Page 1

Manual P/N 820-1557 Rev. B 01/10 2509-7214-01
ATTENTION: Please take a few minutes to thoroughly read this
user’s guide which should be saved for future reference and
passed on to any subsequent owner.
Carbon Monoxide and
Explosive Gas Alarm
User’s Guide
Model: KN-COEG-3 (900-0113)
• 120V AC • 9V Battery Backup • Peak Level Memory
KN-COEG-3
with Digital Display
SINGLE STATION CARBON MONOXIDE
ALARM ALSO SUITABLE FOR USE AS A
RESIDENTIAL GAS DETECTOR
Page 2

Carbon Monoxide Alarm Procedure
1) Operate the Test/Reset button;
2) Call your emergency services (Fire Department or 911);
3) Immediately move to fresh air - outdoors or by an open
door/window. Do a head count to check that all persons are
accounted for. Do not reenter the premises nor move away
from the open door/window until the emergency services
responders have arrived, the premises have been aired out, and
your alarm remains in its normal condition.
4) After following steps 1-3, if the alarm reactivates within a 24
hour period, repeat steps 1-3 and call a qualified appliance
technician to investigate sources of CO from fuel burning
equipment and appliances, and to inspect for proper operation
of equipment.
If problems are identified during this inspection, have the equipment serviced immediately. Note any combustion equipment not
inspected by the technician and consult the manufacturer’s instructions, or contact the manufacturer’s directly for more information
about CO safety and the equipment. Make sure that motor vehicles
are not, or have not been, operating in a garage attached or adjacent to the residence.
Never restart the source of a CO problem until it has been
corrected. Never ignore the sound of the alarm!
If the alarm is sounding, pressing the test/reset button will
terminate the alarm. If the CO condition that caused the alert
in the first place continues, the alarm will reactivate. If the
unit alarms again within six minutes, it is sensing high levels
of CO which can quickly become a dangerous situation.
WARNING:
Activation of the CO
Alarm indicates the presence of Carbon
Monoxide (CO) which can kill you.
PHONE NUMBER:
PHONE NUMBER:
What to do When the Alarm Sounds!
Page 3
Gas Alarm Procedure
When the unit senses either natural gas or propane, the display will
show “GAS” and emit a loud alarm pattern. The alarm pattern for gas
is a 1/2 second beep followed by a 1/2 second of silence then repeating. Know how to respond to a CO or gas emergency.
If the unit alarms for gas:
1) Evacuate the premises;
2) Do not activate any electrical switch or telephone;
3) Contact your fire department.
NOTE: If Gas is present the unit will continue to alarm even if
the “Test/Reset” button is pressed. Unit will stop alarming if
gas is removed.
WARNING:
Activation of the Gas
Alarm indicates the presence of an
explosive gas which can cause an
explosion and/or fire.
PHONE NUMBER:
What to do When the Alarm Sounds!
Page 4

Welcome
Note: Many times throughout this User’s Guide, we will refer to
Carbon Monoxide as “CO”. The words “Gas” or “Explosive Gas”
will refer to Natural Gas or Propane.
This Kidde carbon monoxide (CO) and gas alarm is an important part of
your family’s home safety plan. This alarm has been designed and tested
to detect CO and gas buildup in a residential environment. Your alarm is
for use specifically in the home. As an owner of a CO and gas alarm,
there are some basic facts you should know about for your protection.
Many people think that CO and gas alarms operate like smoke alarms.
Like smoke alarms, CO and gas alarms monitor the air in your home and
sound a loud alarm to warn you of trouble. The way you respond to a
CO and gas alarm is quite different than a smoke alarm. That’s because
a house fire and a CO or gas problem are distinctly different situations. If
your smoke alarm were to alarm, you would quickly be able to judge the
level of danger you were in with your senses. You can see and smell the
smoke, feel the heat, see, and possibly hear the fire burning. You can
also readily see if your smoke alarm is alarming in a non-emergency situation. Because your sense of sight, smell, hearing and touch give you
information, you can almost instantly judge what action to take if you
hear your smoke alarm.
CO is an invisible, odorless, tasteless and non-irritating gas – completely
undetectable to your senses. That’s why it is important to your safety
that you have a CO alarm.
Note: Refer to Section 1 for information about natural gas and propane.
Important Warning Statements
IMPORTANT: This carbon monoxide and gas alarm is designed to
detect carbon monoxide from ANY source of combustion. This
alarm will also detect the presence of natural gas or propane. It is
NOT designed to detect smoke or fire.
WARNING: Carbon monoxide alarms are not smoke alarms. This
carbon monoxide alarm is not a substitute for installing and
maintaining an appropriate number of smoke alarms in your
home.
This carbon monoxide and gas alarm will not sense smoke or fire,
even though carbon monoxide can be generated by fire. For this
reason you must install smoke alarms to provide early warning of
fire and to protect you and your family from fire and its related
hazards.
Page 5

Important Warning Statements
CAUTION: This alarm will only indicate the presence of carbon
monoxide, natural gas or propane at the sensor. Carbon monoxide, natural gas or propane may be present in other areas.
WARNING: This product is intended for use in ordinary indoor
locations of family living units. It is not designed to measure compliance with Occupational Safety and Health Administration
(OSHA), commercial or industrial standards. It is not suitable for
installation in hazardous locations as defined in the National
Electric Code.
The installation of this device should not be used as a substitute
for proper installation, use and maintenance of fuel burning
appliances, including appropriate ventilation and exhaust systems. It does not prevent CO or gas from occurring, nor can it
solve and existing CO or gas problem.
WARNING: This device is designed to protect individuals from
acute effects of carbon monoxide exposure. It may not fully safeguard individuals with specific medical conditions. If in doubt,
consult a medical practitioner.
Individuals with medical problems may consider using warning
devices which provide audible and visual signals for carbon
monoxide concentrations under 30 PPM.
This carbon monoxide and gas alarm requires a continuous supply
of electrical power – it will not work without power. Models
without battery backup will not operate during power failure.
The alarm will detect carbon monoxide primarily and explosive
gas secondarily. CO events will take presidence over explosive
gas events.
This alarm has not been investigated for carbon monoxide detection below 70 PPM.
Contents of This User’s Guide
1. Information About Carbon Monoxide and Explosive Gas
2. Product Features and Specifications
3. Installation Locations
4. Installation Instructions
5. Alarm Characteristics
6. KN-COEG-3 Operating Characteristics
7. Maintenance
8. Limited Warranty
Page 6

General Carbon Monoxide Information
CO is a colorless, odorless and tasteless poison gas that can be fatal
when inhaled. CO inhibits the blood’s capacity to carry oxygen.
Periodically review this alarm manual and discuss your CO alarm emergency procedure with all the members of your family. Never ignore a CO
alarm. A true alarm is an indication of potentially dangerous levels of
CO. CO alarms are designed to alert you to the presence of CO before
an emergency – before most people would experience symptoms of CO
poisoning, giving you time to resolve the problem calmly.
Determine if anyone in the household is experiencing symptoms of CO
poisoning. Many cases of reported CO poisoning indicate that while
victims are aware they are not well, they become so disoriented they are
unable to save themselves by either exiting the building or calling for
assistance. Also, young children and household pets may be the first
affected. You should take extra precautions to protect high-risk persons
from CO exposure because they may experience ill effects from CO at
levels that would not ordinarily affect a healthy adult.
Symptoms of CO Poisoning
The following common symptoms are related to CO poisoning and
should be discussed with ALL members of the household.
Mild Exposure:
Slight headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue (often described as “flu-like”
symptoms).
Medium Exposure:
Severe throbbing headache, drowsiness, confusion, fast heart rate.
Extreme Exposure:
Unconsciousness, convulsions, cardio-respiratory failure, death.
If you experience even mild symptoms of CO poisoning, consult your
doctor immediately!
Carbon Monoxide PPM Levels
Model KN-COEG-3 is equipped with a digital display that shows levels of
CO (displayed in PPM – parts per million). Learn the difference between
dangerous, high, mid and low levels.
Dangerous Levels:
When someone is experiencing symptoms of CO poisoning and CO
readings are generally above 100 PPM. Anytime someone is experiencing
the symptoms of CO poisoning this should be treated as an emergency.
1. Information About Carbon Monoxide
and Explosive Gas
Page 7

See “What to do When the Alarm Sounds” (inside front cover).
High Levels:
Generally above 100 PPM, with no one experiencing symptoms. This
should be treated as an urgent situation. See “What to do When the
Alarm Sounds” (inside front cover).
Mid Levels:
Generally between 50 PPM to 100 PPM. This should be cause for
concern and should not be ignored or dismissed. See “What to do
When the Alarm Sounds” (inside front cover).
Low Levels:
Generally below 50 PPM. Kidde recommends you take action to
eliminate the source of CO. See “What to do When the Alarm Sounds”
(inside front cover).
Possible Sources of Carbon Monoxide
Inside your home, appliances used for heating and cooking are the most
likely sources of CO. Vehicles running in attached garages can also
produce dangerous levels of CO.
CO can be produced when burning any fossil fuel, such as gasoline,
propane, natural gas, oil and wood. It can be produced by any fuelburning appliance that is malfunctioning, improperly installed, or not
ventilated correctly, such as:
• Automobiles, furnaces, gas ranges/stoves, gas clothes dryers, water
heaters, portable fuel burning space heaters and generators,
fireplaces, wood-burning stoves and certain swimming pool heaters.
• Blocked chimneys or flues, back drafts and changes in air pressure,
corroded or disconnected vent pipes, loose or cracked furnace
exchangers.
• Vehicles and other combustion engines running in an open or closed
garage, attached or near a home.
• Burning charcoal or fuel in grills and hibachis in an enclosed area.
Conditions That Can Produce Carbon Monoxide
The following conditions can result in transient CO situations:
• Excessive spillage or reverse venting of fuel-burning appliances caused
by outdoor ambient conditions, such as, wind direction and/or velocity, including high gusts of wind, heavy air in the vent pipes
(cold/humid air with extended periods between cycles).
1. Information About Carbon Monoxide
and Explosive Gas
Page 8

• Negative pressure resulting from the use of exhaust fans.
• Simultaneous operation of several fuel-burning appliances competing
for limited internal air.
• Vent pipe connections vibrating loose from clothes dryers, furnaces, or
water heaters.
• Obstructions in, or unconventional, vent pipe designs which can
amplify the above situations.
• Extended operation of unvented fuel-burning devices (range, oven,
fireplace, etc.).
• Temperature inversions which can trap exhaust gases near the ground.
• Vehicle idling in an open or closed garage, or near a home.
To be safe, know the possible sources of CO in your home. Keep fuelburning appliances and their chimneys and vents in good working condition. Learn the early symptoms of exposure, and if you suspect CO poisoning, move outside to fresh air and get emergency help. Your first line
of defense is an annual inspection and regular maintenance of your
appliances. Contact a licensed contractor or call your local utility company for assistance.
Information About Carbon Monoxide Alarms –
What They Can and Cannot Do:
CO alarms provide early warning of the presence of CO, usually before a
healthy adult would experience symptoms. This early warning is possible,
however, only if your CO alarm is located, installed and maintained as
described in this guide.
Because carbon monoxide is a cumulative poison, long-term exposures
to low levels may cause symptoms, as well as short-term exposures to
high levels. This Kidde unit has a time-weighted alarm – the higher the
level of CO present, the sooner the alarm will be triggered.
This CO alarm can only warn you of the presence of CO. It does not
prevent CO from occurring, nor can it solve an existing CO problem. If
your unit has alarmed and you’ve provided ventilation by leaving your
windows and doors open, the CO buildup may have dissipated by the
time help responds. Although your problem may appear to be
temporarily solved, it’s crucial that the source of the CO is determined
and that the appropriate repairs are made.
1. Information About Carbon Monoxide
and Explosive Gas
Page 9

This CO alarm is designed to act as a monitor; it is not designed for use
as a short-term testing device to perform a quick check for the presence
of CO.
CO alarms have limitations. Like any other electronic device, CO alarms
are not fool-proof. CO alarms have a limited operational life. You must
test your CO alarm weekly, because it could fail to operate at any time.
If your CO alarm fails to test properly, or if its self-diagnostic test reveals
a malfunction, immediately have the unit replaced. This alarm will not
monitor CO levels while in an error condition.
CO alarms can only sense CO that reaches the unit’s sensor. It’s possible
that CO may be present in other areas without reaching the alarm. The
rate and ability that which CO reaches the alarm may be affected by:
• Doors or other obstructions.
• Fresh air from a vent, an open window or other source.
• CO being present on one level of the home and not reach a CO alarm
installed on a different level. (For example, CO in the basement may
not reach an alarm on the second level, near the bedrooms).
For these reasons, we recommend you provide complete coverage by
placing a CO alarm on every level of the home. Please carefully read all
information on properly installing this CO alarm.
CO alarms should not be used to detect the presence of natural gas
(methane), propane, butane, or other combustible fuels.
Instruct children never to touch, unplug or otherwise interfere with the
alarm. Warn children of the dangers of CO poisoning.
General Information About Explosive Gas:
Natural Gas is typically supplied through a main utility line connected to
your home. If you do not live in a rural area you are likely to be a user of
natural gas. Natural gas is much lighter than air and will rise rapidly. If
you are a user of natural gas, mount your CO and Gas alarm 12 inches
away from the ceiling to ensure the earliest opportunity to detect a leak.
Propane is typically supplied to homes via delivery truck in liquid form
and stored near the home in propane tanks. Propane and LP-gas (liquefied petroleum) are often used synonymously. Propane is much heavier
than air and will collect at lower levels. If you are a user of propane,
mount your CO and Gas alarm near the floor to ensure the earliest
opportunity to detect a leak.
1. Information About Carbon Monoxide
and Explosive Gas
Page 10

2. Product Features and Specifications
Blinking
Red Dot
Digital
Display
Carbon
Monoxide
ALARM
Explosive
Gas
ALARM
Test/Reset
Button
Peak Level
Button
Back
Door
Key
Holes
Slide Support for Table Top
and Direct Plug Use
Adapter
Thumb Release
Removable
AC Adapter
Cord
Recess
Power
Cord
Sounder
Alarm
9V Backup
Battery
(shown installed)
Install Backup
Battery
(as shown)
Model KN-COEG-3
with digital display
Both propane and natural gas are colorless and odorless. For safety reasons, an odorant (Mercaptan) is added so that any leak can be detected
by smell. The common detection threshold for smelling the gases is
around 20% of the lower explosion limit (LEL). This can vary greatly
depending on the individuals’ sense of smell and how long they have
been exposed to either gas. The LEL of each of these gases defines the
bottom range of flammability for the gas. Your CO and Gas alarm is calibrated to alarm before 25% of the LEL of either gas detected. Therefore,
it is possible that you may smell gas before the alarm activates.
1. Information About Carbon Monoxide
and Explosive Gas
Page 11

2. Product Features and Specifications
IMPORTANT: Seven (7) years after the initial power up, this alarm
will “beep” two times every 30 seconds to indicate that it is time
to replace the alarm. Replace the alarm immediately! It will not
detect CO in this condition.
To help identify the date to replace the alarm, a label has been affixed to
the side of the alarm. Write the “replace by” date (seven years from
power up) in a permanent marker on this label.
Temperature:
Operating Range: 40°F (4.4°C) to 100°F (37.8°C)
Humidity:
Operating range: 10-95% non-condensing
Audible Alarm:
85+ dB at 10’ @ 3.4±0.5 KHz pulsing alarm
CO Sensor:
Electrochemical
Gas Sensor:
Metal Oxide
Power:
120 volts AC, 60 Hz, 60 mA max, 9 volt battery back-up
Accuracy of Digital Display:
30-999 PPM +/-30% when measured in conditions of 80° F (+/- 10° F),
atmospheric pressure +/- 10% and 40% +/- 3% relative humidity.
Display readings may vary slightly depending on changes in the ambient
condition (temperature, humidity) and the condition of the sensor.
CO Alarm Response Times:
70 PPM = 60-240 min., 150 PPM = 10-50 min., 400 PPM = 4-15 min.
Gas Alarm Response Times:
Before 25% of low explosion limit (LEL) for natural gas or propane is
detected.
Page 12
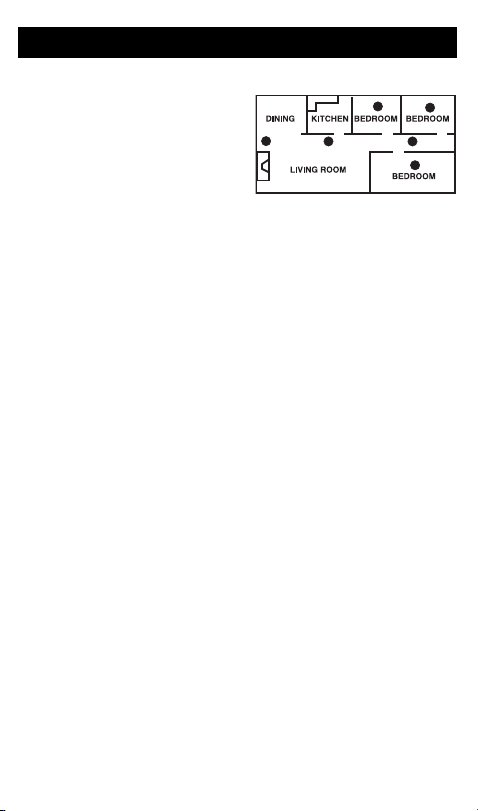
Recommended Installation Locations
CO and Gas alarms should be
mounted in or near bedrooms and
living areas. It is recommended that
you install a CO and Gas alarm on
each level of your home.
When choosing your installation
locations, make sure you can hear
the alarm from all sleeping areas. If
you install only one CO and Gas alarm in your home, install it near bedrooms, not in the basement or furnace room.
• When wall mounting, place out of reach of children. Under no circumstances should children be allowed to handle the CO and Gas
alarm.
• Mounting the CO and Gas alarm should depend on the type of explosive gas you intend to detect:
– If you are a user of natural gas, mount your CO and Gas alarm high
on the wall (no closer than six inches from the ceiling) to ensure the
earliest opportunity to detect a natural gas leak.
– If you are a user of propane, mount your CO and Gas alarm near
the floor to ensure the earliest opportunity to detect a propane
leak.
Locations To Avoid
IMPORTANT: Improper location can affect the sensitive electronic components in this alarm. To avoid causing damage to the unit, to provide
optimum performance, and to prevent unnecessary nuisance alarms:
• Do not install in kitchens, garages or furnace rooms that may expose
the sensor to substances that could damage or contaminate it.
• Do not install in areas where the temperature is colder than 40°F
(4.4°C) or hotter than 100°F (37.8°C) such as crawl spaces, attics,
porches and garages.
• Do not install within 5 ft. of heating or cooking appliances. (Kidde
recommends 15 ft. to prevent nuisance alarms).
• Do not install near vents, flues, chimneys or any forced/unforced air
ventilation openings.
• Do not install near ceiling fans, doors, windows or areas directly
exposed to the weather.
3. Installation Locations
Recommended Locations
Page 13

How to Install Your Alarm
Your Kidde CO and Gas alarm with its removable adapter allows you to
install the alarm as a wall mounted unit, a direct plug unit, or as a table
top unit.
Direct Plug Alarm
In its “as shipped” configuration, all you need
to do is install the 9V backup battery and your
Kidde CO and Gas alarm is ready to be plugged
directly into a wall socket.
To install:
1. Choose a standard 120V unswitched outlet
to plug the alarm into.
2. Pull the slide support out approximately 1/4”
until the slide snaps into place. This will
help support unit in the wall outlet.
3. Plug the alarm into the outlet.
If the outlet is mounted horizontally (sideways):
If you are going to use your alarm as a direct plug and you are going to
plug in to an outlet that is mounted horizontally (sideways), you will
need to rotate the adapter 90˚.
To rotate the adapter:
1. Remove back door by sliding it down and out.
4. Installation Instructions
Back of alarm when
used as direct plug unit
Back of alarm when
used as direct plug unit
• Do not install in dead air spaces, such as peaks of vaulted ceilings or
gabled roofs, where CO or gas may not reach the sensor in time to
provide early warning.
• Do not install this unit near deep-cell large batteries. Large batteries
have emissions that can cause the alarm to perform at less than optimum performance.
• Do not obstruct the vents located on the alarm. Do not place the
alarm where drapes, furniture or other objects block the flow of air to
the vents.
• Do not install on a switched or dimmer-controlled outlet.
3. Installation Locations
Page 14

2. Spread adapter thumb releases out and
carefully turn alarm over. This will allow
adapter to slide out.
3. Lift the adapter completely out of the alarm
and rotate the adapter 90˚ to the right
(clockwise). Snap it firmly back into place.
4. Carefully replace the back door. Insure the
“latches” on all four corners of the door are
lined up, then press the door securely into
place.
5. Plug the alarm into an unswitched wall
socket.
Wall Mounted Alarm
Installation tips for power cord models:
The power cord option provides more flexibility in mounting locations and allows the
alarm to be easily installed at eye level.
For a wall-mounted unit, you will need to
pull out the removable adapter and power
cord.
To install:
1. Follow steps 1 through 4 in the previous
section under “To Rotate the Adapter.”
2. With the adapter removed, pull the
power cord out of the cord recess,
remove the twist tie, and extend the
power cord.
3. With the power cord extended, press the
last few inches of the power cord back
into the cord recess. Gently pull the cord at the bottom of the cord
recess until the cord becomes taught and lays flat in cord recess.
4. Carefully replace the back door. Insure the “latches” on all four corners of the door are lined up, then press the door securely into place.
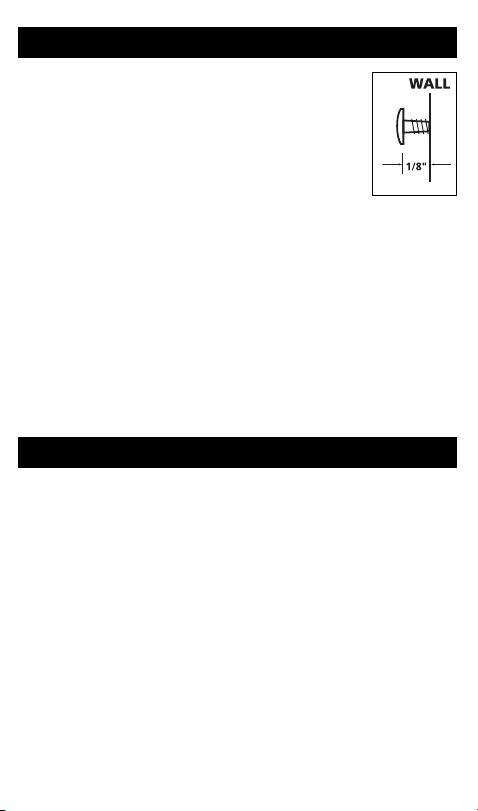
5. Mark the location for the two mounting holes on the wall spaced vertically 2 5/8" apart.
6. If you are mounting the alarm in plaster board or drywall, drill a 3/16"
hole into the wall and insert the plastic anchors provided. Install the
4. Installation Instructions
Back of alarm when
used as a wall mount unit
Back of alarm when
used as direct plug unit
for sideways outlet
Page 15
5. Alarm Characteristics
Carbon Monoxide Alarm Indicator
This CO and Gas alarm is designed to act as a monitor. It is not
designed for use as a short term testing device to perform a quick check
for the presence of CO or gas.
When the alarm senses a dangerous level of CO, the unit will emit a
loud alarm pattern. The alarm pattern is 4 quick beeps followed by 5
seconds of silence. This cycle repeats as long as a dangerous CO conditions exist. The digital display will indicate the CO concentration in parts
per million (PPM).
When the unit senses either natural gas or propane, the display will
show “GAS” and emit a loud alarm pattern. The alarm pattern for gas is
1/2 second beep followed by a 1/2 second of silence then repeating.
In all cases, the unit will detect CO as a priority over gas. If the unit is
detecting gas, then detects an amount of CO to cause an alarm, the
unit will stop alarming for gas and alarm for CO.
two screws provided into the wall or wall anchors
until the screw head is approximately 1/8" from the
wall.
7. Hook the unit over the screw head and into the keyhole in back of the unit.
8. Plug the adapter into an unswitched wall socket.
Table Top Alarm
You can use your CO and Gas alarm as a table top
unit. Follow steps 1 thru 4 above. Instead of mounting
the unit to a wall, pull out the slide support and place
in a location that is easily visible. Be sure the alarm is no more than three
feet from the floor.
Important Labels Provided
Two labels have been provided that have important information on what
to do in case of an alarm. Add the phone number of your emergency
service provider in the space provided. Place one label next to the alarm
after it is mounted, and one label near a fresh air source such as a door
or window.
4. Installation Instructions
Screw Head
Distance
from Wall
Page 16

5. Alarm Characteristics
WARNING: When powered by battery backup only; after four minutes,
this alarm pattern occurs only every 60 seconds, until the alarm is reset
or the CO is eliminated.
• The digital display will show a the PPM of CO or show “GAS” only if
it senses carbon monoxide or gas while in backup mode.
• If gas is detected while on battery backup, the unit will display “GAS”
and alarm in 1/2 second beeps. For the first four minutes after the
unit goes into battery backup operation, the explosive gas sensor will
operate as if on AC power.
However, after four minutes, to extend battery life, the unit will go into
battery conserve mode and will only sample for explosive gas once every
eight minutes. Explosive gas could be present during this 8-minute period without the unit going into alarm. If the alarm is on battery backup
for an extended period of time, replace the battery to ensure maximum
protection is provided. The battery will last only a couple hours in a gas
alarm condition.
WARNING: If at any time you test the alarm and it does not perform as
described, have it replaced immediately.
Whenever the CO and Gas alarm is first powered up, it will sound briefly
to let you know it is receiving power and that the alarm is functioning.
You will see three eights on the digital display, indicating the alarm is in
the start-up mode. The three eights will remain for approximately 20
seconds. You will see a blinking red dot to the lower right of the digital
display. The blinking dot shows that the alarm is operating.
Within 20 seconds, your CO and Gas alarm will start monitoring for CO.
Within 2 minutes your alarm will start monitoring for gas. This alarm will
display a 0 if CO concentrations between 0 and 30 PPM have been
detected within the last 15 seconds. The alarm has begun monitoring
the air for CO and gas and will continue to as long as it receives power.
When the alarm is unplugged or loses power and a good 9V battery is installed: The alarm will automatically switch to its battery back-
up mode and you will notice the following:
• After 4 minutes the digital display will show a blinking dot only – this
helps conserve the battery’s power.
6. Model KN-COEG-3 Operating Characteristics
Page 17

If the battery is low or missing, or if the unit malfunctions, it will display
other readings (and alarm differently) to alert you of specific conditions.
Please familiarize yourself, and other family members, to the difference
between a CO reading and and indication signifying a problem with the
unit itself.
NOTE: When AC power is restored, the alarm will automatically switch
back to normal operating mode.
The alarm will not detect CO or gas if battery is depleted. Replace battery.
The following table illustrates the possible digital displays, describes the
audible alarm patterns, and the recommended actions to take.
6. Model KN-COEG-3 Operating Characteristics
Operating and Alarm Characteristics
LED Display Shows Alarm Sound Unit Status Recommendation
Brief “888” along
with any number
between 100 and 300.
4 quick beeps,
5 seconds
silence,
repeated once
Self checking when
AC powered (Test
button was pressed
or unit was first
powered)
None – CO has not
been detected.
Numbers shown for
test purposes only
Steady “0” displayed. None Normal AC
operation (sensing
no CO) and with a
good battery
None
A display of CO
concentration from
30-999.
4 quick beeps,
5 seconds
silence,
repeating
Alarm condition.
Dangerous
concentrations of
CO detected
Refer to “What to do
When the Alarm
Sounds” (inside front
cover)
“Lb” flashes
alternately with
any number.
One quick
beep every
15 seconds
AC powered and
low or missing
battery
Install or replace 9V
battery
Steady “Err displayed One quick
beep every
30 seconds
Unit malfunction Replace battery.
If “Err” continues,
unit has malfunctioned. Replace
immediately. Unit will
not respond CO
No display alternating
with display of CO
concentration every 60
seconds.
4 quick beeps,
5 seconds
silence,
repeating
every 60 secs
Alarm condition
powered on battery
backup. Dangerous
concentrations of
CO detected
Refer to “What to do
When the Alarm
Sounds” (inside front
cover).
Replace battery
Page 18

Peak Level Memory
When the Peak Level button is pressed and held, the display shows the
highest CO reading taken by the CO alarm since its last reset or power
up. The Peak Level display feature will display levels between 11-999
PPM. Although the Peak Level feature will display levels below 30 PPM,
these levels will not result in an alarm no matter how long the device is
exposed to these levels. The Peak Level feature is helpful in identifying if
you have had a CO reading since resetting the alarm.
Concentrations of CO between 1 and 30 PPM can often occur in normal, everyday conditions. Concentrations of CO below 30 PPM may be
an indication of a transient condition that may appear today and never
reappear. Some CO conditions may start out as low level leaks but could
develop into CO concentrations that may become harmful.
Peak Level Memory Reset
Press the Peak Level button; with the button still pressed, press the
Test/Reset button for two seconds and release. The number on the display will turn to “0”, the memory will be cleared and the alarm will
begin monitoring for CO. The Peak Level memory is also reset when the
unit loses power.
6. Model KN-COEG-3 Operating Characteristics
Operating and Alarm Characteristics
LED Display Shows Alarm Sound Unit Status Recommendation
No display alternating
with “0” every 60
seconds.
None Normal operation
after first 4 minutes
of 9 V battery
operation. Unit
monitoring for CO
Verify AC power is
restored as soon as
possible to conserve
battery.
Replace battery
Display shows
“GAS”
1/2 second
beep, 1/2
second silence,
repeating
Unit has detected gas Refer to “What to do
When the Alarm
Sounds” for Gas
(inside front cover)
Flashing dot None Normal battery-only
operation– unit will
show reading only if
it senses CO or gas
Plug into AC power
as soon possible to
conserve battery
“End” displayed.
Red LED flashes
every 30 seconds
Two quick beeps
every 30 seconds
End of unit life Replace unit immedi-
ately. Unit will not
respond to CO or
Gas
Page 19

7. Maintenance
NOTE: This unit is sealed. The cover is not removable.
Due to the loudness of the alarm, we suggest that you place your
fingers over the sounder opening while testing your alarm.
CAUTION: Continuous exposure to the high sound level of this
alarm over an extended period of time may cause hearing loss.
Testing
Observe the alarm weekly to make sure the red dot is blinking, indicating normal operation.
If the dot is not blinking, unplug the alarm for three minutes, then plug
in again. This will clear the alarm for restart. If the dot does not resume
blinking, your alarm may be malfunctioning.
To test the alarm, press the Test/Reset button. If the alarm is operating
properly, you will notice the following:
• The display shows three “eights”, then shows the word “GAS” while
the alarm is sounding three short “beeps”. Then, the display shows a
number (usually around 200). You will then hear four quick “beeps” –
followed by five seconds of silence – followed by four quick “beeps”
repeating until reset stops. The unit will then show three “eights” for
several seconds. It will then return to monitoring for CO and gas.
Familiarize yourself and household members with the alarm pattern
described above for a CO or gas event. While on AC power, in the event
of a CO or gas incident, the appropriate pattern will continue to repeat
as long as CO or gas is present.
NOTE: Pressing the Test/Reset button tests the functions of the alarm’s
internal components, circuitry and micro-computer. You do not need
to press the Test/Reset button to take a CO or gas reading. CO
readings or the presence of gas are automatically shown on the alarm’s
digital display. If the alarm shows “0”, then no measurable amount of
CO or gas has been sensed by the alarm within the past 15 seconds.
Battery Replacement
NOTE: This CO and Gas alarm is not battery operated. However,
this alarm is equipped with 9 volt battery backup – the 9 volt battery is
to supply short term back-up during a power outage.
When replacing the battery, use one of the following approved brands:
• Duracell MN1604 or MX1604
• Energizer 522
• Gold Peak 1604A
Page 20

7. Maintenance
These batteries can be purchased where you bought the alarm or at a
local hardware store. Use of a different battery may have a detrimental
effect on the alarm operation.
The 9 volt battery is not rechargeable. If the 9 volt battery is missing,
disconnected, or if the battery’s power is low, “Lb” will be displayed
alternately with the current CO reading once every second accompanied
by an audible beep every 15 seconds. If this happens, the battery must
be replaced.
To replace battery:
Remove back door by sliding it down and out. Remove battery by
unsnapping it from the battery clip. Install a new battery by connecting
it to the battery clip and place into the recessed battery cavity. Reinstall
the back door of the unit.
IMPORTANT: Constant exposures to high or low humidity may reduce
battery life. A good safety measure is to replace the battery at least once
a year, or at the same time as you change your clocks for daylight saving
time.
After installing or changing the battery, reinstall your alarm. Test your
alarm by using the Test/Reset button and check that the display is on.
Maintenance Tips
To keep your alarm in good working order, you must follow these steps:
• Test the alarm once a week by pressing the Test/Reset button.
• Vacuum the alarm cover once a month to remove accumulated dust.
• Never use detergents or solvents to clean the alarm. Chemicals can
permanently damage or temporarily contaminate the sensor.
• Avoid spraying air fresheners, hair spray, paint or other aerosols near
the alarm.
• Do not paint the unit. Paint will seal the vents and interfere with
proper sensor operation.
Page 21

7. Maintenance
Move the CO and Gas alarm to a remote location, to prevent possible
damage or contamination of the sensor, prior to performing any of the
following:
• Staining or stripping floors or furniture, painting or wall-papering
• Using aerosols or adhesives
WARNING: Reinstall the CO and Gas alarm as soon as possible to assure
continuous protection.
The following is a list of substances that at high levels can damage the
sensor or cause temporary readings that are not CO readings:
• Ethylene, ethanol, alcohol, iso-propanol, benzene, toluene, ethyl
acetate, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide.
• Also most aerosol sprays, alcohol based products, paint, thinner, solvent, adhesive, hair spray, after shave, perfume, auto exhaust (cold
start) and some cleaning agents.
Page 22
FIVE YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY
Warranty Coverage: The manufacturer warrants to the original consumer purchaser, that
this product (except battery) will be free of defects in material and workmanship for a period
of five (5) years from date of purchase. The manufacturer’s liability hereunder is limited to
replacement of the product, repair of the product or replacement of the product with
repaired product at the discretion of the manufacturer. This warranty is void if the product has
been damaged by accident, unreasonable use, neglect, tampering or other causes not arising
from defects in material or workmanship. This warranty extends to the original consumer
purchaser of the product only.
Warranty Disclaimers: Any implied warranties arising out of this sale, including but not
limited to the implied warranties of description, merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose, are limited in duration to the above warranty period. In no event shall the
Manufacturer be liable for loss of use of this product or for any indirect, special, incidental or
consequential damages, or costs, or expenses incurred by the consumer or any other user of
this product, whether due to a breach of contract, negligence, strict liability in tort or
otherwise. The Manufacturer shall have no liability for any personal injury, property damage
or any special, incidental, contingent or consequential damage of any kind resulting from gas
leakage, fire or explosion. Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied
warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to you. Some states do not allow the
exclusion or limitation of consequential or incidental damages, so the above limitations or
exclusions may not apply to you.
Legal Remedies: This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may also have other
rights that vary from state to state.
Warranty Performance: During the above warranty period, your product will be replaced
with a comparable product if the defective product is returned in a postage paid package to
the following address: Kidde, Customer Service Department, 1016 Corporate Park Drive,
Mebane, NC 27302 USA, together with proof of purchase date. Please include a note
describing the problem when you return the unit. The replacement product will be in
warranty for the remainder of the original warranty period or for six months, whichever is
longer. Other than the cost of postage, no charge will be made for replacement of the
defective product. In many cases the quickest way to exchange your alarm is to return it to
the original place of purchase. If you have questions, call Kidde customer service department.
IMPORTANT: Do not remove unit back cover. Back cover removal will void warranty.
Your Kidde Carbon Monoxide and Gas Alarm is not a substitute for property, disability, life or
other insurance of any kind. Appropriate insurance coverage is your responsibility. Consult
your insurance agent.
Also, Kidde makes no warranty, express or implied, written or oral, including that of
merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose, with respect to the battery.
The above warranty may not be altered except in writing signed by both parties hereto.
QUESTIONS OR FOR MORE INFORMATION
Call our Consumer Hotline at 1-800-880-6788 or contact
us at our website at www.kidde.com
Kidde, 1016 Corporate Park Drive, Mebane, NC 27302
 Loading...
Loading...