Kenwood TK-2206, TK-2202 Service Manual

VHF FM TRANSCEIVER
TK-2202/2206
SERVICE MANUAL
GENERAL .............................................................2
Antenna
(T90-1036-05): TK-2202(K,M)
(KRA-26: Option) TK-2206 (M)
Knob (CH-SELECTOR)
(K29-9318-03)
Knob (VOLUME)
(K29-9309-03)
Cabinet assy
(A02-3852-23)(8CH):
TK-2202(K,M)
(A02-3851-23)(16CH):
TK-2206(M)
SYSTEM SET-UP .................................................2
REALIGNMENT....................................................3
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR .............................. 5
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ....................................... 8
TERMINAL FUNCTION......................................12
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA ................................. 12
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION .........................13
PARTS LIST........................................................14
EXPLODED VIEW...............................................20
PACKING ............................................................ 21
ADJUSTMENT ................................................... 23
PC BOARD
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.....................................32
BLOCK DIAGRAM..............................................36
LEVEL DIAGRAM...............................................38
KSC-31 / KNB-29N / KNB-30A / KBH-10 ......... 39
SPECIFICATIONS............................BACK COVER
© 2004-2 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8677-00 (S) 1246
CONTENTS
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6870-20).......................... 28
Knob (PTT)
(K29-9308-03)
TK-2206 :
Does not come with antenna.
Antenna is available as an option.
Photo is TK-2202.
TK-2202/2206
GENERAL / SYSTEM SET-UP
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians
familiar with similar types of commercial grade communications
equipment. It contains all required service information for the
equipment and is current as of the publication date. Changes
which may occur after publication are covered by either Service
Bulletins or Manual Revisions. These are issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment information,
the full part identification number should be included. This
applies to all parts, components, kits, or chassis. If the part
number is not known, include the chassis or kit number of
which it is a part, and a sufficient description of the required
component for proper identification.
Unit
Model
& destination
TK-2202
TK-2206
TX-RX Unit Frequency range Remarks
K,M
X57-6870-20 136~174MHz
M LOC : 38.4MHz
IF1 : 38.85MHz
PERSONAL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personal
safety:
●
DO NOT transmit until all RF connectors are verified secure
and any open connectors are properly terminated.
●
SHUT OFF and DO NOT operate this equipment near
electrical blasting caps or in an explosive atmosphere.
●
This equipment should be serviced by a qualified technician
only.
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and alignment
procedures contained within.
SYSTEM SET-UP
Merchandise received
License and frequency allocated by FCC
Choose the type of transceiver
Transceiver programming
Are you using the optional antenna?
Are you using the speaker microphone?
NO
NO
Delivery
Frequency range (MHz) RF power Type
TX/RX 136~174
A personal computer (IBM PC or compatible), programming
interface (KPG-22), and programming software (KPG-87D)
are required for programming.
(The frequency, TX power HI/LOW, and signalling data are programmed
for the transceiver.)
YES
YES
KRA-22 or KRA-26
Optional antenna
KMC-17 or KMC-21
Speaker microphone
(Option)
5.0W
TK-2202 (K,M)
TK-2206 (M)
2
REALIGNMENT
TK-2202/2206
REALIGNMENT
1. Modes
User mode
PC mode
Clone mode
Mode Function
User mode For normal use.
PC mode Used for communication between the
Data programming Used to read and write frequency data
mode
PC test mode Used to check the radio using the PC.
Clone mode Used to transfer programming data
Data programming
mode
PC test mode
radio and PC (IBM compatible).
and other features to and from the radio.
This feature is included in the KPG87D.
from one radio to another.
PC tuning mode
2. How to Enter Each Mode
Mode Operation
User mode Power ON
PC mode Received commands from PC
Clone mode
[PTT]+[Side2]+Power ON (Two seconds)
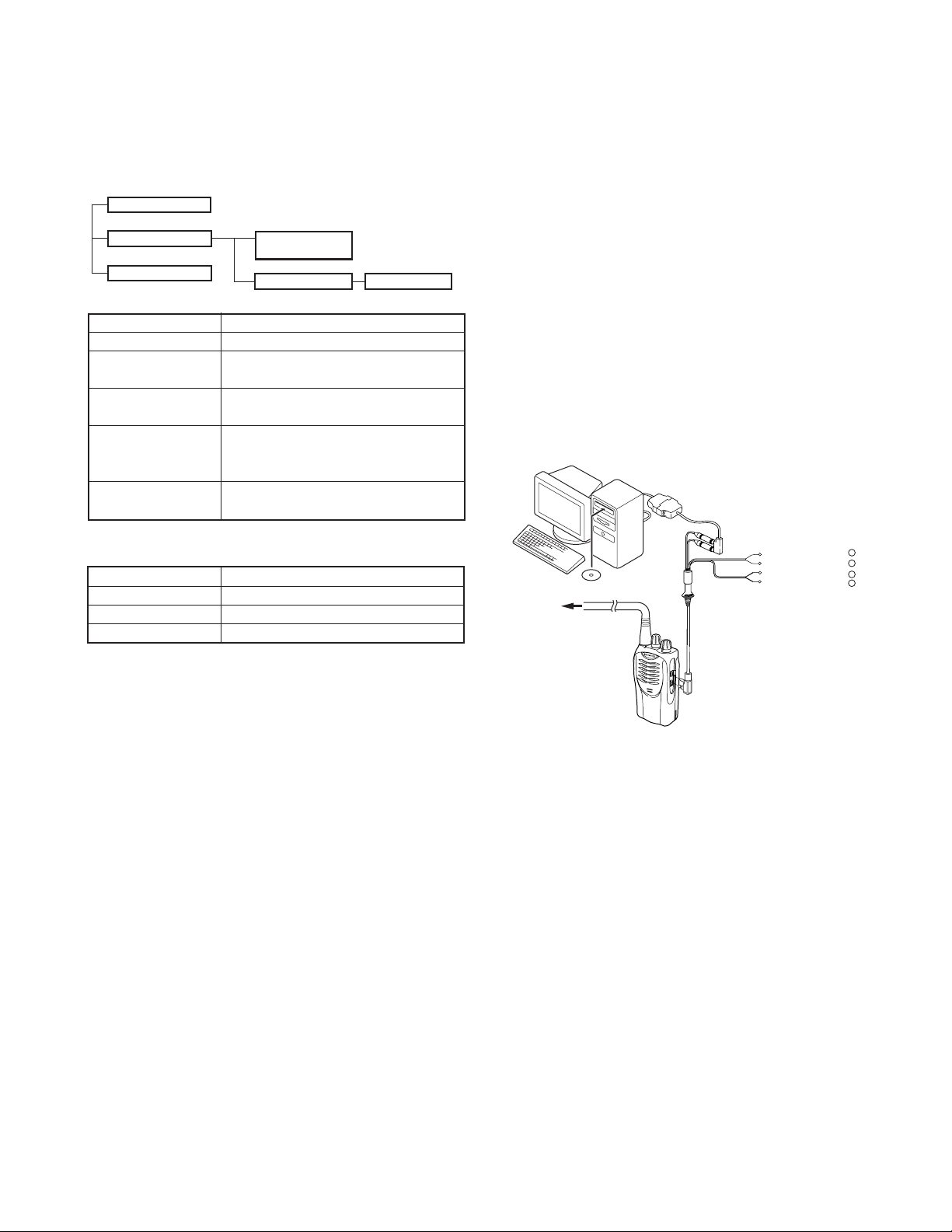
3-3. KPG-22 description
(PC programming interface cable: Option)
The KPG-22 is required to interface the TK-2202/2206 with
the computer. It has a circuit in its D-subconnector (25-pin)
case that converts the RS-232C logic level to the TTL level.
The KPG-22 connects the SP/MIC connector of the TK-2202/
2206 to the computer’s RS-232C serial port.
3-4. Programming software description
KPG-87D is the programming software for TK-2202/2206
supplied on a CD-ROM. This software runs under Windows
98, ME, Windows 2000 or XP on an IBM-PC or compatible
machine.
The data can be input to or read from TK-2202/2206 and
edited on the screen. The programmed or edited data can be
printed out. It is also possible to tune the transceiver.
IBM-PC
KPG-22
Gray +
Gray/Black –
1.5D-XV Lead wire +
1.5D-XV Shield wire –
RF Power meter
or SSG
KPG-87D
Tuning cable
(E30-3216-05)
SP
}
MIC
}
3. PC Mode
3-1. Preface
The TK-2202/ 2206 transceivers are programmed using a
personal computer, a programming interface (KPG-22) and
programming software (KPG-87D).
The programming software can be used with an IBM PC
or compatible. Figure 1 shows the setup of an IBM PC for
programming.
3-2. Connection procedure
1. Connect the TK-2202/2206 to the personal computer with
the interface cable.
2. When the POWER is switched on, user mode can be
entered immediately. When the PC sends a command,
the radio enters PC mode.
When data is transmitting from the transceiver, the red
LED lights.
When data is received by the transceiver, the green LED
lights.
Notes:
• The data stored in the personal computer must match the
model type when it is written into the EEPROM.
• Change the TK-2202/ 2206 to PC mode, then attach the
interface cable.
Fig. 1
4. Clone Mode
4-1. Outline
"Clone Mode" copies the transceiver data to another
transceiver.
The dealer can copy the transceiver data to another
transceiver even without the use of a personal computer.
4-2. Example
The transceiver can copy the programming data to one or
more transceivers via RF communication.
The clone master and clone slave/s must be in Clone mode.
4-3. Operation
1. To switch the clone slave/s to Clone mode, press and hold
the [PTT] and [side2] keys while turning the transceiver
power ON.
2. Wait for 2 seconds. The LED will light orange and the
transceiver will announce "Clone".
3. Select a channel table number using Side1(increment
channel table) and Side2(decrement channnel table) keys.
3

TK-2202/2206
REALIGNMENT
4. To switch the clone master to Clone mode, press and hold
the [PTT] and [side2] keys while turning the transceiver
power ON.
5. Wait for 2 seconds. The LED will light orange and the
transceiver will announce "Clone".
6.
Select the same channel table number as the clone slave/s.
7. Press [PTT] on the clone master to begin data transmission.
When the clone slave starts to receive data, the LED will
light green.
When the clone master finishes sending data, a
"confirmation" tone will sound.
If data transmission fails while cloning, an "error" tone will
sound from the Slave unit.
8. If the cloning fails, no data will be available in the Slave unit
when it is returned to User mode.
9. When the cloning is successful, the Slave unit's "Scan" and
"Key lock" functions will return to their default values (Scan
= OFF, Key lock = OFF).
Notes:
• The dealer can clone data to two or more transceivers by
repeating the above procedures.
• If the transceivers Clone Mode is configured as "Disabled",
the transceiver cannot enter Clone mode.
• The table shown below will cover the frequency tables used
for wireless cloning.
•Clone mode cannot be entered in battery low state.
•A unit cannot be a "Master Unit" if it is unprogrammed. If
[PTT] is pressed, an "error" tone will sound.
• The language used in cloning depends on the "Model type"
setting, not the FPU setting. C, C2, C5 and C6 type
TK-3207 transceivers will use Chinese. Other types English.
• Once a unit is set to be the Master, it cannot be a slave
after the data has been transmitted. This protects the data
in the Master unit.
• Electronic interface may cause a failure in data transfer
during Wireless Clone, such as when waveforms or
electromagnetics are being performed at the workbench.
• Clone mode can be used ONLY by the authorized service
personnel.
• The Clone mode setting must be configured as "Disable"
before being delivered to the end-user.
• To clone, replace the antenna from both the master
transceiver and the slave transceiver with a dummy
load.
• The transmit output power is automatically set to Low
in Clone mode.
Clone Frequency Table
Operating Frequency
Clone
Frequency Table
1 136.000
2 138.000
3 140.000
4 142.000
5 144.000
6 146.000
7 148.000
8 150.000
9 152.000
10 154.000
11 156.000
12 158.000
13 160.000
14 162.000
15 164.000
16 166.000
17 168.000
18 170.000
19 172.000
20 174.000
(MHz)
136~174
4
TK-2202/2206
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
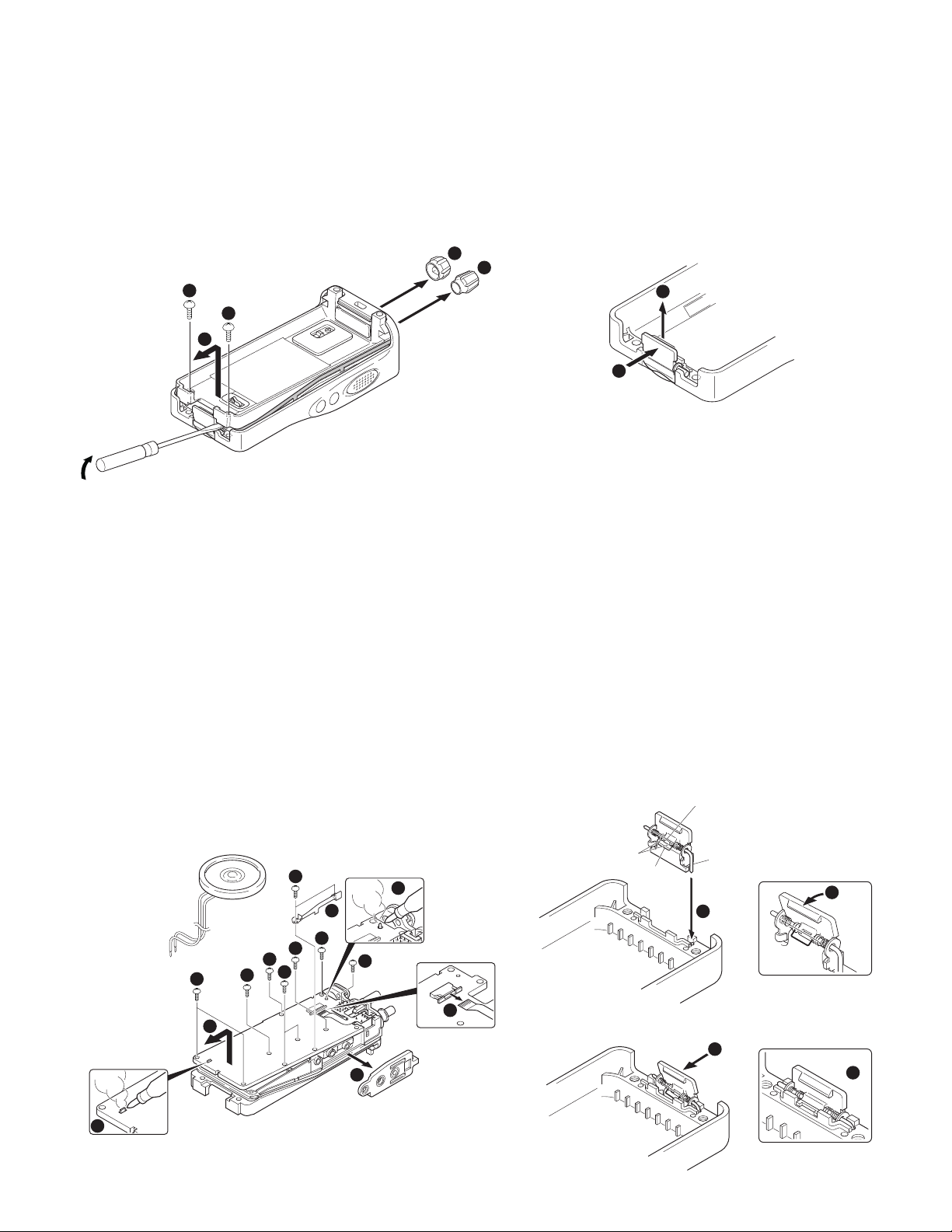
■ Removing the case assembly from the chassis.
1. Remove the volume knob z and channel knob x.
2. Remove the two screws
3. Lift and remove the chassis from the case assembly
(Use a flat-blade screwdriver to easily lift the chassis.)
3
3
4
c
.
v
1
■ Removing the TX-RX unit from the chassis.
1. Remove the packing b from the SP / MIC jack of the TXRX unit.
2. Remove the eleven screws
3. Remove the fixing bracket
4. Remove the solder of the antenna terminal with a soldering
iron
.
,
5. Remove the solder of the positive terminal with a soldering
iron
.
.
Note: You can remove the TX-RX unit from the chassis without
removing the solder at the positive terminal. However,
in this case, you can not attach the packing (G53-1605-
03) that is on the positive terminal to the chassis in
assembling. So, it is advisable to remove the solder on
the positive terminal first.
6. Remove the FPC from the flat cable connector
7. Lift and remove the TX-RX unit from the chassis
fixing the TX-RX unit.
n
of the SP / MIC.
m
/.
Ω.
■ Removing the battery release lever from the case
assembly.
1. Press the upper part of the lever toward the inside of the
.
case assembly. One side of the shaft will be removed
2. Lift and remove the battery release lever from the case
assembly
2
x
.
2
1
z
.
■ Attaching the battery release lever to the case assembly.
1. Insert one side of the shaft into the hole at the lever fitting
section on the case assembly
Caution : The thin spring (G01-4543-04) should be positioned
above the two tabs of the lever.
2. Tilt the battery release lever slightly forward
thick spring (G01-4542-04) is positioned below the case
surface.
3. With the thick spring positioned below the case surface,
attach the other side of the shaft to the case assembly by
pressing the battery release lever
.
v
Caution : Be careful not to tilt the battery release lever too
forward.
If the battery release lever is pushed in this state
where the two tabs come below the case surface,
there is a possibility of damaging the two tabs.
.
z
c
A thin spring
, so that the
x
until it snaps into place
Two tabs
6
7
6
6
6
6
6
9
6
11
8
6
10
5
A thick spring
Shaft
2
1
3
4
5
TK-2202/2206
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
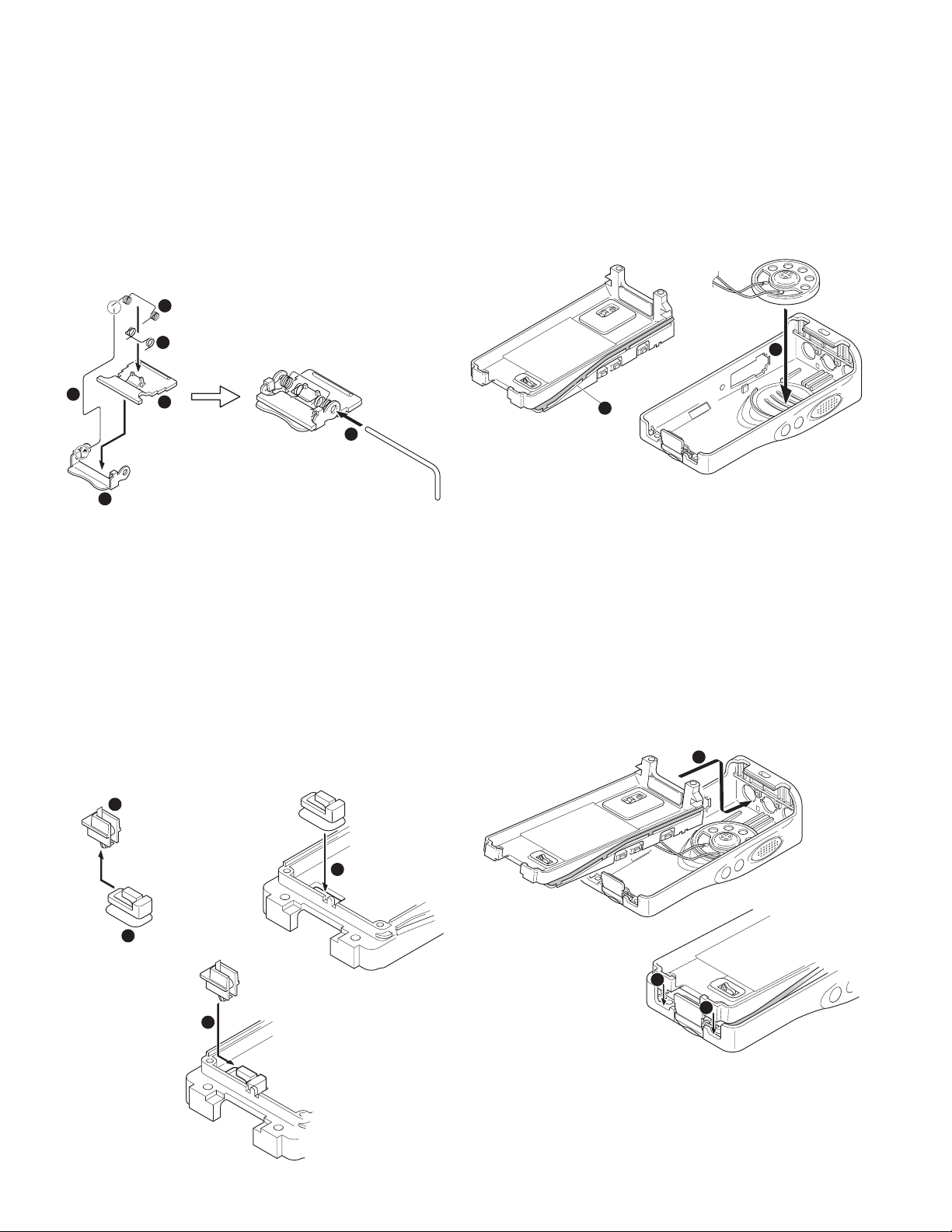
■ Assembling the battery release lever
1. Place the lever x onto the stopper z.
2. Place the thick spring
3. Hook the right and left ends of the thin spring
tabs of the stopper, then place the thin spring onto the
lever
4. Slide the shaft through the hole of the stopper and lever
n
5
.
b
.
4
3
2
1
onto the lever.
c
6
onto the
v
■ Cautions for assembly
1. Attaching the positive terminal to the chassis.
Always attach the positive terminal to the chassis, using
the following procedures, before mounting the TX-RX unit
onto the chassis.
1. Remove the holder assembly
the positive terminal.
2. Mount the packing of the positive terminal into the chassis
hole
3. Mount the holder assembly into the packing of the positive
terminal
c
.
.
v
from the packing z of
x
2. Mounting the chassis to the case assembly.
1. Confirm that the waterproof packing attached to the
circumference of the chassis is securely inserted in the
groove of the chassis
2. Attach the speaker to the speaker recess of the case
assembly
Confirm that the
waterproof packing is
securely inserted in the
groove of the chassis.
3. Insert the upper part of the chassis into the case assembly
.
c
Caution: Take care that the speaker lead wire is not caught
4. Press the chassis
attach them.
Caution: If the packing of the SP / MIC does not come to the
. Make sure the speaker is securely inserted.
x
1
by the microphone element.
correct position after attaching the chassis to the
case assembly, reposition the packing with your
fingers.
.
z
2
and the case assembly together to
v
3
2
3
1
4
4
6
4
TK-2202/2206
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
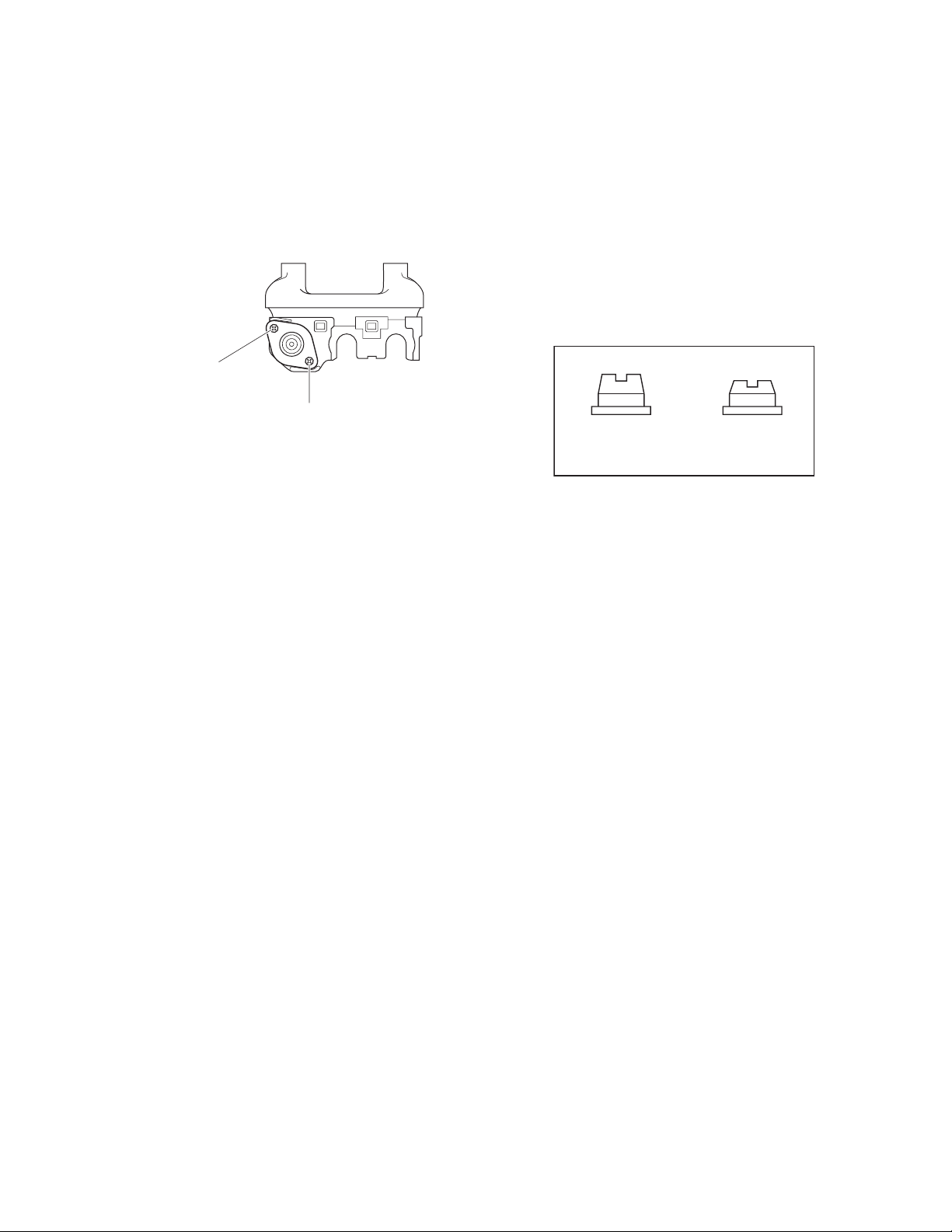
3. Attaching the antenna receptacle to the
chassis.
Screw the antenna receptacle to the chassis in the order
shown in the drawing so that the antenna receptacle comes
to the center of the case hole.
Tighten this screw first.
Tighten this screw second.
4. The nuts of the volume knob and channel
knob
Note that the shapes, colors and heights of nuts of the
volume knob and channel knob are different from one
another. (The nut of volume knob is silver, and the nut of
channel knob is gold)
Use the following jig when removing the nuts of the
volume knob and channel knob.
●
Jig (Part No. : W05-1012-00)
Volume Knob
(Silver)
Channel Knob
(Gold)
7
TK-2202/2206
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
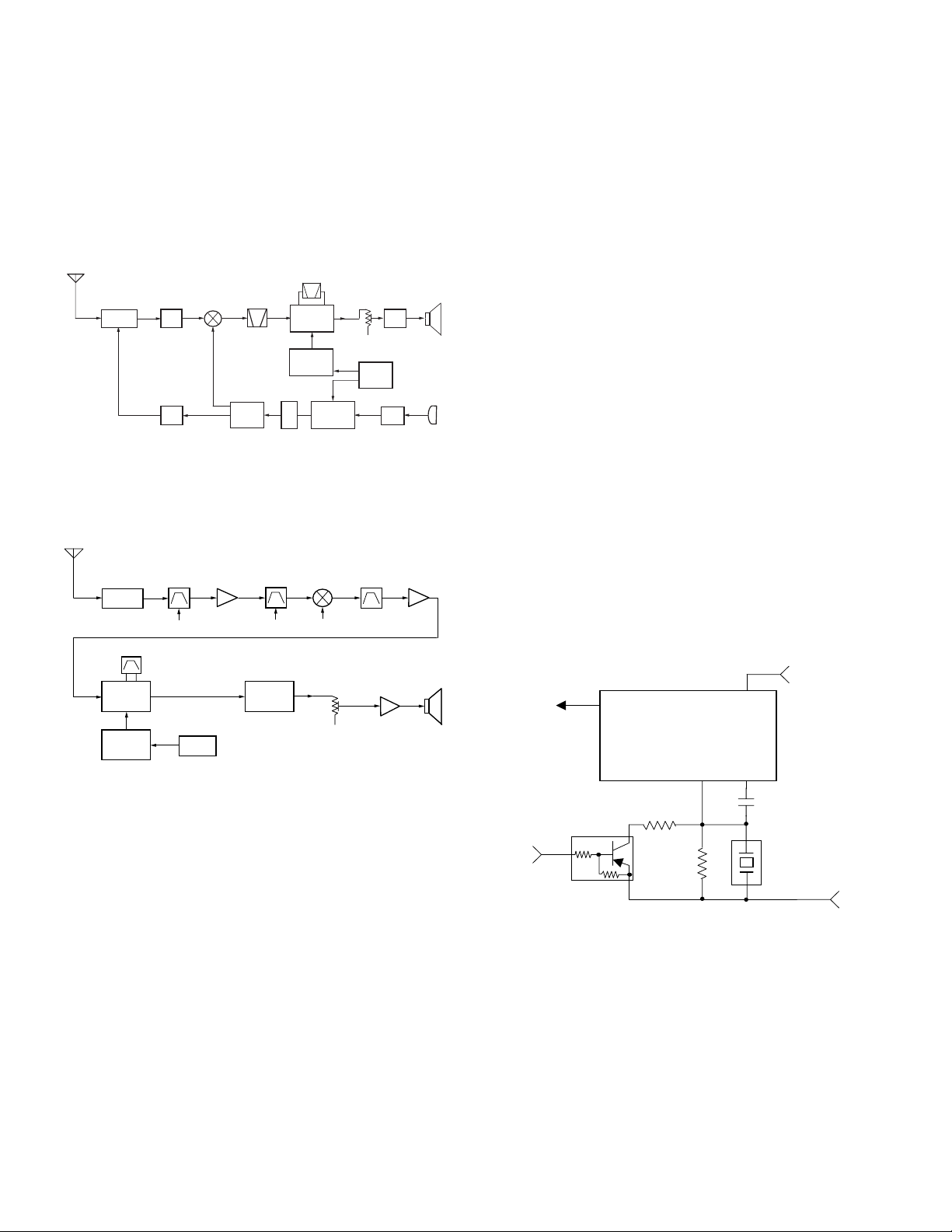
1. Frequency Configuration
The receiver utilizes double conversion. The first IF is 38.85
MHz and the second IF is 450 kHz. The first local oscillator
signal is supplied from the PLL circuit.
The PLL circuit in the transmitter generates the necessary
frequencies. Fig. 1 shows the frequencies.
TX/RX: 136 ~ 174MHz (TK-2202(K,M) TK-2206(M))
ANT
ANT SW
RF
AMP
TX: 136 ~ 174MHz
(TK-2202(K,M) TK-2206(M))
TX
AMP
MCF
38.85MHz
RX: 174.85 ~ 212.85MHz
(TK-2202(K,M) TK-2206(M))
RF
AMP
IF SYSTEM
38.4MHz
X3 multiply
1/2
CF
450kHz
PLL
VCO
TCXO
AF
AMP
MIC
AMP
12.8MHz
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration
2. Receiver
The frequency configuration of the receiver is shown in Fig. 2.
ANT
RF AMP
Q205
BPF
ANT SW
TUNE
IC201
IF,MIX,DET
Q1
X3 multiply
2nd Local
CF201
X1
TCXO
IC301
AQUA
12.8MHz
Fig. 2 Receiver section
1) Front End (RF AMP)
The signal coming from the antenna passes through the
transmit/receive switching diode circuit, (D103,D104,D105
and D106) passes through a BPF (L214 and L213), and is
amplified by the RF amplifier (Q205).
The resulting signal passes through a BPF (L209 and L211)
and goes to the mixer. These BPFs are adjusted by variable
capacitors (D203,D204,D205 and D206). The input voltage
to the variable capacitor is regulated by voltage output from
the microprocessor (IC405).
2) First Mixer
The signal from the front end is mixed with the first local
oscillator signal generated in the PLL circuit by Q1 to
produce a first IF frequency of 38.85 MHz.
The resulting signal passes through the XF201 MCF to cut
the adjacent spurious and provide the opitimun
characteristics, such as adjacent frequency selectivity.
BPF
TUNE
MIXER
Q204
1st Local
AF VOL
MCF
XF201
IC302
AF PA
IF AMP
Q203
SP
MIC
SP
3) IF Amplifier Circuit
The first IF signal is passed through a four-pole monolithic
crystal filter (XF201) to remove the adjacent channel signal.
The filtered first IF signal is amplified by the first IF amplifier
(Q203) and then applied to the lF system IC (IC201). The
IF system IC provides a second mixer, second local
oscillator, limiting amplifier, quadrature detector and RSSI
(Received Signal Strength Indicator). The second mixer
mixes the first IF signal with the 38.4MHz of the second
local oscillator output (TCXO X1) and produces the second
IF signal of 450kHz.
The second IF signal is passed through the ceramic filter
(CF201) to remove the adjacent channel signal. The filtered
second IF signal is amplified by the limiting amplifier and
demodulated by the quadrature detector with the ceramic
discriminator (CD201). The demodulated signal is routed
to the audio circuit.
4) Wide/Narrow Switching Circuit
Narrow and Wide settings can be made for each channel
by switching the demodulation level.
The WIDE (low level) and NARROW (high level) data is
output from IC405, pin 45.
When a WIDE (low level) data is received, Q202 turn on.
When a NARROW (high level) data is received, Q202 turn off.
Q202 turns on/off with the Wide/Narrow data and the
IC201 detector output level is switched to maintain a
constant output level during wide or narrow signals.
Q203
RX_W/N
(IC405)
L : Wide
H : Narrow
AFOUT
Q202
R211
R213
QUAD
IFOUT
C214
IC201
FM IF SYSTEM
CD201
Fig. 3 Wide/Narrow switching circuit
5) Audio Amplifier Circuit
The demodulated signal from IC201 goes to AF amplifier
through IC301.
The signal then goes through an AF volume control , and
is routed to an audio power amplifier (IC302) where it is
amplified and output to the speaker.
5R
8
TK-2202/2206
RECEIVE SIGNALLING
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
6) Squelch
Part of the AF signal from the IC enters the FM IC (IC201)
again, and the noise component is amplified and rectified
by a filter and an amplifier to produce a DC voltage
corresponding to the noise level.
The DC signal from the FM IC goes to the analog port of
the microprocessor (IC405). IC405 determines whether
to output sounds from the speaker by checking whether
the input voltage is higher or lower than the preset value.
To output sounds from the speaker, IC405 sends a high
signal to the SP MUTE line and turns IC302 on through
Q303,Q304,Q305,Q306 and Q316. (See Fig. 4)
7) Receive Signalling
(1) QT/DQT
The output signal from FM IC(IC201) enters the
microprocessor(IC405) through IC301. IC405 determines
whether the QT or DQT matches the preset value, and
controls the SP MUTE and the speaker output sounds
according to the squelch results.
(2) MSK (Fleet Sync)
The MSK input signal from the FM IC goes to pin 31 of IC 301.
The signal is demodulated by MSK demodulator in IC 301.
The demodulated data goes to the CPU for processing.
RECEIVE SIGNALLING
FM IF IC201
IF Amp
BUSY
CPU
IC405
QT/DQT IN
AF CONT
SIGNAL
DTMF
QT/DQT
CLK,DATA,
STD,LOADN
IC301
AQUA
IC302
AF PA
Fig. 4 AF amplifier and squelch
(3) DTMF
The DTMF input signal from the FM IC (IC201) goes to
IC301. The decoded information is then processed by the
CPU.
Q306,316
SW
Q303,304,305
SW
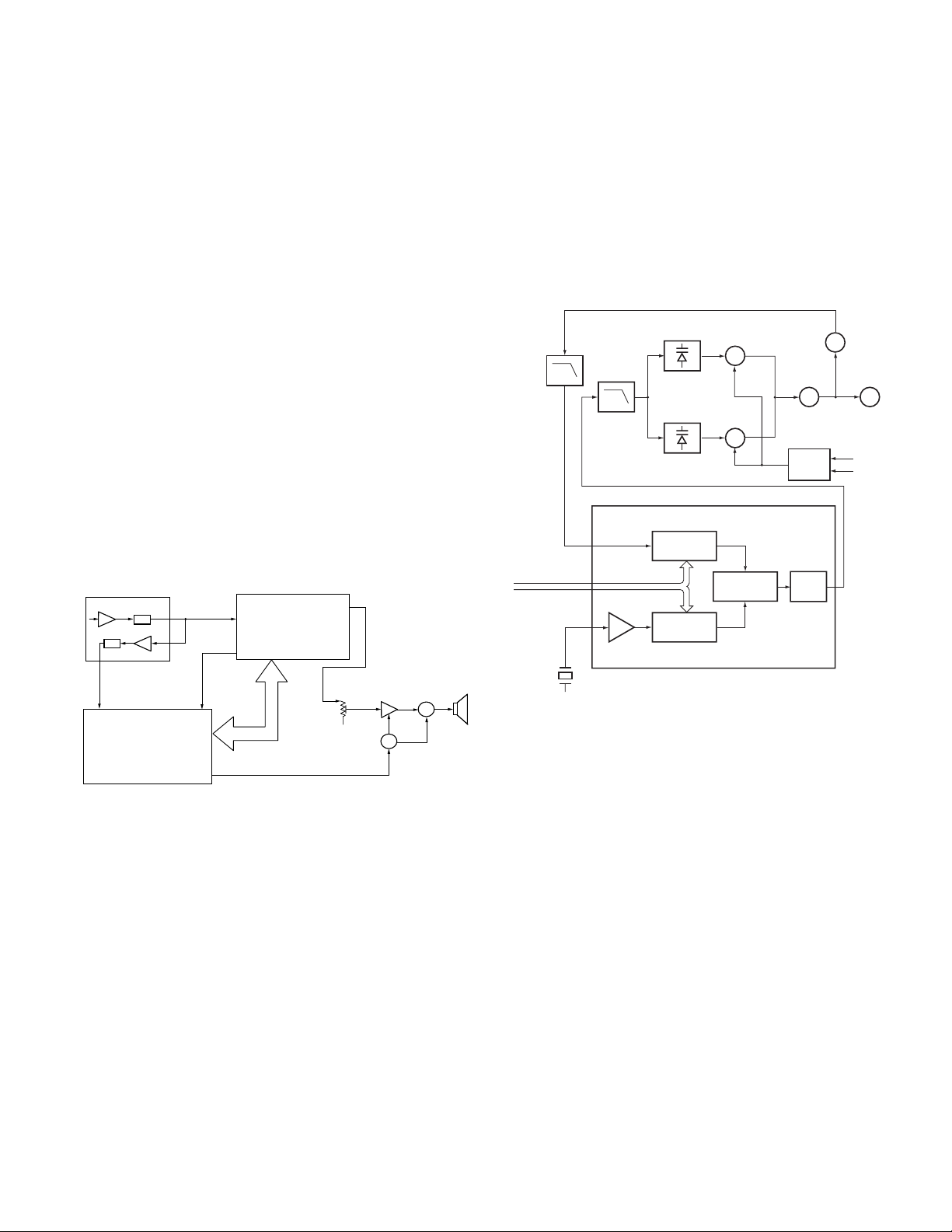
2) VCO
The operating frequency is generated by Q4 in transmit
mode and Q3 in receive mode. The oscillator frequency is
controlled by applying the VCO control voltage, obtained
from the phase comparator, to the varactor diodes (D4 and
D7 in transmit mode and D5 and D9 in receive mode). The
RX pin is set high in receive mode causing Q5 turn on.
The TX pin is set high in transmit mode. The outputs from
Q3 and Q4 are amplified by Q6 and sent to the RF amplifiers.
LPF
LPF
PLL DATA
REF OSC
X1
SP
12.8MHz
D4, 7
D5, 9
PLL IC IC1
1N
1M
Q4
TX VCO
Q3
RX VCO
5kHz/6.25kHz
PHASE
COMPARATOR
5kHz/6.25kHz
Q6
BUFF AMP
Q5, 7
T/R SW
CHARGE
PUMP
Q2
BUFFER
IC2
1/2
RX
TX
Fig. 5 PLL circuit
3) Unlock Detector
If a pulse signal appears at the LD pin of IC1, an unlock
condition occurs, and the DC voltage obtained from C4,R5
and D1 causes the voltage applied to the microprocessor
to go low. When the microprocessor detects this condition,
the transmitter is disabled, ignoring the push-to-talk switch
input signal.
3. PLL Frequency Synthesizer
The PLL circuit generates the first local oscillator signal for
reception and the RF signal for transmission.
1) PLL
The frequency step of the PLL circuit is 2.5,5,6.25 or 7.5kHz.
A 12.8MHz reference oscillator signal is divided at IC1 by a
fixed counter to produce an oscillator (VCO) output signal
which is buffer amplified by Q2 then divided in IC1 by a
programmable counter. The divided signal is compared in
phase with the 5 or 6.25kHz reference signal from the phase
comparator in IC1. The output signal from the phase
comparator is filtered through a low-pass filter and passed
to the VCO to control the oscillator frequency. (See Fig. 5)
4. Transmitter System
1) Microphone Amplifier
The signal from the microphone passes through the IC301.
When encoding DTMF, it is turned OFF for muting the
microphone input signal by IC301.
The signal passes through the Audio processor (IC301) for
the maximum deviation adjustment, and goes to the VCO
modulation input.
9
TK-2202/2206
T
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
IC301
MIC
AGC
LPF
DTMF
IC405
CPU
AQUA
QTVCO
QTTCXO
LPF
LPF
Fig. 6 Microphone amplifier
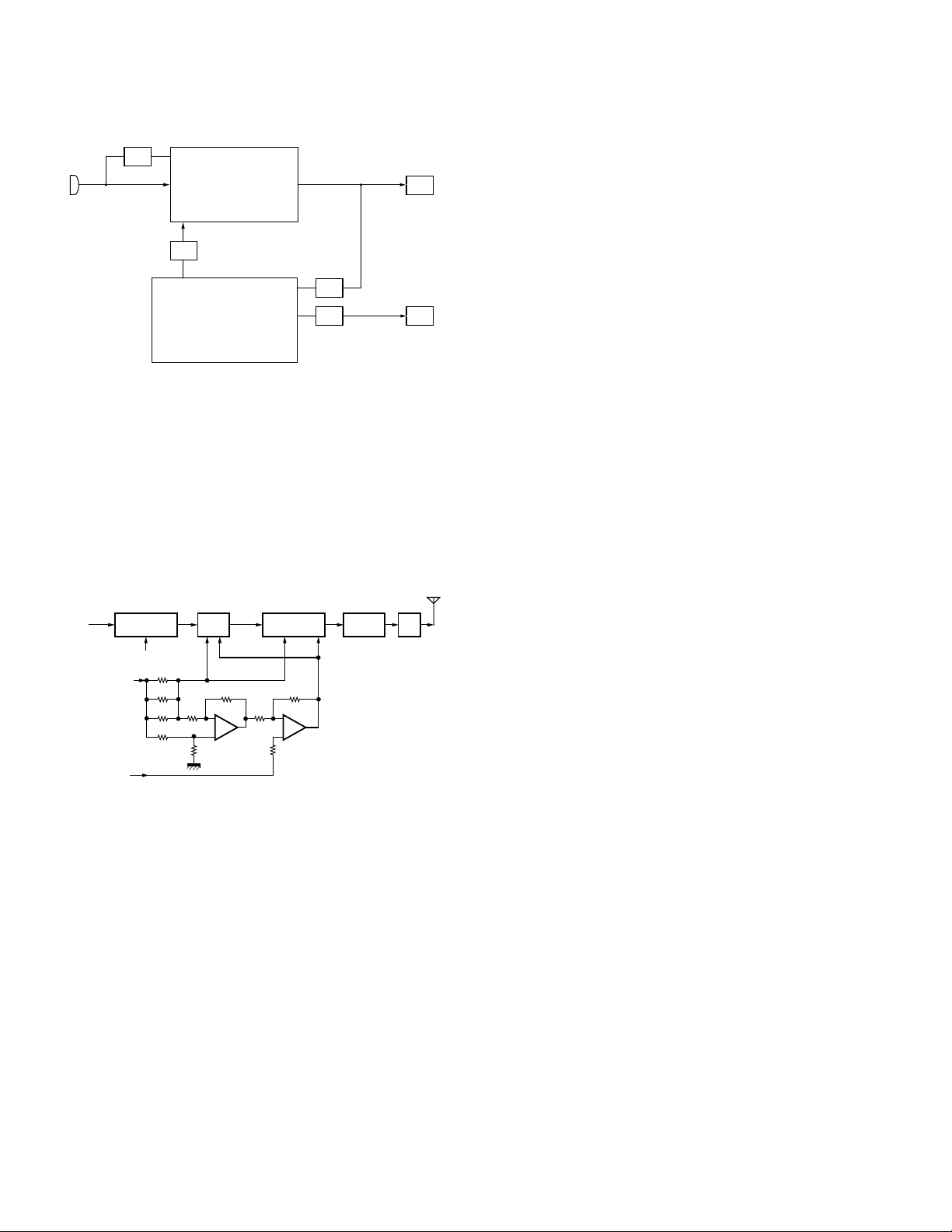
2) Drive and Final Amplifier
The signal from the T/R switch (D101 is on) is amplified by
the pre-drive (Q102) and the drive amplifier (Q103) to 50mW.
The output of the drive amplifier is amplified by the RF power
amplifier (Q106) to 5.0W (1W when the power is low). The
RF power amplifier consists of two MOS FET stages. The
output of the RF power amplifier is then passed through
the harmonic filter (LPF) and antenna switch (D103 and
D104) and applied to the antenna terminal.
D103
From
T/R SW
(D101)
PCTV
(IC405)
Q102
Pre-DRIVE
AMP
5T
+B
R127
R128
R129
Q103 Q106
DRIVE
AMP
IC101
(1/2)
POWER AMP
VDD
RF
IC101
(2/2)
D104
ANT
SW
VGVGVD
Fig. 7 Drive and final amplifier and APC circuit
3) APC Circuit
The APC circuit always monitors the current flowing through
the RF power amplifier (Q106) and keeps a constant current.
The voltage drop at R127, R128 and R129 is caused by the
current flowing through the RF power amplifier and this
voltage is applied to the differential amplifier IC101(1/2).
IC101(2/2) compares the output voltage of IC101(1/2) with
the reference voltage from IC405. The output of IC101(2/2)
controls the VG of the RF power amplifier, drive amplifier
and pre-drive amplifier to make both voltages the same.
The change of power high/low is carried out by the change
of the reference voltage.
The QT,DQT data of the QTVCO Line is output from pin 24
of the CPU. The signal passes through a low pass CR filter,
VCO
mixes with the audio signal, and goes to the VCO modulation
input. TX deviation is adjusted by the CPU.
(2) DTMF
High-speed data is output from pin 2 of the CPU. The signal
passes through a low-pass CR filter, and provides a TX and
X1
TCXO
SP out tone, and is then applied to the audio processor
(IC301). The signal is mixed with the audio signal and goes
to the VCO.
TX deviation is adjusted by the CPU.
(3) MSK (Fleet Sync)
Fleet Sync utilizes 1200bps and 2400bps MSK signal is
output from pin 6 of IC301. And is routed to the VCO.
When encoding MSK, the microphone input signal is muted.
5. Power Supply
There are four 5V power supplies for the microprocessor:
5M,5C,5R, and 5T. 5M for microprocessor is always output
while the power is on. 5M is always output, but turns off when
the power is turned off to prevent malfunction of the
microprocessor.
AN
5C is a common 5V and is output when SAVE is not set to
OFF.
LPF
5R is 5V for reception and output during reception.
5T is 5V for transmission and output during transmission.
6. Control Circuit
The control circuit consists of a microprocessor (IC405) and
its peripheral circuits. It controls the TX-RX unit. IC405 mainly
performs the following:
(1) Switching between transmission and reception by the
PTT signal input.
(2) Reading system, group, frequency, and program data
from the memory circuit.
(3) Sending frequency program data to the PLL.
(4) Controlling squelch on/off by the DC voltage from the
squelch circuit.
(5) Controlling the audio mute circuit by the decode data input.
(6) Transmitting tone and encode data.
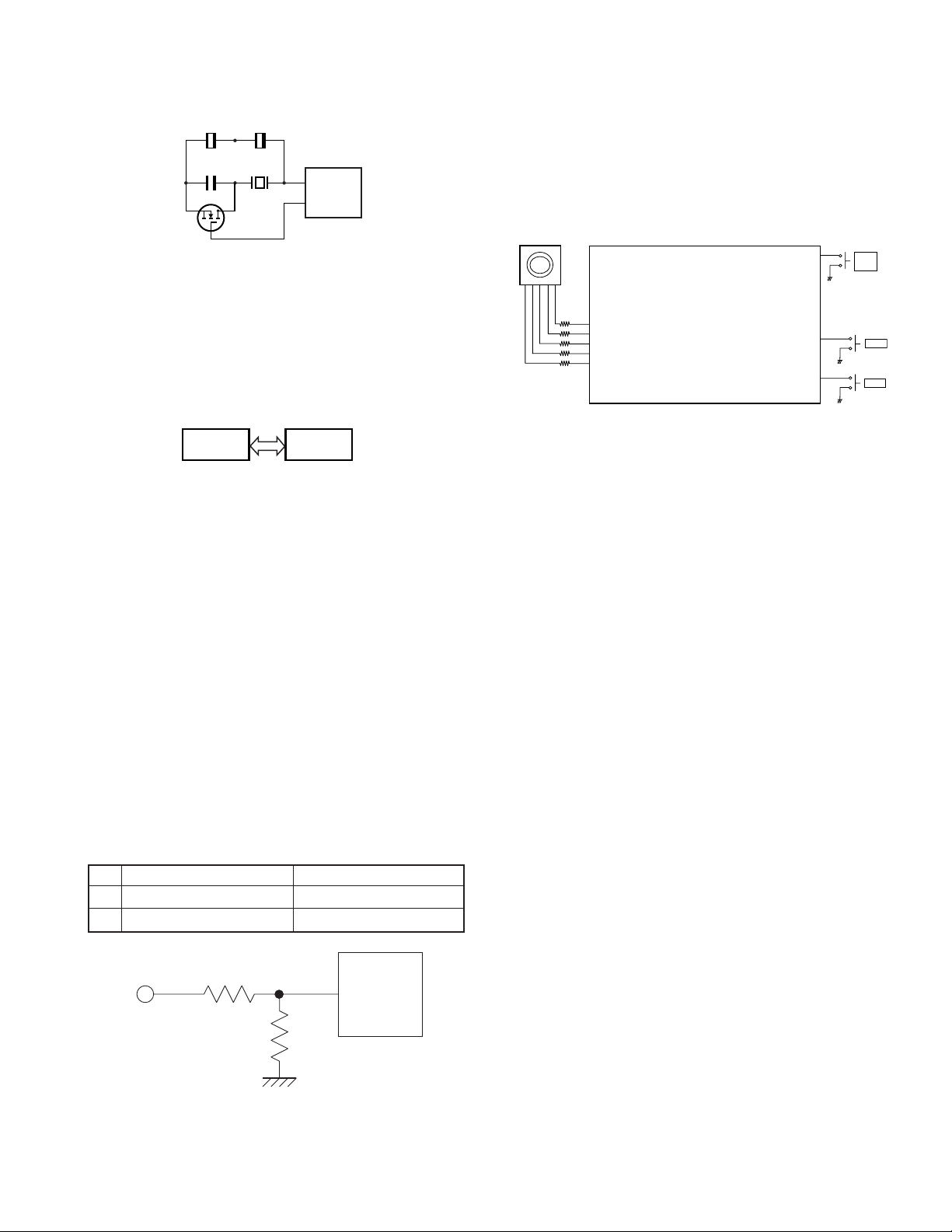
1) Frequency Shift Circuit
The microprocessor (IC405) operates at a clock of
7.3728MHz. This oscillator has a circuit that shifts the
frequency by BEAT SHIFT SW (Q407,Q408).
A beat sound may be able to be evaded from generation if
“Beat Shift” is set to ON when it is generated in the internal
spurious transmission modulated sound of a transceiver.
4) Encode Signalling
(1) QT/DQT
QT,DQT data of the QTTCXO Line is output from pin 28 of
the CPU. The signal passes through a low-pass CR filter
and goes to the TCXO(X1).
10
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
X2
Q407
Q408
Hi: OFF
LOW: ON
Fig. 8 Frequency shift circuit
XOUT
IC405
BSHIFT
TK-2202/2206
7. Control System
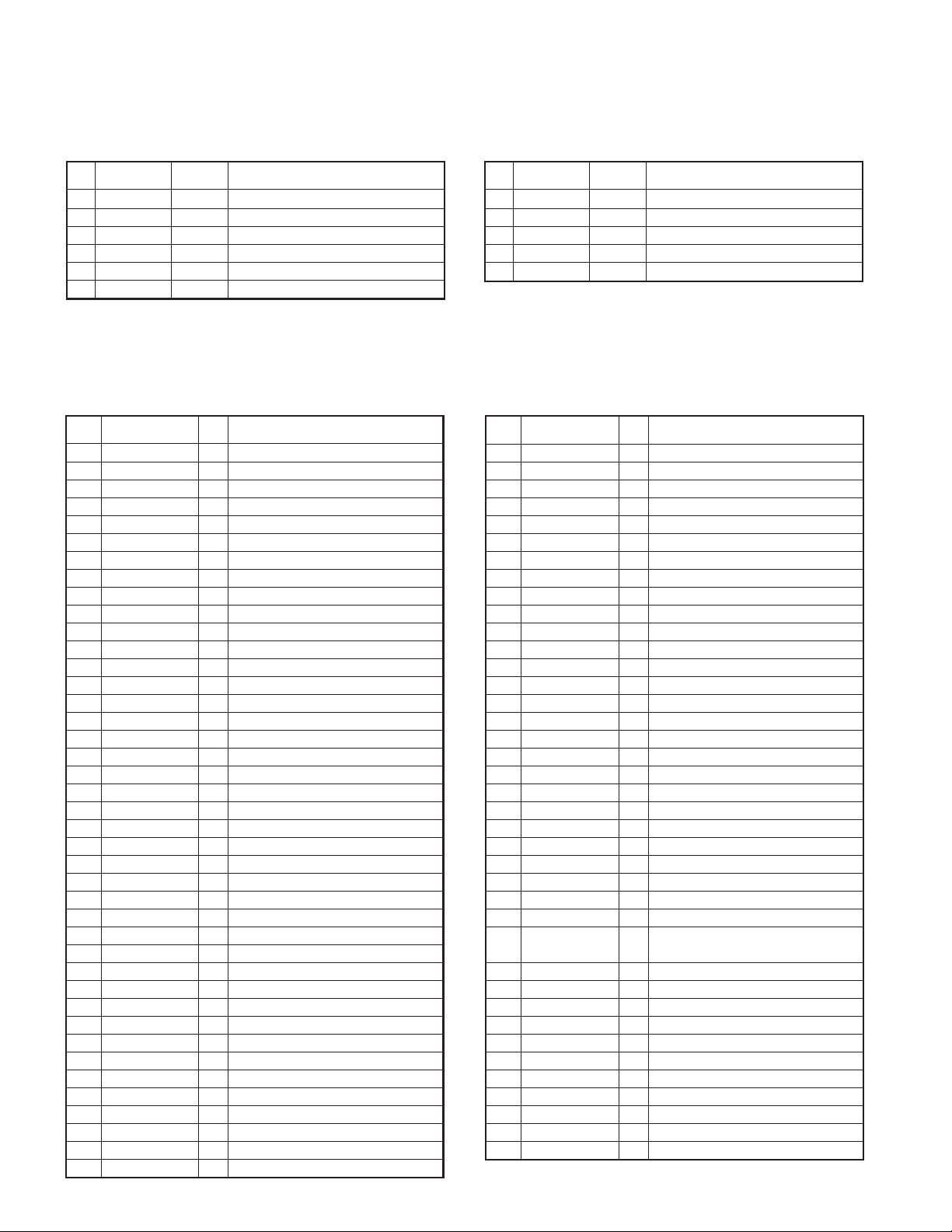
Keys and channel selector circuit.
The signal from the keys and channel selector are directly
input to the microprocessor, as shown in fig. 11.
Channel selector
PTT
27
PTT
SW
2) Memory Circuit
Memory circuit consists of the CPU (IC405) and an EEPROM
(IC406). An EEPROM has a capacity of 64k bits that contains
the transceiver control program for the CPU and data such
as transceiver channels and operating features.
IC405
CPU
IC406
EEPROM
Fig. 9 Memory circuit
3) Low Battery Warning
The battery voltage is checked using by the microprocessor.
The transceiver generates a warning tone when it falls below
the warning voltage shown in the table.
(1)The red LED blinks when the battery voltage falls below
the voltage (1) shown in the table during transmission.
Note:
The transceiver checks the battery voltage during reception
even when, in the FPU, the Battery Warning status function
is set to “On TX” (default setting).
However, the LED does not blink during reception. During
transmission, the LED blinks to generate the warning tone
of a low battery voltage.
50
EN1
49
EN2
48
EN3
47
EN4
46
EN5
IC405
CPU
Fig. 11 Control system
SIDE 1
SIDE 2
74
SW1
75
SW2
(2)The transceiver immediately stops transmission when
the battery voltage falls below the voltage (2) shown in
the table. A message tone beeps while the PTT switch
is released.
Ni-Cd Battery Ni-MH Battery
(1) 6.2[V] 6.2[V]
(2) 5.9[V] 5.9[V]
SB
R404
IC405
88
R406
CPU
Fig. 10 Low battery warning
11
TK-2202/2206
TERMINAL FUNCTION / SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
TERMINAL FUNCTION
■ CN401
Pin
Name
No.
1B IB (Battery Voltage)
2SBOSwitched B
3 SP1 I Audio input
4 SP2 O Audio output
5 GND - GND
6 EN1 I Encoder pulse input
I/O Function
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Microprocessor : 30622MAA-B89GP (TX-RX UNIT : IC405)
■ Pin function
Pin
Port Name I/O Function
No.
1 PCTV O APC/BPF control data output
2 DTMF O DTMF/ Beep output
3NC -NC
4 EEPDAT I/O EEPROM data input/output
5 EEPCLK O EEPROM clock output
6 BYTE - GND
7 GND - GND
8 BSHIFT O Beat shift switch
9NC -NC
10 RESET I CPU reset
11 XOUT O CPU clock (7.3728MHz)
12 VSS - GND
13 XIN I CPU clock (7.3728MHz)
14-15 VCC - +5V
16 INT I Battery voltage monitor input
17 TCLK/DTRDO I Base band IC data input
18 RDF/FD I Base band IC data input
19 SCLK O Base band IC clock output
20 D I/O I/O Base band IC data input / output
21 TDATA/DTRCLK O Base band IC data output
22 DIR O Base band IC data output
23 STD I Base band IC data input
24 QT VCO O QT/DQT output
25 DTRLOADN O Base band IC data output
26 1/2 OSC O 3.6864 MHz (7.3728 MHz/2)
27 PTT I PTT switch input
28 QT TCXO O QT/DQT output
29 TXD O Serial data (FPU/FLASH)
30 RXD I Serial data (FPU/FLASH)
31 GND - GND
32 APCSW O APC switch
33-34 NC - NC
35 DCSW O APC voltage discharge switch
36 TX_W/N O TX Wide/Narrow switch
37 RX_SW O RX VCO switch
38 TX_SW O TX VCO switch
39 GND - GND
40 PLL_UL I PLL unlock detect input
41 PLL_STB O PLL strobe output
42 PLL_DAT O PLL data output
43 PLL_CLK O PLL clock output
12
Pin
No.
10 EN4 I Encoder pulse input
11 EN5 I Encoder pulse input
Pin
No.
53-59 NC - NC
63-64 GND - GND
65-71 NC - NC
78-79 NC - NC
83-87 NC - NC
100 NC - NC
Name
7 EN2 I Encoder pulse input
8 GND - GND
9 EN3 I Encoder pulse input
Port Name I/O Function
44 VCC - +5V
45 RX_W/N O RX Wide/Narrow switch
46 EN5 I Channel selector input
47 EN4 I Channel selector input
48 EN3 I Channel selector input
49 EN2 I Channel selector input
50 EN1 I Channel selector input
51 OPTDET I Headset input detect
52 AF_CONT O Speaker mute
60 VCC - +5V
61 NC - NC
62 VSS - GND
72 LEDTX O Red LED lights control output
73 LEDRX O Green LED lights control output
74 PF1 I SIDE1 key input
75 PF2 I SIDE2 key input
76 SIM1 - GND
77 SIM2 - GND
80 5T_C O 5T control output
81 5R_C O 5R control output
82 5C_C O 5C control output
88 BATT I Battery voltage input
89 RSSI I
90 BUSY I Busy level input
91 VOX I VOX level input
92 QT/DQT_IN I QT/DQT input
93 TH_DET I Thermistor input
94 AVSS - GND
95 NC - NC
96 VREF - +5V
97 AVCC - +5V
98 NC - NC
99 MIC_MUTE O MIC mute
I/O Function
Received Signal Strength
Indicator input
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6870-20)
Ref. No.
IC101 IC Comparator (APC)
IC201 IC FM IF system
IC301 IC Audio processor
IC302 IC AF AMP
IC401 IC Voltage regulator/ 5V
IC402 IC Voltage regulator/ 5V
IC403 IC Voltage detector / Reset
IC404 IC Voltage detector / INT
IC405 IC Microprocessor
IC406 IC EEPROM
Q102 Transistor RF AMP
Q103 FET TX Drive AMP
Q104 Transistor APC switch
Q105 FET APC switch
Q106 FET TX Final AMP
Q107 Transistor APC switch
Q108 FET APC switch
Q109 Transistor APC switch
Q202 Transistor W/N switch / RX
Q203 Transistor IF AMP
Q204 FET Mixer
Q205 FET RF AMP
Q301 Transistor W/N switch / TX
Q302 Transistor MIC AGC
Q303 Transistor DC switch / SP Mute
Q304 Transistor DC switch
Q305 Transistor DC switch / SP Mute
Q306 FET SP Mute switch
Q316 FET SP Mute switch
Q401 Transistor LED switch / Red
Q402 Transistor LED switch / Green
Q403 FET 5T switch
Q404 FET 5R switch
Q405 Transistor 5C switch
Q407 FET Beat Shift switch
Q408 FET Beat Shift switch
Use/Function
IC1 IC PLL system
IC2 IC VCO 1/2 Divider
Q1 Transistor Tripler
Q2 Transistor PLL IC f_in AMP
Q3 FET VCO / RX
Q4 FET VCO / TX
Q5 Transistor DC switch / TX VCO
Q6 FET RF Buffer AMP
Q7 Transistor DC switch / RX VCO
Q8 FET Ripple filter
Q9 Transistor RF AMP
Operation/Condition
TK-2202/2206
Ref. No.
D10
D11 Diode Current steering
D101 Diode TX/RX RF switch
D102 Zener diode APC protect
D103 Diode ANT switch
D104 Diode ANT switch
D105 Diode ANT switch
D106 Diode ANT switch
D202 Diode TX/RX RF switch
D203
D204
D205
D206
D301 Diode Detector
D302 Diode Detector
D303 Diode Isolation
D401 Diode 5V Protection
D402 Diode Reverse Protection
D403 LED LED/ Red
D404 LED LED/ Green
ADDITIONAL PCB
Ref. No.
Q901 FET W/N Switch/ TX
Use/Function
D1 Diode Ripple Filter
Variable
D4
capacitance diode
Variable
D5
capacitance diode
Variable
D7
capacitance diode
Variable
D9
capacitance diode
Variable
capacitance diode
Variable
capacitance diode
Variable
capacitance diode
Variable
capacitance diode
Variable
capacitance diode
Use/Function
Frequency control / TX VCO
Frequency control / RX VCO
Frequency control / TX VCO
Frequency control / RX VCO
Modulator
RF BPF tuning
RF BPF tuning
RF BPF tuning
RF BPF tuning
Operation/Condition
Operation/Condition
13
 Loading...
Loading...