Page 1
Keysight InfiniiVision
1200 X-Series and
EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
Page 2
Notices
CAUTION
WARNING
© Keysight Technologies, Inc. 2005-2020
No part of this manual may be reproduced in
any form or by any means (including
electronic storage and retrieval or translation
into a foreign language) without prior
agreement and written consent from
Keysight Technologies, Inc. as governed by
United States and international copyright
laws.
Manual Part Number
N2137-97015
Edition
Third edition, January 2020
Printed in Malaysia
Published by:
Keysight Technologies, Inc.
1900 Garden of the Gods Road
Colorado Springs, CO 80907 USA
Print History
N2137-97000, September 2018
N2137-97012, January 2019
N2137-97015, January 2020
Warranty
The material contained in this document is
provided "as is," and is subject to being
changed, without notice, in future editions.
Further, to the maximum extent permitted
by applicable law, Keysight disclaims all
warranties, either express or implied, with
regard to this manual and any information
contained herein, including but not limited
to the implied warranties of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose.
Keysight shall not be liable for errors or for
incidental or consequential damages in
connection with the furnishing, use, or
performance of this document or of any
information contained herein. Should
Keysight and the user have a separate
written agreement with warranty terms
covering the material in this document that
conflict with these terms, the warranty
terms in the separate agreement shall
control.
Technology License
The hardware and/or software described in
this document are furnished under a license
and may be used or copied only in
accordance with the terms of such license.
U.S. Government Rights
The Software is "commercial computer
software," as defined by Federal Acquisition
Regulation ("FAR") 2.101. Pursuant to FAR
12.212 and 27.405-3 and Department of
Defense FAR Supplement ("DFARS")
227.7202, the U.S. government acquires
commercial computer software under the
same terms by which the software is
customarily provided to the public.
Accordingly, Keysight provides the Software
to U.S. government customers under its
standard commercial license, which is
embodied in its End User License Agreement
(EULA), a copy of which can be found at
www.keysight.com/find/sweula. The
license set forth in the EULA represents the
exclusive authority by which the U.S.
government may use, modify, distribute, or
disclose the Software. The EULA and the
license set forth therein, does not require or
permit, among other things, that Keysight: (1)
Furnish technical information related to
commercial computer software or
commercial computer software
documentation that is not customarily
provided to the public; or (2) Relinquish to, or
otherwise provide, the government rights in
excess of these rights customarily provided
to the public to use, modify, reproduce,
release, perform, display, or disclose
commercial computer software or
commercial computer software
documentation. No additional government
requirements beyond those set forth in the
EULA shall apply, except to the extent that
those terms, rights, or licenses are explicitly
required from all providers of commercial
computer software pursuant to the FAR and
the DFARS and are set forth specifically in
writing elsewhere in the EULA. Keysight shall
be under no obligation to update, revise or
otherwise modify the Software. With respect
to any technical data as defined by FAR
2.101, pursuant to FAR 12.211 and 27.404.2
and DFARS 227.7102, the U.S. government
acquires no greater than Limited Rights as
defined in FAR 27.401 or DFAR 227.7103-5
(c), as applicable in any technical data.
Safety Notices
A CAUTION notice denotes a hazard.
It calls attention to an operating
procedure, practice, or the like that,
if not correctly performed or
adhered to, could result in damage
to the product or loss of important
data. Do not proceed beyond a
CAUTION notice until the indicated
conditions are fully understood and
met.
A WARNING notice denotes a
hazard. It calls attention to an
operating procedure, practice, or
the like that, if not correctly
performed or adhered to, could
result in personal injury or death.
Do not proceed beyond a WARNING
notice until the indicated
conditions are fully understood and
met.
2 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 3

InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes— At a Glance
Figure 1 InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series 4-Channel Oscilloscope
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 3
Page 4
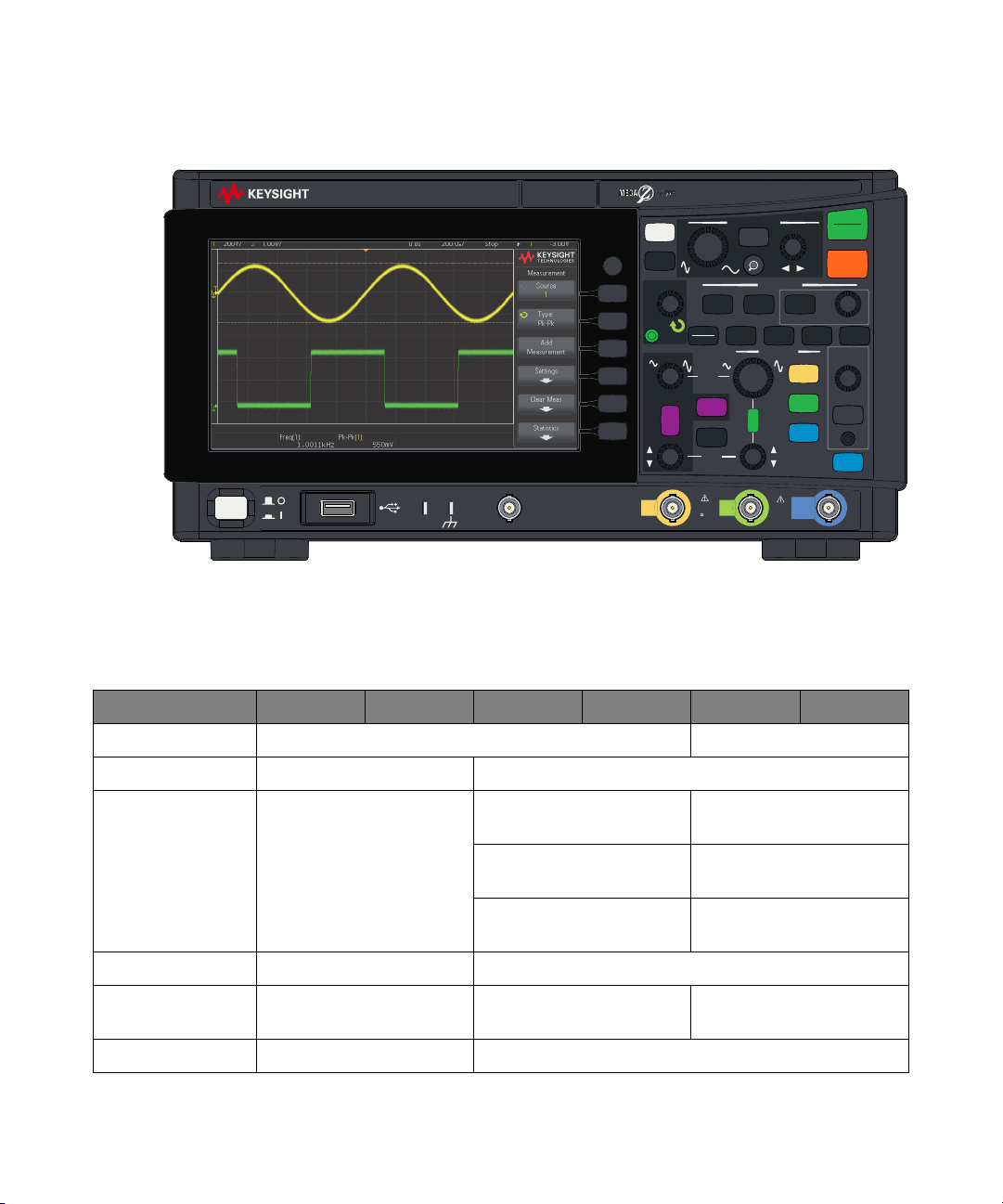
Figure 2 InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series 2-Channel Oscilloscope
Mixed Signal Oscilloscope
MSOX1204G
Digital Storage Oscilloscope
DSOX1202G
200 MHz 2 GSa/s70 MHz 2 GSa/s
InfiniiVision
Push
Fine
Push
Zero
Push to
Select
Force
Entry
Horizontal
Leve-l
Measure
Ver ti ca l
Intensity
Push
for Fine
Push
to Zero
Tri g g e r
Push for 50%
Push to Select
Tri g g e r
FFT
External
Math
Default
Setup
Run
Stop
Single
Wave
Gen
Acquire
2
1
CursorsMeas
Utility
Analyze
Display
Save
to USB
Help
Save
Recall
Auto
Scale
Back
Quick
Action
Demo
Probe
Comp
Ext
Tri g
Gen
Out
Inputs
CH1 and CH2
150V RMS
Input
Ext Trig
30V RMS
~
1M
~
16pF
Demo
Probe
Comp
1
2
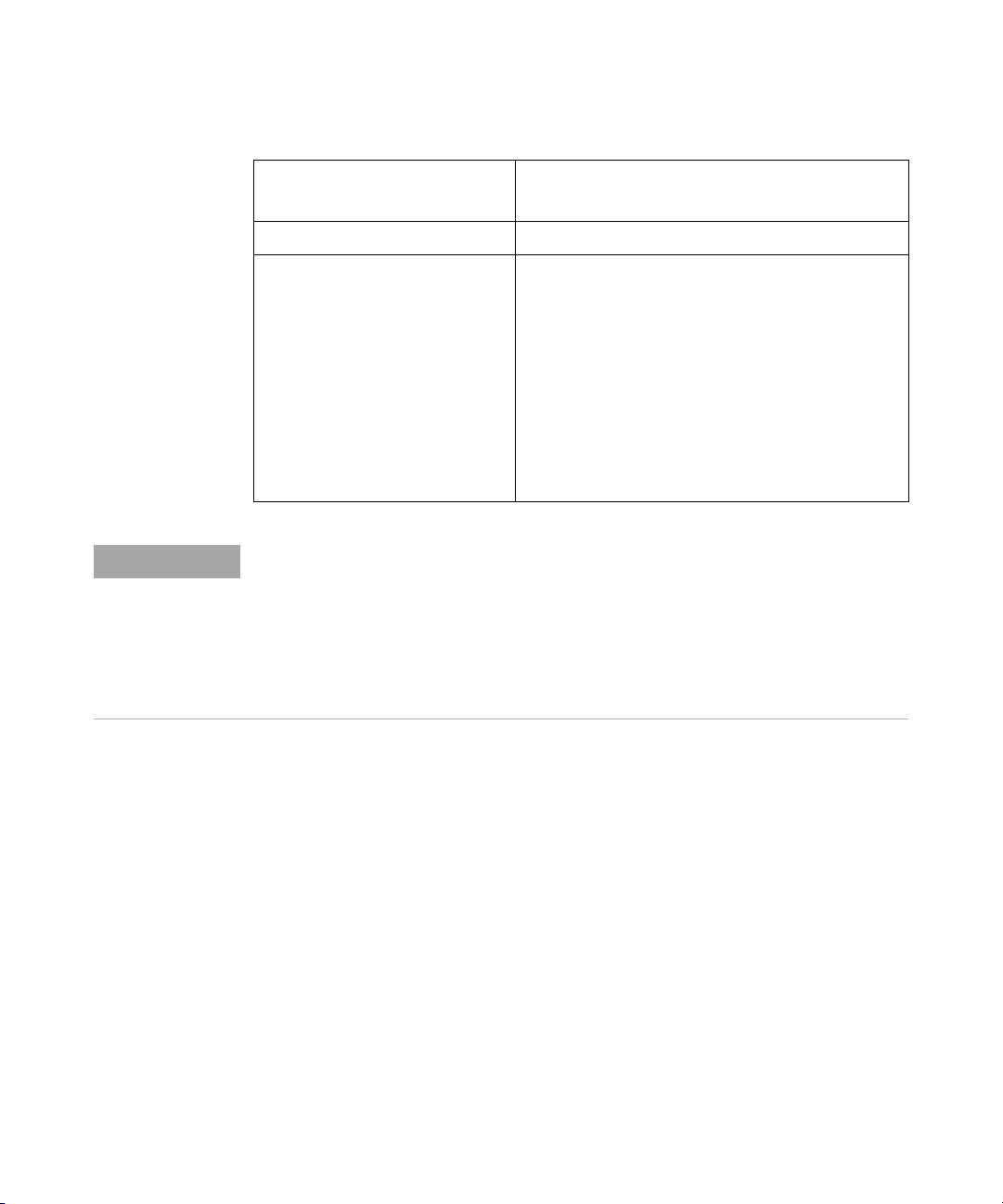
Table 1 InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes Model Numbers, Bandwidths
Model: EDUX1052A EDUX1052G DSOX1202A DSOX1202G DSOX1204A DSOX1204G
Channels: 2 4
Bandwidth: 50 MHz 70 MHz
Bandwidth upgrades: 70 MHz to 100 MHz with
D1202BW1A upgrade
70 MHz to 200 MHz with
D1202BW2A upgrade
100 MHz to 200 MHz with
D1202BW3A upgrade
Sampling rate: 1 GSa/s 2 GSa/s (interleaved), 1 GSa/s (non-interleaved)
Memory: 200 kpts 2 Mpts (1 Mpts when the
External Trig channel is on)
Segmented memory: No Yes
4 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
70 MHz to 100 MHz with
D1200BW1A upgrade
70 MHz to 200 MHz with
D1200BW2A upgrade
100 MHz to 200 MHz with
D1200BW3A upgrade
2 Mpts (interleaved), 1 Mpts
(non-interleaved)
Page 5

Table 1 InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes Model Numbers, Bandwidths (continued)
Model: EDUX1052A EDUX1052G DSOX1202A DSOX1202G DSOX1204A DSOX1204G
Waveform generator: No Yes (20 MHz) No Yes (20 MHz) No Yes (20 MHz)
Mask/limit test: No Yes
The Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G oscilloscopes deliver
these features:
• 7 inch WVGA display.
• 200,000 waveforms/second update rate.
• All knobs are pushable for making quick selections.
• Trigger types: edge, pulse width, and video on EDUX1000-Series models.
DSOX1200-Series models add: pattern, rise/fall time, and setup and hold.
• Serial decode/trigger options for: I
models. DSOX1200-Series models add: CAN, LIN, and SPI.
• Math waveforms: add, subtract, multiply, divide, FFT (magnitude and phase),
and low-pass filter.
• Reference waveforms (2) for comparing with other channel or math waveforms.
• Many built-in measurements.
• G-suffix models have built-in waveform generator with: sine, square, ramp,
pulse, DC, noise.
• USB/LAN ports makes printing, saving, and sharing data easy.
• A Quick Help system is built into the oscilloscope. Press and hold any key to
display Quick Help.
2
C and UART/RS232 on EDUX1000-Series
For more information about InfiniiVision oscilloscopes, see:
www.keysight.com/find/scope
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 5
Page 6
In This Guide
This guide shows how to use the InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G
oscilloscopes.
When unpacking and using the
oscilloscope for the first time, see:
When displaying waveforms and
acquired data, see:
When setting up triggers or changing
how data is acquired, see:
Making measurements and analyzing
data:
• Chapter 1, “Getting Started,” starting on page 21
• Chapter 2, “Horizontal Controls,” starting on page 37
• Chapter 3, “Vertical Controls,” starting on page 47
• Chapter 4, “Analog Bus Display,” starting on page 55
• Chapter 5, “FFT Spectral Analysis,” starting on page 57
• Chapter 6, “Math Waveforms,” starting on page 65
• Chapter 7, “Reference Waveforms,” starting on page
77
• Chapter 8, “Serial Bus Decode/Trigger,” starting on
page 81
• Chapter 9, “Display Settings,” starting on page 83
• Chapter 10, “Labels,” starting on page 91
• Chapter 11, “Triggers,” starting on page 97
• Chapter 12, “Trigger Mode/Coupling,” starting on
page 121
• Chapter 13, “Acquisition Control,” starting on page
129
• Chapter 14, “Cursors,” starting on page 145
• Chapter 15, “Measurements,” starting on page 155
• Chapter 16, “Mask Testing,” starting on page 179
• Chapter 17, “Digital Voltmeter,” starting on page 193
• Chapter 18, “Frequency Response Analysis,” starting
on page 197
When using the built-in waveform
generator, see:
When saving, recalling, or printing,
see:
• Chapter 19, “Waveform Generator,” starting on page
203
• Chapter 20, “Save/Recall (Setups, Screens, Data),”
starting on page 215
• Chapter 21, “Print (Screens),” starting on page 227
6 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 7
When using the oscilloscope's utility
NOTE
functions, see:
For reference information, see: • Chapter 24, “Reference,” starting on page 261
• Chapter 22, “Utility Settings,” starting on page 231
• Chapter 23, “Web Interface,” starting on page 249
When using serial bus triggering and
decode features, see:
• Chapter 25, “CAN Triggering and Serial Decode,”
starting on page 275
• Chapter 26, “I2C Triggering and Serial Decode,”
starting on page 285
• Chapter 27, “LIN Triggering and Serial Decode,”
starting on page 293
• Chapter 28, “SPI Triggering and Serial Decode,”
starting on page 301
• Chapter 29, “UART/RS232 Triggering and Serial
Decode,” starting on page 313
Abbreviated instructions for pressing a series of keys and softkeys
Instructions for pressing a series of keys are written in an abbreviated manner. Instructions for
pressing [Key1], then pressing Softkey2, then pressing Softkey3 are abbreviated as follows:
Press [Key1]> Softkey2 > Softkey3.
The keys may be a front panel [Key] or a Softkey. Softkeys are the six keys located directly
below the oscilloscope display.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 7
Page 8

8 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 9

Contents
InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes—At a
Glance / 3
In This Guide / 6
1 Getting Started
Inspect the Package Contents / 21
Power-On the Oscilloscope / 22
Connect Probes to the Oscilloscope / 23
Maximum input voltage at analog inputs / 23
Do not float the oscilloscope chassis / 23
Input a Waveform / 23
Recall the Default Oscilloscope Setup / 24
Use Autoscale / 24
Compensate Passive Probes / 25
Learn the Front Panel Controls and Connectors / 26
Front Panel Overlays for Different Languages / 33
Learn the Rear Panel Connectors / 33
Learn the Oscilloscope Display / 34
Access the Built-In Quick Help / 36
Select the User Interface Language / 36
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 9
Page 10

2 Horizontal Controls
To adjust the horizontal (time/div) scale / 38
To adjust the horizontal delay (position) / 39
Panning and Zooming Single or Stopped Acquisitions / 40
To change the horizontal time mode (Normal, XY, or Roll) / 40
To display the zoomed time base / 44
To change the horizontal scale knob's coarse/fine adjustment
To position the time reference (left, center, right) / 46
3 Vertical Controls
To turn waveforms on or off (channel or math) / 49
To adjust the vertical scale / 49
To adjust the vertical position / 49
To specify channel coupling / 50
XY Time Mode / 41
setting / 45
To specify bandwidth limiting / 50
To change the vertical scale knob's coarse/fine adjustment
setting / 51
To invert a waveform / 51
Setting Analog Channel Probe Options / 51
To specify the channel units / 52
To specify the probe attenuation / 52
To specify the probe skew / 53
10 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 11

4 Analog Bus Display
5 FFT Spectral Analysis
FFT Measurement Hints / 60
FFT Units / 61
FFT DC Value / 61
FFT Aliasing / 62
FFT Spectral Leakage / 63
6Math Waveforms
To display math waveforms / 66
To perform a math function on an arithmetic operation / 67
To adjust the math waveform scale and offset / 67
Units for Math Waveforms / 67
Math Operators / 68
Add or Subtract / 68
Multiply or Divide / 69
Math Transforms / 70
FFT Magnitude, FFT Phase / 70
Math Filters / 74
Low Pass Filter / 74
7 Reference Waveforms
To save a waveform to a reference waveform location / 77
To display a reference waveform / 78
To scale and position reference waveforms / 79
To adjust reference waveform skew / 79
To display reference waveform information / 80
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 11
Page 12

To save/recall reference waveform files to/from a USB storage
device / 80
8 Serial Bus Decode/Trigger
9 Display Settings
To adjust waveform intensity / 83
To set or clear persistence / 85
To clear the display / 86
To select the grid type / 86
To adjust the grid intensity / 87
To add an annotation / 87
To freeze the display / 89
10 Labels
To turn the label display on or off / 91
To assign a predefined label to a channel / 92
To define a new label / 93
To load a list of labels from a text file you create / 94
To reset the label library to the factory default / 95
11 Triggers
Adjusting the Trigger Level / 99
Forcing a Trigger / 99
Edge Trigger / 99
Pulse Width Trigger / 102
Pattern Trigger / 104
Rise/Fall Time Trigger / 106
12 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 13

Setup and Hold Trigger / 107
Video Trigger / 108
To trigger on a specific line of video / 112
To trigger on all sync pulses / 113
To trigger on a specific field of the video signal / 114
To trigger on all fields of the video signal / 115
To trigger on odd or even fields / 116
Serial Trigger / 118
12 Trigger Mode/Coupling
To select the Auto or Normal trigger mode / 122
To select the trigger coupling / 124
To enable or disable trigger noise rejection / 125
To enable or disable trigger HF Reject / 125
To set the trigger holdoff / 126
External Trigger Input / 127
13 Acquisition Control
Running, Stopping, and Making Single Acquisitions (Run
Control) / 129
Overview of Sampling / 130
Sampling Theory / 131
Aliasing / 131
Oscilloscope Bandwidth and Sample Rate / 131
Oscilloscope Rise Time / 133
Oscilloscope Bandwidth Required / 134
Memory Depth and Sample Rate / 134
Selecting the Acquisition Mode / 135
Normal Acquisition Mode / 136
Peak Detect Acquisition Mode / 136
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 13
Page 14

14 Cursors
15 Measurements
Averaging Acquisition Mode / 138
High Resolution Acquisition Mode / 140
Acquiring to Segmented Memory / 141
Navigating Segments / 142
Infinite Persistence with Segmented Memory / 142
Segmented Memory Re-Arm Time / 142
Saving Data from Segmented Memory / 143
To make cursor measurements / 146
Cursor Examples / 150
To make automatic measurements / 156
Measurements Summary / 157
Snapshot All / 159
Voltage Measurements / 160
Peak-Peak / 160
Maximum / 160
Minimum / 161
Amplitude / 161
Top / 161
Base / 162
Overshoot / 162
Preshoot / 163
Average / 164
DC RMS / 164
AC RMS / 165
Time Measurements / 167
Period / 167
Frequency / 168
14 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 15

Counter / 169
+ Width / 169
– Width / 169
Bit Rate / 169
Duty Cycle / 170
Rise Time / 170
Fall Time / 170
Delay / 170
Phase / 171
X at Min Y / 173
X at Max Y / 173
Count Measurements / 174
Positive Pulse Count / 174
Negative Pulse Count / 174
Rising Edge Count / 175
Falling Edges Count / 175
Measurement Thresholds / 175
Measurement Window with Zoom Display / 177
16 Mask Testing
To create a mask from a "golden" waveform (Automask) / 179
Mask Test Setup Options / 182
Mask Statistics / 184
To manually modify a mask file / 185
Building a Mask File / 188
How is mask testing done? / 191
17 Digital Voltmeter
18 Frequency Response Analysis
To make connections / 197
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 15
Page 16

To set up and run the analysis / 198
To view and save the analysis results / 200
19 Waveform Generator
To select generated waveform types and settings / 203
To specify the expected output load / 206
To use waveform generator logic presets / 207
To add noise to the waveform generator output / 207
To add modulation to the waveform generator output / 208
To set up Amplitude Modulation (AM) / 209
To set up Frequency Modulation (FM) / 210
To set up Frequency-Shift Keying Modulation (FSK) / 212
To restore waveform generator defaults / 213
20 Save/Recall (Setups, Screens, Data)
Saving Setups, Screen Images, or Data / 215
To save setup files / 217
To save BMP or PNG image files / 217
To save CSV, ASCII XY, or BIN data files / 218
Length Control / 219
To save Lister data files / 220
To save reference waveform files to a USB storage device / 220
To save masks / 221
To navigate storage locations / 221
To enter file names / 222
Recalling Setups, Masks, or Reference Waveforms / 222
To recall setup files / 223
To recall mask files / 223
To recall reference waveform files from a USB storage
device / 224
16 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 17

21 Print (Screens)
22 Utility Settings
Recalling Default Setups / 224
Performing a Secure Erase / 224
To print the oscilloscope's display / 227
To set up network printer connections / 229
To specify the print options / 230
To specify the palette option / 230
I/O Interface Settings / 231
Setting up the Oscilloscope's LAN Connection / 232
To establish a LAN connection / 233
Stand-alone (Point-to-Point) Connection to a PC / 234
File Explorer / 234
Setting Oscilloscope Preferences / 236
To choose "expand about" center or ground / 237
To disable/enable transparent backgrounds / 237
To load the default label library / 237
To set up the screen saver / 237
To set Autoscale preferences / 239
Setting the Oscilloscope's Clock / 240
Setting the Gen Out Source / 240
Enabling Remote Command Logging / 241
Performing Service Tasks / 243
To perform user calibration / 243
To perform hardware self test / 244
To perform front panel self test / 244
To export crash log files / 244
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 17
Page 18

23 Web Interface
To display oscilloscope information / 245
To display the user calibration status / 245
To clean the oscilloscope / 245
To check warranty and extended services status / 245
To contact Keysight / 246
To return the instrument / 246
Configuring the [Quick Action] Key / 246
Accessing the Web Interface / 250
Control Instrument / 251
Remote Front Panel / 252
Remote Programming via the Web Interface / 252
Remote Programming with Keysight IO Libraries / 254
Get Image / 254
Save/Recall / 255
Saving Files via the Web Interface / 255
Recalling Files via the Web Interface / 256
Identification Function / 257
Instrument Utilities / 258
Setting a Password / 259
24 Reference
Specifications and Characteristics / 261
Measurement Category / 261
Oscilloscope Measurement Category / 261
Measurement Category Definitions / 262
Maximum Input Voltages / 262
Maximum input voltage at analog inputs / 262
18 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 19

Environmental Conditions / 263
Declaration of Conformity / 263
Probes and Accessories / 263
Software and Firmware Updates / 264
Binary Data (.bin) Format / 264
Binary Data in MATLAB / 265
Binary Header Format / 265
Example Program for Reading Binary Data / 268
Examples of Binary Files / 268
CSV and ASCII XY files / 271
CSV and ASCII XY file structure / 272
Minimum and Maximum Values in CSV Files / 272
Acknowledgements / 273
Product Markings and Regulatory Information / 273
25 CAN Triggering and Serial Decode
Setup for CAN Signals / 275
CAN Triggering / 277
CAN Serial Decode / 279
Interpreting CAN Decode / 280
CAN Totalizer / 281
Interpreting CAN Lister Data / 282
26 I2C Triggering and Serial Decode
Setup for I2C Signals / 285
I2C Triggering / 286
I2C Serial Decode / 290
Interpreting I2C Decode / 291
Interpreting I2C Lister Data / 292
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 19
Page 20

27 LIN Triggering and Serial Decode
Setup for LIN Signals / 293
LIN Triggering / 295
LIN Serial Decode / 297
Interpreting LIN Decode / 299
Interpreting LIN Lister Data / 300
28 SPI Triggering and Serial Decode
Setup for SPI Signals / 301
SPI Triggering / 307
SPI Serial Decode / 309
Interpreting SPI Decode / 311
Interpreting SPI Lister Data / 312
29 UART/RS232 Triggering and Serial Decode
Setup for UART/RS232 Signals / 313
UART/RS232 Triggering / 315
UART/RS232 Serial Decode / 318
Interpreting UART/RS232 Decode / 320
UART/RS232 Totalizer / 321
Interpreting UART/RS232 Lister Data / 322
Index
20 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 21

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
1 Getting Started
Inspect the Package Contents / 21
Power-On the Oscilloscope / 22
Connect Probes to the Oscilloscope / 23
Input a Waveform / 23
Recall the Default Oscilloscope Setup / 24
Use Autoscale / 24
Compensate Passive Probes / 25
Learn the Front Panel Controls and Connectors / 26
Learn the Rear Panel Connectors / 33
Learn the Oscilloscope Display / 34
Access the Built-In Quick Help / 36
Select the User Interface Language / 36
This chapter describes the steps you take when using the oscilloscope for the first
time.
Inspect the Package Contents
• Inspect the shipping container for damage.
If your shipping container appears to be damaged, keep the shipping container
or cushioning material until you have inspected the contents of the shipment
for completeness and have checked the oscilloscope mechanically and
electrically.
• Verify that you received the following items and any optional accessories you
may have ordered:
21
Page 22

1 Getting Started
WARNING
• InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series or EDUX1052A/G oscilloscope.
• Power cord (country of origin determines specific type).
• Oscilloscope probes (one for each analog input channel).
Power-On the Oscilloscope
Requirements
Requirements
To po wer-on the
oscilloscope
Power
Ventilation
Line voltage, frequency, and power:
• ~Line 100-120 Vac, 50/60/400 Hz
• 100-240 Vac, 50/60 Hz
•50W max
The air intake and exhaust areas must be free from obstructions. Unrestricted air
flow is required for proper cooling. Always ensure that the air intake and exhaust
areas are free from obstructions.
The fan draws air in from the left side and bottom of the oscilloscope and pushes it
out behind the oscilloscope.
When using the oscilloscope in a bench-top setting, provide at least 2" clearance
at the sides and 4" (100 mm) clearance above and behind the oscilloscope for
proper cooling.
1 Connect the power cord to the rear of the oscilloscope, then to a suitable AC
voltage source. Route the power cord so the oscilloscope's feet and legs do not
pinch the cord.
2 The oscilloscope automatically adjusts for input line voltages in the range 100
to 240 VAC. The provided line cord is matched to the country of origin.
Always use a grounded power cord. Do not defeat the power cord ground.
22 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
3 Press the power switch.
The power switch is located on the lower left corner of the front panel. The
oscilloscope will perform a self-test and will be operational in a few seconds.
Page 23
Connect Probes to the Oscilloscope
CAUTION
CAUTION
WARNING
1 Connect the oscilloscope probe to an oscilloscope input channel BNC
connector.
2 Connect the probe's retractable hook tip to the point of interest on the circuit or
device under test. Be sure to connect the probe ground lead to a ground point
on the circuit.
Maximum input voltage at analog inputs
150 Vrms, 200 Vpk
Do not float the oscilloscope chassis
Defeating the ground connection and "floating" the oscilloscope chassis will probably
result in inaccurate measurements and may also cause equipment damage. The probe
ground lead is connected to the oscilloscope chassis and the ground wire in the power
cord. If you need to measure between two live points, use a differential probe with
sufficient dynamic range.
Getting Started 1
Input a Waveform
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 23
Do not negate the protective action of the ground connection to the oscilloscope. The
oscilloscope must remain grounded through its power cord. Defeating the ground
creates an electric shock hazard.
The Probe Comp signal is used for compensating probes.
1 Connect an oscilloscope probe from channel 1 to the Demo, Probe Comp terminal
on the front panel.
2 Connect the probe's ground lead to the ground terminal (next to the Demo
terminal).
Page 24

1 Getting Started
WARNING
A voltage source should never be connected to the ground terminal of this instrument.
If, for any reason, the Protective Conductor Terminal is disconnected or not functioning
properly and a voltage source is connected to the equipment's ground terminals, the
entire chassis will be at the voltage potential of the voltage source, and the operator or
bystanders could receive an electric shock.
Recall the Default Oscilloscope Setup
To recall the default oscilloscope setup:
1 Press [Default Setup].
The default setup restores the oscilloscope's default settings. This places the
oscilloscope in a known operating condition.
In the Save/Recall menu, there are also options for restoring the complete factory
settings or performing a secure erase (see Chapter 20, “Save/Recall (Setups,
Screens, Data),” starting on page 215).
Use Autoscale
Use [Auto Scale] to automatically configure the oscilloscope to best display the
input signals.
1 Press [Auto Scale].
You should see a waveform on the oscilloscope's display similar to this:
24 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 25
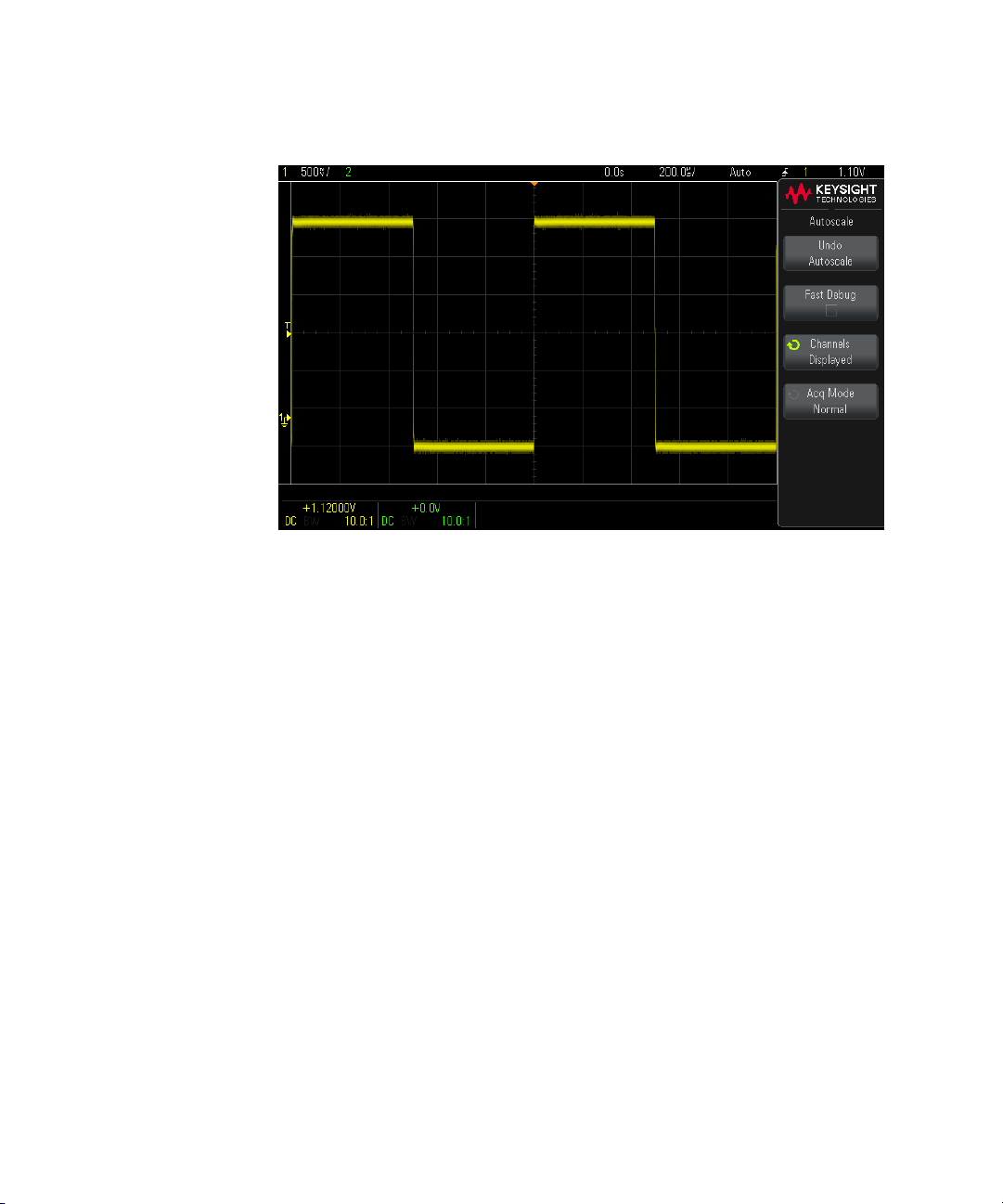
Getting Started 1
2 If you want to return to the oscilloscope settings that existed before, press Undo
Autoscale.
3 If you want to enable "fast debug" autoscaling, change the channels
autoscaled, or preserve the acquisition mode during autoscale, press Fast
Debug, Channels, or Acq Mode.
These are the same softkeys that appear in the Autoscale Preferences menu.
See Chapter 22, “Utility Settings,” starting on page 231.
If you see the waveform, but the square wave is not shaped correctly as shown
above, perform the procedure "Compensate Passive Probes" on page 25.
If you do not see the waveform, make sure the probe is connected securely to the
front panel channel input BNC and to the Demo/Probe Comp terminal.
Compensate Passive Probes
Each oscilloscope passive probe must be compensated to match the input
characteristics of the oscilloscope channel to which it is connected. A poorly
compensated probe can introduce significant measurement errors.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 25
Page 26

1 Getting Started
NOTE
Perfectly compensated
Over compensated
Under compensated
If your probe has a configurable attenuation setting (like the N2140/42A probes do), the 10:1
setting must be used for probe compensation.
1 Input the Probe Comp signal (see "Input a Waveform" on page 23).
2 Press [Default Setup] to recall the default oscilloscope setup (see "Recall the
Default Oscilloscope Setup" on page 24).
3 Press [Auto Scale] to automatically configure the oscilloscope for the Probe
Comp signal (see "Use Autoscale" on page 24).
4 Press the channel key to which the probe is connected ([1], [2], etc.).
5 In the Channel menu, press Probe.
6 In the Channel Probe menu, press Probe Check; then, follow the instructions
on-screen.
If necessary, use a nonmetallic tool (supplied with the probe) to adjust the
trimmer capacitor on the probe for the flattest pulse possible.
On some probes (like the N2140/42A probes), the trimmer capacitor is located
on the probe BNC connector. On other probes (like the N2862/63/90 probes),
the trimmer capacitor is a yellow adjustment on the probe tip.
Learn the Front Panel Controls and Connectors
26 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
7 Connect probes to all other oscilloscope channels.
8 Repeat the procedure for each channel.
On the front panel, key refers to any key (button) you can press.
Page 27

Getting Started 1
6. [Auto Scale] key5. [Default Setup] key
10. Tools keys
1. Power
switch
2. Softkeys
3. [Intensity]
key
4. Entry knob
11. Trigger controls
12. Vertical controls
19. Demo/Probe Comp
and Ground
terminals
15. [Help] key20. USB
Host
port
13. [Wave Gen] key
8. Run Control keys
9. Measure controls
7. Horizontal and Acquisition controls
16. Math
function
controls
18. Waveform
generator
output
17. Analog
channel
inputs
14. [FFT] key
Softkey specifically refers to the six keys next to the display. Menus and softkey
labels appear on the display when other front panel keys are pressed. Softkey
functions change as you navigate through the oscilloscope's menus.
For the following figures, refer to the numbered descriptions in the table that
follows.
Figure 3 InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series 4-Channel Oscilloscopes
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 27
Page 28
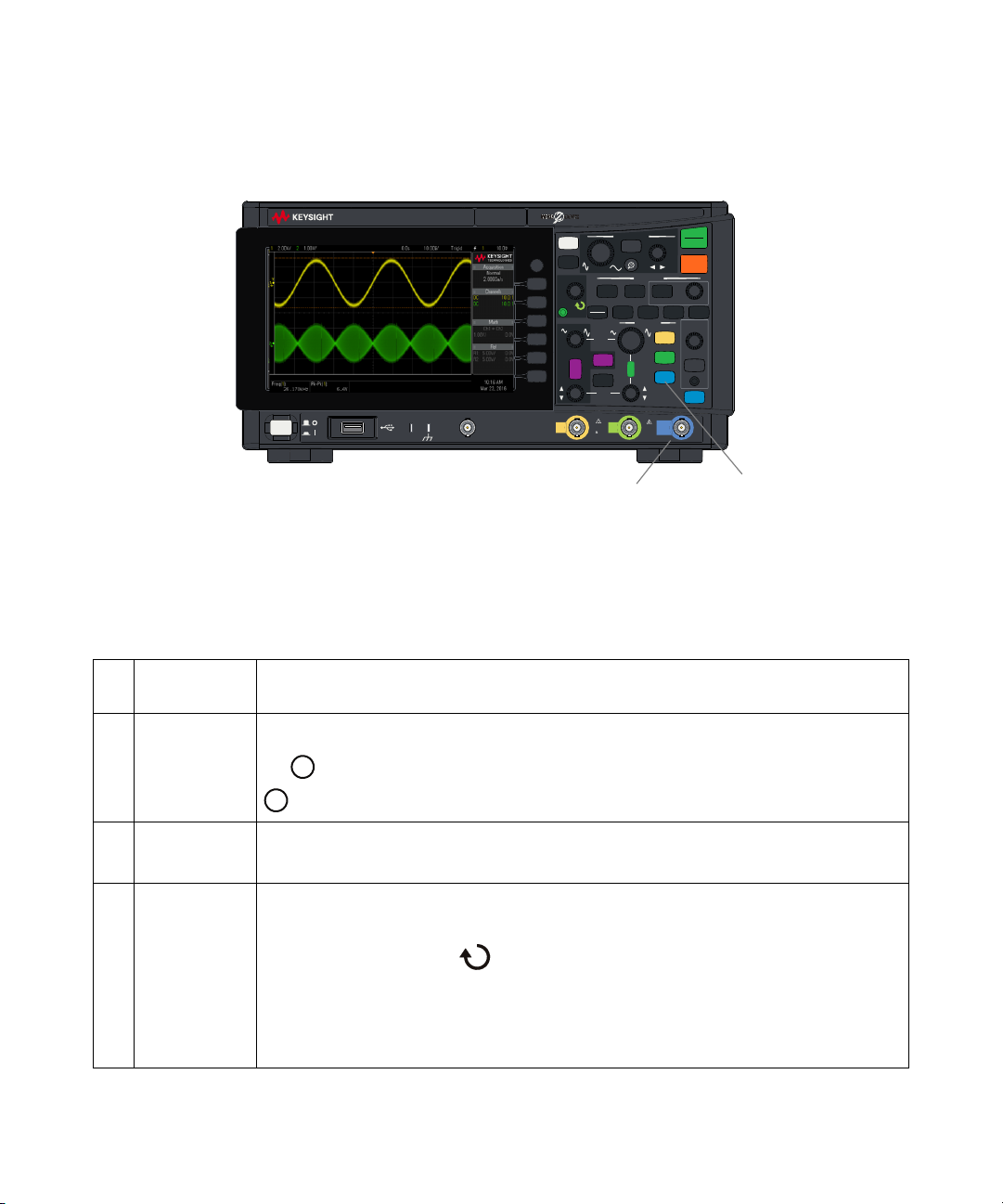
1 Getting Started
Mixed Signal Oscilloscope
MSOX1204G
Digital Storage Oscilloscope
DSOX1202G
200 MHz 2 GSa/s70 MHz 2 GSa/s
InfiniiVision
Push
Fine
Push
Zero
Push to
Select
Force
Entry
Horizontal
Leve-l
Measure
Vert ic al
Intensity
Push
for Fine
Push
to Zero
Trigger
Push for 50%
Push to Select
Trig g e r
FFT
External
Math
Default
Setup
Run
Stop
Single
Wave
Gen
Acquire
2
1
CursorsMeas
Utility
Analyze
Display
Save
to USB
Help
Save
Recall
Auto
Scale
Back
Quick
Action
Demo
Probe
Comp
Ext
Tri g
Gen
Out
Inputs
CH1 and CH2
150V RMS
Input
Ext Trig
30V RMS
~
1M
~
16pF
Demo
Probe
Comp
1
2
22. Ext Trig
external trigger
input
21. [External] key
Back
Back
Figure 4 InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series 2-Channel Oscilloscopes
1. Power switch Press once to switch power on; press again to switch power off. See "Power-On the
Oscilloscope" on page 22.
2. Softkeys The functions of these keys change based upon the menus shown on the display next to the keys.
The Back key moves back in the softkey menu hierarchy. At the top of the hierarchy, the
Back key turns the menus off, and oscilloscope information is shown instead.
3. [Intensity] key Press the key to illuminate it. When illuminated, turn the Entry knob to adjust waveform intensity.
You can vary the intensity control to bring out signal detail, much like an analog oscilloscope.
4. Entry knob The Entry knob is used to select items from menus and to change values. The function of the Entry
knob changes based upon the current menu and softkey selections.
Note that when the Entry knob symbol appears on a softkey, you can use the Entry knob, to
select values.
Often, rotating the Entry knob is enough to make a selection. Sometimes, you can push the Entry
knob to enable or disable a selection. Also, pushing the Entry knob can also make popup menus
disappear.
28 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 29
Getting Started 1
5. [Default Setup]
key
6. [Auto Scale]
key
7. Horizontal and
Acquisition
controls
Press this key to restore the oscilloscope's default settings (details on "Recall the Default
Oscilloscope Setup" on page 24).
When you press the [Auto Scale] key, the oscilloscope will quickly determine which channels have
activity, and it will turn these channels on and scale them to display the input signals. See "Use
Autoscale" on page 24.
The Horizontal and Acquisition controls consist of:
• Horizontal scale knob — Turn the knob in the Horizontal section that is marked to
adjust the time/div setting. The symbols under the knob indicate that this control has the effect
of spreading out or zooming in on the waveform using the horizontal scale.
Push the horizontal scale knob to toggle between fine and coarse adjustment.
• Horizontal position knob — Turn the knob marked to pan through the waveform data
horizontally. You can see the captured waveform before the trigger (turn the knob clockwise) or
after the trigger (turn the knob counterclockwise). If you pan through the waveform when the
oscilloscope is stopped (not in Run mode) then you are looking at the waveform data from the last
acquisition taken.
•[Acquire] key — Press this key to open the Acquire menu where you can select the Normal, XY, and
Roll time modes, enable or disable Zoom, and select the trigger time reference point.
Also you can select the Normal, Peak Detect, Averaging, or High Resolution acquisition modes
and, on DSOX1200-Series models, use segmented memory (see "Selecting the Acquisition
Mode" on page 135).
• Zoom key — Press the zoom key to split the oscilloscope display into Normal and Zoom
sections without opening the Acquire menu.
For more information see Chapter 2, “Horizontal Controls,” starting on page 37.
8. Run Control
keys
When the [Run/Stop] key is green, the oscilloscope is running, that is, acquiring data when trigger
conditions are met. To stop acquiring data, press [Run/Stop].
When the [Run/Stop] key is red, data acquisition is stopped. To start acquiring data, press
[Run/Stop].
To capture and display a single acquisition (whether the oscilloscope is running or stopped), press
[Single]. The [Single] key is yellow until the oscilloscope triggers.
For more information, see "Running, Stopping, and Making Single Acquisitions (Run
Control)" on page 129.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 29
Page 30
1 Getting Started
9. Measure
controls
The measure controls consist of:
•[Analyze] key — Press this key to access analysis features like:
• Trigger level setting.
• Measurement threshold setting.
• Video trigger automatic set up and display.
• Display a bus made up of the analog channel inputs where channel 1 is the least significant bit
and channel 4 is the most significant bit. See also Chapter 4, “Analog Bus Display,” starting
on page 55.
• Enable serial bus decodes. See also Chapter 8, “Serial Bus Decode/Trigger,” starting on page
81.
• Reference waveforms (see Chapter 7, “Reference Waveforms,” starting on page 77).
• Mask testing (see Chapter 16, “Mask Testing,” starting on page 179).
• Digital voltmeter (see Chapter 17, “Digital Voltmeter,” starting on page 193).
• Frequency response analysis on models with a built-in waveform generator (see Chapter 18,
“Frequency Response Analysis,” starting on page 197).
•[Meas] key — Press this key to access a set of predefined measurements. See Chapter 15,
“Measurements,” starting on page 155.
•[Cursors] key — Press this key to open a menu that lets you select the cursors mode and source.
• Cursors knob — Push this knob select cursors from a popup menu. Then, after the popup menu
closes (either by timeout or by pushing the knob again), rotate the knob to adjust the selected
cursor position.
10. Tools keys The Tools keys consist of:
•[Save/Recall] key — Press this key to save oscilloscope setups, screen images, waveform data, or
mask files or to recall setups, mask files or reference waveforms. See Chapter 20, “Save/Recall
(Setups, Screens, Data),” starting on page 215.
• [Utility] key — Press this key to access the Utility menu, which lets you configure the
oscilloscope's I/O settings, use the file explorer, set preferences, access the service menu, and
choose other options. See Chapter 22, “Utility Settings,” starting on page 231.
• [Display] key — Press this key to access the menu where you can enable persistence, adjust the
display grid (graticule) intensity, label waveforms, add an annotation, and clear the display (see
Chapter 9, “Display Settings,” starting on page 83).
• [Quick Action] key — Press this key to perform the selected quick action: measure all snapshot,
print, save, recall, freeze display. and more. See "Configuring the [Quick Action] Key" on
page 246.
•[Save to USB] key — Press this key to perform a quick save to a USB storage device.
30 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 31

Getting Started 1
T
11. Trigger controls The Trigger controls determine how the oscilloscope triggers to capture data. These controls consist
of:
• Level knob — Turn the Level knob to adjust the trigger level for a selected analog channel.
Push the knob to set the level to the waveform's 50% value. If AC coupling is used, pushing the
Level knob sets the trigger level to about 0 V.
The position of the trigger level for the analog channel is indicated by the trigger level icon (if
the analog channel is on) at the far left side of the display. The value of the analog channel trigger
level is displayed in the upper-right corner of the display.
• [Trigger] key — Press this key to select the trigger type (edge, pulse width, video, etc.). See
Chapter 11, “Triggers,” starting on page 97. You can also set options that affect all trigger types.
See Chapter 12, “Trigger Mode/Coupling,” starting on page 121.
•[Force] key — Causes a trigger (on anything) and displays the acquisition.
This key is useful in the Normal trigger mode where acquisitions are made only when the trigger
condition is met. In this mode, if no triggers are occurring (that is, the "Trig'd?" indicator is
displayed), you can press [Force] to force a trigger and see what the input signals look like.
12. Vertical
controls
13. [Wave Gen] key On G-suffix models that have a built-in waveform generator, press this key to access waveform
14. [FFT] key Provides access to FFT spectrum analysis function. See Chapter 5, “FFT Spectral Analysis,” starting
The Vertical controls consist of:
• Analog channel on/off keys — Use these keys to switch a channel on or off, or to access a
channel's menu in the softkeys. There is one channel on/off key for each analog channel.
• Vertical scale knob — Use the knob marked to change the vertical sensitivity (gain) for
the selected analog input channel.
Push the vertical scale knob to toggle between fine and coarse adjustment.
The default mode for expanding the signal is about the ground level of the channel; however, you
can change this to expand about the center of the display.
• Vertical position knob — Use this knob to change the selected analog input channel waveform
vertical position on the display.
The voltage value momentarily displayed in the upper right portion of the display represents the
voltage difference between the vertical center of the display and the ground level ( ) icon. It
also represents the voltage at the vertical center of the display if vertical expansion is set to
expand about ground.
For more information, see Chapter 3, “Vertical Controls,” starting on page 47.
generator functions. See Chapter 19, “Waveform Generator,” starting on page 203.
on page 57.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 31
Page 32

1 Getting Started
15. [Help] key Opens the Help menu where you can display overview help topics, select the Language (see also
"Access the Built-In Quick Help" on page 36), and select training signals that can be output on
the Demo terminal.
16. Math function
controls
17. Analog channel
inputs
18. Waveform
generator
output
19. Demo/Probe
Comp, Ground
terminals
The Math function controls consist of:
•[Math] key — provides access to math (add, subtract, etc.) waveform functions. See Chapter 6,
“Math Waveforms,” starting on page 65.
• Vertical scale knob — Use the knob marked to change the vertical sensitivity (as with
the analog channel vertical controls).
• Vertical position knob — Use the knob to change a math function waveform's vertical position on
the display (as with the analog channel vertical controls).
Attach oscilloscope probes or BNC cables to these BNC connectors.
In the InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series oscilloscopes, the analog channel inputs have 1 MΩ impedance.
Also, there is no automatic probe detection, so you must properly set the probe attenuation for
accurate measurement results. See "Setting Analog Channel Probe Options" on page 51.
On G-suffix models, the built-in waveform generator can output sine, square, ramp, pulse, DC, or
noise on the Gen Out BNC. Press the [Wave Gen] key to set up the waveform generator. See
Chapter 19, “Waveform Generator,” starting on page 203.
You can also send the trigger output signal or the mask test failure signal to the Gen Out BNC
connector. See "Setting the Gen Out Source" on page 240.
• Demo terminal — This terminal outputs the Probe Comp signal which helps you match a probe's
input capacitance to the oscilloscope channel to which it is connected. See "Compensate
Passive Probes" on page 25. The oscilloscope can also output demo or training signals on this
terminal.
• Ground terminal — Use the ground terminal for oscilloscope probes connected to the Demo/Probe
Comp terminal. See the warning in "Input a Waveform" on page 23.
32 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 33

Getting Started 1
20. USB Host port This port is for connecting USB mass storage devices or printers to the oscilloscope.
Connect a USB compliant mass storage device (flash drive, disk drive, etc.) to save or recall
oscilloscope setup files and reference waveforms or to save data and screen images. See
Chapter 20, “Save/Recall (Setups, Screens, Data),” starting on page 215.
To print, connect a USB compliant printer. For more information about printing see Chapter 21,
“Print (Screens),” starting on page 227.
You can also use the USB port to update the oscilloscope's system software when updates are
available.
NOTE: You must Eject a USB mass storage device before unplugging it; otherwise, the device will be
marked as needing repair when connecting to a computer with the Windows operating system (even
though there are no harmful effects to the device).
CAUTION:Do not connect a host computer to the oscilloscope's USB host port. A host computer
sees the oscilloscope as a device, so connect the host computer to the oscilloscope's device port (on
the rear panel). See "Learn the Rear Panel Connectors" on page 33.
21. [External] key Press this key to set external trigger input options. See "External Trigger Input" on page 127.
22. Ext Trig input External trigger input BNC connector. See "External Trigger Input" on page 127 for an
explanation of this feature.
Front Panel Overlays for Different Languages
Front panel overlays, which have translations for the English front panel keys and
label text, are available in many languages. The appropriate overlay is included
when the localization option is chosen at time of purchase.
To install a front panel overlay:
1 Gently pull on the front panel knobs to remove them.
2 Insert the overlay's side tabs into the slots on the front panel.
3 Reinstall the front panel knobs.
Learn the Rear Panel Connectors
For the following figure, refer to the numbered descriptions in the table that
follows.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 33
Page 34

1 Getting Started
2. Kensington lock hole
3. USB Device port
4. LAN port
5. EXT TRIG input (on
4-channel oscilloscopes)
1. Power cord connector
1. Power cord
connector
2. Kensington lock
hole
3. USB Device
port
4. LAN port When the oscilloscope is connected to a network (see "Setting up the Oscilloscope's LAN
15. EXT TRIG input On 4-channel models, the external trigger input BNC connector is on the rear panel.
Attach the power cord here.
This is where you can attach a Kensington lock for securing the instrument.
This port is for connecting the oscilloscope to a host PC. You can issue remote commands from a
host PC to the oscilloscope via the USB device port (see the Programmer's Guide).
Connection" on page 232), the LAN port lets you print to network printers (see Chapter 21, “Print
(Screens),” starting on page 227), access the oscilloscope's built-in web server (see Chapter 23,
“Web Interface,” starting on page 249), and issue remote commands (see the Programmer's Guide).
On 2-channel models, the external trigger input BNC connector is on the front panel.
See "External Trigger Input" on page 127 for an explanation of this feature.
Learn the Oscilloscope Display
The oscilloscope display contains acquired waveforms, setup information,
measurement results, and the softkey definitions.
34 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 35

Getting Started 1
Analog channel
sensitivity
Status line
Analog
channels
and ground
levels
Trigger level
Trigger point,
time reference
Delay
time
Time/
div
Run/Stop
status
Trigger
type
Trigger
source
Measurements
Trigger level
Softkey labels
and information
area
Cursors defining
measurement
Other
waveforms
Figure 5 Interpreting the oscilloscope display
Status line The top line of the display contains vertical, horizontal, and trigger setup information.
Display area The display area contains the waveform acquisitions, channel identifiers, and analog trigger, and
ground level indicators. Each analog channel's information appears in a different color.
Signal detail is displayed using 256 levels of intensity.
For more information about display modes see Chapter 9, “Display Settings,” starting on page 83.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 35
Page 36

1 Getting Started
Back
Back
Softkey labels and
information area
Measurements area When measurements or cursors are turned on, this area contains automatic measurement and cursor
When most front panel keys are pressed, short menu names and softkey labels appear in this area.
The labels describe the softkey functions. Typically, softkeys let you set up additional parameters for
the selected mode or menu.
Pressing the Back key returns through the menu hierarchy until softkey labels are off and the
information area is displayed. The information area contains acquisition, analog channel, math
function, and reference waveform information.
You can also specify that softkey menus turn off automatically after a specified timeout period
([Utility] > Options > Menu Timeout).
Pressing the Back key when the information area is displayed returns to the most recent menu
displayed.
results.
When measurements are turned off, this area displays additional status information describing
channel offset and other configuration parameters.
Access the Built-In Quick Help
To view Quick Help:
1 Press and hold the key, softkey, or knob for which you would like to view help.
Quick Help remains on the screen until another key is pressed or a knob is turned.
Select the User Interface Language
To select the user interface and Quick Help language:
1 Press [Help], then press the Language softkey.
2 Turn the Entry knob until the desired language is selected.
36 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 37

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
2 Horizontal Controls
To adjust the horizontal (time/div) scale / 38
To adjust the horizontal delay (position) / 39
Panning and Zooming Single or Stopped Acquisitions / 40
To change the horizontal time mode (Normal, XY, or Roll) / 40
To display the zoomed time base / 44
To change the horizontal scale knob's coarse/fine adjustment setting / 45
To position the time reference (left, center, right) / 46
The horizontal controls include:
• The horizontal scale and position knobs.
•The [Acquire] key for accessing the Acquire menu.
• The zoom key for quickly enabling/disabling the split-screen zoom display.
The following figure shows the Acquire menu which appears after pressing the
[Acquire] key.
37
Page 38

2 Horizontal Controls
Trigger
point
Time
reference
Delay
time
Time/
div
Trigger
source
Trigger level
or threshold
XY or Roll
mode
Normal
time mode
Zoomed
time base
Time
reference
Figure 6 Acquire Menu
The Acquire menu lets you select the time mode (Normal, XY, or Roll), enable
Zoom, and specify the time reference.
To adjust the horizontal (time/div) scale
38 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
The current sample rate is displayed in the right side information area when
softkey menu labels are off.
1 Turn the large horizontal scale (sweep speed) knob marked to
change the horizontal time/div setting.
Notice how the time/div information in the status line changes.
The ∇ symbol at the top of the display indicates the time reference point.
Page 39

The horizontal scale knob works (in the Normal time mode) while acquisitions are
running or when they are stopped. When running, adjusting the horizontal scale
knob changes the sample rate. When stopped, adjusting the horizontal scale knob
lets you zoom into acquired data. See "Panning and Zooming Single or Stopped
Acquisitions" on page 40.
Note that the horizontal scale knob has a different purpose in the Zoom display.
See "To display the zoomed time base" on page 44.
To adjust the horizontal delay (position)
1 Turn the horizontal delay (position) knob ( ).
The trigger point moves horizontally, pausing at 0.00 s (mimicking a
mechanical detent), and the delay value is displayed in the status line.
Changing the delay time moves the trigger point (solid inverted triangle)
horizontally and indicates how far it is from the time reference point (hollow
inverted triangle ∇). These reference points are indicated along the top of the
display grid.
Figure 6 shows the trigger point with the delay time set to 200 µs. The delay time
number tells you how far the time reference point is located from the trigger point.
When delay time is set to zero, the delay time indicator overlays the time reference
indicator.
Horizontal Controls 2
All events displayed left of the trigger point happened before the trigger occurred.
These events are called pre-trigger information, and they show events that led up
to the trigger point.
Everything to the right of the trigger point is called post-trigger information. The
amount of delay range (pre-trigger and post-trigger information) available
depends on the time/div selected and memory depth.
The horizontal position knob works (in the Normal time mode) while acquisitions
are running or when they are stopped. When running, adjusting the horizontal
scale knob changes the sample rate. When stopped, adjusting the horizontal scale
knob lets you zoom into acquired data. See "Panning and Zooming Single or
Stopped Acquisitions" on page 40.
Note that the horizontal position knob has a different purpose in the Zoom display.
See "To display the zoomed time base" on page 44.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 39
Page 40

2 Horizontal Controls
NOTE
Panning and Zooming Single or Stopped Acquisitions
When the oscilloscope is stopped, use the horizontal scale and position knobs to
pan and zoom your waveform. The stopped display may contain several
acquisitions worth of information, but only the last acquisition is available for pan
and zoom.
The ability to pan (move horizontally) and scale (expand or compress horizontally)
an acquired waveform is important because of the additional insight it can reveal
about the captured waveform. This additional insight is often gained from seeing
the waveform at different levels of abstraction. You may want to view both the big
picture and the specific little picture details.
The ability to examine waveform detail after the waveform has been acquired is a
benefit generally associated with digital oscilloscopes. Often this is simply the
ability to freeze the display for the purpose of measuring with cursors or printing
the screen. Some digital oscilloscopes go one step further by including the ability
to further examine the signal details after acquiring them by panning through the
waveform and changing the horizontal scale.
There is no limit imposed on the scaling ratio between the time/div used to
acquire the data and the time/div used to view the data. There is, however, a
useful limit. This useful limit is somewhat a function of the signal you are
analyzing.
Zooming into stopped acquisitions
The screen will still contain a relatively good display if you zoom-in horizontally by a factor of
1000 and zoom-in vertically by a factor of 10 to display the information from where it was
acquired. Remember that you can make automatic measurements on displayed data only.
To change the horizontal time mode (Normal, XY, or Roll)
1 Press [Acquire].
2 In the Acquire menu, press Time Mode; then, select:
• Normal — the normal viewing mode for the oscilloscope.
40 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 41

Horizontal Controls 2
In the Normal time mode, signal events occurring before the trigger are
plotted to the left of the trigger point (▼) and signal events after the trigger
plotted to the right of the trigger point.
• XY — XY mode changes the display from a volts-versus-time display to a
volts-versus-volts display. The time base is turned off. Channel 1 amplitude
is plotted on the X-axis and Channel 2 amplitude is plotted on the Y-axis.
You can use XY mode to compare frequency and phase relationships
between two signals. XY mode can also be used with transducers to display
strain versus displacement, flow versus pressure, volts versus current, or
voltage versus frequency.
Use the cursors to make measurements on XY mode waveforms.
For more information about using XY mode for measurements, refer to "XY
Time Mode" on page 41.
• Roll — causes the waveform to move slowly across the screen from right to
left. It only operates on time base settings of 50 ms/div and slower. If the
current time base setting is faster than the 50 ms/div limit, it will be set to
50 ms/div when Roll mode is entered.
In Roll mode there is no trigger. The fixed reference point on the screen is the
right edge of the screen and refers to the current moment in time. Events
that have occurred are scrolled to the left of the reference point. Since there
is no trigger, no pre-trigger information is available.
If you would like to pause the display in Roll mode press the [Single] key. To
clear the display and restart an acquisition in Roll mode, press the [Single]
key again.
Use Roll mode on low-frequency waveforms to yield a display much like a
strip chart recorder. It allows the waveform to roll across the display.
XY Time Mode
The XY time mode converts the oscilloscope from a volts-versus-time display to a
volts-versus-volts display using two input channels. Channel 1 is the X-axis input,
channel 2 is the Y-axis input. You can use various transducers so the display could
show strain versus displacement, flow versus pressure, volts versus current, or
voltage versus frequency.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 41
Page 42

2 Horizontal Controls
sinθ =Aor
C
A
B
D
C
Signal must
be cent ered i n
“X”
Measuring
phase difference
Signals 90 degrees
out of phase
Signals
in phase
Example This exercise shows a common use of the XY display mode by measuring the
phase difference between two signals of the same frequency with the Lissajous
method.
1 Connect a sine wave signal to channel 1, and a sine wave signal of the same
frequency but out of phase to channel 2.
2 Press the [Auto Scale] key, press the [Acquire] key; then, press Time Mode and
select "XY".
3 Center the signal on the display with the channel 1 and 2 position ( ) knobs.
Use the channel 1 and 2 volts/div knobs and the channel 1 and 2 Fine softkeys
to expand the signal for convenient viewing.
The phase difference angle (θ) can be calculated using the following formula
(assuming the amplitude is the same on both channels):
Figure 7 XY time mode signals, centered on display
4 Press the [Cursors] key.
42 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
5 Set the Y2 cursor to the top of the signal, and set Y1 to the bottom of the
signal.
Note the ΔY value at the bottom of the display. In this example, we are using
the Y cursors, but you could have used the X cursors instead.
Page 43

Horizontal Controls 2
sinθ =
second Δ Y
first Δ Y
=
1.031
1.688
; θ = 37.65 degrees of phase shift
NOTE
6 Move the Y1 and Y2 cursors to the intersection of the signal and the Y axis.
Again, note the ΔY value.
Figure 8 Phase difference measurements, automatic and using cursors
7 Calculate the phase difference using the formula below.
For example, if the first ΔY value is 1.688 and the second ΔY value is 1.031:
Z-Axis Input in XY Display Mode (Blanking)
When you select the XY display mode, the time base is turned off. Channel 1 is the X-axis
input, channel 2 is the Y-axis input, and the EXT TRIG input is the Z-axis input. If you only want
to see portions of the Y versus X display, use the Z-axis input. Z-axis turns the trace on and off
(analog oscilloscopes called this Z-axis blanking because it turned the beam on and off).
When Z is low (<1.4 V), Y versus X is displayed; when Z is high (>1.4 V), the trace is turned off.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 43
Page 44

2 Horizontal Controls
These markers show the
beginning and end of the
Zoom window
Normal
window
Time/div
for zoomed
window
Time/div
for normal
window
Delay time
momentarily displays
when the Horizontal
position knob is turned
Zoom
window
Signal
anomaly
expanded
in zoom
window
Select
Zoom
To display the zoomed time base
Zoom, formerly called Delayed sweep mode, is a horizontally expanded version of
the normal display. When Zoom is selected, the display divides in half. The top
half of the display shows the normal time/div window and the bottom half
displays a faster Zoom time/div window.
The Zoom window is a magnified portion of the normal time/div window. You can
use Zoom to locate and horizontally expand part of the normal window for a more
detailed (higher-resolution) analysis of signals.
To turn on (or off) Zoom:
1 Press the zoom key (or press the [Acquire] key and then the Zoom softkey).
44 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 45

Horizontal Controls 2
The area of the normal display that is expanded is outlined with a box and the rest
of the normal display is ghosted. The box shows the portion of the normal sweep
that is expanded in the lower half.
To change the time/div for the Zoom window, turn the horizontal scale (sweep
speed) knob. As you turn the knob, the zoomed window time/div is highlighted in
the status line above the waveform display area. The Horizontal scale (sweep
speed) knob controls the size of the box.
The Horizontal position (delay time) knob sets the left-to-right position of the
zoom window. The delay value, which is the time displayed relative to the trigger
point) is momentarily displayed in the upper-right portion of the display when the
delay time ( ) knob is turned.
Negative delay values indicate you're looking at a portion of the waveform before
the trigger event, and positive values indicate you're looking at the waveform after
the trigger event.
To change the time/div of the normal window, turn off Zoom; then, turn the
horizontal scale (sweep speed) knob.
For information about using zoom mode for measurements, refer to "To isolate a
pulse for Top measurement" on page 161 and "To isolate an event for frequency
measurement" on page 168.
To change the horizontal scale knob's coarse/fine adjustment setting
1 Push the horizontal scale knob to toggle between fine and coarse adjustment
of the horizontal scale.
When Fine is enabled, turning the horizontal scale knob changes the time/div
(displayed in the status line at the top of the display) in smaller increments. The
time/div remains fully calibrated when Fine is on.
When Fine is turned off, the Horizontal scale knob changes the time/div setting in
a 1-2-5 step sequence.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 45
Page 46

2 Horizontal Controls
To position the time reference (left, center, right)
Time reference is the reference point on the display for delay time (horizontal
position).
1 Press [Acquire].
2 In the Acquire menu, press Time Ref; then, select:
• Left — the time reference is set to one major division from the left edge of the
display.
• Center — the time reference is set to the center of the display.
• Right — the time reference is set to one major division from the right edge of
the display.
A small hollow triangle (∇) at the top of the display grid marks the position of the
time reference. When delay time is set to zero, the trigger point indicator (▼)
overlays the time reference indicator.
The time reference position sets the initial position of the trigger event within
acquisition memory and on the display, with delay set to 0.
46 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Turning the Horizontal scale (sweep speed) knob expands or contracts the
waveform about the time reference point (∇). See "To adjust the horizontal
(time/div) scale" on page 38.
Turning the Horizontal position ( ) knob in Normal mode (not Zoom) moves the
trigger point indicator (▼) to the left or right of the time reference point (∇). See
"To adjust the horizontal delay (position)" on page 39.
Page 47

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
3 Vertical Controls
To turn waveforms on or off (channel or math) / 49
To adjust the vertical scale / 49
To adjust the vertical position / 49
To specify channel coupling / 50
To specify bandwidth limiting / 50
To change the vertical scale knob's coarse/fine adjustment setting / 51
To invert a waveform / 51
Setting Analog Channel Probe Options / 51
The vertical controls include:
• Multiplexed vertical scale and position knobs for the selected analog channel.
• The channel keys for turning a channel on or off and accessing the channel's
softkey menu.
47
Page 48

3 Vertical Controls
NOTE
NOTE
Channel,
Volts/div
Channel 1
ground
level
Trigger
source
Trigger level
or threshold
Channel 2
ground
level
Keysight recommends always scaling the signal so that the entire waveform is contained
between the top and bottom of the display.
For proper operation of the 1200 X-Series oscilloscope, the channel inputs must not be
overdriven more than ±8 divisions. Exceeding this limit may result in signals that appear
incorrect and may increase crosstalk between the input channels.
To minimize crosstalk between input channels, make sure the channel is not overdriven. Also,
connecting a probe or cable to a channel will reduce crosstalk.
The following figure shows the Channel 1 menu that appears after pressing the [1]
channel key.
The ground level of the signal for each displayed analog channel is identified by
the position of the icon at the far-left side of the display.
48 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 49

To turn waveforms on or off (channel or math)
NOTE
1 Press an analog channel key turn the channel on or off (and to display the
channel's menu).
When a channel is on, its key is illuminated.
Turning channels off
You must be viewing the menu for a channel before you can turn it off. For example, if channel
1 and channel 2 are turned on and the menu for channel 2 is being displayed, to turn channel
1 off, press [1] to display the channel 1 menu; then, press [1] again to turn channel 1 off.
To adjust the vertical scale
1 Turn the large knob above the channel key marked to set the vertical
scale (volts/division) for the channel.
The vertical scale knob changes the analog channel scale in a 1-2-5 step
sequence (with a 1:1 probe attached) unless fine adjustment is enabled (see "To
change the vertical scale knob's coarse/fine adjustment setting" on page 51).
Vertical Controls 3
The analog channel Volts/Div value is displayed in the status line.
The default mode for expanding the signal when you turn the volts/division knob
is vertical expansion about the ground level of the channel; however, you can
change this to expand about the center of the display. See "To choose "expand
about" center or ground" on page 237.
To adjust the vertical position
1 Turn the small vertical position knob ( ) to move the channel's waveform up or
down on the display.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 49
Page 50

3 Vertical Controls
TIP
The voltage value momentarily displayed in the upper right portion of the display
represents the voltage difference between the vertical center of the display and
the ground level ( ) icon. It also represents the voltage at the vertical center of
the display if vertical expansion is set to expand about ground (see "To choose
"expand about" center or ground" on page 237).
To specify channel coupling
Coupling changes the channel's input coupling to either AC (alternating current)
or DC (direct current).
If the channel is DC coupled, you can quickly measure the DC component of the signal by
simply noting its distance from the ground symbol.
If the channel is AC coupled, the DC component of the signal is removed, allowing you to use
greater sensitivity to display the AC component of the signal.
1 Press the desired channel key.
2 In the Channel menu, press the Coupling softkey to select the input channel
coupling:
• DC — DC coupling is useful for viewing waveforms as low as 0 Hz that do not
have large DC offsets.
• AC — AC coupling is useful for viewing waveforms with large DC offsets.
AC coupling places a 10 Hz high-pass filter in series with the input waveform
that removes any DC offset voltage from the waveform.
Note that Channel Coupling is independent of Trigger Coupling. To change trigger
coupling see "To select the trigger coupling" on page 124.
To specify bandwidth limiting
1 Press the desired channel key.
2 In the Channel menu, press the BW Limit softkey to enable or disable bandwidth
limiting.
50 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 51

Vertical Controls 3
When bandwidth limit is on, the maximum bandwidth for the channel is
approximately 20 MHz. For waveforms with frequencies below this, turning
bandwidth limit on removes unwanted high frequency noise from the waveform.
The bandwidth limit also limits the trigger signal path of any channel that has
BW Limit turned on.
To change the vertical scale knob's coarse/fine adjustment setting
1 Push the channel's vertical scale knob (or press the channel key and then the
Fine softkey in the Channel menu) to toggle between fine and coarse
adjustment of the vertical scale.
When Fine adjustment is selected, you can change the channel's vertical
sensitivity in smaller increments. The channel sensitivity remains fully calibrated
when Fine is on.
The vertical scale value is displayed in the status line at the top of the display.
When Fine is turned off, turning the volts/division knob changes the channel
sensitivity in a 1-2-5 step sequence.
To invert a waveform
1 Press the desired channel key.
2 In the Channel menu, press the Invert softkey to invert the selected channel.
When Invert is selected, the voltage values of the displayed waveform are inverted.
Invert affects how a channel is displayed. However, when using basic triggers, the
oscilloscope attempts to maintain the same trigger point by changing trigger
settings.
Inverting a channel also changes the result of any math function selected in the
waveform Math menu or any measurement.
Setting Analog Channel Probe Options
1 Press the probe's associated channel key.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 51
Page 52

3 Vertical Controls
2 In the Channel menu, press the Probe softkey to display the Channel Probe
menu.
The Channel Probe menu lets you select additional probe
parameters such as attenuation factor and units of
measurement for the connected probe.
The Probe Check softkey guides you through the process of
compensating passive probes (such as the N2140A, N2142A,
N2862A/B, N2863A/B, N2889A, N2890A, 10073C, 10074C,
or 1165A probes).
See Also • "To specify the channel units" on page 52
• "To specify the probe attenuation" on page 52
• "To specify the probe skew" on page 53
To specify the channel units
1 Press the probe's associated channel key.
2 In the Channel menu, press Probe.
3 In the Channel Probe menu, press Units; then, select:
• Volts — for a voltage probe.
• Amps — for a current probe.
Channel sensitivity, trigger level, measurement results, and math functions will
reflect the measurement units you have selected.
To specify the probe attenuation
The probe attenuation factor must be set properly for accurate measurement
results.
52 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 53

To set the probe attenuation factor:
1 Press the channel key.
2 Press the Probe softkey until you have selected how you want to specify the
attenuation factor, choosing either Ratio or Decibels.
3 Turn the Entry knob to set the attenuation factor for the connected probe.
When measuring voltage values, the attenuation factor can be set from 0.100:1 to
10000:1 in a 1-2-5 sequence.
When measuring current values with a current probe, the attenuation factor can
be set from 10.0 V/A to 0.0001 V/A.
When specifying the attenuation factor in decibels, you can select values from
-20 dB to 80 dB.
If Amps is chosen as the units and a manual attenuation factor is chosen, then the
units as well as the attenuation factor are displayed.
To specify the probe skew
Vertical Controls 3
When measuring time intervals in the nanoseconds (ns) range, small differences in
cable length can affect the measurement. Use Skew to remove cable-delay errors
between any two channels.
1 Probe the same point with both probes.
2 Press one of the probes associated channel key.
3 In the Channel menu, press Probe.
4 In the Channel Probe menu, press Skew; then, select the desired skew value.
Each analog channel can be adjusted ±100 ns for a total of 200 ns difference.
The skew setting is not affected by pressing [Default Setup] or [Auto Scale].
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 53
Page 54

3 Vertical Controls
54 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 55

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
4 Analog Bus Display
You can display a bus made up of the analog channel inputs and, on 2-channel
oscilloscope models, the external trigger input. Any of the input channels can be
assigned to the bus.
To display an analog bus:
1 Press the [Analyze] key.
2 Press Features; then, select Analog Bus.
3 Press Features again (or push the Entry knob) to enable the analog bus display.
4 To assign channels to the bus, press the Channel softkey, turn the Entry knob to
select the channel, and then press Channel again to include or exclude the
channel in the bus.
5 To specify the analog bus value number base, press Base and turn the Entry
knob to select Hex or Binary.
6 To specify the channel threshold voltage levels, which determines 0 and 1 bit
levels in the bus value, use the Source softkey and the Entry knob to select a
channel, then use the Threshold softkey and Entry knob to specify its threshold
voltage.
You can push the Entry knob to toggle between Source and Threshold softkey
selection.
55
Page 56

4 Analog Bus Display
The bus values display appears at the bottom of the graticule, above any serial
bus waveforms (if present). Channel 1 is the least significant bit and channel 4 is
the most significant bit.
56 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 57

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
5 FFT Spectral Analysis
FFT is used to compute the fast Fourier transform of analog input signals. FFT
takes the digitized time record of the specified source and transforms it to the
frequency domain. When the FFT function is selected, the FFT spectrum is plotted
on the oscilloscope display as magnitude in dBV versus frequency. The readout for
the horizontal axis changes from time to frequency (Hertz) and the vertical readout
changes from volts to dB.
Use the FFT function to find crosstalk problems, to find distortion problems in
analog waveforms caused by amplifier non-linearity, or for adjusting analog filters.
To display a FFT waveform:
1 Press the [FFT] key.
• Source 1 — selects the source for the FFT.
• Settings — displays the FFT Settings menu.
• Span — specifies the frequency range represented by the
width of the display. Divide span by 10 to calculate the
frequency scale per division.
• Center — specifies the frequency at the center vertical grid
line of the display.
57
Page 58

5 FFT Spectral Analysis
NOTE
2 Press the Settings softkey to display additional FFT settings.
• Source 1 — selects the source for the FFT.
• Window— selects a window to apply to your FFT input
signal:
• Hanning — window for making accurate frequency
measurements or for resolving two frequencies that are
close together.
• Flat Top — window for making accurate amplitude
measurements of frequency peaks.
• Rectangular — good frequency resolution and amplitude
accuracy, but use only where there will be no leakage
effects. Use on self-windowing waveforms such as
pseudo-random noise, impulses, sine bursts, and
decaying sinusoids.
• Blackman Harris — window reduces time resolution
compared to a rectangular window, but improves the
capacity to detect smaller impulses due to lower
secondary lobes.
• Vertical Units — lets you select Decibels or VRMS as the units for the FFT
vertical scale.
• Auto Setup — sets the frequency Span and Center to values that will cause
the entire available spectrum to be displayed. The maximum available
frequency is half the FFT sample rate, which is a function of the time per
division setting. The FFT resolution is the quotient of the sampling rate and
the number of FFT points (f
/N). The current FFT Resolution is displayed.
S
Scale and offset considerations
If you do not manually change the FFT scale or offset settings, when you turn the horizontal
scale knob, the span and center frequency settings will automatically change to allow
optimum viewing of the full spectrum.
If you do manually set scale or offset, turning the horizontal scale knob will not change the
span or center frequency settings, allowing you see better detail around a specific frequency.
Pressing the FFT Auto Setup softkey will automatically rescale the waveform and span and
center will again automatically track the horizontal scale setting.
58 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 59

FFT Spectral Analysis 5
3 To make cursor measurements, press the [Cursors] key and set the Source
softkey to Math N.
Use the X1 and X2 cursors to measure frequency values and difference between
two frequency values (ΔX). Use the Y1 and Y2 cursors to measure amplitude in
dB and difference in amplitude (ΔY).
4 To make other measurements, press the [Meas] key and set the Source softkey to
Math N.
You can make peak-to-peak, maximum, minimum, and average dB
measurements on the FFT waveform. You can also find the frequency value at
the first occurrence of the waveform maximum by using the X at Max Y
measurement.
To adjust the FFT waveform scale and offset, use the multiplexed scale and
position knobs next to the [Math] key to re-size and re-position the math
waveform.
The following FFT spectrum was obtained by connecting a 2.5 V, 100 kHz square
wave to channel 2. Set the horizontal scale to 50 µs/div, vertical sensitivity to
1 V/div, Units/div to 20 dBV, Offset to -40.0 dBV, Center frequency to 500 kHz,
frequency Span to 1 MHz, and window to Hanning.
See Also • "FFT Measurement Hints" on page 60
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 59
Page 60

5 FFT Spectral Analysis
NOTE
• "FFT Units" on page 61
• "FFT DC Value" on page 61
• "FFT Aliasing" on page 62
• "FFT Spectral Leakage" on page 63
• "Units for Math Waveforms" on page 67
FFT Measurement Hints
The number of points acquired for the FFT record can be up to 65,536, and when
frequency span is at maximum, all points are displayed. Once the FFT spectrum is
displayed, the frequency span and center frequency controls are used much like
the controls of a spectrum analyzer to examine the frequency of interest in greater
detail. Place the desired part of the waveform at the center of the screen and
decrease frequency span to increase the display resolution. As frequency span is
decreased, the number of points shown is reduced, and the display is magnified.
While the FFT spectrum is displayed, use the [Math] and [Cursors] keys to switch
between measurement functions and frequency domain controls in FFT menu.
FFT Resolution
The FFT resolution is the quotient of the sampling rate and the number of FFT points (fS/N).
With a fixed number of FFT points (up to 65,536), the lower the sampling rate, the better the
resolution.
Decreasing the effective sampling rate by selecting a greater time/div setting will
increase the low frequency resolution of the FFT display and also increase the
chance that an alias will be displayed. The resolution of the FFT is the effective
sample rate divided by the number of points in the FFT. The actual resolution of
the display will not be this fine as the shape of the window will be the actual
limiting factor in the FFTs ability to resolve two closely space frequencies. A good
way to test the ability of the FFT to resolve two closely spaced frequencies is to
examine the sidebands of an amplitude modulated sine wave.
For the best vertical accuracy on peak measurements:
• Make sure the probe attenuation is set correctly. The probe attenuation is set
from the Channel menu if the operand is a channel.
60 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 61

FFT Units
FFT Spectral Analysis 5
• Set the source sensitivity so that the input signal is near full screen, but not
clipped.
• Use the Flat Top window.
• Set the FFT sensitivity to a sensitive range, such as 2 dB/division.
For best frequency accuracy on peaks:
• Use the Hanning window.
• Use Cursors to place an X cursor on the frequency of interest.
• Adjust frequency span for better cursor placement.
• Return to the Cursors menu to fine tune the X cursor.
For more information on the use of FFTs, please refer to Keysight Application Note
243, The Fundamentals of Signal Analysis at
http://literature.cdn.keysight.com/litweb/pdf/5952-8898E.pdf. Additional
information can be obtained from Chapter 4 of the book Spectrum and Network
Measurements by Robert A. Witte.
0 dBV is the amplitude of a 1 Vrms sinusoid. When the FFT source is channel 1 or
channel 2 (or channel 3 or 4 on 4-channel models), FFT units will be displayed in
dBV when channel units is set to Volts and channel impedance is set to 1 MΩ.
FFT units will be displayed in dBm when channel units is set to Volts and channel
impedance is set to 50Ω.
FFT units will be displayed as dB for all other FFT sources or when a source
channel's units has been set to Amps.
FFT DC Value
The FFT computation produces a DC value that is incorrect. It does not take the
offset at center screen into account. The DC value is not corrected in order to
accurately represent frequency components near DC.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 61
Page 62

5 FFT Spectral Analysis
NOTE
FFT Aliasing
When using FFTs, it is important to be aware of frequency aliasing. This requires
that the operator have some knowledge as to what the frequency domain should
contain, and also consider the sampling rate, frequency span, and oscilloscope
vertical bandwidth when making FFT measurements. The FFT resolution (the
quotient of the sampling rate and the number of FFT points) is displayed
on-screen when the FFT menu is open.
Nyquist Frequency and Aliasing in the Frequency Domain
The Nyquist frequency is the highest frequency that any real-time digitizing oscilloscope can
acquire without aliasing. This frequency is half of the sample rate. Frequencies above the
Nyquist frequency will be under sampled, which causes aliasing. The Nyquist frequency is also
called the folding frequency because aliased frequency components fold back from that
frequency when viewing the frequency domain.
Aliasing happens when there are frequency components in the signal higher than
half the sample rate. Because the FFT spectrum is limited by this frequency, any
higher components are displayed at a lower (aliased) frequency.
The following figure illustrates aliasing. This is the spectrum of a 990 Hz square
wave, which has many harmonics. The horizontal time/div setting for the square
wave sets the sample rate and results in a FFT resolution of 1.91 Hz. The displayed
FFT spectrum waveform shows the components of the input signal above the
Nyquist frequency to be mirrored (aliased) on the display and reflected off the right
edge.
62 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 63

Figure 9 Aliasing
FFT Spectral Analysis 5
Because the frequency span goes from ≈ 0 to the Nyquist frequency, the best way
to prevent aliasing is to make sure that the frequency span is greater than the
frequencies of significant energy present in the input signal.
FFT Spectral Leakage
The FFT operation assumes that the time record repeats. Unless there is an
integral number of cycles of the sampled waveform in the record, a discontinuity is
created at the end of the record. This is referred to as leakage. In order to minimize
spectral leakage, windows that approach zero smoothly at the beginning and end
of the signal are employed as filters to the FFT. The FFT menu provides four
windows: Hanning, Flat Top, Rectangular, and Blackman-Harris. For more
information on leakage, see Keysight Application Note 243, The Fundamentals of
Signal Analysis at
http://literature.cdn.keysight.com/litweb/pdf/5952-8898E.pdf.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 63
Page 64

5 FFT Spectral Analysis
64 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 65

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
6 Math Waveforms
To display math waveforms / 66
To perform a math function on an arithmetic operation / 67
To adjust the math waveform scale and offset / 67
Units for Math Waveforms / 67
Math Operators / 68
Math Transforms / 70
Math Filters / 74
Math functions can be performed on analog channels. The resulting math
waveform is displayed in light purple.
You can use a math function on a channel even if you choose not to display the
channel on-screen.
You can:
• Perform an arithmetic operation (like add, subtract, or multiply) on analog input
channels.
• Perform a transform function (like FFT) on an analog input channel.
• Perform a transform function on the result of an arithmetic operation.
65
Page 66

6 Math Waveforms
TIP
To display math waveforms
1 Press the [Math] key on the front panel to display the waveform Math menu.
2 If f(t) is not already shown on the Function softkey, press the
Function sofkey and select f(t): Displayed.
3 Use the Operator softkey to select an operator or transform.
For more information on the operators, transforms, or filters,
see:
• "Math Operators" on page 68
• "Math Transforms" on page 70
• "Math Filters" on page 74
4 Use the Source 1 softkey to select the analog channel on
which to perform math. You can rotate the Entry knob or
repetitively press the Source 1 softkey to make your selection.
If you choose a transform function (FFT) the result is
displayed.
5 If you select an arithmetic operator, use the Source 2 softkey
to select the second source for the arithmetic operation. The
result is displayed.
6 To re-size and re-position the math waveform, see "To adjust the math
waveform scale and offset" on page 67.
Math Operating Hints
If the analog channel or math function is clipped (not fully displayed on screen) the resulting
displayed math function will also be clipped.
Once the function is displayed, the analog channel(s) may be turned off for better viewing of
the math waveform.
The vertical scaling and offset of each math function can be adjusted for ease of viewing and
measurement considerations.
The math function waveform can be measured using [Cursors] and/or [Meas].
66 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 67

To perform a math function on an arithmetic operation
NOTE
To perform an FFT or low-pass filter math function on an arithmetic operation
(add, subtract, or multiply):
1 Press the Function softkey and select g(t): Internal.
2 Use the Operator, Source 1, and Source 2 softkeys to set up an arithmetic
operation.
3 Press the Function softkey and select f(t): Displayed.
4 Use the Operator softkey to select an FFT or low-pass filter math function.
5 Press the Source 1 softkey and select g(t) as the source. Note that g(t) is only
available when you select an FFT or low-pass filter math function in the
previous step.
To adjust the math waveform scale and offset
Use the multiplexed scale and position knobs next to the [Math] key to re-size and
re-position the math waveform.
Math Waveforms 6
Math Scale and Offset are Set Automatically
Any time the currently displayed math function definition is changed, the function is
automatically scaled for optimum vertical scale and offset. If you manually set scale and offset
for a function, select a new function, then select the original function, the original function will
be automatically rescaled.
See Also • "Units for Math Waveforms" on page 67
Units for Math Waveforms
Units for each input channel can be set to Volts or Amps using the Units softkey in
the Channel Probe menu. Units for math function waveforms are:
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 67
Page 68

6 Math Waveforms
Math Operators
Math function Units
add or subtract V or A
multiply
FFT Magnitude dB (decibels) or V RMS.
FFT Phase degrees or radians
A scale unit of U (undefined) will be displayed for math functions when two source
channels are used and they are set to dissimilar units and the combination of units
cannot be resolved.
Math operators perform arithmetic operations (add, subtract, or multiply) on
analog input channels.
• "Add or Subtract" on page 68
• "Multiply or Divide" on page 69
2
, A2, or W (Volt-Amp)
V
Add or Subtract
When you select add or subtract, the Source 1 and Source 2 values are added or
subtracted point by point, and the result is displayed.
You can use subtract to make a differential measurement or to compare two
waveforms.
If your waveforms' DC offsets are larger than the dynamic range of the
oscilloscope's input channels you will need to use a differential probe instead.
68 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 69

Figure 10 Example of Subtract Channel 2 from Channel 1
Math Waveforms 6
See Also • "Units for Math Waveforms" on page 67
Multiply or Divide
When you select the multiply or divide math function, the Source 1 and Source 2
values are multiplied or divided point by point, and the result is displayed.
The divide by zero case places holes (that is, zero values) in the output waveform.
Multiply is useful for seeing power relationships when one of the channels is
proportional to the current.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 69
Page 70

6 Math Waveforms
Figure 11 Example of Multiply Channel 1 by Channel 2
See Also • "Units for Math Waveforms" on page 67
Math Transforms
Math transforms perform a transform function (FFT) on an analog input channel or
on the result of an arithmetic operation.
• "FFT Magnitude, FFT Phase" on page 70
FFT Magnitude, FFT Phase
Using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), the FFT (Magnitude) math function
displays the magnitudes of the frequency content that makes up the source
waveform, and the FFT (Phase) math function shows the phase relationships of the
frequency content. The FFT takes the digitized time record of the specified source
and transforms it to the frequency domain.
The source of the FFT math functions can be analog input channels or an
arithmetic operation g(t).
70 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 71

Math Waveforms 6
The horizontal axis of FFT math functions is frequency (Hertz). For the FFT
(Magnitude) math function, the vertical axis is in decibels or V RMS. For the FFT
(Phase) math function, the vertical axis is in degrees or radians.
Use the FFT (Magnitude) function to find crosstalk problems, to find distortion
problems in analog waveforms caused by amplifier non-linearity, or for adjusting
analog filters.
To display a FFT waveform:
1 Press the [Math] key, press the Function softkey and select f(t), press the Operator
softkey and select FFT (Magnitude) or FFT (Phase).
• More — displays the FFT settings menu.
• Auto Setup — sets the frequency Span and Center to values
that will cause the entire available spectrum to be
displayed. The maximum available frequency is half the
FFT sample rate, which is a function of the time per
division setting. The FFT resolution is the quotient of the
sampling rate and the number of FFT points (f
current FFT Resolution is displayed.
/N). The
S
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 71
Page 72

6 Math Waveforms
2 Press the More softkey to display the FFT settings.
• Source 1 — selects the source for the FFT. (See "To perform
a math function on an arithmetic operation" on
page 67 for information about using g(t) as the source.)
• Span — sets the overall width of the FFT spectrum that you
see on the display (left to right). Divide span by 10 to
calculate the number of Hertz per division. It is possible to
set Span above the maximum available frequency, in
which case the displayed spectrum will not take up the
whole screen. Press the Span softkey, then turn the Entry
knob to set the desired frequency span of the display.
• Center — sets the FFT spectrum frequency represented at
the center vertical grid line of the display. It is possible to
set the Center to values below half the span or above the
maximum available frequency, in which case the displayed
spectrum will not take up the whole screen. Press the
Center softkey, then turn the Entry knob to set the desired
center frequency of the display.
• Window— selects a window to apply to your FFT input signal:
• Hanning — window for making accurate frequency measurements or for
resolving two frequencies that are close together.
• Flat Top — window for making accurate amplitude measurements of
frequency peaks.
• Rectangular — good frequency resolution and amplitude accuracy, but use
only where there will be no leakage effects. Use on self-windowing
waveforms such as pseudo-random noise, impulses, sine bursts, and
decaying sinusoids.
• Blackman Harris — window reduces time resolution compared to a
rectangular window, but improves the capacity to detect smaller impulses
due to lower secondary lobes.
• Vertical Units — For FFT (Magnitude), you can select Decibels or VRMS. For
FFT (Phase), you can select Degrees or Radians.
Use the knobs for the [Math] key to adjust the FFT waveform vertical scale
and offset.
72 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 73

Math Waveforms 6
NOTE
Scale and offset considerations
If you do not manually change the FFT scale or offset settings, when you turn the horizontal
scale knob, the span and center frequency settings will automatically change to allow
optimum viewing of the full spectrum.
If you do manually set scale or offset, turning the horizontal scale knob will not change the
span or center frequency settings, allowing you see better detail around a specific frequency.
Pressing the FFT Auto Setup softkey will automatically rescale the waveform and span and
center will again automatically track the horizontal scale setting.
3 To make cursor measurements, press the [Cursors] key and set the Source
softkey to Math: f(t).
Use the X1 and X2 cursors to measure frequency values and difference between
two frequency values (ΔX). Use the Y1 and Y2 cursors to measure amplitude in
dB and difference in amplitude (ΔY).
4 To make other measurements, press the [Meas] key and set the Source softkey to
Math: f(t).
You can make peak-to-peak, maximum, minimum, and average dB
measurements on the FFT waveform. You can also find the frequency value at
the first occurrence of the waveform maximum by using the X at Max Y
measurement.
The following FFT spectrum was obtained by connecting a 4 V, 75 kHz square
wave to channel 1. Set the horizontal scale to 50 µs/div, vertical sensitivity to
1 V/div, Units/div to 20 dBV, Offset to -60.0 dBV, Center frequency to 250 kHz,
frequency Span to 500 kHz, and window to Hanning.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 73
Page 74

6 Math Waveforms
See Also • "To perform a math function on an arithmetic operation" on page 67
• "FFT Measurement Hints" on page 60
• "FFT Units" on page 61
• "FFT DC Value" on page 61
• "FFT Aliasing" on page 62
• "FFT Spectral Leakage" on page 63
• "Units for Math Waveforms" on page 67
Math Filters
You can use math filters to create a waveform that is the result of a low-pass filter
on an analog input channel or on the result of an arithmetic operation.
• "Low Pass Filter" on page 74
Low Pass Filter
The low-pass filter function applies the filter to the selected source waveform and
display the resut in the math waveform.
74 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 75

Math Waveforms 6
NOTE
The low-pass filter is a 4th order Bessel-Thompson filter.
Use the Bandwidth softkey to select the filter's -3 dB cutoff frequency.
The ratio of the input signal's Nyquist frequency and the selected -3 dB cutoff frequency
affects how many points are available in the output, and under some circumstances, there are
no points in the output waveform.
Figure 12 Example of Low Pass Filter
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 75
Page 76

6 Math Waveforms
76 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 77

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
7 Reference Waveforms
To save a waveform to a reference waveform location / 77
To display a reference waveform / 78
To scale and position reference waveforms / 79
To adjust reference waveform skew / 79
To display reference waveform information / 80
To save/recall reference waveform files to/from a USB storage device / 80
Analog channel or math waveforms can be saved to one of two reference
waveform locations in the oscilloscope. Then, a reference waveform can be
displayed and compared against other waveforms. One reference waveform can
be displayed at a time.
You can adjust the vertical scale and offset of reference waveforms. There is also a
skew adjustment for reference waveforms. Reference waveform scale, offset, and
skew information can optionally be included on the oscilloscope display.
Analog channel, math, or reference waveforms can be saved to a reference
waveform file on a USB storage device. You can recall a reference waveform file
from a USB storage device into one of the reference waveform locations.
To save a waveform to a reference waveform location
1 Press the [Analyze] key.
2 Press Features; then, select R1 or R2.
3 Press Features again (or push the Entry knob) to turn on the reference waveform.
4 Press Save/Clear.
77
Page 78

7 Reference Waveforms
NOTE
5 In the Save/Clear menu, press the Source softkey and turn the Entry knob to
6 Press the Save to R1/R2 softkey to save the waveform to the reference waveform
Reference waveforms are non-volatile — they remain after power cycling or performing a
default setup.
select the source waveform.
location.
To clear a
reference
waveform location
1 Press the [Analyze] key.
2 Press Features; then, select R1 or R2.
3 Press Features again (or push the Entry knob) to turn on the reference waveform.
4 Press Save/Clear.
5 In the Save/Clear menu, press the Clear R1/R2 softkey to clear the reference
waveform location.
Reference waveforms are also cleared by a Factory Default or Secure Erase (see
Chapter 20, “Save/Recall (Setups, Screens, Data),” starting on page 215).
To display a reference waveform
1 Press the [Analyze] key.
2 Press Features; then, select R1 or R2.
3 Press Features again (or push the Entry knob) to turn on the reference waveform.
78 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 79

One reference waveform can be displayed at a time.
Reference Waveforms 7
See Also • "To display reference waveform information" on page 80
To scale and position reference waveforms
1 Display the desired reference waveform (see "To display a reference
waveform" on page 78).
2 Press the Scale softkey and turn the Entry knob to adjust the reference
waveform vertical scale.
3 Press the Offset softkey and turn the Entry knob to adjust the reference
waveform vertical offset.
To adjust reference waveform skew
Once reference waveforms are displayed, you can adjust their skew.
1 Display the desired reference waveform (see "To display a reference
waveform" on page 78).
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 79
Page 80

7 Reference Waveforms
2 Press the Skew softkey and turn the Entry knob to adjust the reference
waveform skew.
To display reference waveform information
1 Press the [Analyze] key.
2 Press Features; then, select R1 or R2.
3 Press Save/Clear.
4 In the Save/Clear menu, press the Display Info softkey to enable or disable
reference waveform information on the oscilloscope display.
5 Press the Transparent softkey to enable or disable transparent information
backgrounds.
This setting is also used for other oscilloscope information on the display, like
mask test statistics, etc.
To save/recall reference waveform files to/from a USB storage device
Analog channel, math, or reference waveforms can be saved to a reference
waveform file on a USB storage device. See "To save reference waveform files to a
USB storage device" on page 220.
You can recall a reference waveform file from a USB storage device into one of the
reference waveform locations. See "To recall reference waveform files from a USB
storage device" on page 224.
80 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 81

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
8 Serial Bus Decode/Trigger
Depending on the oscilloscope model, the following hardware-accelerated serial
decode and trigger features are available:
Serial decode and trigger type: Available on:
CAN (Controller Area Network) DSOX1200-Series models
I2C (Inter-IC) DSOX1200-Series and EDUX1052A/G
models
LIN (Local Interconnect Network) DSOX1200-Series models
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) DSOX1200-Series models
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter)
protocols including RS232 (Recommended Standard 232)
Triggering on
Serial Data
See Also • Chapter 25, “CAN Triggering and Serial Decode,” starting on page 275
In some cases, such as when triggering on a slow serial signal (for example, I2C,
SPI, CAN, LIN, etc.), to stabilize the waveform display, it may be necessary to
switch from the Auto trigger mode to the Normal trigger mode to prevent the
oscilloscope from auto-triggering. You can select the trigger mode by pressing the
[Trigger] key, then the Mode softkey.
Also, the threshold voltage level must be set appropriately for each source
channel. The threshold level for each serial signal can be set in the Signals menu
(press [Analyze] > Features, select Serial Bus, then press the Signals softkey).
• Chapter 26, “I2C Triggering and Serial Decode,” starting on page 285
• Chapter 27, “LIN Triggering and Serial Decode,” starting on page 293
DSOX1200-Series and EDUX1052A/G
models
81
Page 82

8 Serial Bus Decode/Trigger
• Chapter 28, “SPI Triggering and Serial Decode,” starting on page 301
• Chapter 29, “UART/RS232 Triggering and Serial Decode,” starting on page 313
82 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 83

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
9 Display Settings
To adjust waveform intensity / 83
To set or clear persistence / 85
To clear the display / 86
To select the grid type / 86
To adjust the grid intensity / 87
To add an annotation / 87
To freeze the display / 89
To adjust waveform intensity
You can adjust the intensity of displayed waveforms to account for various signal
characteristics, such as fast time/div settings and low trigger rates.
Increasing the intensity lets you see the maximum amount of noise and
infrequently occurring events.
Reducing the intensity can expose more detail in complex signals as shown in the
following figures.
1 Press the [Intensity] key to illuminate it.
This key is located just below the Entry knob.
2 Turn the Entry knob to adjust the waveform instensity.
Waveform intensity adjustment affects analog channel waveforms only (not math
waveforms, reference waveforms, etc.).
83
Page 84

9 Display Settings
Figure 13 Amplitude Modulation Shown at 100% Intensity
Figure 14 Amplitude Modulation Shown at 40% Intensity
84 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 85

To set or clear persistence
With persistence, the oscilloscope updates the display with new acquisitions, but
does not immediately erase the results of previous acquisitions. All previous
acquisitions are displayed with reduced intensity. New acquisitions are shown in
their normal color with normal intensity.
Waveform persistence is kept only for the current display area; you cannot pan
and zoom the persistence display.
To use persistence:
1 Press the [Display] key.
2 In the Display menu, press Persistence.
3 In the Persistence menu, press Persistence; then, turn the Entry knob to select
between:
• Off — turns off persistence.
When persistence is off, you can press the Capture Waveforms softkey to
perform a single-shot infinite persistence. A single acquisition's data is
displayed with reduced intensity, and it remains on the display until you
clear persistence or clear the display.
• ∞ Persistence — (infinite presistence) Results of previous acquisitions are
never erased.
Display Settings 9
Use infinite persistence to measure noise and jitter, to see the worst-case
extremes of varying waveforms, to look for timing violations, or to capture
events that occur infrequently.
• Variable Persistence — Results of previous acquisitions are erased after a
certain amount of time.
Variable persistence gives you a view of acquired data that is similar to
analog oscilloscopes.
When variable persistence is selected, press the Time softkey and use the
Entry knob to specify the amount of time that previous acquisitions are to be
displayed.
The display will begin accumulating multiple acquisitions.
4 To erase the results of previous acquisitions from the display, press the Clear
Persistence softkey.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 85
Page 86

9 Display Settings
The oscilloscope will start to accumulate acquisitions again.
5 To return the oscilloscope to the normal display mode, turn off persistence;
then, press the Clear Persistence softkey.
Turning off persistence does not clear the display. The display is cleared if you
press the Clear Display softkey or if you press the [Auto Scale] key (which also
turns off persistence).
For another method of seeing worst-case extremes of varying waveforms, see
"Glitch or Narrow Pulse Capture" on page 136.
To clear the display
1 Press [Display] > Clear Display.
You can also configure the [Quick Action] key to clear the display. See "Configuring
the [Quick Action] Key" on page 246.
To select the grid type
When the Video trigger type is selected (see "Video Trigger" on page 108), and the
vertical scaling of at least one displayed channel is 140 mV/div, the Grid softkey
lets you select from these grid types:
• Full — the normal oscilloscope grid.
• mV — shows vertical grids, labeled on the left, from -0.3 V to 0.8 V.
• IRE — (Institute of Radio Engineers) shows vertical grids in IRE units, labeled on
the left, from -40 to 100 IRE. The 0.35 V and 0.7 V levels from the mV grid are
also shown and labeled at the right. When the IRE grid is selected, cursor values
are also shown in IRE units. (Cursor values via the remote interface are not in
IRE units.)
The mV and IRE grid values are accurate (and match Y cursor values) when the
vertical scaling is 140 mV/division and the vertical offset is 245 mV.
To select the grid type:
1 Press [Display].
2 In the Display menu, press Grid.
86 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 87

3 In the Grid menu, press the Grid softkey; then, turn the Entry knob to select
the grid type.
To adjust the grid intensity
To adjust the display grid (graticule) intensity:
1 Press [Display].
2 In the Display menu, press Grid.
3 In the Grid menu, press the Intensity softkey; then, turn the Entry knob to
change the intensity of the displayed grid.
The intensity level is shown in the Intensity softkey and is adjustable from 0 to
100%.
Each major vertical division in the grid corresponds to the vertical sensitivity
shown in the status line at the top of the display.
Each major horizontal division in the grid corresponds to the time/div shown in the
status line at the top of the display.
Display Settings 9
To add an annotation
You can add an annotation to the upper left corner of the oscilloscope's display.
The annotation is useful for documentation purposes, to add notes before
capturing screens.
To add an annotation:
1 On the oscilloscope's front panel, press [Display].
2 In the Display menu, press Annotation.
3 In the Annotation menu, press Annotation to enable the annotation.
4 Press Edit.
5 In the Edit Annotation menu:
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 87
Page 88

9 Display Settings
NOTE
• Use the Spell, , , and Delete Character softkeys to enter the annotation
text:
• Spell — press this softkey and turn the Entry knob to select the character
at the current position.
• — press this softkey to enter characters and move the cursor to the
next character position.
• — press this softkey to enter characters and move the cursor to the
previous character position.
• Delete Character — press the or softkeys until the desired character
is highlighted; then, press this softkey to delete the character.
You can use a connected USB keyboard instead of using the Spell (and other) character
editing softkeys.
• Use the Clear softkey to delete all annotation characters.
• Press OK to save the annotation edits.
88 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 89

Display Settings 9
Back
6 Press the Back key to return the the Annotation menu.
7 Press the Text Color softkey and turn the Entry knob to select the annotation
color.
You can choose white, red, or colors that match analog channels, digital
channels, math waveforms, reference waveforms, or markers.
8 Press the Background softkey and turn the Entry knob to select the annotation
background:
• Opaque — the annotation has a solid background.
• Inverted — the annotation's foreground and background colors are switched.
• Transparent — the annotation has a transparent background.
See Also • "To save BMP or PNG image files" on page 217
• "To print the oscilloscope's display" on page 227
To freeze the display
To freeze the display without stopping running acquisitions, you must configure
the [Quick Action] key. See "Configuring the [Quick Action] Key" on page 246.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 89
Page 90

9 Display Settings
1 Once the [Quick Action] key has been configured, press it to freeze the display.
2 To un-freeze the display, press [Quick Action] again.
Manual cursors can be used on the frozen display.
Many activities, such as adjusting the trigger level, adjusting vertical or horizontal
settings, or saving data will un-freeze the display.
90 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 91

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
10 Labels
To turn the label display on or off / 91
To assign a predefined label to a channel / 92
To define a new label / 93
To load a list of labels from a text file you create / 94
To reset the label library to the factory default / 95
You can define labels and assign them to each analog input channel, or you can
turn labels off to increase the waveform display area.
To turn the label display on or off
1 Press [Display] > Labels > Display.
This turns on labels for the displayed analog channels. Labels are displayed at
the left edge of the displayed traces.
The figure below shows an example of displayed labels.
91
Page 92

10 Labels
2 To turn the labels off, press the Display softkey again.
To assign a predefined label to a channel
1 Press [Display] > Labels > Edit.
2 Press the Channel softkey, then turn the Entry knob or successively press the
Channel softkey to select a channel for label assignment.
92 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 93

Labels 10
The figure above shows the list of channels and their default labels. The
channel does not have to be turned on to have a label assigned to it.
3 Press the Library softkey, then turn the Entry knob or successively press the
Library softkey to select a predefined label from the library.
4 Press the Apply New Label softkey to assign the label to your selected channel.
5 Repeat the above procedure for each predefined label you want to assign to a
channel.
To define a new label
1 Press [Display] > Labels > Edit.
2 Press the Channel softkey; then, turn the Entry knob or successively press the
softkey to select a channel for label assignment.
The channel does not have to be turned on to have a label assigned to it. If the
channel is turned on, its current label will be highlighted.
3 Press the Spell softkey; then, turn the Entry knob to select the first character in
the new label.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 93
Page 94

10 Labels
NOTE
Turning the Entry knob selects a character to enter into the highlighted position
shown in the "New label =" line and in the Spell softkey. Labels can be up to ten
characters in length.
4 Press the Enter softkey to enter the selected character and to go to the next
character position.
5 You may position the highlight on any character in the label name by
successively pressing the Enter softkey.
6 To delete a character from the label, press the Enter softkey until the letter you
want to delete is highlighted, then press the Delete Character softkey.
You can use a connected USB keyboard instead of using the Spell (and other) character
editing softkeys.
7 When you are done entering characters for the label, press the Apply New Label
softkey to assign the label to the selected channel.
When you define a new label, it is added to the nonvolatile label list.
Label Assignment
Auto-Increment
When you assign a label ending in a digit, such as ADDR0 or DATA0, the
oscilloscope automatically increments the digit and displays the modified label in
the "New label" field after you press the Apply New Label softkey. Therefore, you
only need to select a new channel and press the Apply New Label softkey again to
assign the label to the channel. Only the original label is saved in the label list. This
feature makes it easier to assign successive labels to numbered control lines and
data bus lines.
To load a list of labels from a text file you create
It may be convenient to create a list of labels using a text editor, then load the
label list into the oscilloscope. This lets you type on a keyboard rather than edit
the label list using the oscilloscope's controls.
You can create a list of up to 75 labels and load it into the oscilloscope. Labels are
added to the beginning of the list. If more than 75 labels are loaded, only the first
75 are stored.
To load labels from a text file into the oscilloscope:
94 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 95

Labels 10
NOTE
NOTE
1 Use a text editor to create each label. Each label can be up to ten characters in
length. Separate each label with a line feed.
2 Name the file labellist.txt and save it on a USB mass storage device such as a
thumb drive.
3 Load the list into the oscilloscope using the File Explorer (press [Utility] > File
Explorer).
Label List Management
When you press the Library softkey, you will see a list of the last 75 labels used. The list does
not save duplicate labels. Labels can end in any number of trailing digits. As long as the base
string is the same as an existing label in the library, the new label will not be put in the library.
For example, if label A0 is in the library and you make a new label called A12345, the new
label is not added to the library.
When you save a new user-defined label, the new label will replace the oldest label in the list.
Oldest is defined as the longest time since the label was last assigned to a channel. Any time
you assign any label to a channel, that label will move to the newest in the list. Thus, after you
use the label list for a while, your labels will predominate, making it easier to customize the
instrument display for your needs.
When you reset the label library list (see next topic), all of your custom labels will be deleted,
and the label list will be returned to its factory configuration.
To reset the label library to the factory default
Pressing the Default Library softkey will remove all user-defined labels from the library and
set the labels back to the factory default. Once deleted, these user-defined labels cannot be
recovered.
1 Press [Utility] > Options > Preferences.
2 Press the Default Library softkey.
This will delete all user-defined labels from the library and set the labels in the
library back to the factory default. However, this does not default the labels
currently assigned to the channels (those labels that appear in the waveform
area).
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 95
Page 96

10 Labels
NOTE
Defaulting labels without erasing the default library
Pressing [Default Setup] sets all channel labels back to the default labels but does not erase
the list of user-defined labels in the library.
96 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 97

Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes
User's Guide
11 Triggers
Adjusting the Trigger Level / 99
Forcing a Trigger / 99
Edge Trigger / 99
Pulse Width Trigger / 102
Pattern Trigger / 104
Rise/Fall Time Trigger / 106
Setup and Hold Trigger / 107
Video Trigger / 108
Serial Trigger / 118
A trigger setup tells the oscilloscope when to acquire and display data. For
example, you can set up to trigger on the rising edge of the analog channel 1 input
signal.
You can adjust the vertical level used for analog channel edge detection by
turning the Trigger Level knob.
In addition to the edge trigger type, you can also set up triggers on pulse widths
or video signals. On DSOX1200-Series models, you can additionally set up
triggers on patterns, rise/fall times, or setup and hold violations.
97
Page 98

11 Triggers
Pre-Trigger Buffer
Post-Trigger Buffer
Acquisition Memory
Trigger Event
You can use any input channel or the EXT TRIG input BNC (see "External Trigger
Input" on page 127) as the source for most trigger types.
Changes to the trigger setup are applied immediately. If the oscilloscope is
stopped when you change a trigger setup, the oscilloscope uses the new
specification when you press [Run/Stop] or [Single]. If the oscilloscope is running
when you change a trigger setup, it uses the new trigger definition when it starts
the next acquisition.
You can use the [Force] key to acquire and display data when triggers are not
occurring.
You can use the [Trigger] key to set options that affect all trigger types (see
Chapter 12, “Trigger Mode/Coupling,” starting on page 121).
You can save trigger setups along with the oscilloscope setup (see Chapter 20,
“Save/Recall (Setups, Screens, Data),” starting on page 215).
Triggers - General
Information
A triggered waveform is one in which the oscilloscope begins tracing (displaying)
the waveform, from the left side of the display to the right, each time a particular
trigger condition is met. This provides stable display of periodic signals such as
sine waves and square waves, as well as nonperiodic signals such as serial data
streams.
The figure below shows the conceptual representation of acquisition memory. You
can think of the trigger event as dividing acquisition memory into a pre-trigger
and post-trigger buffer. The position of the trigger event in acquisition memory is
defined by the time reference point and the delay (horizontal position) setting (see
"To adjust the horizontal delay (position)" on page 39).
98 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
Page 99

Adjusting the Trigger Level
T
NOTE
You can adjust the trigger level for a selected analog channel by turning the
Trigger Level knob.
You can push the Trigger Level knob to set the level to the waveform's 50% value.
If AC coupling is used, pushing the Trigger Level knob sets the trigger level to
about 0 V.
The position of the trigger level for the analog channel is indicated by the trigger
level icon (if the analog channel is on) at the far left side of the display. The
value of the analog channel trigger level is displayed in the upper-right corner of
the display.
The line trigger level is not adjustable. This trigger is synchronized with the power
line supplied to the oscilloscope.
You can also change the trigger level of all channels by pressing [Analyze] > Features and
then selecting Trigger Levels.
Triggers 11
Forcing a Trigger
The [Force] key causes a trigger (on anything) and displays the acquisition.
This key is useful in the Normal trigger mode where acquisitions are made only
when the trigger condition is met. In this mode, if no triggers are occurring (that is,
the "Trig'd?" indicator is displayed), you can press [Force] to force a trigger and see
what the input signals look like.
In the Auto trigger mode, when the trigger condition is not met, triggers are forced
and the "Auto?" indicator is displayed.
Edge Trigger
The Edge trigger type identifies a trigger by looking for a specified edge (slope)
and voltage level on a waveform. You can define the trigger source and slope in
this menu. The trigger type, source, and level (if applicable) are displayed in the
upper-right corner of the display.
Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide 99
Page 100

11 Triggers
1 On the front panel, in the Trigger section, press the [Trigger] key.
2 In the Trigger menu, press the Trigger Type softkey.
3 Press the Trigger Type softkey; then, turn the Entry knob to select Edge.
4 Select the trigger source:
• Analog channel, 1 to the number of channels
• External — triggers on the rear panel EXT TRIG input signal.
• Line — triggers at the 50% level of the rising or falling edge of the AC power
source signal.
• WaveGen — triggers at the 50% level of the rising edge of the waveform
generator output signal. (Not available when the DC or Noise waveforms are
selected.)
• WaveGen Mod (FSK/FM) — when waveform generator FSK or FM modulation is
used, triggers at the 50% level of the rising edge of the modulating signal.
You can choose a channel that is turned off (not displayed) as the source for the
edge trigger.
The selected trigger source is indicated in the upper-right corner of the display
next to the slope symbol:
• 1 through 4 = analog channels.
• E = External trigger input.
• L = Line trigger.
• W = Waveform generator.
5 Press the Slope softkey and select rising edge, falling edge, alternating edges,
or either edge (depending on the selected source). The selected slope is
displayed in the upper-right corner of the display.
100 Keysight InfiniiVision 1200 X-Series and EDUX1052A/G Oscilloscopes User's Guide
 Loading...
Loading...