Page 1
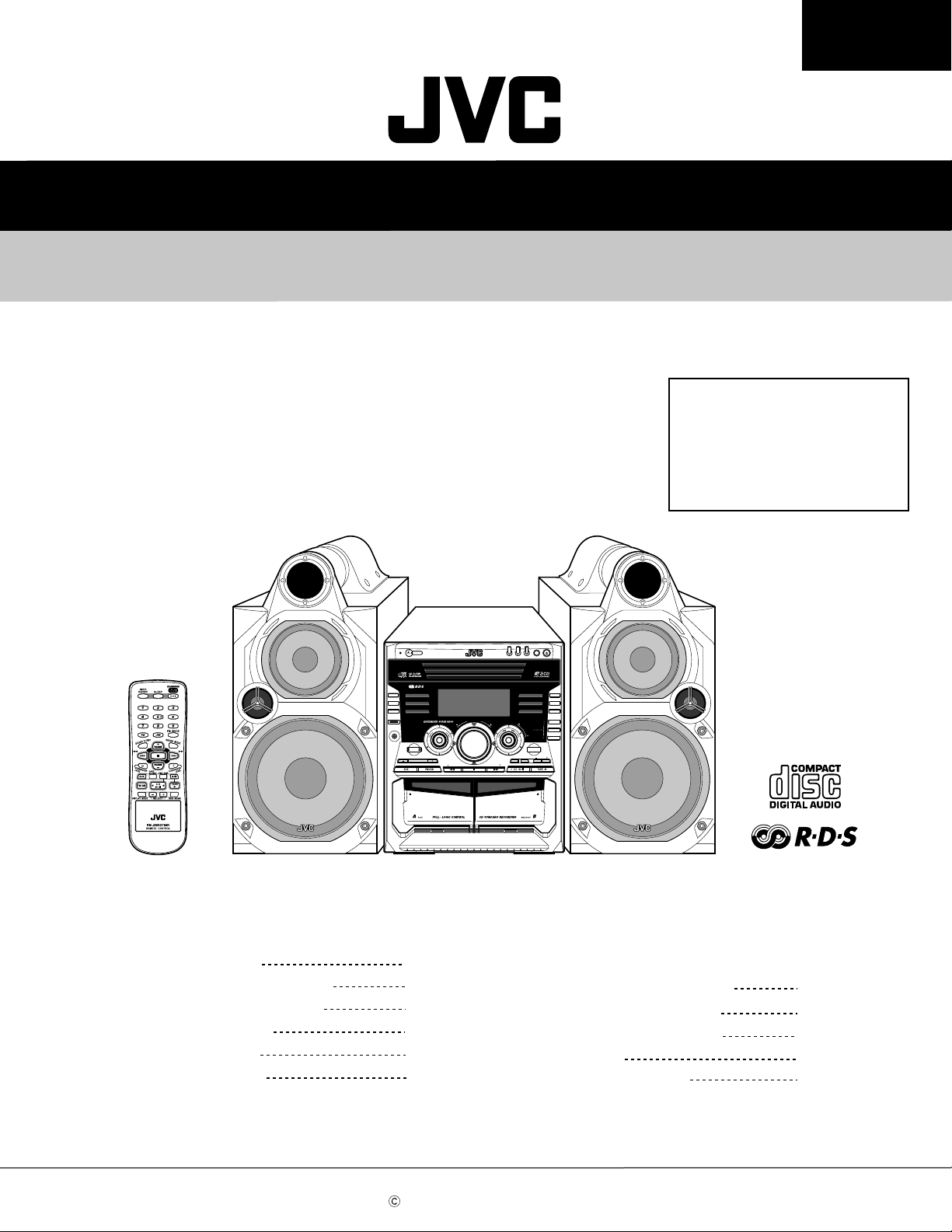
SERVICE MANUAL
COMPACT COMPONENT SYSTEM
MX-GT88
MX-GT88
B ------------------------ U.K.
E ---- Continental Europe
EN ----- Northern Europe
EV ------- Eastern Europe
CD
3
2
CD
CD
1
Area suffix
STANDBY
ECO
COMPACT COMPONENT SYSTEM MX-GT88
REC START
K
OC
R
/ STOP
CD REC
POP
START
DUBBING
CLASSIC
DISPLAY
MP3
PHONES
SOUND
TURBO
SUBWOOFER LEVEL
U
L
M
O
E
V
M
D
O
N
U
D
E
O
S
TUNING
BEEP
DISC CHANGE
REPEAT
DANCE
PROGRAM
HA
LL
RANDOM
STADIUM
CLOCK
/ TIMER
SET
PRESET
CANCEL
/ DEMO
TAPE A / B
SELECT
DISPLAY MODE
RDS MODE
TUNING
EJECTEJECT
SP-MXGT88 SP-MXGT88CA-MXGT88
Contents
Safety Precautions
Important for laser produbts
Preventing static electricity
Disassembly method
Wiring connection
Adjustment method
COPYRIGHT 2003 VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LTD.
1-2
1-4
1-5
1-6
1-19
1-20
Flow of functional operation
until TOC read
Maintenance of laser pickup
Replacement of laser pickup
Trouble shooting
Description of major ICs
1-24
1-25
1-25
1-26
1-30~44
No.22075
Jul. 2003
Page 2
MX-GT88
1. This design of this product contains special hardware and many circuits and components specially for safety
purposes. For continued protection, no changes should be made to the original design unless authorized in
writing by the manufacturer. Replacement parts must be identical to those used in the original circuits. Services
should be performed by qualified personnel only.
2. Alterations of the design or circuitr y of the product should not be made. Any design alterations of the product
should not be made. Any design alterations or additions will void the manufacturer`s warranty and will further
relieve the manufacture of responsibility for personal injury or property damage resulting therefrom.
3. Many electrical and mechanical parts in the products have special safety-related characteristics. These
characteristics are often not evident from visual inspection nor can the protection afforded by them necessarily
be obtained by using replacement components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Replacement par ts which
have these special safety characteristics are identified in the Parts List of Service Manual. Electrical
components having such features are identified by shading on the schematics and by ( ) on the Parts List in
the Service Manual. The use of a substitute replacement which does not have the same safety characteristics
as the recommended replacement parts shown in the Parts List of Service Manual may create shock, fire, or
other hazards.
4. The leads in the products are routed and dressed with ties, clamps, tubings, barriers and the like to be
separated from live parts, high temperature parts, moving parts and/or sharp edges for the prevention of
electric shock and fire hazard. When service is required, the original lead routing and dress should be
observed, and it should be confirmed that they have been returned to normal, after re-assembling.
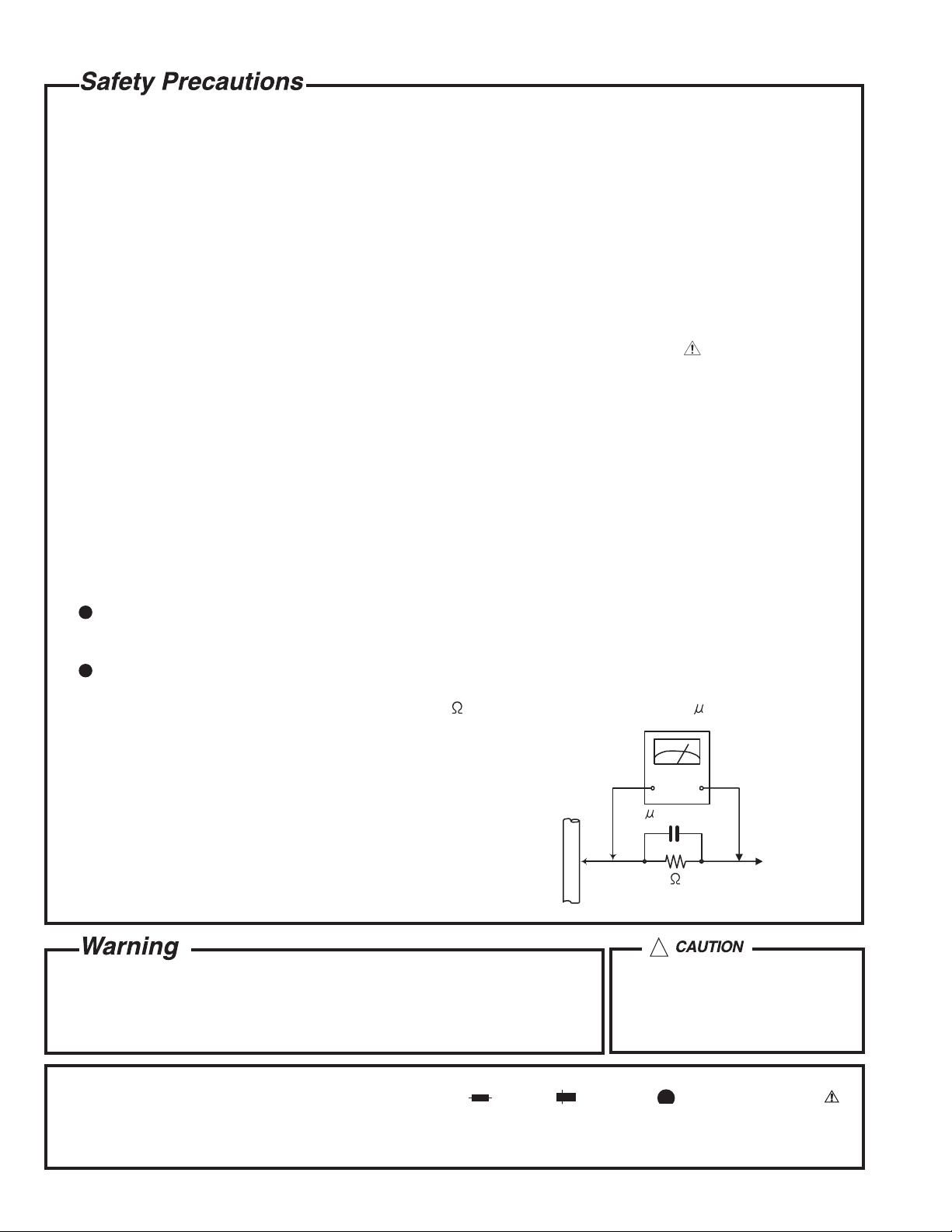
5. Leakage currnet check (Electrical shock hazard testing)
After re-assembling the product, always perform an isolation check on the exposed metal parts of the product
(antenna terminals, knobs, metal cabinet, screw heads, headphone jack, control shafts, etc.) to be sure the
product is safe to operate without danger of electrical shock.
Do not use a line isolation transformer during this check.
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Using a "Leakage Current Tester", measure the leakage
current from each exposed metal parts of the cabinet, particularly any exposed metal part having a return
path to the chassis, to a known good earth ground. Any leakage current must not exceed 0.5mA AC (r.m.s.).
Alternate check method
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Use an AC voltmeter having, 1,000 ohms per volt or more
sensitivity in the following manner. Connect a 1,500 10W resistor paralleled by a 0.15 F AC-type capacitor
between an exposed metal part and a known good earth ground.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor with the AC
voltmeter.
Move the resistor connection to each exposed metal part,
particularly any exposed metal part having a return path to
the chassis, and meausre the AC voltage across the resistor.
Now, reverse the plug in the AC outlet and repeat each
measurement. Voltage measured any must not exceed 0.75 V
AC (r.m.s.). This corresponds to 0.5 mA AC (r.m.s.).
0.15 F AC TYPE
1500 10W
Good earth ground
AC VOLTMETER
(Having 1000
ohms/volts,
or more sensitivity)
Place this
probe on
each exposed
metal part.
!
1. This equipment has been designed and manufactured to meet international safety standards.
2. It is the legal responsibility of the repairer to ensure that these safety standards are maintained.
3. Repairs m ust be made in accordance with the relevant safety standards.
4. It is essential that safety critical components are replaced by approved parts.
5. If mains voltage selector is provided, check setting for local voltage.
Burrs formed during molding may
be left over on some parts of the
chassis. Therefore, pay attention to
such burrs in the case of
preforming repair of this system.
In regard with component parts appearing on the silk-screen pr inted side (parts side) of the PWB diagrams, the
parts that are printed over with black such as the resistor ( ), diode ( ) and ICP ( ) or identified by the " "
mark nearby are critical for safety.
(This regulation does not correspond to J and C version.)
1-2
Page 3
MX-GT88
(U.K only)
1. This design of this product contains special hardware and many circuits and components specially
for safety purposes. For continued protection, no changes should be made to the original
design unless authorized in writing by the manufacturer. Replacement parts must be identical to
those used in the original circuits.
2. Any unauthorised design alterations or additions will void the manufacturer's guarantee ; further more the
manufacturer cannot accept responsibility f or personal injury or property damage resulting therefrom.
3. Essential safety critical components are identified by ( ) on the Parts List and by shading on the
schematics, and must never be replaced by parts other than those listed in the manual. Please note
however that many electrical and mechanical parts in the product have special safety related
characteristics. These characteristics are often not evident from visual inspection. Parts other than
specified by the manufacturer may not have the same safety characteristics as the recommended
replacement parts shown in the Parts List of the Service Manual and may create shock, fire, or
other hazards.
4. The leads in the products are routed and dressed with ties, clamps, tubings, barriers and the
like to be separated from live parts, high temperature parts, moving parts and/or sharp edges
for the prevention of electric shock and fire hazard. When service is required, the or iginal lead
routing and dress should be observed, and it should be confirmed that they have been returned
to normal, after re-assembling.
1. Service should be performed by qualified personnel only.
2. This equipment has been designed and manufactured to meet international safety standards.
3. It is the legal responsibility of the repairer to ensure that these safety standards are maintained.
4. Repairs must be made in accordance with the relevant safety standards.
5. It is essential that safety critical components are replaced by approved parts.
6. If mains voltage selector is provided, check setting for local voltage.
!
Burrs formed during molding may be left over on some parts of the chassis. Therefore,
pay attention to such burrs in the case of preforming repair of this system.
1-3
Page 4
MX-GT88
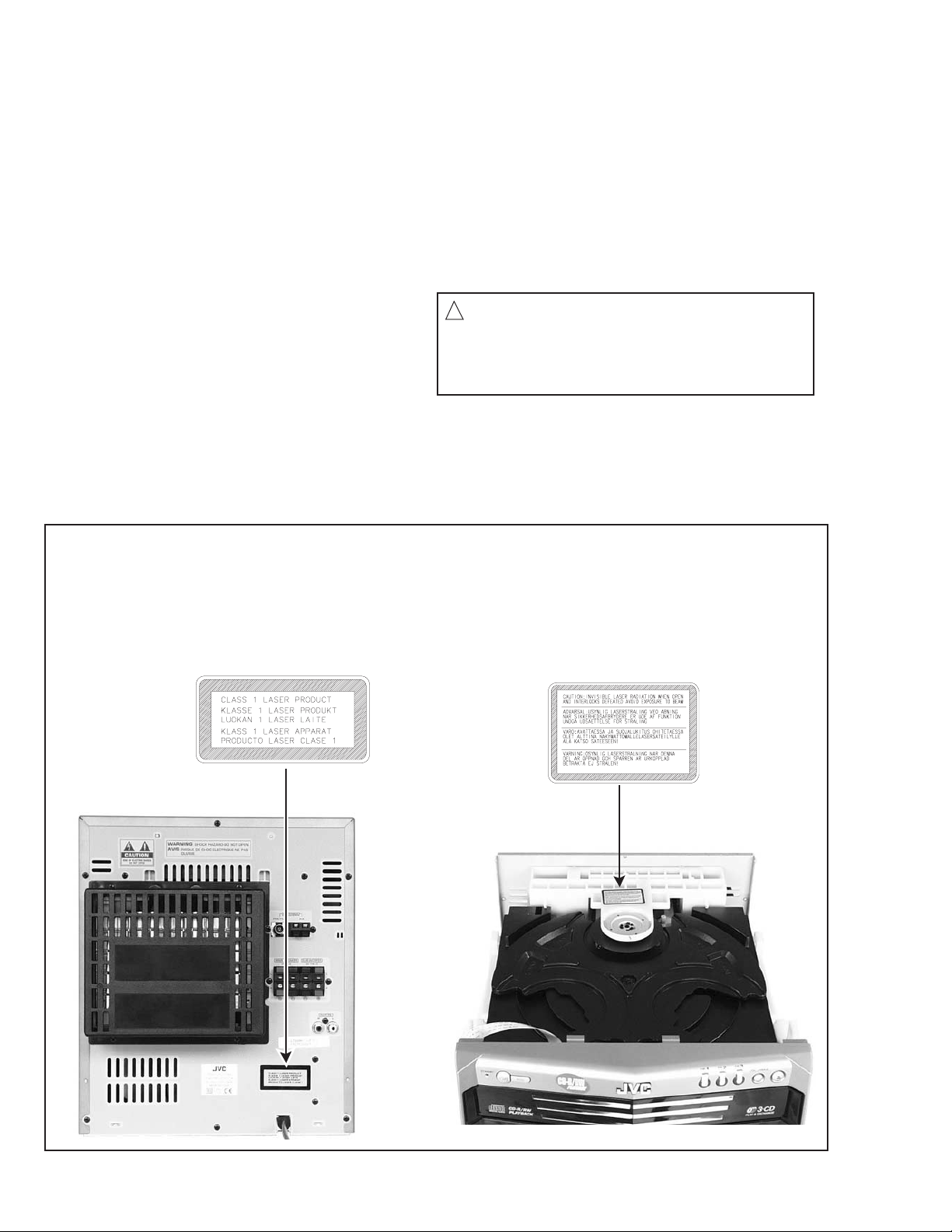
Important for laser products
1.CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
2.DANGER : Invisible laser radiation when open and inter
lock failed or defeated. Avoid direct exposure to beam.
3.CAUTION : There are no serviceable parts inside the
Laser Unit. Do not disassemble the Laser Unit. Replace
the complete Laser Unit if it malfunctions.
4.CAUTION : The compact disc player uses invisible
laserradiation and is equipped with safety switches
whichprevent emission of radiation when the drawer is
open and the safety interlocks have failed or are de
feated. It is dangerous to defeat the safety switches.
5.CAUTION : If safety switches malfunction, the laser is able
to function.
6.CAUTION : Use of controls, adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result in
hazardous radiation exposure.
CAUTION
!
REPRODUCTION AND POSITION OF LABELS
Please use enough caution not to
see the beam directly or touch it
in case of an adjustment or operation
check.
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
WARNING LABEL
1-4
Page 5
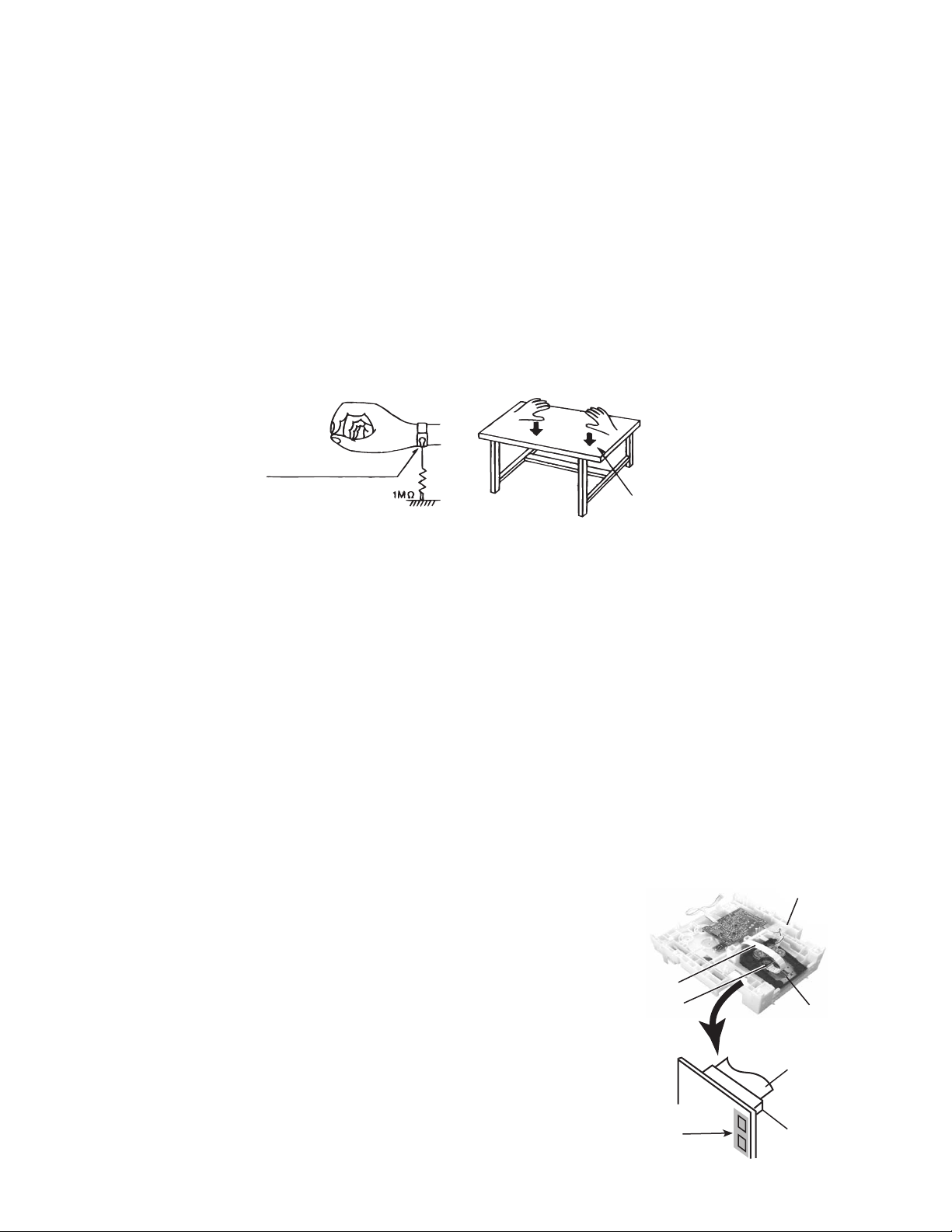
Preventing static electricity
MX-GT88
1. Grounding to prevent damage by static electricity
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), which occurs when static electricity stored in the body, fabric, etc. is discharged,
can destroy the laser diode in the traverse unit (optical pickup). Take care to prevent this when performing repairs.
2. About the earth processing for the destruction prevention by static electricity
In the equipment which uses optical pick-up (laser diode), optical pick-up is destroyed by the static electricity of
the work environment.
Be careful to use proper grounding in the area where repairs are being performed.
2-1 Ground the workbench
Ground the workbench by laying conductive material (such as a conductive sheet) or an iron plate over
it before placing the traverse unit (optical pickup) on it.
2-2 Ground yourself
Use an anti-static wrist strap to release any static electricity built up in your body.
(caption)
Anti-static wrist strap
Conductive material
(conductive sheet) or iron plate
3. Handling the optical pickup
1. In order to maintain quality during transport and before installation, both sides of the laser diode on the
replacement optical pickup are shorted. After replacement, return the shorted parts to their original condition.
(Refer to the text.)
2. Do not use a tester to check the condition of the laser diode in the optical pickup. The tester's internal power
source can easily destroy the laser diode.
4. Handling the traverse unit (optical pickup)
1. Do not subject the traverse unit (optical pickup) to strong shocks, as it is a sensitive, complex unit.
2. Cut off the shorted part of the flexible cable using nippers, etc. after replacing the optical pickup. For specific
details, refer to the replacement procedure in the text. Remove the anti-static pin when replacing the traverse
unit. Be careful not to take too long a time when attaching it to the connector.
3. Handle the flexible cable carefully as it may break when subjected to strong force.
4. It is not possible to adjust the semi-fixed resistor that adjusts the laser power. Do not turn it
Attention when CD mechanism assembly is decomposed
*Please refer to "Disassembly method" in the text for pick-up and how to
detach the CD mechanism assembly.
1. Remove the CD changer unit.
2. Remove the CD changer mechanism.
3. Solder is put up before the card wire is removed from the pickup unit
connector on the CD mechanism assembly.
(When the card wire is removed without putting up solder, the CD pick-up
assembly might destroy.)
4. Please remove solder after connecting the card wire with the pickup unit
connector when you install picking up in the substrate.
Card wire
Picup unit
connector
Soldering
Fig.2
CD changer unit
Fig.1
Card wire
Picup unit
connector
CD changer
mechanism
1-5
Page 6
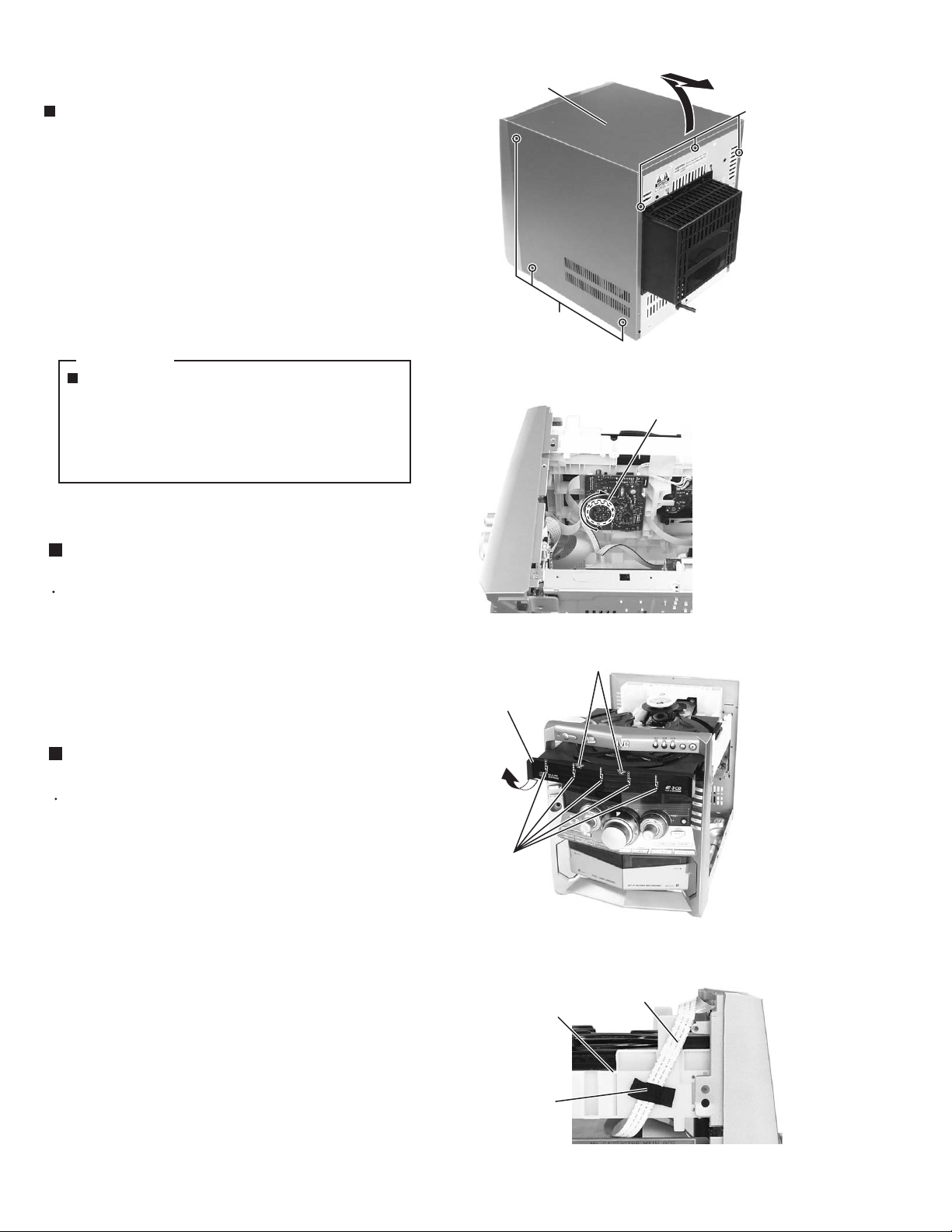
MX-GT88
Disassembly method
Removing the metal cover (See Fig.1)
1.
Remove the three screws A attaching the metal
cover on the back of the body.
2.
Remove the six screws B attaching the metal cover
on both sides of the body.
3.
Remove the metal cover from the body by lifting the
rear part of the cover.
ONE POINT
How to eject the CD tray manually
(see fig.2)
Turn the loading pulley gear at the bottom of
the CD changer unit as shown in Fig.2 and
draw the CD tray toward the front.
Metal cover
A
B
(both sides)
Fig.1
Loading pulley gear
(See <CD changer unit>fig.1)
Removing the CD tray fitting
(See Fig. 3)
Prior to performing the following procedure, eject the
CD tray.
After drawing the lower part of the tray fitting toward
1.
the front, remove the five claws. Then, while moving
the tray fitting upward, remove it.
Removing the CD changer unit
(See Fig.4 to 7)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover and CD tray fitting.
1.
Remove the card wire attached to CD changer unit
on the adhesion tape.
2.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector CW105
on the CD board.
3.
Disconnect the harness from the connector CW104
on the main board.
4.
Remove the two screws C attaching the CD changer
unit to the rear panel.
Fig.2
Joint
CD tray fitting
Claw
Fig.3
Card wire
CD changer unit
5.
Remove the two screws D attaching the CD changer
unit to both sides of the front panel assembly.
6.
Draw the CD changer unit upward from behind while
pulling the rear panel outward.
1-6
Adhesion tape
Fig.4
Page 7
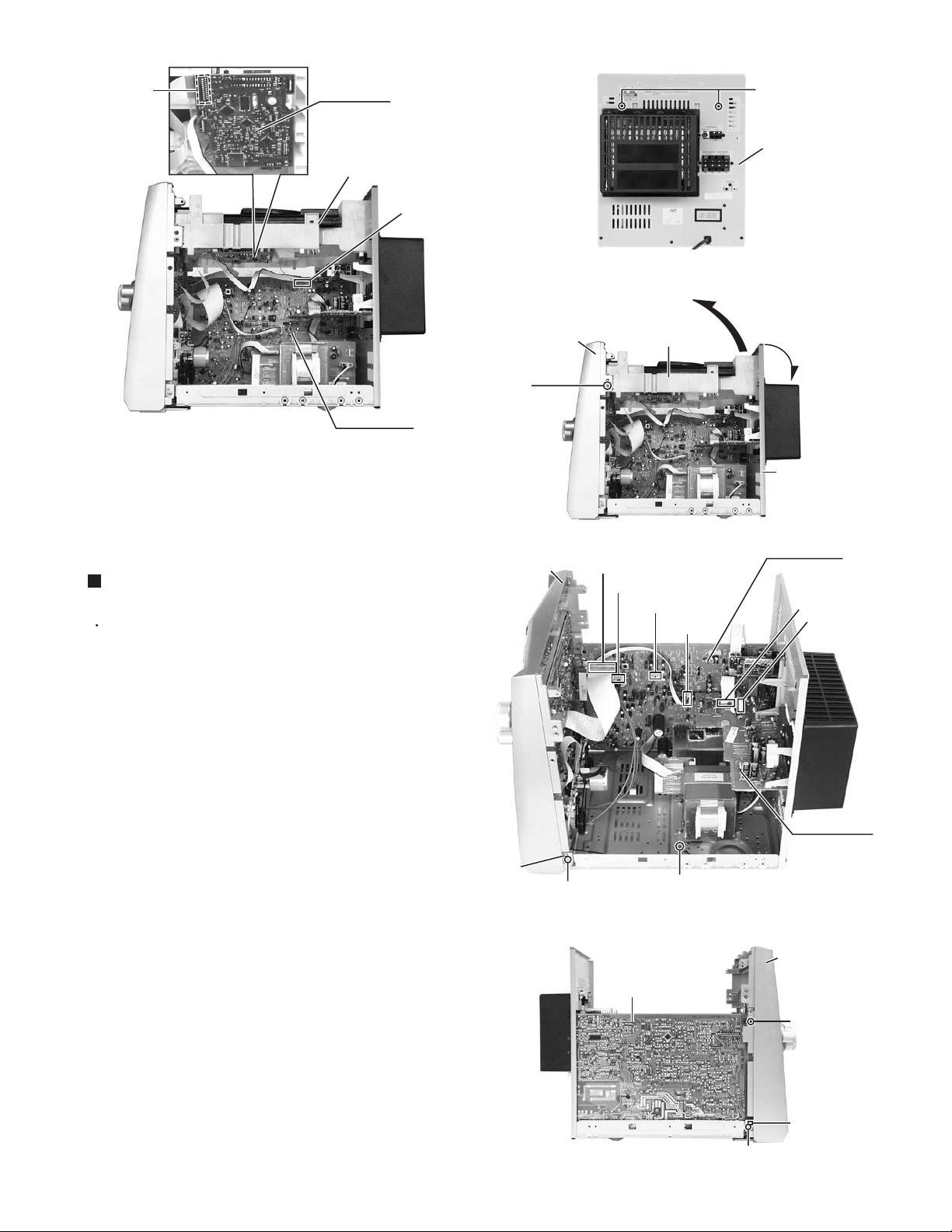
MX-GT88
CW105
CD board
CD changer unit
CW104
Main board
Fig.5
Removing the front panel assembly
(See Fig.8 to 10)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover and CD changer unit.
Front panel
assembly
D
(both sides)
Front panel
assembly
Fig.6
CD changer unit
Fig.7
CW101
CW109
CW110
C
Rear panel
Rear panel
Main board
ACW1
ACW2
CW108
1.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector CW101
on the main board.
2.
Disconnect the harness from the connector CW108,
CW109 and CW110 on the main board.
3.
Remove the screw E fixiing the lug wire.
4.
Remove the two screws F attaching the front panel
assembly to both sides of the body.
5.
Remove the screw G attaching the main board to the
front panel assembly.
6.
Remove the screw H attaching the front panel
assembly to bottom of the body.
7.
Release the two joints1 and two joints2, and detach
the front panel assembly toward the front.
Joint1
(both sides)
(both sides)
F
Fig.8
Main board
Fig.9
E
(fixing the lug wire)
F
(both sides)
Amp. board
Front panel
assembly
G
Joint1
(both sides)
1-7
Page 8
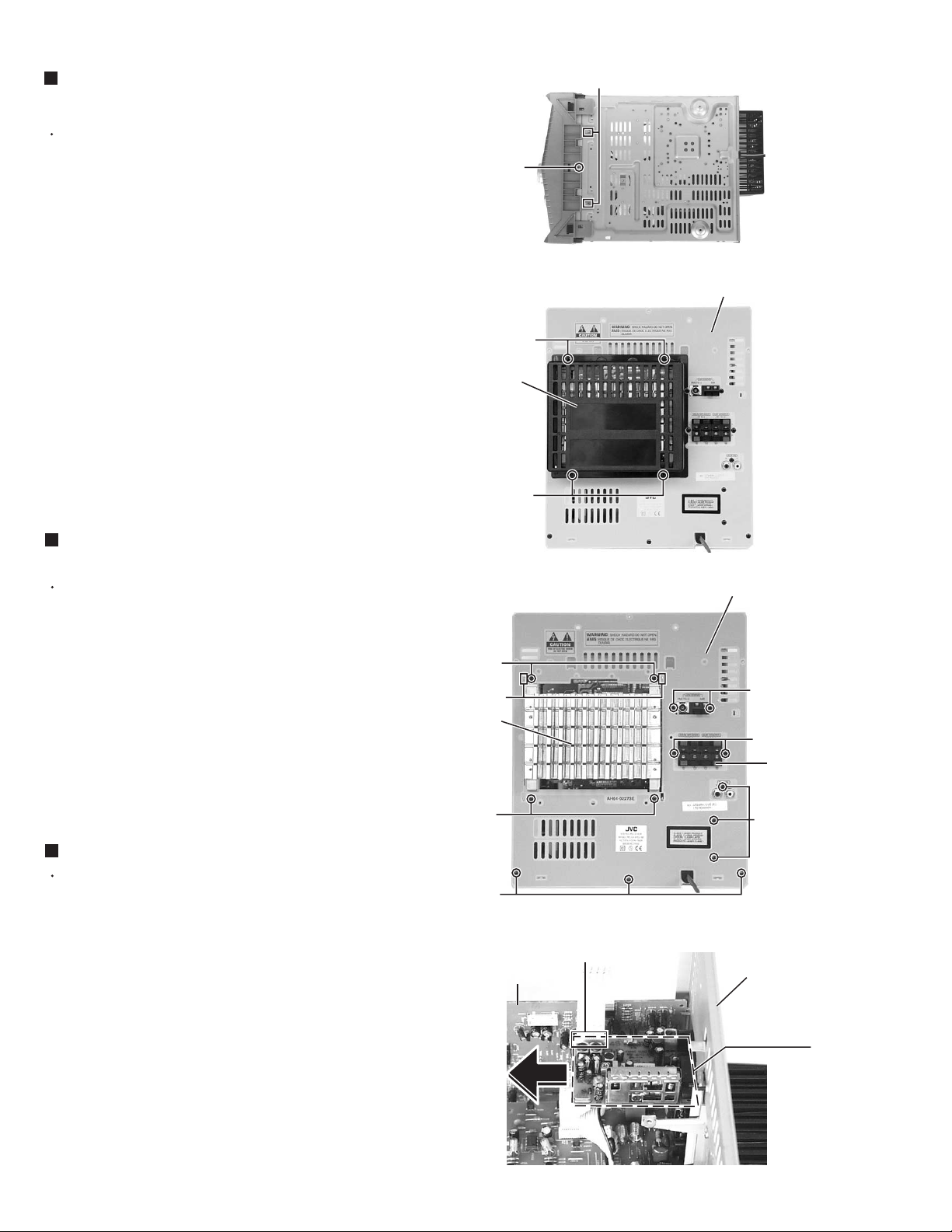
MX-GT88
)
Removing the heat sink & amp. board
(See Fig.8, 11 and 12)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover and CD changer unit.
1.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector ACW1
and the harness from the connector ACW2 on the
amp. board.
2.
Remove the four screws I attaching the heat sink
cover to the rear panel. Remove the heat sink cover.
3.
Remove the four screws J attaching the heat sink
and two screws K attaching the speaker terminal to
the rear panel.
4.
After moving the heat sink upward, remove the
claws. Then pull out the heat sink & amp. board
inward.
Heat sink
cover
H
Joint2
Fig.10
(Bottom side
Rear panel
I
I
Removing the tuner board
(See Fig.12 and 13)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover.
1.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector CON01
on the tuner board.
2.
Remove the two screws L attaching the tuner board
to the rear panel.
Removing the rear panel (See Fig.12)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit, heat sink & amp.
board and tuner board.
1.
Remove the three screws M and three screws N
attaching the rear panel.
J
Claws
Heat sink
J
N
Main board
Fig.11
Rear panel
L
K
Speaker
terminal
M
Fig.12
CON01
Rear panel
1-8
Tuner board
Fig.13
Page 9
MX-GT88
3
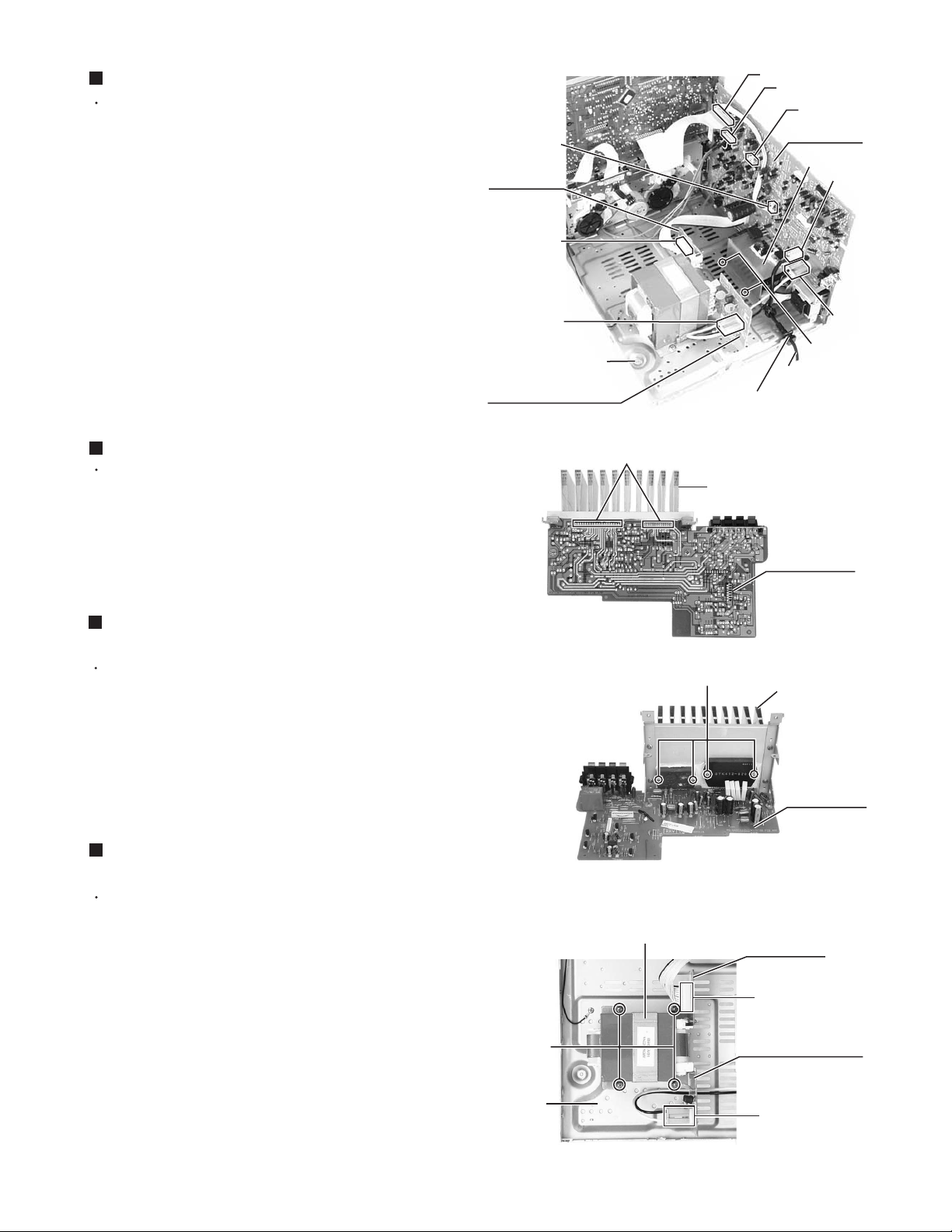
Removing the main board (See Fig. 14)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit and rear panel.
1.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector CW101,
and the harness from the connector CW108,
CW109, CW110 and CW11, and the power cord
from the connector PW103 on the main board.
2.
Disconnect the harness from the connector PCW1
on the fuse board.
3.
Remove the screw G attaching the main board to the
front panel assembly. (See Fig.9)
4.
Remove the two screws O attaching the heat sink to
the bottom chassis.
Removing the power cord (See Fig. 14)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit and rear panel.
CW108
Fuse board
PCW1
PW102
Bottom chassis
Power supply board
Power ICs solder point
CW101
CW109
CW110
Main board
Heat sink
PW10
CW11
O
Power cord
Power cord stopper
Fig.14
Heat sink
1.
Disconnect the power cord from the connector
PW103 on the main board and pull up the power
cord stopper upward.
Removing the power ICs
(See Fig.15 and 16)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit and heat sink &
amp. board.
1.
Unsolder the power ICs solder points.
2.
Remove the four screws P attaching the power ICs
to the heat sink.
Removing the power transformer
(See Fig .17)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit and heat sink &
amp. board.
1.
Disconnect the harness from the connector PW102
on the power supply board.
Fig.15
Fig.16
Power transformer
P
Amp. board
(reverse side)
Heat sink
Amp. board
Fuse board
PCW1
2.
Disconnect the harness from the connector PCW1 on
the fuse board.
3.
Remove the four screws Q attaching the power
transformer on the bottom chassis.
Bottom
chassis
Q
Power supply board
PW102
Fig.17
1-9
Page 10

MX-GT88
<Front panel assembly>
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the front panel assembly.
Removing the CD switch board (See Fig.1)
1.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector UCW03
on the CD switch board.
2.
Remove the five screws A attaching the CD switch
board.
Removing the front board
(See Fig.1 and 2)
1.
Pull out the sound mode knob, volume knob, and
preset knob from the front side of front panel
assembly.
2.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector UCW02
on the front board and the connector on the mecha.
board.
3.
Remove the fifteen screws B attaching the front
board.
B
B
Connector
Mecha.
board
Front panel assembly (inner side)
A
Fig.1
CD switch board
UCW03
Front board
UCW02
UCW01
4.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector UCW01
on the front board.
Removing the headphone jack board
(See Fig.3)
Prior to performing the following procedure remove
the front board.
1.
You can pull out the headphone jack board.
Removing the cassette mechanism
assembly (See Fig.3)
1.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector on the
mecha. board.
2.
Remove the six screws C attaching the cassette
mechanism assembly.
Connector
C
Mecha.
board
Sound mode knob
Volume knob
Preset knob
Fig.2
Front panel assembly (inner side)
Headphone
jack board
C
1-10
C
(fixing the lug wire)
Fig.3
Cassette mechanism
assembly
Page 11
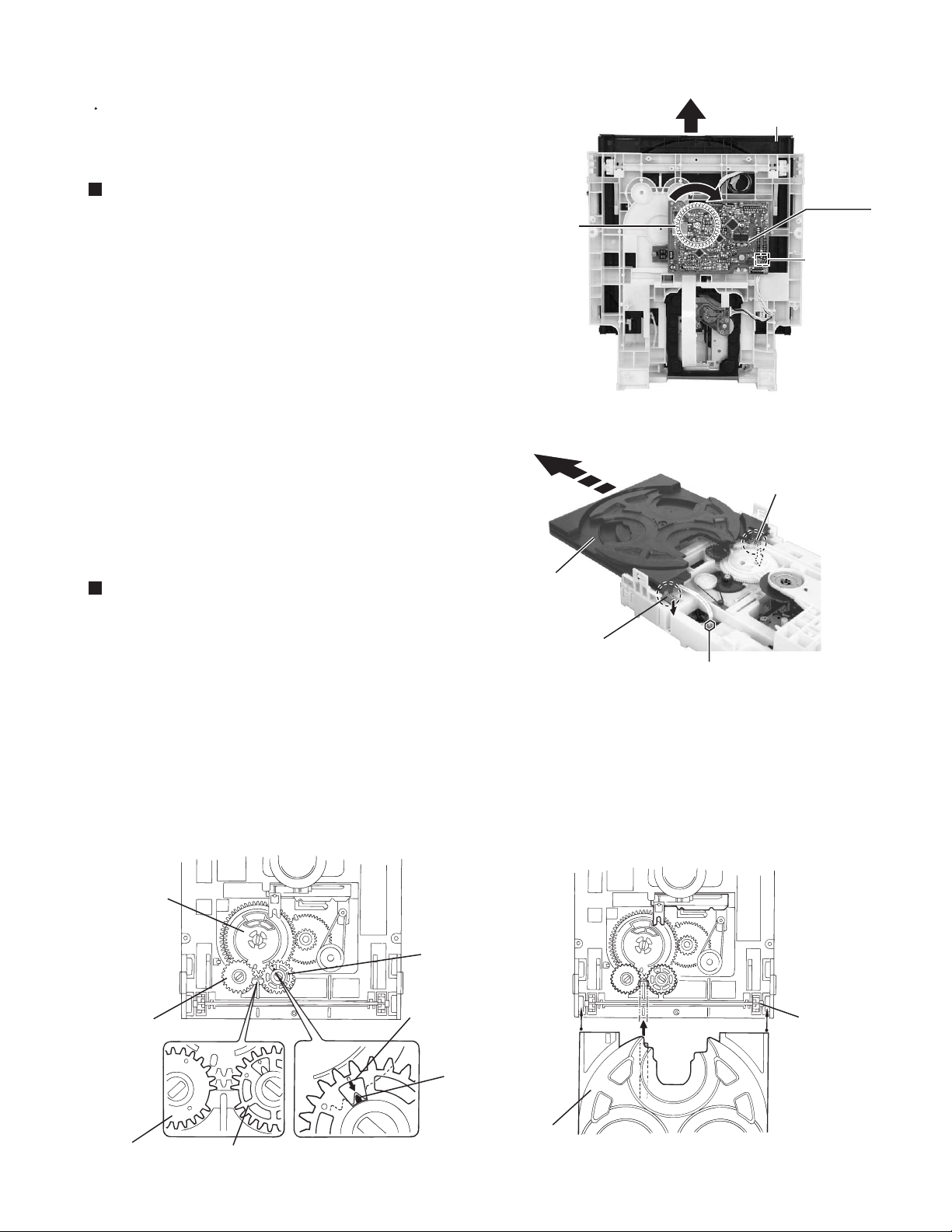
MX-GT88
<CD changer unit>
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the CD changer unit.
Removing the CD tray (See Fig.1 and 2)
1.
Turn the black loading pulley gear on the under side
of the CD changer unit in the direction of the arrow
and draw the CD tray toward the front until it stops.
2.
Disconnect the card wire from connector CW103 on
the CD board.
3.
Push down the two tray stoppers marked a and pull
out the CD tray.
Loading pulley
gear
CD changer uint (reverse side)
CD tray
CD board
CW103
Fig.1
a (Tray stopper)
Reinstall the CD tray (See Fig.3 and 4)
1.
Align the gear-cam with the gear-tray as shown fig.3,
then mount the CD tray.
2.
When assembling the CD tray, take extreme care not
engage with gear - synchro.
Gear-cam
Gear-convert
Gear-cam
timing point
CD tray
a
(Tray stopper)
CW103
(on the CD board)
Fig.2
Gear-tray
Gear-synchro
Gear-convert
Gear-tray
CD tray
Gear-tray
Fig.3 Fig.4
1-11
Page 12
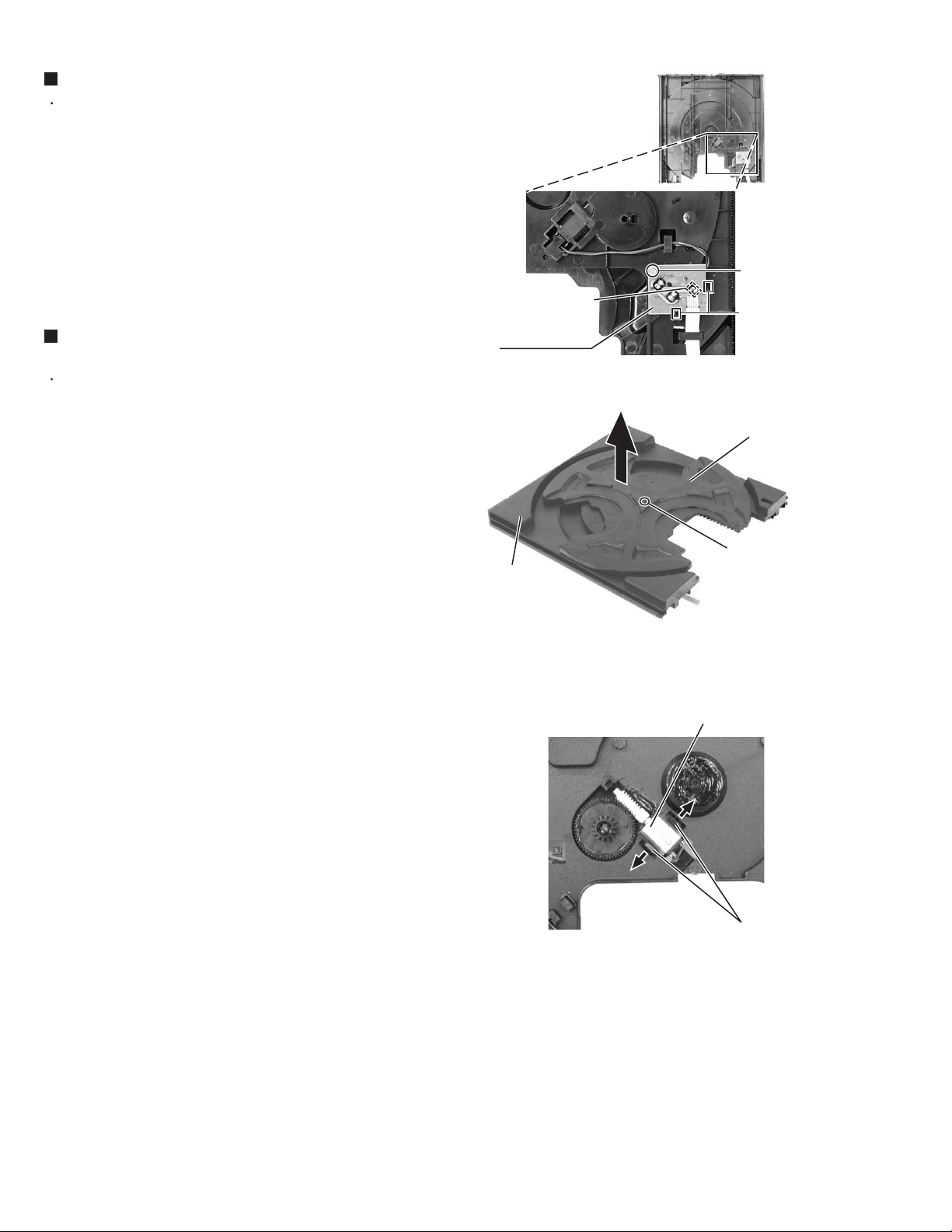
MX-GT88
Removing the sensor board (See Fig.5)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the CD tray.
1.
Remove the screw A attaching the sensor board on
the CD tray.
2.
Remove the sensor board releasing the two tabs a.
3.
Disconnect the harness from the connector CW1 on
the sensor board.
Removing the turn tray motor
(See Fig.6 and 7)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the CD tray and sensor board.
1.
Remove the screw B attaching the turn tray. Detach
the turn tray from the base tray.
2.
Pull outward the tab b attaching the turn tray motor
on the base tray and detach the turn tray motor.
CD tray (reverse side)
A
CW1
Tab a
Sensor board
Fig.5
Turn tray
Introductory notes:
Base tray + Turn tray = CD tray
Base tray
B
Fig.6
Turn tray motor
Base tray (upper side)
Tab b
Fig.7
1-12
Page 13

Removing the belt, the CD board and the
switch board (See Fig.8 and 9)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the CD tray.
1.
Detach the belt from the pulley on the upper side of
the CD changer unit (Do not stain the belt with
grease).
2.
Disconnect the card wire from the pickup unit
connector on the under side of the CD changer unit.
Attention : Solder is put up before the card wire is
removed from the pick-up unit
connector on the CD mechanism
assembly.
(When the card wire is removed without
putting up solder, the CD pick-up unit
assembly might destroy.)
3.
Disconnect the motor wire harness from connector
on the CD board.
4.
Remove the screw C attaching the switch board and
release the two tabs e attaching the switch board
outward and detach the switch board.
5.
Remove the two screws D attaching the CD board.
First release the two tabs f and two tabs g attaching
the motor, then release the CD board.
If the tabs f and g are hard to release, it is
recommendable to unsolder the two soldered parts
on the motor terminal of the CD board.
Tabs e
C
Switch board
CW3
CD changer unit
Fig.8
CD board
D
Tabs g
Soldered parts
CD mechanism board
motor connecter
Pickup unit connector
Card wire
MX-GT88
Belt
Motor
Tabs f
Soldering
Picup unit
connector
Fig.9
1-13
Page 14
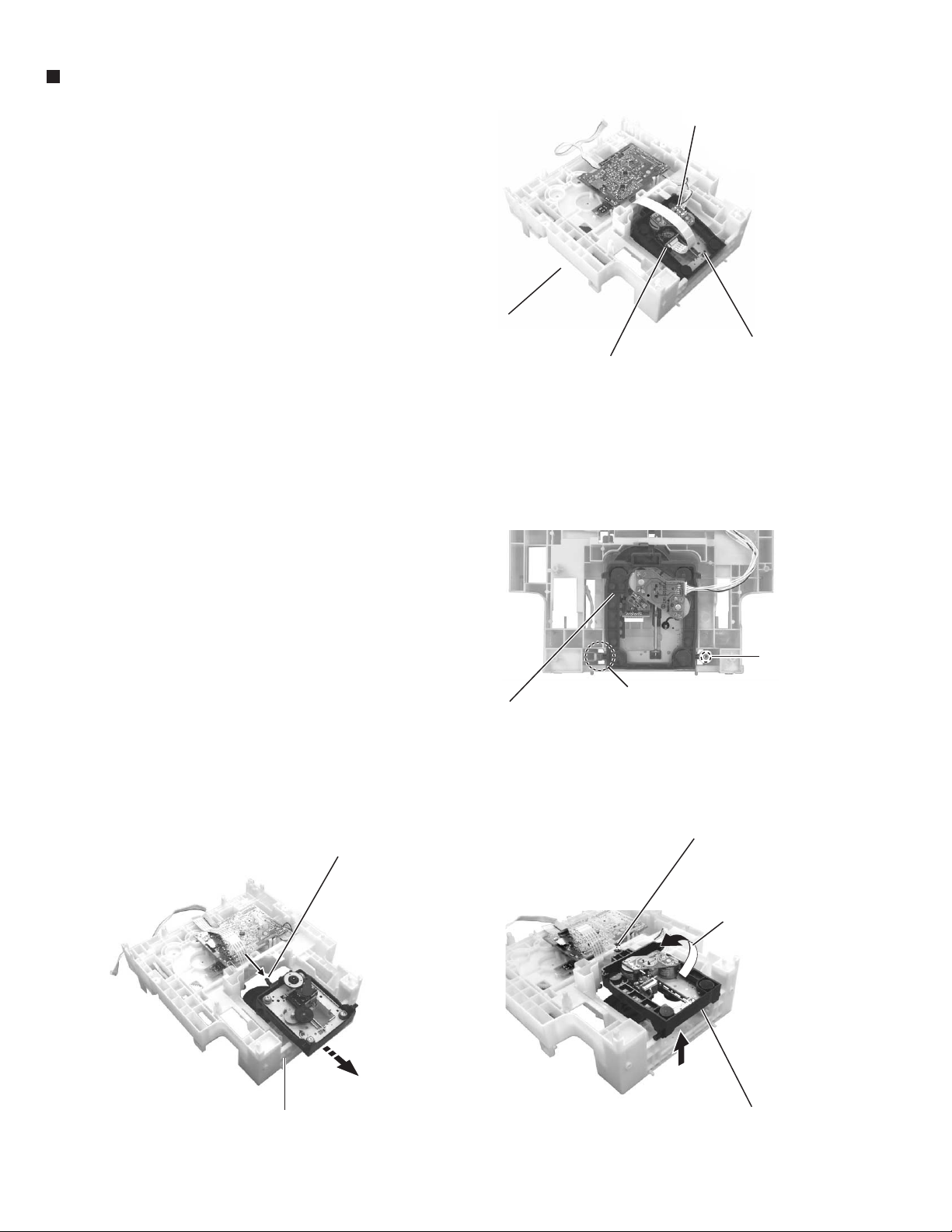
MX-GT88
Removing the CD mechanism holder
assembly (mechanism included)
(See Fig.10 to 13)
1.
Disconnect the harness from connector on the CD
mechanism board in the CD mechanism assembly
on the under side of the CD changer unit. Disconnect
the card wire from the pickup unit connector.
Attention : Solder is put up before the card wire is
removed from the pick-up unit
connector on the CD mechanism
assembly. (Refer to Fig.9)
(When the card wire is removed without
putting up solder, the CD pick-up unit
assembly might destroy.)
Motor connecter
CD changer unit
CD mechanism holder assembly
Pickup unit connector
2.
Remove the screw E attaching the shaft on the right
side of the CD mechanism holder assembly. Pull
outward the stopper fixing the shaft on the left side
and remove the CD mechanism holder assembly
from behind in the direction of the arrow y.
3.
Turn the CD mechanism holder assembly half
around the lift up slide shaft h of the CD mechanism
holder assembly until the turn table is reversed, and
pull out the CD mechanism holder assembly.
Lift up slide shaft
Fig.10
E
Stopper
CD mechanism holder assembly
Fig.11
Lift up slide shaft n
1-14
CD mechanism holder assembly
Fig.13
y
CD mechanism holder assembly
Fig.12
Page 15

MX-GT88
<CD mechanism section>
•
Removing the CD mechanism holder from the CD
chager unit.
(Refer to "Removing the CD mechanism holder
assembly" )
Removing the pickup unit (
1. Removing the cut washer on the feed gear
sleeve and pull out the feed gear.
2. Remove the two screws A fixing the pickup
shaft.
3. Removing the pickup unit.
Removing the motor board
1. Unsolder the motor terminal on the motor board.
2. Remove the moter board.
Removing the feed motor (
Remove the two motor fixing screws at B and
removing the feed motor.
See Fig.1)
(See Fig.2)
See Fig.1)
A
Motor board
Shutter
Cut washer
B
Fig.1
Unsolder
Pickup unit
Feed Gear
Feed motor
Shaft
A
Removing the spindle motor
The spindle motor cannot be removed as a single
unit.
When removing the spindle motor, change the chasis
and turntable together as aunit.
Spindle motor
Unsolder
Fig.2
1-15
Page 16

MX-GT88
<Cassette mechanism section>
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the
cassette mechanism assembly.
Removing the R/P head.
(See Fig.1 and 2)
1.
Remove the screw A on the right side of the R/P
head.
2.
Remove the screw B on the left side of the R/P
head.
Remove the erase head.
1.
Remove the screw C fixing the erase head.
(See Fig.1)
E. Head
R/P Head
C
B
B
Pinch roller
A
Fig.1
A
Remove the pinch roller.
Pull out the pinch roller stopper.
1.
Pull out the pinch roller.
2.
(See Fig.3)
Spring
Pinch roller
R/P Head
Fig.2
Pinch roller
stopper
Fig.3
1-16
Page 17

MX-GT88
Removing the motor
1.
Slide the plastic cover in the direction of the arrow,
and remove the three claws. Then remove the
plastic cover.
2.
Remove the two screws D fixing the motor.
Be careful to grease's splash when the drive belt
comes off.
3.
Unsolder the motor terminal.
(See Fig. 4 to 6)
Removing the mechanism board
1.
Unsolder the four solder parts a and the four solder
parts b.
2.
Remove the two screws E attaching the mecha.
board.
(See Fig. 5)
Removing the flywheel
1.
Remove the cut-washer at c from the capstan shaft,
then remove the flywheel.
When reassembling the flywheel, be sure to use new
washers as they cannot be reused.
(See Fig. 7 and 9)
Solder
part
D
Claw
Fig.4
Motor
b
terminal
Solder
part
a
Solder
part
E
a
Plastic cover
Mecha. board
E
Flywheel
Washer
FR belt
Fig.8
Sleeve
c
FR belt
Drive belt
Motor
Drive belt
Fig.5
Motor
Drive belt
Fig.6
Fig.9
Capstan
washer
Fig.7
1-17
Page 18

MX-GT88
< Speaker section >
It is exchange in a unit.
Please do not decompose as much as possible.
Removing the duct (See Fig. 1)
1.
Remove the foru screws A and two screws B
attaching the duct, and remove the duct.
Duct
B
(both sides)
A
(both sides)
Fig.1
1-18
Page 19

MX-GT88
Wiring connection
Amp. board
0
9
Front board
UCW02
AH39-00295A
3809-001413
ACW2
ACW1
CD switch board
3809-001228
UCW03
UCW04
UCW05
UCW01
9
Power transformer
0
PW102
PCW1
9
0
3809-001121
AH39-00338A
AH39-00466A
CD mechanism
AH39-20561P
CW2
AAN1
CW1
CW3
AH38-12001A
9
0
Color codes are shown below.
1 Brown
2 Red
3 Orange
4 Yellow
5 Green
6 Blue
7 Violet
0
9
8 Gray
9 White
0 Black
0
2
0
2
3809-001034
CW102
CW103
CW105
CW106
9
0
CD board
CW107
CW101
CW104
CW3
AH39-00060A
3809-001211
3809-001434
CON01
0
0
9
3809-001259
9
0
9
0
9
0
CW103
9
0
CW105
CW104
PW103
CW11
CW106
9
0
9
AH39-00247A
0
CW108
Main board
CW110
Tuner board
CW101
CW111
CW109
CW107
9
0
0
9
2
2
0
CW01B
9
0
Headphone J.board
9
AH39-00022A
0
9
2
0
88
9
9
0
9
2
0
AH39-20002D
8
2
8
2
1-19
Page 20

MX-GT88
Adjustment method
1. Tuner
ITEAM
Received FREQ.
Adjustment
point
Output
* Adjustment Location of Tuner PCB
AM(MW) OSC
Adjustment
522~1629 KHz
MO
1~7.0 0.5V
MAIN
PCB
AM(MW) RF
Adjustment
594 KHz
MA
Maximum
Output(Fig.1)
VT GND
TESTER
1-20
Fig.1 OSC Voltage
Page 21

FM THD Adjustment
MX-GT88
SSG FREQ.
98 MHz
Adjustment
point
FM DETECTOR COIL
(FM DET)
Output
60 dB
Minumum Distortion (0.4% below)
(Fig.2)
FM Search Level Adjustment
SSG FREQ.
Adjustment
point
(SVR1)
BEACON
SENSITIVITY
SEMI-VR(10K )
98 MHz
Output
GND
FM
Antenna
Terminal
SET
FM S.S.G
Speaker
Terminal
output
Distortion Meter
Fig.2 IF CENTER and THD Adjustment
28 dB
FM Antenna
Input
Oscilloscope
Input
SET
Output
28 dB(
2dB)
Adjust SVR1 (Fig.3)
*Adjust FM S.S.G level to 28dB
AM(MW) I.F Adjustment
SSG FREQ.
Frequency
450 kHz
522 kHz
Adjustment
point
AM IF
Maximum output (Fig.4)
FM S.S.G
GND
FM IN
Fig.3 FM Auto Search Level Adjustment
60cm
OUTPUT
AM SSG
450KHZ
AM ANT
IN
20 k
AM IF
Speaker Terminal
INPUT
VTVM Oscilloscope
OUTPUT
Fig.4 AM I.F Adjustment
1-21
Page 22

MX-GT88
2. Cassette Deck
To adjust tape speed
Notes
1) Measuring tape:
i) VT-712/MTT-111(or equivalent)
(Tapes recorded with 3kHz)
ii) AC-225/MTT-5512(or equivalent)
2) Connect the cassette deck to the frequency counter
as in fig.1.
Cassette Deck
SPK OUT
Frequency Counter
output
Fig.1
Pre-Setup
Condition
NOR
1 3KHz
SPEED
Control
SPK OUT
(connected to the
frequency counter)
1) Deck 1:VT-712
2) Press PLAY
SW button
To Adjust
Turn VSR1 to
left and right
(FRONT PCB)
3) Deck 2:Same
as above
To adjust plabyback level/REC
Notes
1) Before the actual adjustment, clean the play/recording head.
2) Measuring tape :
i) VT-703/MTT-114N(or equivalent 10kHz AZIMUTH control)
ii) AC-225/MTT-5512(or equivalent)
3) The cassette deck is connections as shown in fig.2.
MAIN PCB
SPK OUT
(GND)
Fig.2
VTVM
In Out
RemarkStandardPre-SetupItemStep
1%
range
Oscilloscope
1. Adjust Deck 1 Play Level
Pre-Setup
Condition
AZIMUTH1 SPK OUT
(VTVM is
connected to
the scope)
1-22
After putting VT-703
into Deck 1
- Press FWD PLAY
button.
To Adjust
Turn the control
screw to as
shownin Fig.3.
Max output
and same phase
(both channels)
RemarkStandardPre-SetupItemStep
After
adjustment
secure it with
REGION
LOCK.
Page 23

2. Adjust Deck 2 Play Level/REC BIAS
MX-GT88
2
AZIMUTH1
Recording
Bias
Voltage
Pre-Setup
Condition
SPK OUT
(VTVM is
connected to
the scope)
Fig.4
Recording /Play head
AZIMUTH control screw
(FWD Play)
After putting VT-703
into Deck 2
1)Press FWD PLAY
button.
After putting AC-225
into Deck 2
1)Press REC PLAY
button.
2)TAPE PCB JCW3,
connectted to VTVM
To Adjust
Turn the control
screw to as
shown in Fig.3.
Turn JSR2L,
JSR2R to the
right and left
Max output
and same phase
(both channels)
CHECK TO
7mV(
0.5mV)
RemarkStandardPre-SetupItemStep
After
adjustment
secure it with
REGION
LOCK.
AZIMUTH control screw
(RVS Play)
Audio OSC.
Fig.3
AUX IN
SET
(MAIN PCB)
IN
TP
SPK OUT
Fig.4
VTVM
IN OUT
Oscilloscope
1-23
Page 24

MX-GT88
Flow of functional operation until TOC read
Power ON
Play Key
RESET a CD LSI
Check Point
Confirm that the voltage at the pin17
of KB9226(IC101) is "L" "H".
LIMIT SW ON
SET Default value of
TE gain, TE balance
Automatic adjusting of
focus bias
Automatic adjusting of
FE offset
Automatic adjusting of
TE offset
LASER power ON
Detection of disk
Confirm that the voltage at the pin33
of KB9226(IC101) is "H" "L" "H".
Confirm that the voltage at the
pin37 of KB9226(IC101) is 3.5V.
Tracking error waveform at TOC reading
Pin 34 of
KB9226
(IC101)
Approx
0.4V
2.50V
Disc states
to rotate
Approx.3.7sec
Disc is rotated
Automatic adjusting of
TE balance
Automatic adjusting of
TE gain
TOC reading
Play a disc
Confirm that the signal from pin24
of KB9226(IC101) is 3.5V as a
accelerated pulse during
approx.1.96s.
Confirm the waveform of
the Tracking error signal
at the pin 34 of KB9226(IC101).
Confirm the eye-pattern
at the pin2 of KB9226(IC101).
1-24
Page 25

Maintenance of laser pickup
MX-GT88
(1) Cleaning the pick up lens
Before you replace the pick up, please try to
clean the lens with a alcohol soaked cotton
swab.
(3) Semi-fixed resistor on the APC PC board
The semi-fixed resistor on the APC printed circuit board which is attached to the pickup is used to adjust the
laser power. Since this adjustment should be performed to match the characteristics of the whole optical block,
do not touch the semi-fixed resistor.
If the laser power is lower than the specified value, the laser diode is almost worn out, and the laser pickup
should be replaced.
If the semi-fixed resistor is adjusted while the pickup is functioning normally, the laser pickup may be damaged
due to excessive current.
(2) Life of the laser diode
When the life of the laser diode has expired,
the following symptoms will appear.
1. The level of RF output (EFM output :
amplitude of eye pattern) will below.
Is the level of
RF OUT under
1.1V 0.2Vp-p?
YES
O.K
NO
Replace it.
Replacement of laser pickup
Turn off the power switch and,disconnect the
power cord from the ac outlet.
Replace the pickup with a normal one.(Refer
to "Pickup Removal" on the previous page)
Plug the power cord in,and turn the power on.
At this time,check that the laser emits for
about 3seconds and the objective lens moves
up and down.
Note: Do not observe the laser beam directly.
Play a disc.
Check the eye-pattern at TP1.
Finish.
1-25
Page 26

MX-GT88
Troubleshooting
1. Amplifier
Power malfunction
No output
1-26
Page 27

2.Tuner malfunction (FM/AM)
MX-GT88
3.Tape
1-27
Page 28

MX-GT88
4.CD
1-28
Page 29

5.CD - MP3 parts
MX-GT88
1-29
Page 30

MX-GT88
Description of major ICs
LC876764 (UIC1) : Microcontroller
1.Pin layout
S47/PF7
S46/PF6
S45/PF5
S44/PF4
S43/PF3
S42/PF2
S41/PF1
S40/PF0
VDD4
S39/PE7
S38/PE6
S37/PE5
S36/PE4
S35/PE3
S34/PE2
S33/PE1
S32/PE0
S31/PD7
S30/PD6
S29/PD5
S28/PD4
S27/PD3
S26/PD2
S25/PD1
S24/PD0
S23/PC7
S22/PC6
S21/PC5
S20/PC4
FIX0
2.Block diagram
8079787776757473727170696867666564636261605958575655545352
P00
P01
P02
P03
P04
P05
P06
P07
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829
CF1
RES
VSS1
XT1/AN10
P16/T1PWML
P30/INT4/T1IN
P31/INT4/T1IN
P32/INT4/T1IN
P33/INT4/T1IN
P17/T1PWMH/BUZ
P34/INT5/T1IN
P35/INT5/T1IN
XT2/AN11
P36/INT5/T1IN
P37/INT5/T1IN
IR PLA
S48/PG0
S49/PG1
S50/PG2
S51/PG3
VSS2
VDD2
P10/SO0
P11/SI0/SB0
P12/SCK0
P13/SO1
P14/SI1/SB1
P15/SCK1
Interrupt Control
Stand-by Control ROM
CF2
VDD1
P80/AN0
P81/AN1
P82/AN2
P83/AN3
P84/AN4
P85/AN5
P86/AN6
P87/AN7/MICIN
51
S19/PC3
50
S18/PC2
49
S17/PC1
48
S16/PC0
47
VDD3
46
S15/T15
45
S14/T14
44
S13/T13
43
S12/T12
42
S11/T11
41
S10/T10
40
S9/T9
39
S8/T8
38
S7/T7
37
S6/T6
36
S5/T5
35
S4/T4
34
S3/T3
33
S2/T2
32
S1/T1
31
30
S0/T0
P73/INT3/T0IN/AN13
P70/INT0/T0LCP/AN8
P71/INT1/T0HCP/AN9
P72/INT2/T0IN/NKIN/AN12
SIO0
SIO1
Timer 0
(High speed clock counter)
Timer 1
Base Timer
VFD Controller
INT 0 - 5
Noise Rejection
CF
RC
MRC
X’ tal
Clock
Generator
Bus Interface
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 7
Port 8
ADC
Weak Signal
Detector
PC
ACC
B Register
C Register
ALU
PSW
RAR
RAM
1-30
Timer 4
Timer 5
Timer 6
Timer 7
Stack Pointer
Watch Dog Timer
Page 31

MX-GT88
3. Pin function (1/2)
Pin name
VSS1, 2
VDD1,2,3,4
FIX0
PORT0
P00 to P07
PORT1
P10 to P17
PORT3
P30 to P37
PORT7
P70 to P73
PORT8
P80 to P87
S0/T0 to
S8/T8
S9/T9 to
S15/T15
S16 to S23
S24 to S31
-
-
-
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
O
I/O
I/O
Power supply (-)
Power supply (+)
Test pin
Set as VSS with the user’s option. (see Note 1)
• 8bit input/output port
• Data direction programmable in nibble units
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified in nibble units
• Input for HOLD release
• Input for port 0 interrupt
• 15V withstand at N-channel open drain output
• 8bit input/output port
• Data direction programmable for each bit
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
• Other pin functions
P10: SIO0 data output
P11: SIO0 data input / bus input / output
P12: SIO0 clock input / output
P13: SIO1 data output
P14: SIO1 data input / bus input / output
P15: SIO1 clock input / output
P16: Timer 1 PWML output
P17: Timer 1 PWMH output / Buzzer output
• 8bit input/output port
• Data direction can be specified for each bit
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
• 15V withstand at N-channel open drain output
• Other functions:
P30 to P33: INT4 input / HOLD release input / Timer 1 event input / Timer 0L
capture input / Timer 0H capture input
P34 to P37: INT5 input / HOLD release input / Timer 1 event input / Timer 0L
capture input / Timer 0H capture input
• 4bit input/output port
• Data direction can be specified for each bit
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
• Other functions
P70: INT0 input / HOLD release input / Timer0L capture input / Output for watchdog timer
P71: INT1 input / HOLD release input / Timer0H capture input
P72: INT2 input / HOLD release input / Timer 0 event input / Timer0L capture input
/ High speed clock counter input
P73: INT3 input(noise rejection filter attached input) / Timer 0 event input
/ Timer 0H capture input
AD input port: AN8(P70), AN9(P71), AN12(P72), AN13(P73)
• 8bit input/output port
• Input/output can be specified in a bit unit
• Other functions:
AD input port: AN0 to AN7
Weak signal detector input port: MICIN(P87)
• Large current output for VFD display controller digit (can be used for segment)
• Large current output for VFD display controller segment/digit
• Output for VFD display controller segment/digit
• Other functions:
High voltage input port: PC0 to PC7
• Output for VFD display controller segment
• Other functions:
High voltage input port: PD0 to PD7
Function I/O
1-31
Page 32

MX-GT88
3. Pin function (2/2)
Pin name
S32 to S39
S40 to S47
S48 to S51
RES
XT1
XT2
CF1
CF2
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
I
I/O
I
O
Function I/O
• Output for VFD display controller segment
• Other functions
High voltage input port: PE0 to PE7
• Output for VFD display controller segment
• Other functions:
High voltage input/output port: PF0 to PF7
• Output for VFD display controller segment
• Other functions:
High voltage input/output port: PG0 to PG3
Reset terminal
• Input for 32.768kHz crystal oscillation
• Other functions:
General purpose input port
When not in use, connect to VDD1.
AD input port: AN10
• Output for 32.768kHz crystal oscillation
• Other functions:
General purpose input port
When not in use, set to oscillation mode and leave open circuit.
AD input port: AN11
Input terminal for ceramic oscillator
Output terminal for ceramic oscillator
KA9258D (IC301) : 4-ch Motor driver
1.Block diagram
28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15
10K
T • S • D
+-
LEVEL SHIFT
VCC VCC
10K
REGULATOR
10K
10K
GND
10K
10K
10K
50K
MUTE
LEVEL SHIFT
-+
1-32
10K
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
GND
Page 33

HA12237 (JIC01) : Audio signal processor
1. Block diagram
TEST
(Open for normal use)
IREF
GND
ALCDET
20
19
18
17
Vcc
16
A
MUTE ON/OFF
REC MUTE OFF/ON
15
14
(REC RETURN ON/OFF)
A/B
13
ALC ON/OFF
High/Normal
11
12
MX-GT88
REC OUT(L)
NC
ALC(L)
REC IN(L)
NC
PB OUT(L)
TAI(L)
EQOUT(L)
PB-EQ(L)
PB-NF2(L)
21
22
23
24
2526
27
28
29
30
EQ
120/60
(Norm/High)
+
31
MUTE
AB
32
33
34
Return SW
35
ALC
Return SW
36
37
38
MUTE
AB
39
EQ
120/60
(Norm/High)
+
40
REC OUT(R)
10
9
NC
8
ALC(R)
7
REC IN(R)
6
NC
5
PB OUT(R)
4
TAI(R)
3
EQOUT(R)
2
PB-EQ(R)
1
PB-NF2(R)
2. Pin function
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Symbol
PB-NF2(R)
PB-EQ(R)
EQOUT(R)
TAI(R)
PBOUT(R)
NC
RECIN(R)
NC
RECOUT(R)
ALC ON/OFF
High/Norm
A/B
MUTE ON/OFF
PB-NF1(L)
Function
PB EQ feed back
NAB output
EQ output
Tape input
PB output
NC pin
REC-EQ input
NC pin
REC output
Mode control input
Mode control input
Mode control input
Mode control input
AIN(L)
Pin No.
RIP
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
REC
IN(L)
Symbol
REC MUTE
OFF/ON
Vcc
GND
IREF
Test mode
RECOUT(L)
NC
RECIN(L)
NC
PBOUT(L)
GND
Return
Function
Mode control input
Vcc pin
GND pin
Equalizer reference
current input
Test mode pin
REC output
NC pin
REC-EQ input
NC pin
PB output
IN(R)
NC
AIN(R)
Pin No.
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
PB-NF1(R)
Symbol
TAI(L)
EQOUT(L)
PB-EQ(L)
PB-NF2(L)
PB-NF(L)
AIN(L)
RIP
BIN(L)
REC-RETURN
GND
BIN(R)
NC
AIN(R)
PB-NF1(R)
Function
Tape input
EQ output
NAB output
PB EQ feed back
PB EQ feed back
PB A deck input
Ripple filter
PB B deck input
REC Return
GND pin
PB B deck input
NC pin
PB A deck input
PB EQ feed back
1-33
Page 34

MX-GT88
KB9226 (IC101) : RF amp. & servo signal processor
1. Pin layout
36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
SLP
FEO
VCC
FEM
FRSH
TEO
FSET
TEM
FLB
FGD
2. Block diagram
37
LD
PD
38
39
PDAC
40
PDBD
PDF
41
42
PDE
43
DCB
MCP
44
45
DCCI
46
DCCO
47
VREF
48
EQC
LPFT
ATSC
RFO
RFM
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
TEIO
TZC/SSTOP
S1L9226X
EQO
EQI
GND
EFMI
FSI
SLO
SLM
SPO
SPM
ASY
EFM
LOCK
WDCK
CLVI
RESET
MLT
MDATA
MCK
ISTAT
TGU
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
EQO
EFMI
DCCI
DCC0
MCP
DCB
VCC/
VDD
FRSH
FSET
FLB
FGD
FSI
45
46
44
43
10
11
EQI
RFO
RFM
4
5
RF AGC & EQ
Control
Focus OK Detect
Defect Detect Mirror
Gen
Focus Servo Loop
- Gain & Phase
Compensation
- Focus Search
- Offset Adjust
- FZC Gen.
6
7
8
9
EQC
Center
Voltage
APC. Laser
Control &
LPC
Tracking Servo Loop
- Gain & Phase
Compensation
- Track Jump
- Offset Adjust
- TZC Gen.
Hardware Logic
- Auto-Sequencer
- Fast Search
- Febias, Focus Servo,
Tracking Offset ADJ.
VREF
Tracking Error
PDE
(RW)
I/V AMP
PDF
41 40424748123
PDBD
39
RF & Focus
Error (CD-RW)
I/V AMP
Sled Servo &
Kick Gen
PDAC
38
37
35
34
33
36
29
28
27
26
25
PD
LD
LPFT
TEIO
TZC&
SSTOP
ATSC
TEO
TEM
SLP
SLO
SLM
- Tracking Balance & Gain
Adjust
- Interruption Detect
29
FEO
- EFM Muting System
30
FEM
1-34
TGU
12
Micom Data Interface Logic Decoder
1413 15 16 17 19 18 20 22 21
ISTAT
MCK
MDATA
MLT
RESET
WDCK
CLVI
LOCK
EFM
Comparator
ASY
EFM
Spindle
Servo LPF
23
24
SPDLO
SPDLM
Page 35

3. Pin function
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
Symbol
RFM
RFO
EQI
EQO
EFMI
VCC
FRSH
FSET
FLB
FGD
FSI
TGU
ISTAT
MCK
MDATA
MLT
RESET
CLVI
WDCK
LOCK
EFM
ASY
SPM
SPO
SLM
SLO
SLP
TEM
TEO
FEM
FEO
GND
TZC/
SSTOP
TEIO
LPFT
ATSC
LD
PD
PDAC
PDBD
PDF
PDE
DCB
MCP
DCCI
DCCO
VREF
EQC
Function
I/O
RF summing amp. inverting input
I
RF summing amp. output
O
RFO DC eliminating input(use by MIRROR, FOK ,AGC & EQ terminal)
I
RF equalizer output
O
EFM slice input. (input impedance 47K)
I
Main power supply
P
Capcitor connection to focus search
I
Filter bias for focus,tracking,spindle
I
Capacitor connection to make focus loop rising band
I
Terminal to change the hign frequency gain of focus loop
I
Focus servo input
I
Connect the component to change the high frequency of tracking Loop
I
Internal status output
O
Micom clock
I
Data input
I
Data latch input
I
Reset input
I
Input the spindle control output from DSP
I
88.2KHz input terminal from DSP
I
Sled run away inhibit pin (L: sled off & tracking gain up)
I
EFM output for RFO slice(to DSP)
O
Auto asymmetry control input
I
Spindle amp. inverting input
I
Spindle amp. output
O
Sled servo inverting input
I
Sled servo output
O
Sled servo noninverting input
I
Tracking servo amp.inverting input
I
Tracking servo amp. output
O
Focus servo amp. inverting input
I
Focus servo amp. output pin
O
Main ground
P
Tracking zero crossing input & Check the position of pick-up wherther inside or not
I
Tracking error output & Tracking servo input
B
Tracking error integration input (to automatic control)
I
Anti-shock input
I
APC amp. output
O
APC amp. input
I
Photo diode A & C RF I/V amp. inverting input
I
Photo diode B & D RF I/V amp. inverting input
I
Photo diode F & tracking(F) I/V amp. inverting input
I
Photo diode E & tracking(E) I/V amp. inverting input
I
Capacitor connection to limit the defect detection
I
Capacitor connection to mirror hold
I
Output pin to connect the component for defect detect
O
Input pin to connect the component for defect detect
I
(VCC+GND)/2 Voltage reference output
O
AGC_equalize level control terminal & capacitor terminal to input in to VCA
I
MX-GT88
1-35
Page 36

MX-GT88
5L9290 (IC201) : Digital signal processor for CDP
1. Pin layout
RCHOUT
VSSA_DAC
VREF
VHALF
VDDA_DAC
LRHOUT
VDDA_PLL
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
VSSD_DAC
VDDD_DAC
SADTI
LRCKI
BCKI
2. Block diagram
VSSA_PLL
VCO1LF
VSSD_PLL
VDDD_PLL
VDDD1_5V
XIN
XOUT
VSSD1_5V
EFMI
LOCK
SMEF
SMON
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
SMDS
WDCK
S5L9290X
DSP+DAC
48-LQFP-0707
LKFS
TESTV
LKFS
RESETB
MLT
MDAT
SOS1
SQCK
SBCK
SQDT
SBDT
MCK
ISTAT
C2PO
S0S1
SQCK
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
DATX
BCKO
LRCKO
SADTO
DATX
C2PO
JITB
SBCK
VDDD3-5V
VSSD2-3V
VDDD2-3V
MUTE
SQDT
VCO1LF
EFMI
LOCK
SMEF
SMDP
SMDS
WDCK
WFCK
RFCK
C4M
XIN
ISTAT
MLT
MDAT
MCK
MUTE
DPLL
CLV
Servo
Timing
Generator
Micom
Interface
Subcode
Out
EFM
Demodulator
ECC
16K
SRAM
Address
Generator
JITB
Interpolator
Interface
SADTO
LRCKO
BCKO
I/O
Digital
Out
SADTI
LRCKI
BCKI
Digital
Filter
1-bit
DAC
PWM
LPF
LCHOUT
RCHOUT
VHALF
VREF
1-36
Page 37

3. Pin function
MX-GT88
NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
28
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
Symbol
VSSA_PLL
VCO1LF
VSSD_PLL
VDDD_PLL
VDDD1-5V
XIN
XOUT
VSSD1
EFMI
LOCK
SMEF
SMDP
SMDS
WDCK
TESTV
LKFS
C4M
RESETB
MLT
MDAT
MCK
ISTAT
S0S1
SQCK
SQDT
MUTE
VDDD2-3V
VSSD2
VDDD3-5V
SBCK
JITB
C2PO
DATX
SADTO
LRCKO
BCKO
BCKI
LRCKI
SADTI
VSSD_DAC
VDDD_DAC
RCHOUT
VSSA_DAC
VREF
VHALF
VDDA_DAC
LCHOUT
VDDA_PLL
I/O
-
O
-
-
I
O
-
I
O
O
O
O
O
I
O
O
I
I
I
I
O
O
I
O
I
-
-
-
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
I
I
I
-
-
O
O
O
O
-
Function
Analog Ground for DPLL
Pump out for VCO1
Digital Ground Separated Bulk Bias for DPLL
Digital Power Separated Bulk Bias for DPLL (3V Power)
Digital Power (5V Power, I/O PAD)
X'tal oscillator input (16.9344MHz)
X'tal oscillator output
Digital Ground (I/O PAD)
EFM signal input
CLV Servo locking status output
LPF time constant control of the spindle servo error signal
Phase control output for Spindle Motor drive
Speed control output for Spindle Motor drive
Word clock output (Normal Speed : 88.2KHz, Double Speed : 176.4KHz)
Various Data/Clock Input
The Lock status output of frame sync
4.2336MHz clock output
System Reset at 'L'
Latch signal input from Micom
Serial data input from Micom
Serial data receiving clock input from Micom
The internal status output to Micom
Subcode sync signal(S0+S1) output
Subcode-Q data transfering bit clock input
Subcode-Q data serial output
System mute at 'H'
Digital Power (3V Power, Internal Logic)
Digital Ground (Internal Logic)
Digital Power (5V Power, I/O PAD)
Subcode data transfering bit clock
Internal SRAM jitter margin status output
C2 pointer output
Digital audio data output
Serial audio data output (48 slot, MSB first)
Channel clock output
Bit clock output
Bit clock input
Channel clock input
Serial audio data input (48 slot, MSB first)
Digital Ground for DAC
Digital Power for DAC (3V Power)
Right-Channel audio output through DAC
Analog Ground for DAC
Referance Voltage output for bypass
Referance Voltage output for bypass
Analog Power for DAC (3V Power)
Left-Channel audio output through DAC
Analog Power for PLL (3V Power)
1-37
Page 38

MX-GT88
KS9274 (IC601) : CD-MP3 decoder
1.Block diagram
2.Pin function
5
6
10
14
15
20
21
22
24
25
26
27
35
36
37
38
39
44
45
46
47
50
51
52
53-62
63
CD-ROM Decoder MP3 Decoder
DRAM CONTROLLER
44-63 35-39
1M 4bits DRAM
CLK
RESETB
FILTER_0
FILTER_1
PLL_BYPASS
CD_DATA
CD_LRCK
CD_BCK
ACLK
BCLK
LRCK
ADAT
MDAT
MCK
MLAT
MDOUT
MINT
DDAT0
DDAT1
WEB
RASB
DDAT2
DDAT3
CASB
DA9-DA0
OEB
I
System clock input
I
System reset actibe LOW
O
820uF to GND940uF to GND
O
When "HIGH" PLL is bypassed, Tied to LOW in normal operation
I
I
I
I
O
O
O
O
I
Write/Read data from MCU to CD-MP3
I
Data strobe signal from MCU
I
Micom command identifier from MCU to CD-MP3
O
Data from CD-MP3 to MCU
O
Intertupt output to MCU
Data BUS
Data BUS
O
Wtite enable
O
Row address strobe
Data BUS
Data BUS
O
Colume address strobe
O
Address output
O
Control output to make data output to "High-Z" at DRAM
DAC
INTERFACE
HOST MCU INTERFACE
HOST MCU
24-2720-22
KA3082 (IC401, IC402) : DC motor driver
1.Pin layout 2.Pin function
Pin No.
BIAS
1234
GND
V
O1
1-38
DRIVER OUT
PRE DRIVER
LOGIC SWITCH
678910
V
V
Z1
CTL
5
V
IN1VIN2
SV
CC
TSD
PV
CC
V
V
O2
Z2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Symbol
GND
VO1
VZ1
VCTL
VIN1
VIN2
SVCC
PVCC
VZ2
VO2
Function
I/O
Ground
Output 1
O
Phase compensation
Motor speed control
I
Input 1
I
Input 2
I
Supply voltage (Signal)
Supply voltage (Power)
Phase compensation
Output 2
O
Page 39

TDA7442D (EIC01) : Audio processor
1.Pin layout
MX-GT88
R_IN3
R_IN2
R_IN1
L_IN1
L_IN2 V
L_IN3
L_IN4
MUXOUTL
IN(L)
MUXOUT(R)
IN(R)
BIN(R)
BOUT(R)
BIN(L)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2.Block diagram
MUXOUT(L)
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
L-IN1
L-IN2
L-IN3
L-IN4
R-IN1
R-IN2
R-IN3
R-IN4
4
50K
5
50K
6
50K
7
50K
3
50K
2
50K
1
50K
28
50K
31.5dB
control
31.5dB
control
MUXOUT(R)
+
2.2 F
+
2.2 F
28
R_IN4
27
LOUT
26
ROUT
25
AGND
24
S
CREF23
SDA
22
SCL
21
DIG-GND
20
TREBLE(R)
19
TREBLE(L)
18
PS1
17
LP
16
15
BOUT(L)
100nF
IN(L)
98
30K
SYMULATED
L+R
30K
1110
IN(R)
PS1
17
RPS1
PS1
90Hz
MUSIC/
SYMULATED
SUPPLY
AGND
CREF
MIXING
AMP
MIXING
AMP
22 F
MUSIC
-
L-R
+
OFF
LPF
EFFECT
9KHz
CONTROL
24 25 2316
LP
V
S
1.2nF
5.6nF
TREBLE-L
18
OFF
SURR
TREBLE
TREBLE
SURR
OFF
Vref
TREBLE-R
5.6nF
5.6K
100nF
100nF
BIN(L)
BOUT(L)
15
14
RB
FIX
BASS
I2C BUS DECODER + LATCHES
BASS
12
BIN(R) BOUT(R)
100nF 100nF
5.6K
FIX
VAR
RB
1319
79dB CONTROL
-
VAR
+
FIX
+
-
SPKR
ATT
MUTE
SPKR
ATT
MUTE
79dB CONTROL
D98AU947A
27
LOUT
21
SCL
22
SDA
20
DIG GND
26
ROUT
BA4560 (FIC02) : Dual op amp.
1.Pin layout
OUT1
– IN1
+ IN1
V
1
2
1ch
+
–
3
EE
4
+
2ch
8
7
6
–
5
V
CC
OUT2
– IN2
+ IN2
1-39
Page 40

MX-GT88
L4959 (PIC02) : Voltage regulator
1.Pin layout
TAB CONNECTED TO PIN 6
2.Block diagram
2/10
V
S
EN 8V
EN 12V(a)
EN 12V(b)
8
7
5
REF
GEN
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
D97AU716A
OUT 12V(a)
V
S
OUT 8.6V
EN 8.6V
EN 12V(a)
GND
EN 12V(b)
N.C.
OUT 5.6V
V
S
OUT 12V(b)
5.6V, 250mA
3
OUT 5.6V
REGULATOR
8.6V, 600mA
REGULATOR
9
OUT 8.6V
SWITCHED
12V, 800mA
REGULATOR
11
OUT 12V(a)
SWITCHED
12V, 1.3A
REGULATOR
1
OUT 12V(b)
SWITCHED
1-40
D97AU569C
3.Pin function
Pin Pins Description
1 OUT 12V (b) 12V/1.3A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
2V
S
3 OUT 5.6V 5.6V/250mA OUTPUT VOLTAGE
4 N.C. not connected
5 EN 12V (b) Enable 12V/1.3A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
6 GND Ground
7 EN 12V (a) Enable 12V/0.8A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
8 EN 8.6V Enable 8.6V/0.6A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
9 OUT 8.6 8.6V/0.6A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
10 V
S
11 OUT 12V (a) 12V/0.8A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
Supply Voltage
Supply Voltage
GND
6
Page 41

M11L1644 (IC602) : DRAM
1. Block diagram
MX-GT88
WE
RAS
CAS
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
CONTROL
CLOCK
GENERATOR
COLUMN
11
ADDRESS
BUFFER
REFRESH
CONTROLLER
REFRESH
COUNTER
11
ADDRESS
BUFFERS(11)
LOGIC
11
ROW
DATA-IN BUFFER
I/O0
.
.
4
I/O3
DATA-OUT
11
COLUMN
BUFFER
CE
DECODER
2048
4
4
SENSE AMPLIFIERS
I/O RATING
2048 x 4
2048 x 2048 x 4
2048
ROW
11
DECODER
MEMORY
ARRAY
2. Pin function
Pin No.
3~11, 14~19, 7
5
21
4
20
2, 3,22, 23
1, 12
13, 24
6
Symbol
A0~A10
RAS
CAS
WE
OE
I/O0~I/O3
Vcc
Vss
NC
I/O
I/O
Vdd GENERATOR
Function
Address Input
Row Address : A0~A10
I
Column Address : A0~A10
Row Address Strobe
I
Column Address Strobe
I
Write Enable
I
Output Enable
I
Data Input/ Ountput
Power (5V or 3.3V)
Ground
-
No Connect
Vcc
Vss
1-41
Page 42

MX-GT88
STK403-070 (FIC01) : Power amp.
1.Pin layout
Ch1
+Vcc
2
2.Block diagram
2
out
Ch1
out
41
3
Ch2
out
5
Ch2
out
6
Ch1
10
Ch1
IN
NF
11
+TRE8SUB9GND-Vcc
7
ST-BY
12
Ch2
NF
13
Ch2
IN
14
7
10
11
Pre Driver IC
CH1
R1
R2
C1
1
SUB
STK412-020 (WIC01) : Power amp.
1.Block diagram
13
TR1 TR4
R5
TR3
R6
TR2
3489 6 125
R8
TR5
R7
TR6
R3
R4
C2
Bias Circuit
1817
Pre Driver IC
CH2
TR41
R41
14
13
1
1-42
14
15
16
TR1
TR3
C2
R4
R5
D1
TR6
R6
R3
R7
TR8
TR7
TR9
TR10
9 118
TR19
TR18
TR20
1012
D2
TR2 TR12
R1
C1
TR4
TR5
R2
TR17
R17
R13
TR16
R16
R14
R15
C12
D12
R11
TR14
TR11
C11
TR13
TR15
R12
D41
D51
TR51
Comaprator
SUB
Comaprator
R51
D42
D43
D53
D52
3
2
7
5
4
6
Page 43

PT8300 (UIC03, UIC04) : DRAM
1.Pin layout
MX-GT88
1
VSS
CLK
LATCH
P15
P14
P13
P12
P11
P10
P9
P8
CLK0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
/RESET
LATCH0
2.Block diagram
PULLUP
27
28
VDD
VSS
1
4
LATCH
CLK
3
26
DI1
/RESET
2
/RESET
CLKO
14
16
DI2
LATCH0
DO2
DO1
13
25
15
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
VDD
PULLUP
DI1
DO2
P0
P1
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6
P7
DI2
DO1
LATCH
RESET
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 P11 P12 P13 P14 P15
CLK
DI
CLK
DI
O0
I0
Q0
RESET
D0
LATCH 16-BIT
SHIFT REGISTER1: 16-BIT SHIFT REGISTER SERIAL TO PARALLEL
SHIFT REGISTER2: 16-BIT SHIFT REGISTER SERIAL TO PARALLEL
O7 O8
I7 I8
O15
I15
Q15
DO
D15
DO
3. Pin function
Pin No.
Pin Name
1
2
/RESET
3
4
5-12
13
14
15,25
26,17
17-24
27
LATCH
P15~P8
LATCHO
CLKO
DO1, DO2
DI1, DI2
P7~P0
PULLUP
28
VSS
CLK
VDD
I/O
Function
-
Ground
I
Reset pin
I
Clock input pin
I
Latch input pin
I/O
Parallel data I/O pins
O
Latch output pin
O
Clock output pin
O
Serial data output pins
I
Serial data input pins
O
Parallel data output pin
I
P8 to P15 control pin for internal pull-up resistor
When P8 to P15 are in the output state, the PULLUP pin must be connected to VDD.
When P8 to P15 are in the input state, the PULLUP pin must be connected to VSS.
-
Power supply pin
1-43
Page 44

MX-GT88
LA72723(IC03) : RDS demodulation
1. Pin layout
VREF
MPXIN
Vdda
Vssa
FLOUT
CIN
TES
XOUT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2. Block Diagram
Vdda
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
Vssa
MPXIN
ANTI ALIASING
FILTER
RDS-ID/READY
16
RDCL
15
RDDA
14
RST
13
MODE
12
Vddd
11
Vssd
10
XIN
9
57kHz
BPF
(SCF)
FLOUTVREF
VREF
SMOOTHING
FILTER
CIN
+
-
PLL
(57kHz)
CLOCK
RECOVERY
(1187.5Hz)
DATA
DECODER
RAM
(128-bits)
Vddd
Vssd
RDDA
RDCL
MODE
TEST
3. Pin functions
Pin
Symbol
No.
1
VREF
2
MPXIN
Vdda
3
4
Vssa
5
FLOUT
6
CIN
TEST
7
8
XOUT
9
XIN
10
Vssd
11
Vddd
12
MODE
13
14
15
16
RST
RDDA
RDCL
RDS-ID
READY
TEST
I/O
O
O
O
O
I/O
O
CLK(4.332MHz)
OSC
XIN XOUT
RDS-ID
DETECT
RST
RDS-ID/
READY
Function
Reference voltage output (Vdda/2)
I
Baseband (multiplexed) signal input
Analog power supply (+5V)
Analog ground
Subcarrier input (filter output)
I
I
Subcarrier input (comparator input)
Test input
Crystal oscillator output (4.332MHz)
I
Crystal oscillator input (exeternal reference input)
Digtal ground
Digtal power supply
I
I
Read mode setting (0:master,1:slave)
RDS-ID/RAM reset (positive polarity)
RDS data output
RDS clock output (master mode)/RDS clock input (slave mode)
RDS-ID/READY output (negative polarity)
1-44
Page 45

< MEMO >
MX-GT88
1-45
Page 46

MX-GT88
VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LIMITED
AV & MULTMEDIA COMPANY AUDIO/VIDEO SYSTEM CATEGORY 10-1,1 chome,Ohwatari-machi,maebashi-city,371-8543,Japan
(No.22075)
Printed in Japan
200307
 Loading...
Loading...