Page 1

KRAMER ELECT RONICS LTD.
USER MANUAL
MODEL:
SID
Step
P/N: 2900-300302 Rev 5
-X1N
-in Co mmander
Page 2
Page 3

Page 4

Contents
1 Introduction 1
2 Getting Started 2
2.1 Achieving the Best Performance 2
2.2 Safety Instruc ti o ns 2
2.3 About the Power Connect Plus™ Feature 3
2.4 Shielded Twisted Pair/Unshielded Twisted Pair 3
2.5 Recycling Kramer Products 3
3 Overview 4
4 Defining the SID-X1N Step-in Commander 6
5 Connecting the SID-X1N 8
5.1 Connecting the Remote Step-In Switch and LED 9
5.2 Connecting the Remote Select Switch and LED 10
5.3 Connecting the Remote Input Selection LEDs 11
6 Principles of Operation 12
6.1 Video Input Selection 12
6.2 Audio Signal Control 13
6.3 Automatic Output Shutdown 13
7 Operating the SID-X1N 14
7.1 Manually Selecting an Input 14
7.2 Taking Control of the Switcher Input 15
7.3 Locking the EDID 15
7.4 Adjusting the UXGA Input Phase 15
8 Configuring and Maintaining the SID-X1N 16
8.1 Setting the Configuration DIP-switch 16
9 Wiring t he Twisted Pair RJ-45 Connectors 18
10 Technical Specifications 19
10.1 Supported Resolutions 20
11 Default EDID 22
11.1 HDMI, DisplayPort and DVI 22
11.2 PC-UXGA 24
12 Remote Commands 26
12.1 Kramer Protocol 2000 Syntax 26
12.2 Kramer Protocol 2000 Instruction Codes 27
12.3 RS-232 Hardware Interface 28
Figures
Figure 1: SID-X1N Step-in Commander Front Panel 6
Figure 2: SID-X1N Step-in Commander Rear Panel 7
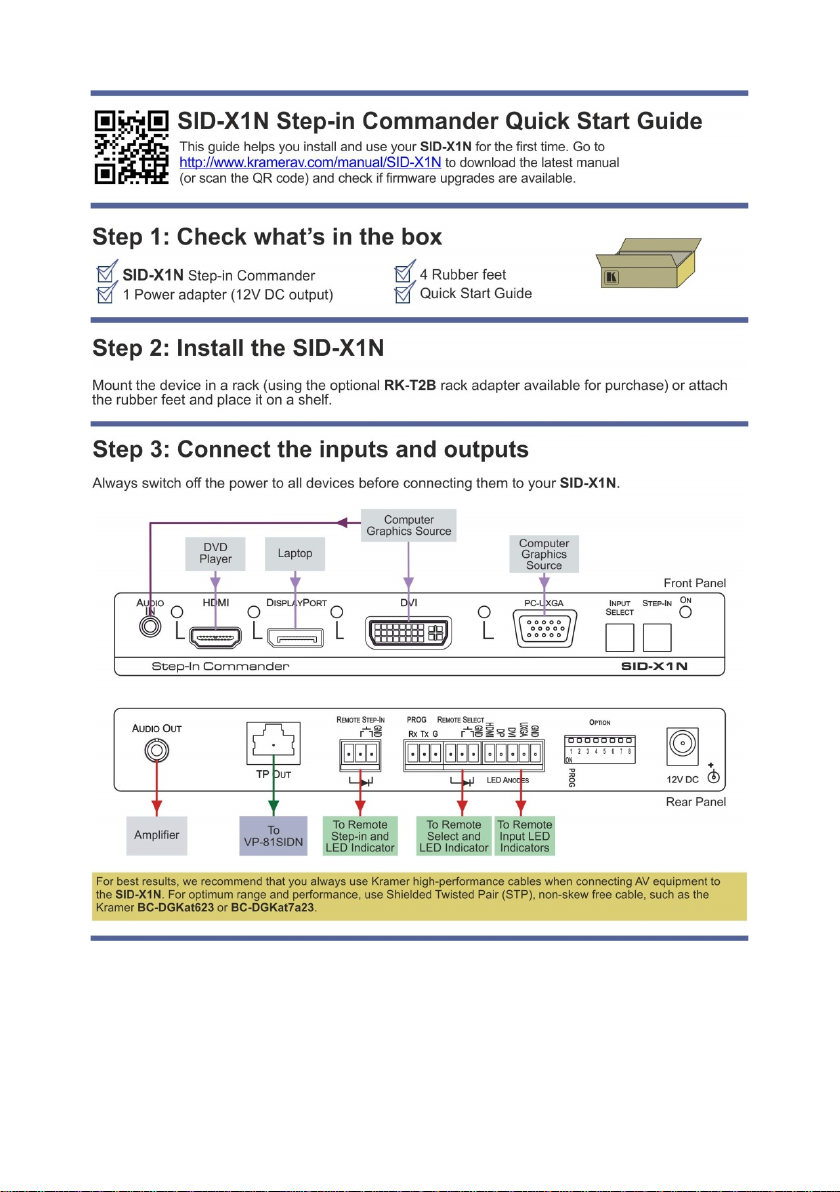
Figure 3: Connecting the SID-X1N Step-in Commander 8
Figure 4: Remote Step-In Switch and LED Wiring 9
Figure 5: Remote Select Switch and LED Wiring 10
Figure 6: Remote Input Indicator LED Connections 11
Figure 7: Remote Input Indicator LED Wiring 11
Figure 8: The Configuration DIP-switch 16
Figure 9: TP Pinout Wiring 18
SID-X1N – Contents i
Page 5

1 Introduction
Welcome to Kramer Electronics! Since 1981, Kramer Electronics has been
providing a world of unique, creative, and affordable solutions to the vast range of
problems that confront video, audio, presentation, and broadcasting professionals
on a daily basis. In recent years, we have redesigned and upgraded most of our
line, making the best even better!
Our 1,000-plus different models now appear in 14 groups that are clearly defined
by function: GROUP 1: Distribution Amplifiers; GROUP 2: Switchers and Routers;
GROUP 3: Control Systems; GROUP 4: Format/Standards Converters; GROUP 5:
Range Extenders and Repeaters; GROUP 6: Specialty AV Products; GROUP 7:
Scan Converters and Scalers; GROUP 8: Cables and Connectors; GROUP 9:
Room Connectivity; GROUP 10: Accessories and Rack Adapters and GROUP 11:
Sierra Video Products; GROUP 12: Digital Signage; and GROUP 13: Audio, and
GROUP 14: Collaboration.
Thank you for purchasing the Kramer MegaTOOLS
®
SID-X1N Step-in
Commander which is ideal for:
• Display systems requiring simple input selection
• Remote monitoring of computer activity in schools and businesses
• Rental/staging applications
• Multimedia and presentation source selection
SID-X1N - Introduction 1
Page 6
Caution:
There are no operator serviceable parts inside the unit
i
!
!
2 Getting Started
We recommend that you:
• Unpack the equipment carefully and save the original box and packaging
materials for possible future shipment
• Review the contents of this user manual
Go to www.kramerav.com/downloads/SID-X1N t o check for up-to-date
user manuals, application programs, and to check if firmware upgrades are
available (where appropriate).
2.1 Achieving the Best Performance
To achieve the best performance:
• Use only good quality connection cables (we recommend Kramer high-
resolution, high-quality cables) t o avoid interferenc e, det eri orat i on in signal
quality due to poor matching, and elevated noise levels (often associated
with low quality cables)
• Do not secure the cables in tight bundles or roll the slack into tight coils
• Avoid interference from neighboring electrical appliances that may adversely
influence signal quality
• Position your Kramer SID-X1N away from moisture, excessive sunlight and
dust
This equipment is to be used only inside a building. It may only be
connected to other equipment that is installed inside a building.
2.2 Safety Instructions
Warning:
Warning:
2 SID-X1N - Getting Started
Use only the Kramer Electronics input power wall
adapter that is provided with the unit
Disconnect the power and unplug the unit from the wall
before installing
Page 7

2.3 About the Power Connect Plus™ Feature
The Power Connect Plus™ feature means that only the SID-X1N needs to be
connected to a power source when the SID-X1N and receiver are within 60m
(197ft) of each other. The Power Connect Plus™ feature applies as long as the
cable can carry power and the distance does not exceed 60m on standard TP
cable. (Heavier gauge cable may be used to extend the Power Connect Plus™
range).
2.4 Shielded Twisted Pair/Unshielded Twisted Pair
Kramer engineers have developed special twisted pair cables to best match our
digital twisted pair products; the Kramer BC-DGKat623 (CAT 6 23 AWG cable),
and the Kramer BC-DGKat7a23 (CAT 7a 23 AWG cable). These specially built
cables significantly outperform regular CAT 6 and CAT 7a cables.
2.5 Recycling Kramer Products
The Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive 2002/96/EC
aims to reduce the amount of WEEE sent for disposal to landfill or incineration by
requiring it to be collected and recycled. To comply with the WEEE Directive,
Kramer Electronics has made arrangements with the European Advanced
Recycling Network (EARN) and will cover any costs of treatment, recycling and
recovery of waste Kramer Electronics branded equipment on arrival at the EARN
facility. For details of Kramer’s recycling arrangements in your particular country
go to our recycling pages at www.kramerav.com/support/recycling/.
SID-X1N - Getting Started 3
Page 8

3 Overview
The SID-X1N accepts an HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI and PC graphics video input, as
well as an unbalanced stereo audio input (which is embedded into the output
signal), and transmits the signal via TP (Twisted Pair) cable to a compatible
switcher or DGKat receiver, (for example, the VP-81SIDN or PT-572+).
The SID-X1N also provides an unbalanced, stereo audio output. When the
SID-X1N is connected to a switcher, it also controls the input and output selection
of the switcher.
In particular the SID-X1N: features:
• HDTV support
• HDMI with x.v.Color™ and 3D
• HDCP compliancy—works with sources that support HDCP repeater mode
Note: When using a MacBook as a source and the content is protected
using HDCP, if the display does not support HDCP, no video is transmitted
• Input signal detection based on video clock presence
• Automatic input selection based on manual selection or last connected input
• Automatic analog audio detection and embedding
• Automatic output shutdown when the input signal is lost (with a configurable
delay)
• Installation up to 50m (164ft) from the switcher, (30m with the TP-574)
• I-EDIDPro™ Kramer Intelligent EDID Processing™ – Intelligent EDID
handling & processing algorithm ensures Plug and Play operation for HDMI
systems
• A lockable EDID
• VGA phase adjustment
4 SID-X1N - Overview
Page 9

• PowerConnectPlus – A single connection to the receiver powers both units.
The higher voltage PowerConnectPlus also powers regular PowerConnect
devices via auto-negotiation
• Equalization and reclocking of the data
• A maximum data rate of 4.95Gbps (1.65Gb per graphics channel)
• Support for digital audio formats
• A MegaTOOLS
®
sized enclosure. Two devices can be mounted in a rack
using the optional RK-T2B adapter
You can control the SID-X1N using the front panel buttons or remotely via contact
closure switches.
SID-X1N - Overview 5
Page 10

#
Feature
Function
2
LED
Lights green when the HDMI input is selected
3
HDMI Connector
Connect to an HDMI source
4
LED
Lights green when the DisplayPort input is selected
5
DP Connector
Connect to a DisplayPort so urc e
7
DVI Connector
Connect to a DVI source
8
LED
Lights green when the PC-UXGA input is selected
9
PC-UXGA
Connector (F)
Connect to a PC graphics sour ce
10
INPUT SELECT Button
Press repeatedly to cycle through the inputs manually to
button will not activate the input
11
STEP-IN Button
Press to activate the input on the switcher that the
SID-X1N is connected to, (see Section 7.2)
12
ON LED
Lights green when the device is powered on
4 Defining the SID-X1N Step-in Commander
Figure 1 defines the front panel of the SID-X1N.
Figure 1: SID-X1N Step-in Commander Front Panel
1 AUDIO IN 3.5mm Mini Jack Conn ect to an unbalanced stereo audi o source
HDMI
DisplayPort
6
DVI
LED Lights green when the DVI input is selected
PC-UXGA
15-pin HD
6 SID-X1N - Defining the SID-X1N Step-in C om m a n der
select an input, (overrides automatic selection, see
Section
7.1).
Note: When the button is lit it is inactive and pressing the
Page 11
#
Feature
Function
Section 4)
specification cable
3
Block
LED
Connect to the anode of the remot e St e p-In LED indicator
4
Switch
Connect to the remote, Step-In switch, (see Section 5.1)
5
RS-232 3-pin Terminal
Block
Connect to the PC via RS-232 to perform a firmware upgrade
6
LED
Connect to the anode of the remot e Inp ut Sel ec t LED indicator,
(see Section 4)
7
Switch
Connect to the remote, Input Select switch, (see Section 5.2)
9
OPTION 8x DIP-switch
Sets the device behavio r, (se e Section 8.1)
10
12V DC Power Connector
Connect to the supplied power adapter, center pin positive
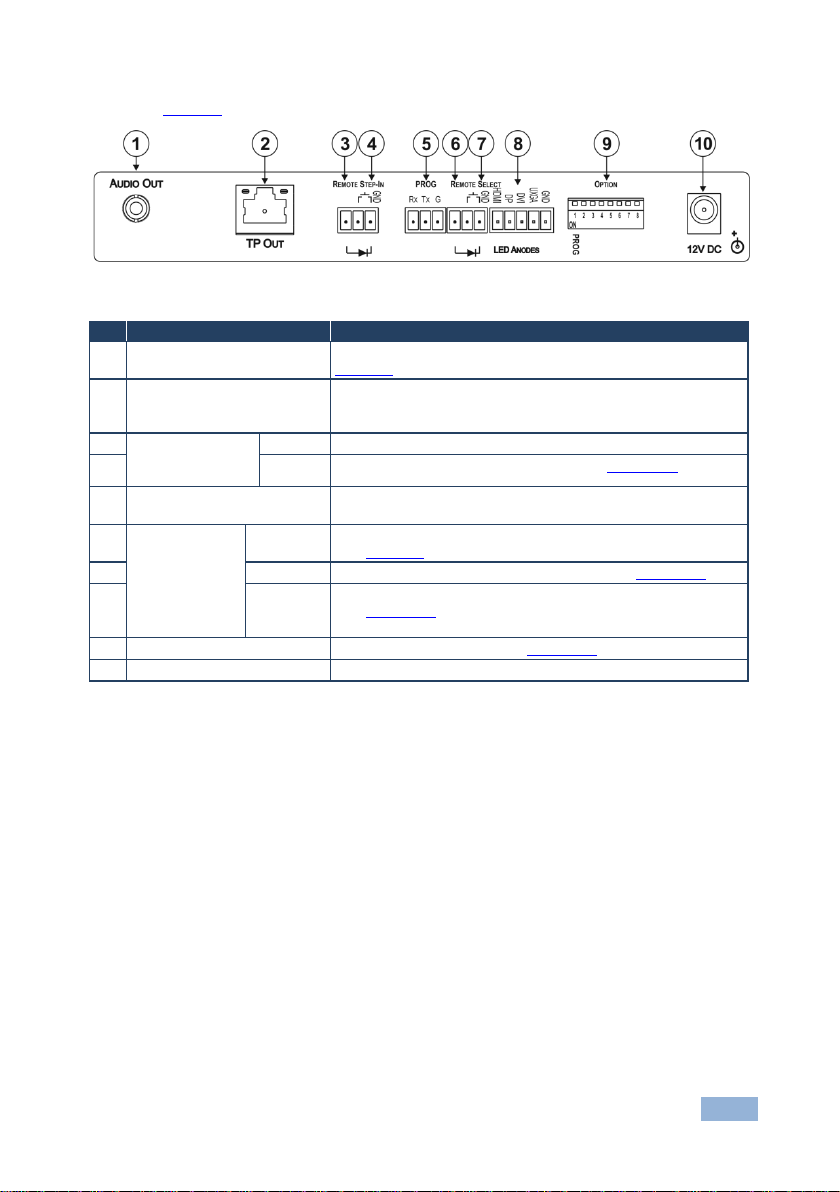
Figure 2 defines the rear panel of the SID-X1N.
Figure 2: SID-X1N Step-in Commander Rear Panel
1 AUDIO OUT 3.5mm Mini Jack Connect to an unbalanced, stereo audio acceptor, (see
2 TP OUT RJ-45 Connector Connect to a compatible switcher or DGKat receiver, (for
REMOTE STEP-IN
3-pin Terminal
PROG
REMOTE
SELECT 8-pin
8 LED HDMI,
Terminal Block
DP, DVI
and UXGA
example, VP-81SIDN or PT-572+) using CAT 6 or higher
Connect to the anodes of the remote input indicators
(see Section 5.3
)
SID-X1N - Defining the SID-X1N Step-in Com m ander 7
Page 12

i
5 Connecting the SID-X1N
Switch off the power to all devices before connecting them to your
SID-X1N. After connecting your SID-X1N connect the power to other
devices.
Figure 3: Connecting the SID-X1N Step-in Commander
To connect the SID-X1N as illustrated in Figure 3:
1. Connect up to four video sources, (for example, a Blu-ray disc player, a
laptop and two computer graphics sources) to the video input connectors.
8 SID-X1N - Connecting the SID-X1N
Page 13

2. Connect the unbalanced stereo audio source, (for example, the audio output
from the laptop) to the AUDIO IN 3.5mm m ini jack.
3. Connect the AUDIO OUT 3.5mm mini jack to the unbalanced, stereo audio
acceptor, (for example, a power amplifier with speakers).
4. Connect the TP OUT RJ-45 connector to a compatible switcher, (for
example, VP-81SIDN).
5. Connect the REMOTE STEP-IN 3-way terminal block to a contact-closure
switch and LED (see Section 5.1
).
6. Connect the REMOTE SELECT 3-way terminal block to a momentary
contact-closure switch and LEDs (see Section 5.2
).
7. Connect the LED ANODES 5-way terminal block to the remote input
indicator LEDs (see Section 5.3
).
8. Connect the power adapter to the SID-X1N and to the mains power.
Note: All LED supplies include a current limiting resistor and are designed to work
with any standard LED.
5.1 Connecting the Remote Step-In Switch and LED
You can connect a remote, contact closure step-in switch to take control of the
input of the attached switcher, as well as a remote step-in LED to the REMOTE
STEP-IN terminal block on the rear panel of the SID-X1N.
Figure 4
illustrates the connections from the terminal block to the switch and LED.
Figure 4: Remote Step-In Switch and LED Wiring
SID-X1N - Connecting the SID-X1N 9
Page 14

To connect a remote step-in switch and LED as illustrated in the example in
Figure 4
:
1. Connect pins 2 and 3 from the terminal block to the remote step-in switch.
2. Connect pin 1 from the terminal block to the anode of the remote step-in
LED.
3. Connect pin 3 from the terminal block to the cathode of the remote step-in
LED.
5.2 Connecting the Remote Select Switch and LED
You can connect a remote, contact closure, input selection switch to activate an
input (momentary contact is sufficient to switch inputs), as well as an indicator
LED to the terminal block on the rear panel of the SID-X1N.
Figure 5
illustrates the connections from the terminal block to the switch and LED.
Figure 5: Remote Select Switch and LED Wiring
To connect a remote selection switch and LED as illustrated in the example
in Figure 5
1. Connect pins 2 and 3 from the terminal block to the remote selec t ion switch.
2. Connect pin 1 from the terminal block to the anode of the remote selection
3. Connect pin 3 from the terminal block to the cathode of the remote selection
10 SID-X1N - Connecting the SID-X1N
:
LED.
LED.
Page 15

5.3 Connecting the Remote Input Selection LEDs
You can connect remote, input selection LEDS to the LED terminal block on the
rear panel of the SID-X1N to indicate which is the active input.
Figure 6
illustrates the connections from the terminal block to the LEDs.
Figure 6: Remote Input Indicator LED Connections
To connect remote input indicator LEDs:
1. Connect pin 1 from the terminal block to the anode of the remote HDMI
indicator LED.
2. Connect pin 2 from the terminal block to the anode of the remote DP
indicator LED.
3. Connect pin 3 from the terminal block to the anode of the remote DVI
indicator LED (see the example in Figure 7
4. Connect pin 4 from the terminal block to the anode of the remote UXGA
indicator LED.
5. Connect pin 5 from the terminal block to the cathode of each LED.
).
Figure 7: Remote Input Indicator LED W iring
SID-X1N - Connecting the SID-X1N 11
Page 16

6 Principles of Operation
This chapter describes the principles of operation of the SID-X1N and comprises:
• Video input selection (see Section 6.1
• Audio signal control (see Section 6.2)
The SID-X1N selects video and audio inputs based on the rules described below.
6.1 Video Input Selection
The video mode selection is set by the DIP-switches (see Section 8.1) to either of
the following:
• Manual
• Last connected
In manual mode the input is selected using the front panel buttons. Only inputs
with a live signal present can be selected.
In last connected mode the SID-X1N selects the input based on which input was
connected last. If the signal on this input is subsequently lost for any reason, the
input with a live signal with the highest priority is automatically selected. The
priority from highest to lowest is:
• HDMI
• DisplayPort
)
• DVI
• PC
Note: In last connected mode, manually selecting an input using the front panel
Input Select button overrides the last-connected automatic selection.
When an input cable is removed, there is a delay of either 0.5 or 3 seconds,
(selectable, see Section 8.1
another input can be automatically selected according to the signal priority shown
above.
12 SID-X1N - Princi ples of Operation
) before automatic switching takes place. After that,
Page 17

DIP-switch
2
DIP-switch
3
3.5mm Mini Jack
Input
Audio on Output
On/Off
On/Off
On/Off
VGA
3.5mm mini jack
Off
On/Off
Inserted
HDMI/DP/DVI
3.5mm mini jack
Not inserted
Embedded HDMI/DP/DVI
On
On/Off
Inserted/Not inserted
HDMI/DP
Embedded HDMI/DP
On
Off
Inserted/Not inserted
DVI
Embedded DVI
On
On
Inserted/Not inserted
3.5mm mini jack
6.2 Audio Signal Control
The Option DIP-switches 2 and 3 (see Section 8.1) control the manner in which
audio is handled.
The following table describes which audio signal is embedded in the output.
6.3 Automatic Output Shutdown
The SID-X1N can disable the output (signal and 5V) when there is no signal for a
specified period in:
• Manual mode—when the signal on the currently selected input is lost
• Automatic mode—when there is no signal on any of the inputs
SID-X1N - Principle s of Oper at io n 13
The delay period is set by the DIP-switch, (see Section 8.1
). At the end of this
period, both the output signal and the power supply to other devices (via
PowerConnect) are disabled.
The return of an input signal on either the currently s elected input (in manual
mode), or on any input (in automatic mode), immediately re-activates the output
and turns on PowerConnect.
Page 18

7 Operating the SID-X1N
This chapter describes the operating procedures of the SID-X1N and comprises:
• Manually selecting an input (see Section 7.1
• Taking control of the switcher input (see Section 7.2)
• Locking the EDID (see Section 7.3)
Powering up the SID-X1N recalls from the non-volatile memory the last settings
that were in force when the device was powered down.
The SID-X1N inputs can be selected remotely via the VP-81SIDN. For details on
how to do so, see the VP-81SIDN User Manual.
7.1 Manually Selecting an Input
Note: When the button is lit it is inactive and pressing the button will not activate
the input.
To manually select an input:
• Press the INPUT SELECT button repeatedly until the required input is active
as indicated by the associated LED.
Note: Only inputs that have an active signal can be selected.
Note: The manual selection overrides any input selection when in last connected
mode and remains in effect until the device is power cycled.
)
14 SID-X1N - Operating the SID-X1N
Page 19

7.2 Taking Control of the Switcher Input
To activate the input of the switcher to which the SID-X1N is connected, press the
STEP-IN button. If the switcher grants the SID-X1N access to the input, the STEPIN button lights. If the switcher does not grant access for some reason, the button
flashes for a few seconds and then does not light. One reason for this may be that
the switcher input connected to the SID-X1N has been set to have a lower priority
than the currently active input.
Note: Input priority on the switcher is set using the Kramer Control Software.
7.3 Locking the EDID
The currently stored EDID can be locked to prevent it from being overwritten. To
lock the current EDID, set DIP-switch 5 to ON (see Section 8.1
Note: The device must be power-cycled after you change this DIP-switch.
7.4 Adjusting the UXGA Input Phase
Adjust the phase to get a clean, sharp picture on the screen, with minimal
horizontal streaking and shimmering.
).
To adjust the UXGA input phase:
• Press and hold the Input Select button to increase the phase repetitively by
one degree per second
• Press and hold the Step-In button to decrease the phase repetitively by one
degree per second
SID-X1N - Operating the SID-X1N 15
Page 20

#
Feature
Function
DIP-switch
Off—Disable updating
audio signals
or manual, (see Section 6.1)
Off—Automatic EDID selection
8 Configuring and Maintaining the SID-X1N
8.1 Setting the Configuration DIP-switch
The 8x dip-switch provides the ability to configure a number of device functions. A
switch that is down is on, a switch that is up is off. By default, switch 2 is down
(on), all the other switches are up (off).
Figure 8: The Configuration DIP-switch
Note: You must power cycle the device if you make any changes to the
DIP-switch.
1 Program Enables firmware updates On—Enable updating
2 General audio
control
3 DVI audio c on tr ol
(active only when
DIP-switch 2 is
on)
4 Video mode input
selection
5 Lock EDID Locks the current EDID, (see
16 SID-X1N - Configuring and Maintaining the SID-X1N
Selects whether the analog
audio is embedded in the
outputs, (see Section 6.2
Selects whether the analog
audio is embedded in the DVI
signal
Sets the video input selection
mode to either last connected
Section 7.3
)
)
On—Use embedded audio for
HDMI and DP; the audio selection
for DVI is selected by DIP-swi t c h 3
Off—The HDMI, DVI and DP inputs
use the analog audio signal if a
3.5mm audio jack is inserted into
the analog audio input. If no jack is
inserted, they use their embedded
On—When switch #2 is on, the
analog audio signal is used wit h the
DVI input
Off—When switch #2 is off, the
embedded audio signal is used in
the DVI input
On—Last connected
Off—Manual
On—Locked EDID
Page 21

#
Feature
Function
DIP-switch
6
Switching delay
Selects the time delay before
When the input signal is lost but the
Off—10 seconds
When the cable is removed:
Off—3 seconds
7
Output disable
Sets the delay time between
shutdown
On—1 minute
8
Output Power
Enables/disables the output
On—Power is always on
switch 7
delay
Control
switching occurs when an
input signal is lost.
Note: The delay is
independent of the input
switching mode
loss of the input signal and
output/PowerConnect
power when the input signal is
lost
cable is not removed:
On—0.5 seconds
On—0.5 seconds
Off—15 minutes
Off—Power is disabled when input
signal is lost after delay set by DIP-
Note: DIP-switch 2 must be set to ON to enable DIP-switch 3 to control the DVI
audio mode selection.
SID-X1N - Configuring and Maintaining the SID-X1N 17
Page 22

PIN
Wire Color
1
Orange / White
2
Orange
3
Green / White
4
Blue 5 Blue / White
6
Green
7
Brown / White
8
Brown
Pair 1
4 and 5
Pair 2
1 and 2
Pair 3
3 and 6
!
9 Wiring the Twisted Pair RJ-45 Connec t ors
When using STP cable, connect/solder the cable shield to the RJ-45 connector
shield. Figure 9
connectors
EIA /TIA 568B
defines the TP pinout using a straight pin-to-pin cable with RJ-45
Figure 9: TP Pinout Wiring
Warning:
18 SID-X1N - Wiring the Twisted Pair RJ-45 Connectors
Using a TP cable that is incorrectly wired will cause
permanent damage to the device
Page 23

1 VGA on a 15-pin HD (F) connector
Audio:
1 Unbalanced stereo audio on a 3.5mm mini jack
OUTPUTS:
1 TP on an RJ-45
1 Unbalanced stereo audio in a 3.5mm mini jack
ANALOG AUDIO
INPUT:
Maximum level—3Vpp
REMOTE LED
IMPEDANCE:
5V, 300Ω approx.
HDCP: Works with sources that support HDCP repeater mode
MAXIMUM DATA
RATE:
4.95Gbps (1.65Gb per grap hi cs c ha nn el)
POWER
CONSUMPTION:
12V DC, 1.1A
STANDARDS:
OPERATING
TEMPERATURE:
0° to +40°C (32° to 104°F)
TEMPERATURE:
COOLING:
Convection, vents
ENCLOSURE TYPE:
Aluminium
mountable
WEIGHT:
0.48kg (1.1lbs) approx.
INCLUDED
ACCESSORIES:
Power adapter
the color of the modular TBUS-10xl)
Specifications are subject to change without notice
For the most updated resolution list, go to our Web site at www.kramerav.com
10 Technical Specifications
INPUTS: Video:
PORTS: 1 RS-232 3-pin terminal block for programming
CONTROLS: Front panel buttons, remote step-in switch, remote input
STANDARDS: HDMI with x.v.Color™ and 3D
MAXIMUM STEP-IN
DISTANCE:
COMPLIANCE
STORAGE
HUMIDITY: 10% to 90%, RHL non-condensing
selection switches, RS-232
50m (164ft) up to 1080p @60Hz @24bpp
CE, UL
–40° to +70°C (–40° to 158°F)
1 HDMI on an HDMI connector
1 DP on a DisplayPort connector
1 DVI-D on a DVI-I connector
DIMENSIONS: 18.8cm x 11.3cm x 2.5cm (7.4” x 4.5” x 1”) W, D, H rack-
OPTIONS: 19“ Rack adapter RK-T2B, RTBUS-12, RTBUS-22, SID-X1NBP
Kit (substitute black top plate for the SID-X1N to blend in with
SID-X1N - Technical Specifications 19
Page 24

Resolution
Refresh Rate
640 x 480p
85Hz; 75Hz; 72Hz; 60H z; 59.95Hz
720 x 480i
30Hz
720 x 480p
60Hz
720 x 576p
50Hz
848 x 480p
60Hz
852 x 480p
60Hz
800 x 600p
85Hz; 75Hz; 72Hz; 60Hz
1024 x 768p
85Hz; 75Hz; 70Hz; 60Hz
1152 x 864p
75Hz
1280 x 768p
60Hz
1280 x 800p
60Hz
1360 x 768p
60Hz
1366 x 768
60Hz; 50Hz
1280 x 960
60Hz
1280 x 1024p
75Hz; 60Hz
1440 x 900p
60Hz
1400 x 1050p
60Hz
1600 x 900p
60Hz
1680 x 1050p
60Hz
1600 x 1200p
60Hz
1080 x 1920p
50Hz; 60Hz; 24Hz;
1080 x 1920i
50Hz; 60Hz;
Resolution
Refresh Rate
640 x 480p
85Hz; 75Hz; 72Hz; 60Hz
848 x 480p
60Hz
800 x 600p
85Hz; 75Hz; 72Hz; 60Hz
1024 x 768p
85Hz; 75Hz; 70Hz; 60Hz
1152 x 864p
75Hz
1280 x 768p
60Hz
1280 x 800p
60Hz
1360 x 768p
60Hz
1366 x 768
60Hz;
1280 x 960
60Hz
1280 x 1024p
75Hz; 60Hz
1440 x 900p
60Hz
1400 x 1050
60Hz
1600 x 900p
60Hz
1680 x 1050p
60Hz
1600 x 1200p
60Hz
1080 x 1920i
60Hz;
10.1 Supported Resolutions
HDMI/DVI
20 SID-X1N - Technical Specifications
DisplayPort
Page 25

Resolution
Refresh Rate
640 x 480p
60Hz
720 x 480p
60Hz
800 x 600p
60Hz
1024 x 768p
60Hz
1280 x 720p
60Hz; 50Hz
1152 x 864
75Hz
1360 x 768
60Hz;
1366 x 768
60Hz; 50Hz
1280 x 960p
60Hz
1280 x 1024p
60Hz
1440 x 900
60Hz
1400 x 1050
60Hz
1920 x 1080p
60Hz
1920 x 1200
60Hz; 50Hz
VGA
SID-X1N - Technical Specifications 21
Page 26

11 Default EDID
Each input on the SID-X1N is loaded with a factory default EDID.
Note: When the SID-X1N is connected to a DVI acceptor, an audio block is added
to the EDID.
11.1 HDMI, DisplayPort and DVI
Monitor
Model name............... SID-X1N
Manufacturer............. KMR
Plug and Play ID......... KMR0672
Serial number............ 505-709990100
Manufacture date......... 2011, ISO week 255
Filter driver............ None
-------------------------
EDID revision............ 1.3
Input signal type........ Digital
Color bit depth.......... Undefined
Display type............. RGB color
Screen size.............. 520 x 320 mm (24.0 in)
Power management......... Standby, Suspend, Active off/sleep
Extension blocs.......... 1 (CEA-EXT)
-------------------------
DDC/CI................... n/a
Color characteristics
Default color space...... Non-sRGB
Display gamma............ 2.20
Red chromaticity......... Rx 0.674 - Ry 0.319
Green chromaticity....... Gx 0.188 - Gy 0.706
Blue chromaticity........ Bx 0.148 - By 0.064
White point (default).... Wx 0.313 - Wy 0.329
Additional descriptors... None
Timing characteristics
Horizontal scan range.... 30-83kHz
Vertical scan range...... 56-76Hz
Video bandwidth.......... 170MHz
CVT standard............. Not supported
GTF standard............. Not supported
Additional descriptors... None
Preferred timing......... Yes
Native/preferred timing.. 1280x720p at 60Hz (16:10)
Modeline............... "1280x720" 74.250 1280 1390 1430 1650 720 725 730 750 +hsync +vsync
Standard timings supported
720 x 400p at 70Hz - IBM VGA
720 x 400p at 88Hz - IBM XGA2
640 x 480p at 60Hz - IBM VGA
640 x 480p at 67Hz - Apple Mac II
640 x 480p at 72Hz - VESA
640 x 480p at 75Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 56Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 60Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 72Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 75Hz - VESA
832 x 624p at 75Hz - Apple Mac II
1024 x 768i at 87Hz - IBM
1024 x 768p at 60Hz - VESA
1024 x 768p at 70Hz - VESA
1024 x 768p at 75Hz - VESA
1280 x 1024p at 75Hz - VESA
22 SID-X1N - Default EDID
Page 27

1152 x 870p at 75Hz - Apple Mac II
1280 x 1024p at 75Hz - VESA STD
1280 x 1024p at 85Hz - VESA STD
1600 x 1200p at 60Hz - VESA STD
1024 x 768p at 85Hz - VESA STD
800 x 600p at 85Hz - VESA STD
640 x 480p at 85Hz - VESA STD
1152 x 864p at 70Hz - VESA STD
1280 x 960p at 60Hz - VESA STD
EIA/CEA-861 Information
Revision number.......... 3
IT underscan............. Supported
Basic audio.............. Supported
YCbCr 4:4:4.............. Supported
YCbCr 4:2:2.............. Supported
Native formats........... 1
Detailed timing #1....... 1920x1080p at 60Hz (16:10)
Modeline............... "1920x1080" 148.500 1920 2008 2052 2200 1080 1084 1089 1125 +hsync +vsync
Detailed timing #2....... 1920x1080i at 60Hz (16:10)
Modeline............... "1920x1080" 74.250 1920 2008 2052 2200 1080 1084 1094 1124 interlace +hsync
+vsync
Detailed timing #3....... 1280x720p at 60Hz (16:10)
Modeline............... "1280x720" 74.250 1280 1390 1430 1650 720 725 730 750 +hsync +vsync
Detailed timing #4....... 720x480p at 60Hz (16:10)
Modeline............... "720x480" 27.000 720 736 798 858 480 489 495 525 -hsync -vsync
CE video identifiers (VICs) - timing/formats supported
1920 x 1080p at 60Hz - HDTV (16:9, 1:1)
1920 x 1080i at 60Hz - HDTV (16:9, 1:1)
1280 x 720p at 60Hz - HDTV (16:9, 1:1) [Native]
720 x 480p at 60Hz - EDTV (16:9, 32:27)
720 x 480p at 60Hz - EDTV (4:3, 8:9)
720 x 480i at 60Hz - Doublescan (16:9, 32:27)
720 x 576i at 50Hz - Doublescan (16:9, 64:45)
640 x 480p at 60Hz - Default (4:3, 1:1)
NB: NTSC refresh rate = (Hz*1000)/1001
CE audio data (formats supported)
LPCM 2-channel, 16/20/24 bit depths at 32/44/48 kHz
CE vendor specific data (VSDB)
IEEE registration number. 0x000C03
CEC physical address..... 1.0.0.0
Maximum TMDS clock....... 165MHz
CE speaker allocation data
Channel configuration.... 2.0
Front left/right......... Yes
Front LFE................ No
Front center............. No
Rear left/right.......... No
Rear center.............. No
Front left/right center.. No
Rear left/right center... No
Rear LFE................. No
Report information
Date generated........... 06/08/2014
Software revision........ 2.60.0.972
Data source.............. File
Operating system......... 6.1.7601.2.Service Pack 1
SID-X1N - Default EDID 23
Page 28

Raw data
00,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,00,2D,B2,72,06,02,00,00,00,FF,15,01,03,80,34,20,78,EA,B3,25,AC,51,30,B4,26,
10,50,54,FF,FF,80,81,8F,81,99,A9,40,61,59,45,59,31,59,71,4A,81,40,01,1D,00,72,51,D0,1E,20,6E,28,
55,00,07,44,21,00,00,1E,00,00,00,FF,00,35,30,35,2D,37,30,39,39,39,30,31,30,30,00,00,00,FC,00,53,
49,44,2D,58,32,4E,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,FD,00,38,4C,1E,53,11,00,0A,20,20,20,20,20,20,01,31,
02,03,1B,F1,48,10,05,84,03,02,07,16,01,23,09,07,07,65,03,0C,00,10,00,83,01,00,00,02,3A,80,18,71,
38,2D,40,58,2C,45,00,07,44,21,00,00,1E,01,1D,80,18,71,1C,16,20,58,2C,25,00,07,44,21,00,00,9E,01,
1D,00,72,51,D0,1E,20,6E,28,55,00,07,44,21,00,00,1E,8C,0A,D0,8A,20,E0,2D,10,10,3E,96,00,07,44,21,
00,00,18,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,47
11.2 PC-UXGA
Monitor
Model name............... SID-X1N
Manufacturer............. KMR
Plug and Play ID......... KMR0672
Serial number............ 505-709990100
Manufacture date......... 2011, ISO week 255
Filter driver............ None
-------------------------
EDID revision............ 1.3
Input signal type........ Analog 0.700,0.000 (0.7V p-p)
Sync input support....... Separate, Composite, Sync-on-green
Display type............. RGB color
Screen size.............. 520 x 320 mm (24.0 in)
Power management......... Standby, Suspend, Active off/sleep
Extension blocs.......... None
-------------------------
DDC/CI................... n/a
Color characteristics
Default color space...... sRGB
Display gamma............ 2.20
Red chromaticity......... Rx 0.674 - Ry 0.319
Green chromaticity....... Gx 0.188 - Gy 0.706
Blue chromaticity........ Bx 0.148 - By 0.064
White point (default).... Wx 0.313 - Wy 0.329
Additional descriptors... None
Timing characteristics
Horizontal scan range.... 30-83kHz
Vertical scan range...... 56-76Hz
Video bandwidth.......... 170MHz
CVT standard............. Not supported
GTF standard............. Not supported
Additional descriptors... None
Preferred timing......... Yes
Native/preferred timing.. 1280x720p at 60Hz (16:10)
Modeline............... "1280x720" 74.250 1280 1390 1430 1650 720 725 730 750 +hsync +vsync
Standard timings supported
720 x 400p at 70Hz - IBM VGA
720 x 400p at 88Hz - IBM XGA2
640 x 480p at 60Hz - IBM VGA
640 x 480p at 67Hz - Apple Mac II
640 x 480p at 72Hz - VESA
640 x 480p at 75Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 56Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 60Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 72Hz - VESA
800 x 600p at 75Hz - VESA
832 x 624p at 75Hz - Apple Mac II
1024 x 768i at 87Hz - IBM
1024 x 768p at 60Hz - VESA
1024 x 768p at 70Hz - VESA
1024 x 768p at 75Hz - VESA
1280 x 1024p at 75Hz - VESA
1152 x 870p at 75Hz - Apple Mac II
1280 x 1024p at 75Hz - VESA STD
1280 x 1024p at 85Hz - VESA STD
24 SID-X1N - Default EDID
Page 29

1600 x 1200p at 60Hz - VESA STD
1024 x 768p at 85Hz - VESA STD
800 x 600p at 85Hz - VESA STD
640 x 480p at 85Hz - VESA STD
1152 x 864p at 70Hz - VESA STD
1280 x 960p at 60Hz - VESA STD
Report information
Date generated........... 11/02/2015
Software revision........ 2.60.0.972
Data source.............. File
Operating system......... 6.1.7601.2.Service Pack 1
Raw data
00,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,00,2D,B2,72,06,02,00,00,00,FF,15,01,03,6E,34,20,78,EE,B3,25,AC,51,30,B4,26,
10,50,54,FF,FF,80,81,8F,81,99,A9,40,61,59,45,59,31,59,71,4A,81,40,01,1D,00,72,51,D0,1E,20,6E,28,
55,00,07,44,21,00,00,1E,00,00,00,FF,00,35,30,35,2D,37,30,39,39,39,30,31,30,30,00,00,00,FC,00,53,
49,44,2D,58,31,4E,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,FD,00,38,4C,1E,53,11,00,0A,20,20,20,20,20,20,00,41,
FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,
FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,
FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,
FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF
SID-X1N - Default EDID 25
Page 30

MSB
LSB
DESTINATION
INSTRUCTION
0 D N5
N4
N3
N2
N1
N0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2nd Byte
INPUT
1
I6
I5
I4
I3
I2
I1
I0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
3rd Byte
OUTPUT
1
O6
O5
O4
O3
O2
O1
O0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
4th Byte
MACHINE NUMBER
1
OVR X M4
M3
M2
M1
M0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
12 Remote Commands
Note: The SID-X1N can be controlled remotely only via DGKat, for example from
the VP-81SID or TP-574, using Kramer Protocol 2000 remote commands.
This protocol uses four bytes of information as defined below. The default data
rate is 9600 baud, with no parity, 8 data bits and 1 stop bit.
This section describes:
• Kramer Protocol 2000 syntax (see Section 12.1
• Kramer Protocol 2000 instruction codes (see Section 12.2)
• RS-232 hardware interface (see Section 12.3)
12.1 Kramer Protocol 2000 Syntax
1st Byte
1st Byte: Bit 7 – Defined as 0
The 6-bit INSTRUCTION defines the function performed by the switcher(s). If a function is performed using the
machine’s keyboard, these bits are set with the INSTRUCTION NO. performed. The instruction codes are defined
according to the table below (INSTRUCTION NO. is the value set in N5…N0).
2nd Byte: Bit 7 – Defined as 1
I6…I0 – INPUT
When switching (i.e. instruction codes 1 and 2), the 7-bit INPUT is set as the input number to be switched. If switching is
done using the machi ne’ s front panel, these bits are set with the INPUT NUMBER switched. For other operations, these
bits are defined according to the table.
3rd Byte: Bit 7 – Defined as 1
O6…O0 – OUTPUT
When switching (i.e. instruction codes 1 and 2), the 7-bit OUTPUT is set as the output number to be switched. I f
switching is done using the machine’s front panel, these bits are set with the OUTPUT NUMBER switched. For other
operations, these bits are defined according to the table.
D – DESTINATION:
N5…N0 – INSTRUCTION
0 – Sends information to the switchers (from the PC)
1 – Sends information to the PC (from the switcher)
)
26 SID-X1N - Remote Commands
Page 31

Instruction
Definition fo r Spec ific Instruction
Notes # Description
Input
Output
0
RESET VIDEO
0 0 1
1
SWITCH VIDEO
Set equal to video input
(0 = disconnect)
Set equal to video output that is
(0 = to all the outputs)
2, 15
2
SWITCH AUDIO
Set equal to audio input
(0 = disconnect)
Set equal to audio output that is
(0 = to all the outputs)
2
3
STORE VIDEO STATUS
Set as SETUP #
To store
To delete
2, 3, 15
4
RECALL VIDEO
STATUS
Set as SETUP #
0
2, 3, 15
5
REQUEST STATUS OF
A VIDEO OUTPUT
Set as SETUP #
Equal to output number whose
status is required
4, 3 6 REQUEST STATUS OF
AN AUDIO OUTPUT
Set as SETUP #
Equal to output number whose
status is required
4, 3
7
VIS SOURCE
Set as input # when
0 – No VIS (immediate)
setting
2, 5, 17, 18
4th Byte: Bit 7 – Defined as 1
Bit 5 – Don’t care
OVR – Machine number override
M4…M0 – MACHINE NUMBER
This byte is used to address machines in a system by their machine numbers. When several machines are controlled
from a single serial port, they are usually configured together and each machine has an individual machin e num b er . If
the OVR bit is set, then all machine numbers accept (implement) the command and the addressed machine replies.
When a single machine is controlled over the serial port, always set M4…M0 to 1, and make sure that the machine itself
is configured as MACHINE NUMBER = 1.
12.2 Kramer Protocol 2000 Instruction Codes
All the values in the table are decimal, unless otherwise stated
that is switched
that is switched
OUTPUT byte = 6;
OR
Set as output # when
OUTPUT byte = 7;
OR
Set as blank period
(in steps of 25ms) when
OUTPUT byte = 32;
OR
Set = 0. *****
NOTES on the above table:
NOTE 2 – These are bi-directional definitions. If the switcher receives the code, it performs the instruction. If
the instruction is performed (due to a keystroke operation on the front panel), then these codes are sent.
For example, if the PC sends HEX code:
01 85 88 83
then the switcher (machine 3) switches input 5 to output 8.
If the user switches input 1 to output 7 using the front panel buttons, the switcher sends HEX code:
41 81 87 83
to the PC.
When the PC sends one of the commands in this group to the switcher, if the instruction is valid, the switcher
replies by sending the same four bytes to the PC that it received (except for the first byte, where the
DESTINATION bit is set high).
NOTE 5 – For the OUTPUT byte set as 6, the VIS source is the input selected using the OUTPUT byte.
Similarly, for the OUTPUT byte set as 7, the VIS source is the output selected using the OUTPUT byte. Note
that on some machines the sync source is not software selectable, but is selected using switches, jumpers,
etc.
switched
switched
1 – Input # 1
2 – External digital sync
3 – External analog sync
4 – Dynamic sync
5 – Inter-machine sync
6 – Input # (INPUT byte)
7 – Output #(INPUT byte)
8 – User-defined sync
32 – RGBHV seamless switching
64 – Set for delayed switch
65 – Execute delayed switch
66 – Cancel delayed switch
SID-X1N - Remote Commands 27
Page 32

NOTE 17 – For clean switching of RGBHV video, the seamless switching option can be used. The blanking
period for the transition of the RGB sources can be set in steps of 25 milliseconds.
For example, to set for 350ms blanking time (14 steps), send HEX code:
07 8E A0 81.
NOTE 18 – Delayed execution switches after a delay dictated by RS-232 control. To do this, the user sends
instruction 7 with the SET FOR DELAYED SWITCH option (64
(instruction 1) or pressing a front panel button. The switch is not executed (unless timed-out) until the
EXECUTE DELAYED SWITCH code is sent, or the SET FOR DELAYED SWITCH code is sent again. (The
mode is automatically cancelled after switching if the EXECUTE command is used).
For example, to connect input 4 to output 3 after a delay, send HEX code:
07 80 C0 81 (set for delayed switch)
01 84 83 81 (switch code)
then, after the required delay, send HEX code:
07 80 C1 81(execute delayed switch)
to implement the switch.
The following sources are supported:
HDMI input : 0x07 0x80 0x81 0x81<CR>
DP input : 0x07 0x80 0x85 0x81<CR>
DVI input : 0x07 0x80 0x89 0x81<CR>
VGA input : 0x07 0x80 0x8C 0x81<CR>
Note: The syntax of the binary values differs according to the terminal
communication software being used. For example, using Hercules, the syntax
appears as follows (for the HDMI input): $07$80$81$81<cr>
12.3 RS-232 Hardware Interface
) before sending the switch command
dec
RS-232 connection between the machine and controller is used for firmware
upgrade procedures and technical maintenance. The default data rate is 115200
baud, with no parity, 8 data bits and 1 stop bit.
Note: Using any additional, non-standard RS-232 commands developed for
internal debugging purposes is not recommended. Such commands are only used
internally for performing firmware upgrades over the RS-232 hardware interface.
28 SID-X1N - Remote Commands
Page 33

Page 34

For the latest information on our products and a list of Kramer distributors, visit our
SAFETY WARNING
Disconnect the unit from the power
supply before opening and servicing
P/N:
2900-300302
Rev:
5
!
Web site where updates to this user manual may be found.
We welcome your questions, comments, and feedback.
Web site: www.kramerav.com
E-mail: info@kramerel.com
 Loading...
Loading...