Page 1

Model 2461 1 kW Pulse Mode Interactive
SourceMeter® Instrument User’s Manual
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Test Equipment Depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176 - TestEquipmentDepot.com
*P246190001A*
2461-900-01A
A Greater Measure of Condence
A Tektr onix Company
Page 2

Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument
Model 2461
User's Manual
© 2015, Keithley Instruments
Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.A.
All rights reserved.
Any unauthorized reproduction, photocopy, or use of the information herein, in whole or in part,
without the prior written approval of Keithley Instruments is strictly prohibited.
TSP®, TSP-Link®, and TSP-Net® are trademarks of Keithley Instruments. All Keithley Instruments
product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of Keithley Instruments. Other brand
names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Document number: 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Page 3

Safety precautions
The following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any associated instrumentation. Although
some instruments and accessories would normally be used with nonhazardous voltages, there are situations where hazardous
conditions may be present.
This product is intended for use by qualified personnel who recognize shock hazards and are familiar with the safety precautions
required to avoid possible injury. Read and follow all installation, operation, and maintenance information carefully before using
the product. Refer to the user documentation for complete product specifications.
If the product is used in a manner not specified, the protection provided by the product warranty may be impaired.
The types of product users are:
Responsible body is the individual or group responsible for the use and maintenance of equipment, for ensuring that the
equipment is operated within its specifications and operating limits, and for ensuring that operators are adequately trained.
Operators use the product for its intended function. They must be trained in electrical safety procedures and proper use of the
instrument. They must be protected from electric shock and contact with hazardous live circuits.
Maintenance personnel perform routine procedures on the product to keep it operating properly, for example, setting the line
voltage or replacing consumable materials. Maintenance procedures are described in the user documentation. The procedures
explicitly state if the operator may perform them. Otherwise, they should be performed only by service personnel.
Service personnel are trained to work on live circuits, perform safe installations, and repair products. Only properly trained
service personnel may perform installation and service procedures.
Keithley Instruments products are designed for use with electrical signals that are measurement, control, and data I/O
connections, with low transient overvoltages, and must not be directly connected to mains voltage or to voltage sources with high
transient overvoltages. Measurement Category II (as referenced in IEC 60664) connections require protection for high transient
overvoltages often associated with local AC mains connections. Certain Keithley measuring instruments may be connected to
mains. These instruments will be marked as category II or higher.
Unless explicitly allowed in the specifications, operating manual, and instrument labels, do not connect any instrument to mains.
Exercise extreme caution when a shock hazard is present. Lethal voltage may be present on cable connector jacks or test
fixtures. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) states that a shock hazard exists when voltage levels greater than
30 V RMS, 42.4 V peak, or 60 VDC are present. A good safety practice is to expect that hazardous voltage is present in any
unknown circuit before measuring.
Operators of this product must be protected from electric shock at all times. The responsible body must ensure that operators
are prevented access and/or insulated from every connection point. In some cases, connections must be exposed to potential
human contact. Product operators in these circumstances must be trained to protect themselves from the risk of electric shock. If
the circuit is capable of operating at or above 1000 V, no conductive part of the circuit may be exposed.
Do not connect switching cards directly to unlimited power circuits. They are intended to be used with impedance-limited
sources. NEVER connect switching cards directly to AC mains. When connecting sources to switching cards, install protective
devices to limit fault current and voltage to the card.
Before operating an instrument, ensure that the line cord is connected to a properly-grounded power receptacle. Inspect the
connecting cables, test leads, and jumpers for possible wear, cracks, or breaks before each use.
When installing equipment where access to the main power cord is restricted, such as rack mounting, a separate main input
power disconnect device must be provided in close proximity to the equipment and within easy reach of the operator.
For maximum safety, do not touch the product, test cables, or any other instruments while power is applied to the circuit under
test. ALWAYS remove power from the entire test system and discharge any capacitors before: connecting or disconnecting
cables or jumpers, installing or removing switching cards, or making internal changes, such as installing or removing jumpers.
Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to the common side of the circuit under test or power line (earth)
ground. Always make measurements with dry hands while standing on a dry, insulated surface capable of withstanding the
voltage being measured.
Page 4

For safety, instruments and accessories must be used in accordance with the operating instructions. If the instruments or
accessories are used in a manner not specified in the operating instructions, the protection provided by the equipment may be
impaired.
Do not exceed the maximum signal levels of the instruments and accessories, as defined in the specifications and operating
information, and as shown on the instrument or test fixture panels, or switching card.
When fuses are used in a product, replace with the same type and rating for continued protection against fire hazard.
Chassis connections must only be used as shield connections for measuring circuits, NOT as protective earth (safety ground)
connections.
If you are using a test fixture, keep the lid closed while power is applied to the device under test. Safe operation requires the use
of a lid interlock.
If a screw is present, connect it to protective earth (safety ground) using the wire recommended in the user documentation.
The symbol on an instrument means caution, risk of danger. The user must refer to the operating instructions located in the
user documentation in all cases where the symbol is marked on the instrument.
The symbol on an instrument means caution, risk of electric shock. Use standard safety precautions to avoid personal
contact with these voltages.
The symbol on an instrument shows that the surface may be hot. Avoid personal contact to prevent burns.
The symbol indicates a connection terminal to the equipment frame.
If this symbol is on a product, it indicates that mercury is present in the display lamp. Please note that the lamp must be
properly disposed of according to federal, state, and local laws.
The WARNING heading in the user documentation explains dangers that might result in personal injury or death. Always read
the associated information very carefully before performing the indicated procedure.
The CAUTION heading in the user documentation explains hazards that could damage the instrument. Such damage may
invalidate the warranty.
Instrumentation and accessories shall not be connected to humans.
Before performing any maintenance, disconnect the line cord and all test cables.
To maintain protection from electric shock and fire, replacement components in mains circuits — including the power
transformer, test leads, and input jacks — must be purchased from Keithley Instruments. Standard fuses with applicable national
safety approvals may be used if the rating and type are the same. Other components that are not safety-related may be
purchased from other suppliers as long as they are equivalent to the original component (note that selected parts should be
purchased only through Keithley Instruments to maintain accuracy and functionality of the product). If you are unsure about the
applicability of a replacement component, call a Keithley Instruments office for information.
To clean an instrument, use a damp cloth or mild, water-based cleaner. Clean the exterior of the instrument only. Do not apply
cleaner directly to the instrument or allow liquids to enter or spill on the instrument. Products that consist of a circuit board with
no case or chassis (e.g., a data acquisition board for installation into a computer) should never require cleaning if handled
according to instructions. If the board becomes contaminated and operation is affected, the board should be returned to the
factory for proper cleaning/servicing.
Safety precaution revision as of January 2013.
Page 5

Introduction ............................................................................................................... 1-1
Table of Contents
Welcome .............................................................................................................................. 1-1
Introduction to this manual ................................................................................................... 1-1
Extended warranty ............................................................................................................... 1-1
Contact information .............................................................................................................. 1-2
CD-ROM contents ................................................................................................................ 1-2
Organization of manual sections .......................................................................................... 1-2
Applications .......................................................................................................................... 1-3
Using the front-panel interface ................................................................................ 2-1
Front panel overview ............................................................................................................ 2-1
Power the instrument on or off ............................................................................................. 2-3
Turn the Model 2461 output on or off ................................................................................... 2-4
Touchscreen display ............................................................................................................ 2-5
Select items on the touchscreen ............................................................................................... 2-5
Scroll bars ................................................................................................................................. 2-6
Interactive swipe screens .......................................................................................................... 2-6
Menu overview .......................................................................................................................... 2-9
Store measurements on a USB flash drive ........................................................................ 2-10
Saving screen captures to a USB flash drive .................................................................... 2-10
Using a remote interface .......................................................................................... 3-1
Remote communications interfaces ..................................................................................... 3-1
Supported remote interfaces ................................................................................................ 3-1
GPIB communications .......................................................................................................... 3-2
Install the GPIB driver software ................................................................................................. 3-2
Install the GPIB cards in your computer .................................................................................... 3-2
Connect GPIB cables to your instrument .................................................................................. 3-2
Set the GPIB address ............................................................................................................... 3-3
LAN communications ........................................................................................................... 3-4
Set up LAN communications on the instrument ........................................................................ 3-4
Set up LAN communications on the computer .......................................................................... 3-5
USB communications ........................................................................................................... 3-6
Connect a computer to the Model 2461 using USB .................................................................. 3-6
Communicate with the instrument ............................................................................................. 3-7
Using the web interface...................................................................................................... 3-10
Connect to the instrument web interface ................................................................................. 3-10
LAN troubleshooting suggestions ............................................................................................ 3-10
Identify the instrument ............................................................................................................. 3-12
Review events in the event log ................................................................................................ 3-12
Determining the command set you will use ....................................................................... 3-12
Page 6

Table of Contents Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
Making basic front-panel measurements ................................................................ 4-1
Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 4-1
Equipment required for this application................................................................................ 4-2
Device connections .............................................................................................................. 4-2
Make front-panel measurements ......................................................................................... 4-2
How to make front-panel measurements .................................................................................. 4-3
Measuring low-resistance devices .......................................................................... 5-1
Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 5-1
Equipment required .............................................................................................................. 5-1
Set up remote communications ........................................................................................... 5-1
Device connections .............................................................................................................. 5-2
Low-resistance measurements ............................................................................................ 5-5
Set up the measurement from the front panel ........................................................................... 5-5
View the measurements on the front-panel GRAPH swipe screen ........................................... 5-6
View the buffer statistics on the front panel ............................................................................... 5-6
Set up the low-resistance application using SCPI commands................................................... 5-6
Set up the low-resistance application using TSP commands .................................................... 5-7
Rechargeable battery measurements ...................................................................... 6-1
Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 6-1
Equipment required .............................................................................................................. 6-3
Device connections .............................................................................................................. 6-4
Automated battery charge and discharge cycle testing ....................................................... 6-6
Set up remote communications ................................................................................................. 6-7
Set up the battery application using SCPI commands .............................................................. 6-7
Set up the battery application using TSP commands ................................................................ 6-9
Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart ............................................... 7-1
Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 7-1
Equipment and software required ........................................................................................ 7-1
Set up remote communications ........................................................................................... 7-2
Device connections .............................................................................................................. 7-2
Generating an I-V sweep using KickStart ............................................................................ 7-4
Configure the Model 2461 to use the KickStart software .......................................................... 7-4
Launch KickStart and set up the test ......................................................................................... 7-5
Run the test and view the graph ................................................................................................ 7-7
View and save the test data in tabular form .............................................................................. 7-8
Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel ....................................................... 8-1
Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 8-1
Equipment required .............................................................................................................. 8-1
Page 7

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Table of Contents
Set up remote communications ........................................................................................... 8-2
Device connections .............................................................................................................. 8-2
Solar panel characterization ................................................................................................ 8-4
Set up the solar panel I-V sweep from the front panel .............................................................. 8-4
Set up the solar panel I-V sweep using SCPI commands ......................................................... 8-6
Set up the solar panel I-V sweep using TSP commands .......................................................... 8-6
Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs ...................................................................... 9-1
Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 9-1
Equipment required .............................................................................................................. 9-1
Set up remote communications ........................................................................................... 9-2
Device connections .............................................................................................................. 9-2
High-speed, high-power pulses from a remote interface ..................................................... 9-4
Define the pulse sweep test parameters ................................................................................... 9-5
Set up the source and measure functions ................................................................................. 9-6
The pulse command's trigger model ......................................................................................... 9-6
Front-panel operations to output a high-current pulse sweep ................................................... 9-7
SCPI commands to output a high-current pulse sweep ............................................................ 9-7
TSP commands to output a high-current pulse train ................................................................. 9-8
Viewing the results on the front panel ....................................................................................... 9-9
Capturing high-power pulse waveforms ............................................................... 10-1
Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 10-1
Equipment required ............................................................................................................ 10-1
Set up remote communications ......................................................................................... 10-2
Device connections ............................................................................................................ 10-2
High-speed, high-power pulses from a remote interface ................................................... 10-4
Define the pulse train test parameters .................................................................................... 10-5
The trigger model of the pulse command ................................................................................ 10-6
Front panel operations to output high-current pulses .............................................................. 10-7
SCPI commands to output high-current pulses ....................................................................... 10-7
TSP commands to output a high-power pulse waveforms ...................................................... 10-8
Viewing the measure waveform on the front panel ................................................................. 10-9
Viewing the source and digitize waveforms simultaneously on the front panel ..................... 10-10
Troubleshooting FAQs ........................................................................................... 11-1
About this section ............................................................................................................... 11-1
Where can I find updated drivers? ..................................................................................... 11-1
How do I upgrade the firmware? ........................................................................................ 11-2
Why can't the Model 2461 read my USB flash drive?........................................................ 11-2
How do I change the command set? ................................................................................. 11-2
Why am I getting a 5074 event code? ............................................................................... 11-3
How do I save the present state of the instrument? .......................................................... 11-4
Why did my settings change? ............................................................................................ 11-4
Page 8

Table of Contents Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
What are the Quick Setup options? ................................................................................... 11-5
Next steps ............................................................................................................... 12-1
Additional Model 2461 information ..................................................................................... 12-1
Page 9

In this section:
Welcome .................................................................................. 1-1
Introduction to this manual ....................................................... 1-1
Extended warranty ................................................................... 1-1
Contact information .................................................................. 1-2
CD-ROM contents .................................................................... 1-2
Organization of manual sections .............................................. 1-2
Applications .............................................................................. 1-3
Section 1
Introduction
Welcome
Thank you for choosing a Keithley Instruments product. The Model 2461 1 kW Pulse Mode Interactive
SourceMeter® Instrument is a precise, low-noise instrument that combines a stable DC power supply,
high-power, high-current source, electronic load, and high-impedance multimeter with pulse, contact
check, and digitize capabilities. This instrument features intuitive setup and control, enhanced signal
quality and range, and better resistivity and resistance capabilities than similar products on the
market.
The Model 2461 can source up to 7 A (10 A pulse), and features 1 A, 4 A, 5 A, 7 A, and 10 A ranges.
With 0.012 percent basic accuracy at 6½-digit resolution, the Model 2461 is a good solution for
testing a wide variety of materials and devices in applications such as power semiconductors, solar
energy, high brightness LEDs, power conversion, electrochemistry, batteries, and more.
Introduction to this manual
This manual provides detailed applications to help you achieve success with your Keithley
Instruments Model 2461. In addition, this manual provides information about the basics of the front
panel to familiarize you with the instrument.
This manual presents an overview of each application, followed by instructions to complete the
application using the front panel, SCPI code, TSP code, or Keithley KickStart Startup Software.
Extended warranty
More information about the commands that are used in these applications is available. Refer to the
SCPI and TSP command reference sections of the Model 2461 Reference Manual. This manual is on
the Product Information CD-ROM that came with your instrument.
Additional years of warranty coverage are available on many products. These valuable contracts
protect you from unbudgeted service expenses and provide additional years of protection at a fraction
of the price of a repair. Extended warranties are available on new and existing products. Contact your
local Keithley Instruments office, sales partner, or distributor for details.
Page 10

Section 1: Introduction Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
1-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Contact information
If you have any questions after you review the information in this documentation, please contact your
local Keithley Instruments office, sales partner, or distributor.
CD-ROM contents
The Model 2461 instrument Interactive SourceMeter® SMU Instruments Product Information CD-ROM
(Keithley Instruments part number 24GDI-950-01) is shipped with each Model 2461 instrument.
The Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter SMU Instrument Product Information CD-ROM
contains:
Quick Start Guide: Provides unpacking instructions, describes basic connections, reviews basic
operation information, and provides a quick test procedure to ensure the instrument is
operational.
User's Manual: Provides application examples that you can use as a starting point to create your
own applications.
Reference Manual: Includes advanced operation topics, maintenance information,
troubleshooting procedures, and in-depth descriptions of programming commands.
KickStart Startup Software Quick Start Guide: Provides instructions for the KickStart Startup
Software, which allows you to quickly make measurements and get results without having to
program test scripts.
Accessories information: Documentation for accessories that are available for the Model 2461.
Organization of manual sections
This manual is organized into the following sections:
Using the front-panel interface (on page 2-1): Describes the basics of using the front-panel
interface.
Using a remote interface (on page 3-1): Describes the basics of remote communications and
using the instrument web interface.
Application examples (see below): Provides detailed examples of how to use the Model 2461 in
some typical situations.
Page 11

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 1: Introduction
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 1-3
Troubleshooting FAQs (on page 11-1): Provides answers to frequently asked questions to help
you troubleshoot common problems encountered with the Model 2461.
Next steps (on page 12-1): Provides information about additional resources that can help you use
the Model 2461.
The PDF version of this manual contains bookmarks for each section. The manual sections are also
listed in the Table of Contents at the beginning of this manual.
For more information about bookmarks, see Adobe® Acrobat® or Reader® help.
Applications
This manual provides application examples that show you how to perform tests from the front panel
and over a remote interface. These applications are presented after the summary information about
the Model 2461. The applications include:
Making basic front-panel measurements (on page 4-1): Demonstrates the basic measurement
functionality using a single Model 2461 and a two-terminal device under test (DUT).
Measuring low-resistance devices (on page 5-1): Demonstrates how to use a Model 2461 to
make low-resistance measurements of a 20 m resistor.
Rechargeable battery measurements (on page 6-1): Demonstrates how to use a single Model
2461 to perform automated battery discharge and charge cycle testing.
Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart (on page 7-1): Demonstrates how use the
Model 2461 to test high-brightness light-emitting diodes (LEDs) using Keithley KickStart Startup
Software.
Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel (on page 8-1): Demonstrates using an I-V sweep to
characterize a solar panel using the Model 2461.
Making pulsed I-V measurements (on page 4-1): Demonstrates how to use the Model 2461
Interactive SourceMeter instrument to generate I-V curves of high-brightness LEDs (HBLEDs)
using the extended range pulsing capabilities of the instrument.
Capturing high-power pulse waveforms (on page 10-1): Demonstrates how to use the Model
2461 Interactive SourceMeter instrument to generate extended operating range, high-power
voltage pulses (up to 10 A at 100 V) and capture both the current and voltage waveforms of
high-power pulses.
Page 12

In this section:
Front panel overview ................................................................ 2-1
Power the instrument on or off ................................................. 2-3
Turn the Model 2461 output on or off ....................................... 2-4
Touchscreen display................................................................. 2-5
Store measurements on a USB flash drive ............................. 2-10
Saving screen captures to a USB flash drive ......................... 2-10
Section 2
Using the front-panel interface
Front panel overview
The front panel of the Model 2461 is shown below. Descriptions of the controls on the front panel
follow the figure.
Figure 1: Model 2461 front panel
Page 13

Section 2: Using the front-panel interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
2-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
POWER switch
Turns the instrument on or off. To turn the instrument on, press the
power switch so that it is in the on position (|). To turn it off, press the
power switch so that it is in the off position (O).
HOME key
Returns the display to the Home screen.
MENU key
Opens the main menu. Press the icons on the main menu to open
source, measure, view, trigger, script, and system screens.
QUICKSET key
Opens a menu of preconfigured setups, including voltmeter,
ammeter, ohmmeter, and power supply. Also allows you to choose
source and measure functions and adjust performance for better
resolution or speed.
HELP key
Opens help for the area or item that is selected on the display. If
there is no selection when you press the HELP key, it displays
overview information for the screen you are viewing.
USB port
Saves reading buffer data and screen snapshots to a USB flash
drive. Also stores and retrieves scripts to and from a USB flash drive.
The flash drive must be formatted as a FAT drive.
Touchscreen
The Model 2461 has a high-resolution, five-inch color touchscreen
display. The touchscreen accesses swipe screens and menu options.
You can access additional interactive screens by pressing the
front-panel MENU, QUICKSET, and FUNCTION keys.
Navigation control
Turning the navigation control: Moves the cursor to highlight a list
value or menu item so that you can select it. Turning the control when
the cursor is in a value entry field increases or decreases the value in
the field.
Pressing the navigation control: Selects the highlighted choice or
allows you to edit the selected field.
ENTER key
Selects the highlighted choice or allows you to edit the selected field.
EXIT key
Returns to the previous screen or closes a dialog box. For example,
press the EXIT key when the main menu is displayed to return to the
Home screen. When you are viewing a subscreen (for example, the
Event Log screen), press the EXIT key to return to the main menu
screen.
FUNCTION key
Displays instrument functions. To select a function, touch the function
name on the screen.
TRIGGER key
Accesses trigger-related settings and operations. The action of the
TRIGGER key depends on the instrument state.
OUTPUT ON/OFF
switch
Turns the output source on or off. The key illuminates when the
source output is on.
Page 14

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 2: Using the front-panel interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 2-3
REMOTE LED
indicator
Illuminates when the instrument is controlled through a remote
interface.
LAN LED indicator
Illuminates when the instrument is connected to a local area network
(LAN).
1588 LED indicator
Illuminates when the instrument is connected to an IEEE-1588
INTERLOCK LED
indicator
Illuminates when the interlock is enabled.
SENSE terminals
Use the SENSE HI and SENSE LO terminal connections to measure
voltage at the device under test (DUT). When you use sense leads,
measurement of the voltage drop across the force leads is
eliminated. This produces more accurate voltage sourcing and
measurement at the DUT.
FORCE terminals
Use FORCE HI and FORCE LO terminal connections to source or
sink voltage or current to or from a device under test (DUT).
FRONT/REAR
TERMINALS switch
Activates the terminals on the front or rear panel. When the
front-panel terminals are active, a green "F" is visible to the left of the
FRONT/REAR switch. When the rear-panel terminals are active, a
yellow "R" is visible to the left of the switch.
Chassis connection
Banana jack connector that provides a chassis connection.
compliant device.
Note that 1588 functionality is not supported at this time. This
functionality will be made available with a firmware update.
Power the instrument on or off
Follow the steps below to connect the Model 2461 to line power and turn on the instrument. The
Model 2461 operates from a line voltage of 100 V to 240 V at a frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. It
automatically senses line voltage and frequency. Make sure the operating voltage in your area is
compatible.
You must turn on the Model 2461 and allow it to warm up for at least one hour to achieve rated
accuracies.
Operating the instrument on an incorrect line voltage may cause damage to the instrument, possibly
voiding the warranty.
The power cord supplied with the Model 2461 contains a separate protective earth (safety
ground) wire for use with grounded outlets. When proper connections are made, the
instrument chassis is connected to power-line ground through the ground wire in the power
cord. In addition, a redundant protective earth connection is provided through a screw on
the rear panel. This terminal should be connected to a known protective earth. In the event
of a failure, not using a properly grounded protective earth and grounded outlet may result
in personal injury or death due to electric shock.
Page 15

Section 2: Using the front-panel interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
2-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Do not replace detachable mains supply cords with inadequately rated cords. Failure to use
properly rated cords may result in personal injury or death due to electric shock.
To connect the power cord:
1. Make sure that the front-panel POWER switch is in the off (O) position.
2. Connect the female end of the supplied power cord to the AC receptacle on the rear panel.
3. Connect the other end of the power cord to a grounded AC outlet.
Figure 2: Model 2461 rear panel
To turn a Model 2461 on or off:
1. Before turning the instrument on, disconnect any devices under test (DUTs) from the Model 2461.
2. To turn your instrument on, press the front-panel POWER switch to place it in the on (|) position.
The instrument displays a status bar as it powers on. The Home screen is displayed when power
on is complete.
3. To turn your instrument off, press the front-panel POWER switch to place it in the off (O) position.
Turn the Model 2461 output on or off
You can turn the Model 2461 output on from the front panel or by sending remote commands.
Turning the Model 2461 output off does not place the instrument in a safe state (an interlock
is provided for this function).
Hazardous voltages may be present on all output and guard terminals. To prevent electrical
shock that could cause injury or death, never make or break connections to the Model 2461
while the instrument is powered on. Turn off the equipment from the front panel or
disconnect the main power cord from the rear of the Model 2461 before handling cables.
Putting the equipment into an output-off state does not guarantee that the outputs are
powered off if a hardware or software fault occurs.
Page 16

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 2: Using the front-panel interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 2-5
When the source of the instrument is turned off, it may not completely isolate the instrument from the
external circuit. You can use the Output Off setting to place the Model 2461 in a known,
noninteractive state during idle periods, such as when you are changing the device under test. The
output-off states that can be selected for a Model 2461 are normal, high-impedance, zero, or guard.
See "Output-off state" in the Model 2461 Reference Manual for additional details.
Using the front panel:
Press the OUTPUT ON/OFF switch. The instrument is in the output-on state when the switch is
illuminated. The instrument is in the output-off state when the switch is not illuminated.
Using SCPI commands:
To turn the output on, send the command:
:OUTPut:STATe ON
To turn the output off, send the command:
:OUTPut:STATe OFF
Using TSP commands:
To turn the output on, send the command:
smu.source.output = smu.ON
To turn the output off, send the command:
smu.source.output = smu.OFF
Touchscreen display
The touchscreen display gives you quick front-panel access to source and measure settings, system
configuration, instrument and test status, reading buffer information, and other instrument
functionality. The display has multiple swipe screens that you can access by swiping the front panel.
You can access additional interactive screens by pressing the front-panel MENU, QUICKSET, and
FUNCTION keys.
Do not use sharp metal objects, such as tweezers or screwdrivers, or pointed objects, such as pens
or pencils, to touch the touchscreen. It is strongly recommended that you use only fingers to operate
the instrument. Use of clean-room gloves to operate the touchscreen is supported.
Select items on the touchscreen
To select an item on the displayed screen, do one of the following:
Touch it with your finger
Turn the navigation control to highlight the item, and then press the navigation control to select it
The following topics describe the Model 2461 touchscreen in more detail.
Page 17

Section 2: Using the front-panel interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
2-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Scroll bars
Some of the interactive screens have additional options that are only visible when you scroll down the
screen. A scroll indicator on the right side of the touchscreen identifies these screens. Swipe the
screen up or down to view the additional options.
The figure below shows a screen with a scroll bar.
Figure 3: Touchscreen window with a scroll bar indicator
Interactive swipe screens
The Model 2461 touchscreen display has multiple screens that you can access by gently swiping left
or right on the lower half of the display. The options available in the swipe screens are described in
the following topics.
Swipe screen heading bar
The heading bar of the swipe screen contains the following options.
Figure 4: Swipe screens, maximized and minimized
Page 18

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 2: Using the front-panel interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 2-7
#
Screen element
Description
1
Minimize indicator
You can swipe down to minimize the swipe screens.
2
Swipe screen indicator
Each circle represents one swipe screen. As you swipe right or left, a different
circle changes color, indicating where you are in the screen sequence. Select a
circle to go to a swipe screen without swiping.
3
Calculations shortcut
Select to open the CALCULATIONS SETTINGS menu.
4
Settings shortcut
Select to open the MEASURE SETTINGS menu for the selected function.
5
Restore indicator
Indicates that you can swipe up to display the swipe screen.
6
Graph shortcut
Select to open the Graph screen.
SOURCE swipe screen
The SOURCE swipe screen shows the present value of the source and the set values for source,
source range, and source limit. You can change the set values from the front panel by selecting the
buttons on this screen.
Figure 5: SOURCE swipe screen
Source function indicators on the right side of the screen signify settings that affect the displayed
source value.
MEAS: Source readback is on and the value shown is the measured value of the source.
PROG: Source readback is off and the value shown is the programmed source value. If the
output is off, the displayed source value is replaced with Output Off.
The icon on the right side of the swipe screen heading bar is a shortcut to the full SOURCE
SETTINGS menu.
Page 19

Section 2: Using the front-panel interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
2-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
SETTINGS swipe screen
The SETTINGS swipe screen gives you front-panel access to some instrument settings. It shows you
the present settings and allows you to change, enable, or disable them quickly.
Figure 6: SETTINGS swipe screen
To disable or enable a setting, select the box next to the setting so that it shows an X (disabled) or a
check mark (enabled).
The icons on the right side of the swipe screen heading bar are shortcuts to the CALCULATIONS
SETTINGS and MEASURE SETTINGS menus.
For descriptions of the settings, use the navigation control to select the button, then press the HELP
key.
STATISTICS swipe screen
The STATISTICS swipe screen contains information about the readings in the active reading buffer.
When the reading buffer is configured to fill continuously and overwrite old data with new data, the
buffer statistics include the data that was overwritten. To get statistics that do not include data that
has been overwritten, define a large buffer size that will accommodate the number of readings you
will make. You can use the Clear Active Buffer button on this screen to clear the data from the
active reading buffer.
Figure 7: Model 2461 STATISTICS swipe screen
USER swipe screen
You can program custom text that appears on the USER swipe screen. For example, you can
program the Model 2461 to show that a test is in process. Refer to the Model 2461 Reference
Manual, "Customizing a message for the USER swipe screen"
Figure 8: USER swipe screen
Page 20

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 2: Using the front-panel interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 2-9
GRAPH swipe screen
The GRAPH swipe screen shows a graphical representation of the readings in the presently selected
reading buffer.
Figure 9: GRAPH swipe screen
To view the graph in the full screen and to access graph settings, select the graph icon on the right
side of the swipe screen header. You can also open the full-function Graph screen by pressing the
MENU key and selecting Graph under Views.
For more information about graphing measurements, see "Graphing" in the Model 2461 Reference
Manual.
Menu overview
To access the main menu, press the MENU key on the Model 2461 front panel. The figure below
shows the organization of the main menu.
Figure 10: Model 2461 main menu
The main menu includes submenus that are labeled in green across the top of the display. Touching
an icon in a submenu opens an interactive screen.
Page 21

Section 2: Using the front-panel interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
2-10 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Store measurements on a USB flash drive
If there is measurement data in the buffer, you can copy it from the Model 2461 to a USB flash drive.
The information is saved in the .csv file format.
To store measurement data:
1. Insert a flash drive into the front-panel USB port.
2. Press the MENU key.
3. In the Measure column, select Reading Buffers.
4. Select the buffer that you want to save.
5. Select Save to USB.
6. Enter a name for the new file.
7. Select the OK button on the displayed keyboard.
8. Select Yes to confirm saving the file.
9. Select OK to close the dialog box.
Saving screen captures to a USB flash drive
You can save the content of the front-panel display to a graphic file. The instrument saves these
graphic files, also known as screen captures, to the USB flash drive in the .png file format.
To save the screen capture:
1. Insert a USB flash drive in the USB port on the front panel of the instrument.
2. Navigate to the screen you want to capture.
3. Press the HOME and ENTER keys. The instrument displays "Saving screen capture."
4. Release the keys.
Page 22

In this section:
Remote communications interfaces.......................................... 3-1
Supported remote interfaces .................................................... 3-1
GPIB communications .............................................................. 3-2
LAN communications................................................................ 3-4
USB communications ............................................................... 3-6
Using the web interface .......................................................... 3-10
Determining the command set you will use ............................ 3-12
Section 3
Using a remote interface
Remote communications interfaces
You can choose from one of several communication interfaces to send commands to and receive
responses from the Model 2461.
You can control the Model 2461 from only one communications interface at a time. The first interface
on which it receives a message takes control of the instrument. If another interface sends a message,
that interface can take control of the instrument. You may need to enter a password to change the
interface, depending on the access mode.
The Model 2461 automatically detects the type of communications interface (LAN, GPIB, or USB)
when you connect to the respective port on the rear panel of the instrument. In most cases, you do
not need to configure anything on the instrument. In addition, you do not need to reboot if you change
the type of interface that is connected.
Supported remote interfaces
The Model 2461 supports the following remote interfaces:
GPIB: IEEE-488 instrumentation general purpose interface bus
Ethernet: Local area network ethernet communications
USB: Type B USB port
TSP-Link: A high-speed trigger synchronization and communications bus that test system
builders can use to connect multiple instruments in a master-and-subordinate configuration
For details about TSP-Link, see "TSP-Link System Expansion Interface" in the Model 2461 Reference
Manual.
Page 23

Section 3: Using a remote interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
3-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
GPIB communications
The Model 2461 GPIB interface is IEEE Std 488.1 compliant and supports IEEE Std 488.2 common
commands and status model topology.
You can have up to 15 devices connected to a GPIB interface, including the controller. The maximum
cable length is the lesser of either:
The number of devices multiplied by 2 m (6.5 ft)
20 m (65.6 ft)
Install the GPIB driver software
You may see erratic bus operation if you ignore these limits.
Check the documentation for your GPIB controller for information about where to acquire drivers.
Keithley Instruments also recommends that you check the website of the GPIB controller for the latest
version of drivers or software.
It is important that you install the drivers before you connect the hardware. This prevents associating
the incorrect driver to the hardware.
Install the GPIB cards in your computer
Refer to the documentation from the GPIB controller vendor for information about installing the GPIB
controllers.
Connect GPIB cables to your instrument
To connect an instrument to the GPIB interface, use a cable equipped with standard GPIB
connectors, as shown below.
Figure 11: GPIB connector
Page 24

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 3: Using a remote interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 3-3
To allow many parallel connections to one instrument, stack the connectors. Each connector has two
screws to ensure that connections remain secure. The figure below shows a typical connection
diagram for a test system with multiple instruments.
To avoid possible mechanical damage, stack no more than three connectors on any one instrument.
To minimize interference caused by electromagnetic radiation, use only shielded GPIB cables.
Contact Keithley Instruments for shielded cables.
Figure 12: Model 2461 IEEE-488 connections
Set the GPIB address
The default GPIB address is 18. You can set the address to any address from 1 to 30 if it is unique in
the system. This address cannot conflict with an address that is assigned to another instrument or to
the GPIB controller.
GPIB controllers are usually set to 0 or 21. To be safe, do not configure any instrument to have an
address of 21. To change the controller address, see the documentation for the controller.
The instrument saves the address in nonvolatile memory. It does not change when you send a reset
command or when you turn the power off and then on again.
Page 25

Section 3: Using a remote interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
3-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
To set the GPIB address from the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Communication. The SYSTEM COMMUNICATIONS window opens.
3. Select the GPIB tab.
4. Next to Address, select the number. The GPIB Address dialog box is displayed.
5. Enter the address.
6. Select OK.
LAN communications
You can communicate with the instrument using a local area network (LAN).
When you connect using a LAN, you can use a web browser to access the internal web page of the
instrument and change some of the instrument settings. For more information, see Using the web
interface (on page 3-10).
The Model 2461 is an LXI version 1.4 Core 2011 compliant instrument that supports TCP/IP and
complies with IEEE Std 802.3 (ethernet LAN). There is one LAN port (located on the rear panel of the
instrument) that supports full connectivity on a 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps network. The Model 2461
automatically detects the speed.
The Model 2461 also supports Multicast DNS (mDNS) and DNS Service Discovery (DNS-SD), which
are useful on a LAN with no central administration.
Contact your network administrator to confirm your specific network requirements before setting up a
LAN connection.
If you have problems setting up the LAN, refer to LAN troubleshooting suggestions (on page 3-10).
Set up LAN communications on the instrument
This section describes how to set up manual or automatic LAN communications on the instrument.
Set up automatic LAN configuration
If you are connecting to a LAN that has a DHCP server or if you have a direct connection between the
instrument and a host computer, you can use automatic IP address selection.
If you select Auto, the instrument attempts to get an IP address from a DHCP server. If this fails, it
reverts to an IP address in the range of 169.254.1.0 through 169.254.254.255.
Both the host computer and the instrument should be set to use automatic LAN configuration.
Though it is possible to have one set to manual configuration, it is more complicated to set up.
Page 26

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 3: Using a remote interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 3-5
To set up automatic IP address selection using the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Communication.
3. Select the LAN tab.
4. For TCP/IP Mode, select Auto.
5. Select Apply Settings to save your settings.
Set up manual LAN configuration
If necessary, you can set the IP address on the instrument manually.
You can also enable or disable the DNS settings and assign a host name to the DNS server.
Contact your corporate information technology (IT) department to secure a valid IP address for the
instrument when placing the instrument on a corporate network.
The instrument IP address has leading zeros, but the computer IP address cannot.
To set up manual IP address selection on the instrument:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Communication.
3. Select the LAN tab.
4. For TCP/IP Mode, select Manual.
5. For IP Address, enter the LAN IP address. You can touch the number you want to change.
6. For Gateway, enter the gateway address.
7. For Subnet, enter the subnet mask.
8. Select Apply Settings to save your settings.
Set up LAN communications on the computer
This section describes how to set up the LAN communications on your computer.
Do not change your IP address without consulting your system administrator. If you enter an
incorrect IP address, it can prevent your computer from connecting to your corporate network or it
may cause interference with another networked computer.
Record all network configurations before modifying any existing network configuration information on
the network interface card. Once the network configuration settings are updated, the previous
information is lost. This may cause a problem reconnecting the host computer to a corporate
network, particularly if DHCP is disabled.
Be sure to return all settings to their original configuration before reconnecting the host computer to a
corporate network. Contact your system administrator for more information.
Wait for the LAN status indicator on the front panel to turn solid green
A solid green LAN status indicator confirms that the instrument was assigned an IP address. Note
that it may take several minutes for the computer and instrument to establish a connection.
Page 27

Section 3: Using a remote interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
3-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Install LXI Discovery Browser software on your computer
You can use the LXI Discovery Browser to identify the IP addresses of LXI-certified instruments.
Once identified, you can double-click the IP address in the LXI Discovery Browser to open the web
interface for the instrument.
Run the LXI Discovery Browser
To run the LXI Discovery Browser software:
1. From the Microsoft Windows Start menu, select Keithley Instruments.
2. Select LXI Discovery Browser.
3. Click LXI Discovery Browser. The Keithley LXI Discovery Browser window is displayed.
The LXI Discovery Browser displays the instruments that it finds on the network and their
associated IP addresses.
4. Double-click an IP address in the LXI Discovery Browser dialog box. The instrument web page for
that instrument opens.
For information about using the web page, refer to Using the web interface (on page 3-10).
USB communications
To use the rear-panel USB port, you must have the Virtual Instrument Software Architecture (VISA)
layer on the host computer. See "How to install the Keithley I/O Layer" in the Model 2461 Reference
Manual for more information.
VISA contains a USB-class driver for the USB Test and Measurement Class (USBTMC) protocol that,
once installed, allows the Microsoft® Windows® operating system to recognize the instrument.
When you connect a USB device that implements the USBTMC or USBTMC-USB488 protocol to the
computer, the VISA driver automatically detects the device. Note that the VISA driver only
automatically recognizes USBTMC and USBTMC-USB488 devices. It does not recognize other USB
devices, such as printers, scanners, and storage devices.
In this section, "USB instruments" refers to devices that implement the USBTMC or
USBTMC-USB488 protocol.
Connect a computer to the Model 2461 using USB
To connect the Model 2461 to a computer using a USB connection, use Keithley Instruments
Model USB-B-1, which is shipped with the instrument.
Each Model 2461 needs its own USB cable to be connected to the computer.
To connect an instrument to a computer using USB:
1. Connect the Type A end of the cable to the computer.
2. Connect the Type B end of the cable to the instrument.
3. Turn on the instrument power. When the computer detects the new USB connection, the Found
New Hardware Wizard starts.
4. If the "Can Windows connect to Windows Update to search for software?" dialog box opens, click
No, and then click Next.
5. On the "USB Test and Measurement device" dialog box, click Next, and then click Finish.
Page 28
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 3: Using a remote interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 3-7
Communicate with the instrument
For the instrument to communicate with the USB device, you must use NI-VISATM. VISA requires a
resource string in the following format to connect to the correct USB instrument:
USB0::0x05e6::0x2461::[serial number]::INSTR
Where:
0x05e6: The Keithley vendor ID
0x2461: The instrument model number
[serial number]: The serial number of the instrument (the serial number is also on the rear
panel)
INSTR: Use the USBTMC protocol
To determine these parameters, you can run the Keithley Configuration Panel, which automatically
detects all instruments connected to the computer.
If you installed the Keithley I/O Layer, you can access the Keithley Configuration Panel through the
Microsoft® Windows® Start menu.
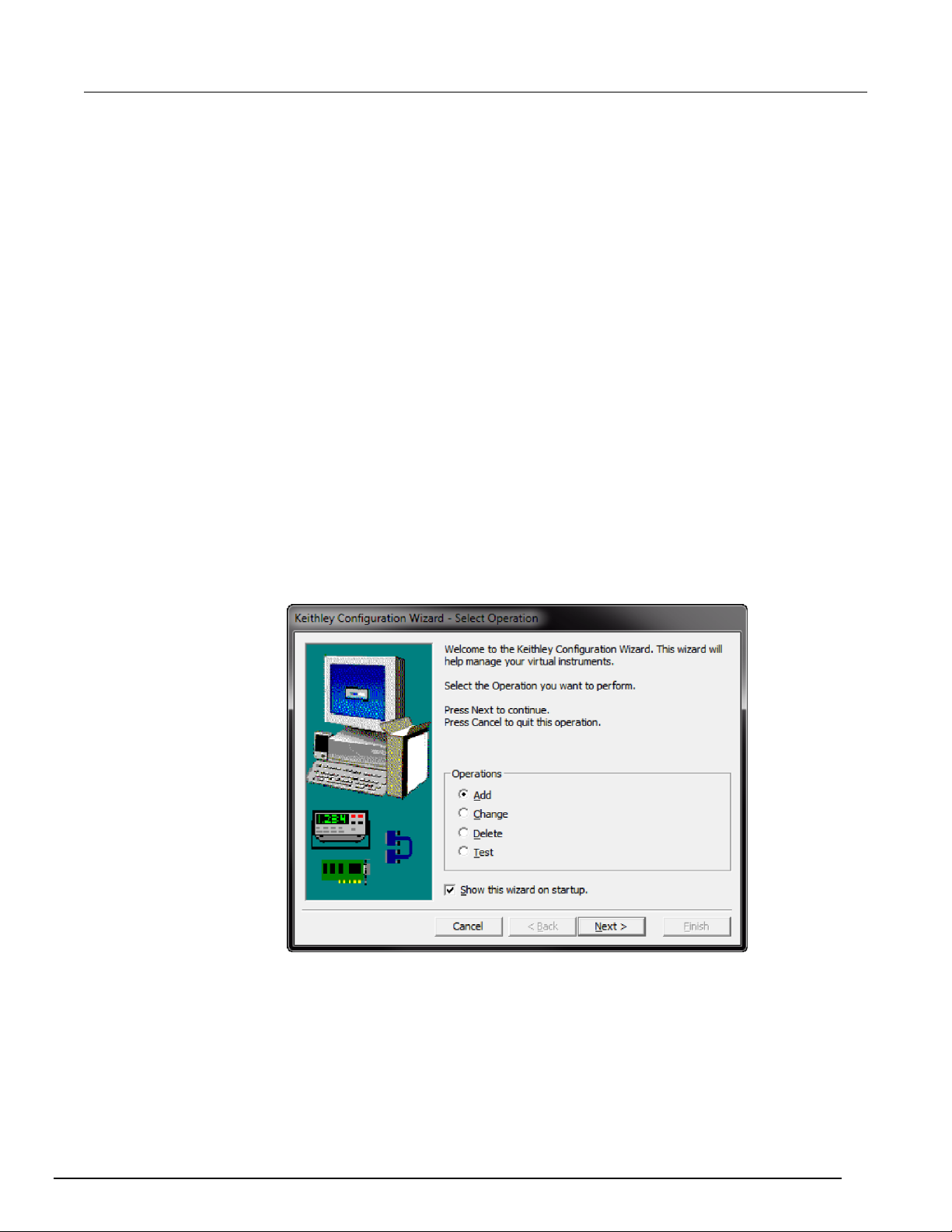
To use the Keithley Configuration Panel to determine the VISA resource string:
1. Click Start > All Programs > Keithley Instruments > Keithley Configuration Panel. The
Select Operation dialog box is displayed.
Figure 13: Select Operation dialog box
2. Select Add.
Page 29
Section 3: Using a remote interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
3-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
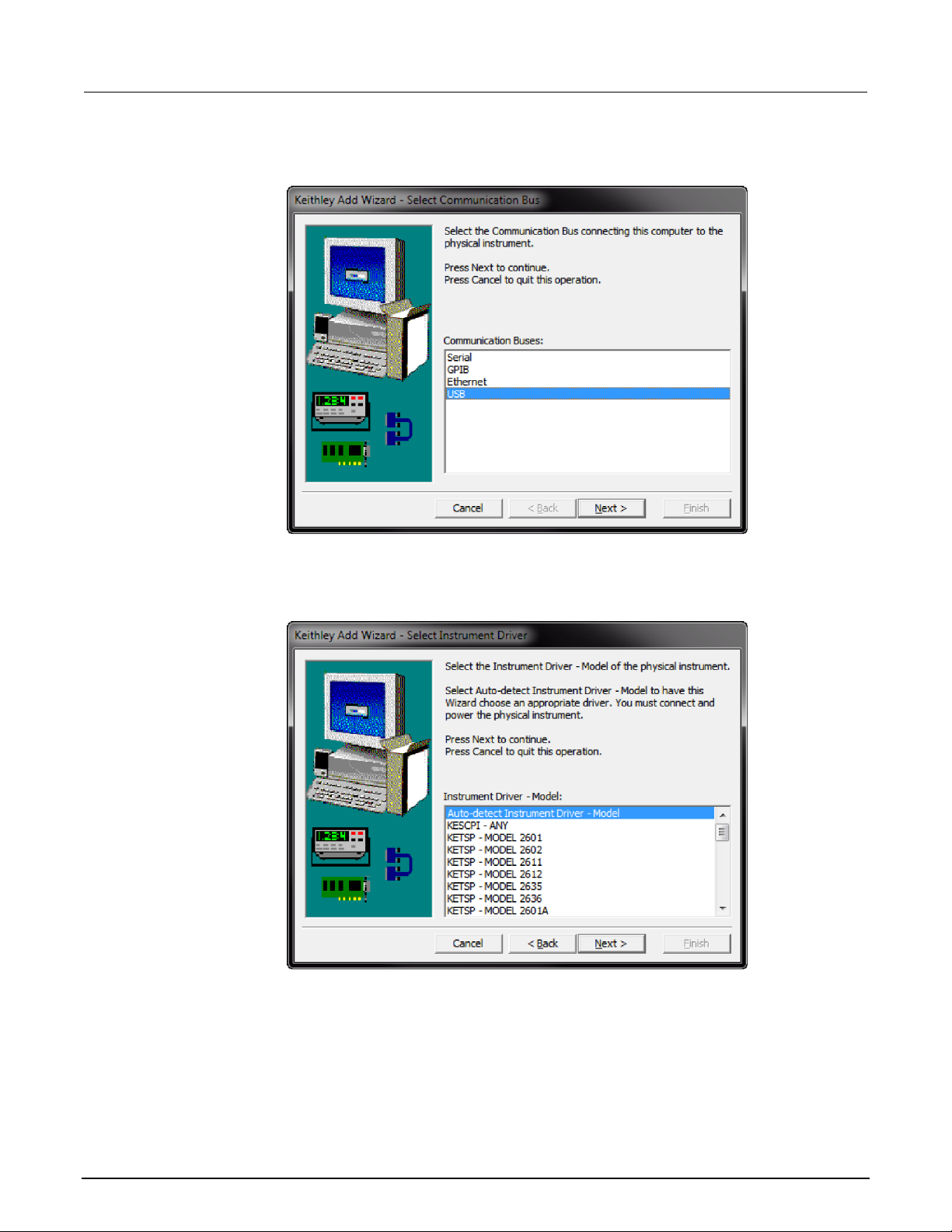
3. Click Next. The Select Communication Bus dialog box is displayed.
Figure 14: Select Communication Bus dialog box
4. Select USB.
5. Click Next. The Select Instrument Driver dialog box is displayed.
Figure 15: Select Instrument Driver dialog box
6. Select Auto-detect Instrument Driver - Model.
7. Click Next. The Configure USB Instrument dialog box is displayed with the detected instrument
VISA resource string visible.
8. Click Next. The Name Virtual Instrument dialog box is displayed.
Page 30
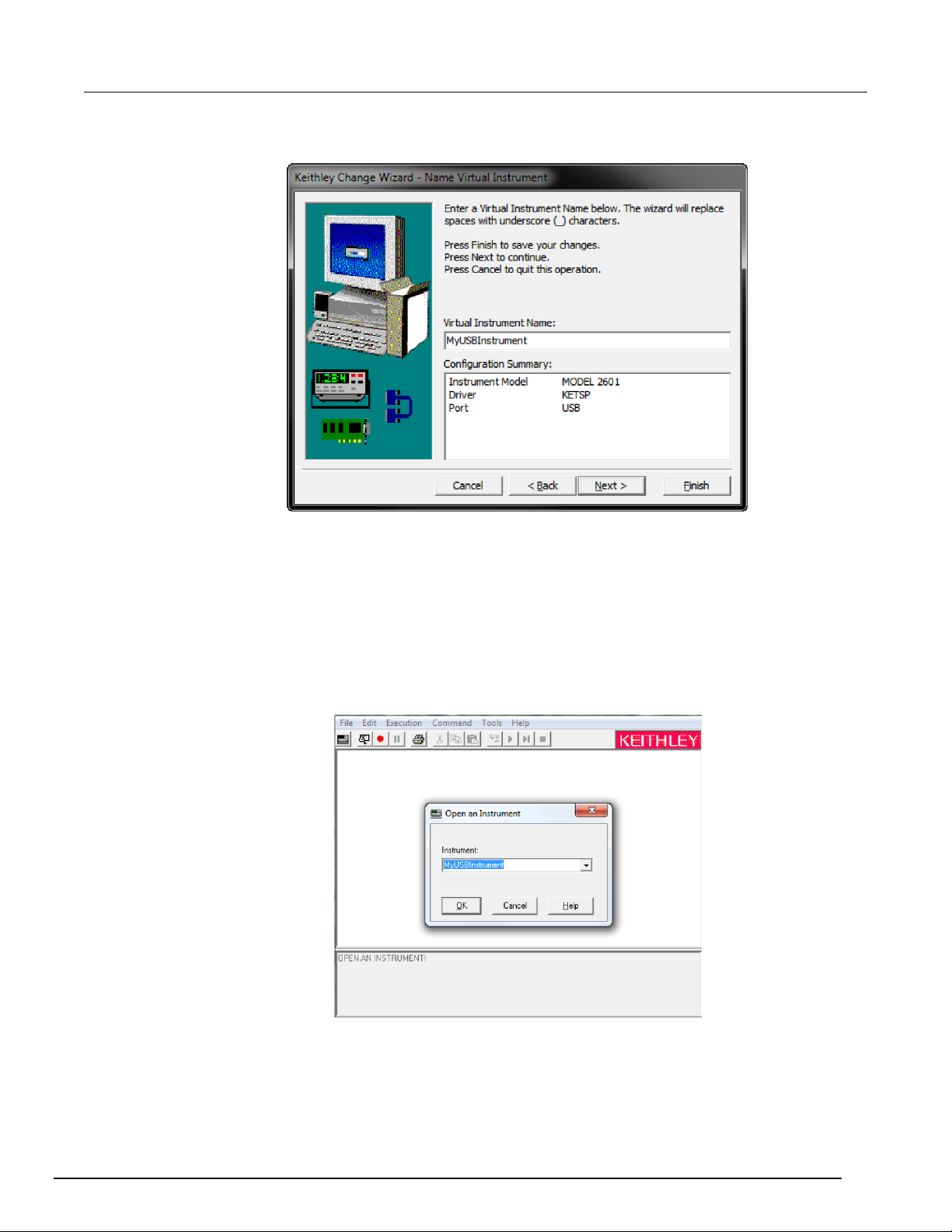
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 3: Using a remote interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 3-9
Figure 16: Name Virtual Instrument dialog box
9. In the Virtual Instrument Name box, enter a name that you want to use to refer to the instrument.
10. Click Finish.
11. Click Cancel to close the Wizard.
12. Save the configuration. From the Keithley Configuration Panel, select File > Save.
Verify the instrument through the Keithley Communicator:
1. Click Start > All Programs > Keithley Instruments > Keithley Communicator.
2. Select File > Open Instrument to open the instrument you just named.
Figure 17: Keithley Communicator Open an Instrument
3. Click OK.
4. Send a command to the instrument and see if it responds.
Page 31

Section 3: Using a remote interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
3-10 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
If you have a full version of NI-VISA on your system, you can run NI-MAX or the VISA Interactive
Control utility. See the National Instruments documentation for information.
If you have the Agilent IO Libraries on your system, you can run Agilent Connection Expert to check
your USB instruments. See the Agilent documentation for information.
Using the web interface
The Model 2461 web interface allows you to make settings and control your instrument through a web
page. The web page includes:
Instrument status.
The instrument model, serial number, firmware revision, and the last LXI message.
An ID button to help you locate the instrument.
A virtual front panel and command interface that you can use to control the instrument.
Download access to a .csv file that contains reading buffer data.
Administrative options and LXI information.
The instrument web page resides in the firmware of the instrument. Changes you make through the
web interface are immediately made in the instrument.
Connect to the instrument web interface
When the LAN and instrument establish a connection, you can open a web page for the instrument.
To access the web interface:
1. Open a web browser on the host computer.
2. Enter the IP address of the instrument in the address box of the web browser. For example, if the
instrument IP address is 192.168.1.101, enter 192.168.1.101 in the browser address box.
3. Press Enter on the computer keyboard to open the instrument web page.
4. If prompted, enter a user name and password. The default is admin for both.
LAN troubleshooting suggestions
If you are unable to connect to the web interface of the instrument, check the following items:
The network cable is in the LAN port on the rear panel of the instrument, not one of the
TSP-Link® ports.
The network cable is in the correct port on the computer. The LAN port of a laptop may be
disabled when the laptop is in a docking station.
The setup procedure used the configuration information for the correct ethernet card.
The network card of the computer is enabled.
The IP address of the instrument is compatible with the IP address on the computer.
The subnet mask address of the instrument is the same as the subnet mask address of the
computer.
Page 32
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 3: Using a remote interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 3-11
You can also try restarting the computer and the instrument. To restart the instrument:
1. Turn the instrument's power off, and then on.
2. Wait at least 60 seconds for the network configuration to be completed.
3. Press the MENU key.
4. Under System, select Communication.
5. Select the LAN tab.
6. Verify the settings.
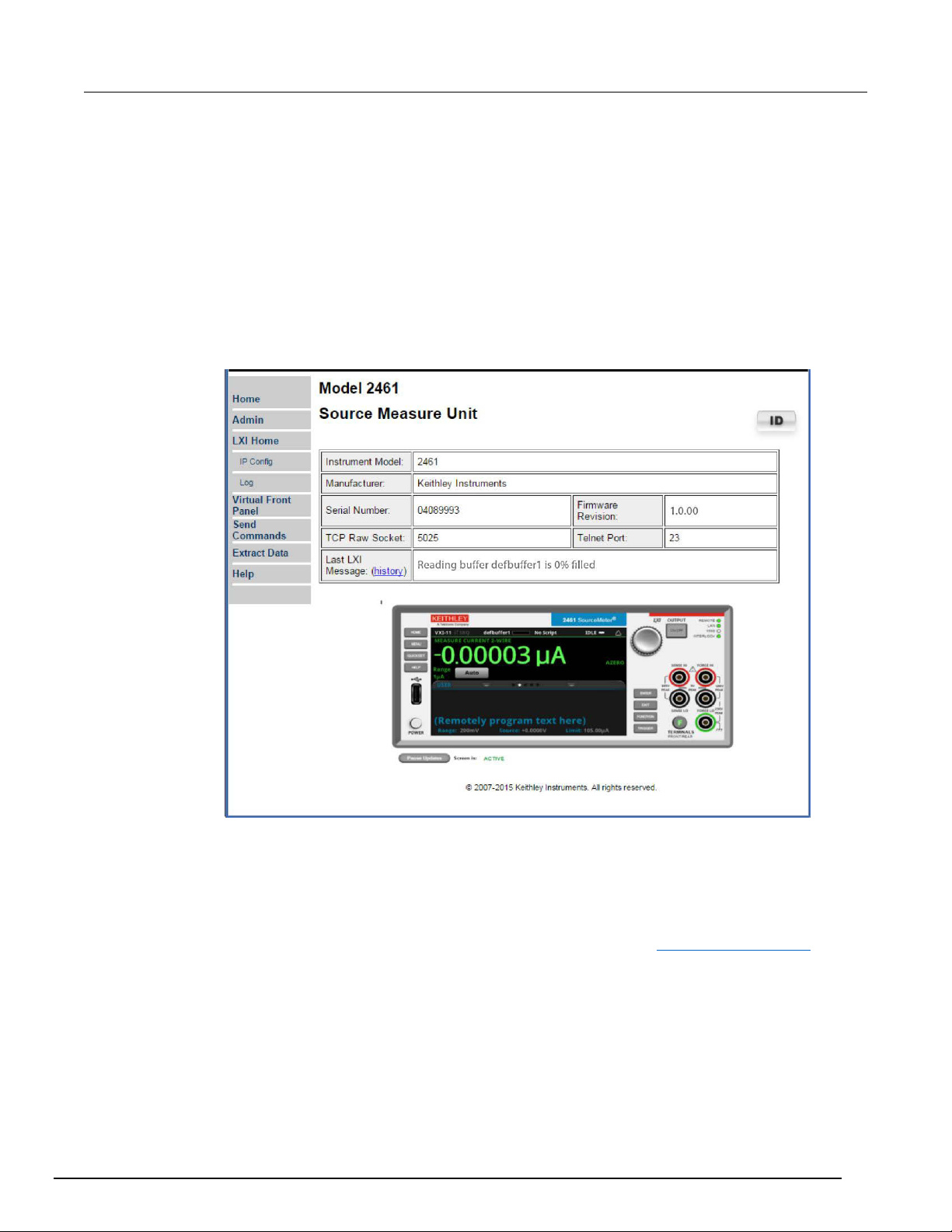
Figure 18: Model 2461 web page
If the above actions do not correct the problem, contact your system administrator.
The Home page of the instrument provides information about the instrument. It includes:
The instrument model number, manufacturer, serial number, and firmware revision number.
The TCP Raw Socket number and Telnet Port number.
The last LXI message. The history link opens the LXI Home page.
The ID button, which allows you to identify the instrument. Refer to Identify the instrument (on
page 3-12).
Page 33

Section 3: Using a remote interface Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
3-12 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Identify the instrument
If you have a bank of instruments, you can click the ID button to determine which one you are
communicating with.
To identify the instrument:
In the middle of the left side of the Home page, click the ID button.
The button turns green and the LAN status indicator on the instrument blinks.
Click the ID button again to return the button to its original color and return the LAN status indicator to
steady on.
Review events in the event log
The event log records all LXI events that the instrument generates and receives. The log includes the
following information:
The EventID column, which shows the event identifier that generated the event.
The System Timestamp column, which displays the seconds and nanoseconds when the event
occurred.
The Data column, which displays the text of the event message.
Determining the command set you will use
You can control the Model 2461 with command sets that are based on the SCPI or Test Script
Processor (TSP®) programming languages. You can change the command set that you use with the
Model 2461. The remote command sets that are available include:
SCPI: An instrument-specific language built on the SCPI standard.
TSP: A scripting programming language that contains instrument-specific control commands that
can be executed from a stand-alone instrument. You can use TSP to send individual commands
To clear the event log and update the information on the screen, click the Refresh button.
or use it to combine commands into scripts.
You cannot combine the command sets.
As delivered from Keithley Instruments, the Model 2461 is set to work with the Model 2461 SCPI
command set.
Using the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. Select the button next to Command Set and select the command set.
4. You are prompted to reboot.
Page 34

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 3: Using a remote interface
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 3-13
To change to the SCPI command set from a remote interface:
Send the command:
*LANG SCPI
Reboot the instrument.
To change to the TSP command set from a remote interface:
Send the command:
*LANG TSP
Reboot the instrument.
To verify which command set is selected:
Send the command:
*LANG?
Page 35

In this section:
Introduction .............................................................................. 4-1
Equipment required for this application .................................... 4-2
Device connections .................................................................. 4-2
Make front-panel measurements .............................................. 4-2
Section 4
Making basic front-panel measurements
Introduction
You can use the Model 2461 to source voltage or current and make measurements from the front
panel.
Make sure you select functions before you make changes to other instrument settings. The options
that you have for settings depend on the functions that are active when you make the changes. If
you make a change that is not compatible with the active functions, you may get unexpected results
or you may receive an event message. Also note that when you select a different function, the
instrument clears the buffer. The applications in this manual illustrate the order in which you should
perform operations for best results.
In this application, you make measurements on a 10 k resistor by sourcing voltage and measuring
current. You can make similar measurements on any two-terminal device under test (DUT) if
appropriate source values are used.
Some of the methods you can use to set up the Model 2461 to make measurements from the front
panel include:
Use Quicksets. Press the QUICKSET key to open a menu of preconfigured setups, including
voltmeter, ammeter, ohmmeter, and power supply setups. It also allows you to choose test
functions and adjust performance for better resolution or speed.
Select source and measure functions. Press the FUNCTION key to select from a list of source
and measure functions.
Use menu options. Press the MENU key to open a menu of options.
After selecting your source and measure functions, select buttons on the Model 2461 Home screen
and Settings swipe screens to change the settings.
You will use a combination of these methods to set up the measurement for this application.
Page 36
Section 4: Making basic front-panel measurements Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
4-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Equipment required for this application
Equipment required for this application:
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter
Two insulated banana cables; you can use the set that is provided with the Model 2461, the
Keithley Instruments Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set
One 10 k resistor to test
Device connections
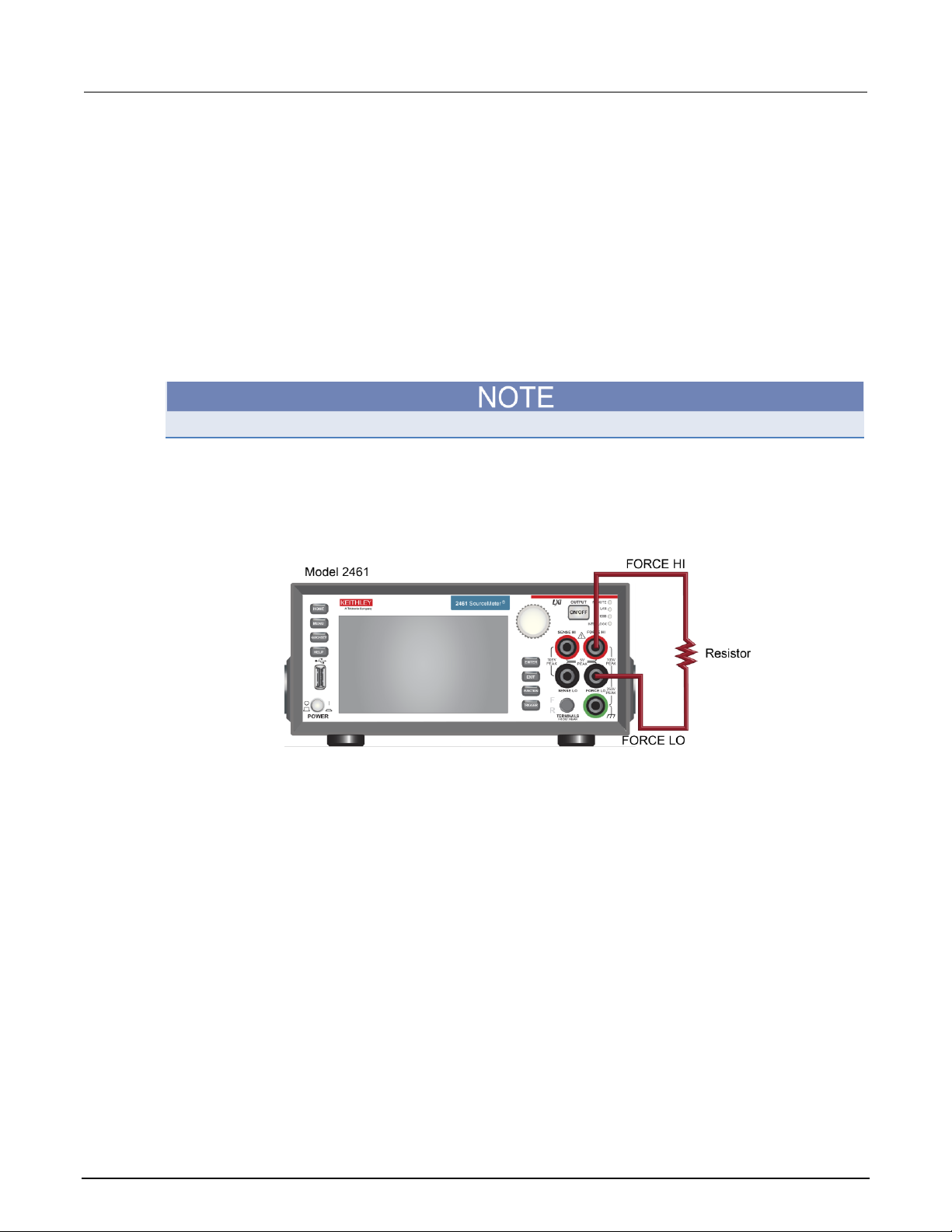
Turn the power to the instrument off before attaching connections to the Model 2461.
Connect the Model 2461 to the resistor in a 2-wire (local sense) configuration. In this configuration,
the device is connected between the FORCE HI and FORCE LO terminals.
The physical connections to the front panel are shown in the following figure.
®
Instrument
Figure 19: Model 2461 2-wire front-panel connections
Make front-panel measurements
For this application, you will:
Select the source and measure functions
Select the source range
Set the source value
Set the source limit
Select the measurement range
Turn on the source output
Observe the readings on the display
Turn off the source output
Page 37

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 4: Making basic front-panel measurements
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 4-3
How to make front-panel measurements
To make a measurement from the front panel:
1. Press the POWER switch on the front panel to turn on the instrument or cycle power if the
instrument is already on.
2. Verify the source and measure function. On the front panel, press the FUNCTION key.
3. Under Source Voltage and Measure, select Current.
4. Select the source range. On the Home screen, under SOURCE V, select the button next to
Range.
5. Select 20 V.
6. Select the source voltage. Under SOURCE V, select the button next to Source.
7. Enter 10 V and select OK.
8. Set the limits for the source. Under SOURCE V, select the button next to Limit.
9. Enter 10 mA and select OK.
10. Select the measurement range. In the MEASURE area of the Home screen, select the button
next to Range.
11. Select Auto.
12. Turn on the output by pressing the OUTPUT ON/OFF switch. The OUTPUT indicator light turns
on.
13. Observe the readings on the display. For the 10 k resistor, typical display values are:
1.00000 mA
+9.99700 V
14. When measurements are complete, turn the output off by pressing the OUTPUT ON/OFF switch.
The OUTPUT indicator light turns off.
Page 38

In this section:
Introduction ............................................................................... 5-1
Equipment required .................................................................. 5-1
Set up remote communications ................................................ 5-1
Device connections .................................................................. 5-2
Low-resistance measurements ................................................. 5-5
Section 5
Measuring low-resistance devices
Introduction
This application example demonstrates how to use the Model 2461 to measure a low-resistance
device.
You may need to make low-resistance measurements (<10 ) in a number of applications. Typical
applications include continuity testing of cables and connectors, substrate vias, and resistors.
Typically, you make these resistance measurements by forcing a current and measuring the resulting
voltage drop. The Model 2461 automatically calculates the resistance. The measured voltage is
usually in the mV range or less. Built-in features of the Model 2461 optimize low-resistance
measurements, such as remote sensing and offset compensation.
Equipment required
Set up remote communications
One Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter
®
Instrument
For front-panel connections, use four insulated banana cables, such as the Keithley Instruments
Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set included with the Model 2461; you will
need another set)
For rear-panel connections, use one Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (provided
with the Model 2461), or you can use one set of Model 2460-BAN Banana Test Leads/Adapter
Cables (with appropriate connections to the device)
One low-resistance device to be tested; the application shown here uses a 20 m resistor
You can run this application from the front panel or any of the supported communication interfaces for
the instrument (GPIB, USB, or ethernet).
The following figure shows the rear-panel connection locations for the remote communication
interfaces. For additional information about setting up remote communications, see Remote
communications interfaces (on page 3-1).
Page 39

Section 5: Measuring low-resistance devices Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
5-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Figure 20: Model 2461 remote interface connections
Device connections
To provide the best measurement accuracy, use the four-wire (Kelvin) measurement method for this
test. This method eliminates the effects of lead resistance on the measurement accuracy. It is the
preferred method when measuring low resistances.
To use the 4-wire connection method:
Connect one set of test leads to the FORCE LO and FORCE HI terminals; this setup forces a
current through the device under test.
Connect the other set of test leads to the SENSE HI and SENSE LO terminals, which measure
the voltage drop across the device under test (DUT).
Page 40
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 5: Measuring low-resistance devices
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 5-3
Hazardous voltages may be present on all output and guard terminals. To prevent electrical
shock that could cause injury or death, never make or break connections to the Model 2461
while the output is on.
To prevent electric shock, test connections must be configured such that the user cannot
come in contact with conductors or any device under test (DUT) that is in contact with the
conductors. It is good practice to disconnect DUTs from the instrument before powering the
instrument. Safe installation requires proper shields, barriers, and grounding to prevent
contact with conductors.
There is no internal connection between protective earth (safety ground) and the LO
terminals of the Model 2461. Therefore, hazardous voltages (more than 30 V
) can appear
rms
on LO terminals. This can occur when the instrument is operating in any mode. To prevent
hazardous voltage from appearing on the LO terminals, connect the LO terminal to
protective earth if your application allows it. You can connect the LO terminal to the chassis
ground terminal on the front panel or the chassis ground screw terminal on the rear panel.
Note that the front-panel terminals are isolated from the rear-panel terminals. Therefore, if
you are using the front-panel terminals, ground to the front-panel LO terminal. If using the
rear-panel terminals, ground to the rear panel LO terminal.
The following figure shows the schematic for the application.
Figure 21: Sourcing current and measuring resistance using a 4-wire configuration
Page 41
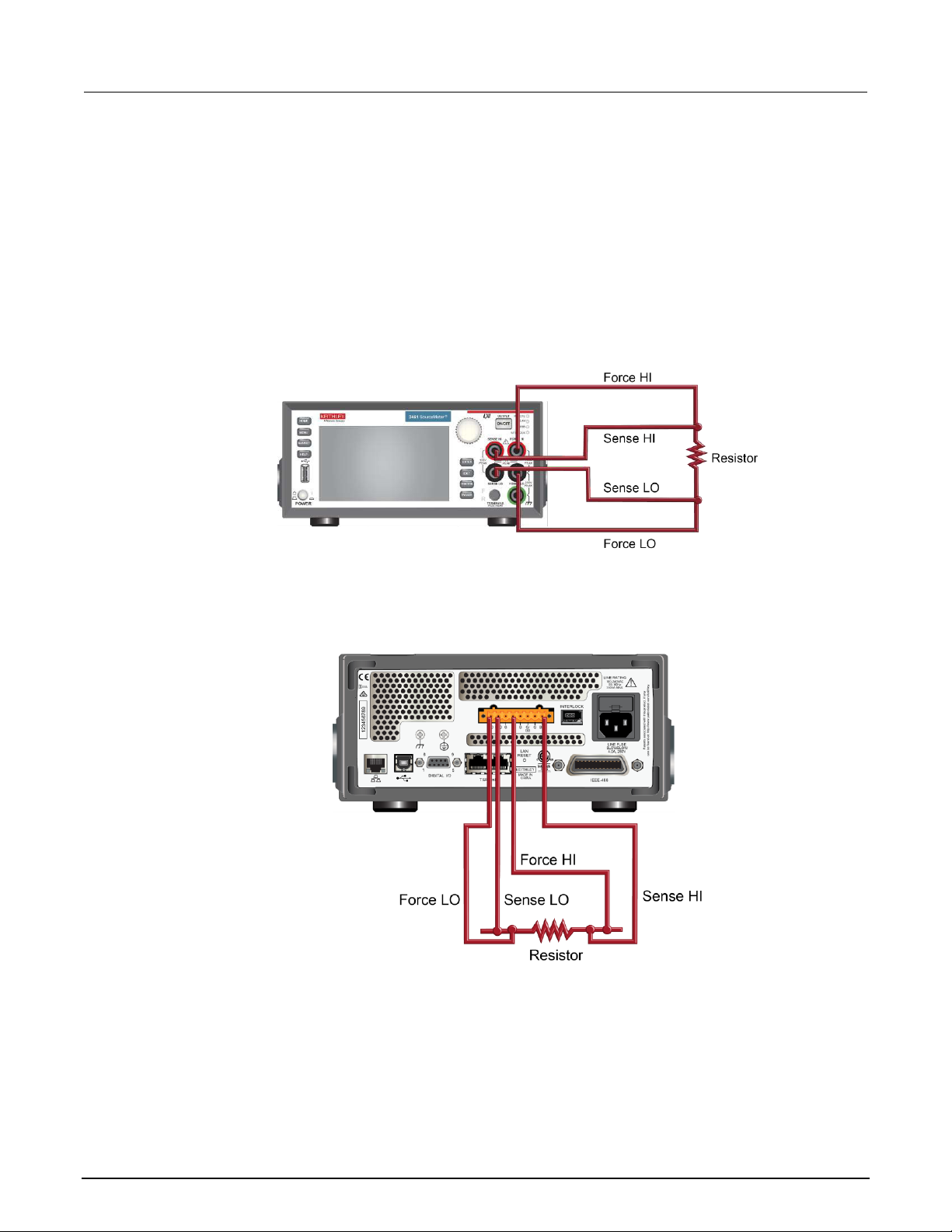
Section 5: Measuring low-resistance devices Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
5-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
You can use either the front-panel or the rear-panel terminals for this application. The following
figures show the physical connections for the front and rear panels. Note that you must use either the
front-panel terminals or rear-panel terminals — you cannot mix connections.
When you connect the leads to the device under test (DUT), notice that the FORCE LO and SENSE
LO connections are attached to one of the DUT leads. Make the FORCE HI and SENSE HI
connections to the other lead. Connect the sense connections as close to the resistor under test as
possible. This 4-wire measurement eliminates the resistance of the test leads in the measurement.
The figure below shows the front-panel connections. You can make these connections with four
insulated banana cables that are rated to the maximum current (10 A), such as two sets of the
Keithley Instruments Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set.
Figure 22: Model 2461 front-panel connections for low-resistance measurements
The figure below shows the rear-panel connections. You can make these connections with either the
Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (included with the Model 2461) or a Model 2460-BAN
Banana Test Leads/Adapter Cable with appropriate cabling.
Figure 23: Model 2461 low-resistance connections on rear panel
Page 42

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 5: Measuring low-resistance devices
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 5-5
Low-resistance measurements
This application demonstrates how to use the Model 2461 to measure a low-resistance device. You
can measure from the front panel or over the remote interface using SCPI code or TSP code.
For this application, you will:
Reset the instrument.
Select the source current and measure resistance function.
Set the current source value.
Select four-wire (remote sense) mode. This eliminates the effect of lead resistance on
measurement accuracy.
Enable offset compensation. This reduces offset caused by thermoelectric voltages. For
information about offset compensation, see "What is offset compensation?" in the Model 2461
Reference Manual.
Turn on the source output and start making measurements.
Generate readings from the front panel or the remote interface.
Turn the source output off.
Set up the measurement from the front panel
To set up the application from the front panel:
1. Make connections from the Model 2461 to the device under test, as described in Device
connections (on page 5-2).
2. Reset the instrument:
a. Press the MENU key.
b. Under System, select Info/Manage.
c. Select System Reset.
d. Select OK.
3. Press the FUNCTION key.
4. Under Source Current and Measure, select Resistance.
5. Press the HOME key.
6. In the SOURCE I area, select the button next to Source. Select the source value.
7. Press the MENU key. Under Measure, select Settings.
8. Next to Sense, select 4-Wire Sense.
9. Next to Offset Compensation, select On.
10. Press the HOME key.
11. Press the OUTPUT ON/OFF switch to enable the output and start making measurements.
12. Press the OUTPUT ON/OFF switch to disable the output and stop making measurements.
The instrument displays the measurements in the MEASURE VOLTAGE area of the Home screen.
Page 43

Section 5: Measuring low-resistance devices Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
5-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
View the measurements on the front-panel GRAPH swipe screen
You can view the resistance measurements as a function of time on the front-panel GRAPH swipe
screen. To access the GRAPH swipe screen, swipe the bottom part of the Home screen to the right.
A graph similar to the one in the figure below is displayed.
Figure 24: GRAPH swipe screen
To see the graph on the full screen, touch the graph icon on the GRAPH swipe bar to open the Graph
screen.
View the buffer statistics on the front panel
You can view the measurement statistics on the Model 2461 front-panel STATISTICS swipe screen,
including:
Peak-to-peak value
Minimum, maximum, and average reading values
Standard deviation
Figure 25: STATISTICS swipe screen
Set up the low-resistance application using SCPI commands
The following sequence of SCPI commands makes 100 low-resistance measurements by sourcing
current and measuring resistance. In this example, the source current magnitude and limit voltage are
set automatically. It uses remote commands to change the front-panel display to show the GRAPH
swipe screen. This allows you to view numeric data at the top of the screen and graphic data at the
bottom of the screen.
Page 44

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 5: Measuring low-resistance devices
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 5-7
You may need to make changes so that this code will run in your programming environment.
Command
Description
*RST
TRIG:LOAD "SimpleLoop", 100
SENS:FUNC "RES"
SENS:RES:RANG:AUTO ON
SENS:RES:OCOM ON
SENS:RES:RSEN ON
DISP:SCR SWIPE_GRAPh
OUTP ON
INIT
*WAI
TRAC:DATA? 1, 100, "defbuffer1", READ, REL
OUTP OFF
Reset the Model 2461.
Configure Simple Loop trigger model
template to make 100 readings.
Set to measure resistance.
Turn on auto range.
Enable offset compensation.
Set to use 4-wire sense mode.
Show the GRAPH swipe screen.
Turn on the output.
Initiate readings.
Wait until finished.
Read the resistance and time values from
defbuffer1.
Turn off the output.
Send the following commands for this example application:
Set up the low-resistance application using TSP commands
The following TSP code is designed to be run from Keithley Instruments Test Script Builder (TSB).
TSB is a software tool that is available from the Keithley Instruments website. You can install and
use TSB to write code and develop scripts for TSP-enabled instruments. Information about how to
use TSB is in the online help for TSB and in the “Introduction to TSP operation” section of the Model
2461 Reference Manual.
To use other programming environments, you may need to make changes to the example TSP code.
By default, the Model 2461 uses the SCPI command set. You must select the TSP command set
before sending TSP commands to the instrument.
To enable TSP commands:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. For Command Set, select TSP.
4. At the prompt to reboot, select Yes.
This sequence of TSP commands makes 100 low-resistance measurements by sourcing current and
measuring resistance. In this example, the source current magnitude and limit voltage are set
automatically. It uses remote commands to change the front-panel display to show the GRAPH swipe
screen. This allows you to view numeric data at the top of the screen and graphic data at the bottom
of the screen. After the code executes, the data is displayed in the Instrument Console of Test Script
Builder.
Page 45

Section 5: Measuring low-resistance devices Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
5-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Send the following commands for this example application:
--Reset the instrument to the default settings
reset()
--Configure the Simple Loop trigger model template to make 100 readings.
trigger.model.load("SimpleLoop", 100)
--Change the view on the front panel to the GRAPH swipe screen.
display.changescreen(display.SCREEN_GRAPH_SWIPE)
--Set to measure resistance, use 4-wire sense,
--and offset compensation.
smu.measure.func = smu.FUNC_RESISTANCE
smu.measure.sense = smu.SENSE_4WIRE
smu.measure.offsetcompensation = smu.ON
--Turn on the output
smu.source.output = smu.ON
--Initiate trigger model and wait until finished.
trigger.model.initiate()
waitcomplete()
--Turn off output
smu.source.output = smu.OFF
--Read the resistance and time values from defbuffer1.
print("Resistance:\tTime:")
for i = 1, 100 do
print(string.format("%f\t%f", defbuffer1[i], defbuffer1.relativetimestamps[i]))
end
Page 46

In this section:
Introduction ............................................................................... 6-1
Equipment required .................................................................. 6-3
Device connections .................................................................. 6-4
Automated battery charge and discharge cycle testing ............ 6-6
Section 6
Rechargeable battery measurements
Introduction
This example application demonstrates how to use a single Model 2461 to perform automated battery
discharge and charge cycle testing.
To prevent personal injury or damage to the Model 2461, do not attempt to charge
nonrechargeable batteries. Some of the batteries that can be charged with a Model 2461
are nickel cadmium (Ni-Cd), nickel metal hydride (Ni-MH), lithium ion (Li-ion), rechargeable
alkaline, and lead acid. If you are working with a battery type that is not listed here, please
contact your local Keithley office, sales partner, or distributor, or call one of our
Applications Engineers to get technical assistance.
Always follow the battery manufacturer's requirements for charging or discharging
batteries using a Model 2461. Failure to properly charge or discharge batteries may cause
them to leak or explode, resulting in personal injury and property damage. Overvoltage and
current protection should be provided in the charge circuit, external to the instrument,
when charging batteries without built-in protection.
Do not charge or discharge batteries that exceed 100 V at 1.0 A, 20 V at 4.0 A, 10 V at 5.0 A,
or 7 V at 7 A.
Page 47

Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
6-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
For both the charging and discharging cycles, you configure the Model 2461 to source voltage and measure
1
Model 2461 is in source mode (VS > VB). Instrument functions as a
power supply; charge current (i) is positive.
2
Model 2461 is in sink mode (Vs < VB). Instrument functions as an
electronic load; discharge current (i) is negative.
current. The following figures show simplified schematics for the charge and discharge cycles.
Figure 26: Model 2461 charge-discharge cycle
Charging
A battery is usually charged using a constant current. To do this, use a Model 2461 as a voltage
source set to the voltage rating of the battery, with the target charging current set as the current limit.
At the start of the test, the battery voltage is less than the voltage output setting of the Model 2461.
As a result, this voltage difference drives a current that is immediately limited to the user-defined
current limit. When in current limit, the Model 2461 acts as a constant current source until it reaches
the programmed voltage level. As the battery becomes fully charged, the current decreases until it
reaches zero or near zero. To prevent safety hazards or damage to the battery, be careful not to
overcharge the battery.
Discharging
When discharging a battery, the Model 2461 operates as a sink because it is dissipating power
instead of sourcing it. The voltage source of the Model 2461 is set to a lower level than the battery
voltage. The current limit sets the discharge rate. When the output is enabled, the current from the
battery flows into the HI terminal of the Model 2461. As a result, the current readings are negative.
The discharge current should stay constant until the battery voltage decreases to the voltage source
setting of the Model 2461.
Page 48

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 6-3
If you are using the current source to charge or discharge batteries, the following precautions must
be observed. Failure to observe these precautions could result in instrument damage that is not
covered by the warranty.
Make sure the external voltage never exceeds the voltage limit setting of the current source. This will
cause excessive current to be drawn from the external battery or source.
Be sure to set the output-off state of the current source for high impedance. This setting opens the
output relay when the output is turned off. With the normal output-off state selected, turning the
output off sets the voltage limit to zero. This 0 V source limit condition will cause excessive current to
be drawn from the external battery or source.
Carefully consider and configure the output-off state, source, and limits before connecting the Model
2461 to a device that can deliver energy. Devices that can deliver energy include voltage sources,
batteries, capacitors, and solar cells. Configure instrument settings before making connections to the
device. Failure to consider the output-off state, source, and limits may result in damage to the
instrument or to the device under test (DUT).
When using the current source as a sink, always set the voltage limit and configure overvoltage
protection (OVP) to levels that are higher than the external voltage level. Failure to do so could result
in excessive current flow into the Model 2461 (> 100 mA) and incorrect measurements.
Equipment required
One Model 2461 High-Current Interactive SourceMeter
For front-panel connections, use four insulated banana cables, such as the Keithley Instruments
Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set included with the Model 2461; you will
need another set)
For rear-panel connections, use one Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (provided
with the Model 2461), or you can use one set of Model 2460-BAN Banana Test Leads/Adapter
Cables (with appropriate connections to the device)
One GPIB, USB, or ethernet cable to connect the Model 2461 to a computer
One rechargeable battery to test
®
Instrument
Page 49
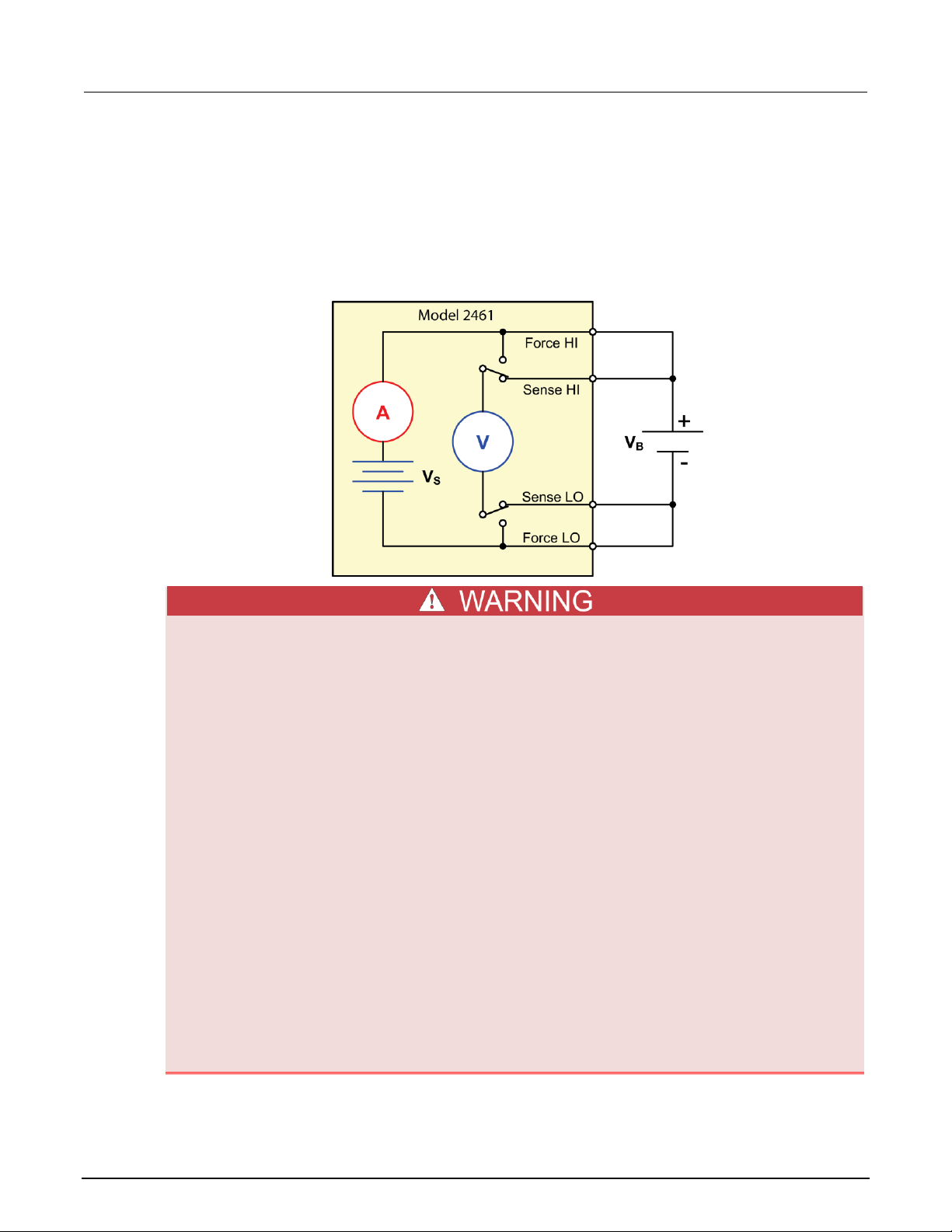
Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
6-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Device connections
To set up the test, connect the Model 2461 to the battery as shown in the following figure. Make a
4-wire (remote sense) connection from the instrument terminals to the battery to eliminate the effects
of the lead resistance. This allows you to measure the battery voltage as closely as possible to the
terminals of the instrument.
Figure 27: Schematic for the Model 2461 battery application
To prevent electric shock, test connections must be configured such that the user cannot
come in contact with conductors or any device under test (DUT) that is in contact with the
conductors. It is good practice to disconnect DUTs from the instrument before powering the
instrument. Safe installation requires proper shields, barriers, and grounding to prevent
contact with conductors.
There is no internal connection between protective earth (safety ground) and the LO
terminals of the Model 2461. Therefore, hazardous voltages (more than 30 V
) can appear
rms
on LO terminals. This can occur when the instrument is operating in any mode. To prevent
hazardous voltage from appearing on the LO terminals, connect the LO terminal to
protective earth if your application allows it. You can connect the LO terminal to the chassis
ground terminal on the front panel or the chassis ground screw terminal on the rear panel.
Note that the front-panel terminals are isolated from the rear-panel terminals. Therefore, if
you are using the front-panel terminals, ground to the front-panel LO terminal. If using the
rear-panel terminals, ground to the rear panel LO terminal.
Be aware that hazardous voltages can appear on the LO terminals even if the terminals are
not presently selected. The TERMINALS FRONT/REAR switch selects the active terminals
for the measurement. It does not disconnect the terminals.
The maximum input voltage between FORCE/SENSE HI and FORCE/SENSE LO 105 V
peak
.
Exceeding this value may create a shock hazard.
The maximum common-mode voltage (the voltage between FORCE/SENSE LO and chassis
ground) is 250 V
. Exceeding this value may cause a breakdown in insulation that can
peak
create a shock hazard.
Page 50
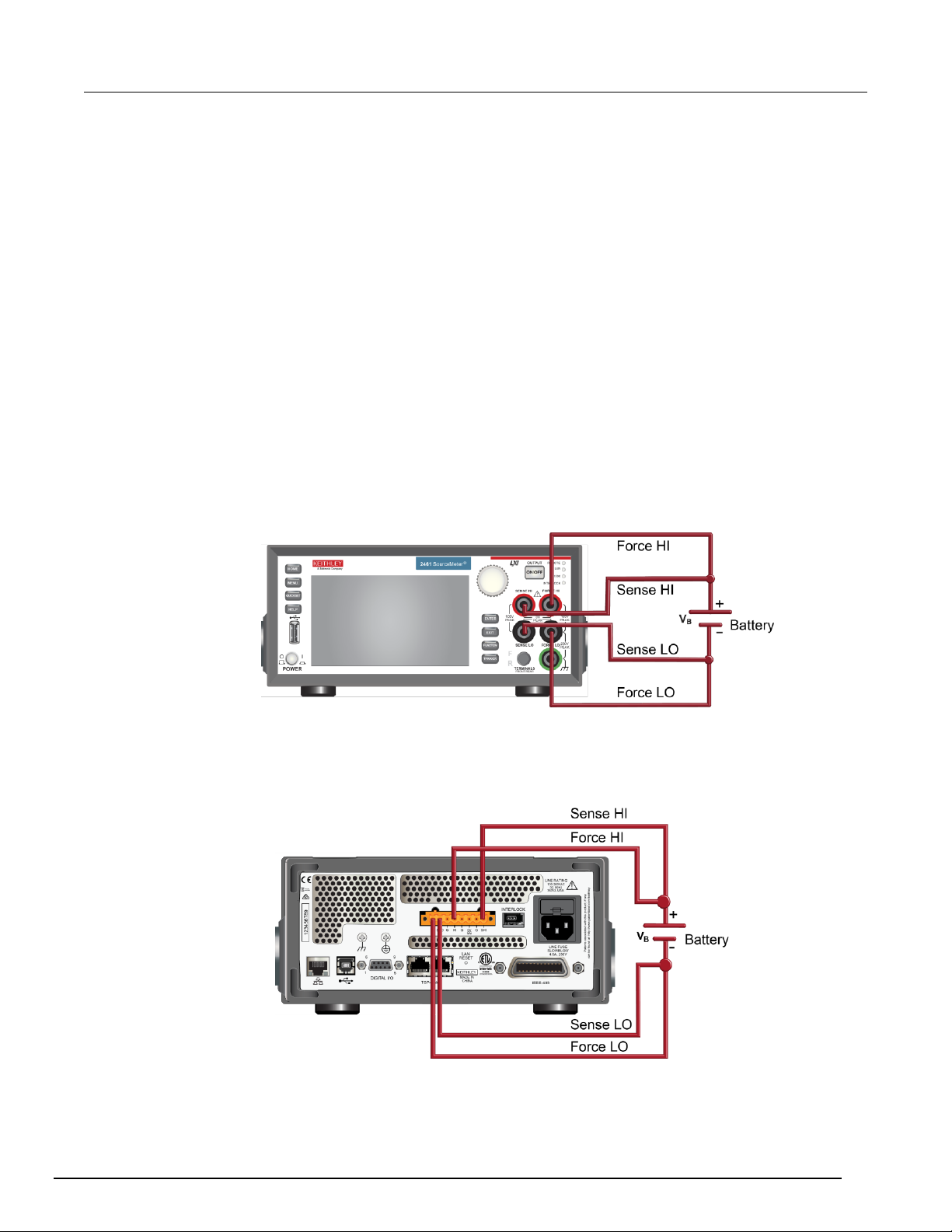
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 6-5
Connect the FORCE HI and SENSE HI output terminals of the Model 2461 to the positive (+) terminal
of the battery. Connect the SENSE LO and FORCE LO outputs to the negative () terminal of the
battery.
Make sure that when the output of the Model 2461 is turned off, it is set to the high-impedance
(High-Z) output-off state. When the high-impedance output-off state is selected, the output relay
opens when the output is turned off. This prevents the battery from draining when the output is off.
You can make test connections to the Model 2461 from the rear or front panel of the instrument.
To set the output-off state to high impedance:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. In the Source column, select Settings.
3. Select the button next to Output Off and select High Impedance.
4. Press the HOME key to return to the Home screen.
The figure below shows the front-panel connections. You can make these connections with four
insulated banana cables that are rated to the maximum current (10 A), such as two sets of the
Keithley Instruments Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set.
Figure 28: Front-panel connections for the battery discharge-charge application
The figure below shows the rear-panel connections. You can make these connections with either the
Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (included with the Model 2461) or a Model 2460-BAN
Banana Test Leads/Adapter Cable with appropriate cabling.
Figure 29: Rear-panel connections for the battery discharge-charge application
Page 51

Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
6-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Automated battery charge and discharge cycle testing
Battery charge and discharge cycles often take several hours, so automating the test is important.
This example demonstrates how to use the Model 2461 to perform an automated battery discharge
test using SCPI commands or TSP commands.
For this application, you will:
Reset the instrument.
Set the measurement to a 4-wire configuration.
Set the instrument to source voltage and measure current.
Select the high impedance output-off mode, which opens the output relay when the Model 2461
output is turned off. Select this mode before connecting the battery to the output. This prevents
the battery from draining when it is connected to the instrument with the output off.
Set the current limit to the current level at which the battery is to be charged or discharged. This
is the load current of the test. Even though the Model 2461 is sourcing voltage, it operates in
constant current mode because it is in current limit until it reaches the desired voltage.
Turn on source readback to enable the Model 2461 to measure the battery voltage while it either
charges or discharges.
Read the load current, source readback voltage, and the relative timestamp.
Monitor the voltage until the battery voltage reaches the specified voltage level and stop the test.
To charge the battery, program the Model 2461 to output a voltage that is equivalent to the voltage
rating of the battery. For example, to charge a 10 V battery, set the Model 2461 to source 10 V. As
the battery fully charges, current decreases until it reaches zero or near zero (battery charged).
To discharge the battery, program the Model 2461 to output a voltage to a lower level than the battery
voltage and set the output-off state to high impedance. In this configuration, the Model 2461 operates
as a sink to discharge the battery. Current from the battery flows into the SENSE HI terminal of the
Model 2461, which results in negative current measurements. As the battery discharges, the current
stays constant.
Page 52

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 6-7
Set up remote communications
This application is configured to run remotely. You can run this application from any of the supported
communication interfaces for the instrument (GPIB, USB, or ethernet).
The following figure shows the rear-panel connection locations for the remote communication
interfaces.
Figure 30: Model 2461 remote interface connections
Set up the battery application using SCPI commands
The SCPI code in this example is configured to discharge a fully charged 1.2 V (2500 mAh) battery to
0.9 V. The Model 2461 is configured to source voltage and measure current. Specifically, the voltage
source is set to 0.9 V and the source limit is set to 2.5 A. The voltage, current, and relative timestamp
values are returned. Measurements are made until the voltage reaches the set level.
You may need to change the current and voltage levels so that they are appropriate for the battery
you are testing.
In the following example code, notice that some of the code is labeled as "Pseudocode." The code
you use for the pseudocode lines will vary based on the programming environment you use.
Page 53
Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
6-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Send the following commands for this example application:
SMU
command or
pseudocode
Commands
Description
SMU
command
OUTP:SMOD HIMP
SENS:CURR:RSEN ON
SOUR:FUNC VOLT
SOUR:VOLT 0.9
ROUT:TERM REAR
SOUR:VOLT:READ:BACK ON
SOUR:VOLT:RANG 2
SOUR:VOLT:ILIM 2.5
SENS:FUNC "CURR"
SENS:CURR:RANG 4
OUTP ON
Turn on high-impedance output mode.
Set to 4-wire sense mode.
Set to source voltage.
Set source level to 0.9 V.
Select the rear-panel connections.
Turn on source readback.
Set source range to 2 V.
Set the source limit to 2.5 mA.
Set to measure current.
Set current range to 4 A.
Turn the output on.
Pseudocode
iteration = 1
voltLimit = 0.9001
current = []
voltage = []
seconds = []
hours = []
while true do:
Create a variable called iteration and
initialize to 1.
Create a variable called voltLimit and
initialize to 0.9001.
Create an empty array for current
measurements.
Create an empty array for voltage
measurements.
Create an empty array for the time values.
Start a while loop.
SMU
command
current[iteration] = READ?
"defbuffer1"
voltage[iteration] = TRAC:DATA?
iteration, iteration,
"defbuffer1", SOUR
seconds[iteration] = TRAC:DATA?
iteration, iteration,
"defbuffer1", REL
Append the current reading to the array
current.
Append the voltage reading to the array
voltage.
Append the time reading to the array
seconds.
Pseudocode
hours[iteration] =
seconds[iteration]/3600
print(voltage[iteration],
current[iteration],
hours[iteration])
if voltage[iteration] <=
voltLimit then:
break
end if
iteration = iteration + 1
delay(10)
end while
Calculate the hours taken at each iteration.
Print the measured values.
Compare the voltage reading from this
iteration to the voltage limit. If the
measured value is less than or equal to the
limit, break out of the loop.
End the if statement.
Increment the iteration count by 1.
Delay for 10 seconds.
End the while loop.
SMU
command
OUTP OFF
Turn the output off.
Page 54
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 6-9
Set up the battery application using TSP commands
The following TSP code is designed to be run from Keithley Instruments Test Script Builder (TSB).
TSB is a software tool that is available from the Keithley Instruments website. You can install and
use TSB to write code and develop scripts for TSP-enabled instruments. Information about how to
use TSB is in the online help for TSB and in the “Introduction to TSP operation” section of the Model
2461 Reference Manual.
To use other programming environments, you may need to make changes to the example TSP code.
By default, the Model 2461 uses the SCPI command set. You must select the TSP command set
before sending TSP commands to the instrument.
To enable TSP commands:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. For Command Set, select TSP.
4. At the prompt to reboot, select Yes.
The TSP code in this example sets the Model 2461 to the source voltage function and measure
current function. To discharge a fully charged 1.2 V battery, the voltage source is set to 0.9 V and the
source limit is set to 2.5 A. The voltage, current, and relative timestamp values are returned.
Measurements are made until the voltage reaches the set level. During the test, these measurements
are shown on the USER swipe screen at the bottom of the screen (see the figure following the
example code).
You may need to change the current and voltage levels so that they are appropriate for the battery
you are testing.
The TSP code in this example also saves all of the current, voltage, and time readings to a USB flash
drive connected to the Model 2461 front panel.
Before connecting the battery to the output terminals, complete the following tasks to prepare the
Model 2461 for the test.
Reset the instrument:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Info/Manage.
3. Select System Reset > OK.
Set the output-off state to High Impedance:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under Source, select Settings.
3. Select the button next to Output Off State and select High Impedance. This output-off state
opens the output relay when the output is turned off, preventing the battery from draining.
Page 55

Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
6-10 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Send the following TSP commands for this example application:
--This code discharges a 2500 mAH 1.2 V battery to 0.9 V with a
--discharge current of 2.5A (1C).
--Before using this code, reset the instrument from the front panel
--and set the output-off state of the Model 2461 to High Impedance
--(High Z). Also, insert a USB flash drive in the front-panel USB
--port to save your readings.
--Clear the buffer.
defbuffer1.clear()
--Measurement settings.
smu.measure.func = smu.FUNC_DC_CURRENT
smu.measure.range = 2.5
smu.measure.sense = smu.SENSE_4WIRE
--Source settings.
smu.source.func = smu.FUNC_DC_VOLTAGE
smu.source.offmode = smu.OFFMODE_HIGHZ
smu.source.level = 0.9
smu.terminals = smu.TERMINALS_REAR
smu.source.range = 0.9
smu.source.readback = smu.ON
smu.source.ilimit.level = 2.5
--Set the voltage limit for the battery to stop discharging.
--Set the variable for the number of iterations.
voltLimit = 0.9001
iteration = 1
--Turn on the source output.
smu.source.output = smu.ON
--Change the display to the USER swipe screen.
display.changescreen(display.SCREEN_USER_SWIPE)
--Keep taking readings in the while loop until the measured voltage
--is equal to the voltage limit.
while true do
--Take a reading and get the current, voltage, and relative timestamp.
curr = smu.measure.read(defbuffer1)
volt = defbuffer1.sourcevalues[iteration]
time = defbuffer1.relativetimestamps[iteration]
hours = time/3600
--Compare the measured voltage to the voltage limit.
--Exit the loop if it has reached the limit.
if volt <= voltLimit then
break
end
--Print the number of completed cycles, the voltage, and the time for the
--iteration. Display the information on the front panel.
print("Completed Cycles: ",iteration, "Voltage: ", volt, "Time: ", time)
display.settext(display.TEXT1, string.format("Voltage = %.4fV", volt))
display.settext(display.TEXT2, string.format("Current = %.2fA, Time = %.2fHrs",
curr, hours))
--Increment the number of iterations and wait 10 seconds.
iteration = iteration + 1
delay(10)
end
--Turn the output off when the voltage limit is reached.
smu.source.output = smu.OFF
--Save the measurements to the USB flash drive.
Page 56
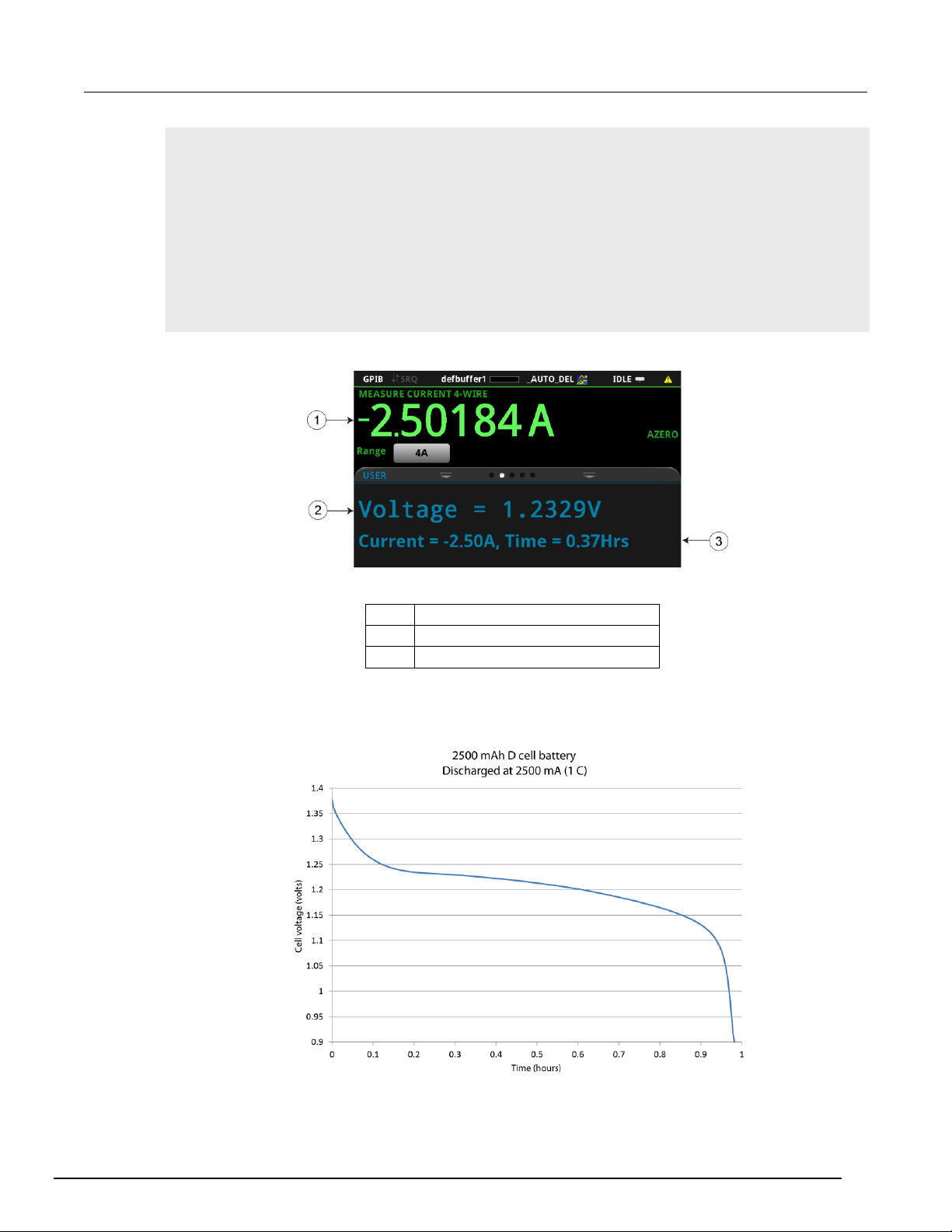
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 6: Rechargeable battery measurements
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 6-11
FileNumber = file.open("/usb1/TestData.csv", file.MODE_WRITE)
1 Measured load current
2 Measured battery voltage
3 Source value and elapsed test time
file.write(FileNumber,"Current,Voltage,Seconds\n")
--Print the measured values in a four-column format.
print("nIteration:\tCurrent:\tVoltage:\tTime:\n")
for i = 1, defbuffer1.n do
print(i, defbuffer1[i], defbuffer1.sourcevalues[i],
defbuffer1.relativetimestamps[i])
file.write(FileNumber, string.format("%g,%g, %g\r\n",defbuffer1.readings[i],
defbuffer1.sourcevalues[i],defbuffer1.relativetimestamps[i]))
end
--Close the .csv file.
file.close(FileNumber)
Figure 31: Model 2461 USER swipe screen showing test results
Figure 32: Results of battery discharge test
Page 57

In this section:
Introduction ............................................................................... 7-1
Equipment and software required ............................................. 7-1
Set up remote communications ................................................ 7-2
Device connections .................................................................. 7-2
Generating an I-V sweep using KickStart ................................. 7-4
Introduction
Section 7
Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart
This example application demonstrates how to generate a current-voltage sweep on a
high-brightness LED using the Keithley KickStart Startup Software and a Model 2461. KickStart
software allows you to set up your instrument and run a test quickly without writing any code. The
data generated by KickStart can be plotted on a graph or viewed in a table. The measurements can
also be saved to a file in .csv file format.
In this example, you will use the KickStart software to configure the Model 2461 to output a voltage
sweep and measure the resulting current on a high-brightness LED. You will then run the test and
graph the data in KickStart.
Equipment and software required
One Model 2461 High-Current Interactive SourceMeter
For front-panel connections, use four insulated banana cables, such as the Keithley Instruments
Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set included with the Model 2461; you will
need another set)
For rear-panel connections, use one Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (provided
with the Model 2461), or you can use one set of Model 2460-BAN Banana Test Leads/Adapter
Cables (with appropriate connections to the device)
One GPIB, USB, or ethernet cable to connect the Model 2461 to a computer
One high-brightness LED
®
Instrument
Page 58

Section 7: Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
7-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Set up remote communications
This application is configured to run remotely. You can run this application from any of the supported
communication interfaces for the instrument (GPIB, USB, or ethernet).
The following figure shows the rear-panel connection locations for the remote communication
interfaces.
Figure 33: Model 2461 remote interface connections
Device connections
For best measurement accuracy and to eliminate the effects of test lead resistance when sourcing
high current, connect the Model 2461 to the device under test (DUT) using the 4-wire sense method.
To use the 4-wire sense connection method:
Connect the FORCE HI and SENSE HI leads to the anode terminal of the LED.
Connect the FORCE LO and SENSE LO leads to the cathode terminal of the LED.
Make the connections as close to the DUT as possible to exclude the test-lead resistance from
the measurement.
Page 59
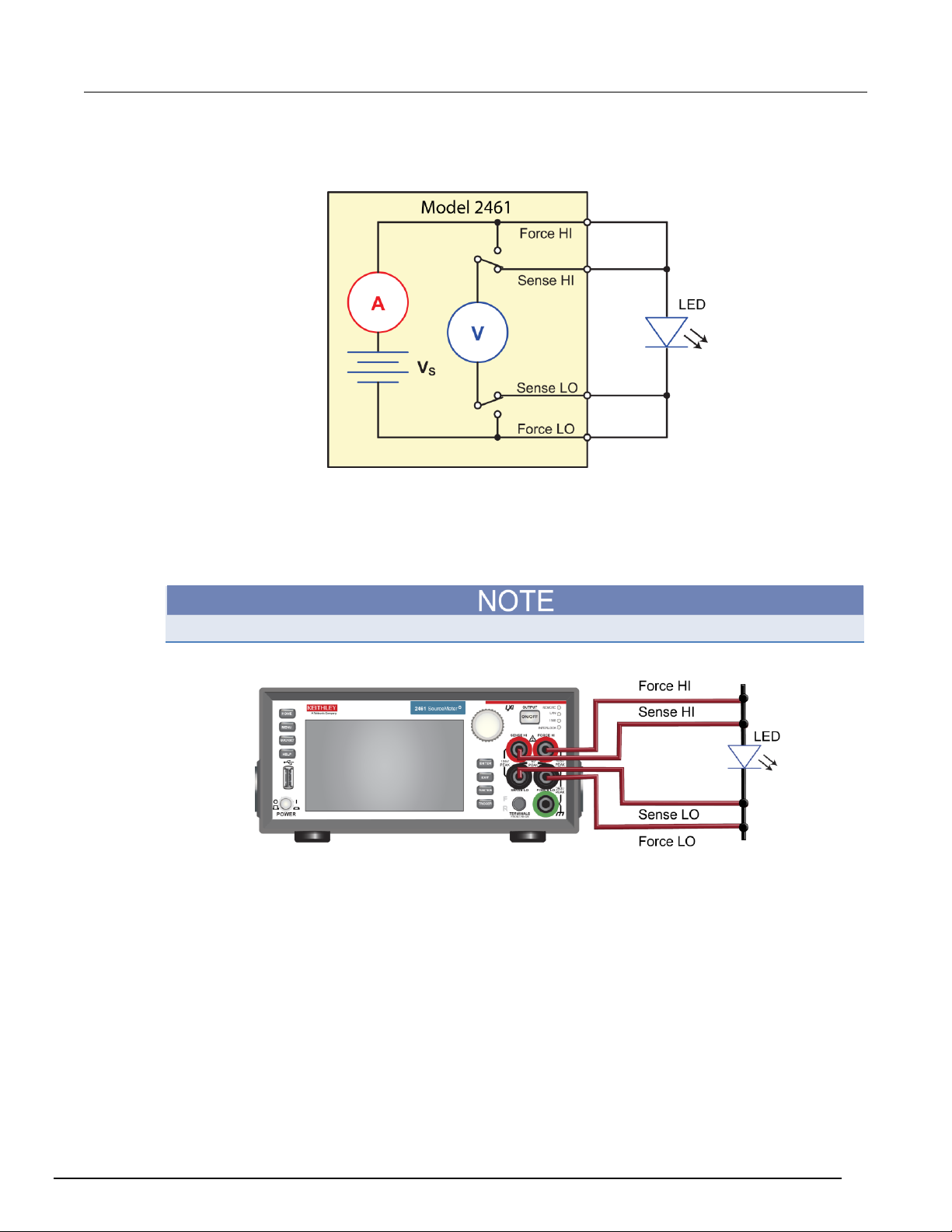
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 7: Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 7-3
The following figure shows the schematic for testing a high-brightness LED.
Figure 34: Model 2461 4-wire rear connections
The following figures show the physical connections for the front and rear panels. Note that you must
use either the front-panel terminals or rear-panel terminals — you cannot mix connections.
The figure below shows the front-panel connections. You can make these connections with four
insulated banana cables that are rated to the maximum current (10 A), such as two sets of the
Keithley Instruments Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set.
Turn the power to the instrument off before attaching connections to the Model 2461.
Figure 35: Model 2461 4-wire front-panel connections to an LED
Page 60

Section 7: Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
7-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
The figure below shows the rear-panel connections. You can make these connections with either the
Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (included with the Model 2461) or a Model 2460-BAN
Banana Test Leads/Adapter Cable with appropriate cabling.
Figure 36: Model 2461 4-wire rear-panel connections to an LED
Generating an I-V sweep using KickStart
This example application uses Keithley KickStart Startup Software to generate a current-voltage
sweep on a high-brightness LED.
In this example application, you will:
Launch the KickStart software
Create a new test project
Select an instrument
Select a test type
Configure the test parameters
Configure and view the graph screen
Run the test
View and save the test data
Configure the Model 2461 to use the KickStart software
The Model 2461 must be set to use the Test Script Processor (TSP®) command set before you can
use the KickStart software. By default, the Model 2461 uses the SCPI command set. You must select
the TSP command set before using KickStart.
To enable TSP commands:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. For Command Set, select TSP.
4. At the prompt to reboot, select Yes.
Page 61

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 7: Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 7-5
Launch KickStart and set up the test
Once the communication cable is connected to the computer and the TSP command set is enabled,
you are ready to launch the KickStart software.
To create a new test project:
1. Launch the KickStart software. The Start Page is displayed, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 37: KickStart Startup Software Start Page
2. On the Start Page, click New KickStart Test. The Save As dialog box opens.
3. Navigate to the location where you want to save your test projects (you do not need to create a
folder; KickStart creates the folder for you). You can also use the default location for KickStart
projects, which is C:\Users\My Documents\Keithley Instruments\KickStart.
4. Enter a name for the test and click Save. The test is saved as a .kst file in a folder with the
name of the test project.
Page 62

Section 7: Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
7-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
5. Click Select Instrument in the bottom left corner of the screen. If the Model 2461 is configured
Source settings
Parameter
Value
Source Mode
Voltage Sweep
Sweep Type
Linear
Start Voltage
2
Stop Voltage
3.7
Step Voltage
0.05
# Of Steps
This is automatically completed based on the
step voltage setting. For this example, the value
is 35.
Current Limit
7
Delay Seconds
0.01
Measure settings
Parameter
Value
Current Measure
Enabled, Auto Range
Voltage Measure
Enabled, Programmed Value
properly, it appears in the Instrument Configuration panel.
6. Right-click Model 2461:1 and select Add Instrument. Information about the connected Model
2461 appears in the bottom half of the Instrument Configuration panel.
Figure 38: Select instrument in the Instrument Configuration
7. At the bottom of the screen, click Select Test Type. The Test Types panel opens on the left side
of the screen, showing the available test types.
8. Right-click the IV Characterizer test type and select Add Test Type. The Source Measure
Settings screen opens.
9. Use the values in the following tables to specify the source and measure parameters for this
application (you can change these values for your own application).
Page 63

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 7: Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 7-7
10. In the lower part of the Measure Settings column, select the button next to Advanced
Advanced settings
Parameter
Value
Input Jacks
Rear
Sensing Mode
4-wire
Output OFF State
Normal
High Capacitance
Off
Offset Compensation
Off
Configuration and set the parameters listed in the following table.
11. To configure the graphing function, select the Graph tab.
12. Click the button next to X-Axis and select Smu1.V (sweep voltage).
13. Click the button next to Y-Axis and select Smu1.I (measure current).
You are now ready to run the test.
Run the test and view the graph
To run the test, select Start Test in the lower right corner of the screen. An I-V sweep is generated
automatically and the results appear in real time on the graph screen. The data on the graph is scaled
automatically as the test progresses.
The following figure shows the result of running this example application.
Figure 39: Results of running an I-V sweep on a high-brightness LED
To save the graph as a .png file, click Graph Image in the Export Data/Graph area of the ribbon at
the top of the screen.
Page 64

Section 7: Generating an I-V sweep on an LED with KickStart Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
7-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
View and save the test data in tabular form
You can also view the results of the test in tabular form by selecting the Sheet tab. The figure below
shows the test results on the Sheet tab.
Figure 40: Test data on the KickStart Sheet tab
To export the data as a .csv or .xlsx file, click Excel Format or CSV Format in the Export
Data/Graph area of the ribbon at the top of the screen.
Page 65

In this section:
Introduction ............................................................................... 8-1
Equipment required .................................................................. 8-1
Set up remote communications ................................................ 8-2
Device connections .................................................................. 8-2
Solar panel characterization ..................................................... 8-4
Section 8
Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel
Introduction
This example application demonstrates how to use the Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter®
Instrument to measure the I-V characteristics of a solar panel.
From the I-V characteristics measured by the Model 2461, you can determine important parameters
about the solar panel, including:
Maximum current (I
Maximum power (P
Open circuit voltage (V
Short-circuit current (I
Because the Model 2461 has four-quadrant source capability, it can sink up to 7 A of cell current as a
function of the applied voltage.
Equipment required
One Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter
For front-panel connections, use four insulated banana cables, such as the Keithley Instruments
Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set included with the Model 2461; you will
need another set)
For rear-panel connections, use one Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (provided
with the Model 2461), or you can use one set of Model 2460-BAN Banana Test Leads/Adapter
Cables (with appropriate connections to the device)
One solar panel
) and voltage (V
max
)
max
)
oc
)
sc
)
max
®
Instrument
Page 66

Section 8: Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
8-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Set up remote communications
You can run this application from the front panel or any of the supported communication interfaces for
the instrument (GPIB, USB, or ethernet).
The following figure shows the rear-panel connection locations for the remote communication
interfaces. For additional information about setting up remote communications, see Remote
communications interfaces (on page 3-1).
Figure 41: Model 2461 remote interface connections
Device connections
Connect the Model 2461 to the solar panel in a 4-wire configuration to provide the best measurement
accuracy and eliminate the effects of the lead resistance on the measurement.
To use the 4-wire connection method:
Connect the FORCE LO and SENSE LO leads to the cathode terminal.
Connect the FORCE HI and SENSE HI leads to the anode terminal.
Make the connections as close to the solar panel as possible to avoid including the resistance of
the test leads in the measurement.
You can use either the front-panel or the rear-panel terminals for this application.
Hazardous voltages may be present on all output and guard terminals. To prevent electrical
shock that could cause injury or death, never make or break connections to the Model 2461
while the output is on.
To prevent electric shock, test connections must be configured such that the user cannot
come in contact with conductors or any device under test (DUT) that is in contact with the
conductors. It is good practice to disconnect DUTs from the instrument before powering the
instrument. Safe installation requires proper shields, barriers, and grounding to prevent
contact with conductors.
Page 67
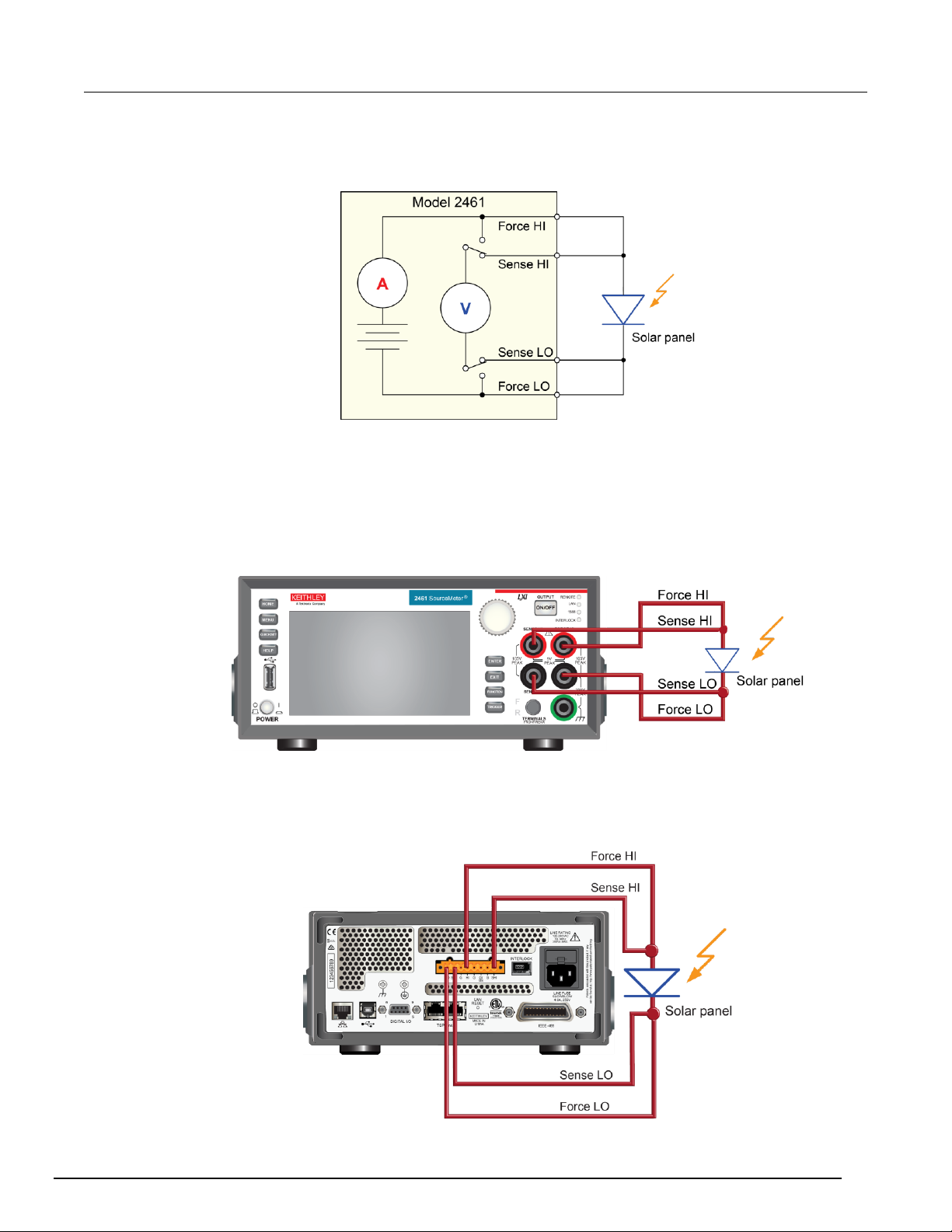
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 8: Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 8-3
The following figure shows the schematic for the application.
Figure 42: Model 2461 connections to a solar panel
The following figures show the physical connections for the front and rear panels. Note that you must
use either the front-panel terminals or rear-panel terminals — you cannot mix connections.
The figure below shows the front-panel connections. You can make these connections with four
insulated banana cables that are rated to the maximum current (10 A), such as two sets of the
Keithley Instruments Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set.
Figure 43: Model 2461 4-wire connections to the front panel
The figure below shows the rear-panel connections. You can make these connections with either the
Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (included with the Model 2461) or a Model 2460-BAN
Banana Test Leads/Adapter Cable with appropriate cabling.
Figure 44: Model 2461 4-wire connections to the rear panel
Page 68

Section 8: Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
8-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Solar panel characterization
This application demonstrates how to use the Model 2461 to characterize a solar panel. The
examples show how to use the front panel, SCPI code over a remote interface, and TSP code over a
remote interface.
For this test, you will:
Reset the instrument.
Select the source voltage function and measure current function.
Set the current limit.
Select four-wire (remote sense) mode.
Set up and generate a voltage sweep.
Initiate the trigger model, which will turn the output on.
Record the measurements.
After the voltage sweep is complete, turn off the output.
Retrieve the measurements.
View the data on the front-panel graph.
You must control the light source for this application; you will run the test with the light source on and
again with the light source off.
Set up the solar panel I-V sweep from the front panel
This is an example of an I-V test that sweeps voltage from 0 V to 20 V in 115 steps and measures the
resulting current. You can then view the data on the graph screen.
To set up the application from the front panel:
1. Make connections to the instrument and device under test (DUT) as described in Device
connections (on page 8-2).
2. Press the POWER switch on the front panel to turn on the instrument.
3. Reset the instrument:
a. Press the MENU key.
b. Under System, select Info/Manage.
c. Select System Reset.
d. Select OK.
4. Press the HOME key.
5. Press the FUNCTION key.
6. Under Source Voltage and Measure, select Current.
Page 69
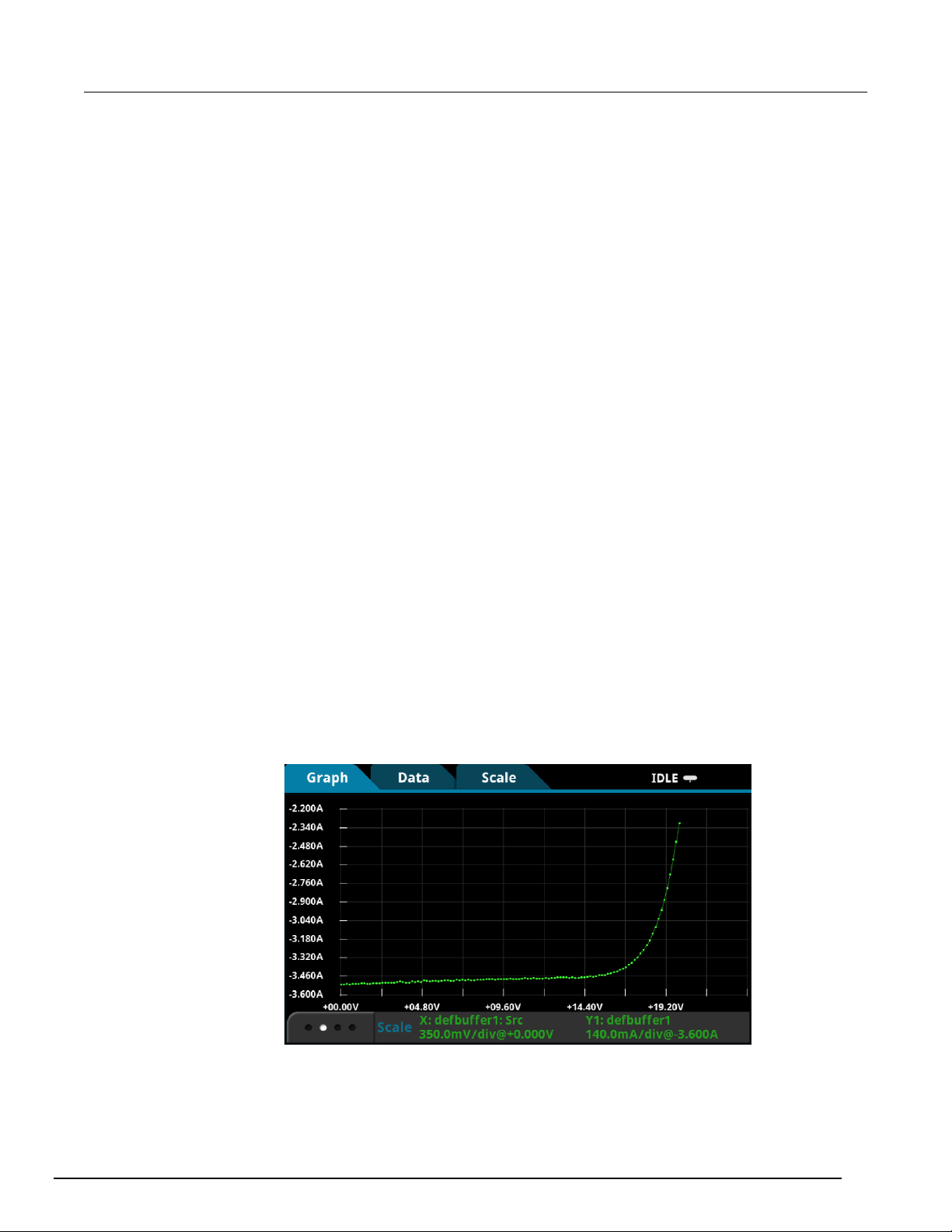
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 8: Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 8-5
7. Press the MENU key.
8. Under Measure, select Settings.
9. Select the button next to Sense and select 4-Wire Sense.
10. Press the MENU key.
11. Under Source, select Sweep.
12. Set the Start level to 0 V and select OK.
13. Set the Stop level to 20 V and select OK.
14. Select the button next to Definition and select Number of Points.
15. Select the button next to Points, enter 115, and select OK.
16. Swipe the SWEEP SETTINGS screen until you see Source Limit.
17. Select the button next to Source Limit, enter 4 A, and select OK.
18. Select the button next to Source Delay and select Specify Delay.
19. Enter 50 ms and select OK.
20. Select Generate. This sets up a trigger model for the sweep.
21. Press the MENU key.
22. Under Measure, select Reading Buffers.
23. Select defbuffer1.
24. Select Clear, select Yes, and select OK.
25. Press the MENU key.
26. Under Views, select Graph.
27. Press the TRIGGER key to initiate the trigger model. The output turns on and a RUN indicator is
visible at the top of the screen while the sweep is running.
28. Press the trigger key again to repeat the sweep.
The following figure shows an example of solar panel I-V measurements on the front-panel graph.
Note that the current is negative on the graph because the Model 2461 is sinking current.
Figure 45: Example of solar panel measurements on the Model 2461 front-panel graph
Page 70
Section 8: Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
8-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Set up the solar panel I-V sweep using SCPI commands
Command
Description
*RST
SENS:FUNC "CURR"
SENS:CURR:RANG:AUTO ON
SENS:CURR:RSEN ON
SOUR:FUNC VOLT
SOUR:VOLT:RANG 20
SOUR:VOLT:ILIM 4
SOUR:SWE:VOLT:LIN 0, 20, 115, 0.05
INIT
*WAI
TRAC:DATA? 1, 115, "defbuffer1", SOUR, READ
Reset the Model 2461.
Set to measure current.
Set to measure with autorange enabled.
Set to use 4-wire sense mode.
Set to source voltage.
Set to the 20 V source range.
Set the current limit to 4 A.
Set to sweep voltage from 0 to 20 V in 115 steps
with a 0.05 s delay.
Initiate the sweep.
Wait until the sweep is finished.
Read the source and measure values from
defbuffer1.
This example sequence of SCPI commands generates an I-V sweep on a solar panel. You may need
to make changes so that this code will run in your programming environment.
In this example, the voltage is swept from 0 V to 20 V in 115 steps. The resulting solar panel current
is measured. The current and voltage measurements are stored in default buffer 1 (defbuffer1).
Send the following commands for this example application:
Set up the solar panel I-V sweep using TSP commands
The following TSP code is designed to be run from Keithley Instruments Test Script Builder (TSB).
TSB is a software tool that is available from the Keithley Instruments website. You can install and
use TSB to write code and develop scripts for TSP-enabled instruments. Information about how to
use TSB is in the online help for TSB and in the “Introduction to TSP operation” section of the Model
2461 Reference Manual.
To use other programming environments, you may need to make changes to the example TSP code.
By default, the Model 2461 uses the SCPI command set. You must select the TSP command set
before sending TSP commands to the instrument.
To enable TSP commands:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. For Command Set, select TSP.
4. At the prompt to reboot, select Yes.
In this example, a linear voltage sweep is configured to output voltage from 0 V to 20 V in 115 steps.
The instrument measures the resulting current from the solar panel during the sweep.
Page 71

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 8: Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 8-7
Send the following commands for this example application:
--Define the number of points in the sweep.
num = 115
--Reset the instrument and clear the buffer.
reset()
--Set the source and measure functions.
smu.measure.func = smu.FUNC_DC_CURRENT
smu.source.func = smu.FUNC_DC_VOLTAGE
--Configure the measurement settings.
smu.terminals = smu.TERMINALS_FRONT
smu.measure.sense = smu.SENSE_4WIRE
smu.measure.autorange = smu.ON
smu.measure.nplc = 1
--Configure the source settings.
smu.source.highc = smu.OFF
smu.source.range = 20
smu.source.readback = smu.ON
smu.source.highc = smu.OFF
smu.source.ilimit.level = 4
smu.source.sweeplinear("SolarPanel", 0, 20, num, 0.05)
--Start the trigger model and wait for it to complete.
trigger.model.initiate()
waitcomplete()
--Define initial values.
voltage = defbuffer1.sourcevalues
current = defbuffer1
isc = current[1]
mincurr = current[1]
imax = current[1]
voc = voltage[1]
vmax = voltage[1]
pmax = voltage[1]*current[1]
--Calculate values.
for i = 1, num do
print(voltage[i],current[i],voltage[i]*current[i])
if (voltage[i]*current[i] < pmax) then
pmax = voltage[i]*current[i]
imax = current[i]
vmax = voltage[i]
end
if math.abs(current[i]) < math.abs(mincurr) then
voc = voltage[i]
end
end
pmax = math.abs(pmax)
imax = math.abs(imax)
print("Pmax=",pmax,",Imax=",imax,",Vmax=",vmax,",Isc=",isc,",Voc=",voc)
--Display values on the Model 2461 front panel.
display.changescreen(display.SCREEN_USER_SWIPE)
display.settext(display.TEXT1, string.format("Pmax = %.4fW", pmax))
display.settext(display.TEXT2, string.format("Isc = %.4fA, Voc = %.2fV", isc, voc))
Page 72
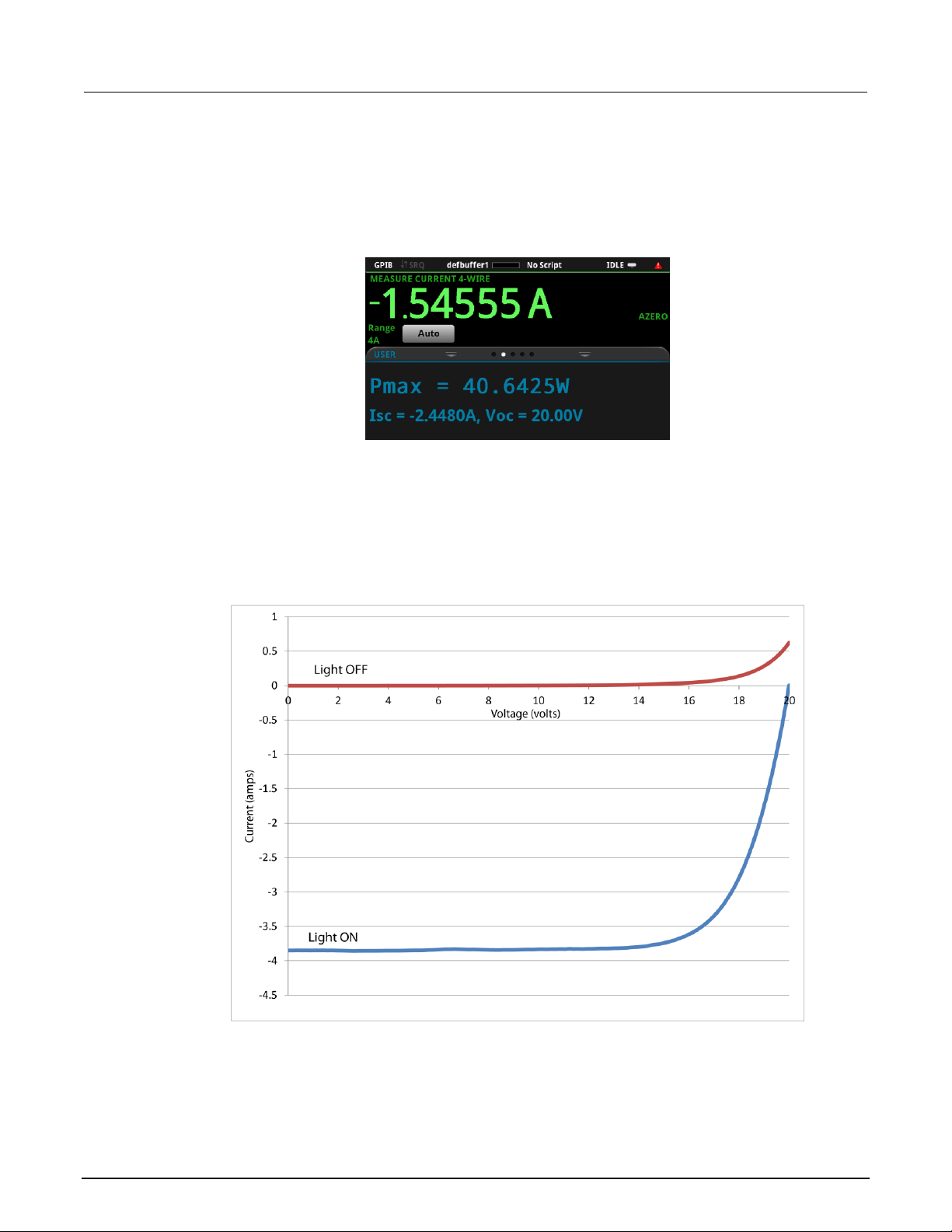
Section 8: Measuring I-V characteristics of a solar panel Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
8-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
In the example above, the instrument is programmed to display custom text on the USER swipe
screen using the display.changescreen and display.settext commands. After the test is
finished, the display will indicate the maximum power (P
), the short circuit current (ISC), and the
max
open circuit voltage (VOC), as shown in the figure below.
Figure 46: Solar panel I-V sweep results on the USER swipe screen
After the code is executed, five values are returned in the Instrument Console of Test Script Builder
(TSB), and the measured current, voltage, and calculated power are displayed on the front panel of
the Model 2461. You can copy the data from the TSB Instrument Console into a spreadsheet
application such as Microsoft® Excel® for graphing and further analysis. The figure below shows the
results of graphing the data in an Excel spreadsheet. Notice that the test on the solar panel was
executed with light (light ON) and in the dark (light OFF).
Figure 47: Solar panel I-V characteristics generated with and without light
Page 73

In this section:
Introduction .............................................................................. 9-1
Equipment required .................................................................. 9-1
Set up remote communications ................................................ 9-2
Device connections .................................................................. 9-2
High-speed, high-power pulses from a remote interface .......... 9-4
Section 9
Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs
Introduction
This example application demonstrates how to use the Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter
instrument to generate I-V curves of high-brightness LEDs (HBLEDs) using the extended range
pulsing capabilities of the instrument. Making pulsed I-V measurements may be necessary to avoid
self-heating effects, device damage, or to observe the response of the HBLED to a pulsed signal.
The trigger model is used to control the timing in pulse mode. The minimum pulse width setting
allowed by the instrument is 150 µs, but a high-voltage or high-current pulse may require a longer
pulse width to settle to the final value you want. The digitizing capability of the Model 2461 can be
used to verify timing accuracy of voltage and current pulses.
Equipment required
One Model 2461 1 kW Pulse Mode Interactive SourceMeter
®
Instrument
For front-panel connections, use four insulated banana cables, such as the Keithley Instruments
Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set included with the Model 2461; you will
need another set)
For rear-panel connections, use one Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (provided
with the Model 2461), or you can use one set of Model 2460-BAN Banana Test Leads/Adapter
Cables (with appropriate connections to the device)
One GPIB, USB, or ethernet cable to connect the Model 2461 to a computer
Page 74

Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
9-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Set up remote communications
This application is configured to run remotely. You can run this application from any of the supported
communication interfaces for the instrument (GPIB, USB, or ethernet).
The following figure shows the rear-panel connection locations for the remote communication
interfaces.
Figure 48: Model 2461 remote interface connections
Device connections
For best measurement accuracy and to eliminate the effects of test lead resistance when sourcing
high current, connect the Model 2461 to the device under test (DUT) using the 4-wire sense method.
To use the 4-wire sense connection method:
Connect the FORCE HI and SENSE HI leads to one end of the DUT.
Connect the FORCE LO and SENSE LO leads to the other end of the DUT.
Make the connections as close the DUT as possible to exclude the test-lead resistance from the
measurement.
Page 75

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 9-3
The following figure shows the schematic for outputting high-current pulses to a resistor.
Figure 49: Model 2461 4-wire connections to a resistor
The following figures show the physical connections for the front and rear panels. The front-panel
connections are safety banana jacks; the rear-panel connection is a screw terminal.
The figure below shows the front-panel connections. You can use four insulated banana cables that
are rated to a maximum current of at least 10 A, such as two sets of the Keithley Instruments Model
8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set is included with the Model 2461).
Figure 50: Model 2461 4-wire connections to the front panel
Page 76

Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
9-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
The figure below shows the rear-panel connections. You can make these connections with either the
Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (included with the Model 2461) or a Model 2460-BAN
Banana Test Leads/Adapter Cable with appropriate cabling.
Figure 51: Model 2461 4-wire connections to the rear panel
High-speed, high-power pulses from a remote interface
In this application, the Model 2461 is configured from a remote interface to generate a high-power
pulse sweep using Test Script Processor (TSP®) commands. A current reading is made during each
pulse.
To ensure precise timing control, you will specify pulse parameters, configure the voltage source and
current measurements and set up the trigger model to control the timing of the pulses and
measurements.
Page 77

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 9-5
Define the pulse sweep test parameters
Test parameter
Value
Definition
configListName
myPulseSweep
The name of the configuration list that contains the pulse
values created by the pulse command.
biaslevel
0 V
Sets the offset voltage of the pulse sweep.
start
0 V
Sets the starting value of the pulse sweep.
stop
4.15 V
Sets the ending value of the pulse sweep.
pulsewidth
0.8 ms
Sets the time at the amplitude level for each pulse.
measureEnable
smu.ON
Enables measurements at the top of each pulse. Turning this
feature off makes the instrument source pulses without
measuring.
bufferName
defbuffer1
Sets the buffer in which the measurement data will be stored.
delay
0 ms
Sets the delay before each pulse.
offTime
19 ms
Sets the time at the bias level.
count
1
Sets the number of times the sweep is repeated.
xBiasLimit
1 A
Sets the current limit between pulses when the bias level of
the voltage is sourced.
xPulseLimit
10 A
Sets the current limit during the pulse when the pulse level of
voltage is sourced.
failAbort
smu.OFF
Abort the pulse sweep if bias or pulse source limit is
exceeded.
Dual
smu.OFF
If enabled, sets the pulses to sweep back to the starting
value.
The following pulse parameters, which define the magnitude and timing of the pulse sweep, will be
entered into the pulse command to generate the configuration list and trigger model necessary for the
pulses. The actual values for these test parameters will vary depending on your specific application.
Page 78

Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
9-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
The following figure illustrates these test parameters.
Figure 52: Model 2461 Pulse Sweep Diagram
Set up the source and measure functions
To generate high-speed, high-current pulses and measure the voltage during each pulse, it is
important to configure the measure and source functions appropriately.
The pulse command will report an error if the set measure time is longer than the pulse width.
To minimize measure time:
Set the voltage measure range to a fixed range.
Set the integration rate of the measurement to 0.01 NPLC (166.67 µs at 60 Hz line frequency).
Run autozero once to perform a one-time autozero operation before the start of the trigger model.
For more precise source times:
Turn off the source readback feature. If you want to use source readback, you must allow enough
time for two measurements: The voltage measurement and the current source measurement.
Set the source delay time to zero.
The pulse command's trigger model
The built-in pulse settings screen and the remote pulse commands configure the trigger model of the
Model 2461 to generate the pulses. Executing the pulse command or generating a pulse setup from
the front panel will take a snapshot of the active source and measure settings of the Model 2461.
These settings are saved to configuration lists. The trigger model recalls the settings in the
configuration lists, triggers the pulse and measure using constant delays, and loops to create the
specified number of pulses. The trigger model must be generated again if source or measure settings
(such as NPLC and autozero) are changed and you want these settings to be applied to the pulse
trigger model.
Page 79

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 9-7
Front-panel operations to output a high-current pulse sweep
You can use the pulse settings screen to configure the Model 2461 for pulsing from the front panel of
the instrument. It is important to set the instrument’s measure range to a level that will fit the pulse
limit magnitude before entering the pulse settings screen. If the pulse limit is set higher than the
measure range, the instrument produces an error when you press the Generate button. In this
example, the instrument is set to measure current and source voltage. The source range is set to
auto and the measure range is set to 10 A.
To access the pulse settings screen:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under Source, select Pulse.
All of the pulse specific settings used in this example can be set on this menu screen, including the
type of pulse (Pulse Train, Linear Sweep with Steps, Linear Sweep with Points or Logarithmic
Sweep). This example uses the Linear Sweep Points option to generate the voltage sweep.
Enter the parameters from Define the pulse sweep test parameters (on page 9-5) into the option
fields. The pulse setup is not saved until you press the Generate button. The Generate button notifies
the instrument to save all of the source, measure, and pulse settings in configuration lists and the
trigger model.
To create and run the pulse configuration lists and trigger models:
1. Select Linear Sweep Points from the list of pulse types.
2. Enter all pulse parameters into the applicable boxes.
3. Press Generate at the top of the screen to save the configuration.
4. Press the Trigger button to generate the pulses.
SCPI commands to output a high-current pulse sweep
:SOURce:FUNC VOLTage
:SOURce:VOLTage:READ:BACK OFF
:SENSe:FUNC "CURRent"
:SENSe:CURRent:RSENse ON
:SENSe:CURRent:RANGe 10
:SENSe:CURRent:NPLC .01
:SENSe:CURRent:AZERo OFF
:SOURce:PULSe:SWEep:VOLTage:LINear 0, 0, 4.15, 100, .0008, 1, "defbuffer1", 0,
.019, 1, 1, 10, 0, 0
:INIT
*WAI
Page 80

Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
9-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
TSP commands to output a high-current pulse train
The following TSP code is designed to be run from Keithley Instruments Test Script Builder (TSB).
TSB is a software tool that is available from the Keithley Instruments website. You can install and
use TSB to write code and develop scripts for TSP-enabled instruments. Information about how to
use TSB is in the online help for TSB and in the “Introduction to TSP operation” section of the Model
2461 Reference Manual.
To use other programming environments, you may need to make changes to the example TSP code.
By default, the Model 2461 uses the SCPI command set. You must select the TSP command set
before sending TSP commands to the instrument.
To enable TSP commands:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. For Command Set, select TSP.
4. At the prompt to reboot, select Yes.
This following example code generates 100 pulses with a magnitude varying from 0 to 4.15 V and a
pulse width of 0.8 ms. The load is a green high-brightness LED. The current readings are stored in
the default buffer, defbuffer1.
Send the following commands for this application:
Reset the instrument()
--Set up the pulse parameters (user-specified).
configListName = "myPulseSweep"
bias_level = 0
start = 0
stop = 4.15
-- Specify 100 points in the sweep.
points = 100
pulse_width = 0.8e-3
MeasureEnable = smu.ON
bufferName = defbuffer1
delay = 0
offTime = 19e-3
-- Do the sweep one time.
count = 1
xBiasLimit = 1
xPulseLimit = 10
failAbort = smu.OFF
-- The sweep goes from start to stop, but not back down again.
dual = 0
--Set the source to output voltage.
smu.source.func = smu.FUNC_DC_VOLTAGE
smu.source.readback = smu.OFF
--Set up the measure functions.
smu.measure.func = smu.FUNC_DC_CURRENT
smu.measure.sense = smu.SENSE_4WIRE
Page 81
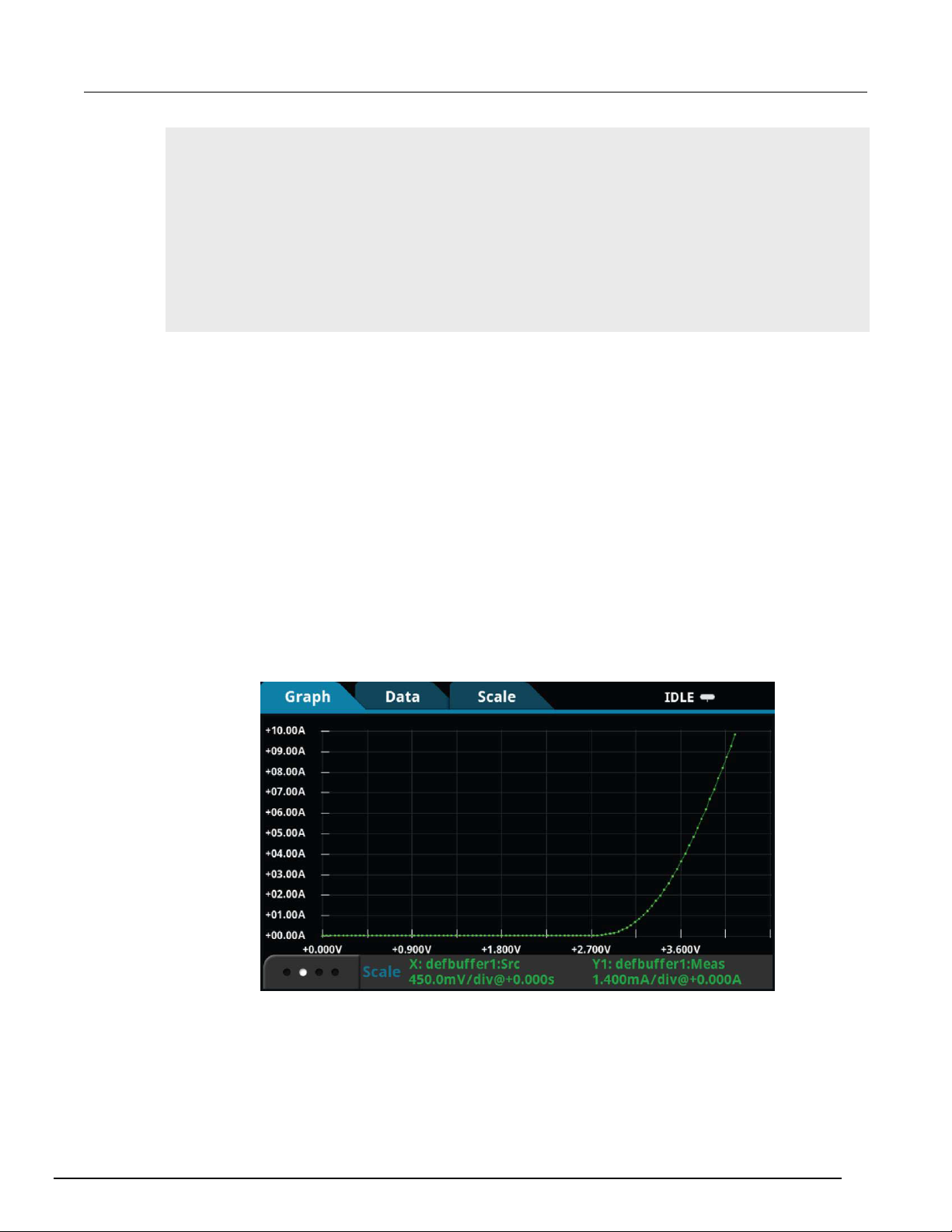
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 9-9
smu.measure.range = 10
smu.measure.nplc = .01
smu.measure.autozero.enable = smu.OFF
--Send the pulse sweep command to set up the trigger model and configuration lists.
smu.source.pulsesweeplinear(configListName, bias_level, start, stop, points,
pulse_width, MeasureEnable, bufferName, delay, offTime, count, xBiasLimit,
xPulseLimit, failAbort, dual)
--Initiate trigger model and wait until finished.
trigger.model.initate()
waitcomplete()
Viewing the results on the front panel
The I-V characteristics of the diode can be seen on the front panel of the instrument using the
graphing function.
To view the graph:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under View, select Graph.
The default settings for the graph show time on the x-axis and the measure results on the y-axis.
However, it is possible to plot current and voltage against each other to generate an I-V plot.
To enable I-V graphing:
1. In the graph screen, select the Data tab located at the top of the screen.
2. Under the Graph Type option, select Scatter/IV.
3. Select the Graph tab located at the top of the screen to return to the graph.
Figure 53: Front panel view of the I-V curve
Page 82
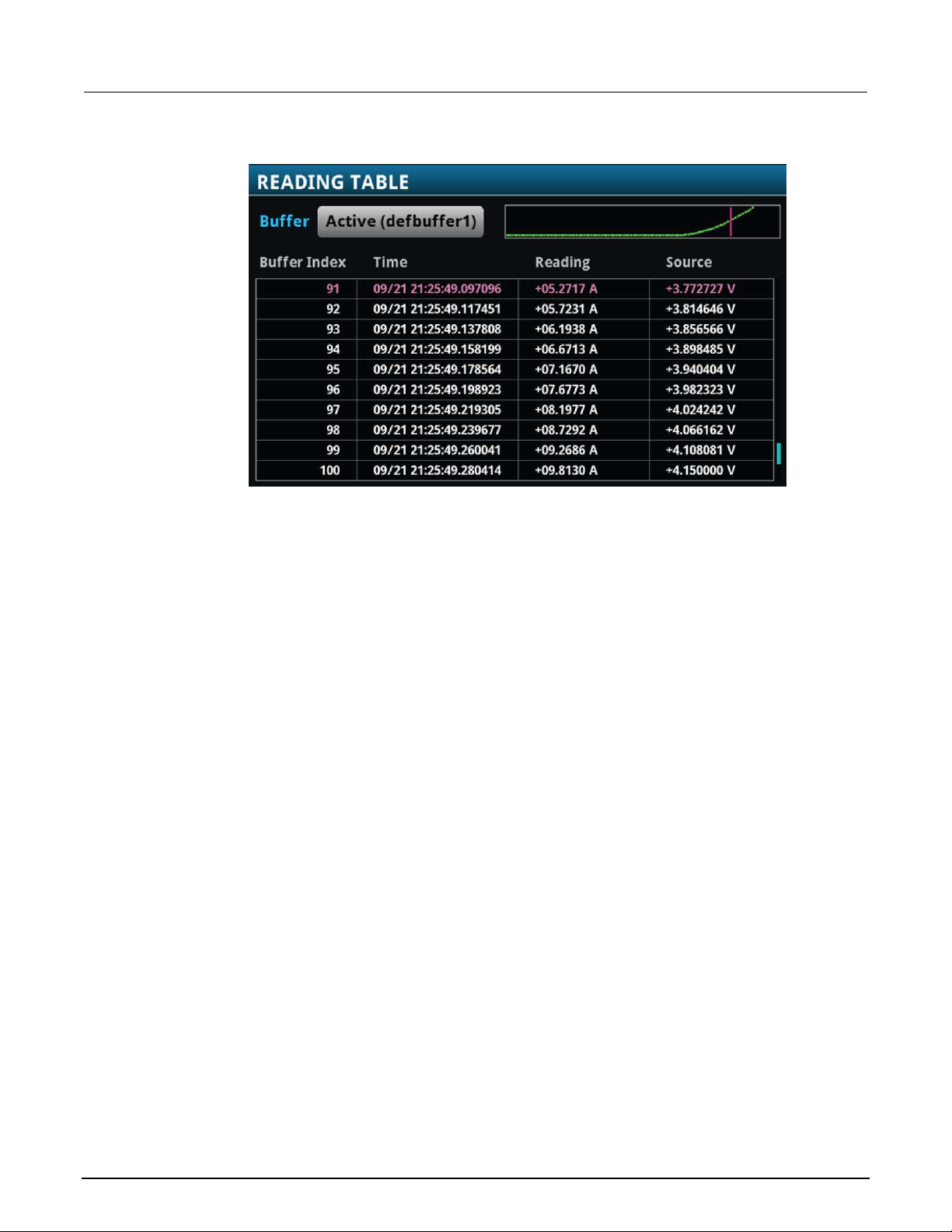
Section 9: Pulse Testing High-Brightness LEDs Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
9-10 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Figure 54: Reading table showing measurement results
Page 83

In this section:
Introduction ............................................................................ 10-1
Equipment required ................................................................ 10-1
Set up remote communications .............................................. 10-2
Device connections ................................................................ 10-2
High-speed, high-power pulses from a remote interface ........ 10-4
Section 10
Capturing high-power pulse waveforms
Introduction
In addition to a traditional integrating ADC, the Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter also features a
fast-sampling ADC. The fast digitizing ADC of the Model 2461 allows the instrument to take
measurements at high speed, with capabilities similar to an oscilloscope. This allows you to capture
data at up to one million samples per second and store up to 5 million readings with timestamps. This
feature allows simultaneous current and voltage measurements without any additional hardware, and
offers 18-bit resolution, providing for high accuracy, even at high speed. The fast ADC of the Model
2461 allows this instrument to be used in a broad range of applications, such as negative bias
temperature instability (NBTI) testing and transient thermal analysis.
This example application demonstrates how to use the Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter
instrument to generate extended operating range, high-power voltage pulses (up to 10 A at 100 V),
and capture both the current and voltage waveforms of high-power pulses. This technique is useful
for testing and troubleshooting the transient response of high-power devices.
Equipment required
One Model 2461 1 kW Pulse Mode Interactive SourceMeter
®
Instrument
For front-panel connections, use four insulated banana cables, such as the Keithley Instruments
Model 8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set included with the Model 2461; you will
need another set)
For rear-panel connections, use one Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (provided
with the Model 2461), or you can use one set of Model 2460-BAN Banana Test Leads/Adapter
Cables (with appropriate connections to the device)
One GPIB, USB, or ethernet cable to connect the Model 2461 to a computer
Page 84

Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
10-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Set up remote communications
This application is configured to run remotely. You can run this application from any of the supported
communication interfaces for the instrument (GPIB, USB, or ethernet).
The following figure shows the rear-panel connection locations for the remote communication
interfaces.
Figure 55: Model 2461 remote interface connections
Device connections
For best measurement accuracy and to eliminate the effects of test lead resistance when sourcing
high current, connect the Model 2461 to the device under test (DUT) using the 4-wire sense method.
To use the 4-wire sense connection method:
Connect the FORCE HI and SENSE HI leads to one end of the DUT.
Connect the FORCE LO and SENSE LO leads to the other end of the DUT.
Make the connections as close the DUT as possible to exclude the test-lead resistance from the
measurement.
Page 85
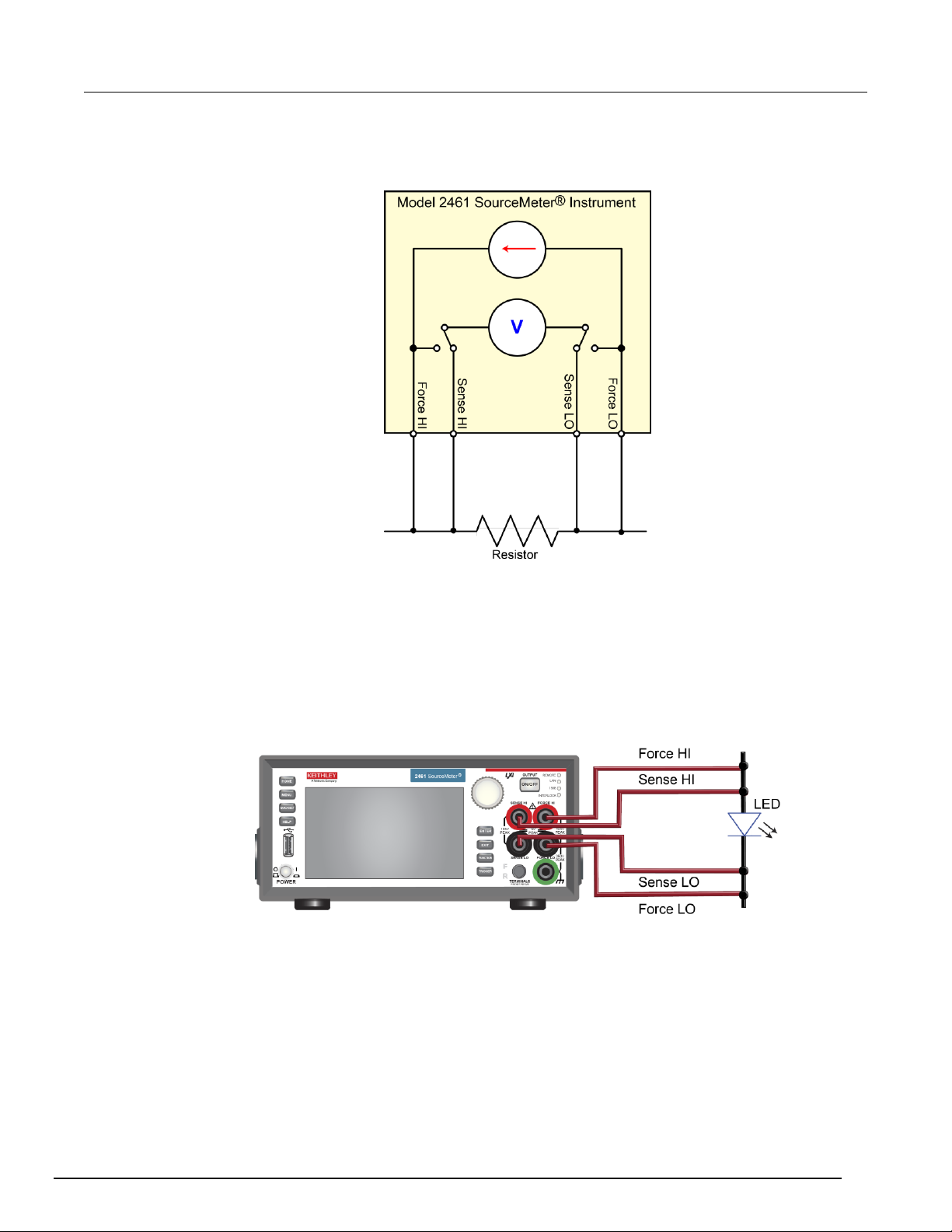
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 10-3
The following figure shows the schematic for outputting high-current pulses to a resistor.
Figure 56: Model 2461 4-wire connections to a resistor
The following figures show the physical connections for the front and rear panels. The front-panel
connections are safety banana jacks; the rear-panel connection is a screw terminal.
The figure below shows the front-panel connections. You can use four insulated banana cables that
are rated to a maximum current of at least 10 A, such as two sets of the Keithley Instruments Model
8608 High-Performance Clip Lead Set (one set is included with the Model 2461).
Figure 57: Model 2461 4-wire connections to the front panel
Page 86
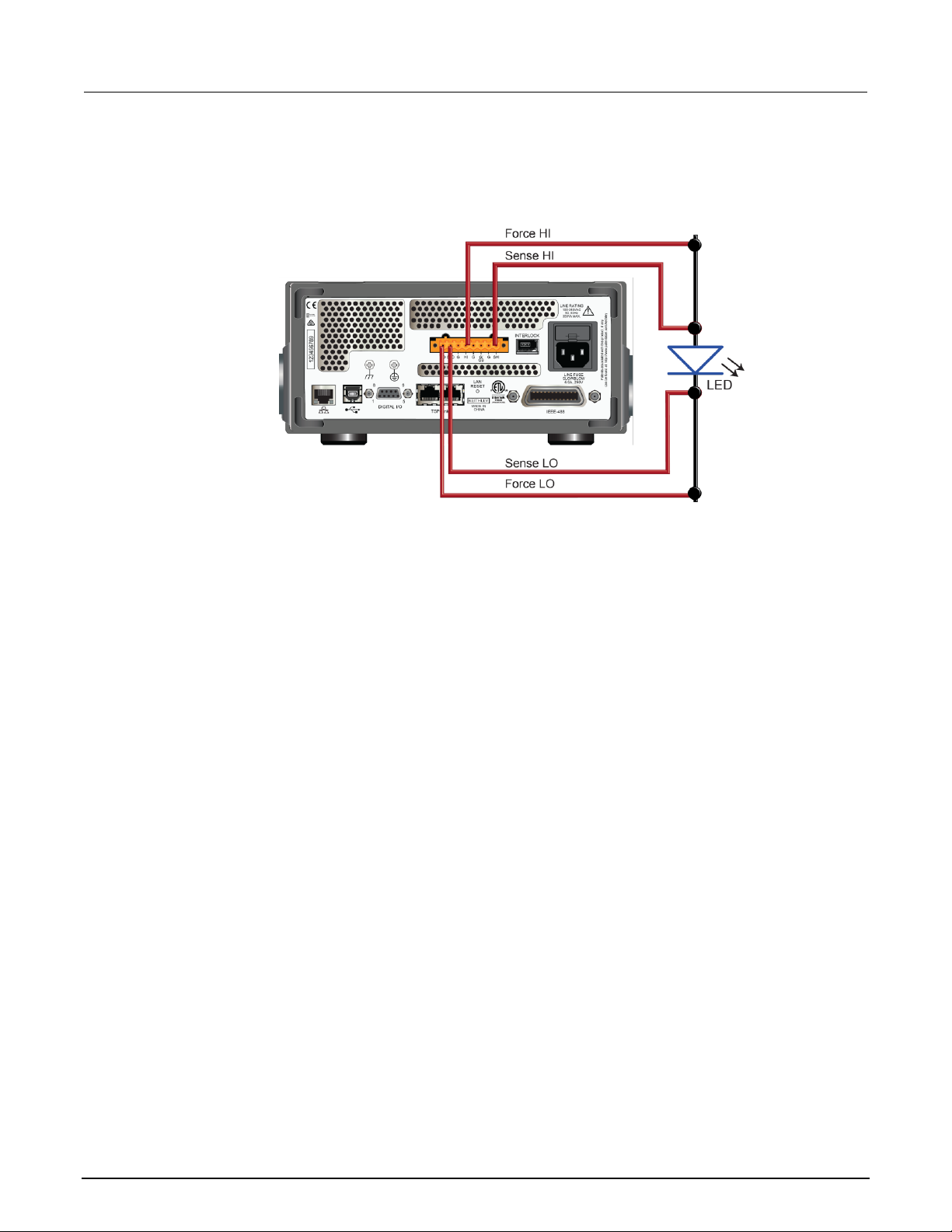
Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
10-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
The figure below shows the rear-panel connections. You can make these connections with either the
Model 2460-KIT Screw-Terminal Connector Kit (included with the Model 2461) or a Model 2460-BAN
Banana Test Leads/Adapter Cable with appropriate cabling.
Figure 58: Model 2461 4-wire connections to the rear panel
High-speed, high-power pulses from a remote interface
In this application, the Model 2461 is configured from a remote interface to generate a high-power
pulse sweep using Test Script Processor (TSP®) commands. A current reading is made during each
pulse.
To ensure precise timing control, you will specify pulse parameters, configure the voltage source and
current measurements and set up the trigger model to control the timing of the pulses and
measurements.
Page 87
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 10-5
Define the pulse train test parameters
Test parameter
Value
Definition
configListName
myPulses
Sets the name of the configuration list containing the pulse
values created by the pulse command.
bias_level
0 A
Sets the offset current of the pulse train.
pulse_level
10 A
Sets the amplitude current of each pulse from zero (not
from the bias level).
pulse_width
1 ms
Sets the time at the amplitude level for each pulse.
measureEnable
smu.ON
Enables digitizer measurements.
bufferName
defbuffer1
Sets the buffer in which the measurement data will be
stored.
delay
10 ms
Sets delay before each pulse.
offTime
19 ms
Sets the time at the bias level.
count
1
Sets the number of pulses in a train.
xBiasLimit
2 V
Sets the voltage limit between pulses when the bias level
of the current is sourced.
xPulseLimit
21 V
Sets the voltage limit during the pulse when the pulse level
of current is sourced.
failAbort
smu.OFF
Abort the pulse train if bias or pulse source limit is
exceeded.
The following pulse parameters, which define the magnitude and timing of the pulse train, will be
entered into the pulse command to generate the configuration list and trigger model necessary for the
pulses. The actual values for these test parameters will vary depending on your specific application.
Page 88
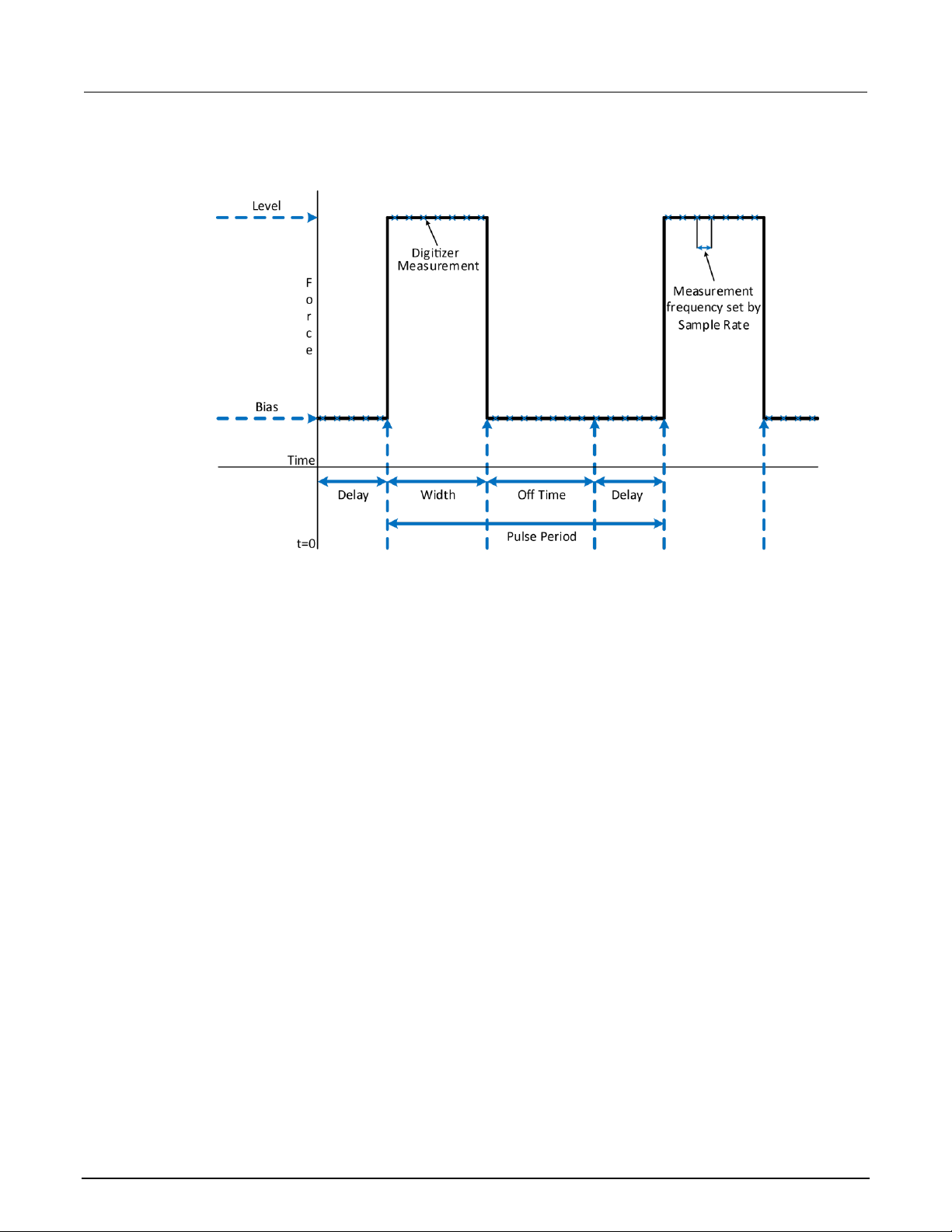
Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
10-6 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
The following figure illustrates these test parameters.
Figure 59: Timing diagram for the example
The trigger model of the pulse command
The built-in pulse settings screen and the remote pulse commands configure the trigger model of the
Model 2461 to generate the pulses. Executing the pulse command or generating a pulse setup from
the front panel takes a snapshot of the active source and digitize settings of the Model 2461. These
settings are saved to configuration lists. When you initiate the trigger model, the instrument recalls the
settings in the configuration lists, triggers the pulse and digitize actions using constant delays, and
loops to create the number of specified pulses.
The trigger model must be generated again if source or digitize settings (such as Sample Rate and
Source Readback) are changed and you want these settings to be applied to the pulse trigger model.
Page 89

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 10-7
Front panel operations to output high-current pulses
You can use the Pulse Settings screen to configure the Model 2461 for pulsing from the front panel of
the instrument. It is important to set the digitize range to a level that will fit the pulse limit magnitude
before you make changes to the Pulse Settings screen. In this example, the instrument is configured
to source current and measure voltage. The source range is set to auto and the measure range is set
to 20 V.
To access the pulse settings screen:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under Source, select Pulse.
You can set all of the pulse specific settings used in this example on this menu screen, including the
type of pulse (Pulse Train, Linear Sweep with Steps, Linear Sweep with Points, or Logarithmic
Sweep). This example uses the Pulse Train option to generate the pulse.
Enter all of the parameters from Define the pulse train test parameters into the option fields. The
pulse setup is not saved until the Generate button is pressed. The Generate button notifies the
instrument to save all of the source, digitize, and pulse settings in configuration lists and the trigger
model.
To create and run the pulse configuration lists and trigger models:
1. Select Pulse Train from the list of pulse types.
2. Enter all pulse parameters into the applicable boxes.
3. Press Generate at the top of the screen to save the configuration.
4. Press the Trigger button to execute the pulses.
SCPI commands to output high-current pulses
:SOURce:FUNC CURRent
:SOURce:CURRent:READ:BACK ON
:DIGitize:FUNC "VOLTage"
:DIGitize:VOLTage:RSENse ON
:DIGitize:VOLTage:RANGe 20
:DIGitize:VOLTage:SRATe 500000
:TRACe:POINTS 1000000, defbuffer1
:ROUTe:TERMinals FRONT
:SOURce:PULSe:TRain:CURRent 0, 10, .001, 1, 1, "defbuffer1", .001, .099, 2, 21, 0
:Init
*WAI
Page 90

Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
10-8 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
TSP commands to output a high-power pulse waveforms
The following TSP code is designed to be run from Keithley Instruments Test Script Builder (TSB).
TSB is a software tool that is available from the Keithley Instruments website. You can install and
use TSB to write code and develop scripts for TSP-enabled instruments. Information about how to
use TSB is in the online help for TSB and in the “Introduction to TSP operation” section of the Model
2461 Reference Manual.
To use other programming environments, you may need to make changes to the example TSP code.
By default, the Model 2461 uses the SCPI command set. You must select the TSP command set
before sending TSP commands to the instrument.
To enable TSP commands:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. For Command Set, select TSP.
4. At the prompt to reboot, select Yes.
The following example code generates 1 pulse with a magnitude of 10 A and a pulse width of 1 ms.
The load creates the data shown below was a 2 ohm, 50 W resistor. The voltage and current
waveforms capture at 500 kS/s each and the readings are stored in the default buffer defbuffer1.
---Reset the instrument
reset()
--Set up the pulse parameters (user-specified).
configListName = "myPulses"
bias_level = 0
pulse_level = 10
pulse_width = 1e-3
count = 1
MeasureEnable = smu.ON
bufferName = defbuffer1
delay = 1e-3
offTime = 99e-3
xBiasLimit = 2
xPulseLimit = 21
failAbort = smu.OFF
--Set the source to output current.
smu.source.func = smu.FUNC_DC_CURRENT
smu.source.readback = smu.ON
--Set up the measure functions.
smu.digitize.func = smu.FUNC_DIGITIZE_VOLTAGE
smu.digitize.sense = smu.SENSE_4WIRE
smu.digitize.range = 20
smu.digitize.samplerate = 500000
defbuffer1.capacity = 1000000
--Send the pulse train command to set up the trigger model and config lists.
smu.source.pulsetrain(configListName, bias_level, pulse_level, pulse_width, count,
MeasureEnable, bufferName, delay, offTime, xBiasLimit, xPulseLimit, failAbort)
---Initiate trigger model and wait until finished.
trigger.model.initiate()
waitcomplete()
Page 91
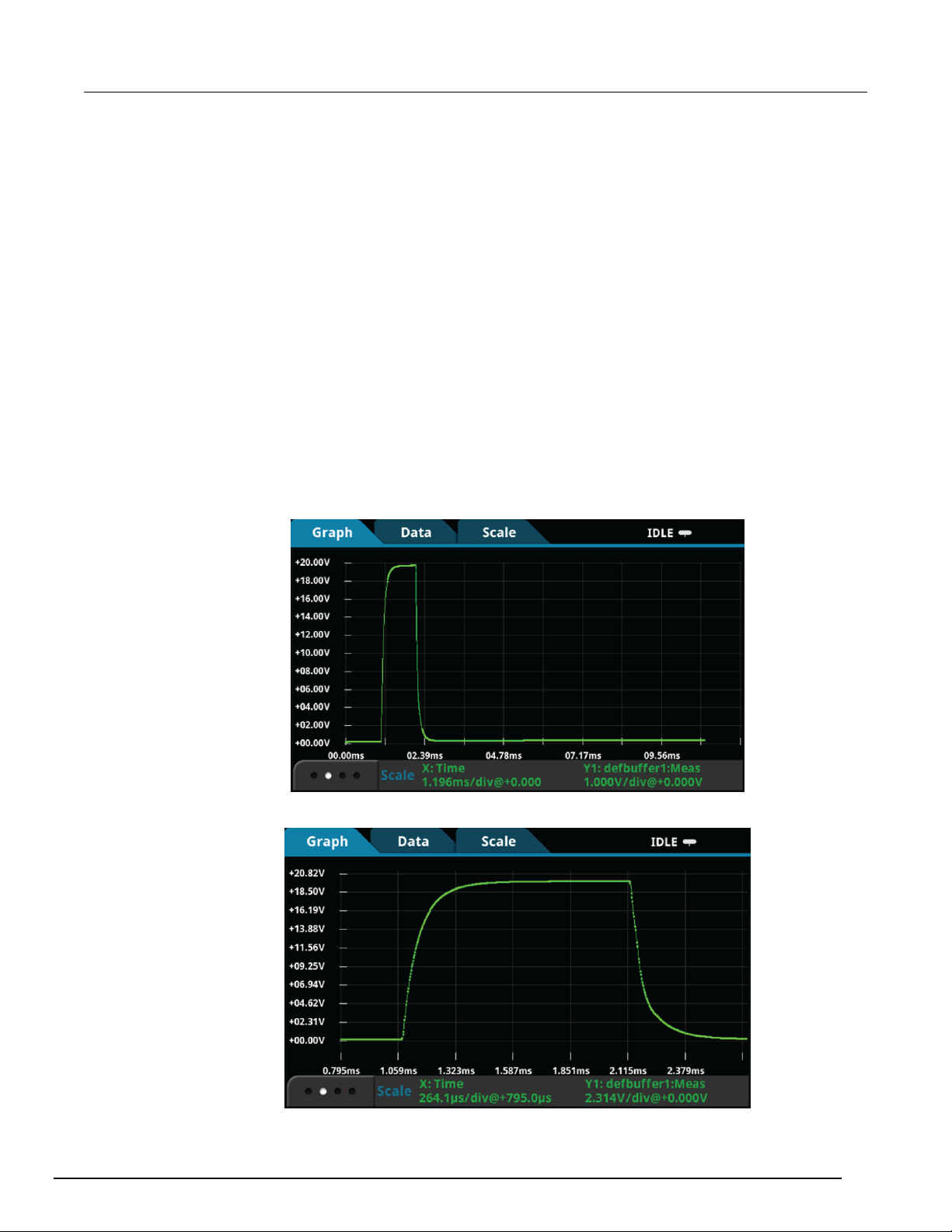
Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 10-9
Viewing the measure waveform on the front panel
You can view the I-V characteristics of the diode on the front panel of the instrument using the built-in
graphing functions.
To view the graph:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under View, select Graph.
The displayed graph with vary depending on the type of Scaling selected. The best way to get an
overview of all of the data is to set the X-axis scaling method to All.
To change the graph scaling to All:
1. In the graph screen, select the Scale tab at the top of the screen.
2. Under the X-axis Method option, select All.
3. Select the Graph tab at the top of the screen to return to the graph.
Once the scaling is set to All, the graph shown below appears. You can then pinch and zoom on the
relevant portions of the waveform. The following graph shows a zoomed version of the waveform.
Figure 60: Front-panel view of voltage digitize waveform
Figure 61: Front-panel view of voltage digitize waveform zoomed in
Page 92

Section 10: Capturing high-power pulse waveforms Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
10-10 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
Viewing the source and digitize waveforms simultaneously on the front panel
In this example, you enable source readback to capture the current source waveform and the voltage
digitize waveform. You can plot the two waveforms together on the same graph to examine time
dependencies between the two waveforms. This technique is very powerful and enables you to get a
detailed look at the pulse response of your DUT.
To plot the source waveform stored in defbuffer1:
1. In the graph screen, select the Data tab at the top of the screen.
2. Select Add Trace on the right side of the screen.
3. Select defbuffer1 from the list of reading buffers.
4. Select Source in the list of Buffer Elements.
5. Select the Graph tab at the top of the screen to return to the graph.
See the Model 2461 Reference Manual for more information on graphing operations. Both the source
trace and the digitize trace are displayed on the graph. Pinching and zooming on the touch screen
manipulates the Y-axis of the active trace and the X-axis of both traces. To switch between active
traces, press the trace button on the lower left of the screen.
Figure 62: Front-panel view of voltage digitize and current source waveforms
Page 93

In this section:
About this section ................................................................... 11-1
Where can I find updated drivers? .......................................... 11-1
How do I upgrade the firmware? ............................................ 11-2
Why can't the Model 2461 read my USB flash drive? ............. 11-2
How do I change the command set? ...................................... 11-2
Why am I getting a 5074 event code? .................................... 11-3
How do I save the present state of the instrument? ............... 11-4
Why did my settings change? ................................................. 11-4
What are the Quick Setup options? ........................................ 11-5
About this section
Section 11
Troubleshooting FAQs
This section is helps you find answers to the most common questions encountered with the Model
2461. For additional FAQs, please see the "Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)" section of the Model
2461 Reference Manual.
Where can I find updated drivers?
For the latest drivers and additional support information, see the Keithley Instruments support
website.
To see what drivers are available for your instrument:
1.
2. Enter the model number of your instrument.
3. Select Software Driver from the list.
If you use the native LabVIEWTM or IVI driver, you must configure the Model 2461 to use the SCPI
command set. For information on changing the command set, refer to How do I change the
command set? (on page 11-2)
Page 94

Section 11: Troubleshooting FAQs Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
11-2 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
How do I upgrade the firmware?
Do not turn off power or remove the USB flash drive until the upgrade process is complete.
You can upgrade or downgrade the firmware from the front panel or from the virtual front panel.
Refer to "Using the Model 2461 virtual front panel" in the Model 2461 Reference Manual for
information.
From the front panel or virtual front panel:
1. Copy the firmware file (.upg file) to a USB flash drive.
2. Verify that the firmware file is in the root subdirectory of the flash drive and that it is the only
firmware file in that location.
3. Disconnect any input and output terminals that are attached to the instrument.
4. Turn on instrument power.
5. Insert the flash drive into the USB port on the front panel of the instrument.
6. From the instrument front panel, press the MENU key.
7. Under System, select Info/Manage.
8. To upgrade to a newer version of firmware, select Upgrade to New.
9. To return to a previous version of firmware, select Downgrade to Older.
10. If the instrument is controlled remotely, a message is displayed. Select Yes to continue.
11. When the upgrade is complete, reboot the instrument.
Why can't the Model 2461 read my USB flash drive?
Verify that the flash drive is formatted with the FAT file system. The Model 2461 only supports FAT
drives.
In Microsoft® Windows®, you can check the file system by checking the properties of the USB flash
drive.
How do I change the command set?
You can change the command set that you use with the Model 2461. The remote command sets that
are available include:
SCPI: An instrument-specific language built on the SCPI standard.
TSP: A scripting programming language that contains instrument-specific control commands that
can be executed from a stand-alone instrument. You can use TSP to send individual commands
or use it to combine commands into scripts.
Page 95

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 11: Troubleshooting FAQs
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 11-3
You cannot combine the command sets.
As delivered from Keithley Instruments, the Model 2461 is set to work with the Model 2461 SCPI
command set.
To set the command set from the front panel:
1. Press the MENU key.
2. Under System, select Settings.
3. Select the button next to Command Set.
4. Select the command set.
5. You are prompted to reboot.
To verify which command set is selected from a remote interface:
Send the command:
*LANG?
To change to the SCPI command set from a remote interface:
Send the command:
*LANG SCPI
Reboot the instrument.
To change to the TSP command set from a remote interface:
Send the command:
*LANG TSP
Reboot the instrument.
Why am I getting a 5074 event code?
The instrument provides an interlock circuit on the rear panel. You must enable this circuit in order for
the instrument to set source voltages greater than ±42 V DC. If you try to assign a high-voltage output
and turn the source on when the interlock is not asserted, you see event code 5074, "Output voltage
limited by interlock."
The Model 2461 is provided with an interlock circuit that must be positively activated in
order for the high voltage output to be enabled. The interlock helps facilitate safe operation
of the equipment in a test system. Bypassing the interlock could expose the operator to
hazardous voltages that could result in personal injury or death.
If the safety interlock is not asserted and the source is turned on, the following actions occur:
The nominal output is limited to less than ±42 V.
The front-panel INTERLOCK indicator is not illuminated.
To recover from this error, properly engage the interlock using a safe test fixture before turning on the
Model 2461 output.
Page 96

Section 11: Troubleshooting FAQs Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual
11-4 2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015
How do I save the present state of the instrument?
You can save the settings in the instrument as a script using the front-panel menus or from a remote
interface. After they are saved, you can recall the script or copy it to a USB flash drive.
From the front panel:
1. Configure the Model 2461 to the settings that you want to save.
2. Press the MENU key.
3. Under Scripts, select Create Setup. The CREATE SETUP window is displayed.
4. Select Create. A keyboard is displayed.
5. Use the keyboard to enter the name of the script.
6. Select the OK button on the displayed keyboard. The script is added to internal memory.
Using SCPI commands:
Configure the instrument to the settings that you want to save. To save the setup, send the
command:
*SAV <n>
Where <n> is an integer from 0 to 4.
In the front-panel script menus, the setups saved with the *SAV command have the name Setup0x,
where x is the value you set for <n>.
Using TSP commands:
Configure the instrument to the settings that you want to save. To save the setup, send the
command:
createconfigscript("setupName")
Where setupName is the name of the setup script that will be created.
Why did my settings change?
Many of the commands in the Model 2461 are saved with the source or measure function that was
active when you set them. For example, assume you have the measure function set to current and
you set a value for display digits. When you change the measure function to voltage, the display digits
value changes to the value that was last set for the voltage measure function. When you return to the
current measure function, the display digits value returns to the value you set previously.
Page 97

Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter® Instrument User's Manual Section 11: Troubleshooting FAQs
2461-900-01 Rev. A / November 2015 11-5
What are the Quick Setup options?
The QUICKSET key opens a screen that provides access to function selection, performance
adjustments, and quick setups.
The Function button on the Quickset menu allows you to select a source or measure function. The
options are the same as those available when you use the front-panel FUNCTION key.
The Performance slider allows you to adjust speed and resolution. As you increase speed, you lower
the amount of resolution. As you increase resolution, you decrease the reading speed. These settings
take effect the next time a measurement is made.
The Performance slider allows you to adjust speed and resolution. As you increase speed, you lower
the amount of resolution. As you increase resolution, you decrease the reading speed. These settings
take effect the next time the output is turned on and measurements are made.
The Quick Setups allow you to set the instrument to operate as a Voltmeter, Ammeter, Ohmmeter, or
Power Supply.
When you select a Quick Setup, the instrument turns the output on. Carefully consider and configure
the appropriate output-off state, source, and limits before connecting the Model 2461 to a device that
can deliver energy, such as other voltage sources, batteries, capacitors, or solar cells. Configure the
settings that are recommended for the instrument before making connections to the device. Failure
to consider the output-off state, source, and limits may result in damage to the instrument or to the
device under test (DUT).
Page 98

In this section:
Additional Model 2461 information ......................................... 12-1
Additional Model 2461 information
Section 12
Next steps
This manual has prepared you to start using your new Model 2461 Interactive SourceMeter®
Instrument for your application. For more detailed information, refer to the Keithley Instruments Model
2461 Reference Manual.
For related documentation, software tools, and drivers, see the Product Information CD-ROM.
The Knowledge Center, which contains the following handbooks:
The Low Level Measurements Handbook: Precision DC Current, Voltage, and Resistance
Measurements
Switching Handbook: A Guide to Signal Switching in Automated Test Systems
Application notes
Updated drivers
Information about related products
Your local Field Applications Engineer can help you with product selection, configuration, and usage.
Check the website for contact information.
Page 99

All Keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of Keithley Instruments.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
All other trademarks and trade names are the property of their respective companies.
A Greater Measure of Confidence
8/14
 Loading...
Loading...