Page 1

PDF provided by Conference Room AV
Kramer VP-796A 9x4 4K UHD HDBaseT, Presentation Switcher Scaler, Analog Audio
Page 2

VP-796(A) / VP-797(A) / VP-798(A)
Operating Instructions
Page 3

COPYRIGHT
This document and the software described within it are copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under
copyright laws, neither the documentation nor the software may be copied, photocopied, reproduced,
translated, or reduced to electronic medium or machine readable form, in whole or in part, without
prior written consent of Kramer UK Ltd ("Kramer"). Failure to comply with this condition may result in
prosecution.
Kramer does not warrant that this product package will function properly in every hardware/software
environment.
Although Kramer has tested the hardware, firmware, software and reviewed the documentation,
KRAMER MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH RESPECT TO
THIS HARDWARE, FIRMWARE, SOFTWARE OR DOCUMENTATION, THEIR QUALITY, PERFORMANCE,
MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THIS SOFTWARE AND DOCUMENTATION
ARE LICENSED 'AS IS', AND YOU, THE LICENSEE, BY MAKING USE THEREOF, ARE ASSUMING THE ENTIRE
RISK AS TO THEIR QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE.
IN NO EVENT WILL KRAMER BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE SOFTWARE OR
DOCUMENTATION, even if advised of the possibility of such damages. In particular, and without
prejudice to the generality of the foregoing, Kramer has no liability for any programs or data stored or
used with Kramer software, including costs of recovering such programs or data.
Copyright (c) 2016 All World-wide Rights Reserved
All trademarks acknowledged
Kramer operates a policy of continued product improvement, therefore specifications are subject to
change without notice as products are updated or revised.
E&OE.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
2
Page 4

Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................ 6
1.1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW .......................................................................................................................... 6
1.2 PACKING LIST .................................................................................................................................. 7
2. BASIC SWITCHER SET-UP .............................................................................................................. 8
3. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................ 11
3.1 FRONT PANEL LAYOUT .................................................................................................................... 11
3.2 INPUT VIDEO CONNECTOR OVERVIEW ............................................................................................... 12
3.3 REAR PANEL LAYOUT ...................................................................................................................... 13
3.4 OUTPUT CONNECTOR OVERVIEW .................................................................................................... 13
3.5 PRODUCT SPECIFICATION ................................................................................................................ 14
3.5.1 Power Supply Requirement ................................................................................................ 14
3.5.2 Input Specifications ............................................................................................................ 14
3.5.3 Output Specifications ......................................................................................................... 15
3.5.4 Analog Audio ...................................................................................................................... 17
3.5.5 Supported formats ............................................................................................................. 18
4. UNIT CONTROL ........................................................................................................................... 19
5. FRONT PANEL CONTROL ............................................................................................................ 19
5.1 MAIN MENU ................................................................................................................................ 19
5.2 INPUT .......................................................................................................................................... 20
5.3 OUTPUT ....................................................................................................................................... 21
5.3.1 Display Type ....................................................................................................................... 21
5.3.2 Gamma/Colour .................................................................................................................. 22
5.3.3 Output Config ..................................................................................................................... 23
5.4 COLOUR (INPUT CHANNEL ADJUSTMENTS ) ........................................................................................ 24
5.4.1 Black-Level Offset ............................................................................................................... 24
5.4.2 Black-Level ......................................................................................................................... 24
5.4.3 Contrast ............................................................................................................................. 24
5.4.4 Saturation .......................................................................................................................... 24
5.4.5 Hue ..................................................................................................................................... 24
5.4.6 RGB values ......................................................................................................................... 24
5.4.7 Colour Temp ....................................................................................................................... 25
5.4.8 Input Gamma ..................................................................................................................... 25
5.5 GEOMETRY ................................................................................................................................... 26
5.5.1 Picture Format ................................................................................................................... 26
5.5.2 Overscan ............................................................................................................................ 27
5.5.3 Pan Tilt Zoom (PTZ) ............................................................................................................ 27
5.6 VIDEO WALL ................................................................................................................................. 29
5.6.1 Auto Zoom .......................................................................................................................... 29
5.6.2 Units Wide/Units High ....................................................................................................... 29
5.6.3 Horizontal Pos/Vertical Pos ............................................................................................... 29
5.7 ENHANCEMENT ............................................................................................................................. 30
5.7.1 Sharpness ........................................................................................................................... 30
5.7.2 Detail .................................................................................................................................. 30
5.8 SYSTEM ........................................................................................................................................ 31
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
3
Page 5

5.8.1 User .................................................................................................................................... 31
5.8.2 Names/Profiles ................................................................................................................... 31
5.8.3 Input Config ........................................................................................................................ 31
5.8.4 Menu Settings .................................................................................................................... 34
5.8.5 Network Settings ................................................................................................................ 34
5.8.6 Security Settings ................................................................................................................. 35
5.8.7 Factory Defaults ................................................................................................................. 35
5.9 AUDIO ......................................................................................................................................... 36
5.9.1 Mic 1,2 Level, Mix, Mute ................................................................................................... 36
5.9.2 Balance, Treble, Bass ......................................................................................................... 36
5.9.3 Audio Setup ........................................................................................................................ 36
5.10 STATUS .................................................................................................................................... 38
6. WEB BROWSER CONTROL .......................................................................................................... 39
6.1 CONNECTING TO THE UNIT .............................................................................................................. 39
6.2 WEB PAGE MENU ORIENTATION ....................................................................................................... 40
6.3 SOFTWARE UPDATE ....................................................................................................................... 43
6.4 BACKUP AND RESTORE .................................................................................................................... 43
6.5 LOGO AND CUSTOM TEST PATTERN CAPTURE .................................................................................. 44
7. FIRMWARE UPDATE ................................................................................................................... 45
7.1 USB UPDATE ................................................................................................................................ 45
7.2 WEB BROWSER UPDATE ................................................................................................................. 45
8. ENVIRONMENTAL AND EMC ...................................................................................................... 46
8.1 RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS ......................................................................................... 46
8.2 STORAGE ...................................................................................................................................... 46
8.3 CE AND FCC COMPLIANCE .............................................................................................................. 46
8.4 PAT TESTING ................................................................................................................................ 46
APPENDIX A ....................................................................................................................................... 47
FRONT PANEL MENU TREE ................................................................................................................ 47
APPENDIX B ....................................................................................................................................... 54
FRONT PANEL AUDIO MENU TREE ..................................................................................................... 54
APPENDIX C ....................................................................................................................................... 59
SINGLE LINK DVI-U PINOUT ............................................................................................................... 59
APPENDIX D ...................................................................................................................................... 60
RS-232 PINOUT .................................................................................................................................. 60
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
4
Page 6

SAFETY WARNINGS
THERE ARE NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTS WITHIN THE UNIT. REMOVAL OF THE TOP
COVER WILL EXPOSE THE USER TO DANGEROUS VOLTAGES. DO NOT OPERATE THE UNIT
WITHOUT THE TOP COVER INSTALLED.
ENSURE THAT ALL ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS (INCLUDING THE MAINS PLUG AND ANY
EXTENSION LEADS) COMPLY WITH ELECTRICAL SAFETY REGULATIONS.
CONNECT ONLY LOW VOLTAGE ISOLATED CIRCUITS TO THE INPUT AND OUTPUT
CONNECTORS. IF ANY QUESTIONS REGARDING THIS ISSUE, PLEASE CONSULT
QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL.
TO PREVENT SHOCK OR FIRE HAZARD DO NOT EXPOSE THIS EQUIPMENT TO RAIN OR
MOISTURE. IF SUCH EXPOSURE OCCURS, REMOVE THE POWER CABLE FROM THE
MAINS OUTLET AND HAVE THE EXPOSED UNIT CHECKED BY QUALIFIED SERVICE
PERSONNEL.
DO NOT OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT IF IT APPEARS THAT IS NOT OPERATING NORMALLY,
OR IF IT IS DAMAGED IN ANY WAY. REMOVE THE POWER CABLE FROM THE MAINS
OUTLET AND CONSULT QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL.
DO NOT REMOVE ANY FIXED COVERS UNLESS YOU ARE A QUALIFIED SERVICE
PERSONNEL. ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE POWER CABLE FROM THE MAINS OUTLET
BEFORE ANY COVER IS REMOVED.
THIS EQUIPMENT CONTAINS NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTS. REFER ALL SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE TO QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
5
Page 7

1. Introduction
This manual explains how to operate your VP-796(A) / VP-797(A) / VP-798(A) Scaler-Switcher.
If you have any questions relating to this or any other product supplied by Kramer please visit
our web site www.kramerelectronics.com.
1.1 System Overview
The VP-796(A) / VP-797(A) / VP-798(A) line of products feature excellent image processing algorithms
for the very best in scaling, motion-adaptive de-interlacing and automatic film 3:2 and 2:2 pull-down
correction. The new generation of Kramer products significantly outperforms the capabilities of
benchmark competitor products.
In addition to full 4K processing, new and unique technology allows for seamless switching between
different inputs as fast as ¼ of a second.
VP-796(A) / VP-797(A) / VP-798(A) feature with a flexible, high performance video input front end that
allows them to accept and process a wide variety of inputs. HDMI, DVI and Display Port video with
HDCP encryption is supported, as are computer graphics inputs in SVGA analogue and HDMI/DVI
digital formats. Analogue support also includes true component video in YPbPr and RGBS formats as
well as composite (CVBS) inputs.
A high performance video decoder is utilized with 4x oversampling and 3D Y/C separation for
outstanding video image clarity. The output frame rate can lock to the input frame rate dynamically
without frame rate conversion in order to reduce system latency; or it can be set to a fixed output
frame rate, e.g. for driving basic screens which are not 50Hz-compatible. The output format can also
lock to an externally provided synchronization signal on various models (see model matrix).
3GSDI/HDSDI/SDI digital formats are supported on VP-797 and VP-798 (see model matrix below).
Outputs are available in HDMI/DVI digital formats as well as 3GSDI and HDBaseT (see model matrix
below). All outputs are active simultaneously, except in the cases where the formats are not
compatible. For example, for the PC graphic formats that are not supported by the SDI standards, the
3GSDI output will be disabled. Also note that if an HDCP encrypted signal is connected to the DP,
HDMI or DVI input, the HDMI and DVI output signals will be similarly HDCP encrypted and the 3GSDI
output will be disabled. HDCP capability can be switched off per input, so that a source can transmit
non-protected content material.
The Pan, Tilt and Zoom (PTZ) feature allows users to select a ‘region of interest’, ROI, of the input image
to fill the screen and pan and tilt within it.
The Video Wall feature allows multiple units to work synchronously and be part of a large matrix
configuration, up-to 4x4. Each unit automatically crops a section of the input video image and displays
it on the corresponding projector or screen.
Models VP-798 and VP-798A support edge blending allowing brightness adjustments in certain regions
to match the brightness of overlapping areas.
All units can be operated via the front panel display and rotary knob, or through a built-in web page, or
via an API interface. The API manual is published separately and is available on our website.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
6
Page 8
Model
VP-
796 VP-797 VP-798
VP-796A
VP-797A
VP-798A
VP-796A/VP-797A/VP-798A models include 8 stereo audio inputs and two microphone inputs with
Phantom Power. An embedded audio mixer allows mixing of the mic inputs to any analog or digital
audio signal. Each unit includes a 30W stereo audio power amplifier allowing direct connection to
loudspeakers. Separate line level outputs are also provided for connecting to external amplifier
systems.
3G SDI & Genlock
HDBaseT
Pro-Blend
Audio Models
1.2 Packing List
1) 3 pin plug IEC mains cable
2) CD (w/ documentation)
3) Quick Start Guide (QSG)
7
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 9

2. Basic Switcher Set-Up
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
8
Page 10

© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
9
Page 11

© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
10
Page 12

Front Panel Shortcuts:
Standby + Esc
3. System Description
3.1 Front Panel Layout
The front panel includes several buttons allowing the user to select between the different inputs and
to perform other functions, a jog wheel and an LCD screen. From the front panel you can navigate the
menus, select the an input and direct access to key functions. The front panel layout is similar
between the different models except for the SDI, HDBT selection keys. Only models featuring these
inputs included these buttons.
VP-796 / VP-796A
VP-797 / VP-797A / VP-798 / VP-798A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 – Standby key: By pressing the Standby key, the unit is put into standby mode. This is indicated by a
“STANDBY” message on the LCD with the back light turned off. When the unit starts up, the red
Standby key flashes. Once the unit is operational, the Standby key is solid red.
2 – Input channel selection keys: All input channels can be directly selected. The active channel key is
illuminated.
3 – Test Pattern key: Directly activates a Test Pattern. Use the jog wheel to scroll through the
available test patterns.
4 – Direct function keys: Four functions can be directly accessed by pressing their assigned key:
Freeze (stop/resume live video), PTZ (activate/deactivate Pan Tilt Zoom), Logo (show/skip a
predefined logo), Blank (blank the output screen/resume live video).
5 – Menu navigational keys: When the Menu/Sel key acts as an Enter or Select key for menu
changes. A jog wheel is used for menu navigation and changing values. To exit the menu or any
submenu press the Esc key or navigate to the Exit item and press the Menu/Sel key or press the jog
wheel.
6 – Front Panel LCD: Displays the Menus on a 4-line display
7 – Jog wheel: The wheel is used for navigating through the menu system and making value changes.
The jog wheel has a push function the creates the same effect as pushing the Menu/Sel key.
Keypad unlock: Esc + Menu/Sel
Mode reset: Esc + CV
Factory reset: Esc + YPbPr (in live operation or at power up)
Set output mode to 720p: Esc + VGA
Firmware version:
( press the menu button to exit )
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
11
Page 13
Model
Dedicated Genlock
3.2 Input Video Connector Overview
VP-796
VP-796A
2x 3G-SDI/HD
via BNC
Display Port
via DP connector
2x HDMI (UHD,4K)
via HDMI connector
HDBaseT
via RJ45 connector
DVI & analogue (RGB/RGB/YPbPr)
via DVI-U
VGA analogue via 15HDD
Composite Video
via BNC
HDMI (HD)
Via HDMI connector
VP-797
VP-797A
VP-798
VP-798A
12
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 14

3.3 Rear Panel Layout
The rear panel features all input and output connectors, communication ports and the power supply
connector.
VP-796
VP-796A
VP-797 / VP-798
VP-797A / VP-798A
1 2 3 4 5 6/ 7 8 9/10 11 12 13/ 14 15 16 17
1 - 2x SD/HD-SDI/3G-SDI input 2 - HDBaseT (UHD/4k) input
3 - Display Port (UHD/4k) input 4 - 2x HDMI-1 & 2 (UHD/4k) input
5 - S/PDIF output 6 - VGA Input
7 - DVI-U (DVI-D and YPbPr through a cable adapter) 8 - 1x HDMI-3 (HD) input
9 - Composite Video 2 (BNC) 10 - Genlock input (BNC)
11 - 3G-SDI output 12 - HDBT (UHD/4k) output
13 - RS232 port 14 - DVI/HDMI1 (HD) output and
15 - HDMI2 (UHD/4k) output 16 - TCP/IP and 2x USB
17 - Power supply connector
3.4 Output Connector Overview
Model VP-796 VP-797 VP-798
1x 3G-SDI/HD via BNC
1x HDMI (UHD,4K) via HDMI connector
HDBaseT via RJ45 connector
DVI-D/HDMI via DVI-U
Audio Connectors
VP-796A
VP-797A
VP-798A
13
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 15

3.5 Product Specification
This section provides technical specification for all models. The following topics are discussed:
Power Supply Requirements
Input Specifications
Output Specifications
Supported Formats
Communication Specifications
3.5.1 Power Supply Requirement
100V-264VAC 50/60Hz connected via a standard IEC connector located on the rear panel.
3.5.2 Input Specifications
3.5.2.1 Video Inputs
Composite via BNC connector
Signal formats Composite (CVBS)
Standards NTSC, PAL, SECAM
Composite (CVBS) input level 1V p-p nominal incl. sync
Input Impedance 75 Ohms
3.5.2.2 Component Video Inputs
Via DVI-U connector and appropriate adapter cable
YPbPr (YUV), YPbPrS and RGsB component video, menu selectable.
Signal formats 484i (480i) and 576i (SD), 480p, 576p (ED), 720p, 1080i at 50, 59.94 and 60Hz
and 1080p at 23.98, 24, 25, 29.97 and 30Hz.
Please note this input does not support Computer SVGA signals which should be connected via
the Computer SVGA input, The SVGA input supports the separate H & V syncs.
3.5.2.3 3G-SDI Input
Format: SD-SDI, HD-SDI and 3G-SDI YCbCr 4:2:2 serial digital component video
Input impedance: 75 ohms.
SMPTE 292M, SMPTE 259M-C and SMPTE 424M compliant, accepts 484i, 576i, 720, 1080i and
1080p single link formats at 270Mb, 1.485Gb or 2.97Gb rates.
3.5.2.4 Computer (SVGA) Inputs VESA formats
Signal formats: DOS, VGA – WUXGA up to 165MHz pixel clock
RGB video level: 0.7V - 1.0V
RGB input impedance: 75 Ohms
Sync format : Separate H & V sync at TTL/5V levels.
3.5.2.5 HDMI & DVI Inputs
HDMI with or without HDCP, 36-bit video compatible.
DVI-D input with or without HDCP
Signal formats - video
SD: 625i (576i) and 525i (480i) in double-rate formats;
ED: 480p, 576p;
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
14
Page 16
HD: 1280x720p, 1920x1080i, 1920x1080psf; 1920x1080p 23.97, 24, 25, 29.94, 30, 50, 59.94 &
60Hz; 2048x1080p 23.97, 24, 25, 29.94, 30, 50, 59.94 & 60Hz.
HDMI 1 and HDMI 2 support: 4K signals: 3840x2160p & 4096x2160p 23.97, 24, 25, 29.94, 30,
50, 59.94 & 60Hz (50, 59.94 & 60Hz supported in YUV 4:2:0 colour space format),
Signal formats – computer
Common VESA graphics formats from VGA to 4k up to 297 MHz (HDMI 1 and HDMI 2) and 225
MHz (HDMI 3) pixel clock
3.5.2.6 DP Input
Display Port without HDCP, 36-bit video compatible.
Signal formats as HDMI 1 and HDMI 2.
3.5.2.7 HDBT Input
Uncompressed HD video over RJ45 connector and max.100m CAT5e cable (or better)
CAT5e/CAT6 for 100m and signals with less than 225MHz Pixel Clock
CAT6a/CAT7 for 100m and signals up to 297MHz Pixel Clock
Signal formats as HDMI 1 and HDMI 2.
HDMI-1 and HDMI-2 and HDBT inputs support RGB and YUV 4:2:0 colour space formats.
Signals with YUV 4:4:4 and YUV 4:2:2 colour space formats need to be connected to the HDMI3 or
DVI input.
Graphics formats with odd numbered horizontal active pixels, e.g. 1365x768 are not supported.
3.5.3 Output Specifications
All output channels are active simultaneously, provided that the input signal is not HDCP encrypted. All
units include an HDMI, and a DVI-U connectors for DVI/HDMI connectivity. Some models feature a BNC
connector for 3G-SDI signals and an RJ-45 connector supporting HDBaseT capability. The DVI-D
connector supports HDMI with 36-bit video and audio formats when connected to a suitable HDMI
receiver. The colour depth of the HDMI signal is determined by a menu selection and the capabilities of
the monitor.
Interlaced outputs are only supported on models with 3G-SDI output.
3.5.3.1 3G-SDI Output
Format: SD-SDI, HD-SDI and 3G-SDI YCbCr 4:2:2 serial digital component video
Input impedance: 75 ohms.
SMPTE 292M, SMPTE 259M-C and SMPTE 424M compliant, accepts 484i, 576i, 720, 1080i and
1080p single link formats at 270Mb, 1.485Gb or 2.97Gb rates.
3.5.3.2 HDMI & DVI Outputs
HDMI with or without HDCP, 36-bit video compatible.
DVI-D input with or without HDCP
Signal formats - video
SD: 625i (576i) and 525i (480i) in double-rate formats;
ED: 480p, 576p;
15
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 17
Output Channel
Output Format
HDMI
PCM up to 8ch, up to 24Bit, up to 192kHz sampling rate
SDI PCM up to 8ch, up to 24Bit,
48kHz sampling rate
SPDIF
PCM up to 2ch, up to 24Bit, up to 96kHz sampling rate
HD: 1280x720p, 1920x1080i, 1920x1080psf; 1920x1080p 23.97, 24, 25, 29.94, 30, 50, 59.94 &
60Hz; 2048x1080p 23.97, 24, 25, 29.94, 30, 50, 59.94 & 60Hz.
HDMI 1 and HDMI 2 support: 4K signals: 3840x2160p & 4096x2160p 23.97, 24, 25, 29.94, 30,
50, 59.94 & 60Hz (50, 59.94 & 60Hz supported in YUV 4:2:0 colour space format),
Signal formats – computer
Common VESA graphics formats from VGA to 4k up to 297 MHz (HDMI 1 and HDMI 2) and 225
MHz (HDMI 3) pixel clock
3.5.3.3 HDBT Output
Uncompressed HD video over RJ45 connector and max.100m CAT5e cable (or better)
CAT5e/CAT6 for 100m and signals with less than 225MHz Pixel Clock
CAT6a/CAT7 for 100m and signals up to 297MHz Pixel Clock
Signal formats as HDMI 1 and HDMI 2.
3.5.3.4 HDCP Output encryption
When the input signal is HDCP encrypted, the DVI-D, HDMI and HDBaseT outputs will also be
encrypted and the 3G-SDI output will be disabled. If the display device does not support
HDCP, the output will be black and a message indicating that the presence of an HDCP signal
will be shown on the screen.
The user can turn off the unit’s HDCP compliance to allow non-encrypted content to pass
through the unit. This is an important feature specially when using a MAC computer as the
source. The MAC will encrypt its output signal if a compliant device is seen attached to its
output regardless of the copy protection requirements of the content. By turning off HDCP,
the MAC will see a non-compliant device and therefore will not encrypt its output. When
HDCP compliance is turned off, encrypted sources will not be displayed.
3.5.3.5 Audio Output
Audio embedded in HDMI and SDI video streams is passed through the system and re-embedded into
the HDMI and SDI output signals.
Also, the unit features a S/PDIF coaxial digital audio output connector for monitoring audio of the HDMI
and SDI channel.
When HDMI is selected as the input channel, the HDMI EDID is read by a video source such as a Blu- Ray
Player. The unit allows the source to provide the formats shown under output formats for HDMI in the
below table. All formats are re-embedded into the HDMI output data stream, those which are not
allowed on the SDI or SPDIF output are muted on the individual channels.
(incl. 32kHz,44.1kHz,48kHz,96kHz,192kHz)
(incl. 32kHz,44.1kHz,48kHz,96kHz)
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
16
Page 18

3.5.4 Analog Audio
Units supporting audio include up-to 8 analog stereo Inputs, two microphone Inputs with phantom
power and an audio mixer.
Analog stereo signals are connected to the unit via 3.5 mm jack sockets, except for the CV input that is
associated with two RCA connectors. Using the audio menu, any video input can be link with any
audio input and mixed with the mic inputs.
Audio models also include stereo audio power amplifier supporting 15W RMS loudspeaker per output
and separate stereo balanced line level audio outputs for external amplifier systems. The analog
stereo outputs are available on two phoenix connectors.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
17
Page 19
CVT 1.30MA/VESA
3.5.5 Supported formats
Horiz.
Active
Pixels
640 480
720 480i
720 480p
720 576i
720 576p
800 600
1024 768
1280 720
1280 768
1280 800
1280 1024
1360 768
1366 768
1440 900
1400 1050
1600 1200
1680 1050
1920 1080i
1920 1080p
1920 1200
2048 1080
2048 1200
2560 1080
2560 1440
2560 1600
3840 2160
4096 2160
Vert.
Active
Lines
60 59.94 50 30 29.97 25 24 23.98
Vertical Refresh Rate (Hz) Outputs
DVI
HDMI
HDBT
3GSDI
EIA/CEA-861-B Format
EIA/CEA-861-B Format
EIA/CEA-861-B Format
001M9/VESA DMT
001MA/VESA DMT
001M3/VESA DMT
VESA CVT 002MA
EIA/CEA-861-B Format
EIA/CEA-861-B Format
VESA CVT 002MA-
EIA/CEA-861-F VIC=86
VESA CVT 004M-R
VESA CVT 004M-R
EIA/CEA-861-F VIC=93
EIA/CEA-861-F VIC=98
Specification
VESA DMT
6 (NTSC)
17 (PAL)
VESA DMT
VESA DMT
4
VESA CVT
VESA CVT
VESA DMT
VESA DMT
proprietary
DMT
VESA CVT
VESA DMT
5
5
R/VESA DMT
proprietary
proprietary
18
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 20

4. Unit Control
All models can be controlled via the front panel, a web page built-in into the unit or an API protocol
interface. The next two chapters describe the Front Panel and Web Browser control methods. The API
interface can be found in a separate document available on our web site.
5. Front Panel Control
You can enter the main menu by pressing the Menu/Sel key from the status screen. You can use the
jog wheel and Menu/Sel and Esc buttons to navigate through the different menus.
A complete diagram of the menu tree is shown in Appendix A. The audio menu tree for units fitted
with the audio option is shown in Appendix B.
Next, is a brief description of the functions and settings available from the front panel menus.
5.1 Main Menu
The main menu lists the selected input channel and 6 sub menus. The 6 sub menus are:
Output
Colour
Geometry
Video Wall
Enhancement
System
Each menu includes an Exit entry to return to the previous level. Some adjustments are not applicable
to all signal types or operating modes, in which case those non-applicable functions will be greyed out
and are not accessible.
The unit is designed to have separate memories for all the settings in each section. All Input parameters
are specific to your chosen input channel and input signal type, and are not global to the unit. For
example, if you change the settings for the composite video channel, you will not affect the settings you
may have made in the DVI channel.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
19
Page 21

5.2 Input
This menu provides an additional method of selecting the desired input.
Depending on the specific model, some of these input selections may not be available.
Test patterns can be selected even when there are no inputs connected to the unit. Different test
patterns can be selected by scrolling the jog wheel.
Settings:
SDI-1
SDI-2
Display Port
HDMI-1
HDMI-2
HDBaseT
DVI
HDMI-3
VGA
YPbPr/RGB
Composite Video
Test Pattern
Default : HDMI-1
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
20
Page 22

5.3 Output
This menu contains adjustments related with the outputs of the unit.
5.3.1 Display Type
5.3.1.1 Output Mode (Resolution)
The selected output resolution should match the native resolution of the imaging device to avoid
double scaling.
The 3GSDI output does not feature the PC resolutions, only 480i/p, 576i/p, 720p and 1080i/p output
modes are supported.
Settings: See the Supported format table
Default : 1920x1080p
5.3.1.2 Frame Rate
As with the output resolution, the output frame rate should match the native frame of the imaging
device. Some frame rates may not be available depending on the selected resolution.
In auto mode the output frame rate follows the input frame rate if it supported by the output resolution.
If the input frame rate is not supported by the output resolution, then the unit determines the output
frame according to a procedure programmed in the software.
Settings: 60 Hz, 59.94 Hz, 50 Hz, 48 Hz, 25Hz, 24 Hz, 23.97, Auto
Default : 59.94Hz
5.3.1.3 I/O Lock
From this menu, the user can select the genlock mode of the unit. If I/O Lock is off, the output free-runs
with a fixed refresh rate determined by the frame rate setting. In this mode, the output vertical refresh
sync deviates slightly from the input vertical refresh sync, even if both are set at the same rate,
occasionally causing frame dropping or repeat.
If I/O Lock is set to On, the output refresh rate follows the input video refresh rate if possible. If not, the
output is operated with a fixed refresh rate determined by the frame rate setting.
If I/O Lock is set to Genlock, the output refresh rate will follow the vertical sync of the signal connected
to the Genlock BNC connector. Genlock is achieved when the Genlock vertical sync rate matches the
vertical sync rate set in the output menu. Valid combinations are 50Hz/50Hz, 59.94Hz/59.94H and
60Hz/60Hz. If genlock is not achieved, the output frame rate refresh rate is determined by the frame
rate setting.
The LCD main status menu indicates the genlock status: (I/O Locked or Genlocked) or in free run mode
(Free Run).
In order to achieve clean switch between input selections, follow the locking settings described in the
table below.
21
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 23

I/O Lock =
On
I/O Lock = Genlock
I/O Lock = Off
Auto Frame Rate
Never Clean
Always Clean
Depends on Inputs
Fixed Frame Rate (any)
Never Clean
Always Clean
Always Clean
(Lock to i/p video)
(Free Run)
If the output Frame rate is set to Auto, Genlock signals all genlock signals can be accepted. On the
other hand, if a specific frame is selected, for example 60Hz, a Genlock reference signal od 60Hz can
only be accepted and the unit will not lock to a 50Hz reference signal.
If the output Frame rate is set to Auto and I/O lock is off, input switching may-not be clean. Clean
switching will depend how close the frame rates of the current and next input channel are.
Settings: Off, On, Genlock (for models supporting genlock)
Default : Off (Free Run)
5.3.1.4 Frame Rate (Enable)
From this menu the user can choose the output frame rates that the unit can output. This is done to
prevent the unit from outputting frame rates that cannot be accepted by the display.
Settings: 60 Yes/No, 50 Hz Yes/No, 48 Yes/No, 30/29.97Hz Yes/No, 25 Yes/No, 24/23.98 Yes/No
Default : 60Hz Yes, 50Hz Yes, 48Hz No, 30/29.97Hz Yes, 25Yes, 24/23.98Hz Yes
5.3.2 Gamma/Colour
5.3.2.1 Native Colour Temp
Native Colour Temp allows the user to select from pre-configured colour temperatures to match the
display. If this value is the same as the Colour Temp value in the (Input) Colour menu, no conversion is
performed.
Settings: 3700, 5500, 6500, 7500, 9300, 10000
Default : 6500K
5.3.2.2 Output Gamma
Output gamma allows to re-gamma video signals with pre-configured gamma values to match the
display. Input gamma and output gamma both default to 2.2. If they are both set to the same value,
there is no effect on the image.
If you need to reduce the level of certain color in the image, select a higher value for the input colour
Temp in the Colour menu, or a lower number for the Native Colour Temp in the Output menu.
Settings: 1.0 to 3.0 in steps of 0.1
Default : 2.2
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
22
Page 24

5.3.3 Output Config
5.3.3.1 Display
Internally, the output interface processes data at a full ten bits per colour. The colour depth on the
HDMI outputs is determined by the supported standard of the attached monitor or device when set to
DVI/HDMI.
DVI 1.0 and HDMI 1.1/1.2 devices are set at 24 bit, for HDMI 1.3 or later compliant devices it is up to 36
bit. The DVI forced selection will output video with 24 bit colour depth irrespective of the supported
standard of the attached monitor.
Settings: DVI forced, DVI/HDMI
Default : HDMI
5.3.3.2 HDCP
HDCP encryption support on the output can be switched off as is in the input. This means the unit
pretends to be non-HDCP compliant on the DVI/HDMI output port and consequently does not encrypt
data. At the same time, HDCP is also turned off at the input ports. This allows the unit to accept nonHDCP encrypted data. If the source however, is HDCP encrypted, then the output will be black.
Settings: On, Off
Default : On
5.3.3.3 DVI Colour Space and DVI Range
When set to Default CEA, the output modes have limited range, and VESA modes have full range.
Therefore, an incoming limited range mode is either passed through when the output is set to a CEA
output mode or expanded when the output is set to a VESA mode. An incoming full range mode is
either compressed when the output is set to a CEA output mode or passed through when the output
is set to a VESA mode.
If the HDMI/DVI output does not operate properly, the range can be changed manually. A limited
video range is only using the following greyscale for video information - 8 Bit System: 0x10 .. 0xEF, 10
Bit System: 0x040 .. 0x03BF, 12 Bit System: 0x100 .. 0xEFF.
Settings : Color Space: RGB or YPbPr / Range: Default, Limited, and Full
Default : RGB & Full
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
23
Page 25

5.4 Colour (Input Channel Adjustments )
5.4.1 Black-Level Offset
Used to select 7.5 IRE black level set-up adjustment. Should always be set to 7.5 IRE for HDMI video
and NTSC video inputs and should usually be off for PAL analog video inputs.
Settings: 0 IRE, 7.5 IRE
Default : 0 IRE
5.4.2 Black-Level
Black level controls the offset applied to the video signal. (same as the brightness control on a TV)
Settings: -50 to 50 in steps of 1
Default : 0
5.4.3 Contrast
Contrast controls the gain applied to the video signal.
Settings: -50 to 50 in steps of 1
Default : 0
5.4.4 Saturation
Controls the video colour saturation, (applies individually to all video inputs but not computer input
signals or formats).
Settings: -50 to 50 in steps of 1
Default : 0
5.4.5 Hue
Adjusts the colour hue of NTSC signals. This is not applicable for computer input signals or formats.
Settings: -50 to 50 in steps of 1
Default : 0
5.4.6 RGB values
This is a user-defined colour temperature setting where R,G,B gain (white balance) and offset/bias
(black balance) can be adjusted separately in order to match the display device. This control is not
available for output modes with colour space format YUV 4:2:0.
Settings : Red/Green/Blue Gain/Bias : -512 to 512
Default : 0
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
24
Page 26

5.4.7 Colour Temp
A preset range of Colour Temperature allowing the user to select from pre-configured colour
temperatures to match the colour temperature of the incoming signal. If this value Native Colour
Temp value in the Output menu are the same, no conversion is performed.
Settings: 3700K, 5500K, 6500K, 7500K, 9300K, 10000K
Default : 6500K
5.4.8 Input Gamma
Set this value to match the gamma of the input signal. Input and output gamma both default to 2.2. If
they are both set to the same value, there is no effect on the image.
Settings: 1.0 to 3.0 in steps of 0.1
Default : 2.2
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
25
Page 27

5.5 Geometry
This menu contains adjustments associated with setting up position, aspect ratio and scale of the
input signal.
5.5.1 Picture Format
This menu allows users to select the displayed aspect ratio when the input signal aspect ratio is
different to the display panel’s aspect ratio. Some aspect ratios may not be applicable to all signal
types, in which case selecting a non-applicable aspect ratio conversion will have no effect on the
displayed image.
Original: Preserves the aspect ratio of the incoming image and scales the image to fit into the size of
the panel. Depending on the aspect ratio of the panel the image is either bordered by the right/left
side or bottom/top of the panel. Non-used areas of the panel are displayed black (letterboxed).
Full Screen: Scales the image to the size of the panel without preserving the aspect ratio.
Crop: Preserves the aspect ratio and scales the image to fill the screen. Depending on the aspect ratio
of the panel either the top/bottom or right/left areas of the image are cropped.
Anamorphic: Scales the input image such that it is displayed with a 16:9 aspect ratio when displayed
on the screen. The image is further scaled to fit into the size of the panel. Depending on the aspect
ratio of the panel the image is then either bordered by the right/left side or bottom/top of the panel.
Non-used areas of the panel are displayed black (letterboxed).
Settings: Original, Full Screen, Crop, Anamorphic
Default: Original
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
26
Page 28

5.5.2 Overscan
Overscan is used to slightly zoom into the image. Therefore, the border area of an image is no longer
displayed on the screen. This cuts off unwanted features at the top or bottom from e.g. head switching
in legacy video images.
Settings: 0 to 10 in steps of 1
Default: 0
5.5.3 Pan Tilt Zoom (PTZ)
This menu provides settings to zoom and shrink the image, pan horizontally and tilt vertically within the
image. PTZ can be switched on or off and the settings can be saved per input channel or globally, i.e. if
applied globally the same PTZ settings are applied when switching input channels or changing the input
mode.
The Zoom setting allows zooming into the image or shrink it.
When Aspect Lock is set to On, vertical zoom is disabled and the horizontal zoom or shrink factor is also
used to vertically adjust the image. In this mode the aspect ratio is preserved.
When Aspect Lock is Off, horizontal and vertical scaling factors are set separately, regardless of the
input image aspect ratio.
27
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 29

Off raster panning is also allowed, i.e., the image can be shifted outside the active area of the display.
The PTZ settings can be set to the default settings with the reset button.
Settings: On/Off
Default: Off
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
28
Page 30

5.6 Video Wall
The Video Wall menu provides controls to set up multiple units in a multi-screen application.
Multiple screens are stitched together to provide a bigger display with higher resolution than a single
display. Each display is driven by a separate unit.
In a multi projection display, the individual projections typically are chosen to overlap to give seamless
transitions. Multiple LED walls or LCD/Plasma screens do not have overlapping regions and the blend
Width is set to zero. When using Video Wall to drive one single large screen, it is essential that all
units are I/O locked or genlocked, otherwise motion tear will be observed at the boundaries of the
image processed by each unit.
5.6.1 Auto Zoom
Switches on the auto zoom resizing the video image to display the assigned part of the total image.
When Auto zoom is turned on, the processor will cut and scale the portion of the picture selected by
the matrix size and position selected as described next
Settings: On/Off
Default: Off
5.6.2 Units Wide/Units High
The dimensions of the multi-screen display is defined with this menu. The maximum number of screen
supported is 16. This function is used in conjunction with the next function.
Settings: Units Wide: 1, 2, 3, 4 / Units High: 1, 2, 3, 4
Default: Units Wide: 1 / Units High: 1
5.6.3 Horizontal Pos/Vertical Pos
These settings provides the coordinates of the segment of the total image that the unit will process (cut
out and resize). This function is used in conjunction with the previous function to select the blend
regions to be provided even when auto zoom is turned off.
Settings: 0 to 3 indicating co-ordinates 0,0, to 3,3 for the maximum matrix size of 16
Default : 0, 0
In the example below a 4K image is split into four 1080p quadrants in a 2x2 configuration. All units are
set to I/O lock to prevent image tear between the four displays.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
29
Page 31

5.7 Enhancement
The enhancement menu provides image enhancement functions. Note that the enhancement settings
apply only to video input signal and not to computer graphics signals.
5.7.1 Sharpness
Control of the sharpening enhancement filters' levels. These are peaking filters to improve highfrequency response. Note that setting this control too high on a signal which already has good high
frequency response will cause ringing or ghosting.
Settings: -4 to 4 in steps of 1
Default : 0
5.7.2 Detail
This filter provides powerful 2D image enhancement which can be used to greatly improve detail
definition and clarity without causing image ringing or ghosting. It improves both horizontal and vertical
detail. Correct setting of the detail enhance filter can make SD signals look virtually indistinguishable
from true HD. At setting 0 the filter is switched off, with setting 3 providing the highest effect.
Settings: 0, 1, 2, 3
Default : 1
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
30
Page 32

5.8 System
This selection contains functions which are more applicable to system operation than to picture
adjustment.
5.8.1 User
Several unit settings can be stored under a user name. Different users can store their preferred settings
and recall them by selecting their user name.
User settings are stored automatically and no special action is required by the user. For example, if the
setting is changed from USER1 to USER2, then all of unit’s parameters at the time of the change will be
stored under USER1. When the unit is changed back to USER1, the USER1 settings will be loaded back t
the unit.
Using the Web interface, any number of settings can also be stored/restored to/from the PC.
Settings: USER 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 10
Default : USER 1
5.8.2 Names/Profiles
The Names/Profiles menu provides input masks to rename the generic input channels and user names.
User names and input channel names can be changed to any word with a maximum of 12 alpha numeric
characters with a value range of 0-9, A-Z and blank.
The unit itself can be given a name. The default name is VIDEOPROC. This name followed by the MAC
address is used by the web server and being displayed in the unit line of the web page.
5.8.3 Input Config
Inputs can be configured through the following sub-menus:
5.8.3.1 Analog Inputs
5.8.3.1.1 VGA Setup:
Frequency (Clock) and phase can also be altered manually, as the vertical and horizontal
position
Settings: 0 to 32
Default : 0
Colour Space
Settings: RGB or YCbCr
Default : RGB
The greyscale range can be reduced by switching from full to limited (see range values
discussed in the output config section)
Settings: Full / Limited
Default : Full
A reset button to factory defaults is provided, to return the phase, clock and positional
settings to the original positions.
The preferred video mode can be selected in the EDID Input Format menu. This setting can
force the source to output a certain video mode provided the driver of the graphic card reads
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
31
Page 33

the preferred timing in the EDID. Most likely the PC needs to be rebooted for the driver to
notice the EDID change.
Default : 1920x1080p
5.8.3.1.2 RGB/YPbPr Setup:
Same as VGA Setup, except there is no concept of EDID with component video
and thus no EDID Input Format menu.
o CVBS Setup:
CCS is a filter to reduce luminance to chrominance cross talk of composite video
signals (only) which appears as a coarse rainbow pattern or random colours in
regions of fine details.
Default : On
5.8.3.2 Digital Inputs
5.8.3.2.1 DP Config:
The automatic HDMI Colour Space and Range settings can be overwritten in this menu.
Colour space
Settings: RGB or YCbCr, if Auto setting does not give the desired result
Default: Auto
Range
Settings: Limited. Full or Auto range.
Default: Auto
Deep Color: The EDID can be configured to enable deep colour capability. The unit can
process colour depth of 24/30 per channel. Deep Colour can be off, if the source outputs
24bits, or set to on when the source outputs 30bits. The detected source output colour
depth is reported on the corresponding menu.
Settings: On/Off
Default: Off
EDID In: The preferred video resolution can be selected in the EDID Input Format menu.
This setting can force the source to output the selected format provided the driver of the
graphic card takes notice of the preferred timing in the EDID. The PC most likely has to be
rebooted for the driver to take notice.
Default : 1920x1080p
5.8.3.2.2 HDMI 1, HDMI 2, HDMI 2, DVI & HDBT Config.
Colour space
Settings: RGB or YCbCr, if Auto setting does not give the desired result
Default: Auto
Range
Settings: Limited. Full or Auto range.
Default: Auto
Deep Color: The EDID can be configured to enable deep colour capability. The unit can
process colour depth of 24/30/36bit per channel. Deep Colour can be off if the source
outputs 24bit, or set to on if the source outputs either 30bit or 36bit. The detected source
output colour depth is reported on the corresponding menu.
Settings: On/Off
Default: Off
EDID In: The preferred video resolution can be selected in the EDID Input Format menu.
This setting can force the source to output the selected format provided the driver of the
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
32
Page 34

graphic card takes notice of the preferred timing in the EDID. The PC most likely has to be
rebooted for the driver to take notice.
Default : 1920x1080p
HDCP: When setting HDCP Input to off, the unit pretends to be non HDCP compliant
allowing the source to not encrypt data. The source will only non-encrypt only when the
material is not protected. When the HDCP capability is set to off, the output is
unencrypted and this menu item is greyed out.
Settings: On/Off
Default: On
5.8.3.2.3 DVI Config
The preferred video mode for DVI input can be selected. This setting may force the source
to output a certain video mode provided the driver of the graphic card takes notice of the
preferred timing in the EDID. The PC most likely has to be rebooted for the driver to take
notice.
Settings: HDMI / DVI only
Default: HDMI
5.8.3.2.4 HDMI Audio Support
The audio capabilities of the HDMI port can be configured by means of overwriting the
EDID. The unit described in this manual is part of an audio/video processing chain and
devices behind the unit may not be able to cope with advanced audio. The unit can signal
the source to match with the audio capabilities of the display (setting Match Display 1/2),
or to be S/PDIF friendly or to be SDI friendly (48kHz PCM only, 2ch or 8ch). If the unit is set
to Full the capabilities of the unit are communicated by means of the EDID to an audio
source.
Settings: On/Off
Default: On
5.8.3.2.5 SDI Setup
SDI audio input is routed to the HDMI and 3GSDI output connector. Two consecutive SDI
audio channels can be output on the HDMI/3GSDI output interface. The group can be
chosen. Or all eight SDI audio channels can be transmitted
Settings: Stereo ch(1,2)/(3,4)/(5,6)/(7,8)/Multichannel
Default: Stereo ch (1,2)
5.8.3.3 Test Pattern Setup
When the menu is off, the test pattern can be selected by turning the jog wheel. For unit
control through a web browser or to set up a certain default test pattern please use the
input configuration menu.
Custom test patterns loaded into the unit through the web interface, and selected as the
other test patterns.
A test tone to accompany the test pattern can be switched on and off.
Default: Pattern: SMPTE / Test Tone: Off
5.8.3.4 Input Enable
Individual selections are provided to enable to disable each input
Settings: On or Off for each Input
Default: All on
5.8.3.5 Switching Transition:
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
33
Page 35

The switching transition can be selected to be Freeze, Blank, Fast Fade and Slow Fade.
Freeze : Halts the prior channel image until the new channel image is stable. Freeze is
the default mode.
Blank : Switches the output to a black screen instead of the last shown image.
Fast and Slow Fade : Fades between the channels with different transition times
Settings: Freeze, Blank, Fast Fade and Slow Fade
Default: Freeze
5.8.4 Menu Settings
This menu allows users to change the menu display time, i.e. the time after which the LCD menu is
switched back to the main status screen again with no user interaction.
From this menu you can change the language and also lock the keyboard. To unlock the keyboard a
combination of keys has to be pressed at the same time. The locking of the keyboard is indicated by a
message that the keypad is locked. The message also specifies the key press combination necessary to
unlock the unit. When successfully unlocking the keypad the message shows up: Keypad unlocked.
The backlight level of the LCD can be set in this menu.
The background colour of the web pages can be changed from dark to light to match the ambient
conditions.
5.8.4.1.1 Language
Settings: English (AE), English (BE), Deutsch
Default: English (AE)
5.8.4.1.2 Keypad Lock
Settings: Off, Menu Only, All Keys
Default: Lock: Off
5.8.4.1.3 Menu Time
Settings: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, Infinite
Default: 15 secs
5.8.4.1.4 LCD Backlight
Settings: 0 ..10
Default: 10
5.8.4.1.5 Jog Push Enable
Settings: On, Off
Default: On
5.8.4.1.6 Web Colors
Settings: Dark, Light
Default: Dark
5.8.5 Network Settings
The Network Settings menu allows users to configure the unit´s TCP/IP address. Under Address Type a
static or DHCP leased address can be chosen. The static address, gateway address and netmask needs
to be entered manually.
34
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 36

Make sure you p
ush the Apply button for
the
setting changes
The Network Settings menu provides information on the DHCP Status and IP address assigned to the
unit, as well as the fixed MAC Address programmed into the unit. The DHCP status can be Off when a
static assignment is used. When DHCP is on, the menu displays the leased address. If the lease is
unsuccessful, the menu displays “none”
When changing from DHCP to Static mode or vice versa it is strongly recommended that you cycle the
power to the unit in order the change is properly recognized by other devices on the network.
Settings: Static, DHCP
Default: DHCP
5.8.6 Security Settings
The password for ftp and web access to the unit can be changed in this menu.
FTP password Default: user
WWW password : Off
5.8.7 Factory Defaults
This button allows users to restore all settings to the default values of the unit, allowing the unit to
return to a known (good) system state. A confirmation is requested prior to actual system settings
restore.
to become effective
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
35
Page 37

5.9 Audio
This selection contains functions required to manage the audio inputs and outputs
5.9.1 Mic 1,2 Level, Mix, Mute
The Level setting defines the audio level for the Microphone inputs. Mix adjustment controls the mixing
between Mic and the selected audio source.
Settings:
Level: -12 to +60
Mix : 0 to 100 (100 is full microphone sound)
Mute: Yes, No
Default :
Level: -6
Mix : 50
Mute: No
5.9.2 Balance, Treble, Bass
Balance highlights the sound from the left or right output channels. Treble adjusts high frequency
sounds and bass the low frequency sounds.
Settings:
Balance: -100 to +100
Treble : -15 to +15
Bass: -15 to +15
Default :
Balance: 0
Treble : 0
Bass: 0
5.9.3 Audio Setup
5.9.3.1 Audio Delay (Available in future software release)
This settings allows the users to adjust the delay between the video and audio sources. This
feature is used to correct lip-sync issues
Settings: -100 to 500 ms
Default : 0 ms
5.9.3.2 Input Level
Input level adjusts the gain of the incoming audio signal
Settings: -12 to +6 db
Default : 0 db
5.9.3.3 Input Mode
Defines whether the incoming audio signal is stereo and mono
Settings: Stereo / Mono
Default : Stereo
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
36
Page 38

5.9.3.4 Input Mute
Enables of the mute function for the selected audio source
Settings: Yes / No
Default : No
5.9.3.5 Amp Gain
Amp gain adjusts the gain for the D-power amp driving speakers.
Settings: 0 to +38 db
Default : 0 db
5.9.3.6 Audio Assign
This menu allows users to assign any analog audio source or mics to the selected input. If the
selected input is digital, the user can also select the audio that is embedded to the video
signal. These selections can be performed on per input basis or globally.
5.9.3.6.1 Config
Selects whether the Audio assignments are done per source or globally
Settings: Per Inp / Globally
Default : Per Inp
5.9.3.6.2 Audio In
This menu is enabled when the audio assignments are done globally. If an Analog source is
selected, the user can also choose the analog audio source from the next menu (Analog In). If
a Digital source is selected, the embedded audio in the selected audio source will be used.
Settings: Stereo Analog / Analog with Mic / Digital
Default : Stereo Analog
5.9.3.6.3 Analog In
This menu is enabled when the audio assignments are done globally. From this menu the user
selects the audio source to be assigned to the selected input
Settings: CVBS / HDBaseT / Display Port / HDMI 1 / HDMI 2 / VGA / DVI / HDMI 3
Default : CVBS
5.9.3.6.4 Analog Inputs
This menu is enabled when the audio assignments are done per Input.
For each of the analog video sources the user can select a Stereo Analog source or a Stereo
analog source with the mics. The user can also selected which of the analog source will be
assigned to the input.
Settings: Stereo Analog / Analog with mic
Default : Stereo Analog
For the analog audio source:
Settings: CVBS / HDBaseT / Display Port / HDMI 1 / HDMI 2 / VGA / DVI / HDMI 3
Default : The corresponding analog input associated with the video input
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
37
Page 39

5.9.3.6.5 Digital Inputs
This menu is enabled when the audio assignments are done per Input.
For each of the digital video sources the user can select a Stereo Analog source, a Stereo
analog source with the mics, or the corresponding embedded audio within the video signal. If
an analog source is selected, the user can also selected which of the analog source will be
assigned to the input.
Settings: Stereo Analog / Analog with Mic / Digital
Default : Digital
If an analog audio source is selected :
Settings: CVBS / HDBaseT / Display Port / HDMI 1 / HDMI 2 / VGA / DVI / HDMI 3
Default : The corresponding analog input associated with the video input
5.9.3.7 Mic Config
This menu allows users to enable phantom power for condenser mics. When phantom power
is enabled, a voltage of +48V is sent to the condenser microphone via the XLR socket.
5.9.3.8 Audio Out Mute
This menu allows users to mute audio output source individually.
5.10 Status
This menu provides status information of the connections to the HDMI2, DVI/HDMI1 and HDBT outputs.
The unit reads the EDID of the attached monitor and makes decision based on its capabilities and the
configuration of the unit (Deep Colour and HDCP support). The type of attached monitor (DVI or HDMI),
video bit depth (8, 10 or 12 bit per colour channel) and HDCP encryption (on/off) is displayed.
38
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 40

When changing from DHCP to Static mode or vice versa
, it is strongly
6. Web Browser Control
The unit can be remotely controlled from a PC or any mobile device. No additional software needs to
be installed on the PC. The PC web browser is used as the graphical user interface for all control items.
To connect to the unit the TCP/IP address of the unit has to be entered into the address list box of the
web browser in the following format http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. The TCP/IP address assigned to the unit
can be found in the System/Network Settings menu.
6.1 Connecting to the unit
The Network Settings menu of the unit allows to configure the unit’s TCP/IP address. Under Address
Type a static or DHCP leased address mode can be selected. he factory default of the unit is DHCP. The
static address and Netmask needs to be entered manually.
The Network Settings menu provides information on the DHCP Status and the IP address assigned to
the unit as well as the fixed MAC Address of the unit. The DHCP status is Off when the static
assignment is selected. If the unit has an assigned address, then the menu displays the address, or
“None” if the lease was not successful.
recommended that you cycle the power to the unit in order the
change is properly recognized by other devices on the network
After the correct IP address is entered into the address bar, the web browser starts to load the
menus mirroring the status of the unit. All menu items are shown as their respective buttons, sliders
and list boxes and can be accessed and altered with the PC mouse or corresponding navigational key
presses.
From the web Browser, under security settings, the user name and Password can be turned on. The
default settings are:
User Name: user
Password: user
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
39
Page 41

6.2 Web page menu Orientation
The main page of the web browser is shown below. The Unit ID is displayed on the first line and is
composed of the identifier PV7 followed by the MAC address. The firmware version number and
information on the input mode are listed next.
Under the information pane the available input channels are shown and can be activated directly.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
40
Page 42
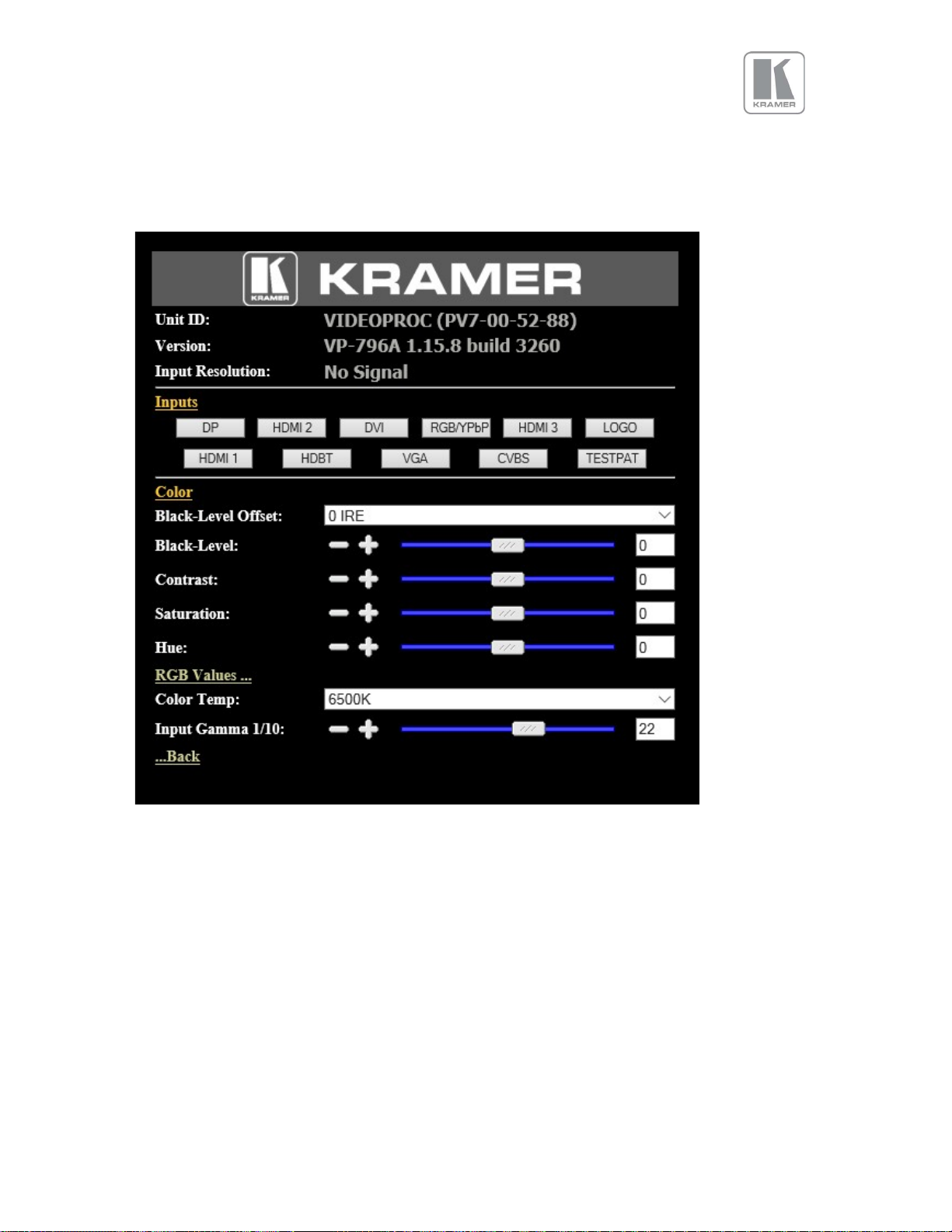
The menu system can be navigated with the PC mouse. Move the mouse pointer over the menu item
and click the left mouse button to open a submenu. Submenus have three dots followed by the menu
name. Move the mouse pointer over the Back item and click the left mouse button to go back to the
prior menu.
Menu items can be lists, sliders or alpha numeric fields.
A list item can be activated by moving the mouse pointer over the list item and clicking the left mouse
button. The list comes up and an item can be selected by moving the mouse pointer to the desired value
(here: 0 IRE) and clicking the left mouse button again.
A slider value can be changed by moving the mouse pointer over the slider, click and hold the left mouse
button and move the mouse to the right or left to decrease or increase the value. Also, the slider can
be controlled in single steps with the mouse wheel. Or by moving the mouse pointer over the – or +
fields and clicking the left mouse button..
Values can be entered directly in the field beneath the slider. Click into the field, enter the new value
through the PC keyboard and click with the left mouse button to any location outside the field to update
to the new value.
41
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 43

Renaming the input channel is used as an example to explain the alpha numeric field changes. Move
the mouse pointer into the alpha numeric field and click on the left mouse button. The cursor can be
controlled with the right/left and back space keys of the PC keyboard. The new name for the input
channel can be entered.
The new name is stored when clicking with the left mouse button to any location outside the field.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
42
Page 44

6.3 Software Update
A page for file uploads is provided. Browse a firmware file (extension .bin) and select it. The path and
name will be shown in the field left to the Browse button. Now click the update button.
6.4 Backup and restore
The unit set-ups can be backed up to a PC and restored later through the web browser When pressing
the Backup button a l file download dialog box appears. The default name of a backup is nvram.bin.
This name can be changed and stored on the PC in any location.
To restore the unit’s settings, browse and select the file on your PC. The selected file will be shown in
the field left to the Browse button. Now press the restore button.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
43
Page 45

6.5 LOGO and Custom Test Pattern Capture
Any image in PNG format can be selected from your PC and loaded to the unit to be used as a LOGO.
This name can be changed and stored on the PC in any location. The image size limitation is 64MB.
From the same menu you can select up-to four images and download them as custom test patterns.
These images will appear as Custom1,2,3 or 4 in the Test pattern menu
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
44
Page 46

7. Firmware Update
The latest firmware is found on Kramer’s download website at:
There are two methods of updating your unit’s firmware. First, through a USB port with a USB
memory drive and second, through TCP/IP connection with the web server.
7.1 USB update
From the firmware dropdown menu, select the
“PV7S PQV6xx_HQU7xx_LED7xx-2\xxxx.bin” file
where XXXX is the latest firmware built number.
Download the .bin file and rename it “PV7update.bin”
Copy the file to the root directory of a USB memory stick
Power Off the unit and plug the USB drive into one of the USB ports
Power On the unit and wait few seconds for the message to remove the USB drive
After the USB is removed, the unit will continue the boot-up process.
Wait until the boot up processes is completed, and the status menu appears on the front
panel screen. The Status menu indicates the detected source, Output resolution and I/O lock
state.
7.2 Web Browser update
To update via the web server, please follow the steps outlined previously in the web browser control
chapter.
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
45
Page 47

8. ENVIRONMENTAL AND EMC
8.1 Recommended Operating Conditions
Temperature 0oC to 40oC
Humidity (non-condensing) 5% to 95%
8.2 Storage
Temperature -25oC to +85oC
Humidity 0% to 95%
8.3 CE and FCC Compliance
CE: This product complies with the requirements of 2004/108/EC Electromagnetic
Compatibility Directive, and 2006/95/EC Low Voltage Directive. Compliance is to EN55022
Class A.
FCC: WARNING: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
A digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at their own expense.
The user is cautioned that changes and modifications made to the equipment without
approval of the manufacturer could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
It is suggested that the user use only shielded and grounded signal cables to ensure
compliance with FCC rules.
8.4 PAT Testing
Earth continuity testing under PAT regulations shall be done to the product with 8A or 10A only. A test
with 25A may damage the product.
Since the unit is classified as an IT equipment, according to the IEE Code of Practice, the test can also
be performed with 20-200mA. If this method is not available, and a high current test is to be used
instead, a 8A or 10A test is also acceptable (a minimum of 1.5 times of the unit’s internal 5A fuse).
You have to be careful where you connect the earth bond test lead when using 8A or 10A. Always
connect the test lead (mains earth) to the metal chassis. DO NOT CONNECT to the connectors of the
rear panel (signal earth), because you may damage the unit beyond repair.
46
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 48

Factory Defaults
HDMI-1
3GSD I-1
3GSD I-2
HDBT
Di spl ay Type
O/P Mod e
1920x1080p
4096x2160p
Fra me Rate
59.94Hz
23.98Hz ... 60Hz
I/O Lock
Off
Off
Source
Genl ock
Ge nlock Offsets
H Offset
V Offs et
Fra me Rate s
Yes
No
Ga mma/ Col or
Na tive Col or
6500K
3700K
6500K
7500K
9300K
10000K
Outp ut Gamma
2.2
1.0 ... 3.0
Outp ut Confi g
HDMI
Di spla y
HDCP
On
On Off
RGB
YPbPr
ne xt pa ge
APPENDIX A
Front Panel Menu Tree
Vol ume
In put
Outp ut
0 .. 63.5 db
2
2
Di spl ayPort
HDMI-1
HDMI-2
1
VGA
DVI
CV
RGB/YPbPr
HDMI-3
TP
LOGO
640x480p......
2
2
5500K
DVI /HDMI
DVI Forced
DVI Colo rspa ce
47
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 49
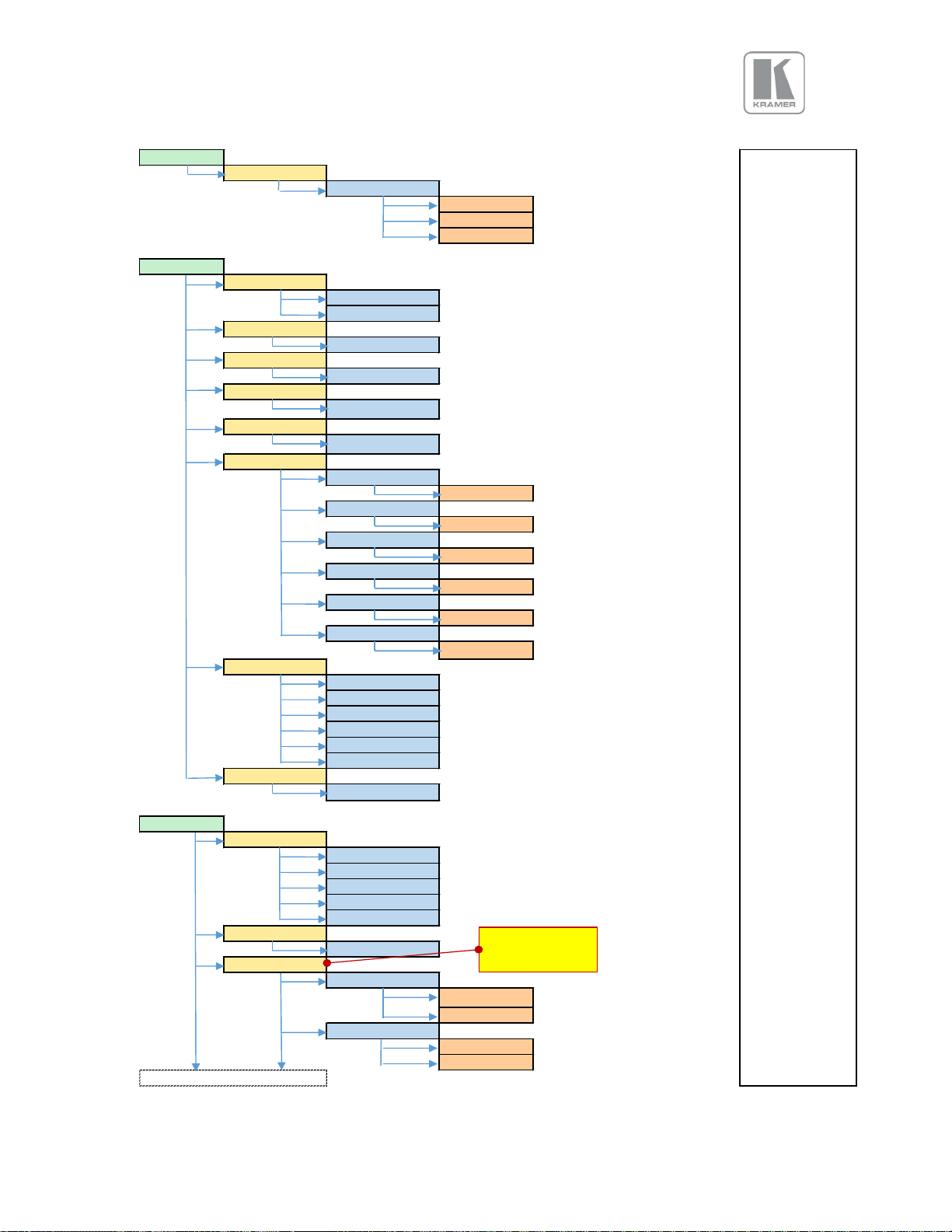
RGB
Output Config
DVI Range
Full
Full
Limi ted
Auto
BL-Offset
0 IRE
0 IRE
7.5 IRE
Bl ack-Level
0
-50 ... ... 50 s teps
Contra st
0
-50 ... ... 50 s teps
Sa turati on
0
Hue
0
RGB Va lues
Red Bi as
0
-512 ... 512
Red Ga in
0
-512 ... 512
Green Bias
0
-512 ... 512
Green Gain
0
-512 ... 512
Bl ue Bias
0
-512 ... 512
Bl ue Gain
0
Color Temp
6500K
3700K
5500K
6500K
7500K
9300K
10000K
Input Gamma
2.2
Pict. Format
Full Screen
Origina l
Full Screen
Crop
Ana morph ic
The aterscope
Overs can
0
0%.. 10%
Pan/Til t/Zoo m
PTZ Enabl e
On
PTZ Setti ng
Global
Gl oba l
Us e pe r-mode
ne xt pa ge
Output
Color
-50 ... ... 50 s teps
-50 ... ... 50 s teps
Geometry
1.0 ... 3.0
-512 ... 512
Off
Input
Channel(s)
Off
48
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 50

Pan /Til t/Zoo m
Pan
0
-50% ... 50%
Tilt0-50% ... 50%
Zoo m H
0
25% ...400%
Aspe ct Lock
On
Zoo m V
0
PTZ Res et
Auto Zoom
Off
Off
On
Uni ts Wide
1
1,2,3,4
Uni ts Hi gh
1
1,2,3,4
H-Position
0
0,1,2,3
V-Pos iti on
0
0,1,2,3
Bezel Wi dth
L(eft) Bezel
0
0 to 50 pxl s
R(i ght) Bezel
0
0 to 50 pxl s
T(op) Bezel
0
0 to 50 pxl s
B(ottom) Be zel
0
0 to 50 pxl s
Sharp nes s
0
-4 ... 4 s teps
De tails
1
0 ... 3 s teps
Us er
User 1
User 1 ... Us er 10
Name s/Profiles
Uni t Name
VIDEOPROC
In put Na mes
3GSDI-1
3GSDI-2
HDBT
ne xt pa ge
Geometry
Vide o Wa ll
Enh ance ment
Off
On
25% ...400%
Enabled when
Aspect Lock is
System
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
VIDEOPROC
2
2
Di splayPort
HDMI-1
HDMI-2
1
VGA
DVI
Manualedit
49
Page 51
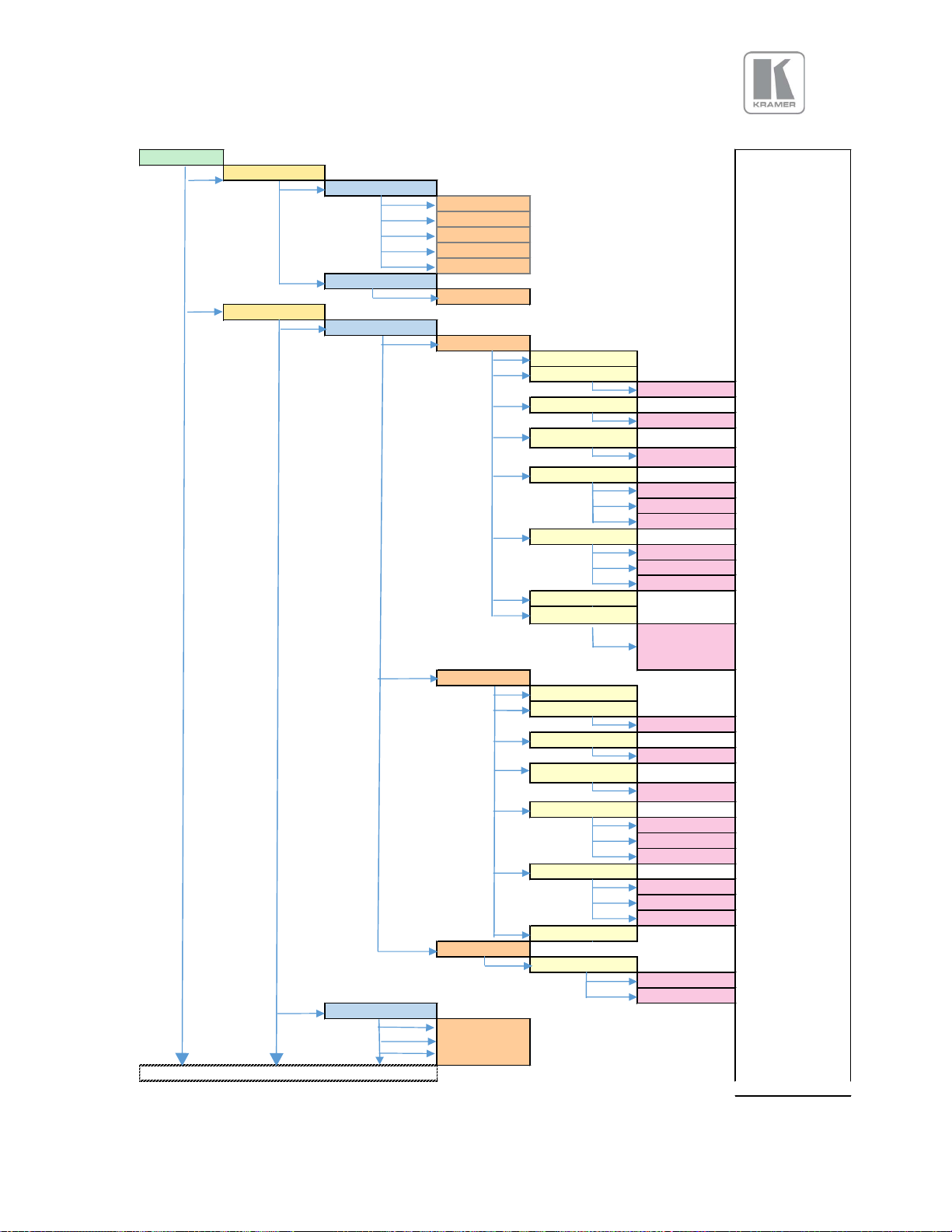
Na me s/Profiles
In put Na mes
Us er Name s
User 1 to 10
In put Con fi g
Ana log I nputs
VGA Setup
Clock
0
Pha se
0
0 ... 31 s teps
H-Position
0
0
ColorSpa ce
RGB
RGB
YCbCr
Auto
Ra nge
Full
Full
Limi ted
Auto
Res et Mode
4096x2160p60
RGB/YPbPr
Clock
0
Pha se
0
0 ... 31 s teps
H-Position
0
0
ColorSpa ce
RGB
RGB
YCbCr
Auto
Ra nge
Full
Full
Limi ted
Auto
Res et Mode
CVBS Setup
CCS
On
Off
On
Di gita l I nputs
DP Confi g
HDMI 1 Confi g
HDM 2 Config
ne xt pa ge
System
CV
RGB/YPbPr
HDMI-3
TestPatte rn
LOGO
V-Pos iti on
-3 .. +3
EDI D IN 1920x1080p/59.95
1920x1080p
23.98 ...
V-Pos iti on
0
0
0
50
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 52
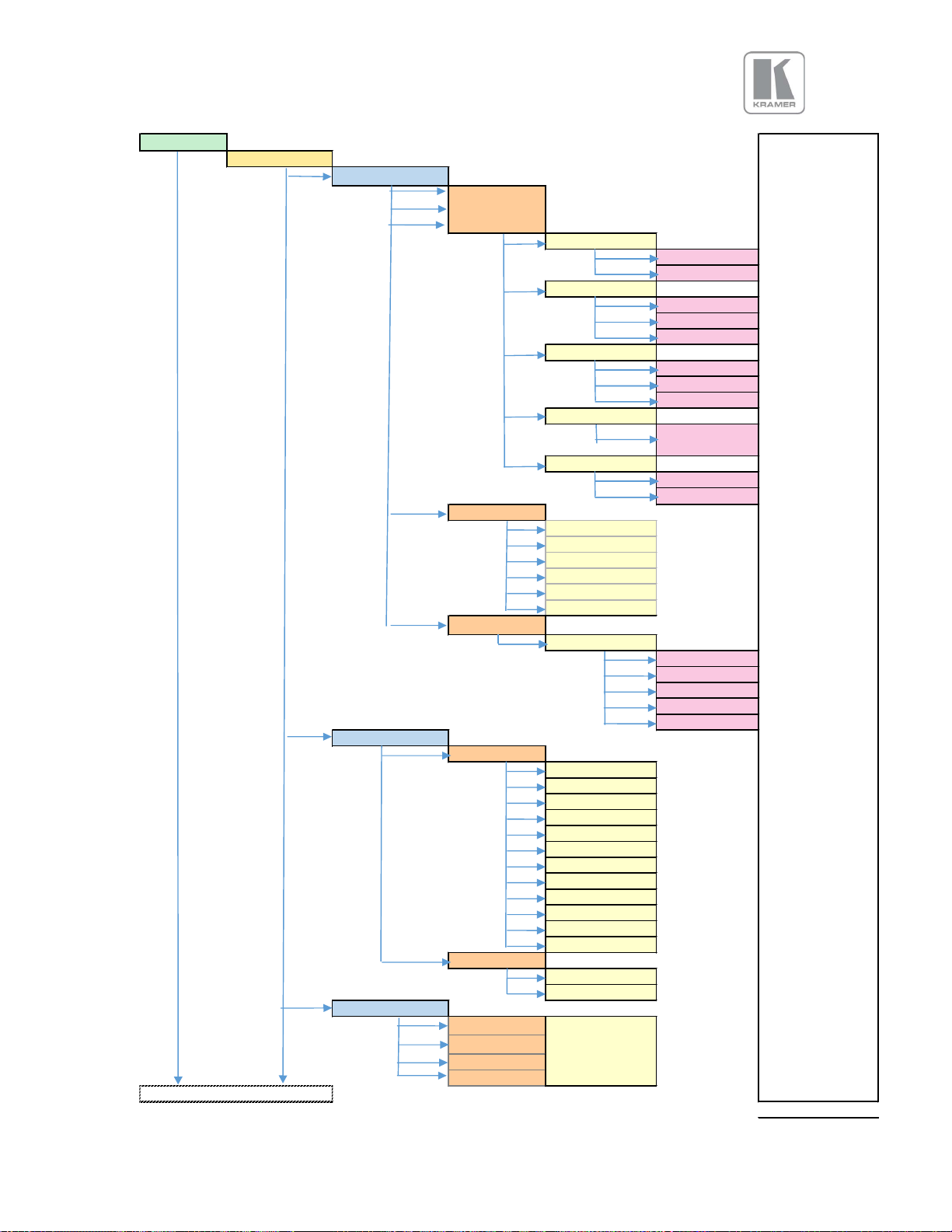
Input Confi g
HDBT Confi g1
DVI Confi g
HDMI 3 Confi g
Col orspace
RGB
RGB
YCbCr
Auto
Auto
Full
Limi ted
Auto
Auto
On
Off
1920x1080p 59.94
On
On
HDMI Au dio
Full
Full
Match Di s pla y 1
S/PDIF frie ndl y
SDI Setup
Aud io Map
Stereo ch(1,2)
Stereo ch(1,2)
Ste reo ch(3,4)
Ste reo ch(5,6)
Ste reo ch(7,8)
Mul tichannel
Test Pattern Se tup
Tes t Pat.
SMPTE
Red curta in
Gre en curtain
Bl ue curta in
Gre y V bars
Gre y H b ars
As pect Tes t
Mul ti Te st
Wa rp Adjus t
SMPTE
PLUGE
Cus tom 1-2-3-4
Logo
Tes t Tone
Off
On
Off
In put Enabl e
On
3GSDI-1
3GSDI-2
ne xt page
System
Di gita l I nputs
Ra nge
Dee p Col or
EDI D In
HDCP
Match Di s pla y 2
SDI friendly 2-ch
SDI friendly 8-ch
2
1920x1080p23.98
.. 4096x2160p60
Off
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
2
2
Di spl ayPort
HDMI-1
On / Off
51
Page 53

Input Con fig
In pu t En abl e
3GSDI-1
3GSDI-2
HDBT
Swi tching
Freeze
Freeze
Bl ank
Fa st Fad e
Sl ow Fad e
Menu Settings
Langu age
English (AE)
English (BE
De utsch
Off
All Keys
Menu Time
15 sec
5 sec
10 sec
15 sec
20 sec
25 sec
30 sec
Infi nite
LCD Ba cklight
10
0 ..10
Jog Pus h Ena ble
On
On
Off
Web Colors
Dark
Da rk
Light
Addres s Type
DHCP
DHCP
Sta tic
IP
NETGWApply
Se curi ty Se ttings
FTP Pa sswd
user
us er
ne xt pa ge
System
2
2
Di splayPort
HDMI-1
HDMI-2
1
VGA
DVI
CV
RGB/YPbPr
HDMI-3
TP
LOGO
English (AE)
On / Off
Network Se ttings
Keypa d Lock
Off
Menu Onl y
Enabled for Static
addresses; Manual entry
is required
52
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 54
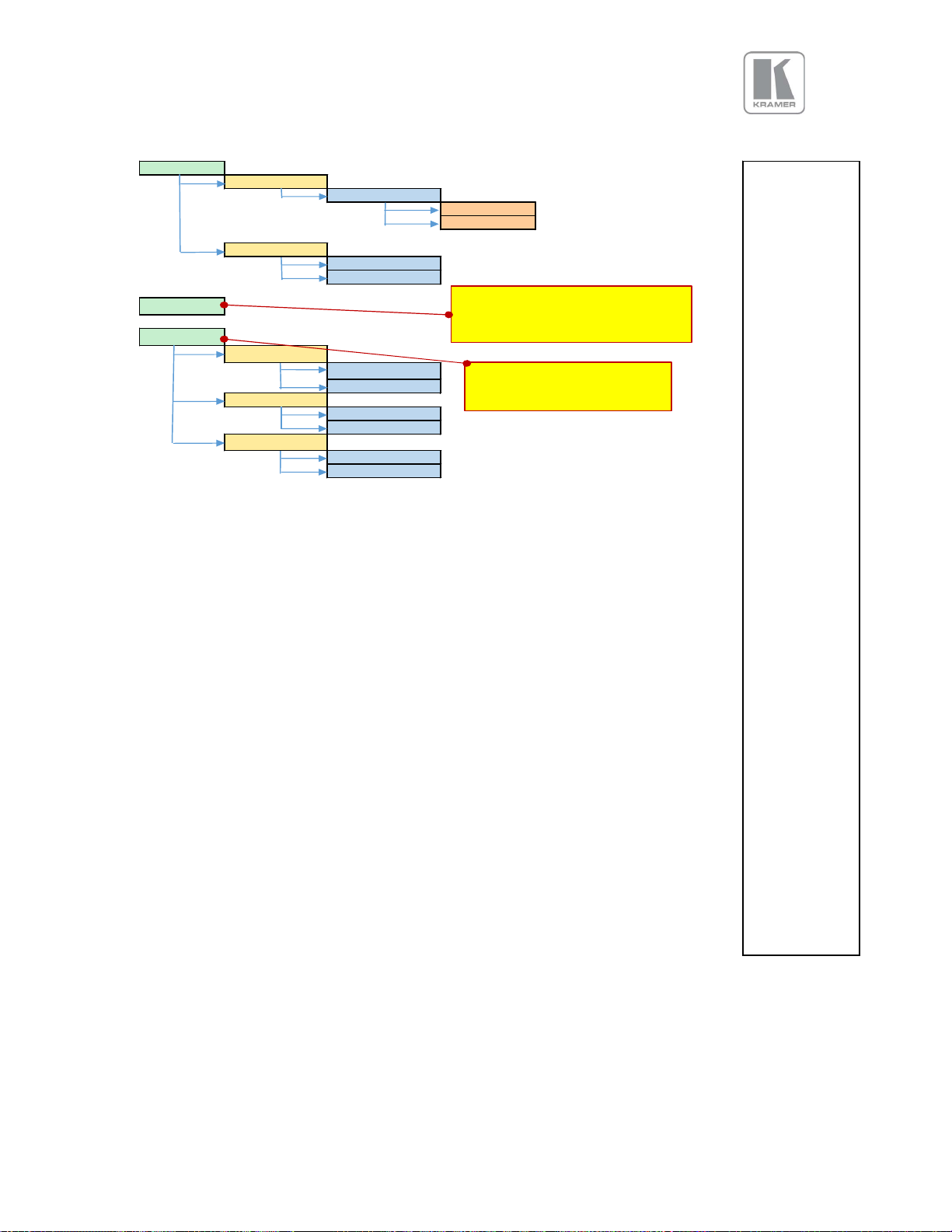
Securi ty Se ttings
WWW Pas swd
Off
On
Off
Fa ctory Defau lts
Can cel
Fa ctory Defau lts
Bi t Dep th 8,10,12
DVI
HDCP
Bi t Dep th 8,10,12
HDB T1HDCP
Bi t Dep th 8,10,12
System
Audio
Sta tus
HDMI
HDCP
A completeAudio menu is
presented in the next section
Reports on the status of
devices connected to the unit
53
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 55

Mono
Yes
Global
Digital
APPENDIX B
Volume
Input
Output
Color
Geometry
Video Wall
Enhancement
System
Audio
Front Panel Audio Menu Tree
-63.5 .. 0 db
Mic1 Level
-6.0 ... 60.0
Mic1 Mix
0 ... 100 %
Mic1 Mute
No/ Ye s
Mic2 Level `
-6.0 ... 60.0 db
Mic2 Mix
0 ... 100 %
Mic2 Mute
No/ Ye s
Balance
-100 ... 100
Treble
-15.0 ... 15.0
Bass
-15.0 ... 15.0
Audio Setup
Audio Delay
-100 ... 300 ms
Input Level
-12.0 ... 6.0 db
Input Mode
Stereo
Input Mute
Amp Gain
Audio Assign
next page
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
No
0 ... 39
Config
Per Input
Audio In
Stereo Analog
Analog with Mics
54
Page 56

Digital
Audio
Audio Setup
Audio Assign
Analog In
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
Analog Inputs
VGA Audio
Stereo Analog
Analog with Mics
Digital
VGA Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
RGB/YPbPr
Stereo Analog
Analog with Mics
next page
RGB/YPbPr Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
CVBS Audio
Stereo Analog
Analog with Mics
Digital
CVBS Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
Exit
55
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 57

Digital
Audio
Audio Setup
Audio Assign
Digital Inputs
SDI1 Audio
Stereo Analog
Analog with Mics
SDI1 Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
SDI2 Audio
Stereo Analog
Analog with Mics
Digital
SDI2 Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
DP Audio
Stereo Analog
Analog with Mics
Digital
DP Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
HDMI1 Audio
Digital
Analog with Mics
Digital
HDMI1 Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
next page
56
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 58

Digital
Audio
Audio Setup
Audio Assign
Digital Inputs
HDMI2 Audio
Stere o Analog
Analog with Mics
HDMI2 Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
HDBT Audio
Stere o Analog
Analog with Mics
Digital
HDBT Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
HDMI3 Audio
Stere o Analog
Analog with Mics
Digital
HDMI3 Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
DVI Audio
Digital
Analog with Mics
Digital
DVI Analog
CVBS
HDBaseT
Display Port
HDMI 1
HDMI 2
VGA
DVI
HDMI 3
Exit
Exit
next page
57
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 59

© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
58
Page 60

TMDS
data 2
−
Pin 5 TMDS data 4+
Pin 7 DDC data
Pin 9 TMDS data 1
− Digital green
−
Pin 11
TMDS data 1/3 shield
Pin 13
Pin 24
TMDS clock
− Digital clock
−
C2 Analog green
C4 Analog horizontal sync
APPENDIX C
Single Link DVI-U Pinout
Pin 1
Pin 2 TMDS data 2+ Digital red+
Pin 3 TMDS data 2/4 shield
Pin 4 TMDS data 4−
Pin 6 DDC clock
Pin 8 Analog vertical sync
Pin 10 TMDS data 1+ Digital green+
Pin 12
Pin 14 +5 V Power for monitor when in standby
Pin 15 Ground Return for pin 14 and analog sync
Pin 16 Hot plug detect
Pin 17 TMDS data 0− Digital blue and digital sync
Pin 18 TMDS data 0+ Digital blue+ and digital sync
Pin 19 TMDS data 0/5 shield
Pin 20
Pin 21
Pin 22 TMDS clock shield
Pin 23 TMDS clock+ Digital clock+
Digital red−
C1 Analog red
C3 Analog blue
C5 Analog ground Return for R, G, and B signals
59
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
Page 61
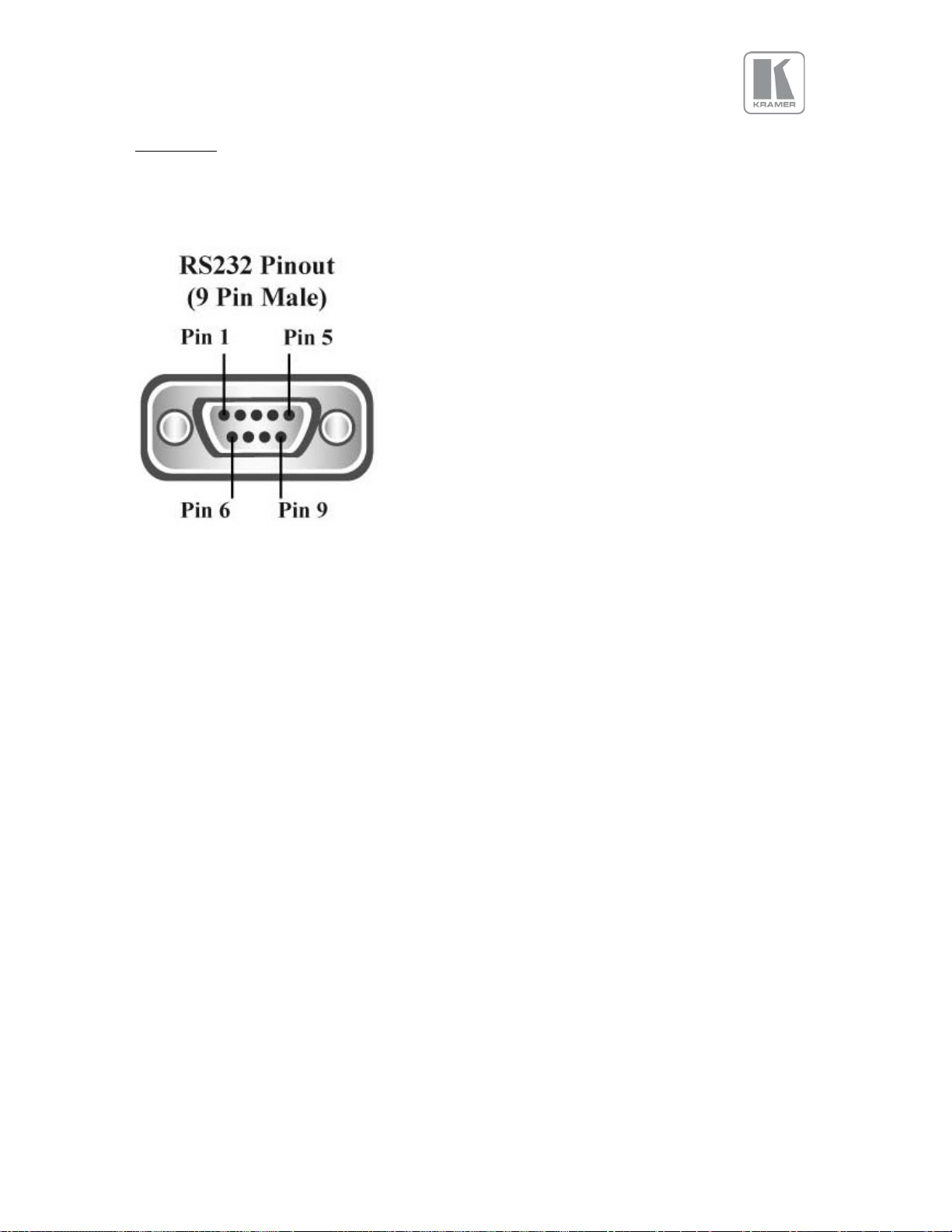
APPENDIX D
RS-232 Pinout
Pin 2 Received Data
Pin 3 Transmit Data
Pin 5 Signal Ground
© KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD. Issue 1-13 July 28, 2016
60
 Loading...
Loading...