Page 1

I
l
Test Equipment Depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176 - TestEquipmentDepot.com
nstruction Manua
Models 7015-S and 7015-C
40-Channel Solid-State Multiplexer Cards
Contains Operating and Servicing Information
7015-901-01 Rev. A / 6-93
Page 2

WARRANTY
Keithley Instruments, Inc. w
arrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of 1 year from
date of shipment.
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables, rechargeable batteries, diskettes, and documentation.
During the warranty period, we will, at our option, either repair or replace any product that proves to be defective.
To exercise this warranty, write or call your local Keithley representative, or contact Keithley headquarters in Cleveland, Ohio. You
will be given prompt assistance and return instructions. Send the product, transportation prepaid, to the indicated service facility.
Repairs will be made and the product returned, transportation prepaid. Repaired or replaced products are warranted for the balance
of the original warranty period, or at least 90 days.
LIMITATION OF W
This warranty does not apply to defects resulting from product modification without Keithle
ARRANTY
y’s express written consent, or misuse
of any product or part. This warranty also does not apply to fuses, software, non-rechargeable batteries, damage from battery leakage, or problems arising from normal wear or failure to follow instructions.
THIS WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR USE. THE REMEDIES PROVIDED HEREIN
ARE BUYER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES.
NEITHER KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC. NOR ANY OF ITS EMPLOYEES SHALL BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF ITS INSTRUMENTS AND SOFTWARE EVEN IF KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC., HAS BEEN ADVISED IN ADVANCE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. SUCH EXCLUDED DAMAGES SHALL INCLUDE, BUT ARE NOT LIMITED TO: COSTS
OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION, LOSSES SUSTAINED AS THE RESULT OF INJURY TO ANY PERSON, OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY.
CHINA: Keithley Instruments China • Y
FRANCE: Keithley Instruments SARL • BP 60 • 3 Allée des Garays • 91122 Palaiseau Cédex • 33-1-60-11-51-55 • Fax: 33-1-60-11-77-26
GERMANY: Keithley Instruments GmbH • Landsberger Strasse 65 • D-82110 Germering, Munich • 49-89-8493070 • Fax: 49-89-84930759
GREAT BRITAIN: Keithley Instruments, Ltd. • The Minster • 58 Portman Road • Reading, Berkshire, England RG3 1EA • 44-1189-596469 • Fax: 44-1189-575666
ITALY: Keithley Instruments SRL • Viale S. Gimignano 38 • 20146 Milano • 39-2-48303008 • Fax: 39-2-48302274
NETHERLANDS: Keithley Instruments BV • Avelingen West 49 • 4202 MS Gorinchem • 31-(0)183-635333 • Fax: 31-(0)183-630821
SWITZERLAND: Keithley Instruments SA • Kriesbachstrasse 4 • 8600 Dübendorf • 41-1-8219444 • Fax: 41-1-8203081
TAIWAN: Keithley Instruments Taiwan • 1FL., 85 Po Ai Street • Hsinchu, Taiwan • 886-3-572-9077 • Fax: 886-3-572-9031
uan Chen Xin Building, Room 705 • 12 Yumin Road, Dewai, Madian • Beijing 100029 • 8610-62022886 • Fax: 8610-62022892
1/99
Page 3

Models 7015-S and 7015-C Instruction Manual
©1993, Keithley Instruments, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Cleveland, Ohio, U. S. A.
First Printing June 1993
Document Number: 7015-901-01 Rev. A
Page 4

Manual Print History
The print history shown below lists the printing dates of all Revisions and Addenda created for this manual. The
Revision Level letter increases alphabetically as the manual undergoes subsequent updates. Addenda, which are
released between Revisions, contain important change information that the user should incorporate immediately
into the manual. Addenda are numbered sequentially. When a new Revision is created, all Addenda associated
with the previous Revision of the manual are incorporated into the new Revision of the manual. Each new Revision includes a revised copy of this print history page.
Revision A (Document Number 7015-901-01) ...................................................................................June 1993
All Keithley product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Page 5

Safety Precautions
The following safety precautions should be observed before using
this product and any associated instrumentation. Although some instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations where hazardous conditions
may be present.
This product is intended for use by qualified personnel who recognize shock hazards and are familiar with the safety precautions required to avoid possible injury. Read the operating information
carefully before using the product.
The types of product users are:
Responsible body is the individual or group responsible for the use
and maintenance of equipment, for ensuring that the equipment is
operated within its specifications and operating limits, and for ensuring that operators are adequately trained.
Operators use the product for its intended function. They must be
trained in electrical safety procedures and proper use of the instrument. They must be protected from electric shock and contact with
hazardous live circuits.
Maintenance personnel perform routine procedures on the product
to keep it operating, for example, setting the line voltage or replacing consumable materials. Maintenance procedures are described in
the manual. The procedures explicitly state if the operator may perform them. Otherwise, they should be performed only by service
personnel.
Service personnel are trained to work on live circuits, and perform
safe installations and repairs of products. Only properly trained service personnel may perform installation and service procedures.
Users of this product must be protected from electric shock at all
times. The responsible body must ensure that users are prevented
access and/or insulated from every connection point. In some cases,
connections must be exposed to potential human contact. Product
users in these circumstances must be trained to protect themselves
from the risk of electric shock. If the circuit is capable of operating
at or above 1000 volts, no conductive part of the circuit may be
exposed.
As described in the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) Standard IEC 664, digital multimeter measuring circuits
(e.g., Keithley Models 175A, 199, 2000, 2001, 2002, and 2010) are
Installation Category II. All other instruments’ signal terminals are
Installation Category I and must not be connected to mains.
Do not connect switching cards directly to unlimited power circuits.
They are intended to be used with impedance limited sources.
NEVER connect switching cards directly to AC mains. When connecting sources to switching cards, install protective devices to limit fault current and voltage to the card.
Before operating an instrument, make sure the line cord is connected to a properly grounded power receptacle. Inspect the connecting
cables, test leads, and jumpers for possible wear, cracks, or breaks
before each use.
For maximum safety, do not touch the product, test cables, or any
other instruments while power is applied to the circuit under test.
ALWAYS remove power from the entire test system and discharge
any capacitors before: connecting or disconnecting cables or jumpers, installing or removing switching cards, or making internal
changes, such as installing or removing jumpers.
Exercise extreme caution when a shock hazard is present. Lethal
voltage may be present on cable connector jacks or test fixtures.The
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) states that a shock
hazard exists when voltage levels greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V
peak, or 60VDC are present. A good safety practice is to expect
that hazardous voltage is present in any unknown circuit before
measuring.
Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to the
common side of the circuit under test or power line (earth) ground.
Always make measurements with dry hands while standing on a
dry, insulated surface capable of withstanding the voltage being
measured.
Page 6

The instrument and accessories must be used in accordance with its
specifications and operating instructions or the safety of the equipment may be impaired.
Do not exceed the maximum signal levels of the instruments and accessories, as defined in the specifications and operating information, and as shown on the instrument or test fixture panels, or
switching card.
When fuses are used in a product, replace with same type and rating
for continued protection against fire hazard
Chassis connections must only be used as shield connections for
measuring circuits, NOT as safety earth ground connections.
If you are using a test fixture, keep the lid closed while power is applied to the device under test. Safe operation requires the use of a
lid interlock.
If a screw is present, connect it to safety earth ground using the
wire recommended in the user documentation.
!
The symbol on an instrument indicates that the user should refer to the operating instructions located in the manual.
The symbol on an instrument shows that it can source or measure 1000 volts or more, including the combined effect of normal
and common mode voltages. Use standard safety precautions to
avoid personal contact with these voltages.
The WARNING heading in a manual explains dangers that might
result in personal injury or death. Always read the associated information very carefully before performing the indicated procedure.
The CAUTION heading in a manual explains hazards that could
damage the instrument. Such damage may invalidate the warranty.
Instrumentation and accessories shall not be connected to humans.
Before performing any maintenance, disconnect the line cord and
all test cables.
To maintain protection from electric shock and fire, replacement
components in mains circuits, including the power transformer, test
leads, and input jacks, must be purchased from Keithley Instruments. Standard fuses, with applicable national safety approvals,
may be used if the rating and type are the same. Other components
that are not safety related may be purchased from other suppliers as
long as they are equivalent to the original component. (Note that selected parts should be purchased only through Keithley Instruments
to maintain accuracy and functionality of the product.) If you are
unsure about the applicability of a replacement component, call a
Keithley Instruments office for information
To clean an instrument, use a damp cloth or mild, water based
cleaner. Clean the exterior of the instrument only. Do not apply
cleaner directly to the instrument or allow liquids to enter or spill
on the instrument. Products that consist of a circuit board with no
case or chassis (e.g., data acquisition board for installation into a
computer) should never require cleaning if handled according to instructions. If the board becomes contaminated and operation is affected, the board should be returned to the factory for proper
cleaning/servicing.
Rev. 2/99
Page 7

Model 7015-C, 7015-S
40-Channel Solid State Multiplexer Cards
MULTIPLEX CONFIGURATION: Four independent 1×10 2-pole
multiplex banks or two independent 1×10 4-pole multiplex banks.
Adjacent banks can be connected together. Jumpers can be removed to
isolate any bank from the backplane.
CONTACT CONFIGURATION: 2-pole Form A (Hi, Lo).
CONNECTOR TYPE:
7015-C: 96-pin male DIN connector.
7015-S: Screw terminal, #16AWG maximum wire size, with .092 inch
O.D. 28 conductors per card maximum. #22AWG typical wire size
with .062 inch O.D. 88 conductors per card maximum.
MAXIMUM SIGNAL LEVEL: 175V peak between any two pins, 34mA
resistive load, 0.3VA max., 1 × 106V•Hz max.
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE: 175V peak, any pin to chassis.
CONTACT TYPE: Solid state switch.
CHANNEL RESISTANCE (per conductor): < 210Ω.
Bank A
H I
Channel 1
LO
Channels 2-9
H I
Channel 10
LO
CONTACT POTENTIAL:
7015-C:<5µV per channel contact pair.
7015-S: <4µV per channel contact pair.
OFFSET CURRENT: < 1nA.
ACTUATION TIME: <500µs.
ISOLATION:
Bank: >109Ω, <25 pF.
Channel to Channel: >109Ω, <50 pF.
Differential: Configured as 1×10: >109Ω, <100pF.
Common Mode: Configured as 1×10: >109Ω, <375pF.
INSERTION LOSS (50Ω Source, 1MΩ Load): <0.1dB below 250kHz,
<3dB below 500kHz.
ENVIRONMENT: Operating: 0° to 50°C, up to 35°C at 80% RH.
Configured as 1×40: >109Ω, <200pF.
Configured as 1×40: >109Ω, <1100pF.
Storage: –25°C to 65°C.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
H I
Output
LO
J
J
H I
Backplane
LO
Banks B-C
Bank D
H I
LO
Channels 2-9
H I
Channel 10
LO
Channel 1
J
J
JJ
H I
Output
LO
J
J
H I
Backplane
LO
Page 8

Table of Contents
1 General Information
1.1 Introduction.......................................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Features ................................................................................................................................................................ 1-1
1.3 Warranty information........................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.4 Manual addenda ................................................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.5 Safety symbols and terms .................................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.6 Specifications ....................................................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.7 Unpacking and inspection .................................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.7.1 Inspection for damage.................................................................................................................................. 1-2
1.7.2 Shipment contents ........................................................................................................................................ 1-2
1.7.3 Instruction manual........................................................................................................................................ 1-2
1.7.4 Repacking for shipment ...............................................................................................................................1-3
1.8 Optional accessories............................................................................................................................................. 1-3
2 Mutliplexing Basics
2.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Basic multiplexer configurations .........................................................................................................................2-1
2.2.1 Multiplexer bank-to-bank jumpers............................................................................................................... 2-2
2.2.2 Backplane jumpers....................................................................................................................................... 2-5
2.3 Typical multiplexer switching schemes ............................................................................................................... 2-6
2.3.1 Single-ended switching ................................................................................................................................ 2-6
2.3.2 Differential switching ..................................................................................................................................2-6
2.3.3 Sensing ......................................................................................................................................................... 2-6
2.4 Multiplexer expansion.......................................................................................................................................... 2-8
2.4.1 Multi-card switching systems ......................................................................................................................2-8
2.4.2 Mainframe multiplexer expansion ...............................................................................................................2-9
i
Page 9

3 Card Connections & Installation
3.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................................3-1
3.2 Handling precautions............................................................................................................................................3-1
3.3 Connections ..........................................................................................................................................................3-1
3.3.1 Bank-to-bank jumpers ..................................................................................................................................3-2
3.3.2 Backplane jumpers .......................................................................................................................................3-3
3.3.3 Screw terminal connector card .....................................................................................................................3-4
3.3.4 Multi-pin (mass termination) connector card ...............................................................................................3-6
3.4 Typical connection schemes...............................................................................................................................3-10
3.4.1 Single card system......................................................................................................................................3-10
3.4.2 Two-card system ........................................................................................................................................3-13
3.4.3 Multiple-card systems ................................................................................................................................3-13
3.4.4 Two-mainframe system ..............................................................................................................................3-13
3.5 Model 7015 installation and removal .................................................................................................................3-18
4 Operation
4.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................................4-1
4.2 Maximum signal levels.........................................................................................................................................4-1
4.3 Mainframe control of multiplexer card ................................................................................................................4-1
4.3.1 Channel assignments ....................................................................................................................................4-1
4.3.2 Front panel control .......................................................................................................................................4-3
4.3.3 IEEE-488 bus operation ...............................................................................................................................4-4
4.4 Multiplexer applications.......................................................................................................................................4-5
4.4.1 High-speed scanning ....................................................................................................................................4-5
4.4.2 Resistor testing .............................................................................................................................................4-7
4.4.4 Testing with matrix cards ...........................................................................................................................4-10
4.4.3 Transistor current gain testing ....................................................................................................................4-10
4.5 Measurement considerations ..............................................................................................................................4-12
4.5.1 Thermoelectric potentials ...........................................................................................................................4-12
4.5.2 Channel resistance ......................................................................................................................................4-13
4.5.3 Path isolation ..............................................................................................................................................4-14
4.5.4 Magnetic fields ...........................................................................................................................................4-15
4.5.5 Radio frequency interference .....................................................................................................................4-15
4.5.6 Ground loops ..............................................................................................................................................4-15
4.5.7 Keeping connectors clean...........................................................................................................................4-16
4.5.8 Scanning speed considerations ...................................................................................................................4-16
5 Service Information
5.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................................5-1
5.2 Handling and cleaning precautions ......................................................................................................................5-1
5.3 Performance verification .....................................................................................................................................5-2
5.3.1 Environmental conditions.............................................................................................................................5-2
5.3.2 Recommended equipment ............................................................................................................................5-2
5.3.3 Multiplexer card connections .......................................................................................................................5-3
5.3.4 Channel resistance tests................................................................................................................................5-3
5.3.5 Offset current tests........................................................................................................................................5-4
5.3.6 Contact potential tests...................................................................................................................................5-6
5.3.7 Bank and channel-to-channel isolation tests ................................................................................................5-7
5.3.8 Differential and common-mode isolation tests...........................................................................................5-11
ii
Page 10

5.4 Special handling of static-sensitive devices....................................................................................................... 5-13
5.5 Principles of operation .......................................................................................................................................5-13
5.5.1 Block diagram ............................................................................................................................................ 5-13
5.5.2 ID data circuits ........................................................................................................................................... 5-14
5.5.3 Relay control .............................................................................................................................................. 5-15
5.5.4 Power-on safeguard.................................................................................................................................... 5-15
5.6 Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................................. 5-16
5.6.1 Troubleshooting equipment .......................................................................................................................5-16
5.6.2 Troubleshooting access .............................................................................................................................. 5-16
5.6.3 Troubleshooting Procedure ........................................................................................................................ 5-16
6 Replaceable Parts
6.1 Introduction.......................................................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.2 Parts lists .............................................................................................................................................................. 6-1
6.3 Ordering information ........................................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.4 Factory service ..................................................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.5 Component layouts and schematic diagrams .......................................................................................................6-1
iii
Page 11

×
×
×
List of Illustrations
2 Multiplexing Basics
Figure 2-1 Model 7015 simplified schematic .............................................................................................................. 2-2
Figure 2-2 Four 1
Figure 2-3 Two 1
Figure 2-4 One 1
Figure 2-5 Model 7001/7002 analog backplane .......................................................................................................... 2-5
Figure 2-6 Bank connections to backplane .................................................................................................................. 2-6
Figure 2-8 Differential switching example .................................................................................................................. 2-7
Figure 2-9 Sensing example......................................................................................................................................... 2-7
Figure 2-7 Single-ended switching example................................................................................................................ 2-7
Figure 2-10 Two separate multiplexer systems ............................................................................................................. 2-8
Figure 2-11 Multiplexer input expansion example ........................................................................................................ 2-9
Figure 2-12 Mixed card type example ......................................................................................................................... 2-10
10 multiplexer configuration (jumpers not installed) .................................................................. 2-3
20 multiplexer configuration (jumpers installed) ........................................................................ 2-3
40 multiplexer configuration (jumpers installed) ......................................................................... 2-4
3 Card Connections & Installation
Figure 3-1 Bank-to-bank jumper locations .................................................................................................................. 3-2
Figure 3-2 Bank-to-bank jumper terminal identification............................................................................................. 3-2
Figure 3-3 Bank-to-bank jumper installation............................................................................................................... 3-3
Figure 3-4 Backplane jumpers ..................................................................................................................................... 3-4
Figure 3-5 Model 7015 screw terminal connector card ............................................................................................... 3-4
Figure 3-6 Typical screw terminal connections........................................................................................................... 3-5
Figure 3-7 Cable clamp for screw terminal connector card......................................................................................... 3-5
Figure 3-8 Typical round cable connection techniques ............................................................................................... 3-8
Figure 3-9 Model 7011-MTR connector pinout .......................................................................................................... 3-9
Figure 3-10 Model 7011-KIT-R (with/cable) assembly ................................................................................................ 3-9
Figure 3-11 Single-card system example (multi-pin connector card).......................................................................... 3-11
Figure 3-12 Single card system example (screw terminal connector card) ................................................................. 3-12
Figure 3-13 Two-card system example (multi-pin connector card) ............................................................................ 3-14
Figure 3-14 Two-card system example (screw terminal connector card).................................................................... 3-15
Figure 3-15 Two-mainframe system example (multi-pin connector card) .................................................................. 3-16
Figure 3-16 Two-mainframe system example (screw terminal connector card) ......................................................... 3-17
Figure 3-17 Model 7015 card installation in Model 7001 ........................................................................................... 3-19
Figure 3-18 Model 7015 card installation in Model 7002 ........................................................................................... 3-19
v
Page 12

4 Operation
Figure 4-1 Channel status display ................................................................................................................................ 4-2
Figure 4-2 Display organization for multiplexer channels........................................................................................... 4-2
Figure 4-3 Model 7015 programming channel assignments ........................................................................................ 4-3
Figure 4-4 High-speed scanning connections............................................................................................................... 4-6
Figure 4-5 Four-wire resistance testing........................................................................................................................ 4-8
Figure 4-6 Low-resistance testing ................................................................................................................................ 4-9
Figure 4-7 Configuration for current gain test ........................................................................................................... 4-11
Figure 4-8 Connecting multiplexer and matrix cards together................................................................................... 4-12
Figure 4-9 Thermoelectric generation ........................................................................................................................ 4-13
Figure 4-10 Channel resistance .................................................................................................................................... 4-13
Figure 4-11 Path isolation resistance............................................................................................................................ 4-14
Figure 4-12 Voltage attenuation by path isolation resistance ...................................................................................... 4-14
Figure 4-13 Power line ground loops ........................................................................................................................... 4-15
Figure 4-14 Eliminating ground loops ......................................................................................................................... 4-16
5 Service Information
Figure 5-1 Path resistance test connections.................................................................................................................. 5-4
Figure 5-2 Differential and common mode offset current test connections................................................................. 5-5
Figure 5-3 Contact potential test connections .............................................................................................................. 5-6
Figure 5-4 Bank isolation test connections .................................................................................................................. 5-7
Figure 5-5 Channel-to-channel isolation test connections ........................................................................................... 5-9
Figure 5-6 Differential isolation test connections ...................................................................................................... 5-11
Figure 5-7 Common-mode isolation test connections................................................................................................ 5-13
Figure 5-8 Model 7015 block diagram....................................................................................................................... 5-14
Figure 5-9 Start and stop sequences ........................................................................................................................... 5-15
Figure 5-10 Transmit and acknowledge sequence ....................................................................................................... 5-15
vi
Page 13

List of Tables
3 Card Connections & Installation
Table 3-2 Bank-to-bank jumpers (on connector card)................................................................................................. 3-2
Table 3-3 Backplane jumpers (on relay card).............................................................................................................. 3-3
Table 3-6 Multipin card terminal identification ..........................................................................................................3-6
Table 3-7 Mass termination accessories ...................................................................................................................... 3-7
4 Operation
Table 4-7 Paired Channels in 4-pole Operation ..........................................................................................................4-7
5 Service Information
Table 5-2 Verification equipment................................................................................................................................ 5-2
Table 5-8 Bank isolation test summary ....................................................................................................................... 5-8
Table 5-9 Channel-to-channel isolation test summary ................................................................................................ 5-9
Table 5-12 Differential and common-mode isolation testing...................................................................................... 5-12
Table 5-16 Recommended troubleshooting equipment............................................................................................... 5-16
Table 5-17 Troubleshooting procedure .......................................................................................................................5-17
vii
Page 14

×
1
General Information
1.1 Introduction
This section contains general information about the Model
7015 40-Channel Solid-State Multiplexer Card.
There are two basic versions of this multiplexer card; the
Model 7015-S and the Model 7015-C. The Model 7015-S assembly consists of a screw terminal connector card and a relay card. External test circuits are wired directly to the screw
terminals of the connector card. Also available from Keithley
is the Model 7015-ST, which is an extra screw terminal connector card. With an extra connector card, you can wire a
second test system without disturbing the wiring configura
tion of the first test system.
The Model 7015-C assembly consists of a multi-pin (mass
termination) connector card and the relay card. External test
circuit connections to the multiplexer are made via the 96pin male DIN connector on the connector card. Keithley offers a variety of optional accessories that can be used to make
connections to the connector card (see paragraph 1.8).
The rest of Section 1 is arranged in the following manner:
1.7 Unpacking and inspection
1.8 Repacking for shipment
1.9 Optional accessories
1.2 Features
The Model 7015 is a solid-state, two-pole, quad, 1
tiplexer card. Some of the key features include:
• Solid-state relays for fast switching, indefinite “contact” life, and quiet operation.
• Low contact potential and offset current for minimal effects on low-level signals.
• The connector board detaches from the relay board allowing easy access to the screw terminals (Model 7015S) and jumpers.
• Easy jumper configuration of one, two, three or four
multiplexer banks.
• Backplane jumpers. Cutting jumpers disconnects multiplexer bank outputs from the Model 7001 or Model
7002 analog backplane.
10 mul-
1.2 Features
1.3 Warranty information
1.4 Manual addenda
1.5 Safety symbols and terms
1.6 Specifications
1.3 Warranty information
Warranty information is located on the inside front cover of
this instruction manual. Should your Model 7015 require
warranty service, contact the Keithley representative or authorized repair facility in your area for further information.
1-1
Page 15

General Information
×
When returning the multiplexer card for repair, be sure to fil
out and include the service form at the back of this manual in
order to provide the repair facility with the necessary information.
1.4 Manual addenda
Any improvements or changes concerning the multiplexer
card or manual will be explained in an addendum included
with the card. Addenda are provided in a page replacement
format. Simply replace the obsolete pages with the new pages.
1.5 Safety symbols and terms
The following symbols and terms may be found on an instrument or used in this manual.
!
The symbol on an instrument indicates that the user
should refer to the operating instructions located in the instruction manual.
1.7 Unpacking and inspection
1.7.1 Inspection for damage
The Model 7015 is packaged in a re-sealable, anti-static bag
to protect it from damage due to static discharge and from
contamination that could degrade its performance. Before removing the card from the bag, observe the following precautions on handling.
Handling Precautions:
1. Always grasp the card by the side edges and shields. Do
not touch the board surfaces or components.
2. When not installed in a Model 7001/7002 mainframe,
keep the card in the anti-static bag and store it in the original packing carton.
After removing the card from its anti-static bag, inspect it for
any obvious signs of physical damage. Report any such damage to the shipping agent immediately.
1.7.2 Shipment contents
The WARNING heading used in this manual explains dangers that might result in personal injury or death. Always
read the associated information very carefully before performing the indicated procedure.
The CAUTION heading used in this manual explains hazards that could damage the multiplexer card. Such damage
may invalidate the warranty.
1.6 Specifications
Model 7015 specifications are found at the front of this manual. These specifications are exclusive of the multiplexer
mainframe specifications
The following items are included with every Model 7015 order:
• Model 7015 Quad 1
• Model 7015 Instruction Manual
• Additional accessories as ordered
10 Multiplexer Card
1.7.3 Instruction manual
If an additional instruction manual is required, order the
manual package, Keithley part number 7015-901-00. The
manual package includes an instruction manual and any pertinent addenda.
1-2
Page 16

General Information
1.7.4 Repacking for shipment
Should it become necessary to return the Model 7015 for repair, carefully pack the unit in its original packing carton or
the equivalent, and include the following information:
• Advise as to the warranty status of the multiplexer card.
• Write ATTENTION REPAIR DEPARTMENT on the
shipping label.
• Fill out and include the service form located at the back
of this manual.
1.8 Optional accessories
The following accessories are available for use with the
Model 7015:
Model 7015-ST This screw terminal connector card is
identical to the one provided with the Model 7015-S assembly. An extra screw terminal connector card allows you to
wire a second test system without disturbing the wiring configuration of the first connector card
Model 7011-KIT-R This connection kit includes a 96-pin
female DIN connector that will mate directly to the connector on the Model 7015-C or to a standard 96-pin male DIN
bulkhead connector (see Model 7011-MTR). This connector
uses solder cups for connections to external circuitry. It includes an adapter for a round cable and the housing.
Model 7011-MTC-2 This 2-meter round cable assembly
is terminated with a 96-pin female DIN connector on each
end. It will mate directly to the connector on the Model
7015-C and to a standard 96-pin male DIN bulkhead connector (see Model 7011-MTR).
Model 7011-MTR This 96-pin male DIN bulkhead con-
nector uses solder cups for connections to external circuitry.
It will mate to the Model 7011-KIT-R connector, and Model
7011-MTC-2 cable assembly.
1-3
Page 17

×
×
×
2
Multiplexing Basics
2.1 Introduction
This section covers the basics for multiplex switching and is
arranged as follows:
2.2 Basic multiplex configurations: Covers the basic
multiplex configurations: quad 1
20 configuration and single 1
nificance of the backplane jumpers is also c vered here.
2.3 Typical multiplex switching schemes: Explains
some of the basic ways a multiplexer can be used to switch
source or measure applications. Covers single-ended switching, differential (floating) switching and sensing.
10 configuration, dual 1
40 configuration. The sig-
2.4 System expansion: Discusses the various configura
tions that are possible by using multiple cards.
2.2 Basic multiplexer configurations
A simplified schematic of the Model 7015 multiplexer card
is shown in Figure 2-1. It is organized as four
plexer banks. Each bank has 10 inputs and one output. Twopole switching is provided for each multiplexer input, with
HI and LO switched. Two or more banks can be jumpered together to expand multiplexer inputs, and backplane jumpers
provide bank connections to a second card installed in a
Model 7001 or Model 7002 mainframe.
1 ×
10 multi-
2-1
Page 18

Multiplexing Basics
×
×
×
×
×
×
7015
110
Inputs
Bank A
Bank B
Outputs
Bank C
Bank D
110
110
110
HI
LO
(Solid State Switching)
Figure 2-1
Model 7015 simplified s hematic
Input (1 of 40)
HI
Bank
Switching Topology
for all Channels
LO
HI
LO
HI
LO
Bank to Bank
Note : Factory Configuration shown
C
Jumpers
D
Jumpers
HI
LO
Backplane Jumpers
(to 7001/7002 Analog
Backplane)
HI
LO
2.2.1 Multiplexer bank-to-bank jumpers
Jumpers are installed on the connector card to connect multiplexer banks together to form a 1
jumper set connects two adjacent banks together. These
jumper sets are included with the Model 7015.
The bank-to-bank jumpers allow you to configure the multiplexer card in a variety of ways. Typical multiplexer config
urations include:
40 multiplexer. Each
• Four 1
10 multiplexers; no jumpers installed (Figure
2-2).
•Two 1
20 multiplexers; Bank A jumpered to Bank B,
Bank C jumpered to Bank D (Figure 2-3).
• One 1
40 multiplexer; all bank-to-bank jumpers in-
stalled (Figure 2-4).
Other combinations are possible, including multiplexers of
various sizes (in multiples of 10 channels). For example, you
could install jumpers to configure the card as one 1
one 1
10 multiplexer.
30 and
Refer to Section 3 for information on installing bank-to-bank
jumpers.
2-2
Page 19

F
Multiplexing Basics
Inputs
1
Bank A
10
2
2
2
Output A
1
Bank B
10
1
Bank C
10
1
Bank D
10
2
2
2
2
2
2
Figure 2-2
Four 1 × 10 multiplexer configu ation (jumpers not installed)
Inputs
1
Bank A
10
1
Bank B
10
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Output B
Output C
Output D
Output A
2
Jumpers
1
Bank C
10
1
Bank D
10
2
2
2
2
2
2
Output C
2
Jumpers
igure 2-3
Two 1 × 20 multiplexer configu ation (jumpers installed)
2-3
Page 20

Multiplexing Basics
F
Bank A
Bank B
Bank C
Bank D
Inputs
1
10
1
10
1
10
1
10
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Output A
2
Jumpers
2
Jumpers
2
Jumpers
igure 2-4
One 1 × 40 multiplexer configu ation (jumpers installed)
2-4
Page 21

Multiplexing Basics
2.2.2 Backplane jumpers
There are four pairs of backplane jumpers located on the relay card. With the jumpers installed, the banks of the multiplexer card are connected to the analog backplane of the
Model 7001/7002 allowing expansion with a second card installed in the mainframe. With the jumpers removed (cut),
the multiplexer card is isolated from another card installed in
the same mainframe.
Model 7001/7002
Card 1 Card 2
H
L
G
H
Row 1 or Bank A
Row 2 or Bank B
The three-pole analog backplane of the Model 7001/7002
mainframe is shown in Figure 2-5. Through this analog backplane, the banks of a Model 7015 multiplexer card, installed
in one slot, can be connected to the banks (or rows) of a compatible card installed in another slot of the mainframe.
Note that the Model 7002 also has backplane jumpers, which
can be used to isolate cards into two groups of fi e.
Analog
Backplane
H
L
G
H
Figure 2-5
Model 7001/7002 analog backplane
H = High
L = Low
G = Guard
L
G
H
L
G
H
L
G
Row 3 or Bank C
Row 4 or Bank D
L
G
H
L
G
H
L
G
Row = Matrix Card (7012)
Bank = MUX Card (7015)
2-5
Page 22

Multiplexing Basics
Ω
Ω
Figure 2-6 shows how each bank of the Model 7015 is connected to the backplane. Notice that since the Model 7015 is
a two-pole card, there is no connection made to the Guard
terminal of the backplane. The Model 7015 is shipped from
the factory with the backplane jumpers installed.
7001/7002
Analog
Backplane
H
L
G
H
L
H = High
L = Low
G = Guard
7015
Bank
(1 of 4)
Backplane
Jumpers
Figure 2-6
Bank connections to backplane
Removing (cutting) the backplane jumpers isolates the card
from the backplane, and subsequently, any card installed in
an other slot. For information on removing the jumpers, refer
to Section 3.
NOTE
The Model 7001/7002 does not provide an
analog backplane for the non-701X series
cards. As a result, any of these cards installed in one slot in the mainframe is electrically isolated from any card(s) installed
in an other slot. The only way to connect a
Model 7015 to one of these cards is to wire
them together using the connector blocks
or terminals.
2.3 Typical multiplexer switching schemes
The following paragraphs describe some basic switching
schemes that are possible with a two-pole switching multiplexer. These switching schemes include some various
shielding configurations to help minimize noise pickup in
sensitive measurement applications. These shields are shown
connected to chassis ground. For some test configurations
shielding may prove to be more effective with shields connected to circuit common or LO. Chassis ground is accessible at the rear panel of the Model 7001/7002.
2.3.1 Single-ended switching
In the single-ended switching configuration, the source or
measure instrument is connected to the DUT through a single pathway, as shown in Figure 2-7. The instrument is connected to the output of one of the banks, and the DUT is
shown connected to one of the inputs for that bank.
2.3.2 Differential switching
The differential or floating switching configuration is shown
in Figure 2-8. The advantage of using this configuration is
that the terminals of the source or measure instrument are not
confined to the same pathway. Each terminal of the instrument can be switched to any available input in the test system.
2.3.3 Sensing
Figure 2-9 shows how the multiplexer card can be configure
to use instruments that have sensing capability. The main advantage of using sensing is to cancel the effects of switch
card path resistance (<210
tance of external cabling. Whenever path resistance is a consideration, sensing should be used.
, <130
typical) and the resis-
2-6
Page 23

Multiplexing Basics
HI
LO
Source or
Measure
Figure 2-7
Single-ended switching example
LO
Bank A-D Input 1-10
H
Out In
L
7015
Bank A, B Input 1-10
HI
Out In
Out In
H
L
H
L
Optional
Shield
DUT
DUT
Source or
Measure
Figure 2-8
Differential switching example
Source HI
Sense HI
Sense LO
Source LO
Source or
Measure
Figure 2-9
Sensing example
Bank C, D Input 1-10
Bank A, B
7015
H
Out In
L
H
Out In
L
Input 1-10
7015
Bank C, D Input 1-10
DUT
2-7
Page 24

Multiplexing Basics
×
×
×
2.4 Multiplexer expansion
With the use of additional switching cards and mainframes,
larger systems can be configured. Each Model 7001 Switch
System mainframe will accommodate up to two cards, and
the Model 7002 Switch System mainframe can accommodate up to 10 cards.
2.4.1 Multi-card switching systems
Separate switching systems
Multiple single-card systems can be configured by removing
the backplane jumpers from each additional card. All cards
will be controlled by the same mainframe, but they will be
electrically isolated from each other. Figure 2-10 shows an
example using two Model 7015 multiplexer cards.
Multiplexer input expansion
You can double the number of multiplexer inputs by simply
installing two “as shipped” Model 7015s in the Model 7001
mainframe. Similarly, the number of multiplexer inputs can
be increased by a factor of 10 by installing 10, “as shipped”
Model 7015s in a Model 7002. By leaving the backplane
jumpers installed, the banks of the multiplexer card installed
in slot 1 (CARD 1) are automatically connected to the banks
of the multiplexer card installed in slot 2 (CARD 2) through
the analog backplane (and with any remaining cards installed
in a Model 7002).
Figure 2-11 shows an example of input expansion. Each
Model 7015 card is configured as four 1
10 multiplexers.
By connecting the banks together (via Model 7001/7002 analog backplane), the resulting multiplexer system has 20 2pole inputs for each of the four banks. Note that, if all the
bank-to-bank jumpers on any card are installed (as shipped),
the result would be a single 1
80 multiplexer. A total of 10
Model 7015 cards installed in a Model 7002 would yield a
single 1
400 multiplexer with all bank-to-bank jumpers in-
stalled.
NOTE
Connecting any two banks on one card together also connects the corresponding
banks of the backplane together. Thus, the
corresponding banks of other card(s) will
be connected together even if the bank-tobank jumpers on those cards are not installed.
110
Bank A
110
Bank B
110
Bank C
110
Bank D
Four 1x10 Multiplexers
Figure 2-10
Two separate multiplexer systems
Card 1
7015
7001/7002
Backplane
Backplane
Jumpers
Removed
Analog
Card 2
7015
110
110
110
110
Four 1x10 Multiplexers
2-8
Page 25

Card 1
7001/7002
Analog
Backplane
Multiplexing Basics
Card 2
110
7015
Bank A
110
Bank B
110
Bank C
110
Bank D
Quad 1x10 Multiplexers
Quad 1x20 Multiplexer
Figure 2-11
Multiplexer input expansion example
Mixing card types
Different types of cards can be used together to create some
unique switching systems. For example, you could have a
Model 7015 multiplexer card installed in one slot and a Model 7012 matrix card installed in another slot.
110
7015
110
110
110
Quad 1x10 Multiplexers
Backplane
Jumpers
installed
multiplexer banks. On the multiplexer card, the bank-tobank jumpers must be removed to maintain isolation between matrix rows. See the instruction manual for the Model
7012 for complete information on the matrix card.
2.4.2 Mainframe multiplexer expansion
Figure 2-12 shows one possible switching system using a
matrix card and a multiplexer card. The backplane jumpers
for both the matrix and multiplexer cards must be installed.
This arrangement allows matrix rows to be connected to
Multiplexer systems using up to 12 or 60 multiplexer cards
are possible by using six Model 7001 or 7002 mainframes together. Each Model 7015 added to the system provides 40
additional inputs. Paragraph 3.4.3 explains how to connect a
test system using two mainframes.
2-9
Page 26

Multiplexing Basics
110
1
2
Rows
3
4
Notes : 1. Models 7015 and 7012 backplane jumpers
must be installed.
2. Model 7015 bank-to-bank jumpers must be
removed.
Figure 2-12
Mixed card type example
Card 1
7012
Columns
4 x 10 Matrix
7001/7002
Backplane
Card 2
7015
110
110
110
110
Inputs
Bank A
Bank B
Bank C
Bank D
Quad 1 x 10 Mux
2-10
Page 27

3
Card Connections & Installation
3.1 Introduction
WARNING
The procedures in this section are intended only for qualified service personnel. Do not perform these procedures
unless qualified to do so. Failure to recognize hazards and observe normal
safety precautions could result in personal injury or death.
The information in this section is arranged as follows:
3.2 Handling precautions: Explains precautions that
must be followed to prevent contamination to the multiplexer card assembly. Contamination could degrade
the performance of the multiplexer card.
3.3 Connections: Covers the basics for connecting exter-
nal circuitry to the two available connector cards for
the multiplexer; the screw terminal connector card and
the multi-pin connector card.
3.2 Handling precautions
To maintain high-impedance isolation, care should be taken
when handling the relay card to avoid contamination from
such foreign materials as body oils. Such contamination can
substantially lower leakage resistances, thus degrading performance.
To avoid possible contamination, always grasp the relay and
connector cards by the side edges or shields. Do not touch
the board surfaces, components, or areas adjacent to the electrical contacts. Dirt build-up over a period of time is another
possible source of contamination. To avoid this problem, operate the mainframe and multiplexer card in a clean environment.
If a card becomes contaminated, it should be thoroughly
cleaned as explained in paragraph 5.2.
3.3 Connections
3.4 Typical connection schemes: Provides some typical
connection schemes for single card, two-card and twomainframe system configurations.
3.5 Model 7015 installation: Provides a procedure to in-
stall the multiplexer card assembly in the Model 7001
or Model 7002 mainframe.
This paragraph provides the basic information needed to
connect your external test circuitry to the multiplexer. It includes the installation of the bank-to-bank jumpers on the
connector card, installation/removal of backplane jumpers
on the relay card, and detailed information on making external connections to the two available connector cards.
3-1
Page 28

Card Connections & Installation
WARNING
The following connection information is
intended to be used by qualified service
personnel. Failure to recognize hazards
and observe standard safety precautions
could result in personal injury or death.
3.3.1 Bank-to-bank jumpers
As explained in paragraph 2.2.1, the banks of the multiplexer
card can be connected together (using plug-in jumpers) to
form larger multiplexers. The locations of the bank-to-bank
jumper terminals for both connector cards are shown in Figure 3-1.
Terminal identification is provided by Figure 3-2. On the
drawing, the six terminal pairs are labeled W100 through
W105. The top three terminal pairs (W101, W103 and
W105) are used to connect the LO terminals of the banks together. The bottom terminal pairs (W100, W102 and W104)
are used to connect the HI terminals of the banks together.
Table 3-1 summarizes the purpose of each jumper.
Bank
A to B
LO
W101
HI
W100
Bank
B to C
W103
W102
Figure 3-2
Bank-to-bank jumper terminal identificatio
Table 3-1
Bank-to-bank jumpers (on connector card)
Installed
jumper* Connection
W101
W100
W103
W102
W105
W104
*See Figure 3-1 for location.
Bank A LO to Bank B LO
Bank A HI to Bank B HI
Bank B LO to Bank C LO
Bank B HI to Bank C HI
Bank C LO to Bank D LO
Bank C HI to Bank D HI
Bank
C to D
W105
W104
Jumper Terminals
A. Screw Terminal Connector
Card (Model 7015-S)
Figure 3-1
Bank-to-bank jumper locations
3-2
Bank-to-Bank
Bank-to-Bank
Jumper Terminals
B. Multi-pin Connector Card
(Model 7015-C)
Page 29

Card Connections & Installation
Referring to Figure 3-1 for jumper locations, perform the following steps to install bank-to-bank jumpers:
1. If mated together, separate the relay card from the connector card by removing the mounting screw and pulling
the two cards away from each other. Remember to handle the cards only by the edges and shields to avoid contamination.
2. Refer to Figure 3-2 and Table 3-1 to determine which
jumpers to install.
3. Using Figure 3-3 as a guide, install the jumpers on the
appropriate terminal pairs.
Jumper
Jumper Terminal
Pair
Figure 3-3
Bank-to-bank jumper installation
1. If mated together, separate the relay card from the connector card by removing the mounting screw and pulling
the two cards away from each other. Remember to handle the cards only by the edges and shields to avoid contamination.
2. Use Figure 3-4 and Table 3-2 to locate the jumpers that
are to be removed.
3. It is not necessary to unsolder the jumpers from the PC
board. Using a pair of wire cutters, cut both ends of each
jumper, then remove each cut jumper completely.
Table 3-2
Backplane jumpers (on relay card)
Jumper* Backplane connection
W100
W101
W102
W103
W104
W105
W106
W107
*See Figure 3-4 for location.
Bank A HI
Bank A LO
Bank B HI
Bank B LO
Bank C HI
Bank C LO
Bank D HI
Bank D LO
3.3.2 Backplane jumpers
The Model 7001 and Model 7002 mainframes have an analog backplanes that allow the banks of a Model 7015 multiplexer to be internally connected to a compatible switching
card installed in another slot (see paragraph 2.4.1 for details).
The backplane jumpers for the multiplexer card assembly are
located on the relay card as shown in Figure 3-4, and Table
3-2 summarizes jumper connections. The card is shipped
from the factory with the jumpers installed.
Jumper removal
Perform the following steps to remove backplane jumpers:
Jumper installation
Referring to Figure 3-4 for jumper locations, perform the following steps to install backplane row jumpers:
1. If mated together, separate the relay card from the connector card by removing the mounting screw and pulling
the two cards away from each other. Remember to handle the cards only by the edges and shields to avoid contamination.
2. Physically remove a cut jumper by unsoldering the two
cut ends from the PC board.
3. Install a new #22 AWG jumper wire (Keithley P/N J-
15), and solder it to the PC board.
4. Remove the solder flux from the PC board. The cleaning
procedure is explained in paragraph 5.2.
3-3
Page 30

Card Connections & Installation
Backplane Jumpers
7015 Relay Card
W100
W101
W102
W103
W104
W105
W106
W107
Figure 3-4
Backplane jumpers
3.3.3 Screw terminal connector card
The screw terminal connector card is shown in Figure 3-5.
Connections are made directly to the screw terminals of the
twelve terminal blocks. Each screw terminal will accommodate #16-22 AWG wire.
3-4
Figure 3-5
Model 7015 screw terminal connector card
Page 31

Figure 3-7
Cable clamp for screw terminal connector card
Clips
Screw
Card Connections & Installation
Wiring procedure
Perform the following procedure to wire circuitry to the
screw terminal connector card:
WARNING
Make sure all power is off and that any
stored energy in external circuitry is discharged.
1. If mated together, separate the connector card from the
relay card by removing the mounting screw and pulling
the two cards away from each other. Remember to handle the cards only by the edges and shields to avoid contamination.
2. Using an insulated screwdriver, connect the circuitry to
the appropriate terminals. Figure 3-6 shows how the output of Bank A would be connected to a DMM.
3. Referring to Figure 3-7, remove the top half of the cable
clamp as follows:
A. Loosen the cable clamp screw enough to disengage
it from the bottom half of the cable clamp.
B. Using your thumb and forefinge , press the retaining
clips inward and, with your other hand, remove the
top half of the clamp.
4. Route wires under wire guide/connector shim.
5. Route the wires through the bottom half of the cable
clamp.
6. Replace the top half of the clamp. It simply snaps onto
the bottom half of the clamp. Tighten the cable clamp
screw. The clamp serves as a strain relief for terminal
block wires.
7. Mate the connector card to the relay card. The Model
7015 is now ready to be installed in the Model 7001 or
Model 7002 mainframe. See paragraph 3.5 for details.
#16 - 22 AWG Wires
Bank A
H
Output
L
H
CH 1
L
H
CH 2
L
H
CH 3
L
Figure 3-6
Typical screw terminal connections
HI
DMM
LO
3-5
Page 32

Card Connections & Installation
3.3.4 Multi-pin (mass termination) connector
card
Since connections to external circuitry are made at the 96-pin
male DIN bulkhead connector, there is no need to separate
the connector card from the relay card. If the connector card
is separated from the relay card, carefully mate them together and install the supplied 4-40 mounting screw. Be sure to
handle the cards by the edges and shields to avoid contamination.
Table 3-3
Multipin card terminal identificatio
Mux
Terminal
Bank A
Input 1 HI
LO
Input 2 HI
LO
Input 3 HI
LO
Input 4 HI
LO
Input 5 HI
LO
Input 6 HI
LO
Input 7 HI
LO
Input 8 HI
LO
Input 9 HI
LO
Input 10 HI
LO
Output HI
LO
Connector
Desig.
1a-32c
32c
32b
32a
31c
31b
31a
30c
30b
30a
29c
29b
29a
28c
28b
28a
27c
27b
27a
26c
26b
26a
25c
Schem.
Desig.
1-96
Terminal
Bank B
96
Input 1 HI
64
3295Input 2 HI
6331Input 3 HI
9462Input 4 HI
3093Input 5 HI
6129Input 6 HI
9260Input 7 HI
2891Input 8 HI
5927Input 9 HI
9058Input 10 HI
2689Output HI
Mux
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
Connector
Desig.
1a-32c
24c
24b
24a
23c
23b
23a
22c
22b
22a
21c
21b
21a
20c
20b
20a
19c
19b
19a
18c
18b
18a
17c
Schem.
Desig.
1-96
88
56
2487Input 2 HI
5523Input 3 HI
8654Input 4 HI
2285Input 5 HI
5321Input 6 HI
8452Input 7 HI
2083Input 8 HI
5119Input 9 HI
8250Input 10 HI
1881Output HI
Terminal identification for the DIN connector of the multipin connector card is provided by Table 3-3. This connector
will mate to a 96-pin female DIN connector.
Keithley has a variety of cable and connector accessories
available to accommodate connections from the connector
card to test instrumentation and DUT (devices under test). In
general, these accessories, which are summarized in Table 34, utilize a round cable assembly for connections.
Mux
Terminal
Bank C
Input 1 HI
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
Connector
Desig.
1a-32c
16c
16b
16a
15c
15b
15a
14c
14b
14a
13c
13b
13a
12c
12b
12a
11c
11b
11a
10c
10b
10a
9c
Schem.
Desig.
1-96
Terminal
Bank D
80
Input 1 HI
48
1679Input 2 HI
4715Input 3 HI
7846Input 4 HI
1477Input 5 HI
4513Input 6 HI
7644Input 7 HI
1275Input 8 HI
4311Input 9 HI
7442Input 10 HI
1073Output HI
Mux
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
LO
Connector
Desig.
1a-32c
8c
8b
8a
7c
7b
7a
6c
6b
6a
5c
5b
5a
4c
4b
4a
3c
3b
3a
2c
2b
2a
1c
Schem.
Desig.
1-96
72
40
8
71
39
7
70
38
6
69
37
5
68
36
4
67
35
3
66
34
2
65
Notes: 1. Pins 9a and 9b (pins 9 and 41 on schematic) are shield.
2. Short pin 1a to 1b on the mating connector (pins 1 and 33 on schematic) to allow the output relays on the connector card to close.
Pins of the Model 7015-C mass termination connector can be identified in one of three ays:
1. Mux terminal, consisting of banks A-D and inputs 1-10.
2. Connector description, consisting of rows a-c and columns 1-32.
3. Schematic and component layout designation (1-96).
3-6
Page 33

Table 3-4
Mass termination accessories
Model Description
7011-KIT-R 96-pin female DIN connector and
housing for round cable.
Card Connections & Installation
male DIN connector. The output relays will close only when
the Model 7011-MTC-2 cable assembly is connected to card.
If building your own cable assembly, you must make sure
that it shorts pin 1a to 1b of the card connector (Table 3-3)
when it is mated to the card. Shorting pin 1a to 1b allows the
output relays to close.
7011-MTC-2 Two-meter round cable assembly ter-
minated with a 96-pin female DIN
connector on each end.
7011-MTR 96-pin male DIN bulkhead connec-
tor.
Typical connection techniques
All external circuitry, such as instrumentation and DUTs,
that you wish to connect to the multiplexer card must be terminated with a single 96-pin female DIN connector. The following connection techniques provide some guidelines and
suggestions for wiring your circuitry.
WARNING
Before beginning any wiring procedures, make sure all power is off, and
any stored energy in external circuitry is
discharged.
Round cable assemblies
cable connection techniques using accessories available
from Keithley.
In Figure 3-8A, connections are accomplished using a Model
7011 MTC-2 cable and a Model 7011-MTR bulkhead connector. The two-meter round cable is terminated with a 96pin female DIN connector at each end. This cable mates directly to the multi-pin connector card and to the bulkhead
connector. The bulkhead connector has solder cups to allow
direct connection to instrumentation and DUT. Figure 3-9
provides the pinout for the bulkhead connector.
In Figure 3-8B, connections are accomplished using a Model
7011 MTC-2 cable assembly that is cut in half. The 96-pin
female DIN connector on one end of the cable mates directly
to the multi-pin connector card. The unterminated end of the
cable is wired directly to instrumentation and DUT. The other half of the cable assembly could be used for a second
switching card.
Figure 3-8 shows typical round
NOTE
External circuitry should be connected
(plugged in) only with the mainframe
power off, after the Model 7015 assembly
is installed in the Model 7001 or 7002
mainframe. Installation is covered in paragraph 3.5.
Output relays
for each of the four output banks. These output relays are
normally open to prevent any hazardous voltages (via the
mainframe backplane) from appearing on the pins of the
The multi-pin connector card uses a relay
In Figure 3-8C, connections are accomplished using a custom-built cable assembly that consists of a Model 7011-KITR connector and a suitable round cable. Hitachi cable part
number N2807-P/D-50TAB is a 50-conductor cable. Two of
these cables can be used to supply 100 conductors.The connector has solder cups to accommodate the individual wires
of the unterminated cable. Figure 3-10 provides an exploded
view of the connector assembly and shows how the cable is
connected. The connector end of the resultant cable assembly mates directly to the multi-pin connector card. The unterminated end of the cable assembly is wired directly to
instrumentation and DUT.
3-7
Page 34

Card Connections & Installation
A)
B)
C)
Multi-Pin
Connector
Card
Multi-Pin
Connector
Card
Multi-Pin
Connector
Card
7011-MTC-2
cable assembly
7011-MTC-2
(Cut in Half)
Wire instrumentation and
DUT to bulkhead connector
(See Figure 3-9 and Table 3-3
for terminal identification)
7011-MTR
bulkhead connector
Wire directly to
instrumentation
and DUT
Wire directly to
instrumentation
and DUT
Cable
Figure 3-8
Typical round cable connection techniques
7011-Kit-R
Connector Kit
Notes : Figure 3-10 provides an exploded view showing
how the connector (with cable) is assembled.
Cable Hitachi p/n N2807-P/D-50TAB is a
50-conductor round cable. Two of these cables
can be used to supply 100 conductors.
3-8
Page 35
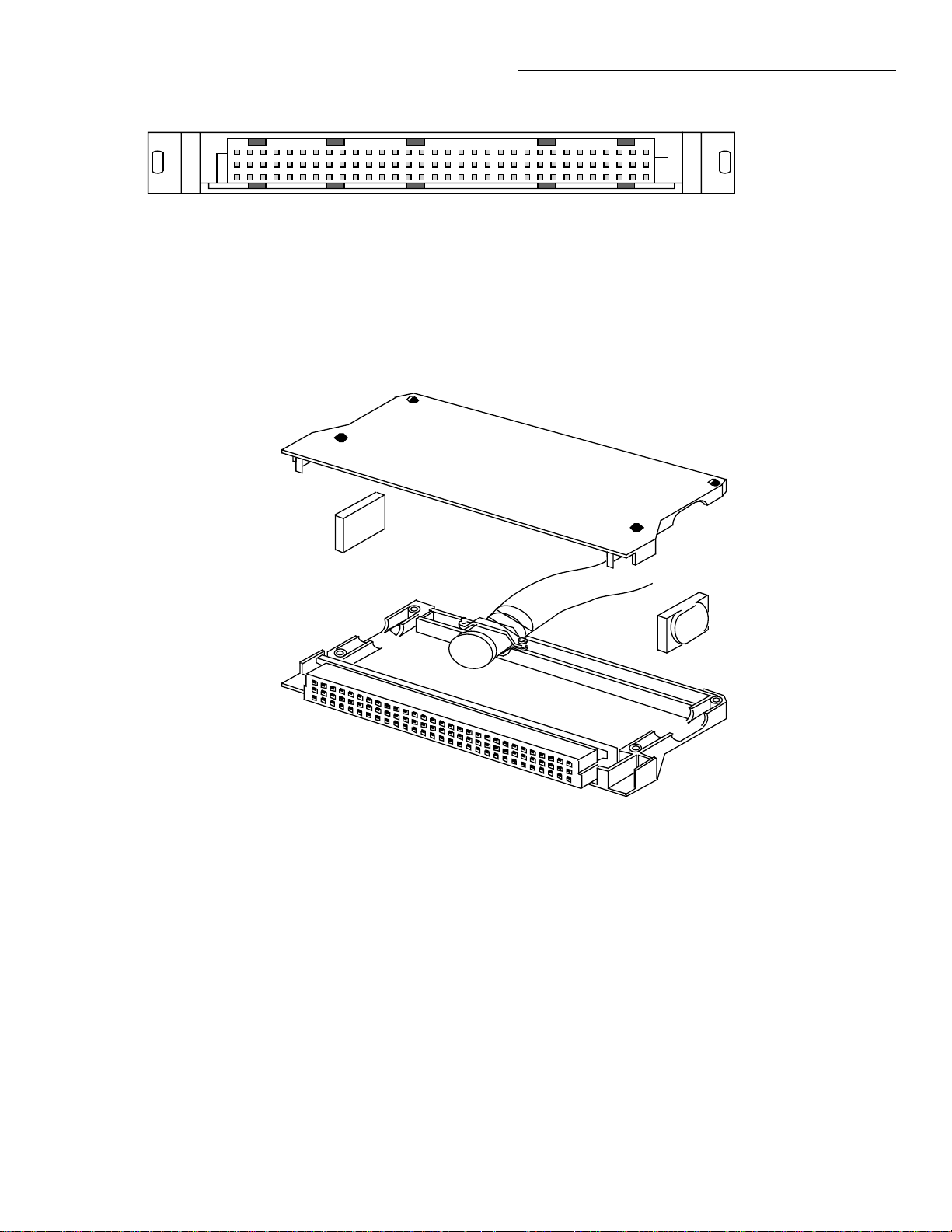
Note : See Table 3-3 for terminal
identification.
Figure 3-9
Model 7011-MTR connector pinout
Card Connections & Installation
3231302928272625242322212019181716151413121110987654321
c
b
a
View from solder
cup side of
connector
Figure 3-10
Model 7011-KIT-R (with/cable) assembly
3-9
Page 36

Card Connections & Installation
×
3.4 Typical connection schemes
The following information provides some typical connection
schemes for single card, two-card and two-mainframe system configurations. Connection schemes for the multi-pin
connector card use some of the techniques presented in paragraph 3.3.2. Keep in mind that these are only examples to
demonstrate various ways to wire a test system. Connection
details for both connector cards (multi-pin and screw terminal connector cards) are provided in paragraph 3.3.
3.4.1 Single-card system
Figure 3-11 shows external connections for a single-card
system that uses the multi-pin connector card. This singlecard system is configured as two 1
so, the appropriate bank-to-bank jumpers must be installed
to connect Banks A and B together and Banks C and D together.
Instrumentation and DUTs are hard-wired to the Model
7011-MTR male bulkhead connector. This connector has
solder cups that will accept wire sizes up to #24 AWG. The
test system is connected to the multiplexer using the Model
7011-MTC-2 round cable assembly. This cable mates direct-
20 multiplexers. To do
ly to both the external bulkhead connector and the Model
7015-C multiplexer card assembly. Note that the bulkhead
connector is shown mounted to a fixture to help keep the cabling stable during the test.
The single-card system in Figure 3-12 is identical to the system in the previous illustration except for the connection
scheme. The system in Figure 3-12 uses the screw terminal
connector card. With this card, single-conductor connections
are made directly from the terminal blocks of the connector
card to instrumentation and DUTs.
When using a single-card system, make sure that the card remains electrically isolated from any other switching cards.
There are several ways to ensure isolation for a single card in
the Model 7001 or Model 7002 mainframe:
1. Vacate other mainframe slots. If there are Model 701X
cards installed in other slots, remove them.
2. Remove the backplane jumpers on the multiplexer card.
Doing so will disconnect the card from the analog backplane of the mainframe.
3. Remove the backplane jumpers from switching cards installed in all other slots.
3-10
Page 37

Card Connections & Installation
HI and LO to
Instrument
Instrument
Banks A and B
HI and LO to
Banks C and D
84 Individual Conductors
1201 20
DUT Test Fixture
Fixture for
Bulkhead
Connector
7011-MTR
Bulkhead
Connector
7015-C
7011-MTC-2
Cable Assembly
1
20
1
20
DUTs
1
20
1
20
7015-C
(Dual 1x20)
Simplified Equivalent Circuit
Figure 3-11
Single-card system example (multi-pin connector card)
Instruments
Notes: Bank-to-Bank jumpers installed
as follows :
Bank A connected to Bank B
Bank C connected to Bank D
3-11
Page 38

Card Connections & Installation
HI and LO to
Instrument
Instrument
Banks A and B
HI and LO to
Banks C and D
7015-S
DUTs
1
20
1
20
1
20
1
20
(Dual 1x20)
Simplified Equivalent Circuit
120
120
DUT Test Fixture
Notes: Bank-to-bank jumpers installed
as follows :
Bank A connected to Bank B
Bank C connected to Bank D
Instruments
Figure 3-12
Single-card system example (screw terminal connector card)
3-12
Page 39

×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
Card Connections & Installation
3.4.2 Two-card system
Both Figure 3-13 and Figure 3-14 show a system using two
multiplexer cards installed in one Model 7001 mainframe to
configure a single 1
configured as a single 1
jumpers (both cards) are installed to connect Banks A, B, C,
and D together. By leaving the backplane jumpers of both
cards installed, the banks of Card 1 are connected to the
banks of Card 2 through the analog backplane of the Model
7001 mainframe resulting in the 1
Figure 3-13 shows how external connections can be made for
the multi-pin connector cards. In this example, a single Model 7011-MTC-2 round cable assembly is cut in half to provide two cables, each of which is unterminated at one end.
The unterminated ends of the two cables are hard-wired to
the instrument and DUT as shown in the drawing. The other
ends of these cables mate directly to the Model 7015-C multiplexer card assemblies.
Figure 3-14 shows how external connections can be made for
the screw terminal connector card. Single conductor connections are made directly from the screw terminals of the connector card to the instrument and DUT.
80 multiplexer system. Each card is
40 multiplexer. All bank-to-bank
80 configuration.
3.4.3 Multiple-card systems
The same general system configuration shown in Figure 3-13
and Figure 3-14 can be expanded further by substituting a
Model 7002 mainframe for the Model 7001. Since a single
Model 7002 can hold 10 cards, a 1
configured using 10 Model 7015 cards in a single mainframe.
400 multiplexer can be
3.4.4 Two-mainframe system
Both Figure 3-15 and Figure 3-16 show a system using three
multiplexer cards installed in two Model 7001 mainframes to
configure a single 1
configured as a single 1
jumpers of all three cards must be installed to connect Banks
A, B, C, and D together.
By leaving the backplane jumpers of the cards in mainframe
#1 installed, the banks of Card 1 are connected to the banks
of Card 2 through the analog backplane of the Model 7001
mainframe resulting in a 1
connections from the instrument to the card in the second
mainframe connect the banks of all three cards together to
form the 1
to the Two-card System (see previous paragraph) except that
a third multiplexer card (installed in a second mainframe) is
added.
Figure 3-15 shows the connection scheme for the multi-pin
connector cards. External circuit connections to the Model
7001 #1 mainframe are identical to the ones used for the
Two-card System. The third multiplexer card (installed in
Model 7001 #2 mainframe) shows how a custom-built cable
can be used to make connections to external circuitry. A suitable round cable can be constructed using a 96-pin female
DIN connector (Model 7011-KIT-R) with two lengths of Hitachi cable P/N N2807-P/D-50TAB. This cable contains 50
conductors; two lengths provide 100 conductors. This cable
will mate to the Model 7015-C multiplexer card assembly.
The unterminated end of the cable is connected directly to
the instrument and DUT. Notice that the bank connections
for the third multiplexer card are made at the instruments.
120 multiplexer system. This system is similar
120 multiplexer system. Each card is
40 multiplexer. Bank-to-bank
80 configuration. External bank
Figure 3-16 shows connections for the screw terminal connector card. Single conductor connections are made directly
from the screw terminals of the connector card to the instrument and DUT.
3-13
Page 40

Card Connections & Installation
HI and LO to
Instrument
Banks A thru D
7011-MTC-2
Cable Assembly
(Cut in half to
provide two cables)
7015C
7015C
7001
C
A
R
D
1
C
A
R
D
2
1
40
Card 1 (1x40)
1
40
DUTs
41
80
1
40
Card 2 (1x40)
41
80
Single 1x80 Multiplexer
Simplified Equivalent Circuit
Figure 3-13
Two-card system example (multi-pin connector card)
DUT Test Fixture
Instruments
7001
Analog
Backplane
41 80
Notes: 1. All bank-to-bank jumpers
(both cards) must be installed.
2. Backplane jumpers (both
cards) must be installed.
3-14
Page 41

Instrument
164 individual
conductors
(#22 AWG)
7001
7015-S
7015-S
Card Connections & Installation
C
A
R
D
1
C
A
R
D
2
1
DUT Test Fixture
Card 1 (1x40)
1
40
DUTs
41
80
1
40
Card 2 (1x40)
41
80
Single 1x80 Multiplexer
Simplified Equivalent Circuit
Figure 3-14
Two-card system example (screw terminal connector card)
Instruments
7001
Analog
Backplane
41 8040
Notes: 1. All bank-to-bank jumpers
(both cards) must be installed.
2. Backplane jumpers (both
cards) must be installed.
3-15
Page 42

Card Connections & Installation
DUT Test Fixture
81 120
7011-Kit-R
Connector Kit
Cable
Instrument
7011-MTC-2
Cable Assembly
(Cut in half to
provide two cables)
140
DUT Test Fixture
7001 #2
C
7001 #1
A
R
Trigger Link
D
1
I
N
C
A
R
O
D
U
2
T
C
A
R
Trigger Link
D
1
I
N
C
A
R
O
D
U
2
T
7015-C
Not Used
7015-C
7015-C
41 80
Trigger
Link
Cable
7001 #1
Card 1 (1x40)
1
1
40
40
41
Card 2 (1x40)
41
7001
Analog
Backplane
DUTs
80
80
7001 #2
Card 1 (1x40)
81
120
Single 1x120 Multiplexer
Simplified Equivalent Circuit
Figure 3-15
Two-mainframe system example (multi-pin connector card)
Instruments
External
Bank
Connections
Notes: 1. Backplane jumpers for both cards installed
in 7001 #1 must be installed.
2. All bank-to-bank jumpers, on all three
cards, must be installed.
3-16
Page 43

244 Individual
Conductors
(#22 AWG)
DUT Test Fixture
81 120
Instrument
7015-S
Not Used
7015-S
7015-S
7001 #2
C
A
R
Trigger Link
D
1
I
N
C
A
R
O
D
U
2
T
7001 #1
C
A
R
Trigger Link
D
1
I
N
C
A
R
O
D
U
2
T
Card Connections & Installation
Trigger
Link
Cable
DUTs
7001 #1
Card 1 (1x40)
1
1
40
40
Card 2 (1x40)
41
41
80
80
7001 #2
Card 1 (1x40)
81
120
Single 1x120 Multiplexer
Simplified Equivalent Circuit
41140 80
DUT Test Fixture
Instruments
7001
Analog
Backplane
External
Bank
Connections
Notes: 1. Backplane jumpers for both cards installed
in 7001 #1 must be installed.
2. All bank-to-bank jumpers, on all three
cards, must be installed.
Figure 3-16
Two-mainframe system example (screw terminal connector card)
3-17
Page 44

Card Connections & Installation
3.5 Model 7015 installation and removal
This paragraph explains how to install and remove the Model
7015 multiplexer card assembly from the Model 7001 or
Model 7002 mainframe.
WARNING
Installation or removal of the Model
7015 is to be performed by qualified service personnel. Failure to recognize and
observe standard safety precautions
could result in personal injury or death.
NOTE
If using the screw terminal connector card,
make sure your external circuitry is wired
to the card (as explained in paragraph
3.3.1) before installing the card assembly
in the Model 7001 or Model 7002 mainframe.
mainframe), and disconnect their line
cords. Make sure all power is removed
and any stored energy in external circuitry is discharged.
1. Mate the connector card to the relay card if they are separated. Install the supplied 4-40 screw at the end of the
card to secure the assembly. Make sure to handle the
cards by the edges and shields to prevent contamination.
2. Facing the rear panel of the mainframe, select the slot
that you wish to install the card in.
3. Referring to Figure 3-17 or Figure 3-18 for Model 7015C installation or Model 7015-S installation, feed the
multiplexer card assembly into the desired slot such that
the edges of the relay card ride in the rails.
4. With the ejector arms in the unlocked position, push the
card assembly all the way into the mainframe until the
arms engage into the ejector cups, then push both arms
inward to lock the card into the mainframe.
5. Tighten ground screw shown in Figure 3-17 and Figure
3-18.
CAUTION
To prevent contamination to the multiplexer card that could degrade performance, handle the card assembly only
by the edges and shields.
Multiplexer card installation
Perform the following steps to install the multiplexer card assembly in the Model 7001 or Model 7002 mainframe:
WARNING
Turn off all instrumentation power (including the Model 7001 or Model 7002
WARNING
Failure to tighten the ground screw may
result in a shock hazard or damage to
the multiplexer card.
Multiplexer card removal
To remove the multiplexer card assembly, first loosen the
ground screw, unlock the card by pulling the latches outward, then pull the card assembly out of the mainframe. Remember to handle the card assembly by the edges and shields
to avoid contamination that could degrade performance.
3-18
Page 45

Card Connections & Installation
Tighten Ground
Screw
KEITHLEY
KEITHLEY
CAUTION:
CAUTION:
Figure 3-17
Model 7015 card installation in Model 7001
Ejector Arms
(Open Position)
WARNING:
WARNING:
NO INTERNAL OPERATOR SERVICABLE PARTS,SERVICE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
NO INTERNAL OPERATOR SERVICABLE PARTS,SERVICE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
C
A
7015-S SOLID STATE MULTIPLEXER
MADE IN USA
7015-C SOLID STATE MULTIPLEXER
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD,REPLACE FUSE WITH SAME TYPE AND RATING.
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD,REPLACE FUSE WITH SAME TYPE AND RATING.
R
D
1
C
A
R
D
2
I
N
O
U
T
TRIGGER LINK
Ejector Arms
(Locked Position)
DIGITAL I/O
CHANNEL
READY
LINE
RATING
90-250
V
50-400
Hz
40VA
MAX
IEEE
EXTERNAL
TRIGGER
-
488
Ejector Arms
(open position)
Ejector Arms
(locked position)
INTERCONNECTION, INSTALLATION AND REMOVAL OF CARDS BY QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL ONLY.
WARNING:
CARD 1 CARD 2 CARD 3 CARD 4
7015-S SOLID STATE MULTIPLEXER
KEITHLEY
WARNING:
NO INTERNAL OPERATOR SERVICEABLE PARTS, SERVICE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
7015-C SOLID STATE MULTIPLEXER
KEITHLEY
Figure 3-18
Model 7015 card installation in Model 7002
Tighten ground screw
3-19
Page 46

±
4
Operation
4.1 Introduction
This section contains detailed information on operating the
Model 7015 and is formatted as follows:
4.2 Maximum signal levels: Summarizes the maximum
signal levels of the Model 7015 multiplexer card assembly.
4.3 Mainframe control of multiplexer card: Summarizes
programming steps to control the multiplexer card
from the Model 7001 or Model 7002.
4.4 Multiplexer switching examples: Provides some typ-
ical applications for using the Model 7015.
4.5 Measurement considerations: Reviews a number of
considerations when using the Model 7015 to make
measurements.
4.2 Maximum signal levels
To prevent damage to the solid-state relays, never exceed the
following maximum signal levels:
175V peak between any two pins, 34mA resistive load,
0.3VA max, 1 × 10
6
V•Hz max.
4.3 Mainframe control of multiplexer card
The following information pertains to the Model 7015 SolidState Multiplexer Card. It assumes that you are familiar with
operation of the Model 7001 or Model 7002 mainframe.
If you are not familiar with operation of the mainframe, it is
recommended that you proceed to Getting Started (Section
3) of the mainframe Instruction Manual after reading the following information.
4.3.1 Channel assignments
CAUTION
To prevent damage to the card, do not
exceed its maximum signal level specifications.
Do not use the Model 7015 to switch inductive loads, or the solid-state relays
may sustain damage.
The Model 7001 has a channel status display (Figure 4-1)
that provides the real-time state of each available channel.
The left portion of the display is for slot 1 (Card 1), and the
right portion is for slot 2 (Card 2). The Model 7002 displays
channel assignments for each card slot, as shown in Figure
4-2.
The Model 7015 card contains 40 channels and is made up
of four banks (Bank A, B, C, and D) of 10 multiplexer inputs
4-1
Page 47

Operation
as shown in the illustration. Model 7002 row assignments are
shown in parentheses.
To control the multiplexer (mux) card from the mainframe,
each multiplexer input must have a unique CHANNEL assignment that includes the slot number in which the card is
installed. The CHANNEL assignments for the multiplexer
card are provided in Figure 4-3. Each CHANNEL assignment is made up of the slot designator (1 or 2 for the Model
7001; 1-10 for the Model 7002) and the multiplexer channel.
Model 7001 Display
CARD 1 CARD 2
1 234567 89101 234567 8910
= Open Channel
= Closed Channel
To be consistent with Model 7001/7002 operation, the slot
designator and mux input are separated by exclamation
points (!). Some examples of CHANNEL assignments are as
follows:
CHANNEL 1!1 = Slot 1, Channel 1 (Input 1 of Bank A)
CHANNEL 1!40 = Slot 1, Channel 40 (Input 10 of Bank D)
CHANNEL 2!23 = Slot 2, Channel 23 (Input 3 of Bank C)
CHANNEL 2!36 = Slot 2, Channel 36 (Input 6 of Bank D)
Figure 4-1
Channel status display
(Row 1)
Bank A
(Row 2)
Bank B
(Row 3)
Bank C
(Row 4)
Bank D
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
1
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
1
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
1
Model 7002 designations shown in parentheses
10
10
10
10
Figure 4-2
Display organization for multiplexer channels
4-2
Page 48

Operation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1!1
1!2
1!3
1!4
1!5
1!6
1!7
1!8
1!9
1!10
1!12
1!22
1!32
A. Slot 1 (Card 1)
1!11
1!21
1!31
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
2!2
2!12
2!22
2!32
B. Slot 2 (Card 2)
2!1
2!11
2!21
2!31
Examples : 1!18 = Slot 1, Channel 18 (Input 8, Bank B)
2!36 = Slot 2, Channel 36 (Input 6, Bank D)
Note : For Model 7002 slots 3-10, substitute slot
number for first number in channel assignments.
Figure 4-3
Model 7015 programming channel assignments
1!13
1!23
1!33
2!3
2!13
2!23
2!33
1!14
1!24
1!34
2!4
2!14
2!24
2!34
1!15
1!25
1!35
2!5
2!15
2!25
2!35
1!16
1!26
1!36
2!6
2!16
2!26
2!36
1!17
1!27
1!37
2!7
2!17
2!27
2!37
1!18
1!28
1!38
2!8
2!18
2!28
2!38
1!19
1!29
1!39
2!9
2!19
2!29
2!39
1!20
1!30
1!40
2!10
2!20
2!30
2!40
4.3.2 Front panel control
Closing and opening channels
A multiplexer channel is closed from the front panel by simply keying in the CHANNEL assignment and pressing
CLOSE. For example, to close channel 36 (Input 6 of Bank
D) of a multiplexer card installed in slot 2, key in the following channel list, and press CLOSE:
SELECT CHANNELS 2!36
The above closed channel can be opened by pressing OPEN
or OPEN ALL. The OPEN key opens only the channels specified in the channel list, and OPEN ALL opens all channels.
The following display is an example of a channel list that
consists of several channels:
SELECT CHANNELS 2!1, 2!3, 2!22-2!25
Notice that channel entries are separated by commas (,). A
comma is inserted by pressing ENTER or the right cursor
key ( ). The channel range is specified by using the hyphen (-) key to separate the range limits. Pressing CLOSE
will close all the channels specified in the channel list. Pressing OPEN (or OPEN ALL) will open the channels.
Scanning channels
Multiplexer channels are scanned by creating a scan list and
configuring the Model 7001 or Model 7002 to perform a
scan. The scan list is created in the same manner as a channel
list (see Closing and Opening Channels). However, the scan
list is specified from the “SCAN CHANNEL” display mode.
(The SCAN LIST key toggles between the channel list and
the scan list.) The following shows an example of a scan list:
SCAN CHANNELS 2!1, 2!3, 2!21-2!25
4-3
Page 49

Operation
When a scan is performed, the channels specified in the scan
list will be scanned in the order that they are presented in the
scan list.
A manual scan can be performed by using the RESET default conditions of the Model 7001 or Model 7002. RESET
is selected from the SAVESETUP menu of the main MENU.
When RESET is performed, the mainframe is configured for
an infinite number of manual scans. The first press of STEP
takes the mainframe out of the idle state. The next press of
STEP will close the first channel specified in the scan list.
Each subsequent press of STEP will select the next channel
in the scan list.
4.3.3 IEEE-488 bus operation
Bus operation is demonstrated using HP BASIC 4.0. The
programming statements assume that the primary address of
the mainframe is 07.
commands. These commands are listed as follows:
*RST
:TRIGger:SEQuence:COUNt:AUTo ON
:ROUTe:SCAN <list>
:INIT
The first command resets the mainframe to a default scan
configuration. The second command automatically sets the
channel count to the number of channels in the Scan List, the
third command defines the Scan List, and the fourth command takes the mainframe out of the idle state.
The following program will perform a single scan through all
40 channels of a multiplexer card installed in slot 1:
10 OUTPUT 707; “*RST”
20 OUTPUT 707; “:trig:seq:coun:auto on”
30 OUTPUT 707; “:scan (@ 1!1:1!40)”
40 OUTPUT 707; “:init”
50 END
Closing and opening channels
The following SCPI commands are used to close and open
channels:
:CLOSe <list>
:OPEN <list>|ALL
The following statement closes channels 1!1, and 1!3
through 1!11:
OUTPUT 707; “:clos (@ 1!1, 1!3:1!11)”
Notice that the colon (:) is used to separate the range limits.
Either of the following statements will open channels 1!1,
and 1!3 through 1!11:
OUTPUT 707; “:open (@ 1!1, 1!3:1!11)”
OUTPUT 707; “:open all”
Scanning channels
There are many commands associated with scanning. However, it is possible to configure a scan using as little as four
Line 10 Selects a default configuration for the scan.
Line 20 Sets channel count to the scan-list-length.
Line 30 Defines the scan list.
Line 40 Take the Model 7001/7002 out of the idle state.
The scan is configured to start as soon as this
command is executed.
When the above program is run, the scan will be completed
as rapidly as possible. An additional relay delay can be added
to the program to slow down the scan for viewing. The program is modified by adding line 25 to slow down the scan.
Also, Line 5 is added to the beginning of the program to ensure that all channels are open before the scan is started.
5 OUTPUT 707; “:open all”
10 OUTPUT 707; “*RST”
20 OUTPUT 707; “:trig:seq:coun:auto on”
25 OUTPUT 707; “:trig:del 0.25”
30 OUTPUT 707; “:scan (@ 1!1:1!40)”
40 OUTPUT 707; “:INIT”
50 END
Line 5 Opens all channels.
Line 25 Sets a 1/4 second delay after each channel closes.
4-4
Page 50

Operation
4.4 Multiplexer applications
The following paragraphs discuss some typical applications
for the Model 7015. These applications include various
forms of resistor testing, transistor testing, as well as a discussion of how to combine the Model 7015 with a matrix
card to increase switching versatility.
Although many Model 7015 applications are similar to those
of cards using conventional mechanical relays, the solidstate switching used by the Model 7015 offers several distinct advantages over more traditional mechanical switching
methods:
• Faster switching for more rapid scanning.
• Indefinite “contact” life with little or no change in on
characteristics regardless of the number of switching
cycles.
• Noise-free operation.
pole connection scheme shown, a total of 40 DUTs per card
can be tested at high scanning rates (with break-before-make
off; Model 7002 only). The type of measurement can vary,
although some sort of voltage measurements are usually
made using the setup shown.
To provide synchronization between scanner card channel
closure and multimeter measurements, a trigger link cable is
connected between the multimeter and switching mainframe, as shown in Figure 4-4C. A total of six instruments
can be connected together using the trigger link, allowing the
system to be expanded to a maximum of one multimeter and
fi e switching mainframes. Five Model 7001s can accommodate a total of 10 Model 7015 cards, for testing up to 400
DUTs. Similarly, fi e Model 7002 mainframes can hold a total of 50 Model 7015 cards for testing a maximum of 2,000
DUTs.
To optimize measuremernt speed using this test configura
tion:
4.4.1 High-speed scanning
The Model 7015 and its host Model 7001/7002 mainframe
can be used with a Model 2001 Multimeter to perform highspeed scanning, as shown in Figure 4-4. Using the typical 2-
• Use the trigger link.
• Operate the Model 2001 in the semi-synchronous trigger and burst modes.
• Turn break-before-make off (Model 7002 only).
4-5
Page 51

Operation
WARNING:
NO INTERNAL OPERATOR SERVICABLE PARTS,SERVICE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
WARNING:
NO INTERNAL OPERATOR SERVICABLE PARTS,SERVICE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
CAUTION:
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD,REPLACE FUSE WITH SAME TYPE AND RATING.
CAUTION:
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD,REPLACE FUSE WITH SAME TYPE AND RATING.
7015
PREV
DCV ACV DCI ACI Ω2 Ω4 FREQ TEMP
DISPLAY
NEXT
REL TRIG STORE RECALL
POWER
INFO LOCAL CHAN SCAN CONFIG MENU EXIT ENTER
FILTER MATH
2001 MULTIMETER
RANGE
AUTO
RANGE
Model 2001 Multimeter
2001 Multimeter
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
Input HI
HI
350V
1100V
PEAK
PEAK
LO
500V
INPUTS
PEAK
F
R
Input LO
FRONT/REAR
2A 250V
AMPS
CAL
Single 1x40 MUX DUTs
A. Test Configuration
M
7015
B. Simplified Equivalent Circuit
1
40
40
(40)
DUT
7001 Switch System 2001 Multimeter
7015-C SOLID STATE MULTIPLEXER
KEITHLEY
Trigger Link OUT
Figure 4-4
High-speed scanning connections
INPUT
1100V
!
HI LO
SENSE
Ω 4 WIRE
PEAK
350V
PEAK
500V
PEAK
OPTION SLOT
AMPS
2A MAX
AMPS
FUSE
2A, 250V
Trigger Link
Cable (8501)
C. Trigger Link Connections
EXTERNAL
TRIGGER
INPUT
MADE IN
U.S.A.
METER
COMPLETE
OUTPUT
DIGITAL I/O
IN OUT
TRIGGER
LINK
LINE RATING
LINE FUSE
90-134VAC
SLOWBLOW
180-250VAC
55VA MAX
IEEE-488
(CHANGE IEEE ADDRESS
WITH FRONT PANEL MENU)
1/2A, 250V
50, 60, 400HZ
Trigger Link IN
4-6
Page 52

Operation
4.4.2 Resistor testing
The Model 7015 can be used to test a number of resistors using only one test instrument or a group of instruments. Such
tests include four-wire resistance measurements using a
DMM, and low-resistance measurements using a separate
current source and sensitive digital voltmeter.
Two-wire resistance tests
The Model 7015 should not normally be used for two-wire
resistance testing because of the relatively high on resistance
(<210 Ω ; <130 Ω typical) of the solid-state relays. However,
if the DUT resistance is >100k Ω , errors caused by multiplexer card path resistance can be kept to under 0.25%.
Four-wire resistance tests
More precise measurements over a wider range of system
and DUT conditions can be obtained by using the four-wire
measurement scheme shown in Figure 4-5. Here, separate
sense leads from the Model 2001 Multimeter are routed
through the multiplexer card to the resistor under test. The
extra set of sense leads minimizes the effects of voltage
drops across the card relay contacts that supply the test current to the DUT. (The current through the sense leads is negligible, resulting in virtually no voltage drop across the sense
lead relay contacts.) Note, however, that an extra two poles
of switching per device are required for four-wire resistance
measurements. For this reason, only 20 resistors per card can
be tested using this configuration. Also note that the Model
2001 is limited to the 200 Ω range and above because the
sense lead resistance is too high for the 20 Ω range.
The Model 7015 can be configured for 20 channels of 4-pole
operation by isolating Banks A and B from Banks C and D,
and by programming the Model 7001/7002 mainframe for
the 4-pole mode. (See Section 4 of the Model 7001/7002 Instruction Manual.) Bank jumper removal is described in
paragraph 3.3.1. To configure the connector card for 4-pole
operation, remove only the jumpers between Banks B and C
(W102 and W103). The resulting paired channels are shown
in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1
Paired Channels in 4-pole Operation
7001/7002
CHANNEL
assignment
1 1 and 21 Bank A, In 1 and
2 2 and 22 Bank A, In 2 and
3 3 and 23 Bank A, In 3 and
4 4 and 24 Bank A, In 4 and
5 5 and 25 Bank A, In 5 and
6 6 and 26 Bank A, In 6 and
7 7 and 27 Bank A, In 7 and
8 8 and 28 Bank A, In 8 and
9 9 and 29 Bank A, In 9 and
10 10 and 30 Bank A, In 10 and
11 11 and 31 Bank B, In 1 and
12 12 and 32 Bank B, In 2 and
13 13 and 33 Bank B, In 3 and
14 14 and 34 Bank B, In 4 and
15 15 and 35 Bank B, In 5 and
16 16 and 36 Bank B, In 6 and
17 17 and 37 Bank B, In 7 and
18 18 and 38 Bank B, In 8 and
19 19 and 39 Bank B, In 9 and
20 20 and 40 Bank B, In 10 and
Channel
pair in
4-pole
Bank C, In 1
Bank C, In 2
Bank C, In 3
Bank C, In 4
Bank C, In 5
Bank C, In 6
Bank C, In 7
Bank C, In 8
Bank C, In 9
Bank C, In 10
Bank D, In 1
Bank D, In 2
Bank D, In 3
Bank D, In 4
Bank D, In 5
Bank D, In 6
Bank D, In 7
Bank D, In 8
Bank D, In 9
Bank D, In 10
Connection
designations
4-7
Page 53

Operation
7015
PREV
DCV ACV DCI ACI Ω2 Ω4 FREQ TEMP
DISPLAY
NEXT
REL TRIG STORE RECALL
POWER
INFO LOCAL CHAN SCAN CONFIG MENU EXIT ENTER
FILTER MATH
Model 2001 Multimeter
2001 MULTIMETER
RANGE
AUTO
RANGE
Input HI
Sense Ω
HI
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1100V
PEAK
PEAK
LO
500V
INPUTS
PEAK
F
R
FRONT/REAR
2A 250V
AMPS
CAL
Input LO
20
1
1
20
DUTs
(20)
21
Sense Ω
LO
40
Dual 1x20 MUX
Note : Jumpers between
Banks B and C are
removed.
A. Test Configuration
Figure 4-5
Four-wire resistance testing
Ω
2001
Multimeter
Input HI
Sense Ω HI
Sense Ω LO
Input LO
7015
B. Simplified Equivalent Circuit
R
DUT
4-8
Page 54

Operation
Low-level resistance measurements
Many times, it is necessary to make resistance measurements
with either lower voltage sensitivity or higher currents than
are available with ordinary DMMs. Examples of cases where
low-level resistance measurements may be necessary include
the testing of PC board traces, contacts, bus bars, and low-resistance shunts.
Figure 4-6 shows a typical test configuration for a switching
system capable of testing a number of low resistance devices.
The Model 220 Current Source forces current through the
device under test, while the Model 182 Sensitive Digital
Voltmeter measures the resulting voltage across the device.
Since low voltage levels are being measured, thermal EMF
offsets generated by relay and connector contacts will have a
KEITHLEY
182 SENSITIVE DIGITAL VOLTMETER
TRG
SRQ
REM
TALK
LSTN
detrimental effect on measurement accuracy unless steps are
taken to avoid them. Thermal EMF effects can be virtually
eliminated by taking two voltage measurements, E
and E
1
the first with the current, I, fl wing in one direction, and the
second with a current, I, of the same magnitude fl wing in
the opposite direction. The resistance can then be calculated
as follows:
E
2E–1
----------------=
R
2I
Note that simply reversing the current source polarity will result in a 2 × accuracy specification change. To avoid this
problem, matrix switching could be added to the test system
to reverse the current. See paragraph 4.4.4.
7015
HI
1
1
,
2
Model 182
220 Current Source
182
Nanovoltmeter
V
182 Input
220 Output
20
LO
HI
LO
20
Dual 1x20 MUX
20
DUTs
(20)
1
R
Figure 4-6
Low-resistance testing
220 Currrent
Source
7015
DUT
4-9
Page 55

Operation
4.4.3 Transistor current gain testing
The DC or static common-emitter current gain of a transistor
can be determined by biasing the transistor for a specific value of base current, I
rent, I
. The DC common-emitter current gain, β , of the
C
transistor is then determined as follows:
Figure 4-7 shows the test configurationand equivalent circuit
for the current gain test. The Model 224 Current Source is
used to source the base current, I
Source supplies the collector-emitter voltage, V
collector current, I
meter. Switching among the transistors being tested is, of
course, performed by the Model 7015 multiplexer card.
In order to perform the current gain test, the voltage source
is first set to the desired value of V
then set to a base current value that will result in the desired
value of I
as measured by the DMM. The current gain can
C
then be calculated as outlined above.
Because of the 130 Ω (typical) channel resistance of the
Model 7015, collector current values should be kept as small
as possible to minimize voltage drops across the relay contacts. For example, a 1mA collector current will result in a
nominal 0.1 to 0.2V voltage drop across the relay contacts.
, and then measuring the collector cur-
B
I
C
β
-----=
I
B
. The Model 230 Voltage
B
, and the
CE
, is measured by the Model 2001 Multi-
C
. The current source is
CE
4.4.4 Testing with matrix cards
The Model 7015 can be added to a matrix switching system
to enhance the test capabilities of that system. The following
paragraphs discuss an overall multiplexer/matrix switching
system.
Multiplexer and matrix card connections
Figure 4-8 shows a typical system using Model 7012 and
7015 cards together. In this instance, the multiplexer card is
configured as four 1 × 10 multiplexers. Note that rows of the
matrix card are connected to the banks of the multiplexer
card through the analog backplane of the mainframe; no external wiring is necessary to connect the two cards together.
In this application, the DUTs are connected to the bank inputs on the multiplexer card, allowing a large number of
DUTs to be switched through the matrix card. Also, the instruments are connected to the columns on the matrix card.
This particular configuration is best suited for applications
requiring a large number of DUTs to be connected to several
instruments. In other cases, the test configuration may call
for a large number of instruments and few DUTs. In those
situations, the instruments would be connected to the multiplexer inputs, and the DUTs would be connected to the columns.
4-10
Page 56

Operation
Measure
I
C
Source
V
CE
Source
I
B
PREV
DCV ACV DCI ACI Ω2 Ω4
DISPLAY
NEXT
REL TRIG STORE RECALL
POWER
INFO LOCAL CHAN SCAN CONFIG MENU EXIT ENTER
Model 230
Voltage Source
Output
Model 224
Current Source
2001 MULTIMETER
FREQ TEMP
FILTER MATH
Model 2001
Multimeter
RANGE
AUTO
RANGE
SENSE
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
PEAK
LO
INPUTS
FR
FRONT/REAR
2A 250V
AMPS
CAL
Output
Common
INPUT
1100V
PEAK
500V
PEAK
Amps
LO
HI
A. Test Configuration
7015
1
20
1
20
Dual 1x20 MUX
B
B
DUT (20)
C
E
1
20
C
E
224
Current
Source
Figure 4-7
Configuration for cur ent gain test
I
I
C
β =
I
B
I
B
DUT
V
CE
C
V
Multimeter
+
230 Voltage
Source
-
2001
B. Simplified Equivalent Circuit
4-11
Page 57

Operation
DUTs
(10)
DUTs
(10)
DUTs
(10)
DUTs
(10)
Backplane
Jumpers
2
1
10
2
2
1
10
2
2
1
10
2
2
1
10
2
2
2
A
2
B
C
2
D
Rows
1
2
3
4
Instruments
7001/7002
7015
Multiplexer
Card
Note : The 7015 Bank-to-Bank
jumpers must be removed.
Backplane
Figure 4-8
Connecting multiplexer and matrix cards together
4.5 Measurement considerations
Many measurements made with the Model 7015 are subject
to various effects that can seriously affect low-level measurement accuracy. The following paragraphs discuss these effects and ways to minimize them.
4.5.1 Thermoelectric potentials
Thermoelectric potentials (thermal EMFs) are small electric
potentials generated by differences in temperature at circuit
connecting points such as multiplexer card terminals and
connectors. Thermal EMFs can also be generated by the solid-state relays themselves.
7012 Matrix Card
Thermoelectric generation
Figure 4-9 shows a representation of how thermal EMFs are
generated. The test leads are made of the A material, while
the source under test is the B material. The temperatures between the junctions are T1 and T2.
In the unlikely event that the two junction temperatures are
identical, the thermal EMFs will exactly cancel because the
generated potentials oppose one another. More often, the two
junction temperatures will differ, and considerable thermal
EMFs will be generated.
4-12
Page 58

Figure 4-10
Channel resistance
R
DUT
R
CHANNEL
DUT MUX
Card
= DUT Resistance
= Channel Resistance
= Measured Resistance
= R
DUT
+ R
CHANNEL
R
DUT
R
CHANNEL
R
M
R
M
R
M
Operation
T
1
The thermal EMF developed by dissimilar metals A
and B in a series circuit is:
= Q
E
T
( T1 – T2 )
AB
ABA
T
2
E
Temperature of the A to B
junction in °C
Temperature of the B to A
junction in °C
Thermoelectric voltage
coefficient of material A with
respect to B, µV/°C
HI
T
LO
Voltmeter
Figure 4-9
Thermoelectric generation
Minimizing thermal EMFs caused by solid-state relays
should be repeated whenever the range is changed for best
accuracy.
4.5.2 Channel resistance
Channel resistance is the equivalent resistance between the
input and output terminals of the multiplexer card. With conventional mechanical relays, the channel resistance is generally low enough to be negligible. However, the solid-state
relays used in the Model 7015 have an on resistance of
<210 Ω (<130 Ω typical), which can be a consideration in
many applications.
The channel resistance of the multiplexer card is in series
with the equivalent resistance of the DUT, as shown in Figure 4-10, and it adds to R
through the card, the channel resistance can significantly affect measurement accuracy, particularly for DUT resistance
values less than 100k Ω . For other types of measurements,
any current that fl ws through the card will cause a voltage
drop across R
CHANNEL
, resulting in similar measurement er-
rors.
. When measuring resistance
DUT
Since thermal EMFs generated by the solid-state relays are
largely a function of the operating temperature of those relays, thermal EMF generation can be minimized by keeping
the power dissipation in relays to a minimum. (To do so, simply minimize the current fl wing through the card at a given
voltage.) Not only will the relays switching the power be affected, but adjacent relays on the relay card circuit board can
also be affected by heating, although usually to a lesser degree. Also, minimizing on time will reduce thermal EMFs.
Nulling residual thermal offsets
Even if all reasonable precautions are taken, some residual
thermal offsets may still be present. These offsets can be
minimized by using the measuring instrument’s offset-compensated ohms feature if available. Also, the zero or relative
feature can be used to null them out. To do so, place the instrument on the range to be used for the measurement, and
short the end of the connecting cable nearest the measured
source (first disconnect the cable from the source to avoid
shorting out the source). After allowing the reading to settle,
press the zero or rel button to null the offset, then make your
measurement as usual. Note that it may be necessary to rezero often to counteract thermal drifts, and the rel process
4-13
Page 59

Operation
The effects of channel resistance can be minimized by following a few basic rules:
• When measuring resistance, use only the four-wire
measurement technique for resistances less than
100kΩ.
• When measuring voltage, use an instrument with high
input impedance.
• Whenever possible, keep the current fl wing through
the card to an absolute minimum.
4.5.3 Path isolation
The path isolation is simply the equivalent impedance between any two test paths in a measurement system. Ideally,
the path isolation should be infinite, but the actual resistance
and distributed capacitance of the card, cables, and connectors results in less than infinite path isolation values for these
devices.
Path isolation resistance forms a signal path that is in parallel
with the equivalent resistance of the DUT, as shown in Figure 4-11. For low-to-medium device resistance values, path
isolation resistance is seldom a consideration; however, it
can seriously degrade measurement accuracy when testing
high-impedance devices. The voltage measured across such
a device, for example, can be substantially attenuated by the
voltage divider action of the device source resistance and
path isolation resistance, as shown in Figure 4-12. Also,
leakage currents can be generated through these resistances
by voltage sources in the system.
R
DUT
E
DUT
DUT
= Source Resistance of DUT
R
DUT
E
= Source EMF of DUT
DUT
R
= Path Isolation Resistance
PATH
R
= Input Resistance of Measuring Instrument
IN
Figure 4-11
Path isolation resistance
E
DUT
E
OUT
R
DUT
=
R
PATH
MUX
Card
R
E
DUT
DUT
R
+
R
PATH
R
R
PATH
PATH
IN
Measuring
Instrument
V
4-14
Figure 4-12
Voltage attenuation by path isolation resistance
Any differential isolation capacitance affects DC measurement settling time as well as AC measurement accuracy.
Thus, it is often important that such capacitance be kept as
low as possible. Although the distributed capacitance of the
multiplexer card is generally fi ed by design, there is one
area where you do have control over the capacitance in your
system – the connecting cables. To minimize capacitance,
keep all connecting cables as short as possible.
Page 60

Operation
4.5.4 Magnetic fields
When a conductor cuts through magnetic lines of force, a
very small current is generated. This phenomenon will frequently cause unwanted signals to occur in the test leads of a
switching system. If the conductor has sufficient length, even
weak magnetic fields like those of the earth can create suffi
cient signals to affect low-level measurements.
Three ways to reduce these effects are: (1) reduce the lengths
of the test leads, (2) minimize the exposed circuit area, and
(3) keep test leads and equipment stationary. In extreme cases, magnetic shielding may be required. Special metal with
high permeability at low flux densities (such as mu metal) is
effective at reducing these effects.
Even when the conductor is stationary, magnetically induced
signals may still be a problem. Fields can be produced by
various signals such as the AC power line voltage. Large inductors such as power transformers can generate substantial
magnetic fields, so care must be taken to keep the switching
and measuring circuits a good distance away from these potential noise sources.
At high current levels, even a single conductor can generate
significant fields. These effects can be minimized by using
twisted pairs, which will cancel out most of the resulting
fields
RFI can be minimized in several ways. The most obvious
method is to keep the equipment and signal leads as far away
from the RFI source as possible. Shielding the switching
card, signal leads, sources, and measuring instruments will
often reduce RFI to an acceptable level. In extreme cases, a
specially-constructed screen room may be required to suffi
ciently attenuate the troublesome signal.
Many instruments incorporate internal filtering that may
help to reduce RFI effects in some situations. In some cases,
additional external filtering may also be required. Keep in
mind, however, that filtering may have detrimental effects on
the desired signal.
4.5.6 Ground loops
When two or more instruments are connected together, care
must be taken to avoid unwanted signals caused by ground
loops. Ground loops usually occur when sensitive instrumentation is connected to other instrumentation with more
than one signal return path such as power line ground. As
shown in Figure 4-13, the resulting ground loop causes current to fl w through the instrument LO signal leads and then
back through power line ground. This circulating current develops a small but undesirable voltage between the LO terminals of the two instruments. This voltage will be added to
the source voltage, affecting the accuracy of the measurement.
4.5.5 Radio frequency interference
RFI (Radio Frequency Interference) is a general term used to
describe electromagnetic interference over a wide range of
frequencies across the spectrum. Such RFI can be particularly troublesome at low signal levels, but it can also affect measurements at high levels if the problem is of sufficien
severity.
RFI can be caused by steady-state sources such as radio or
TV signals, or some types of electronic equipment (microprocessors, high speed digital circuits, etc.), or it can result
from impulse sources, as in the case of arcing in high-voltage
environments. In either case, the effect on the measurement
can be considerable if enough of the unwanted signal is
present.
Signal Leads
Instrument 1 Instrument 2 Instrument 3
Ground Loop
Current
Power Line Ground
Figure 4-13
Power line ground loops
4-15
Page 61

Operation
Figure 4-14 shows how to connect several instruments together to eliminate this type of ground loop problem. Here,
only one instrument is connected to power line ground.
Instrument 1 Instrument 2 Instrument 3
Power Line Ground
Figure 4-14
Eliminating ground loops
Ground loops are not normally a problem with instruments
having isolated LO terminals. However, all instruments in
the test setup may not be designed in this manner. When in
doubt, consult the manual for all instrumentation in the test
setup.
4.5.7 Keeping connectors clean
As is the case with any high-resistance device, the integrity
of connectors can be compromised if they are not handled
properly. If connector insulation becomes contaminated, the
insulation resistance will be substantially reduced, affecting
high-impedance measurement paths.
Oils and salts from the skin can contaminate connector insulators, reducing their resistance. Also, contaminants present
in the air can be deposited on the insulator surface. To avoid
these problems, never touch the connector insulating material. In addition, the multiplexer card should be used only in
clean, dry environments to avoid contamination.
If the connector insulators should become contaminated, either by inadvertent touching, or from air-borne deposits, they
can be cleaned with a cotton swab dipped in clean methanol.
After thorough cleaning, they should be allowed to dry for
several hours in a low-humidity environment before use, or
they can be dried more quickly using dry nitrogen.
4.5.8 Scanning speed considerations
One key advantage of the Model 7015 is the faster switching
times affordable by the solid-state relays. The following
paragraphs discuss considerations for taking full advantage
of this faster switching speed while scanning.
Break-before-make (Model 7002 only)
Normally, break-before-make is enabled to ensure that the
presently closed channel fully opens before the subsequent
channel in the scan list closes. While this feature does protect
the mux card and external circuits, it also slows down the
scanning speed somewhat. To maximize scanning speed, disable break-before-make operation. Note, however, that caution should be used, as simultaneous connection of two or
more active sources may damage the mux card or external
circuits. Break-before-make can be enabled or disabled by
using the appropriate selection in the GENERAL MENU
(Model 7002 only).
4-16
Page 62

5
Service Information
WARNING
The information in this section is intended only for qualified service personnel. Some of the procedures may expose
you to hazardous voltages that could result in personal injury or death. Do not
attempt to perform these procedures
unless you are qualified to do so.
5.1 Introduction
This section contains information necessary to service the
Model 7015 multiplexer card and is arranged as follows:
5.2 Handling and cleaning precautions: Discusses han-
dling precautions and methods to clean the card should
it become contaminated.
5.3 Performance verification: Covers the procedures
necessary to determine if the card meets stated specifications
5.4 Special handling of static-sensitive devices: Re-
views precautions necessary when handling staticsensitive devices.
5.2 Handling and cleaning precautions
Because of the high-impedance areas on the Model 7015,
care should be taken when handling or servicing the card to
prevent possible contamination. The following precautions
should be taken when servicing the card.
Handle the card only by the edges and shields. Do not touch
any board surfaces or components not associated with the repair. Do not touch areas adjacent to electrical contacts. When
servicing the card, wear clean cotton gloves.
Do not store or operate the card in an environment where
dust could settle on the circuit board. Use dry nitrogen gas to
clean dust off the board if necessary.
Should it become necessary to use solder on the circuit
board, use an OA-based (organic activated) flux. Remove the
flux from the work areas when the repair has been completed. Use pure water along with clean cotton swabs or a clean
soft brush to remove the flux.Take care not to spread the flu
to other areas of the circuit board. Once the flux has been removed, swab only the repaired area with methanol, then
blow dry the board with dry nitrogen gas.
5.5 Principles of operation: Briefly discusses circuit op-
eration.
5.6 Troubleshooting: Presents some troubleshooting tips
for the Model 7015 including relay replacement precautions.
After cleaning, the card should be placed in a 50 ° C low humidity environment for several hours before use.
5-1
Page 63

Service Information
5.3 Performance verification
The following paragraphs discuss performance verificatio
procedures for the Model 7015, including path resistance,
offset current, contact potential, and isolation.
With the Model 7015’s backplane jumpers installed, the performance verification procedures must be performed with
only one multiplexer card (the one being checked) installed
in the Model 7001/7002 mainframe. These conditions do not
apply if the backplane jumpers are removed.
CAUTION
Contamination will degrade the performance of the card. To avoid contamination, always grasp the card by the side
edges. Do not touch the connectors, and
do not touch the board surfaces or components. On plugs and receptacles, do
not touch areas adjacent to the electrical
contacts.
NOTE
Failure of any performance verificatio
test may indicate that the multiplexer card
is contaminated. See paragraph 5.2 for information on cleaning the card.
5.3.1 Environmental conditions
All verification measurements should be made at an ambient
temperature between 18 ° and 28 ° C, and at a relative humidity of less than 70%.
5.3.2 Recommended equipment
Table 5-1 summarizes the equipment necessary for performance verification, along with an application for each unit.
Table 5-1
Verification equipmen
Description Model or number Specifications Applications
DMM Keithley Model 2001 2kΩ; 50ppm Channel resistance
Electrometer w/voltage source Keithley Model 617 10pA, 100pA;
1.6% 100V
source; 0.2%
Sensitive Digital Voltmeter Keithley Model 182 3mV; 60ppm Contact potential
Switching mainframe Keithley Model 7001 or
7002
Triax cable (unterminated) Keithley Model 7025 Offset current
Low thermal cable (unterminated) Keithley Model 1484 Contact potential
All
Offset current, path isolation
5-2
Page 64

Service Information
5.3.3 Multiplexer card connections
The following information summarizes methods that can be
used to connect test instrumentation to the two connector
cards. Detailed connection information is provided in Section 3.
Model 7015-S Instrumentation can simply be hard-wired
directly to the screw terminals of the connector card. Jumper
wires should be kept as short as possible.
Model 7015-C One method to make instrument connec-
tions to the multiplexer card is by hard-wiring a 96-pin female DIN connector then mating it to the connector on the
Model 7015-C. Input and output shorting connections can
also be done at the connector. The connector in the Model
7011-KIT-R connection kit (see Table 3-3) can be used for
this purpose. Pin identification for the connector is provided
by Figure 3-8.
CAUTION
After making solder connections to a
connector, remove solder flux as explained in paragraph 5.2. Failure to
clean the solder connections could result
in degraded performance preventing
the card from passing verification tests.
Before pre-wiring any connectors or plugs, study the following test procedures to fully understand the connection requirements.
1. Turn off the Model 7001/7002 if it is on.
2. Turn on the Model 2001, and allow it to warm up for one
hour before making measurements.
3. Connect all input terminals of Bank A together to form
one common terminal, as shown in Figure 5-1.
4. Set the Model 2001 to the 2k Ω range, and connect the
four test leads to the INPUT and SENSE jacks.
5. Short the four test leads together and enable REL. Leave
REL enabled for the entire test.
6. Connect INPUT HI and SENSE HI of the Model 2001
to the common terminal (jumper on Bank A inputs). It is
recommended that the physical connections be made at
inputs 1 and 10 of Bank A, as shown in Figure 5-1.
7. Connect INPUT LO and SENSE LO to the HI (H) terminal of Bank A.
8. Install the Model 7015 in slot 1 (CARD 1) of the Model
7001/7002.
9. Turn on the Model 7001/7002, and program it to close
Channel 1!1 (Bank A, Input 1). Verify that the resistance
of this path is <210 Ω .
10. Open Channel 1!1 and close Channel 1!2 (Bank A, Input
2). Verify that the resistance of this path is <210 Ω .
11. Using the basic procedure in steps 9 and 10, check the
resistance of Bank A HI (H) terminal paths for Inputs 3
through 10 (Channels 1!3 through 1!10).
12. Turn off the Model 7001/7002, and move the INPUT
LO and SENSE LO test leads to the LO (L) terminal of
Bank A.
13. Repeat steps 9 through 11 to check the LO (L) terminal
paths of Bank A (Channels 1!1 through 1!10).
14. Repeat the basic procedure in steps 1 through 13 for
Banks B through D (Channels 1!11 through 1!40).
5.3.4 Channel resistance tests
Perform the following steps to verify that each relay is closing properly and that the channel resistance is within specification.
5-3
Page 65

Service Information
PREV
DCV ACV DCI ACI Ω2 Ω4
DISPLAY
NEXT
POWER
FILTER MATH
REL TRIG STORE RECALL
INFO LOCAL CHAN SCAN CONFIG MENU EXIT ENTER
Model 2001 Multimeter
(Measure 4-Wire Ohms)
Note : Connections are set
up to test Bank A HI
2001 MULTIMETER
FREQ TEMP
SENSE
Ω 4 WIRE
350V
PEAK
INPUTS
F
RANGE
AUTO
FRONT/REAR
RANGE
CAL
INPUT
HI
1100V
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
R
2A 250V
AMPS
Sense Ω LO
Sense Ω HI
Input HI
Input LO
Jumpers
1 3456789102
A
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
Bank Inputs
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
H
L
H
L
Figure 5-1
Path resistance test connections
5.3.5 Offset current tests
These tests check leakage current between HI (H) and LO
(L) (differential offset current) and from HI (H) and LO (L)
to chassis (common-mode offset current) of each pathway. In
general, these tests are performed by simply measuring the
leakage current with an electrometer. In the following procedure, the Model 617 is used to measure the leakage current.
Test connections are shown in Figure 5-2.
Perform the following procedure to check offset current:
1. Turn off the Model 7001/7002 if it is on, and remove any
jumpers or wires connected to the multiplexer card.
2. Connect the triax cable to the Model 617, but do not
connect it to the multiplexer card at this time.
3. Turn on the Model 617, and allow the unit to warm up
for two hours before testing. After warm-up, select the
200pA range, and enable zero check and zero correct in
that order. Leave zero correct enabled for the entire procedure. Also, be certain that V- Ω , GUARD is OFF and
that the ground strap is connected to LO.
4. Connect the triax cable to Bank A HI and LO, as shown
in Figure 5-2A.
5. Install the Model 7015 in slot 1 (CARD 1) of the Model
7001/7002.
Model 7015
6. Turn on the Model 7001/7002, and program the unit to
close Channel 1!1 (Bank A, Input 1).
7. On the Model 617, disable zero check, and allow the
reading to settle. Verify that the reading is <1nA. This
specification is the offset (leakage) current of the pathway.
8. Enable zero check on the Model 617 and open Channel
1!1 from the front panel of the Model 7001/7002.
9. Repeat the basic procedure in steps 6 through 8 to check
the rest of the pathways (Inputs 2 through 10) of Bank A
(Channels 1!2 through 1!10).
10. Turn off the Model 7001/7002, and change the electrometer connections to Bank B.
11. Repeat the basic procedure in steps 6 through 10 to
check Bank B, Inputs 1 through 10 (Channels 1!11
through 1!20).
12. Repeat the basic procedure in steps 6 through 11 for
Banks C and D (Channels 1!21 through 1!40).
13. Turn off the Model 7001/7002 and change the electrometer connections, as shown in Figure 5-2B. Note that
electrometer HI is connected to HI and LO of the Bank
A output, which are jumpered together. Electrometer
LO is connected to chassis.
14. Repeat steps 6 through 12 to check that the common
mode offset current is <1nA.
5-4
Page 66

Model 7025
Unterminated
Triax Cable
INPUT
Model 617
(Measure Current)
Note : Setup shown is configured
to test Bank A pathways for
offset current.
HI (Red)
LO (Black)
Bank Inputs
1 3456789102
A
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
Model 7015
A) Differential
Service Information
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
H
L
H
L
Model 7025
Unterminated
Triax Cable
INPUT
1 3456789102
A
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
Model 617
(Measure Current)
Note : Setup shown is configured
to test Bank A pathways for
offset current.
HI (Red)
LO (Blk)
Short
B) Common-Mode
Figure 5-2
Differential and common mode offset current test connections
Bank Inputs
Model 7015
H
L
H
L
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
5-5
Page 67

Service Information
5.3.6 Contact potential tests
These tests check the EMF generated by each relay contact
pair (H and L) for each pathway. The tests simply consist of
using a sensitive digital voltmeter (Model 182) to measure
the contact potential.
Perform the following procedure to check contact potential
of each path:
1. Turn off the Model 7001/7002 if it is on.
2. Place jumpers between Banks A-B, B-C, and C-D.
3. Turn on the Model 182, and allow the unit to warm up
to achieve rated accuracy.
4. Place a short between HI to LO on each input (Channels
1-40).
5. Place a short between HI to LO on output Bank D (long
enough to cut with wire cutters).
6. Connect the Model 182 input leads to HI and LO output
Bank A using copper wires.
7. Install the Model 7015 in slot 1, and turn the Model
7001/7002 on.
8. Allow Models 7001/7002, 7015 and 182 to warm up for
two hours.
9. Select the 3mV range on the Model 182.
10. Press REL READING (on the Model 182) to null out internal offsets. Leave REL READING enabled for the
entire procedure.
11. Turn off the Model 7001/7002. Remove the Model 7015
from slot 1. Cut the short on B and D output HI to LO.
12. Install the Model 7015 in the Model 7001/7002 slot 1,
and turn power on.
13. Wait 15 minutes.
14. Program the Model 7001/7002 to close Channel 1!1.
15. After settling, verify that reading on the Model 182 is
within required limits (see specifications). This measurement represents the contact potential of the pathway.
16. From the Model 7001/7002, open Channel 1!1.
17. Repeat steps 12 through 14 for all 40 channels.
Model 1484
Low Thermal Cable
(Unterminated)
KEITHLEY
182 SENSITIVE DIGITAL VOLTMETER
Model 182
Note : Setup shown is configured
to test Bank A thru D
relays for contact potential.
Figure 5-3
Contact potential test connections
Low thermal short.
Clean high purity
Bank Inputs
1 3456789102
A
HI
LO
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
copper (1 of 40)
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
H
L
H
L
Model 7015
5-6
Page 68

Service Information
5.3.7 Bank and channel-to-channel isolation tests
Bank isolation tests check the leakage resistance between adjacent banks. Channel-to-channel isolation tests check the
leakage resistance between a Bank Output connection and a
Bank Input connection with an adjacent Bank Input relay
closed. In general, the tests are performed by applying a voltage (100V) across the leakage resistance and then measuring
the current. The isolation resistance is then calculated as R =
V/I. In the following procedure, the Model 617 functions as
both a voltage source and an ammeter. In the V/I function,
the Model 617 internally calculates the resistance from the
known voltage and current levels and displays the resistive
value.
Perform the following steps to check bank and channel-tochannel isolation:
1. Turn off the Model 7001/7002 if it is on, and remove any
jumpers or test leads connected to the multiplexer card.
2. Turn on the Model 617, and allow the unit to warm up
for two hours before testing.
3. On the Model 617, select the 2pA range, and enable zero
check and zero correct in that order. Leave zero correct
enabled for the entire procedure.
4. Connect the electrometer to the Model 7015, as shown
in Figure 5-4.
5. Install the Model 7015 in slot 1 of the Model 7001/7002,
and turn on the mainframe.
6. On the Model 617, select the 20pA range and release
zero check.
7. On the Model 617, press SUPPRESS to cancel offset
current, then enable zero check.
WARNING
The following steps use high voltage
(100V). Be sure to remove power from
the circuit before making connection
changes.
8. On the Model 617, set the voltage source for +100V, and
select the 20nA current range. Make sure the voltage
source is in standby.
9. Place the Model 617 in the V/I measurement function by
pressing SHIFT OHMS.
10. Program the Model 7001/7002 to close Channels 1!1
and 1!12 (Bank A, Input 1 and Bank B, Input 2).
Banana to Banana Cable
Ground Link
Removed
INPUT
Source V and
Measure V/I
Model 617
Unterminated
Banana Cables
Note : Setup shown is configured
to test isolation between
Bank A and Bank B.
Figure 5-4
Bank isolation test connections
Model 7025
Unterminated
Triax Cable
HI
(Red)
Bank Inputs
1 3456789102
A
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
Model 7015
H
L
H
L
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
5-7
Page 69

Service Information
Ω
Ω
Ω
11. On the Model 617, disable zero check, and press OPERATE to source +100V.
12. After allowing the reading on the Model 617 to settle,
verify that it is >1G Ω (10
9
). This measurement is the
leakage resistance (bank isolation) between Bank A, Input 1 and Bank B, Input 2.
13. Place the Model 617 voltage source in standby, and enable zero check.
14. Turn off the Model 7001/7002, and move the electrometer connections to Banks B and C.
15. Install the Model 7011 in slot 1 of the mainframe, and
turn on the Model 7001.
16. Program the Model 7001/7002 to close Channels 1!12
and 1!23 (Bank B, Input 2 and Bank C, Input 3).
17. On the Model 617, disable zero check, and press OPERATE to source +100V.
18. After allowing the reading on the Model 617 to settle,
verify that it is >1G Ω (10
9
).
19. Place the Model 617 voltage source in standby, and enable zero check.
20. Turn off the Model 7001/7002 and move the electrometer connections to Banks C and D.
21. Install the Model 7015 in slot 1 of the mainframe, and
turn on the Model 7001/7002.
22. Using Table 5-2 as a guide, repeat the basic procedure of
steps 16 through 18 for the rest of the path pairs (test
numbers 3 through 9 in the table).
23. Place the Model 617 voltage source in standby, and enable zero check.
NOTE
Refer to the following procedure to check
channel-to-channel isolation.
24. Turn off the Model 7001/7002, and connect the Model
617 to the card as shown in Figure 5-5.
25. Install the Model 7015 in slot 1 of the Model 7001/7002,
and turn on the mainframe.
26. Program the Model 7001/7002 to close Channel 1!2
(Bank A, Input 2). Make sure all other channels are
open.
27. On the Model 617, disable zero check, and press OPERATE to source 100V.
28. After allowing the reading on the Model 617 to settle,
verify that it is >1G Ω (10
9
).
29. Place the Model 617 voltage source in standby, and enable zero check.
30. Using Table 5-3 as a guide, perform tests 2 through 9 for
the remaining Bank A Inputs. Remember to move Bank
Input connections as indicated in the table.
31. Use Table 5-3 (test numbers 10 through 36) and the
above procedure to test Banks B, C, and D.
Table 5-2
Bank isolation test summary
Test
number Bank isolation Test equipment location Channels closed*
1 Bank A, Input 1 to Bank B, Input 2 Bank A and Bank B 1!1 and 1!12
2 Bank B, Input 2 to Bank C, Input 3 Bank B and Bank C 1!12 and 1!23
3 Bank C, Input 3 to Bank D, Input 4 Bank C and Bank D 1!23 and 1!34
4 Bank C, Input 4 to Bank D, Input 5 Bank C and Bank D 1!24 and 1!35
5 Bank C, Input 5 to Bank D, Input 6 Bank C and Bank D 1!25 and 1!36
6 Bank C, Input 6 to Bank D, Input 7 Bank C and Bank D 1!26 and 1!37
7 Bank C, Input 7 to Bank D, Input 8 Bank C and Bank D 1!27 and 1!38
8 Bank C, Input 8 to Bank D, Input 9 Bank C and Bank D 1!28 and 1!39
9 Bank C, Input 9 to Bank D, Input 10 Bank C and Bank D 1!29 and 1!40
*Assumes Model 7015 installed in slot 1 of mainframe. Programmed as slot (1) and channel.
5-8
Page 70

Model 7025
Unterminated
Banana to Banana Cable
Ground Link
Removed
INPUT
Source V and
Measure V/I
Model 617
Unterminated
Banana Cables
Note : Setup shown is configured
to test isolation between
path 1!1 and 1!2.
Triax Cable
HI
(Red)
Figure 5-5
Channel-to-channel isolation test connections
Jumper
1 3456789102
A
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
Bank Inputs
Model 7015
Service Information
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
H
L
H
L
Table 5-3
Channel-to-channel isolation test summary
Test
number Channel-to-channel isolation Test equipment location
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
*Assumes Model 7015 installed in slot 1 of mainframe. Programmed as slot (1) and channel.
Bank A, Input 1 to Bank A, Input 2
Bank A, Input 2 to Bank A, Input 3
Bank A, Input 3 to Bank A, Input 4
Bank A, Input 4 to Bank A, Input 5
Bank A, Input 5 to Bank A, Input 6
Bank A, Input 6 to Bank A, Input 7
Bank A, Input 7 to Bank A, Input 8
Bank A, Input 8 to Bank A, Input 9
Bank A, Input 9 to Bank A, Input 10
Bank A and Input 1
Bank A and Input 2
Bank A and Input 3
Bank A and Input 4
Bank A and Input 5
Bank A and Input 6
Bank A and Input 7
Bank A and Input 8
Bank A and Input 9
Channel
closed*
1!2
1!3
1!4
1!5
1!6
1!7
1!8
1!9
1!10
5-9
Page 71

Service Information
Table 5-3 (continued)
Channel-to-channel isolation test summary
Test
number Channel-to-channel isolation Test equipment location
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
Bank B, Input 1 to Bank B, Input 2
Bank B, Input 2 to Bank B, Input 3
Bank B, Input 3 to Bank B, Input 4
Bank B, Input 4 to Bank B, Input 5
Bank B, Input 5 to Bank B, Input 6
Bank B, Input 6 to Bank B, Input 7
Bank B, Input 7 to Bank B, Input 8
Bank B, Input 8 to Bank B, Input 9
Bank B, Input 9 to Bank B, Input 10
Bank C, Input 1 to Bank C, Input 2
Bank C, Input 2 to Bank C, Input 3
Bank C, Input 3 to Bank C, Input 4
Bank C, Input 4 to Bank C, Input 5
Bank C, Input 5 to Bank C, Input 6
Bank C, Input 6 to Bank C, Input 7
Bank C, Input 7 to Bank C, Input 8
Bank C, Input 8 to Bank C, Input 9
Bank C, Input 9 to Bank C, Input 10
Bank D, Input 1 to Bank D, Input 2
Bank D, Input 2 to Bank D, Input 3
Bank D, Input 3 to Bank D, Input 4
Bank D, Input 4 to Bank D, Input 5
Bank D, Input 5 to Bank D, Input 6
Bank D, Input 6 to Bank D, Input 7
Bank D, Input 7 to Bank D, Input 8
Bank D, Input 8 to Bank D, Input 9
Bank D, Input 9 to Bank D, Input 10
Bank B and Input 1
Bank B and Input 2
Bank B and Input 3
Bank B and Input 4
Bank B and Input 5
Bank B and Input 6
Bank B and Input 7
Bank B and Input 8
Bank B and Input 9
Bank C and Input 1
Bank C and Input 2
Bank C and Input 3
Bank C and Input 4
Bank C and Input 5
Bank C and Input 6
Bank C and Input 7
Bank C and Input 8
Bank C and Input 9
Bank D and Input 1
Bank D and Input 2
Bank D and Input 3
Bank D and Input 4
Bank D and Input 5
Bank D and Input 6
Bank D and Input 7
Bank D and Input 8
Bank D and Input 9
Channel
closed*
1!12
1!13
1!14
1!15
1!16
1!17
1!18
1!19
1!20
1!22
1!23
1!24
1!25
1!26
1!27
1!28
1!29
1!30
1!32
1!33
1!34
1!35
1!36
1!37
1!38
1!39
1!40
5-10
*Assumes Model 7015 installed in slot 1 of mainframe. Programmed as slot (1) and channel.
Page 72

Ω
Service Information
5.3.8 Differential and common-mode isolation
tests
These tests check the leakage resistance (isolation) between
HI (H) and LO (L) (differential), and from HI (H) and LO (L)
to chassis (common-mode) of every bank and channel. In
general, the test is performed by applying a voltage (100V)
across the terminals and then measuring the leakage current.
The isolation resistance is then calculated as R = V/I. In the
following procedure, the Model 617 functions as a voltage
source and an ammeter. In the V/I function, the Model 617
internally calculates the resistance from the known voltage
and current levels, and displays the resistance value.
Perform the following steps to check differential and common mode isolation:
1. Turn off the Model 7001/7002 if it is on, and remove any
jumpers and test leads connected to the multiplexer
card.
2. Turn on the Model 617, and allow the unit to warm up
for two hours for rated accuracy.
3. On the Model 617, select the 2pA range, and enable zero
check and zero correct in that order. Leave zero correct
enabled for the entire procedure.
WARNING
The following steps use high voltage
(100V). Be sure to remove power from
the circuit before making connection
changes.
4. On the Model 617, set the voltage source for +100V, and
select the 200nA current range. Make sure the voltage
source is still in standby.
5. Place the Model 617 in the V/I measurement function by
pressing SHIFT OHMS.
6. With the Model 617 in standby, connect the electrometer
to Bank A of the multiplexer card, as shown in Figure 5-
6.
7. Install the Model 7015 in slot 1 (CARD 1) of the mainframe, and turn on the Model 7001/7002.
8. Make sure all the relays are open. (Press OPEN ALL on
the Model 7001/7002.)
9. On the Model 617, disable zero check, and press OPERATE to source 100V.
10. After allowing the reading on the Model 617 to settle,
verify that it is >1G Ω (10
9
). This measurement is the
differential leakage resistance (isolation) of Bank A.
11. Place the Model 617 in standby, and enable zero check.
Banana to Banana Cable
Ground Link
Removed
INPUT
Model 617
Unterminated
Banana Cable
Note : Setup shown is configured to
test isolation between HI and
LO of Bank A.
Figure 5-6
Differential isolation test connections
Model 7025
Unterminated
Triax Cable
HI
(Red)
Bank Inputs
1 3456789102
A
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
Model 7015
H
L
H
L
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
5-11
Page 73

Service Information
Ω
Ω ).
12. Program the Model 7001/7002 to close Channel 1!1
(Bank A, Input 1).
13. On the Model 617, disable zero check, and press OPERATE to source +100V.
14. After allowing the reading on the Model 617 to settle,
verify that it is also >1G Ω (10
9
). This measurement
checks the differential isolation of Input 1.
15. Using Table 5-4 as a guide, repeat the basic procedure in
steps 11 through 14 to test Inputs 2 through 10 of Bank
A (test numbers 3 through 11 of the table).
16. Use Table 5-4 (test numbers 12 through 42) and the
above procedure to test Banks B, C and D.
17. Place the Model 617 voltage source in standby, and enable zero check.
NOTE
Refer to Figure 5-7 for the following procedure to check common mode isolation.
18. Turn off the Model 7001/7002, and connect the electrometer to the Model 7015 as shown in Figure 5-7.
19. Repeat steps 4 through 16 to check common mode isolation. Verify that each reading is >1G Ω (10
9
Table 5-4
Differential and common-mode isolation testing
Test
number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Differential or common
mode isolation
Bank A
Bank A, Input 1
Bank A, Input 2
Bank A, Input 3
Bank A, Input 4
Bank A, Input 5
Bank A, Input 6
Bank A, Input 7
Bank A, Input 8
Bank A, Input 9
Bank A, Input 10
Channel
closed*
None
1!1
1!2
1!3
1!4
1!5
1!6
1!7
1!8
1!9
1!10
Table 5-4 (continued)
Differential and common-mode isolation testing
Test
number
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
*Assumes Model 7015 installed in slot 1 of mainframe. Programmed as slot (1) and channel.
Differential or common
mode isolation
Bank B
Bank B, Input 1
Bank B, Input 2
Bank B, Input 3
Bank B, Input 4
Bank B, Input 5
Bank B, Input 6
Bank B, Input 7
Bank B, Input 8
Bank B, Input 9
Bank B, Input 10
Bank C
Bank C, Input 1
Bank C, Input 2
Bank C, Input 3
Bank C, Input 4
Bank C, Input 5
Bank C, Input 6
Bank C, Input 7
Bank C, Input 8
Bank C, Input 9
Bank C, Input 10
Bank D
Bank D, Input 1
Bank D, Input 2
Bank D, Input 3
Bank D, Input 4
Bank D, Input 5
Bank D, Input 6
Bank D, Input 7
Bank D, Input 8
Bank D, Input 9
Bank D, Input 10
Channel
closed*
None
1!11
1!12
1!13
1!14
1!15
1!16
1!17
1!18
1!19
1!20
None
1!21
1!22
1!23
1!24
1!25
1!26
1!27
1!28
1!29
1!30
None
1!31
1!32
1!33
1!34
1!35
1!36
1!37
1!38
1!39
1!40
5-12
Page 74

Model 7025
Unterminated
Banana to Banana Cable
Ground Link
Removed
INPUT
Source V and
Measure V/I
Model 617
Unterminated
Banana Cable
Note : Setup shown is configured
to test isolation between
Bank A and chassis ground.
Triax Cable
(Red)
Figure 5-7
Common-mode isolation test connections
HI
Jumper
Bank Inputs
1 3456789102
A
B
C
D
HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL HL
Model 7015
Service Information
H
L
H
L
Bank
Outputs
H
L
H
L
5.4 Special handling of static-sensitive devices
CMOS and other high-impedance devices are subject to possible static discharge damage because of the high-impedance
levels involved. When handling such devices, use the precautions listed below.
NOTE
In order to prevent damage, assume that all
parts are static-sensitive.
1. Such devices should be transported and handled only in
containers specially designed to prevent or dissipate
static build-up. Typically, these devices will be received
in anti-static containers made of plastic or foam. Keep
these parts in their original containers until ready for installation or use.
2. Remove the devices from their protective containers
only at a properly-grounded workstation. Also, ground
yourself with an appropriate wrist strap while working
with these devices.
3. Handle the devices only by the body; do not touch the
pins or terminals.
4. Any printed circuit board into which the device is to be
inserted must first be grounded to the bench or table.
5. Use only anti-static type de-soldering tools and grounded-tip soldering irons.
5.5 Principles of operation
The following paragraphs discuss the basic operating principles for the Model 7015, and can be used as an aid in troubleshooting the card. The schematic drawing of the card is
shown on drawing number 7015-106, located at the end of
Section 6.
5.5.1 Block diagram
Figure 5-8 shows a simplified block diagram of the Model
7015. Key elements include the relay drivers and solid-state
relays, as well as the ROM, which contains card ID and configuration information. These various elements are discussed
in the following paragraphs.
5-13
Page 75

Service Information
To Mainframe
To Mainframe
Figure 5-8
Model 7015 block diagram
+5V
CLK
Data
Strobe
Enable
ID CLK
ID DATA
+6V
Relay
Drivers
U100U103,
U105
ROM
U104
Solid State
Relays
K100-K179
User connections
5.5.2 ID data circuits
Upon power-up, card identification information from each
card is read by the mainframe. This ID data includes such information as card ID, hardware settling time, and relay configuration information.
ID data is contained within an on-card EEPROM (U104). In
order to read this information, the sequence described below
is performed on power-up.
1. The IDDATA line (pin 6 of U104) is set from high to low
while the IDCLK line (pin 5 of U104) is held high. This
transition initiates a start command to the ROM to transmit data serially to the mainframe (Figure 5-9).
2. The mainframe sends the ROM address location to be
read over the IDDATA line. The ROM then transmits an
acknowledge signal back to the mainframe, and it then
transmits data at that location back to the mainframe
(Figure 5-10).
3. The mainframe then transmits an acknowledge signal,
indicating that it requires more data. The ROM will then
sequentially transmit data after each acknowledge signal it receives.
4. Once all data is received, the mainframe sends a stop
command, which is a low-to-high transition of the IDDATA line with the IDCLK line held high (see Figure 5-9).
5-14
Page 76

Figure 5-9
Start and stop sequences
IDCLK
IDDATA
Start Bit Stop Bit
Service Information
IDCLK
189
IDDATA
(Data output
from mainframe
or ROM)
IDDATA
(Data output
from mainframe
or ROM)
Start
Figure 5-10
Transmit and acknowledge sequence
5.5.3 Relay control
Card relays are controlled by serial data transmitted via the
relay DATA line. A total of fi e bytes for each card are shifted in serial fashion into latches located in the card relay driver ICs, U100-U103, U105. The serial data is clocked in by
the CLK line. As data overfl ws one register, it is fed out the
Q’S line of the register down the chain.
Once all fi e bytes have shifted into the card, the STROBE
line is set high to latch the relay information into the Q outputs of the relay drivers, and the appropriate relays are ener-
Acknowledge
gized. Note that a relay driver output goes low to energize the
corresponding relay.
5.5.4 Power-on safeguard
Upon power-up, the relay driver outputs are inhibited for
about 200msec to avoid random engagement. The output enable (OE) signal is generated by circuitry located in the
mainframe.
5-15
Page 77

Service Information
5.6 Troubleshooting
5.6.1 Troubleshooting equipment
Table 5-5 summarizes recommended equipment for troubleshooting the Model 7015.
Table 5-5
Recommended troubleshooting equipment
Manufacturer
Description
Multimeter Keithley 2001 Measure DC voltages
Oscilloscope TEK 2243 View logic waveforms
Switching
mainframe
5.6.2 Troubleshooting access
In order to gain access to the relay card top surface to measure voltages under actual operation conditions, perform the
following steps (Model 7001 only):
1. Disconnect the connector card from the relay card.
2. Remove the Model 7001 cover.
3. Install the relay card in the CARD 1 slot location.
4. Turn on Model 7001 power to measure voltages (see following paragraph).
and model Application
Keithley 7001 Control card
WARNING
Lethal voltages are present within the
7001 mainframe. Some of the procedures may expose you to hazardous
voltages. Observe standard safety precautions for dealing with live circuits.
Failure to do so could result in personal
injury or death.
CAUTION
Observe the following precautions when
troubleshooting or repairing the switch
card:
To avoid contamination, which could
degrade card performance, always handle the card only by the handle and side
edges. Do not touch edge connectors,
board surfaces, or components on the
card. Also, do not touch areas adjacent
to electrical contacts on connectors.
Use care when removing parts from the
PC board to avoid pulling traces away
from the circuit board. Before attempting to remove a part, use an appropriate
de-soldering tool, such as a solder sucker, to clear each mounting hole completely free of solder. Each pin must be
free to move in its mounting hole before
removal.
5.6.3 Troubleshooting Procedure
Table 5-6 summarizes switch card troubleshooting.
5-16
Page 78

Table 5-6
Troubleshooting procedure
Step Item/component Required condition Comments
Service Information
1 Ground
(P2001, pins 3, 4, 15, 16)
2 K100-K178 even-numbered
relays, pins 1 and 2
3 U104, pin 8 +5VDC Logic voltage.
4 U104, pin 5 IDCLK pulses During power-up only.
5 U104, pin 6 IDDATA pulses During power-up only.
6 U100, pin 7 STROBE pulse End of relay update sequence.
7 U100, pin 2 CLK pulses During relay update sequence only.
8 U100, pin 3 DATA pulses During relay update sequence only.
9 U100-U103, U105,
pins 10-18
+6VDC Relay voltage.
Low with relay energized; high
with relay de-energized.
All voltages referenced to digital ground.
Relay driver outputs.
5-17
Page 79

Service Information
5-18
Page 80

6
Replaceable Parts
6.1 Introduction
This section contains replacement parts information, schematic diagrams, and component layout drawings for the
Model 7015.
6.2 Parts lists
Parts lists for the various circuit boards are included in tables
integrated with schematic diagrams and component layout
drawings for the boards. Parts are listed alphabetically in order of circuit designation.
6.3 Ordering information
To place an order, or to obtain information concerning replacement parts, contact your Keithley representative or the
factory (see inside front cover for addresses). When ordering
parts, be sure to include the following information:
6.4 Factory service
If the card is to be returned to Keithley Instruments for repair,
perform the following:
1. Complete the service form at the back of this manual,
and include it with the card.
2. Carefully pack the card in the original packing carton.
3. Write ATTENTION REPAIR DEPT on the shipping label.
Note: It is not necessary to return the switching mainframe
with the card.
6.5 Component layouts and schematic diagrams
Component layout drawings and schematic diagrams are included on the following pages integrated with the parts lists:
7015-100 Component Layout, Solid-State Relay Card for
7015-S and 7015-C.
1. Card model number (7015)
2. Card serial number
3. Part description
4. Circuit description, if applicable
5. Keithley part number
7015-106 Schematic, Solid-State Relay Card for 7015-S
and 7015-C.
NOTE
The Models 7015-S and 7015-C use the
same relay card. Only the connector cards
are different.
6-1
Page 81

Replaceable Parts
7015-160 Component Layout, Terminal Block Board for
7015-S.
7015-166 Schematic, Terminal Block Board for 7015-S.
7015-170 Component Layout, Mass Terminated Card for
7015-C.
7015-176 Schematic, Mass Terminated Card for 7015-C.
6-2
Page 82

Table 6-1
Parts List, Solid-State Relay Card (Models 7015-C and 7015-S)
Replaceable Parts
Circuit
Desig. Description
EJECTOR ARM
SHIELD
STANDOFF, #4-40X.812LG
STANDOFF #2 CLEARANCE
C109,110
C101,102,103,105,
106,107,108
C100,C104
CR101
J1002,1003
P2001
R140
R100-139
K100-179
U100-103,105
U104
CAP, 10UF,-20+100%,25V,ALUM ELEC
CAP,.1UF,20%,50V,CERAMIC
CAP,150PF,10%,1000V,CERAMIC
DIODE,SILICON,IN4006 (D0-41)
CONN, 48-PIN, 3-ROWS
CONNECTOR, 32-PIN, 2-ROWS
RES,10K,5%,1/4W,COMPOSITION OR FILM
RES,2K,5%,1/4,COMPOSITION OR FILM
RELAY
IC, 8-BIT SERIAL-IN LATCH DRIVER,5841A
EPROM PROGRAM
Keithley
Part No.
7011-301B
7011-305B
ST-137-20
ST-204-1
C-314-10
C-365-.1
C-64-150P
RF-38
CS-736-2
CS-775-1
R-76-10K
R-76-2K
RL-167
IC-536
7015-800A01
W100-107,109
JUMPER
J-15
6-3
Page 83

sz
KK
Page 84

TC17-100
25917
B2
Page 85

25917
B2
Page 86

Table 6-2
Parts List,Terminal Block Board (Model 7015-S)
Replaceable Parts
Circuit
Desig. Description
TOP CLAMP
CABLE CLAMP
SHIELD
J1006,1009,1012,1015
J1004,1005,1007,1008,
1010,1011
P1002,1003
W100-105
CONN, 6 PIN
CONN, 8 PIN
CONNECTOR, 48-PIN, 3 ROWS
CONN,BERG,2 PIN
Keithley
Part No.
7011-302B
7011-304-5C
7011-305B
TE-115-6
TE-115-8
CS-748-3
CS-339-2
6-4
Page 87

Page 88

Page 89

Table 6-3
Parts List, Mass Terminated Card (Model 7015-C)
Replaceable Parts
Circuit
Desig. Description
BRACKET
CONNECTOR SHIM
SHIELD
STANDOFF
C101,102
C103
CR101-105
E101,102
J1004
K101-104
P1002,1003
Q101-103
R103,104
R106
R109
R108,110
R105
R111
R107
CAP,1UF,20%,50V, CERAMIC
CAP,.1UF,20%,50V,CERAMIC
DIODE,SILICON,IN4148 (DO-35)
FERRITE BEAD
CONN, 96-PIN, 3 ROWS
RELAY, ULTRA-SMALL POLARIZED TF2E-5V
CONNECTOR, 48-PIN, 3 ROWS
TRANS,N CHAN MOSPOW FET,2N7000 (TO-92)
RES, 1M, 10%, 1/2W, COMPOSITION
RES,10,5%,1/4W,COMPOSITION OR FILM
RES,100K,5%,1/4W,COMPOSITION OR FILM
RES,10K,5%,1/4W,COMPOSITION OR FILM
RES, 68, 5%, 1/4W, COMPOSITION OR FILM
RES,10K,1%,1/8W,METAL FILM
RES,4.99K,1%,1/8W,METAL FILM
Keithley
Part No.
7011-307
7011-309A
7011-311A
ST-203-1
C-237-1
C-365-.1
F-28
CT-1
CS-514
RL-149
CS-748-3
TG-195
R-1-1M
R-76-10
R-76-100K
R-76-10K
R-76-68
R-88-10K
R-88-4.99
U101
U102
W100-105
IC,QUAD 2 INPUT NOR,74HC02
IC, DUAL, VOLTAGE COMPARATOR, LM393
CONN,BERG,2 PIN
IC-412
IC-343
CS-339-2
6-5
Page 90

Page 91

Page 92

Index
Numerics
7011-KIT-R 1-3
7011-MTC-2 1-3
7011-MTR 1-3
7015-ST 1-3
B
Backplane jumpers 2-5, 3-3
Bank and channel-to-channel isolation
tests 5-7
Bank-to-bank jumpers 3-2
Basic multiplexer configurations 2-1
Block diagram 5-13
Break-before-make 4-16
C
Card Connections & Installation 3-1
Channel assignments 4-1
Channel resistance 4-13
Channel resistance tests 5-3
Closing and opening channels 4-3, 4-4
Component layouts and schematic dia-
grams 6-1
Connections 3-1
Contact potential tests 5-6
F
Factory service 6-1
Features 1-1
Four-wire resistance tests 4-7
Front panel control 4-3
G
General Information 1-1
Ground loops 4-15
H
Handling and cleaning precautions 5-1
Handling precautions 3-1
High-speed scanning 4-5
I
ID data circuits 5-14
IEEE-488 bus operation 4-4
Inspection for damage 1-2
Installation and removal 3-18
Instruction manual 1-2
L
Low-level resistance measurements 4-9
M
Magnetic fields 4-15
Mainframe control of multiplexer card 4-1
Mainframe multiplexer expansion 2-9
Manual addenda 1-2
Maximum signal levels 4-1
Measurement considerations 4-12
Minimizing thermal EMFs 4-13
Mixing card types 2-9
Multi-card switching systems 2-8
Multi-pin (mass termination) connector
card 3-6
Multiple-card systems 3-13
Multiplexer and matrix card connections
4-10
Multiplexer applications 4-5
Multiplexer bank-to-bank jumpers 2-2
Multiplexer card connections 5-3
Multiplexer card installation 3-18
Multiplexer card removal 3-18
Multiplexer expansion 2-8
Multiplexer input expansion 2-8
Multiplexer switching schemes 2-6
Multiplexing Basics 2-1
D
Differential and common-mode isolation
tests 5-11
Differential switching 2-6
E
Environmental conditions 5-2
J
Jumper installation 3-3
Jumper removal 3-3
K
Keeping connectors clean 4-16
N
Nulling residual thermal offsets 4-13
O
Offset current tests 5-4
Operation 4-1
Optional accessories 1-3
Ordering information 6-1
Output relays 3-7
i-1
Page 93

P
Parts lists 6-1
Path isolation 4-14
Performance verification 5-2
Power-on safeguard 5-15
Principles of operation 5-13
R
Radio frequency interference 4-15
Recommended equipment 5-2
Relay control 5-15
Repacking for shipment 1-3
Replaceable Parts 6-1
Resistor testing 4-7
Round cable assemblies 3-7
S
Safety symbols and terms 1-2
Scanning channels 4-3, 4-4
Scanning speed considerations 4-16
Screw terminal connector card 3-4
Sensing 2-6
Separate switching systems 2-8
Service Information 5-1
Shipment contents 1-2
Single-card system 3-10
Single-ended switching 2-6
Special handling of static-sensitive devic-
es 5-13
Specifications 1-2
T
Testing with matrix cards 4-10
Thermoelectric generation 4-12
Thermoelectric potentials 4-12
Transistor current gain testing 4-10
Troubleshooting 5-16
Troubleshooting access 5-16
Troubleshooting equipment 5-16
Troubleshooting Procedure 5-16
Two-card system 3-13
Two-mainframe system 3-13
Two-wire resistance tests 4-7
Typical connection schemes 3-10
Typical connection techniques 3-7
U
Unpacking and inspection 1-2
W
Warranty information 1-1
Wiring procedure 3-5
i-2
Page 94

Service Form
Model No. Serial No. Date
Name and Telephone No.
Company
List all control settings, describe problem and check boxes that apply to problem.
Intermittent
❏
❏
IEEE failure
Front panel operational
❏
Display or output (check one)
Drifts
❏
❏
Unstable
❏
Overload
❏
Calibration only
❏
Data required
(attach any additional sheets as necessary)
Show a block diagram of your measurement system including all instruments connected (whether power is turned on or not).
Also, describe signal source.
Analog output follows display
❏
❏
Obvious problem on power-up
All ranges or functions are bad
❏
Unable to zero
❏
❏
Will not read applied input
❏
CertiÞcate of calibration required
Particular range or function bad; specify
❏
❏
Batteries and fuses are OK
Checked all cables
❏
Where is the measurement being performed? (factory, controlled laboratory, out-of-doors, etc.)
What power line voltage is used? Ambient temperature? ¡F
Relative humidity? Other?
Any additional information. (If special modiÞcations have been made by the user, please describe.)
Be sure to include your name and phone number on this service form
.
Page 95

Keithley Instruments, Inc.
28775 Aurora Road
Cleveland, Ohio 44139
Printed in the U.S.A
 Loading...
Loading...