Page 1

VDV Scout® Pro 2
•
VOICE, DATA, AND VIDEO
•
AND SPLIT PAIRS
• • •
TONE GENERATOR
•
•
AUTO POWER-OFF
VDV501-098
VDV Scout® Pro 2 LT
VDV501-108
ENGLISH
Page 2

ENGLISH
VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 & VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT
The Klein Tools VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 is a portable voice-data-video cable tester. It tests and troubleshoots RJ11, RJ12,
®
Pro
2 LT combines these features with length measurement.
Section headers in
are relevant only to VDV501-108 VDV Scout
are relevant only to VDV501-108 VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT.
VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 and VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT:
6.4" x 2.8" x 1.4" (16.3 x 7.1 x 3.6 cm)
•
Weight:
9.0 oz. (255 g) with battery and remote
•
Operating Temperature:
32° to 122°F (0° to 50°C)
•
Storage Temperature:
-4° to 140°F (-20° to 60°C)
•
10% to 90%, non-condensing
Maximum Voltage
between any two connector pins
without damage:
RJ Jack:
66V DC or 55V AC
•
66V DC or 55V AC
•
Battery Life
•
Standby:
4 years
•
Active:
425 hours
Cable Types:
Shielded or unshielded; Cat-7, Cat-7a,
Cat-6a, Cat6, Cat-5e, Cat-5, Cat-4, Cat-3, Coax
Maximum RJ Cable Length:
0 to 1,000 ft. (305 m)
•
Minimum Cable Length for Split Pair Detection
•
Maximum Coax Cable Length:
100 ohms maximum DC
Capacitance
•
1 ft. (0.3 m)
•
constant (or 30nF total capacitance)
•
Accuracy):
±
±
WARNINGS
To ensure safe operation and service of the tester, follow these instructions. Failure to observe these warnings can
result in severe injury or death.
•
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 is designed for use on unenergized cabling systems. Connecting the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 to
®
Pro 2. Visually inspect an RJ
of the jack unless the plug is specifically designed for that purpose.
SYMBOLS:
WARNING:
Potential for personal injury.
Caution: Potential for damage or destruction to equipment.
Always wear approved eye protection.
Conformité Européenne. Conforms with European Economic Area directives.
This symbol indicates that equipment and its accessories shall be subject to a separate collection
and correct disposal.
RED
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT ONLY
Page 3
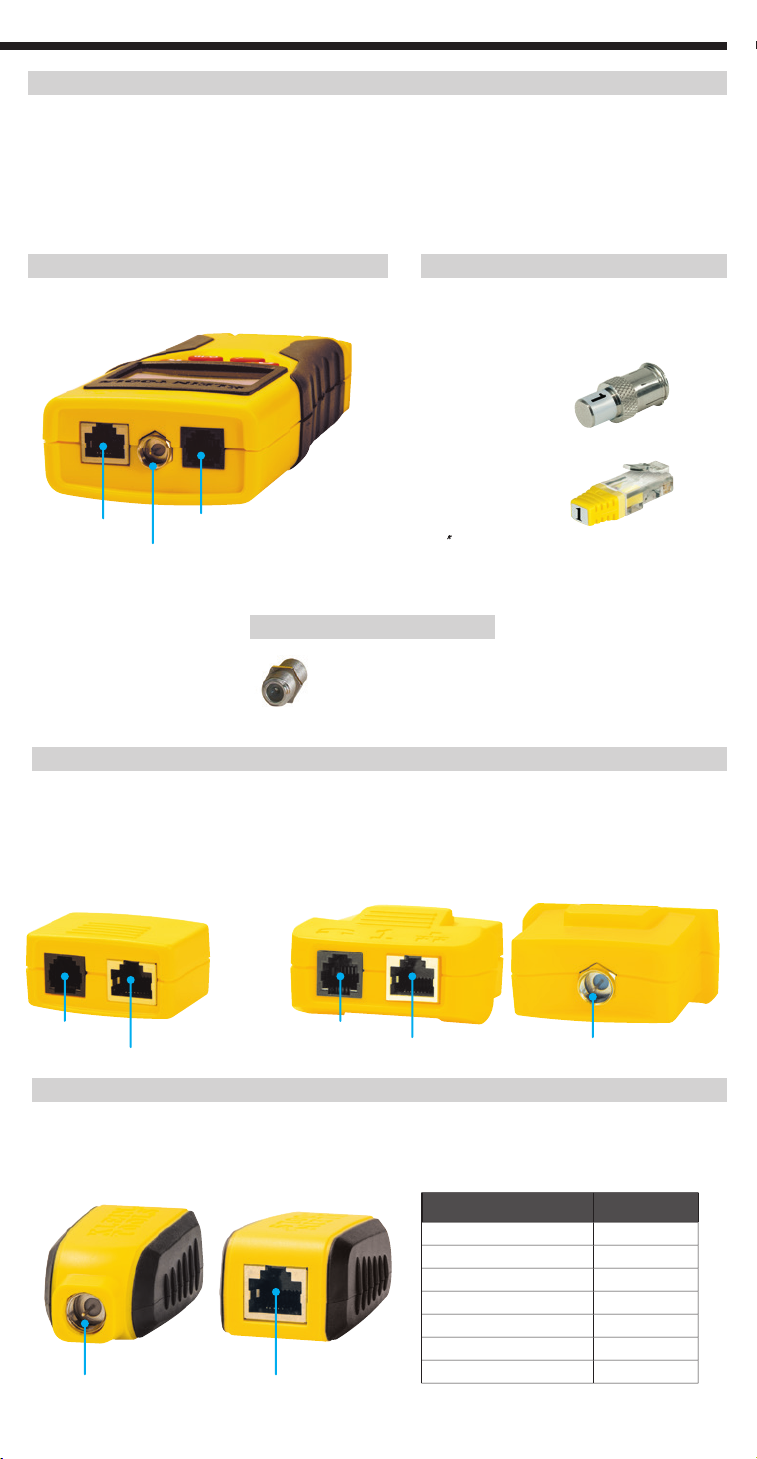
3
VDV526-055
Use for cable location identification mapping and continuity testing. Remotes display on tester
as Remote IDs #2-8.
Self-Storing Remote
VDV999-109
Video cable, coaxial cable, RG6 cable, RG59 cable.
2 twisted pair cable, 3 twisted pair cable, Cat3.
VDV SCOUT
®
PRO 2 OR VDV SCOUT
®
PRO 2 LT
CoaxMap™ Location ID Remote
VDV512-056
LanMap™ Location ID Remotes cannot
be used to determine continuity.
SELF-STORING ID REMOTES
TEST-N-MAP™ ID REMOTES
Barrel Connector
Use with F-connector port
Use for cable location identification mapping and/or continuity testing. Self-storing remotes display on tester
as Remote ID #1.
Front
Self-Storing Test-n-Map™ ID Remote
VDV999-110
VDV999-110
Test-n-Map™ Remote ID #
VDV501-112
3
VDV501-113
4
VDV501-114
5
VDV501-115
6
VDV501-116
VDV501-117
8
VDV501-118
Back
Use for cable location identification mapping.
Included in kit or sold separately.
Part #
Page 4
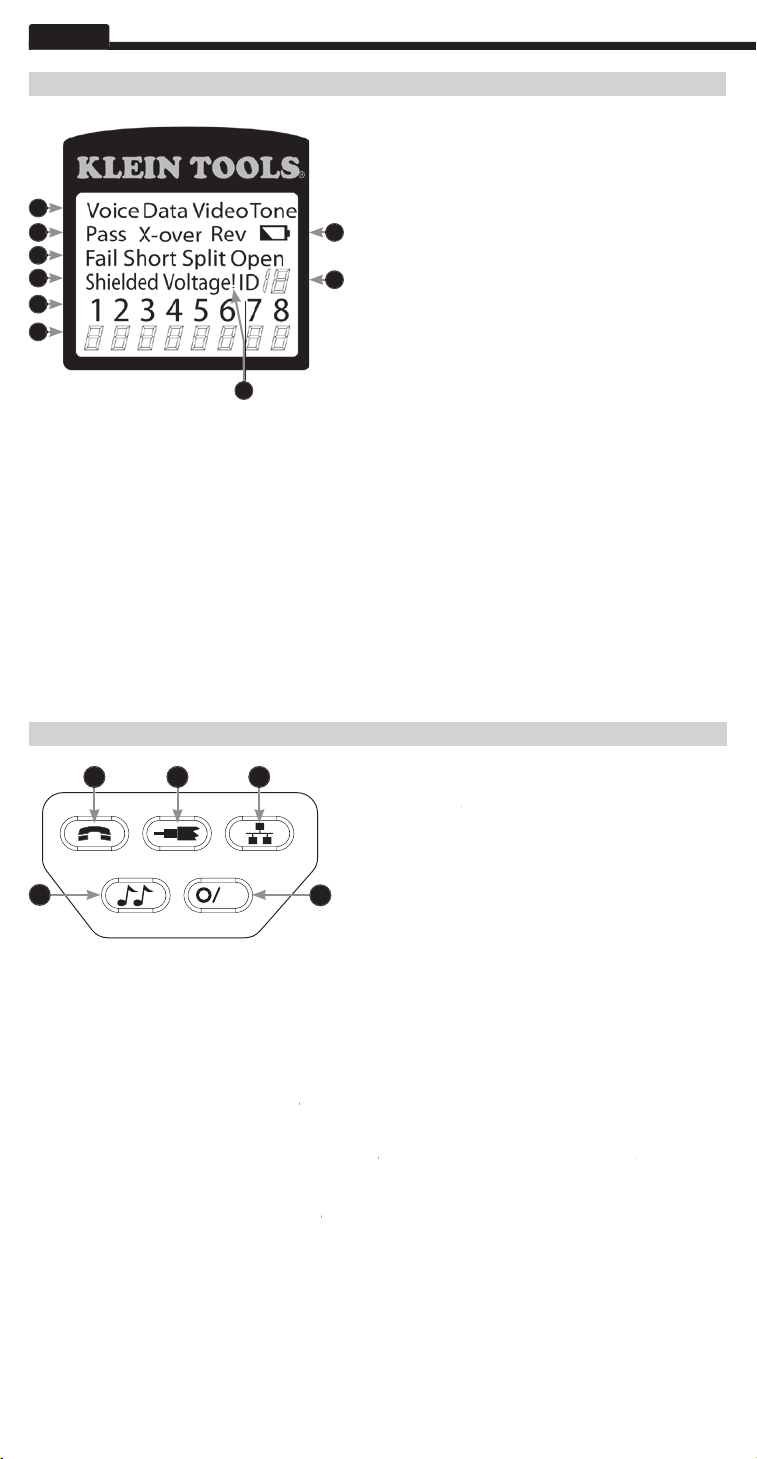
ENGLISH
1.
Mode:
The top line of the display shows the cable type test
2. Pass/Special Cables:
“Pass” will be on if the cable is a
one wired voice cable or a video cable with no faults. In
addition, the “X-over” illuminates if a properly wired cross-
over (uplink) cable is recognized, or the “Rev” illuminates if
the cable is a properly wired reverse-pinned voice cable. The
wire map will show actual pin connections.
3. Cable Faults:
The “Fail” icon will be on only if the cable is
error takes precedence over miswires and the appropriate
designated pairs are not twisted together in the cable, an
AC signal fault.
A. Voice:
VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 will turn off after 20 seconds automatically.
tests are run continuously and the display updated until the O/
Three hash marks will alternately light up on the display to
show the tester is in continuous mode. Continuous mode is
B. Video:
4. Shield:
“Shielded” illuminates when a shielded data cable is properly connected at both ends. It will be flashing if there is a
short to a wire in the cable along with that pin number and the “Short” indicator.
5. Tester-End Wire Map:
The top line displays the pins on the tester end in order. These pins are mapped to the pins on the
6. Remote-End Wire Map:
The bottom line displays the corresponding pin on the remote-end. Dash lines on the remote line
the equivalent of 10k
Ω
to 100k
Ω
of DC resistance.
7. Battery Low:
The battery low symbol illuminates when the battery is nearing depletion. The symbol will begin to flash when the
8. Location ID:
9. Voltage Detected Warning:
for voltage is performed before each test and if found, no test is run. The tester should be disconnected immediately from the
source of the voltage.
only for the F-connector, because the video continuity test is the same as the ID test. The test loops continuously until the O/ID
C. Data:
Scout
®
Pro 2 will turn off after 20 seconds automatically. If the button is pressed and held until “LOOP ON” is displayed, tests
are run continuously and the display updated until the O/ID button is pressed or after 5 minutes of no change in results. Three
finding intermittent problems.
When Tone is pressed, the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 begins sending an audio tone for the connector last tested with the pins
and cadence previously selected for that connector type. To change the connector type, press a different connector type button.
through the available tone cadences. To turn the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 off, press the O/ID button. The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 will
turn off automatically 60 minutes after the last button press. The tone is compatible only with analog tone tracers such as the
E. Off/ID:
®
Pro 2 when it is on in any mode. With the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 off, pressing the
O/ID button starts the ID test mode. The ID test mode scans for all possible ID types – voice, video and data. The “ID” icon and
a progression of “o” are displayed on the bottom line of the display to indicate scanning is active. If no ID remotes are found,
“Open” is displayed. When an ID remote is found, the connector type and the ID number are displayed. If multiple ID remotes
are found, the ID or fault is displayed in sequence. The test loops continuously until the O/ID button is pressed or for 5 minutes
after last change in ID status.
The RJ jacks share internal connections so only one RJ cable can be connected at a time for accurate cable test results.
®
Pro
2 may be connected at the same time.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A B C
D
ID
E
Page 5
5
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 OWNERS: PLEASE SKIP TO PAGE 7.
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT uses the capacitive properties of a cable to measure its length. One end of the cable should be connected
to the corresponding port on the top of the tester. The other end should be left disconnected or attached to the self-storing remote.
The Length Constant sections below discuss the best practices to follow when measuring length in order to achieve the most
accurate results.
The length constant refers to the electrical characteristic of a cable used to characterize length. Every cable has an associated length
constant in units of picofarads per foot. Setting the length constant on the tester is important to obtaining an accurate measurement
from the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT. The default length constants are as follows:
•
•
The length constant can sometimes be provided by the manufacturer of the cable (see EDITING LENGTH CONSTANT section). You
from 10pF/ft. to 40pF/ft.
consistency of the cable along its length.
The length constant can vary from cable to cable, even of the same type produced by the same manufacturer. It can also vary
over the length of one cable because the length constant is dependent on the physical properties of the cable, which may not be
consistent throughout the entire cable. The change in wire pair spacing through the cable can vary the length constant along the
When setting the length constant using a length of cable, the cable should be at least 50 ft. long. This will yield a ±2% uncertainty (1
®
Pro
2 LT will test for length on the first pair with no faults found. In
constant by 0.1pF. Hold down to scroll through values quickly.
and release to measure length of a cable connected to the
will decrease the length constant by 0.1pF. Hold down to scroll
through values quickly.
®
Pro 2 LT will test for
While the tester is off, press and hold for three seconds to enter Tone mode (see general Keypad
section). While the tester is off, press and release to enter Length Measurement mode. In Length Measurement mode, press
and release again to briefly show the length constant. Press and hold for three seconds to enter Length Constant Edit mode.
Connect one end of the cable under test to the RJ45 port
other end of the cable unterminated.
2.
to enter length mode.
3.
or the phone button
or the video button
on
the keypad to begin the test on the Ethernet cable or phone cable or coax cable,
4.
(Optional) press
or
repeatedly to select the pair of wires
that should be
5.
Read the length measurement
as shown.
A phone or data cable under test can be unterminated (open) or terminated by an
or 2 ft. greater than the actual measurement. In this case, subtract 1 or 2 ft. from
the reading to obtain the actual measurement. Coax cable under test must be left.
F G H
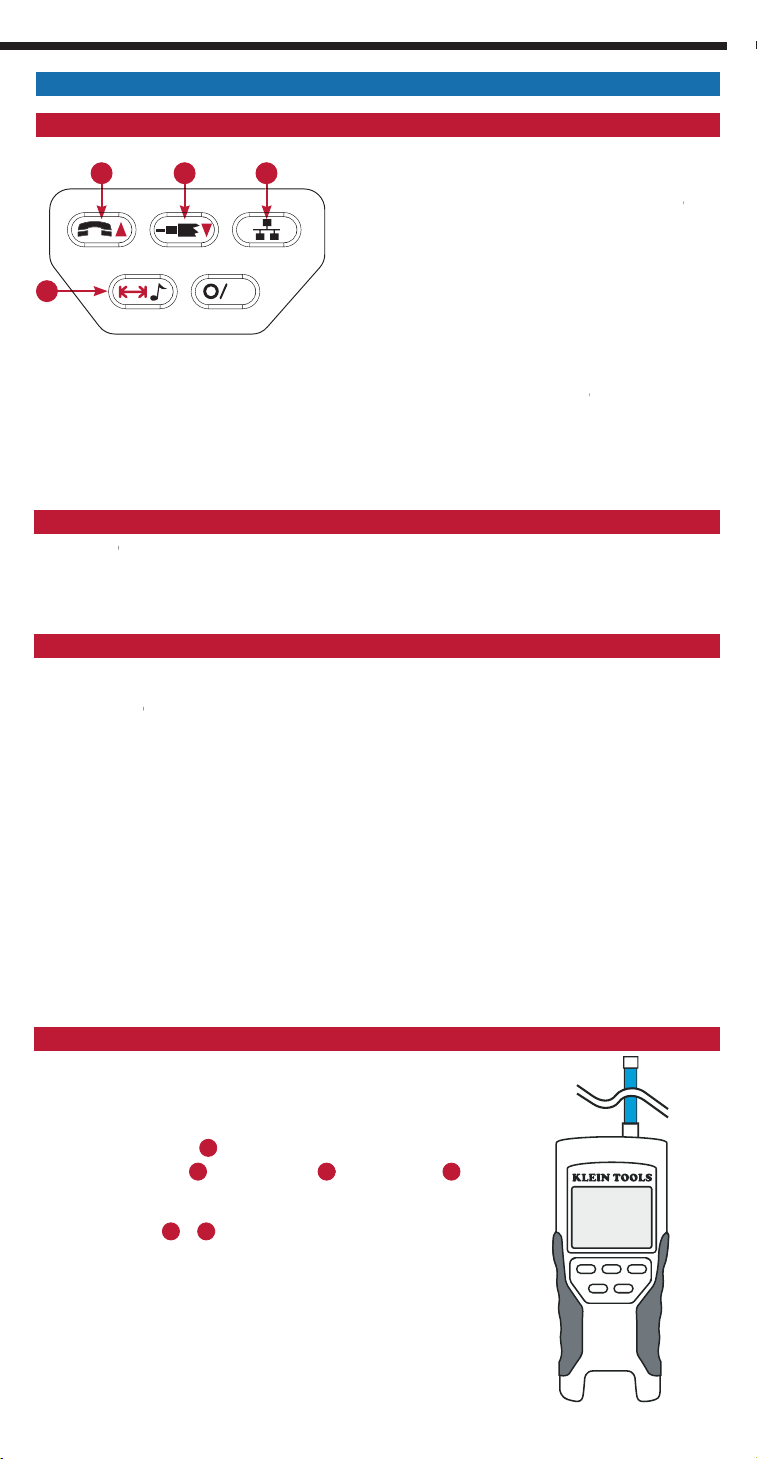
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT KEYPAD
F. Voice/Up Arrow:
I
H. Data:
I. Tone/Length Measurement:
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – MEASURING LENGTH OVERVIEW
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – LENGTH CONSTANT
Voice:
Data:
Video:
ID
G. Video/Down Arrow:
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – MEASURING LENGTH
I
H
H
F
F
G
Page 6

6
ENGLISH
Test Running Continuously
Cable Type
Assure the tester is off
and the screen is blank.
2.
to enter length mode.
3.
again.
The length constant will be displayed
on the screen for three seconds.
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT stores a separate length constant for each of the three cable types (voice, data, and video).
1.
MEASURING LENGTH
section
to set up the correct type of cable.
2.
for three seconds until EDIT CAP is shown
on the screen.
3.
and Down Arrow
to increment or decrement the length constant
in units of 0.1pF to the desired
value. The screen will switch back and forth between
the length measurement and the length constant value
every two seconds while no buttons are pressed.
4.
again
to return to length measurement.
should be 50 ft. or greater.
Cut or obtain a length of cable of the same type you would like to measure.
Measure the cable using standard methods (pad
2.
MEASURING LENGTH
section
to set up the cable to be tested.
3.
for three seconds until EDIT CAP is shown
on the screen.
4.
and Down Arrow
to increment or decrement the length constant
in units of 0.1pF. The screen will
switch back and forth between the length measurement and the length constant value every two seconds while no buttons are
still be changed while the length measurement is being viewed in this mode.
5.
again to return to
You may now measure
other unknown lengths of cable.
Assure the tester is off
and the screen is blank.
2.
to enter length mode.
3.
and video button
at the same time.
The screen will show "METERS" or "Ft." momentarily, then
show the length measurement in the unit selected.
"0_0" for 0.0 meters. Length constants are displayed in pF/ft. or pF/m depending on the selected unit measurement mode.
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – MEASURING LENGTH
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – DISPLAYING LENGTH CONSTANT
I
I
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – LENGTH CONSTANT EDIT MODE
I
F
G
I
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – DETERMINING LENGTH CONSTANT
I
F
G
I
VDV SCOUT® PRO 2 LT – CHANGING UNIT OF MEASUREMENT
I
F
G
Page 7

7
TESTING CONTINUITY - OVERVIEW
When testing for continuity of a cable, you are checking that all conductors within a cable are connected properly from one end
to the other.
connected (a "short").
TESTING CONTINUITY - TERMINATED OR INSTALLED RJ45/RJ12 CABLE
Testing Continuity
1
Testing Continuity
Testing Continuity-Installed
1
8-wire Ethernet cables can have an additional set of errors. A miswire simply means that the pin on one side of the cable is not
connected to the identical pin on the other side of the cable (for example, pin 2 on one side is connected to pin 6 on the other side).
Certain pairs of conductors are required to be twisted together from endpoint to endpoint. These errors are called split pairs, and
can be present in cables that don't have any miswires.
Testing continuity is not the same as testing bandwidth. Other testers exist for verifying the amount of data that can pass through
a cable.
Connect one end of the cable under test
to the RJ45 port (if you are testing an Ethernet cable) or RJ12 port (if you are
testing a phone cable) located at the top of the main tester body. If testing a wall port, connect a known good patch cable
from the wall plate to the appropriate port at the top of the main tester body.
Connect the other end of the cable
under test to the corresponding port on the testing remote (LOCATION ONLY ID remotes
cannot be used). If testing a wall port, connect a known good patch cable
†
from the wall port to the appropriate port on the
testing remote.
3.
or the phone button
on the keypad to begin the test on the Ethernet cable or phone cable,
of the test using the
Wiring and Display Examples
section.
†
Only Klein Tools Universal RJ12 Jumper Cable (VDV726-125) or an approved equivalent should be used in the RJ45 jack of
the Test-n-Map™ ID Remotes. Using a non-universal RJ11/12 patch cable could result in damaged contact pins.
TESTING CONTINUITY - TERMINATED OR INSTALLED COAX CABLE
Testing Continuity
Testing Continuity-Installed
Testing Continuity-Term Coax
1
1 2 3
Testing Continuity
Testing Continuity-Installed
Testing Continuity-Term Coax
Testing Continuity- Installed Coax
1
1 2 3
Attach barrel connector
to the open coax port on the top of the main tester body.
Connect one end of the cable
to the barrel connector at the top of the main tester body.
3.
attach a second barrel connector to the other end of the cable under test.
This step is not necessary if testing an installed coax cable
(cable attached to a wall plate).
4.
Connect a numbered CoaxMap™ Location ID Remote
to the second barrel connector
or
attach one of the
Test-n-Map™ ID Remotes
to the barrel connector.
5.
on the keypad to begin the test on the coax cable.
6.
using the
Wiring and Display Examples
section.
Test
Test Remotes
or
or
Test
Test Remotes
or
Test
Test
or
C
A
B
Page 8

8
ENGLISH
®
The first and most convenient way to identify installed cables is by using location ID remotes. Using location ID remotes, you can trace
any manual tracing.
The second way to identify cables is using the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2's built-in analog tone generator. The tester will place a low-frequency
voltage on the cable. By using an analog tone probe (Klein Tools VDV526-054, VDV500-060, or most other manufacturers’ analog
tone probes, sold separately), a cable can be identified by the tone it is carrying. This technique only allows one cable to be traced per
tone generator, but has additional benefits like the ability to trace a cable manually behind certain wall materials, or trace unterminated
cables of non-standard types.
LanMap™ Location ID Remotes cannot be used to verify continuity
snaps into the bottom of the tester or the Test-n-Map™ ID Remotes (included in some kits, or sold separately) can be used to test
continuity of data or phone cables. However,
CoaxMap™ Location ID Remotes can be used to verify continuity and identify
coax
cables. Any numbered CoaxMap™ Location ID Remote can be used to test continuity.
Testing Continuity
Testing Continuity-Installed
Testing Continuity-Term Coax
Testing Continuity- Installed Coax
1 2 3
1
1
1 2 3
of each room that needs to be identified. Write down
2.
Take the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 to the wiring closet or router
(the source of the internet connection).
3.
Connect an unknown cable to the RJ45 port
on the top of the tester.
4.
on the keypad to begin the ID test on the Ethernet cable. The LCD will read "Data ID#" where "#" is
the ID number of the LanMap™ Location ID Remote connected to the other side of the cable. Compare this number to the
5.
Repeat steps 3 and 4 for each unknown cable
1
1 2 3
of each room that needs to be identified.
Write down pairs of numbers and room names for later.
2.
Take the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 to the wiring closet or cable splitter
(the source of the cable connection).
3.
Connect an unknown cable to the video port
on the top of the tester.
4.
on the keypad to begin the ID test on the coax cable. The LCD will read " Video ID#" where "#" is
the ID number of the CoaxMap™ Location ID Remote connected to the other side of the cable. Compare this number to the
5.
Repeat steps 3 and 4 for each unknown cable
until all have been labeled. You can use these labels to determine which
Ethernet and coax cable can be identi ed simultaneously.
When both cables are connected at the same time and the ID
E
E
Page 9

9
1
1 2 3
Connect a known working patch cable
to the RJ45 port (if you are tracing an Ethernet cable) or RJ12 port (if you are
tracing a phone cable) located at the top of the main tester body.
2.
Connect the other end of the patch cable
to the wall port at the satellite location of the cable under test (not at the
wiring closet).
3.
D
on the keypad to initialize the tone generation. Press it repeatedly to change the tone cadence
from a steady low or high tone to a warbling slow or fast tone.
4.
or the phone button
will be placed on.
5.
Take the analog tone probe to the wiring closet or router
6.
entering the wiring closet. The tone will be loudest at the cable that the
VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 is connected. Mark the cable with a label.
7.
Repeat steps 2-6
for each room that has installed cable.
1
1 2 3
Attach barrel connector
to the open coax port on the top of the main tester body.
2.
Connect a known working patch cable
to the barrel connector at the top of the main tester body.
3.
Connect the other end of the patch cable
to the wall port at the satellite location of the cable under test (not at the
wiring closet).
4.
Press the tone button
on the keypad to initialize the tone generation. Press it repeatedly to change the tone cadence
from a steady low or high tone to a warbling slow or fast tone.
5.
to place the tone on the coax output port.
6.
Take the analog tone probe to the wiring closet or cable splitter
7.
entering the wiring closet. The tone will be loudest at the cable that the
VDV Scout
Pro 2 is connected to. Mark the cable with a label.
8.
Repeat steps 2-7
for each room that has installed cable.
C
A
D
B
Page 10

ENGLISH
TESTING CONTINUITY & CABLE IDENTIFICATION SIMULTANEOUSLY – INSTALLED RJ45/RJ12 CABLE
Attach a numbered Test-n-Map™ ID Remote to the RJ45/RJ12 port
of each room that needs to be identified using a known
good patch cable
‡
comparing/identifying the cables later.
2.
Take the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 to the distribution point
(often a wiring closet, switch or router at the other end of the cable
3.
Connect an unknown cable to the RJ45 port
on the top of the tester.
4.
or phone button
on the keypad to begin the test on the Ethernet or phone cable, respectively. The
side of the cable.
5.
Compare this number to the remote number/room pair list you made in step 1
and mark the cable with a piece of labeled
tape, print a label or mark with a permanent ink pen. The LCD will also display the results of the continuity test. These results
should be interpreted using the
Wiring and Display Examples
section.
6.
Repeat steps 4 and 5 for each unknown cable
should be connected to the cable splitter, or to troubleshoot intermittent connections in the future.
‡
Only Klein Tools Universal RJ12 Jumper Cable (VDV726-125) or an approved equivalent should be used in the RJ45 jack of the
Test-n-Map™ ID Remotes. Using a standard RJ11/12 patch cable could result in damaged contact pins.
TESTING CONTINUITY & CABLE IDENTIFICATION SIMULTANEOUSLY – OVERVIEW
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 has the capability of simultaneously testing continuity and providing cable location identification for up to eight
®
Pro 2 series testers come with
either the standard self-storing remote #1 or the Self-Storing Test-n-Map™ ID Remote #1. Test-n-Map™ ID Remotes #2 through #8
are included in some kits, or sold separately in the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 Test-n-Map™ ID Remote Kit (VDV770-827).
VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 Test-n-Map™ ID Remote Kit (VDV770-827)
C
A
Page 11

TESTING CONTINUITY & CABLE IDENTIFICATION SIMULTANEOUSLY – INSTALLED COAX CABLE
Attach a numbered Test-n-Map™ ID Remote to the F-connector port
of each room. Write down the number of the remote and
of the room number/description in which it is placed for comparing/identifying the cables later.
2.
Take the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 to the distribution point
(often a wiring closet, switch or router at the other end of the cable
3.
Connect an unknown cable to the video port
on top of the tester using a barrel connector.
4.
B
on the keypad to begin the test on the coax cable. The LCD will display “Video ID#” where “#” is the
5.
Compare this number to the remote number/room pair list you made in step 1
and mark the cable with a piece of labeled
tape, print a label or mark with a permanent ink pen. The LCD will also display the results of the continuity test. These results
should be interpreted using the
Wiring and Display Examples
section.
6.
Repeat steps 4 and 5 for each unknown cable
should be connected to the cable splitter, or to troubleshoot intermittent connections in the future.
Does the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 measure cable length?
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 does not measure cable length. The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2
does measure cable length.
2.
Does the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT use Time Domain Re ectometry (TDR)?
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 LT does not use TDR to measure cable length. The capacitive properties of a cable are used to determine
the cable length.
3.
Does the VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 test the bandwidth of the cable?
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 only performs continuity related tests and split pair testing.
4.
The screen is ashing “3” and “6” with “U” underneath them when I try to test the continuity of an Ethernet cable.
What's wrong?
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 only tests continuity on cables terminated with the Self-Storing Remote or a Test-n-Map™ ID Remote.
5.
The screen is ashing “For ID Test Only” with an ID number showing when I try to test the continuity of an Ethernet cable.
What's wrong?
The VDV Scout
®
Pro 2 only tests continuity on cables terminated with the self-storing remote or Test-n-Map™ ID Remotes.
6.
When I am testing continuity of an Ethernet or phone cable, there are 3 vertical hash marks moving across the right side of
the screen. What does this mean?
or the phone button
for about 3 seconds. In coax continuity mode, loop mode is always
active. In tone generation mode, the vertical hash marks indicate the tone is active.
7.
How do I know which end of a cable is bad?
®
Pro 2. Assuming that the cable is not
damaged somewhere in its length (i.e. it's a brand new cable), you can sometimes determine which end to redo based on the
diagnostic message. For instance, if the cable says there is this miswire:
Then you can usually determine which end just by looking closely again at your terminations through the clear plug. For opens
and shorts, it is not as easy to determine whether a pin is making contact with the wire just from observation. It could also be
8.
Why don't I hear anything when the tester is in the tone mode?
®
Pro 2.
C
A
Page 12

ENGLISH
WIRING AND DISPLAY EXAMPLES
Properly Wired T568A UTP:
T568B is electrically identical to T568A, but swaps the green and orange pairs. Either standard will work as long as the same
standard is used at both ends of a run or patch cable. Mixing “A” and “B” creates a cross-over cable.
T568A Cable with a miswire and unrecognized continuity:
1 and
2 pins on the
VDV Scout
®
Pro 2
are connected to pins 2 and 1 at
the remote-end. The pins with this error are flashing. The “U” for
the remote pin numbers indicates an unrecognizable continuity was
detected that is neither a short or open. An ID remote connected to the
VDV Scout
®
Pro 2
when in cable test mode would also show this error.
T568A Cable with a Miswire and Unrecognized Continuity:
T568A Cable with a Short and an Open:
The 1-2 pair pins are shorted together and the 7-8 pair is open. The pins with the errors are
flashing. Dash lines (-) on the bottom (remote) display line indicate the short, while no numbers on the bottom line indicate the open pair.
T568A Cable with a Short and Open:
T568A Cable with Split Pairs:
T568A Cable with Split Pairs:
A common error in building a cable is to put all the pairs in pin sequence 1-2, 3-4, 5-6 and 7-8. This will
produce the correct continuity, but the pairs are designated to be on pins 3-6 and 4-5 in the middle of the connector for compatibility with
phone wiring. This wiring error is only detected by the split pair test since the designated pairs are not twisted together.
8
Page 13

WIRING AND DISPLAY EXAMPLES
Coax Cable Properly Wired with ID Remote #1:
The #1 ID remote is used to terminate a properly wired coax cable. The video test passes,
Coax Cable with an Open:
There is a break in the cable continuity. A break in the shield or in the center wire can cause an open fault. The
cable does not pass and the ID remote number on the other end of the cable cannot be determined.
Coax Cable with a Short:
The center wire of the cable is connected to the shield, creating a short. The cable does not pass and the ID remote
Page 14

450 Bond Street
www.kleintools.com
ENGLISH
®
Pro 2 with a #1 Phillips head screwdriver.
2. Disconnect battery cable and recycle exhausted battery.
3. Acquire a 9 volt alkaline battery (IEC 6LR61, ANSI/NEDA 1640A).
4. Connect battery cable to new battery observing polarity and place into battery compartment.
5. Replace battery door and screw, taking care not to over-tighten it.
WARRANTY
www.kleintools.com/warranty
Turn instrument off and disconnect any cables. Clean the instrument by using a damp cloth. Do not use abrasive cleaners
or solvents.
STORAGE
tures or humidity. After a period of storage in extreme conditions exceeding the limits mentioned in the Specifications
section, allow the instrument to return to normal operating conditions before using it.
Tools for proper disposal options.
 Loading...
Loading...