Precision
Miter Gauge System
OWNER’S MANUAL
Item# KMS7102
www.kregtool.com • 800.447.8638
FT4032
Version 3 - 4/2014

2.
Safety Guidelines
General Safety Rules
WARNING! To reduce the risk of injury, user must read the instruction manual.
!
WARNING! Read all instructions. Failure to follow all instructions listed below may result in electric shock, fi re and/or serious injury. The term
!
“power tool” in all of the warnings listed below refers to your mains-operated (corded) power tool or battery-operated (cordless) power tool.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
1) Work area safety
a) Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered or dark areas invite accidents.
b) Don’t use power tools in a dangerous environment. Don’t use power tools in damp or wet locations, or expose them to rain.
c) Do not operate power tools in explosive atmospheres, such as in the presence of fl ammable liquids, gases or dust. Power tools create sparks which may ignite the dust or fumes.
d) Keep children and bystanders away while operating a power tool. Distractions can cause you to lose control.
e) Make your workshop child proof with padlocks, master switches, or by removing starter keys.
2) Electrical safety
a) Power tool plugs must match the outlet. Never modify the plug in any way. Do not use any adapter plugs with earthed (grounded) power tools. Unmodifi ed plugs and matching outlets
will reduce risk of electric shock.
b) Ground electric tools. If the tool is equipped with a three-prong plug, it should only be plugged into a grounded three-hole electrical outlet. If the proper outlet is not available, have one
installed by a qualifi ed electrician. Never remove the third prong or modify the provided plug in any way.
c) Avoid body contact with earthed or grounded surfaces such as pipes, radiators, ranges and refrigerators. There is an increased risk of electric shock if your body is earthed
or grounded
d) Do not expose power tools to rain or wet conditions. Water entering a power tool will increase the risk of electric shock.
e) Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord for carrying, pulling, or unplugging the power tool. Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp edges, or moving parts. Damaged or entangled
cords increase the risk of electric shock.
f) Use a proper extension cord and make sure it is in good condition. When using an extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to carry the current your machine draws. An
undersized cord causes a drop in line voltage resulting in loss of power and overheating. When operating a power tool outdoors, use an extension cord suitable for outdoor use.
3) Personal safety
a) Stay alert, watch what you are doing, and use common sense when operating a power tool. Do not use a power tool while you are tired or under the infl uence of drugs,
alcohol, or medication. Do not allow familiarity gained from frequent use of a tool to replace safe work practices. A moment of inattention while operating power tools may result
in serious personal injury.
b) Always wear safety glasses. Everyday eyeglasses only have impact resistant lenses, they are NOT safety glasses.
c) Use safety equipment. Use a face or dust mask when the cutting operation is dusty. Safety equipment such as a dust mask, non-skid safety shoes, hard hat, or hearing protection
used for appropriate conditions reduces personal injuries.
d) Avoid accidental starting. Ensure the switch is in the off-position before plugging in. Carrying power tools with your fi nger on the switch or plugging in power tools that have the
switch on invites accidents.
e) Remove any adjusting key or wrench before turning the power tool on. A wrench or a key left attached to a rotating part of the power tool may result in personal injury.
f) Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and balance at all times. This enables better control of the power tool in unexpected situations.
g) Secure workpieces. Use clamps or a vise to hold work when practical. This is safer than using your hand and it frees both hands to operate the tool.
h) Never stand on the machine. Serious injury could occur if the tool tips or if the cutting tool is unintentionally contacted.
i) Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or jewelry. Keep your hair, clothing and gloves away from moving parts. Loose clothes, jewelry or long hair can be caught in moving parts.
j) If devices are provided for the connection of dust extraction and collection facilities, ensure these are connected and properly used. Use of these devices can reduce dust-related hazards.
4) Power tool use and care
a) Keep guards in place, properly adjusted, and in working order.
b) Do not force the power tool. Use the correct power tool for your application. The tool will do the job better and safer at the feed rate for which it was designed.
c) Use the right tool or accessory. Don’t a force tool or attachment to do a job for which it was not designed.
d) Do not use the power tool if the switch does not turn it on and off. Any power tool that cannot be controlled with the switch is dangerous and must be repaired.
e) Disconnect the plug from the power source and/or the battery pack from the power tool before making any adjustments, changing accessories, or storing power tools.
Such preventive safety measures reduce the risk of starting the power tool accidentally.
f) Never leave tool running unattended. Turn power off. Don’t leave tool until it comes to a complete stop.
g) Store idle power tools out of the reach of children and do not allow persons unfamiliar with the power tool or these instructions to operate the power tool. Power tools are
dangerous in the hands of untrained users.
h) Maintain power tools. Check for misalignment or binding of moving parts, breakage of parts and any other condition that may affect power tool operation. If damaged,
have the power tool repaired before use. Many accidents are caused by poorly maintained power tools.
i) Keep cutting tools sharp and clean. Properly maintained cutting tools with sharp cutting edges are less likely to bind and are easier to control.
j) Use the recommended speed for the cutting tool or accessory and workpiece material.
k) Only use parts and accessories recommended by the manufacturer. Consult the owner’s manual for recommended accessories. Using improper accessories may cause personal injury .
l) Use the power tool, accessories, bits, and blades in accordance with these instructions and in the manner intended for the particular type of power tool, taking into
account the working conditions and the work to be performed. Use of the power tool for operations different from those intended could result in a hazardous situation.
5)Avoid kickback when operating your power tool. Kickbacks can cause serious injury, property damage, or death. A kickback usually occurs when the workpiece or cut-off piece
binds or becomes trapped between a spinning blade or bit and the machine fence and is violently ejected. To avoid kickback:
a) Always use a sharp blade or bit.
b) On a tablesaw, ensure that both the saw blade and rip fence are parallel to the miter-gauge slots. See your tablesaw owner’s manual for instructions on making these adjustments.
c) Plan your tablesaw cuts to avoid binding. Never use the rip fence and the miter gauge at the same time to support a workpiece. The cut-off can bind and kick back.
d) Never cut freehand. The workpiece should always be supported by either the miter gauge or the machine fence, but not both.
e) Use hold-downs, featherboards, push sticks, and push blocks where appropriate to guide the workpiece during the cut. These accessories protect your hands from injury.
f) When using a featherboard while making through cuts on a tablesaw, always position the featherboard on the in-feed side and at least 2” in front of the blade.
g) Never position a featherboard adjacent to or on the out-feed side of a blade or bit, or in any confi guration that would cause the workpiece or waste to be pushed into or
pinch the blade or bit. Positioning a featherboard in this manner can cause the workpiece or waste to kick back, resulting in serious personal injury.
6) Service
a) Have your power tool serviced by a qualifi ed repair person using only identical replacement parts. This will ensure that the safety of the power tool is maintained.
Safety Guidelines
3.
General Safety Rules
7) Additional safety rules for the Precision Miter Gauge System
a) Read this manual and these safety guidelines. Follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines for the tool on which you are using this accessory. Learn the applications and
limitations of the tool as well as the hazards specifi c to it. Operating the power tool before understanding safe and proper use could result in personal injury.
b) Ensure that the handle is tight and the fence extrusion T-knobs are secure prior to starting the power tool.
c) Keep hands away from a moving blade or bit when operating the machine. Never reach near a moving blade or bit to clear debris. Turn off the power tool and wait for the blade
or bit to come to a complete stop.
d) Always support long boards on both the infeed and the outfeed ends.
e) Always securely hold workpieces against the machine table and miter gauge or fence.
f) This miter-gauge system is designed for a specifi c application. Do not modify and/or use it for any other application. If you have questions about the miter gauge,
DO NOT use it until you contact Kreg Tool Company and receive advice.
WARNING! This product contains one or more chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
!
California Proposition 65
WARNING! Dust created by sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities may contain chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or
!
other reproductive harm. Examples of these chemicals are:
a) Lead from lead-based paints
b) Crystalline silica from bricks, cement, and other masonry products
c) Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated lumber
Your risk from exposure to these chemicals depends on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure, work in a well-ventilated area with approved safety equipment, such
as a dust mask specifi cally designed to fi lter out microscopic particles.
Miter Gauge Assembly
ATTENTION
!
These instructions show how to assemble the Precision Miter Gauge System for use on the left-hand side of the blade. To use the
Precision Miter Gauge on the right-hand side of the blade, assemble the Swing Stop™ to be the mirror image of the one shown
in the Swing Stop™ drawing. You can use the measuring tape included with the miter gauge on the right side of the blade by
installing it to read upside down so that measurements from the blade read left to right. To purchase a left-to-right reading version
of the measuring tape, contact Customer Service at 1-800-447-8638.
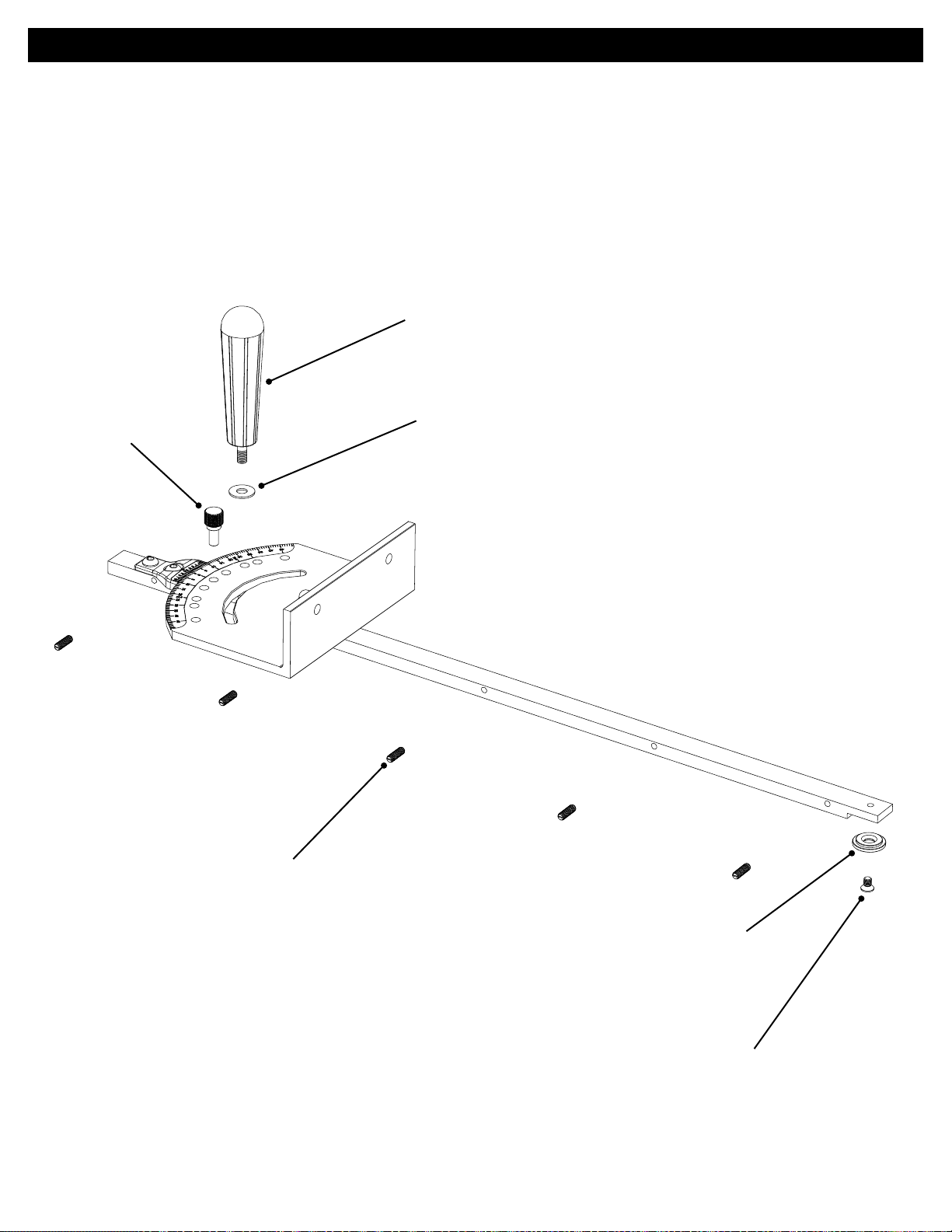
4.
(1) Positioning pin
FT4056
Assembly - Miter Gauge
Miter Gauge
Parts Diagram
(1) Handle
FT4029
(1) ¼" nylon washer
FT4030
(5) #10-32 x ⅝" nylon set screws
FT4102
(1) T-slot washer
FT4057
(1) #10-32 x 5/16" fl at head machine screw
FT4207
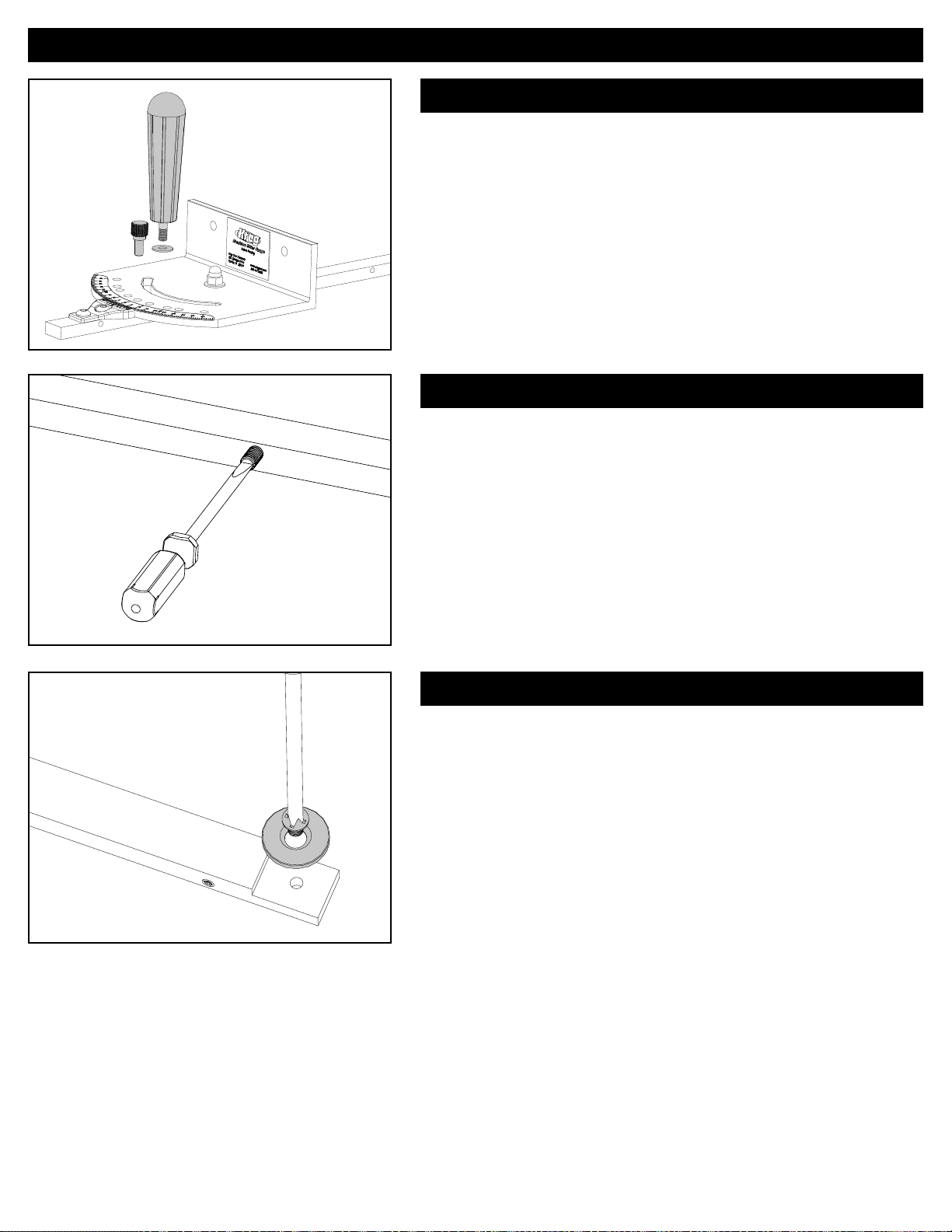
Assembly - Miter Gauge
Install the miter-gauge handle
Set the miter-gauge angle to zero and insert the positioning pin into
the zero-angle positive-stop hole. Slip the ¼" nylon washer onto the
threaded stud on the handle and thread the handle into the guide bar.
Tighten the handle.
Adjust the guide bar
Using a small, fl at-blade screwdriver, thread fi ve #10-32 x ⅝" nylon set
screws into the holes in the side of the guide bar. Drive all of them from
the same side until they just start to project from the opposite side. Testfi t the miter gauge in your saw miter slot. Adjust each screw, removing
and replacing the miter gauge as necessary, until the miter gauge slides
smoothly all along the miter slot without any side-to-side play.
5.
Attach the T-slot washer (for saws with T-profi le miter-gauge slots only)
For a saw with a T-shaped miter-gauge slot, fasten the T-slot washer
to the bottom face of the notch at the leading end of the guide bar with
the #10-32 x 5/16" fl athead machine screw. Tighten the screw, being
careful not to strip the threads in the aluminum bar.
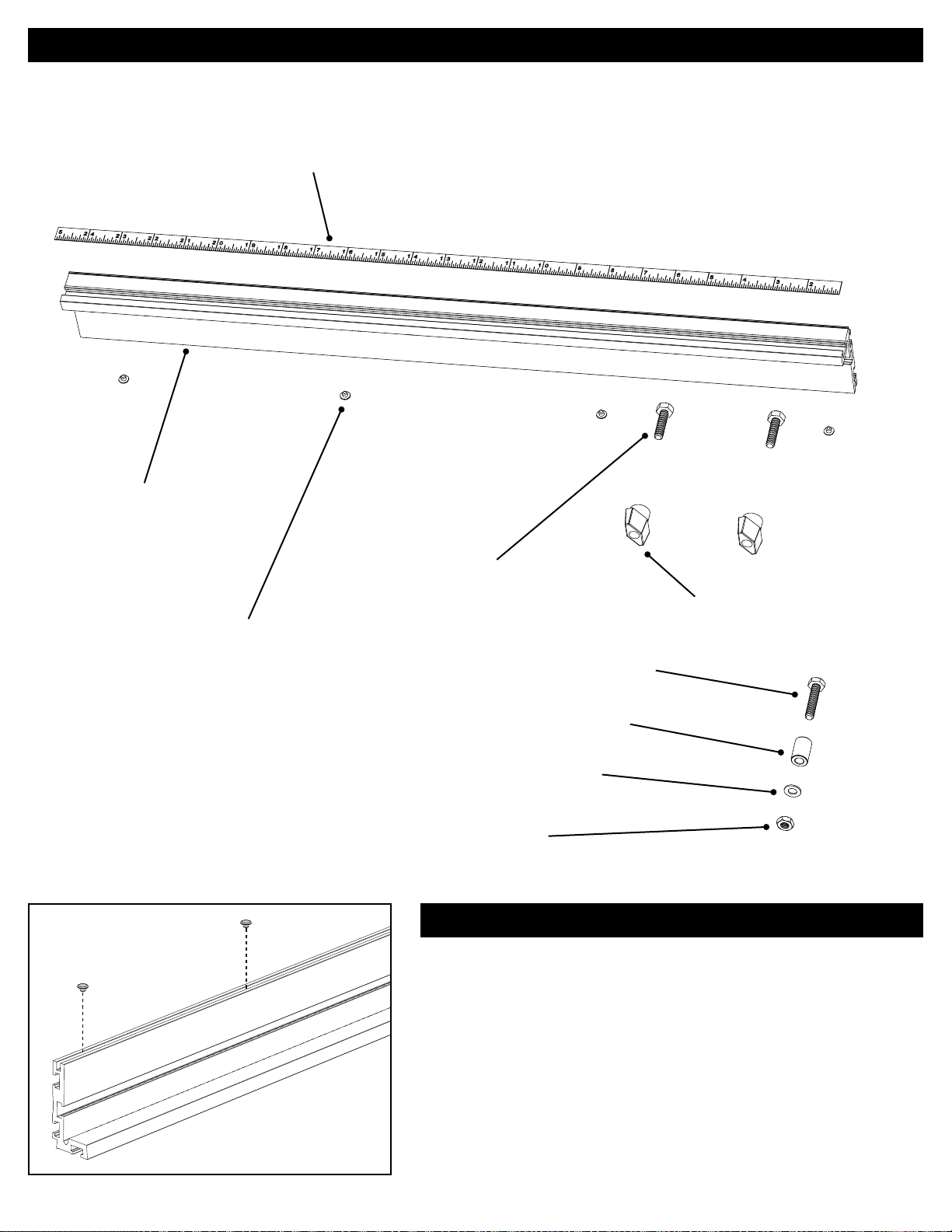
6.
Assembly - Fence
Fence Assembly
(1) 48" right-to-left reading self-adhesive tape
FT4047
(1) Fence extrusion
KMS7702
(6) Glides
FT4055
(2) ¼"-20 x 1" hex head bolts
FT4139
(1) ¼"-20 x 1¼" hex head bolt
FT4059
Parts Diagram
(2) T-knobs
DK1313
(1) Fence Stop
FT4203
(1) ¼" brass washer
DK1504
(1) ¼"-20 hex nut
DK1510
Install the fence glides
Press the four plastic glides into the groove in the bottom of the fence,
placing one about 1" from each end and the other two spaced evenly
between them.
Assembly - Fence
Attach the fence to the miter-gauge head
Slide the heads of two ¼"-20 x 1¼" hex head bolts into the T-slot in the
back of the fence. Insert the bolts into the holes in the face of the miter
gauge head. Thread on the T-knobs. You’ll fi ne-tune the fence position
later.
7.
Adhere the measuring tape
Before installing the self-adhesive measuring tape, make sure the
shallow groove in the top of the fence is clean and dry. To hold the
miter gauge steady while you install the tape, place the miter gauge in
the saw miter-gauge slot. Cut the tape at the 1” mark and the 25" mark
using sturdy scissors or metal snips.
Peel the backing from the 1" end of the measuring tape, exposing
about one inch of the adhesive. Fold the backing so it protrudes from
the tape at an angle. Align the tape 1” mark with the right-hand end of
the fence (the end nearest to the saw blade) and press the tape into
the shallow groove in the rail. With the fi rst inch of tape adhered, pull
the backing from under the tape, pressing the tape into the groove as
you continue to remove the backing. Should you attach the scale in the
wrong position, immediately remove and reposition it, and then fi rmly
press it in place.
8.
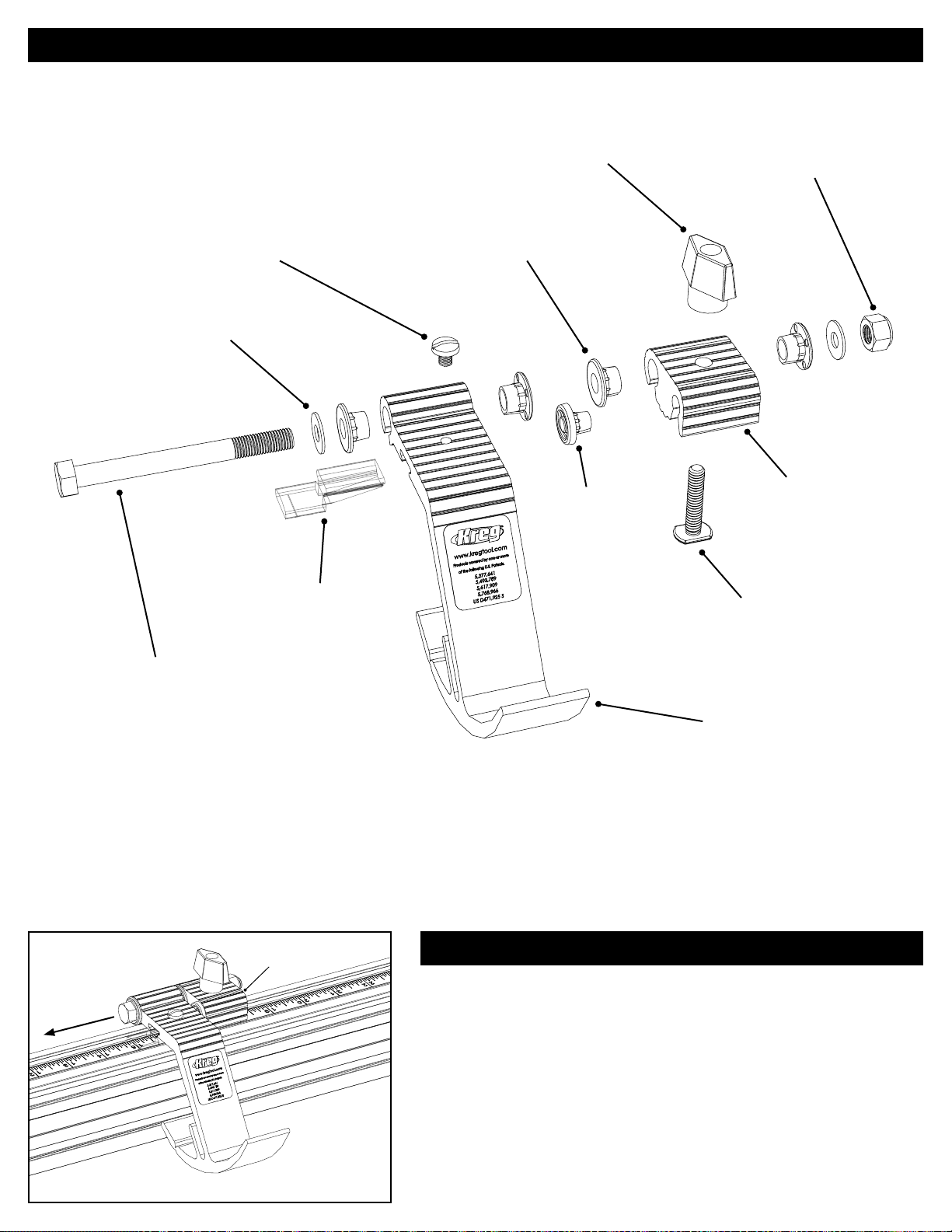
Assembly - Swing Stop
TM
Swing Stop
TM
Parts Diagram
(1) #10-32 x ¼" nylon machine screw
FT4064
(2) 5/16" brass washer
FT4137
(1) T-knob
DK1313
(4) Fence-stop bushing
FT4257
(1) Support button
FT4258
(1) 5/16"-24 lock nut
FT4061
(1) Base
FT4262
(1) Lens
FT4063
(1) 5/16"-24 x 3¼" hex head bolt
FT4060
(1) ¼"-20 x 1¼" T-bolt
FT4212
(1) Arm
FT4261
Assemble the stop
Referring to the drawing above, assemble the Swing Stop™. When installing the 5/16"-24 x 3¼" hex head bolt that
joins the arm to the base, tighten the lock nut enough to eliminate side-to-side play but still allow the arm to move
freely. (Raise and release the arm. It should fall slowly.) When installing the lens cursor, position the red line about
⅜" from edge of the arm.
! ATTENTION
Base
Assemble the Swing Stop™ with the arm on the blade or bit side of
Blade
the base.
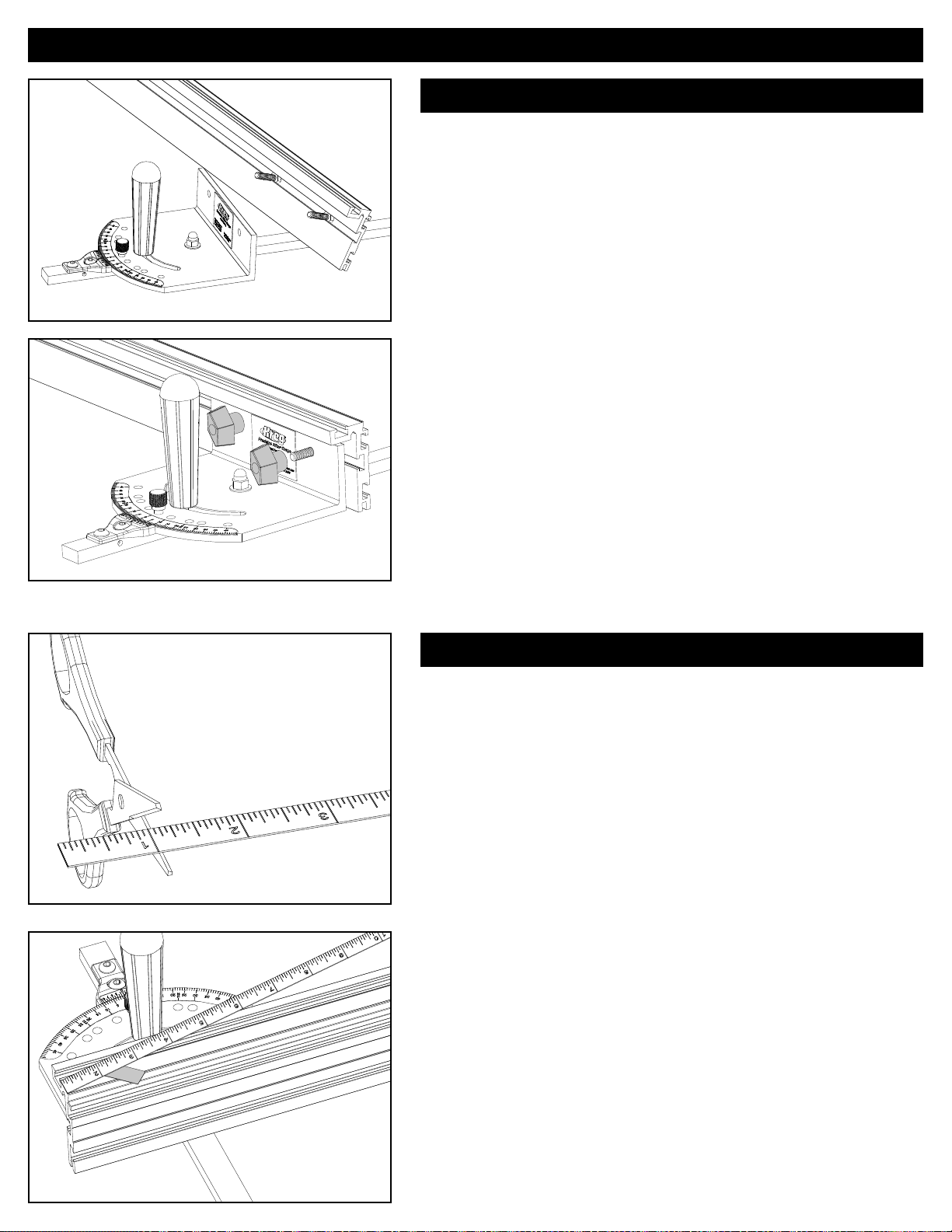
Assembly - Swing Stop
Position the fence and calibrate Swing Stop™
With the miter gauge in place on your machine (a tablesaw in this
example) ensure that the guide bar slides easily in the miter-gauge
slot without side-to-side play. Disconnect the tablesaw from power
and raise the blade. Loosen the two T-knobs that secure the fence to
the head, and position the end of the fence ⅝” from the saw blade.
Tighten the knobs. Loosen the handle, remove the positioning pin,
and rotate the miter-gauge head in both directions to make sure the
fence does not contact the blade. If there is interference, loosen the
T-knobs and slide the fence away from the blade. Return the mitergauge head to the zero-degree position, insert the positioning pin, and
tighten the handle.
Use a steel shop ruler (one with the zero mark fl ush with the end) to
position the stop arm 3" from the blade. Let the blade teeth graze the
end of the ruler. (Do not use the cursor and measuring tape to position
the stop arm.) Tighten the stop T-knob.
Loosen the nylon machine screw that secures the lens cursor to the
arm and position the lens with the red line exactly over the 3” mark on
the measuring tape. Tighten the nylon screw.
TM
9.
Make a test cut to confi rm the 3" length. Adjust the cursor position as
necessary and make another test cut.
To install the fence stop, slide the head of the ¼"-20 x 1¼" hex head
bolt into the T-slot in the back of the fence on the side of the mitergauge head closest to the blade. Slip the fence-stop bushing over the
bolt and thread on the hex nut. Slide the fence stop against the edge
of the miter-gauge head and tighten the nut. Now you can reposition
the fence, for example moving the fence closer to the blade to support
a workpiece when making an angled cut, and return it to perfect
calibration for right-angle cuts simply by repositioning the fence with the
stop against the edge of the miter-gauge head.
! ATTENTION - Bevel Cuts
Any time the blade is tilted toward the miter gauge, always check to see if any part of the miter gauge contacts the blade
before turning on the saw. If there is interference, move the fence away from the blade. This may require removing the fence
stop and then recalibrating the fence after making the bevel cut.
10.
Using the Miter Gauge
Adjusting the miter gauge to pre-set angles
The miter gauge head features positive stops at 0, 10, 22½, 30, and 45 degrees. To use these stops, simply loosen the handle,
remove the positioning pin, rotate the miter-gauge head to the desired angle, drop the positioning pin in place, and tighten the handle.
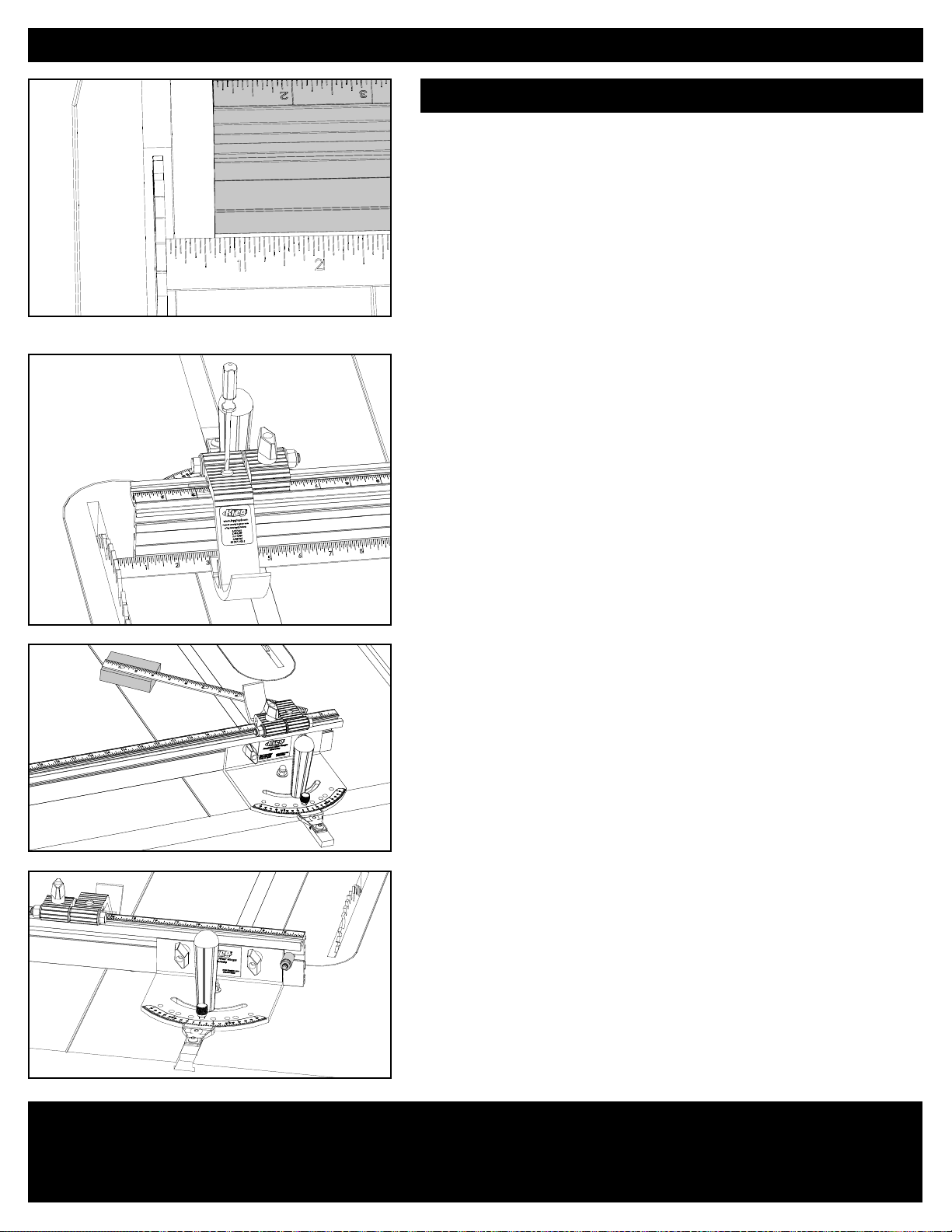
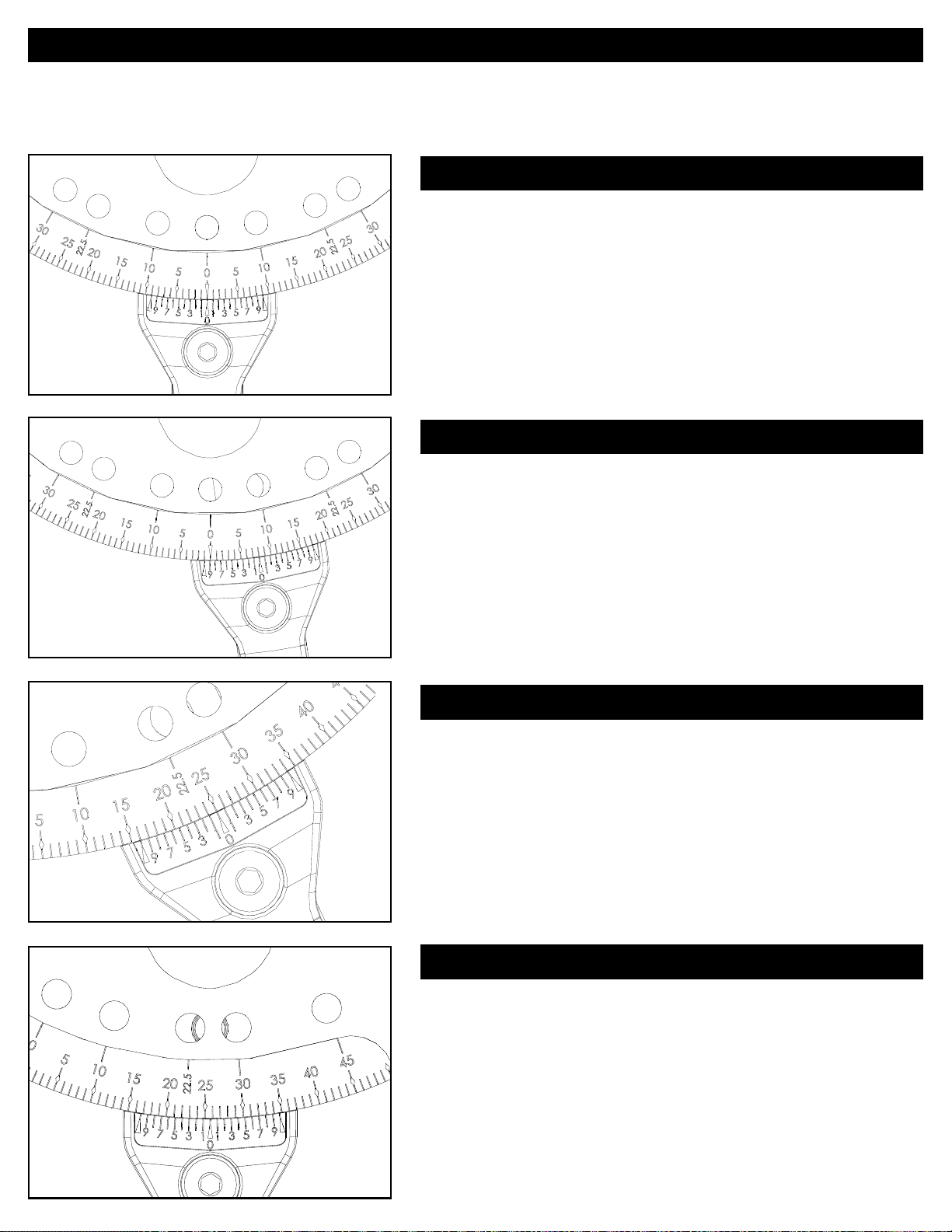
1. Setting fractional angles
The miter gauge is equipped with an upper scale that measures
angles in whole degrees and a lower Vernier scale that measures
angles in 1/10th-degree fractions. These scales allow you to set
whole-degree angles and any 1/10th-degree fraction between.
2. Setting fractional angles
To set a whole-degree angle, line up the degree mark on the upper
scale with the zero arrow on the Vernier scale, and tighten the handle.
3. Setting fractional angles
To set an angle between whole degrees (25.7 degrees in this
example), rotate the miter-gauge head until the arrow on the Vernier
scale lines up with the whole degree mark. (In this example, we rotate
the head clockwise.)
4. Setting fractional angles
To arrive at the 25.7-degree setting, locate the “7” to the right of
zero on the Vernier scale. Continue rotating the miter-gauge head
clockwise until the desired 1/10th-degree mark on the Vernier scale
aligns with the nearest whole-degree mark on the upper scale. (In this
example, the “7” mark on the Vernier scale aligns with the “32” on the
upper scale.)
Note: When rotating the miter gauge head clockwise, use the 1/10thdegree scale to the right of zero on the Vernier scale. When rotating
counterclockwise, use the 1/10th-degree scale to the left of zero.

Using the Miter Gauge
Using shop-built accessories with your miter gauge
The T-slots along the length of the fence allow you to attach auxiliary fences, custom shop-made stops, or other jigs and fi xtures
using standard ¼" hex head bolts. You also can use ¼" toilet-fl ange bolts available from hardware stores or home centers.
Adding an auxiliary fence
An auxiliary fence provides a renewable surface that can be extended
beyond the path of the blade to support a workpiece, resulting in
smooth crosscuts with minimum chipping. The auxiliary fence must be
¾" thick, 2⅝" high, and any length that suits your application, and can
be made from solid wood, plywood, particleboard, or medium-density
fi berboard (MDF). Attach the auxiliary fence with 1/4"-20 x ¾" hex
head bolts, ¼" washers, and nuts. Drill ¼" holes with ¾" counterbores
11/16" deep. The auxiliary fence can be repositioned or replaced
without effecting the Swing Stop™ calibration.
11.
! ATTENTION
To use the Swing Stop™ with an auxiliary fence, you must modify
the stop arm so it properly seats against the fence when lowered,
as shown in this section. Once the stop arm has been altered,
it must be used with an auxiliary fence. The stop will not work
correctly if used without the auxiliary fence.
Modifying the stop arm for an auxiliary fence
A groove (break line) is incorporated into the stop arm to provide a
simple means to shorten this portion of the Swing Stop™ for use
with a ¾”-thick auxiliary fence. If you intend to use an auxiliary fence,
remove the breakaway section of the arm, as shown.
Three Simple Steps
1. Firmly hold the stop arm in your hand or a vise.
2. Use pliers to grip the breakaway portion of the stop arm and
snap off this piece.
3. File or sand the rough edge smooth.

12.
WARRANTY
WARRANTY
KREG PRECISION MITER GAUGE SYSTEM
Kreg Tool Company products are warranted
to be free of defects in materials and
workmanship for a period of one (1) year
from the date of delivery to the original
purchaser. This warranty is extended only to
the original purchaser and covers only Kreg
products purchased directly from Kreg Tool
Company and its authorized distributors.
During the warranty period, Kreg Tool
Company, at its option, will repair or replace
any product or component part thereof
proving defective. This warranty applies
only to products used in accordance with
proper operation, maintenance, and safety
procedures set forth in catalogs, manuals,
and other instructional materials furnished by
Kreg Tool Company.
This warranty is in effect only if the warranty
registration card included with the product is
fully and properly completed and returned to
Kreg Tool Company within ten (10) days from
the date of delivery to the original purchaser.
This warranty is null and void if the product
has been subjected to (1) neglect, improper
service, or improper storage; (2) misuse,
abuse, accident, or other circumstances
beyond Kreg Tool Company control; and
(3) modifi cation, alteration, tampering,
disassembly, or repairs executed outside
of the Kreg Tool Company factory or not
authorized by Kreg Tool Company. This
warranty does not cover normal wear and
tear, corrosion, abrasion, or damage due to
natural causes or acts of God.
To obtain warranty service, contact the
distributor from whom you purchased your
Kreg product or contact Kreg Tool Company
directly. Proof of purchase is required to
secure remedy under the terms of this
warranty. Kreg Tool Company assumes no
responsibility for products returned without
prior authorization. Kreg Tool Company
obligations under this warranty shall be
exclusively limited to repairing or replacing
products determined to be defective upon
delivery to and inspection by Kreg Tool
Company. Under no circumstance shall
Kreg Tool Company be liable for incidental
or consequential damages resulting from
defective products, nor shall Kreg Tool
Company liability exceed the purchase price
of the product.
This constitutes Kreg Tool Company’s
sole warranty. Any and all other warranties
implied by law, including any warranties for
merchantability or fi tness for a particular
purpose, are hereby limited to the duration of
this warranty. Kreg Tool Company shall not
be liable for any loss, damage or expense
directly or indirectly related to the use of
Kreg products or from any other cause or for
consequential damages including without
limitation, loss of time, inconvenience, and
loss of production. The warranty contained
herein may not be modifi ed and no other
warranty, expressed or implied, shall be
made by or on behalf of Kreg Tool Company.
The following information will be useful in the event warranty service is required.
Date of Purchase: ____/____/____
Purchased From: ____________________________________________
Keep a copy of your purchase invoice with this form.
Kreg Tool Company 201 Campus Drive Huxley, IA 50124

Precision
Miter Gauge System
GUIDE D’UTILISATION
Article #KMS7102
www.kregtool.com • 800.447.8638
FT4032
Version 3 - 4/2014

2.
Consignes de sécurité
Règles de sécurité générales
AVERTISSEMENT! Afi n de réduire les risques de blessure, l’utilisateur doit lire le manuel d’instructions.
!
AVERTISSEMENT! Lisez toutes les instructions. Le non-respect des instructions ci-dessous peut entraîner un choc électrique, un incendie ou des
!
blessures graves. Le terme « outil électrique » utilisé dans tous les avertissements qui fi gurent ci-dessous désigne les outils électriques alimentés
sur secteur (à fi l) ou alimentés par piles (sans fi l).
CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS
1) Mesures de sécurité dans l’aire de travail
a) L’aire de travail doit être propre et bien éclairée. Une aire de travail encombrée ou peu éclairée augmente le risque d’accident.
b) N’utilisez pas un outil électrique dans un environnement dangereux. N’utilisez pas un outil électrique dans un endroit mouillé ou humide et ne l’exposez pas à la pluie.
N’utilisez pas un outil électrique dans un endroit mouillé ou humide et ne l’exposez pas à la pluie.
c) N’utilisez pas d’outils électriques dans une atmosphère explosive, par exemple en présence de liquides, de vapeurs ou de poussières infl ammables. Les outils électriques
produisent des étincelles susceptibles d’enfl ammer ces poussières ou ces vapeurs.
d) Gardez les enfants et les autres personnes à l’écart lorsque vous utilisez un outil électrique. Une distraction peut vous faire perdre la maîtrise de l’outil.
e) Empêchez les enfants d’accéder à l’atelier en utilisant des cadenas et un interrupteur général ou en retirant les clés du commutateur d’allumage.
2) Consignes de sécurité relatives à l’électricité
a) Les fi ches des outils électriques doivent correspondre à la prise. Ne modifi ez jamais la fi che de quelque façon que ce soit. N’utilisez pas d’adaptateur avec les outils
électriques mis à la terre. L’utilisation de fi ches non modifi ées dans les prises compatibles réduit les risques de choc électrique.
b) Branchez les outils électriques sur une prise mise à la terre. Un outil muni d’une fi che à trois broches ne doit être branché que sur une prise de courant à trois alvéoles mise à la terre.
Si vous ne disposez pas d’une telle prise, demandez à un électricien qualifi é d’en installer une avant d’utiliser l’outil. Ne retirez jamais la troisième broche et ne modifi ez jamais la fi che.
c) Évitez de toucher à des surfaces mises à la terre, par exemple un tuyau, un radiateur, une cuisinière ou un réfrigérateur. Le contact du corps avec une surface mise à la terre
augmente les risques de choc électrique.
d) N’exposez pas les outils électriques à la pluie ou à tout autre environnement humide. Les risques de choc électrique sont plus élevés si l’eau s’infi ltre dans un outil électrique.
e) N’utilisez pas le cordon d’alimentation de façon abusive. Ne transportez jamais un outil électrique en le tenant par son cordon, et ne tirez jamais sur le cordon pour le débrancher.
Tenez le cordon d’alimentation éloigné des sources de chaleur, de l’huile, des objets coupants et des pièces mobiles. Les risques de choc électrique sont plus élevés si le cordon
d’alimentation est endommagé ou emmêlé.
f) Utilisez une rallonge appropriée et assurez-vous qu’elle est en bon état. Utilisez une rallonge qui convient au courant consommé par la machine. Une rallonge de calibre insuffi sant
entraînera une baisse de la tension secteur, une perte de puissance et une surchauffe. Lorsque vous utilisez un outil électrique à l’extérieur, servez-vous d’une rallonge conçue pour
être utilisée à l’extérieur.
3) Sécurité personnelle
a) Soyez vigilant, prêtez attention à ce que vous faites et faites preuve de bon sens lorsque vous utilisez un outil électrique. N’utilisez pas un outil électrique lorsque vous ressentez de la
fatigue ou lorsque vous êtes sous l’effet de drogues, d’alcool ou de médicaments. L’habitude liée à l’utilisation fréquente d’un outil ne remplace pas une méthode de travail sécuritaire.
Un moment d’inattention pendant que vous utilisez des outils électriques peut occasionner des blessures graves.
b) Portez toujours des lunettes de sécurité. Les lunettes ordinaires sont seulement munies de verres résistants aux chocs et ne peuvent PAS être considérées comme des lunettes de sécurité.
c) Utilisez de l’équipement de sécurité. Portez un masque facial ou un masque antipoussières quand la coupe produit beaucoup de poussière. Le port d’équipement de sécurité, comme un
masque antipoussières, des chaussures de sécurité antidérapantes, un casque de protection et des protecteurs auditifs, lorsque les conditions l’exigent, réduit les risques de blessures.
d) Évitez les mises en marche accidentelles de l’outil. Assurez-vous que l’interrupteur de l’outil est à la position d’arrêt avant de le brancher. Le fait de transporter un outil électrique en
gardant le doigt sur l’interrupteur ou de le brancher tandis que son interrupteur est en position de marche augmente les risques d’accident.
e) Retirez toutes les clés de réglage de l’outil électrique avant de mettre celui-ci en marche. Une clé de réglage oubliée sur un outil rotatif peut occasionner des blessures graves.
f) Ne vous penchez pas trop en avant. Gardez une posture sécuritaire et un bon équilibre en tout temps. Cela vous permet de mieux maîtriser l’outil électrique lorsque des situations
inattendues se présentent.
g) Fixez bien la pièce à travailler. Utilisez des colliers de serrage ou un étau pour fi xer la pièce sur laquelle vous travaillez, au besoin. Cette technique est plus sécuritaire que l’utilisation
de vos mains et vous permet de garder les mains libres pour faire fonctionner l’outil.
h) Ne vous tenez jamais debout sur l’outil. Des blessures graves peuvent survenir s’il se renverse ou si l’outil tranchant est accidentellement mis en marche.
i) Habillez-vous convenablement. Ne portez pas de vêtements amples ni de bijoux. Gardez vos cheveux, vos vêtements et vos gants loin des pièces mobiles. Les vêtements
amples, les bijoux et les cheveux longs risquent de se prendre dans les pièces mobiles.
j) Si un dispositif permet de raccorder un dépoussiéreur, assurez-vous que celui-ci est branché et utilisé correctement. L’usage de ces dispositifs contribue à réduire les dangers liés à la poussière.
4) Utilisation et entretien d’un outil électrique
a) Gardez les protecteurs en place, bien réglés et en bon état de fonctionnement.
b) Ne forcez pas l’outil électrique. Utilisez l’outil électrique approprié à la tâche que vous envisagez. L’utilisation appropriée de l’outil selon la vitesse d’alimentation prévue permet
d’obtenir de meilleurs résultats, de façon plus sécuritaire.
c) Utilisez l’outil ou l’accessoire approprié. Ne tentez pas d’utiliser un outil ou l’un de ses accessoires pour effectuer un travail pour lequel il n’est pas conçu.
d) N’utilisez pas l’outil électrique si l’interrupteur ne fonctionne pas. Tout outil qui ne peut pas être contrôlé par l’interrupteur est dangereux et doit être réparé.
e) Débranchez la fi che de la prise ou retirez le bloc-piles de l’outil électrique avant d’effectuer des réglages, de changer d’accessoire ou de le ranger. Ces mesures de sécurité
préventives réduisent les risques de mettre accidentellement l’outil électrique en marche.
f) Ne laissez jamais l’outil en marche sans supervision. Coupez l’alimentation électrique. Ne vous éloignez pas de l’outil tant qu’il ne s’est pas complètement arrêté.
g) Rangez les outils électriques inutilisés hors de la portée des enfants et ne laissez pas les personnes ne connaissant pas bien l’outil ou ces instructions utiliser l’outil.
Les outils électriques sont dangereux s’ils se retrouvent entre les mains d’utilisateurs qui ne savent pas s’en servir.
h) Entretenez les outils électriques. Vérifi ez les pièces mobiles pour vous assurer qu’elles ne sont pas désalignées, enrayées, brisées ou dans un état qui pourrait nuire au fonctionnement
de l’outil électrique. Si elles sont endommagées, faites-les réparer avant d’utiliser l’outil. De nombreux accidents sont provoqués par des outils électriques mal entretenus.
i) Gardez vos outils tranchants affûtés et propres. Des outils tranchants bien entretenus et dont les lames sont affûtées risquent moins de se bloquer et sont plus faciles à maîtriser.
j) Utilisez la vitesse recommandée pour l’outil de coupe, l’accessoire et la pièce à travailler.
k) N’utilisez que des pièces et des accessoires recommandés par le fabricant. Consultez la liste des accessoires recommandés dans le guide d’utilisation. L’utilisation d’accessoires
inappropriés peut causer des blessures.
l) Utilisez l’outil électrique, les accessoires, les embouts et les lames conformément aux instructions et aux fi ns pour lesquelles l’outil a été conçu, en tenant compte des conditions de
travail et des tâches à effectuer. L’utilisation de l’outil électrique à des fi ns autres que celles pour lesquelles il a été conçu pourrait entraîner une situation dangereuse.
5)Évitez les rebonds lorsque vous utilisez votre outil électrique. Les rebonds peuvent causer des blessures graves, des dommages matériels ou la mort. Un rebond se produit
généralement lorsque la pièce à travailler ou un morceau se retrouvent coincés entre une lame de scie ou un foret et le guide de la machine et sont ensuite projetés violemment en l’air.
Pour éviter les rebonds :
a) Utilisez toujours une lame coupante ou un foret bien affûté.
b) Sur une scie à table, assurez-vous que la lame de scie et le guide longitudinal sont parallèles aux rainures du guide d’onglet. Consultez le guide d’utilisation de votre scie à table pour
savoir comment effectuer ces réglages.
c) Planifi ez vos coupes avec la scie à table pour éviter les blocages. N’utilisez jamais le guide longitudinal et le guide d’onglet simultanément pour supporter la pièce. La partie coupée peut
se bloquer et faire un rebond.
d) N’effectuez jamais une coupe à main libre. La pièce doit toujours être supportée par le guide d’onglet ou le guide de la machine, mais pas les deux simultanément.
e) Utilisez des chevilles de retenue, des guides d’appui, des poussoirs et des blocs poussoirs au besoin pour guider la pièce durant la coupe. Ces accessoires vous évitent de vous couper les mains.
f) Lorsque vous effectuez des coupes transversales sur une scie à table avec un guide d’appui à languettes, placez toujours le guide d’appui à languettes sur le côté d’alimentation et à au
moins 5,08 cm de l’avant de la lame.
g) Ne placez jamais un guide d’appui à languettes vis-à-vis d’une lame ou d’un trépan, ou derrière ceux-ci, ou réglé de manière à ce que la pièce ou les retailles soient poussées vers la
lame ou le foret, ou s’y coincent. Un tel positionnement du guide d’appui à languettes peut faire rebondir la pièce ou les retailles et causer de graves blessures.

Consignes de sécurité
3.
Règles de sécurité générales
6) Réparation
a) Demandez à un technicien qualifi é qui utilise seulement des pièces de rechange identiques aux pièces d’origine d’effectuer l’entretien de votre outil électrique. Vous vous
assurerez ainsi de respecter les consignes de sécurité de l’outil électrique.
7) Règles de sécurité supplémentaires pour le système de guide d’onglet de précision.
a) Lisez attentivement ce manuel et ces consignes de sécurité. Suivez les consignes de sécurité du fabricant de l’outil sur lequel vous utilisez cet accessoire. Assurez-vous de connaître
le fonctionnement et les restrictions de l’outil ainsi que les risques potentiels liés à son utilisation. L’utilisation de cet outil électrique sans comprendre la méthode sécuritaire et adéquate
peut entraîner des blessures graves.
b) Assurez-vous que la poignée et les boutons en T du profi lé du guide sont bien serrés avant de démarrer l’outil électrique.
c) Gardez vos mains loin d’une lame ou d’un foret en mouvement lorsque vous utilisez l’appareil. Ne placez jamais votre main près d’une lame ou d’un foret en mouvement pour
enlever les débris. Arrêtez l’outil électrique et attendez l’arrêt complet de la lame ou du foret.
d) Dans le cas des longs panneaux, placez toujours un support sous l’extrémité d’entrée et un support sous l’extrémité de sortie.
e) Tenez toujours les pièces fermement contre la table de la machine et le guide d’onglet ou le guide.
f) Ce système de guide d’onglet est conçu pour une utilisation précise. Ne le modifi ez pas et ne l’utilisez pas à d’autres fi ns. Si vous avez des questions au sujet du guide
d’onglet, NE l’utilisez PAS avant d’avoir communiqué avec Kreg Tool Company et d’avoir reçu des conseils.
AVERTISSEMENT! Cet article contient un ou plusieurs produits chimiques reconnus par l’État de la Californie comme étant la cause de cancers et d’anomalies congénitales ou d’autres
!
problèmes liés aux fonctions reproductrices. Lavez-vous les mains après l’avoir manipulé.
Proposition 65 de la Californie
AVERTISSEMENT! La poussière causée par le ponçage mécanique, le sciage, le polissage, le perçage et d’autres activités liées à la construction peut contenir des produits chimiques
!
reconnus par l’État de la Californie comme étant la cause de cancers et d’anomalies congénitales ou d’autres problèmes liés aux fonctions reproductrices. Voici quelques exemples
de ces produits chimiques :
a) le plomb provenant de peintures à base de plomb;
b) la silice cristalline provenant de la brique, du ciment ou d’autres matériaux de maçonnerie;
c) l’arsenic et le chrome provenant du bois d’œuvre traité avec un produit chimique.
Les risques liés à l’exposition à ces produits chimiques dépendent du nombre de fois où vous effectuez ce type de travaux. Afi n de limiter votre exposition à ces produits, travaillez dans
un endroit bien ventilé en vous munissant de l’équipement de sécurité approuvé tel qu’un masque antipoussières conçu spécialement pour fi ltrer les particules microscopiques.
Ensemble de guide d’onglet
AVERTISSEMENT!
!
Ces instructions présentent la manière d’assembler le guide d’onglet de précision pour une utilisation du côté gauche de la
lame. Pour utiliser le guide d’onglet du côté droit de la lame, assemblez la butée Swing Top™ de sorte qu’elle soit symétrique
à l’illustration. Vous pouvez utiliser le ruban à mesurer inclus avec le guide d’onglet sur le côté droit de la lame en l’installant de
manière à effectuer une lecture inversée et à donner ainsi les mesures de la lame de gauche à droite. Pour vous procurer un
ruban à mesurer gradué de gauche à droite, communiquez avec le service à la clientèle au 1 800 447-8638.

4.
Assemblage : Guide d’onglet
Schéma des pièces du
guide d’onglet
(1) poignée
FT4029
(1) goupille de
positionnement
FT4056
(1) rondelle en nylon de ¼ po
FT4030
(5) vis de calage en nylon 10-32 × ⅝ po
FT4102
(1) rondelle à rainure en T
FT4057
(1) vis à métaux à tête plate 10-32 × 5/16 po
FT4207

Assemblage : guide d’onglet
Installation de la poignée du guide d’onglet
Réglez l’angle du guide d’onglet à zéro degré et insérez la goupille
de positionnement dans le trou de butée fi xe à zéro degré. Glissez la
rondelle en nylon de ¼ po sur la tige fi letée de la poignée et vissez la
poignée dans le guide-chaîne. Serrez la poignée.
Réglage du guide-chaîne
À l’aide d’un petit tournevis à tête plate, vissez cinq vis de calage
10-32 × ⅝ po en nylon dans les trous situés sur le côté du guidechaîne. Vissez-les tous du même côté jusqu’à ce qu’ils émergent du
côté opposé. Vérifi ez l’ajustement du guide d’onglet dans la rainure de
l’onglet de votre scie. Ajustez chaque vis en retirant et en replaçant le
guide d’onglet au besoin jusqu’à ce que celui-ci glisse en douceur le
long de la rainure de l’onglet sans mouvement latéral.
5.
Fixation de la rondelle à rainure en T
(pour les scies à rainure de guide d’onglet en T seulement)
Pour une scie à rainure de guide d’onglet en T, serrez la rondelle à
rainure en T sur la face inférieure de l’encoche au niveau de l’extrémité
avant du guide-chaîne à l’aide de la vis à métaux à tête plate 10-32 ×
5/16 po. Serrez la vis en faisant attention à ne pas abîmer le fi letage
dans la barre en aluminium.

6.
Assemblage : guide
(1) ruban à mesurer autoadhésif gradué de
droite à gauche de 121,92 cm
FT4047
Schéma des pièces
de l’assemblage du guide
(1) profi lé du guide
KMS7702
(6) glissières
FT4055
(2) boulons à tête
hexagonale de ¼-20 × 1 po
FT4139
(1) boulon à tête hexagonale de ¼-20 × 1¼ po
FT4059
(1) butée de guide
FT4203
(1) rondelle en laiton de ¼ po
DK1504
(1) écrou hexagonal de ¼ × 20 po
DK1510
Installation des glissières de guide
(2) boutons en T
DK1313
Poussez les quatre glissières en plastique dans la rainure au fond du
guide en en plaçant une à environ 2,54 cm de chaque extrémité et les
deux autres à intervalles réguliers.

Assemblage : guide
Fixation du guide sur la tête du guide d’onglet
Glissez les têtes de deux boulons à tête hexagonale de ¼-20 x 1 ¼
po dans la rainure en T située à l’arrière du guide. Insérez les boulons
dans les trous sur la face avant de la tête du guide d’onglet. Vissez les
boutons en T. Vous règlerez la position du guide plus tard.
7.
Ajout du ruban à mesurer
Avant d’installer le ruban à mesurer autoadhésif, assurez-vous que
la rainure peu profonde sur le dessus du guide est propre et sèche.
Lors de l’installation du ruban à mesurer, maintenez le guide d’onglet
en place en le plaçant dans la rainure du guide d’onglet sur la scie.
Coupez le ruban à mesurer aux marques de 2,54 cm et de 63,5 cm à
l’aide de ciseaux robustes ou d’une cisaille à métaux.
Retirez une bande de 2,54 cm de la pellicule protectrice du ruban à
mesurer à partir de l’extrémité où fi gure la marque de 2,54 cm. Pliez
la pellicule protectrice de sorte qu’elle forme un angle avec le ruban
à mesurer. Alignez la marque de 2,54 cm avec l’extrémité droite du
guide (l’extrémité la plus proche de la lame de scie), puis collez le
ruban dans la rainure peu profonde pratiquée dans la traverse. Une fois
cette bande de 2,54 cm de ruban collée, retirez le reste de la pellicule
protectrice et collez le ruban dans la rainure à mesure que vous retirez
la pellicule protectrice. Si vous fi xez la règle graduée de la mauvaise
manière, retirez-la immédiatement, repositionnez-la et mettez-la bien
en place.

8.
Assemblage : butée Swing Stop
Schéma des pièces de
la butée Swing Stop
(1) vis à métaux de 10-32 x ¼ po en nylon
FT4064
(2) rondelles en laiton de 5/16 po
FT4137
TM
(1) bouton en T
DK1313
(4) bagues pour les
butées de guide
FT4257
TM
(1) écrou de blocage
de 5/16-24 po
FT4061
(1) base
FT4262
(1) boulon à tête hexagonale
de 5/16-24 × 3¼ po
FT4060
(1) lentille
FT4063
(1) bouton de
soutien
FT4258
(1) boulon en T de
¼-20 × 1 ¼ po
FT4212
(1) bras
FT4261
Assemblage de la butée
En vous reportant à l’illustration ci-dessus, assemblez la butée Swing Stop™. Lorsque vous insérez le boulon à tête
hexagonale de 5/16-24 × 24-3¼ po qui raccorde le bras à la base, serrez l’écrou de blocage suffi samment pour empêcher
tout mouvement latéral tout en permettant au bras de bouger librement. (Soulevez, puis relâchez le bras. Il devrait retomber
lentement.) Lors de l’installation du curseur à lentille, placez la ligne rouge à environ 9,5 mm du bord du bras.
Lame
Base
ATTENTION!
Assemblez la butée Swing Stop™ en plaçant le bras sur le côté lame
ou foret de la base.

Assemblage : butée Swing Stop
Positionnement du guide et calibrage de la butée Swing Stop™
Le guide d’onglet étant en place sur votre machine (une scie à table
dans cet exemple), assurez-vous que le guide-chaîne glisse librement
dans la rainure du guide d’onglet sans aucun mouvement latéral.
Débranchez la scie à table, puis soulevez la lame. Desserrez les
deux boutons en T qui fi xent le guide à la tête et placez l’extrémité du
guide à 16 mm de la lame de scie.Vissez les boutons. Desserrez la
poignée, retirez la goupille de positionnement, puis faites tourner la
tête du guide d’onglet dans les deux sens pour vérifi er que le guide
n’entre pas en contact avec la lame. Si c’est le cas, desserrez les
boutons en T et glissez le guide loin de la lame. Remettez la tête
du guide d’onglet sur la position à zéro degré, insérez la goupille de
positionnement, puis resserrez la poignée.
Utilisez une règle en acier normale (avec la marque du zéro à son
extrémité) pour placer le bras de la butée à 7,62 cm de la lame. Les
dents de la lame doivent effl eurer l’extrémité de la règle. (N’utilisez pas
le curseur et le ruban à mesurer pour positionner le bras de butée.)
Vissez le bouton en T de la butée.
Desserrez la vis à métaux en nylon qui maintient le curseur à lentille
sur le bras et positionnez la lentille de manière à placer la ligne rouge
exactement au-dessus de la marque de 7,62 cm du ruban à mesurer.
Serrez la vis en nylon.
TM
9.
Coupez une pièce pour confi rmer la longueur de 7,62 cm. Réglez la
position du curseur au besoin, puis coupez une autre pièce.
Pour installer la butée du guide, glissez la tête du boulon à tête
hexagonale de ¼-20 × 1¼ po dans la rainure en T au dos du guide, du
côté de la tête du guide d’onglet le plus proche de la lame. Glissez la
bague de la butée du guide autour du boulon et vissez-la sur l’écrou
hexagonal. Glissez la butée du guide contre le bord de la tête du guide
d’onglet et serrez l’écrou. Vous pouvez maintenant repositionner le
guide en rapprochant, par exemple, le guide de la lame pour soutenir
une pièce lors d’une coupe en biseau et le remettre sur le calibrage
parfait pour des coupes droites en repositionnant simplement le guide
avec la butée placée contre le bord de la tête du guide d’onglet.
ATTENTION! - Coupes en biseau
Dès lors que la lame est inclinée vers le guide d’onglet, vérifi ez toujours si une partie quelconque du guide d’onglet entre en
contact avec la lame avant de mettre la scie en marche. Si c’est le cas, éloignez le guide de la lame. Il peut alors s’avérer
nécessaire de retirer la butée du guide et de calibrer à nouveau le guide après la coupe en biseau.

10.
Utilisation du guide d’onglet
Réglage du guide d’onglet à des angles prédéfi nis
La tête du guide d’onglet présente des butées fi xes à 0, 10, 22½, 30 et 45 degrés. Pour utiliser ces butées, il suffi t de desserrer
la poignée, retirer la goupille de positionnement, faire pivoter la tête du guide d’onglet à l’angle souhaité, mettre la goupille de
positionnement en place et resserrer la poignée.
1. Défi nition des angles fractionnaires
Le guide d’onglet est équipé d’une échelle supérieure qui mesure les
angles en degrés entiers ainsi que d’une échelle à vernier inférieure
qui mesure les angles en fractions de 1/10
permettent de défi nir des angles en degrés entiers et toute fraction de
1/10e de degré entre ceux-ci.
e
de degré. Ces échelles
2. Défi nition des angles fractionnaires
Pour défi nir un angle en degrés entiers, alignez le repère de l’échelle
supérieure avec la fl èche du zéro sur l’échelle à vernier et serrez la
poignée.
3. Défi nition des angles fractionnaires
Pour défi nir un angle situé entre des degrés entiers (25,7 degrés dans
cet exemple), faites tourner la tête du guide d’onglet jusqu’à ce que
la fl èche sur l’échelle à vernier s’aligne avec le repère de l’angle en
degrés entiers. (Dans cet exemple, nous tournons la tête dans le sens
des aiguilles d’une montre.)
4. Défi nition des angles fractionnaires
Pour arriver à la valeur de 25,7 degrés, repérez le « 7 » à droite du
zéro sur l’échelle à vernier. Continuez à tourner la tête du guide
d’onglet dans le sens des aiguilles d’une montre jusqu’à aligner le
repère du 1/10e de degré souhaité sur l’échelle à vernier avec le repère
de degré entier le plus proche sur l’échelle supérieure. (Dans cet
exemple, le repère « 7 » sur l’échelle à vernier s’aligne au repère« 32 »
sur l’échelle supérieure.)
Remarque : Lorsque vous tournez la tête du guide d’onglet dans le
sens des aiguilles d’une montre, utilisez l’échelle des 1/10e de degrés
à droite du zéro sur l’échelle à vernier. Lorsque vous tournez la tête
du guide d’onglet dans le sens contraire des aiguilles d’une montre,
utilisez l’échelle des 1/10e de degrés à gauche du zéro.

Utilisation du guide d’onglet
11.
Utilisation d’accessoires montés en usine avec le guide d’onglet
Les rainures en T le long du guide permettent de fi xer des guides auxiliaires, des butées personnalisées montées en usine ou
d’autres gabarits et supports à l’aide de boulons à tête hexagonale de ¼ po. Vous pouvez également utiliser des boulons d’ancrage
au sol de ¼ po, disponibles dans les quincailleries ou les centres de rénovation.
Ajout d’un guide auxiliaire
Un guide auxiliaire offre une surface renouvelable pouvant être étendue
au-delà de la trajectoire de la lame pour soutenir une pièce travaillée
et vous permettant ainsi d’effectuer des coupes transversales avec un
minimum d’ébrèchement. Le guide auxiliaire doit avoir une épaisseur
de 19,05 mm, une hauteur de 6,67 cm et la longueur adéquate pour
votre application. Il peut être en bois massif, en contreplaqué, en
panneau de particules ou en panneau de fi bres à densité moyenne
(MDF). Fixez le guide auxiliaire à l’aide de boulons à tête hexagonale
de ¼-20 × ¾ po, de rondelles de ¼ po et d’écrous. Percez des trous de
6,35 mm d’une profondeur de 17,46 mm avec des lamages de 19,05
mm. Vous pouvez repositionner ou remplacer le guide auxiliaire sans
impact sur le calibrage de la butée Swing Stop™.
ATTENTION!
Pour pouvoir utiliser la butée Swing Stop™ avec un guide
auxiliaire, vous devez modifi er le bras de butée de sorte qu’il
repose correctement contre le guide lorsqu’il est abaissé, comme
illustré dans cette section. Une fois le bras modifi é, vous devez
l’utiliser avec un guide auxiliaire. La butée ne fonctionnera pas
correctement sans le guide auxiliaire.
Modifi cation du bras de butée pour un guide auxiliaire
Une rainure (ligne de rupture) est pratiquée dans le bras de butée
pour vous permettre de raccourcir cette partie de la butée Swing
Stop™ en vue de l’utilisation d’un guide auxiliaire d’une épaisseur
de 19,05 mm. Si vous comptez utiliser un guide auxiliaire, retirez la
section cassable du bras comme illustré.
Trois étapes simples
1. Tenez le bras de butée fermement dans votre main ou dans
un étau.
2. Serrez la partie cassable du bras de butée avec une pince et
rompez-la.
3. Limez ou poncez le rebord.

12.
Garantie
Garantie
SYSTÈME DE GUIDE D’ONGLET DE PRÉCISION KREG
Les produits de Kreg Tool Company sont
garantis contre tout défaut de matériaux et de
fabrication pendant une période de un (1) an
à compter de la date de livraison à l’acheteur
initial. La présente garantie ne s’applique
qu’à l’acheteur initial et couvre uniquement
les produits Kreg achetés directement auprès
de Kreg Tool Company et de ses distributeurs
autorisés. Durant la période de garantie, Kreg
Tool Company réparera ou remplacera tout
produit ou toute pièce jugés défectueux à sa
discrétion. La présente garantie s’applique
uniquement aux produits utilisés de manière
adéquate et conformément aux procédures
d’entretien et de sécurité indiquées dans les
catalogues, les guides et tout autre manuel
d’instructions fournis par Kreg Tool Company.
La présente garantie est valide seulement
si la carte d’enregistrement de la garantie
incluse avec le produit a été dûment remplie
et retournée à Kreg Tool Company dans les
dix (10) jours suivant la date de livraison à
l’acheteur initial.
La présente garantie est nulle et non
avenue si le produit (1) a été négligé, mal
entretenu ou rangé de façon inadéquate;
(2) a fait l’objet d’un usage inapproprié ou
abusif, a subi un accident ou a été soumis
à toute autre circonstance indépendante de
la volonté de Kreg Tool Company; et (3) a
été modifi é, transformé, manipulé, démonté
ou réparé ailleurs qu’à l’usine de Kreg Tool
Company ou d’une façon non autorisée par
Kreg Tool Company. La présente garantie
ne couvre pas l’usure normale, la corrosion,
l’abrasion ni les dommages découlant
de causes naturelles ou de cas de force
majeure.
Pour effectuer une réclamation au titre de la
garantie, communiquez avec le distributeur
auprès de qui vous avez acheté le produit ou
communiquez directement avec Kreg Tool
Company. Une preuve d’achat est nécessaire
pour obtenir une réparation conformément
aux conditions de la présente garantie.
Kreg Tool Company n’est aucunement
responsable des produits retournés sans
autorisation préalable. Les obligations
de Kreg Tool Company prévues par la
présente garantie se limitent exclusivement
à la réparation ou au remplacement des
produits jugés défectueux après avoir été
livrés à Kreg Tool Company et inspectés
par cette dernière. Kreg Tool Company ne
peut en aucun cas être tenue responsable
des dommages accessoires ou consécutifs
découlant des produits défectueux, et la
responsabilité de Kreg Tool Company ne peut
excéder le prix d’achat du produit.
Ce qui précède constitue l’unique garantie
de Kreg Tool Company. Toutes les autres
garanties prévues par la loi, y compris
toute garantie de qualité marchande ou
de conformité à un usage particulier, sont
limitées, par les présentes, à la durée de
cette garantie. Kreg Tool Company n’est pas
responsable des pertes, des dommages ni
des dépenses découlant, directement ou
indirectement, de l’utilisation des produits
Kreg ou de toute autre cause, ni des
dommages consécutifs, y compris sans
toutefois s’y limiter, la perte de temps, les
désagréments et la perte de production. La
garantie décrite aux présentes ne peut être
modifi ée, et aucune autre garantie, qu’elle
soit expresse ou implicite, ne peut être offerte
par Kreg Tool Company ou en son nom.
Les renseignements suivants seront utiles si vous devez effectuer une réclamation au titre de la garantie.
Date d’achat : ____/____/____
Nom du détaillant : ____________________________________________
Conservez une copie de votre reçu original avec ce formulaire.
Kreg Tool Company 201 Campus Drive Huxley, IA 50124

Precision
Miter Gauge System
MANUAL DEL PROPIETARIO
Artículo #KMS7102
www.kregtool.com • 800.447.8638
FT4032
Version 3 - 4/2014

2.
Pautas de seguridad
Normas generales de seguridad
! ADVERTENCIA Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, el usuario debe leer el manual de instrucciones.
!
! ADVERTENCIA Lea todas las instrucciones. Si no se siguen todas las instrucciones que se detallan a continuación, es posible que se produzcan
!
descargas eléctricas, incendios o lesiones graves. El término “herramienta eléctrica” que aparece en todas las advertencias a continuación se
refi ere a la herramienta eléctrica conectada a la línea principal (con cable) o a la herramienta eléctrica funcionando a batería (inalámbrica).
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES
1) Seguridad en el área de trabajo
a) Mantenga el área de trabajo limpia y bien iluminada. Las áreas desordenadas u oscuras aumentan las posibilidades de accidentes.
b) No use herramientas eléctricas en entornos peligrosos. No utilice herramientas eléctricas en áreas húmedas o mojadas, ni las exponga a la lluvia.
c) No utilice herramientas eléctricas en atmósferas en las que exista riesgo de explosión, por ejemplo, en presencia de líquidos infl amables, gases o polvo. Las herramientas eléctricas
producen chispas que podrían encender el polvo o los vapores.
d) Mantenga a los niños y transeúntes alejados durante la operación de una herramienta eléctrica. Las distracciones pueden hacerle perder el control.
e) Haga que su taller sea a prueba de niños por medio de candados e interruptores maestros, o retirando las llaves de arranque.
2) Seguridad eléctrica
a) Los enchufes de las herramientas eléctricas deben encajar en el tomacorriente. Nunca modifi que el enchufe de ninguna manera. No utilice ningún enchufe adaptador con herramientas
eléctricas con puesta a tierra. Los enchufes sin modifi caciones y que encajan en los tomacorrientes reducen el riesgo de descarga eléctrica.
b) Herramientas eléctricas con puesta a tierra. Si la herramienta está equipada con un enchufe de tres clavijas, solo debe enchufarse en un tomacorriente de tres orifi cios con puesta a
tierra. Si no se cuenta con un enchufe adecuado, pídale a un electricista califi cado que instale uno. Nunca retire la tercera clavija ni modifi que el enchufe incluido de ninguna manera.
c) Evite el contacto del cuerpo con superfi cies conectadas a tierra, como tuberías, radiadores, estufas o refrigeradores. Existe un gran riesgo de descarga eléctrica si su cuerpo tiene
conexión a tierra.
d) No exponga las herramientas eléctricas a la lluvia ni a condiciones de humedad. Si ingresa agua en una herramienta eléctrica, aumentará el riesgo de descarga eléctrica.
e) No maltrate el cable. Nunca use el cable para transportar, jalar o desenchufar la herramienta eléctrica. Mantenga el cable alejado del calor, el aceite, los bordes fi losos o las piezas en
movimiento. Los cables dañados o enredados aumentan el riesgo de descarga eléctrica.
f) Use una extensión eléctrica apropiada y asegúrese de que esté en buen estado. Cuando utilice una extensión eléctrica, asegúrese de utilizar una que sea lo sufi cientemente resistente
como para conducir la corriente que su equipo necesita. Un cable de tamaño menor que el requerido causará una baja en el voltaje de la línea. Esto podría provocar un corte de
energía y sobrecalentamiento. Cuando utilice una herramienta eléctrica en exteriores, use una extensión eléctrica adecuada para uso en exteriores.
3) Seguridad personal
a) Manténgase alerta, observe lo que hace y actúe con sentido común al operar una herramienta eléctrica. No utilice una herramienta eléctrica si está cansado o bajo los efectos de
drogas, alcohol o medicamentos. No permita que la familiaridad obtenida por el uso de una herramienta reemplace las prácticas de un trabajo seguro. Un momento de desatención
mientras opera herramientas eléctricas puede provocar lesiones personales graves.
b) Use gafas de seguridad en todo momento. Las gafas comunes solamente poseen lentes resistentes a impactos, pero NO son gafas de seguridad.
c) Utilice un equipo de seguridad. Use una protección o mascarilla antipolvo cuando la operación de corte desprenda demasiado polvo. El equipo de seguridad, como mascarillas
antipolvo, zapatos de seguridad antideslizantes, casco o protección para los oídos, que se usa para crear condiciones apropiadas, reduce las lesiones personales.
d) Evite los arranques accidentales. Asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en la posición de apagado antes de enchufarlo. Transportar herramientas eléctricas con el dedo en el interruptor
o enchufar herramientas eléctricas que tienen el interruptor encendido aumentan las posibilidades de accidentes.
e) Retire todas las llaves de ajuste o llaves inglesas antes de encender la herramienta eléctrica. Si se deja una llave inglesa o una llave conectada a una pieza giratoria de la herramienta
eléctrica, se pueden producir lesiones personales.
f) No se extienda demasiado. Mantenga una posición y un equilibrio adecuados en todo momento. Esto permite un mejor control de la herramienta eléctrica en situaciones inesperadas.
g) Asegure las piezas de trabajo. Use abrazaderas o una prensa para sostener la pieza de trabajo cuando sea práctico. Es más seguro que usar las manos y, de este modo, ambas
manos quedan libres para operar la herramienta.
h) Nunca se pare sobre la máquina. Si la herramienta se voltea o si toca accidentalmente la herramienta de corte, puede producir lesiones graves.
i) Use ropa adecuada. No use ropa holgada o joyas. Mantenga el cabello, la ropa y los guantes lejos de las piezas en movimiento. La ropa holgada, las joyas o el cabello largo pueden
quedar atrapados en las piezas giratorias.
j) Si se proporcionan dispositivos para la conexión de instalaciones de extracción y recolección de polvo, asegúrese de que se conecten y se usen debidamente. El uso de estos
dispositivos puede disminuir los peligros relacionados con el polvo.
4) Uso y cuidado de herramientas eléctricas
a) Mantenga los protectores en su lugar, ajustados de manera correcta y en buenas condiciones de funcionamiento.
b) No fuerce la herramienta eléctrica. Utilice la herramienta eléctrica adecuada para su aplicación. La herramienta realizará un trabajo más seguro y de mejor calidad al ritmo de trabajo
para el que fue diseñada.
c) Use la herramienta o el accesorio correctos. No fuerce una herramienta o un accesorio para hacer un trabajo para el que no fue diseñado.
d) No utilice la herramienta eléctrica si el interruptor no enciende ni apaga. Cualquier herramienta eléctrica que no pueda controlarse con el interruptor es peligrosa y debe repararse.
e) Desconecte el enchufe de la fuente de alimentación o la batería de la herramienta eléctrica antes de realizar cualquier ajuste, cambiar accesorios o almacenar herramientas eléctricas.
Este tipo de medidas de seguridad preventivas reduce el riesgo de arranques accidentales de la herramienta eléctrica.
f) Nunca deje la herramienta en funcionamiento sin supervisión. Desconecte la alimentación. No suelte la herramienta hasta que no se detenga por completo.
g) Almacene las herramientas eléctricas que no estén en uso fuera del alcance de los niños y no permita que personas no familiarizadas con la herramienta o estas instrucciones la
operen. Las herramientas eléctricas son peligrosas en manos de usuarios sin capacitación.
h) Realice mantenimiento a las herramientas eléctricas. Revise si hay desalineación o agarrotamiento de piezas móviles o si están rotas, así como cualquier otra condición que pueda
afectar la operación de la herramienta eléctrica. Si se daña, haga reparar la herramienta eléctrica antes de usarla. Muchos accidentes son producto del mantenimiento incorrecto de las
herramientas eléctricas.
i) Mantenga las herramientas de corte afi ladas y limpias. Las herramientas de corte que se mantienen adecuadamente, con sus bordes de corte afi lados, tienen un riesgo menor de
trabarse y son más fáciles de controlar.
j) Utilice la velocidad recomendada para la herramienta de corte o el accesorio y el material de la pieza de trabajo.
k) Solo use piezas y accesorios recomendados por el fabricante. Consulte el manual del propietario para conocer los accesorios recomendados. Usar accesorios incorrectos puede
causar lesiones personales.
l) Use la herramienta, los accesorios, las brocas y las hojas según estas instrucciones, y de la manera adecuada para el tipo de herramienta eléctrica en particular, considerando las
condiciones de trabajo y el trabajo que se va a realizar. El uso de la herramienta eléctrica en operaciones distintas para las que fue diseñada podría crear una situación de peligro.
5) Evite los contragolpes al operar una herramienta eléctrica. Los contragolpes pueden causar lesiones graves, daño a la propiedad o la muerte. Generalmente, un contragolpe se
produce cuando una pieza de trabajo o una pieza de corte se atascan o quedan atrapadas entre una cuchilla o broca en movimiento y la guía de la máquina, y son expulsadas con
fuerza. Para evitar un contragolpe:
a) Use siempre una hoja o una broca afi ladas.
b) En la sierra de masa, asegúrese de que tanto la hoja de sierra como la guía de corte estén ubicadas en paralelo con las ranuras del cartabón de inglete. Para obtener instrucciones
para hacer estos ajustes, consulte el manual del propietario de su sierra de masa.
c) Planifi que los cortes de la sierra de masa para evitar atascamientos. Nunca use la guía de corte y el cartabón de inglete al mismo tiempo para apoyar una pieza de trabajo. La pieza de
corte puede atascarse y efectuar un contragolpe.
d) Nunca realice un corte con mano libre. La pieza de trabajo debe estar siempre sostenida por el cartabón de inglete o la guía de la máquina, pero no por ambos.
e) Cuando sea necesario, use sujeciones, tablas con canto biselado, varillas de empuje y bloques de empuje para guiar la pieza de trabajo durante el corte. Estos accesorios protegen
sus manos de cualquier lesión.
f) Cuando use una tabla con canto biselado mientras realiza cortes en una sierra de masa, coloque siempre la tabla con canto biselado en el lado de la alimentación y al menos 2 pulg
(5,10 cm) delante de la hoja.
g) Nunca coloque una tabla con canto biselado junto a la hoja o broca, ni en la parte de la alimentación exterior de la hoja o broca, tampoco la coloque de manera tal que pudiera
ocasionar que la pieza de trabajo o el desperdicio ingresen o se pellizquen en la hoja o broca. Colocar una tabla con canto biselado de esta manera puede ocasionar que la pieza de
trabajo o el desperdicio retrocedan, lo cual podría ocasionar un daño grave.

Pautas de seguridad
Normas generales de seguridad
6) Reparación
a) Permita que solo una persona capacitada repare la herramienta eléctrica, utilizando solo piezas de repuesto idénticas. Esto mantendrá la seguridad de la herramienta eléctrica.
7) Normas de seguridad adicionales para el sistema de cartabón de inglete Precision
a) Lea este manual y estas pautas de seguridad. Siga las pautas de seguridad del fabricante de la herramienta en la que usa este accesorio. Conozca las aplicaciones y las limitaciones
de la herramienta, además de sus peligros específi cos. Es posible que si se opera la herramienta eléctrica antes de comprender su utilización segura y adecuada, se produzcan
lesiones personales.
b) Asegúrese de que la manija esté apretada y que las perillas en T de extrusión de la guía estén fi jas antes de arrancar la herramienta eléctrica.
c) Mantenga las manos alejadas de la hoja o broca en movimiento mientras opera la máquina. Nunca se acerque a la hoja o broca en movimiento para limpiar los desechos. Apague la
herramienta eléctrica y espere a que la hoja o la broca se detengan por completo.
d) Siempre dé apoyo a tablas largas tanto en el extremo de alimentación como de salida.
e) Asegure siempre las piezas de trabajo colocadas sobre la mesa de la máquina y al cartabón de inglete o guía.
f) Este sistema de cartabón de inglete está diseñado para una aplicación específi ca. No la modifi que ni la use para otra aplicación. Si tiene preguntas sobre el cartabón de inglete, NO lo
use antes de comunicarse con Kreg Tool Company y recibir consejo.
ADVERTENCIA Este producto contiene una o más sustancias químicas reconocidas por el estado de California como causantes de cáncer, defectos congénitos u otros daños en el
!
aparato reproductivo. Lávese las manos después de manipularlo.
Propuesta 65 de California
ADVERTENCIA El polvo producido por el lijado, serruchado, trituración, taladrado eléctrico y otras actividades de construcción puede contener sustancias químicas reconocidas por
!
el estado de California como causantes de cáncer, defectos congénitos u otros daños en el aparato reproductivo. Algunos ejemplos de estos químicos son:
a) Plomo de pinturas a base de plomo
b) Sílice cristalina de ladrillos, cemento y otros productos de mampostería
c) Arsénico y cromo de madera tratada con químicos
3.
El riesgo que corre debido a la exposición a estos químicos varía dependiendo de la frecuencia con que realiza este tipo de trabajo. Para reducir la exposición, trabaje en un área bien
ventilada y utilice un equipo de seguridad aprobado, como una mascarilla antipolvo, específi camente diseñado para fi ltrar partículas microscópicas.
Ensamble del cartabón de inglete
ATENCIÓN
!
Estas instrucciones muestran cómo armar el cartabón de inglete Precision para usar en el lado izquierdo de la hoja. Para usar el
cartabón de inglete Precision en el lado derecho de la hoja, arme el Swing Stop™ para que sea igual y opuesto al que se muestra
en el dibujo de Swing Stop™. Puede usar la cinta métrica que se incluye con el cartabón de inglete en el lado derecho de la hoja al
instarlo para que se lea de arriba a abajo, de modo tal que las medidas de la hoja se lean de izquierda a derecha. Para comprar la
versión de lectura de izquierda a derecha de la cinta métrica, comuníquese con el Servicio al cliente al 1-800-447-8638.

4.
Ensamble - Cartabón de inglete
Diagrama de las piezas
del cartabón de inglete
(1) Manija
FT4029
(1) Pasador de
posicionamiento
FT4056
(1) Arandela de nailon de ¼ pulg (0,63 cm)
FT4030
(5) Tornillos de ajuste de nailon
#10-32 x 5/8 pulg
FT4102
(1) Arandela con ranura en T
FT4057
(1) Tornillo de cabeza plana de #10-32 x 5/16 pulg
FT4207

Ensamble - Cartabón de inglete
Instalación de la manija del cartabón de inglete
Establezca el ángulo del cartabón de inglete en cero e inserte
el pasador de posicionamiento en el orifi cio del tope positivo del
ángulo cero. Deslice la arandela de nailon de ¼ pulg (0,63 cm) en el
montante roscado en la manija y enrosque la manija en la barra de
guía. Apriete la manija.
Ajuste de la barra guía
Con un destornillador de cabeza plana pequeño, enrosque cinco
tornillos de fi jación de nailon de #10-32 x ⅝ pulg en los orifi cios en el
lado de la barra guía. Pase cada uno desde el mismo lado hasta que
comiencen a aparecer en el lado opuesto. Pruebe el calce del cartabón
de inglete en la ranura de inglete de la sierra. Ajuste cada tornillo, quite
o reemplace el cartabón de inglete según sea necesario, hasta que el
cartabón de inglete se deslice sin problemas por la ranura de inglete,
sin ninguna holgura lateral.
5.
Coloque la arandela con ranura en T
(solamente para sierras con ranuras de cartabón de inglete con perfi l en T)
Para una sierra con ranura de cartabón de inglete con perfi l en T,
coloque la arandela con ranura en T en la cara inferior de la muesca
en el extremo principal de la barra guía con el tornillo de cabeza plana
#10-32 x 5/16 pulg. Apriete el tornillo; tenga cuidado de no rodar las
roscas en la barra de aluminio.

6.
(1) Cinta autoadhesiva con lectura de derecha
a izquierda de 48 pulg (121,90 cm)
FT4047
(1) Extrusión de la guía
KMS7702
Ensamble - Guía
Diagrama de las piezas
de ensamble de la guía
(6) Rieles
FT4055
(1) Perno de cabeza hexagonal de ¼ pulg -20 x 1¼ pulg
FT4059
(1) Arandela de latón de ¼ pulg (0,63 cm)
DK1504
(1) Tuerca hexagonal de ¼ pulg-20
DK1510
(2) Pernos de cabeza hexagonal
de ¼ pulg-20 x 1 pulg
FT4139
(1) Tope de guía
FT4203
Instalación de los rieles de la guía
Presione los cuatro rieles de plástico en la ranura en la parte inferior
de la guía y coloque uno a aproximadamente 1 pulg (2,54 cm) de
cada extremo y los otros dos espaciados de forma pareja entre ellos.
(2) Perillas en T
DK1313

Ensamble - Guía
Fije la guía a la cabeza del cartabón de inglete
Deslice las cabezas de los dos pernos de cabeza hexagonal de ¼
pulg-20 x 1 ¼ pulg en la ranura en T en la parte posterior de la guía.
Inserte los pernos en los orifi cios ubicados en la cara de la cabeza del
cartabón de inglete. Enroque en las perillas en T. Luego, ajustará con
precisión la posición de la guía.
7.
Adhesión de la cinta métrica
Antes de aplicar la cinta métrica autoadhesiva, asegúrese de que la
ranura poco profunda en la parte superior de la guía esté limpia y seca.
Para mantener fi jo al cartabón de inglete mientras instala la cinta,
coloque el cartabón de inglete en la ranura del cartabón de inglete de
la sierra. Corte la cinta en la marca de 1 pulg (2,54 cm) y la marca de
25 pulg (63,50 cm) con tijeras resistentes o tijeras para metal.
Despegue el refuerzo del extremo marcado en 1 pulg (2,54 cm) de
la cinta métrica y exponga aproximadamente 1 pulg (2,54 cm) del
adhesivo. Pliegue el refuerzo para que sobresalga de la cinta en un
ángulo. Alinee la marca en 1 pulg (2,54 cm) de la cinta con el extremo
derecho de la guía (el extremo más cercano a la hoja de la sierra) y
presione la cinta en la ranura poco profunda en el riel. Con los primeros
2,54 cm de la cinta adheridos, jale el refuerzo restante debajo de la
cinta y presione fi rmemente la cinta en la ranura a medida que sigue
retirando el refuerzo. En el caso de colocar la escala en la posición
incorrecta, retírela inmediatamente y vuelva a posicionarla, y luego
presione fi rmemente en su lugar.

8.
Diagrama de las piezas
del Swing Stop
TM
Ensamble - Swing Stop
(1) Perilla en T
DK1313
TM
(1) Contratuerca de
5/16 pulg-24
FT4061
(1) Tornillo para metal de nailon
#10-32 x ¼ pulg
FT4064
(2) Arandela de latón de 5/16 pulg (0,79 cm)
FT4137
(1) Lentes
FT4063
(1) Perno de cabeza hexagonal
de 5/16 pulg-24 x ¾ pulg
FT4060
(4) Conector para tope
de guía
FT4257
(1) Botón de apoyo
FT4258
(1) Base
FT4262
(1) Perno en T de ¼
pulg-20 x 1¼ pulg
FT4212
(1) Brazo
FT4261
Ensamble del tope
Use como referencia el dibujo anterior y ensamble el Swing Stop™. Al instalar el perno de cabeza hexagonal de 5/16 pulg-24
x 3 1/4 pulg que une al brazo con la base, apriete la contratuerca lo sufi ciente como para eliminar la holgura lateral, pero de
manera tal que permita el libre movimiento del brazo. (Suelte el brazo y libérelo. Debería caer lentamente). Al instalar el cursor
del lente, coloque la línea roja a aproximadamente 3/8 pulg (0,95 cm) del borde del brazo.
ATENCIÓN
Base
Ensamble el Swing Stop™ con el brazo en el lado de la base de la
Hoja
hoja o broca.

Ensamble - Swing Stop
Colocación de la guía y calibración del Swing Stop™
Con el cartabón de inglete colocado en la máquina (una sierra de
mesa, en este ejemplo), asegúrese de que la barra guía se deslice
fácilmente por la ranura del cartabón de inglete sin ninguna holgura
lateral. Desconecte la sierra de mesa de la fuente de alimentación
y levante la hoja. Afl oje las dos perillas en T que fi jan la guía a la
cabeza y coloque el extremo de la guía a 5/8 pulg (0,62 cm) de la hoja
de la sierra. Ajuste las perillas. Afl oje la manija, retire el pasador de
posicionamiento y gire la cabeza del cartabón de inglete en ambas
direcciones para asegurarse de que la guía no entre en contacto con la
hoja. Si hay interferencia, afl oje las perillas en T y deslice la guía para
quitarla de la hoja. Vuelva a colocar la cabeza del cartabón de inglete
en la posición de grado cero, inserte el pasador de posicionamiento y
apriete la manija.
Use una regla de metal de taller (una con la marca en cero al ras con
el extremo) para posicionar el brazo de tope a 3 pulg (7,62 cm) de la
hoja. Permita que los dientes de la hoja rocen el extremo de la regla.
(No use el cursor ni la cinta métrica para posicionar el brazo de tope).
Apriete la perilla en T del tope.
Afl oje el tornillo para metal de nailon que fi ja el cursor del lente al brazo
y coloque el lente con la línea roja exactamente sobre la marca de 3
pulg (7,62 cm) en la cinta métrica. Apriete el tornillo de nailon.
TM
9.
Realice un corte de prueba para confi rmar la longitud de 3 pulg
(7,62 cm). Ajuste la posición del cursor según sea necesario y realice
otro corte de prueba.
Para instalar el tope de la guía, deslice la cabeza del perno de cabeza
hexagonal 1/4 pulg-20 x 1 1/4 pulg en la ranura en T en la parte
posterior de la guía en T lateral de la cabeza del cartabón de inglete
más cercano a la hoja. Deslice el conector para tope de guía por el
perno y enrosque la tuerca hexagonal. Deslice el tope de la guía contra
el borde de la cabeza del cartabón de inglete y apriete la tuerca. Ahora
puede cambiar la posición de la guía, por ejemplo, puede mover la guía
más cerca de la hoja para dar soporte a la pieza de trabajo cuando se
realiza un corte en ángulo y puede regresarla a la calibración perfecta
para los cortes en ángulo recto, al posicionar solamente la guía con el
tope contra el borde de la cabeza del cartabón de inglete.
ATENCIÓN – Cortes biselados
Siempre que la hoja se incline hacia el cartabón de inglete, revise para ver si alguna parte del cartabón de inglete hace
contacto con la hoja, antes de girar en la sierra. Si hay interferencia, mueva la guía para quitarla de la hoja. Es posible que
esto requiera que se retire el tope de la guía, y luego que se vuelva a calibrar la guía después de realizar el corte biselado.

10.
Cómo usar el cartabón de inglete
Ajuste del cartabón de inglete en los ángulos preestablecidos
La cabeza de cartabón de inglete cuenta con topes positivos en los grados 0, 10, 22 ½, 30 y 45. Para usar estos topes, solo afl oje
la manija, retire el pasador de posicionamiento y gire la cabeza del cartabón de inglete al ángulo deseado, suelte el pasador de
posicionamiento en su lugar, y apriete la manija.
1. Cómo establecer ángulos fraccionales:
El cartabón de inglete cuenta con una escala superior que mide los
ángulos en grados enteros y una escala Vernier inferior que mide
los ángulos en fracciones de 1/10 grados. Estas escalas le permiten
establecer ángulos de grados enteros y cualquier fracción de ángulo
de 1/10 grados entremedio.
2. Cómo establecer ángulos fraccionales:
Para establecer un ángulo de grado entero, alinee la marca de grado
en la escala superior con la fl echa de cero en la escala de Vernier, y
apriete la manija.
3. Cómo establecer ángulos fraccionales:
Para establecer un ángulo entre los grados enteros (25,7 grados, en
este ejemplo), gire la cabeza del cartabón de inglete hasta que la
fl echa en la escala de Vernier se alinee con la marca de grado entero.
(En este ejemplo, rotamos la cabeza hacia la derecha).
4. Cómo establecer ángulos fraccionales:
Para llegar a establecer un ángulo de 25,7 grados, ubique el “7” a la
derecha del cero en la escala de Vernier. Continúe la rotación de la
cabeza del cartabón de inglete hacia la derecha hasta que la marca
deseada de 1/10 grados en la escala de Vernier se alinee con la
marca de grado entero más cercana en la escala superior. (En este
ejemplo, la marca de “7” en la escala de Vernier se alinea con el “32”
de la escala superior).
Nota: Al rotar la cabeza del cartabón de inglete hacia la derecha, use
una escala de 1/10 grados hacia la derecha del cero en la escala de
Vernier. Al rotar la cabeza del cartabón de inglete hacia la izquierda,
use una escala de 1/10 grados hacia la izquierda del cero en la
escala de Vernier.

Cómo usar el cartabón de inglete
Cómo usar accesorios fabricados en taller con el cartabón de inglete
Las ranuras en T junto con el largo de la guía le permiten fi jar guías auxiliares, topes fabricados en taller personalizados u otras
plantillas y ensambles con los pernos de cabeza hexagonal de ¼ pulg estándares. También, puede usar los pernos de brida del
inodoro disponibles en ferreterías o centros para el hogar.
Cómo agregar una guía auxiliar
Una guía auxiliar proporciona una superfi cie renovable que puede
extenderse hasta sobrepasar el recorrido de la hoja a fi n de dar
soporte a la pieza de trabajo y, como resultado, obtener cortes
transversales suaves con un mínimo desportillado. La guía auxiliar
debe tener un espesor de 3/4 pulg (1,90 cm), una altura de 2 5/8
pulg (6,67 cm) y cualquier largo que se adapte a la aplicación; puede
construirse con madera sólida, madera contrachapada, panel de
aglomerado o madera de densidad media (MDF). Fije la guía auxiliar
con pernos de cabeza hexagonal de 1/4 pulg-20 x 3/4 pulg, arandelas
de 1/4 pulg (0,63 cm) y tuercas. Taladre orifi cios de 1/4 pulg (0,63 cm)
con orifi cios escariados de 3/4 pulg (1,90 cm) y 11/16 pulg (1,75 cm)
de profundidad. La guía auxiliar puede volver a colocarse o puede
reemplazarse sin afectar la calibración del Swing Stop™.
11.
ATENCIÓN
Para usar el Swing Stop™ con la guía auxiliar, debe modifi car el
brazo de tope de modo que se asiente adecuadamente contra la
guía cuando se baja, como se muestra en esta sección. Una vez
que se haya modifi cado el brazo de tope, debe usarse con una
guía auxiliar. El tope no funcionará correctamente si no se usa
con una guía auxiliar.
Cómo modifi car el brazo de tope para una guía auxiliar
Se ha agregado una ranura (línea de quiebre) en el brazo de corte con
el motivo de ofrecer un método simple para acortar esta porción del
Swing StopTM, para usarlo con la guía auxiliar de 3/4 pulg (1,90 cm) de
espesor. Si desea usar una guía auxiliar, retire la sección de interrupción
del brazo, como se muestra.
Tres pasos sencillos
1. Sostenga con fi rmeza el brazo de tope con la mano o
una prensa.
2. Use unas pinzas para sujetar la porción de separación del
brazo de tope, y luego saque esa pieza a presión.
3. Lime o lije el borde áspero hasta que quede suave.

12.
Garantía
Garantía
SISTEMA DE CARTABÓN DE INGLETE PRECISION KREG
Los productos Kreg Tool Company
están garantizados contra defectos en
los materiales y la mano de obra por un
período de un (1) año a partir de la fecha de
entrega al comprador original. Esta garantía
se extiende solo al comprador original y
cubre solo productos Kreg comprados
directamente de Kreg Tool Company y de
sus distribuidores autorizados. Durante el
periodo de garantía, Kreg Tool Company,
a su criterio, reparará o reemplazará
cualquier producto o componente del
producto que presente defectos. Esta
garantía se aplica solo a productos usados
siguiendo procedimientos de funcionamiento,
mantenimiento y seguridad adecuados y
establecidos en catálogos, manuales y otros
materiales educativos proporcionados por
Kreg Tool Company.
Esta garantía entra en vigor solo si se
completa la tarjeta de registro de garantía
incluida con el producto de forma adecuada
y se devuelve a Kreg Tool Company dentro
de los diez (10) días que siguen a la fecha de
entrega al comprador original.
Esta garantía queda nula y sin validez, si el
producto ha sido sometido a (1) negligencia,
servicio inadecuado, o almacenamiento
inadecuado; (2) maltrato, uso inadecuado,
accidente u otras circunstancias fuera
del control de Kreg Tool Company;
y (3) modifi caciones, manipulación,
desensamblaje o reparaciones realizadas
fuera de la fábrica de Kreg Tool Company
o no autorizadas por Kreg Tool Company.
Esta garantía no cubre el desgaste normal la
corrosión, la abrasión o daños causados por
fenómenos naturales.
Para obtener el servicio de garantía,
comuníquese con el distribuidor a quien le
compró el producto Kreg o directamente con
Kreg Tool Company. Se exigirá una prueba
de compra para validar el recurso según
los términos de esta garantía. Kreg Tool
Company no asume ninguna responsabilidad
por productos devueltos sin autorización
previa. La responsabilidad de Kreg Tool
Company, según esta garantía, se limita
exclusivamente a la reparación o reemplazo
de los productos hallados defectuosos a
la entrega y según la inspección de Kreg
Tool Company. Bajo ninguna circunstancia
Kreg Tool Company será responsable por
daños accidentales o resultantes causados
por productos defectuosos; asimismo, la
responsabilidad de Kreg Tool Company
no será superior al precio de compra del
producto.
La presente constituye la única garantía de
Kreg Tool Company. Cualquier otra garantía
implícita por la ley, lo que incluye cualquier
garantía de comerciabilidad o idoneidad para
un fi n particular, están por tanto limitadas al
tiempo a la duración de esta garantía. Kreg
Tool Company no será responsable por
pérdidas, daños o gastos relacionados de
forma directa o indirecta al uso de productos
Kreg ni por ninguna otra causa o daño
resultante, lo que incluye pero no se limita
a pérdidas de tiempo, molestias y pérdidas
de producción. La garantía descrita en el
presente documento no puede modifi carse.
Además, ninguna garantía adicional, expresa
o implícita, puede hacerse por Kreg Tool
Company ni en su nombre.
La siguiente información será útil en el caso que se requiera el servicio de la garantía.
Fecha de compra: ____/____/____
Comprado en: ____________________________________________
Conserve una copia de su factura de compra con este formulario.
Kreg Tool Company 201 Campus Drive Huxley, IA 50124
 Loading...
Loading...