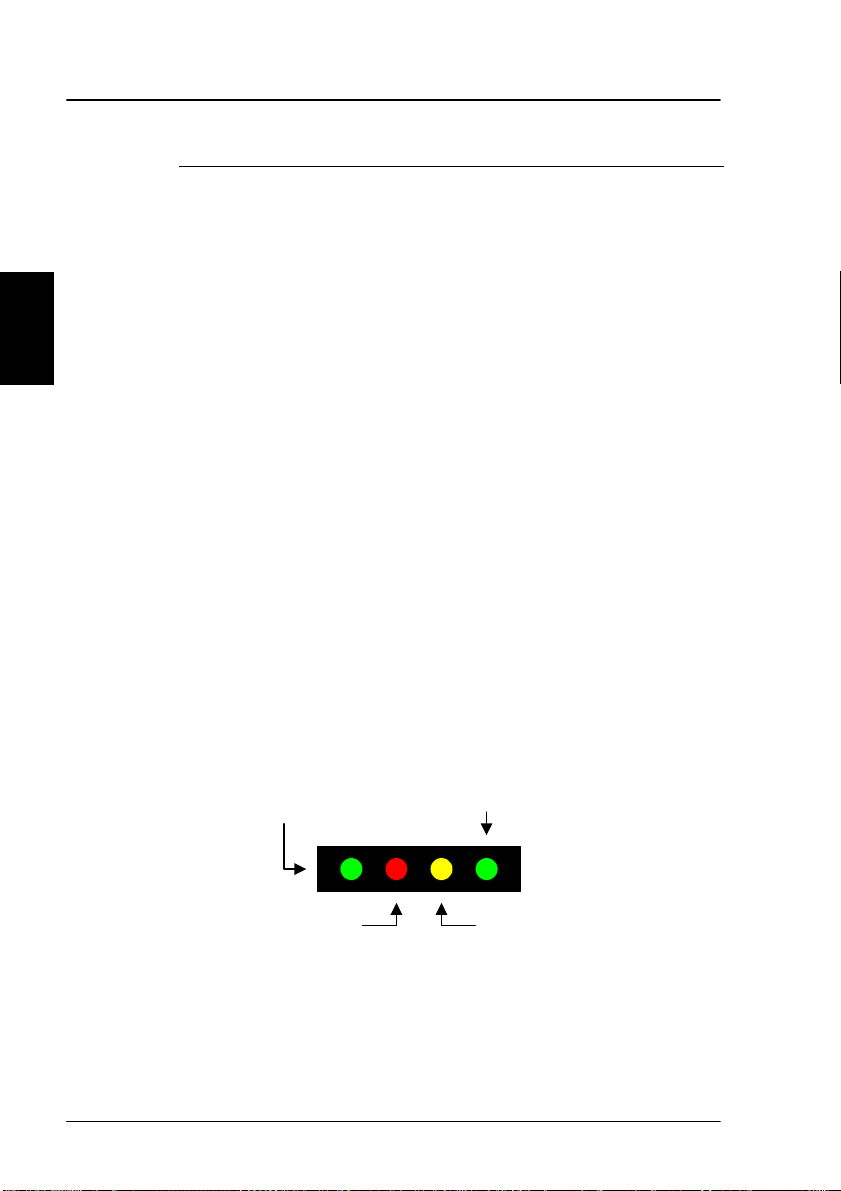
There are four LED’s under the LCD display (see below).
There are four LED’s under the LCD display (see below).
From left to right they are Power (GREEN) – Alarm (RED) –
From left to right they are Power (GREEN) – Alarm (RED) –
Connected (AMBER) – Synchronization (GREEN).
Connected (AMBER) – Synchronization (GREEN).
Power
Synchronization
14 May 2005
Alarm Connection
Page 26

The Handset Introduction
POWER LED (GREEN): The Power LED indicates that the
system is powered up.
ALARM LED (RED): The Alarm LED will illuminate when the
system detects a fault. An error code will also be displayed
in the LCD and in the error log.
CONNECTION LED (AMBER): The Connection LED will flash
when a call is ringing at the receiving end and will
illuminate steady when a connection is made.
SYNCHRONIZATION LED (GREEN): This is a dual function
LED. Initially, the LED will illuminate when the system has
synchronization with a satellite. When the system has
established a data call, the LED assumes its secondary
function as a data transfer light. When data is being
transferred (sent or received), the LED will light. This is a
quick visual reference during data communications.
2
May 2005 15
Page 27

2
Introduction The Handset
2.4.2 Function Buttons
The Function buttons, as shown above, enables the user to
enter the menu system of the transceiver and change
various settings. Each button is described in detail below.
Some of the function buttons have a 2nd function shown in
italics at the upper right corner of the function button. To
use this 2nd function of a function button, press the "2nd"
button and then press the function button.
Key Function
16 May 2005
This key has two functions.
1) If system is ‘ON’, this key will either –
by a single press - enter the top level
of the menu system (see section 4.3
Menu System) or – by holding down
for about 5 sec. - power down the
system.
2) If system is ‘OFF’, this key will force
Page 28

The Handset Introduction
Key Function
the system to power up.
This use of this key is depending on the
present MMI status.
In the Menu system
current submenu until main level is reached.
When asked YES or NO
key will be interpreted as a ‘NO’ response.
When entering data
will cancel the entry.
This use of this key is depending on the
present MMI status.
In the Menu system
chosen submenu.
When asked YES or NO
key will be interpreted as a ‘YES’ response.
When entering data
will accept the entry.
This key has two functions.
The primary function is to clear
entered character. It is similar in function to
the backspace key on a PC.
The secondary function is to insert
characters. This is used when inserting new
Inmarsat Mobile Numbers (IMN’s), Phonebook
entries, etc.
This key has two functions.
The primary function is to scroll upwards
menu items not shown on the 2-line display of
the LCD.
this key will exit the
by the system, this
into the system, this key
this key will enter the
by the system, this
into the system, this key
the last
new
to
2
May 2005 17
Page 29

2
Introduction The Handset
Key Function
previously
between normal
previously
to
The secondary function is to edit
entered information.
This key has two functions.
The primary function is toggle
mode and alphanumeric mode.
The secondary function is to delete
entered information.
This key is used to access secondary key
functions.
This key has two functions.
The primary function is to scroll downwards
menu items not shown on the 2-line display of
the LCD.
The secondary function is presently not used.
This key toggles between ‘on hook’ and ‘off
hook’.
2.4.3 Alpha-Numeric Section
The keypad can be in normal (numeric) mode or alpha
mode. Normal mode is used to enter digits (phone
numbers) whereas alpha mode is used to enter letters
(names in the phone book). The
between the two modes. The display indicates if in alpha
mode. In alpha mode each of the numeric keys (plus
can be used to select between subsets of the alphabet (and
certain special characters) by pressing the key a number of
times until the wanted letter/character is shown on the
display. To insert the letter C it is necessary to press
times in alpha mode. Below is an overview of the relevant
keys in alpha mode.
18 May 2005
is used to toggle
)
3
Page 30

The Handset Introduction
Key Toggles between when pressed in alpha mode
- ? ! , . : ’ $ ( ) + / 1
A B C 2
D E F 3
G H I 4
J K L 5
M N O 6
P Q R S 7
T U V 8
W X Y Z 9
0 or Move cursor (forced)
2
May 2005 19
Page 31

Introduction The Handset
Key Toggles between when pressed in alpha mode
<space>
2
A number of keys have a 2
Key Function
Recalls the last dialed number.
Not used
Shortcut to the area selection submenu, see
section 4.3.2 A.
Used to establish a fax call from the handset
if the fax does not have a keypad. See
section 4.1.3 Fax Call.
Not used.
Toggles the handset microphone ‘ON’ or
‘OFF’.
Toggles the cradle speaker ‘ON’ or ‘OFF’.
Shows C/No “signal strength” in the display.
Pressing
previous state.
Sets the brightness of the LED's. See section
4.4.15 below LED Dimm.
Short cut to the Help desk menu. See section
4.3.5 below Help Desk.
or returns to the
nd
function.
20 May 2005
Page 32

The Handset Introduction
Key Function
Insert an entry (for example in phone book)
Edit an existing entry (for example in phone
book)
Delete an existing entry (for example in
phone book)
Not used.
2
May 2005 21
Page 33

Page 34

Get Ready to Make a Call Getting Started
3 Getting Started
3.1 Get Ready to Make a Call
3.1.1 How to Power-Up the System.
There are two ways to power up the system:
• Power Key on handset
• Power Button on back panel of Transcei v er Unit
The handset power button is also the menu button. To
power up you may simply press the button once.
The transceiver power button is placed on the back panel of
the unit. See figure below.
3
Press and hold the power button for a few seconds until the
green LED on the front of the terminal lights up.
May 2005 23
Page 35

Getting Started Get Ready to Make a Call
3
The display and all LED's on the handset will light up for a
few seconds.
Below is a view of the normal handset display readout,
while the System is booting.
Initialising
AORE:
Wait for NCS
AORE:
Wait for NCS
24 May 2005
Page 36

Get Ready to Make a Call Getting Started
AORE:
Wait for GPS
The system may stay in the “Wait for GPS” state for an
extended period, if e.g. the antenna has been turned off for
a long time or there is not a free view to the GPS satellites.
The time to get the GPS position may be several minutes.
When the display reads “READY” as shown above, the
system is ready to make and receive calls.
AORE: LESNAME
READY
3.1.2 How to Shut Down the System.
Note: To make sure that writing to the configuration
module is completed, please wait at least 10 seconds
after any changes to the configuration, before
shutting the system down.
To shut down the system from the handset, you press the
button for 3 sec. The display now shows that if you
press the key for further 4 sec the terminal will power
down. The display counts down to zero, but by releasing
the button any time before it reaches zero, you may abort
the power down procedure.
3
May 2005 25
Page 37

Getting Started Use of PIN Codes.
To shut down the system from the transceiver press and
hold the power button for a few seconds, until the handset
display shows the message shown below.
3
Release the button and the system will shut down.
Note: After a shut down please wait at least 5
seconds, before trying to power up the system again.
3.2 Use of PIN Codes.
Access to some terminal functionality is restricted by PIN
codes. Two different kinds of User PIN codes are used in
the system: one for the Super User and one for the Service
User.
Both PIN codes are composed of digits between 0 and 9
and the length must be between 4 and 8 digits.
The normal everyday user (Normal User) can make and
receive calls, access the phonebook, chose an ocean region
and a default LES, read the alarm log and status and make
calls from the Helpdesk. For a description of these
functions refer to section 4.3 “Menu System”. All other
functionality has to be carried out by a Super User or a
Service User.
Thrane F33
Goodbye
Super User
The Super User has the same rights as the Normal User. In
addition the Super User can access the Super User menu
(see section 4.4 for details). A Super User will typically be
a person responsible for setting up and maintaining the
system. It is only possible to have one Super User PIN
26 May 2005
Page 38

Normal Calls Getting Started
code. If the code is entered incorrectly 3 times, the PIN
becomes blocked. A blocked Super User PIN can only be
unblocked by a PUK code or the Service User. The factory
PIN code is ‘12345678’.
Service User PIN
The Service User has access to all functionality in the Fleet
system, which is accessible through the handset. Only T&T
and/or the supplier of the equipment will normally know
this PIN. If the PIN is entered incorrectly 3 times, the PIN
becomes blocked. Only a PUK code can unblock a blocked
Service User PIN. Refer to the “TT-3088A SAILOR Fleet33
Installation Manual” for the use of the service menu.
3.3 Normal Calls
3.3.1 Calling From the TT-3088A
When making calls from a handset or from a fax keypad
just type in the phone number as if you were making an
international call (with prefix for automatic international
calls equal to 00).
3
Example:
To dial the number of Thrane & Thrane (+45 39558800),
press:
for international calls
for country code then
followed by
or .
The display on the terminal handset will show how the call
proceeds.
May 2005 27
Page 39

Getting Started Normal Calls
You hang up by pressing . After hanging up, the display
will show how long the call lasted.
Connected:
00:01:59
The Phone Book can also be used to initiate a call, either by
selecting an entry in the phone book or by using the short
code. See section 4.1.1 for details.
3
3.3.2 Calling To the TT-3088A
Calling the terminal or a device connected to the terminal
is similar to making international calls. The specific IMNnumber (a terminal may have more numbers as different
services exist and more devices may be connected to the
different hardware interfaces of the terminal) has to be
preceded by one of the five possible international access
codes. This depends on whether you know which area the
terminal is within or not:
870: Area of terminal not known
(Requires that the LES supports Mobility Management).
871: AORE
872: POR
873: IOR
874: AORW
To call a terminal positioned in IOR, dial:
00873 followed by the IMN number.
28 May 2005
Page 40

Data Calls Getting Started
3.4 Data Calls
Please note: The data connection services are only
available when the vessel is positioned inside an area
with Spot Beam coverage.
3.4.1 MPDS Connection
The Mobile Packet Data Service (MPDS) provides the
mobile user with an economic and flexible data connection.
The user is only charged by the transferred traffic (in MB).
This means that for applications like Web browsing, email
services, IP/LAN connectivity, small to medium size file
transfer, the MPDS will be the most economic and
convenient solution. The maximum data transfer rate is 64
kbit/s to the terminal and 28 kbps from the terminal.
A connection can be started automatically by an application
like Internet Explorer or Outlook Express. The connection
can also be established manually. In windows, open DialUp networking and double click the appropriate icon. Enter
username and password if necessary. Click ‘Connect’. Wait
for the connection to be completed, indicated by a ‘Dial -up
Networking’ icon in the task bar tray.
3
To disconnect: Right click the tray icon and choose
‘Disconnect’.
See section 5.2.1 on how to setup the computer and
transceiver for an MPDS connection.
While in MPDS mode the TT-3088A is flagged busy in the
Inmarsat network. This means that the Fleet system is not
able to receive any incoming calls until it returns to normal
idle mode. However, the user can enable the Call Waiting
Notification feature. This allows the system to receive voice
May 2005 29
Page 41

Getting Started Data Calls
calls during an ongoing MPDS call. For further information
about this feature, see section 3.4.2.
3.4.2 Call waiting
As indicated in the previous section the user can enabl e the
Call Waiting Notification in order to receive incoming voice
calls during an MPDS session. The enabling can optionally
be restricted to specific phone numbers.
The 4-wire and 2-wires interfaces can be configured for
3
usage for the Call Waiting Notification. When the
notification arrives, the user is notified by a special ringing
tone and a message is shown in the display if the 4-wire
handset is selected for the service.
In case of an incoming call during an MPDS session with
the Call Waiting Notification enabled, the user has three
options:
1. The user can reject the pre-emption of the MPDS
connection by pressing “*” or “Exit” on the 4-wire
handset (if enabled) or by taking an enabled 2-wire
phone off hook, pressing “*” and placing the phone on
hook again. The ringing stops on all handsets that are
configured for the service.
2. The user can accept the pre-emption of the MPDS
connection by pressing “OK” or “#” on the 4-wire
handset (if enabled) or by taking an enabled 2-wire
phone off hook, pressing “#” and placing the phone on
hook again. The MPDS session is now deregistered and
the call gets through after a short while. The phone(s)
to which the call is routed starts ringing and the call
can be answered. Note that the call can be answered
on another interface than the interface that was used
to accept the call – e.g. a fax will normally only be
30 May 2005
Page 42

Data Calls Getting Started
routed to a specific RJ11 connector and not the 4-wire
handset.
3. The user may also choose to do nothing. After a certain
time the notification stops and the pre-emption of the
MPDS connection is implicitly rejected, if no other lines
have accepted the notification.
Configuration of the Call Waiting notification is described in
paragraph 4.4.24.
3.4.3 9600 Data Connection
9.6 kbps data is a circuit switched service, i.e. you have
the 9.6 kbps speed all the time, and you pay for the time
you are connected. This service will be the most economic
solution for batch data transfers.
The connection can be established manually. In windows,
open Dial-Up networking and double click the appropriate
icon. Enter username and password if necessary. Click
‘Connect’. Wait for the connection to be completed,
indicated by a ‘Dial-up Networking’ icon in the task bar
tray.
To disconnect: Right click the tray icon and choose
‘Disconnect’.
See section 5.2.2 on how to setup the computer and
transceiver for a 9.6 kbps data connection.
3
May 2005 31
Page 43

Page 44

Call Functions Operation
4 Operation
4.1 Call Functions
4.1.1 Calls Using the Phone Book
The phone book can be used to initiate calls, either by
selecting an entry in the phone book, and then pressing
or , or by using the short code. The latter is done
by pressing
afterwards will establish the call. Pressing
show the actual number and the call can then be
established by pressing
the last dialed number, thus
will redial the last number.
followed by the short code. Pressing
instead will
or . Short code 0 contains
or followed by
4
4.1.2 Call From Handset Connected to RJ11
Making a call from a (normal 2-wire PSTN) phone
connected to one of the two analogue RJ11 interfaces is
done in the same way as a call from the handset. Just keep
in mind to press the
terminal, that the number is complete.
To Call Thrane & Thrane in Denmark (country code 45) is
done by pressing the following keys on the phone:
When using one of the RJ11 analogue interfaces please
make sure that the selected interface is configured for a
service, which supports voice. See section 4.4.21.Routing
May 2005 33
key in order to signal the
Page 45

Operation Call Functions
The display on the handset will show how the call proceeds.
After hanging up (on the 2-wire phone), the display will
show how long the call lasted.
4.1.3 Fax Calls
Fax calls can be made whether the fax has a keypad or
not.
Calls from a fax with keypad are done as international calls
followed by
(country code 45) press the following keys on the fax:
. To call Thrane & Thrane in Denmark
4
Please make sure that the analogue RJ11 interface to which
the fax is connected is configured for a service, which
supports fax.
The display on the handset will show how the call proceeds.
After hanging up, the display will show how long the call
lasted.
Calls from a fax without keypad are done by using the
keypad on the terminal handset. To call Thrane & Thrane in
Denmark (country code 45) press the following keys on the
SAILOR Fleet handset:
Then press the start-button on the fax.
To hang up after faxing please refer to fax user manual.
34 May 2005
Page 46

Using the Menu System Operation
4.1.4 Internal Calls
It is possible to make internal calls between the RJ11 (2
wire) interfaces. To initiate a call press the interface code
from the table below and then
Interface Interface Code Interface port
RJ11 #1 2 X1
RJ11 #2 3 X2
.
4.2 Using the Menu System
The level of access to the menus is divided into 3 groups of
users. A Normal User, a Super User and a Service User.
The Normal User has access to normal everyday functions.
The Super User has the same rights, but can additionally
access different setup menus. The Service User menu is
only accessible to the supplier or Thrane & Thrane. Both
Super User and Service User menus are protected by PIN
codes.
To access the menu system press:
To scroll through menus use the keys
To enter a submenu press:
To exit to a previous level press:
An entry in the menu system can also be reached by
pressing
and a number corresponding to the entry
.
.
and .
.
4
May 2005 35
Page 47

Operation Menu System – All Users
level, e.g. pressing will access the 'Alarm Log'
menu.
The complete menu tree can be found in Appendix A Menu Tree.
4.3 Menu System – All Users
This section describes the functions in the menu system
available to all users.
4.3.1 Phonebook
4
Phonebook
Area
LES
Mailbox
Helpdesk
Alarm log
Status
Super User
Service User
01 TT
02 TT2
01 539558800
02 5395588xx
Hint
to view the
Press
last nine digits of the
phonenumber
The terminal PhoneBook contains 99 entries. Each entry contains the following information:
• Name
• Telephone number
• Short code
The telephone number includes call prefix for automatic
calls and international access code. The telephone number
can hold up to 22 digits.
The name can hold from 0 to 16 characters.
36 May 2005
Page 48

Menu System – All Users Operation
The short code can be used for quick access when dialing.
To use the short code, press
press
again to dial.
The list of entries in the phone book is sorted according to
short code.
An entry in the phone book is displayed as a short code
and a name if in alpha mode or as a short code and a
telephone number if in normal mode.
Use
to select an entry and press . The phone
number is displayed.
or to dial.
Press
Inserting an entry in the phone book from within the phone
book menu is done in the following way. In this example
the number to T&T, 004539558800, with short code 14 is
inserted.
<short code> and
THRANE
4
Editing or deleting an entry is done by selecting the entry
in the phone book and pressing
respectively.
May 2005 37
and
Page 49

Operation Menu System – All Users
4.3.2 Area
4
Phonebook
Area
LES
Mailbox
Helpdesk
Alarm log
Status
Super User
Service User
None
*Automatic
W-Atlantic
E-Atlantic
Indian
Pacific
Spare1
Spare2
Spare3
Spare4
The Area menu is used to select satellite/ocean region. The possible options are:
• None (no satellite is selected)
• Automatic (automatic satellite selection)
• W-Atlantic (AOR-W satellite)
• E-Atlantic (AOR-E satellite)
• Indian (IOR satellite)
• Pacific (POR satellite)
• Spare 1 (for future use)
• Spare 2 (for future use)
• Spare 3 (for future use)
• Spare 4 (for future use)
If Automatic is selected the system will search through
the options and select based on signal strength.
To change the selection: Choose an area and press
.
The selection will be marked with an *.
The coverage map can be found in the FleetCP
configuration program (see section 5.1 System Set-up ).
38 May 2005
Page 50

Menu System – All Users Operation
4.3.3 LES
Phonebook
Area
LES
Mailbox
Helpdesk
Alarm log
Status
Super User
Service User
The LES li st contains a list of those LES operators, which
may be selected as gateway to the terrestrial network. The
last used LES will be marked with * and this LES will also
be the first LES tried next time the terminal is logged on.
Use
to select. The Area selected in section 4.3.2 A, will
decide, which LES's will be available for selection (see
section 4.4.23 LES Config for further information about LES
configuration).
001: LES001
002: LES002
003: LES003
004: LES004
005: LES005
006:
007:
008: LES008
009: LES009
.
.
.
.
4
May 2005 39
Page 51

4
Operation Menu System – All Users
4.3.4 Mailbox
Phonebook
Area
LES
Mailbox
Helpdesk
Alarm log
Status
Super User
Service User
The Mailbox feature is not supported by all LES operators. The feature handles messages sent from the LES operator. If a call is made to a terminal, which is busy, switched off, etc. the LES operator may offer the facility to record a short message. When the terminal again becomes operational a message is sent indicating that the LES operator has recorded a short message for the terminal.
List Empty
The
symbol in the handset display indicates the
presence of such messages.
Each message can be seen in the Mailbox menu and
contains the following information:
• LES Access Code
• Service type (voice, fax, data).
To View a entry, select the message and press
. See
how to delete a message in section 4.4.21 Mail Box.
40 May 2005
Page 52

Menu System – All Users Operation
4.3.5 Help Desk
Phonebook
Area
LES
Mailbox
Helpdesk
Alarm log
Status
Super User
Service User
The Help Desk is a secondary phone book that can be used for storing up to 10 support phone numbers (e.g. Thrane & Thrane support centers).
Editing/inserting and deleting entries is done in exactly the
same way as with the phone book, but it can only be done
from the super user menu. Each entry contains a phone
number, name of the entry, and a LES access code.
Press to access
the menu directly.
H.Desk empty
4
May 2005 41
Page 53

4
Operation Menu System – All Users
4.3.6 Alarm Log
Phonebook
Area
LES
Mailbox
Helpdesk
Alarm log
Status
Super User
Service User
View alarms
The Alarm Log, logs all the alarms i n the system (cf. 6.1 List of Error messages). From this menu, the alarm can be viewed only. To clear the alarm list see section 4.4.17. Scroll through the list, using the of the Alarm name, indicates that the alarm is still active. Select an alarm for viewing, by pressing for an alarm contains an alarm description and the time and date when the alarm occurred. See section 6.1 for a list of alarms.
*FEU
*POSITION
.
.
.
keys. A * in front
. Each entry
The alarm log can contain up to 20 entries. The log will
wrap around when the log is full.
42 May 2005
Page 54

Menu System – All Users Operation
4.3.7 Status
Phonebook
Area
LES
Mailbox
Helpdesk
Alarm log
Status
Super User
Service User
The Status menu has the following sub menus:
C/NO
Transceiver
RF Block
Bulletin
Antenna
GPS Info
• C/No
• Transceiver
• RF Block
• Bulletin
• Antenna
• GPS Info
C/No:
Choosing C/No will display the signal strength in dBHz.
Pressing
will return to the previous state.
Transceiver
Release date: Software release date.
Unit Type: Type of unit.
Serial No.: T&T serial number.
ISN: Inmarsat serial number.
PCB No.: Serial number of main CPU board.
Forward ID: Terminals Forward ID number.
SW Ver.: Software version.
RF Block
RX Frequency: Receiving frequency in MHz.
4
May 2005 43
Page 55

4
Operation Menu System – All Users
TX Frequency: Transmitting frequency in MHz
Freq. offset: Frequency offset between 0-1500 Hz.
Acc. offset: Acc offset between 0-1500 Hz.
AGC: AGC between 0-1024.
Gain: Gain between 0-256.
TX level: TX level equals LOW or OK.
Lo1-Lo3: Lox In or Out of lock.
Temperature: Temperature in deg. C.
Power mode: Power mode in sleep or normal.
Bulletin
Ocean Region: AORW, A ORE, POR or IOR.
NSR state: Not initialized, initializing or initialized.
Type: Mini-M or NG
Bulletin page 1-6: Page 1 to 255 or Inval id.
Spot beam ID: Spot beam ID number between 1-255.
SU CC Rxed: Between 0000-9999.
SU CC Txed: Between 0000-9999.
Antenna
The antenna information is divided into two parts: F
E
nd Unit and Antenna Control Unit and is primarily
intended for service use.
ront
FEU: Unit type:
Serial no.:
SW version:
Mode:
Power:
Temperature:
Cable loss:
Reset count:
Date:
If cable loss is 100%, it means that the cable loss
compensation is at its maximum, and may therefore not be
able to compensate fully for the cable loss. A cable with a
lower RF loss should be used.
44 May 2005
Page 56

Menu System – All Users Operation
ACU: Unit type:
Serial no.:
State:
Input power:
Control ver.:
Loader ver.:
FPGA ver.:
SU ver.:
RX2 ver.:
Loader CRC:
Control CRC:
FPGA CRC:
Config CRC:
GPS Info
PositionInfo: Not ready or Latitude and Longitude.
Heading: Not ready, heading 0-360 degrees or
Heading N/A Low speed (If speed is
equal to or below 1 knot).
Speed: Not ready or speed in knots.
UTC Time: Not ready or YYYY:MM:DD HH:MM:SS
Internal GPS: Not ready or Active and ready.
4
May 2005 45
Page 57

T
T
4
Operation Menu System - Super User
4.4 Menu System - Super User
This section contains a description of the items in the
Super User Menu. Please remember that the
be used to toggle short codes on and off.
4.4.1 Call Logs
------------Call logs
Routing
Data Setup
Contrast
Logged Calls
otal time
otal MPDS
Clear log
Start time
Phone number
Duration
OID
Area
LES acc.code
button can
The Call log menu has the following sub-menus
• Logged calls
• Total Time
• Total MPDS
• Clear log
By entering the Logged calls menu it is possible to inspect
information about each of the outgoing calls made on the
terminal. The following information is logged for each call:
• Start time of call.
• Destination phone number.
• Duration of call
• Originating ID. (Description of service used).
• Ocean region used.
• LES access code.
46 May 2005
Page 58

Menu System - Super User Operation
• Terrestrial network identity (always 0).
• Call priority.
• Number of received bytes in MPDS.
• Number of transmitted bytes in MPDS.
• Total number of bytes in MPDS.
Total Time shows the total accumulated call time since
last reset.
Total MPDS shows the total accumulated number of bytes,
used in MPDS sessions.
To clear the Call Log select the Clear Log menu. Press
to clear or
to abort.
The call log can contain up to 100 entries. After that it will
do a wrap around and start overwriting the oldest entry.
A warning will be generated when the call log contains
more than 70 entries. You may then back up your log data
by Fleet CP PC software. If you also clear the log, you will
get a warning again when 30 entries are left.
4
4.4.2 Routing
Routing
Data Setup
Contrast
May 2005 47
Handset #1
RJ11 #1
RJ11 #2
RS232
Ethernet
MiniM voice
{IMN}#
---------------
9.6K Fax
{IMN}
---------------
9.6K Data
*{IMN}
--------------.
.
.
Page 59

4
Operation Menu System - Super User
This menu has been divided into a submenu pr. interface
plus a print menu:
• Handset #1
• RJ11 #1
• RJ11 #2
• RS-232 #1
• Ethernet
Note 1: The IMN-number has to be defined, before
the service can be routed to an interface. The service
will not be listed in the routing table, unless it has an
IMN-number defined.
Note 2: Some users want the IMN number to reflect
the corresponding telephone number. In this case
the user should EDIT the default IMN number. The
INSERT function is only for adding additional IMN
numbers (or for creating the first IMN in case the list
is empty).
When entering one of the above submenus it is possible to
scroll through a list of all relevant IMN-numbers for the
interface. In the handset menu, you will see all IMN’s
associated with voice: i.e. mini-M voi ce. If an IMN has an
incoming route to an interface it is marked with “*”. If it
has an outgoing route to an interface, it is marked with a
“#”. It is possible to change the routing-status for each
IMN to the opposite by pressing
for outgoing.
It is possible to route one IMN to more interfaces. E.g. an
IMN can be routed to both RJ11 interfaces at the same
time. This will make it possible, to have an incoming call
being routed to two 2-wire phones simultaneous.
48 May 2005
for incoming and
Page 60

Menu System - Super User Operation
4.4.3 Data Setup
Routing
Data setup
Contrast
This menu is used to setup baud rate and dataflow control
for the RS-232 interface. The following settings can be
configured.
Baud Rate: 115200-1200
Flow Ctrl: None | Xon/Xoff | Hardware
+++mode: Disabled | Enabled
Result codes: Disabled | Enabled
Baud Rate
Flow ctrl
+++mode
Result codes
End Data
115200
57600
38400
.
.
1200
4
4.4.4 Contrast
Call logs
Routing
Data setup
Contrast
The display contrast of the handset can be adjusted. To
change the contrast level, select the Contrast menu and
adjust the value with
between 1 and 8. Default value is 4.
May 2005 49
Press to Adjust
Contrast
4.====
and . Setting can be adjusted
Page 61

Operation Menu System - Super User
4.4.5 Ring Setup
4
Ring Setup
Key Beep
Set UTC Ti me
Set UTC Da te
Ring setup gives the possibility to change the ringing tone and the handset volume. Adjustable values are:
Ring Volume: Off|1|2|3|4, default i s 4.
Ring Cadence: 1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8, default is 1.
Both settings are adjusted with
4.4.6 Key Beep
Ring Setup
Key Beep
Set UTC Tim e
Set UTC Da te
Ring Volume
Ring Cadence
Press to Adjust
and .
Key beep
Off
Press to Adjust
Ring
4.==
Volume
==
Key Beep, the sound that's heard when a key is pressed, can be set to Off, 1, 2, 3 or 4. The setting is adjusted with
and . Key Beep is default off.
50 May 2005
Page 62

Menu System - Super User Operation
4.4.7 Set UTC Time
Ring Setup
Ring Setup
Key Beep
Key Beep
Set UTC Time
Set UTC Time Set UTC Date
Set UTC Date Language
The current UTC time can be viewed and modified. The
time is displayed in 24 hour format {hh:mm}. Enter a new
time and press
is set to a non-UTC time a clock error message will appear
after a while. By pressing *, the GPS time is automatically
transferred.
Edit time
17:29
to update or to cancel. If the clock
4.4.8 Set UTC Date
Ring Setup
Key Beep
Set UTC Time
Set UTC Date
The current UTC date can be viewed and modified. The
date is displayed in the format {yyyy:mm:dd}. Enter a
new date and press
pressing *, the GPS date is automatically transferred.
Edit Date
2005-05-23
4
to update or to cancel. By
May 2005 51
Page 63

4
Operation Menu System - Super User
4.4.9 Disclose Pos.
Disclose Pos
Allowed Dial
Ph.BookDial
Auto Prefix
It is possible to disable the automatic reporting of posi tion,
from the GPS system. This menu gives the option to
change this. Select ‘Reveal Pos’ or ‘Don't reveal’ with the
and key. Select function with the key. Current
status is marked with a *.
Note: Disabling automatic reporting of position,
means that the terminal will report spot beam ID
instead.
*Reveal Pos
Dont Reveal
Press to Sc
Press
to select
roll
4.4.10 Allowed Dial
Press to insert mas
Press
Disclose Pos
Allowed Dial
Ph.BookDial
Auto Prefix
to delete mas
List empty
Allowed Dial is a function that allows the Super User to specify a phone number mask, to restrict outgoing calls.
A phone number matches a dial mask, if the number
contains at least as many digits as the mask and when the
52 May 2005
k
k
Page 64

Menu System - Super User Operation
digits in the mask matches the corresponding digits in the
phone number, starting from the first digit.
to insert a mask and to delete an
Press
entry.
Examples:
Mask 00453955
Valid number 004539558800
Valid number 004539558888
Invalid number 39558800
Invalid number 004539
The terminal can contain up to 99 entries and each entry
can be 22 digits long.
The phone number you enter in the dialer for making an
MPDS connection, is a dummy number that is not used.
Therefore the “Allowed Dial” list has no effect on MPDS
connecting.
4
4.4.11 Ph.Book Dial
Press to Scroll
Press
Disclose Pos
Allowed Dial
Ph.BookDial
Auto Prefix
When this function is enabled, Normal User will only be
able to make calls using the phone book or the Help desk
from a SAILOR handset.
May 2005 53
to select
*Disabled
Enabled
Page 65

Operation Menu System - Super User
Use and to scroll between ‘Enable’ or ‘Disable’ and
press
to select.
The function is by default disabled.
4.4.12 Auto Prefix
4
Disclose Pos
Allowed Dial
Ph.BookDial
Auto Prefix
Press to insert pref
Press
A prefix, e.g. 0045 for Denmark, can automatically be
added to any dialed number. The prefix is not added to
numbers dialed from the phonebook. One prefix number
with up to 22 characters can be defined. By default no Auto
Prefix number is specified. Press
and
to delete the prefix.
4.4.13 BarServiceIn
BarServicIn
BarServicOut
LED Dimm
Ant. Setup
MiniM Voice
MPDS
9600 Fax
9600 Data
to delete pre
Prefix no.
0045
to insert a prefix
Press
Press
ix
fix
Barre
*Not badrred
to Scroll
to
select
All incoming calls on a specific service can be barred. Scroll
through the services with
54 May 2005
. Select the service with
Page 66

Menu System - Super User Operation
. The service can then be set to ‘Barred’ or ‘Not barred’
with
and .
4.4.14 BarServiceOut
BarServicIn
BarServicOut
LED Dimm
Ant. Setup
MiniM Voice
MPDS
9600 Fax
9600 Data
All outgoing calls on a specific service can be barred. Scroll
through the services with
. Select the service with
. The service can then be set to ‘Barred’ or ‘Not barred’
with
and .
*Barred
Not barred
Press to Scroll
Press
to select
4
4.4.15 LED Dimm
BarServicIn
BarServicOut
LED Dimm
Ant. Setup
The brightness of the 4 Handset LED's can be adjusted. To change the brightness level, select the LED Dimm menu and adjust the value with adjusted to Bright, Dimm and Off. Default value is Bright.
May 2005 55
Press to Scroll
to select
Press
*Bright
Dimm
Off
and . Setting can be
Page 67

4
Operation Menu System - Super User
4.4.16 Ant.Setup
Ant.Setup
Alarm Log
Warning Log
The Ant.Setup menu has the following sub menus: Reset ACU: This function will reset the ACU in the
antenna. The DC power running in the antenna cable will
be turned of for a few seconds, causing the ACU to restart.
This can be useful if the antenna control freezes or locks
up.
Set time out: This function sets the number of seconds
the system waits without a satellite signal before it
assumes the tracking is lost. Valid range is 1 to 300
seconds. Default is 130 seconds. Press
changes.
Reset ACU
Set time out
Num. Skyscan
Mount Pos.
Upload FEU
Set T
ime Out
130
to validate
Num. Skyscan: Enables the user to define the number of
sky scans. Valid range is 1 to 10 scans. Default is 1 scan.
Press
to validate changes.
Mount Pos.: Because of the build in GPS, the antenna is
capable of finding the satellite within a few seconds. A
heading of the ship is also needed, but since the GPS does
not supply the antenna with this information, a relative
angle of the antenna compared to the ships bow, has to be
known. Select the antennas mounted position, relative to
the ships bow. Valid angles are 0, 90, 180, and 270 deg,
positive in a clockwise direction. Default angle is 0 deg.
Changes must confirmed by pressing
56 May 2005
.
Page 68

R
R
T
f
Menu System - Super User Operation
Upload FEU: If a new FEU (Part of the antenna) is
installed, this command will upload software to the FEU,
thereby pairing the system software with FEU. If the FEU
software version in the antenna is different from the
version that is stored in the system, you will get a warning.
You may then use the “Upload FEU” command to remove
this difference.
4.4.17 Alarm log
LED Dimm
Ant. Setup
Alarm Log
Warning Log
View log
Clear log
Audio Alarm
*NS
*FEU
.
.
On
Of
NS
Corrupt
-----------ime
17:42
------------
Date
11-Feb-02
4
The Alarm Log, logs all the alarms in the system. From this menu, the alarm can be viewed and cleared. To clear the alarm list, select the submenu "Clear alarms" and confirm the message "Delete all?" by pressing through the alarm list, using the
keys. A * in front
. Scroll
of the Alarm name, indicates that the alarm is still active.
Select an alarm for viewing, by pressing
. Each entry
for an alarm contains an alarm description and the time
and date when the alarm occurred. See section 6.1 for a
list of alarms.
The alarm log can contain up to 20 entries. The log will
wrap around when the log is full.
May 2005 57
Page 69

4
Operation Menu System - Super User
You may get an audio alarm when an alarm is added to the
alarm log. This may be turned on and off by entering the
Audio Alarm menu.
4.4.18 Warning Log
LED Dimm
Ant. Setup
Alarm Log
Warning Log
The Warning Log logs the warnings in the system.
Warnings are not as serious as alarms. From this menu,
the warnings can be viewed and cleared. To clear the
warning list, select the submenu "Clear log" and confirm
the message "Delete all?" by pressing
the warning log, using the
warning name, indicates that the warning is still active.
Select a warning for viewing, by pressing
for a warning contains a warning description and the time
and date when the warning occurred.
View log
Clear log
. Scroll through
keys. A * in front of the
. Each entry
4.4.19 Help Desk
Help Desk. Please refer to section 4.3.5.
58 May 2005
Page 70

Menu System - Super User Operation
4.4.20 PIN codes
Alarm Log
Warning log
Help Desk
PIN Codes
SU-PIN Chg
Type New PIN
_
The PIN codes menu is where the Super User PIN is changed. For a description of the pin codes, see section 3.2 Use of PIN Codes. The PIN codes menu has the following sub menu.
SU-PIN Chg: The Super User PIN is changed here. Type
the new PIN and press
to accept the change.
4.4.21 Mail Box
4
Press to view message
Press
to delete a message
Mail Box
RJ11 Setup
LES Config
List Empty
The Mailbox feature handles messages being sent from the LES operator. If a call is made to a terminal, which is busy, switched off, etc. the LES operator may offer the facility to record a short message. When the terminal again becomes operational a message is sent indicating that the
May 2005 59
Page 71

Operation Menu System - Super User
LES operator has recorded a short message for the
terminal.
symbol in the handset display indicates the
The
presence of such messages.
Each message can be seen in the Mailbox menu and
contains the following information:
• LES Access Code
• Service type (voice, fax, data).
The following operations are possible:
• View entries
• Delete entries.
4
To View an entry, select the message and press
delete an entry, select the message and press
4.4.22 RJ11 Setup
Mail Box
RJ11 Setup
LES Config
2-wire phones, connected to the RJ11 interfaces, may vary
in sensitivity. The output volume from the interfaces can
therefore be adjusted. The volume can be set to High,
Volume
PABX
Press
Press
RJ11 #1-2
*High
Medium
Low
to Scroll
to se
lect
. To
.
Normal mode
PABX mode
60 May 2005
Page 72

r
Menu System - Super User Operation
Medium or Low. The setting is adjusted with and
and selected with
. The default value is High.
4.4.23 LES Config
Mail Box
RJ11 Setup
LES Config
Default LES
PreferredLES
Reset LES
Distress LES
*W-Atlantic
E-Atlantic
Pacific
Indian
Spare 1
Spare 2
Spare 3
Spare 4
001: Comsat
002: BT
003: KDD
004: Teleno
005: OTE
006:
007:
008: FRAC
009: ST12
.
.
.
.
4
This menu is used to select a list of LES operators. It
contains the following sub menus:
• Default LES
• PreferredLES
• Reset LES
The Default LES list contains a list of those LES operators,
which may be selected as gateway to the terrestrial
network. The last used LES will be marked with * and this
LES will also be the first LES tried next time the terminal is
logged on. If there's no LES list selected under Allowed or
Preferred LES, the Default LES list will contain the LES list
from the satellite bulletin board, meaning all available LES
in the selected Ocean region. Use
and to select
a Ocean region and then a LES.
May 2005 61
Page 73

4
_
Operation Menu System - Super User
You may also edit the LES names in the “Default LES” list.
to start editing the selected name. You may
Press
clear the name by pressing
An Allowed LES list can be selected under the Service
User menu. If an Allowed LES list exists, only the LES's in
this list can be selected under Default and Preferred LES.
An Allowed LES list contains all available LES operators in
the selected ocean region. Those operators marked with *
can be used as Default LES operators and thus appears in
the Default LES list above. If all LES operators are allowed
and can be used there are no markings.
As there are many operators, you can use PreferredLES
to make selections easier. The Preferred LES list can be
used to indicate in which order LES operators should
appear on the Default LES list. This is done by pressing
.
for each LES intended to be on the list and in the
order they should appear in the Default LES list. Press
to update the preferred LES list. To remove a LES from the
list, press
and then to update the list.
The Reset LES command reset all the LES names to
default names.
4.4.24 Additional Features
Mail Box
RJ11 Setup
LES Config
Add. Features
62 May 2005
STU Setup
STU PIN
STU
Disabled
Page 74

Menu System - Super User Operation
The Additional Features contains one sub menu: STU
Setup (Secure Telephone Unit). To enable the STU service
a PIN code must be entered. The PIN code can be
retrieved from your distributor. If the PIN code is
successfully entered a new screen appears. Here the
service can be enabled or disabled. Use
and
to change. Press to leave the sub menu.
to toggle
4.4.25 Data Limits
RJ11 Setup
LES Config
Add. Features
Data Limits
The Data Limits menu enables the user to enter an upper
limit for the use of each high speed connection. This
feature is an effective way of preventing that a user by
mistake forgets to close a connection.
MPDS
9600 Data
Limit OFF
000000 Kb
Limit OFF
00:00 hh:mm
4
The Data Limits menu contains two sub menus MPDS and
ISDN. Use
The MPDS sub menu contains two parameters Limit and a
value for the maximum allowed amount of kilobytes that
can be transferred in each call. Limit can be either ON or
OFF. If set to ON the MPDS connection will automatically
be closed down if the transferred data amount gets beyond
the entered maximum value. If set to OFF, there will be no
limits for the amount of data that can be transferred. Use
to and to choose among them.
to select Limit and to manipulate. To enter a
maximum limit press
enter a value and press
sub menu.
May 2005 63
. Then use the numeric buttons to
to save. Press to leave the
Page 75

Operation Menu System - Super User
The ISDN sub menu contains two parameters Limit and a
maximum duration for each call. Limit can be either ON
or OFF. If set to ON the call will automatically be closed
down if the call has lasted longer than the entered
maximum duration. If set to OFF, there will be no
boundaries on the call duration. Use
and
to manipulate. To enter a maximum call duration
press
. Then use the numeric buttons to enter the
duration in hours and minutes and press
to select Limit
to save. Press
to leave the sub menu.
4.4.26 Call Waiting Notification
4
Add.Features
Data Limits
Call Waiting
---------
------
Support
Limit Calls
Handset
RJ11
Pend. Time
Caller #1-5
Disabled
Enabled
Dial Spec.
Notification
Ring Tone
Notification
Ring Tone
Pend. Time
0030
Number
Ring Tones
Yes / No
Ring Tone 1-8
RJ11 #1-3
Ring Type 1-8
Caller # No
Handset
RJ11
The Call Waiting menu contains a number of sub menus.
Use
to and to choose among them. Press
to save the changes and press leave a menu. Please
refer to section 3.4.2 for general information about the Call
Waiting Notification.
64 May 2005
Page 76

Menu System - Super User Operation
The first menu item is Support and it is used for enabling
or disabling the Call Waiting Notification service. A third
option “Dial Spec.“ makes it possible to control the
Support setting using the AT shell command
settings by pressing
and press leave the menu.
1
. Choose the
The second menu item is Limit Calls. The user may not
want all calls to interrupt the MPDS sessions. It is possible
to enter up to five phone numbers that are allowed to
interrupt the MPDS sessions while all others will be
rejected. If Limit Calls is set to “Enabled” only the five
phone numbers are allowed to interrupt. If Limit Calls is
set to “Disabled” all calls are allowed to interrupt. The
third option “Dial Spec.“ makes it possible to control the
Limit Calls setting using the AT command
2
. Please note
that the Limit Calls service is not supported by the LES at
present time. However, it will most likely be available in
near future. Choose the settings by pressing
and press
leave the menu.
The third menu item is Handset and it contains two sub
items: Notification and Ring Tone. Notification can be
either Yes or No and it controls whether or not the 4-Wire
Handset should be used for Call Waiting Notification. Ring
Tone can be used for choosing among the 8 Ring Tones.
4
1
If “Dial Spec.“ is chosen, support of Call Waiting Notification can
be controlled using the AT shell command “+WCWNS=<value>”
during the MPDS call setup. Possible values for the AT shell
command are: 0 =
2
If “Dial Spec.“ is chosen the Limit Calls setting can be
controlled using the AT command
MPDS call setup. Possible values are: 0 =
ENABLED.
May 2005 65
DISABLED, 1 = ENABLED, 2 = AUTOMATIC.
2
“+WCWNR=<value> during the
DISABLED, 1 =
Page 77

4
Operation Menu System - Super User
Choose the settings by pressing and press leave
the menu.
The fourth menu item is RJ11 and it contains two sub
items: Notification and Ring Tone. Notification can be
either Yes or No for each of the three RJ11 2-wire
connectors. The item Ring Tone can be used for choosing
a common 2-wire ring tone among eight ring tones. The
ring tones are described with the two symbols ‘#’ (sound)
and ‘ ‘ (no sound). Choose the settings by pressing
and press leave the menu.
The fifth menu item is Pending Time and this value is by
default set to 30 seconds. The Call Waiting Notification will
continue for a number of seconds corresponding to the
value of Pending Time. If the user chooses to ignore the
notification for a longer period the incoming call will be
ignored. Enter a value and press
the menu. Press to leave the menu without saving.
The last menu items are Caller #1-5 and each of these
can contain a phone number that is allowed to interrupt the
MPDS sessions if this is enabled in the menu item Limit
Calls. Each number can be individually associated with a
ring tone and with the 4-Wire handset and/or a number of
the RJ11 2-Wire connectors. Configuration is done as
described in the menu items Handset and RJ11.
to save when leaving
66 May 2005
Page 78

System Set-up using FleetCP PC Programs
5 PC Programs
5.1 System Set-up using FleetCP
System set-up can be managed from a PC program called
FleetCP, instead of from the handset. FleetCP can be
installed from the enclosed CD-ROM. The following pages
contain a short introduction to FleetCP. The picture below
shows the initial screen, when the program is started.
Connect the transceiver to PC using a standard RS-232.
When connected, clicking the red R button on the top
toolbar will read the current configuration from the
terminal. Clicking the red W button, will write any changes
to the terminal.
May 2005 67
5
Page 79

PC Programs System Set-up using FleetCP
The functions can be selected by clicking in the left menu
window. The menu window is divided into the following
groups: Phonebook, Help Desk, Phone Setup, Antenna
Setup, General Status, Alarm Status, Call Log, Antenna
Alignment, Debug Utilities and Terminal Window.
5.1.1 The Map
Clicking the map will show the Azimuth and Elevation to
the satellites reachable in that area. See picture below.
5
The status bar in the lower part of the window, will show
longitude and latitude as the cursor is moved around the
screen.
68 May 2005
Page 80

System Set-up using FleetCP PC Programs
5.1.2 Pin Codes
The status of the PIN codes can be seen on the right side of
the status bar. If no PIN codes are entered, all locks will be
red and locked. Click the appropriate button to enter or
change a PIN code. See picture below. If a PIN is entered,
the lock will become unlocked and turn green. At the same
time a new logout button will appear next to the PIN code
buttons. Clicking this button resets the status of the all PIN
codes.
If a change to the configuration is made without entering a
PIN code first, a prompt will appear when the write button
is pressed, asking for the PIN. See below.
To read more about PIN codes see section 3.2 Use of PIN
Codes.
May 2005 69
5
Page 81

PC Programs System Set-up using FleetCP
5.1.3 Phonebook
Phonebook entries is made by selecting Phonebook and
right clicking in the phonebook area. Entries here can be
modified or deleted in the same way. See picture below.
Further information can be found 4.3.1 Phonebook.
5
Inserting, editing and deleting entries in the Helpdesk
works in a similar way. See the Installation Manual for
further information.
70 May 2005
Page 82

System Set-up using FleetCP PC Programs
5.1.4 Satellite Setup
Satellite Setup offers an easy way of setting up Allowed,
Preferred and default LES. LES operators are dragged and
dropped between the three tables. Setup is made for each
ocean region. See picture below.
Read more about LES configuration in section 4.4.23 LES
Config.
May 2005 71
5
Page 83

PC Programs System Set-up using FleetCP
5.1.5 Routing
To route calls, use the table in the Routing window. Click in
the cell that correspond to service/interface that is to be
changed. Click the * or # button in lower part of the screen
to define it as a incoming or outgoing call. To add a IMN,
click the New IMN/ID button. See picture.
5
See section 4.4.2 Routing and IMN Config in the
Installation manual for a detailed explanation about
routing, IMN and ID's.
72 May 2005
Page 84

System Set-up using FleetCP PC Programs
5.1.6 Setting up Time and Date
To correct the time/date or in the future, the language, use
the MMI setup window. Click the Use PC time button to
import the time and date from the PC clock. If the clock is
set to a non-UTC time a clock error message will appear on
the 4-W handset on the transceiver after a while.
May 2005 73
5
Page 85

PC Programs System Set-up using FleetCP
5.1.7 Barring Services
In the security window call restrictions can be enabled or
disabled and an Auto prefix inserted.
5
See section 4.4.10 Allowed Dial, 4.4.13 BarServiceIn and
4.4.14 BarServiceOut for more details.
74 May 2005
Page 86

System Set-up using FleetCP PC Programs
5.1.8 Settings
In the Cradle/Handset window it is possible to setup ring
type, ring volume, LED brightness and display contrast.
RS-232 parameters of the terminal can be changed in the
RS-232 window.
May 2005 75
5
Page 87

PC Programs System Set-up using FleetCP
5.1.9 Antenna
The antenna setup gives a possibility to change Long term
failure timeout, number of allowed sky scans and the
antennas mount position relative to the ships bow. See
section 4.4.16 Ant.Setup for details. The antenna can be
rebooted by clicking the Reset ACU button.
The terminal window makes it possible to run AT
commands in the same way as the Windows program
5
HyperTerminal.
76 May 2005
Page 88

Set-up Using RS-232 PC Programs
5.2 Set-up Using RS-232
The illustrations below shows a typical hardware setup for
a MPDS or 9.6 kps data connection using the RS-232
interface.
MPDS or 9.6 kps data Hardware Connection.
For a MPDS or 9.6 kps data session, connect a RS-232
cable between the COM port of the computer and the RS232 interface on the Fleet system.
5.2.1 Set-up for MPDS
The terminal is connected to a PC or similar equipment via
a standard RS-232 cable. In this manual, the setup of a PC
running a MS-Windows operating system is described.
Configuring the TT-3088A
The transceiver has to be configured for the right ocean
region and LES operator that provides the MPDS service.
This is done using the handset user interface.
May 2005 77
5
Page 89

PC Programs Set-up Using RS-232
The transceivers RS-232 configuration shall be (using the
handset user interface):
• Baud Rate: 115200 baud
• Flow control: Hardware
Setting up your PC
In this section the setting up of a MS-Windows based PC is
described in general terms covering Windows 95, 98, 2000
and NT. The screen dumps below is from Windows 98. For
a detailed description with more screen dumps of the
installations, you are referred to the Application Note
“Configuring SAILOR Fleet77 for MPDS” on your MES
Software distribution disk or at our web site
www.thrane.com.
Step 1: Install a standard modem
• From the Control Panel select Modems and add a
Standard modem. Do not let Windows detect the
modem, but manually choose a standard 28800 bps
Modem.
5
• Select the appropriate COM port (i.e. the COM port that
is connected to the terminal.
• Set maximum speed to 115200
• Set Data bits = 8, Parity = None and Stop bits = 1
78 May 2005
Page 90

Set-up Using RS-232 PC Programs
Important:
• Enter Advanced settings and type the initialization
command AT+WS45=4 in the Extra settings field. This
string is transferred to the terminal when setting up a
connection. If the MPDS connection is to use another LES
than the one already selected, you use the initialization
command = AT+WS45=4;+WLES=XXX, where XXX is
the LES number.
• If the terminal is to stay in MPDS mode with no activity,
for longer periods of time, then the automatic
“disconnect when idle” setting in Windows must be
disabled. Refer to your Windows manual on how to do
this.
5
May 2005 79
Page 91

PC Programs Set-up Using RS-232
Step 2: Create a Dial-up connection
Open Dial-up Networking from My computer. Click “Make
new connection”
• Select the standard modem defined during step 1 as the
dial up device
• Enter a dummy telephone number (the number is not
used but has to be defined – write e.g. “123” as the
phone number
5
• Give the connection a recognizable name e.g. MPDS
connection
80 May 2005
Page 92

Set-up Using RS-232 PC Programs
Include TCP/IP as allowed network protocol and use default
TCP/IP settings (Server assigned IP address, Server
assigned name server addresses etc.)
5.2.2 Set-up for 9600 Data
The correct routing has to be configured via the handset.
See section 4.4.2 on how to route the data interface.
In the example below, is shown how to setup an Internet
connection via 9.6K data interface.
Step 1: Install a modem
• From the Control Panel select Modems and add a
modem.
• Let Windows detect the modem automatically.
May 2005 81
5
Page 93

PC Programs Set-up Using RS-232
5
82 May 2005
Step 2: Create a Dial-up connection
Open Dial-up Networking from My computer. Click “Make
new connection”
• Select the Lasat modem defined during step 1 as the dial
up device
• Enter the telephone number to the Internet Service
Provider. Remember country code and area code if
necessary.
Page 94

Set-up Using RS-232 PC Programs
• Give the connection a recognizable name e.g. ISDN
connection
Include TCP/IP as allowed network protocol and use TCP/IP
settings (Server assigned IP address, Server assigned
name server addresses etc.) as recommended by the ISP.
5
May 2005 83
Page 95

PC Programs Set-up using Ethernet/PPPoE
After this the connection can be made as described in
section 3.4.1 MPDS Connection.
Please note: The data connection services are only
available when the vessel is positioned inside an area
with Spot Beam coverage.
5.3 Set-up using Ethernet/PPPoE
This chapter describes the set-up and operation of data
connections via Ethernet and PPPoE using various PPPoE
clients.
5.3.1 Windows XP with Built-in PPPoE Client
Prerequisites
The PC must have an Ethernet adapter and Windows XP
installed and both must be operational. There must be a
network connection between the PC and the Fleet system.
5
As an example the the transceiver can be connected to the
computer through a switch or hub or directly using a
crossover cable.
Setting up the Connection
1. From the “Start” menu select “Settings” then “Network
Connections” and then “Create New Connection”.
This brings up the “New Connection Wizard”.
2. Click “Next”.
3. Select “Connect to the Internet” and click “Next”.
4. Select “Setup my connection manually” and click
“Next”.
84 May 2005
Page 96

Set-up using Ethernet/PPPoE PC Programs
5. Select “Connect using broadband connection requiring
user name and password” and click “Next”.
6. Type a name for the connection, e.g. ”MPDS via PPPoE”
and click “Next”.
7. Select “Anyone” and click “Next”.
8. Type a random user name and password and click
“Next”.
9. Select the shortcut on desktop option.
10. Click “Finish”.
11. Now click the new shortcut on the desktop named
“MPDS via PPPoE”. The SAILOR F33 system should now
make the connection.
Note:
Because of the relatively long set-up time for a data
connection, the PPPoE connection may some times time
out.
5
5.3.2 Windows 2000 WinPoET PPPoE Client
The data connection via Ethernet and PPPoE can be
established using various PPPoE clients.
The PPPoE client WinPoet can be obtained through your
local Thrane & Thrane distributor and works for both
Macintosh and PC.
Prerequisites
The computer must have a working Ethernet adapter.
Connect the transceiver to the computer through a switch
or hub or connect directly using a crossover cable.
May 2005 85
Page 97

PC Programs Set-up using Ethernet/PPPoE
Installation
The WinPoET program will most likely be installed from a
CD.
1. Double click the ‘Setup.exe’ icon, and the installation
begins.
5
86 May 2005
2. Click ‘Next’ and ‘Yes’ to accept the accept license
agreement.
Page 98

Set-up using Ethernet/PPPoE PC Programs
3. Choose the installation directory and click ‘Next’ to
install. The program will now be installed.
4. When done click ‘Finish’ to restart the computer
5. Find the shortcut on the desktop called ‘WinPoET
Broadband Connection Manager’ and double click.
May 2005 87
5
Page 99

PC Programs Set-up using Ethernet/PPPoE
6. Enter random user name and password and then click
‘START’.
The status field tells you how far you have reached in the
connection process.
After a successful authentication the status of the terminal
will be ‘Connected’. The user is now capable of using the
Internet like with any traditional connection.
5
88 May 2005
Page 100

List of Error messages Troubleshooting
6 Troubleshooting
6.1 List of Error messages
6.1.1 Satellite Network Messages
Within the satellite network a number of messages are
defined to indicate the network status. This section
describes the possible messages (Cause Codes) that might
be displayed in the TT-3620G Handset.
Cause Code Description Event
1001 Normal
(not shown in
the handset)
1011 Called party is
busy.
1012 Called party is
busy
1021 No User MES is clearing the call because
May 2005 89
MES is clearing the call as instructed by
the relevant MES terminal equipment.
MES is rejecting the call beca use the
specified MES terminal number is
currently busy, and MES has not been
authorized to divert calls which are
addressed to that number
MES is clearing the fixed-originated call
because subsequent to the acceptance of
the call and the signaling of the identity of
the mobile terminal to which the call will
actually be routed, that terminal has
become busy and hence cannot be rung
6
 Loading...
Loading...