Page 1
Keysight N777-C Series
Tunable Laser Family
N7776C Tunable Laser Source
N7778C Tunable Laser Source
N7779C Tunable Laser Source
Programming
Guide
Page 2
Notices
CAUTION
WARNING
© Keysight Technologies 2021
No part of this manual may be reproduced
in any form or by any means (including
electronic storage and retrieval or translation into a foreign language) without prior
agreement and written consent from
Keysight Technologies as governed by
United States and international copyright
laws.
Manual Part Number
N7770-90C02
Edition
Edition 2.1, February 2021
Keysight Technologies Deutschland GmbH
Herrenberger Strasse 130,
71034 Böblingen, Germany
Technology Licenses
The hardware and/or software described in
this document are furnished under a
license and may be used or copied only in
accordance with the terms of such license.
U.S. Government Rights
The Software is “commercial computer
software,” as defined by Federal Acquisition
Regulation (“FAR”) 2.101. Pursuant to FAR
12.212 and 27.405-3 and Department of
Defense FAR Supplement
(“DFARS”) 227.7202, the U.S. government
acquires commercial computer software
under the same terms by which the
software is customarily provided to the
public. Accordingly, Keysight provides the
Software to U.S. government customers
under its standard commercial license,
which is embodied in its End User License
Agreement (EULA), a copy of which can
be found at:
http://www.keysight.com/find/sweula.
The license set forth in the EULA represents
the exclusive authority by which the U.S.
government may use, modify, distribute, or
disclose the Software. The EULA and the
license set forth therein, does not require
or permit, among other things, that
Keysight: (1) Furnish technical information
related to commercial computer software
or commercial computer software
documentation that is not customarily
provided to the public; or (2) Relinquish to,
or otherwise provide, the government
rights in excess of these rights customarily
provided to the public to use, modify,
reproduce, release, perform, display, or
disclose commercial computer software or
commercial computer software documentation. No additional government requirements beyond those set forth in the EULA
shall apply, except to the extent that those
terms, rights, or licenses are explicitly
required from all providers of commercial
computer software pursuant to the FAR and
the DFARS and are set forth specifically in
writing elsewhere in the EULA. Keysight
shall be under no obligation to update,
revise or otherwise modify the Software.
With respect to any technical data as
defined by FAR 2.101, pursuant to FAR
12.211 and 27.404.2 and DFARS 227.7102,
the U.S. government acquires no greater
than Limited Rights as defined in FAR
27.401 or DFAR 227.7103-5 (c), as
applicable in any technical data.
Warranty
THE MATERIAL CONTAINED IN THIS
DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED "AS IS," AND IS
SUBJECT TO BEING CHANGED, WITHOUT
NOTICE, IN FUTURE EDITIONS. FURTHER,
TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY
APPLICABLE LAW, KEYSIGHT DISCLAIMS
ALL WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WITH REGARD TO THIS MANUAL
AND ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED
HEREIN, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. KEYSIGHT SHALL
NOT BE LIABLE FOR ERRORS OR FOR
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH THE
FURNISHING, USE, OR PERFORMANCE OF
THIS DOCUMENT OR ANY INFORMATION
CONTAINED HEREIN. SHOULD KEYSIGHT
AND THE USER HAVE A SEPARATE
WRITTEN AGREEMENT WITH WARRANTY
TERMS COVERING THE MATERIAL IN THIS
DOCUMENT THAT CONFLICT WITH THESE
TERMS, THE WARRANTY TERMS IN THE
SEPARATE AGREEMENT WILL CONTROL.
Safety Notices
A CAUTION notice denotes a hazard.
It calls attention to an operating
procedure, practice, or the like that,
if not correctly performed or adhered
to, could result in damage to the
product or loss of important data.
Do not proceed beyond a CAUTION
notice until the indicated conditions
are fully understood and met.
A WARNING notice denotes a hazard.
It calls attention to an operating
procedure, practice, or the like that,
if not correctly performed or adhered
to, could result in personal injury or
death. Do not proceed beyond a
WARNING notice until the indicated
conditions are fully understood and
met.
2 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 3

Safety Summary
General This product is a Protection Class 1 instrument (provided with a protective earth terminal)
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation
of this instrument. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings or
operating instructions in the product manuals violates safety standards of design,
manufacture, and intended use of the instrument. Keysight Technologies assumes no
liability for the customer's failure to comply with these requirements. Product manuals
are provided on the Web. Go to www.keysight.com and type in your product number in
the Search field at the top of the page.
and has been manufactured and tested according to international safety standards. The
protective features of this product may be impaired if it is used in a manner not specified
in the operation instructions.
All Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) used in this product are Class 1 LEDs as per
IEC 60825-1:2014.
Environment Conditions
Tempe rat ure
Before Applying Power
Ground the Instrument
Do Not Operate in an
Explosive Atmosphere
This instrument is intended for indoor use in an Overvoltage Category II, pollution degree
2 environment. It is designed to operate at a maximum relative humidity of 85% RH,
non-condensing and at altitudes of up to 2000 meters. Refer to the specifications tables
for the AC mains voltage requirements and ambient operating temperature range.
The instrument should be protected from temperature extremes and changes in
temperature that may cause condensation within it.
The operating temperature is from 10 °C to +35 °C
The storage temperature is from –40 °C to +70 °C (Option D00, standard front panel)
___________________________ __ –30 °C to +70 °C (Option D01, touchscreen display)
Verify that all safety precautions are taken. The power cable inlet of the instrument serves
as a device to disconnect from the mains in case of hazard. The instrument must be
positioned so that the operator can easily access the power cable inlet. When the
instrument is rack mounted the rack must be provided with an easily accessible mains
switch.
To minimize shock hazard, the instrument chassis and cover must be connected to an
electrical protective earth ground. The instrument must be connected to the AC power
mains through a grounded power cable, with the ground wire firmly connected to an
electrical ground (safety ground) at the power outlet. Any interruption of the protective
(grounding) conductor or disconnection of the protective earth terminal will cause a
potential shock hazard that could result in personal injury.
Do not operate the instrument in the presence of flammable gases or fumes.
Do Not Remove the
Instrument Cover
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 3
Operating personnel must not remove instrument covers. Component replacement and
internal adjustments must be made only by qualified personnel.
Instruments that appear damaged or defective should be made inoperative and secured
against unintended operation until they can be repaired by qualified service personnel.
Page 4
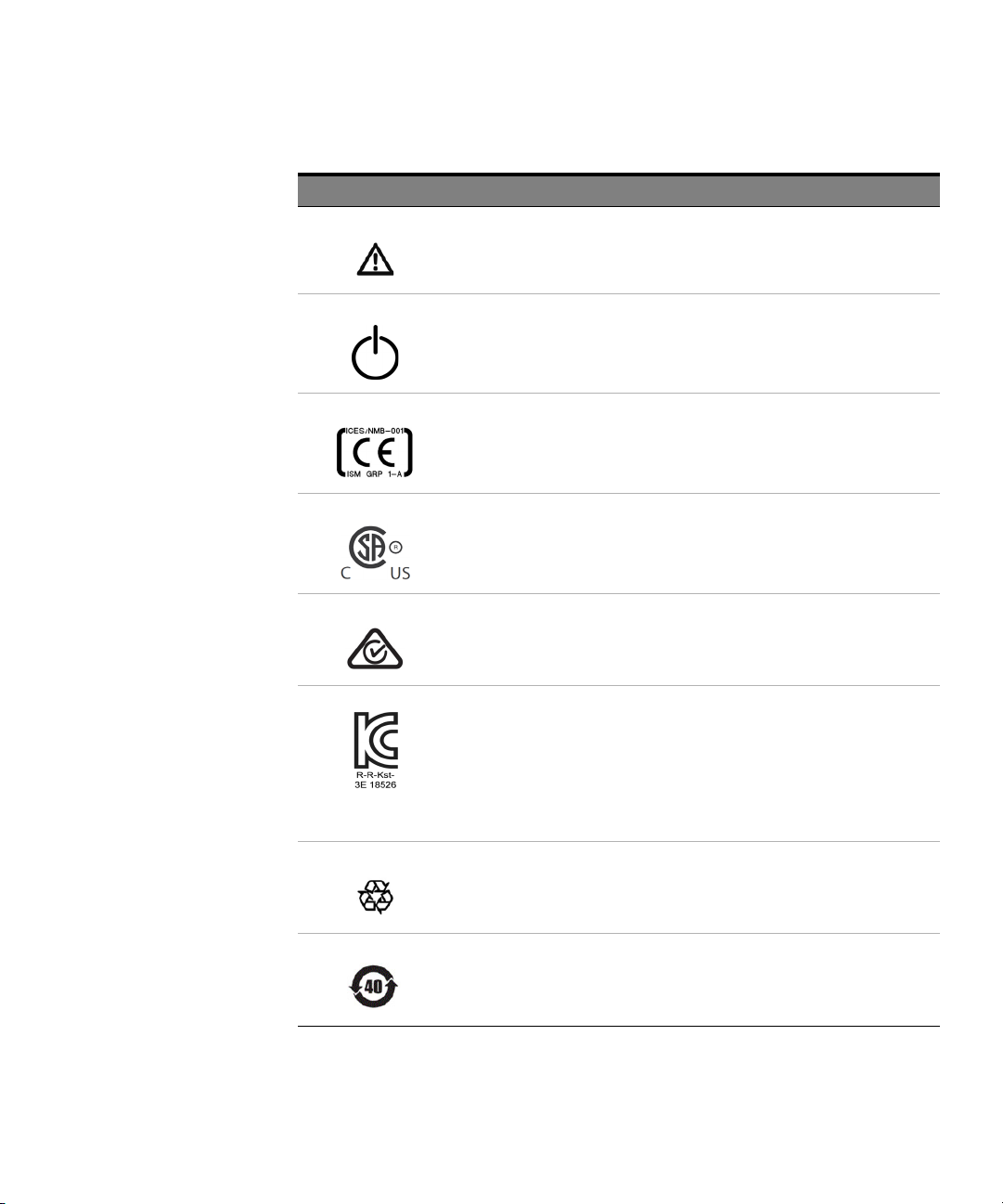
Instrument Markings
Instrument Marking Description
The instruction manual symbol. The product is marked with this warning symbol when it
is necessary for the user to refer to the instructions in the manual.
Standby supply. Unit is not completely disconnected from AC mains when switch is
off.
The CE mark is a registered trademark of the European Community.
The CSA mark with the 'c' and 'us' subscript indicates the instrument is certified to the
applicable Canadian and United States of America standards respectively.
The RCM mark is a registered trademark of the Australian Communications and Media
Authority
This symbol is a South Korean Class A EMC Declaration, with the product identification
code "R-R-Kst-3E18526".
R - Identification of authorization prefix.
R - Identification of basic certification information.
Kst - Identification of applicant's information
3E18526 - Product identification.
This is a Class A instrument suitable for professional use and in electromagnetic
environment outside of the home.
The recycling symbol indicates the general ease with which the instrument can be
recycled.
China Restricted Substance Product Label. The EPUP (environmental protection use
period) number in the center indicates the time period during which no hazardous
or toxic substances or elements are expected to leak or deteriorate during normal
use and generally reflects the expected useful life of the product.
4 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 5
South Korean Class A EMC Declaration
ۉࡅ߄έה
ࢇЕ߶הࡈˁ߾۰یࡈଟּࢶࡳԻࢶଢ۽ૡɼձ؇ࡵԻ۰ɼࢽࡈˁ߾۰ی
ࡈଜЕˁࡉࢷળɾۺࢂࡉԮɼݡТЬ
یࡈ ߇ΰחࡵ߶הࡈ ؏ܞݦࢢ߾փ ࢶࡈଞЬ
Information to the user:
This instrument has been conformity assessed for used in business environments. In a
residential environment this equipment may caused radio interference.
This EMC statement applies to the equipment only for use in business environment.
Compliance and Environmental Information
Table 1 Compliance and Environmental Information
Safety Symbol Description
This product complies with WEEE Directive (2002/96/EC) marking requirements.
The affixed label indicates that you must not discard this electrical/electronic
product in domestic household waste.
Product Category: With reference to the equipment types in WEEE Directive Annex I,
this product is classed as a “Monitoring and Control instrumentation” product.
Do not dispose in domestic household waste.
To return unwanted products, contact your local Keysight office, or see
http://about.keysight.com/en/companyinfo/environment/takeback.shtml for more
information.
Declaration of Conformity
Declarations of Conformity for this product and for the Keysight products may be
downloaded from the Web. Go to http://www.keysight.com/go/conformity.
You can then search by product number to find the latest Declaration of Conformity.
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 5
Page 6

Page 7

Contents
1 Introduction to Programming
Safety Summary 3
Instrument Markings 4
South Korean Class A EMC Declaration 5
Compliance and Environmental Information 5
Declaration of Conformity 5
Message Queues 10
How the Input Queue Works 10
Clearing the Input Queue 10
The Output Queue 10
The Error Queue 10
Programming and Syntax Diagram Conventions 12
Short Form and Long Form 12
Command and Query Syntax 13
Common Commands 16
Common Command Summary 16
Common Status Information 17
2 Command Summary
Command Summary 20
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 7
Page 8

Contents
3 Instrument Setup and Status
IEEE-Common Commands 28
Status Reporting – The STATus Subsystem 34
Interface/Instrument Behaviour Settings – The SYSTem
Subsystem 41
System Communicate - The :SYST:COMMunicate sub tree 45
4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Root Layer Command 58
Signal Generation – The SOURce Subsystem 61
Configure Subsystem Commands 81
Triggering - The TRIGger Subsystem 84
5 Error Codes
Error Strings 88
8 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 9

Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family
Programming Guide
1 Introduction to
Programming
Message Queues / 10
Programming and Syntax Diagram Conventions / 12
Common Commands / 16
This chapter gives general information on how to control your instrument
remotely.
Descriptions for the actual commands for the instruments are given in the
following chapters. The information in these chapters is specific to the
N777-C tunable laser source instruments.
Page 10

1 Introduction to Programming
Message Queues
How the Input Queue Works
Clearing the Input Queue
The Output Queue
The instrument exchanges messages using an input and an output queue.
Error messages are kept in a separate error queue.
The input queue is a FIFO queue (first-in first-out). Incoming bytes are
stored in the input queue. The parser starts if the LF character is received.
Switching the power off, or sending a Device Interface Clear signal, causes
commands that are in the input queue, but have not been executed to be
lost.
The output queue contains responses to query messages. The instrument
transmits any data from the output queue when a controller addresses the
instrument as a talker.
Each response message ends with a LF (0A
the query has an error, the output queue remains empty.
The Message Available bit (MAV, bit 4) is set in the Status Byte register
whenever there is data in the output queue.
). If no query is received, or if
16
The Error Queue
The error queue is 30 errors long. It is a FIFO queue (first-in first-out). That
is, the first error read is the oldest error to have occurred. For example:
1 If no error has occurred, the error queue contains:
o error"
+ 0, "N
2 After a command such as wav:pow, the error queue now contains:
+ 0, "N
o error"
-113, "Undefined header"
3 If the command is immediately repeated, the error queue now
contains:
+ 0, "No error"
-113, "Undefined header"
-113, "Undefined header"
10 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 11

Introduction to Programming 1
If more than 29 errors are put into the queue, the message:
-350, "Queue overflow"
is placed as the last message in the queue.
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 11
Page 12

1 Introduction to Programming
Programming and Syntax Diagram Conventions
A program message is a message containing commands or queries that
you send to the instruments. The following are a few points about program
messages:
• You can use either upper-case or lower-case characters.
• You can send several commands in a single message. Each command
must be separated from the next one by a semicolon (;).
• A command message is ended by a line feed character (LF).
• You can use any valid number/unit combination.
In other words, 1500NM,1.5UM and 1.5E-6M are all equivalent.
If you do not specify a unit, then the default unit is assumed. The
default unit for the commands are given with command description in
the next chapter.
Short Form and Long Form
The instrument accepts messages in short or long forms.
For example, the message
:STATUS:OPERATION:ENABLE 768
is in long form.
The short form of this message is
:STAT:OPER:ENAB 768
In this manual, the messages are written in a combination of upper and
lower case. Upper case characters are used for the short form of the
message.
For example, the above command would be written
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle
The first colon can be left out for the first command or query in your
message. That is, the example given above could also be sent as
STAT:OPER:ENAB 768
12 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 13

Command and Query Syntax
All characters not between angled brackets must be sent exactly as
shown.
The characters between angled brackets (<...>) indicate the kind of data
that you should send, or that you get in a response. You do not type the
angled brackets in the actual message.
Descriptions of these items follow the syntax description. The following
types of data are most commonly used:
string is ascii data. A string is contained between double quotes ("...") or single quotes (‘...’).
value is numeric data in integer (12), decimal (34.5) or exponential format (67.8E-9).
wsp is a white space.
Other kinds of data are described as required.
The characters between square brackets ([...]) show optional information
that you can include with the message.
The bar (
a or b, but not both simultaneously.
Extra spaces are ignored, so spaces can be inserted to improve readability.
Introduction to Programming 1
|) shows an either-or choice of data, for example, a|b means either
Units
Where units are given with a command, usually only the base units are
specified. The full sets of units are given in the table below.
Table 2 Units and allowed Mnemonics
Unit Default Allowed Mnemonics
meters M PM, NM, UM, MM, M
decibel DB MDB, DB
second S NS, US, MS, S
decibel/1mW DBM MDBM, DBM
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 13
Page 14

1 Introduction to Programming
NOTE
Unit Default Allowed Mnemonics
Hertz HZ HZ, KHZ, MHZ, GHZ, THZ
Watt Watt PW, NW, UW, MW, Watt
meters per second M/S NM/S, UM/S, MM/S, M/S
Data Types
With the commands you give parameters to the instrument and receive
response values from the instrument. Unless explicitly specified these data
are given in ASCII format. The following types of data are used:
• Boolean data may only have the values 0 or 1.
• Integer range is given for each individual command.
• Float variables may be given in decimal or exponential writing (0.123 or
123E-3).
All Float values conform to the 32 bit IEEE Standard, that is, all Float
values are returned as 32-bit real values.
•A string is contained between double quotes (
‘...’). When the instrument returns a string, it is always included in " ".
(
• When a register value is given or returned (for example *ESE), the
decimal values for the single bits are added. For example, a value of
nine means that bit 0 and bit 3 are set.
• Larger blocks of data are given as Binary Blocks, preceded by
“#<H><Len><Block>”; <H> represents the number of digits, <Len>
represents the number of bytes, and <Block> is the data block. For
example, for a Binary Block with 1 digit and 6 bytes this is: #16TRACES.
The block represents an array of numbers. Each number has the byte
ordering least significant byte first, also called LSBfirst, little-endian or
Intel byte ordering.
"...") or single quotes
Note that within your program, calculations with wavelengths may require
double-precision 64-bit floats to provide the desired resolution.
14 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 15

Slot and Channel Numbers
Each module is identified by a slot number and a channel number. For
commands that require you to specify a channel, the slot number is
represented by [n] in a command and the channel number is represented
by [m].
The slot number represents the module’s position in the mainframe. The
slot number for N777-C is always 0.
Channel numbers are not used for N777-C.
Introduction to Programming 1
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 15
Page 16

1 Introduction to Programming
NOTE
Common Commands
Common Command Summary
The IEEE 488.2 standard has a list of reserved commands, called common
commands. Some of these commands must be implemented by any
instrument using the standard, others are optional.
Your instrument implements all the necessary commands, and some
optional ones. This section describes the implemented commands.
Table 3 on page -16 provides a summary of the common commands.
Table 3 Common Command Summary
Command Parameter Function Page
*CLS Clear Status Command page 28
*ESE Standard Event Status Enable Command page 28
*ESE? Standard Event Status Enable Query page 29
*ESR? Standard Event Status Register Query page 29
*IDN? Identification Query page 30
*OPC Operation Complete Command page 30
*OPC? Operation Complete Query page 30
*OPT? Options Query page 31
*RST Reset Command page 31
*STB? Read Status Byte Query page 32
*TST? Self Test Query page 32
*WAI Wait Command page 33
These commands are described in more detail in IEEE-Common Commands on
page 28.
16 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 17
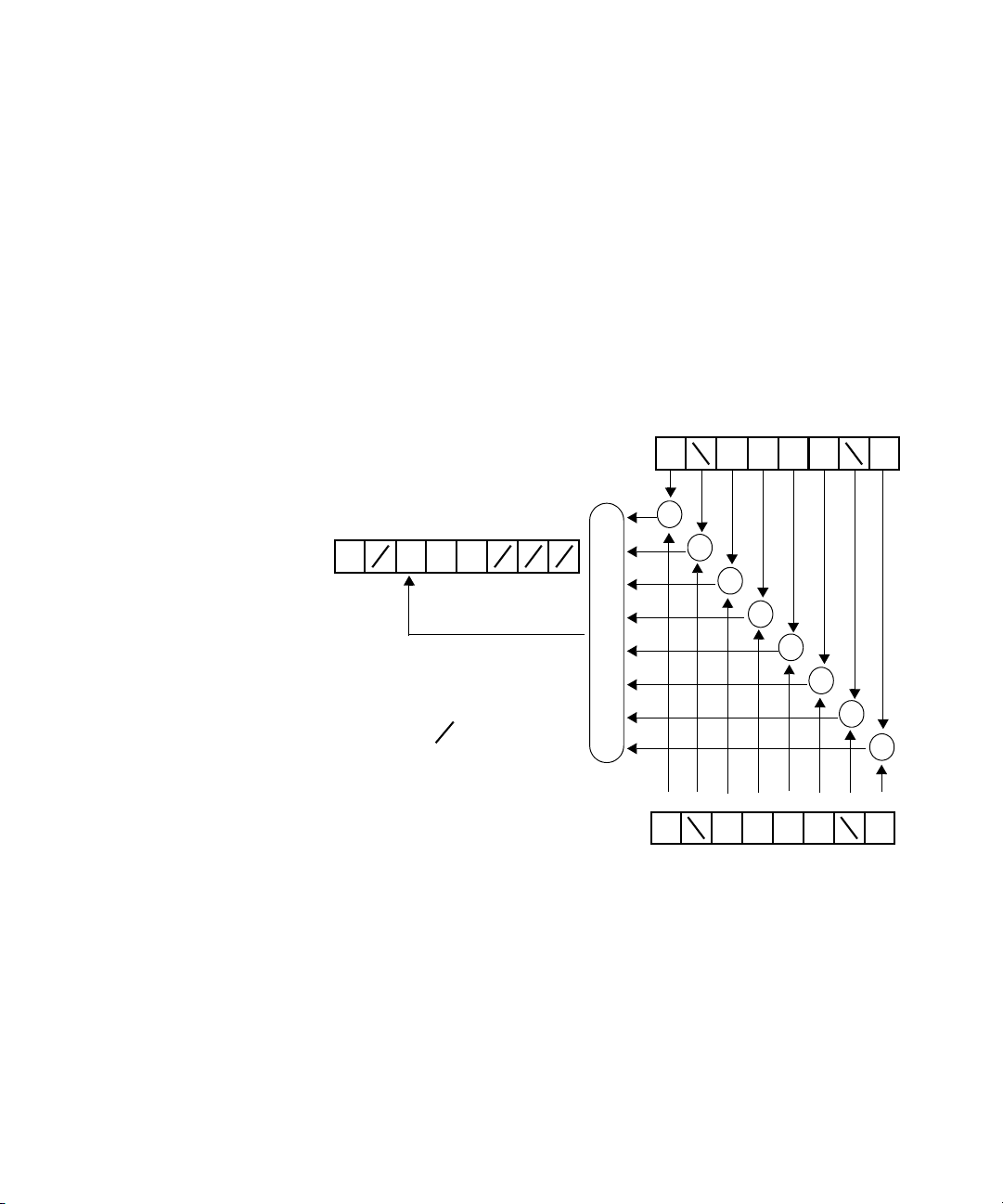
Common Status Information
01234567
*STB? returns the Status Byte Register
Status
OSB ESB QSB
*ESR? returns the Standard Event Status Register
001
01234567
Event
100000
Status
Register
01234567
Event
111111
Status
Enable
Mask
*ESE sets the Standard Event Status Enable Mask
&
&
&
&
&
&
&
&
OR
Byte
All bits shown as are unused
0
MAV
There are three registers for the status information. Two of these are
status-registers and one is an enable-registers. These registers conform to
the IEEE Standard 488.2-1987. You can find further descriptions of these
registers under *ESE, *ESR?, and *STB?.
Figure 1 shows how the Standard Event Status Enable Mask (SESEM) and
the Standard Event Status Register (SESR) determine the Event Status Bit
(ESB) of the Status Byte.
Introduction to Programming 1
Figure 1 The Event Status Bit
The SESR contains the information about events that are not slot specific.
The SESEM allows you to choose the event that may affect the ESB of the
Status Byte. If you set a bit of the SESEM to zero, the corresponding event
cannot affect the ESB. The default is for all the bits of the SESEM to be set
to 0.
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 17
Page 18

1 Introduction to Programming
NOTE
The questionable and operation status systems set the Operational Status
Bit (OSB) and the Questionable Status Bit (QSB).
Unused bits in any of the registers change to 0 when you read them.
18 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 19

Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family
Programming Guide
2 Command Summary
Command Summary / 20
This chapter lists commands relating to the N777-C series tunable laser
source instruments.
Each of these summaries contains a page reference for more detailed
information about the particular command later in this manual.
Page 20

2 Command Summary
Command Summary
The commands are ordered in a command tree. Every command belongs
to a node in this tree.
The root nodes are also called the subsystems. A subsystem contains all
commands belonging to a specific topic. In a subsystem there may be
further subnodes.
Table 4 on page 20 gives an overview of the command tree. You see the
nodes, the subnodes, and the included commands.
Table 4 Command Summary
Command Page
CONFigure Subsystem
:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:ACTual? Page 81
:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:NUMBer? Page 81
:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:PRESet Page 81
20 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:CANCel Page 82
:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:RECall Page 82
:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:SAVE Page 82
:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:ERASe Page 83
Command Page
SOURce Subsystem
:SOURce0:AM:COHCtrl:COHLevel? Page 61
:SOURce0:AM:COHCtrl:COHLevel Page 61
:SOURce0:AM:SOURce? Page 62
:SOURce0:AM:SOURce Page 62
:SOURce0:AM:STATe Page 62
:SOURce0:AM:STATe? Page 63
Page 21

Command Summary 2
Command Page
:SOURce0:READout:DATA? Page 63
:SOURce0:READout:POINts? Page 63
:SOURce0:WAVelength:CORRection:ARA Page 64
:SOURce0:WAVelength:CORRection:ZERO Page 64
:SOURce0:WAVelength:FREQuency Page 64
:SOURce0:WAVelength:FREQuency? Page 65
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CHECkparams? Page 66
:SOURce0:WAVelength:REFerence? Page 65
:SOURce0:WAVelength:REFerence:DISPlay Page 65
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CYCLes Page 67
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CYCLes? Page 67
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:DWELl Page 68
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:FLAG? Page 69
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:DWELl? Page 68
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging Page 69
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging? Page 70
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:MODE Page 70
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:MODE? Page 71
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:PMAX? Page 71
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:REPeat Page 71
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:REPeat? Page 72
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SOFTtrigger Page 72
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SPEed Page 73
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SPEed? Page 73
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt Page 73
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP? Page 75
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt? Page 73
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 21
Page 22

2 Command Summary
Command Page
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP Page 74
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:[STATe] Page 75
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:[STATe]? Page 76
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:PREVious Page 76
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:NEXT Page 76
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:[WIDTh] Page 77
:SOURce0:POWer[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]? Page 77
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:[WIDTh]? Page 77
:SOURce0:POWer[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]? Page 78
:SOURce0:POWer:STATe Page 78
:SOURce0:POWer:STATe? Page 79
:SOURce0:POWer:UNIT Page 79
:SOURce0:POWer:UNIT? Page 79
Command Page
STATus Subsystem
:STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]? Page 34
:STATus:OPERation:CONDition? Page 34
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle Page 35
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle? Page 35
:STATu s0: OPER atio n:CONDition? Page 36
:STATus0:OPERation[:EVENt]? Page 35
:STATus0:OPERation:ENABle Page 37
:STATus0:OPERation:ENABle? Page 37
:STATu s:P RESe t Pag e 37
:STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]? Page 38
22 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 23

Command Summary 2
Command Page
:STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition? Page 38
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle Page 38
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle? Page 39
:STATus0:QUEStionable[:EVENt]? Page 39
:STATus0:QUEStionable:CONDition? Page 39
:STATus0:QUEStionable:ENABle Page 40
:STATus0:QUEStionable:ENABle? Page 40
Command Page
SYSTem Subsystem
:SYSTem:DATE Page 41
:SYSTem:DATE? Page 41
:SYSTem:HELP:HEADers? Page 41
:SYSTem:HELP:ERRors? Page 42
:SYSTem:TIME Page 42
:SYSTem:PRESet Page 43
:SYSTem:TIME? Page 43
:SYSTem:ERRor[:NEXT]? Page 43
:SYSTem:ERRor:COUNt? Page 43
:SYSTem:VERSion? Page 44
:SYSTem:REBoot Page 44
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:AUTOip:ENABle? Page 45
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:AUTOip:ENABle Page 46
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:CANCel Page 46
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway Page 46
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway? Page 46
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 23
Page 24

2 Command Summary
Command Page
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway:CURRent? Page 47
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DHCP:ENABle? Page 47
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DHCP:ENABle Page 47
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname? Page 48
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname Page 48
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname:CURRent? Page 48
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname Page 48
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname? Page 49
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname:CURRent? Page 49
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver? Page 49
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver Page 50
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver:CURRent? Page 50
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IDN Page 50
24 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress Page 50
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress? Page 51
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress:CURRent? Page 51
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:MACaddress? Page 51
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:ENABle? Page 52
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:ENABle Page 52
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:SERVer? Page 52
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:SERVer Page 52
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DESCription? Page 53
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DESCription Page 53
::SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:RESet Page 53
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:RESTart Page 54
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SAVE Page 54
Page 25

Command Summary 2
Command Page
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk? Page 54
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk Page 55
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk:CURRent? Page 55
Command Page
TRIGger Subsystem
:TRIGger Page 84
:TRIGger[n]:INPut Page 84
:TRIGger[n]:INPut? Page 85
:TRIGger[n]:OUTPut? Page 85
:TRIGger[n]:OUTPut Page 85
:TRIGger:CONFiguration Page 86
:TRIGger:CONFiguration? Page 86
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 25
Page 26

Page 27

Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family
Programming Guide
3 Instrument Setup and
Status
IEEE-Common Commands / 28
Status Reporting – The STATus Subsystem / 34
Interface/Instrument Behaviour Settings – The SYSTem Subsystem / 41
System Communicate - The :SYST:COMMunicate sub tree / 45
This chapter gives descriptions of commands that you can use when
setting up your instrument. The commands are split into the following
separate subsytems:
• IEEE specific commands that were introduced in Common Commands on
page 16.
• STATus subsystem commands that relate to the status model.
• SYSTem subsystem commands that control the serial interface and
internal data.
Page 28

3 Instrument Setup and Status
IEEE-Common Commands
Command: *CLS
Syntax: *CLS
Common Commands on page 16 gave a brief introduction to the
IEEE-common commands which can be used with the instruments. This
section gives fuller descriptions of each of these commands.
Description: The Clear Status (*CLS) command clears the status byte by emptying the error queue and clearing all the event registers
Parameters: none
Response: none
Example: *CLS
(SESR) including the Data Questionable Event Register, the Standard Event Status Register, the Standard Operation Status
Register and any other registers that are summarized in the status byte.
Command: *ESE
Syntax: *ESE<wsp><value>
Description: The standard Event Status Enable command (*ESE) sets bits in the Standard Event Status Enable Mask (SESEM) that enable
Parameters: The bit value for the register (a 16-bit signed integer value):
0 ≤ value ≤ 255
the corresponding bits in the standard event status register (SESR).
The register is cleared:
at power-on,
by sending a value of zero.
The register is not changed by the *RST and *CLS commands.
Bit Mnemonic Decimal Value
7 (MSB) Power On 128
6Not Used 64
5 Command Error 32
4 Execution Error 16
3 Device Dependent Error 8
2Query Error 4
28 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 29

1Not Used 2
0 (LSB) Operation Complete 1
Response: none
Example: *ESE 255
Command: *ESE?
Syntax: *ESE?
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Description: The standard Event Status Enable query *ESE? returns the contents of the Standard Event Status Enable Mask (see *ESE
for information on this register).
Parameters: none
Response: The bit value for the register (a 16-bit signed integer value).
Example: *ESE? −> +255
Command: *ESR?
Syntax: *ESR?
Description: The standard Event Status Register query *ESR? returns the contents of the Standard Event Status Register. The register
is cleared after being read.
parameters none
response The bit value for the register (a 16-bit signed integer value):
Bit Mnemonic Decimal Value
7 (MSB) Power On 128
6Not used 64
5 Command Error 32
4 Execution Error 16
3 Device Dependent Error 8
2Query Error 4
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 29
Page 30

3 Instrument Setup and Status
1Not used 2
0 (LSB) Operation Complete 1
Example: *ESR? -> +128
Command: *IDN?
Syntax: *IDN?
Description: The IDeNtification query *IDN? gets the instrument identification over the interface.
Parameters: none
Response: The identification, for example:
MMMMMMMM
mmmm
ssssssss
rrrrrrrrrr
Example: *IDN? -> Keysight Technologies,N7776C,N71130PP02,V1.000
manufacturer, for example Keysight Technologies
instrument model number (for example N7776C)
serial number
firmware revision level
Command: *OPC
Syntax: *OPC
Description: Generates the OPC message in the standard event status register when all pending overlapped operations have been
Parameters: none
Response: none
Example: *OPC
Command: *OPC?
Syntax: *OPC?
Description: The OPeration Complete query *OPC? parses all program message units in the input queue, sets the operation complete bit
completed.
in the Standard Event Status register, and places an ASCII ’1’ in the output queue, when the contents of the input queue
have been processed.
Taking advantage of this feature, and using *OPC? in a loop to query until the instrument returns 1, can lead to useful gains
in program execution efficiency.
30 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 31

Parameters: none
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Response: 1 is returned if all modules are ready to execute a new operation.
0 is returned if any module is busy.
Example: *OPC? -> 1
Command: *OPT?
Syntax: *OPT?
Description: The OPTions query *OPT? returns the modules installed in your instrument.
Parameters: none
Response: Returns the part number of all installed modules, separated by commas.
Slots are listed starting with the lowest slot number, that is, slot 0 for the 8164A/B and Slot 1 for the 8163A/B and 8166A/B.
If any slot is empty or not recognised, two spaces are inserted instead of the module’s part number. See the example below,
where slots 1 and 4 are empty.
Example: *OPT? -> N7776C, , , ,
Command: *RST
Syntax: *RST
Description: The ReSeT command *RST sets the mainframe and all modules to the reset setting (standard setting) stored internally.
The instrument is placed in the idle state awaiting a command. The *RST command clears the error queue.
The *RST command is equivalent to the *CLS command AND the syst:preset command.
The following are not changed:
Instrument interface address
Service request enable register (SRE)
Standard Event Status Enable Mask (SESEM)
To prevent this, use the CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:PRESet command to keep the previously stored settings in
non-volatile RAM.
Parameters: none
Response: none
Example: *RST
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 31
Page 32

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: *STB?
Syntax: *STB?
Description: The STatus Byte query *STB? returns the contents of the Status Byte register.
Parameters: none
Response: The bit value for the register (a 8-bit signed integer value):
Bit Mnemonic Decimal Value
7 (MSB) Operation Status (OSB) 128
6 Not used 64
5 Event Status Bit (ESB) 32
4 Message Available (MAV) 16
3 Questionable Status (QSB) 8
2 Not used 0
1 Not used 0
Example: *STB? -> +32
Command: *TST?
Syntax: *TST?
Description: The self-TeST query *TST? makes the instrument perform a self-test and place the results of the test in the output queue. If
Parameters: none
Response: Selftest failed 1
Example: *TST? -> 0
32 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
0 Not used 0
the self-test fails, the results are also put in the error queue. We recommend that you read self-test results from the error
queue. No further commands are allowed while the test is running. After the self-test the instrument is returned to the
setting that was active at the time the self-test query was processed. The self-test does not require operator interaction
beyond sending the *TST? query.
A value of zero indicates no errors.
Page 33

Command: *WAI
Syntax: *WAI
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Description: The WAIt command prevents the instrument from executing any further commands until the current command has finished
executing. Some module firmware includes commands that set a "StatNOPC" flag during execution to indicate that the
module is busy. *WAI blocks all commands until every module hosted by the instrument is no longer busy. All pending
operations, are completed during the wait period.
Parameters: none
Response: none
Example: *WAI
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 33
Page 34

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Status Reporting – The STATus Subsystem
The Status subsystem allows you to return and set details from the Status
Model.
Command: :STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?
Syntax: :STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?
Description: Returns the Operational Status Event Summary Register (OSESR).
Parameters: none
Response: The sum of the results for the module (a 16-bit unsigned integer value, where 0 ≤ value ≤ 65535):
Bits
15 -1 Not used
0 Summary
Example: :stat:oper? -> +0
Command: :STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
Syntax: :STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
Description: Reads the Operational Status Condition Summary Register.
Parameters: none
Response: The sum of the results for the module (a 16-bit unsigned integer value, where 0 ≤ value ≤ 65535):
Bits
15 - 1 Not used
0 Summary 1
Example: :stat:oper:cond? -> +0
34 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 35

Command: :STATus:OPERation:ENABle
Syntax: :STATus:OPERation:ENABle<wsp><value>
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Description: Sets the bits in the Operational Status Enable Summary Mask (OSESM) that enable the contents of the OSESR to affect the
Status Byte (STB).
Setting a bit in this register to 1 enables the corresponding bit in the OSESR to affect bit 7 of the Status Byte.
Parameters: The bit value for the OSESM as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
The default value is 65535.
Response: none
Example: :stat:oper:enab 128
Command: :STATus:OPERation:ENABle?
Syntax: :STATus:OPERation:ENABle?
Description: Returns the OSESM for the OSESR
Parameters: none
Response: The bit value for the operation enable mask as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
Example: :stat:oper:enab? -> +128
Command: :STATus0:OPERation[:EVENt]?
Syn tax: :STATu s0:OPERation[:EVENt]?
Description: Returns the Operational Slot Status Event Register (OSSER) of the laser module.
Parameters: none
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 35
Page 36

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Response: The results for the individual slot events (a 16-bit unsigned integer value, where 0 ≤ value ≤ 65535):
Bit
8-16
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Example: :stat0:oper? -> +0
Command: :STATus0:OPERation:CONDition?
Syntax: :STATus0:OPERation:CONDition?
Description: Returns the Operational Slot Status Condition Register of the laser module.
Parameters: none
Response: The results for the individual slot events (a 16-bit unsigned integer value, where 0 ≤ value ≤ 65535):
Bit
8-16
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Mnemonic
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Slot n: shutter has been opened
Slot n: Zeroing ongoing
Not used
Slot n: Coherence Control has been switched on
Slot n: Laser has been switched on
Mnemonic
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Shutter open
Zeroing ongoing
Not used
Coherence Control is switched on
Laser is switched on
Decimal Value
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
2
1
Decimal Value
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
2
1
Example: :stat0:oper:cond? -> +0
36 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 37

Command: :STATus0:OPERation:ENABle
Syntax: :STATus0:OPERation:ENABle<wsp><value>
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Description: Sets the bits in the Operation Slot Status Enable Mask (OSSEM) for the laser module that enable the contents of the
Operation Slot Status Event Register (OSSER) to affect the OSESR.
Setting a bit in this register to 1 enables the corresponding bit in the OSSER and OSESR.
Parameters: The bit value for the OSSEM as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
Response: none
Example: :stat0:oper:enab 128
Command: :STATus0:OPERation:ENABle?
Syntax: :STATus0:OPERation:ENABle?
Description: Returns the OSSEM of the laser module
Parameters: none
Response: The bit value for the OSSEM as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
Example: :stat0:oper:enab? -> +128
Command: :STATus:PRESet
Syn tax: : STATus: PRE Set
Description: Presets all bits in all OPERation and QUEStionable status systems to 0.
Parameters: none
Response: none
Example: :stat:pres
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 37
Page 38

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: :STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
Syntax: :STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
Description: Returns the Questionable Status Event Summary Register (QSESR).
Parameters: none
Response: The sum of the results for the QSESR as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
Bits Mnemonics Decimal Value
15 - 1 Not used 0
0 Slot 0 summary 1
Example: :stat:ques? -> +0
Command: :STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Syntax: :STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Description: Returns the Questionable Status Condition Summary Register.
Parameters: none
Response: The sum of the results for the Questionable Status Condition Summary Register as a 16-bit unsigned integer value
Example: :stat:ques:cond? -> +0
Command: :STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle
Syntax: :STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle<wsp><value>
Description: Sets the bits in the Questionable Status Enable Summary Mask (QSESM) that enable the contents of the QSESR to affect the
38 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
(0 .. +65535)
Bits Mnemonics Decimal Value
15 - 1 Not used
0 Slot 0 summary 1
Status Byte (STB).
Setting a bit in this register to 1 enables the corresponding bit in the QSESR to affect bit 3 of the Status Byte.
Page 39

Instrument Setup and Status 3
Parameters: The bit value for the questionable enable mask as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 ..+65535)
The default value is 65535.
Response: none
Example: :stat:ques:enab 128
Command: :STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle?
Syntax: :STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle?
Description: Returns the QSESM for the event register
Parameters: none
Response: The bit value for the QSEM as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
Example: :stat:ques:enab? -> +128
Command: :STATus0:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
Syntax: :STATus0:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
Description: Returns the questionable status of slot n - the Questionable Slot Status Event Register (QSSER).
Parameters: none
Response: The results for the individual slot events (a 16-bit unsigned integer value, where 0 ≤ value ≤ 65535):
Bit
16 - 2
1
0
Every nth bit is the summary of the laser module.
Example: :stat0:oper? -> +0
Command: :STATus0:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Syntax: :STATus0:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Description: Returns the Questionable Slot Status Condition Register for the laser module.
Parameters: none
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 39
Mnemonic
Not Used
Slot n: A Zeroing operation has failed
Slot n: Excessive Value has occurred
Decimal Value
2
1
Page 40

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Response: The results for the individual slot events (a 16-bit unsigned integer value, where 0 ≤ value ≤ 65535):
Bit
16 - 2
1
0
Every nth bit is the summary of slot n.
Example: :stat0:ques:cond? -> +0
Command: :STATus0:QUEStionable:ENABle
Syn tax: : STATus0:QUEStionable:ENABle<wsp><value>
Description: Sets the bits in the Questionable Slot Status Enable Mask (QSSEM) for slot n that enable the contents of the Questionable
Slot Status Register (QSSR) for the laser module to affect the QSESR.
Setting a bit in this register to 1 enables the corresponding bit in the QSSER and QSESR.
Parameters: The bit value for the QSSEM as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
Response: none
Example: :stat0:ques:enab 128
Mnemonic
Not Used
Slot n: A Zeroing operation has failed
Slot n: Excessive Value has occurred
Decimal Value
2
1
Command: :STATus0:QUEStionable:ENABle?
Syn tax: : STATus0:QUEStionable:ENABle?
Description: Returns the QSSEM for slot n
Parameters: none
Response: The bit value for the QSSEM as a 16-bit unsigned integer value (0 .. +65535)
Example: :stat0:ques:enab? -> +128
40 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 41

Instrument Setup and Status 3
Interface/Instrument Behaviour Settings – The SYSTem Subsystem
The SYSTem subsystem lets you control the instrument’s serial interface.
You can also control some internal data (like date, time, and so on)
Command: :SYSTem:DATE
Syntax: :SYSTem:DATE<wsp><year>,<month>,<day>
Description: Sets the instrument’s internal date.
Parameters: the first value is the year (four digits),
the second value is the month, and
the third value is the day.
Response: none
Example: :syst:date 2019, 10, 12
Command: :SYSTem:DATE?
Syntax: :SYSTem:DATE?
Description: Returns the instrument’s internal date.
Parameters: none
Response: The date in the format year, month, day (16-bit signed integer values)
Example: :syst:date? -> +2019,+10,+12
Command: :SYSTem:HELP:HEADers?
Syntax: :SYSTem:HELP:HEADers?
Description: Returns a list of commands.
Parameters: none
Response: Returns a list of commands
Example: :syst:help:head? -> Returns a list of all commands
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 41
Page 42

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: :SYSTem:HELP:ERRors?
Syntax: :SYSTem:HELP:ERRors?
Description: Return an overview about all Errorcodes and a short description.
Parameters: none
Response: String list of error codes
Example: :syst:help:err? -> +0,"No error",-100,"Command error",- 101,"Invalid character",-102,"Syntax error",-103,
Command: :SYSTem:PRESet
Syntax: :SYSTem:PRESet
Description: Sets the instrument to the standard settings. This command has the same function as the Preset hardkey.
Parameters: none
Response: none
Example: :SYST:PRES
"Invalid separator",-104,"Data type error",-105,"GET not allowed",-108,"Parameter not allowed",...
Pressing the "LAN Reset" Button for a short time has the same effect.
Long pressing of the "LAN Reset" Button resets the LAN Parameter.
The following are not affected by this command:
the interface address,
the output and error queues,
the Service Request Enable register (SRE),
the Status Byte (STB),
the Standard Event Status Enable Mask (SESEM), and
the Standard Event Status Register (SESR).
NOTE: This will also erase all saved configurations. To prevent this, use
the:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:PRESet on page 81 command to keep previous stored settings in the NVRAM.
Command: :SYSTem:TIME
Syntax: :SYSTem:TIME<wsp><hour>,<minute>,<second>
Description: Sets the instrument’s internal time.
42 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 43

Instrument Setup and Status 3
Parameters: 24-hour time format: hours (0-23), minutes (0-59), seconds (0-59).
Response: none
Example: :syst:time 20,15,30
Command: :SYSTem:TIME?
Syntax: :SYSTem:TIME?
Description: Returns the instrument’s internal time.
Parameters: none
Response: The time in the format hour, minute, second. Hours are counted 0...23 (24 hour time format).
Example: :syst:time? -> +20,+15,+30
Command: :SYSTem:ERRor[:NEXT]?
Syntax: :SYSTem:ERRor[:NEXT]?
Description: Returns the next error from the error queue.
Parameters: none
Response: The number of the latest error, and its meaning.
Example: :syst:err? -> -113,"Undefined header"
Command: :SYSTem:ERRor:COUNt?
Syntax: :SYSTem:ERRor:COUNt?
Description: Returns the total no. of errors.
Parameters: none
Response: The total count of errors.
Example: :syst:err:coun? -> 20
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 43
Page 44

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: :SYSTem:VERSion?
Syntax: :SYSTem:VERSion?
Description: Returns the SCPI revision to which the instrument complies.
Parameters: none
Response: The revision year and number.
Example: :syst:vers? −> 2019.0
Command: :SYSTem:REBoot
Syntax: :SYSTem:REBoot
Description: Reboots the instrument.
Parameters: none
Response: None
Example: :syst:reb
44 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 45

System Communicate - The :SYST:COMMunicate sub tree
NOTE
We recommend you change network settings using the local user
interface.
The instrument does not close open connections when restarting the network
interface (:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:RESTart). This means the number of
possible connections is reduced by the number of previously open connections.
However, the instrument does make sure connections are still alive. It should
release unused open connections after about two minutes.
Some notes on DHCP/AutoIP/DNS
• If DHCP is enabled but no DHCP server is found, the instrument tries to
use AutoIP as a fallback. This may take about 2 minutes.
• Depending on the available network capabilities, the instrument tries to
tell the DNS server its host name or read the host and domain named it
has been assigned.
Instrument Setup and Status 3
MAC address:
The Media Access Control (MAC) number is a unique number associated
with each network adapter.
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:AUTOip:ENABle?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:AUTOip:ENABle?
Description: Check whether Automatic IP addressing is enabled or disabled.
Parameters: None
Response: Boolean (0 | 1)
Example: :SYST:COMM:ETH:AUTO:ENAB?
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 45
Page 46

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:AUTOip:ENABle
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:AUTOip:ENABle
Description: Enable or disable whether IP addresses can be created automatically by the instrument. Automatic IP addressing is only
Parameters: Boolean (0 | 1 | off | on)
Response: None
Example: :SYST:COMM:ETH:AUTO:ENAB 1
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:CANCel
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:CANCel
Description: Undo all changes to the network parameters that have been made since the last save, reboot or ":syst:comm:eth:restart"
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :SYST:COMM:ETH:CANC
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway
Description: Set the default gateway.
used if DHCP is enabled, but the instrument cannot find a DHCP server.
command.
Parameters: string (Up to four groups of up to 3 digits, groups separated by ".". Groups with leading zeros are interpreted as octal
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dgat “192.168.101.11“
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway?
Description: Get the default gateway.
46 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
numbers.)
Page 47

Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dgat? -> “192.168.101.11“
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway:CURRent?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DGATeway:CURRent?
Description: Get the currently used default gateway.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dgat:curr? -> “192.168.101.11“
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DHCP:ENABle?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DHCP:ENABle?
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Description: Check whether DHCP is enabled or disabled.
Parameters: None
Response: Boolean (0 | 1)
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dhcp:enab? -> 1
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DHCP:ENABle
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DHCP:ENABle
Description: Enable or disable DHCP
Parameters: Boolean (0 | 1 | off | on)
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dhcp:enab on
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 47
Page 48

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname?
Description: Get the domain name.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dom? -> “.companyname.com”
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname
Description: Set the domain name (used if DHCP is disabled).
Parameters: String
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dom “.companyname.com”
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname:CURRent?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DOMainname:CURRent?
Description: Get the currently used domain name.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:dom:curr? -> “.companyame.com”
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname
Description: Set the host name.
48 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 49

Instrument Setup and Status 3
Parameters: string (maximum 19 characters, though not all characters can be used)
The default host name is K-P...P-S...S; where P...P is the product Number, and S...S is as many of the last digits of the serial
number as it takes to get a 15 character host name.
If you set an empty host name (""), the host name will be set to its default value.
Response: none
Example: :syst:comm:eth:host “N7776C”
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname?
Description: Get the host name.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:host? -> “K-N7776C-0PP03”<END
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname:CURRent?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:HOSTname:CURRent?
Description: Get the current host name.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:host:curr? -> "K-N7776C-12345"
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver?
Description: Get the defined (DNS) nameserver for name resolution.
Parameters: None
Response: IP Address String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:nser? -> "1.1.1.1", "2.2.2.2"
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 49
Page 50

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver
Description: Set one or two nameservers for name resolution. (used if DHCP is disabled).
Parameters: IP Address String
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:nser "1.1.1.1"
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver:CURRent?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NSERver:CURRent?
Description: Get the DNS server addresses assigned from your DHCP sever (this is only valide if DHCP is available and enabled.
Parameters: None
Response: IP Address String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:nser:curr? ->
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IDN
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IDN
Description: The LAN LED on the front panel of the instrument flashes for identification.
Parameters: Boolean (0 | 1 | off | on)
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:idn 1
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress
Description: Set the IP address of the system manually (used if DHCP is disabled).
50 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
"10.127.72.11","10.127.90.11"
Page 51

Instrument Setup and Status 3
Parameters: String (Up to four groups of up to 3 digits, groups separated by ".". Groups with leading
zeroes are interpreted as octal numbers.)
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:ipad “192.132.13.2”
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress?
Description: Get the manually set IP address of the system.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:ipad? -> “192.132.13.2”
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress:CURRent?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:IPADdress:CURRent?
Description: Get the current IP address of the instrument.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:ipad:curr? -> “192.132.13.2”
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:MACaddress?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:MACaddress?
Description: Get the MAC address of the network adapter.
Parameters: None
Response: String (hexadecimal value).
Example: :syst:comm:eth:mac? -> "00-07-E0-14-AE- 08"
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 51
Page 52

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:ENABle?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:ENABle?
Description: Returns the usage of a NTP Server
Parameters: None
Response: Boolean (0 | 1)
Example: :syst:comm:eth:ntp:enab? -> 1
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:ENABle
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:ENABle
Description: Disables or enables instrument's use of NTP.
Parameters: Boolean (0 | 1)
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:ntp:enab 1
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:SERVer?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:SERVer?
Description: Get the defined Network Time Protocol (NTP) server for clock synchronization.
Parameters: None
Response: Address String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:ntp:serv? -> "pool.ntp.org"
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:SERVer
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:NTP:SERVer
Description: Get the defined Network Time Protocol (NTP) server for clock synchronization.
The acronym NTP stands for Network Time Protocol, a protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems.
52 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 53

Parameters: Address String
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:ntp:serv "pool.ntp.org"
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DESCription?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DESCription?
Description: Get the desired mDNS service name.
Parameters: None
Response: Quoted string of up to 260 characters
Example: :syst:comm:eth:desc? -> "Keysight N777-C - 42321"
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DESCription
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:DESCription
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Description: Set the desired mDNS service name.
Parameters: Quoted string of up to 260 characters
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:desc "Keysight N777-C - 42321"
Command: ::SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:RESet
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:RESet
Description: Press the "LAN Reset" button for a long time has the same effect.
Pressing the "LAN Reset" button for a short time is the same as system:preset command.
DHCP On
AutoIP On
NTP Off
Hostname is a concatenation of product number and serial number.
The password for the web based LAN configuration interface is reset to ‘keysight’.
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 53
Page 54

3 Instrument Setup and Status
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:res
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:RESTart
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:RESTart
Description: Restart the system’s network interface with the new parameters.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:rest
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SAVE
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SAVE
Description: Save the system’s network interface parameters.
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:save
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk?
Description: Get the subnet mask.
This command only works if the instrument has a working network connection at the time the command is issued.
If not you either have to wait until the instrument decides on an IP address using AutoIP or reboot the instrument.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:smas? -> “255.255.255.0”
54 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 55

Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk
Description: Set the subnet mask.
Instrument Setup and Status 3
Parameters: String (Up to four groups of up to 3 digits, groups separated
by ".". Groups with leading zeroes are interpreted as octal
numbers.)
Response: None
Example: :syst:comm:eth:smas “255.255.255.0“
Command: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk:CURRent?
Syntax: :SYSTem:COMMunicate:ETHernet:SMASk:CURRent?
Description: Get the currently used subnet mask.
Parameters: None
Response: String
Example: :syst:comm:eth:smas:curr? -> “255.255.255.0”
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 55
Page 56

Page 57

Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family
Programming Guide
4 Measurement
Operations & Settings
Root Layer Command / 58
Signal Generation – The SOURce Subsystem / 61
Configure Subsystem Commands / 81
Triggering - The TRIGger Subsystem / 84
This chapter gives descriptions of commands that you can use when you
are setting up or performing measurements. The commands are split up
into the following subsystems:
Root layer commands that take power measurements, configures
triggering, and return information about the mainframe and it’s slots.
SOURce subsystem commands that control Laser Source modules, DFB
source modules, Tunable Laser modules, and Return Loss Modules with
internal laser sources.
Configure subsystem commands that control all instruments.
TRIGger subsystem commands that control triggering.
Page 58

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Root Layer Command
Command: :LOCK
Syntax: :LOCK<wsp><boolean>, <value>
Description: Switches the lock off and on.
Parameters: A boolean value: 0 or OFF: switch lock off
Response: none
Example: :lock 1,1234 - 1234 is the default password
Command: :LOCK?
Syntax: :LOCK?
Description: Queries the current state of the lock.
Parameters: none
Response: A boolean value: 0: lock is switched off
Example: :lock? -> 1
Lasers cannot be switched on, if you switch the lock on. Lasers are switched off immediately when you switch the lock on.
1 or ON: switch lock on
<value> is the four-figure lock password.
1: lock is switched on
58 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 59

Command: :SLOT[n]:EMPTy?
Syntax: :SLOT[n]:EMPTy?
Description: Queries whether a device is connected for compatibility reasons.
Parameters: None
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: A boolean value: 0: there is a module in the slot
examples: :slot0:empt? -> 0 An optical head is connected to the optical head interface
Command: :SLOT[n]:IDN?
Syntax: :SLOT[n]:IDN?
Description: Returns information about the device.
Parameters: None
Response: MMMMMMMM
mmmm
ssssssss
rrrrrrrrrr
Example: :slot0:idn? ->
Keysight Technologies,N7776C,N711300002,V4.016
See *IDN? on page 30 for information on mainframe identity strings,
and :SLOT[n]:IDN? on page 59 for information on module identity strings.
Command: :SLOT[n]:OPTions?
manufacturer
instrument model number (for example N7776C)
serial number
date of firmware revision
1: the module slot is empty
module in slot 1
Syntax: :SLOT[n]:OPTions?
Description: Returns information about device's options.
Parameters: None
Response: A string.
Example: :slot0:opt? -> 216
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 59
Page 60

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Command: :SLOT[n]:TST?
Syntax: :SLOT[n]:TST?
Description: Returns the latest selftest results for a device for compatibility reasons.
Parameters: None
Response: Returns +0
Example: :slot0:tst? -> +0
Command: :SPECial:REBoot
Syntax: :SPECial:REBoot
Description: Reboots the device.
Parameters: none
Response: none
Example: :spec:reb
60 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 61

Signal Generation – The SOURce Subsystem
The IEEE 488.2 standard has a list of reserved commands, called source
commands. Some of these commands must be implemented by any
instrument using the standard, others are optional. Your instrument
implements all the necessary commands, and some optional ones.
This section provides the description of these commands.
Command: :SOURce0:AM:COHCtrl:COHLevel?
Syntax: :SOURce0:AM:COHCtrl:COHLevel<wsp><value>?<wsp>[MIN | MAX | DEF]
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Description: Queries the current level of coherence, when using Coherence Control. Coherence is expressed on an arbitrary scale from
1 to 100%. A 100% coherence level corresponds to maximum coherence length and minimum linewidth.
Parameters: Optional MIN: returns the minimum programmable value (1%)
MAX: returns the maximum programmable value (100%)
DEF: returns the default preset (*RST) value.
Response: Returns the currently set excursion level as a percentage between 1 and 100.
Example: :sour0:am:cohc:cohl? -> 1.00000000e+00
Affects: N7778C and N7779C
Command: :SOURce0:AM:COHCtrl:COHLevel
Syntax: :SOURce0:AM:COHCtrl:COHLevel<wsp><value>[MIN | MAX | DEF]
Description: Sets the level of coherence, when using coherence control, on an arbitrary scale from 1 to 100%. A 100% coherence level
corresponds to maximum coherence length and minimum linewidth. The coherence level required for a specific linewidth
and coherence length can vary between modules.
Parameters: The excursion level as a percentage of its maximum value.
Also allowed: MIN: minimum programmable value (1%)
MAX: maximum programmable value (100%)
DEF: default preset (*RST) value.
Response: None
Example: :sour0:am:cohc:cohl 50
Affects: N7778C and N7779C
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 61
Page 62

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Command: :SOURce0:AM:SOURce?
Syntax: :SOURce0:AM:SOURce?
Description: Returns the type or source of the modulation of the laser output.
Parameters: None
Response: +1: coherence control
Example: :sour0:am:sour? -> +1
Affects: N7778C and N7779C
Command: :SOURce0:AM:SOURce
Syntax: :SOURce0:AM:SOURce<wsp> |COHCtrl|WVLLocking|1|5
Description: Selects the type or source of the modulation of the laser output.
Parameters: COHCtrl or 1: coherence control
Response: None
Example: :sour0:am:sour COHC
Affects: Coherence control is only available with N7778C and N7779C
Command: :SOURce0:AM:STATe
Syntax: :SOURce0:AM:STATe<wsp> OFF|ON|0|1
+5: wavelength locking
WVLLocking or 5: wavelength locking
Wavelength locking is only available with N7776C
Description: Enables and disables amplitude modulation of the laser output.
Parameters: A boolean value: OFF or 0: amplitude modulation disabled (default)
Response: None
Example: :sour0:am:stat 0
Affects: All N777-C laser sources
62 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
ON or 1: amplitude modulation enabled.
Page 63

Command: :SOURce0:AM:STATe?
Syntax: :SOURce0:AM:STATe?
Description: Returns the current state of amplitude modulation.
Parameters: none
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: A boolean value: 0: modulation is disabled
1: modulation is enabled
Example: :sour0:am:stat? -> 0
Affects: All N777-C laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:READout:DATA?
Syntax: :SOURce0:READout:DATA?<wsp> LLOG|PMAX
Description: Returns the data as a binary stream from either a lambda logging operation or the maximum power the laser can produce at
each wavelength.
Parameters: • LLOGging: Returns a binary stream that contains each wavelength step of the lambda logging operation, see
:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging. Each binary block is an 8-byte long double in Intel byte order.
• PMAX: Returns a binary stream that contains the maximum power the laser can produce at each wavelength. Each binary
block is a 8-byte long double (the wavelength value) followed by a 4-byte long float (the power value). The stream is in
Intel byte order.
Response: A binary stream in Intel byte order.
Example: :sour0:read:data? llog -> the data as a binary stream
Affects: All N777-C laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:READout:POINts?
Syntax: :SOURce0:READout:POINts?<wsp>LLOGging|PMAX
Description: Returns the number of datapoints that the :READout:DATA? command will return.
Parameters: • LLOGging: Returns the number of wavelength steps for a lambda logging operation.
• PMAX: Returns the number of datapoints (each datapoint contains a value for wavelength and power).
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 63
Page 64

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Response: The number of datapoints as an integer value.
Example: :sour0:read:poin? pmax -> +27
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:CORRection:ARA
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:CORRection:ARA
Description: Realigns the laser cavity.
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:corr:ara
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:CORRection:ZERO
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:CORRection:ZERO
Description: Executes a wavelength zero.
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:corr:zero
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:FREQuency
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:FREQuency<wsp><value> [THZ|GHZ|MHZ|KHZ|HZ]
Description: Sets the frequency difference used to calculate a relative wavelength. The output wavelength is made up of the reference
64 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
wavelength and this frequency difference.
The default units for frequency are Hertz.
The output wavelength[l] is set from the base wavelength (l0) and the frequency offset (df ).
The formula for calculating the output wavelength is:
where c is the speed of light in a vacuum (2.990 x 108 ms-1)
Page 65

Parameters: The frequency difference is a float value in Hz.
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:freq -10THZ
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:FREQuency?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:FREQuency?
Description: Returns the frequency difference used to calculate a relative wavelength.
Parameters: None
Response: Returns the frequency difference as a float value in Hz.
Example: :sour0:wav:freq? -> -1.00000000E+013
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:REFerence?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:REFerence?
Description: Returns the reference wavelength (l0).
Parameters: None
Response: The wavelength as a float value in meters.
Example: :sour0:wav:ref? -> +1.5500000E-006
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:REFerence:DISPlay
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:REFerence:DISPlay
Description: Sets the reference wavelength to the value of the output wavelength (l -> l0), that is, sets the frequency offset (df) to zero.
Parameters: None
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 65
Page 66

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:ref:disp
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources and DFB modules
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CHECkparams?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CHECkparams?
Description: Returns whether the currently set sweep parameters (sweep mode, sweep start, stop, width, etc.) are consistent. If there is a
Parameters: None
Response: A string with a detailed description of a configuration problem, or "0,OK" if the sweep os configured correctly. The responses
sweep configuration problem, the laser source is not able to pass a wavelength sweep.
shown below are all the possible configuration problem strings:
Message Description
368,LambdaStop <=LambdaStart start wavelength must be smaller
369,sweepTime < min the total time of the sweep is too
370,sweepTime > max the total time of the sweep is too
371,triggerFreq > max the trigger frequency (calculated
372,step < 0.1 pm step size too small
373,triggerNum > max the number of triggers exceeds
374,LambdaLogging = On AND Modulation
= On AND ModulationSource!
= CoherenceControl
375,LambdaLogging = On AND TriggerOut!
= StepFinished
than stop wavelength
small
large
from sweep speed divided by
sweep step) is too large
the allowed limit
The only allowed modulation
source with the lambda logging
function is coherence control.
lambda logging only works "Step
Finished" output trigger configuration
376,Lambda logging in stepped mode lambda logging can only be done in
377,step not multiple of <x> the step size must be a multiple of
66 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
continuous sweep mode
the smallest possible step size
Page 67

Measurement Operations & Settings 4
378, triggerFreq < min the number of triggers exceeds
379, Continuous Sweep AND Modulation
= On
380, LambdaStart < min sweep start is too small
381, LambdaStop > max sweep stop is too large
Example: :sour0:sour0:wav:swe:chec? -> "0,OK"
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CYCLes
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CYCLes<wsp><value>|MIN|MAX|DEF|0
Description: Sets the number of cycles.
Cannot be set while a sweep is running.
Parameters: The number of cycles is an integer value.
Also allowed are: MIN: minimum programmable value
MAX: maximum programmable value
DEF: This is not the preset (*RST) default value but is half the sum of, the minimum
programmable value and the maximum programmable value 0: cycles continuously.
Response: None
the allowed limit
379,Continuous Sweep = On
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:cycl 3
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CYCLes?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:CYCLes?[<wsp>MIN|MAX|DEF]
Description: Returns the number of cycles.
Parameters: None
Also allowed are: MIN: minimum programmable value
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 67
MAX: maximum programmable value
DEF: This is not the preset (*RST) default value but is half the sum of, the minimum
programmable value and the maximum programmable value 0: cycles continuously.
Page 68

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Response: The number of cycles as a signed integer value.
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:cycl? -> +3
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:DWELl
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:DWELl<wsp><value>|MIN|MAX|DEF[NS|US|MS|S]
Description: Sets the dwell time. Can only be used when sweep is stepped.
Parameters: The dwell time as a float value.
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:dwel 500ms
Cannot be set while a sweep is running.
If you specify no units in your command, seconds are used as the default.
Also allowed are: MIN: minimum programmable value
MAX: maximum programmable value
DEF: This is not the preset (*RST) default value but is half the sum of, the minimum
programmable value and the maximum programmable value
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:DWELl?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:DWELl?[<wsp>MIN|MAX|DEF]
Description: Returns the dwell time. Can only be used when sweep is stepped.
Parameters: None
Also allowed are: MIN: minimum programmable value
Response: The dwell time in seconds.
MAX: maximum programmable value
DEF: This is not the preset (*RST) default value but is half the sum of, the minimum
programmable value and the maximum programmable value
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:dwel? -> +5.00000000E-001
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
68 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 69

Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:FLAG?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:FLAG?
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Description: The sweep flag is used to find out when logging data is available and when the next sweep cycle may be triggered.
It may also be used as a sweep cycle counter, where: flag/2 = number of sweep cycles
The flag is:
• only used in continuous sweep
• set to 0 at start/end of sweep
• incremented when the sweep is waiting for a trigger
• incremented when logging data is available
• an odd number when, waiting for a trigger
• an even number when, logging data may be read
If the trigger input isn’t configured to start a sweep cycle the flag is increased by two when the logging data is available.
If no logging data is calculated, because the user doesn’t want lambda logging, the flag is incremented at the end of the
sweep cycle regardless
Sweep state Flag
start 0
sweep waiting for trigger 1
trigger ->
first cycle | start moving back | do some postprocessing | logging data available
sweep waiting for next trigger 3
Parameters: none
Response: The current sweep flag value as a signed integer value
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:flag? -> +30
Affects: All tunable laser modules except N7779C.
2
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging<wsp>OFF|ON|0|1
Description: Switches lambda logging on or off. Lambda logging is a feature that records the exact wavelength of a tunable laser module
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 69
when a trigger is generated during a continuous sweep. You can read this data using the :READout:DATA? command.
The following settings are the prerequisites for Lambda Logging:
Set :WAVelength:SWEep:MODE to CONTinuous.
Set :TRIGger[n][:CHANnel[m]]:OUTPut to STFinished (step finished)
Set :AM:STATe[l] to OFF
If any of the above prerequisites are not met, then when the sweep is started the status "Sweep parameters inconsistent" will
be returned and Lambda Logging will automatically be turned off.
Page 70

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Lambda logging is disabled at the end of a sweep.
Generally, a continuous sweep can only be started if:
• the trigger frequency, derived from the sweep speed and sweep step, is <= 1 MHz
• the number of triggers, calculated from the sweep span and sweep span, is <=1048576
• the start wavelength is less than the stop wavelength.
In addition, a continuous sweep with lambda logging requires:
• the trigger output to be set to step finished
• modulation set to off.
Parameters: 0 or OFF:
1 or ON:
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:llog 1
Affects: All tunable laser modules that support continuous sweep.
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging?
Description: Returns the state of lambda logging.
Parameters: None
Response: A boolean value: 0 – lambda logging is switched off
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:llog? -> 1
Affects: All tunable laser modules that support continuous sweeps.
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:MODE
switch lambda logging off
switch lambda logging on
1 – lambda logging is switched on
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:MODE<wsp><mode>
Description: Sets the sweep mode.
Cannot be set while a sweep is running.
Parameters: STEPped:
MANual:
CONTinuous:
70 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Stepped sweep mode
Manual sweep mode
Continuous sweep mode
Page 71

Response: none
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:mode STEP
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:MODE?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:MODE?
Description: Returns the sweep mode.
Parameters: None
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: STEP:
MAN:
CONT:
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:mode? -> STEP
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:PMAX?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:PMAX?<wsp><start wavelength>,<stop wavelength>
Description: Returns the power to the highest permissible power for the selected wavelength sweep.
Parameters: start wavelength:
stop wavelength:
Response: The highest permissible power for the selected wavelength sweep as a float value.
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:pmax? 1540nm,1550nm -> +3.5500000E-004
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:REPeat
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:REPeat<wsp><mode>
Stepped sweep mode
Manual sweep mode
Continuous sweep mode
The wavelength at which the sweep starts as a float value.
The wavelength at which the sweep starts as a float value.
Description: Sets the repeat mode. Applies in stepped-sweep and manual sweep modes. The N7776C, N7777C and N7778C also support
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 71
TWOWay mode in continuous sweep mode.
Page 72

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Parameters: ONEWay:
TWOWay:
Response: none
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:rep twow
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:REPeat?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:REPeat?
Description: Returns the repeat mode.
Parameters: None
Response: ONEWay:
TWOWay:
Every stepped or continuous sweep cycle starts at the start wavelength of the sweep and ends at the stop
wavelength of the sweep
Every odd sweep cycle starts at the start wavelength of the sweep, and every even sweep cycle starts at the
stop wavelength of the sweep.
Set the start and stop wavelength of the sweep using :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt
on page 73 and :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP on page 74 respectively.
Every stepped or continuous sweep cycle starts at the start wavelength of the sweep and ends at the
stop wavelength of the sweep
Every odd sweep cycle starts at the start wavelength of the sweep, and every even sweep cycle starts at
the stop wavelength of the sweep.
Set the start and stop wavelength of the sweep using
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt on page 73 and
:SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP on page 74 respectively.
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:rep? -> ONEW
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SOFTtrigger
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SOFTtrigger
Description: Softtrigger does the same as a normal (hardware) trigger at the backplane.
Parameters: None
72 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Usage:
- Trigger input configuration: Start Sweep
- Start Sweep
- SoftTrigger
Page 73

Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: None
Example: :sour0:sour0:wav:swe:soft
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SPEed
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SPEed<wsp><speed>[NM/S|UM/S|MM/S|M/S|MIN|MAX]
Description: Sets the speed for continuous sweeping.
Cannot be set while a sweep is running.
Parameters: Speed as a float value in meters per second (m/s).
Response: none
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:spe 10nm/s
Affects: All tunable laser modules that support continuous sweeps.
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SPEed?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:SPEed? [MIN|MAX]
Description: Returns the speed for continuous sweeping.
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:spe? +8.00000000e-08
Affects: All tunable laser modules that support continuous sweeps.
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt<wsp><startvalue>[PM|NM|UM|MM|M|MIN|MAX]
Description: Sets the starting point of the sweep.
Cannot be set while a sweep is running.
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 73
Page 74

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Parameters: The wavelength at which the sweep starts as a float value.
Response: none
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:star 1500nm
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STARt?[<wsp>MIN|MAX]
Description: Returns the starting point of the sweep.
Parameters: optional MIN Returns the minimum start wavelength available.
Response: The wavelength at which the sweep starts as a float value in meters.
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:star? -> +1.50000000E-006
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
If you specify no units in your command, meters are used as the default.
Also allowed are:
MIN: minimum programmable value
MAX: maximum programmable value
This value is sweep speed dependent.
MAX Returns the maximum start wavelength available.
This value is sweep speed dependent.
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP<wsp><stop value>[PM|NM|UM|MM|M|MIN|MAX]
Description: Sets the end point of the sweep.
Cannot be set while a sweep is running.
Parameters: The wavelength at which the sweep ends as a float value in meters.
74 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
If you specify no units in your command, meters are used as the default.
MIN Sets the minimum stop wavelength available.
This value is sweep speed and mode dependent.
MAX Sets the maximum stop wavelength available.
This value is sweep speed and mode dependent.
Page 75

Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:stop 1550nm
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STOP?[<wsp>MIN|MAX]
Description: Returns the end point of the sweep.
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Parameters: optional MIN Returns the minimum start wavelength available.
Response: The wavelength at which the sweep ends as a float value in meters.
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:stop? -> +1.55000000E-006
Affects: All tunable laser modules
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:[STATe]
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:[STATe]<wsp>STOP|0|STARt|1|PAUSe|2|CONTinue|3
Description: Stops, starts, pauses or continues a wavelength sweep.
Parameters: 0 or STOP:
1 or STARt:
2 or PAUSe:
3 or CONTinue:
If you enable lambda logging (see :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:LLOGging on page 69 ) and modulation
(see :SOURce0:AM:STATe on page 62 ) simultaneously, a sweep cannot be started.
Generally, a continuous sweep can only be started if:
the trigger frequency, derived from the sweep speed and sweep step, is <=1MHz
the number of triggers, calculated from the sweep span and sweep span, is <=1048576
the start wavelength is less than the stop wavelength.
In addition, a continuous sweep with lambda logging requires:
the trigger output to be set to step finished modulation set to off.
This value is sweep speed dependent.
MAX Returns the maximum start wavelength available.
This value is sweep speed dependent.
Stop the sweep.
Start a sweep, run sweep.
Pause the sweep. (doesn’t apply for continuous sweep)
Continue a sweep. (doesn’t apply for continuous sweep)
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 75
Page 76

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Response: none
Example: :sour0:wav:swe STOP
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:[STATe]?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:[STATe]?
Description: Returns the state of a sweep.
Parameters: None
Response: +0:
Example: :sour0:wav:swe? -> +0
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:NEXT
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:NEXT
Description: Performs the next sweep step in stepped sweep if it is paused or in manual sweep.
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:step:next
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:PREVious
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:PREVious
Description: Performs one sweep step backwards in stepped sweep if it is paused or in manual sweep.
+1:
+2:
Sweep is not running
Sweep is running
Sweep paused
Parameters: None
76 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 77

Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:step:prev
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:[WIDTh]
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:[WIDTh]<wsp><value>[PM|NM|UM|MM|M|MIN|MAX]
Description: Sets the width of the sweep step.
In continuous sweep mode, the end of a step is used for triggering.
Parameters: The width of the sweep step as a float value.
If you specify no units in your command, meters are used as the default.
MIN: Sets the minimum step width available.
MAX: Sets the maximum step width available.
Response: None
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:step 5nm
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:[WIDTh]?
Syntax: :SOURce0:WAVelength:SWEep:STEP:[WIDTh]?[<wsp>MIN|MAX]
Description: Returns the width of the sweep step
Parameters: optional MIN Returns the minimum step width available.
MAX Returns the maximum step width available.
Response: The sweep step as a float value in meters.
Example: :sour0:wav:swe:step? -> +5.00000000E-009
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:POWer[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]
Syntax: :SOURce0:POWer[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]<wsp><value>[PW|NW|UW|MW|Watt|DBM]|MIN|MAX
Description: Sets the power of the laser output.
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 77
Page 78

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
The instrument may not be able to output a signal with the maximum programmable power, it will output a signal with the
maximum power. Use the :WAVelength:SWEep:PMAX:CURRent? to query the maximal possible power at output. Current
output power is minimum of this command or :WAVelength:SWEep:PMAX:CURRent?
The default units are DBM or W, depending on the unit selected using the following command:
:SOURce0:POWer:UNIT on page 79.
Parameters: Any value in the specified range (see the appropriate User’s Guide).
Also allowed are: MIN: minimum programmable value
Response: None
Example: :sour0:pow 5mW
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:POWer[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]?
Syntax: :SOURce0:POWer[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]?<wsp>[MIN|DEF|MAX]
Description: Returns the amplitude level of the output power.
Parameters: Also allowed are: MIN: minimum amplitude level
Response: Amplitude level relevant to the current value or specified parameter (if MIN, MAX, or DEF are chosen as a parameter).
Example: :sour0:pow? -> +8.00000000E-004
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
The value returned is the actual amplitude that is output, which may be different from the value set for the output. If these
two figures are not the same, it is indicated in the :STATus:OPERation register.
MAX: maximum programmable value
DEF: This is not the preset (*RST) default value, but is the maximum programmable level
MAX: maximum amplitude level
DEF: default value
Command: :SOURce0:POWer:STATe
Syntax: :SOURce0:POWer:STATe<wsp><boolean>
Description: Switches the laser of the chosen source on or off.
Parameters: A boolean value: 0: Laser Off
78 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
1: Laser On
Page 79

Response: None
Example: :sour0:pow:stat 1
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:POWer:STATe?
Syntax: :SOURce0:POWer:STATe?
Description: Queries the laser state of the chosen source.
Parameters: None
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: A boolean value: 0: Laser Off
Example: :sour0:pow:stat? -> 1
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:POWer:UNIT
Syntax: :SOURce0:POWer:UNIT<wsp>DBM|0|Watt|1
Description: Sets the power units
Parameters: 0 or DBM:
1 or W:
Response: None
Example: :sour0:pow:unit w
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
Command: :SOURce0:POWer:UNIT?
Syntax: :SOURce0:POWer:UNIT<wsp>DBM|0|Watt|1
Description: Return the current power units
dBm (default)
Watts
1: Laser On
Parameters: 0:1:dBm
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 79
Watts
Page 80

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Response: none
Example: :sour0:pow:unit? -> 0
Affects: All N777-C tunable laser sources
80 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 81

Configure Subsystem Commands
This section provides the description of the following commands.
Command: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:ACTual?
Syntax: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:ACTual?
Description: Get the index of the setting currently being used.
Parameters: None
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: int
A value >0 is returned if the setting has been stored in FLASH memory (using :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:SAVE), or
has been recalled from FLASH memory (using :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:RECall), and has not been changed since.
0 is returned if the setting has not yet been stored. 0 is returned if the FLASH setting has been deleted
(using:CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:ERASe) since the last recall or store. -1 is returned if the setting was changed but
has not been saved yet.
Example: :conf:meas:sett:act? → +2
Affects: All instruments
Command: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:NUMBer?
Syntax: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:NUMBer?
Description: Get the number of settings. In addition to the settings spaces in FLASH memory, the working memory can hold a setting.
Parameters: None
Response: int
Example: :conf:meas:sett:numb? → +1
Affects: All instruments
Command: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:PRESet
Syntax: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:PRESet
Description: Resets the setting values in the working memory. In contrast to the *RST and System:Preset commands, the previous stored
Parameters: None
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 81
settings remain in nonvolatile RAM and can be recalled again.
Page 82

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Response: None
Example: :conf:meas:sett:pres
Affects: All instruments
Command: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:CANCel
Syntax: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:CANCel
Description: Discard all the changes to the setting since the last save or recall
Parameters: None
Response: None
Example: :conf:meas:sett:canc
Affects: All instruments
Command: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:RECall
Syntax: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:RECall
Description: Recall a setting from FLASH memory
Parameters: Integer
Response: None
Example: :conf:meas:sett:rec 1
Affects: All instruments
Command: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:SAVE
Syntax: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:SAVE
Description: Recall a setting from FLASH memory
Parameters: Integer
Response: None
Example: :conf:meas:sett:save 1
Affects: All instruments
82 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 83

Command: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:ERASe
Syntax: :CONFigure:MEASurement:SETTing:ERASe
Description: Erase a setting from memory
Parameters: Integer
Response: None
Example: :conf:meas:sett:eras 1
Affects: All instruments
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 83
Page 84

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Triggering - The TRIGger Subsystem
The TRIGger Subsystem allows you to configure how the instrument reacts
to incoming or outgoing triggers.
Command: :TRIGger
Syntax: :TRIGger<wsp>NODEA|1|NODEB|2
Description: Generates a hardware trigger.
Parameters: 1 or NODEA:
2 or NODEB:
A hardware trigger cannot be effective in the DISabled triggering mode but can be effective in DEFault, PASSthrough or
LOOPback triggering modes, see :TRIGger:CONFiguration on page 86 for information on triggering modes.
Is identical to a trigger at the Input Trigger Connector.
Generates trigger at the Output Trigger Connector.
:TRIGger on page 84 describes the :TRIGger command for advanced users.
Response: None
Example: :trig 1
Command: :TRIGger[n]:INPut
Syntax: :TRIGger[n]:INPut<wsp><trigger response>
Description: Sets the incoming trigger response and arms the module.
Parameters: IGNore:
NEXTstep:
SWStart:
Response: None
Example: :trig0:inp ign
Affects: All tunable laser modules
Ignore incoming trigger.
Perform next step of a stepped sweep.
Start a sweep cycle.
84 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 85

Command: :TRIGger[n]:INPut?
Syntax: :TRIGger[n]:INPut?
Description: Returns the incoming trigger response.
Parameters: None
Measurement Operations & Settings 4
Response: IGNore:
NEXTstep:
SWStart:
Example: :trig0:inp? -> ign
Affects: All tunable laser modules
Command: :TRIGger[n]:OUTPut
Syntax: :TRIGger[n]:OUTPut
Description: Specifies when an output trigger is generated and arms the module.
Parameters: DISabled:
STFinished:
SWFinished:
SWSTarted:
Response: None
Example: :trig0:outp dis
Affects: All tunable laser modules
Command: :TRIGger[n]:OUTPut?
Ignore incoming trigger.
Perform next step of a stepped sweep.
Start a sweep cycle.
Never.
When a sweep step finishes.
When sweep cycle finishes.
When a sweep cycle starts.
Syntax: :TRIGger[n]:OUTPut?
Description: Returns the condition that causes an output trigger.
Parameters: none
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 85
Page 86

4 Measurement Operations & Settings
Response: DISabled:
Example: :trig0:outp? -> dis
Affects: All tunable laser modules
Command: :TRIGger:CONFiguration
Syntax: :TRIGger:CONFiguration
Description: Sets the hardware trigger configuration with regard to Output and Input Trigger Connectors.
Parameters: 0 or DISabled:
Response: none
Example: :trig:conf dis
affects All modules
STFinished:
SWFinished:
SWSTarted:
1 or DEFault:
2 or PASSthrough:
3 or LOOPback:
Never.
When a sweep step finishes.
When sweep cycle finishes.
When a sweep cycle starts.
Trigger connectors are disabled.
The Input Trigger Connector is activated, the incoming trigger response for each
slot.
A trigger at the Input Trigger Connector generates a trigger at the Output Trigger
Connector automatically. No triggers from the instrument at the output.
The same as PASSthrough. This is included for compatibility reasons.
Command: :TRIGger:CONFiguration?
Syntax: :TRIGger:CONFiguration?
Description: Returns the hardware trigger configuration.
Parameters: None
Parameters: 0 or DISabled:
1 or DEFault:
2 or PASSthrough:
3 or LOOPback:
Example: :trig:conf? -> DEF
affects All modules
86 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Trigger connectors are disabled.
The Input Trigger Connector is activated, the incoming trigger response for each slot.
A trigger at the Input Trigger Connector generates a trigger at the Output Trigger
Connector automatically. No triggers from the instrument at the output.
The same as PASSthrough. This is included for compatibility reasons.
Page 87

Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family
Programming Guide
5 Error Codes
Error Strings / 88
This chapter gives information about error codes used with the N777-C
series tunable laser source instruments.
Page 88

5 Error Codes
Error Strings
Error strings in the range -100 to -183 are defined by the SCPI standard,
downloadable from: http://www.ivifoundation.org/docs/scpi-99.pdf
String descriptions taken from this standard (VERSION 1999.0 May, 1999),
whether in whole or in part, are enclosed by [ ].
Table 1 Overview for Supported Strings
Error
Number String
0 "No error"
-100 "Command Error"
-101 "Invalid character"
-102 "Syntax error"
-103 "Invalid separator"
-104 "Data type error"
-105 "GET not allowed"
-108 "Parameter not allowed"
-109 "Missing parameter"
-110 "Command header error"
[This is the generic syntax error used when a more specific error cannot be detected. This code
indicates only that a Command Error as defined in IEEE 488.2,11.5.1.1.4 has occurred.]
[A syntactic element contains a character which is invalid for that type; for example, a header
containing an ampersand, SETUP&. This error might be used in place of error -114 and perhaps
some others.]
[An unrecognized command or data type was encountered; for example, a string was received
when the device does not accept strings.]
[The parser was expecting a separator and encountered an illegal character; for example, the
semicolon was omitted after a program message unit]
[The parser recognized a data element different than one allowed; for example,numeric or string
data was expected but block data was encountered.]
[A Group Execute Trigger was received within a program message (see IEEE488.2, 7.7).]
[More parameters were received than expected for the header]
[Fewer parameters were received than required for the header]
-111 "Header separator error"
88 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Page 89

Error
Number String
Error Codes 5
-112 "Program mnemonic too long"
[The header contains more than twelve characters (see IEEE 488.2, 7.6.1.4.1).]
-113 "Undefined header"
[The header is syntactically correct, but it is undefined for this specific device; for example, *XYZ is
not defined for any device.]
-114 "Header suffix out of range"
-115 "Unexpected number of parameters"
-120 "Numeric data error"
[This error, as well as errors -121 through -129, are generated when parsing a data element which
appears to be numeric, including the nondecimal numeric types. This error message is used if the
device cannot detect a more specific error.]
-121 "Invalid character in number"
[An invalid character for the data type being parsed was encountered; for example, an alpha in a
decimal numeric]
-123 "Exponent too large"
[The magnitude of the exponent was larger than 32000 (see IEEE 488.2,7.7.2.4.1).]
-124 "Too many digits"
[The mantissa of a decimal numeric data element contained more than 255 digits excluding
leading zeros (see IEEE 488.2, 7.7.2.4.1).]
-128 "Numeric data not allowed"
[A legal numeric data element was received, but the device does not accept one in this position for
the header.]
-130 "Suffix error"
-131 "Invalid suffix"
-134 “Suffix too long”
-138 “Suffix not allowed”
-140 "Character data error"
-141 “Invalid character data”
-144 "Character data too long"
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 89
[The suffix does not follow the syntax described in IEEE 488.2, 7.7.3.2, or thesuffix is inappropriate
for this device.]
[The suffix contained more than 12 characters (see IEEE 488.2, 7.7.3.4).]
[A suffix was encountered after a numeric element which does not allow suffixes.]
[Either the character data element contains an invalid character or the particular element received
is not valid for the header.]
Page 90

5 Error Codes
Error
Number String
-148 “Character data not allowed”
-150 “String data error”
-151 “Invalid string data”
-158 “String data not allowed”
-160 "Block data error"
-161 “Invalid block data”
-168 “Block data not allowed”
-170 “Expression error”
-171 “Invalid expression”
[A legal character data element was encountered where prohibited by the device.]
[This error, as well as errors -151 through -159, are generated when parsing a string data element.
This error message is used when the device cannot detect a more specific error.]
[A string data element was expected, but was invalid for some reason (see IEEE 488.2, 7.7.5.2); for
example, an END message was received before the terminal quote character.]
[A string data element was encountered but was not allowed by the device at this point in parsing.]
[A block data element was expected, but was invalid for some reason (see IEEE 488.2, 7.7.6.2); for
example, an END message was received before the length was satisfied.]
[A legal block data element was encountered but was not allowed by the device at this point in
parsing.]
[This error, as well as errors -171 through -179, are generated when parsing an expression data
element. This particular error message is used when the device cannot detect a more specific
error.]
[The expression data element was invalid (see IEEE 488.2, 7.7.7.2); for example, unmatched
parentheses or an illegal character.]
-178 “Expression data not allowed”
-180 "Macro error"
-181 “Invalid outside macro definition”
-183 “Invalid inside macro definition”
-184 "Macro parameter error"
90 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
[A legal expression data was encountered but was not allowed by the device at this point in
parsing.]
[Indicates that a macro parameter placeholder ($<number) was encountered outside of a macro
definition.]
[Indicates that the program message unit sequence, sent with a *DDT or *DMC command, is
syntactically invalid (see IEEE 488.2, 10.7.6.3).]
Page 91

Error
Number String
Error Codes 5
-185 “Subop out of range”
Description:
Suboperations are parameters that are passed to refine the destination of a command. They are
used to address slots, channels, laser selections and GPIB/SCPI register levels. This error is
generated if the parameter is not valid in the current context or system configuration.
Example:
This error occurs if the user queries the status of a summary register and passes an invalid status
level (also see "Status for 816x" on page 28 programmer's guide).
Note:
Incorrect slots and channels addresses are handled by error code -301
-200 “Execution error (StatExecError)"
Description:
This error occurs when the current function, instrument or module state (or status) prevents the
execution of a command. This is a generic error which can occur for a number of reasons.
Example:
When a powermeter has finished a logging application and data is available, the user is not able to
reconfigure the logging application parameters. First, the user must stop the logging application.
-201 "Invalid while in local"
"Please be patient - GPIB currently locked out"
Description:
Some operations block the complete system. Since no sensible measurements are possible while
this is true, the GPIB is locked out.
Example:
When ARA, Lambda zeroing or zeroing is executing on a TLS module, the GPIB is not accessible.
-202 "Settings lost due to rtl"
-203 "Command protected"
-210 "Trigger error"
-211 “Trigger ignored”
-212 “Arm ignored”
-213 “Init ignored”
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 91
Description:
A trigger has been detected but ignored because of timing contraints. (For Example: average time
to large).
Description:
The user can set the automatic re-arming option for input and output trigger events (see Error
Strings
on page 88). When this error occurs, the device ignores the setting because the current
module status does not allow the change of trigger settings.
Description:
The INIT:IMM command initiates a trigger and completes a full measurement cycle. The continuous
measurement must be DISABLED. This error code is generated if the module is still in cont.
measurement mode.
Page 92

5 Error Codes
Error
Number String
-214 "Trigger deadlock"
-215 "Arm deadlock"
-220 "Parameter error (StatParmError)”
-220 -220, "Parameter error (StatParmOutOfRange)"
-220 "Parameter error (StatParmIllegalVal)"
-221 "Settings conflict (StatParmInconsistent)"
Description:
The user has passed a parameter that cannot be changed in this way. The device cannot detect one
of the following more specific errors:
Description:
The user has passed a parameter that exceeds the valid range for this parameter.
Description:
The user has passed a parameter that does not match a value in a list of possible values.
Description:
The user has passed a parameter that conflicts with other already configured parameters.
Example:
There are constrains for TLS sweep parameters: this error is generated when lambda step size
exceeds the difference between start and stop wavelength.
If error -221 is returned after you try to start a wavelength sweep, one of the following cases of
sweep parameter inconsistency has occurred:
Continuous Sweep mode AND l Start is less than l Stop.
Continuous Sweep mode AND Sweep Time is too short. Adjust Sweep Speed, l Start, or l Stop.
Continuous Sweep mode AND Sweep Time is too long. Adjust Sweep Speed, l Start, or l Stop.
Continuous Sweep mode AND Trigger Frequency is too high. Adjust Step Size. Trigger Frequency is
the Sweep Speed divided by the Step Size.
Stepped Sweep mode AND Lambda Logging Enabled.
Continuous Sweep mode AND Lambda Logging Enabled AND Output trigger mode not set to
STFinished (Step finished).
Continuous Sweep mode AND Lambda Logging is Enabled AND Modulation Source is not set to
OFF.
Continuous Sweep mode AND Lambda Logging is Enabled AND Sweep Cycles is not set to 1.
-222 "Data out of range (StatParmTooLarge)"
-222 "Data out of range (StatParmTooSmall)"
92 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
Description:
The user has passed a continuous parameter that is too large.
Example:
Wavelength 1800nm when maximum wavelength is 1700nm.
Description:
The user has passed a continuous parameter that is too small.
Example:
Wavelength 700nm when minimum wavelength is 800nm.
Page 93

Error
Number String
Error Codes 5
-223 “Too much data”
Description:
A function returns more data or the user requests more data than the application is able to handle.
Example:
A tunable laser source produces more data when lambda values of a sweep are stored than the
816x instrument is able to handle. Use the new SENSE:FUNC:RES:BLOCK? command to split the
data aquisition into multiple parts.
-224 “Illegal parameter value”
[Used where exact value, from a list of possibles, was expected.]
-225 "Out of memory"
Description:
The request application or function cannot be executed because the instrument runs out of
memory.
-226 "Lists not same length"
-230 "Data corrupt or stale"
-231 "Data questionable (StatValNYetAcc)"
Description:
The data that is retured is not accurate or reliable. The user should repeat the operation. The
reason for this error is unspecific.
Example:
A powermeter configured a long average time has not completed its current measurement cycle
when the user queries the current power.
-231 "Data questionable (StatRangeTooLow)"
Description:
As -231 (StatValNYetAcc) but for a more specific reason: The powermeter readout data is not
reliable because the currently set (manual) range does not correspond with the input power.
-240 "Hardware error"
-241 "Hardware missing"
-250 "Mass storage error"
-251 "Missing mass storage"
-252 "Missing media"
-253 "Corrupt media"
-254 "Media full"
-255 "Directory full"
-256 "File name not found"
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 93
Page 94

5 Error Codes
Error
Number String
-257 "File name error"
-258 "Media protected"
-260 "Expression error"
-261 "Math error in expression (StatUnitCalculationError)"
-270 "Macro error"
-271 "Macro syntax error"
-272 “Macro execution error”
-273 “Illegal macro label”
-274 "Macro parameter error"
-275 "Macro definition too long"
-276 “Macro recursion error”
-277 “Macro redefinition not allowed”
Description:
This may occur when the user attempts to transform data in a way that is currently not possible.
Example:
When a powermeter is measuring very small power values in dBm (such as noise power), negative
power values in Watt may also be present (such as when the powermeter calibration wavelength
does not correspond to the wavelength of input signal). The instrument cannot transform negative
Watt values to dBm because the logarithm of a negative value is not defined.
[Indicates that a syntactically legal macro program data sequence could not beexecuted due to
some error in the macro definition (see IEEE 488.2, 10.7.6.3.)]
[Indicates that the macro label defined in the *DMC command was a legal string syntax, but could
not be accepted by the device (see IEEE 488.2, 10.7.3 and 10.7.6.2); for example, the label was too
long, the same as a common command header, or contained invalid header syntax.]
[Indicates that a syntactically legal macro program data sequence could not be executed because
the device found it to be recursive (see IEEE 488.2, 10.7.6.6).]
[Indicates that a syntactically legal macro label in the *DMC command could not be executed
because the macro label was already defined (see IEEE 488.2,10.7.6.4).]
-278 “Macro header not found”
-280 "Program error"
-281 "Cannot create program"
-282 "Illegal program name"
94 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
[Indicates that a syntactically legal macro label in the *GMC? query could not be executed because
the header was not previously defined.]
Page 95

Error
Number String
-283 "Illegal variable name"
Error Codes 5
-284 "Function currently running (StatModuleBusy)"
Description:
This error is generated when a function is currently running on a module so that it cannot process
another command.
Example:
When a powermeter is running a logging application, you are not able to configure the logging
application parameters (also see -200).
-285 "Program syntax error"
-286 "Program runtime error"
-290 "Memory use error"
-291 "Out of memory"
-292 "Referenced name does not exist"
-293 "Referenced name already exists"
-294 "Incompatible type"
-300 "Device-specific error"
-303 "Module slot empty or slot / channel invalid"
Description:
The user has send a command to an empty slot.
-310 “System error”
[Indicates that some error, termed “system error” by the device, has occurred. This code is
device-dependent.]
-311 "Memory error"
-312 "PUD memory lost"
-313 "Calibration memory lost"
-314 "Save/recall memory lost"
-315 "Configuration memory lost"
-320 "Storage fault"
-321 “Out of memory”
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 95
[An internal operation needed more memory than was available.]
Page 96

5 Error Codes
Error
Number String
-330 “Self-test failed”
-340 "Calibration failed"
-350 “Queue overflow”
-360 "Communication error"
-361 "Parity error in program message"
-362 "Framing error in program message"
-363 "Input buffer overrun"
-365 "Time out error"
-368 "LambdaStop<=LambdaStart"
-369 "sweepTime < min"
-370 "sweepTime > max"
-371 "triggerFreq > max"
-372 "step < min"
-373 "triggerNum > max"
-374 "LambdaLogging = On AND Modulation = On AND ModulationSource! = CoherenceControl"
Description:
You have started the self test, but the module has detected an error while executing it
[A specific code entered into the queue in lieu of the code that caused the error. This code
indicates that there is no room in the queue and an error occurred but was not recorded.]
-375 "LambdaLogging = On AND TriggerOut! = StepFinished"
-376 "Lambda logging in stepped mode"
-377 "step not multiple of 0.1pm"
-378 "triggerFreq < min"
-400 “Query error”
-410 “Query INTERRUPTED”
96 Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide
[This is the generic query error for devices that cannot detect more specific errors. This code
indicates only that a Query Error as defined in IEEE 488.2, 11.5.1.1.7 and 6.3 has occurred.]
[Indicates that a condition causing an INTERRUPTED Query error occurred (see IEEE 488.2,
6.3.2.3); for example, a query followed by DAB or GET before a response was completely sent.]
Page 97

Error
Number String
Error Codes 5
-420 “Query UNTERMINATED”
-430 “Query DEADLOCKED”
-440 “Query UNTERMINATED after indef resp”
[Indicates that a condition causing an UNTERMINATED Query error occurred (see IEEE 488.2,
6.3.2.2); for example, the device was addressed to talk and an incomplete program message was
received.]
[Indicates that a condition causing an DEADLOCKED Query error occurred (see IEEE 488.2,
6.3.1.7); for example, both input buffer and output buffer are full and the device cannot continue.]
[Indicates that a query was received in the same program message after an query requesting an
indefinite response was executed (see IEEE 488.2, 6.5.7.5).]
Keysight N777-C Series Tunable Laser Family Programming Guide 97
Page 98

This information is subject to
change without notice.
© Keysight Technologies 2021
Edition 2.1, February 2021
www.keysight.com
 Loading...
Loading...