Page 1

i55 / i65 Scanners
A-61527
User’s
Guide
Page 2

Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Scanner features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Safety information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
MSDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Safety precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
User precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Safety and regulatory agency approvals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Environmental information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
EMC statements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
United States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Japan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Acoustic emission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Power system connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
What’s in the box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Site specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Installing the scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Installing the Kodak Driver Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Making connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Verifying for a USB port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Connecting the USB cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
SCSI connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
SCSI interface device ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Setting the SCSI terminator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Connecting the power cord to the scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Set up the input and output trays. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Unlocking the scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Turning on the scanner and finalizing Kodak Driver Software
installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Installing application software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Scanner components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Front view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Under the flatbed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
ADF Inside view. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Back view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Indicator lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3 Using the Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Turning the scanner on and off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Adjusting the input tray . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Installing and adjusting the output tray. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Lifting the flatbed cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Start and stop scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Document preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Scanning your documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Verifying your scanner installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Viewing test images . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Application software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
A-61527 May 2005 i
Page 3

4 Image Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Common terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Making camera selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Scan Validation Tool dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Starting the Scan Validation Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Using the TWAIN Datasource . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Buttons on the Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . 34
The Imaging tab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Scanning bi-tonal images . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Scanning color images . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Scanning grayscale images . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
The Paper tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Cropping values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Additional paper selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Compression tab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
The Dropout tab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
The Multifeed tab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
The Options tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
The Setup tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
The Info tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Using the ISIS Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Scanner Settings dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Buttons on the Scanner Settings dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Image Processing settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Page size and layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
More Scanner Settings dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Image Control options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Color Dropout options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Scanner Control dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Multi-Feed Detection options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Energy Saving features of the scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Transport Timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Defining the Scan area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Scan Area dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
5 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Cleaning procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Cleaning the feed rollers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Cleaning the feed module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Cleaning the imaging area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Cleaning the platen glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Replacement procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Replacing the feed module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Replacing the paper feed roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Replacing the input tray . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Replacing the flatbed cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Locking the scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Supplies and consumables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
ii A-61527 May 2005
Page 4

6 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Indicator lights and error codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Clearing a document jam . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Getting service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Problem solving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Scanner not working . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Testing for USB connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
USB connection issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Appendix A Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Appendix B Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
A-61527 May 2005 iii
Page 5

1 Introduction
The Kodak i55 and i65 Scanners are compact document scanners
perfect for workgroups and other decentralized applications. These
scanners have a 50-page automatic document feeder that scans 32
pages per minute at 200 dpi (bi-tonal), including a flatbed for nonfeedable documents. For your image processing needs, the TWAIN
Datasource and ISIS Driver are included with the Kodak i55/i65
Scanners.
• Kodak i55 Scanner — desktop simplex color scanner
• Kodak i65 Scanner — desktop duplex color scanner
This User’s Guide provides information and procedures for the Kodak
i55 and i65 Scanners using the TWAIN Datasource and ISIS Driver.
The information in this guide is for use with both scanner models unless
otherwise noted.
A-61527 May 2006 1
Page 6

Scanner features • Easy to use
• Small, compact size
• Scans up to 21.6 x 86 cm (8.5 x 34 in.) using the automatic document
feeder when the host PC is configured with adequate memory. See
the section entitled, “System requirements” for more information.
• Scans up to 8.5 x 11.69 inches / A3 using the flatbed
• Scans 32 ppm (200 dpi, bi-tonal, duplex, portrait orientation) lettersize documents
• Choose color, bi-tonal, grayscale, simultaneous bi-tonal and
grayscale, or simultaneous bi-tonal and color
• Easy cleaning and maintenance
• Output resolutions from 75 to 600 dpi
• Bundled ISIS and TWAIN drivers
• Length checking based on multi-feed detection
• Choice of USB 2.0 or SCSI II interface
Safety information
MSDS Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for chemical products are
available on the Kodak website at: www.kodak.com/go/msds. When
accessing the MSDSs from the website, you will be required to provide
the catalog number of the consumable you want the Material Safety
Data Sheet for. See the section entitled, “Supplies and consumables”
later in this guide for a listing of supplies and catalog numbers.
Safety precautions • Use only the power supply that was provided with the scanner (Sino-
American model SA60-24).
IMPORTANT: Do not substitute another power supply model or another
manufacturer’s power supply.
• Be sure to use the proper AC power source.
• Avoid danger of electric shock. Only use the scanner and power
supply indoors in a dry location.
• Do not install the scanner in a humid or dusty area.
2 A-61527 May 2006
Page 7
User precautions Users and their employer need to observe the common sense
precautions applicable to the operation of any machinery. These
include, but are not limited to, the following:
• Do not wear loose clothing, unbuttoned sleeves, etc.
• Do not wear loose jewelry, bracelets, bulky rings, long necklaces, etc.
• Hair length should be kept short, using a hair net if needed, or tying
long hair up in a bundle.
• Remove all other loose objects from the area that could be drawn into
the machine.
• Take sufficient breaks to maintain mental alertness.
• Follow the recommended Kodak cleaning procedures. Do not use air,
liquid or gas spray cleaners. These cleaners only displace the dust,
dirt or debris to another location within the scanner, which could
cause the scanner to malfunction.
Supervisors should review their practices and make compliance with
these precautions as a part of the job description for operation of the
Kodak i55/i65 Scanners or any mechanical device.
Safety and regulatory agency approvals
The Kodak i55 and i65 Scanners conform to applicable national and
international product safety and electronic emission regulatory
requirements. This includes, but is not limited to, the following:
Country or Region Safety Approval Safety Mark Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC Mark
Australia
Canada CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950 C - UL Canada ICES - 003 Issue 3 Class B
China GB4943 CCC
“S&E”
European Union
Germany EN 60950 TUV GS
International IEC 60950 CISPR 22 Class B
Japan VCCI Class B VCCI
Tai wan CNS 13438 Class B BSMI
United States UL 60950 UL CFR 47 Part 15 Subpart B
CE EN 55022
AS/NZS CISPR 22 Class B C-Tick
GB 9254 Class B
GB 17625.1 Harmonics
ITE Emissions Class B
EN61000-3-2
Powerline harmonics
EN 61000-3-3 Flicker
EN 55024 ITE Immunity
FCC Class B
CCC
“S&E”
CE
A-61527 May 2006 3
Page 8

Environmental information
• The Kodak i55 and i65 Scanners are designed to meet worldwide
environmental requirements.
• Guidelines are available for the disposal of consumable items that
are replaced during maintenance or service; follow local regulations
or contact Kodak locally for more information.
• The Kodak i55 and i65 Scanners contain lead in the circuit board
solder, glass lens and mercury in the lamps. Disposal of this material
may be regulated due to environmental considerations. For disposal
or recycling information, contact your local authorities or, in the USA,
visit the Electronics Industry Alliance website: www.eiae.org.
• The product packaging is recyclable.
• The Kodak i55 and i65 Scanners are Energy Star compliant and are
shipped from the factory with the default time set to 15 minutes.
EMC statements
United States This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class B digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
additional suggestions.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate
the equipment. Where shielded interface cables have been provided
with the product or specified additional components or accessories
elsewhere defined to be used with the installation of the product, they
must be used in order to ensure compliance with FCC regulation.
4 A-61527 May 2006
Page 9

Japan This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary
Control Council for interference by information Technology Equipment
(VCCI). If this is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic
environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use the
equipment according to the instruction manual.
Acoustic emission Maschinenlärminformationsverordnung – 3, GSGV
Der arbeitsplatzbezogene Emissionswert beträgt <70 db(A).
[Machine Noise Information Ordinance — 3, GSGV
The operator-position noise emission value is <70 dB(A).]
Power system connection
This product is also designed for Norwegian IT power system with
phase-to-phase voltage 230V.
A-61527 May 2006 5
Page 10

2 Getting Started
What’s in the box Before you begin open the box and check the contents:
• Kodak i55 or i65 Scanner (with input tray and flatbed cover)
• Output tray
• Feed module
• USB 2.0 cable
• Power supply
• Power cord bundle(s)
• Welcome Folio which includes:
- Bundled installation and application CD(s)
- Registration sheets
- Printed User’s Guide, English
-Quick Tips Guide
- Quick Installation Guide
- Service Contact sheets
- Miscellaneous flyers
6 A-61527 May 2006
Page 11

System requirements Following is the recommended system configurations to run Kodak i55
and i65 Scanners.
Optimum requirements to match scanner capabilities:
• Intel Pentium IV, 2.5 GHz processor:
- 512 MB RAM for scanning documents no longer than 35.56 cm
(14 in.) in length in color, grayscale, or bi-tonal at 400 dpi.
- 2 GB RAM for scanning documents no longer than 86.36 cm
(34 in.) in length in color, grayscale, or bi-tonal at 400 dpi.
- 2 GB RAM for scanning documents no longer than 35.56 cm
(14 in.) in length in color, grayscale, or bi-tonal at 600 dpi.
- 3 GB RAM for scanning documents no longer than 86.36 cm
(34 in.) in length in grayscale or bi-tonal at 600 dpi
• USB port 2.0 (best) or SCSI II
• Windows 2000 Professional or Windows XP (Professional/Home)
• 15 MB free hard disk space is required to install the drivers.
Applications and image storage will require additional hard disk
space.
• CD-ROM drive
Minimum requirements to allow basic scanner operation:
The following minimum requirements may not achieve the rated speed
of the scanner.
• Intel Pentium III, 1 GHz processor, 512 MB RAM
• USB port 1.1 or SCSI
• Windows 2000 Professional, Windows ME, Windows 98SE, or
Windows XP (Professional/Home)
• 15 MB free hard disk space is required to install the drivers.
Applications and image storage will require additional hard disk
space.
• CD-ROM drive
NOTE: The ability to scan longer documents or very high resolutions is
somewhat dependent on the available host PC memory.
Differences in memory use between scanning applications may
account for some issues scanning a long document at very high
resolution. While the memory guidelines above are
conservative, your experience may vary depending on your host
PC configuration and scanning application.
A-61527 May 2006 7
Page 12

Installation Unpack the scanner carefully and check the contents. If any items are
missing or damaged, contact your authorized dealer immediately.
Site specifications Place the scanner:
• in a clean area with temperature and relative humidity typical of an
office environment.
IMPORTANT: Only use the scanner and power supply indoors in a dry
location.
• in a location out of sunlight. Direct exposure to sun or excessive heat
may cause damage to the unit and will affect image quality.
• on a stable, level work surface capable of supporting 7.5 kg
(16.5 lbs.). Tilted or uneven surfaces may cause mechanical or
paper-feeding problems.
• within 1.52 meters (5 feet) of an easily accessible electrical power
outlet.
Keep the scanner box and packing materials for shipping purposes.
Installing the scanner Install the scanner in the following order:
1. Install the Kodak Driver Software.
2. Verify that you have either a USB or SCSI connection and connect
the cables between your scanner and the PC.
3. Connect the power cord to the scanner.
4. Set up the input and output trays.
5. Unlock the scanner.
6. Turn on the scanner.
7. Restart the PC (required for SCSI II connection) to finalize the
Kodak Driver Software installation.
8. Install other supplied applications (optional).
IMPORTANT:
• Install the Kodak Driver Software on the host PC before you
connect the scanner.
• For best performance, use USB 2.0 when possible.
8 A-61527 May 2006
Page 13
Installing the Kodak Driver Software
Install the Kodak Driver Software before connecting the scanner to
your PC. The Kodak Driver Software consists of the Kodak Scanner
Drivers using the TWAIN Datasource and ISIS Driver to be used with
either USB and SCSI II connections.
1. Insert the Kodak i55/i65 Scanner Installation CD in the CD-ROM
drive. The installation program starts automatically.
NOTE: If the CD does not start automatically, open the My
Computer icon on your desktop. Double-click the icon for
your CD-ROM drive, then double-click on Setup.exe.
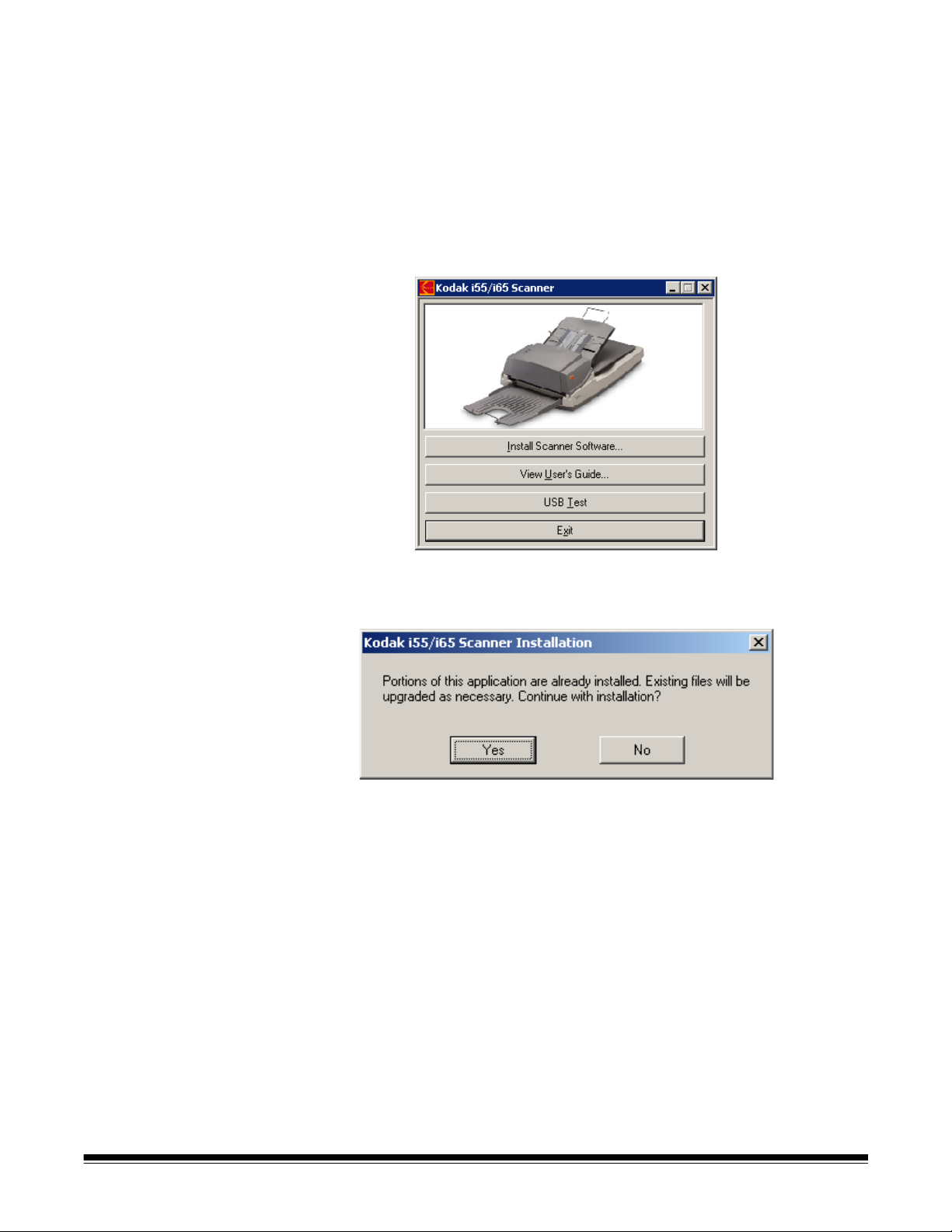
2. Select Install Scanner Software.
The Kodak i55/i65 Scanner Installation window may be displayed:
NOTE: This window may or may not be displayed depending upon what
was previously installed on your computer.
A-61527 May 2006 9
Page 14

3. Click Yes. The Welcome window will be displayed:
4. Click Next. The Software License Agreement window will be
displayed:
5. After reading the agreement, click I Agree to continue.
10 A-61527 May 2006
Page 15
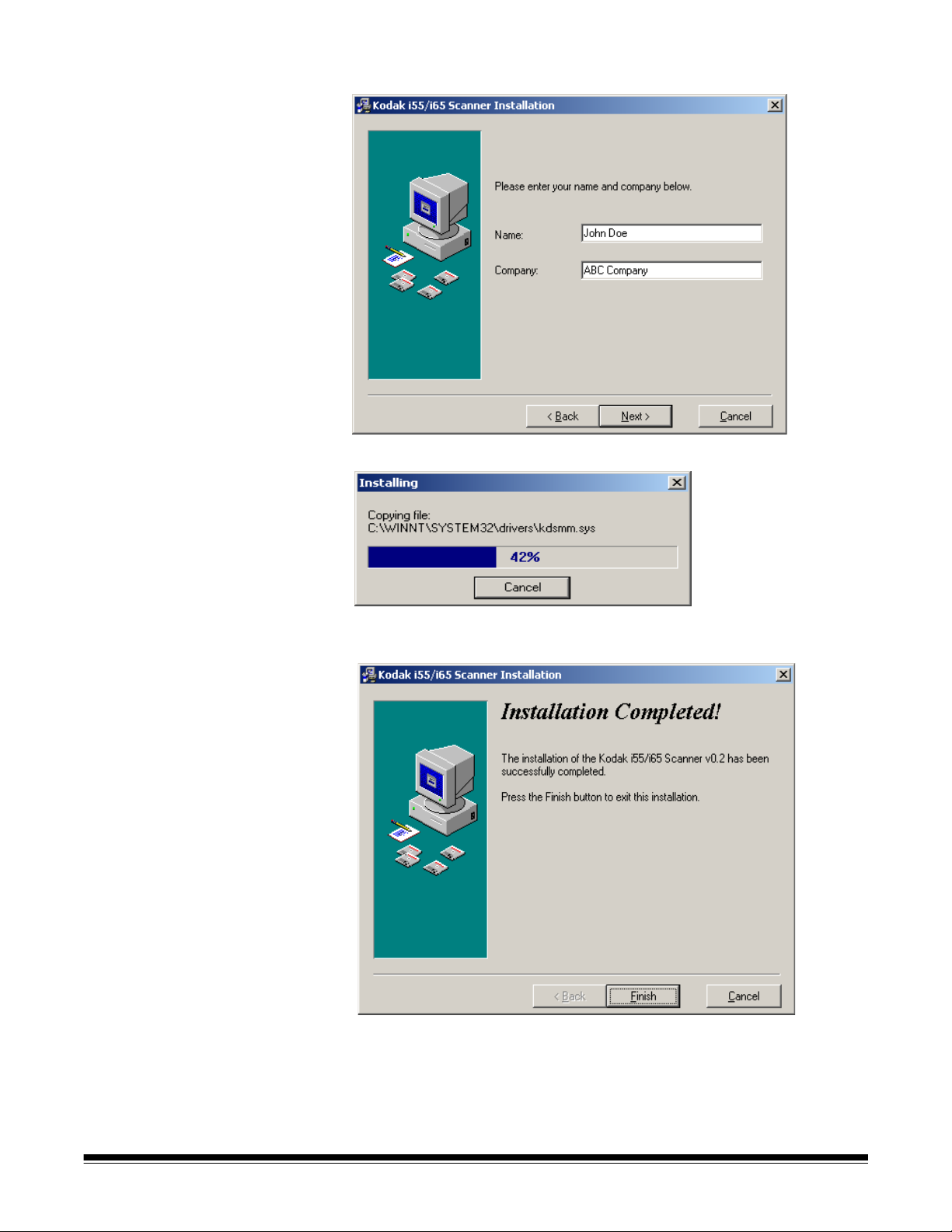
6. Enter your name and company name and click Next.
7. When the installation is complete, the following dialog box will be
displayed:
8. Click Finish.
A-61527 May 2006 11
Page 16
Making connections The Kodak i55/i65 Scanners can accommodate either a USB or SCSI
connection. Depending upon whether you are connecting USB or SCSI,
go to the one of the following sections.
USB connections
Verifying for a USB port After you install the Kodak Driver Software, check for the presence and
version of a USB port.
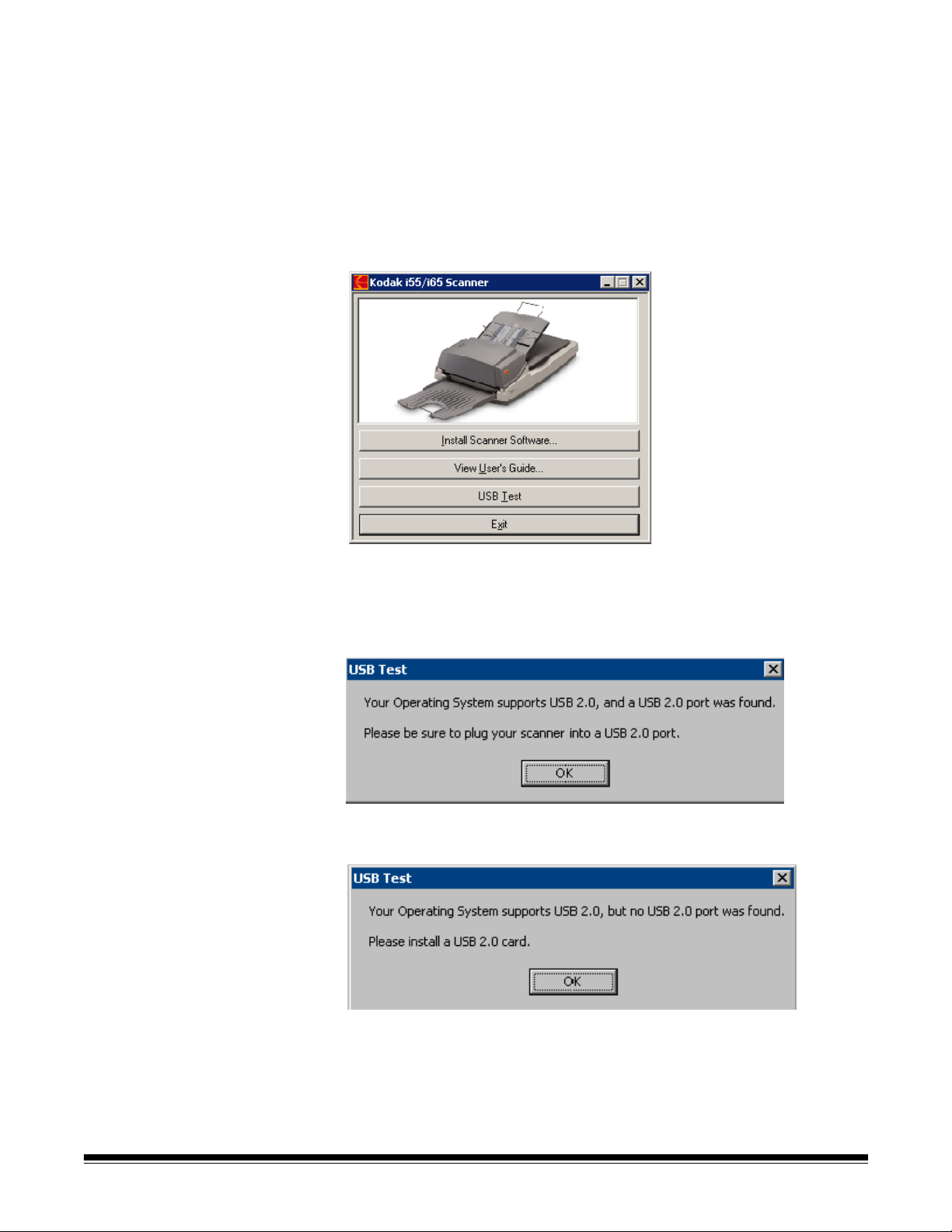
• Select USB Test.
The USB verification tool will check your operating system and
hardware capability to determine if you need to install a USB card.
• If a functioning USB 2.0 port is present, the following window will be
displayed. Click OK and proceed with the next section.
• If your PC does not have a USB 2.0 port installed, you should install a
USB 2.0 Accessory card..:
• If you get any message other than either of the messages above, see
the section entitled, “USB connection issues” in Chapter 6,
Troubleshooting.
12 A-61527 May 2006
Page 17
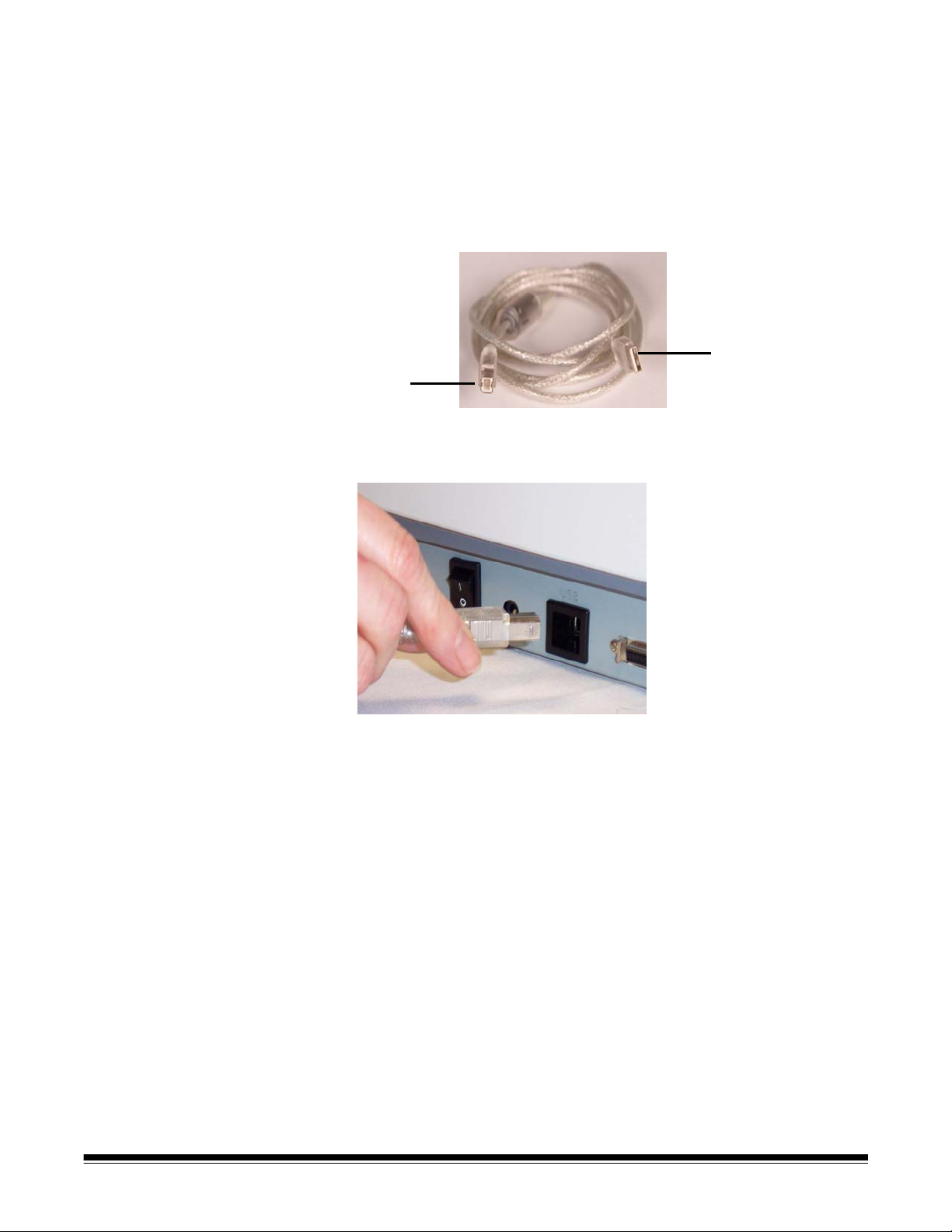
Connecting the USB cable IMPORTANT: If you have not installed the Kodak Driver Software,
do that now before proceeding.
The following instructions explain the connection of the USB cable
between your scanner and PC. You need to identify the USB port on
your PC. If you installed a USB 2.0 card, use that port, otherwise use
the USB port on your PC.
The USB cable supplied with your scanner has two different ends.
A
B
1. Attach the B end of the USB cable to the scanner USB port, located
on the back of the scanner.
2. Attach the A end of the USB cable to the proper USB port on your
PC.
A-61527 May 2006 13
Page 18

SCSI connections IMPORTANT: Be sure the PC is off while you are doing the steps in
the “SCSI connections” section.
Connect the SCSI signal cable as shown below.
1. Attach a SCSI cable to the SCSI port.
NOTE: There are two SCSI ports on the scanner. This is a SCSI II
pass-through connection. Plug the SCSI cable into either
port using a 50-pin, high-density connector to connect to
the scanner.
2. Attach the other end of the SCSI cable to your PC SCSI port.
SCSI interface device ID Kodak does not recommend several devices on a SCSI chain with our
scanner. However, if there is more than one SCSI device on the chain,
you may need to adjust the SCSI ID selector on the scanner. This
selector assigns a specific device ID to the scanner. If the assignment
conflicts with an existing SCSI device, select a new ID.
NOTE: The factory SCSI ID setting for the scanner is 6. SCSI ID 0 is
usually assigned to an internal hard disk drive and 7, 8, and 9
are used for diagnostic purposes. The scanner will not operate
properly if the SCSI ID is set to 7, 8, or 9.
• Using a suitable tool, turn the SCSI ID selector switch until the arrow
points to the desired ID number.
14 A-61527 May 2006
Page 19

Setting the SCSI terminator The scanner comes with a built-in SCSI terminator. The terminator ON/
OFF switch is located on the scanner between the SCSI cable
connectors.
• If the scanner is the only or the last device in a SCSI chain, place the
terminator switch in the ON position.
• If the scanner is to be located between the computer and another
SCSI device, place the terminator switch in the OFF position. Kodak
does not recommend the scanner to be connected between devices
in a SCSI chain.
Connecting the power cord to the scanner
When the drivers have been installed, connect the power supply and
power cord to the scanner. Make sure that the power outlet is located
within 1.52 meters (5 feet) of the scanner and is easily accessible.
Before proceeding, be sure the power to the scanner is off.
1. Select the appropriate AC power cord for your region from the
supply of power cords packed with your scanner.
NOTE: The power cord for the United States/Canada and China
look very similar. The difference is the United States/
Canadian power cord has holes in the prongs, and the
Chinese power cord does not.
United States
and Canada
China
2. Attach the power cord for your power type to the power supply.
A-61527 May 2006 15
Page 20
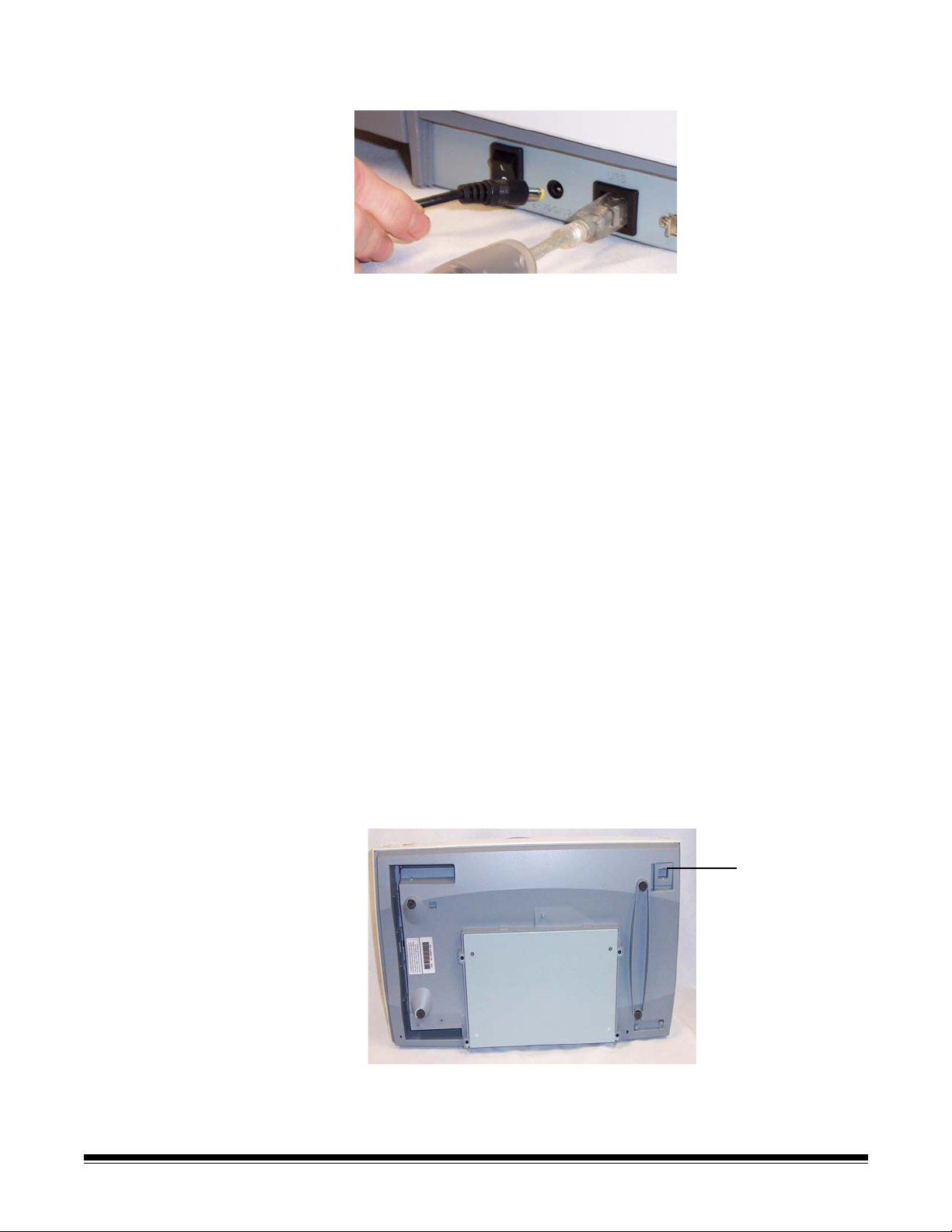
3. Plug the output power cord from the power supply into the power
port on the scanner.
4. Plug the input power cord into the wall outlet.
Set up the input and output trays
Detailed procedures and illustrations for installing and adjusting the
input and output trays can be found in Chapter 3, Using the Scanner.
Following is a brief outline of these procedures to get you started.
1. Lift the input tray to about a 45° angle.
2. Pull the input tray wire leg down.
3. Place the wire leg on the top of the clips on the flatbed cover and
press down to snap the wire leg into the clips.
4. Install the output tray by inserting the three tabs on the output tray
into the three slots on the automatic document feeder.
Unlocking the scanner The scanner has a shipping switch that locks the scanner’s flatbed
camera to avoid causing damage during transportation.
• Unlock the shipping switch before you power up the scanner.
• Lock the shipping switch before moving the scanner to a new
location. See the section entitled, “Locking the scanner” in Chapter 5
for procedures.
To unlock the scanner:
1. Place the scanner in an upright position on its front.
2. Unlock the scanner by moving the shipping switch (located on the
bottom of the scanner) down into the unlocked position.
Shipping
switch
3. Place the scanner back in its normal position.
16 A-61527 May 2006
Page 21

Turning the scanner on/ finalizing Kodak Driver Software installation
When the USB and/or SCSI cable and power connections have been
made, and the Kodak Software Drivers have been properly installed,
the installation will be complete when the PC and the scanner have
been powered up in the proper sequence.
1. Turn off the host PC.
2. Use the power switch on the back of the scanner to turn the scanner
on (I).
When you turn on the scanner, the scanner goes through a series of
self-tests, the green LED indicator will flash. When it is finished and
ready to scan, the indicator will stop flashing and stay lit. If the
scanner does not pass the self-test, refer to Chapter 6,
Troubleshooting.
3. Turn on the host PC.
Installing application software
The following screens are based on Windows 2000. However,
depending on the computer operating system you are using, these
screens may be different.
Your operating software will now auto detect the scanner.
4. To test the scanner, refer to the section entitled “Verifying your
scanner installation” in Chapter 3.
If the driver installation was unsuccessful, see the section entitled,
“Scanner not working” in Chapter 6, Troubleshooting.
The Kodak Scan Validation Tool is installed by default when installing
the Kodak Driver Software. Refer the section entitled, “Verifying your
scanner installation” in Chapter 3 for instructions and use.
Other scanning applications are also provided. If you choose to use one
of these applications, or another image capture application not
provided, see the User Guide’s provided with these applications for
instructions on how to install and use the software.
A-61527 May 2006 17
Page 22
Scanner components
Front view
Input tray
Side guides
Indicator lights
Output tray extension
Input tray extension
Balance wire
Flatbed cover
ADF cover
Output tray
Indicator lights — these indicator lights indicate the conditions of the
scanner. See the section entitled “Indicator lights” later in this section.
Side guides — slide the guides in or out to accommodate the
document size you want to scan. The balance wire must be lifted up
before you can adjust the side guides.
Input tray — place documents face-down in the input tray for scanning.
The input tray holds up to 50 documents.
Input tray extension — pull out to accommodate documents longer
than 36 cm (14 in.).
Balance wire — place the documents to be scanned in the input tray
and lower the balance wire to keep the documents in place and aid in
document feeding.
Flatbed cover — lift this cover to access the flatbed. The flatbed cover
can be easily lifted up to provide more clearance for scanning thick
books on the flatbed.
ADF cover — the ADF (automatic document feeder) lifts up to provide
access for maintenance and jam clearance.
Output tray — collects the scanned documents.
Output tray extension — pull out this extension when scanning
documents longer than A4 (8.5 x 11 inches).
18 A-61527 May 2006
Page 23

Under the flatbed cover
Reference
mark
Glass platen
Reference
frames
Reference mark — position the document you want to scan up against
the reference mark to ensure the entire document will be scanned.
Glass platen — place the document face-down on the glass platen for
scanning.
Reference frames — these reference frames, located around the
perimeter of the glass platen, provide a reference as to where to align
the document on the flatbed.
ADF Inside view
Feed module
Rollers
Release tab
Imaging area
Paper Feed
roller
Release tab
Feed module — provides smooth document feeding and separation of
various sizes, thicknesses and textures of documents.
Rollers — provides smooth document feeding of various sizes,
thicknesses and textures of documents.
Release tabs — use these tabs to release the Paper Feed roller cover
when you change the Paper Feed roller.
Imaging area — for optimum image quality keep the imaging area
clean.
A-61527 May 2006 19
Page 24

Back view
SCSI ports
Power
switch
Power
port
USB port
Terminator
switch
Power switch — turns the scanner on and off.
Power port — connects the power cord to the scanner.
USB port — connects the scanner to the PC.
SCSI ports — two 50-pin, high-density connectors provide SCSI
connections to the scanner.
Terminator switch — allows you to turn SCSI termination on or off if
the scanner is at the middle or the end of a SCSI chain.
SCSI ID selector — allows you to assign a specific SCSI device ID to
the scanner.
Indicator lights There are three indicator lights on the ADF.
When you first turn on the scanner, all three lights illuminate
momentarily and then flash as the scanner goes through a series of
self-tests. The lights will flash accordingly.
SCSI ID
selector
Power (green) — illuminates and stays on for power.
Ready (green)
• flashes when the lamps are warming up
• illuminates when the scanner is ready to scan
• off when the scanner is in Standby mode
Error (red) — illuminates or flashes when there is an error condition.
NOTE: When the scanner is in Energy Star Saving mode, all the
indicators will be off.
20 A-61527 May 2006
Page 25

3 Using the Scanner
Turning the scanner on and off
Adjusting the input tray
• Press the power switch on the back of the scanner to turn the
scanner on (I) or off (O).
When you turn on the scanner, it will go through a series of self-tests.
When completed, the green indicator light will remain on and constant.
Documents are placed into the input tray to be scanned through the
automatic document feeder.
To adjust the input tray:
1. Lift the input tray to about a 45° angle.
2. Pull the input tray wire leg down.
3. Place the wire leg on the top of the clips on the flatbed cover.
4. Press down slightly on the input tray to snap the wire leg into the
clips.
A-61527 May 2006 21
Page 26

To accommodate longer documents (longer than 36 cm / 14 in.):
• Pull the input tray extension wire out to the desired length.
The input tray has side guides that can be adjusted to accommodate
the size of the documents you are scanning.
To adjust the side guides:
• Move the side guides in/out to the desired position.
22 A-61527 May 2006
Page 27

Installing and adjusting the output tray
The output tray receives scanned documents from the automatic
document feeder after they are scanned. Before scanning documents,
be sure the output tray is properly installed and adjusted.
To install and adjust the output tray:
1. Hold the output tray at about a 30° angle.
2. Insert the three tabs on the output tray into the three slots on the
automatic document feeder.
Lifting the flatbed cover
Start and stop
scanning
3. Lower the tray to lock it into place.
4. Pull the output tray extension wire out to the desire length.
If you have a large book you want to scan (i.e., telephone book), you
can lift the flatbed cover to provide easy access to the flatbed.
Before you start scanning, make sure the scanner is on and ready for
operation, which is indicated by the green indicator light being on and
constant.
Scanning is controlled by software developed for your application. To
start and stop scanning, refer to the documentation provided with your
application software.
A-61527 May 2006 23
Page 28

Document preparation
• A batch of documents to be fed into the scanner must be arranged so
the leading edges of all documents are aligned and centered in the
input tray; this allows the feeder to introduce documents into the
scanner one at a time.
• Staples and paper clips on documents may damage the scanner and
documents. Remove all staples and paper clips before scanning.
• Documents should be in good condition.
Paper Weights: 60 g/m
Minimum Document Size: 9.4 x 14 cm (3.7 x 5.5 in.)
Maximum Document Size:
• Automatic Document Feeder — 21.6 x 86 cm (8.5 x 34 in.)
NOTE: Long Paper mode will scan document lengths from 35.56 cm
(14 in.) to 86.36 cm (34 in.) when the host PC is configured
with adequate memory (see “System requirements” for more
information regarding memory requirements). See Chapter 4,
Image Processing for more information regarding Long Paper
mode.
• Flatbed — 21.6 x 29.7 cm (8.5 x 11.69 in.)
Paper Types: Bond, Laser, Inkjet, Offset
NOTE: Chemically coated papers may cause excessive wear/swelling
of the rollers.
Paper inks: All inks on the paper must be dry before scanning is
started. This includes: Standard offset printing, Inkjet printer, Thermal
transfer, Handwriting inks.
Correction Fluids: Liquid Paper®, Tipp-Ex®, Wite-out®, and other
similar correction fluids.
2
to 105 g/m2 (16 to 28 lbs.)
24 A-61527 May 2006
Page 29

Scanning your
Using the ADF
documents
Standard paper size documents should feed easily through the scanner.
• Lift the balance wire and place the documents you want to scan facedown into the input tray of the scanner.
Using the flatbed
Use the flatbed to scan documents that cannot be scanned using the
ADF.
1. Lift the flatbed cover.
2. Place the document face down on the glass platen.
3. Position the document with the upper right corner aligned with the
reference mark.
A-61527 May 2006 25
Page 30

Verifying your scanner installation
Kodak provides a test application called the Kodak Scan Validation
Tool. This section describes how to use this tool to perform a basic scan
function which includes feeding paper and viewing captured images on
your PC.
The following steps help you to verify that your scanner installation was
successful. If this procedure is successful, you will be ready to use your
scanner. If it is not successful, go back and review the installation
procedures outlined in the section entitled, “Installing the scanner” in
Chapter 2.
NOTE: Detailed descriptions of all the options on the Scan Validation
Tool dialog boxes can be found in Chapter 4, Image Processing.
Before you begin, be sure the scanner is on and ready to scan.
1. Select Start>Programs>Kodak>Document Imaging>Scan
Validation Tool. The Scan Validation Tool dialog box will be
displayed. Select TWAIN (or ISIS) for the Driver Types and Kodak
Scanner i55/i65 as the Driver. The Scan Validation Tool dialog box
will be displayed.
2. Click the Scanner icon to access the Kodak Scanner Properties
dialog box.
26 A-61527 May 2006
Page 31

3. Select Defaults.
A confirmation message, Reset all values to factory defaults? will
be displayed.
4. Click OK. This resets the software to the factory-installed default
settings. The factory default settings are set to capture bi-tonal
images. For a Kodak i55 Scanner one side of the document will be
scanned. For a Kodak i65 Scanner both sides of the document will
be scanned.
5. Click OK on the Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box.
A-61527 May 2006 27
Page 32

The Scan Validation Tool screen will be displayed. Be sure Save
Images To Files is checked and click one of the four icons to
display the images in the Scan Validation Tool window
6. Lift the balance wire and place some sample documents face-down
into the input tray of the scanner.
Balance
wire
7. Click the Start button on the Scan Validation Tool.
The documents will be scanned and displayed in the Scan
Validation Tool window.
NOTE: If the scanner is in lamp saver mode, a message will be
displayed that the lamps need sufficient time to warm up.
After the images have been displayed, your scanner installation
verification is completed.
8. Click the Close box to exit the Scan Validation Tool.
28 A-61527 May 2006
Page 33

Viewing test images The images you scanned can be found in the TWAIN folder on the C
drive. Files will be named using the following naming convention:
image0000001A.jpg is a front image; image0000001B.jpg is a back
image. Double-click on this file to open and view the captured image.
Because factory default settings were used, the image quality may not
be optimized to meet your needs. To learn more about image
processing features, go to Chapter 4, Image Processing. The Image
Processing chapter provides detailed descriptions of the available
image processing features.
When testing has been completed, delete the test images.
Application software Some scanning applications are available on the CDs packed with your
scanner.
You may also use other capture applications. See the User’s Guide
provided with these applications for instructions on how to use the
software.
A-61527 May 2006 29
Page 34

4 Image Processing
Overview This chapter introduces concepts that may be new to many users. The
Kodak i55 and i65 Scanners provide the ability to process scanned
images to improve their quality. Using these features the scanner can
sometimes make the scanned image look better than the original
document. Basic image processing concepts are reviewed in this
chapter to help you take advantage of these powerful features.
Image processing refers to several separate features of the scanner
that allow you to automatically adjust each image in a certain way that
may improve the resulting images. Common examples of image
processing features are correcting any skew in the fed document,
cutting the edges of the image off to remove any unneeded border or
cleaning up extraneous “noise” on the image. The idea is to do this
automatically so you can get better images with a minimum amount of
rework.
The information that follows describes the image processing features
by walking you through the Scan Validation Tool. The same options
should be available on the user interface of the software application you
are using (i.e., Kodak Capture Software). All fields on the Scan
Validation Tool are described in this chapter.
Common terms Following are a few common terms that are used throughout this
chapter:
Bi-tonal or Binary — black-and-white.
Color — full color image, grayscale is derived from the color scan.
Simplex — indicates that only one side of the document (the front side)
will be scanned, creating a single page image.
Duplex — indicates that both sides of the document will be scanned,
creating two page images.
Cameras — it is important to understand the concept of “cameras”, the
component in the scanner that is used to scan your documents.
The Kodak i55 Scanner is a simplex scanner. The camera has the
ability to separate color and bi-tonal/binary data simultaneously. This
means it scans one-sided documents; a front color image and a front bitonal/binary image, allowing you to capture one side of a document
either in color/grayscale or black-and-white at the same time.
The Kodak i65 Scanner is a duplex scanner. The cameras have the
ability to separate color and bi-tonal/binary data simultaneously. This
means it scans both sides of a two-sided document; a front color
image, a rear color image, a front bi-tonal/binary image, and a rear bitonal/binary image, allowing you to capture both sides of a document in
either color/grayscale, black-and-white, or a combination of color/
grayscale and black-and-white.
30 A-61527 May 2006
Page 35

When you use the Kodak Scan Validation Tool, you will need to select
which camera(s) you want to use to scan your document to get the
desired results. You can use the following examples as a guide when
making camera selections.
Making camera selections
When you launch the Kodak Scan Validation Tool, you will be making
selections on the dialog boxes to set up your images for scanning test
documents. Both TWAIN and ISIS have camera selection boxes that
refer to the cameras within the scanners. Following are some examples
of choosing the correct camera for the desired results. For the purpose
of these examples, the TWAIN Datasource has been used.
Example 1: scanning a two-sided color document both sides in
color
If you want to scan a two-sided color document, make your camera
selections as follows:
Camera selection Result - Side 1 Result - Side 2
• Select both Front Color and Rear Color. Depending on which
camera (in this example, Front Color) is highlighted, will depend on
which side of the document is scanned first. The result is two images
in color.
Example 2: scanning a two-sided color document, front side only
in bi-tonal
If you want to scan only the front side of a color document in black-andwhite, make your camera selections as follows:
Camera selection Original - Side 1 Result - Side 1
• Select and highlight Front Bitonal. The resultant image will be the
front side of the document in black-and-white.
A-61527 May 2006 31
Page 36

Scan Validation Tool dialog box
The Scan Validation Tool (SVT) is a diagnostic application that Kodak
provides with most Kodak scanners. The SVT user interface allows
access to all the features of the scanner and is a good way to verify that
the scanner is working properly. The Scan Validation Tool allows you to
verify scanner functionality using both the TWAIN Datasource and the
ISIS Driver.
Displays the user interface
for the selected driver.
Starts the scanner
Allows you to select
the directory to store
scanned images and
their file names. Only
available when Save
Images to Files is selected.
Stops the scanner
Closes the image viewer
(no images will be
displayed)
Scans one page
Displays one
image at a time
Displays the
License Key
window
Displays four
images at a time
Displays eight
images at a time
Displays two
images at a time
Display Every enter the sampling rate of the images you wish to
display while scanning. For example, to see every image, enter a value
of 1. To see every tenth image, enter a value of 10.
Last File displays the full path and file name for the last stored
image.
Tota l displays the total number of images scanned during the current
Scan Validation Tool session.
32 A-61527 May 2006
Page 37

Starting the Scan Validation Tool
1. Select Start>Run or select Programs>Kodak>Document
Imaging>Scan Validation Tool. Enter the filename or choose
Browse to locate the ScanValidation.exe file.
2. Select TWAIN (or ISIS) for the Driver Type and the Kodak Scanner
i55/i65 Scanner as the Driver. The Scan Validation Tool dialog box
will be displayed.
3. Double-click the Scanner icon to access the Kodak Scanner
Properties dialog box.
A-61527 May 2006 33
Page 38

Using the TWAIN Datasource
The TWAIN Datasource is a piece of software that communicates with
your Kodak Scanner. It is provided with the i55 and i65 Scanners. Many
scanning applications support the TWAIN standard and this datasource
can be used to interface with these applications.
This section provides descriptions of the scanner features using options
on the TWAIN tabs and how to set these options. If you are using the
TWAIN Datasource, follow the procedures in this section to set up your
scanner. If you are using the ISIS Driver, see the section entitled,
“Using the ISIS Driver” later in this chapter.
For the purpose of this manual, all displayed dialog boxes assume the
features on the Kodak i65 Scanner (duplex scanner). If you have a
Kodak i55 Scanner (simplex scanner) options are limited to simplex
scanning only.
Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box
Buttons on the Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box
The Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box allows you to review and
configure the scanner’s settings. It consists of several tabbed windows
each of which will be described within this chapter. Click on each tab to
set all the desired values. You do not have to click OK until you have
made all selections on all of the tabs.
The buttons at the bottom of the dialog box are described below:
Defaults when you select Defaults, the message Reset all values
to factory defaults? will be displayed. Clicking Yes on this message
will reset all values on all tabs to the factory default settings.
Copy copies the settings of the front camera to the rear camera for
the selected camera (bi-tonal, color or grayscale). For example, if you
have Front Bi-tonal highlighted, these values will be copied to the
Rear Bi-tonal camera. If you have Front Color highlighted, these
values will be copied to the Rear Color camera. This option is only
available for the Kodak i65 Scanner.
OK saves the values set on all tabs.
Cancel closes the dialog box without saving any changes.
34 A-61527 May 2006
Page 39

The Imaging tab The Imaging tab allows you to define several image processing values
that can be applied to your scanner.
The Camera Selection box lists the available sides (front and rear)
of any document where you can define individual image processing
values. For detailed information about the cameras, refer to the
beginning of this chapter, “Making camera selections”.
On the Kodak i65 Scanner there is a separate camera for each side of
the document being scanned. The Kodak Scanner drivers allow you to
control the camera settings independently. Some settings apply only to
bi-tonal images, other settings apply to color images. By selecting the
appropriate camera and image type you can control the scanner’s
output.
• If you have a Kodak i55 Scanner, you can select either Front Color
and/or Front Bi-tonal. This means you can scan the front side of a
document depending on how the documents are placed in the feeder
and create one or two images.
• If you have a Kodak i65 Scanner, you can select any individual
camera (i.e., Front Color, Rear Color, Front Bi-tonal and/or Rear
Bi-tonal) or any combination of the cameras. This means you can
scan the front side, rear side or both sides of a document and create
between one and four images.
• Whatever is highlighted in the Camera Selection box determines the
values available on the Imaging, Paper, Compression and Dropout
tabs.
NOTE: What is highlighted is not necessarily selected. Make sure
that the highlighted area you are making changes to is on the
selected camera if you want to see these settings reflected in
the final image.
A-61527 May 2006 35
Page 40

Scanning bi-tonal images Bi-tonal images are scanned images that are made up of only black-
and-white elements. The descriptions below are for bi-tonal images
only.
Binarization is the process of converting a grayscale or color image to
a bi-tonal image. There are several different methods of performing this
conversion. Two of the options Kodak provides are iThresholding and
Adaptive Threshold Processing.
These options are applied to grayscale scanned images and output a
bi-tonal electronic image. Thresholding and Adaptive Threshold
Processing separate the foreground information from the background
information even when the background color or shading varies, and the
foreground information varies in color quality and darkness. Different
types of documents may be scanned using the same image processing
parameters and still result in excellent scanned images.
• iThresholding: selecting iThresholding allows the scanner to
dynamically evaluate each document to determine the optimal
threshold value to produce the highest quality image. This allows
scanning of mixed document sets with varying quality (i.e., faint text,
shaded backgrounds, color backgrounds) to be scanned using a
single setting thus reducing the need for document sorting.
When using iThresholding, only Contrast may be adjusted.
• Adaptive Thresholding (ATP): the Adaptive Threshold Processor
separates the foreground information in an image (i.e., text, graphics,
lines, etc.) from the background information (i.e., white or non-white
paper background).
When using Adaptive Thresholding, Threshold and Contrast may be
adjusted.
36 A-61527 May 2006
Page 41

When Adaptive Thresholding is selected, Contrast values may range
from 1 to 100.
Fixed thresholding ATP
disabled
ATP enabled
Fixed Processing used for black-and-white and other high contrast
documents. A single level is set to determine the black-and-white
transition. The threshold is programmable over the entire density range.
Fixed thresholding sets Contrast to 0. If Fixed Processing is selected,
Contrast is not available.
64-Level Bayer Dither, 64-Level 45 Degree Clustered Dot Screen
and 64-Level Dispersed Dot Screen represent alternative
screening options to emulate a grayscale image.
Noise Filter occasionally small dots or specks appear in the
background of a scanned image. These specks increase file
compression size and usually contain no image information. Using the
Noise Filter on documents containing very fine detail (e.g., the dot on
an "i" in 4-point type) may cause information to be lost. It is
recommended that you do not use Noise Filter when scanning
documents with text smaller than 7-point type.
Noise Filter can be used with bi-tonal images only and is front/rear
independent. Choose (none), Lone Pixel or Majority Rule.
• Lone Pixel reduces random noise on bi-tonal images by converting a
single black pixel surrounded by white to white or by converting a
single white pixel surrounded by black to black.
A-61527 May 2006 37
Page 42

• Majority Rule sets the central pixel value in a matrix according to the
majority of white or black pixels in a matrix.
No Noise Filter Used Lone Pixel
Image Filter used to enhance images containing dot matrix text and/
or images printed with shaded or colored backgrounds using halftone
screens. This filter effectively eliminates noise caused by the halftone
screen. Choose (none) or Halftone Removal.
• Halftone Removal is used to enhance images containing dot matrix
text and/or images with shaded or colored backgrounds using
halftone screens. This filter effectively eliminates noise caused by the
halftone screen.
Contrast % sets the image contrast by adjusting the difference
between black-and-white, thereby making an image sharper or softer.
In a low contrast setting, the difference between black-and-white is
small, so the image is softer. In a high contrast setting, the difference
between black-and-white is large, so the image is clearer. Select a
contrast value from 1 to 100. The default is 50.
Contrast 1
Contrast 60
Contrast 100
Adjust the contrast setting by dragging the Contrast sliding bar to the
left or right to achieve the desired contrast setting, or you can enter a
value (1 to 100) in the Contrast text box. Scan the document to check
the contrast.
38 A-61527 May 2006
Page 43

Threshold used to convert a grayscale image to a bi-tonal image.
The thresholding value is an integer ranging from 0 to 255. A low
threshold value produces a lighter image, and can be used to subdue
backgrounds and subtle, unneeded information. A high threshold value
produces a darker image, and can be used to help pick up faint images.
Adjust the threshold setting by dragging the Threshold sliding bar to the
left or right to achieve the desired threshold setting, or you can enter a
value (0 to 255) in the Threshold text box. Scan the document to check
the threshold.
200 dpi; 80 Threshold
20 Contrast
200 dpi; 80 Threshold
100 Contrast
Resolution or dots per inch (dpi) indicates the scanning resolution,
which largely determines the quality of the scanned image. The greater
the resolution, the better the reproduction. However, scanning at a
higher resolution also increases scanning time and file size. The
industry standard is 200 dpi (about 8 pixels/mm).
Choose a resolution value from the drop down list. The default value is
200 dpi. Available resolutions are 75, 100, 150, 200, 240, 300, 400 or
600.
Polarity the host PC provides information to the scanner defining
whether the image should be stored in standard or reverse polarity. The
default polarity is Black on a White background. Reverse polarity is
White on a Black background.
Black on White polarity White on Black polarity
A-61527 May 2006 39
Page 44

Color Table Not applicable for bi-tonal images. See the next section
“Scanning color images”.
Paper Source — provides the following options:
• ADF: select this option when using the scanner in continuous feed
mode.
• Flatbed: select this option when using the flatbed for scanning
documents that cannot be scanned when used the automatic
document feeder, such as thick or bound documents (books).
• ADF/Flatbed: if you select this option, and no documents are in the
ADF, the scanner will automatically use the flatbed.
40 A-61527 May 2006
Page 45

Scanning color images The descriptions below are for scanning color images only.
Resolution or dots per inch (dpi) indicates the scanning resolution,
which largely determines the quality of the scanned image. The greater
the resolution, the better the reproduction. However, scanning at a
higher resolution also increases scanning time and file size.
Choose a resolution value from the drop down list. The default is 200
dpi. Available resolutions are: 75, 100, 150, 200, 240, 300, 400 or 600.
Color Tables the selection of a color table effects how the scanner
reproduces the color of a scanned document. Color Tables are look-up
tables that store color descriptions which can be used for gamma
correction of images being transferred between different equipment
(i.e., scanners, printers, monitors, etc.). You can choose from the three
Kodak default color tables: Pictures, Text and Text with Pictures, or if
you have created your own custom color tables using the Brightness
and Contrast Control, these tables will also be available. For more
information on the Brightness and Contrast Control, see the Reference
Guide, A-61506.
Paper Source — provides the following options:
• ADF: select this option when using the scanner in continuous feed
mode.
• Flatbed: select this option when using the flatbed for scanning
documents that cannot be scanned when used the automatic
document feeder, such as thick or bound documents (books).
• ADF/Flatbed: if you select this option, and no documents are in the
ADF, the scanner will automatically use the flatbed.
A-61527 May 2006 41
Page 46

Scanning grayscale images The descriptions below are for scanning grayscale images only.
Resolution or dots per inch (dpi) indicates the scanning resolution,
which largely determines the quality of the scanned image. The greater
the resolution, the better the reproduction. However, scanning at a
higher resolution also increases scanning time and file size.
Choose a resolution value from the drop down list. The default is 200
dpi. Available resolutions are: 75, 100, 150, 200, 240, 300, 400 or 600.
Color Tables the selection of a color table effects how the scanner
reproduces the color of a scanned document. Color Tables are look-up
tables that store color descriptions which can be used for gamma
correction of images being transferred between different equipment
(i.e., scanners, printers, monitors, etc.). The selection of a color table
effects how the scanner reproduces the color of a scanned document.
You can choose from the three Kodak default color tables: Pictures,
Text and Text with Pictures, or if you have created your own custom
color tables using the Brightness and Contrast Control , these tables will
also be available. For more information on the Brightness and Contrast
Control, see the Reference Guide, A-61506.
Convert Color to Grayscale enable this option when you want the
captured image to be 8-bit grayscale instead of 24-bit color.
Paper Source — provides the following options:
• ADF: select this option when using the scanner in continuous feed
mode.
• Flatbed: select this option when using the flatbed for scanning
documents that cannot be scanned when used the automatic
document feeder, such as thick or bound documents (books).
• ADF/Flatbed: if you select this option, and no documents are in the
ADF, the scanner will automatically use the flatbed.
42 A-61527 May 2006
Page 47

The Paper tab The Paper tab allows you to define values relating to image output (i.e.,
cropping values, rotation, paper size and units of measure).
Camera selection box lists the available sides of an image that you
can define individual image processing values.
The display window on the right will display the cropping area you are
altering. The cropping area will change as values are being altered.
Cropping values Cropping allows you to capture a portion of the document being
scanned. Cropping options can be used independently with color/
grayscale and bi-tonal images and are also front and rear side
independent, however for simultaneous output scanning color/
grayscale and bi-tonal cropping must be the same per side.
• On an i55 Scanner one cropping option can be assigned per
document.
• On an i65 Scanner two cropping options can be set per document.
Cropping select one of the following options:
• Automatic: dynamically adjusts the cropping window for different
document sizes based upon the edges of the image. Use this option
for batches of mixed-sized documents.
• Aggressive: selecting this option will eliminate any residual white/
gray border on any image edges. When using Aggressive cropping,
there is a possibility that a small amount of image data from the edge
of the document may be lost.
A-61527 May 2006 43
Page 48

• Relative to Document (zone processing): (used for batches of
same-sized documents) — zone processing is a floating fixed crop
window (the zone) located relative to the upper left corner of a
document. It allows you to select an area on the document to be
delivered in either color/grayscale or bi-tonal format (a separate
window for both bi-tonal and color/grayscale may be defined).
Different parameters may be selected for both the front and rear of
the image.
This option may be used in conjunction with Automatic cropping
where a separate color/grayscale or bi-tonal area to be saved is
desired. It is useful in applications where a photograph, signature,
embossment or seal appears in a consistent area for an application
(you may want that small area in color/grayscale and the rest in bitonal).
• Fixed to Transport (used for batches of same-sized documents):
allows you to define the area or zone to be imaged. If you select this
option, enter the x and y offset values, width and length. You can
enter the desired values in the fields or use the arrow keys to define
the desired area. The Display window will show image placement as
you change the values.
The following options are only available when Fixed to Transport or
Relative to Document is selected.
- X-Offset the distance from the left end of the scanner to the
left edge of the scanning area.
- Y-Offset — the position from the top end of the document to the
top end of the scanning area.
- Width — the width of the scanning area.
- Length — the length of the scanning area.
- Center Frame automatically calculates the x-offset for centerfed feeding based upon document size selected.
- Rotate Frame automatically calculates the offset values based
upon feed orientation of the document size selected (landscape
vs. portrait).
NOTES:
• You can scan documents longer than 35.56 cm (14 in.) and less than
86 cm (34 in.) when the host PC is configured with adequate memory
(see “System requirements” for more information).
• Automatic and Relative to Document cropping in Flatbed mode
work well in most cases. When the scanner cover is removed to
accommodate large magazines, books, or other bound material or
when the flatbed glass becomes dirty, Automatic cropping
performance may not be as desired. In these cases, you might try
using the Image Edge Fill option or scanning in Fixed cropping mode
and more carefully aligning the document on the flatbed.
44 A-61527 May 2006
Page 49

Automatic Deskew select this option to automatically deskew a
document within ±0.3 degrees of the leading edge of the document.
This option is only available if you have Automatic cropping selected.
Image Edge Fill — fills the edges of a scanned image, after all other
image processing options have been applied, by covering the area in
Black or White (as selected). Select a value in the Top, Left, Right
and/or Bottom area(s) from each side of the scanned image to be
filled.
NOTE: When using this option, be careful not to enter a value too large
as it could fill in image data that you want to keep.
Additional paper selections In addition to cropping values that can be applied using the Paper tab,
the following options are available:
Preset Front/Rear Size the default paper size is set when a scanner
is first selected. You can choose a different paper size using the dropdown list box.
Units defines the primary measurement system. Inches,
Centimeters, Picas, Points, 20th of Points, and Pixels are available.
A-61527 May 2006 45
Page 50

The Compression tab Compression squeezes a file to decrease the total size. Bi-tonal images
are normally compressed using a CCITT standard called Group IV,
often used in conjunction with TIFF files. Color and grayscale images
are often compressed using JPEG techniques.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is a file format standard commonly
used for bi-tonal images. It is often used in conjuction with the CCITT
Group IV compression standard to reduce image file size. Color and
grayscale images can be saved in this format too, but they are often
found uncompressed and are, therefore, quite large. Use the
Compression tab to select compression settings.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Editor Group). This group developed and
lent their name to a file compression standard for color and grayscale
images that is widely used by scanners, digital cameras and software
applications. On Microsoft Windows-based systems, a file with the
extension .jpg has normally been compressed using this standard.
Camera Selection box lists the available sides (Front Color, Rear
Color, etc.) of an image that you can define individual image processing
values.
Compression the i55/i65 Scanners can be configured to output bi-
tonal, grayscale, and color images in various supported formats and
resolutions independent of each other and each side of the image.
These options vary based on the type of scanner.
For bi-tonal scanning the following compressions are available:
• CCITT Group 4 TIFF
• (none) uncompressed TIFF
46 A-61527 May 2006
Page 51

The following color/grayscale compression options are available:
• JPEG — JPEG compression offers a JPEG quality of Draft, Good,
Better, Best, Superior.
- Draft: smallest file size with draft image quality
- Good: larger file size with good image quality
- Better: larger file size with better image quality
- Best: larger file size with the best image quality
- Superior: largest file size with superior image quality
• (none) produces an uncompressed bitmap.
A-61527 May 2006 47
Page 52

The Dropout tab Electronic Color Dropout is used to eliminate a form’s background so
that a document management system may automatically — through
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and ICR (Intelligent Character
Recognition) technology — read pertinent data without interference
from the lines and boxes of the form. The i55/i65 Scanners can dropout
either red, green or blue. The Dropout tab allows you to select the
desired dropout color and alter the filter threshold and background.
Camera Selection box electronic color drop-out is available only for
bi-tonal and grayscale images.
Color Dropout choose the color you want to eliminate: (none)
Remove Red, Remove Green, Remove Blue.
Filter Threshold the value that is used to identify the color which will
be dropped out. This value is applied to the color area. Color with a
Red/Green/Blue component more than the entered value is dropped.
This setting determines how much of the selected color is dropped out.
A lower value will leave more of the selected color in, while a higher
value will drop more of the selected color out.
Background this value will be substituted in the grayscale (pre-
thresholded) image for the color being removed. Therefore, this value
should be higher than the threshold value selected on the Imaging tab
for this pixel to become the background color. For example, if you are
scanning a white document with a green form and you have selected a
bi-tonal threshold value of 127, you should choose an electronic color
drop-out background value greater than 127 so the substituted pixel will
be white in the dropped-out image.
48 A-61527 May 2006
Page 53

The Multifeed tab Multi-feed Detection aids in document processing by detecting
documents that may go through the feeder overlapped.
Length Detection choose the minimum length of the document that
can be scanned with a multi-feed being detected. The Display window
will show the size of the document as you change the value. You can
select to display this amount in Inches, Centimeters, Picas, Points,
20th of Points or Pixels. A value of 0 indicates no length detection.
Length detection is best used when scanning same-sized documents.
Multifeed Stops Scanning if this option is not selected, the scanner
will log the condition but continue to operate. You can choose the sound
you would like the PC to make to alert you of a multifeed.
To choose a sound:
• Click on the Browse button and choose the desired .wav file.
A-61527 May 2006 49
Page 54

The Options tab The Options tab allows you to set Image Transfer and Transport
control.
Image Transfer Order if you are using simultaneous output
scanning (bi-tonal and color/grayscale) for either side, this option
controls the order in which the scanner returns image data. For
example, if you are scanning color and bi-tonal and you select Bi-tonal
Image, the scanner will return the bi-tonal front image, then the front
color image.
Transport Timeout allows you to set a transport timeout value. This
value is the amount of time the scanner will wait after the last document
enters the transport before the transport timeout action is taken. You
can specify a time delay setting from 1 to 30 seconds.
Energy Saving Features of Scanner allows you to set the amount
of time the scanner will remain inactive before the scanner goes into an
idle state. Choices are: (none) and 5 to 60 minutes. The default is 15
minutes.
Blank Image Detection — use the slider bar to specify the image size
(KB), below which an image is determined to be blank. Images with
sizes less than the size number you select will not be created. If you
use this option, you must specify a blank image size for each image
output type (Bi-tonal, Grayscale and Color) not just one. The default
for this option is None, which means that you will keep all images.
50 A-61527 May 2006
Page 55

The Setup tab The Setup tab allows you to download firmware and set the scanner
clock. The Setup tab is only available wh en running the Scan V alidatio n
Tool, via the TWAIN Datasource.
Package the scanner firmware runs your Kodak i55/i65 Scanners.
The value displayed in the Current field is the version of firmware
currently in use by your scanner. Periodically Kodak releases updated
versions of firmware which are available through Kodak Service and
Support. When Download is selected, the Select Scanner Firmware
dialog box will be displayed.
Download… this option is used to download the latest version of
firmware to your scanner.
Configure displays the local time, UTC (Universal Time Clock) and
the scanner serial number.
Lock camera — click this button to lock the scanner’s flatbed camera
assembly. This is normally done before shipping the scanner to avoid
damage to the flatbed camera. Refer to the section entitled, “Locking
the scanner” in Chapter 2 for more information and procedures.
A-61527 May 2006 51
Page 56

The Info tab The Info tab displays information that is pertinent to your scanner.
52 A-61527 May 2006
Page 57

Using the ISIS Driver The ISIS Driver is a piece of software that communicates with the
scanner. This driver is created and maintained by Pixel Translations,
Inc. and is provided with the scanner by Kodak. Many scanning
applications support ISIS drivers and this driver can be used to
interface with them.
This section provides descriptions of the options on the ISIS dialog
boxes and how to set these options.
For the purpose of this manual, all displayed dialog boxes assume the
features available on the Kodak i65 Scanner. If you have a Kodak i55
Scanner all options are limited to simplex scanning only.
Scanner Settings dialog box
Buttons on the Scanner Settings dialog box
See the section entitled, “Starting the Scan Validation Tool” earlier in
this chapter to access the Scanner Settings dialog box.
Following are descriptions of the buttons located at the bottom of the
dialog box.
More displays the More Scanner Settings dialog box. This dialog
box provides additional image processing settings unique to the Kodak
i55/i65 Scanners.
Area displays the Scan Area dialog box.
Copy this function is only available when using the scanner in
duplex mode. The Copy button provides a convenient way to set up the
color, grayscale or binary image settings on one side and transfer them
to the other. For example, if you highlight and set up Front Binary, you
can use the Copy button to duplicate those settings for Rear Binary.
About displays the About dialog box. The About dialog box provides
detailed information such as the driver version number, certification
status and the version of QuickDriver used to develop this driver.
A-61527 May 2006 53
Page 58

Default when you select Default, the values will be reset to the
factory defaults.
OK saves the values set on all dialog boxes.
Cancel closes the dialog box without saving any changes.
Camera Settings area
The selections in the Camera area list the available sides (front and
back) of an image where you can define individual image processing
values. Options include: Front Color, Front Binary, Back Color and Back
Binary. For detailed information about Camera selection, see the
section entitled, “Making camera selections” earlier in Chapter 4.
On the Kodak i65 Scanner there is a separate camera for each side of
the document being scanned. The Kodak Scanner drivers allow you to
control the camera settings independently. Some settings apply only to
binary (black-and-white) images, others apply to color/grayscale
images. By selecting the appropriate camera and image type, you can
control the scanner’s output.
When starting the configuration process, use the steps below as a
guide:
1. Check the images you wish to capture (Enable camera settings).
2. Select the order to transfer the images (Color First or Binary First).
3. Configure each image by highlighting it (Configure).
Enable camera settings select the desired checkbox to enable the
Front Color, Front Binary, Back Color or Back Binary settings as
desired. This indicates the images you wish to capture and transfer to
the host PC. (It is possible to capture only rear images.) Enable your
selection by putting a checkmark in the desired box.
Color First/Binary First define the transfer order by selecting the
Color First or Binary First radio button. This determines which image
is transferred to the host PC first when using simultaneous output
scanning. For example, if you are scanning front color and front binary
and you select Binary First the scanner will return the front binary
image, then the front color image.
54 A-61527 May 2006
Page 59

Configure highlight the image you want to setup. As you select the
image, other options will become available on the Scanner Settings
dialog box. The availability of these options is dependent upon the
selection you make.
Convert Color to Grayscale this option is only available when
configuring color cameras. When selected, the scanner will convert the
color image data to grayscale before making it available to the host PC.
Image Processing settings The other options on this dialog box allow you to define image
processing values that can be applied to your scanner.
Scan Source the host PC provides information to the scanner
defining whether to scan one or both sides of the document. Simplex
indicates that only one side (front side) of the document will be
scanned. Simplex – Back indicates that only one side (back side) of
the document will be scanned. Duplex indicates that both sides of the
document will be scanned.
Also select one of the following options:
• ADF: select this option when using the scanner in continuous feed
mode.
• Flatbed: select this option when using the flatbed for scanning
documents that cannot be scanned when used the automatic
document feeder, such as thick or bound documents (books).
• ADF/Flatbed: if you select this option, and no documents are in the
ADF, the scanner will automatically use the flatbed.
Dots per inch (dpi) or Resolution indicates the scanning resolution,
which largely determines the quality of the scanned image. The greater
the resolution, the better the reproduction. However, scanning at a
higher resolution also increases scanning time and file size.
Choose a resolution value from the drop-down list. The default is 200
dpi. Available resolutions are: 75, 100, 150, 200, 240, 300, 400 and
600.
A-61527 May 2006 55
Page 60

Cropping allows you to capture a portion of the document being
scanned. All cropping options can be used with color/grayscale and
binary images. Front and Rear cropping are independent, however, for
simultaneous output scanning, color/grayscale and binary cropping
must be the same per side. Only one cropping option can be assigned
per image. Select one of the following options:
• Automatic: dynamically adjusts the cropping window for different
document sizes based on the edges of the image. Use this option for
56 A-61527 May 2006
Page 61

NOTES:
• You can scan documents larger than 35.56 cm (14 in.) and less than
86 cm (34 in.) in length when the host PC is configured with adequate
memory (see “System requirements” for more information regarding
memory requirements).
• Automatic and Relative to Document cropping in Flatbed mode
work well in most cases. When the scanner cover is removed to
accommodate large magazines, books, or other bound material or
when the flatbed glass becomes dirty, Automatic cropping
performance may not be as desired. In these cases, you might try
using the Image Edge Fill option or scanning in Fixed cropping mode
and more carefully aligning the document on the flatbed.
Page size and layout The default paper size is set when a scanner is first selected. You can
choose a different paper size using the drop-down list box.
NOTE: The Page Size and Page Layout selections also appear on the
Scan Area dialog box. If you make a change on the Scanner
Settings dialog box, the same selections will appear on the
Scan Area dialog box and vice versa.
The Page Layout area allows you to select either Portrait or Landscape.
• Portrait will display the image orientation in the shape of a
conventional portrait, where height is greater than width.
• Landscape will display the image orientation in the shape of a
conventional landscape painting, where width is greater than height.
A-61527 May 2006 57
Page 62

Binarization is the process of converting a grayscale or color image to
a binary image. There are several different methods of performing this
conversion. The following descriptions are for binary images only.
The following binarization options work on grayscale scanned images
and outputs a bi-tonal electronic image. Their strength lies in the ability
to separate the foreground information from the background information
even when the background color or shading varies, and the foreground
information varies in color quality and darkness. Different types of
documents may be scanned using the same image processing
parameters and results in excellent scanned images.
Available binarization options are:
• iThresholding: selecting iThresholding allows the scanner to
dynamically evaluate each document to determine the optimal
threshold value to produce the highest quality image. This allows
scanning of mixed document sets with varying quality (i.e., faint text,
shaded backgrounds, color backgrounds) to be scanned using a
single setting thus reducing the need for document sorting.
When using iThresholding, only Contrast may be adjusted.
• Fixed Processing (FP): used for black-and-white and other high
contrast documents. A single level is set to determine the black-andwhite transition. The threshold is programmable over the entire
density range. Fixed thresholding sets the contrast to 0. If Fixed
Processing is selected, Contrast is not available.
• Adaptive Thresholding (ATP): the Adaptive Threshold Processor
separates the foreground information in an image (i.e., text, graphics,
lines, etc.) from the background information (i.e., white or non-white
paper background).
When using Adaptive Thresholding, Threshold and Contrast may be
adjusted. Contrast values may range from 1 to 100. A Contrast value
of 100 is considered fully adaptive thresholding.
Fixed thresholding ATP disabled ATP enabled
58 A-61527 May 2006
Page 63

Dithering a method used to simulate gray levels. When selected,
the Dithering options are available.
• 64-Level Bayer Dither, 64-Level 45 Degree Clustered Dot Screen
and 64-Level Dispersed Dot Screen: these represent alternative
screening options to emulate gray.
Contrast % sets the image contrast by adjusting the difference
between black-and-white, thereby making an image sharper or softer.
Contrast is only available for binary images.
In a low contrast setting, the difference between black-and-white is
small, so the image is softer. In a high contrast setting, the difference
between black-and-white is large, so the image is clearer. Select a
contrast value from 1 to 100. The default is 50.
Contrast 1
Contrast 60
Contrast 100
Manual is always selected for binary images. Adjust the Contrast
setting by dragging the Contrast sliding bar to the left or right to achieve
the desired Contrast setting. Scan the document to check the contrast.
Threshold thresholding is used to convert a grayscale image into a
binary (1 bit/pixel) image. The thresholding value ranges from 0 to 255.
The default is 90. A low threshold value will produce a lighter image,
and can be used to subdue backgrounds and subtle, unneeded
information. A high threshold value will produce a darker image, and
can be used to help pick up faint images.
A-61527 May 2006 59
Page 64

Adjust the Threshold setting by dragging the Threshold sliding bar to
the left or right to achieve the desired Threshold setting. Scan the
document to check the threshold.
200 dpi; 80 Threshold; 20 Contrast 200 dpi; 80 Threshold; 100 Contrast
Lighten, Normal and Darken are used as quick sets to adjust the
threshold. Lighten = 72, Normal = 90 and Darken = 128.
60 A-61527 May 2006
Page 65

More Scanner Settings dialog box
Additional image processing values unique to the i55/i65 Scanners are
available when you choose the More button on the Scanner Settings
dialog box.
Camera settings area
The selections in the Camera area list the available sides (front and
back) of an image where you can define individual image processing
values.
When starting the configuration process, use the steps below as a
guide:
1. Check the images you wish to capture (Enable camera settings).
2. Select the order to transfer the images (Color First/Binary First).
3. Configure each image by highlighting it (Configure).
Enable camera settings select the desired checkbox to enable the
Front Color, Front Binary, Back Color or Back Binary settings as
desired. This indicates the images you wish to capture and transfer to
the host PC. (It is possible to capture only rear images.) You can enable
your selection by putting a checkmark in the desired box.
Color First/Binary First define the transfer order by selecting the
Color First or Binary First radio button. This determines which image
is transferred to the host PC first when using simultaneous output
scanning. For example, if you are scanning front color and front binary
and you select Binary First the scanner will return the front binary
image, then the front color image.
Configure highlight the image you want to setup. As you select the
image, other options will become available on the More Scanner
Settings dialog box. The availability of these options is dependent upon
the selection you make.
A-61527 May 2006 61
Page 66

Convert Color to Grayscale this option is only available when
configuring color cameras. When selected, the scanner will convert the
color image data to grayscale before making it available to the host.
Scan Source the host PC provides information to the scanner
defining whether to scan one or both sides of the document. Simplex
indicates that only one side (front side) of the document will be
scanned. Simplex – Back indicates that only one side (rear side) of the
document will be scanned. Duplex indicates that both sides of the
document will be scanned.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Editor Group) Quality. This group developed
and lent their name to a file compression standard for color and
grayscale images that is widely used by scanners, digital cameras and
software applications. On Microsoft Windows-based systems, a file with
the extension .jpg has normally been compressed using this standard.
JPEG compression offers a JPEG quality of Draft, Good, Better, Best
and Superior.
• Draft smallest file size with draft image quality.
• Good larger file size with good image quality.
• Better larger file size with better image quality.
• Best larger file size with the best image quality.
• Superior largest file size with superior image quality.
Image Edge Fill — fills the edges of a scanned image, after all other
image processing options have been applied, by covering the area in
Black or White (as selected). Select a value in the Top, Left, Right
and/or Bottom area(s) from each side of the scanned image to be
filled.
• When using this option, be careful not to enter a value too large as it
could fill in image data that you want to keep.
Image Control options The following Image Control options are available:
Deskew check this option to automatically deskew a document
within ±0.3 degrees of the leading edge of the document. Automatic
deskew can detect up to a 45-degree skew and correct up to a 24degree angle at 200 dpi or a 10-degree skew angle at 300 dpi. This
option is not available when you have Fixed to Transport or Relative
to Document cropping selected.
NOTE: To prevent data loss, the document must have all four corners
within the image path.
62 A-61527 May 2006
Page 67

Halftone Removal used to enhance images containing dot matrix
text and/or images with shaded or colored backgrounds using halftone
screens. This filter effectively eliminates noise caused by the halftone
screen. This option is only applied to binary images.
Polarity the host PC provides information to the scanner defining
whether the image should be stored in standard or reverse polarity. The
default polarity is Black on a White background. Reverse polarity is
White on a Black background.
Black on White polarity White on Black polarity
Noise filter — occasionally small dots or specks appear in the
background of a scanned image. These specks increase file
compression size and usually contain no image information. Using the
Noise Filter on documents containing very fine detail (e.g., the dot on
an "i" in 4-point type) may cause information to be lost. It is
recommended that you do not use the Noise Filter when scanning
documents with text smaller than 7-point type.
Noise Filter can be used with binary images only and is Front/Rear
independent. Choose None, Lone Pixel or Majority Rule.
• Lone Pixel reduces random noise on binary images by converting a
single black pixel surrounded by white to white or by converting a
single white pixel surrounded by black to black.
• Majority Rule sets the central pixel value in a matrix according to the
majority of white or black pixels in a matrix.
No Noise Filter Used Lone Pixel
A-61527 May 2006 63
Page 68

Color Dropout options Electronic color dropout is used to eliminate a form’s background so
that a document management system may automatically — through
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and ICR (Intelligent Character
Recognition) technology — read pertinent data without interference
from the lines and boxes of the form. You can select the desired
dropout color, and alter the filter threshold and background.
Electronic color dropout is available only for binary and grayscale
images.
Dropout Color the i55/i65 Scanners can drop out red, green or blue.
None is the default.
Background Value this value will be substituted in the grayscale
(pre-thresholded) image for the color being removed. Therefore, this
value should be higher than the threshold value selected on the
Scanner Settings dialog box for this pixel to become the background
color. The default value is 245. For example, if you are scanning a white
document with a green form and you have selected a binary threshold
value of 127, you should choose an electronic color dropout
background value greater than 127 so the substituted pixel will be white
in the dropped-out image.
Threshold value the value that is used to identify the color which
will be dropped out. This value is applied to the color area. Color with a
Red/Green/Blue component more than the entered value is dropped.
This setting determines how much of the selected color is dropped out.
A lower value will leave more of the selected color in, while a higher
value will drop more of the selected color out. The default value is 175.
64 A-61527 May 2006
Page 69

Scanner Control dialog box
Selecting the Scanner Control button on the More Scanner Settings
dialog box displays the Scanner Control dialog box.
This dialog box allows you to set multi-feed detection and transport
control. The settings in this dialog box do not affect the quality of the
image.
OK saves the values set on the dialog box.
Multi-Feed Detection options
Cancel closes the dialog box without saving any changes.
Length Detection this option can be enabled or disabled. The
default is disabled. If Length Detection is enabled, enter the maximum
length. This is the minimum length of the document that can be
scanned with a multi-feed being detected. Length detection is used
when scanning same-sized documents to check for overlap. For
example, if you are scanning 8.5 x 11-inch (A4) documents in portrait
mode, you may want to enter a value of 11.25 inches (28.57 cm) in the
Maximum Length field.
Units — defines the primary measurement system. Pixels, Inches,
and Centimeters are available.
Auto Set when enabled, will automatically set the maximum length
value to .50-inch (1.27 cm) greater than the length of the currently
selected page size.
Stop scanner on Multi-Feed — when enabled, the scanner will stop
when a multi-feed is encountered.
Sound Alarm on Multi-Feed — when enabled, the scanner will alert
you with the sound you selected when a multi-feed is encountered.
Sound — select this option to choose the sound you would like your
PC to make to alert you of a multi-fed document.
To choose a sound:
1. Click on the Sound button to display the Open dialog box.
2. Choose the desired .wav file.
3. Click Open on the dialog box and the sound will be saved.
A-61527 May 2006 65
Page 70

Energy Saving features of the scanner
Transport timeout This feature allows you to set a transport timeout value. This value is
Blank image detection Use the slider bar to specify the image size (KB), below which an image
Energy Star allows you to set the amount of time the scanner will
remain inactive before the scanner goes into an idle state (sleep mode).
Choices are: 0 to 60 minutes.
the amount of time the scanner will wait after the last document enters
the transport before the transport timeout action is taken. You can
specify a time delay setting from 1 to 300 seconds. The default is 10
seconds.
is determined to be blank. Images with sizes less than the size number
you select will not be created. If you use this option, you must specify a
blank image size for each image type (Bi-tonal, Gray and Color) you
want to delete. The default for this option is None, which means that
you will keep all images dialog box.
Defining the Scan area The Scan Area dialog box is only available for images when the
Cropping option selected on the Scanner Settings dialog box is either
Fixed to Transport or Relative to Document cropping.
To access the Scan Area dialog box, select Area on the Scanner
Settings dialog box.
NOTE: Select the side and image to be defined by highlighting Front
Color/Grayscale, Front Binary, Back Color/Grayscale, Back
Binary or as appropriate based on the cropping option selected
for each of these in the Scanner Settings dialog box. The scan
areas defined for all camera selections are independent.
66 A-61527 May 2006
Page 71

Scan Area dialog box The Scan Area dialog box allows you to define the amount of image
data which is returned to the host. The area can be defined in Pixels,
Inches or Centimeters.
The Scan Area dialog box is only available when Fixed to Transport or
Relative to Document is selected on the Scanner Settings dialog box.
Page size and layout the default paper size is set when a scanner
is first selected. You can choose a different paper size using the dropdown list box.
NOTE: The Page Size and Page Layout selections also appear on the
Scanner Settings dialog box. If you make a change on the Scan
Area dialog box, the same selections will appear on the Scanner
Settings dialog box and vice versa.
The Page Layout area allows you to select either Portrait or
Landscape.
Portrait will display the image orientation in the shape of a
conventional portrait, where height is greater than width.
Landscape will display the image orientation in the shape of a
conventional landscape painting, where width is greater than height.
Area:
X the distance from the left end of the scanner to the left-edge of the
scanning area.
Y — the position from the top end of the document to the top end of the
scanning area.
Width — the width of the scanning area.
Height — the height of the scanning area.
Snap causes the dimensions of the Area box to be controlled in fixed
1/8-inch increments. This option is not available in Pixels mode.
A-61527 May 2006 67
Page 72

5 Maintenance
Cleaning procedures Your scanner needs to be cleaned periodically. If documents do not
feed easily, if several documents feed at the same time or if streaks
appear on your images, it is time to clean your scanner. The section
entitled, “Supplies and consumables” at the end of this chapter
provides a listing of the supplies required to clean your scanner.
IMPORT ANT: Use only non-flammable cleaners such as those provided
through Kodak Parts Services. Do not use household
cleaners.
Do not use cleaners in confined areas, use with adequate
ventilation.
Do not use cleaners on hot surfaces. Allow surfaces to
cool to ambient temperature before use.
68 A-61527 May 2006
Page 73

Cleaning the feed module
1. Remove the feed module by squeezing the plastic clamps that hold
the feed module in place and lift it out of position.
2. Wipe the feed module from top to bottom with a roller cleaning pad.
3. Reinstall the feed module by pushing the feed module into position
aligning the feed module into the slots until it snaps into place.
A-61527 May 2006 69
Page 74

Cleaning the imaging area
1. Remove dust and debris from this area by using a Staticide wipe or
a small brush. Be careful not to scratch the glass when cleaning.
Use caution when cleaning the upper and lower white
background strips. Be careful not to catch the small black tabs
with the Staticide wipe. These tabs are fragile and can bend or
break.
IMPORTANT: Staticide wipes contain isopropanol which can cause
eye irritation and dry skin. Wash your hands with soap
and water after performing maintenance procedures.
Refer to MSDS for more information.
2. Wipe the imaging area again with an almost-dry Staticide wipe to
remove any streaks.
3. When finished, close the ADF cover.
Cleaning the platen glass To clean the smudges and fingerprints on the platen glass:
1. Open the flatbed cover.
2. Wipe the flatbed platen glass with a fresh Staticide wipe.
3. Wipe the flatbed platen glass with a dry Staticide wipe.
70 A-61527 May 2006
Page 75

Replacement
This section provides procedures for replacing the following parts.
procedures
Replacing the feed module
• Feed module life varies depending upon paper types (chemically
treated papers), environment and cleanliness.
• Paper Feed roller life varies depending upon paper types
(chemically treated papers), environment and cleanliness.
• Input tray and flatbed cover only needs to be replaced if they get
damaged.
Degradation of feeder performance, multiple feeds, stoppages, etc.
indicate a need to change the feed module. Failure to clean regularly,
and/or use of non-recommended cleaning solvents can shorten the
feed module life.
For additional feed modules, see the section entitled, “Supplies and
consumables” later in this chapter.
1. Open the ADF cover.
2. Squeeze the plastic clamps that hold the feed module in place and
lift it out of position.
3. Push the new feed module into position, aligning the new feed
module into the slots, until it snaps into place.
4. Close the ADF cover.
A-61527 May 2006 71
Page 76

Replacing the paper feed roller
1. Open the ADF cover.
2. Lift the tabs and remove the paper feed roller cover.
3. Remove the paper feed roller.
72 A-61527 May 2006
Page 77

4. Insert the new paper feed roller by aligning the tabs into the slots
and pressing the roller into place.
Ta b
Slot
5. Reinsert the paper feed roller cover and snap it into place.
6. Close the ADF cover.
A-61527 May 2006 73
Page 78

Replacing the input tray If the input tray needs to be reinstalled or replaced, use the following
procedure:
1. Remove the flatbed cover from the scanner by lifting the flatbed
cover straight up.
2. Raise the input tray as shown and gently lift the input tray out of the
slots.
Pins and slots
To install a new input tray
1. Align the pins on the input tray with the slots on the flatbed cover (as
shown in the illustration above) and push the input tray into place.
2. Lower the input tray against the flatbed cover.
3. Replace the flatbed cover on the scanner.
74 A-61527 May 2006
Page 79

Replacing the flatbed cover
If the flatbed cover needs to be reinstalled or replaced, use the
following procedure.
1. Remove the flatbed cover from the scanner by lifting the flatbed
cover straight up.
2. Install the new flatbed cover by aligning the pins into the holes on
the scanner base and setting the flatbed cover into place.
Locking the scanner The TWAIN Datasource provides a Lock camera option which moves
the camera into position before physically locking the scanner with the
shipping switch. ISIS does not provide this option. For TWAIN
datasource users follow the procedure below.
1. Turn on the host PC and start the Scan Validation Tool.
NOTE: For detailed instructions on starting the Scan Validation Tool,
see the section entitled “Starting the Scan Validation Tool” in
Chapter 4, Image Processing.
A-61527 May 2006 75
Page 80

2. Access the Setup tab and click the Lock Camera button.
The following messages will be displayed:
3. Click OK on both messages.
4. Lock the scanner by moving the shipping switch (located at the
bottom of the scanner) back to the locked position.
76 A-61527 May 2006
Page 81

Supplies and
Contact your scanner supplier to order supplies and parts.
consumables
Description CAT No.
Kodak Feed Module
Kodak Digital Science Roller Cleaning Pads 853 5981
Staticide Wipes for Kodak Scanners 896 5519
Kodak i55/i65 Feed Roller Kit 154 4303
162 3362
A-61527 May 2006 77
Page 82

6 Troubleshooting
Occasionally you may encounter a situation with your scanner where it
may not function properly. Refer to the information in this chapter to
help you resolve the situation before calling Technical Support.
Indicator lights and error codes
Clearing a document jam
The indicator lights provide information on the current state of the
scanner.
Flashing green: indicates the scanner is warming up from a power
saving mode and preparing to scan.
Steady green: indicates the scanner is ready to scan.
Flashing red: indicates a scanner error, such as the ADF cover is
open.
If your scanner stops scanning due to a document jam, follow the
procedures below:
1. Open the ADF cover.
2. Remove any jammed documents from inside the scanner.
3. Close the cover.
Getting service If your scanner needs service, go to the website at:
www.kodak.com/go/docimaging
There you can find out how best to obtain service for your scanner for
your region.
78 A-61527 May 2006
Page 83

Problem solving Use the chart below as a guide to check possible solutions to problems
you may encounter when using the Kodak i55/i65 Scanner.
Problem Possible Solution
Scanner will not scan; no LED display
Image quality is:
•poor
• decreased
• lines or streaks
Documents are jamming
When the scanner is powered up, it
makes noise and does not come to the
Ready state.
You can specify an image from the
scanner, but the scanner or computer
crashes when scanning.
Make sure that:
• the power cord is plugged securely into the back of scanner and the
wall outlet.
• the power light is illuminated on the power supply.
• the power switch is on.
• the wall outlet is not defective (call a licensed electrician).
• the PC and/or the scanner was not restarted after installing the
software.
• Clean the imaging area. See the procedures in Chapter 5,
Maintenance.
Make sure that:
• the input tray and side guides are adjusted for the width of the
documents you are scanning.
• the output tray is adjusted for the length of the documents you are
scanning.
• all documents meet the specifications for size, weight and type as
outlined in the section entitled, “Document preparation”.
• the scanner is clean.
• the feed module is installed properly and securely in place.
• The shipping switch was not unlocked. Unlock it. See the section
entitled “Unlocking the scanner” in Chapter 2.
• The scanner is not located on a level surface. This may cause the
scanner to function improperly.
• Verify that the SCSI or USB cable is plugged in correctly.
• Only two SCSI terminators can be connected to the SCSI chain: one is
at the end of the SCSI device and the other is already in the host
A-61527 May 2006 79
Page 84

Problem Possible Solution
Image has clipped corners
Images are not being cropped correctly
Roller marks appear on the document
after scanning
Images have black background bleedthrough
If your images have clipped corners, the skew angle was too large for the
scanner to handle.
• Be sure documents are placed in the input tray with the edges aligned
and the side guides positioned correctly to accommodate the size
documents you are feeding to avoid large skew angles.
• If you are scanning large stacks of documents, separate the documents
into smaller stacks.
If auto or aggressive cropping is enabled, and your images are not
being cropped correctly, clean the white background strips in the imaging
area.
• See the procedures in Chapter 5, Maintenance “Cleaning the imaging
area”.
If you are scanning images that are smaller than 9.4 x 14 cm (3.7 x 5.5
in.) documents may intermittently be cut off.
• Do not use auto or aggressive cropping.
Clean the rollers. See the procedures in Chapter 5, Maintenanc e.
When scanning translucent documents, black bleed-through may be
displayed on the image. To minimize this, adjust the Contrast value or
select Fixed Processing to improve the image. For more information on
Contrast and Fixed Processing, see Chapter 4, Image Processing.
80 A-61527 May 2006
Page 85

Scanner not working If your scanner is not working, you may need to reinstall the drivers. To
verify this:
1. Click the My Computer icon and click the right mouse button.
2. Select Properties.
3. Click on the Hardware tab and select Device Manager.
A-61527 May 2006 81
Page 86

4. From the Device Manager screen, select Imaging devices. If the
Kodak i55/i65 Scanner appears with a ? before the name, you need
to reinstall the driver software.
5. Double-click on the Kodak Scanner i65 (or i55). The Scanner
Properties dialog box will be displayed. Select the Driver tab.
6. Click Update Driver. The Upgrade Device Driver Wizard will be
displayed.
82 A-61527 May 2006
Page 87

7. Click Next.
8. Click Next.
9. Insert the Kodak Installation CD in the CD-ROM drive and locate the
KDS folder. Locate and select the kdssti.in file.
10.Click Open and proceed with the prompts to install the driver.
A-61527 May 2006 83
Page 88

Testing for a USB connection
When the Kodak device drivers for the Kodak i55 and i65 Scanners are
installed, a copy of the USB test software will also be installed. It will be
located in this folder by default along with the Kodak Scan Validation
Tool software:
C:\program files\Kodak\Document Imaging\usbtst.exe
If you run this executable (usbtst.exe), it will display a set of USB values
and protocols. At this time, the software application will function in all
operating systems, but will only be valid with the Windows XP system.
If a shortcut of the executable is created, and the /test switch is added
to the end of the “Target:” path (to the right of the quotes), then when it
is launched from the shortcut, it will run the dialog boxes as listed above
and function accordingly with all the operating systems.
To verify USB port speed with the scanner, run the Scan Validation Tool
software, and select the Info tab. USBSCAN/x.x will be displayed in
parentheses in the Driver: box. x.x is the speed the scanner is actually
communicating.
84 A-61527 May 2006
Page 89

USB connection issues The USB verification tool will check your operating system and
hardware capability to determine if you have a functioning USB 2.0 or if
you need to install a USB card.
Your operating system is correctly configured to support USB 2.0.
If a functioning USB 2.0 port is present, this dialog box will be
displayed.
Your operating system supports USB 2.0, however, a USB 1.1 port
was found
• If your PC does not have a USB 2.0 port installed, install a USB 2.0
Accessory card.
• If a USB 2.0 port or card is installed and the USB test tool does not
recognize the USB card as 2.0, install or update the drivers for that
card.
Your operating system only supports USB 1.1
There are some host PC operating systems that do not support USB
2.0, but support USB 1.1 (e.g., Windows 98SE). The Kodak i55 and i65
Scanners are rated and designed to operate with USB 2.0, but will
function in a USB 1.1 port, however, the scanner will only perform at a
USB 1.1 speed.
Solutions:
• Update your operating system to one that supports USB 2.0, such as,
Windows 2000 or Windows XP.
• You may add a USB 2.0 card but will function only as a USB 1.1.
A-61527 May 2006 85
Page 90

You do not need to install any additional USB card(s)
The host PC operating system only supports USB 1.1 and does not
support USB 2.0, but it found a USB port. The Kodak i55 and i65
Scanners are rated and designed to operate with USB 2.0, but will
function in a USB 1.1 port, however, the scanner will only perform at a
USB 1.1 speed.
Solution: Update your operating system to one that supports USB 2.0.
such as, Windows 2000 or Windows XP. You can also verify what the
scanner port speed is running at by using the Scan Validation Tool
application with the scanner.
USB will not work
This operating system will not support a USB port. It is recommended
to upgrade the operating system to support USB, such as Windows
98SE, Windows 2000 or Windows XP.
86 A-61527 May 2006
Page 91

Appendix A Specifications
Scanner Type/Speed
Scanning Technology CCD type
Output Resolutions 75, 100, 150, 200, 240, 300, 400 and 600 dpi
File Format Output BMP, TIFF, JPEG, PDF (with bundled software)
Scan Area Automatic Document Feeder:
ADF Capacity 50 sheets (A4, 20 lb. paper)
Recommended Daily
Volume
Illumination Cold Cathode Fluorescent
Electrical requirements 100 - 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz
Scanner Dimensions Height: 19.9 cm / 7.8 in.
Scanner Weight Kodak i55 Scanner: 6.7 kg / 14.8 lbs.
Host Connection USB 2.0 or SCSI II
Operating Temperature 10°C to 35°C (50°F to 95°F)
Humidity 20 to 80%
Environmental Factors Energy Star qualified scanners
Scanner Power Voltage: 24.0 Vdc; Current: 2.0 A
Power Consumption i55 Standby: <20 watts
Acoustic Noise
(Sound Power level)
• i55 Scanner: simplex color scanner with an automatic document feeder, 32
pages per minute (portrait), 200 dpi, bi-tonal
• i65 Scanner: duplex color scanner with an automatic document feeder, 32
pages per minute (portrait), 200 dpi, bi-tonal
Grayscale output bit depth is: 8
Color capture bit depth is: 48
Color output bit depth is: 24
• Maximum — 21.6 x 86 cm (8.5 x 34 in.) when the host PC is configured with
adequate memory.
• Minimum — 9.4 x 14 cm (3.7 x 5.5 in.)
Flatbed: Up to 21.6 x 29.7 cm (8.5 x 11.69)
1,500
Width: 56.7 cm / 22.3 in.
Depth: 35 cm / 13.8 in.
Kodak i65 Scanner: 7.5 kg / 16.5 lbs.
i55 Running: <30 watts
Sleep mode: <12 watts
i65 Standby: <30 watts
i65 Running: <40 watts
Sleep mode: <12 watts
Operating: less than 58 dB
Standby: less than 46 dB
A-61527 May 2006 87
Page 92

Appendix B Warranty Information - United States
Warranty Subject to the WARRANTY LIMITATIONS herein, Kodak warrants its products
to function properly during the warranty period. Warranty period starts from the
date of initial installation, when installed within one year from date of shipment.
(If the purchase price does not include installation, the warranty becomes
effective 14 days from date of shipment). KODAK warrants that Product shall
conform to the applicable specifications separately provided by KODAK and
shall be free from manufacturing related defects in materials and
workmanship. The warranty covers the purchaser of the equipment, as well as
anyone else who owns it during the warranty period.
Warranty repair coverage
If the product does not function properly during the warranty period, Kodak will
provide for telephone support and/or on-site maintenance, including any
adjustments and/or replacement of parts, [except Image Maintenance Kits,
supply items and consumables, such as disc, paper, ribbons, print heads, feed
rollers and all other items as referenced in the Manufacturer's Manual(s)]
required to maintain Products in an operating condition which is consistent with
Manufacturer's published specifications, without charge during Kodak’s normal
working hours (usually 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m., Monday through Friday). Parts
removed from the product and replaced at no-charge will become the property
of Kodak.
How to obtain service Call Kodak’s Customer Support Center at 1 (800) 356-3253. The Equipment
Service Identifier (Kodak K-number located on the equipment) must be
provided.
Warranty limitations A. Circumstances beyond Kodak's control (such as Customer overriding,
bypassing or defeating interlock switches on Products).
B. Misuse, abuse, failure to follow Manufacturer's Product operating
instructions.
C. Warranty service is limited to the United States.
KODAK MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR
STATUTORY, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR THE WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE FOR THIS PRODUCT.
REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT WITHOUT CHARGE ARE KODAK'S ONLY
OBLIGATIONS UNDER THIS WARRANTY. KODAK WILL NOT BE
RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE SALE, USE, OR IMPROPER
FUNCTIONING OF THIS PRODUCT, REGARDLESS OF THE CAUSE.
SUCH DAMAGES FOR WHICH KODAK WILL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE,
INCLUDE, BUT ARE NOT LIMITED TO, LOSS OF REVENUE OR
PROFIT, DOWNTIME COSTS, LOSS OF USE OF THE PRODUCT, LOSS
OF DATA, COST OF ANY SUBSTITUTE PRODUCT, FACILITIES OR
SERVICES OR CLAIMS OF CUSTOMERS FOR SUCH DAMAGES.
This limitation of liability will not apply to claims for injury to persons or damage
to property caused by the sole negligence or fault of KODAK or by persons
under its direction or control.
88 A-61527 May 2006
Page 93

EASTMAN KODAK COMPANY
Document Imaging
Rochester, New York 14650
www.kodak.com/go/docimaging
Kodak is a trademark of Eastman Kodak
Company.
A-61527 5/2005
©Eastman Kodak Company, 2005
 Loading...
Loading...