Page 1

IPMI Firmware User Guide
for the
AM4010
Module
Manual ID: 36363, Rev. Index 1.1
Firmware: SK-IPMI-AM4010, EKS Idx 0101
June 12, 2007
Page 2

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
1. Copyright
Copyright © 2007 Kontron AG
Kontron Modular Computers makes no representations or warranties with respect to the
contents or use of this manual, and specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of
merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Kontron Modular Computers makes no representations or warranties with respect to this
embedded Linux package, and specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of
merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Permission is granted to make and distribute verbatim copies of this manual provided that the
copyright notice and this permission notice are preserved on all copies.
Permission is granted to copy and distribute modified versions of this documentation under
the conditions for verbatim copying, provided also that the entire resulting derived work is
distributed under the terms of a permission notice identical to this one.
Permission is granted to copy and distribute translations of this documentation into another
language, under the above conditions for modified versions.
The PICMG® and CompactPCI® names and the PICMG®, CompactPCI®, ATCA®, and
AdvancedTCA® logos are registered trademarks and AdvancedMC is a trademark of the PCI
Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group.
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
I2C is a trademark of Phillips Semiconductors.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
All other trademarks, registered trademarks, and trade names are the property of their
respective owners.
Page 2 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 3
2. Revision History
IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
Manual/Product Title:
Manual ID Number: xxxxx
Revision Index Brief Description of Changes Date of Issue
Draft / 0.0 Initial Issue May 3, 2007
1.0 Completed May 22, 2007
1.1 Revised June 12, 2007
IPMI Firmware User Guide for the AM4010 Module
Imprint
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH may be contacted via the following:
MAILING ADDRESS TELEPHONE AND E-MAIL
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH +49 (0) 800-SALESKONTRON
Sudetenstraße 7 sales@kontron.com
D - 87600 Kaufbeuren Germany
For further information about other Kontron products, please visit our Internet web site:
www.kontron.com
Disclaimer
Copyright © 2007 Kontron AG. All rights reserved. All data is for information purposes only
and not guaranteed for legal purposes. Information has been carefully checked and is believed
to be accurate; however, no responsibility is assumed for inaccuracies. Kontron and the
Kontron logo and all other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their
respective owners and are recognized. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 3
Page 4

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
3. Contents
1. Copyright............................................................................................................................2
2. Revision History.................................................................................................................3
3. Contents..............................................................................................................................4
4. Introduction ........................................................................................................................6
4.1 Acronym Definitions..................................................................................................6
4.2 Related Documentation..............................................................................................7
5. Introduction ........................................................................................................................8
5.1 IPMI in AdvancedMC / AdvancedTCA Environment...............................................8
5.2 The Module Management Controller Hardware ........................................................8
6. MMC Firmware..................................................................................................................9
6.1 Key Features...............................................................................................................9
6.2 Supported IPMI Commands.....................................................................................10
6.2.1 Standard commands..........................................................................................10
6.2.2 OEM Commands and Extensions.....................................................................17
6.2.2.1 Get Device ID command with OEM extensions..........................................17
6.2.2.2 Set Firmware Parameters..............................................................................18
6.2.2.3 Set Control State (Firmware Hub, Boot Order)............................................19
6.2.2.4 Get Control State (Firmware Hub, Boot Order)...........................................19
6.2.2.5 OEM Module Quiescence Feedback............................................................20
6.3 Sensors Implemented on the AM4010.....................................................................22
6.3.1 Sensor List........................................................................................................22
6.3.2 OEM Event / Reading Types............................................................................25
6.4 Firmware Code.........................................................................................................27
6.4.1 Structure and functionality ...............................................................................27
6.4.2 Firmware Upgrade............................................................................................27
6.5 Firmware Configuration...........................................................................................27
6.6 Firmware / Module Identification ............................................................................28
6.7 FRU Information ......................................................................................................28
6.7.1 Structure and functionality ...............................................................................28
6.7.2 Download .........................................................................................................28
6.8 E-Keying...................................................................................................................29
6.9 PCI Express Clock Source........................................................................................29
6.10 BIOS Supervisory and Automated Firmware Hub Switch.......................................29
Page 4 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 5

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.11 Hot Swap ..................................................................................................................29
6.12 LAN functions..........................................................................................................31
6.12.1 Overview ..........................................................................................................31
6.12.2 Setting up the Ethernet channel........................................................................31
6.12.2.1 Setup by BIOS menu................................................................................31
6.12.2.2 Setup by ipmitool or IPMI commands .....................................................31
6.12.3 Setup of user and password..............................................................................31
6.12.4 IPMI over LAN (IOL)......................................................................................32
6.12.5 Serial over LAN (SOL) ....................................................................................32
6.13 OS Support / Tools...................................................................................................33
6.13.1 DOS..................................................................................................................33
6.13.2 Linux.................................................................................................................33
6.13.3 Windows...........................................................................................................33
7. IPMI Communication LEDs.............................................................................................34
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 5
Page 6

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
4. Introduction
4.1 Acronym Definitions
AMC Advanced Mezzanine Card
BSP Board Support Package
DMI Desktop Management Interface
FRU Field Replaceable Unit
FWH Firmware Hub
2
C Inter-Integrated Circuit
I
IPMB Intelligent Platform Management Bus
IPMB-0 AdvancedTCA shelf-level IPMB
IPMB-L Local, on-carrier IPMB that links the carrier IPMC with the MMCs of installed modules
IPMC Intelligent Platform Management Controller located on AMC carrier
IPMI Intelligent Platform Management Interface
IOL IPMI over LAN. An MMC is accessed via LAN, not IPMB
KCS Keyboard Controller Style
MMC Module Management Controller – an IPMI controll er located on the AMC mo dule
MP Management Power
PICMG PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturer Group
PWR Payload Pow er
SDR Sensor Data Record
SDRR Sensor Data Record Repository
SEL System Event Log
SMBIOS System Management BIOS
SMS System Management Software (designed to run under the OS)
SOL Serial over LAN. A serial interface is redirected by LAN using the RM CP+ protocol.
Page 6 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 7

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
4.2 Related Documentation
IPMI specifications: (http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/spec.htm)
• IPMI-Intelligent Platform Management Interface Specification. Second Generation
v2.0, February 12, 2004 (part)
• [2] IPMI- Platform Management FRU Information Storage Definition v1.0,
Document Revision 1.1, September 1999
PICMG specifications: http://www.picmg.org
• PICMG® AMC.0 R1.0 - Advanced Mezzanine Card Base Specification
• PICMG® AMC.1 R1.0 - PCI Express and Advanced Switching on AdvancedMC
• PICMG® AMC.2 R1.0 – AMC Gigabit Ethernet/10 Gigabit XAUI Ethernet
Open tool’s documentation
• [1] Ipmitool documentation: http://ipmitool.sourceforge.net
• OpenIPMI documentation: http://www.openipmi.sourceforge.net
Kontron manuals and specifications: http://www.kontron.com/
• AM4010 User’s Guide
• [3] AM4010 Linux Board Support Package
As a hot-swappable field replaceable unit (FRU), the AM4010 follows the stringent carrier
grade RASM feature set, namely - Reliability, Availability, Serviceability, Maintainability.
Built in accordance to the AMC.0 specification, the AM4010 is also AMC.1 and AMC.2
compliant and is easily managed via IPMI v1.5/v2.0.
As with every Advanced Mezzanine Card (AMC) the AM4010 is equipped with a Module
Management Controller (MMC).
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 7
Page 8

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
5. Introduction
5.1 IPMI in AdvancedMC / AdvancedTCA Environment
The Module Management Controller is a crucial component of any AMC module. Besides
acting as a regular IPMI management controller (sensor monitoring, event logging, etc.), it
also provides an interface to all necessary data related to module power requirements and
implemented interfaces (E-Keying). Further, it plays an active role in the module hot swap
state management. The carrier IPMI Controller (IPMC) communicates with the MMC using
the local IPMB (IPMB-L) bus. In an ATCA/AMC environment, it is the IPMC that actually
turns on/off module (payload) power. However, before the IPMC enables the module payload
power, various criteria must be satisfied by both the carrier and the module, including power
requirements and capabilities, matching interfaces, current module hot swap state, and any
other special conditions as specified by the Shelf Manager policy.
5.2 The Module Management Controller Hardware
On the AM4010 module, the MMC is implemented using the Renesas H8S/2166 controller
with 512 kB of internal flash and 40 kB of RAM. An additional 1 MB serial EEPROM chip
provides redundant firmware image storage. A separate 32 kB serial EEPROM chip is used
for firmware private data and 4 kB FRU Inventory storage.
The MMC circuit implements two local Keyboard Style Interfaces (KCS) with interrupt
support for communication with system side management software and the IPMB-L bus for
interconnection with the IPMC.
IPMI over LAN (IOL) is supported by two Ethernet channels.
The MMC implements a wide range of sensors that permit the monitoring of:
• main power voltages: +12V (PWR), +5V, +3.3V, +3.3V (MP), +1.5V, +1.8V,
+0.9V (DDR)
• temperatures: CPU die, MCH die, board inlet and outlet near CPU, board inlet and
outlet near MCH
• Power Good, LAN links, IPMB link, NMI and SMI lines, board reset, post code,
boot error, processor hot (>100 °C), IPMB-L state, Health error, IPMI watchdog
etc.
Page 8 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 9

6. MMC Firmware
6.1 Key Features
• compliant with the related IPMI and PICMG® specifications (refer to 4.2, Related
Documentation)
• firmware designed and specially made for AdvancedMC environments
• supports two KCS interfaces with interrupt support
• supports the local IPMB (IPMB-L) interface
• out of band management and monitoring using IPMB-L interface permits access to
sensors regardless of module CPU state
• sensor thresholds fully configurable
• sensor names prefixed with AMC module Bay ID (A1…4, B1…4)
• Usable in µTCA slots 1…12. Sensor names for slots 9…12 are prefixed with
R9…R12
IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
• complete IPMI watchdog functionality
• complete FRU functionality (refer to 6.7)
• firmware can be updated in the field (refer to 6.4.2)
• two firmware banks implemented, firmware bank management is done by the open
tool ipmitool (function fwum) [1] (refer to 6.4.1)
• downloading new firmware image does not break currently running firmware
activities (refer to 6.4.2).
• manual and automatic firmware image roll-back (in case of upgrade failure). Refer
to 6.4.2.
• firmware customizable per BIOS menu or per OEM IPMI commands (refer to 6.5)
• interoperable with other AMC, ATCA, or IPMI solutions
• OEM board supervision and control extensions such as firmware hub select and
boot order configuration (refer to 6.2.2)
• BIOS supervisor and automated switch to recover image from second firmware
hub (refer to 6.10)
• Serial over LAN (SOL, refer to 6.12.5) support
• IPMI over LAN (IOL, refer to 6.12.4) support
• Graceful shutdown support (refer to 6.11)
• “Health” LED shows heartbeat and pulses if a KCS interface is active. The “out-
of-service” (OOS) LED pulses when IPMB-L is active (refer to 7).
• If the carrier supplies an external clock 3 the module will use it. Otherwise the
module will use the internal PCIe clock (refer to 6.9).
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 9
Page 10
IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
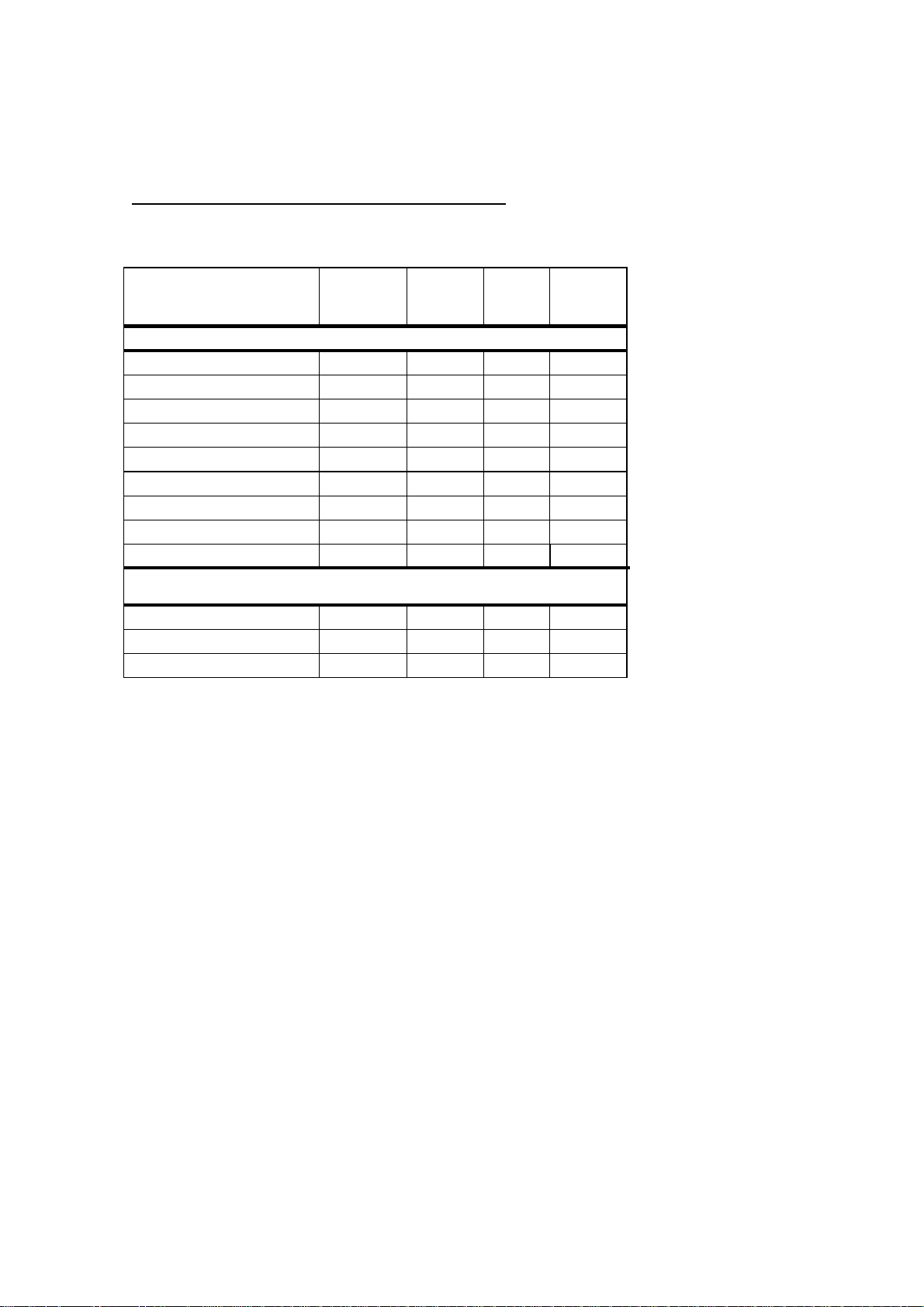
6.2 Supported IPMI Commands
6.2.1 Standard commands
Part of the command list in IPMI specification 2.0
M = mandatory, O = optional
IPMI 2.0
Spec. section
NetFn CMD
Kontron
support
On MMC
IPM Device “Global” Commands
Get Device ID 20.1 App 01h M / Yes [3]
Cold Reset 20.2 App 02h
Warm Reset 20.3 App 03h
Get Self Test Results 20.4 App 04h
Manufacturing Test On 20.5 App 05h
Set ACPI Power State 20.6 App 06h
Get ACPI Power State 20.7 App 07h
Get Device GUID 20.8 App 08h
Broadcast “Get Device ID”
BMC Watchdog Timer
Commands
Reset Watchdog Timer 27.5 App 22h O / Yes
Set Watchdog Timer 27.6 App 24h
Get Watchdog Timer 27.7 App 25h
20.9 App 01h
M
O / Yes
O / No
O / Yes
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
M / Yes
O
O / Yes
O / Yes
Page 10 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 11
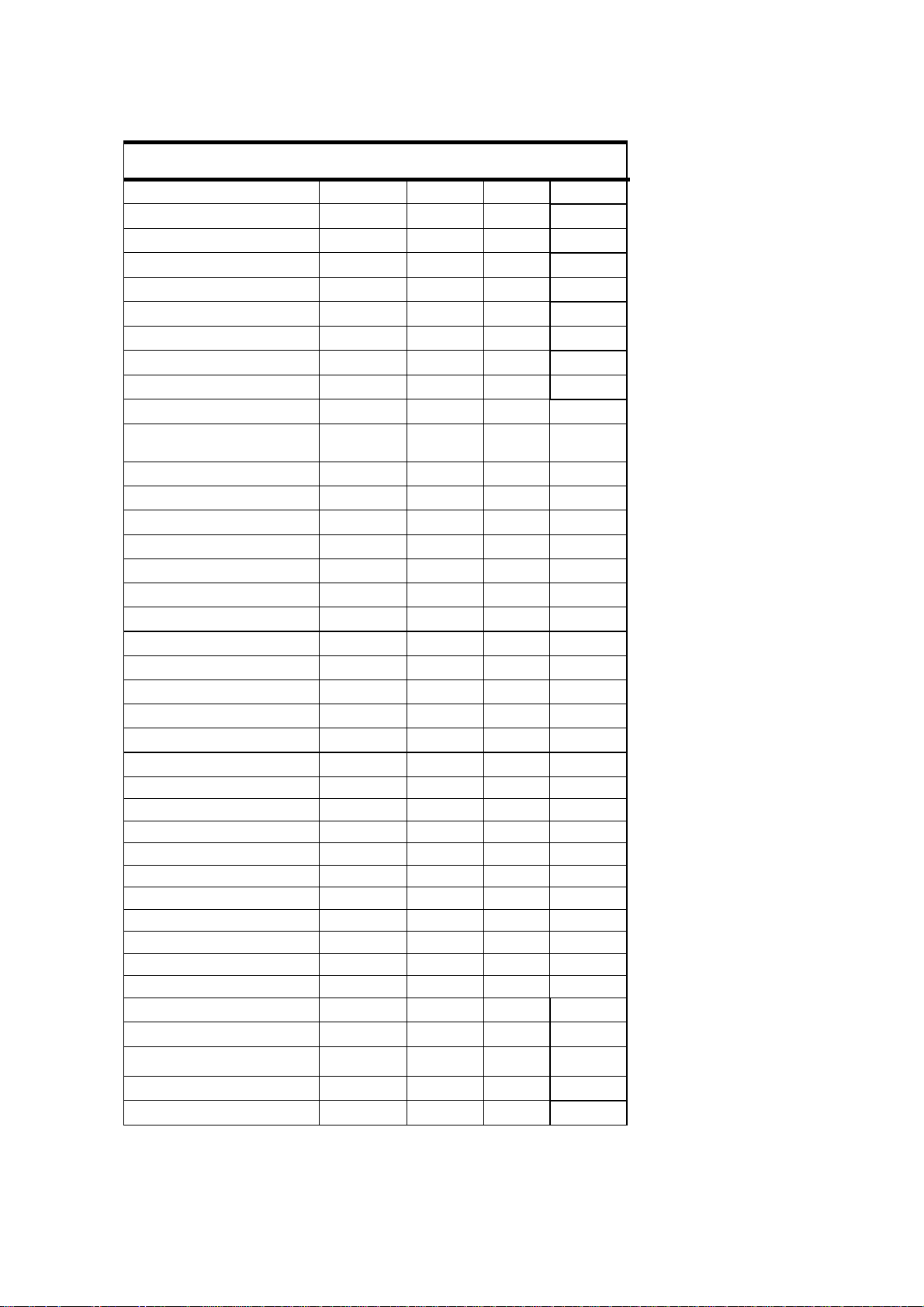
IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
BMC Device and Messaging
Commands
Set BMC Global Enables 22.1 App 2Eh O / Yes
Get BMC Global Enables 22.2 App 2Fh
Clear Message Flags 22.3 App 30h
Get Message Flags 22.4 App 31h
Enable Message Channel Receive 22.5 App 32h
Get Message 22.6 App 33h
Send Message 22.7 App 34h
Read Event Message Buffer 22.8 App 35h
Get BT Interface Capabilities 22.9 App 36h
Get System GUID 22.14 App 37h
Get Channel Authentication
Capabilities
Get Session Challenge 22.15 App 39h
Activate Session 22.17 App 3Ah
Set Session Privilege Level 22. 18 App 3Bh
Close Session 22.19 App 3Ch
Get Session Info 22.20 App 3Dh
Get AuthCode 22.21 App 3Fh
Set Channel Access 22.22 App 40h
Get Channel Access 22.23 App 41h
Get Channel Info 22.24 App 42h
Set User Access 22.26 App 43h
Get User Access 22.27 App 44h
Set User Name 22.28 App 45h
Get User Name 22.29 App 46h
Set User Password 22.30 App 47h
Activate Payload 24.1 App 48h
Deactivate Payload 24.2 App 49h
Get Payload Activation Status 24.4 App 4Ah
Get Payload Instance Info 24.5 App 4Bh
Set User Payload Access 24.6 App 4Ch
Get User Payload Access 24.7 App 4Dh
Get Channel Payload Support 24.8 App 4Eh
Get Channel Payload Version 24.9 App 4Fh
Get Channel OEM Payload Info 24.10 App 50h
Master Write-Read 22.11 App 52h
Get Channel Cipher Suits 22.15 App 54h
Suspend/Resume Payload
Encryption
Set Channel Security Keys 22.25 App 56h
Get System Interface Capabilities 22.9 App 57h
22.13 App 38h
24.3 App 55h
O
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / No
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / No
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / No
O / Yes
O / No
O / Yes
O / No
O / No
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 11
Page 12

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
Chassis Device Commands
Get Chassis Capabilities 28.1 Chassis 00h O / Yes
Get Chassis Status 28.2 Chassis 01h
Chassis Control 28.3 Chassis 02h
Chassis Reset 28.4 Chassis 03h
Chassis Identify 28.5 Chassis 04h
Set Chassis Capabilities 28.7 Chassis 05h
Set Power Restore Policy 28.8 Chassis 06h
Get System Restart Cause 28.11 Chassis 07h
Set System Boot Options 28.12 Chassis 08h
Get System Boot Options 28.13 Chassis 09h
Get POH Counter 28.14 Chassis 0Fh
Event Commands
Set Event Receiver 29.1 S/E 01h
Get Event Receiver 29.2 S/E 02h
Platform Event (a.k.a. “Event
Message”)
PEF and Alerting Commands O
Get PEF Capabilities 30.1 S/E 10h
Arm PEF Postpone Timer 30.2 S/E 11h
Set PEF Configuration Parameters 30.3 S/E 12h
Get PEF Configuration Parameters 30.4 S/E 13h
Set Last Processed Event ID 30.5 S/E 14h
Get Last Processed Event ID 30.6 S/E 15h
Alert Immediate 30.7 S/E 16h
PET Acknowledge 30.8 S/E 17h
29.3 S/E 03h
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / Yes [1]
M
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
Page 12 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 13

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
Sensor Device Commands M
Get Device SDR Info 35.2 S/E 20h
Get Device SDR 35.3 S/E 21h
Reserve Device SDR Repository 35.4 S/E 22h
Get Sensor Reading Factors 35.5 S/E 23h
Set Sensor Hysteresis 35.6 S/E 24h
Get Sensor Hysteresis 35.7 S/E 25h
Set Sensor Threshold 35.8 S/E 26h
Get Sensor Threshold 35.9 S/E 27h
Set Sensor Event Enable 35.10 S/E 28h
Get Sensor Event Enable 35.11 S/E 29h
Re-arm Sensor Events 35.12 S/E 2Ah
Get Sensor Event Status 35.13 S/E 2Bh
Get Sensor Reading 35.14 S/E 2Dh
Set Sensor Type 35.15 S/E 2Eh
Get Sensor Type 35.16 S/E 2Fh
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
O / No
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / No
O / No
M / Yes
O / No
O / No
FRU Device Commands M
Get FRU Inventory Area Info 34.1 Storage 10h
Read FRU Data 34.2 Storage 11h
Write FRU Data 34.3 Storage 12h
SDR Device Commands
Get SDR Repository Info 33.9 Storage 20h O / No
Get SDR Repository Allocation
Info
Reserve SDR Repository 33.11 Storage 22h
Get SDR 33.12 Storage 23h
Add SDR 33.13 Storage 24h
Partial Add SDR 33. 14 Storage 25h
Delete SDR 33.15 Storage 26h
Clear SDR Repository 33.16 Storage 27h
Get SDR Repository Time 33.17 Storage 28h
Set SDR Repository Time 33.18 Storage 29h
Enter SDR Repository Update
Mode
Exit SDR Repository Update Mode 33.20 Storage 2Bh
Run Initialization Agent 33.21 Storage 2Ch
33.10 Storage 21h
33.19 Storage 2Ah
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
O
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 13
Page 14

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
SEL Device Commands
Get SEL Info 40.2 Storage 40h O / No
Get SEL Allocation Info 40.3 Storage 41h
Reserve SEL 40.4 Storage 42h
Get SEL Entry 40.5 Storage 43h
Add SEL Entry 40.6 Storage 44h
Partial Add SEL Entry 40.7 Storage 45h
Delete SEL Entry 40.8 Storage 46h
Clear SEL 40.9 Storage 47h
Get SEL Time 40.10 Storage 48h
Set SEL Time 40.11 Storage 49h
Get Auxiliary Log Status 40.12 Storage 5Ah
Set Auxiliary Log Status 40.13 Storage 5Bh
LAN Device Commands
Set LAN Configuration Parameters 23.1 Transport 01h O / Yes
Get LAN Configuration Parameters 23.2 Transport 02h
Suspend BMC ARPs 23.3 Transport 03h
Get IP/UDP/RMCP Statistics 23.4 Transport 04h
Serial/Modem Device Commands
Set Serial/Modem Configuration 25.1 Transport 10h O / No
Get Serial/Modem Configuration 25.2 Transport 11h
Set Serial/Modem Mux 25.3 Transport 12h
Get TAP Response Codes 25.4 Transport 13h
Set PPP UDP Proxy Transmit Data 25.5 Transport 14h
Get PPP UDP Proxy Transmit Data 25.6 Transport 15h
Send PPP UDP Proxy Packet 25.7 Transport 16h
Get PPP UDP Proxy Receive Data 25.8 Transport 17h
Serial/Modem Connection Active 25.9 Transport 18h
Callback 25.10 Transport 19h
Set User Callback Options 25.11 Transport 1Ah
Get User Callback Options 25.12 Transport 1Bh
SOL Activating 26.1 Transport 20h
Get SOL Configuration Parameters 26.2 Transport 21h
Set SOL Configuration Parameters 26.3 Transport 22h
O
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O
O / No
O / Yes
O / Yes
O
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
Page 14 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 15

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
Bridge Management Commands
(ICMB)
Get Bridge State [ICMB] Bridge 00h O / No
Set Bridge State [ICMB] Bridge 01h
Get ICMB Address [ICMB] Bridge 02h
Set ICMB Address [ICMB] Bridge 03h
Set Bridge Proxy Address [ICMB] Bridge 04h
Get Bridge Statistics [ICMB] Bridge 05h
Get ICMB Capabilities [ICMB] Bridge 06h
Clear Bridge Statistics [ICMB] Bridge 08h
Get Bridge Proxy Address [ICMB] Bridge 09h
Get ICMB Connector Info [ICMB] Bridge 0Ah
Get ICMB Connection ID [ICMB] Bridge 0Bh
Send ICMB Connection ID [ICMB] Bridge 0Ch
Discovery Commands (ICMB)
Prepare For Discovery [ICMB] Bridge 10h O / No
Get Addresses [ICMB] Bridge 11h
Set Discovered [ICMB] Bridge 12h
Get Chassis Device ID [ICMB] Bridge 13h
Set Chassis Device ID [ICMB] Bridge 14h
Bridging Commands (ICMB)
Bridge Request [ICMB] Bridge 20h O / No
Bridge Message [ICMB] Bridge 21h
Event Commands (ICMB)
Get Event Count [ICMB] Bridge 30h O / No
Set Event Destination [ICMB] Bridge 31h
Set Event Reception State [ICMB] Bridge 32h
Send ICMB Event Message [ICMB] Bridge 33h
Get Event Destination [ICMB] Bridge 34h
Get Event Reception State [ICMB] Bridge 35h
OEM Commands for Bridge
NetFn
OEM Commands [ICMB] Bridge C0h-FEh O / No
Other Bridge Commands
Error Report [ICMB] Bridge FFh O / No
O
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O
O / No
O
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O / No
O
O
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 15
Page 16

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
AdvancedTCA®[10]
Get PICMG Properties 3-9 PICMG 00h M / Yes
Get Address Info 3-8 PICMG 01h
Get Shelf Address Info 3-13 PICMG 02h
Set Shelf Address Info 3-14 PICMG 03h
FRU Control 3-22 PICMG 04h
Get FRU LED Properties 3-24 PICMG 05h
Get LED Color Capabilities 3-25 PICMG 06h
Set FRU LED State 3-26 PICMG 07h
Get FRU LED State 3-27 PICMG 08h
Set IPMB State 3-51 PICMG 09h
Set FRU Activation Policy 3-17 PICMG 0Ah
Get FRU Activation Policy 3-18 PICMG 0Bh
Set FRU Activation 3-16 PICMG 0Ch
Get Device Locator Record ID 3-29 PICMG 0Dh
Set Port State 3-41 PICMG 0Eh
Get Port State 3-42 PICMG 0Fh
Compute Power Properties 3-60 PICMG 10h
Set Power Level 3-62 PICMG 11h
Get Power Level 3-61 PICMG 12h
Renegotiate Power 3-66 PICMG 13h
Get Fan Speed Properties 3-63 PICMG 14h
Set Fan Level 3-65 PICMG 15h
Get Fan Level 3-64 PICMG 16h
Bused Resource 3-44 PICMG 17h
Get IPMB Link Info 3-49 PICMG 18h
AMC
Set AMC Port State
Get AMC Port State
PICMG® 3.0
Table
AMC.0 Table
Table 3-27
Table 3-28
PICMG
PICMG
M
N/A
N/A
N/A
M / Yes [2]
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
M / Yes
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
19h O / Yes
20h O / Yes
[1] Response byte 2: hours, byte 3: minutes after module start. Bytes 4..6: void
[2] Request byte 3: = only 04h (quiesced) implemented.
[3] Has oem extensions. Please refer to 6.2.2.1, Get Device ID command with OEM
extensions
Page 16 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 17

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.2.2 OEM Commands and Extensions
6.2.2.1 Get Device ID command with OEM extensions
LUN NetFn CMD
Get Device ID command with OEM extensions 00h App = 06h 01h
Byte Data Field
Request Data - -
Response Data
1 Completion Code
2:12 Regular Get Device ID Command response fields
Release index (e.g. 101 denotes release index 1.01)
13
Please note: Some tools offer this as “SDR version”.
14 Module Geographical Address (site number):
1 … 8 = Module in AMC bay A1, A2 ,A3, A4, B1, B2, B3, B4
or in µTCA slot 1 … 8 with bus addresses
72h, 74h, 76h, 78h, 7ah, 7ch, 7eh, 80h
9 …12 = Module in µTCA slot 9 … 12 with bus addresses
82h, 84h, 86h,88h
0, > 12 = Module position is not in range. The IPMB-L bus is
switched off (ref. to 8.3).
15 Reserved
16 Reserved
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 17
Page 18

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.2.2.2 Set Firmware Parameters
The command below permits the selection of interrupts to be used during KCS
communication. The value of FFh instructs MMC not to drive the interrupt request line at
all, while the value of 07h forces it to use the ISA style IRQ7 line. Please refer to chapter
6.5 of this manual for further details regarding MMC configuration.
LUN NetFn CMD
Set Firmware Parameters 03h OEM = 3Eh 05h
Byte Data Field
Request data
1 Reserved
B4h
2 Reserved
90h
3 Reserved
91h
4 Reserved
8Bh
5 Cmd Flags
[6:2] Reserved
[1] 0b = get only
[0] 0b = do not reset
6 Operating Modes
[7:5] Reserved
[4] Reserved
[3:1] Reserved
[0] Reserved (=1b)
7 IRQ number
FFh = do not use interrupts
0Ah = use IRQ10
0Bh = use IRQ11
Any other values Reserved.
Response data
Page 18 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
1 Completion code
2 Cmd Flags
3 Operating Modes
4 IRQ number
Page 19

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.2.2.3 Set Control State (Firmware Hub, Boot Order)
LUN NetFn CMD
Set Control State (Firmware Hub, Boot Order) 00h OEM = 3Eh 20h
Byte Data Field
Request data
1 Control ID
00h: Firmware Hub Flash Select
9Dh: Boot Order Configuration
2 Control State (refer to AM4010 User Guide)
00h .. 01h for control ID = Firmware Hub Flash Select
00h .. FFh for control ID = Boot Order Configuration.
(These settings are stored in EEPROM and applied (to logic) each
time the MMC detects power-on)
00h: No override, boot as usual
01h: Next boot device is: Floppy
02h: Next boot device is: HDD
03h: Next boot device is: CD
04h: Next boot device is: Network
Response data
1 Completion code
6.2.2.4 Get Control State (Firmware Hub, Boot Order)
LUN NetFn CMD
Get Control State (Firmware Hub, Boot Order) 00h OEM = 3Eh 21h
Byte Data Field
Request data 1 Control ID
00h Firmware Hub Flash Select
9Dh Boot Order Configuration
1 Completion code Response data
4 Control State (refer to AM4010 User Guide)
00h .. 01h for control ID = Firmware Hub Flash Select
00h .. FFh for control ID = Boot Order Configuration
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 19
Page 20

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.2.2.5 OEM Module Quiescence Feedback
Overview
Please refer to 6.11, Hot Swap.
If the OS doesn’t fully support ACPI this command provides support to control a graceful
shut down of the AM4010. There is a Graceful Reboot and Shutdown Daemon (grnsd) for
Linux included in the newest Linux BSPs being offered by Kontron. It works as being
described in the following (refer to “Usage for a self written shut down daemon” below).
If ACPI is fully supported this command can be used to set a timeout time for the case
that the ACPI means (ACPI daemon etc.) are unable to shut down the system in time. As a
default value at system start this time is set to 0 (endless wait).
Usage for a self written shut down daemon
This command normally is used by a shut down daemon in a non ACPI supporting
software environment. If a timeout time has to be set to avoid an endless waiting for the
sleep state the daemon calls this command after system start with the “set quiesce wait
timeout” bit set and the “Quiesce wait timeout” time <> 0. Afterwards the daemon calls
this command cyclically with the “OS daemon present” bit set. When the MMC gets a
FRU Control (Quiesce) request from the carrier (e.g. during a Hot Swap sequence) it sets
the “quie s c e r e q u est ( FR U C o n t r o l)” b i t in its command response. Afte r the daemon
sees this bit set in the response it should shut down the system. After having set the
“quiesce request (FRU Control)” bit the MMC starts the timeout timer (if a timeout
time was defined) and monitors the sleep signal line to recognize the sleep state
which should be caused by the shut down. When the MMC detects the sleep state
(signal) or it receives a command with the “quiescence acknowledge” bit set or the
tim e o u t t i m e r h a s e x p i r e d , t h e M M C sends a “Module Hot Swap event” message to the
carrier, and in the following the payload power will be switched off.
If no daemon is announced as present
If no command call announces that a daemon is present, the MMC automatically uses the
default timeout time 0 (endless wait) during the Hot Swap process. But if the timeout time
was set to a value 1…255 by this time will be used in any case while waiting for the sleep
state (signal).
LUN NetFn CMD
OEM Module Quiescence Feedback 00h OEM = 3Eh 40h
Request data 1 Control bits:
Byte Data Field
[7] - 1b = set quiesce wait timeout
[6] - 1b = quiescence acknowledge (OS ready)
[5] - 1b = OS daemon present
[4:0] Reserved
Page 20 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 21

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
2 Quiesce wait timeout [sec]
a) An OS daemon is present (refer to bits above):
This is the maximum time from the moment on that the
MMC receives FRU Control (Quiesce) request until
it sends back the appropriate Module Hot Swap event
message.
b) No OS daemon is present (refer to bits above):
This is the maximum time from the moment on that the
MMC receives FRU Control (Quiesce) request until
it sends back the appropriate Module Hot Swap event
message.
If sleep state is recognized before timeout then the
Module Hot Swap event message will be sent
immediately. If the time is set to 0 (default after reset)
then the Module Hot Swap event message will only be
sent after recognition of sleep state (signal).
Response data
Settings changed with this command are volatile (in particular quiesce timeout and OS
daemon present). Bits [6:5] are always settable, but once the quiesce request comes they
cannot be cleared until quiescence state is entered and exited.
1 Completion code: 00h
2 Control bits:
[7] - Reserved
[6] - 1b = quiescence acknowledge (OS ready)
[5] - 1b = OS daemon present
[4] - 1b = quiesce request (FRU Control)
[3] - Reserved
[2] - 1b = graceful reboot request (FRU Control)
[1] - 1b = quiescence reached (MMC acknowledge)
[0] - 1b = module hot swap switch opened
3 Quiesce wait timeout (valid only if OS daemon present = 1)
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 21
Page 22

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.3 Sensors Implemented on the AM4010
The MMC includes many sensors for voltage or temperature monitoring and various others
for pass/fail type signal monitoring.
Every sensor is associated with a Sensor Data Record (SDR). Sensor Data Records contain
information about the sensors identification such as sensor type, sensor name, sensor unit.
SDRs also contain the configuration of a specific sensor such as threshold/hystheresis, event
generation capabilities that specifies sensor behavior. Some field of the sensor SDR are
configurable through IPMI v1.5 command and are set to built-in initial value. Finally one
field which is the sensor owner must reflect the module addresses that allow the AMC Carrier
to identify the owner of the SDR when it is scanned from the module management controller
and merged within the AMC Carrier Device SDR repository.
From IPMI perspective, the MMC is set up as a satellite management controller (SMC). It
does support sensor devices, and uses the IPMI static sensor population feature of IPMI v1.5.
All SDRs can be queried using Device SDR commands to the MMC.
The sensor name in its SDR has a name prefix which after module insertion is automatically
adapted to the physical position of the module in a carrier or in a µTCA chassis. The format
of this prefix is
• in AMC bay 1…8 or µTCA slot 1…8: ‘A1:’, ‘A2:’, ‘A3:’, ‘A4:’, ‘B1:’, ‘B2:’, ‘B3:’,
‘B4:’.
• in µTCA slot 9…12: ‘R9:’, ‘Ra:’, ‘Rb:’, ‘Rc:’.
Please note that in the case that the module is installed elsewhere, then the IPMB-L address of
the module is unknown and the interface is off.
Module sensors that have been implemented are listed in the sensor list below.
6.3.1 Sensor List
For OEM (Kontron) specific sensor types and codes in the following table please refer to
chapter 6.3.2.
SENSOR TYPE
SENSOR
NAME
(CODE) /
EVENT/READING
TYPE (CODE)
IPMI Info-1 OEM Firmware Info 1
(C0h) / OEM (70h)
IPMI Info-2 OEM Firmware Info 2
(C0h) / OEM (71h)
IPMI Watchdog Watch dog (23h) /
Sensor-specific
FRU Agent OEM (C5h) / Discrete
(0Ah)
Ass. Mask
/ Deass.
Mask /
Reading
Mask
0003h /
0000h /
7FFFFh
0003h /
0000h /
7FFFFh
010Fh /
0000h /
010Fh
0140h /
0000h /
0147h
DESCRIPTION
For internal use only N
For internal use only N
Watchdog 2 Y
FRU agent N
Causes red
Health LED
on error
Page 22 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 23

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
ModuleHotSwap OEM (F2h) / Sensor-
specific
IPMBL State OEM (C3h) / Sensor-
specific
Storage Err Management subsystem
health (28h) / Sensorspecific
Board Reset OEM (C4h) / Sensor-
specific
Board 3.3V Voltage (02h) / Threshold (
01h)
Board 3.3vIPM Voltage (02h) / Threshold (
01h)
Board 12.0v Voltage (02h) / Threshold (
01h)
Board 1.8V Voltage (02h) / Threshold (
01h)
Board Vtt0.9V Voltage (02h) / Threshold (
01h)
Board 5.0V Voltage (02h) / Threshold (
01h)
Board 1.5V Voltage (02h) / Threshold (
01h)
Temp CPU Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Temp MCH Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Temp CPU In Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Temp AMC Out Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Temp AMC In Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Temp CPU Out Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
CPU status Processor (07h) / Sensor-
specific (6Fh)
0007h /
0000h /
0007h
000Fh /
0000h /
000Fh
0002h /
0000h
04DEh /
0000h
2204h /
2204h /
1212h
2204h /
2204h /
1212h
2204h /
2204h /
1212h
2204h /
2204h /
1212h
2204h /
2204h /
1212h
2204h /
2204h /
1212h
2204h /
2204h /
1212h
0280h /
3280h /
1818h
0280h /
3280h /
1818h
0280h /
3280h /
1818h
0280h /
3280h /
1818h
0280h /
3280h /
1818h
0280h /
3280h /
1818h
0002h /
0002h /
0002h
Hot swap sensor N
State of IPMB-L bus
Storage error N
Board reset event Y
Board 3.3V supply Y
AMC Management
Power (MP) 3.3V
AMC Payload Power
(PWR) 12V
Board 1.8V supply Y
DDR termination
supply
Board 5V supply Y
Board 1.5V supply Y
CPU die temperature Y
MCH die temperature Y
Inlet temperature
near CPU
Outlet temperature
near AMC connector
Inlet temperature
near AMC connector
Outlet temperature
near CPU
CPU thermal alarm
sensor
N
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 23
Page 24

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
POST Value OEM Post Value (C6h) /
OEM (78h)
FWH0 Boot Err Boot Error (1Eh) / Sensor-
specific
FWH1 Boot Err Boot Error (1Eh) / Sensor-
specific
Pwr Good Power supply (08h) / OEM
(77h)
Pwr Good Evt Power supply (08h) / OEM
(77h)
Board NMI Critical interrupt (13h) /
Digital discrete (03h)
SMI Timeout Critical interrupt (13h) /
Digital discrete (03h)
Lan Front0 Lk LAN (27h) / Sensor-
specific
Lan Front1 Lk LAN (27h) / Sensor-
specific
Lan AMC0 Link LAN (27h) / Sensor-
specific
Lan AMC1 Link LAN (27h) / Sensor-
specific
Health Error Platform Alert (24h) /
Digital discrete (03h)
MMC Reboot Platform Alert (24h) /
Digital discrete (03h)
Ver change Version change (2Bh) /
Digital discrete (03h)
Proc hot>100C OEM (CFh) / Digital
discrete (03h)
0000h /
0000h /
00FFh
0008h /
0008h /
0008h
0008h /
0008h /
0008h
0000h /
0000h /
18B7h
0000h /
18B7h /
18B7h
0002h /
0000h /
0003h
0002h /
0000h /
0003h
0000h /
0000h /
0003h
0000h /
0000h /
0003h
0000h /
0000h /
0003h
0000h /
0000h /
0003h
0000h /
0000h /
0003h
0002h /
0000h /
0003h
0002h /
0000h /
0003h
0002h /
0000h /
0003h
POST Value (from
host I/O port 80h)
Firmware Hub 0 boot
error
Firmware Hub 1 boot
error
Statuses of all power
lines
Power fail events for
all power lines
CPU NMI signal N
Time out during SMI
processing
LAN Front link status
or LAN port 8 status
(if supported by the
module)
LAN port 9 status (if
supported by the
module)
LAN port 0 status N
LAN port 1 status N
Aggregate states
(power, temperatures
etc.). Visualization
by the Health LED.
MMC reboot active
state. Is asserted
during boot time.
Version change N
Monitors the CPU’s
“Processor Hot“
signal ( > 100 C)
N
Y
Y
N
Y
N
N
N
Y
N
N
Page 24 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 25

6.3.2 OEM Event / Reading Types
IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
OEM
SENSOR
EVENT/READING
TYPE (CODE)
Firmware Info 1 (C0h) 70h Internal Diagnostic Data
Firmware Info 2 (C0h) 71h Internal Diagnostic Data
Board Reset (C4h) 6Fh (sensor type
specific)
OEM
TYPE (CODE)
DESCRIPTION
Sensor-specific
Offset
00h Reserved
01h HwPowerReset
02h PCIReset
03h HwWatchDogReset
04h SoftReset
05h Reserved
06h ColdReset
07h IPMICommand
08h Reserved
Event
IPMBL State (C3h) 6Fh (sensor type
specific)
Post Value (C6h) 6Fh (sensor type
specific)
09h Reserved
0Ah BMCWatchdog
Sensor
discrete State
08h IPMB-L running
others IPMB-L not running
Sensor
discrete State
Bits [7:0] Post Value (read from host I/O port
Bits [15:8] Reserved
Meaning
Meaning
80h)
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 25
Page 26

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
i.e. for
Power Good /
Power Good Event
77h
Sensor-specific
Offset
0h 12V good
1h 5V good
2h 3V3 good
3h Reserved
4h 1V8 good
5h 1V5 good
6h Reserved
7h vccCore good
8h Reserved
9h 1V1 good
Ah Reserved
Bh 3V3IPMI good
Ch 0V9 good
Event
Hot swap sensor (F2h) 6Fh (sensor type
specific)
Sensor-specific
Offset
00h Handle close
01h Handle open
02h Quiesced
Event
Page 26 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 27

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.4 Firmware Code
6.4.1 Structure and functionality
MMC firmware code is organized into boot code and operational code, both of which are
stored in a flash module. Upon an MMC reset, the MMC executes the boot code and performs
the following:
1- Self test to verify the status of its hardware and memory.
2- Performs a checksum of the operational code.
3- Communicates with the Firmware Upgrade Manager (FWUM) in order to inform the MC
watchdog that the actual MMC firmware is suitable for execution. Upon successful
verification of the operational code checksum, the firmware will jump to the operational code.
Operational code is upgradeable in-the-field.
6.4.2 Firmware Upgrade
The standard way to upgrade the MMC’s operational code is to use the open tool ‘ipmitool’
[1] together with an image file. Ipmitool allows the downloading (‘ipmitool download …’)
and activation (‘ipmitool upgrade’) of the new operational code and saves an existing one.
The rollback to the formerly running operational code is possible as well (‘ipmitool
rollback’)..
All IPMI interfaces which are offered by ipmitool are usable (KCS interface, IPMB bus,
LAN). This allows local upgrade or remote upgrade.
Files which contain an image of operational code have the module type (AM4010) and the
string “FWUM” in its name.
During the download process the currently running operational code operates as usual until
the upgrade command is issued. During the upgrade process the MMC is off line for about 45
seconds when the boot code is re-organizing the firmware storage and afterwards starts the
new operational code. If this doesn’t succeed after a time out the boot code performs an
automatic rollback to the last working operational code.
6.5 Firmware Configuration
For software that uses the local KCS connection to the MMC, it may be may be more
favorable to set up interrupt based KCS communications. This may help to speed up data
exchange via KCS considerably. By default, the MMC does not generate interrupts to the
local CPU at all. The best way to change this is to use the IPMI menu in BIOS (Advanced ->
IPMI 1.5 Configuration -> KCS-SMS IRQ). Possible options are: IRQ10, IRQ11 or disabled
(default setting).
Another method of interrupt configuration is to do it ‘manually’ executing an ‘OEM Set
Firmware Parameters Command’ (refer to 6.2.2.2, Set Firmware Parameters.
It is strongly recommended to make changes in this area with the help of the BIOS. The BIOS
code creates an ‘IPMI Device Information Record (Type 38h)’ entry in the SMBIOS Table.
The information provided there includes: IPMI specification revision (v1.5), type of
supported interface (KCS), its base address (CA2h) and interrupt number for it (10, 11 or
none), and the IPMB address of the controller (depending on the module slot/bay). Some of
this information may be needed by software drivers or applications, for example the Linux
OpenIPMI driver looks for the SMBIOS IPMI entry while detecting system interfaces and it
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 27
Page 28

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
does make usage of the interrupt number provided there. Making changes ‘manually’ leaves
SMBIOS IPMI entry with not-up-to-date values until next reboot.
6.6 Firmware / Module Identification
There are two ways to determine via IPMI that a MMC resides on an AM4010.
1. The response on the IPMI command “Get Device ID” offers among others the the
following response data:
• Manufacturer ID = 3A98h (Kontron IANA ID)
• Device ID = 04h (H8S2166)
• Product ID = 4010
• Firmware Revision - depends on running firmware.
2. The Device ID String which can be found by reading the the Management Controller
Device Locator Record (SDR Type 12h) contains the string “AM4010”. For a module
being placed in bay B3 the Device ID String will be “B3: AM4010”.
6.7 FRU Information
6.7.1 Structure and functionality
The MMC provides 4 kB non-volatile storage space for FRU information. Some of the data
stored there, like Module Current Requirements record or E-Keying information (refer to
AMC.0 specification for details), are mandatory for module functionality in the ATCA/AMC
environment. Refer to [2] Platform Management FRU Information Storage Definition
document for details).
Please note that missing FRU information will prevent the AMC module from being accepted
by the carrier controller during the Hot Swap process and the module will get no payload
power.
Full low level access to read or write a module’s FRU Information is provided by regular
IPMI FRU Device commands. Please be careful when writing FRU information directly using
standard IPMI commands. Damaging the FRU Information may lead to a non working
payload.
To avoid this danger there exists a Kontron Linux tool ‘frum’ (refer to section 12.2), which
allows to display and partially modify FRU data. E.g. the ‘frum’ tool makes it easy to modify
Product Info Area fields (like Product Version or Product Serial Number).
6.7.2 Download
Normally the user needs not download the FRU information because the module is shipped
with the data which describes best the module capabilities and requirements. Remember that
FRU information might be damaged by a write access to the IPMI FRU Device using
standard IPMI commands.
Page 28 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 29

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
If needed the standard way to download FRU information to the module is to use the open
tool ‘ipmitool’ [1] for the download of an image file. Ipmitool allows the downloading
(‘ipmitool fru write …’). The rollback to the formerly running operational code is possible as
well (‘ipmitool rollback’).
All IPMI interfaces which are offered by ipmitool are usable (KCS interface, IPMB bus,
LAN). This allows local upgrade or remote upgrade. Note that the KCS interface is only
usable on a powered payload.
6.8 E-Keying
E-Keying has been defined in the AMC.0 R1.0 Specification to prevent module damage,
prevent misoperation, and verify bay connection compatibility. The FRU data contains the
AMC point-to-point connectivity record as described in Section 3.9.2 of the AMC.0 R1.0
specification. The Set/Get AMC Port State IPMI commands defined by the AMC.0
specification are used by the carrier for either granting or rejecting the E-keys.
6.9 PCI Express Clock Source
The PCI-E reference clock may be generated locally by the module (default configuration) or
acquired via the AMC connector (common/external reference clock). The standard FRU EKeying data for the AM4010 contains an AMC Link Descriptor for the PCI-E clock. If an
external clock is available the carrier’s IPMC provides it by a “Set AMC Port State”
command. The appropriate control signal is latched by the on-board FPGA during payload
power on and cannot be changed until payload power off.
The common reference clock provided by the carrier may be slightly modulated (Spread
Spectrum Clock - SSC). Standard FRU E-Keying data for AM4010 contains two AMC Link
Descriptors for the PCI-E channel, describing how the module works with non-SSC or with
SSC. The carrier’s IPMC makes this selection during E-keying by “Set AMC Port State”
commands“. The clock selection will be latched by the on-board FPGA during payload power
on and can’t be changed until payload power off.
6.10 BIOS Supervisory and Automated Firmware Hub Switch
After each payload reset, the MMC expects a special message from the BIOS i.e. the BIOS
checksum report. If the checksum (computed by the BIOS boot block) is incorrect or the
message itself is not available within 15 seconds after payload reset, then the currently used
firmware hub is assumed to contain an invalid or a corrupted BIOS image. In this case an
automatic switch to another firmware hub is done and another reset is initiated and the “Boot
Error (Invalid boot sector) event” for the failing firmware hub is generated. Refer to 6.3.1,
sensors ‘FWHx Boot Err’. x = 0..1 .
6.11 Hot Swap
As a hot-swappable field replaceable unit (FRU), the AM4010 also follows the same stringent
carrier grade RASM feature set, namely - Reliability, Availability, Serviceability,
Maintainability. When offered in combination with AdvancedTCA platforms, TEM (Telecom
Equipment Manufacturers) clients literally conserve valuable system AdvancedTCA system
slots. The AM010 supports Full Hot Swap capability as per PICMG 3.0. It can be removed
from or installed in the system while it is on (without powering-down the system). Please
refer to the PICMG 3.0 specification for additional details.
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 29
Page 30

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
During Hot Swap of a working module the payload side has to be shut down automatically on
command of the MMC and the end of shut down has to be signalled back to the MMC.
Because the AM4010 supports ACPI, an OS on payload side which supports this too makes
shut down very easy. If the OS doesn’t support ACPI there is a special method to be used.
Method 1. The payload OS supports ACPI
Requirements:
• ACPI support must be enabled in the BIOS menu.
• The ACPI daemon must be active.
• An ACPI power button event must result in a sleep state.
Part of the Hot Swap 0peration sequence to be processed by MMC and OS:
• On command of the carrier controller the MMC simulates the pressing and release of
the “power button” to force an ACPI event.
• The ACPI daemon detects this ACPI event and initiates the shut down of the payload
software system.
• At the end of shut down the payload hardware system reports the sleep state to the
MMC by setting the appropriate signal line.
• The MMC detects the sleep state and reports this to the carrier controller so that the
Hot Swap processing can be continued and finished.
By default the MMC waits endless for the sleep state. If an endless wait shall be avoided
in each case it is possible to set a timeout time after which the system will be switched off
unconditionally. For the setting of the timeout refer to 6.2.2.5, OEM Module Quiescence
Feedback.
Method 2. The payload OS does not support ACPI
Requirements:
• At system start on payload side the Kontron shutdown daemon ‘grnsd’ has to be
started. It is included in the Linux board support packages for the AM4010 (refer to
[3]). This daemon communicates cyclically with the MMC for the exchange of states,
commands and acknowledges. For this it uses the “OEM Module Quiescence
Feedback” command. Refer to 6.2.2.5. In principle it plays the same role as the ACPI
daemon of method 1, above.
Part of the Hot Swap 0peration sequence to be processed by MMC and OS:
• On command of the carrier controller the MMC sets a “shut down request” flag.
• The grnsd daemon recognizes this request in the response to its cyclical “OEM
Module Quiescence Feedback” command and initiates the shut down of the payload
software system.
• At the end of the shut down process the grnsd daemon informs the MMC by setting
the appropriate flag when calling the “OEM Module Quiescence Feedback” command.
• The MMC reports this to the carrier controller so that the Hot Swap processing can be
continued and finished.
By default the MMC waits endless for this information. If an endless wait shall be avoided
in each case it is possible to set a timeout time after which the system will be switched off
unconditionally. For the setting of the timeout refer to 6.2.2.5, OEM Module Quiescence
Feedback.
Page 30 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 31

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.12 LAN functions
6.12.1 Overview
The two Ethernet channels which reside on port 0 (channel 0) and port 1 (channel 1) at the
AMC Fabric Interface can – in parallel to their ‘normal’ use - be used for the following
special purposes:
• IPMI over LAN (IOL)
• Serial over LAN
Common for both kinds of communication is the use of the RMCP/RMCP+ for the packing of
the data to be transferred. On Ethernet the port 623 is used for transfers with this protocol.
While IOL serves to transport IPMI commands and their responses the SOL serves to
transport any serial data. In each case the MMC serves as a protocol encoder and decoder.
Please note that IOL is able to use both RMCP and RMCP+ protocols. SOL works only with
the RMCP+ protocol.
6.12.2 Setting up the Ethernet channel
There are two methods to prepare the MMC’s SOL and IOL LAN parameters for the two
possible Ethernet channels:
• During the BIOS setup
• By use of the open tool ‘ipmitool’ or IPMI commands
The setup methods are compatible i.e. both methods show the parameters which are set by the
other one.
The setup is separate for both channels. When the MAC addresses are set the ones which are
programmed into the hardware have to be re-used. This is a restriction. The IP addresses
being used by ‘normal’ payload use and IOL/SOL use may differ but need not differ as long
as the RMCP port 623 is not used in parallel.
6.12.2.1 Setup by BIOS menu
The BIOS setup menu “Advanced>IPMI 1.5 Configuration>Set LAN Configuration” offers
the setting of some LAN parameters for both channels (1, 2). After this setup IOL is not yet
ready for use. Refer to 6.12.2.2, Setup by ipmitool or IPMI commands.
6.12.2.2 Setup by ipmitool or IPMI commands
The open tool ipmitool offers commands for the setup of the two Ethernet channels. All
possible options are showed by issuing
ipmitool lan set
If ipmitool is not usable the LAN parameters can be set by using the generic IPMI commands
which are defined for this.
To enable the LAN support after parameter setup this command has to be issued:
ipmitool lan set access on
6.12.3 Setup of user and password
The open tool ipmitool offers commands for the listing and manipulation of user accounts for
channel 1 and 2. An overview can be obtained by putting in
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 31
Page 32

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
Ipmitool user
The predefined users for a channel can be listed by the command
Ipmitool user <channel 1, 2>.
The AM4010 has for every channel these predefinitions in non volatile memory:
ID Name Callin Link Auth IPMI Msg Channel Priv Limit
1 false true true USER
2 admin false true true ADMINISTRATOR
Please note that admin’s password is preset with ‘kontron’.
Changed users and passwords stay valid after payload power off.
6.12.4 IPMI over LAN (IOL)
IPMI over LAN is used for to communicate with an IPMI controller as e.g. the AM4010’s
MMC via LAN using the RMCP or RMCP+ protocol. The data which is transferred are IPMI
commands and the responses to them.
The open tool ‘ipmitool’ can serve as a control program and user interface for this. ipmitool
allows to issue generic IPMI commands as e.g.:
ipmitool -I lanplus -H 192.168.3.189 -U admin -P admin raw 6 1
or to call complex functions like ‘mc .info’:
ipmitool -I lanplus -H 192.168.3.189 -U admin -P admin mc info
This uses many generic IPMI commands to get all needed information.
6.12.5 Serial over LAN (SOL)
Serial over LAN connects the COM1 or /dev/ttyS0 respectively of the AM4010’s payload
side to an Ethernet channel. The MMC resides between this serial interface and one of the
Ethernet channels. It serves as an encoder and a decoder for the used RMCP+ protocol and
controls the data stream. Outside the AM4010 e.g. the open tool ipmitool can be used to drive
the SOL session i.e. it offers a console function to communicate via Ethernet with the
AM4010’s serial interface.
The serial interface can be used as a connection to
1) a user program on the AM4010 payload
2) the BIOS console redirection function. Refer to the BIOS setup menu
“Advanced>Console Redirection”. There the serial parameters for this purpose can be
set. Please note that after BIOS start, the OS gets active in most cases (except e.g.
DOS) and the console redirection stops working because the OS doesn’t use BIOS
functions to drive the console.
3) a Linux login console. This can be activated after payload start e.g. by the command
getty –h 115200 /dev/ttyS0
4) etc.
SOL supports and requires serial hardware handshake. This should be activated for the serial
port. Otherwise transmitted data might get lost. In any case the same serial parameters for the
used payload side serial interface and the MMC’s serial interface have to be used. The
parameters for the MMC’s serial interface can be set by the “ipmitool sol set …” command.
Calling “ipmitool sol set” shows all options that can be set.
Other commands which are possible are showed when issuing “ipmitool sol help”.
Page 32 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
Page 33

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
6.13 OS Support / Tools
6.13.1 DOS
There is a low-level DOS command line tool provided by Intel that allows hex-formatted
IPMI commands to be sent to the management controller via KCS interface. The IPMI
Command Test Tool can be found at: http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/tools.htm
6.13.2 Linux
Normally all drivers and kernel modules needed for communication between the payload
sided software and the MMC firmware via the KCS interface come with the distribution.
Newest sources can be downloaded from http://openipmi.sourceforge.net
downloaded the OpenIPMI project as well. The OpenIPMI library package includes some
applications and the needed libraries. One of the applications is ‘ipmicmd’ which makes it
possible to send and receive raw IPMI sequences; another, the ‘ipmi_ui’, provides a higher
level interface and thus it does not require deep IPMI knowledge from the user side.
Another very useful all-in-one tool is the ipmitool ( http://ipmitool.sourceforge.net ). It
provides a user friendly interface to many IPMI features and extensions, for example to
PICMG LED control and Kontron FWUM.
. There may be
There is a Kontron Modular Computers’ IPMI ToolKit which contains some tools for the
customer for the monitoring and the maintenance of some IPMI functionalities.
The following command line tools are included in the IPMI ToolKit:
• frum: display and modification of FRU data
• temptool: selection, display, and storage of temperature and voltage sensor values
All these tools are OpenIPMI based. This toolkit is available on the “AMC Kit CD”. If this
CD was not shipped with your module then please contact our support ( support@kontron-
modular.com ).
Please refer to the manual "MAN_LIN_IPMI_TOOLKIT_0103.pdf" being included in the
package.
6.13.3 Windows
Intel provides KCS reference drivers for Windows and the IPMI Conformance Test Suite
(ICTS), they are available at the following address:
http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/tools.htm
ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1 © 2007 Kontron AG Page 33
Page 34

IPMI Firmware User Guide: AM4010
7. IPMI Communication LEDs
There are three IPMI communication LEDs on the face plate.
LED 0
Color: Blue
Position: Bottom right
Labeled: ./.
Meaning: Indicates the Hot Swap state of the inserted and powered module.
Meaning: On: Module may be extracted.
Blinking: Hot Swap active, don’t extract
Off: Module in normal operation. Don’t extract.
Index in “Get/Set LED State” commands: 0
LED 1
Color: Red
Position: Top left
Labeled: by a crossed out plus sign
Meaning: Indicates the “Out Of Service” state of the powered module.
Behavior: Solid red = module out of service
Off = module powered/running
Pulsing red = Traffic on the IPMB-L bus
Index in “Get/Set LED State” commands: 1
LED 2
Color: Green / red
Position: Top right
Labeled: by a plus sign Meaning: Indicates the “Health” state of a running/powered module.
Behavior: Blinking slow: Module MMC is running, showing its heart beat.
Pulsing: The KCS interface is active.
Solid: Module MMC not running or firmware is a non heart
beat version (version dependent, standard is heart beat).
Off: Module MMC not running.
Is green: No health error detected (refer to sensor “Health Error “,
6.3.1).
Is red: Health error detected.
Index in “Get/Set LED State” commands: 2
Page 34 © 2007 Kontron AG ID: 36363, Rev. 1.1
 Loading...
Loading...