Page 1
Installation
Automatic Transfer Switches
Models:
KSSB
30- 1200 Amps
TP-7191 4/21
Page 2

Product Identification Information
Product identification numbers determine service parts.
Record the product identification numbers in the spaces
below immediately after unpacking the products so that
the numbers are readily available for future reference.
Record field-installed kit numbers after installing the
kits.
Transfer Switch Identification Numbers
Record the product identification numbers from the
transfer switch nameplate.
Model Designation
Serial Number
Accessories
- Alarm Board
- Battery Module
- California OSHPD Approval
- Controller Disconnect Switch
- Current Monitoring
- Digital Meter
- Heater
- IBC Seismic Certification
- I/O Module, Standard (max. 4) qty:
- I/O Module, High Power (max. 4) qty:
- Load Shed
- Line-Neutral Monitoring
- Supervised Transfer Switch
- SurgeProtectionDevice(SPD)
-
-
-
-
Controller Identification
Record the controller description from the generator set
operation manual, spec sheet, or sales invoice.
Controller Description
Page 3

Table of Contents
Safety Precautions and Instructions 5........................................................
Introduction 9..............................................................................
List of Related Literature 9.....................................................
Service Assistance 10........................................................................
Section 1 Product Description 11.............................................................
1.1 Purpose 11.............................................................
1.2 Nameplate 11...........................................................
1.3 Model Designation 12....................................................
Section 2 Installation 13......................................................................
2.1 Introduction 13..........................................................
2.2 Receipt of Unit 13........................................................
2.2.1 Inspection 13....................................................
2.2.2 Lifting 13.......................................................
2.2.3 Storage 14......................................................
2.2.4 Unpacking 14...................................................
2.3 Installation 14...........................................................
2.4 IBC Seismic Certification 15...............................................
2.5 Manual Operation, Model KSS Switches 16.................................
2.5.1 Manual Operation, 30- 230 Amp Switches 16........................
2.5.2 Manual Operation, 230A/600V and 260- 1200 Amp Switches 17........
2.6 Controller Connections 19................................................
2.6.1 Controller Input and Output Connections 20.........................
2.6.2 Harness Connection 20...........................................
2.6.3 Controller Ground 20.............................................
2.7 Electrical Wiring 21......................................................
2.7.1 Source and Load Connections 21..................................
2.7.2 Engine Start Connection 23.......................................
2.7.3 Auxiliary Contacts 24.............................................
2.8 Communication and Accessory Connections 25..............................
2.9 Functional Tests 25......................................................
Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections 27......................................
3.1 Introduction 27..........................................................
3.2 Communication Connections 27...........................................
3.2.1 USB Port SiteTech Connection 27..................................
3.2.2 Modbus Connection 27...........................................
3.2.3 Ethernet Connection 29...........................................
3.3 Accessory Modules 31...................................................
3.3.1 Accessory Module Mounting 31....................................
3.3.2 Input/Output (I/O) Modules 32.....................................
3.3.3 External Battery Supply Module (EBSM) 33.........................
3.3.4 Alarm Module 34................................................
3.4 Heater 36...............................................................
Section 4 Scheduled Maintenance 39..........................................................
Section 5 Functional Tests and Setup 41......................................................
5.1 Introduction 41..........................................................
5.2 Manual Operation Test 41.................................................
5.3 Voltage Check 41........................................................
5.4 Lamp Test 42
TP-7191 4/21 Table of Contents 3
...........................................................
Page 4

Table of Contents, continued
5.5 Automatic Operation Test 42..............................................
5.6 System Setup 43........................................................
5.7 Exerciser Setup 43.......................................................
5.8 User Interface Cover 43..................................................
5.9 Startup Notification 43....................................................
Appendix A Abbreviations 45................................................................
TP-7191 4/21Table of Contents4
Page 5
Safety Precautions and Instructions
IMPORT ANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS.
Electromechanical equipment,
including generator sets, transfer
switches, switchgear, and accessories,
can cause bodily harm and pose
life-threatening danger when
improperly installed, operated, or
maintained. To prevent accidents be
aware of potential dangers and act
safely. Read and follow all safety
precautions and instructions. SAVE
THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
This manual hasseveral types of safety
precautions and instructions: Danger,
Warning, Caution, and Notice.
DANGER
DANGER indicates a hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, will
result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
WARNING indicates a hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
CAUTION indicates a hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, could
result in minor or moderate injury.
NOTICE
NOTICE is used to address practices
not related to physical injury.
Safety decals affixed to the equipment
in prominent places alert the operator
or service technician to potential
hazards and explain how to act safely.
The decals are shown throughout this
publication to improve operator
recognition. Replace missing or
damaged decals.
Accidental Starting
WARNING
Accidental starting.
Can cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect the battery cables before
working on the generator set.
Remove the negative (- ) lead first
when disconnecting the battery.
Reconnect the negative (- ) lead last
when reconnecting the battery.
Disabling the generator set.
Accidental starting can cause
severe injury or death. Before
working on the generator set or
equipment connected to the set,
disable the generator set as follows:
(1) Move the generator set master
switch to the OFF position.
(2) Disconnect the power to the battery
charger. (3) Remove the battery
cables, negative (- ) lead first.
Reconnect the negative (- ) lead last
when reconnecting the battery. Follow
these precautions to prevent starting of
the generator set by an automatic
transfer switch, remote start/stop
switch, or engine start command from a
remote computer.
(Decision-Makerr 3+ and 550
Generator Set Controllers)
Disabling the generator set.
Accidental starting can cause
severe injury or death. Before
working on the generator set or
equipment connected to the set,
disable the generator set as follows:
(1) Press the generator set off/reset
button to shut down the generator set.
(2) Disconnect the power to the battery
charger, if equipped. (3) Remove the
battery cables, negative (- ) lead first.
Reconnect the negative (- ) lead last
when reconnecting the battery. Follow
these precautions to prevent the
starting of the generator set by the
remote start/stop switch.
(RDC, DC, RDC2, DC2,
Decision-Makerr 3000, 3500 and
6000 Generator Set Controllers)
Disabling the generator set.
Accidental starting can cause
severe injury or death. Before
working on the generator set or
equipment connected to the set,
disable the generator set as follows:
(1) If the controller is not already in the
MAN (manual) mode, press the
Controller Mode button and then press
the MAN mode button. (2) If the
generator set is running, press and hold
the Manual- Stop button for at least
2 seconds to stop the generator set.
(3) Press the Controller Mode button
and then press the controller Off mode
button. (4) Disconnect the power to the
battery charger, if equipped.
(5) Remove the battery cables,
negative (- ) lead first. Reconnect the
negative (- ) lead last when
reconnecting the battery. Follow these
precautions to prevent the starting of
the generator set by the remote
start/stop switch.
(Decision-Makerr 8000 Controller)
Hazardous Voltage/
Moving Parts
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Only authorized personnel should
open the enclosure.
TP-7191 4/21 5Safety Precautions and Instructions
Page 6

Grounding electrical equipment.
Hazardous voltagewill cause severe
injury or death. Electrocution is
possible whenever electricity is
present. Ensure you comply with all
applicable codes and standards.
Electrically ground the generator set,
transfer switch, and related equipment
and electrical circuits. Turn off the main
circuit breakers of all power sources
before servicing the equipment. Never
contact electrical leads or appliances
when standing in water or on wet
ground because these conditions
increase the risk of electrocution.
Removing the transfer switch from
bypass/isolation models. Hazardous
voltage will cause severe injury or
death. Bypass and isolate the transfer
switch before removing it from the
enclosure. The bypass/isolation switch
is energized. Do not touch the isolation
contact fingers or the control circuit
terminals.
Short circuits. Hazardous
voltage/current will cause severe
injury or death. Short circuits can
cause bodily injury and/or equipment
damage. Do not contact electrical
connections with tools or jewelry while
making adjustments or repairs.
Remove all jewelry before servicing the
equipment.
Making line or auxiliary
connections. Hazardous voltage
will cause severe injury or death. To
prevent electrical shock deenergize the
normal power source before making
any line or auxiliary connections.
Servicing the transfer switch.
Hazardous voltagewill cause severe
injury or death. Deenergize all power
sources before servicing. Turn off the
main circuit breakers of all transfer
switch power sources and disable all
generator sets as follows: (1) Move all
generator set master controller
switches to the OFF position. (2)
Disconnect power to all battery
chargers. (3) Disconnect all battery
cables, negative (- ) leads first.
Reconnect negative (- ) leads last when
reconnecting the battery cables after
servicing. Follow these precautions to
prevent the starting of generator sets
by an automatic transfer switch, remote
start/stop switch, or engine start
command from a remote computer.
Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all
jewelry. (2) Stand on a dry, approved
electrically insulated mat. (3) Test
circuits with a voltmeter to verify that
they are deenergized.
(Decision-Makerr 3+ and 550
Generator Set Controllers)
Servicing the transfer switch.
Hazardous voltagewill cause severe
injury or death. Deenergize all power
sources before servicing. Turn off the
main circuit breakers of all transfer
switch power sources and disable all
generator sets as follows: (1) Pressthe
generator set off/reset button to shut
down the generator set. (2) Disconnect
power to all battery chargers. (3)
Disconnect all battery cables, negative
(- ) leads first. Reconnect negative (- )
leads last when reconnecting the
battery cables after servicing. Follow
these precautions to prevent the
starting of generator sets by an
automatic transfer switch, remote
start/stop switch, or engine start
command from a remote computer.
Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all
jewelry. (2) Stand on a dry, approved
electrically insulated mat. (3) Test
circuits with a voltmeter to verify that
they are deenergized.
(RDC, DC, RDC2, DC2,
Decision-Makerr 3000, 3500 and
6000 Generator Set Controllers)
Testing live electrical circuits.
Hazardous voltage or current will
cause severe injury or death. Have
trained and qualified personnel take
diagnostic measurements of live
circuits. Use adequately rated test
equipment with electrically insulated
probes and follow the instructions of the
test equipment manufacturer when
performing voltage tests. Observe the
following precautions when performing
voltage tests: (1) Remove all jewelry.
(2) Stand on a dry, approved electrically
insulated mat. (3) Do not touch the
enclosure or components inside the
enclosure. (4) Be prepared for the
system to operate automatically.
(600 volts and under)
Heavy Equipment
WARNING
Unbalanced weight.
Improper lifting can cause severe
injury or death and equipment
damage.
Use adequate lifting capacity.
Never leave the transfer switch
standing upright unless it is securely
bolted in place or stabilized.
Notice
NOTICE
Improper operator handle usage.
Use the manual operator handle on the
transfer switch for maintenance
purposes only . Return the transfer
switch to the normal position. Remove
the manual operator handle, if used,
and store it in the place provided on the
transfer switch when service is
completed.
TP-7191 4/216 Safety Precautions and Instructions
Page 7

NOTICE
Foreign material contamination.
Cover the transfer switch during
installation to keep dirt, grit, metal drill
chips, and other debris out of the
components. Cover the solenoid
mechanism during installation. After
installation, use the manual operating
handle to cycle the contactor to verify
that it operates freely. Do not use a
screwdriver to force the contactor
mechanism.
NOTICE
Electrostatic discharge damage.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
damages electronic circuit boards.
Prevent electrostatic discharge
damage by wearing an approved
grounding wrist strap when handling
electronic circuit boards or integrated
circuits. An approved grounding wrist
strap provides a high resistance (about
1 megohm), not a direct short,to
ground.
TP-7191 4/21 7Safety Precautions and Instructions
Page 8

Notes
TP-7191 4/218 Safety Precautions and Instructions
Page 9

Introduction
This manual provides installation instructions for the
Kohlerr Model KSSB Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS).
Model KSSB transfer switches are equipped with the
Kohler MPACr 1200 controller.
Model KSSB is used in some places in this manual to
indicate that this document applies to an updated
version of the model KSS automatic transfer switch. The
letter B is NOT used in the model designation or Quick
Ship (QS) specification numbers used for ordering the
product.
A separate manual provided with the transfer switch
covers the transfer switch controller operation. See List
of Related Materials for the document part number.
Information in this publication represents data available
at the time of print. Kohler Co. reserves the right to
change this literature and the products represented
without notice and without any obligation or liability
whatsoever.
Read this manual and carefully follow all procedures
and safety precautions to ensure proper equipment
operation and to avoid bodily injury. Read and follow the
Safety Precautions and Instructions section at the
beginning of this manual. Keep this manual with the
equipment for future reference.
The equipment service requirements are very important
to safe and efficient operation. Inspect parts often and
perform required service at the prescribed intervals.
See the controller Operation manual for the service
schedule. Obtain service from an authorized service
distributor/ dealer to keep equipment in top condition.
List of Related Literature
A separate manual covers the transfer switch controller
and related accessories. The Service Manual contains
service instructions for transfer switch power switching
devices and electrical controls.
The following table lists the part numbers for related
literature.
Literature Item Part Number
Specification Sheet, Model KSSB G11-150
Specification Sheet, Decision-Makerr
MPAC 1200 Controller
Operation Manual, Decision-Makerr
MPAC 1200 Controller
Wiring Diagram Manual, Model KC/KSSB TP-7195
Service Manual, Model KC/KSSB TP-6920
G11-127
TP-6866
TP-7191 4/21 9Introduction
Page 10

Service Assistance
For professional advice on generator set power
requirements and conscientious service, please contact
your nearest Kohler distributor or dealer.
D Visit the Kohler Co. website at KOHLERPower.com.
D Look at the labels and decals on your Kohler product
or review the appropriate literature or documents
included with the product.
D Call toll free in the US and Canada 1-800-544-2444.
D Outside the US and Canada, call the nearest regional
office.
Headquarters Europe, Middle East, Africa
(EMEA)
Kohler EMEA Headquarters
Netherlands B.V.
Kristallaan 1
4761 ZC Zevenbergen
The Netherlands
Phone: (31) 168 331630
Fax: (31) 168 331631
Asia Pacific
Kohler Asia Pacific Headquarters
Singapore, Republic of Singapore
Phone: (65) 6264-6422
Fax: (65) 6264-6455
China
North China Regional Office, Beijing
Phone: (86) 10 6518 7950
(86) 10 6518 7951
(86) 10 6518 7952
Fax: (86) 10 6518 7955
East China Regional Office, Shanghai
Phone: (86) 21 6288 0500
Fax: (86) 21 6288 0550
India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka
India Regional Office
Bangalore, India
Phone: (91) 80 3366208
(91) 80 3366231
Fax: (91) 80 3315972
Japan, Korea
North Asia Regional Office
Tokyo, Japan
Phone: (813) 3440-4515
Fax: (813) 3440-2727
TP-7191 4/2110 Service Assistance
Page 11
Section 1 Product Description
1.1 Purpose
An automatic transfer switch (ATS) transfers electrical
loads from a normal (preferred) source of electrical
power to an emergency (standby) source when the
normal source falls outside the acceptable electrical
parameters.
When the normal (preferred) source fails, the ATS
signals the emergency (standby) source generator set
to start. When the emergency (standby) source reaches
acceptable levels and stabilizes, the ATS transfers the
load from the normal (preferred) source to the
emergency (standby) source. The AT S continuously
monitors the normal (preferred) source and transfers
the load back when the normal (preferred) source
returns and stabilizes. After transferring the load back to
the normal (preferred) source, the ATS removes the
generator start signal, allowing the generator set to shut
down.
Figure 1-2 shows a typical installation block diagram.
Normal
(Utility)
Power
Switching
Device
Power
Emergency
(Generator)
Power
Automatic Transfer Switch
To Load
Generator
Start Generator
Electrical
Controls
TS-003
Figure 1-2 Typical ATS Block Diagram
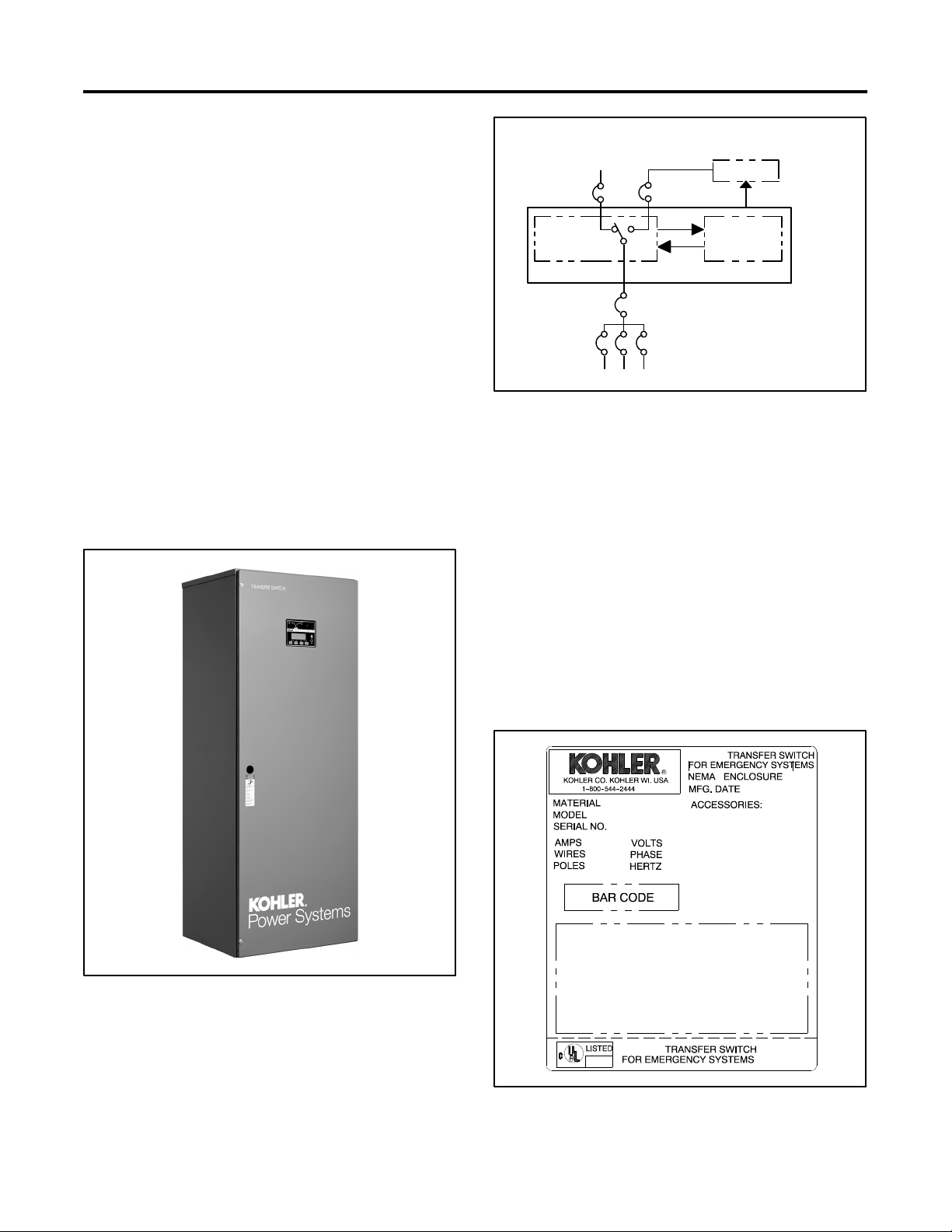
1.2 Nameplate
A nameplate attached to the controller cover on the
inside of the enclosure door includes a model
designation, a serial number, ratings, and other
information about the transfer switch. See Figure 1-3.
The serial number is also shown on a label inside the
transfer switch enclosure.
Figure 1-1 Automatic Transfer Switch
Copy the model designation, serial number, and
accessory information from the nameplate to the spaces
provided in the Product Identification Information
section inside the frontcover of this manual for use when
requesting service or parts.
GM21291
Figure 1-3 Typical Transfer Switch Nameplate
TP-7191 4/21 11Section 1 Product Description
Page 12

1.3 Model Designation
Model Controls Voltage Enclosure Current Rating MiscellaneousMechanismTransition
Record the transfer switch model designation in the boxes. The transfer switch model designation defines
characteristics and ratings as explained below.
Poles
Note: The letter B is not used after KSS in the model designation shown on the ATS nameplate or used for
ordering the product.
Sample Model Designation: KSS-AMTA-0400S
Model
K: Kohler
Mechanism
S: Standard (Specific Breaker)
Transiti on
S: Standard
Controller
A:
Decision-Makerr MPAC 1200, Automatic
B:
Decision-Makerr MPAC 1200, Non-Automatic
Voltage/Frequency
C: 208 Volts / 60 Hz K: 440 Volts/60 Hz
D: 220 Volts / 50 Hz M: 480 Volts /60 Hz
F: 240 Volts / 60 Hz N: 600 Volts / 60 Hz
G: 380 Volts/50 Hz P: 380 Volts /60 Hz
H: 400 Volts / 50 Hz R: 220 Volts / 60 Hz
J: 416 Volts / 50 Hz S: 400 Volts/60 Hz
Number of Poles/Wires
N: 2 Poles/ 3 Wires, Solid Neutral
T: 3 Poles/4 Wires, Solid Neutral
V: 4 Poles /4 Wires, Switched Neutral
W: 4 Poles/4 Wires, Overlapping Neutral
Enclosure
A: NEMA 1 D: NEMA 4
B: NEMA 12 F: NEMA 4X
C: NEMA 3R G: Open Unit
Current, Amps
0030 0200 0600
0070 0230 0800
0104 0260 1000
0150 0400 1200
Connections
S: Standard
Note: Some selections are not available for every model.
Contact your Kohler distributor for availability.
TP-7191 4/2112 Section 1 Product Description
Page 13
Section 2 Installation
2.1 Introduction
Kohlerr transfer switches are shipped factory-wired,
factory-tested, and ready for installation. Have the
equipment installed only by trained and qualified
personnel, and verify that the installation complies with
applicable codes and standards. Switch installation
includes the following steps:
D Unpack and inspect the transfer switch upon receipt.
D Verify that the transfer switch voltage and frequency
ratings match the voltages and frequencies of the
sources.
D Install the transfer switch.
D Check the manual operation.
D Connect the controller harness and ground lead.
D Connect the generator set engine start leads.
D Connect the normal power source (utility),
emergency power source (generator set), and load
circuits.
D Connect accessories, if provided.
D Check voltages and operation.
2.2 Receipt of Unit
2.2.1 Inspection
At the time of delivery, inspect the packaging and the
transfer switch for signs of shipping damage. Unpack
the transfer switch as soon as possible and inspect the
exterior and interior for s hipping damage. If damage
and/or rough handling is evident, immediately file a
damage claim with the transportation company.
2.2.2 Lifting
WARNING
Unbalanced weight.
Improper lifting can cause severe
injury or death and equipment
damage.
Use adequate lifting capacity.
Never leave the transfer switch
standing upright unless it is securely
bolted in place or stabilized.
Protect the switch against damage before and during
installation.
Note: A protective device such as a molded-case circuit
breaker or fused disconnect switch MUST be
installed on both sources of incoming power for
circuit protection and used as a disconnect
device.
The functional tests in Section 5 are a necessary part of
the installation. Be sure to perform the functional tests,
which include voltage checks and operation tests,
before putting the transfer switch into service.
Refer to Figure 2-1 for the approximate weight of the
transfer switch in a Type 1 enclosure. For open units and
other enclosures, refer to the dimension drawing. Use a
spreader bar to lift the transfer switch. Attach the bar
only to the enclosure’s mounting holes or lifting
brackets; do not lift the unit any other way. Close and
latch the enclosure door before moving the unit.
Weight kg (lb.)
Amps
30- 200 28 (62) 30 (65) 31 (68)
230
(208- 480V)
230(600V)
260- 600
800 220 (485) 231 (510) 238 (525)
1000 — 231 (510) 238 (525)
1200 — 356 (785) 379 (835)
2-Pole 3-Pole 4-Pole
52 (115) 56 (123) 59 (131)
179 (395) 183 (403) 188 (414)
Figure 2-1 Approximate Weights, Type 1 Enclosures
TP-7191 4/21 13Section 2 Installation
Page 14

2.2.3 Storage
Store the transfer switch in its protective packing until
final installation. Protect the transfer switch at all times
from moisture, construction grit, and metal chips. Avoid
storage in low-temperature and high-humidity areas
where moisture could condense on the unit. See
Figure 2-2 for acceptable storage temperatures.
Plan the installation. Use the dimensions given on the
enclosure dimension (ADV) drawings. Select a
mounting site that complies with local electrical code
restrictions for the enclosure type. Mount the transfer
switch as close to the load and power sources as
possible. Allow adequate space to fully open the
enclosure and to service the switch. Provide cable
bending space and clearance to live metal parts.
Environmental Specifications
Operating Temperature -20Cto70C(-4Fto158F)
Storage Temperature -40Cto85C(-40Fto185F)
Humidity 5% to 95% noncondensing
Figure 2-2 Environmental Specifications
2.2.4 Unpacking
Allow the equipment to warm to room temperature for at
least 24 hours before unpacking to prevent
condensation on the electrical apparatus. Use care
when unpacking to avoid damaging transfer switch
components. Remove d irt and packing material that
may have accumulated in the transfer switch or any of its
components.
Note: Do not use compressed air to clean the switch.
Cleaning with compressed air can cause debris
to lodge in the components and damage the
switch.
For 600- 800 amp transfer switches, remove the lag
screws that secure the transfer switch to the shipping
skid. For 1000- 1200 amp transfer switches, open the
enclosure door to remove the lag screws that secure the
transfer switch to the skid.
2.3 Installation
NOTICE
Foreign material contamination. Cover the transfer switch
during installation to keep dirt, grit, metal drill chips, and other
debris out of the components. Cover the solenoid mechanism
during installation. After installation, use the manual operating
handle to cycle the contactor to verify that it operates freely.
Do not use a screwdriver to force the contactor mechanism.
The transfer switch may use both American Standard and
metric hardware. Use the correct size tools to prevent
rounding of the bolt heads and nuts.
Outdoor installations. Transfer switches with
NEMA 3R, 4, or 4X enclosures can be installed
outdoors. In locations with very high ambient
temperatures, installation in a shaded area or a location
with the enclosure door facing away from direct sunlight
is recommended.
Prepare the foundation. Ensure that the supporting
foundation for the enclosure is level and straight. Refer
to the applicable enclosure outline drawing for all
mounting details including door opening space.
For bottom cable entry, if used, install conduit stubs in
the foundation. Refer to the enclosure dimension
drawing f or the conduit stub locations. When pouring a
concrete floor, use interlocking conduit spacer caps or a
wood or metal template to maintain proper conduit
alignment.
Installation of seismically certified transfer
switches. Seismic certification must be requested
when the transfer switch is ordered. See Section 2.4 and
thetransferswitchdimension(ADV)drawingsfor
additional installation requirements for transfer switches
with seismic certification.
Install the ATS. Mount 30- through 600-amp transfer
switches to a wall or other rigid vertical supporting
structure. Clearance holes through the back of each
enclosure are provided for mounting. Level the
enclosure and use shims if needed to make it plumb.
Verify that the door hinges are vertical to avoid d istortion
of the enclosure or door.
Bolt 800- through 1200-amp automatic transfer
switches directly to floor mounting pads. Use shims if
needed to plumb the enclosure. Verify that the door
hinges are vertical to avoid distortion of the enclosure or
door.
Check the system voltage and frequency.Compare
the voltage and frequency shown on the transfer switch
nameplate to the source voltage and frequency. Do not
install the transfer switch if the system voltage and
frequency are different from the nominal normal (utility)
source voltage and frequency or the nominal
emergency source voltage and frequency shown on the
generator set nameplate.
TP-7191 4/2114 Section 2 Installation
Page 15

2.4 IBC Seismic Certification
Automatic transfer switches with seismic certification
must be installed according to the instructions in this
section. Also refer to ADV-7456, the Certificate of
Compliance provided with the ATS, and the installation
(ADV) drawings for the transfer switch.
Abbreviations:
ACI: American Concrete Institute
IBC: International Building Coder
Design spectral response acceleration at short
S
DS:
period, as determined in Section 1615.1.3 of
the IBC
: Equipment response modification factor
R
p
: Equipment importance factor
I
p
: In-structure equipment amplification factor
a
p
Refer to the International Building Coder for more
information.
General Seismic Installation Notes (for ATS only):
1. Anchors used for seismic installation must be
designed in accordance with ACI 355.2- 04.
Suggested manufacturers include Simpson,
Ramset, and Hilti.
2. Anchors must be installed to a minimum
embedment of 8x the anchor diameter.
3. Anchors must be installed in minimum 4000 psi
compressive strength normal weight concrete.
Concrete aggregate must comply with ASTM C33.
Installation in structural lightweight concrete is not
permitted unless otherwise approved by the
structural engineer of record.
4. Anchors must be installed to the required torque
specified by the anchor manufacturer to obtain
maximum loading.
5. Anchors must be installed to the anchor spacing
required to obtain maximum load and edge
distance required to obtain maximum load unless
otherwise approved by the structural engineer of
record.
6. Anchors used for seismic installation must be
designed and rated to resist seismic loading in
accordance with ACI 355.2- 04 and documented in
a report by a reputable testing agency (for
example, the Evaluation Service Report issued by
the International Code Council).
7. Wide washers must be installed at each anchor
location between the anchor head and equipment
for tension load distribution. See applicable ADV
drawing for specific anchor information and washer
dimensions.
8. Equipment installed on a housekeeping pad
requires the housekeeping pad thickness to be at
least 1.5x the anchor embedment depth.
9. All housekeeping pads must be seismically
designed and dowelled or cast into the building
structure as approved by the structural engineer of
record.
10. Rebar reinforcing in the housekeeping pad is
required for all installations.
11. Concrete and rebar reinforcing must be designed
in accordance with ACI 318- 05.
12. Wall-mounted equipment must be installed to a
rebar reinforced structural concrete wall that is
seismically designed and approved by the
engineer of record to resist the added seismic
loads from components being anchored to the wall.
13. Floor-mounted equipment (with or without a
housekeeping pad) must be installed to a rebar
reinforced structural concrete floor that is
seismically designed and approved by the
engineer of record to resist the added seismic
loads from components being anchored to the
floor.
14. When installing to a floor or wall, rebar interference
must be considered.
15. Equipment attached to any structural floor or wall
other than those constructed of structural concrete
and designed to accept the seismic loads from the
mounted equipment are beyond the scope of this
specification.
16. Installation to light-weight concrete over steel
decking is beyond the scope of this specification.
17. Installation to concrete block or cinder block walls
is beyond the scope of this specification.
TP-7191 4/21 15Section 2 Installation
Page 16
2.5 Manual Operation, Model KSS
Switches
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
2.5.1 Manual Operation, 30- 230 Amp
Switches
The 30- 230 amp standard-transition models have an
attached manual operating handle. See Figure 2-3.
Note: For 230A/600V models, see Section 2.5.2.
Manual Operation Test Procedure, 30- 230 Amp
Transfer Switches
1. Disable the generator set to prevent starting and
disconnect all power sources before manually
operating the transfer switch.
Servicing the transfer switch. Hazardous voltage will
cause severe injury or death. Deenergize all power sources
before servicing. Turn off the main circuit breakers of all
transfer switch power sources and disable all generator sets
as follows: (1) Press the generator set off/reset button to shut
down the generator set. (2) Disconnect power to all battery
chargers. (3) Disconnect all battery cables, negative (- ) leads
first. Reconnect negative (- ) leads last when reconnecting the
battery cables after servicing. Follow these precautions to
prevent the starting of generator sets by an automatic transfer
switch, remote start/stop switch, or engine start command
from a remote computer. Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all jewelry. (2) Stand on a
dry,approved electrically insulated mat. (3) Test circuits with a
voltmeter to verify that they are deenergized.
Note: A manual operation handle is provided on the
transfer switch for maintenance purposes only.Do
not use the manual operation handle to transfer
the load with the power connected.
Use the manual operation handle to check the manual
operation before energizing the transfer switch. Use the
following manual operation procedures to verify that the
contactor operates smoothly without binding.
Note: A contactor in normal and serviceable condition
operates smoothly without binding. Do not place
the transfer switch into service if the contactor
does not operate smoothly; contact an
authorized distributor/dealer to service the
contactor.
2. To manually operate the transfer switch, turn the
attached handle by hand. See Figure 2-3. The
maintenance handle turns in the opposite direction
of the weight. It should operate smoothly without
any binding. If it does not, check for shipping
damage or construction debris.
3. Return the transfer switch to the Normal position.
2
1
3
1. Handle
2. Position indicators
3. Weight
4. Floating Weight
4
Figure 2-3 Manual Operation Handle, 30- 230 Amp
Switches
229
TP-7191 4/2116 Section 2 Installation
Page 17
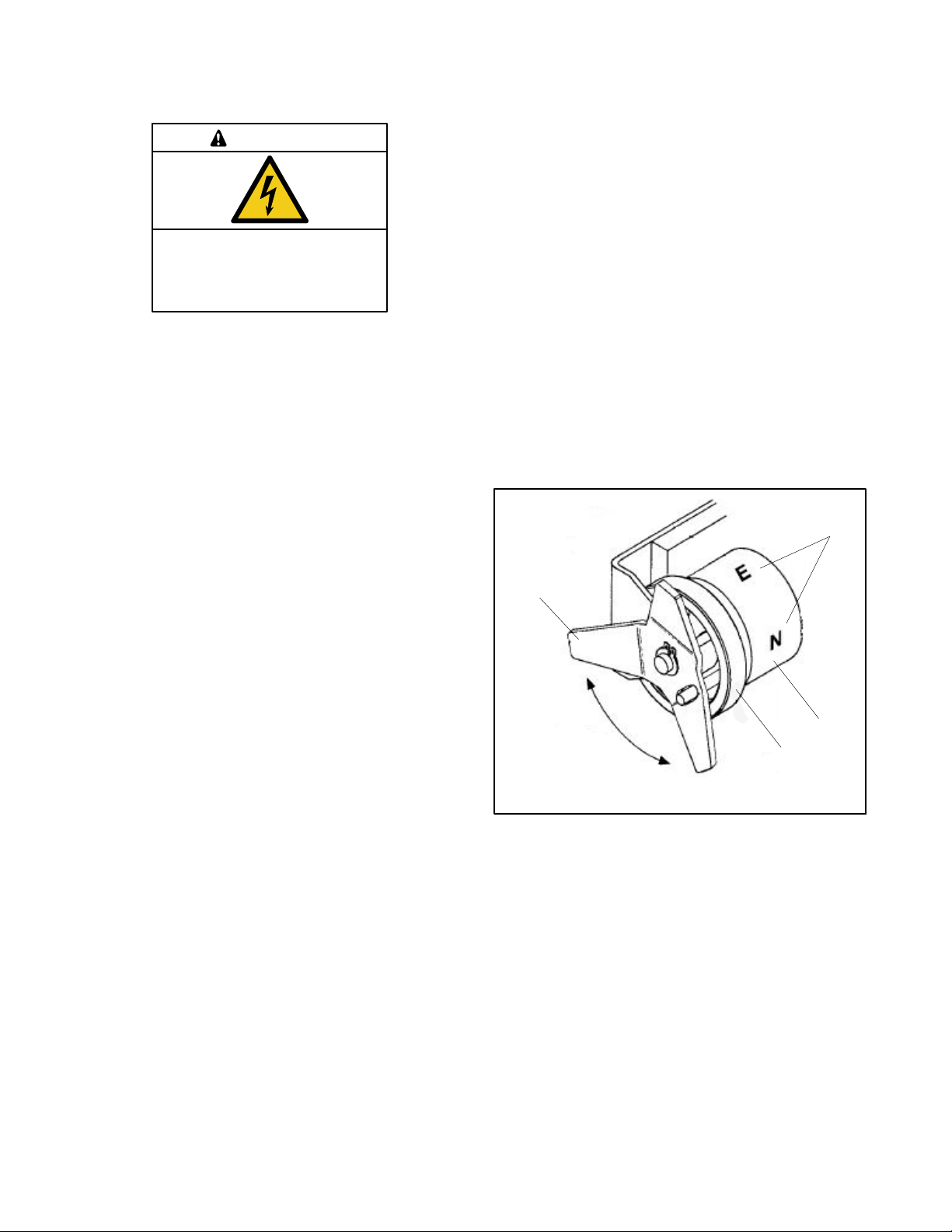
2.5.2 Manual Operation, 230A/600V and
260- 1200 Amp Switches
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
NOTICE
Improper operator handle usage. Use the manual operator
handle on the transfer switch for maintenance purposes only.
Return the transfer switch to the normal position. Remove the
manual operator handle, if used, and store it in the place
provided on the transfer switch when service is completed.
The 260- 1200 amp standard-transition models use a
detachable manual operating handle.
Manual Operation Test Procedure, 230A/600V and
260- 1200 Amp Standard-Transition Transfer
Switches
1. Disable the generator set to prevent starting and
disconnect all power sources before manually
operating the transfer switch.
2. Remove the maintenance handle from the clip(s)
on the left side of the transfer switch frame. See
Figure 2-4.
3. 230- 600 amp switches: See Figure 2-5. Insert
the maintenance handle into the hole in the shaft on
the left side of the operator.
1
2
202
1. Maintenance handle
2. Storage clip(s)
Figure 2-4 Detachable Handle Storage (typical)
800- 1200 amp switches: See Figure 2-7. Insert
the maintenance handle into the hole in the molded
hub on the left side of the operator.
4. Move the maintenance handle up or down as
shown to manually operate the transfer switch. It
should operate smoothly without any binding. If it
does not, check for shipping damage or
construction debris. See Figure 2-6.
5. Return the transfer switch to the Normal position.
6. Remove the maintenance handle and store it on the
frame in the clips provided.
Note: Verify that the maintenance handle has been
removed before proceeding.
TP-7191 4/21 17Section 2 Installation
Page 18

1
1
1
2
N
E
3
N
1. Handle
2. Hub
3. Position indicators (right side of contactor):
O = open, C = closed
Figure 2-5 Manual Operation, 260- 600 Amp
Switches
E
2
E
283
3
N
ATS Position
E
Normal
N
E
Emergency
N
Handle Indicators
Up
E:O
upper contacts open
N:C
lower contacts closed
E:C
upper contacts closed
N:O
Down
lower contacts open
Note: If Normal and Emergency connections are reversed,
this operation is also reversed.
Figure 2-6 Maintenance Handle Positions,
260- 1200 Amp Switches
1. Maintenance handle
2. Hub
3. Position indicators (right side of contactor):
O = open, C = closed
Figure 2-7 Manual Operation, 800- 1200 Amp
Switches
202
TP-7191 4/2118 Section 2 Installation
Page 19

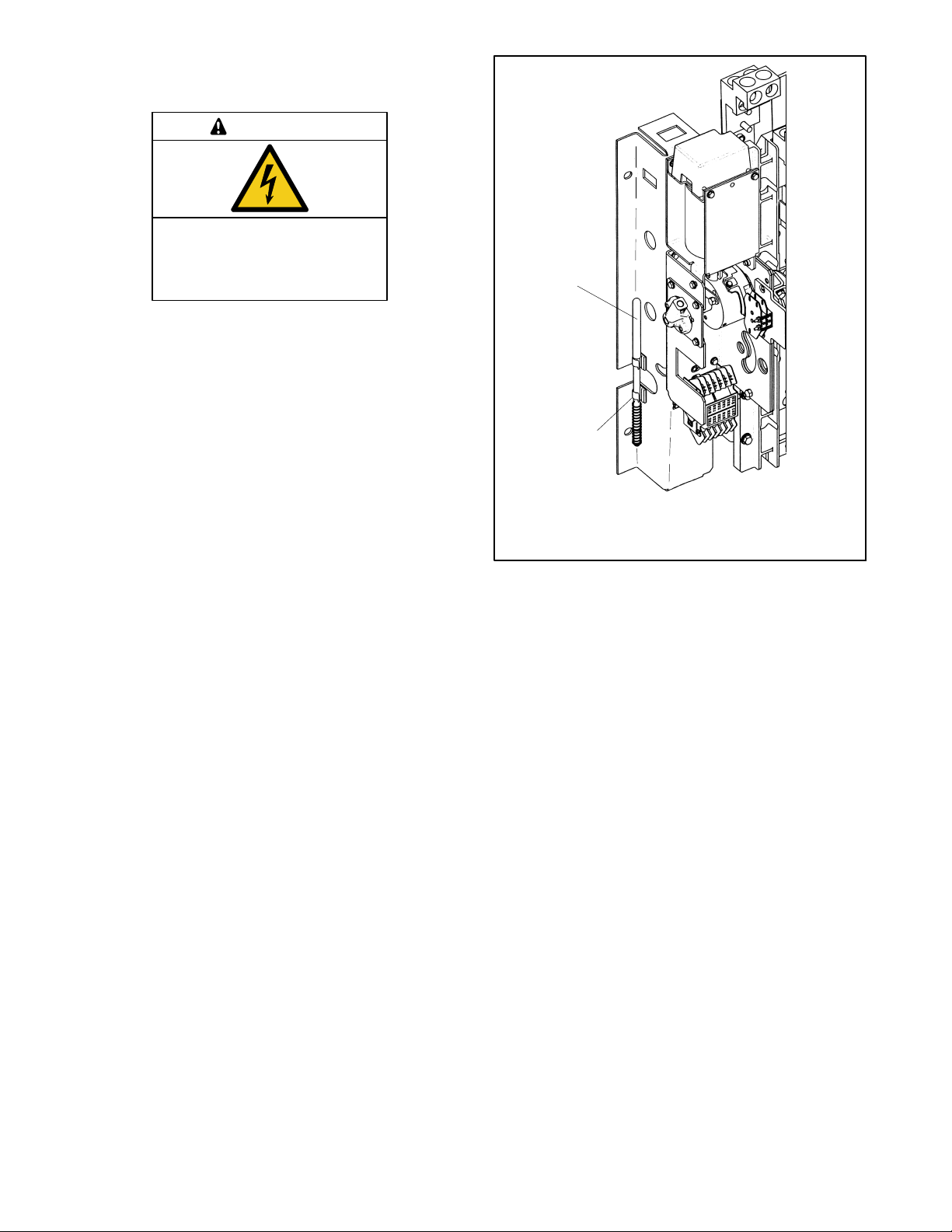
2.6 Controller Connections
The c ontroller is mounted in a plastic housing on the
inside of the transfer switch enclosure door.
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
NOTICE
Electrostatic discharge damage. Electrostatic discharge
(ESD) damages electronic circuit boards. Prevent
electrostatic discharge damage by wearing an approved
grounding wrist strap when handling electronic circuit boards
or integrated circuits. An approved grounding wrist strap
provides a high resistance (about 1 megohm), not a direct
short, to ground.
2
1
Figure 2-8 shows the locations of the connectors on the
controller. It is not necessary to open the cover to access
the Ethernet, Modbusr, and input/output connectors.
Opening the cover. If necessary, open the plastic
housing by pushing up on the latch on the bottom of the
cover and swinging the cover up and out. The cover is
hinged at the top. Lift the cover off the hinges to remove
it completely, if necessary.
Note: Always replace the cover before energizing the
transfer switch controls.
3
4
5
6
8
7
1. Standard input/output connection
2. RS-485 connection TB2
3. Connection for optional current sensing kit
4. Optional I/O module connection P16
5. Access openings to optional RJ-45 connector
6. Latch
7. Ground wire
8. Contactor harness connection
Figure 2-8 Controller
Modbus is a registered trademark of Schneider Electric.
TP-7191 4/21 19Section 2 Installation
GM85884
Page 20

2.6.1 Controller Input and Output
Connections
The controller provides connections for two
programmable inputs and two programmable outputs.
See Figure 2-8 for the connector location and
Figure 2-9 for the I/O connection specifications.
Each input has a signal and a return connection. The
outputs are C form contacts with ratings of
500 mA @ 120 VAC. See Figure 2-10 for connections.
Use #12- 24 AWG wire and tighten the connections to
0.5Nm(4.4in.lbs.).
For additional input and output connections, optional
input/output modules are available. See Section 3.3 for
instructions.
Main Board I/O Specifications
Output contact type Isolated form C (SPDT)
Output contact rating 1amp@30VDC,
500 mA @120 VAC
I/O terminals wire size #12- 24 AWG
Figure 2-9 Main Board I/O Specifications
2.6.2 Harness Connection
Verify that the contactor harness is connected at the
controller base (or at the controller disconnect switch, if
equipped). See Figure 2-11.
Note: Verify that the power is disconnected before
connecting or disconnecting the contactor
harness.
2.6.3 Controller Ground
Verify that the grounding wire is connected from the
controller’s lower left mounting stud to the enclosure.
This connection provides proper grounding that does
not rely upon the door hinges.
TB1
6
Output 1 NO
Output 1 C
Output 1 NC
Input 1B
Input 1A
1
12
Output 2 NO
Output 2 C
Output 2 NC
Input 2B
Input 2A
7
NC = normally closed
NO = normally open
C=common
Figure 2-10 Input and Output Connections
6866
1
2
1. Contactor Harness Connection
2. Ground Connection
GM85844
Figure 2-11 Contactor Harness and Controller
Ground Connections
TP-7191 4/2120 Section 2 Installation
Page 21

2.7 Electrical Wiring
All internal electrical connections are factory-wired and
tested. Field installation includes connecting the
sources, loads, generator start circuit(s), and auxiliary
circuits, if used.
Note: A protective device such as a molded-case circuit
breaker or fused disconnect switch MUST be
installed on both sources of incoming power for
circuit protection and use as a disconnect device.
Refer to the wiring diagrams provided with the transfer
switch. Observe all applicable national, state, and local
electrical codes during installation.
Install DC, control, and communication system wiring
in separate conduit from AC power wiring.
It is not necessary to remove pole covers from the
transfer switch for cabling. If you do remove them,
reinstall them carefully.
WARNING
Accidental starting.
Can cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect the battery cables before
working on the generator set.
Remove the negative (- ) lead first
when disconnecting the battery.
Reconnect the negative (- ) lead last
when reconnecting the battery.
Servicing the transfer switch. Hazardous voltage will
cause severe injury or death. Deenergize all power sources
before servicing. Turn off the main circuit breakers of all
transfer switch power sources and disable all generator sets
as follows: (1) Press the generator set off/reset button to shut
down the generator set. (2) Disconnect power to all battery
chargers. (3) Disconnect all battery cables, negative (- ) leads
first. Reconnect negative (- ) leads last when reconnecting the
battery cables after servicing. Follow these precautions to
prevent the starting of generator sets by an automatic transfer
switch, remote start/stop switch, or engine start command
from a remote computer. Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all jewelry. (2) Stand on a
dry,approved electrically insulated mat. (3) Test circuits with a
voltmeter to verify that they are deenergized.
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
Making line or auxiliary connections. Hazardous voltage
will cause severe injury or death. To prevent electrical
shock deenergize the normal powersource before making any
line or auxiliary connections.
Grounding electrical equipment. Hazardous voltage will
cause severe injury or death. Electrocution is possible
whenever electricity is present. Ensure you comply with all
applicable codes and standards. Electrically ground the
generator set and related equipment and electrical circuits.
Turn off the main circuit breakers of all power sources before
servicing the equipment. Never contact electrical leads or
appliances when standing in water or on wet ground because
these conditions increase the risk of electrocution.
NOTICE
Foreign material contamination. Cover the transfer switch
during installation to keep dirt, grit, metal drill chips, and other
debris out of the components. Cover the solenoid mechanism
during installation. Afterinstallation, use the manual operating
handle to cycle the contactor to verify that it operates freely.
Do not use a screwdriver to force the contactor mechanism.
2.7.1 Source and Load Connections
Determine the cable size. Refer to the transfer switch
dimension drawing to determine the cable size and
number of cables required for the transfer switch. Make
sure that the cables are suitable for use with the transfer
switch lugs. Watertight conduit hubs may be required for
outdoor use.
Drill the entry holes. Cover the transfer switch to
protect it from metal chips and construction grit. Then
drill entry holes for the conductors at the locations
shown on the enclosure drawings. Remove debris from
the enclosure with a vacuum cleaner.
Note: Do not use compressed air to clean the switch.
Cleaning with compressed air can cause debris
to lodge in the components and damage the
switch.
TP-7191 4/21 21Section 2 Installation
Page 22

Install and test the power cables. Leave sufficient
slack in the power leads to reach all of the power
connecting lugs on the power switching device. Test the
power conductors before connecting them to the
transfer switch. Installing power cables in conduit, cable
troughs and ceiling-suspended hangers often requires
considerable force. Pulling cables can damage
insulation and stretch or break the conductor’s strands.
Test the cables after pulling them into position and
before they are connected to verify that they are not
defective and that they were not damaged during
installation.
Install the cable spacers provided with 150- 230 amp
switches as shown in Figure 2-12.
1
1½inch
approximate
127
1
1. Cable spacers
Figure 2-12 Cable Spacers for 150 - 230 Amp
Switches
Connect the cables. Be careful when stripping
insulation from the cables; avoid nicking or ringing the
conductor. Clean cables with a wire brush to remove
surface oxides before connecting them to the terminals.
Apply joint compound to the connections of any
aluminum conductors.
Refer to the wiring diagram provided with the switch.
The connection points on the contactor are labeled
Normal, Emergency, and Load. Be sure to follow the
phase markings (A, B, C, and N). For single-phase
systems, connect to A and C.
Tighten the lugs. Verify that all connections are
consistent with drawings before tightening the lugs.
Tighten all cable lug connections to the torque values
shown on the label on the switch. (See Figure 2-14 for a
typical rating/torque label.) Carefully wipe off any
excess joint compound after tightening the terminal
lugs.
For load connections to bus bars, use a compression
washer, flat washer, and a minimum grade 5 bolt and
torque the connections to the values in Figure 2-13.
Bolt Torque
Bolt Size, inches
ft. lb. Nm
1/4 7 9.5
5/16 12 16.3
3/8 20 27.1
1/2 50 67.8
5/8 95 128.8
3/4 155 210.2
Figure 2-13 Tightening Torque for Bus Bars
SUITABLEFOR CONTROL OF MOTORS, ELEC
DISCHARGE AND TUNGSTEN LAMPS, ELEC HEATING EQPT, WHERE THE SUM OF MOTOR FULLLOAD AMPSAND AMPS OF OTHER LOADS DOES
NOT EXCEED THE SWITCH AMP RATING AND THE
TUNGSTEN LOAD DOES NOT EXCEED % OF
SWITCH RATING, 240V MAX.
WHEN PROTECTED BY A CIRCUIT BREAKER
WITHOUT AN ADJUSTABLE SHORT-TIME R ESPONSE
ONLY OR BY FUSES THIS TRANSFER SWITCH IS
RATED FOR USE ON ACIRCUI TCAPABLE OF
DELIVERING NOT MORE THEN THE RMS SYMM
AMPS AT THE VOLTAGE SHOWN.
RMS SYMM
MAX
AMPS
X1000
35
22 600
42 480 GE SGL4,SGP4,TB4, 400
THLC4,TLB4 400
SGLA,SGL6,SGP6,TB6
SKHA,SKL8,SKP8,TKL
42 480I-T-ECJD6,HHJD6, 400
HHJXD6,HJD6,SCJD6,SHJD6
CLD6,HHLD6,HHLXD6,HLD6,
SCLD6,SHLD6
CMD6,HMD6,HND6,MD6,MXD6,
SCMD6,SHMD6,SMD6,SND6 800
42 480 SQUARE D LC ,LI
MH
42 480 WESTH HKD,KDC,LCL, 400
TRI- PAC LA
HLD
TRI- PACNB 800
42 480 ABB S5
S6
42 480 MERLIN GERIN
CJ600
BREAKER/MFR/TYPE
VOLTS
480 ANY
ANY
ANY
ANY
ANY
ANY
100
AMPS
MAX
PER NEC
PER NEC
600
800
400
600
600
800
600
800
400
600
400
800
600
Note: Connect the source and load pha ses as
indicated by the markings and dra wings to
prevent short circuits and to prevent phasesensitive load devices from malfunctioning or
operating in reverse.
200 480 FUSE ANY CLASS J
USE 75 C MIN. CU/AL WIRE FOR PO WER
CONNECTIONS. USE 60 C MIN. CU WIRE FOR
CONTROLS.
1
USE COPPER OR ALUMINUM WIRE
FOR POWER TERMINA LS
RECOMMENDED TIGHTENING
TORQUE 600 IN- LBS
483500- 007
REV
600
B
1. Torque specification
Figure 2-14 Typical Rating/Torque Label
007
TP-7191 4/2122 Section 2 Installation
Page 23

2.7.2 Engine Start Connection
WARNING
Accidental starting.
Can cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect the battery cables before
working on the generator set.
Remove the negative (- ) lead first
when disconnecting the battery.
Reconnect the negative (- ) lead last
when reconnecting the battery.
Disabling the generator set. Accidental starting can
cause severe injury or death. Before working on the
generator set or equipment connected to the set, disable the
generator set as follows: (1) Press the generator set off/reset
button to shut down the generator set. (2) Disconnect the
power to the battery charger, if equipped. (3) Remove the
battery cables, negative (- ) lead first. Reconnect the negative
(- ) lead last when reconnecting the battery. Follow these
precautions to prevent the starting of the generator set by the
remote start/stop switch.
Prevent the generator set from starting by pressing the
OFF button on the generator controller; disconnecting
power to the generator engine start battery charger, if
installed; and disconnecting all generator engine start
battery cables, negative (- ) leads first.
Connect the generator set remote starting circuit to the
engine start connections. On 30- 230 amp models, the
engine start terminals are located on the transfer switch
contactor assembly and labeled with a decal. See
Figure 2-15. On larger models, the engine start terminal
block is located on a bracket on the right side of the
enclosure. See Figure 2-16 for the location of theengine
start terminal block. Refer to the generator set
installation manual for wire size specifications.
6126
1
14
15
16 (Do not use)
1. Engine start contacts 14 and 15
Figure 2-15 Engine Start Contacts, 30- 230 Amp
Switches
1
Engine Start Contacts
Contact Rating 2 A @ 30 VDC/250 VAC
ref ADV- 8570
1. Engine start connection terminal block location
Figure 2-16 Engine Start Contact Terminal Block,
230A/600V and 260- 1200 Amp Switches
TP-7191 4/21 23Section 2 Installation
Page 24

2.7.3 Auxiliary Contacts
Connect the auxiliary contacts to customer-supplied
alarms, remote indicators, or other devices. Auxiliary
contacts provide contacts that close when the transfer
switch is in the Normal position and contacts that close
when the transfer switch is in the Emergency position.
Figure 2-17 lists the number of contacts available by
ATS model and size (amps).
D On 30- 230 Ampunits, the contacts are located on the
right side of the contactor. See Figure 2-18.
D On 230A/600V and 260- 1200 Amp units, the
contacts are located on the left side of the contactor.
See Figure 2-19. See Figure 2-20 for typical
connections.
Refer to the wiring diagrams provided with the transfer
switch for specific auxiliary contact connection
information.
Follow the wire size and tightening torque specifications
shown on the decal on the transfer switch.
STANDARD
31
1
6126
29
Auxiliary Position Indicating Contacts
(rated 10 amps @ 32 VDC/250 VAC)
Number of Contacts Indicating
Switch Rating,
Amps
30- 230 2, 2 1, 1
260- 1200 8, 8 —
Normal, Emergency
Standard
Optional
Figure 2-17 Auxiliary Contacts
32 30
13 11
STANDARD
12
10
35 33
OPTIONAL
36
34
1. Auxiliary contacts (contacts shown with contactor in Normal
position)
Figure 2-18 Auxiliary Contacts, 30- 230 Amp Transfer
Switches
TP-7191 4/2124 Section 2 Installation
Page 25

GM115522
Figure 2-20 Typical Auxiliary Contact Connection,
1
230- 1200 Amp Transfer Switches (see
Figure 2-19 and schematic diagram)
2.8 Communication and
Accessory Connections
ref GM110688
See Section 3 for accessory and communication
connection instructions.
2.9 Functional Tests
After completion of the mechanical installation and all
electrical connections, perform the functional tests
described in Section 5. The procedures in Section 5 are
required to complete the installation and startup of the
transfer switch.
1
ref GM10757
1. Auxiliary contacts (see the schematic diagram for contacts
closed on Normal or closed on Emergency)
Figure 2-19 Auxiliary Contact Connection Locations,
230A/600V and 260- 1200 Amp Transfer
Switches
TP-7191 4/21 25Section 2 Installation
Page 26

Notes
TP-7191 4/2126 Section 2 Installation
Page 27
Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
3.1 Introduction
This section explains the connection of communication
cables and selected accessories.
Also refer to the following documentation for instructions
to install, connect, and operate optional accessories.
D Transfer switch wiring diagrams.
D Installation instructions or diagrams provided with
loose accessory kits.
D Controller Operation Manual. See List of Related
materials in the Introduction section of this manual for
document numbers.
3.2 Communication Connections
The Decision-Makerr MPAC 1200 controller is
equipped with a USB port and a Modbus port with an
RS-485 connector. An Ethernet communication board is
optional.
3.2.1 USB Port SiteTech Connection
1
GM85888
1. USB connection (below port cover)
Figure 3-1 USB Connection for SiteTech
3.2.2 Modbus Connection
DANGER
A personal computer and Kohlerr SiteTecht software
can be used for changing controller settings. Use a USB
cable to connect the controller to a personal computer.
See Figure 3-1 for the USB port location on the front of
the controller assembly. Remove the small port cover
anduseaUSBcablewithamini-Bconnectortoconnect
the controller’s USB port to the computer.
See TP-6701, SiteTech Software Operation Manual, for
instructions to use the software. Disconnect the USB
cable from the controller and replace the port cover
when finished.
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
Servicing the transfer switch. Hazardous voltage will
cause severe injury or death. Deenergize all power sources
before servicing. Turn off the main circuit breakers of all
transfer switch power sources and disable all generator sets
as follows: (1) Press the generator set off/reset button to shut
down the generator set. (2) Disconnect power to all battery
chargers. (3) Disconnect all battery cables, negative (- ) leads
first. Reconnect negative (- ) leads last when reconnecting the
battery cables after servicing. Follow these precautions to
prevent the starting of generator sets by an automatic transfer
switch, remote start/stop switch, or engine start command
from a remote computer. Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all jewelry. (2) Stand on a
dry,approved electrically insulated mat. (3) Test circuits with a
voltmeter to verify that they are deenergized.
See Figure 3-2 for the RS-485 Modbus connector
location.
Use serial connections to TB2 on the controller to
connect the transfer switch to a personal computer for
system monitoring, the optional remote annunciator, or
a Modbus network. See Figure 3-4.
Notice that a 121 ohm terminating resistor is
recommended on the last device in a network. If there is
TP-7191 4/21 27Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 28

only one device, a terminating resistor may be required
depending on the cable distance and communication
speed. Long cables and high speeds will increase the
need for a terminating resistor.
TheserialportisanisolatedRS-485portwith
connection speeds of 9.6, 19.2, and 57.6 kbps. Use
shielded twisted-pair cable to connect to the RS-485
connectors on the controller’s terminal strip TB2 for
serial connections. For connectionto a PC, use a USB to
RS-485 converter.
Input
1
GND1
Cable shield
A1 (- )
B1 (+)
3
Connect the Modbus input and output to the terminals
shown in Figure 3-3. Use #12-24 AWG shielded,
twisted-pair wire. Belden cable #9841 or equivalent is
recommended. Connect one end of the shield to
ground. Leave the other end of the shield disconnected.
Tighten the connections to 0.5 Nm (4.4 in. lb.).
Use Modbus RTU (remote terminal unit) protocol for
communication through the serial port. A map of the
Modbus codes for this controller is available. Contact
your local distributor/dealer.
Note: Modbusr applications require a Modbus
software driver written by a trained and qualified
systems programmer.
1
2
TB2
4
GND1
B1 (+)
6
A1 (- )
Cable shield
Output
Customer connections
Figure 3-3 Modbus RS-485 Connections
GM85884
1. RS-485 Modbus connections
2. Access opening for RS-485 cables
Figure 3-2 Modbus Connections (controller cover
removed for illustration only)
TP-7191 4/2128 Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 29

3.2.3 Ethernet Connection
PC
PCPC
USB port
USB to RS-485 port
converter
Terminating resistor
may be required [
(121 Ohms)
USB port
USB to RS-485
port converter
RS-485 *
RS-485 *
RS-485 *
RS-485 *
In
Out
In
Out
In
Out
In
Out
Device
Device
Device
Last
Device
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
Servicing the transfer switch. Hazardous voltage will
cause severe injury or death. Deenergize all power sources
before servicing. Turn off the main circuit breakers of all
transfer switch power sources and disable all generator sets
as follows: (1) Press the generator set off/reset button to shut
down the generator set. (2) Disconnect power to all battery
chargers. (3) Disconnect all battery cables, negative (- ) leads
first. Reconnect negative (- ) leads last when reconnecting the
battery cables after servicing. Follow these precautions to
prevent the starting of generator sets by an automatic transfer
switch, remote start/stop switch, or engine start command
from a remote computer. Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all jewelry. (2) Stand on a
dry,approved electrically insulated mat. (3) Test circuits with a
voltmeter to verify that they are deenergized.
Terminating resistor [,
(121 Ohms)
* Use Belden #9841 or equivalent shielded, twisted-pair
communication cable for RS-485 connections. Ground
one end of the cable shield. Leave the other end of the
cable shield disconnected.
[ Long cables and high communication speeds will require
a terminating resistor. Use 121 ohm resistor X-6058-27.
Figure 3-4 Serial Connections
The Ethernet communication accessory board is
required for connection to the Ethernet. The Ethernet
communication board is an optional accessory for the
MPAC 1200 controller. The communication board
connects to the controller board as shown in Figure 3-5.
1
1
2
GM85884
1. Ethernet communication board with RJ-45 connector
2. Access opening for Ethernet cable
Figure 3-5 Ethernet Board (controller cover
removed for illustration only)
The Ethernet communication accessory board allows
the transfer switch to be connected to a building’s
Ethernet network to communicate with personal
computers connected to the same subnet.
TP-7191 4/21 29Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 30

Note: For an ethernet connection, obtain an IP address
and subnet mask number fr om the local system
administrator.
Ethernet Port. The ethernet port is a standard RJ-45
jack. See Figure 3-5 for the location of the Ethernet port.
Use Category 5e or better cable to connect the
controller to the building’s network.
Use the controller’s Setup menus or a personal
computer connected to the controller’s USB port and
Kohler SiteTech software to set the communication
parameters. The Ethernet communication board may
have a default IP address assigned at the factory for test
purposes. See Figure 3-6. Change the IP address to
an address owned by the user. See the controller
operation manual for instructions to set the
communication parameters.
The transfer switch controller does not operate as a
Modbus-to-Ethernet converter for other devices in a
network. For multiple device networks connected to the
personal computer through the Ethernet, use a
Modbus-to-Ethernet converter for the other devices in
the network. See Figure 3-7 and instruction sheet
TT-1405, provided with the converter, for connection
instructions.
The controller can communicate with up to five (5)
simultaneous TCP/IP (ethernet) connections. These
five connections do not include the RS-485 serial port. In
the extreme case, five users may be communicating
with the controller via TCP/IP network connections and
another may be communicating through the serial port,
for a total of six (6) communication channels. As the
controller is asked to communicate with more and more
outside devices, the communication will slow down.
Modbusr TCP/IP
Category 5e
PC
IP xx.xx.xx.02
Note: The PC and the ATS must be on the same subnet.
Note: A crossover cable can be used to connect the PC
to the ATS controller through the Ethernet port.
Figure 3-6 Remote Network (Ethernet) Connection
Modbusr
TCP/IP
PC
IP xx.xx.xx.02
Modbusr
TCP/IP
Ethernet
Network
Ethernet
Network
Modbusr TCP/IP
Category 5e
Modbusr TCP/IP
Category 5e
Modbusr TCP/IP
Category 5e
Converter,
Modbusr/Ethernet
IP xx.xx.xx.05
Modbusr
RTU
RS-485
MPAC
Controller with
Ethernet comm.
board
IP xx.xx.xx.03
MPAC
Controller with
Ethernet comm.
board
IP xx.xx.xx.03
Device
Device
RS-485
RS-485
PC
IP xx.xx.xx.01
Figure 3-7 Ethernet Connections to Multiple-Device Network
Terminating resistor
(121 Ohms)
Device
Device
RS-485
Last device
TP-7191 4/2130 Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 31
3.3 Accessory Modules
3.3.1 Accessory Module Mounting
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
Servicing the transfer switch. Hazardous voltage will
cause severe injury or death. Deenergize all power sources
before servicing. Turn off the main circuit breakers of all
transfer switch power sources and disable all generator sets
as follows: (1) Press the generator set off/reset button to shut
down the generator set. (2) Disconnect power to all battery
chargers. (3) Disconnect all battery cables, negative (- ) leads
first. Reconnect negative (- ) leads last when reconnecting the
battery cables after servicing. Follow these precautions to
prevent the starting of generator sets by an automatic transfer
switch, remote start/stop switch, or engine start command
from a remote computer. Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all jewelry. (2) Stand on a
dry,approved electrically insulated mat. (3) Test circuits with a
voltmeter to verify that they are deenergized.
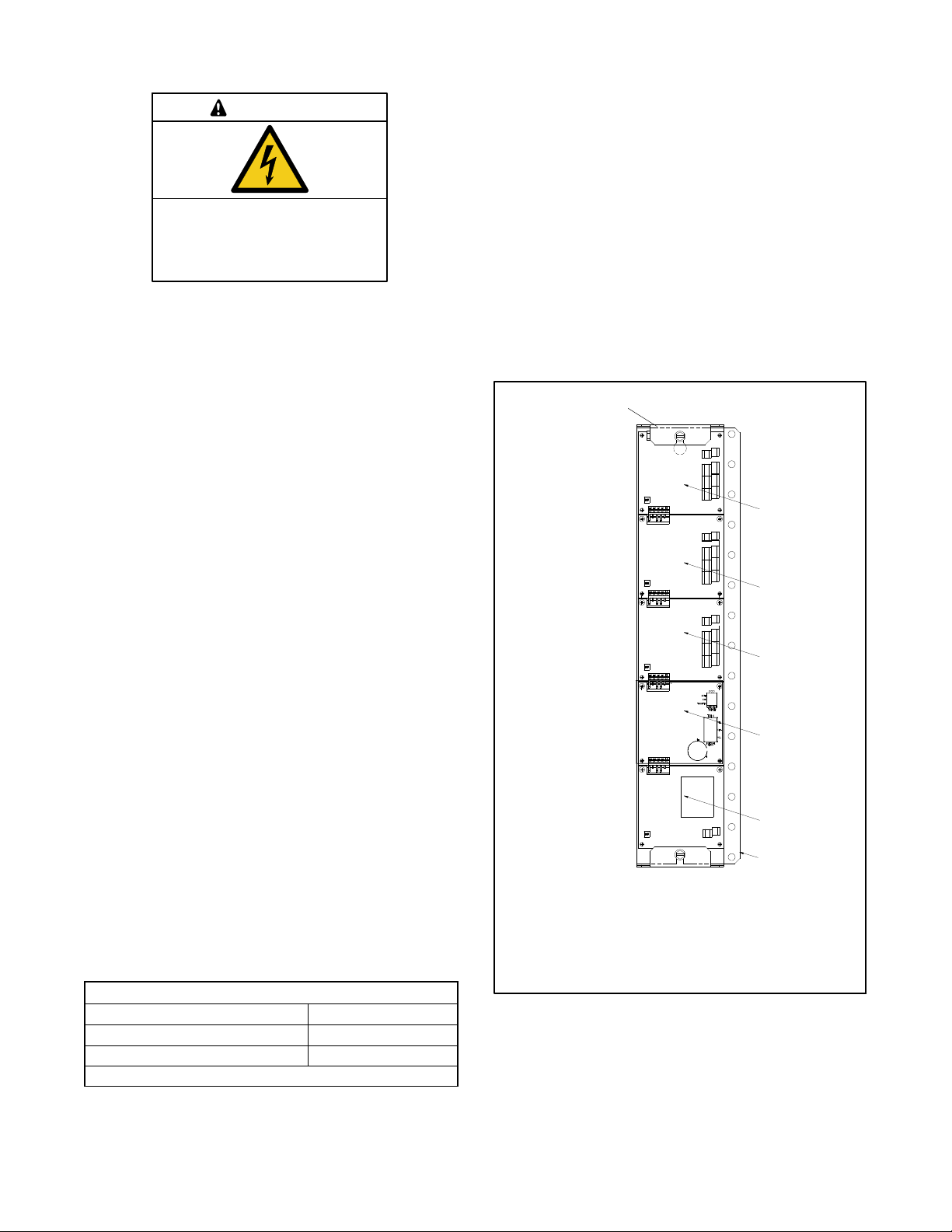
Mount the accessory modules on the module mounting
plate. Starting at the end of the module mounting
assembly nearest the cable connection, install any I/O
modules first, then install the alarm board, if used. The
external battery module, if used, must be the last
module. See Figure 3-9. The alarm board has a fixed
Modbus address = 5.
Note: Some models may have the I/O module
assembly installed with the cable connection end
pointing to the side or the bottom. Regardless of
the actual orientation of the assembly, the I/O
modules must be installed closest to the cable
connection, followed by the alarm module and
then the external battery module, if used.
1
2
Accessory modules are available with the MPAC 1200
controller. This section provides specifications and field
connection information for factory-installed accessory
modules. If the modules are not factory-installed, follow
the instructions provided with the kits to install the
mounting assembly and modules.
The transfer switch uses a standard bus system for
connecting accessory modules to the controller. This
bus incorporates a standard serial communication
interface for passing data back and forth between the
main logic board and the assemblies on the expansion
bus.
The module mounting kit holds up to five optional
modules. Add t he current draw for all modules installed
to determine the total current draw. See Figure 3-8. The
total current drawn by all modules must not exceed 300
mA. If an External Battery Module is installed and
connected to a battery, there is no current restriction.
The External Battery Module, if used, must be the last
board on the bus.
Module Current Draw Specifications, mA
Alarm Module 75
Standard I/O Module 75
High Power I/O Module 100
Note: EBSM required if total current is higher than 300 mA.
Figure 3-8 Module Current Requirements
1. Cable connection (defined as the TOP regardless of
orientation)
2. I/O modules (if equipped)
3. Alarm module (if equipped)
4. External battery module (must be last, if equipped)
5. Mounting plate
Figure 3-9 Module Mounting
2
2
3
4
5
GM46258
TP-7191 4/21 31Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 32

3.3.2 Input/Output (I/O) Modules
Two types of input/output modules are available. The
standard I/O Module has two inputs and six outputs. The
high-power I/O module has two inputs and three
outputs. See Figure 3-10 through Figure 3-13 for I/O
module illustrations and specifications.
1
2
1
2
3
4
1. Input LEDs 7 and 8 for inputs 1 and 2
2. Input connector (see Figure 3-14)
3. Output connector
4. Output LEDs 1- 6
GM41093
Figure 3-10 Standard Input/Output Module
Inputs
Available Inputs 2
Input Definition Contact Closure
Current 5mAMax
Connection Type Terminal Strip
Wire Size #14-24 AWG
Max Distance 700 feet
Outputs
Outputs Available 6
Contact Type Form C (SPDT)
Contact Voltage Rating
Connection Type Terminal Strip
Wire Size #14-24 AWG
2A@30VDC
500 mA @ 125 VAC
Figure 3-11 Standard I/O Module Specifications
3
4
1. Input LEDs 1 and 2
2. Input connector (see Figure 3-14)
3. Output connector
4. Output LEDs 3- 5 for outputs 1, 2, and 3
GM42186
Figure 3-12 High-Power Input/Output Module
Inputs
Available Inputs 2
Input Definition Contact Closure
Current 5mAMax
Connection Type Terminal Strip
Wire Size #14-24 AWG
Max Distance 700 feet
Outputs
Outputs Available 3
Contact Type Form C (SPDT)
12 A @ 24 VDC
Contact Voltage Rating
Connection Type Terminal Strip
Wire Size #14-24 AWG
12 A @ 250 V AC
10 A @ 277 V AC
2A@480VAC
Environmental Specifications
Temperature -40Cto85C(-40Fto185F)
Humidity 35% to 85% noncondensing
Figure 3-13 High-Power I/O Module Specifications
TP-7191 4/2132 Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 33
Use 14-24 AWG cable to connect to inputs and outputs.
See Figure 3-14.
3.3.3 External Battery Supply Module
(EBSM)
LEDs on the module circuit board light to indicate that
each input or output is active.
Note: Each I/O module must have unique address.
Use the address DIP switches on the I/O module to
assign a unique (different) address to each module as
shown in Figure 3-15. Assign addresses in order from 1
to 4. An LED for each DIP switch lights to indicate that
theswitchisclosed.
The alarm module’s fixed address is 5. The battery
module’s fixed address is 6.
See the controller operation manual for instructions to
assign functions to each input and output. Inputs and
outputs can also be assigned using a personal
computer with Kohlerr SiteTecht software or over
Modbus. See TP-6701, SiteTech Operation Manual, or
TP-6113, Modbus Protocol Manual.
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
The external battery supply module kit allows
connection to the generator set engine start battery(ies)
or other batteries to provide 12 VDC power to the ATS
controller. The external battery supply module kit is
required for the following applications:
D Systems using extended engine start time
delays. The EBSM provides power to the ATS
controller during extended time delays longer than 15
seconds, when neither the Normal nor the
Emergency source is available.
D Installations with frequent utility power outages.
The EBSM provides power to the ATS controller when
neither source is available, preserving the controller’s
backup battery.
D Transfer switches equipped with multiple
accessory modules that require a total of more
than 300 mA current. SeeFigure3-8.
The EBSM produces 2 amps at 12 VDC with 9- 36 VDC
input. The EBSM input is reverse-polarity protected.
The EBSM outputs a low battery voltage signal when the
external battery voltage falls below 11 VDC for a 12-volt
system or 22 VDC for a 24-volt system. The module is
showninFigure3-16.
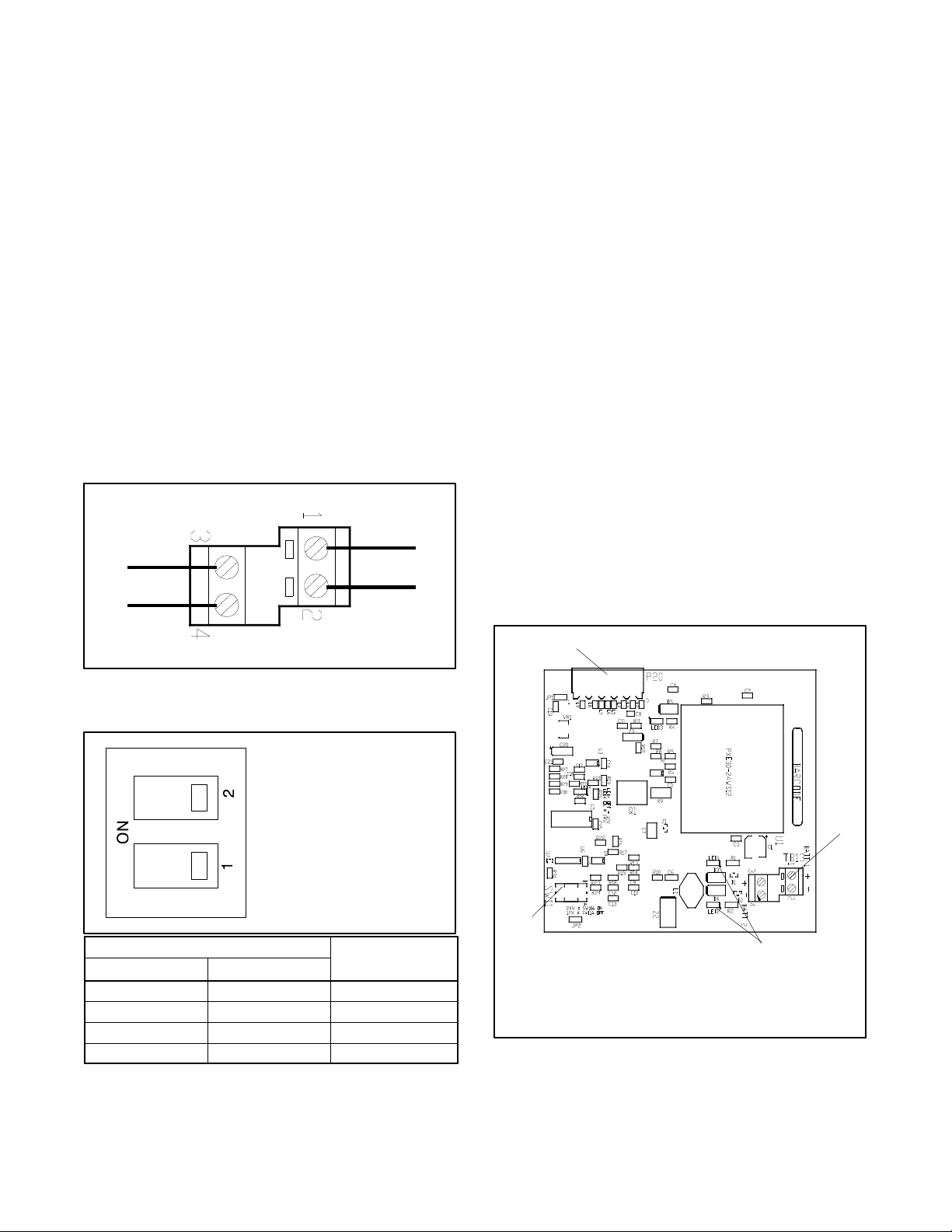
Figure 3-14 I/O Module Input Connections
(TB1 or TB10)
Both switches OFF
Address=1 shown
DIP Switch
1 2
Off Off 1
On Off 2
Off On 3
On On 4
Address
Figure 3-15 Address DIP Switch Settings
refGM41093
1
4
2
1. Connector P20
2. LED indicators
3. Battery input connection terminal block TB13
4. 12/24 volt DIP switch SW11-1. OFF=12 VDC, ON = 24 VDC
Figure 3-16 External Battery Supply Module
3
GM42227-A
TP-7191 4/21 33Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 34

The external battery supply module kit includes one
external battery supply circuit board and the circuit
board mounting components. A module mounting kit is
required for installation of the external battery supply
module. See Section 3.3.1. Obtain a module mounting
kit if one is not already installed and follow the
instructions provided with the kits to install the mounting
assembly and modules.
ThebatteryvoltageselectionDIPswitchSW11-1allows
selection between 12-volt and 24-volt systems for low
battery voltage sensing and indication. Connect one or
two batteries to the external battery supply module. Use
a battery charger to maintain the battery(ies) connected
to the EBSM.
DIP Switch SW11-1 Setting Battery Voltage
OFF 12 VDC
ON 24 VDC
Figure 3-17 Battery Voltage Selection
EBSM Connection and Voltage Setting
1. Use #14-28 AWG wire to connect one or two
batteries to terminal block TB13. (A second battery
can be connected but is not required.) Follow the
markingontheboardforthepositive(+)and
negative (- ) connections. See Figure 3-16 and
Figure 3-17.
3.3.4 Alarm Module
See Figure 3-18 for the optional alarm module. A
module mounting kit is required for installation of the
alarm module. See Section 3.3.1.
The functions provided by this board are:
D 90 dB Audible alarm (any alarm function can be
programmed to trigger the audible alarm)
D Chicago alarm operation
D Preferred source selection
D Supervised transfer control (supervised transfer
control switch required)
D Connection for external alarm
The alarm board has a fixed address = 5.
1
2
Note: If the battery connections are reversed, red
LED1 or LED2 will light. See Figure 3-16.
2. Set voltage selector switch SW11-1 to 12 or
24VDC. See Figure 3-16 and Figure 3-17. Switch
SW11-2 is not used.
Note: The EBSM has no address switches but
must be the last board on the bus.
4
1. Supervised Transfer Switch Connection, P22
2. External Alarm Connection, TB 14
3. Alarm Indicator, LED1
4. DIP Switches
Figure 3-18 Alarm Module
GM40764
3
TP-7191 4/2134 Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 35
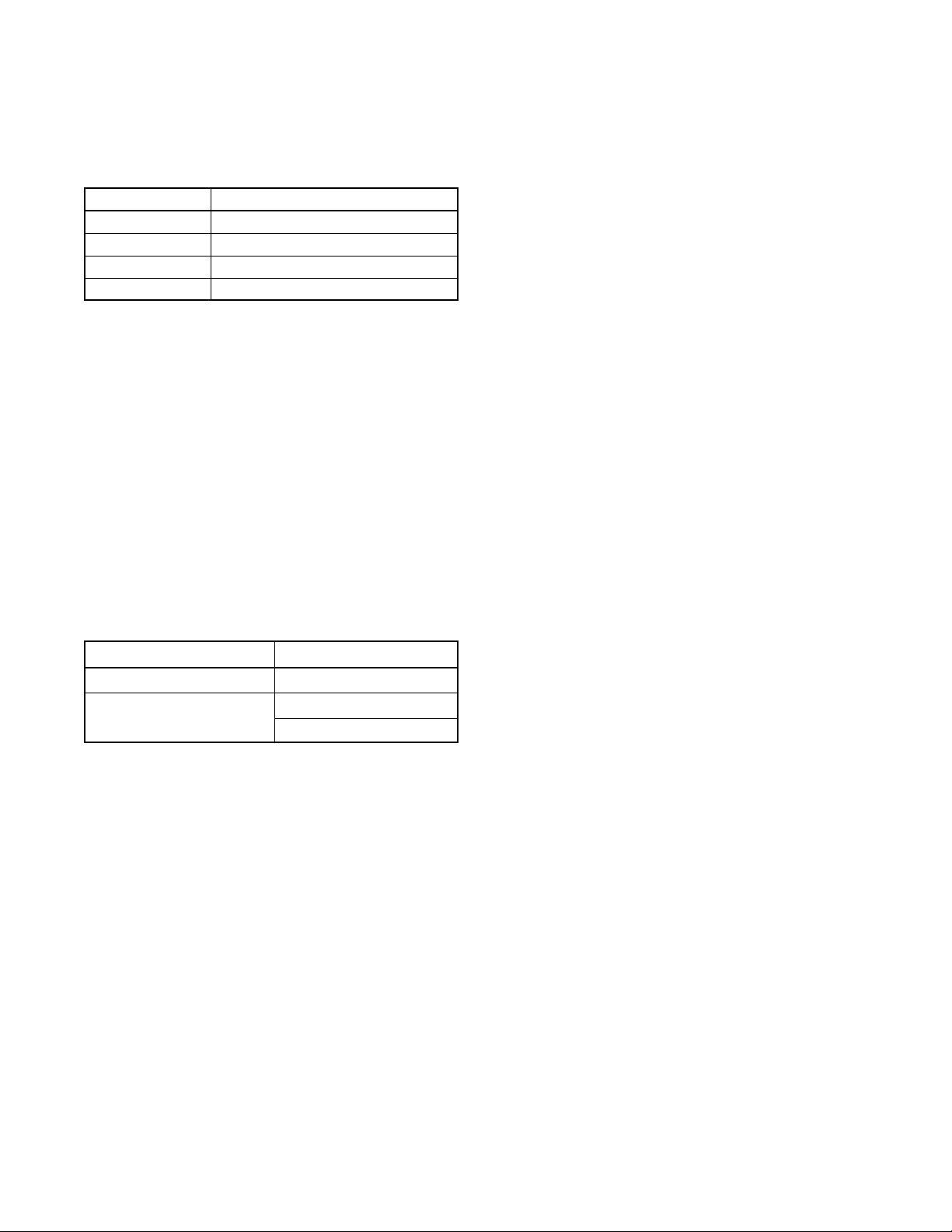
Alarm Board DIP Switches
Audible Alarm Setup
There are four DIP switches on the alarm module board.
Some of the switches are not used. See Figure 3-19. To
enable the preferred source s election, set DIP switch 1
to ON. If the supervised transfer switch is installed on the
ATS,setDIPswitch2toON.
DIP Switch Function
1 Preferred source selection
2 Supervised transfer enable
3 Not used
4 Not used
Figure 3-19 Alarm Board DIP Switches
Preferred Source Selection
The alarm module is required for preferred source
selection. To enable the preferred source selection, set
DIP switch 1 to ON. Then see the controller operation
manual for instructions to select Source N or Source E
as the preferred source.
External Alarm
A customer-supplied external alarm horn can be
connected to the alarm module at terminal block TB14.
Connect to the normally open or normally closed contact
as recommended by the alarm manufacturer’s
instructions. See Figure 3-20.
Item Specification
Wire Size #12-22 AWG Cu
Contact Voltage Rating
500mA@120VAC
250mA@240VAC
The alarm board is equipped with a 90 dB audible alarm.
The audible alarm can be set to sound under selected
fault conditions. Use the Common Alarms Setup menu
to assign functions to the audible alarm. See the
controller operation manual for instructions to set
Audible Alarm: Y for each function that should trigger the
alarm.
Alarm Operation, Normal Mode
In Normal Mode, the horn sounds anytime a fault event
happens in the system. The horn continues to sound
unless the alarm silence button is pressed. When the
fault is cleared, the alarm silence is ended and reset for
the next alarm.
Alarm Operation, Chicago Alarm Mode
Chicago Alarm mode requires the horn to sound and a
lamp or LED to light when the switch is in the emergency
(non-preferred) position. The horn continues to sound
unless the alarm silence button is pressed. When the
fault is cleared, the alarm silence is ended and reset for
the next alarm.
For Chicago Alarm Mode, use the Common Alarm
Setup menu to assign the necessary faults and
conditions to the audible alarm. See the controller
operation manual for instructions to assign common
faults. Be sure to assign the Contactor in Standby
condition to trigger the audible alarm.
A remote alarm or indicator light can also be connected
to the alarm board to indicate the alarm condition, as
described previously. See External Alarm.
Figure 3-20 External Alarm Connection
Specifications
TP-7191 4/21 35Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 36

Alarm Silence Mode
In Alarm Silence Mode, the horn is disabled. Alarm
Silenced appears on the display and the system alert
LED lights.
The Alarm Silenced condition can be assigned to a
programmable output. See the controller operation
manual for instructions to assign outputs.
Instructions to Silence the Alarm in Normal and
Chicago Alarm Modes
When the alarm is activated, the word Alarm appears on
the main display menu above the first button. See
Figure 3-21. Press the Alarm button to open the Reset
menu. Then press the button labeled Reset to silence
the alarm.
System Ready
LD Exer 12/14 @ 16:00
Norm 480V Emer 480V
Alarm View Set Test
Reset
To Silence Alarm
BYReset Main
Reset
Status or Fault Description
Alarm Silenced
BYReset Main
Figure 3-21 Alarm Silence
3.4 Heater
DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect all power sources before
opening the enclosure.
Servicing the transfer switch. Hazardous voltage will
cause severe injury or death. Deenergize all power sources
before servicing. Turn off the main circuit breakers of all
transfer switch power sources and disable all generator sets
as follows: (1) Press the generator set off/reset button to shut
down the generator set. (2) Disconnect power to all battery
chargers. (3) Disconnect all battery cables, negative (- ) leads
first. Reconnect negative (- ) leads last when reconnecting the
battery cables after servicing. Follow these precautions to
prevent the starting of generator sets by an automatic transfer
switch, remote start/stop switch, or engine start command
from a remote computer. Before servicing any components
inside the enclosure: (1) Remove all jewelry. (2) Stand on a
dry,approved electrically insulated mat. (3) Test circuits with a
voltmeter to verify that they are deenergized.
An anti-condensation heater kit is available. The strip
heater is controlled by a hygrostat to raise the
temperature inside the enclosure above the dew point to
prevent condensation. Figure 3-22 shows a typical
location of the heater kit components inside the
enclosure.
The installer must connect 120 VAC power to the
terminal block near the hygrostat. See Figure 3-23 and
Figure 3-24. The heater and hygrostat are connected to
power through a 15-amp circuit breaker.
The relative humidity setting on the hygrostat is
adjustable from 35% to 95%. A setting of 65% is
recommended.
Because of space limitations in the smaller enclosures,
30- 225 Amp Model KSS switches can include either an
enclosure heater or a surge protection device (SPD),
but not both.
TP-7191 4/2136 Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 37

1
2
Right Side View
1. Hygrostat assembly, see Figure 3-23
2. Strip heater with guard
1
2
3
GM71056
1. Circuit breaker
2. Relative humidity adjustment c ontrol
3. 120 VAC power connection terminal block (or transformer for
some kits)
Figure 3-23 Hygrostat Assembly, Typical
refADV- 8570
Figure 3-22 Heater Location, Typical
TP-7191 4/21 37Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 38

GM71278
Figure 3-24 Heater Connections
TP-7191 4/2138 Section 3 Communication and Accessory Connections
Page 39

Section 4 Scheduled Maintenance
Regular preventive maintenance ensures safe and
reliable operation and extends the life of the transfer
See the Service Assistance section in this manual for
how to locate a local distributor/dealer.
switch. Preventive maintenance includes periodic
testing, cleaning, inspection, and replacement of worn
or missing components.
The transfer switch controller Operation Manual
contains the Service Schedule and other maintenance
information. Refer to the Operation Manual shipped with
Have maintenance or service performed by a local
authorized distributor/dealer. Maintenance and service
the transfer switch, or see Figure 4-1 for the Operation
Manual part number.
must comply with all applicable codes and standards.
Keep records of all maintenance or service.
Operation Manual Part Number
Operation Manual, Decision-Makerr MPAC 1200 Controller
TP-6866
Figure 4-1 Operation Manual
TP-7191 4/21 39Section 4 Scheduled Maintenance
Page 40

Notes
TP-7191 4/2140 Section 4 Scheduled Maintenance
Page 41

Section 5 Functional Tests and Setup
5.1 Introduction
Be sure to perform all of the functional tests described in
this section before putting the transfer switch into
operation.
The functional tests include the following checks:
D Manual Operation Test
D Voltage Checks
D Lamp Test
D Automatic Operation Test
Note: Perform these checks in the order presented to
avoid damaging the ATS.
Read all instructions on the labels affixed to the
automatic transfer switch before proceeding.
To complete the installation, follow the instructions in
this section to:
D Set the time, date, and exercise schedule on the
controller.
D Perform the system startup procedures listed on the
startup form.
D Register the unit using the Kohlerr online Warranty
Processing System.
5.2 Manual Operation Test
If you have not already done so, test the contactor
manual operation before proceeding to the voltage
check and electrical operation test.
Note: Disable the generator set and disconnect the
power by opening the circuit breakers or switches
for both sources before manually operating the
transfer switch.
5.3 Voltage Check
The voltage, frequency, and phasing of the transfer
switch and the power sources must be the same to avoid
damage to loads and the transfer switch. Compare the
voltage and frequency ratings of the utility source,
transfer switch, and generator set, and verify that the
ratings are all the same.
Use the voltage check procedure explained in this
section to verify that the voltages and phasing of all
power sources are compatible with the transfer switch
before connecting the power switching device and
controller wire harnesses together.
Follow the instructions provided with the generator set
to prepare the generator set for operation.
Read and understand all instructions on installation
drawings and labels on the switch. Note any optional
accessories that have been furnished with the switch
and review their operation.
Note: Source N is the source connected to the normal
side of the contactor. Source E is the source
connected to the emergency side of the
contactor. Verify that the source leads are
connected to the correct lugs before proceeding.
The voltage check procedure requires the following
equipment:
D A digital voltmeter (DVM) with electrically insulated
probes capable of measuring the rated voltage and
frequency
D A phase rotation meter
Follow the instructions in the Installation Section to
check the transfer switch manual operation.
A contactor in normal and serviceable condition
transfers smoothly without binding when operated
manually. Do not place the transfer switch into service if
the contactor does not operate smoothly without
binding; contact an authorized distributor/dealer to
service the contactor.
TP-7191 4/21 41Section 5 Functional Tests and Setup
Page 42

DANGER
Hazardous voltage.
Will cause severe injury or death.
Only authorized personnel should
open the enclosure.
4. Use a phase rotation meter to check the phase
rotation at the Source N (normal) terminals. Rewire
thetransferswitchSourceNterminalstoobtainthe
correct phase sequence if necessary.
Note: The default setting for the phase rotation on
the controller is ABC. If the application uses
a phase rotation of BAC, refer to the
controller Operation Manual for instructions
to change the phase rotation setting on the
controller.
T esting live electrical circuits. Hazardous voltage or
current will cause severe injury or death. Have trained and
qualified personnel take diagnostic measurements of live
circuits. Use adequately rated test equipment with electrically
insulated probes and follow the instructions of the test
equipment manufacturer when performing voltage tests.
Observe the following precautions when performing voltage
tests: (1) Remove all jewelry. (2) Stand on a dry, approved
electrically insulated mat. (3) Do not touch the enclosure or
components inside the enclosure. (4) Be prepared for the
system to operate automatically.
(600 volts and under)
Voltage Check Procedure
1. If Source N is a generator set, move the generator
set master switch to the RUN position. The
generator set should start.
2. Close the Source N circuit breaker or switch.
3. Use a voltmeter to check the Source N (normal)
phase-to-phase and phase-to-neutral (if
applicable) terminal voltages and frequency.
a. If Source N is the utility and the measured input
does not match the voltage and frequency
shown on the transfer switch nameplate,
STOP! Do not proceed further in installation
because the transfer switch is not designed for
the application—call your distributor/dealer to
order the correct transfer switch.
b. If Source N is a generator set and the generator
set output voltage and frequency do not match
the nominal system voltage and frequency
shown on the transfer switch nameplate, follow
the manufacturer’s instructions to adjust the
generator set. The automatic transfer switch
will only function with the rated system voltage
and frequency specified on the nameplate.
5. If the source is a generator set, stop the generator
set by moving the master switch to the OFF
position.
6. Disconnect Source N by opening upstream circuit
breakers or switches.
7. Repeat steps 1 through 5 for Source E. Then
proceed to step 8.
8. Disconnect both sources to the transfer switch by
opening the circuit breakers or switches.
9. Close and lock the transfer switch enclosure door.
10. Reconnect both power sources by closing the
circuit breakers or switches.
11. Move the generator set master switch to the AUTO
position.
Note: If the engine cooldown time delay setting is
not set to zero (default setting), the
generator set may start and run until the
Engine Cooldown Time Delay ends.
12. Perform the lamp test and then proceed to the
automatic operation test.
5.4 Lamp Test
Refer to the controller Operation Manual for instructions
to perform a lamp test. Verify that all controller LEDs or
lamps light during the test.
5.5 Automatic Operation Test
Check the transfer switch’s automatic control system
immediately after the voltage check. Refer to the
controller Operation Manual for instructions to run the
automatic operation test.
Note: Close and lock the enclosure door before starting
the test procedure.
TP-7191 4/2142 Section 5 Functional Tests and Setup
Page 43

5.6 System Setup
5.8 User Interface Cover
Set the controller’s current time and date. See the
controller Operation Manual for instructions.
The transfer switch is factory-set with default settings for
time delays and other parameters. See the controller
Operation Manual for instructions to view and change
settings, if necessary.
Note: Use caution when changing transfer switch
settings. The source voltage and frequency
settings must match the values shown on the
transfer switch nameplate.
5.7 Exerciser Setup
Set the exerciser to start and run the generator set at
least once a week. See the controller Operation Manual
for instructions.
The gasket-sealed, hinged user interface cover
prevents unauthorized access to the transfer switch
controls and protects the user interface from harsh
environmental conditions. The cover is available as an
optional accessory for NEMA 1 enclosures. NEMA 3R
enclosures include the cover as standard equipment.
Use a customer-supplied padlock to lock the cover.
5.9 Startup Notification
Perform the system start up procedure explained on the
Startup Notification Form. The Startup Notification Form
covers all equipment in the power system. Complete the
Startup Notification Form and register the power system
using t he Kohlerr online Warranty Processing System.
TP-7191 4/21 43Section 5 Functional Tests and Setup
Page 44

Notes
TP-7191 4/2144 Section 5 Functional Tests and Setup
Page 45

Appendix A Abbreviations
The following list contains abbreviations that may appear in this publication.
A, amp ampere
ABDC after bottom dead center
AC alternating current
A/D analog to digital
ADC advanced digital control;
adj. adjust, adjustment
ADV advertising dimensional
Ah amp-hour
AHWT anticipatory high water
AISI American Iron and Steel
ALOP anticipatory low oil pressure
alt. alternator
Al aluminum
ANSI American National Standards
AO anticipatory only
APDC Air Pollution Control District
API American Petroleum Institute
approx. approximate, approximately
APU Auxiliary Power Unit
AQMD Air Quality Management District
AR as required, as requested
AS as supplied, as stated, as
ASE American Society of Engineers
ASME American Society of
assy. assembly
ASTM American Society for Testing
ATDC after top dead center
ATS automatic transfer switch
auto. automatic
aux. auxiliary
avg. average
AVR automatic voltage regulator
AWG American Wire Gauge
AWM appliance wiring material
bat. battery
BBDC before bottom dead center
BC battery charger, battery
BCA battery charging alternator
BCI Battery Council International
BDC before dead center
BHP brake horsepower
blk. black (paint color), block
blk. htr. block heater
BMEP brake mean effective pressure
bps bits per second
br. brass
BTDC before top dead center
Btu British thermal unit
Btu/min. British thermal units per minute
C Celsius, centigrade
cal. calorie
CAN controller area network
CARB California Air Resources Board
CAT5 Category 5 (network cable)
CB circuit breaker
CC crank cycle
cc cubic centimeter
CCA cold cranking amps
ccw. counterclockwise
CEC Canadian Electrical Code
cert. certificate, certification, certified
cfh cubic feet per hour
analog to digital converter
drawing
temperature
Institute
Institute (formerly American
Standards Association, ASA)
suggested
Mechanical Engineers
Materials
charging
(engine)
cfm cubic feet per minute
CG center of gravity
CID cubic inch displacement
CL centerline
cm centimeter
CMOS complementary metal oxide
com communications (port)
coml commercial
Coml/Rec Commercial/Recreational
conn. connection
cont. continued
CPVC chlorinated polyvinyl chloride
crit. critical
CSA Canadian Standards
CT current transformer
Cu copper
cUL Canadian Underwriter’s
CUL Canadian Underwriter’s
cu. in. cubic inch
cw. clockwise
CWC city water-cooled
cyl. cylinder
D/A digital to analog
DAC digital to analog converter
dB decibel
dB(A) decibel (A weighted)
DC direct current
DCR direct current resistance
deg., degree
dept. department
dia. diameter
DI/EO dual inlet/end outlet
DIN Deutsches Institut fur Normung
DIP dual inline package
DPDT double-pole, double-throw
DPST double-pole, single-throw
DS disconnect switch
DVR digital voltage regulator
2
E
PROM, EEPROM
E, emer. emergency (power source)
ECM electronic control module,
EDI electronic data interchange
EFR emergency frequency relay
e.g. for example (exempli gratia)
EG electronic governor
EGSA Electrical Generating Systems
EIA Electronic Industries
EI/EO end inlet/end outlet
EMI electromagnetic interference
emiss. emission
eng. engine
EPA Environmental Protection
EPS emergency power system
ER emergency relay
ES engineering special,
ESD electrostatic discharge
est. estimated
E-Stop emergency stop
etc. et cetera (and so forth)
substrate (semiconductor)
Association
Laboratories
Laboratories
e. V. (also Deutsche Industrie
Normenausschuss)
electrically-erasable
programmable read-only
memory
engine control module
Association
Association
Agency
engineered special
exh. exhaust
ext. external
F Fahrenheit, female
FHM flat head machine (screw)
fl. oz. fluid ounce
flex. flexible
freq. frequency
FS full scale
ft. foot, feet
ft. lb. foot pounds (torque)
ft./min. feet per minute
ftp file transfer protocol
ggram
ga. gauge (meters, wire size)
gal. gallon
gen. generator
genset generator set
GFI ground fault interrupter
GND,
gov. governor
gph gallons per hour
gpm gallons per minute
gr. grade, gross
GRD equipment ground
gr. wt. gross weight
H x W x D height by width by depth
HC hex cap
HCHT high cylinder head temperature
HD heavy duty
HET high exhaust temp., high
hex hexagon
Hg mercury (element)
HH hex head
HHC hex head cap
HP horsepower
hr. hour
HS heat shrink
hsg. housing
HVAC heating, ventilation, and air
HWT high water temperature
Hz hertz ( cycles per second)
IBC International Building Code
IC integrated circuit
ID inside diameter, identification
IEC International Electrotechnical
IEEE Institute of Electrical and
IMS improved motor starting
in. inch
in. H
in. Hg inches of mercury
in. lb. inch pounds
Inc. incorporated
ind. industrial
int. internal
int./ext. internal/external
I/O input/output
IP internet protocol
ISO International Organization for
J joule
JIS Japanese Industry Standard
k kilo (1000)
Kkelvin
kA kiloampere
KB kilobyte (2
KBus Kohler communication protocol
kg kilogram
ground
engine temp.
conditioning
Commission
Electronics Engineers
O inches of water
2
Standardization
10
bytes)
TP-7191 4/21 Appendix 45
Page 46

2
kg/cm
kgm kilogram-meter
kg/m
kilograms per square
centimeter
3
kilograms per cubic meter
kHz kilohertz
kJ kilojoule
km kilometer
kOhm, k kilo-ohm
kPa kilopascal
kph kilometers per hour
kV kilovolt
kVA kilovolt ampere
kVAR kilovolt ampere reactive
kW kilowatt
kWh kilowatt-hour
kWm kilowatt mechanical
kWth kilowatt-thermal
Lliter
LAN local area network
L x W x H length by width by height
lb. pound, pounds
3
lbm/ft
pounds mass per cubic feet
LCB line circuit breaker
LCD liquid crystal display
LED light emitting diode
Lph liters per hour
Lpm liters per minute
LOP low oil pressure
LP liquefied petroleum
LPG liquefied petroleum gas
LS left side
L
wa
LWL low water level
sound power level, A weighted
LWT low water temperature
m meter, milli (1/1000)
Mmega(10
3
m
3
m
3
m
units), male
cubic meter
/hr. cubic meters per hour
/min. cubic meters per minute
6
when used with SI
mA milliampere
man. manual
max. maximum
MB megabyte (2
20
bytes)
MCCB molded-case circuit breaker
MCM one thousand circular mils
meggar megohmmeter
MHz megahertz
mi. mile
mil one one-thousandth of an inch
min. minimum, minute
misc. miscellaneous
MJ megajoule
mJ millijoule
mm millimeter
mOhm, mmilliohm
MOhm, Mmegohm
MOV metal oxide varistor
MPa megapascal
mpg miles per gallon
mph miles per hour
MS military standard
ms millisecond
m/sec. meters per second
mtg. mounting
MTU Motoren-und Turbinen-Union
MW megawatt
mW milliwatt
F microfarad
N, norm. normal (power source)
NA not available, not applicable
nat. gas natural gas
NBS National Bureau of Standards
NC normally closed
NEC National Electrical Code
NEMA National Electrical
Manufacturers Association
NFPA National Fire Protection
Association
Nm newton meter
NO normally open
no., nos. number, numbers
NPS National Pipe, Straight
NPSC National Pipe, Straight-coupling
NPT National Standard taper pipe
thread per general use
NPTF National Pipe, Taper-Fine
NR not required, normal relay
ns nanosecond
OC overcrank
OD outside diameter
OEM original equipment
manufacturer
OF overfrequency
opt. option, optional
OS oversize, overspeed
OSHA Occupational Safety and Health
OSHPD Office of Statewide Health
Administration
Planning and Development
(California)
OV overvoltage
oz. ounce
p., pp. page, pages
PC personal computer
PCB printed circuit board
pF picofarad
PF power factor
ph., phase
PHC Phillipsr head Crimptiter
(screw)
PHH Phillipsr hex head (screw)
PHM pan head machine (screw)
PLC programmable logic control
PMG permanent magnet generator
pot potentiometer, potential
ppm parts per million
PROM programmable read-only
memory
psi pounds per square inch
psig pounds per square inch gauge
pt. pint
PTC positive temperature coefficient
PTO power takeoff
PVC polyvinyl chloride
qt. quart, quarts
qty. quantity
R replacement (emergency)
power source
rad. radiator, radius
RAM random access memory
RDO relay driver output
ref. reference
rem. remote
Res/Coml Residential/Commercial
RFI radio frequency interference
RH round head
RHM round head machine (screw)
rly. relay
rms root mean square
rnd. round
RO read only
ROM read only memory
rot. rotate, rotating
rpm revolutions per minute
RS right side
RTDs Resistance Temperature
Detectors
RTU remote terminal unit
RTV room temperature vulcanization
RW read/write
SAE Society of Automotive
Engineers
scfm standard cubic feet per minute
SCR silicon controlled rectifier
s, sec. second
SI Systeme international d’unites,
International System of Units
SI/EO side in/end out
sil. silencer
SMTP simple mail transfer protocol
SN serial number
SNMP simple network management
protocol
SPDT single-pole, double-throw
SPST single-pole, single-throw
spec specification
specs specification(s)
sq. square
sq. cm square centimeter
sq. in. square inch
SMS short message service
SS stainless steel
std. standard
stl. steel
tach. tachometer
TB terminal block
TCP transmission control protocol
TD time delay
TDC top dead center
TDEC time delay engine cooldown
TDEN time delay emergency to
normal
TDES time delay engine start
TDNE time delay normal to
emergency
TDOE time delay off to emergency
TDON time delay off to normal
temp. temperature
term. terminal
THD total harmonic distortion
TIF telephone influence factor
tol. tolerance
turbo. turbocharger
typ. typical (same in multiple
locations)
UF underfrequency
UHF ultrahigh frequency
UIF user interface
UL Underwriter’s Laboratories, Inc.
UNC unified coarse thread (was NC)
UNF unified fine thread (was NF)
univ. universal
URL uniform resource locator
(web address)
US undersize, underspeed
UV ultraviolet, undervoltage
Vvolt
VAC volts alternating current
VAR voltampere reactive
VDC volts direct current
VFD vacuum fluorescent display
VGA video graphics adapter
VHF very high frequency
Wwatt
WCR withstand and closing rating
w/ with
WO write only
w/o without
wt. weight
xfmr transformer
TP-7191 4/2146 Appendix
Page 47

Page 48

TP-7191 4/21
E 2021 Kohler Co. All rights reserved.
KOHLER CO., Kohler, Wisconsin 53044
Phone 920-457-4441, Fax 920-459-1646
For the nearest sales/service outlet in the
US and Canada, phone 1-800-544-2444
KOHLERPower.com
 Loading...
Loading...