Page 1

COMMAND CH18-750
HORIZONTAL CRANKSHAFT
SERVICE MANUAL
Page 2

Contents
Section 1. Safety and General Information ............................................................................
Section 2. Special Tools ..........................................................................................................
Section 3. Troubleshooting .....................................................................................................
Section 4. Air Cleaner and Air Intake System ........................................................................
Section 5. Fuel System and Governor....................................................................................
Section 5A. LPG Fuel Systems ...............................................................................................
Section 5B. Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) Fuel System ......................................................
1
2
3
4
5
5A
5B
Section 6. Lubrication System ................................................................................................
Section 7. Retractable Starter .................................................................................................
Section 8. Electrical System and Components .....................................................................
Section 9. Disassembly ...........................................................................................................
Section 10. Inspection and Reconditioning ...........................................................................
Section 11. Reassembly...........................................................................................................
Section 12. Clutch ....................................................................................................................
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Page 3
Safety and General Information
Section 1
Safety and General Information
Safety Precautions
To ensure safe operation please read the following statements and understand their meaning. Also
refer to your equipment manufacturer's manual for other important safety information. This manual
contains safety precautions which are explained below. Please read carefully.
WARNING
Warning is used to indicate the presence of a hazard that can cause severe personal injury, death,
or substantial property damage if the warning is ignored.
CAUTION
Caution is used to indicate the presence of a hazard that will or can cause minor personal injury or
property damage if the caution is ignored.
Section 1
1
NOTE
Note is used to notify people of installation, operation, or maintenance information that is important
but not hazard-related.
For Y our Safety!
These precautions should be followed at all times. Failure to follow these precautions could result in injury to yourself
and others.
WARNING
Accidental Starts can cause severe
injury or death.
Disconnect and ground spark plug
leads before servicing.
Accidental Starts!
Disabling engine. Accidental starting
can cause severe injury or death.
Before working on the engine or
equipment, disable the engine as follows:
1) Disconnect the spark plug lead(s). 2)
Disconnect negative (-) battery cable
from battery.
WARNING
Rotating Parts can cause severe
injury.
Stay away while engine is in
operation.
Rotating Parts!
Keep hands, feet, hair, and clothing away
from all moving parts to prevent injury.
Never operate the engine with covers,
shrouds, or guards removed.
Hot Parts can cause severe burns.
Do not touch engine while operating
or just after stopping.
Hot Parts!
Engine components can get extremely
hot from operation. To prevent severe
burns, do not touch these areas while the
engine is running - or immediately after it
is turned off. Never operate the engine
with heat shields or guards removed.
WARNING
1.1
Page 4

Section 1
Safety and General Information
WARNING
Explosive Fuel can cause fires and
severe burns.
Do not fill the fuel tank while the
engine is hot or running.
Explosive Fuel!
Gasoline is extremely flammable and its
vapors can explode if ignited. Store
gasoline only in approved containers, in
well ventilated, unoccupied buildings,
away from sparks or flames. Do not fill
the fuel tank while the engine is hot or
running, since spilled fuel could ignite if
it comes in contact with hot parts or
sparks from ignition. Do not start the
engine near spilled fuel. Never use
gasoline as a cleaning agent.
WARNING
WARNING WARNING
Carbon Monoxide can cause severe
nausea, fainting or death.
Avoid inhaling exhaust fumes, and
never run the engine in a closed
building or confined area.
Lethal Exhaust Gases!
Engine exhaust gases contain poisonous
carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide is
odorless, colorless, and can cause death if
inhaled. Avoid inhaling exhaust fumes,
and never run the engine in a closed
building or confined area.
WARNING
Uncoiling Spring can cause severe
injury.
Wear safety goggles or face
protection when servicing
retractable starter.
Explosive Gas can cause fires and
severe acid burns.
Charge battery only in a well
ventilated area. Keep sources of
ignition away.
Explosive Gas!
Batteries produce explosive hydrogen gas
while being charged. To prevent a fire or
explosion, charge batteries only in well
ventilated areas. Keep sparks, open
flames, and other sources of ignition
away from the battery at all times. Keep
batteries out of the reach of children.
Remove all jewelry when servicing
batteries.
Before disconnecting the negative (-)
ground cable, make sure all switches are
OFF. If ON, a spark will occur at the
ground cable terminal which could cause
an explosion if hydrogen gas or gasoline
vapors are present.
Cleaning Solvents can cause severe
injury or death.
Use only in well ventilated areas
away from ignition sources.
Flammable Solvents!
Carburetor cleaners and solvents are
extremely flammable. Keep sparks,
flames, and other sources of ignition
away from the area. Follow the cleaner
manufacturer’s warnings and
instructions on its proper and safe use.
Never use gasoline as a cleaning agent.
1.2
Spring Under T ension!
Retractable starters contain a powerful,
recoil spring that is under tension.
Always wear safety goggles when
servicing retractable starters and
carefully follow instructions in the
"Retractable Starter" Section 7 for
relieving spring tension.
CAUTION
Electrical Shock can cause injury.
Do not touch wires while engine is
running.
Electrical Shock!
Never touch electrical wires or
components while the engine is running.
They can be sources of electrical shock.
Page 5

Engine Identification Numbers
When ordering parts, or in any communication
involving an engine, always give the Model,
Specification and Serial Numbers, including letter
suffixes if there are any.
The engine identification numbers appear on a decal,
or decals, affixed to the engine shrouding. See Figure
1-1. An explanation of these numbers is shown in
Figure 1-2.
Section 1
Safety and General Information
1
Identification Decal
Figure 1-1. Engine Identification Decal Location.
A. Model No.
Command Engine
Horizontal Crankshaft
Horsepower
17 = 17 HP
18 = 18 HP
20 = 20 HP
22 = 22 HP
23 = 23 HP
25 = 25 HP
26 = 26 HP
B. Spec. No.
Engine Model Code
Code Model
62 CH18
64 CH20
66 CH22 (624 cc)
68 CH25
76 CH22/23 (674 cc)
78 CH26
C H 18 S
or
62500
Numerical Designation
730
740
745
750
or
Variation of
Basic Engine
Version Code
S = Electric Start
CH730-0001
CH740-0001
CH745-0001
CH750-0001
Complete Spec Number
(Incorporating Model No.
with V ariation No. of
Basic Spec.)
C. Serial No.
Year Manufactured Code
Code Year
21 1991
22 1992
23 1993
24 1994
25 1995
26 1996
27 1997
28 1998
29 1999
Figure 1-2. Explanation of Engine Identification Numbers.
3305810334
Factory Code
Code Year
30 2000
31 2001
32 2002
33 2003
34 2004
35 2005
36 2006
37 2007
1.3
Page 6
Section 1
Safety and General Information
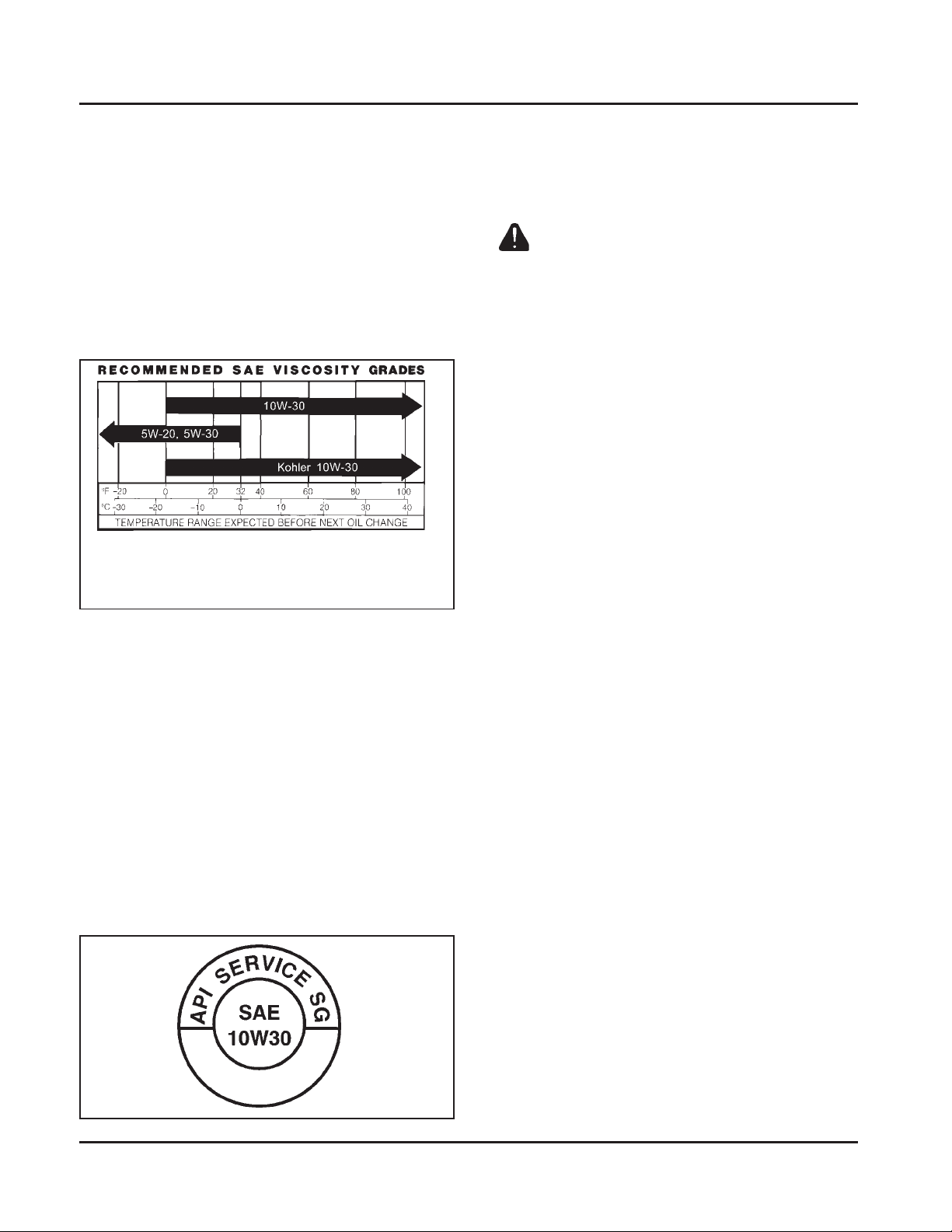
Oil Recommendations
Using the proper type and weight of oil in the
crankcase is extremely important. So is checking oil
daily and changing oil regularly. Failure to use the
correct oil, or using dirty oil, causes premature engine
wear and failure.
Oil Type
Use high-quality detergent oil of API (American
Petroleum Institute) Service Class SG, SH, SJ or higher.
Select the viscosity based on the air temperature at the
time of operation as shown in the following table.
**
*
*Use of synthetic oil having 5W-20 or 5W-30 rating is
acceptable, up to 4°C (40°F).
**Synthetic oils will provide better starting in
extreme cold (below -23°C (-10°F).
Refer to Section 6 - “Lubrication System” for detailed
procedures on checking the oil, changing the oil and
changing the oil filter.
Fuel Recommendations
WARNING: Explosive Fuel!
Gasoline is extremely flammable and its vapors can explode if
ignited. Before servicing the fuel system, make sure there are no
sparks, open flames or other sources of ignition nearby as these
can ignite gasoline vapors. Disconnect and ground the spark plug
leads to prevent the possibility of sparks from the ignition system.
General Recommendations
Purchase gasoline in small quantities and store in clean,
approved containers. A container with a capacity of 2
gallons or less with a pouring spout is recommended.
Such a container is easier to handle and helps eliminate
spillage during refueling.
Do not use gasoline left over from the previous season,
to minimize gum deposits in your fuel system and to
ensure easy starting.
Do not add oil to the gasoline.
NOTE: Using other than service class SG, SH, SJ or
higher oil or extending oil change intervals
longer than recommended can cause engine
damage.
NOTE: Synthetic oils meeting the listed
classifications may be used with oil changes
performed at the recommended intervals.
However, to allow piston rings to properly
seat, a new or rebuilt engine should be
operated for at least 50 hours using standard
petroleum based oil before switching to
synthetic oil.
A logo or symbol on oil containers identifies the API
service class and SAE viscosity grade. See Figure 1-3.
Do not overfill the fuel tank. Leave room for the fuel to
expand.
Fuel Type
For best results, use only clean, fresh, unleaded gasoline
with a pump sticker octane rating of 87 or higher. In
countries using the Research method, it should be 90
octane minimum.
Unleaded gasoline is recommended as it leaves less
combustion chamber deposits and reduces harmful
exhaust emissions. Leaded gasoline is not recommended
and must not be used on EFI engines, or on other models
where exhaust emissions are regulated.
Gasoline/Alcohol blends
Gasohol (up to 10% ethyl alcohol, 90% unleaded gasoline
by volume) is approved as a fuel for Kohler engines.
Other gasoline/alcohol blends are not approved.
Gasoline/Ether blends
Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE) and unleaded
gasoline blends (up to a maximum of 15% MTBE by
volume) are approved as a fuel for Kohler engines. Other
gasoline/ether blends are not approved.
Figure 1-3. Oil Container Logo.
1.4
Page 7
Periodic Maintenance Instructions
Section 1
Safety and General Information
WARNING: Accident al Start s!
Disabling engine. Accidental starting can cause severe injury or death. Before working on the engine or equipment,
disable the engine as follows: 1) Disconnect the spark plug lead(s). 2) Disconnect negative (-) battery cable from battery.
Maintenance Schedule
These required maintenance procedures should be performed at the frequency stated in the table. They should
also be included as part of any seasonal tune-up.
Maintenance RequiredFrequency
• Fill fuel tank Section 5
Daily or Before
Starting Engine
Every 25 Hours
Every 100 Hours
Every 200 Hours
Every 250 Hours
Annually or
Every 500 Hours
Every 500 Hours
Every 1500 Hours
¹Perform these maintenance procedures more frequently under extremely dusty, dirty conditions.
²Only requried for Denso starters. Not necessary on Delco starters. Have a Kohler Engine Service Dealer perform this service.
³Cleanout Kits 25 755 20-S (black) or 25 755 21-S (gold) allow cooling areas to be cleaned without removing shrouds.
• Check oil level. Section 6
• Check air cleaner for dirty1, loose, or damaged parts. Section 4
• Check air intake and cooling areas, clean as necessary1. Section 4
• Service precleaner element1. Section 4
• Replace air cleaner element1. Section 4
• Change oil. (More frequently under severe conditions.) Section 6
• Remove cooling shrouds and clean cooling areas
• Check oil cooler fins, clean as necessary (if equipped). Section 6
• Check spark plug condition and gap. Section 8
• Change oil filter. Section 6
• Change fuel filter (carbureted engines). Section 5
• Replace heavy-duty air cleaner element and check inner element1. Section 4
• Have bendix starter drive serviced2. Section 8
• Have solenoid shift starter disassembled and cleaned2. Section 8
• Have crankshaft splines lubricated2. Section 2
• Replace fuel filter1 (EFI engines). Section 5B
1,3
. Section 4
Refer to:
1
Storage
If the engine will be out of service for two months or
more, use the following storage procedure:
1. Clean the exterior surfaces of the engine. On
Electronic Fuel Injected (EFI) engines, avoid
spraying water at the wiring harness or any of
the electrical components.
2. Change the oil and oil filter while the engine is
still warm from operation. See “Change Oil and
Oil Filter” in Section 6.
3. The fuel system must be completely emptied, or
the gasoline must be treated with a stabilizer to
prevent deterioration. If you choose to use a
stabilizer, follow the manufacturer’s
recommendations, and add the correct amount
for the capacity of the fuel system.
Fill the fuel tank with clean, fresh gasoline. Run
the engine for 2 to 3 minutes to get stabilized fuel
into the rest of the system. Close the fuel shut-off
valve when the unit is being stored or
transported.
To empty the system, run the engine until the
tank and the system are empty.
4. Remove the spark plugs and add one tablespoon
of engine oil into each spark plug hole. Install the
spark plugs, but do not connect the plug leads.
Crank the engine two or three revolutions.
5. On equipment with an EFI engine, disconnect the
battery or use a battery minder to keep the
battery charged during storage.
6. Store the engine in a clean, dry place.
1.5
Page 8
Section 1
Safety and General Information
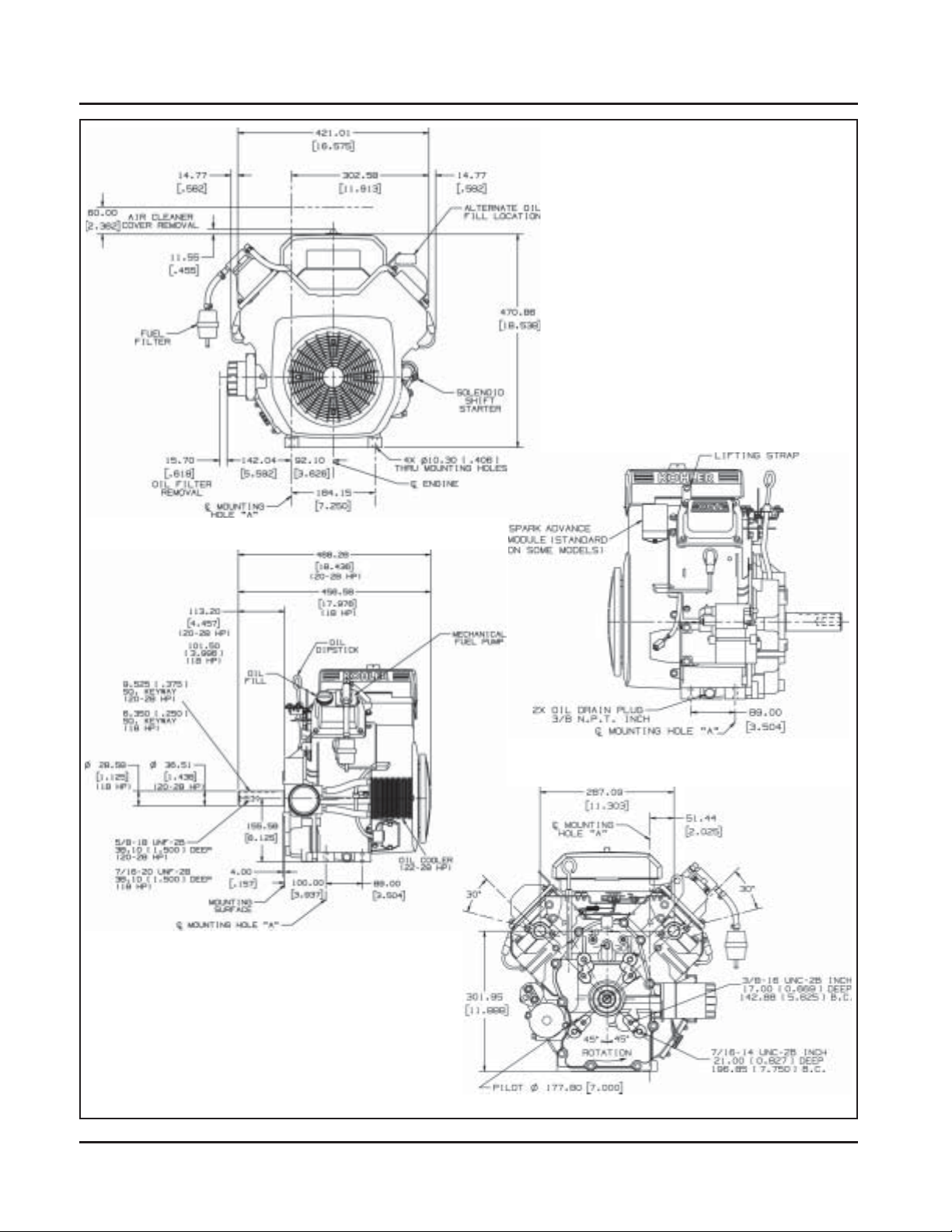
Dimensions in millimeters.
Inch equivalents shown in [ ].
Figure 1-4. Typical Engine Dimensions CH Series with Standard Flat Air Cleaner.
1.6
Page 9
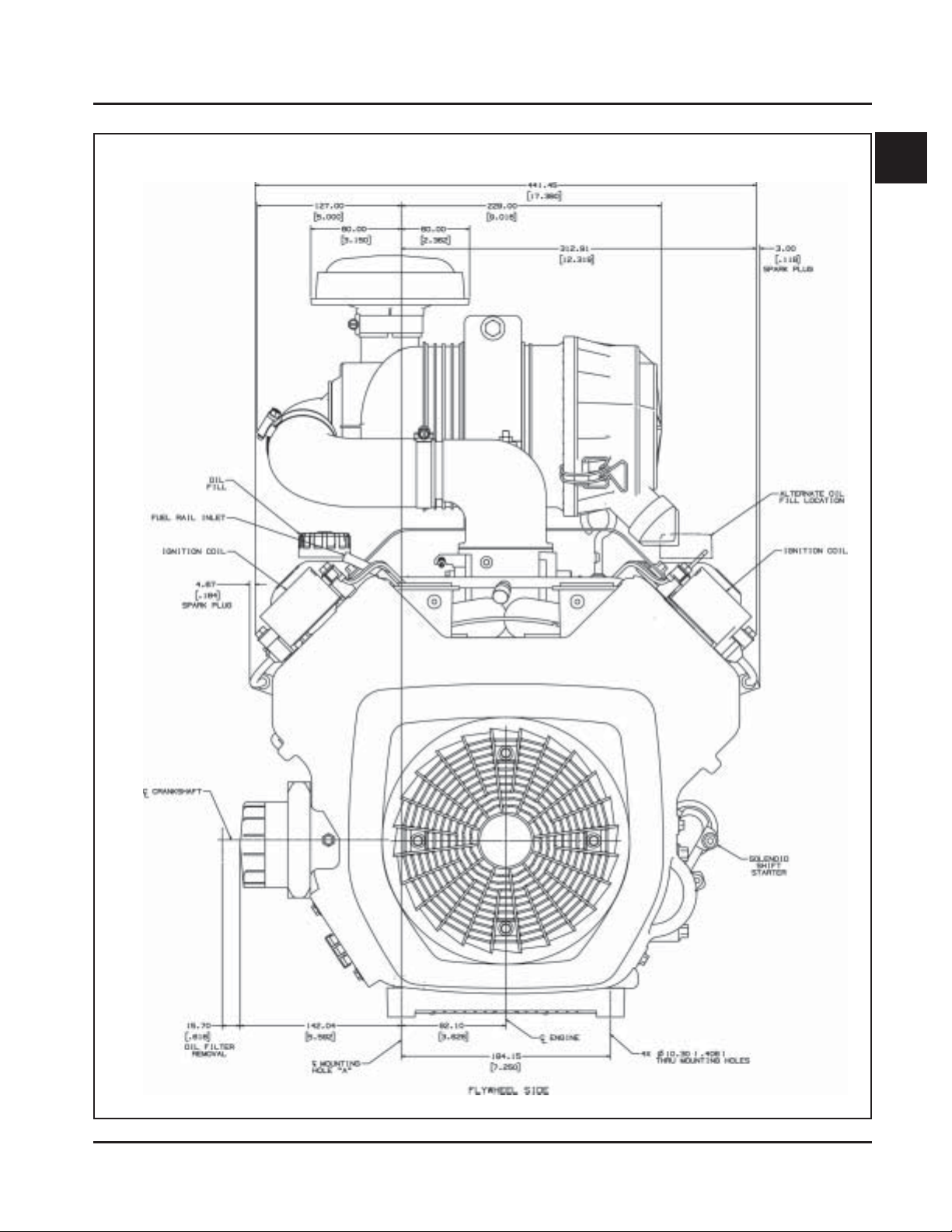
Section 1
Safety and General Information
Dimensions in millimeters.
Inch equivalents shown in [ ].
1
Figure 1-5. T ypical Engine Dimensions CH EFI Series with Heavy-Duty Air Cleaner.
1.7
Page 10

Section 1
Safety and General Information
General Specifications¹
Power (@ 3600 RPM, exceeds Society of Automotive Engineers-Small Engine Test Code J1940.)
CH18 ........................................................................................................................................ 13.4 kW (18 HP)
CH20 ........................................................................................................................................ 14.9 kW (20 HP)
CH22 ........................................................................................................................................ 16.4 kW (22 HP)
CH23 ........................................................................................................................................ 17.2 kW (23 HP)
CH25, CH730 .......................................................................................................................... 18.6 kW (25 HP)
CH26 ........................................................................................................................................ 19.4 kW (26 HP)
CH740 ...................................................................................................................................... 20.1 kW (27 HP)
CH745 ...................................................................................................................................... 20.9 kW (28 HP)
CH750 ...................................................................................................................................... 22.3 kW (30 HP)
Peak Torque
CH18 @ 2200 RPM ................................................................................................................. 43.6 N·m (32.2 ft. lb.)
CH20 @ 2400 RPM ................................................................................................................. 44.3 N·m (32.7 ft. lb.)
CH22 @ 2400 RPM ................................................................................................................. 49.1 N·m (36.2 ft. lb.)
CH23 @ 2400 RPM ................................................................................................................. 54.1 N·m (37.9 ft. lb.)
CH25 @ 2200 RPM ................................................................................................................. 54.0 N·m (39.5 ft. lb.)
CH730 @ 2400 RPM ............................................................................................................... 55.4 N·m (40.9 ft. lb.)
CH26 @ 2800 RPM ................................................................................................................. 54.2 N·m (40.0 ft. lb.)
CH740 @ 2400 RPM ............................................................................................................... 57.3 N·m (42.3 ft. lb.)
CH745 @ 2600 RPM ............................................................................................................... 57.9 N·m (42.7 ft. lb.)
CH750 @ 2400 RPM ............................................................................................................... 64.4 N·m (47.5 ft. lb.)
Bore
CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) .................................................................................................. 77 mm (3.03 in.)
CH22/23 (674 cc) .................................................................................................................... 80 mm (3.15 in.)
CH25, CH26, CH730-750 ....................................................................................................... 83 mm (3.27 in.)
Stroke
CH18-745 ................................................................................................................................ 67 mm (2.64 in.)
CH750 ...................................................................................................................................... 69 mm (2.7 in.)
Displacement
CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) .................................................................................................. 624 cc (38 cu. in.)
CH22/23 (674 cc) .................................................................................................................... 674 cc (41 cu. in.)
CH25, CH26, CH730-745 ....................................................................................................... 725 cc (44 cu. in.)
CH750 ...................................................................................................................................... 755 cc (46 cu. in.)
Compression Ratio
CH18, CH20, CH22/23 ........................................................................................................... 8.5:1
CH25, CH26, CH730-745 ....................................................................................................... 9.0:1
CH750 ...................................................................................................................................... 9.4:1
Dry Weight
CH18, CH20, CH22/23 ........................................................................................................... 41 kg (90 lb.)
CH25, CH26, CH730-745 ....................................................................................................... 43 kg (94 lb.)
CH750 ...................................................................................................................................... 48 kg (105 lb.)
Oil Capacity (w/filter) - approximate,
determined by oil filter and oil cooler used ............................................................................. 1.6-1.8 L (1.7-1.9 U.S. qt.)
¹Values are in Metric units. Values in parentheses are English equivalents. Lubricate threads with engine oil
prior to assembly.
1.8
Page 11

General Specifications¹ cont.
Section 1
Safety and General Information
Angle of Operation - Maximum (At Full Oil Level) All Directions ................... 25°
Blower Housing and Sheet Metal
M5 Fasteners Torque ................................................................................................ 6.2 N·m (55 in. lb.) into new holes
4.0 N·m (35 in. lb.) into used holes
M6 Fasteners Torque ................................................................................................ 10.7 N·m (95 in. lb.) into new holes
7.3 N·m (65 in. lb.) into used holes
Rectifier-Regulator Fastener Torque ................................................................... 1.4 N·m (12.6 in. lb.)
Camshaft
End Play (With Shim) ............................................................................................ 0.076/0.127 mm (0.0030/0.0050 in.)
Running Clearance ................................................................................................. 0.025/0.063 mm (0.0010/0.0025 in.)
Bore I.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 20.000/20.025 mm (0.7874/0.7884 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 20.038 mm (0.7889 in.)
Camshaft Bearing Surface O.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 19.962/19.975 mm (0.7859/0.7864 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 19.959 mm (0.7858 in.)
1
Carburetor and Intake Manifold
Intake Manifold Mounting Fastener Torque
Torque in Two Stages ..................................................................................... first to 7.4 N·m (66 in. lb.)
finally to 9.9 N·m (88 in. lb.)
Carburetor Mounting Screw Torque M6 ............................................................ 6.2-7.3 N·m (55-65 in. lb.)
Adapter (for Heavy Duty Air Cleaner) Mounting Fastener Torque ................ 7.3 N·m (65 in. lb.)
Connecting Rod
Cap Fastener Torque (torque in increments)
8 mm straight shank ............................................................................................ 22.7 N·m (200 in. lb.)
8 mm step-down .................................................................................................. 14.7 N·m (130 in. lb.)
6 mm straight shank ............................................................................................ 11.3 N·m (100 in. lb.)
Connecting Rod-to-Crankpin Running Clearance
New .................................................................................................................. 0.030/0.055 mm (0.0012/0.0022 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 0.070 mm (0.0028 in.)
Connecting Rod-to-Crankpin Side Clearance .................................................... 0.26/0.63 mm (0.0102/0.0248 in.)
Connecting Rod-to-Piston Pin Running Clearance........................................... 0.015/0.028 mm (0.0006/0.0011 in.)
Piston Pin End I.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 17.015/17.023 mm (0.6699/0.6702 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 17.036 mm (0.6707 in.)
¹Values are in Metric units. Values in parentheses are English equivalents. Lubricate threads with engine oil
prior to assembly.
1.9
Page 12

Section 1
Safety and General Information
Crankcase
Governor Cross Shaft Bore I.D.
6 mm Shaft
New .................................................................................................................. 6.025/6.050 mm (0.2372/0.2382 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 6.063 mm (0.2387 in.)
8 mm Shaft
New .................................................................................................................. 8.025/8.075 mm (0.3159/0.3179 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 8.088 mm (0.3184 in.)
Breather Cover Fastener Torque .......................................................................... 7.3 N·m (65 in. lb.)
Oil Drain Plug Torque ............................................................................................ 13.6 N·m (10 ft. lb.)
Closure Plate
Closure Plate Fastener Torque .............................................................................. 24.4 N·m (216 in. lb.)
Crankshaft
End Play (Free) ........................................................................................................ 0.070/0.590 mm (0.0028/0.0230 in.)
End Play (With Thrust Bearing Components) ................................................... 0.070/0.270 mm (0.0028/0.0100 in.)
Except CH25 Engines Below Serial No. 2403500008 .......................................... 0.050/0.750 mm (0.0020/0.0295 in.)
Crankshaft Bore (In Crankcase)
New .................................................................................................................. 40.965/41.003 mm (1.6128/1.6143 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 41.016 mm (1.6148 in.)
Crankshaft to Sleeve Bearing (Crankcase)
Running Clearance - New ............................................................................ 0.03/0.09 mm (0.0012/0.0035 in.)
Crankshaft Bore (In Closure Plate) - New .......................................................... 40.987/40.974 mm (1.6136/1.6131 in.)
Crankshaft Bore (In Closure Plate)-to-Crankshaft
Running Clearance - New ............................................................................ 0.039/0.074 mm (0.0015/0.0029 in.)
Flywheel End Main Bearing Journal
O.D. - New ....................................................................................................... 40.913/40.935 mm (1.6107/1.6116 in.)
O.D. - Max. Wear Limit .................................................................................. 40.84 mm (1.608 in.)
Max. Taper ....................................................................................................... 0.022 mm (0.0009 in.)
Max. Out-of-Round ........................................................................................ 0.025 mm (0.0010 in.)
Closure Plate End Main Bearing Journal
O.D. - New ....................................................................................................... 40.913/40.935 mm (1.6107/1.6116 in.)
O.D. - Max. Wear Limit .................................................................................. 40.84 mm (1.608 in.)
Max. Taper ....................................................................................................... 0.022 mm (0.0009 in.)
Max. Out-of-Round ........................................................................................ 0.025 mm (0.0010 in.)
Connecting Rod Journal
O.D. - New ....................................................................................................... 35.955/35.973 mm (1.4156/1.4163 in.)
O.D. - Max. Wear Limit .................................................................................. 35.94 mm (1.415 in.)
Max. Taper ....................................................................................................... 0.018 mm (0.0007 in.)
Max. Out-of-Round ........................................................................................ 0.025 mm (0.0010 in.)
1.10
Page 13

Section 1
Safety and General Information
Crankshaft cont.
Crankshaft T.I.R.
PTO End, Crank in Engine ............................................................................. 0.279 mm (0.0110 in.)
Entire Crank, in V-Blocks .............................................................................. 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
Cylinder Bore
Cylinder Bore I.D.
New - CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) ............................................................... 77.000/77.025 mm (3.0315/3.0325 in.)
New - CH22/23 (674 cc) ................................................................................. 80.000/80.025 mm (3.1496/3.1506 in.)
New - CH25, CH26, CH730-750 ................................................................... 82.988/83.013 mm (3.2672/3.2682 in.)
Max. Wear Limit - CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) .......................................... 77.063 mm (3.0340 in.)
Max. Wear Limit - CH22/23 (674 cc) ............................................................ 80.065 mm (3.1522 in.)
Max. Wear Limit - CH25, CH26, CH730-750 .............................................. 83.051 mm (3.2697 in.)
Max. Out-of-Round ........................................................................................ 0.12 mm (0.0047 in.)
Max. Taper ....................................................................................................... 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
Cylinder Head
Cylinder Head Fastener Torque
Hex Flange Nut - Torque in Two Stages ...................................................... first to 16.9 N·m (150 in. lb.)
finally to 33.9 N·m (300 in. lb.)
1
Head Bolt - Torque in Two Stages ................................................................ first to 22.6 N·m (200 in. lb.)
finally to 41.8 N·m (370 in. lb.)
Max. Out-of-Flatness .............................................................................................. 0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Rocker Arm Screw Torque .................................................................................... 11.3 N·m (100 in. lb.)
Fan/Flywheel
Fan Fastener Torque ............................................................................................... 9.9 N·m (88 in. lb.)
Flywheel Retaining Screw Torque ....................................................................... 66.4 N·m (49 ft. lb.)
Governor
Governor Cross Shaft-to-Crankcase Running Clearance
6 mm Shaft............................................................................................................. 0.013/0.075 mm (0.0005/0.0030 in.)
8 mm Shaft............................................................................................................. 0.025/0.126 mm (0.0009/0.0049 in.)
Governor Cross Shaft O.D.
6 mm Shaft
New .................................................................................................................. 5.975/6.012 mm (0.2352/0.2367 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 5.962 mm (0.2347 in.)
8 mm Shaft
New .................................................................................................................. 7.949/8.000 mm (0.3129/0.3149 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 7.936 mm (0.3124 in.)
Governor Gear Shaft-to-Governor Gear Running Clearance ......................... 0.015/0.140 mm (0.0006/0.0055 in.)
Governor Gear Shaft O.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 5.990/6.000 mm (0.2358/0.2362 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 5.977 mm (0.2353 in.)
Governor Lever Nut Torque ................................................................................. 6.8 N·m (60 in. lb.)
1.11
Page 14

Section 1
Safety and General Information
Ignition
Spark Plug Type (Champion®or Equivalent) ..................................................... RC12YC, XC12YC, or Platinum 3071
Spark Plug Gap ....................................................................................................... 0.76 mm (0.030 in.)
Spark Plug Torque .................................................................................................. 24.4-29.8 N·m (18-22 ft. lb.)
Ignition Module Air Gap ....................................................................................... 0.28/0.33 mm (0.011/0.013 in.)
Ignition Module Fastener Torque ......................................................................... 4.0-6.2 N·m (35-55 in. lb.)
Speed Sensor Air Gap (EFI engines) ..................................................................... 1.50 ± 0.25 mm (0.059 ± 0.010 in.)
Muffler
Muffler Retaining Nut Torque .............................................................................. 24.4 N·m (216 in. lb.)
Oil Filter
Oil Filter Torque ...................................................................................................... 3/4-1 turn after gasket contact
Oil Cooler
Oil Cooler/Adapter Nipple Torque ...................................................................... 27 N·m (20 ft. lb.)
Piston, Piston Rings, and Piston Pin
Piston-to-Piston Pin Running Clearance ............................................................ 0.006/0.017 mm (0.0002/0.0007 in.)
Piston Pin Bore I.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 17.006/17.012 mm (0.6695/0.6698 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 17.025 mm (0.6703 in.)
Piston Pin O.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 16.995/17.000 mm (0.6691/0.6693 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 16.994 mm (0.6691 in.)
Top Compression Ring-to-Groove Side Clearance
CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) ........................................................................... 0.040/0.080 mm (0.0016/0.0031 in.)
CH22/23 (674 cc) ............................................................................................. 0.030/0.076 mm (0.0012/0.0030 in.)
CH25, CH26, CH730-750 ............................................................................... 0.025/0.048 mm (0.0010/0.0019 in.)
Middle Compression Ring-to-Groove Side Clearance
CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) ........................................................................... 0.040/0.080 mm (0.0016/0.0031 in.)
CH22/23 (674 cc) ............................................................................................. 0.030/0.076 mm (0.0012/0.0030 in.)
CH25, CH26, CH730-750 ............................................................................... 0.015/0.037 mm (0.0006/0.0015 in.)
Oil Control Ring-to-Groove Side Clearance
CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) ........................................................................... 0.060/0.202 mm (0.0024/0.0080 in.)
CH22/23 (674 cc) ............................................................................................. 0.046/0.196 mm (0.0018/0.0077 in.)
CH25, CH26, CH730-750 ............................................................................... 0.026/0.176 mm (0.0010/0.0070 in.)
1.12
Page 15

Section 1
Safety and General Information
Piston, Piston Rings, and Piston Pin cont.
Top and Center Compression Ring End Gap
New Bore - CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) ...................................................... 0.25/0.45 mm (0.0098/0.0177 in.)
New Bore - CH22/23 (674 cc) ........................................................................ 0.18/0.46 mm (0.0071/0.0181 in.)
New Bore - CH25, CH26, CH730-745 .......................................................... 0.25/0.56 mm (0.0100/0.0224 in.)
Used Bore (Max.) - CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) .......................................... 0.77 mm (0.030 in.)
Used Bore (Max.) - CH22/23 (674 cc) ............................................................ 0.80 mm (0.0315 in.)
Used Bore (Max.) - CH25, CH26, CH730-750 .............................................. 0.94 mm (0.037 in.)
Piston Thrust Face O.D.²
New - CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) ............................................................... 76.967/76.985 mm (3.0302/3.0309 in.)
New - CH22/23 (674 cc) ................................................................................. 79.963/79.979 mm (3.1481/3.1488 in.)
New - CH25, CH26, CH730-750 ................................................................... 82.986 mm (3.2671 in.)
Max. Wear Limit - CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) .......................................... 76.840 mm (3.0252 in.)
Max. Wear Limit - CH22 (674 cc) ................................................................. 79.831 mm (3.1430 in.)
Max. Wear Limit - CH25, CH26, CH730-750 .............................................. 82.841 mm (3.2614 in.)
Piston Thrust Face-to-Cylinder Bore² Running Clearance
New - CH18, CH20, CH22 (624 cc) ............................................................... 0.014/0.057 mm (0.0005/0.0022 in.)
New - CH22/23 (674 cc) ................................................................................. 0.021/0.062 mm (0.0008/0.0024 in.)
New - CH25, CH26, CH730-750 ................................................................... 0.001/0.045 mm (0.039/0.0018 in.)
1
Speed Control Bracket
Fastener Torque ....................................................................................................... 10.7 N·m (95 in. lb.) into new holes
7.3 N·m (65 in. lb.) into used holes
Starter Assembly
Thru Bolt Torque
UTE/Johnson Electric, Eaton (Inertia Drive) ............................................... 4.5-5.7 N·m (40-50 in. lb.)
Nippondenso (Solenoid Shift) ...................................................................... 4.5-7.5 N·m (40-84 in. lb.)
Delco-Remy (Solenoid Shift) ......................................................................... 5.6-9.0 N·m (49-79 in. lb.)
Mounting Screw Torque (All) ............................................................................... 15.3 N·m (135 in. lb.)
Brush Holder Mounting Screw Torque
Delco-Remy Starter ........................................................................................ 2.5-3.3 N·m (22-29 in. lb.)
Solenoid (Starter)
Mounting Hardware Torque
Nippondenso Starter ..................................................................................... 6.0-9.0 N·m (53-79 in. lb.)
Delco-Remy Starter ........................................................................................ 4.0-6.0 N·m (35-53 in. lb.)
Nut, Positive (+) Brush Lead Torque
Nippondenso Starter ..................................................................................... 8.0-12.0 N·m (71-106 in. lb.)
Delco-Remy Starter ........................................................................................ 8.0-11.0 N·m (71-97 in. lb.)
Stator
Mounting Screw Torque ........................................................................................ 6.2 N·m (55 in. lb.)
²Measure 6 mm (0.236 in.) above the bottom of the piston skirt at right angles to the piston pin.
1.13
Page 16

Section 1
Safety and General Information
Valve Cover
Valve Cover Fastener Torque
Gasket Style Cover ................................................................................................. 3.4 N·m (30 in. lb.)
Black O-Ring Style Cover
w/Shoulder Screws ........................................................................................ 5.6 N·m (50 in. lb.)
w/Flange Screws and Spacers ...................................................................... 9.9 N·m (88 in. lb.)
Yellow or Brown O-Ring Style Cover w/Integral Metal Spacers .................... 6.2 N·m (55 in. lb.)
Valves and Valve Lifters
Hydraulic Valve Lifter to Crankcase Running Clearance ................................ 0.0241/0.0501 mm (0.0009/0.0020 in.)
Intake Valve Stem-to-Valve Guide Running Clearance ................................... 0.038/0.076 mm (0.0015/0.0030 in.)
Exhaust Valve Stem-to-Valve Guide Running Clearance ................................ 0.050/0.088 mm (0.0020/0.0035 in.)
Intake Valve Guide I.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 7.038/7.058 mm (0.2771/0.2779 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 7.134 mm (0.2809 in.)
Exhaust Valve Guide I.D.
New .................................................................................................................. 7.038/7.058 mm (0.2771/0.2779 in.)
Max. Wear Limit............................................................................................. 7.159 mm (0.2819 in.)
Valve Guide Reamer Size
Standard .......................................................................................................... 7.048 mm (0.2775 in.)
0.25 mm O.S. .................................................................................................... 7.298 mm (0.2873 in.)
Intake Valve Minimum Lift ................................................................................... 8.07 mm (0.3177 in.)
Exhaust Valve Minimum Lift ............................................................................... 8.07 mm (0.3177 in.)
Nominal Valve Seat Angle .................................................................................... 45°
1.14
Page 17
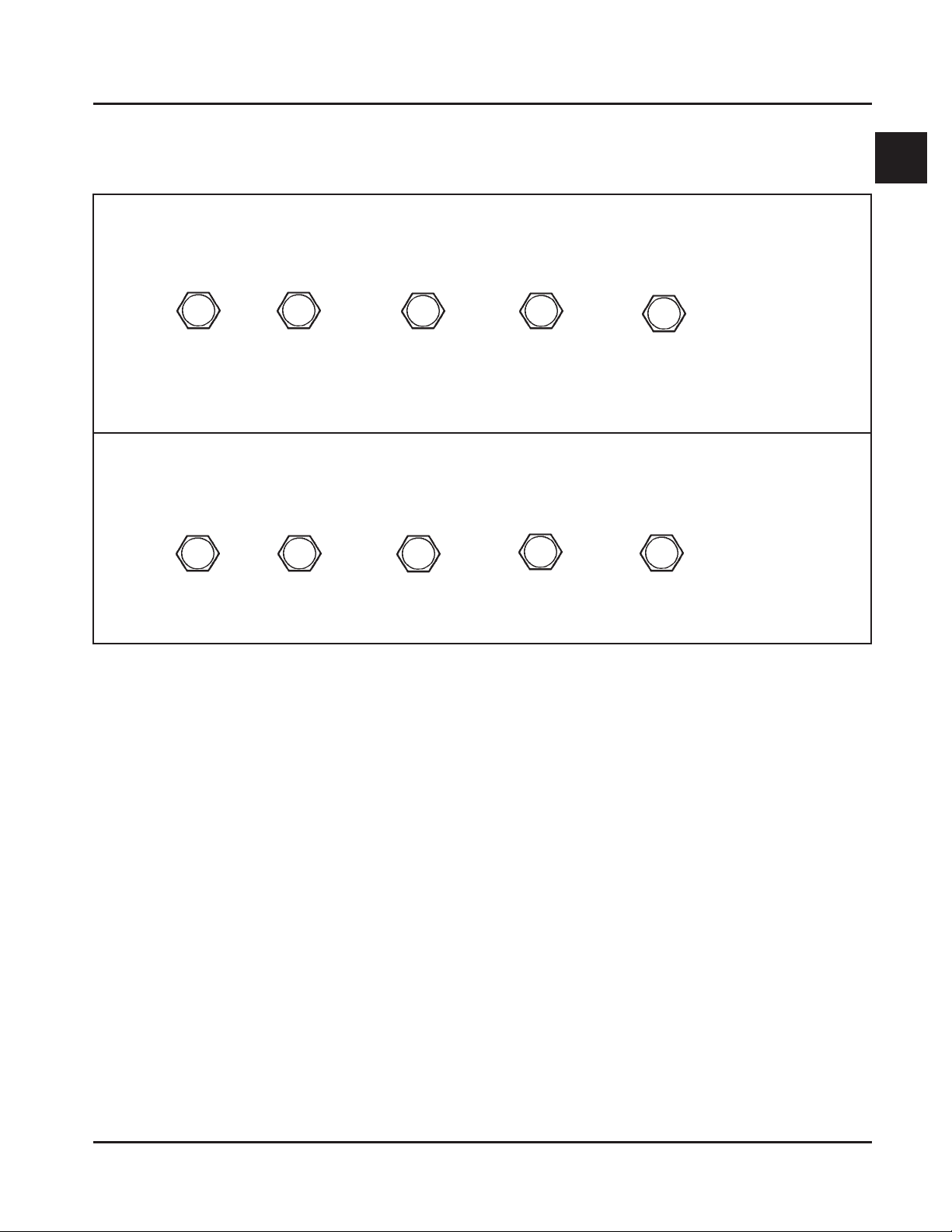
General Torque Values
Section 1
Safety and General Information
Metric Fastener T orque Recommendations for St andard Applications
Tightening Torque: N·m (in. lb.) + or - 10%
Property Class
4.8
Size
M4 1.2 (11) 1.7 (15) 2.9 (26) 4.1 (36) 5.0 (44) 2.0 (18)
M5 2.5 (22) 3.2 (28) 5.8 (51) 8.1 (72) 9.7 (86) 4.0 (35)
M6 4.3 (38) 5.7 (50) 9.9 (88) 14.0 (124) 16.5 (146) 6.8 (60)
M8 10.5 (93) 13.6 (120) 24.4 (216) 33.9 (300) 40.7 (360) 17.0 (150)
5.8
8.8 10.9 12.9
Noncritical
Fasteners
Into Aluminum
Tightening Torque: N·m (ft. lb.) + or - 10%
Property Class
4.8
M10 21.7 (16) 27.1 (20) 47.5 (35) 66.4 (49) 81.4 (60) 33.9 (25)
M12 36.6 (27) 47.5 (35) 82.7 (61) 116.6 (86) 139.7 (103) 61.0 (45)
M14 58.3 (43) 76.4 (55) 131.5 (97) 184.4 (136) 219.7 (162) 94.9 (70)
5.8
8.8
10.9
12.9
Noncritical
Fasteners
Into Aluminum
1
1.15
Page 18
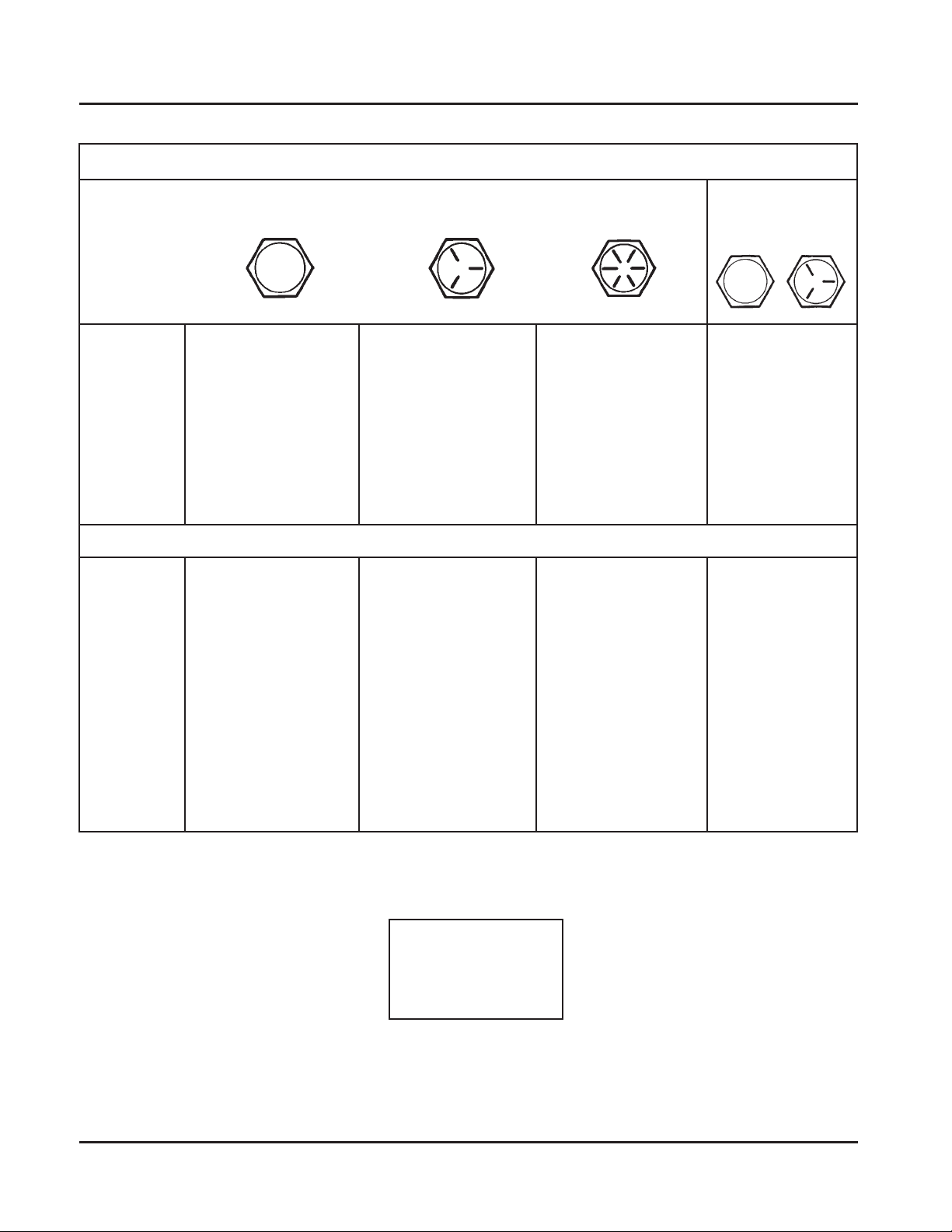
Section 1
Safety and General Information
English Fastener T orque Recommendations for St andard Applications
Tightening Torque: N·m (in. lb.) + or - 20%
Bolts, Screws, Nuts and Fasteners
Assembled Into Cast Iron or Steel
Grade 2 Grade 5 Grade 8
Size
8-32 2.3 (20) 2.8 (25) --------- 2.3 (20)
10-24 3.6 (32) 4.5 (40) --------- 3.6 (32)
10-32 3.6 (32) 4.5 (40) --------- ---------
1/4-20 7.9 (70) 13.0 (115) 18.7 (165) 7.9 (70)
1/4-28 9.6 (85) 15.8 (140) 22.6 (200) ---------
5/16-18 17.0 (150) 28.3 (250) 39.6 (350) 17.0 (150)
5/16-24 18.7 (165) 30.5 (270) --------- ---------
3/8-16 29.4 (260) --------- --------- ---------
3/8-24 33.9 (300) --------- --------- ---------
Grade 2 or 5
Fasteners Into
Aluminum
Tightening Torque: N·m (ft. lb.) + or - 20%
Size
5/16-24 --------- ---------- 40.7 (30) --------3/8-16 --------- 47.5 (35) 67.8 (50) --------3/8-24 --------- 54.2 (40) 81.4 (60) --------7/16-14 47.5 (35) 74.6 (55) 108.5 (80) --------7/16-20 61.0 (45) 101.7 (75) 142.4 (105) --------1/2-13 67.8 (50) 108.5 (80) 155.9 (115) --------1/2-20 94.9 (70) 142.4 (105) 223.7 (165) --------9/16-12 101.7 (75) 169.5 (125) 237.3 (175) --------9/16-18 135.6 (100) 223.7 (165) 311.9 (230) --------5/8-11 149.2 (110) 244.1 (180) 352.6 (260) --------5/8-18 189.8 (140) 311.9 (230) 447.5 (330) --------3/4-10 199.3 (150) 332.2 (245) 474.6 (350) --------3/4-16 271.2 (200) 440.7 (325) 637.3 (470) ---------
Torque
Conversions
N·m = in. lb. x 0.113
N·m = ft. lb. x 1.356
in. lb. = N·m x 8.85
ft. lb. = N·m x 0.737
1.16
Page 19
Section 2
Section 2
Tools & Aids
Tools & Aids
Certain quality tools are designed to help you perform specific disassembly, repair, and reassembly procedures.
By using tools designed for the job, you can properly service engines easier, faster, and safer! In addition, you’ll
increase your service capabilities and customer satisfaction by decreasing engine downtime.
Here is the list of tools and their source.
Separate Tool Suppliers:
Kohler Tools
Contact your source
of supply.
slooT
noitpircseD .oNtraP/ecruoS
SE Tools
415 Howard St.
Lapeer, MI 48446
Phone 810-664-2981
Toll Free 800-664-2981
Fax 810-664-8181
)seireSM&K(looTgnimiTraeGecnalaB
.enignegnilbmessanehwnoitisopdemitnisraegecnalabdlohoT
Design Technology Inc.
768 Burr Oak Drive
Westmont, IL 60559
Phone 630-920-1300
S-6055452relhoK
)753-YylremroF(
2
IFEtiKecivreS
etalPyalpdnEtfahsmaC
.yalpdnetfahsmacgnikcehcroF
retseTnwodkaeLrednilyC
.nrowerasevlavro,sgnir,notsip,rednilycfidnanoitneternoitsubmocgnikcehcroF
erawtfoScitsongaiD)IFE(noitcejnIleuFcinortcelE
.CPpotkseDropotpaLhtiwesU
.enigneIFEnapugnittesdnagnitoohselbuortroF
elbaliavAstnenopmoClaudividnI
retseTerusserP
thgiLdioN
retpadA°09
sreilPpmalCrekiteO
eriWdeR,gulPedoC
eriWeulB,gulPedoC
)seireSSC(looTgnidloHleehwylF 70428-RLKslooTES
relluPleehwylF
.enignemorfleehwylfevomeroT
50428-RLKslooTES
S-5016752relhoK
S-3216752relhoK
S-1016742relhoK
.cnIygolonhceTngiseD
910-ITD
120-ITD
320-ITD
520-ITD
720-ITD
920-ITD
80428-RLKslooTES
2.1
Page 20
Section 2
Tools & Aids
).tnoc(slooT
noitpircseD .oNtraP/ecruoS
hcnerWpartSleehwylF
.lavomergnirudleehwylfdlohoT
looTretfiLevlaVciluardyH
.sretfilciluardyhllatsnidnaevomeroT
retseTmetsySnoitingI
.DCtpecxe,smetsysllanotuptuognitsetroF
.metsysnoitingi)DC(egrahcsideviticapacnotuptuognitsetroF
)seireSM&K(hcnerWtesffO
.stungniniaterlerrabrednilycllatsnierdnaevomeroT
tiKtseTerusserPliO
.erusserplioyfirevdnatsetoT
)tnerructlov021(retseTrotalugeR-reifitceR
)tnerructlov042(retseTrotalugeR-reifitceR
.srotaluger-reifitcertsetotdesU
elbaliavAstnenopmoClaudividnI
ssenraHtseTrotalugeRORP-SC
edoiDhtiwssenraHtseTrotalugeRlaicepS
retseT)MAS(eludoMecnavdAkrapS
KRAPS-TRAMShtiwsenigneno)MASDdnaMASA(MASehttsetoT
.™
)tfihSdioneloS(looTgnidloHhsurBretratS
.gnicivresgnirudsehsurbdlohoT
90428-RLKslooTES
S-8316752relhoK
S-1055452relhoK
S-2055442relhoK
01428-RLKslooTES
S-6016752relhoK
S-0216752relhoK
S-1416752relhoK
.cnIygolonhceTngiseD
130-ITD
330-ITD
S-0416752relhoK
61428-RLKslooTES
)evirDaitrenI(looTgniRgniniateRretratS
.)sretratsOCSAFgnidulcxe(sgnirgniniaterevirdllatsnierdnaevomeroT
)sretratSllA(tiKgnicivreSretratS
.sehsurbdnasgnirgniniaterevirdllatsnierdnaevomeroT
elbaliavAtnenopmoClaudividnI
)tfihSdioneloS(looTgnidloHhsurBretratS
)evitcudnIlatigiD(retemohcaT
.enignenafo)MPR(deepsgnitarepognikcehcroF
retseTerusserP/muucaV
.retemonamretawaotevitanretlA
)seireSM&K(remaeRediuGevlaV
.noitallatsniretfasediugevlavgnizisroF
)CHO,dnammoC,sigeA,egaruoC(tiKecivreSediuGevlaV
.sediugeulavnrowgnicivresroF
S-8116752relhoK
11428-RLKslooTES
61428-RLKslooTES
.cnIygolonhceTngiseD
011-ITD
S-2216752relhoK
31428-RLKslooTES
51428-RLKslooTES
2.2
Page 21

sdiA
noitpircseD .oNtraP/ecruoS
tnacirbuLtfahsmaC )316ZZrapslaV( S-4175352relhoK
esaerGcirtceleiD )166GdraugavoN/EG( S-1175352relhoK
esaerGcirtceleiD )orP-leF( leS-irbuL
tnacirbuLevirDretratScirtcelE )evirDaitrenI( S-1075325relhoK
tnacirbuLevirDretratScirtcelE )tfihSdioneloS(S-2075325relhoK
Section 2
Tools & Aids
2
®
etitcoL
.resnepsidlosoreazo4niydoByvaeH0095
tnalaeSenociliSVTR
S-7079552relhoK
.esurofdevorppaera,detsilesohtsahcus,stnalaesVTRtnatsiserlio,desab-emixoylnO
®
etitcoL
®
etitcoL
0195
®
etitcoL
®
etitcoL
®
etitcoL
895kcalBartlU
785eulBartlU
reppoCartlU
.scitsiretcarahcgnilaestsebrofdednemmocerera0195ro0095.soN
tnacirbuLevirDenilpS S-2175352relhoK
2.3
Page 22
Section 2
Tools & Aids
Special Tools You Can Make
Flywheel Holding Tool
A flywheel holding tool can be made out of an old
junk flywheel ring gear as shown in Figure 2-1, and
used in place of a strap wrench.
1. Using an abrasive cut-off wheel, cut out a six
tooth segment of the ring gear as shown.
2. Grind off any burrs or sharp edges.
3. Invert the segment and place it between the
ignition bosses on the crankcase so that the tool
teeth engage the flywheel ring gear teeth. The
bosses will lock the tool and flywheel in
position for loosening, tightening or removing
with a puller.
2. Remove the studs of a Posi-Lock rod or grind off
the aligning steps of a Command rod, so the joint
surface is flat.
3. Find a 1 in. long capscrew with the correct
thread size to match the threads in the
connecting rod.
4. Use a flat washer with the correct I.D. to slip on
the capscrew and approximately 1” O.D. (Kohler
Part No. 12 468 05-S). Assemble the capscrew
and washer to the joint surface of the rod, as
shown in Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-1. Flywheel Holding Tool.
Rocker Arm/Crankshaft Tool
A spanner wrench to lift the rocker arms or turn the
crankshaft may be made out of an old junk connecting
rod.
1. Find a used connecting rod from a 10 HP or
larger engine. Remove and discard the rod cap.
Figure 2-2. Rocker Arm/Crankshaf t T ool.
2.4
Page 23

Section 3
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Guide
When troubles occur, be sure to check the simple
causes which, at first, may seem too obvious to be
considered. For example, a starting problem could be
caused by an empty fuel tank.
Some general common causes of engine troubles are
listed below. Use these to locate the causing factors.
Refer to the specific section(s) within this service
manual for more detailed information.
Engine Cranks But Will Not Start
1. Empty fuel tank.
2. Fuel shut-off valve closed.
3. Poor fuel, dirt or water in the fuel system.
4. Clogged fuel line.
5. Spark plug lead(s) disconnected.
6. Key switch or kill switch in “off” position.
7. Faulty spark plugs.
8. Faulty ignition module(s).
9. SMART-SPARK
10. Carburetor solenoid malfunction.
11. Diode in wiring harness failed in open circuit
mode.
12. Vacuum fuel pump malfunction, or oil in vacuum
hose.
13. Vacuum hose to fuel pump leaking/cracked.
14. Battery connected backwards.
15. Safety interlock system engaged.
Engine Starts But Does Not Keep Running
1. Restricted fuel tank cap vent.
2. Poor fuel, dirt or water in the fuel system.
3. Faulty or misadjusted choke or throttle controls.
4. Loose wires or connections that short the kill
terminal of ignition module to ground.
5. Faulty cylinder head gasket.
6. Faulty carburetor.
7. Vacuum fuel pump malfunction, or oil in vacuum
hose.
8. Leaking/cracked vacuum hose to fuel pump.
9. Intake system leak.
malfunction (applicable models).
™
Section 3
Troubleshooting
10. Diode in wiring harness failed in open circuit
mode.
Engine Starts Hard
1. PTO drive is engaged.
2. Dirt or water in the fuel system.
3. Clogged fuel line.
4. Loose or faulty wires or connections.
5. Faulty or misadjusted choke or throttle controls.
6. Faulty spark plugs.
7. Low compression.
8. Weak spark.
9. Fuel pump malfunction causing lack of fuel.
10. Engine overheated-cooling/air circulation
restricted.
11. Quality of fuel.
12. Flywheel key sheared.
13. Intake system leak.
Engine Will Not Crank
1. PTO drive is engaged.
2. Battery is discharged.
3. Safety interlock switch is engaged.
4. Loose or faulty wires or connections.
5. Faulty key switch or ignition switch.
6. Faulty electric starter or solenoid.
7. Seized internal engine components.
Engine Runs But Misses
1. Dirt or water in the fuel system.
2. Spark plug lead disconnected.
3. Poor quality of fuel.
4. Faulty spark plug(s).
5. Loose wires or connections that intermittently
ground the ignition kill circuit.
6. Engine overheated.
7. Faulty ignition module or incorrect air gap.
8. Carburetor adjusted incorrectly.
9. SMART-SPARK
models).
malfunction (applicable
™
3
3.1
Page 24

Section 3
Troubleshooting
Engine Will Not Idle
1. Dirt or water in the fuel system.
2. Stale fuel and/or gum in carburetor.
3. Faulty spark plugs.
4. Fuel supply inadequate.
5. Idle speed adjusting screw improperly set.
6. Idle fuel adjusting needle improperly set (some
models).
7. Low compression.
8. Restricted fuel tank cap vent.
9. Engine overheated-cooling system/air circulation
problem.
Engine Overheats
1. Air intake/grass screen, cooling fins, or cooling
shrouds clogged.
2. Excessive engine load.
3. Low crankcase oil level.
4. High crankcase oil level.
5. Faulty carburetor.
6. Lean fuel mixture.
7. SMART-SPARK™ malfunction (applicable
models).
Engine Knocks
1. Excessive engine load.
2. Low crankcase oil level.
3. Old or improper fuel.
4. Internal wear or damage.
5. Hydraulic lifter malfunction.
6. Quality of fuel.
7. Incorrect grade of oil.
Engine Loses Power
1. Low crankcase oil level.
2. High crankcase oil level.
3. Dirty air cleaner element.
4. Dirt or water in the fuel system.
5. Excessive engine load.
6. Engine overheated.
7. Faulty spark plugs.
8. Low compression.
9. Exhaust restriction.
10. SMART-SPARK
models).
11. Low battery.
12. Incorrect governor setting.
malfunction (applicable
™
Engine Uses Excessive Amount of Oil
1. Incorrect oil viscosity/type.
2. Clogged or improperly assembled breather.
3. Breather reed broken.
4. Worn or broken piston rings.
5. Worn cylinder bore.
6. Worn valve stems/valve guides.
7. Crankcase overfilled.
8. Blown head gasket/overheated.
Oil Leaks from Oil Seals, Gaskets
1. Crankcase breather is clogged or inoperative.
2. Breather reed broken.
3. Loose or improperly torqued fasteners.
4. Piston blowby or leaky valves.
5. Restricted exhaust.
External Engine Inspection
Before cleaning or disassembling the engine, make a
thorough inspection of its external appearance and
condition. This inspection can give clues to what
might be found inside the engine (and the cause)
when it is disassembled.
• Check for buildup of dirt and debris on the
crankcase, cooling fins, grass screen, and other
external surfaces. Dirt or debris on these areas
are causes of higher operating temperatures and
overheating.
• Check for obvious fuel and oil leaks, and
damaged components. Excessive oil leakage can
indicate a clogged or improperly-assembled
breather, worn/damaged seals and gaskets, or
loose or improperly-torqued fasteners.
• Check the air cleaner cover and base for damage
or indications of improper fit and seal.
• Check the air cleaner element. Look for holes,
tears, cracked or damaged sealing surfaces, or
other damage that could allow unfiltered air into
the engine. Also note if the element is dirty or
clogged. These could indicate that the engine has
been under serviced.
• Check the carburetor throat for dirt. Dirt in the
throat is further indication that the air cleaner is
not functioning properly.
3.2
• Check the oil level. Note if the oil level is within
the operating range on the dipstick, or if it is low
or overfilled.
Page 25

Section 3
Troubleshooting
• Check the condition of the oil. Drain the oil into a
container - the oil should flow freely. Check for
metal chips and other foreign particles.
Sludge is a natural by-product of combustion; a
small accumulation is normal. Excessive sludge
formation could indicate overrich carburetion,
weak ignition, overextended oil change interval
or wrong weight or type of oil was used, to name
a few.
NOTE: It is good practice to drain oil at a
location away from the workbench. Be
sure to allow ample time for complete
drainage.
Cleaning the Engine
After inspecting the external condition of the engine,
clean the engine thoroughly before disassembling it.
Also clean individual components as the engine is
disassembled. Only clean parts can be accurately
inspected and gauged for wear or damage. There are
many commercially available cleaners that will
quickly remove grease, oil, and grime from engine
parts. When such a cleaner is used, follow the
manufacturer’s instructions and safety precautions carefully.
Make sure all traces of the cleaner are removed before
the engine is reassembled and placed into operation.
Even small amounts of these cleaners can quickly
break down the lubricating properties of engine oil.
Basic Engine Tests
Crankcase Vacuum Test
A partial vacuum should be present in the crankcase
when the engine is operating. Pressure in the
crankcase (normally caused by a clogged or
improperly assembled breather) can cause oil to be
forced out at oil seals, gaskets, or other available
spots.
To test the crankcase vacuum with the manometer:
1. Insert the stopper/hose into the oil fill hole. Leave
the other tube of manometer open to
atmosphere. Make sure the shut off clamp is
closed.
2. Start the engine and run at no-load high speed
(3200 to 3750 RPM).
3. Open the clamp and note the water level in the
tube.
The level in the engine side should be a
minimum of 10.2 cm (4 in.) above the level in the
open side.
If the level in the engine side is less than specified
(low/no vacuum), or the level in the engine side
is lower than the level in the open side
(pressure), check for the conditions in the table
on page 3.4.
4. Close the shut off clamp before stopping the
engine.
To test the crankcase vacuum with the Vacuum/
Pressure Gauge Kit (see Section 2):
1. Remove the dipstick or oil fill plug/cap.
2. Install the adapter into the oil fill/dipstick tube
opening, upside down over the end of a small
diameter dipstick tube, or directly into engine if
a tube is not used.
3. Push the barbed fitting on the gauge solidly into
the hole in the adapter.
4. Start the engine and bring it up to operating
speed (3200-3600 RPM).
3
Crankcase vacuum is best measured with either a
water manometer or a vacuum gauge (see Section 2).
Complete instructions are provided in the kits.
5. Check the reading on the gauge. If the reading is
to the left of “0” on the gauge, vacuum or
negative pressure is indicated. If the reading is to
the right of “0” on the gauge, positive pressure is
present.
Crankcase vacuum should be 4-10 (inches of
water) If the reading is below specification, or if
pressure is present, check the following table for
possible causes and remedies.
3.3
Page 26

Section 3
Troubleshooting
No Crankcase Vacuum/Pressure in Crankcase
Possible Cause
1. Crankcase breather clogged or inoperative.
2. Seals and/or gaskets leaking. Loose or
improperly torqued fasteners.
3. Piston blowby or leaky valves (confirm by
inspecting components).
4. Restricted exhaust.
Compression T est
Some of these engines are equipped with an automatic
compression release (ACR) mechanism. Because of the
ACR mechanism, it is difficult to obtain an accurate
compression reading. As an alternative, perform a
cylinder leakdown test.
Cylinder Leakdown T est
A cylinder leakdown test can be a valuable
alternative to a compression test. By pressurizing the
combustion chamber from an external air source you
can determine if the valves or rings are leaking, and
how badly.
Cylinder Leakdown Tester (see Section 2) is a
relatively simple, inexpensive leakdown tester for
small engines. The tester includes a quick disconnect
for attaching the adapter hose, and a holding tool.
Leakdown T est Instructions
1. Run engine for 3-5 minutes to warm it up.
2. Remove spark plug(s) and air filter from engine.
3. Rotate the crankshaft until the piston (of cylinder
being tested) is at top dead center of the
compression stroke. Hold the engine in this
position while testing. The holding tool supplied
with the tester can be used if the PTO end of the
crankshaft is accessible. Lock the holding tool
onto the crankshaft. Install a 3/8" breaker bar
into the hole/slot of the holding tool, so it is
perpendicular to both the holding tool and
crankshaft PTO.
Solution
1. Disassemble breather, clean parts thoroughly,
check sealing surfaces for flatness, reassemble,
and recheck pressure.
2. Replace all worn or damaged seals and gaskets.
Make sure all fasteners are tightened securely.
Use appropriate torque values and sequences
when necessary.
3. Recondition piston, rings, cylinder bore, valves,
and valve guides.
4. Repair/replace restricted muffler/exhaust
system.
If the flywheel end is more accessible, use a
breaker bar and socket on the flywheel nut/
screw to hold it in position. An assistant may be
needed to hold the breaker bar during testing. If
the engine is mounted in a piece of equipment, it
may be possible to hold it by clamping or
wedging a driven component. Just be certain that
the engine cannot rotate off of TDC in either
direction.
4. Install the adapter into the spark plug hole, but
do not attach it to the tester at this time.
5. Connect an air source of at least 50 psi to the
tester.
6. Turn the regulator knob in the increase
(clockwise) direction until the gauge needle is in
the yellow “set” area at the low end of the scale.
7. Connect the tester quick-disconnect to the
adapter hose while firmly holding the engine at
TDC. Note the gauge reading and listen for
escaping air at the carburetor intake, exhaust
outlet, and crankcase breather.
8. Check your test results against the following
table:
3.4
Page 27

Section 3
Troubleshooting
Leakdown Test Results
Air escaping from crankcase breather ........................................................ Defective rings or worn cylinder.
Air escaping from exhaust system .............................................................. Defective exhaust valve/improper seating.
Air escaping from carburetor....................................................................... Defective intake valve/improper seating.
Gauge reading in “low” (green) zone .......................................................... Piston rings and cylinder in good
condition.
Gauge reading in “moderate” (yellow) zone .............................................. Engine is still usable, but there is some
wear present. Customer should start
planning for overhaul or replacement.
Gauge reading in “high” (red) zone ............................................................. Rings and/or cylinder have considerable
wear. Engine should be reconditioned or
replaced.
3
3.5
Page 28

Air Cleaner and Air Intake System
Air Cleaners
Section 4
General
Most engines are equipped with a replaceable, highdensity paper air cleaner element, surrounded by an
oiled foam precleaner, and housed under a flat outer
cover. This is typically referred to as the standard air
cleaner assembly. See Figures 4-1 and 4-4. Some
engines utilize a heavy-duty style air cleaner as shown
in Figure 4-12.
Figure 4-1. Standard Air Cleaner.
4
Figure 4-2. Removing Latch Style Cover.
Cover
Air Cleaner Element
Precleaner
Standard Air Cleaner
Service
Check the air cleaner daily or before starting the
engine. Check for and correct any buildup of dirt and
debris, along with loose or damaged components.
NOTE: Operating the engine with loose or damaged
air cleaner components could allow
unfiltered air into the engine, causing
premature wear and failure.
Figure 4-3. Removing Knob Style Cover .
Precleaner Service
If so equipped, wash and reoil the precleaner every 25
hours of operation (more often under extremely dusty
or dirty conditions).
To service the precleaner, perform the following steps:
1. Unhook the latches or loosen the retaining knob,
and remove the cover.
2. Remove the foam precleaner from the paper air
cleaner element.
4.1
Page 29

Section 4
Air Cleaner and Air Intake System
3. Wash the precleaner in warm water with
detergent. Rinse the precleaner thoroughly until
all traces of detergent are eliminated. Squeeze out
excess water (do not wring). Allow the precleaner
to air dry.
4. Saturate the precleaner with new engine oil.
Squeeze out all excess oil.
5. Reinstall the precleaner over the paper air cleaner
element.
6. Reinstall the air cleaner cover. Secure the cover
with the two latches or the retaining knob.
Element Cover
Element
Figure 4-4. Air Cleaner Components.
Wing Nut
Precleaner
Seal
Figure 4-6. Removing Elements.
Figure 4-7. Removing Rubber Seal from Bracket.
Paper Element Service (Standard Type)
Every 100 hours of operation (more often under
extremely dusty or dirty conditions), replace the paper
element. Follow these steps:
Figure 4-5. Removing Element Cover Wing Nut.
4.2
1. Unhook the latches or loosen the retaining knob,
and remove the cover.
2. Remove the wing nut, element cover, and paper
element with precleaner (if so equipped).
3. Remove the precleaner (if so equipped) from the
paper element. Service the precleaner as
described in "Precleaner Service".
4. Do not wash the paper element or use
pressurized air, as this will damage the element.
Replace a dirty, bent, or damaged element with a
genuine Kohler element. Handle new elements
carefully; do not use if the sealing surfaces are
bent or damaged.
Page 30
Section 4
Air Cleaner and Air Intake System
5. Check the seal for any damage or deterioration.
Replace as necessary. See Figure 4-7.
6. Reinstall the seal, paper element, precleaner,
element cover, and wing nut.
7. Reinstall the air cleaner cover and secure with the
latches or the retaining knob.
NOTE: Make sure the correct depth air cleaner
element and rubber seal are used for the
engine spec involved. Some engines use
a deeper or extra capacity air cleaner and
a longer rubber seal.
4
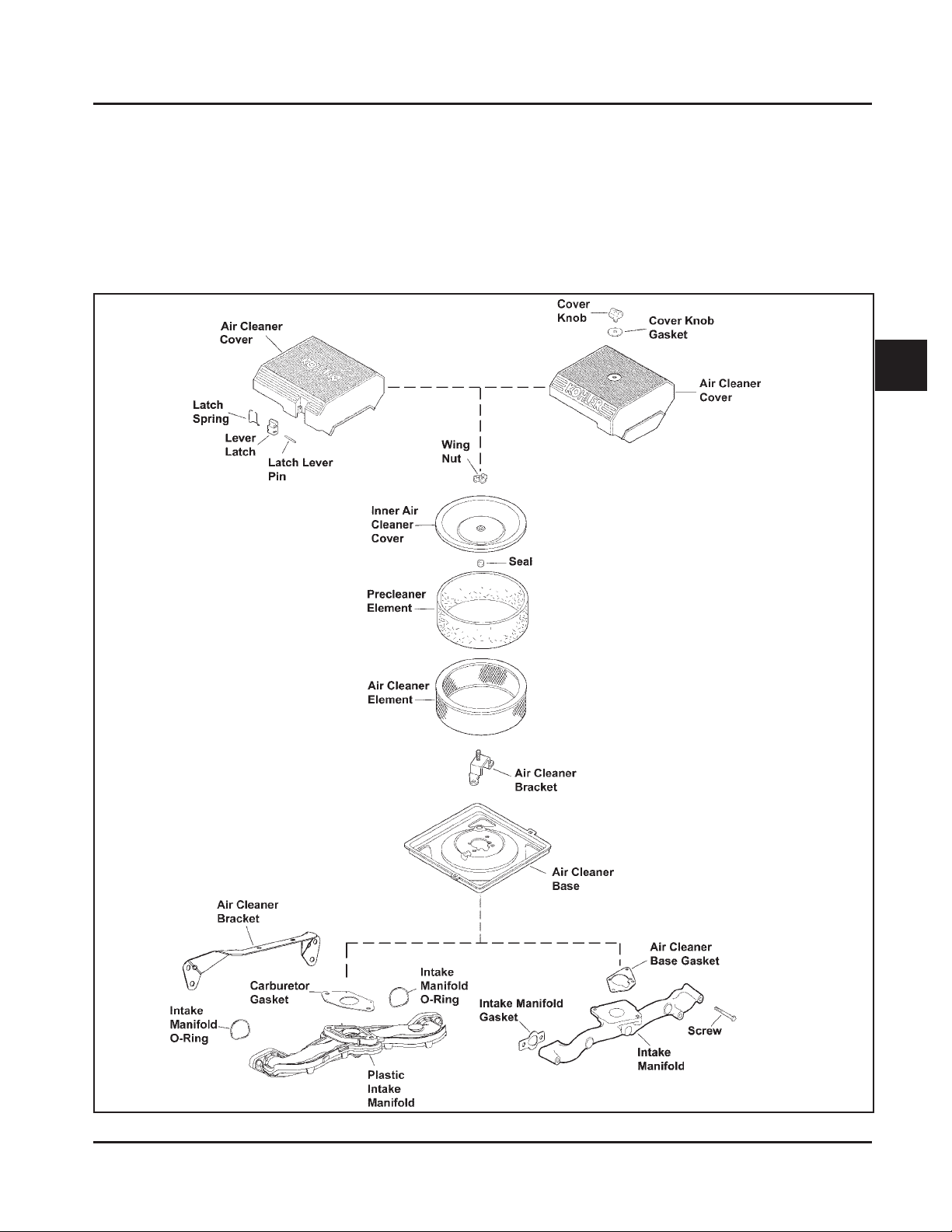
Figure 4-8. Exploded View of St andard Air Int ake System Component s.
4.3
Page 31

Section 4
Air Cleaner and Air Intake System
Figure 4-9. Bracket Retaining Screw.
Air Cleaner Element Cover and Seal - Make sure
element cover is not bent or damaged. Make sure the
wing nut and seal are in place to ensure the element is
sealed against leakage.
Air Cleaner Base - Make sure the base is secured
tightly to the carburetor and not cracked or damaged.
Breather Tube - Make sure the tube is attached to both
the air cleaner base and the breather cover.
NOTE: Damaged, worn or loose air cleaner
components can allow unfiltered air into the
engine causing premature wear and failure.
Tighten or replace all loose or damaged
components.
Rear Mounting
Screws
Figure 4-10. Rear Mounting Screws (Used with
Plastic Intake Manifold).
Complete Disassembly and Reassembly Standard Type
If the base plate on the standard type has to be
removed, proceed as follows:
1. Remove air cleaner components as described
earlier.
2. Remove the hex flange screws securing the
bracket and base. See Figures 4-9 and 4-10.
Remove the bracket.
3. Pinch the sealing collar on the breather hose and
push it down through the hole in the air cleaner
base. Carefully feed the upper section of the
breather tube down through the base. See Figure
4-11.
4. Remove the base and gasket.
5. Reverse the procedure to reinstall new or serviced
components. Torque screws to 9.9 N·m (88 in. lb.).
Heavy-Duty Air Cleaner
Figure 4-11. Breather Tube.
Air Cleaner Components
Whenever the air cleaner cover is removed, or the
paper element or precleaner are serviced, check the
following:
4.4
General
The heavy-duty air cleaner consists of a cylindrical
housing, typically mounted to a bracket off the upper
valve cover screws, and connected with a formed
rubber hose to an adapter on the carburetor or throttle
body/intake manifold (EFI units). The air cleaner
housing contains a paper element and inner element,
designed for longer service intervals. The system is
CARB/EPA certified and the components should not be
altered or modified in any way.
Page 32

Figure 4-12. Heavy-Duty Air Cleaner .
To Service
Every 250 hours of operation (more often under
extremely dusty or dirty conditions), replace the
paper element and check the inner element. Follow
these steps.
1. Unhook the two retaining clips and remove the
end cap from the air cleaner housing.
Section 4
Air Cleaner and Air Intake System
4. Do not wash the paper element and inner
element or use compressed air, this will damage
the elements. Replace dirty, bent or damaged
elements with new genuine Kohler elements as
required. Handle the new elements carefully; do
not use if the sealing surfaces are bent or
damaged.
5. Check all parts for wear, cracks, or damage.
Replace any damaged components.
6. Install the new inner element, followed by the
outer element. Slide each fully into place in the
air cleaner housing.
7. Reinstall the end cap so the dust ejector valve is
down, and secure with the two retaining clips.
See Figure 4-12.
Removal
1. Remove the upper valve cover screws on each
side, securing the main bracket, and loosen the
hose clamp on the adapter inlet, or remove the
adapter mounting screws.
4
2. Pull the air cleaner element out of the housing.
See Figure 4-13.
Inner
Element
Figure 4-13. Removing Elements.
3. After the element is removed, check the condition
of the inner element. It should be replaced
whenever it appears dirty, typically every other
time the main element is replaced. Clean the area
around the base of the inner element before
removing it, so dirt does not get into the engine.
Element
2. Lift the entire air cleaner assembly off the engine.
Disassemble or service as required.
Installation
1. Install the main mounting bracket with the center
section up and the cutout around the carburetor,
aligning the mounting holes with the four upper
valve cover holes.
2. Install and torque the four valve cover mounting
screws to specified torque value.
3. Reconnect the hose to the adapter and tighten the
clamp, or install a new adapter gasket (if the
adapter was separated from the carburetor), and
torque the mounting fasteners to 7.3 N·m
(65 in. lb.).
NOTE: Adapter configurations may vary
depending on engine and application
involved. Two adapters are shown in
Figure 4-14.
4.5
Page 33

Section 4
Air Cleaner and Air Intake System
Figure 4-14. Adapters for Heavy-Duty Air Cleaners.
Air Intake/Cooling System
To ensure proper cooling, make sure the grass screen,
cooling fan fins, and external surfaces of the engine
are kept clean at all times.
Every 100 hours of operation (more often under
extremely dusty or dirty conditions), remove the
blower housing and other cooling shrouds. *Clean the
cooling fins and external surfaces as necessary. Make
sure the cooling shrouds are reinstalled.
*Cleanout kits, Kohler Part No. 25 755 20-S (black) or
25 755 21-S (gold), are recommended to aid
inspection and cleanout of the cooling fins. See
Figure 4-15.
NOTE: Operating the engine with a blocked grass
screen, dirty or plugged cooling fins, and/or
cooling shrouds removed, will cause engine
damage due to overheating.
Figure 4-15. Cleanout Kit Installed on Blower
Housing.
4.6
Page 34

Fuel System and Governor
Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Section 5
Description
The Command horizontal twins use three different
types of fuel systems; carbureted, electronic fuel
injection (EFI), or gaseous. Gaseous fuel systems can
be either liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or LP) or
natural gas (NG). Some dual-fuel engines have a
combination system, which allows the operator to
select either gasoline or LP.
This section covers the standard carbureted fuel
systems. The gaseous systems are covered in
subsection 5A and the EFI systems are covered in
subsection 5B. The governor systems used are covered
at the end of this section.
WARNING: Explosive Fuel!
Gasoline is extremely flammable and its vapors can explode
if ignited. Store gasoline only in approved containers, in
well ventilated, unoccupied buildings, away from sparks or
flames. Do not fill the fuel tank while the engine is hot or
running, since spilled fuel could ignite if it comes in contact
with hot parts or sparks from ignition. Do not start the
engine near spilled fuel. Never use gasoline as a cleaning
agent.
Fuel System Components
The typical carbureted fuel system and related
components include the following:
Fuel then enters the carburetor float bowl and is
drawn into the carburetor body. There, the fuel is
mixed with air. This fuel-air mixture is then burned in
the engine combustion chamber.
Fuel Recommendations
5
General Recommendations
Purchase gasoline in small quantities and store in
clean, approved containers. A container with a
capacity of 2 gallons or less with a pouring spout is
recommended. Such a container is easier to handle
and helps eliminate spillage during refueling.
• Do not use gasoline left over from the previous
season, to minimize gum deposits in your fuel
system and to ensure easy starting.
• Do not add oil to the gasoline.
• Do not overfill the fuel tank. Leave room for the
fuel to expand.
Fuel T y pe
For best results, use only clean, fresh, unleaded
gasoline with a pump sticker octane rating of 87 or
higher. In countries using the Research fuel rating
method, it should be 90 octane minimum.
• Fuel Tank
• Fuel Lines
• In-line Fuel Filter
• Fuel Pump
• Carburetor
Operation
The fuel from the tank is moved through the in-line
filter and fuel lines by the fuel pump. On engines not
equipped with a fuel pump, the fuel tank outlet is
located above the carburetor inlet allowing gravity to
feed fuel to the carburetor.
Unleaded gasoline is recommended as it leaves less
combustion chamber deposits and reduces harmful
exhaust emissions. Leaded gasoline is not
recommended and must not be used on EFI engines,
or on other models where exhaust emissions are
regulated.
Gasoline/Alcohol blends
Gasohol (up to 10% ethyl alcohol, 90% unleaded
gasoline by volume) is approved as a fuel for Kohler
engines. Other gasoline/alcohol blends are not
approved.
5.1
Page 35

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Gasoline/Ether blends
Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE) and unleaded
gasoline blends (up to a maximum of 15% MTBE by
volume) are approved as a fuel for Kohler engines.
Other gasoline/ether blends are not approved.
Fuel Filter
Most engines are equipped with an in-line fuel filter.
Periodically inspect the filter and replace with a
genuine Kohler filter every 200 operating hours.
Fuel Line
In compliance with CARB Tier III Emission
Regulations, carbureted engines with a “Family”
identification number beginning with “6” or greater
(See Figure 5-1), must use Low Permeation SAE 30 R7
rated fuel line; certified to meet CARB requirements.
Standard fuel line may not be used. Order
replacement hose by part number through a Kohler
Engine Service Dealer.
IMPORTANT ENGINE INFORMATION
THIS ENGINE MEETS U.S. EPA AND CA 2005
AND LATER AND EC STAGE II (SN:4) EMISSION
REGS FOR SI SMALL OFF–ROAD ENGINES
FAMILY 6 KHXS.7252 PH
TYPE APP
DISPL. (CC)
MODEL NO.
N11236
SPEC. NO.
SERIAL NO.
BUILD DA TE
OEM PROD. NO.
EMISSION COMPLIANCE PERIOD:
EPA: CARB:
CERTIFIED ON:
REFER TO OWNER'S MANUAL FOR HP RATING,
SAFETY, MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
1-800-544-2444 www.kohlerengines.com
KOHLER CO. KOHLER, WISCONSIN USA
Figure 5-1. “Family” Number Location.
5.2
Page 36

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Fuel System T ests
When the engine starts hard, or turns over but will not start, it is possible that the problem is in the fuel system.
To find out if the fuel system is causing the problem, perform the following tests.
Troubleshooting – Fuel System Related Causes
T est Conclusion
1. Check the following:
a. Make sure the fuel tank contains clean, fresh,
proper fuel.
b. Make sure the vent in fuel tank is open.
c. Make sure the fuel valve is open.
d. Make sure vacuum and fuel lines to fuel
pump are secured and in good condition.
2. Check for fuel in the combustion chamber.
a. Disconnect and ground spark plug leads.
b. Close the choke on the carburetor.
c. Crank the engine several times.
d. Remove the spark plug and check for fuel at
the tip.
3. Check for fuel flow from the tank to the fuel
pump.
a. Remove the fuel line from the inlet fitting of
fuel pump.
b. Hold the line below the bottom of the tank.
Open the shut-off valve (if so equipped) and
observe flow.
4. Check the operation of fuel pump.
a. Remove the fuel line from the inlet fitting of
carburetor.
b. Crank the engine several times and observe
flow.
2. If there is fuel at the tip of the spark plug, fuel is
reaching the combustion chamber.
If there is no fuel at the tip of the spark plug,
check for fuel flow from the fuel tank (Test 3).
3. If fuel does flow from the line, check for faulty
fuel pump (Test 4).
If fuel does not flow from the line, check the fuel
tank vent, fuel pickup screen, in-line filter, shutoff valve, and fuel line. Correct any observed
problem and reconnect the line.
4. If fuel does flow from the line, check for faulty
carburetor. (Refer to the "Carburetor" portions of
this section.)
If fuel does not flow from the line, check for a
clogged fuel line. If the fuel line is unobstructed,
check for overfilled crankcase and/or oil in pulse
line. If none of the checks reveal the cause of the
problem, replace the pump.
5
5.3
Page 37

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Fuel Pump
General
These engines are equipped with either a pulse or
mechanical fuel pump. See Figures 5-2 and 5-3. The
pumping action is created by either the oscillation of
positive and negative pressures within the crankcase
through a hose, or by direct lever/pump actuation off
rocker arm movement. The pumping action causes the
diaphragm on the inside of the pump to pull fuel in
on its downward stroke and to push it into the
carburetor on its upward stroke. Internal check valves
prevent fuel from going backward through the pump.
Outlet Line (to Carburetor)
Pulse Fuel
Pump
Pulse Line
Inlet Line
NOTE: On most models, the pulse line is
connected to a fitting on the crankcase,
while on early models, it is connected to
the valve cover.
4. Install the new fuel pump using the hex flange
screws. Torque the hex flange screws to 2.3 N·m
(20 in. lb.).
NOTE: Make sure the orientation of the new
pump is consistent with the removed
pump. Internal damage may occur if
installed incorrectly.
5. Connect the pulse line to the pulse fitting.
6. Connect the fuel lines to the inlet and outlet
fittings.
Replacing the Mechanical Pump
The mechanical pump is an integral part of the valve
cover assembly and not serviced separately. See Figure
5-3.
1. Disconnect the fuel lines from the inlet and outlet
fittings.
Figure 5-2. Pulse Style Fuel Pump.
Performance
Minimum fuel delivery rate must be 7.5 L/hr.
(2 gal./hr.) with a pressure at 0.3 psi and a fuel lift of
18 in. from carburetor inlet. A 1.3 L/hr. (0.34 gal./hr.)
fuel rate must be maintained at 5 Hz.
Fuel Pump - Replacement
Replacing the Pulse Fuel Pump
Replacement pumps are available through your
source of supply. To replace the pulse pump follow
these steps:
1. Disconnect the fuel lines from the inlet and outlet
fittings.
2. Remove the hex flange screws securing the fuel
pump.
3. Remove the pulse line that connects the pump to
the crankcase or valve cover.
2. Follow the procedure for replacing the valve
cover (Sections 9 and 11).
3. Reconnect the fuel lines to the inlet and outlet
fittings.
Outlet Line (to
Carburetor)
Mechanical
Fuel Pump
Inlet Line
Figure 5-3. Mechanical Fuel Pump.
5.4
Page 38

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Carburetor
General
Engines in this series are equipped with Keihin fixed
main jet carburetors. CH18-740 engines use a onebarrel carburetor. Most applications use a fuel shutoff solenoid installed in place of the fuel bowl
retaining screw, and also contain an accelerator
pump. All carburetors feature a self-relieving choke
like or similar to the one shown in the exploded view
on page 5.10. CH750 engines use a Keihin BK twobarrel carburetor on a matching intake manifold. This
carburetor with related servicing and adjustments is
covered beginning on page 5.11.
Troubleshooting - Carburetor Related Causes
Condition
1. Engine starts hard, runs roughly
or stalls at idle speed.
2. Engine runs rich (indicated by
black, sooty exhaust smoke,
misfiring, loss of speed and power,
governor hunting, or excessive
throttle opening).
1. Low idle fuel mixture (some models)/speed improperly adjusted.
Adjust the low idle speed tab, then adjust the low idle fuel needle.
2a. Clogged air cleaner. Clean or replace.
b. Choke partially closed during operation. Check the choke lever/
linkage to ensure choke is operating properly.
c. Low idle fuel mixture is improperly adjusted. Adjust low idle
fuel needle (some models).
d. Float level is set too high. Separate carburetor air horn from
carburetor body, adjust float to specification.
e. Dirt under the fuel inlet needle. Remove needle; clean needle and
seat and blow with compressed air.
f. Bowl vent or air bleeds plugged. Remove low idle fuel adjusting
needle. Clean vent, ports, and air bleeds. Blow out all passages
with compressed air.
g. Leaky, cracked or damaged float. Submerge float to check for
leaks.
WARNING: Explosive Fuel
Gasoline is extremely flammable and its vapors can explode if
ignited. Store gasoline only in approved containers, in well
ventilated, unoccupied buildings, away from sparks or flames.
Do not fill the fuel tank while the engine is hot or running,
since spilled fuel could ignite if it comes in contact with hot
parts or sparks from ignition. Do not start the engine near
spilled fuel. Never use gasoline as a cleaning agent.
Possible Cause/Probable Remedy
5
3. Engine runs lean (indicated by
misfiring, loss of speed and power,
governor hunting or excessive
throttle opening).
4. Fuel leaks from carburetor. 4a. Float level set too high. See Remedy 2d.
3a. Low idle fuel mixture is improperly adjusted. Adjust low idle
fuel needle (some models).
b. Float level is set too low. Separate carburetor air horn from
carburetor body, adjust float specification.
c. Idle holes plugged; dirt in fuel delivery channels. Remove low
idle fuel adjusting needle. Clean main fuel jet and all passages;
blow out with compressed air.
b. Dirt under fuel inlet needle. See Remedy 2e.
c. Bowl vents plugged. Blow out with compressed air.
d. Carburetor bowl gasket leaks. Replace gasket.
5.5
Page 39

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Troubleshooting Checklist
When the engine starts hard, runs roughly or stalls at
low idle speed, check the following areas before
adjusting or disassembling the carburetor.
• Make sure the fuel tank is filled with clean, fresh
gasoline.
• Make sure the fuel tank cap vent is not blocked
and that it is operating properly.
• Make sure fuel is reaching the carburetor. This
includes checking the fuel shut-off valve, fuel
tank filter screen, in-line fuel filter, fuel lines and
fuel pump for restrictions or faulty components
as necessary.
• Make sure the air cleaner base and carburetor are
securely fastened to the engine using gaskets in
good condition.
• Make sure the air cleaner element (including
precleaner if equipped) is clean and all air cleaner
components are fastened securely.
When current is removed the pin extends blocking
the main fuel jet and preventing fuel from entering
the carburetor.
One-Barrel Carburetor
Fuel Shut-off Solenoid
T wo-Barrel Carburetor
• Make sure the ignition system, governor system,
exhaust system, and throttle and choke controls
are operating properly.
If the engine is hard-starting, runs roughly, or stalls at
low idle speed, it may be necessary to adjust or service
the carburetor.
High Altitude Operation
When operating the engine at altitudes of 1500 m
(5000 ft.) and above, the fuel mixture tends to get overrich. This can cause conditions such as black, sooty
exhaust smoke, misfiring, loss of speed and power,
poor fuel economy, and poor or slow governor
response.
To compensate for the effects of high altitude, special
high altitude jet kits are available. The kits include a
new main jet, slow jet (where applicable), necessary
gaskets and O-Rings. Refer to the parts manual for the
correct kit number.
Fuel Shut-off Solenoid
Most carburetors are equipped with a fuel shut-off
solenoid. The solenoid is attached in place of the fixed
main jet screw on the flywheel side of the carburetor.
See Figure 5-4. The solenoid has a spring-loaded pin
that retracts when 12 volts is applied to the lead,
allowing fuel flow through the main jet.
Fuel Shut-off Solenoid
Figure 5-4. Fuel Shut-off Solenoid.
Below is a simple test, made with the engine off, that
can determine if the solenoid is functioning properly:
1. Shut off fuel and remove the solenoid from the
carburetor. When the solenoid is loosened and
removed, gas will leak out of the carburetor.
Have a container ready to catch the fuel.
2. Wipe the tip of the solenoid with a shop towel or
blow it off with compressed air, to remove any
remaining fuel. Take the solenoid to a location
with good ventilation and no fuel vapors present.
You will also need a 12 volt power source that can
be switched on and off.
3. Be sure the power source is switched “off”.
Connect the positive power source lead to the red
lead of the solenoid. Connect the negative power
source lead to the solenoid bracket.
4. Turn the power source “on” and observe the pin
in the center of the solenoid. The pin should
retract with the power “on” and return to its
original position with the power off. Test several
times to verify operation.
5.6
Page 40

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Carburetor Adjustments (CH18-740)
General
In compliance with government emission standards,
the carburetor is calibrated to deliver the correct airto-fuel mixture to the engine under all operating
conditions. The high-speed mixture is preset and
cannot be adjusted. Pre-compliance carburetors
contain a low idle fuel adjusting needle, on “certified”
compliance carburetors, both the low and high speed
mixture circuits are pre-established and cannot be
adjusted. The low idle speed (RPM) is the only
adjustment available. See Figures 5-5 and 5-6.
Depending on model and application, engines may
also be equipped with a “Governed Idle System.” If
equipped with a “Governed Idle System”, refer to
“Models with Governed Idle System” when
performing any carburetor adjustment, as an
additional step to the listed adjustment procedure(s)
is required.
Low Idle Speed
Adjustment
Low Idle Fuel
Adjusting Needle
NOTE: Carburetor adjustments should be made
only after the engine has warmed up.
Adjusting Low Idle Speed and Fuel (Some Models)
To adjust the carburetor idle speed, see Figure 5-5 and
follow these steps.
1. With the engine stopped, turn the low idle fuel
adjusting needle in clockwise until it bottoms
lightly.
NOTE: The tip of the idle fuel adjusting needle
is tapered to critical dimensions.
Damage to the needle and the seat in the
carburetor body will result if the needle
is forced.
2. Now turn the adjusting needle out
counterclockwise 1-1/2 turns.
3. Start the engine and run at half throttle for 5 to 10
minutes to warm up. The engine must be warm
before making final settings. Check that the
throttle and choke plates can fully open.
5
Main Jet
Location
Figure 5-5. Pre-Compliance Carburetor with Low
Idle Adjustment.
Low Idle
Speed
Adjustment
Fuel Shut-Off
Solenoid (Main
Jet Location)
NOTE: The carburetor has a self-relieving
choke. Choke plate and shaft assembly is
spring loaded. Check to make sure plate
moves freely and is not binding and
affecting idle fuel delivery.
4. Place the throttle control into the “idle” or “slow”
position. Turn the low idle speed adjusting screw
in or out to obtain a low idle speed of 1200 RPM
(± 75 RPM). Check the speed using a tachometer.
NOTE: The actual low idle speed depends on
the application. Refer to the equipment
manufacturer’s recommendations. The
low idle speed for basic engines is 1200
RPM. To ensure best results when setting
the low idle fuel needle, the low idle
speed should be 1200 RPM (± 75 RPM).
5. Turn the low idle fuel adjusting needle in
(slowly) until engine speed decreases and then
back out approximately 3/4 turn to obtain the best
low speed performance.
6. Recheck the idle speed using a tachometer and
readjust the speed as necessary.
Figure 5-6. “Certified” Compliance Carburetor.
5.7
Page 41

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Models with Governed Idle System
An optional governed idle control system is supplied
on some engines. The purpose of this system is to
maintain a desired idle speed regardless of ambient
conditions (temperature, parasitic load, etc.) that may
change. Engines with this feature contain a small
secondary spring connected between the governor
lever and the lower adjustment tab of the main
bracket. See Figure 5-7.
The system requires an additional procedure for
setting the idle speed. If speed adjustments are
required proceed as follows.
Hold Throttle
Lever Against
Screw
1. Make any necessary speed or control
adjustments following the appropriate
instructions covered in this section.
2. Move the throttle control to the idle position.
Hold the governor lever away from the
carburetor, or hold the throttle lever so it is tight
against the idle speed adjusting screw, to negate
the governor activation. See Figure 5-8. Check
the speed with a tachometer and adjust it to 1500
RPM.
3. Release the governor lever and allow the engine
to return to the governed idle speed. Check it
with a tachometer against the equipment
manufacturers recommended idle speed.
Governed Idle Speed (RPM) is typically 300 RPM
(approximate) higher than the low idle speed. If
adjustment is necessary, bend the adjusting tab
on the speed control assembly to set. See Figure
5-7.
Figure 5-8. Holding Throttle Lever Against Idle
Stop Screw (One-Barrel Carburetor).
Servicing
Float
It is not necessary to remove the carburetor from the
engine to check and adjust the float.
1. Remove the air cleaner and breather hose. Refer
to Section 9 – ‘‘Disassembly”.
2. Disconnect the fuel line from the carburetor. See
Figure 5-9.
3. Clean dirt and debris from exterior of carburetor.
4. Remove the four screws holding the two
carburetor halves together. Carefully lift the
upper body off the carburetor body and
disconnect choke linkage.
Governed
Idle Spring
Figure 5-7. Governed Idle Spring Location.
5.8
Screws
Fuel Line
Tab
Figure 5-9. Carburetor Detail.
5. Hold the carburetor upper body so that the float
assembly hangs vertically and rests lightly
against the fuel inlet needle. The fuel inlet needle
should be fully seated, but the needle tip should
not be depressed. See Figure 5-10.
Page 42

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
NOTE: The fuel inlet needle tip is spring loaded.
Make sure the float assembly rests
against the fuel inlet needle without
depressing the tip.
6. The correct float height adjustment is 22 mm
(0.86 in.), measured from the float bottom to the
air horn casting. Adjust the float height by
carefully bending the tab.
NOTE: Be sure to measure from the casting
surface, not the rubber gasket surface.
7. If proper float height adjustment cannot be
achieved, check to see if the fuel inlet needle is
dirty, obstructed or worn. Remove the brass
screw and float assembly to remove the fuel inlet
needle.
Tab
2. Remove the four screws and carefully separate
the air horn assembly from the carburetor body.
3. Loosen the screw securing the float assembly to
the air horn and remove the float, float shaft and
fuel inlet needle.
4. Remove the slow jet from the carburetor body.
NOTE: The main jet is a fixed jet and can be
removed if required. Fixed jets for high
altitude are available.
5. Remove the black cap on the end of the choke
shaft only if it is necessary to inspect and clean
the shaft spring.
6. Remove the low idle speed adjusting screw and
spring from the carburetor body.
7. In order to clean the ‘‘off-idle’’ vent ports and
bowl vent thoroughly, use a good carburetor
solvent (like Gumout
air through the idle adjusting needle hole. Be
careful to use a suitable shop rag to prevent
debris from hitting someone.
™
). Blow clean compressed
5
Float
Figure 5-10. Carburetor Float Adjustment.
8. Once the proper float height is obtained,
carefully lower the carburetor air horn assembly
onto the carburetor body, connecting the choke
linkage. Install the four screws. Torque the
screws to 1.7 N·m (15 in. lb.). See Figure 5-9.
9. Connect the fuel line.
10. Install the breather hose and air cleaner
assembly, following the steps in Section 11 –
‘‘Reassembly”.
Disassembly
Disassemble the carburetor using the following steps.
See Figure 5-11.
1. Remove the air cleaner, breather hose and
carburetor. Refer to Section 9 – “Disassembly”.
8. Remove the preformed rubber gasket only if it is
to be replaced. If it is removed for any reason,
replace it.
Inspection/Repair
Carefully inspect all components and replace those
that are worn or damaged.
• Inspect the carburetor body for cracks, holes and
other wear or damage.
• Inspect the float for cracks, holes, and missing or
damaged float tabs. Check the float hinge and
shaft for wear or damage.
• Inspect the fuel inlet needle and seat for wear or
damage.
• Inspect the tip of the low idle fuel adjusting
needle for wear or grooves.
• The choke plate is spring loaded. Check to make
sure it moves freely on the shaft.
5.9
Page 43

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
NOTE: The choke and throttle plate assemblies
are staked and matched to the shafts at
the factory. They are not serviceable
items.
Always use new gaskets when servicing or
reinstalling carburetors. Repair kits are available
which include new gaskets and other components.
These kits are described on the next page.
Reassembly
Reassemble the carburetor using the following steps.
See Figure 5-11.
1. Assemble the fuel inlet needle to the float tab.
Install the float, float shaft and inlet needle to the
2
4
5
6
7
9
1
3
15
8
air horn. Tighten the screw. Check float height
using the procedure found previously in the
‘‘Adjustments’’ subsection.
2. Install the slow jet with the stepped end toward
the bottom of the carburetor. Make sure jet is
fully seated.
3. Install the low idle adjusting needle and spring.
4. Assemble the upper body onto the lower
carburetor body using the four screws. Torque
the screws to 1.7 N·m (15 in. lb.).
5. Install the carburetor on the engine following the
procedures in Section 11 – ‘‘Reassembly.’’
1. Carburetor Upper Body (Choke)
2. Self-relieving Choke
3. Body Gasket (Formed Rubber)
4. Slow Speed Jet
5. Inlet Needle Valve
6. Clip
7. Float Pin
8. Float Assembly (Kit)
9. Carburetor Lower Body (Throttle)
10. Main Jet
11. Idle Fuel Adjusting Needle (some models)
12. Solenoid Seat
13. Fuel Shut-off Solenoid (Kit)
14. Idle Speed Adjusting Screw
15. Jet (Accelerator Pump Carburetor only)
16. Accelerator Pump Cover
17. Diaphragm
18. Diaphragm Spring
19. O-Ring
20. Rubber Boot
21. Bushing
22. Return Spring
10
11
14
12
13
Figure 5-11. CH18-740 Carburetor – Exploded V iew .
5.10
#
See Note on Page 5.11
21
20
22
Accelerator Pump Version Only
19
17
18
19
16
Page 44

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Components such as the throttle and choke shaft
assemblies, throttle plate, choke plate, low idle fuel
needle, and others, are available separately.
Always refer to the Parts Manual for the engine being
serviced, to ensure the correct repair kits and
replacement parts are ordered. Service/repair kits
available for the carburetor and affiliated
components are:
Carburetor Repair Kit
Float Kit
High Altitude Kit (1525-3048 m/5,000-10,000 ft.)
High Altitude Kit (over 3048 m/10,000 ft.)
Solenoid Assembly Kit
Accelerator Pump Seal and Bushing Kit
Accelerator Pump Diaphragm Kit
Choke Repair Kit
#
NOTE: If accelerator pump rod movement is
restricted or corrosion exists in the pump
rod housing hole; use a 0.153 in. (3.9 mm) or
No. 23 drill and carefully clean (resize) the
hole to restore proper operation. Blow out
the hole with air and lightly lubricate with
oil on reassembly.
Carburetor
Keihin BK T wo-Barrel Carburetor (CH750)
The carburetor used on CH750 engines is a Keihin
two-barrel side draft design with fixed main jets. See
Figure 5-12. A self-relieving choke similar to that used
on single venturi carburetors is also contained in the
design. The circuits within the carburetor function as
described following:
Slow & Mid-Range Circuit:
At low speeds the engine operates only on the slow
circuit. As a metered amount of air is drawn through
the slow air bleed jets, fuel is drawn through the two
main jets and further metered through the slow jets.
Air and fuel are mixed in the body of the slow jet and
exit to the transfer port. From the transfer port the air
fuel mixture is delivered to the idle progression
chamber. From the idle progression chamber the air
fuel mixture is metered through the idle port
passages. At low idle when the vacuum signal is
weak, the air/fuel mixture is controlled by the setting
of the idle fuel adjusting screws. This mixture is then
mixed with the main body of air and delivered to the
engine. As the throttle plate opening increases, greater
amounts of air/fuel mixture are drawn in through the
fixed and metered idle progression holes. As the
throttle plate opens further the vacuum signal
becomes great enough so the main circuit begins to
work.
Main (High-Speed) Circuit:
At high speeds/loads the engine operates on the main
circuit. As a metered amount of air is drawn through
the four air jets, fuel is drawn through the main jets.
The air and fuel are mixed in the main nozzles and
then enter the main body of airflow, where further
mixing of the fuel and air occurs. This mixture is then
delivered to the combustion chamber. The carburetor
has a fixed main circuit; no adjustment is possible.
Carburetor Adjustments
Adjustment
NOTE: Carburetor adjustments should be made
only after the engine has warmed up.
5
Float Circuit:
The fuel level in the bowl is maintained by the float
and fuel inlet needle. The buoyant force of the float
stops fuel flow when the engine is at rest. When fuel
is being consumed, the float will drop and fuel
pressure will push the inlet needle away from the
seat, allowing more fuel to enter the bowl. When
demand ceases, the buoyant force of the float will
again overcome the fuel pressure, rising to the
predetermined setting and stop the flow.
The carburetor is designed to deliver the correct fuelto-air mixture to the engine under all operating
conditions. The main fuel jet is calibrated at the
factory and is not adjustable*. The idle fuel adjusting
needle is also set at the factory and normally does not
need adjustment.
Depending on model and application, engines may
also be equipped with a “Governed Idle System.” If
equipped with a “Governed Idle System”, refer to
“Models with Governed Idle System” when
performing any carburetor adjustment, as an
additional step to the listed adjustment procedure(s)
is required.
5.11
Page 45

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
*NOTE: Engines operating at altitudes above
approximately 1500 m (5000 ft.) may require
a special ‘‘high altitude’’ main jet. Refer to
‘‘High Altitude Operation.’’
If, however, the engine is hard-starting or does not
operate properly, it may be necessary to adjust or
service the carburetor.
Low Idle Fuel Adjustments
(With Limiters)
Low Idle Speed
(RPM) Adjustment
Screw
Fuel Solenoid
Figure 5-12. Keihin T wo-Barrel Carburetor.
2. Place the throttle control into the “idle” or
“slow” position. Adjust the low idle speed to
1200 RPM*. Follow the “Adjusting the Low Idle
Speed (RPM)” procedure.
3. Low Idle Fuel Needle(s) Setting: Place the
throttle into the “idle” or “slow” position.
a. Turn one of the low idle fuel adjusting needles
out (counterclockwise) from the preliminary
setting until the engine speed decreases (rich).
Note the position of the needle. Now turn the
adjusting needle in (clockwise). The engine
speed may increase, then it will decrease as
the needle is turned in (lean). Note the
position of the needle. Set the adjusting
needle midway between the rich and lean
settings. See Figure 5-13.
b. Repeat the procedure on the other low idle
adjustment needle.
4. Recheck/adjust the Low Idle Speed (RPM), to the
specified setting.
Carburetor Adjustment
Low Idle Speed (RPM) Adjustment
1. Low Idle Speed (RPM) Setting: Place the throttle
control into the “idle” or “slow” position. Set the
low idle speed to 1200 RPM* (± 75 RPM) by
turning the low idle speed adjusting screw in or
out. Check the speed using a tachometer.
*NOTE: The actual low idle speed depends on the
application. Refer to the equipment
manufacturer’s recommendations. The low
idle speed for basic engines is 1200 RPM. To
ensure best results when setting the low idle
fuel needle, the low idle speed should be
1200 RPM (± 75 RPM).
Low Idle Fuel Adjustment
NOTE: Engines will have fixed low idle or limiter
caps on the two idle fuel adjusting needles.
Step 3 can only be performed within the
limits allowed by the cap. Do not attempt to
remove the limiter caps.
1. Start the engine and run at half throttle for 5 to
10 minutes to warm up. The engine must be
warm before doing steps 2, 3, and 4.
Adjust to
Lean
Midpoint
Rich
Left Side Right Side
Figure 5-13. Optimum Low Idle Fuel Settings.
Adjust to
Midpoint
Rich
Lean
Models with Governed Idle System
An optional governed idle control system is supplied
on some engines. The purpose of this system is to
maintain a desired idle speed regardless of ambient
conditions (temperature, parasitic load, etc.) that may
change. Engines with this feature contain a small
secondary spring connected between the governor
lever and the lower adjustment tab of the main
bracket. See Figure 5-14.
The system requires an additional procedure for
setting the idle speed. If speed adjustments are
required proceed as follows.
5.12
Page 46

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
1. Make any necessary speed or control
adjustments following the appropriate
instructions covered in this section.
2. Move the throttle control to the idle position.
Hold the governor lever away from the
carburetor, or hold the throttle lever so it is tight
against the idle speed adjusting screw, to negate
the governor activation. See Figure 5-15. Check
the speed with a tachometer and adjust it to 1500
RPM.
3. Release the governor lever and allow the engine
to return to the governed idle speed. Check it
with a tachometer against the equipment
manufacturers recommended idle speed.
Governed Idle Speed (RPM) is typically 300 RPM
(approximate) higher than the low idle speed. If
adjustment is necessary, bend the adjusting tab
on the speed control assembly to set. See Figure
5-14.
Carburetor Servicing
Float Replacement
If symptoms described in the carburetor
troubleshooting guide indicate float level problems,
remove the carburetor from the engine to check and/
or replace the float. Use a float kit to replace the float,
pin, float valve, clip and screw.
1. Perform the removal procedures for the Heavy
Duty Air Cleaner and Carburetor outlined in
Section 9 “Disassembly.”
2. Clean the exterior surfaces of dirt or foreign
material before disassembling the carburetor.
Remove the four mounting screws and carefully
separate the fuel bowl from the carburetor. Do
not damage the inner or bowl O-Ring. Transfer
any remaining fuel into an approved container.
Save all parts. Fuel can also be drained prior to
bowl removal by loosening/removal of the bowl
drain screw. See Figure 5-16.
5
Governed
Idle Spring
Tab
Figure 5-14. Governed Idle Spring Location.
Hold Throttle
Lever Against
Screw
Fuel Bowl
Bowl Drain Screw
Figure 5-16. Fuel Bowl Removed From Carburetor.
Figure 5-15. Holding Throttle Lever Against Idle
Stop Screw (Two-Barrel Carburetor).
5.13
Page 47

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
3. Remove the float pin screw and lift out the old
float, pin and inlet needle. See Figure 5-17.
Discard all of the parts. The seat for the inlet
needle is not serviceable, and should not be
removed.
Figure 5-17. Removing Float and Inlet Needle.
4. Clean the carburetor bowl and inlet seat areas as
required, before installing the new parts.
5. Attach the inlet needle to the plastic tang of the
float with the wire clip. The formed 90° lip
should point up, with the needle valve hanging
down. See Figure 5-18.
Figure 5-19. Installing Float Assembly.
7. Hold the carburetor body so the float assembly
hangs vertically and rests lightly against the fuel
inlet needle. The inlet needle should be fully
seated but the center pin of the needle (on
retainer clip end) should not be depressed. Check
the float height adjustment.
NOTE: The inlet needle center pin is spring loaded.
Make sure the float rests against the fuel inlet
needle without depressing the center pin.
8. The correct float height setting is 17 mm
(0.669 in.) ± 1.5 mm (0.059 in.), measured from
the float bottom to the body of the carburetor. See
Figure 5-20. Replace the float if the height is
different than the specified setting. DO NOT
attempt to adjust by bending float tab.
Figure 5-18. Float and Inlet Needle Details.
6. Install the float and inlet needle down into the
seat and carburetor body. Install the new pivot
pin through the float hinge and secure with the
new retaining screw. See Figure 5-19.
5.14
Figure 5-20. Checking Float Height.
NOTE: Be sure to measure from the casting surface,
not the rubber gasket, if still attached.
Page 48

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
9. When the proper float height is obtained,
carefully reinstall the fuel bowl, using new
O-Rings onto the carburetor. Secure with the
four original screws. Torque the screws to
2.5 ± 0.3 N·m (23 ± 2.6 in. lb.). See Figure 5-21.
Figure 5-21. Installing Fuel Bowl.
10. Install the carburetor and the heavy-duty air
cleaner as outlined in Section 11 “Reassembly.”
Disassembly/Overhaul
1. Clean the exterior surfaces of dirt or foreign
material before disassembling the carburetor.
Remove the four mounting screws and separate
the fuel bowl from the carburetor. Transfer any
remaining fuel into an approved container.
Remove and discard the old O-Rings. Fuel can
also be drained prior to bowl removal by
loosening/removal of the bowl drain screw. See
Figure 5-22.
Fuel Bowl
NOTE: Further disassembly of the fuel bowl is not
necessary unless the Fuel Solenoid Kit, or
Fuel Bowl Kit (obtained separately), will also
be installed.
2. Remove the float pin screw and lift out the old
float, pin, and inlet needle. See Figure 5-23.
Discard all the old parts. The seat for the inlet
needle is not serviceable, and should not be
removed.
5
Figure 5-23. Removing Float and Inlet Needle.
3. Use an appropriate size flat screwdriver, and
carefully remove the two main jets from the
carburetor. Note and mark the jets by location
for proper reassembly. The main jets may be
size/side specific. After the main jets are
removed, the main nozzles can be removed out
through the bottom of the main towers. Note the
orientation/direction of the nozzles. The end with
the two raised shoulders should be out/down
adjacent to the main jets. Save the parts for
cleaning and reuse. See Figure 5-24.
Bowl Drain Screw
Figure 5-22. Fuel Bowl Removed From Carburetor.
Main Nozzles
Main Jets
Figure 5-24. Main Jets and Nozzles Removed.
5.15
Page 49

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
4. Remove the screw securing the flat washer and
ground lead (if equipped), from the top of the
carburetor; then carefully pull (lift) out the two
slow jets. The slow jets may be sized/side
specific, mark or tag for proper reassembly. Note
the small O-Ring on the bottom of each jet. See
Figures 5-25 and 5-26. Save parts for cleaning
and reuse unless a Jet Kit is also being installed.
Clean the slow jets using compressed air. Do not
use wire or carburetor cleaner.
6. Clean the carburetor body, main jets, vent ports,
seats, etc. using a good commercially available
carburetor solvent. Keep away from plastic or
rubber parts if non-compatible. Use clean, dry
compressed air to blow out the internal channels
and ports. Do not use metal tools or wire to clean
orifices and jets. Inspect and thoroughly check
the carburetor for cracks, wear, or damage.
Inspect the fuel inlet seat for wear or damage.
Check the spring loaded choke plate to make sure
it moves freely on the shaft.
7. Clean the carburetor fuel bowl as required.
8. Install the two main nozzles into the towers of
the carburetor body. The end of the main nozzles
with the two raised shoulders should be out/
down (adjacent to the main jets). Make sure the
nozzles are completely bottomed. Carefully
install the main jets into the towers of the
carburetor body on the appropriate side, as
identified when removal was performed. See
Figure 5-27.
Figure 5-25. Removing Screw and Washer.
Slow (Idle Fuel) Jets
O-Ring
Figure 5-26. Slow Jets and O-Ring Detail.
5. Remove the idle speed (RPM) adjustment screw
and spring from the carburetor. Discard the parts.
NOTE: The carburetor is now disassembled for
appropriate cleaning and installation of the
parts in the overhaul kit. Further disassembly
is not necessary. The throttle shaft assembly,
fuel inlet seat, idle fuel adjustment screws
with limiter, and carburetor body, are nonserviceable items and should not be removed.
The choke shaft assembly is serviceable,
however it should not be removed unless a
Choke Repair Kit will be installed.
Nozzle End with
T wo Shoulders
(Out/Down)
Figure 5-27. Installing Main Nozzles and Main Jets.
9. Make sure the O-Ring near the bottom of each
slow jet is new, or in good condition. Align and
insert the two slow jets into the top of
carburetor. See Figure 5-26.
10. Install the large flat retaining washer and secure
with the mounting screw, attaching the ground
lead if originally secured by the screw.
11. Install the new idle speed (RPM) adjustment
screw and spring onto the carburetor. Thread in
until 3 or 4 threads are exposed, as an initial
adjustment. See Figure 5-28.
Main Jets
5.16
Page 50

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Figure 5-28. Installing Idle Speed Adjusting Screw
and Spring.
12. Attach the inlet needle to the plastic tang of the
float with the wire clip. The formed 90° lip
should point up, with the needle valve hanging
down. See Figure 5-29.
Figure 5-29. Float and Inlet Needle Details.
13. Install the float and inlet needle down into the
seat and carburetor body. Install the new pivot
pin through the float hinge and secure with the
new retaining screw. See Figure 5-30.
Figure 5-30. Installing Float Assembly.
14. Hold the carburetor body so the float assembly
hangs vertically and rests lightly against the fuel
inlet needle. The inlet needle should be fully
seated but the center pin of the needle (on
retainer clip end) should not be depressed. Check
the float height adjustment.
NOTE: The inlet needle center pin is spring loaded.
Make sure the float rests against the fuel inlet
needle without depressing the center pin.
15. The correct float height setting is 17 mm
(0.669 in.) ± 1.5 mm (0.059 in.), measured from
the float bottom to the body of the carburetor.
See Figure 5-31. Replace the float if the height is
different than the specified setting. Do not
attempt to adjust by bending float tab.
5
Figure 5-31. Checking Float Height.
NOTE: Be sure to measure from the casting surface,
not the rubber gasket, if still attached.
5.17
Page 51

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
16. When the proper float height is obtained,
carefully reinstall the fuel bowl, using new
O-Rings onto the carburetor. Secure with the
four original screws. Torque the screws to
2.5 ± 0.3 N·m (23 ± 2.6 in. lb.). See Figure 5-32.
Figure 5-32. Installing Fuel Bowl.
Choke Repair
1. Remove the carburetor from the engine. Discard
the old mounting gaskets for the air cleaner and
carburetor.
5. Use a screw extractor (easy-out) and remove the
original choke shaft bushing with the old choke
lever from the carburetor housing. Save the
bushing to use as a driver for installing the new
bushing. Discard the old lever.
6. Clean the I.D. of both choke shaft bores as
required.
7. Insert the new bushing through the new choke
lever from the outside, and start the bushing in
the outer shaft bore. Position the choke lever so
the protruding boss on the carburetor housing is
between the two stops formed in the choke lever.
See Figure 5-34.
Stops
Boss
2. Clean the areas around the choke shaft and the
self-relieving choke mechanism thoroughly.
3. Remove and discard the plastic cap from the end
of the choke lever/shaft assembly.
4. Note the position of the spring legs and the choke
plate for correct reassembly later. See Figure
5-33. Remove the two screws attaching the choke
plate to the choke shaft. Pull the shaft out of the
carburetor body and discard the removed parts.
Figure 5-34. Assembling Choke Lever .
8. Turn the old bushing upside down and use it as a
driver to carefully press or tap the new bushing
into the carburetor body until it bottoms. Check
that the choke lever pivots freely without
restriction or binding. See Figure 5-35.
Figure 5-33. Choke Details.
5.18
Figure 5-35. Installing Bushing.
Page 52

9. Install the new return spring onto the new choke
shaft, so the upper leg of the spring is between
the two formed “stops” on the end of the choke
shaft. See Figure 5-36.
NOTE: Make sure it stays in this location during the
following step.
Figure 5-36. Choke Shaft and Spring Details.
10. Slide the choke shaft and spring into the
carburetor. Pivot (preload) the shaft and set the
inner leg of the spring, against the formed stop
within the choke lever as originally assembled.
See Figure 5-33. The opposing leg of the spring
must still be between the formed “stops” of the
choke shaft.
11. Place a drop of Loctite® on the threads of each
new screw. Position and install the new choke
plate to the flat side of the choke shaft. Start the
two screws. Close the choke and check the plate
alignment within the carburetor throat, then
tighten the screws securely. Do not overtighten.
See Figure 5-37.
Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Figure 5-37. Installing Choke Plate.
12. Check for proper operation and free movement of
the parts. Install the new cap.
Always use new gaskets when servicing or
reinstalling carburetors. Repair kits are available
which include new gaskets and other components.
Service/repair kits available for Keihin BK two-barrel
carburetors and affiliated components are:
Carburetor Overhaul Kit
Float Kit
Fuel Solenoid Kit
Choke Repair Kit
Bowl Kit
High Altitude Kit (1525-3048 m/5,000-10,000 ft.)
High Altitude Kit (Over 3048 m/10,000 ft.)
5
5.19
Page 53

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
26
32
27
31
22
24
28
4
5
6
2
3
30
29
23
25
7
9
1
21
20
17
18
19
1. Carburetor Body Subassembly
2. Idle Speed Screw
8
3. Idle Speed Spring
4. Screw
9
5. Ground Lead
6. Retaining Washer
7. Slow Jet - RH Side
8. Slow Jet - LH Side
9. O-Ring (Slow Jet) (2)
10. Fuel Bowl
11. O-Ring (Fuel Bowl - Upper)
12. O-Ring (Fuel Bowl - Lower)
13. Drain Screw
14. Bowl Screw (4)
15. Fuel Solenoid
16. Sealing Washer
17. Float
18. Pin
19. Screw
20. Float Clip
21. Float Valve/Inlet Needle
22. Main Nozzle - Right Side
23. Main Nozzle - Left Side
24. Main Jet - Right Side
25. Main Jet - Left Side
26. Choke Dust Cap
27. Choke Shaft
28. Spring
29. Bushing
30. Choke Lever
31. Choke Plate
32. Choke Plate Screw (2)
11
12
13
16
Figure 5-38. Keihin BK Two-Barrel Carburetor - Exploded View.
5.20
10
14
15
Page 54

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Governor
General
The governor is designed to hold the engine speed
constant under changing load conditions. Most
engines are equipped with a centrifugal flyweight
mechanical governor. Some engines utilize an
optional electronic governor, which is shown and
covered on page 5.23. The governor gear/flyweight
mechanism of the mechanical governor is mounted
inside the crankcase and is driven off the gear on the
camshaft. This governor design works as follows:
• Centrifugal force acting on the rotating governor
gear assembly causes the flyweights to move
outward as speed increases. Governor spring
tension moves them inward as speed decreases.
Governor Spring
Cross Shaft
Governor Arm
Hex Nut
Throttle
Linkage
Figure 5-39. Governor Linkage.
• As the flyweights move outward, they cause the
regulating pin to move outward.
• When load is applied and the engine speed and
governor gear speed decreases, the governor
spring tension moves the governor arm to open
the throttle plate wider. This allows more fuel
into the engine, increasing the engine speed. As
the speed reaches the governed setting, the
governor spring tension and the force applied by
the regulating pin will again offset each other to
hold a steady engine speed.
Adjustments
NOTE: Do not tamper with the governor setting.
Overspeed is hazardous and could cause
personal injury.
General
The governed speed setting is determined by the
position of the throttle control. It can be variable or
constant, depending on the engine application.
Initial Adjustment
NOTE: EFI engines require a special initial
adjustment procedure, which is covered in
subsection 5B. Refer to “Initial Governor
Adjustment” in that section for setting the
governor on EFI-equipped engines.
Procedure – Carburetor Equipped Engines
Make this adjustment whenever the governor arm is
loosened or removed from the cross shaft. See Figure
5-39 and adjust as follows:
1. Make sure the throttle linkage is connected to the
governor arm and the throttle lever on the
carburetor.
5
• The regulating pin contacts the tab on the cross
shaft causing the shaft to rotate.
• One end of the cross shaft protrudes through the
crankcase. The rotating action of the cross shaft is
transmitted to the throttle lever of the carburetor
through the external throttle linkage. See Figure
5-39.
• When the engine is at rest, and the throttle is in
the “fast” position, the tension of the governor
spring holds the throttle plate open. When the
engine is operating, the governor gear assembly is
rotating. The force applied by the regulating pin
against the cross shaft tends to close the throttle
plate. The governor spring tension and the force
applied by the regulating pin balance each other
during operation, to maintain engine speed.
2. Loosen the hex nut holding the governor lever to
the cross shaft.
3. Move the governor lever toward the carburetor
as far as it will move (wide open throttle) and
hold in this position.
4. Insert a nail into the hole on the cross shaft and
rotate the shaft counterclockwise as far as it will
turn, then tighten hex nut securely.
5.21
Page 55

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Sensitivity Adjustment
Governor sensitivity is adjusted by repositioning the
governor spring in the holes of the governor lever. If
speed surging occurs with a change in engine load, the
governor is set too sensitive. If a big drop in speed
occurs when normal load is applied, the governor
should be set for greater sensitivity. See Figure 5-40
and adjust as follows:
1. To increase the sensitivity, move the spring closer
to the governor cross shaft.
2. To decrease the sensitivity, move the spring
away from the governor cross shaft.
High Speed (RPM) Adjustment (Refer to Figure 5-41.)
1. With the engine running, move the throttle
control to fast. Use a tachometer to check the
RPM speed.
2. Loosen the lock nut on high speed adjusting
screw. Turn the screw outward to decrease, or
inward to increase the RPM speed. Check RPM
with a tachometer.
3. When the desired RPM speed is obtained,
retighten the lock nut.
NOTE: When the throttle and choke control cables
are routed side-by-side, especially under a
single clamp, there must be a small gap
between the cables to prevent internal
binding. After the high-speed setting has
been completed, check that there is a gap of
at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) between the
control cables.
Governor
Lever
Figure 5-40. Governor Sensitivity Adjustments.
Left Side Pull
Choke Control Lever #1
Choke Control Cable
Throttle
Control
Cable
Kill Switch Adjusting Screw
Dual Control High
Speed Lever Stop Screw
"Do Not Remove"
Figure 5-41. Governor Control Connections.
Kill Switch
High Speed
Adjusting
Screw
High Speed
Control Lever
Throttle Control Lever #2
Choke Linkage
Z Bend
Throttle Control Cable
Choke
Control
Cable
Right Side Pull
5.22
Page 56

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Electronic Governor
General
The electronic governor regulates engine speed at
varying loads. It consists of a governor control unit,
digital linear actuator and linkage.
5
4
3
2
1
Figure 5-42. Electronic Governor Assembly .
1. Digital Linear Actuator
2. Throttle Linkage
3. Linkage Spring
4. Choke Linkage
5. Throttle Lever Adapter
Governor Control Unit (GCU) senses engine speed by
pulse voltage inputs from the ignition modules. The
GCU regulates the engine speed by variable input
voltage from a customer-supplied potentiometer or a
single pole, single throw (SPST) switch.
Potentiometer Specifications:
Wiper Voltage
0-1
1-9
9-16
SPST Switch Specifications:
Switch Position
Open
Closed
GCU Safety Features
In the event of an engine overspeed condition, the
GCU will shut down the engine by grounding the
ignition modules.
The GCU will shut down the engine by grounding the
ignition when power to the GCU is lost.
Linkage
The throttle linkage spring will fully open the throttle
plate if the linkage becomes detached from the DLA.
This will create an overspeed condition causing the
engine to shut down. The DLA shaft will have to be
manually screwed back into the body, and then
retracted before reassembling the linkage.
Engine Speed (RPM)
1860 low speed endpoint
variable speed endpoint
3600 high speed endpoint
Engine Speed (RPM)
1860 low speed endpoint
3600 high speed endpoint
5
Governor Control Unit
Figure 5-43. Electronic Governor Assembly .
Digital Linear Actuator (DLA)
Energizing the bi-directional digital linear actuator
coils in the proper sequence, causes the threaded shaft
to move out of, or back into the rotor, in precise linear
increments. When power is removed, the actuator
shaft remains in position. The DLA must initialize
(fully extend) to move the throttle plate to the closed
position, and partially open for starting. Correct
adjustment of the DLA is critical to achieve the full
range of throttle plate movement. See Adjustment
Procedure.
Adjustment Procedure
The DLA must be in the fully retracted position
during assembly. The full range of throttle plate
movement will not be achieved if the DLA is partially
extended when assembled. Loosen the two DLA
mounting plate screws located on the top of the
actuator plate. With the throttle linkage centered in
the U-Clip at the end of the DLA shaft, slide the DLA
bracket assembly back until the throttle plate is fully
open. Torque the mounting plate screws to 2.5 N·m
(22 in. lb.).
5.23
Page 57

Section 5
Fuel System and Governor
Troubleshooting Procedure
Engine starts, but will not continue to run
1. Check the linkage connection between the DLA
and throttle plate.
2. Verify the DLA initializes when power is
supplied (key switch in the start or run position).
3. Test the potentiometer wiper output voltage (if
equipped).
4. Test the SPST switch (if equipped).
5. Check the wire harness and connections.
Engine does not run at the expected speed
1. Check to see that the throttle linkage and DLA
have full range of motion having no mechanical
interference.
2. Test the potentiometer wiper voltage (if
equipped).
3. Test the SPST switch (if equipped).
5.24
Page 58

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
WARNING: Explosive Fuel!
LPG is extremely flammable, is heavier than air, and tends to settle in low areas where a spark or flame could ignite the gas.
Do not start or operate this engine in a poorly ventilated area where leaking gas could accumulate and endanger the safety of
persons in the area.
Proper service and repair of LPG fuel systems requires qualified technicians and special equipment. Many states
require special licensing or certification for LPG repair shops and/or technicians. Check state and local
regulations before attempting any adjustment, service, or repair of the LPG system or components. Faulty
repairs by unqualified or underqualified personnel can have very serious ramifications. The information in this
segment is for the exclusive use of qualified LPG service providers.
5A
LPG Fuel System Components
The typical “liquid withdrawal” LPG fuel system consists of the following components:
• LPG Fuel Tank (Liquid Withdrawal)
• Electric Lock-Off/Filter Assembly
• Vaporizer
• LPG Regulator (Combination Primary/Secondary/Vacuum Lock-Off)
• LPG Carburetor
• High Pressure Fuel Line(s)
• Vacuum Line
Fuel Line
Vaporizer
Vacuum Line
Figure 5A-1.
Lock-Off/Filter
Assembly
LPG Regulator
5A.1
Page 59

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
Operation
In a liquid withdrawal system, the Liquefied
Petroleum Gas (LPG) is released from the bottom of
the supply tank under high pressure. Upon opening
the shut-off valve on the tank, liquid fuel travels out
through the high pressure line to the electric lock-off/
filter assembly. The lock-off opens internally when the
key switch is turned “on,” permitting filtered fuel to
flow to the vaporizer. The vaporizer is mounted in the
flow of the discharged cooling air. It absorbs heat from
the cooling air and transfers it to the fuel, changing the
liquefied petroleum to a vapor or gaseous state, while
partially stepping down the fuel pressure. The gas/
vapor flows under this decreased pressure to the
regulator where it is further reduced to a usable,
regulated pressure. The regulator, activated by intake
manifold vacuum, controls fuel flow to the carburetor.
In the venturi of the carburetor, the fuel vapor is
mixed with incoming air from the air cleaner in the
correct ratio for efficient combustion.
Troubleshooting Checklist
If the engine starts hard, runs roughly, or stalls, check
the following areas.
• Make sure the LPG fuel tank is filled and shut-off
valve is fully opened.
• Make sure fuel is reaching the carburetor.
• Make sure the air cleaner element and precleaner
are clean and all components are fastened
securely.
• Make sure the ignition, governor, exhaust,
throttle, and choke control systems are all
operating properly.
• Check compression.
If engine continues to start hard, run roughly, or stall
after these checks have been made, use the following
troubleshooting guide.
Engine cranks but will not start
1. LPG fuel tank closed, low, or empty.
2. Lock-off not opening electrically, preventing fuel
flow to vaporizer.
3. Fuel filter (located inside lock-off) dirty or
blocked.
4. Insufficient vacuum signal, regulator not opening.
a. Vacuum line between carburetor and
regulator cracked, leaking, kinked, or pinched.
b. Carburetor loose.
c. Intake manifold loose or leaking.
d. Excessive internal engine wear.
5. Faulty regulator.
a. Primary valve not opening.
b. Diaphragm spring adjustment incorrect.
c. Idle adjustment screw incorrectly set.
d. Vent(s) blocked/restricted.
6. Restricted/blocked fuel line.
7. Blocked carburetor fuel circuit.
8. Loose/leaking fuel enrichment hose (Impco
carburetor system).
Hard starting, runs roughly, or stalls at idle speed
1. LPG fuel tank low.
2. Vacuum line between carburetor and regulator
pinched, cracked, or leaking.
3. Carburetor idle speed set too low (should be at
least 1200 RPM).
4. Carburetor idle circuit restricted.
5. Dirty/restricted air cleaner.
6. Dirty/restricted lock-off filter.
7. Frozen/malfunctioning regulator. Check/adjust
primary pressure.
8. Excessive external load on engine.
9. Excessive internal wear.
10. Loose/leaking fuel enrichment hose (Impco
carburetor system).
Irregular or inconsistent idle
1. Improper operation/adjustment of regulator, idle
adjustment screw, throttle opening, and/or engine
governor.
2. Secondary valve in regulator not closing. Readjust
idle screw (couterclockwise) so valve can close
fully against seat.
3. Loose/leaking vacuum line.
4. Loose carburetor mounting and/or line
connections.
5. Damaged diaphragm(s) within regulator.
6. Debris in regulator. Flush debris from drain plug
or remove regulator from system, disassemble
body and remove debris.
7. Dirt or debris in carburetor. Remove carburetor,
disassemble and clean/service as required. If
venturi (Impco carburetor) removal is performed,
mark its orientation to the carburetor body for
proper reinstallation.
8. Loose/leaking fuel enrichment hose (Impco
carburetor system).
5A.2
Page 60

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
Engine stalls during operation
1. No fuel.
2. Faulty lock-off or blocked filter.
3. Improper governor setting.
4. Damaged diaphragms within regulator.
5. Vacuum line leaking, loose, or pinched.
6. Restricted fuel line.
7. Loose/leaking fuel enrichment hose (Impco
carburetor system).
Low power
1. Air cleaner or exhaust system dirty/restricted.
2. Low fuel.
3. Rich gas condition (flooding) through regulator.
a. Dirty/restricted valves in regulator.
b. Damaged primary diaphragm in regulator.
4. No fuel.
a. Electric lock-off not opening, filter blocked, or
restriction within fuel line.
b. Leaking, loose, or cracked vacuum line from
carburetor to regulator.
c. Leaking, or loose intake system components.
d. Regulator primary valve not opening.
e. Secondary, or vacuum lock-off diaphragm
within regulator leaking.
f. Low pressure rubber hose kinked.
g. Frozen regulator.
5. Improper ignition timing.
6. Loose/incorrect throttle lever/clamp bracket
positioning.
7. Loose or incorrectly positioned high speed
throttle plate stop.
Engine runs lean
1. Electrical problem causing intermittent lock-off
operation, or lock-off is faulty.
2. Filter in lock-off dirty or restricted.
3. Restriction in fuel system.
4. Idle holes plugged; dirt in fuel delivery channels.
5. Carburetor fuel circuit restriction.
6. Loose/leaking fuel enrichment hose (Impco
carburetor system).
LPG Carburetor Adjustment s
General
The LPG carburetor and regulator are designed to
deliver the correct fuel-to-air mixture to the engine
under all operating conditions. The high and low idle
fuel mixture settings are preset at the factory, and
cannot be adjusted. These engines are equipped with
an Impco or Nikki carburetor. See Figure 5A-2 and
5A-3. Although both carburetors function similarly,
each is unique and should not be interchanged.
Load Block Assembly
Fuel Enrichment
Hose
Venturi
Retaining
Screw
Fuel Inlet
Figure 5A-2. Impco Carburetor.
Choke Plate/Shaft Assembly
Rear Plug
with Sealing
Washer
Fuel Inlet
Plastic Bushing
Figure 5A-3. Nikki Carburetor.
Idle Speed
Adjusting Screw
Transfer
Chamber
Cover
Vacuum Port
Idle Speed
Adjusting Screw
5A
High fuel consumption
1. Fuel leak. Check lines, connections, and system
components for leaks with soapy water. Fix any
leaks immediately.
2. Incorrectly set regulator, or leakage from valves
in regulator. Readjust, service, or replace
regulator as required.
3. Dirty air cleaner or precleaner.
4. Choke plate in carburetor not opening
completely.
Impco carburetors also incorporate the use of an
external ‘‘Load Block’’ assembly, which controls the
final fuel flow to the carburetor for all throttle
positions except idle. See Figure 5A-2. Calibrated and
flow-matched to the carburetor, it functions similarly
to preset fuel mixture settings in other carburetors.
The load block assembly is not available separately,
nor is any internal servicing permitted or possible. If a
problem is encountered and determined to be caused
by the load block, the carburetor should be replaced.
5A.3
Page 61

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
High Altitude Operation
The standard carburetor calibrations will provide
proper operation up to altitudes of 1500 m (5000 ft.).
No internal changes are necessary or available for
either carburetor.
NOTE: Carburetor adjustments should be made only
after the engine has warmed up.
Idle Speed Adjustment
1. Start the engine and run at half throttle for 5 to 10
minutes. Check that the throttle and choke (Nikki
carburetor) plates can open fully.
2. Place the throttle control into the “idle” or
“slow” position. Turn the low idle speed
adjusting screw (See Figure 5A-2 or 5A-3) in or
out, to obtain a low idle speed of 1200 RPM (± 75
RPM), or set to application specifications. Check
the speed using a tachometer.
NOTE: The actual low idle speed (RPM) depends on
the application. Refer to the equipment
manufacturer’s recommendations. The low
idle speed for basic engines is 1200 RPM.
Impco Carburetor
1. Turn off fuel supply at tank.
2. Remove the air cleaner, breather hose, fuel line,
vacuum hose, choke, and throttle linkages.
Remove the mounting hardware, carburetor, and
gaskets from the engine. Discard the gaskets.
3. The carburetor venturi may be removed for
inspection and appropriate cleaning.
a. Remove the four screws securing the air
cleaner adapter and gasket to the carburetor.
See Figure 5A-4.
LPG Fuel System Component Service
LPG Carburetor - Cleaning
The carburetor may be cleaned if necessary. Removal
from the engine and limited disassembly will aid in
cleaning.
NOTE: Impco Carburetor: Do not loosen or alter the
mounted position of the clamping brackets
and/or stop collar on the throttle shaft. Each
is preset, in correlation to a specific position
of the throttle plate (shaft), or acts as a stop.
None of these attached components,
including the throttle plate or shaft, requires
disassembly or removal for any carburetor
servicing. All the components on the throttle
shaft should be left intact. If the settings of
any one of these is inadvertently loosened or
altered, each must be checked/reset, or
performance and operation will be affected.
Refer to the procedure included in the
reassembly/installation sequence to check or
reset.
Figure 5A-4.
b. Important: Mark a small line on the outer
edge of the venturi for proper orientation and
reinstallation later.
c. Loosen the venturi retaining screw on the side
of the carburetor body and lift out the
venturi. See Figure 5A-5.
5A.4
Figure 5A-5.
Page 62

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
4. Inspect the overall condition of the fuel
enrichment hose attached to the carburetor. It
must be free of cracks, deterioration, and damage.
Disconnect the fuel enrichment hose from the
carburetor fittings to clean or check condition as
required. See Figure 5A-6. Replace with a new
Kohler high pressure hose (LP rated) if the
condition is questionable in any way. Secure new
hose using new clamps.
Figure 5A-6.
Nikki Carburetor
1. Turn off fuel supply at tank.
2. Remove the air cleaner, breather hose, fuel line,
vacuum hose, choke, and throttle linkages.
Remove the nuts, carburetor, and gaskets from
the engine. Discard the gaskets.
3. Remove the fuel transfer chamber cover by
removing the three screws. See Figure 5A-3.
Carefully remove the cover and gasket. Discard
the gasket.
4. The main jet is fixed and nonadjustable, but may
be accessed for cleaning by removing the rear
plug and sealing washer. Discard the washer.
5. In order to clean the off-idle transfer passages
and carburetor thoroughly, use a good carburetor
cleaner and follow the manufacturer's
instructions. Blow clean, compressed air through
the passages and make sure all are open before
reassembling. Do not use wire or metal objects to
clean passages or carburetor body.
5A
5. Clean all parts as required, use a good carburetor
cleaner, following the manufacturer's
instructions. Blow clean, compressed air through
all the passages. Do not poke or probe into the
load block assembly as damage can be done,
resulting in serious operational problems. See
Figure 5A-7.
Figure 5A-7.
LPG Carburetor - Inspection
1. Inspect the carburetor body and removable
venturi (Impco carburetor) for cracks, holes, and
other wear or damage.
2. Check the choke shaft (Nikki carburetor only)
and the throttle shaft for wear and free
movement.
NOTE: Do not attempt to disassemble or
remove either shaft from the carburetor
body, including the mounted clamp
brackets on Impco style carburetors. The
screws, attaching the choke and throttle
plate to their respective shafts are staked
or bonded to prevent loosening. The
plate(s) and shaft(s) are not available
separately. If detrimental wear or
damage is found in any of the parts, the
carburetor should be replaced.
5A.5
Page 63

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
LPG Carburetor - Reassembly
Impco Carburetor
1. Slide the venturi into the carburetor body,
aligning the position mark made prior to
removal. Correctly installed, the discharge holes
should not be visible from the top.
2. Secure with the venturi retaining screw. Torque
the screw to 4.0 N·m (36 in. lb.).
3. Install a new adapter gasket and mount the air
cleaner adapter onto the carburetor with the four
screws. Torque the screws to 4.0 N·m (36 in. lb.).
4. Install a new carburetor gasket onto the intake
manifold adapter, followed by the carburetor.
Install and finger tighten the mounting fasteners.
5. Connect the ‘‘Z’’ end of the throttle linkage and
the dampening spring to the throttle clamp
bracket on the throttle shaft. Attach the opposite
end of linkage and spring to the governor lever.
NOTE: The clamp brackets and stop collar
mounted on the throttle shaft should still
be in their original positions (See Figure
5A-2), and not require any readjustment/
resetting. Continue with steps 6 and 7. If
the mounted position of any one of these
was affected or changed, it will be
necessary to check and reset the position
of each before proceeding. Follow the
complete instructions listed after step 7,
then continue with steps 6 and 7.
Idle Speed Clamp Bracket Position
1. Counting the number of turns, back the idle
speed adjustment screw off (counterclockwise),
so only 1 to 1 1/2 of the threads are visible. See
Figure 5A-8.
Idle Speed
Clamp
Bracket
Mounting
Screw
Figure 5A-8. Backing Off Idle Speed Screw.
2. Loosen the clamp bracket mounting screw, and
pivot the throttle shaft to fully close the throttle
plate. See Figure 5A-9.
6. Manually move the governor lever toward the
carburetor as far as it will go.
7. Check that the throttle plate is now fully open or
reposition the carburetor slightly on the
mounting screws so it is fully open. Torque the
mounting screws to 9.9 N·m (88 in. lb.).
Instructions for Checking/Positioning the Clamp
Brackets Mounted on the Throttle Shaft
Use only if the position or mounting of the clamp
bracket(s) has been disturbed. Figures show the
carburetor removed from the engine for clarity.
5A.6
Figure 5A-9. Closing Throttle Plate.
3. Hold the throttle plate closed and rotate the
clamp bracket until the end of the screw contacts
the stop. Insert a 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) feeler gauge
between the carburetor housing and the side of
the clamp bracket to set the endplay, then tighten
the mounting screw securely. See Figure 5A-10.
Page 64

Figure 5A-10. Tightening Idle Speed Clamp
Mounting Screw.
4. Reset the idle speed adjustment screw back to the
original position.
High Speed/Stop Collar Position
1. Make sure the idle speed clamp position has
already been checked or properly set.
Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
3. Insert a 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) feeler gauge between
the side of the stop collar and the carburetor
housing, then check or set the position of the stop
collar. The head of the mounting screw must be
in contact with the carburetor boss from the back
(hose/fitting) side, preventing any further
rotation over center. Set or adjust the stop collar
as required. See Figure 5A-12.
High Speed Stop
Collar
Figure 5A-12. Adjusting/Setting Stop Collar .
5A
2. Rotate and hold the throttle shaft so the throttle
plate is fully open/perfectly vertical. See Figure
5A-11.
High Speed Stop
Collar
Figure 5A-11. Full Throttle Position.
4. Tighten the screw securely.
NOTE: After the idle speed clamp bracket and the
high speed stop collar positions have been
set, check that the throttle shaft pivots freely
without binding or restriction.
Throttle Linkage Clamp Bracket Position
Carburetor must be assembled to engine with linkage
attached to set this position.
1. The throttle linkage clamp bracket should be
positioned as shown in Figure 5A-13 on the idle
speed clamp bracket side of the throttle shaft.
Throttle
Linkage
Clamp Bracket
Figure 5A-13. Throttle Linkage Clamp Bracket
Position.
5A.7
Page 65

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
2. Manually move the governor lever, with the
throttle linkage connected, toward the carburetor as
far as it will go. Hold it in this position.
3. Looking down the throat of the carburetor, check
that the throttle plate is in the full throttle position
and that the head of the high speed collar stop
screw is in contact with the carburetor boss. If not,
loosen the carburetor mounting screws and
reposition the carburetor slightly. Torque the
carburetor mounting screws to 9.9 N·m (88 in. lb.).
NOTE: If additional adjustment is required,
loosen the throttle linkage clamp bracket
mounting screw, set the throttle shaft to
the full throttle position against the head
of the stop screw, and retighten the clamp
mounting screw securely. See Figure
5A-14.
6. Check to be sure all system connections are tight.
7. Reset idle RPM and recheck high idle (governed
speed) after starting and allowing sufficient
warm-up time.
Electric Lock-Off/Filter Assembly - Functional Test
The electric lock-off can be easily tested to verify that
it is functional. Remove it from the system for testing.
Using a 12 volt power supply or battery, connect one
wire lead to the positive (+) lead of power supply, and
touch remaining wire lead to negative (-) lead of
power supply. When connection is made, an audible
“click” should be heard indicating the opening of the
lock-off. While energized, blow compressed air
through it to determine if it is blocked or restricted.
Figure 5A-14. Tightening Throttle Linkage Clamp
Bracket.
Nikki Carburetor
1. Reinstall the rear plug with a new sealing washer.
Tighten the plug securely.
2. Reinstall fuel transfer chamber cover with a new
gasket. Secure with the three screws.
3. Install new carburetor mounting gasket on
manifold studs, followed by the carburetor and
new air cleaner base gasket.
4. Reconnect the throttle and choke linkages, and
the fuel and vacuum lines.
5. Reinstall the air cleaner base and breather tube.
Secure base with two mounting nuts. Torque nuts
to 9.9 N·m (88 in. lb.). Install the rest of the air
cleaner system.
Figure 5A-15.
Figure 5A-16.
Electric Lock-Off/Filter Assembly - Filter Service
The filter inside the lock-off assembly should be
replaced every 500 hours of operation, or if it becomes
blocked or restricted. Cleaning of the filter element is
not recommended. Order a replacement filter element
by the appropriate Kohler part number.
5A.8
Page 66

V aporizer Assembly
The outer surface of the vaporizer should be kept free
of dirt and debris accumulation, which will cause a
loss of vaporization efficiency. Visual inspection and
necessary cleaning should be performed on a regular
basis, more frequently under dusty or dirty
conditions. The vaporizer should be disassembled,
cleaned, and serviced using a rebuild kit every 1500
hours or if a problem is encountered.
Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
Figure 5A-18. Impco (Beam) Regulator.
5A
Figure 5A-17.
LPG Regulator
The regulator controls both the pressure and flow of
fuel within the LP system. It is comprised of both a
primary and secondary chamber, which are dependent
upon one another. Two different styles of regulators
are used, based upon the system involved. The Impco
(Beam) regulator is shown in Figure 5A-18, and the
Nikki regulator is shown in Figure 5A-19. Although
the basic design and operating principles are similar,
due to system differences the regulators should not be
interchanged.
Figure 5A-19. Nikki Regulator.
Following are separate sections covering the theory of
operation and general service information for each
style of regulator. Detailed service/repair instructions
are included in the rebuild kit for each regulator.
5A.9
Page 67

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
Impco (Beam) Regulator (See Figure 5A-20)
LPG vapor enters at point (A), then passes into
primary area (B) at point (28), where pressure is
reduced from up to 250 psi at the tank to 4.5 psi in
area (B). Fuel pressure against diaphragm (2)
overcomes spring (3) and as movement increases,
spring (5) will close lever (6). The primary diaphragm
breather (not shown in drawing) is vented to
secondary chamber so that rupture of this diaphragm
would direct fuel into the carburetor.
Fuel now moves through passage (E), past secondary
valve (25) into secondary area (C). As negative
pressure (vacuum) is created at the carburetor venturi
and is transmitted through the dry-gas hose to
chamber (C) secondary diaphragm (12) is drawn
down and contacts the secondary lever (16). Fuel will
flow in proportion to air velocity through the
carburetor venturi, ensuring an ideal mixture at all
engine speeds.
Whenever the engine is operating, the vacuum
diaphragm (10) is down against the floor (H) and the
spring (11) is compressed. The idle and starting
adjustment is made with a tamper-resistant screw (17)
which regulates the whisker wire system (not shown),
opening up the secondary orifice slightly (but only
when the vacuum diaphragm is drawn down). Very
little vacuum is needed to start this vacuum
diaphragm travel: 0.2 in. Mercury to start and 0.5 in.
Mercury for full travel. The instant the engine stops
rotating, loss of vacuum in section (D) releases
diaphragm (10) causing bumper (K) to push against
secondary lever (16), overcoming action of whisker
wire and ensuring 100% lock-off.
1
20
2
3
4
6
7
8
1. 1/8-27 NPT Plug
2. Primary Diaphragm Assembly
3. Primary S pring
4. Expansion Plug
5. Secondary Diaphragm Spring
6. Primary Lever Assembly
7. Fillister Head Screw
8. Primary Pivot Pin
9. Torx Head Screw
10. Vac Lock Diaphragm
Assembly
11. Vac Lock Spring
Figure 5A-20.
14
19
17
5
25
E
B
H
K
D
C
28
A
12. Secondary Diaphragm
13. Pan Head Screw
14. Secondary Lever Spring
15. Secondary Pivot Pin
16. Secondary Lever
17. Adjustment Screw
18. Pan Head Screw
19. Expansion Plug
20. Diaphragm Gasket
21. Split Lock Washer
15
18
16
13
12
11
10
9 21
Assembly
This patented Beam design will lock off primary
pressures up to five times in excess of normal and
permits starting without priming or choking.
5A.10
Page 68

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
Nikki Regulator Primary Chamber
(See Figure 5A-21)
The primary chamber reduces the high pressure fuel
flow from the tank and vaporizer down to
approximately 4 psi. Fuel flowing from the vaporizer
enters the inlet of the regulator under approximately
76 kPa (11 psi) of pressure. There it is delivered to the
primary chamber (3) through the clearance between
the primary valve (1) and valve seat (2). As fuel
continues to flow and the primary chamber
approaches 29 kPa (4 psi), the primary diaphragm (4)
overcomes the tension of the diaphragm spring (5). As
the diaphragm (4) and contact button (6) move up, the
primary lever spring (8) pushes the primary lever (7)
up, in turn closing the primary valve (1) and stopping
the flow of fuel. As fuel is consumed and the pressure
in the primary chamber drops below 29 kPa (4 psi), the
diaphragm spring (5) tension will be greater than the
fuel pressure, causing the primary diaphragm (4) to be
pushed down. This causes the contact button (6), to
push the primary lever (7) down, in turn opening the
primary valve (1) and admitting more fuel. In this
manner, the pressure within the primary chamber is
maintained at a relatively constant 29 kPa (4 psi).
9
5
6
3
7
4
1
2
Nikki Regulator Secondary Chamber
(See Figure 5A-22)
The secondary chamber further reduces the fuel
pressure from the 29 kPa (4 psi) of the primary
chamber to near 0 kPa (0 psi) pressure, to prevent
excessive fuel flow to the carburetor. Fuel enters the
secondary chamber (13) through the clearance
between the secondary valve (11) and the valve seat
(12). While the engine is operating, and fuel is being
drawn from the secondary chamber, the secondary
diaphragm (14) is raised by atmospheric pressure,
simultaneously lifting the secondary valve lever (16),
opening the secondary valve (11), allowing fuel to
flow. When the engine is running at idle, there may
not be enough vacuum created in the carburetor
venturi to overcome the tension of the secondary
diaphragm spring (15), and the secondary diaphragm
cannot open the valve. Under those conditions, the
idle adjusting screw (18), and balance spring (19) are
used to apply just enough pressure on the diaphragm
(14) to maintain sufficient fuel flow for idle operation.
The vacuum lock-off mechanism is located in the
secondary chamber. When the engine is running,
manifold vacuum above the diaphragm (17) draws it
up, so the secondary valve can function normally.
When the engine is stopped, manifold vacuum is
terminated, and the diaphragm relaxes and pushes
down on the secondary valve lever, preventing any
fuel flow or leakage through the regulator.
5A
8
To Secondary Chamber
1. Primary Valve 6. Contact Button
2. Primary Valve Seat 7. Primary Valve Lever
3. Primary Chamber 8. Primary Lever Spring
4. Primary Diaphragm 9. Primary Pressure
5. Primary Diaphragm Spring Adjustment
Figure 5A-21. Primary Chamber.
Fuel
Inlet
From Primary
Chamber
12
11
To
Carburetor
11. Secondary Valve 16. Secondary Valve Lever
12. Secondary Valve Seat 17. Vacuum Lock-Off
13. Secondary Chamber Diaphragm
14. Secondary Diaphragm 18 . Idle Adjust Screw
15. Secondary Diaphragm Spring 19. Balance Spring
18
15
16
17
19
To Intake
Manifold
14
Figure 5A-22. Secondary Chamber.
13
5A.11
Page 69

Section 5A
LPG Fuel Systems
Preventative Maintenance
The regulator is preset at the factory and generally
requires no further adjustment. No periodic service is
required. Over time, depending on fuel quality,
operating environment, and system performance, fuel
deposits can accumulate inside the regulator. Those
regulators containing a drain plug (Nikki) should be
drained every 500 hours to remove any accumulated
deposits. See Figure 5A-23.
Regulator Drain Plug
Figure 5A-23. Regulator Drain Plug (Some Models).
Regulator Service
Every 1500 hours it is recommended that
disassembly, cleaning, and resetting of the regulator
be performed using the regulator rebuilding kit
available. Specific instructions are included in the
rebuilding kit. Perform the regulator service
following the instructions provided. As all
adjustments and settings must be reset using specific
test equipment, this must be performed by qualified
LP personnel only.
Impco (Beam) Regulator Service
Kohler repair kit 24 757 40-S should be used to service
the regulator every 1500 hours, or whenever cleaning
and servicing is required.
Nikki Regulator Service
Kohler repair kit 24 757 39-S should be used every
1500 hours.
1. Turn supply valve off, run engine out of fuel, and
turn off ignition switch.
2. Disconnect and ground the spark plug leads.
3. Remove the 1/8" pipe plug from bottom of
regulator and drain any accumulated deposits.
See Figure 5A-23.
4. Reinstall plug using pipe sealant with Teflon
(Loctite® 592 or equivalent) on threads and
tighten securely. If required, a replacement plug
is available as Kohler Part No. X-75-23-S.
®
5A.12
Page 70

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Section 5B
Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)
Fuel System
Contents Page(s)
Description
Initial Starting/Priming Procedure...................................................................................................................... 5B.2
Fuel Recommendations ........................................................................................................................................ 5B.2
EFI Fuel System Components .............................................................................................................................. 5B.3
Operation ................................................................................................................................................................ 5B.3
Important Service Notes ....................................................................................................................................... 5B.4
Electrical Components
Electronic Control Unit (ECU).................................................................................................................... 5B.4-5B.5
Engine Speed Sensor .................................................................................................................................... 5B.5-5B.6
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) and Initialization Procedures ............................................................ 5B.7-5B.10
Engine (Oil) Temperature Sensor ........................................................................................................... 5B.10-5B.11
Oxygen Sensor .......................................................................................................................................... 5B.11-5B.13
Electrical Relay ......................................................................................................................................... 5B.13-5B.14
Fuel Injectors ............................................................................................................................................. 5B.14-5B.17
Ignition System ......................................................................................................................................... 5B.17-5B.18
Spark Plugs........................................................................................................................................................... 5B.18
Wiring Harness ........................................................................................................................................ 5B.18-5B.19
Battery Charging System................................................................................................................................... 5B.19
5B
Fuel Components
Fuel Pump ................................................................................................................................................. 5B.19-5B.20
Fuel Pressure Regulator ........................................................................................................................... 5B.20-5B.22
Fuel Filter .............................................................................................................................................................. 5B.22
Fuel Rail ................................................................................................................................................................ 5B.22
Fuel Line .................................................................................................................................................... 5B.22-5B.23
Throttle Body/Intake Manifold Assembly ....................................................................................................... 5B.23
Idle Speed Adjustment (RPM) ................................................................................................................ 5B.23-5B.24
Initial Governor Adjustment................................................................................................................... 5B.24-5B.26
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Guide ....................................................................................................................................... 5B.26
Electrical System ....................................................................................................................................... 5B.27-5B.33
Fuel System .......................................................................................................................................................... 5B.34
Fault Codes ................................................................................................................................................ 5B.34-5B.42
Troubleshooting Flow Chart ................................................................................................................... 5B.42-5B.43
Flow Chart Diagnostic Aids .................................................................................................................... 5B.44-5B.45
EFI Service Tools ............................................................................................................................. Refer to Section 2
5B.1
Page 71

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Description
WARNING
Explosive Fuel can cause fires and
severe burns.
Fuel system ALWAYS remains under
HIGH PRESSURE.
WARNING: Explosive Fuel!
Gasoline is extremely flammable and its vapors can explode
if ignited. Store gasoline only in approved containers, in
well ventilated, unoccupied buildings, away from sparks or
flames. Do not fill the fuel tank while the engine is hot or
running, since spilled fuel could ignite if it comes in contact
with hot parts or sparks from ignition. Do not start the
engine near spilled fuel. Never use gasoline as a cleaning
agent.
The EFI fuel system remains under high pressure, even
when the engine is stopped. Before attempting to service
any part of the fuel system, the pressure must be relieved.
Pressure Tester, (part of EFI Service Kit, see Section 2) has an
integral relief valve. Connect the black tester hose to the test
valve in the fuel rail. Route the clear hose into a portable
gasoline container. Depress the button on the tester relief valve.
Initial Starting/Priming Procedure
Important: The EFI fuel system must be purged of air
(primed) prior to the initial start up, and/or any time
the system has been disassembled or the fuel tank run
dry.
1. Locate the electronic control unit (ECU) for the
EFI system. Check the part number on the end.
If the Part No. is 24 584 28 or higher, the ECU
has a built-in priming feature.
a. Turn the key switch to the “on/run”
position. You will hear the fuel pump cycle
on and off. When the fuel pump stops
cycling (approximately one minute), the
system is primed; start the engine.
2. For plastic-cased ECU’s below 24 584 28-S, the
system can be primed by manually cycling the
fuel pump.
a. Turn the key switch to the “on/run”
position. The fuel pump will run for about
three seconds and stop. Turn the switch off
and back on to restart the fuel pump.
Repeat this procedure until the fuel pump
has cycled five times, then start the engine.
3. The system can also be primed similar to
relieving pressure.
a. Connect the pressure gauge as described
above for relieving fuel pressure. Depress
and hold the release button and crank the
engine until the air is purged and fuel is
visible in the discharge tube. If fuel is not
visible after 10 seconds, stop cranking and
allow the starter to cool for 60 seconds.
Priming Without a Test Valve in Fuel Rail:
1. Crank the engine in 10-15 second intervals,
allowing a 60 second cool-down period between
cranking intervals, until the engine starts.
NOTE: The number of cranking intervals necessary
will depend on the individual system design,
and/or where the system has been
disassembled.
Fuel Recommendations
General Recommendations
Purchase gasoline in small quantities and store in
clean, approved containers. An approved container
with a capacity of 2 gallons or less with a pouring
spout is recommended. Such a container is easier to
handle and helps prevent spillage during refueling.
• Do not use gasoline left over from the previous
season, to minimize gum deposits in your fuel
system, and to ensure easy starting.
• Do not add oil to the gasoline.
• Do not overfill the fuel tank. Leave room for the
fuel to expand.
Fuel Type
Do not use leaded gasoline, as component damage
will result. Any costs/damages incurred as a result of
using leaded fuel will not be warranted. Use only
clean, fresh, unleaded gasoline with a pump sticker
octane rating of 87 or higher. In countries using the
Research method, it should be 90 octane minimum.
5B.2
Page 72

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Gasoline/Alcohol blends
Gasohol (up to 10% ethyl alcohol, 90% unleaded
gasoline by volume) is approved as a fuel for Kohler
EFI engines. Other gasoline/alcohol blends are not
approved.
Gasoline/Ether blends
Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE) and unleaded
gasoline blends (up to a maximum of 15% MTBE by
volume) are approved as a fuel for Kohler EFI engines.
Other gasoline/ether blends are not approved.
EFI Fuel System Components
General
The Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system is a complete
engine fuel and ignition management design. The
system includes the following principal components:
• Fuel Pump
• Fuel Filter
• Fuel Rail
• Fuel Line(s)
• Fuel Pressure Regulator
• Fuel Injectors
• Throttle Body/Intake Manifold
• Engine Control Unit (ECU)
• Ignition Coils
• Engine (Oil) Temperature Sensor
• Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
• Speed Sensor
• Oxygen Sensor
• Wire Harness Assembly & Affiliated Wiring,
• Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL)
Operation
The EFI system is designed to provide peak engine
performance with optimum fuel efficiency and lowest
possible emissions. The ignition and injection functions
are electronically controlled, monitored and
continually corrected during operation to maintain the
theoretical ideal or “stoichiometric” air/fuel ratio of
14.7:1.
The central component of the system is the Motronic
Engine Control Unit (ECU) which manages system
operation, determining the best combination of fuel
mixture and ignition timing for the current operating
conditions.
An electric fuel pump is used to move fuel from the
tank through the fuel line and in-line fuel filter. A fuel
pressure regulator maintains a system operating
pressure of 39 psi and returns any excess fuel to the
tank. At the engine, fuel is fed through the fuel rail and
into the injectors, which inject it into the intake ports.
™
The ECU controls the amount of fuel by varying the
length of time that the injectors are “on.” This can
range from 1.5-8.0 milliseconds depending on fuel
requirements. The controlled injection of the fuel
occurs each crankshaft revolution, or twice for each
4-stroke cycle. One-half the total amount of fuel
needed for one firing of a cylinder is injected during
each injection. When the intake valve opens, the fuel/
air mixture is drawn into the combustion chamber,
ignited, and burned.
The ECU controls the amount of fuel injected and the
ignition timing by monitoring the primary sensor
signals for engine temperature, speed (RPM), and
throttle position (load). These primary signals are
compared to preprogrammed “maps” in the ECU
computer chip, and the ECU adjusts the fuel delivery
to match the mapped values. An oxygen sensor
provides continual feedback to the ECU based upon
the amount of unused oxygen in the exhaust,
indicating whether the fuel mixture being delivered is
rich or lean. Based upon this feedback, the ECU further
adjusts fuel input to reestablish the ideal air/fuel ratio.
This operating mode is referred to as “closed loop”
operation. The EFI system operates “closed loop”
when all three of the following conditions are met:
a. The oil temperature is greater than 35°C (95°F).
b. The oxygen sensor has warmed sufficiently to
provide a signal (minimum 375°C, 709°F).
c. Engine operation is at a steady state (not starting,
warming up, accelerating, etc.).
During “closed loop” operation the ECU has the
ability to readjust temporary and learned adaptive
controls, providing compensation for changes in
overall engine condition and operating environment,
so it will be able to maintain the ideal air/fuel ratio of
14.7:1. The system requires a minimum engine oil
temperature greater than 55°C (130°F) to properly
adapt. These adaptive values are maintained as long as
the ECU is “powered up” by the battery.
During certain operating periods such as cold starts,
warm up, acceleration, etc., an air/fuel ratio richer than
14.7:1 is required and the system operates in an “open
loop” mode. In “open loop” operation the monitoring
of exhaust gases (output) is not used, and the
controlling adjustments are based on the primary
sensor signals and programmed maps only. The
system operates “open loop” whenever the three
conditions for closed loop operation (above) are not
being met.
5B
5B.3
Page 73

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Important Service Notes!
• Cleanliness is essential and must be maintained
at all times when servicing or working on the EFI
system. Dirt, even in small quantities, can cause
significant problems.
• Clean any joint or fitting with parts cleaning
solvent before opening to prevent dirt from
entering the system.
• Always depressurize the fuel system through the
test valve in fuel rail before disconnecting or
servicing any fuel system components. See fuel
warning on page 5B.2.
• Never attempt to service any fuel system
component while engine is running or ignition
switch is ‘‘on.’’
• Do not use compressed air if the system is open.
Cover any parts removed and wrap any open
joints with plastic if they will remain open for
any length of time. New parts should be removed
from their protective packaging just prior to
installation.
Electrical Components
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Figure 5B-1. “35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU.
• Avoid direct water or spray contact with system
components.
• Do not disconnect or reconnect the wiring
harness connector to the control unit or any
individual components with the ignition ‘‘on.’’
This can send a damaging voltage spike through
the ECU.
• Do not allow the battery cables to touch opposing
terminals. When connecting battery cables attach
the positive (+) cable to positive (+) battery
terminal first, followed by negative (-) cable to
negative (-) battery terminal.
• Never start the engine when the cables are loose
or poorly connected to the battery terminals.
• Never disconnect battery while engine is running.
• Never use a quick battery charger to start the
engine.
• Do not charge battery with key switch ‘‘on.’’
Figure 5B-2. “24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU.
Figure 5B-3. “32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU.
• Always disconnect negative (-) battery cable lead
before charging battery, and also unplug harness
from ECU before performing any welding on
equipment.
5B.4
Page 74

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Three different styles of ECU’s have been utilized in EFI
production. The first style is easily identified by its
metal case with large 35 pin connector block, and also
as MA 1.7. See Figure 5B-1. The second and third styles
have plastic cases, but are smaller in overall size. These
have either a 24 pin or 32 pin connector block and
identified as MSE 1.0 or MSE 1.1 respectively. See
Figures 5B-2 and 5B-3. Basic function and operating
control remains the same between the three, however,
due to differences in the internal circuitry as well as
the wiring harness, none of the ECU’s are
interchangeable. Certain individual service/
troubleshooting procedures also apply, where
applicable, they are covered individually as: “35 Pin”
(MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU, “24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) PlasticCased ECU, or “32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU.
General
The ECU is the brain or central processing computer of
the entire EFI fuel/ignition management system.
During operation, sensors continuously gather data
which is relayed through the wiring harness to input
circuits within the ECU. Signals to the ECU include:
ignition (on/off), crankshaft position and speed (RPM),
throttle position, oil temperature, exhaust oxygen
levels, and battery voltage. The ECU compares the
input signals to the programmed maps in its memory
to determine the appropriate fuel and spark
requirements for the immediate operating conditions.
The ECU then sends output signals to set the injector
duration and ignition timing.
To prevent engine over-speed and possible failure, a
“rev-limiting” feature is programmed into the ECU. If
the maximum RPM limit (4125 RPM on MA 1.7, 4500
RPM on MSE 1.0 & MSE 1.1) is exceeded, the ECU
suppresses the injection signals, cutting off the fuel
flow. This process repeats itself in rapid succession,
limiting operation to the preset maximum.
Service
Never attempt to disassemble the ECU. It is sealed to
prevent damage to internal components. Warranty is
void if the case is opened or tampered with in any
way.
All operating and control functions within the ECU
are preset. No internal servicing or readjustment may
be performed. If a problem is encountered, and you
determine the ECU to be faulty, contact your source of
supply. Do not replace the ECU without factory
authorization.
The relationship between the ECU and the throttle
position sensor (TPS) is very critical to proper system
operation. If the TPS or ECU is changed, or the
mounting position of the TPS is altered, the applicable
“TPS Initialization Procedure” (see pages 5B.8 or 5B.9)
must be performed to restore the synchronization.
Engine Speed Sensor
5B
The ECU continually performs a diagnostic check of
itself, each of the sensors, and the system performance.
If a fault is detected, the ECU turns on the Malfunction
Indicator Light (MIL) on the equipment control panel,
stores the fault code in its fault memory, and goes into
a default operating mode. Depending on the
significance or severity of the fault, normal operation
may continue, or “limp home” operation (slowed
speed, richer running) may be initiated. A technician
can access the stored fault code using a “blink code”
diagnosis flashed out through the MIL. An optional
computer software diagnostic program is also
available, see Section 2.
The ECU requires a minimum of 7.0 volts to operate.
The adaptive memory in the ECU is operational the
moment the battery cables are connected, however the
adapted values are lost if the battery becomes
disconnected for any reason. The ECU will “relearn”
the adapted values if the engine is operated for 10-15
minutes at varying speeds and loads after the oil
temperature exceeds 55°C (130°F).
Figure 5B-4. Engine Speed Sensor .
5B.5
Page 75

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
General
The engine speed sensor is essential to engine
operation; constantly monitoring the rotational speed
(RPM) of the crankshaft. A ferromagnetic 60-tooth ring
gear with two consecutive teeth missing is mounted on
the flywheel. The inductive speed sensor is mounted
1.5 ± 0.25 mm (0.059 ± 0.010 in.) away from the ring
gear. During rotation, an AC voltage pulse is created
within the sensor for each passing tooth. The ECU
calculates engine speed from the time interval between
the consecutive pulses. The two-tooth gap creates an
interrupted input signal, corresponding to specific
crankshaft position (84° BTDC) for cylinder #1. This
signal serves as a reference for the control of ignition
timing by the ECU. Synchronization of the inductive
speed pickup and crankshaft position takes place
during the first two revolutions each time the engine is
started. The sensor must be properly connected at all
times. If the sensor becomes disconnected for any
reason, the engine will quit running.
Service
The engine speed sensor is a sealed, non-serviceable
assembly. If “Fault Code” diagnosis indicates a problem
within this area, check and test as follows.
1. Check the mounting and air gap of sensor. It must
be 1.5 mm ± 0.25 mm (0.059 ± 0.010 in.).
2. Inspect the wiring and connections for damage or
problems.
3. Make sure the engine has resistor type spark
plugs.
4. Disconnect main harness connector from ECU.
6. Disconnect the speed sensor connector from
wiring harness. It is the connector with one heavy
black lead (see Figure 5B-5). Viewing the
connector as shown (dual aligning rails on top),
test the resistance between the terminals
indicated. A reading of 750-1000
be obtained.
Dual Aligning Rails
Corresponds
To #3 (MetalCased ECU) or #10
(Plastic-Cased
ECU) In Main
Connector.
Figure 5B-5. Speed Sensor Connector .
7. a. If the resistance is incorrect, remove the screw
securing the sensor to the mounting bracket
andreplace the sensor.
b. If the resistance in step 5 was incorrect, but
the resistance of the sensor alone was correct,
test the main harness circuits between the
sensor connector terminals and the
corresponding pin terminals in the main
connector. Correct any observed problem,
reconnect the sensor, and perform step 5
again.
Test Terminals
ΩΩ
Ω should again
ΩΩ
Corresponds T o
#21 (Metal-Cased
ECU) or #9
(Plastic-Cased
ECU) In Main
Connector.
5. Connect an ohmmeter between the designated pin
terminals in the plug:
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: #3 and #21
pin terminals.
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: #9 and #10
pin terminals.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU: #9 and
#10 pin terminals.
See pages 5B.28-5B.33 according to ECU style. A
resistance value of 750-1000
temperature (20°C, 68°F) should be obtained.
If resistance is correct, check the mounting, air gap,
toothed ring gear (damage, runout, etc.), and
flywheel key.
5B.6
ΩΩ
Ω at room
ΩΩ
Page 76

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
2
1
3
Mounted on the throttle body/intake manifold and
operated directly off the end of the throttle shaft, the
TPS works like a rheostat, varying the voltage signal
to the ECU in direct correlation to the angle of the
throttle plate. This signal, along with the other sensor
signals, is processed by the ECU and compared to the
internal preprogrammed maps to determine the
required fuel and ignition settings for the amount of
load.
The correct position of the TPS is established and set
at the factory. Do not loosen the TPS or alter the
mounting position unless absolutely required by fault
code diagnosis or throttle shaft service. If the TPS is
loosened or repositioned the appropriate “TPS
Initialization Procedure” (pages 5B.8-5B.10) must be
performed to reestablish the baseline relationship
between the ECU and the TPS.
Service
The TPS is a sealed, non-serviceable assembly. If
diagnosis indicates a bad sensor, complete
replacement is necessary. If a blink code indicates a
problem with the TPS, it can be tested as follows:
5B
4
1. Throttle V alve Shaft
2. Resistor Track
3. Wiper Arm w/Wiper
4. Electrical Connection
Figure 5B-6. Throttle Position Sensor Details.
General
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is used to indicate
throttle plate angle to the ECU. Since the throttle (by
way of the governor) reacts to engine load, the angle
of the throttle plate is directly proportional to the load
on the engine.
Mounted Throttle
Position Sensor
Figure 5B-7. TPS Location.
1. Counting the number of turns, back out the idle
speed adjusting screw (counterclockwise) until
the throttle plates can be closed completely.
2. Disconnect the main harness connector from the
ECU, but leave the TPS mounted to the throttle
body/manifold.
3. Connect the ohmmeter leads as follows:
(See chart on pages 5B.28, 5B.31, or 5B.32).
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Red
(positive) ohmmeter lead to #12 pin terminal, and
Black (negative) ohmmeter lead to #27 pin
terminal.
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Red
(positive) ohmmeter lead to #8 pin terminal, and
Black (negative) ohmmeter lead to #4 pin
terminal.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU: Red
(positive) ohmmeter lead to #8 pin terminal, and
Black (negative) ohmmeter lead to #4 pin
terminal.
Hold the throttle closed and check the resistance. It
should be 800-1200
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
5B.7
Page 77

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
4. Leave the leads connected to the pin terminals as
described in step 3. Rotate the throttle shaft
slowly counterclockwise to the full throttle
position. Monitor the dial during rotation for
indication of any momentary short or open
circuits. Note the resistance at the full throttle
position. It should be 1800-3000
5. Disconnect the main wiring harness connector
from the TPS, leaving the TPS assembled to the
manifold. Refer to the chart below and perform
the resistance checks indicated between the
terminals in the TPS switch, with the throttle in
the positions specified.
Throttle
Position
Closed
Closed
Full
Full
Any
If the resistance values in steps 3, 4, and 5 are
within specifications, go to step 6.
If the resistance values are not within
specifications, or a momentary short or open
circuit was detected during rotation (step 4), the
TPS needs to be replaced, go to step 7.
Between
Terminals
2 & 3
1 & 3
2 & 3
1 & 3
1 & 2
Resistance
Value (Ω)
800-1200
1800-3000
1800-3000
800-1200
1600-2500
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
Continuity
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
7. Remove the two mounting screws from the TPS.
Save the screws for reuse. Remove and discard
the faulty TPS. Install the replacement TPS and
secure with the original mounting screws.
a. Reconnect both connector plugs.
b. Perform the appropriate “TPS Initialization
Procedure” integrating the new sensor to the
ECU.
TPS Initialization Procedure
For “35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU and
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU only
1. Check that the basic engine, all sensors, fuel, fuel
pressure, and battery are good and functionally
within specifications.
Important!
2. Remove/disconnect ALL external loads from
engine (belts, pumps, electric PTO clutch,
alternator, rectifier-regulator, etc.).
3. Start the engine and allow it to warm up for 5-10
minutes, so oil temperature is above 55°C (130°F).
4. Move the throttle control to the idle position and
allow engine to stabilize for a minimum of one
minute.
6. Check the TPS circuits (input, ground) between
the TPS plug and the main harness connector for
continuity, damage, etc. See chart on pages 5B.28,
5B.31, or 5B.32.
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Pin
Circuits #12 and #27.
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Pin
Circuits #8 and #4.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU: Pin
Circuits #8 and #4.
a. Repair or replace as required.
b. Turn the idle speed screw back in to its
original setting.
c. Reconnect connector plugs, start engine and
retest system operation.
5. Install a heavy rubber band around the throttle
lever and the manifold boss, to firmly hold the
throttle against the idle stop. On some EFI
engines there is a dampening spring on the end of
the idle speed screw. The dampening spring (if
used) should be fully compressed and the tab on
the throttle lever in direct contact with the speed
screw. Adjust the idle speed to 1500 RPM, using a
tachometer.
6. Shut off engine.
7. Locate the service connector plug in the wiring
harness.
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Connect a
jumper wire from the TPS initialization pin #8
(gray wire) to the ground pin (black wire), or use
the jumper plug with the red jumper wire. See
Figure 5B-8.
5B.8
Page 78

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Connect a
jumper wire from the TPS initialization pin #24
(violet wire) to the battery voltage pin (red wire),
or use the jumper plug with the blue jumper
wire. See Figure 5B-9.
Figure 5B-8. Service Connector Plug, Metal-Cased
ECU Harness.
b. If light stays on or blinking ceases
prematurely, the procedure was unsuccessful
and must be repeated. Possible causes for
unsuccessful learning may be: 1) Movement
occurred in either the TPS or throttle shaft
during procedure, 2) Crankshaft movement/
rotationwas detected by the speed sensor
during procedure, 3) Throttle plate position
was out of learnable range (recheck the 1500
RPM idle speed adjustment), or 4) Problem
with ECU or TPS.
9. When the initialization procedure has been
successfully completed, turn off the key switch,
remove the jumper wire or connector, and
remove the rubber band from the throttle lever.
10. Disconnect negative (-) battery cable temporarily
to clear all learned adjustments.
11. Reconnect the battery cable and all external loads.
Readjust the idle speed to the equipment
manufacturer’s specified setting and recheck the
high-speed, no-load RPM setting. Observe the
overall performance.
5B
Figure 5B-9. Service Connector Plug, PlasticCased ECU Harness.
8. Hold throttle against idle speed stop screw, turn
the ignition switch to “on” position (do not start
engine), and observe the Malfunction Indicator
Light (MIL).
a. The light should blink on/off quickly for
approximately 3 seconds and then go off and
stay off, indicating the initialization procedure
has been successful.
TPS Initialization Procedure
For “32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU Only
(“Auto-Learn” Initialization)
1. Check that the basic engine, all sensors, fuel, fuel
pressure, and battery are good and functionally
within specifications.
Important!
2. Remove/disconnect ALL external loads from the
engine (belts, pumps, electric PTO clutch,
alternator, rectifier-regulator, etc.).
3. Locate the service connector plug in the wiring
harness. To initiate the TPS auto-learn function,
connect a jumper wire from the TPS initialization
pin #24 (violet wire) to the battery voltage pin
(red wire), or use the jumper plug with the blue
jumper wire. If using the PC-based diagnostic
tool and software (see Section 2), go to “Special
Tests” and follow the prompts to complete.
4. Start the engine and immediately observe the
Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL). The light
should start blinking 4 consecutive times every 2
seconds.
5B.9
Page 79

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
5. Remove the jumper wire or plug from the service
connector plug in wiring harness.
6. Run the engine at full throttle (above 3000 RPM),
to warm up the engine and initiate O
function in “closed-loop” operation.
7. Watch the “MIL”. When the light starts blinking
rapidly, (5 blinks per second), move the throttle
lever to the low idle speed position. Check and
adjust the idle speed to 1500 RPM, using a
tachometer. The lamp should continue to blink
rapidly for another 30 seconds before switching
to a slow blink.
8. When the “MIL” blinks slowly, do not do
anything but wait until the “MIL” shuts off. This
indicates that this procedure has been completed
successfully.
9. Shut off the engine.
If the learn procedure was successfully
completed, the external loads removed/
disconnected in Step 2 may be reconnected.
If the procedure was unsuccessful see Steps a.
and b. following.
a. If during this procedure, the “MIL” goes back
into blinking 4 consecutive blinks every 2
seconds, the engine and O
cooled down and out of “closed-loop”
operation, prohibiting the learning from
occurring. Repeat Steps 6-9.
b. If during the procedure with the engine
running, the “MIL” stays “on” continuously,
for more than 15 seconds, turn off the ignition.
Then initiate the fault code sequence, by doing
three consecutive key-on/key-off cycles
leaving the key “on” in the last sequence,
(each key-on/key-off sequence must be less
than 2.5 seconds long). The fault detected
must be corrected before the “auto-learn”
function can be re-initiated. The PC-based
diagnostic tool and software may be used to
read out the fault code and assist with the
troubleshooting and repair.
sensor have
2
sensor
2
Engine (Oil) T emperature Sensor
Figure 5B-10. Engine (Oil) T emperature Sensor.
General
The engine (oil) temperature sensor (Figure 5B-10) is
used by the system to help determine fuel
requirements for starting, (a cold engine needs more
fuel than one at or near operating temperature).
Mounted in the oil filter adapter housing, it has a
temperature-sensitive resistor that extends into the oil
flow. The resistance changes with oil temperature,
altering the voltage sent to the ECU. Using a table
stored in its memory, the ECU correlates the voltage
drop to a specific temperature. Using the fuel delivery
“maps”, the ECU then knows how much fuel is
required for starting at that temperature.
Service
The temperature sensor is a sealed, non-serviceable
assembly. A faulty sensor must be replaced. If a blink
code indicates a problem with the temperature sensor,
it can be tested as follows:
1. Remove the oil temperature sensor from the
adapter housing and cap or block the adapter
hole.
2. Wipe sensor clean and allow it to reach room
temperature (20°C, 68°F).
3. Unplug the main harness connector from the
ECU.
4. With the sensor connected, check the oil
temperature sensor circuit resistance. The value
should be 2375-2625
5B.31, or 5B.32.
ΩΩ
Ω. See chart on pages 5B.28,
ΩΩ
5B.10
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Check
between the #14 and #27 pin terminals.
Page 80

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Check
between the #6 and #4 pin terminals.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU: Check
between the #6 and #4 pin terminals.
5. Unplug the sensor connector and check sensor
resistance separately. Resistance value should
again be 2375-2625
a. If the resistance is out of specifications,
replace the temperature sensor.
b. If it is within specifications, proceed to Step 6.
6. Check the temperature sensor circuits (input,
ground) from the main harness connector to the
corresponding terminal in the sensor plug for
continuity, damage, etc.
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Pin circuits
#14 and #27.
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Pin
circuits #6 and #4.
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
The tip of the sensor, protruding into the exhaust gas,
is hollow (see cutaway Figure 5B-12). The outer
portion of the tip is surrounded by the exhaust gas,
with the inner portion exposed to the ambient air.
When the oxygen concentration on one side of the tip
is different than that of the other side, a voltage signal
typically cycling between 0.2 and 1.0 volt is generated
between the electrodes and sent to the ECU. The
voltage signal tells the ECU if the engine is straying
from the ideal 14.7:1 fuel mixture, and the ECU then
adjusts the injector pulse accordingly.
12
1. Connection Cable
2. Disc Spring
3. Ceramic Support Tube
4. Protective Sleeve
4
3
5. Contact Element
6. Sensor Housing
7. Active Ceramic Sensor
8. Protective Tube
5
6
8
7
5B
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU: Pin
circuits #6 and #4.
Oxygen Sensor
Figure 5B-11. Oxygen Sensor .
General
The oxygen sensor functions like a small battery,
generating a voltage signal to the ECU, based upon
the difference in oxygen content between the exhaust
gas and the ambient air.
Figure 5B-12. Cutaway of Oxygen Sensor .
The oxygen sensor can function only after being
heated by exhaust temperatures to a minimum of
375°C (709°F). A cold oxygen sensor will require
approximately 1-2 minutes at moderate engine load to
warm sufficiently to generate a voltage signal. Proper
grounding is also critical. The oxygen sensor grounds
through the metal shell, so a good, solid, unbroken
ground path back through the exhaust system
components, engine, and wiring harness is required.
Any disruption or break in the ground circuit can
affect the output signal and trigger misleading fault
codes. Keep that in mind when doing any
troubleshooting associated with the oxygen sensor.
The oxygen sensor can also be contaminated by leaded
fuel, certain RTV and/or other silicone compounds,
carburetor cleaners, etc. Use only those products
indicated as “O² Sensor Safe.”
Service
Like the other sensors already discussed, the oxygen
sensor is a non-serviceable component. Complete
replacement is required if it is faulty. The sensor and
wiring harness can be checked as follows.
NOTE: All tests should be conducted with a good
quality, high-impedance, digital VOA meter
for accurate results.
5B.11
Page 81

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
1. Oxygen sensor must be hot (minimum of 400°C,
725°F). Run engine for about 5 minutes. With the
engine running, disconnect the oxygen sensor lead
from the wiring harness. Set VOA meter for DC
volts and connect the red lead to the disconnected
sensor lead, and the black lead to the sensor shell.
Check for a voltage reading between 0.2 v-1.0 v.
a. If voltage is in the specified range, go to Step 2.
b. If the voltage is not in the specified range,
reconnect the oxygen sensor lead. With the
lead connected, probe or connect the sensor
connection with the red VOA meter lead.
Attach the black VOA meter lead to a known
good ground location. Start and run the engine
at 3/4 throttle and note the voltage output.
The reading should cycle between 0.2 v-1.0 v,
which indicates the oxygen sensor is
functioning normally and also the fuel
delivery controlled by the ECU is within
prescribed parameters. If the voltage readings
show a steady decline, bump the governor
lever to make the engine accelerate very
quickly and check the reading again. If voltage
momentarily increases and then again
declines, without cycling, engine may be
running lean due to incorrect TPS initialization.
Shut off the engine, perform TPS initialization,
and then repeat the test. If TPS initialization
cannot be achieved, perform step c.
previous checkpoint. For example, if the reading
is too low at points on the crankcase, but correct
voltage is indicated when the black lead is
touched to the skin of the muffler, the flange
joints at the exhaust ports become suspect.
3. With sensor still hot (minimum of 400°C, 752°F),
switch meter to the Rx1K or Rx2K scale and check
the resistance between the sensor lead and sensor
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω, go to
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω, the
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω, go to
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω, the
ΩΩ
case. It should be less than 2.0 K
a. If the resistance is less than 2.0 K
Step 4.
b. If the resistance is greater than 2.0 K
oxygen sensor is bad, replace it.
4. Allow the sensor to cool (less than 60°C, 140°F)
and retest the resistance with the meter set on the
Rx1M scale. With sensor cool, the resistance
should be greater than 1.0 M
a. If the resistance is greater than 1.0 M
Step 5.
b. If the resistance is less than 1.0 M
sensor is bad, replace it.
5. With the oxygen sensor disconnected and engine
not running, disconnect the main harness
connector from the ECU and set the meter to the
Rx1 scale. Check the circuit continuity as follows:
c. Replace the oxygen sensor (page 5B.13). Run
the engine long enough to bring the new
sensor up to temperature and repeat the output
test from step 1. The cycling voltage from 0.2
to 1.0 volt should be indicated.
2. Move the black voltmeter lead to the engine
ground location and repeat the output test. The
same voltage (0.2 v-1.0 v) should be indicated.
a. If the same voltage reading exists, go on to
Step 3.
b. If the voltage output is no longer correct, a bad
ground path exists between the sensor and the
engine ground. Touch the black lead at various
points, backtracking from the engine ground
back toward the sensor, watching for a voltage
change at each location. If the correct voltage
reading reappears at some point, check for a
problem (rust, corrosion, loose joint or
connection) between that point and the
5B.12
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Check for
continuity from pin #9 of the ECU connector (see
page 5B.28) to the shell of the oxygen sensor, and
from pin #10 to the sensor connector terminal of
the main harness. Both tests should indicate
continuity.
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Check for
continuity from pin #15 of the ECU connector
(see page 5B.31) to the shell of the oxygen sensor,
and from pin #11 to the sensor connector terminal
of the main harness. Both tests should indicate
continuity.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic Cased ECU: Check for
continuity from pin #19 of the ECU connector
(see page 5B.32) to the shell of the oxygen sensor,
and from pin #20 to the sensor terminal of the
main harness. Both tests should indicate
continuity.
Page 82

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
a. If there is no continuity displayed in either of
the tests, check the harness circuit for breaks
or damage, and the connections for poor
contact, moisture, or corrosion. If no
continuity was found in the first test, also
check for a poor/broken ground path back
through the exhaust system, engine, and
mounting (sensor is grounded through its
shell).
b. If continuity is indicated, go to step 6.
6. With the key switch in the ‘‘on/run’’ position,
using a high impedance voltmeter, check the
voltage from the wiring harness oxygen sensor
connector to the engine ground location. Look for
a steady voltage from 350-550 mv (0.35-0.55 v).
a. If voltage reading is not as specified, move the
black voltmeter lead to the negative post of
the battery, to be certain of a good ground. If
the voltage is still not correct, the ECU is
probably bad.
b. If voltage readings are correct, clear the fault
codes and run the engine to check if any fault
codes reappear.
T o Replace Oxygen Sensor
1. Disconnect the oxygen sensor connector from
wiring harness.
2. Loosen and remove the oxygen sensor from the
exhaust manifold/muffler assembly.
3. Apply anti-seize compound sparingly to threads
of new oxygen sensor, if none already exists. DO
NOT get any on the tip as it will contaminate the
sensor. Install sensor and torque to 50-60 N·m
(37-44 ft. lb.).
4. Reconnect the lead to wiring harness connector.
Make sure it can not contact hot surfaces, moving
parts, etc.
Electrical Relay
Figure 5B-13. Electrical Relay .
General
The electrical relay is used to supply power to the
injectors, coils, and fuel pump. When the key switch is
turned “on” and all safety switch requirements met,
the relay provides 12 volts to the fuel pump circuit,
injectors, and ignition coils. The fuel pump circuit is
continuously grounded, so the pump is immediately
activated and pressurizes the system. Activation of the
ignition coils and injectors is controlled by the ECU,
which grounds their respective circuits at the proper
times.
Service
A malfunctioning relay can result in starting or
operating difficulties. The relay and related wiring can
be tested as follows:
1. Disconnect the relay connector plug from the
relay.
2. Connect black lead of VOA meter to a chassis
ground location. Connect red lead to the #86
terminal in relay connector (see Figure 5B-14). Set
meter to test resistance (Rx1). Turn ignition
switch from “off” to “on”. Meter should indicate
continuity (ground circuit is completed) for 1 to 3
seconds. Turn key switch back off.
5B
5. Test run the engine.
5B.13
Page 83

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Terminal #85 Ignition Switch
Voltage
Terminal #87A Not used
Terminal #30 Permanent Battery Voltage
Terminal #87 Feed T o Ignition
Coils, Fuel
Injectors, and
Fuel Pump
Terminal #86 ECU
Controlled
Ground
Figure 5B-14. Relay Connector.
a. Clean the connection and check wiring if
circuit was not completed.
3. Set meter for DC voltage. Touch red tester lead to
the #30 terminal in relay connector. A reading of
12 volts should be indicated at all times.
4. Connect red lead of meter to the #85 terminal in
relay connector. Turn key switch to the “on”
position. Battery voltage should be present.
6. Attach ohmmeter leads to the #30 and #87
terminals in relay. Initially, there should be no
continuity. Using a 12 volt power supply, connect
the positive (+) lead to the #85 terminal, and touch
the negative (-) lead to the #86 terminal. When 12
volts is applied, the relay should activate and
continuity should exist (circuit made) between
the #30 and #87 terminals. Repeat the test several
times. If, at any time the relay fails to activate the
circuit, replace the relay.
Fuel Injectors
a. No voltage present indicates a problem in the
wiring or at the connector.
b. If voltage is present, the wiring to the
connector is good. Turn ignition switch ‘‘off’’
and proceed to test 5 to test the relay.
T erminal #86 ECU Controlled
Ground
T erminal #87 - Feed
to Ignition Coils,
Fuel Injectors,
and Fuel Pump
T erminal #85 Terminal
#87A -
Ignition
Switch V olt age
Not Used
T erminal #30 Permanent
Battery V oltage
Figure 5B-15. Relay Terminal Details.
5. Connect an ohmmeter (Rx1 scale) between the
#85 and #86 terminals in the relay. There should
be continuity. See Figure 5B-15.
Figure 5B-16. Style 1 Fuel Injector.
Figure 5B-17. Style 2 Fuel Injector.
General
The fuel injectors mount into the intake manifold, and
the fuel rail attaches to them at the top end.
Replaceable O-Rings on both ends of the injector
prevent external fuel leakage, and also insulate it from
heat and vibration. A special clip connects each
injector to the fuel rail, retaining it in place.
5B.14
Page 84

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
When the key switch is on and the relay is closed, the
fuel rail is pressurized, and voltage is present at the
injector. At the proper instant, the ECU completes the
ground circuit, energizing the injector. The valve
needle in the injector is opened electromagnetically,
and the pressure in the fuel rail forces fuel down
through the inside. The “director plate” at the tip of
the injector (see inset) contains a series of calibrated
openings which directs the fuel into the manifold in a
cone-shaped spray pattern.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Service
Injector problems typically fall into three general
categories: electrical, dirty/clogged, or leakage. An
electrical problem usually causes one or both of the
injectors to stop functioning. Several methods may be
used to check if the injectors are operating.
1. With the engine running at idle, feel for
operational vibration, indicating that they are
opening and closing.
2. When temperatures prohibit touching, listen for a
buzzing or clicking sound with a screwdriver or
mechanic’s stethoscope (see Figure 5B-19).
Listen Here
5B
7
Multi-Orifice
Director Plate with
Calibrated Opening
1. Filter strainer in fuel supply
2. Electrical connection
3. Solenoid winding
4. V alve housing
Figure 5B-18. Fuel Injector Details.
The injector is opened and closed once for each
crankshaft revolution, however, only one-half the
total amount of fuel needed for one firing is injected
during each opening. The amount of fuel injected is
controlled by the ECU and determined by the length
of time the valve needle is held open, also referred to
as the “injection duration” or “pulse width”. It may
vary in length from 1.5-8 milliseconds depending on
the speed and load requirements of the engine.
5. Armature
6. V alve body
7. V alve needle
Figure 5B-19. Checking Injectors.
3. Disconnect the electrical connector from an
injector and listen for a change in idle
performance (only running on one cylinder) or a
change in injector noise or vibration.
If an injector is not operating, it can indicate either a
bad injector, or a wiring/electrical connection problem.
Check as follows:
NOTE: Do not apply voltage to the fuel injector(s).
Excessive voltage will burn out the
injector(s). Do not ground the injector(s) with
the ignition “on”. Injector(s) will open/turn
on if relay is energized.
1. Disconnect the electrical connector from both
injectors. Plug the 12 volt Noid Light (part of EFI
Service Kit, see Section 2) in one connector.
5B.15
Page 85

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Figure 5B-20. V olt Noid Light.
2. Make sure all safety switch requirements are met.
Crank the engine and check for flashing of noid
light. Repeat test at other connector.
Check all electrical connections, connectors, and
wiring harness leads if resistance is incorrect.
Injector leakage is very unlikely, but in those rare
instances it can be internal (past the tip of the valve
needle), or external (weeping around the injector
body). See Figure 5B-21. The loss of system pressure
from the leakage can cause hot restart problems and
longer cranking times. To check for leakage it will be
necessary to remove the blower housing, which may
involve removing the engine from the unit.
a. If flashing occurs, use an ohmmeter (Rx1
scale) and check the resistance of each
injector across the two terminals. Proper
resistance is 12-20
correct, check whether the connector and
injector terminals are making a good
connection. If the resistance is not correct,
replace the injector following steps 1-8 and
13-16 below.
b. If no flashing occurs, reattach connectors to
both injectors. Disconnect the main harness
connector from the ECU and the connector
from the relay. Set the ohmmeter to the Rx1
scale and check the injector circuit resistance
as follows:
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Check
the resistance between the relay terminal #87
and pin #35 in main connector. Resistance
should be 4-15
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU:
Check the resistance between relay terminal
#87 and pin #16 in main connector. Then
check resistance between relay terminal #87
and pin #17. Resistance should be 4-15
each circuit.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU:
Check the resistance between relay terminal
#87 and pin #14 in the main connector. Then
check the resistance between relay terminal
#87 and pin #15. Resistance should be 4-15
for each circuit.
ΩΩ
Ω. If injector resistance is
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω for
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω
ΩΩ
Check For Leaks
Figure 5B-21. Injector Inspection Points.
1. Engine must be cool. Depressurize fuel system
through test valve in fuel rail.
2. Disconnect spark plug leads from spark plugs.
3. Remove the air cleaner outer cover, inner wing
nut, element cover and air cleaner element/
precleaner. Service air cleaner components as
required.
4. Remove the two screws securing the air cleaner
base to throttle body manifold. Remove the air
cleaner base to permit access to the injectors.
Check condition of air cleaner base gasket,
replace if necessary.
5. Remove the flywheel screen if it overlaps the
blower housing.
6. If the engine has a radiator-type oil cooler
mounted to the blower housing, remove the two
oil cooler mounting screws.
7. Remove the blower housing mounting screws.
Note the location of the plated (silver) screw
attaching the rectifier-regulator ground lead.
Remove the blower housing.
5B.16
Page 86

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
8. Thoroughly clean the area around and including
the throttle body/manifold and the injectors.
9. Disconnect the throttle linkage and damper
spring from the throttle lever. Disconnect the TPS
lead from the harness.
10. Remove the manifold mounting bolts and
separate the throttle body/manifold from the
engine leaving the TPS, fuel rail, air baffle,
injectors and line connections intact. Discard the
old gaskets.
11. Position the manifold assembly over an
appropriate container and turn the key switch
“on” to activate the fuel pump and pressurize the
system. Do not turn switch to “start” position.
12. If either injector exhibits leakage of more than
two to four drops per minute from the tip, or
shows any sign of leakage around the outer shell,
turn the ignition switch off and replace injector as
follows.
13. Depressurize the fuel system following the
procedure in the fuel warning on page 5B.2.
Remove the two fuel rail mounting screws.
14. Clean any dirt accumulation from the sealing/
mounting area of the faulty injector(s) and
disconnect the electrical connector(s).
injector clogging include higher than normal
operating temperatures, short operating intervals, and
dirty, incorrect, or poor quality fuel. Cleaning of
clogged injectors is not recommended; they should be
replaced. Additives and higher grades of fuel can be
used as a preventative measure if clogging has been a
problem.
Ignition System
General
A high voltage, solid state, battery ignition system is
used with the EFI system. The ECU controls the
ignition output and timing through transistorized
control of the primary current delivered to the coils.
Based on input from the speed sensor, the ECU
determines the correct firing point for the speed at
which the engine is running. At the proper instant, it
releases the flow of primary current to the coil. The
primary current induces high voltage in the coil
secondary, which is then delivered to the spark plug.
Each coil fires every revolution, but every other spark
is “wasted.”
Service
Except for removing the spark plug lead by
unscrewing it from the secondary tower (see Figure
5B-22), no coil servicing is possible. If a coil is
determined to be faulty, replacement is necessary. An
ohmmeter may be used to test the wiring and coil
windings.
5B
15. Pull the retaining clip off the top of the injector(s)
and remove from manifold.
16. Reverse the appropriate procedures to install the
new injector(s) and reassemble the engine. Use
new O-Rings any time an injector is removed
(new replacement injectors include new O-Rings).
Lubricate O-Rings lightly with oil. Torque the fuel
rail and blower housing mounting screws to
3.9 N·m (35 in. lb.), and the intake manifold and
air cleaner mounting screws to 9.9 N·m
(88 in. lb.).
Injector problems due to dirt or clogging are generally
unlikely, due to the design of the injectors, the high
fuel pressure, and the detergent additives in the
gasoline. Symptoms that could be caused by dirty/
clogged injectors include rough idle, hesitation/
stumble during acceleration, or triggering of fault
codes related to fuel delivery. Injector clogging is
usually caused by a buildup of deposits on the
director plate, restricting the flow of fuel, resulting in
a poor spray pattern. Some contributing factors to
Figure 5B-22. Ignition Coil.
NOTE: Do not ground the coils with the ignition
‘‘on,’’ as they may overheat or spark.
T esting
1. Disconnect the main harness connector from ECU.
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Locate pins
#1 and #19 in the 35 pin connector. See page 5B.28.
5B.17
Page 87

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Locate
pins #22 and #23 in the 24 pin connector. See page
5B.31.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic Cased ECU: Locate
pins #30 and #31 in the 32 pin connector. See page
5B.32.
2. Disconnect connector from relay and locate
terminal #87 in connector.
3. Using an ohmmeter set on the Rx1 scale, check
the resistance in circuits as follows:
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU: Check
between terminal #87 and pin #1 for coil #1.
Repeat the test between terminal #87 and pin #19
for coil #2.
“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU: Check
between terminal #87 and pin #22 for coil #1.
Repeat the test between terminal #87 and pin #23
for coil #2.
“32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU: Check
between terminal #87 and pin #30 for coil #1.
Repeat the test between terminal #87 and pin #31
for coil #2.
A reading of 1.8-4.0
the wiring and coil primary circuits are OK.
ΩΩ
Ω in each test indicates that
ΩΩ
4. If the secondary resistance is not within
the specified range, unscrew the spark
plug lead nut from the coil secondary
tower and remove the plug lead. Repeat
step b. 3, testing from the secondary
tower terminal to the red primary
terminal. If resistance is now correct, the
coil is good, but the spark plug lead is
faulty, replace the lead. If step b. 2
resistance was incorrect and/or the
secondary resistance is still incorrect, the
coil is faulty and needs to be replaced.
Spark Plugs
EFI engines are equipped with Champion® RC12YC
(Kohler Part No. 12 132 02-S) resistor style spark
plugs. Equivalent alternate brand plugs can also be
used, but must be a resistor style plug or permanent
damage to the ECU will occur in addition to affecting
operation. Proper spark plug gap is 0.76 mm
(0.030 in.).
Wiring Harness
The wiring harness used in the EFI system connects
the electrical components, providing current and
ground paths for the system to operate. All input and
output signaling occurs through a special all weather
connector that attaches and locks to the ECU (see
Figures 5B-23, 5B-24, and 5B-25).
a. If reading(s) are not within specified range,
check and clean connections and retest.
b. If reading(s) are still not within the specified
range, test the coils separately from main
harness as follows:
1. Disconnect the red and black primary
leads from the coil terminals.
2. Connect an ohmmeter set on the Rx1
scale to the primary terminals. Primary
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
5B.18
resistance should be 1.8-2.5
3. Disconnect the secondary lead from the
spark plug. Connect an ohmmeter set on
the Rx10K scale between the spark plug
boot terminal and the red primary
terminal. Secondary resistance should be
13,000-17,500
ΩΩ
Ω.
ΩΩ
Figure 5B-23. “35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU
Connector and O-Ring.
Page 88

Fuel Components
Fuel Pump
Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Figure 5B-24. “24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU
Connector.
Figure 5B-25. “32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU
Connector.
The condition of the wiring, connectors, and terminal
connections is essential to system function and
performance. Corrosion, moisture, and poor
connections are more likely the cause of operating
problems and system errors than an actual
component. Refer to the ‘‘Troubleshooting –
Electrical’’ section for additional information.
Battery Charging System
EFI engines are equipped with either a 15 or 25 amp
charging system to accommodate the combined
electrical demands of the ignition system and the
specific application. Charging system troubleshooting
information is provided in Section 8.
Internal
Figure 5B-26. Fuel Pump Styles.
General
An electric fuel pump is used to transfer fuel in the
EFI system. Depending on the application, the pump
may be inside the fuel tank, or in the fuel line near the
tank. The pumps are rated for a minimum output of
25 liters per hour at 39 psi. The pumps have an
internal 60-micron filter. In addition, the in-tank style
pumps will have a pre-filter attached to the inlet. Inline pump systems may also have a filter ahead of the
pump on the pick-up/low pressure side. The final
filter is covered separately on page 5B.22.
When the key switch is turned “on” and all safety
switch requirements are met, the ECU through the
relay, activates the fuel pump, which pressurizes the
system for start-up. If the key switch is not promptly
turned to the “start” position, the engine fails to start,
or the engine is stopped with the key switch “on” (as
in the case of an accident), the ECU switches off the
pump preventing the continued delivery of fuel. In
this situation, the MIL will go on, but it will go back
off after 4 cranking revolutions if system function is
OK. Once the engine is running, the fuel pump
remains on.
Service
The fuel pumps are non-serviceable and must be
replaced if determined to be faulty. If a fuel delivery
problem is suspected, make certain the pump is being
activated through the relay, all electrical connections
are properly secured, the fuses are good, and a
minimum of 7.0 volts is being supplied. If during
cranking, voltage drops below 7.0 volts, a reduction of
fuel pressure may occur resulting in a lean starting
condition. If required, testing of the fuel pump and
relay may be conducted.
External
5B
5B.19
Page 89

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
1. Connect the black hose of Pressure Tester (part of
EFI Service Kit, see Section 2), to the test valve in
the fuel rail. Route the clear hose into a portable
gasoline container or the equipment fuel tank.
2. Turn on the key switch to activate the pump and
check the system pressure on the gauge. If system
pressure of 39 psi ± 3 is observed, the relay, fuel
pump, and regulator are working properly. Turn
the key switch off and depress the valve button
on the tester to relieve the system pressure.
a. If the pressure is too high, and the regulator is
outside the tank (just down line from the
pump), check that the return line from the
regulator to the tank is not kinked or blocked.
If the return line is good, replace the regulator
(see ‘‘Regulator Service’’ on page 5B.21).
b. If the pressure is too low, install in-line ‘‘T’’
between the pump and regulator and retest
the pressure at that point. If it is too low there
also, replace the fuel pump.
3. If the pump did not activate (step 2), disconnect
the plug from the fuel pump. Connect a DC
voltmeter across the terminals in the plug, turn
on the key switch and observe if a minimum of 7
volts is present. If voltage is between 7 and 14,
turn key switch off and connect an ohmmeter
between the terminals on the pump to check for
continuity.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
Figure 5B-27. External Fuel Pressure Regulators
with Base.
a. If there was no continuity between the pump
terminals, replace the fuel pump.
b. If the voltage was below 7, test the wiring
harness and relay as covered in the ‘‘Electrical
Relay’’ section.
4. If voltage at the plug was good, and there was
continuity across the pump terminals, reconnect
the plug to the pump, making sure you have a
good connection. Turn on the key switch and
listen for the pump to activate.
a. If the pump starts, repeat steps 1 and 2 to
verify correct pressure.
b. If the pump still does not operate, replace it.
5B.20
Figure 5B-28. Internal Fuel Pressure Regulator.
General
The fuel pressure regulator assembly maintains the
required operating system pressure of 39 psi ± 3. A
rubber-fiber diaphragm (see Figure 5B-29) divides the
regulator into two separate sections; the fuel chamber
and the pressure regulating chamber. The pressure
regulating spring presses against the valve holder
(part of the diaphragm), pressing the valve against the
valve seat. The combination of atmospheric pressure
and regulating spring tension equals the desired
operating pressure. Any time the fuel pressure against
the bottom of the diaphragm exceeds the desired (top)
pressure, the valve opens, relieving the excess
pressure, returning the excess fuel back to the tank.
Page 90

Pressure
Regulating
Spring
Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Pressure
Regulating
Chamber
Diaphragm
Valve
Inlet Port
Return Port (to tank)
Figure 5B-29. Fuel Pressure Regulator Details.
Service
Depending on the application, the regulator may be
located in the fuel tank along with the fuel pump, or
outside the tank just down line from the pump. The
regulator is a sealed, non-serviceable assembly. If it is
faulty, it must be separated from the base/holder
assembly and replaced as follows:
1. Shut engine off, make sure engine is cool, and
disconnect the negative (-) battery cable.
2. Depressurize fuel system through test valve in
fuel rail (see fuel warning on page 5B.2).
3. Access the regulator assembly as required and
clean any dirt or foreign material away from the
area.
Valve Seat
Fuel Chamber
Outlet Port
(to fuel rail)
5B
Figure 5B-30. External Regulators and Base/
Holders.
Figure 5B-31. Internal Regulator and Base/Holder.
4. External Regulator -
Based upon the style of regulator used (see Figure
5B-30):
a. Remove the two screws securing the
mounting bracket to the regulator housing.
Remove the O-Ring and pull the regulator out
of the housing.
b. Remove the snap ring and remove regulator
from base/holder.
Internal (In-Tank) Regulator -
Remove the three screws securing the retaining
ring and regulator in the base/holder assembly.
Grasp and pull the regulator out of the base/
holder. See Figure 5B-31.
5. Always use new O-Rings and hose clamps
when installing a regulator. A new replacement
regulator will have new O-Rings already
installed. Lubricate the O-Rings (external
regulator) with light grease or oil.
6. a. Install the new regulator by carefully pushing
and rotating it slightly into the base or
housing.
b. External Regulators with Square Base
Housing Only; Install a new O-Ring between
the regulator and the mounting bracket. Set
the mounting bracket into position.
c. Secure the regulator in base with the original
retaining ring or screws. Be careful not to dent
or damage the body of the regulator as
operating performance can be affected.
7. Reassemble any parts removed in step 3.
5B.21
Page 91

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
8. Reconnect the negative (-) battery cable.
9. Recheck regulated system pressure at fuel rail test
valve.
Fuel Filter
EFI engines use a high-volume, high-pressure, 10-15
micron, in-line fuel filter.
Figure 5B-32. In-Line Fuel Filter.
General
The fuel rail is a formed tube assembly that feeds fuel
to the top of the injectors. The tops of the injectors fit
into formed cups in the fuel rail. When the rail is
fastened to the manifold, the injectors are locked into
place. A small retaining clip provides a secondary
lock. Incorporated into the fuel rail is a pressure relief/
test valve for testing operating pressure or relieving
fuel system pressure for servicing. The fuel supply
line is attached to the barbed end of the fuel rail with
an Oetiker hose clamp.
Service
The fuel rail is mounted to the throttle body/intake
manifold. It can be detached by removing the two
mounting screws and the injector retaining clips.
Thoroughly clean the area around all joints prior to
any disassembly. No specific servicing is required
unless operating conditions indicate that it needs
internal cleaning or replacement.
Fuel Line
Service
Fuel filter replacement is recommended every 1500
hours of operation or more frequently under
extremely dusty or dirty conditions. Use only the
specified filter, and install it according to the
directional arrows. Do not use a substitute filter as
operating performance and safety can be affected.
Relieve system pressure through the safety valve in
the fuel rail before servicing.
Fuel Rail
Fuel Rail
TPS
Locking Clip
Figure 5B-33. Manifold Assembly .
Fuel
Injector
Figure 5B-34. High Pressure Fuel Line.
General
Special low permeation high-pressure fuel line with
an SAE30 R9 rating is required for safe and reliable
operation, due to the higher operating pressure of the
EFI system. If hose replacement is necessary, order
Fuel Line Service Kit, Part No. 25 111 37-S (containing
60" of high-pressure hose and 10 Oetiker clamps), or
use only the type specified. Special Oetiker clamps
(Kohler Part No. 24 237 05-S) are used on all fuel line
connections to prevent tampering and safety hazards
with the high fuel pressure. The old clamp must be
cut to open a connection, so replacement is necessary
each time. Oetiker Clamp Pliers (part of EFI Service
Kit, see Section 2) is used to crimp the replacement
clamps.
5B.22
Page 92

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
CAUTION:
Fuel lines between the fuel pump and fuel rail must be made
from SAE 30 R9 fuel line. Standard fuel line (SAE 30 R7)
may only be used between the fuel tank and pump (5/16”
ID) and for the return line from the pressure regulator to
the tank (1/4” ID). All high-pressure fuel line connections
must be secured with Oetiker Clamps (Kohler Part No.
24 237 05-S), installed/crimped with the corresponding
pliers.
Throttle Body/Intake Manifold Assembly
Low Idle Speed
Adjusting Screw
Throttle Body
Intake Manifold
Fuel Rail
For starting and warm up, the ECU will adjust the
fuel and ignition timing, based upon ambient
temperature, engine temperature, and loads present.
In cold conditions, the idle speed will probably be
higher than normal for a few moments. Under other
conditions, the idle speed may actually start lower
than normal, but gradually increase to the established
setting as operation continues. Do not attempt to
circumvent this warm up period, or readjust the idle
speed during this time. The engine must be completely
warmed up for accurate idle speed adjustment.
Adjustment Procedure
1. Make sure there are no fault codes present in the
ECU memory.
2. Start the engine and allow it to fully warm up
and establish closed looped operation
(approximately 5-10 min.).
3. Place the throttle control in the ‘‘idle/slow’’
position and check the idle speed with a
tachometer. Turn the idle speed screw in or out as
required to obtain 1500 RPM, or the idle speed
specified by the equipment manufacturer.
5B
Figure 5B-35. Upper Intake Manifold.
General
The EFI engines have no carburetor, so the throttle
function (regulate incoming combustion airflow) is
incorporated in the intake manifold assembly. The
manifold consists of a one-piece aluminum casting
which also provides mounting for the fuel injectors,
throttle position sensor, fuel rail, air baffle, idle speed
screw, and air cleaner assembly.
Service
The throttle body/intake manifold is serviced as an
assembly, with the throttle shaft, throttle plates, and
idle speed adjusting screw installed. The throttle shaft
rotates on needle bearings (non-serviceable), capped
with rubber seals to prevent air leaks.
Idle Speed Adjustment (RPM)
General
The idle speed is the only adjustment that may be
performed on the EFI system. The standard idle speed
setting for EFI engines is 1500 RPM, but certain
applications might require a different setting. Check
the equipment manufacturer’s recommendation.
4. The low idle speed adjustment can affect the high
speed setting. Move the throttle control to the full
throttle position and check the high speed. Adjust
as necessary to 3750 RPM (no load), or the speed
specified by the equipment manufacturer.
Idle Speed Screw Dampening Spring
A small dampening spring (Kohler Part No.
24 089 42-S) is attached to the end of the idle speed
screw of some EFI engines to help stabilize no load
operating speeds. See Figure 5B-36.
5B.23
Page 93

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Dampening
Spring
(Some Models)
Figure 5B-36. Idle Speed Screw Details.
The idle speed adjustment procedure remains the
same for engines with or without a dampening spring.
Typically, no periodic servicing is necessary in this
area. If however, removal/replacement of the
dampening spring is required, reinstall it as follows:
1-3 mm (0.039-0.117 in.)
Exposed Length Off End
Of Adjustment Screw
Idle Speed Screw
If the governor/throttle components are all intact, but
you think there may be a problem with the
adjustment, follow Procedure A to check the setting. If
the governor lever was loosened or removed, go
immediately to Procedure B to perform the initial
adjustment.
A. Checking the Initial Adjustment
1. Unsnap the plastic linkage bushing attaching the
throttle linkage to the governor lever. See Figure
5B-37. Unhook the damper spring from the lever,
separate the linkage from the bushing, and
remove the bushing from the lever. Mark the hole
position and unhook the governor spring from
the governor lever.
Throttle
Linkage
Linkage
Bushing
Damper
Spring
1. Thread the spring onto the end of idle screw
leaving 1-3 mm (0.039-0.117 in.) of the spring
extending beyond the end of the idle speed screw.
2. Secure spring onto the screw with a small amount
of Permabond
adhesive. Do not get any adhesive on free coils of
spring.
3. Start the engine and recheck the idle speed
settings, after sufficient warm up. Readjust as
required.
™
LM-737 or equivalent Loctite
®
Initial Governor Adjustment
The initial governor adjustment is especially critical
on EFI engines because of the accuracy and sensitivity
of the electronic control system. Incorrect adjustment
can result in overspeed, loss of power, lack of
response, or inadequate load compensation. If you
encounter any of these symptoms and suspect them to
be related to the governor setting, the following
should be used to check and/or adjust the governor
and throttle linkage.
Figure 5B-37. Throttle Linkage/Governor Lever
Connection.
2. Check if the engine has a high-speed throttle stop
screw installed in the manifold casting boss. See
Figure 5B-38.
High-Speed
Throttle Stop Screw
Figure 5B-38. Throttle Details.
5B.24
Page 94

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
a. On engines without a stop screw, pivot the
throttle shaft and plate assembly into the “Full
Throttle” position. Insert a 1.52 mm (0.060 in.)
feeler gauge between the rear tang of the
throttle shaft plate and the underside of the
manifold boss. Use a locking pliers (needle
nose works best) to temporarily clamp the
parts in this position. See Figure 5B-39.
Feeler Gauge
Figure 5B-39. Inserting Feeler Gauge (Engines
Without Stop Screw).
B. Setting the Initial Adjustment
1. Check the split where the clamping screw goes
through the governor lever. See Figure 5B-41.
There should be a gap of at least 1/32". If the tips
are touching and there is no gap present, the lever
should be replaced. If not already installed,
position the governor lever on the cross shaft, but
leave the clamping screw loose.
5B
Figure 5B-41. Checking ‘‘Split’’ of Clamp.
b. On engines with a stop screw, pivot the
throttle shaft and plate into the “Full Throttle”
position, so the tang of the throttle shaft plate
is against the end of the high-speed stop
screw. See Figure 5B-38. Temporarily clamp in
this position.
3. Rotate the governor lever and shaft
counterclockwise until it stops. Use only enough
pressure to hold it in that position.
4. Check how the end of the throttle linkage aligns
with the bushing hole in the governor lever. See
Figure 5B-40. It should fall in the center of the
hole. If it doesn’t, perform the adjustment
procedure as follows.
2. Follow the instructions in Step 2 of ‘‘Checking the
Initial Adjustment,’’ then reattach the throttle
linkage to the governor lever with the bushing
clip. It is not necessary to reattach the damper or
governor springs at this time.
3. Insert a nail into the hole in the top of the cross
shaft. Using light pressure, rotate the governor
shaft counterclockwise as far as it will turn, then
torque the hex nut on the clamping screw to
6.8 N·m (60 in. lb.). See Figure 5B-42. Make sure
that the governor arm has not twisted up or
down after the nut has been tightened.
Figure 5B-40. Throttle Link in Center of Hole.
Figure 5B-42. Adjusting Governor Shaft.
5B.25
Page 95

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
4. Verify that the governor has been set correctly.
With the linkage still retained in the “Full
Throttle” position (Step 2), unsnap the bushing
clip, separate the linkage from the bushing, and
remove the bushing from the lever. Follow Steps
3 and 4 in ‘‘Checking the Initial Adjustment’’.
5. Reconnect the dampening spring into its
governor lever hole from the bottom. Reinstall
the bushing and reattach the throttle linkage. See
Figure 5B-37. Reattach the governor spring in the
marked hole.
6. Start the engine and allow it to fully warm up
and establish closed loop operation
(approximately 5-10 min.). Check the speed
settings and adjust as necessary, first the low idle
speed, and then the high speed setting.
Troubleshooting
General
When troubleshooting a problem on an engine with
EFI, basic engine operating problems must be
eliminated first before faulting the EFI system
components. What appears to be an EFI problem
could be something as simple as a fuel tank with
debris in the bottom or a plugged vent. Be sure the
engine is in good mechanical operating condition, and
all other systems are functional before attempting to
troubleshoot the EFI system.
Engine starts hard or fails to start when hot
1. Faulty spark plugs
2. Fuel pump not running
3. Fuel pressure low
4. Insufficient fuel delivery
5. TPS offset incorrect (Initialization)
6. Speed sensor loose or faulty
7. TPS faulty
8. Engine temperature sensor faulty
9. Faulty injectors
Engine stalls or idles roughly (cold or warm)
1. Faulty spark plugs
2. Insufficient fuel delivery
3. TPS offset incorrect
4. TPS faulty
5. Faulty engine temperature sensor
6. Faulty injectors
Engine misses, hesitates, or stalls under load
1. Fuel injector(s), fuel filter, fuel line, or fuel pickup dirty/restricted
2. Dirty air cleaner
3. Insufficient fuel pressure or fuel delivery
4. Vacuum (intake air) leak
5. Improper governor setting, adjustment or
operation
6. Speed sensor malfunction
7. TPS faulty, mounting problem or "TPS
Initialization Procedure" incorrect
8. Bad coil(s), spark plug(s), or wires
Troubleshooting Guide
Engine starts hard or fails to start when cold
1. Fuel pump not running
2. Faulty spark plugs
3. Old/stale fuel
4. Incorrect fuel pressure
5. Speed sensor loose or faulty
6. TPS offset incorrect (initialization)
7. TPS faulty
8. Engine temperature sensor faulty
9. Faulty coils
10. Low system voltage
11. Faulty injectors
5B.26
Low Power
1. Faulty/malfunctioning ignition system
2. Dirty air filter
3. Insufficient fuel delivery
4. Improper governor adjustment
5. Plugged/restricted exhaust
6. One injector not working
7. Basic engine problem exists
8. TPS faulty or mounting exists
9. Throttle plates in throttle body/intake manifold
not fully opening to WOT stop (if so equipped)
Page 96

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Electrical System
The EFI system is a 12 VDC negative ground system,
designed to operate down to a minimum of 7.0 volts. If
system voltage drops below this level, the operation of
voltage sensitive components such as the ECU, fuel
pump, and injectors will be intermittent or disrupted,
causing erratic operation or hard starting. A fully
charged, 12 volt battery with a minimum of 350 cold
cranking amps is important in maintaining steady and
reliable system operation. Battery condition and state
of charge should always be checked first when
troubleshooting an operational problem.
Keep in mind that EFI-related problems are more often
caused by the wiring harness or connections than by
the EFI components. Even small amounts of corrosion
or oxidation on the terminals can interfere with the
milliamp currents used in system operation. Cleaning
the connectors and grounds will solve problems in
many cases. In an emergency situation, simply
disconnecting and reconnecting the connectors may
clean up the contacts enough to restore operation, at
least temporarily.
If a fault code indicates a problem with an electrical
component, disconnect the ECU connector and test for
continuity between the component connector
terminals and the corresponding terminals in the ECU
connector using an ohmmeter. Little or no resistance
should be measured, indicating that the wiring of that
particular circuit is OK. An illustrated listing of
numerical terminal locations, for each style of ECU/
connector is provided on pages 5B.28, 5B.31, or 5B.32.
5B.28 for “35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU
5B.31 for “24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU
5B.32 for “32 Pin” (MSE 1.1) Plastic-Cased ECU
NOTE: When performing voltage or continuity tests,
avoid putting excessive pressure on or
against the connector pins. Flat pin probes
are recommended for testing to avoid
spreading or bending the terminals.
5B
5B.27
Page 97

Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
“35 Pin” (MA 1.7) Metal-Cased ECU Systems
Pin #
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
Component
Ignition Coil #1
Not used
Engine Speed Sensor
ECU Production Test Terminal
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
TPS Initialization Terminal
Engine Ground
O2 Sensor
Not Used
Throttle Position Sensor
Not Used
Oil Temperature Sensor
Not Used
ECU Permanent Battery Voltage
ECU Switched Battery Voltage
Engine Ground
Ignition Coil #2
Vehicle Ground
Engine Speed Sensor
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Throttle Position Sensor
Not Used
Throttle Position Sensor/Oil Temperature Sensor
Power Relay
Not Used
Not Used
Malfunction Indicator Light
Not Used
Vehicle Ground
Not Used
Fuel Injectors
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
5B.28
Page 98

Page 99

Page 100

“24 Pin” (MSE 1.0) Plastic-Cased ECU Systems
Section 5B
EFI Fuel System
Pin #
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
Function
Permanent Battery Voltage
Switched Ignition Voltage
Safety Switch
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) and Temperature Sensor Ground
Not Used
Oil Temperature Sensor Input
Not Used
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Input
Speed Sensor Input
Speed Sensor Ground
Oxygen Sensor Input
Not Used (Oxygen Sensor Ground if needed)
Diagnostic Line
Throttle Position Supply Voltage
Battery Ground
Injector 1 Output
Injector 2 Output
Main Relay Output
Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL)
Not Used (Tach Output if needed)
Not Used
Ignition Coil #1 Output
Ignition Coil #2 Output
TPS Initialization Terminal
10
11
12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
5B
5B.31
 Loading...
Loading...