Page 1
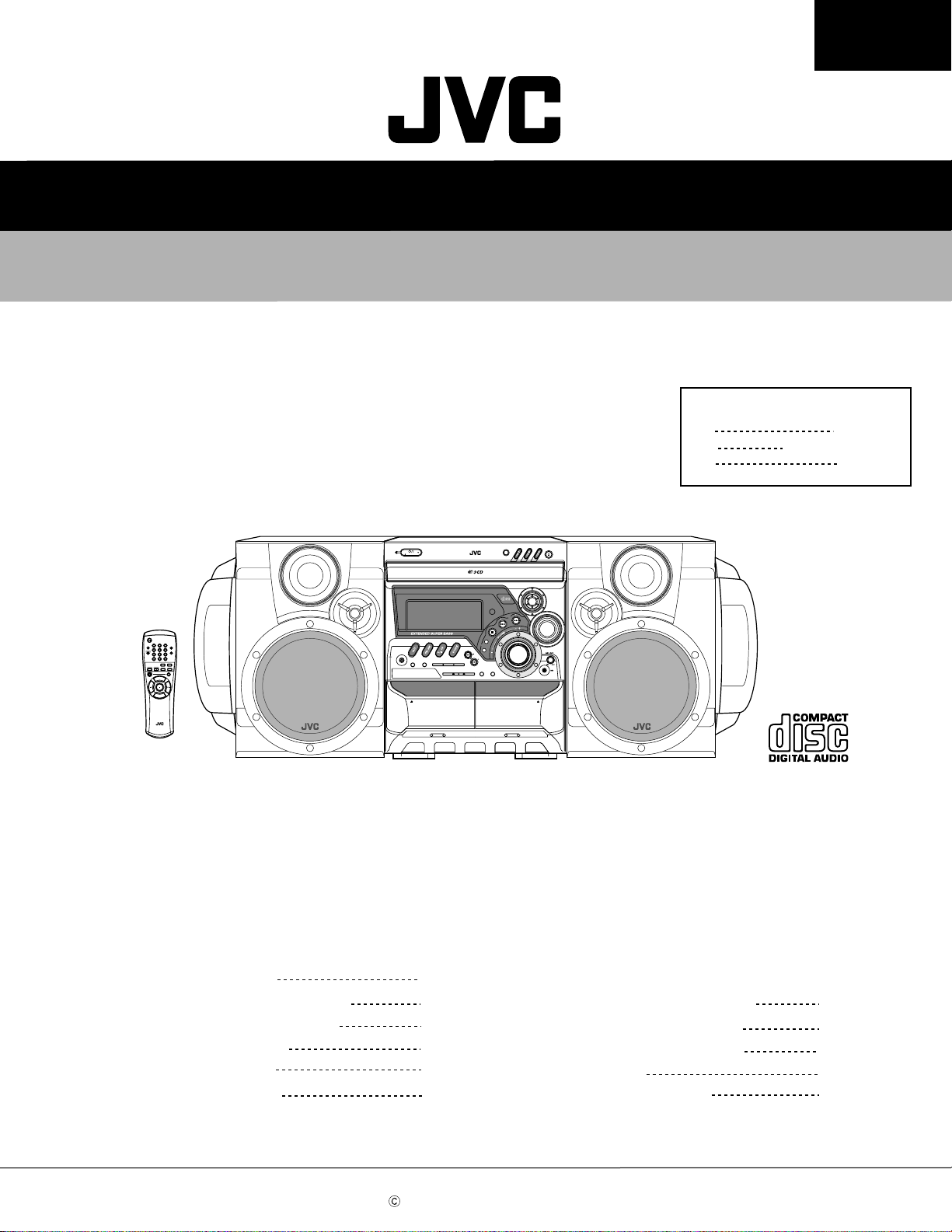
SERVICE MANUAL
COMPACT COMPONENT SYSTEM
Area Suffix
MX-G50
US
UW
UY
MX-G50
Singapore
Brazil,Mexico,Peru
Argentina
STANDBY/ON
SUBWOOFER
12
3
SLEEP
LEVEL
456
SOUND
AUX
MODE
78
9
FM MODE
+10
10
zzzzz
ECHO
FADE
TAPE
FM/AM
TAPE A/B
MUTING
DISC SKIP
CD
/
+
VOLUME
VOLUME
–
RM–SMXG50U REMOTE CONTROL
SP-MXG50
(No MIC jack and MIC LEVEL volume for UY ver.)
Contents
Safety Precautions
Important for laser products
Preventing static electricity
Disassembly method
Wiring connection
Adjustment method
STANDBY
STANDBY/ON
PHONES
COMPU PLAY CONTROL
COMPACT COMPONENT SYSTEM
CLOCK
DISPLAY
/
TIMER
REPEAT PROGRAM
REC START
/STOPCDREC START
EJECT
FULL - LOGIC CONTROL
PLAY
A
1-2
1-3
1-4
1-5
1-20
1-21
DISC CHANGE
PLAY & EXCHANGE
MX-G50
CANCEL
/DEMO
TUNING
RANDOM
TAPE A
DUBBING
CD SYNCHRO RECORDING
CD-R/RW PLAYBACK
SOUND
MODE
COMPACT
DIGITAL AUDIO
SUBWOOFER
PRESET
SET
TAPE B
LEVEL
EJECT
REC/PLAY
B
SP-MXG50CA-MXG50
Flow of functional operation
until TOC read
Maintenance of laser pickup
Replacement of laser pickup
Trouble shooting
Description of major ICs
1-25
1-26
1-26
1-27
1-30~43
COPYRIGHT 2001 VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LTD.
No.20978
Jul. 2001
Page 2
MX-G50
1. This design of this product contains special hardware and many circuits and components specially for safety
purposes. For continued protection, no changes should be made to the original design unless authorized in
writing by the manufacturer. Replacement parts must be identical to those used in the original circuits. Services
should be performed by qualified personnel only.
2. Alterations of the design or circuitry of the product should not be made. Any design alterations of the product
should not be made. Any design alterations or additions will void the manufacturer`s warranty and will further
relieve the manufacture of responsibility for personal injury or property damage resulting therefrom.
3. Many electrical and mechanical parts in the products have special safety-related characteristics. These
characteristics are often not evident from visual inspection nor can the protection afforded by them necessarily
be obtained by using replacement components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Replacement parts which
have these special safety characteristics are identified in the Parts List of Service Manual. Electrical
components having such features are identified by shading on the schematics and by ( ) on the Parts List in
the Service Manual. The use of a substitute replacement which does not have the same safety characteristics
as the recommended replacement parts shown in the Parts List of Service Manual may create shock, fire, or
other hazards.
4. The leads in the products are routed and dressed with ties, clamps, tubings, barriers and the like to be
separated from live parts, high temperature parts, moving parts and/or sharp edges for the prevention of
electric shock and fire hazard. When service is required, the original lead routing and dress should be
observed, and it should be confirmed that they have been returned to normal, after re-assembling.
5. Leakage currnet check (Electrical shock hazard testing)
After re-assembling the product, always perfor m an isolation check on the exposed metal parts of the product
(antenna terminals, knobs, metal cabinet, screw heads, headphone jack, control shafts, etc.) to be sure the
product is safe to operate without danger of electrical shock.
Do not use a line isolation transformer during this check.
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Using a "Leakage Current Tester", measure the leakage
current from each exposed metal parts of the cabinet, particularly any exposed metal part having a return
path to the chassis, to a known good earth ground. Any leakage current must not exceed 0.5mA AC (r.m.s.).
Alternate check method
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Use an AC voltmeter having, 1,000 ohms per volt or more
sensitivity in the following manner. Connect a 1,500 10W resistor paralleled by a 0.15 F AC-type capacitor
between an exposed metal part and a known good earth ground.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor with the AC
voltmeter.
Move the resistor connection to each exposed metal part,
particularly any exposed metal part having a return path to
the chassis, and meausre the AC voltage across the resistor.
Now, reverse the plug in the AC outlet and repeat each
measurement. Voltage measured any must not exceed 0.75 V
AC (r.m.s.). This corresponds to 0.5 mA AC (r.m.s.).
0.15 F AC TYPE
1500 10W
Good earth ground
AC VOLTMETER
(Having 1000
ohms/volts,
or more sensitivity)
Place this
probe on
each exposed
metal part.
!
1. This equipment has been designed and manufactured to meet international safety standards.
2. It is the legal responsibility of the repairer to ensure that these safety standards are maintained.
3. Repairs m ust be made in accordance with the relevant safety standards.
4. It is essential that safety critical components are replaced by approved parts.
5. If mains voltage selector is provided, check setting for local voltage.
Burrs formed during molding may
be left over on some parts of the
chassis. Therefore, pay attention to
such burrs in the case of
preforming repair of this system.
In regard with component parts appearing on the silk-screen pr inted side (parts side) of the PWB diagrams, the
parts that are printed over with black such as the resistor ( ), diode ( ) and ICP ( ) or identified by the " "
mark nearby are critical for safety.
When replacing them, be sure to use the parts of the same type and rating as specified by the manufacturer.
(Except the J and C version)
1-2
Page 3
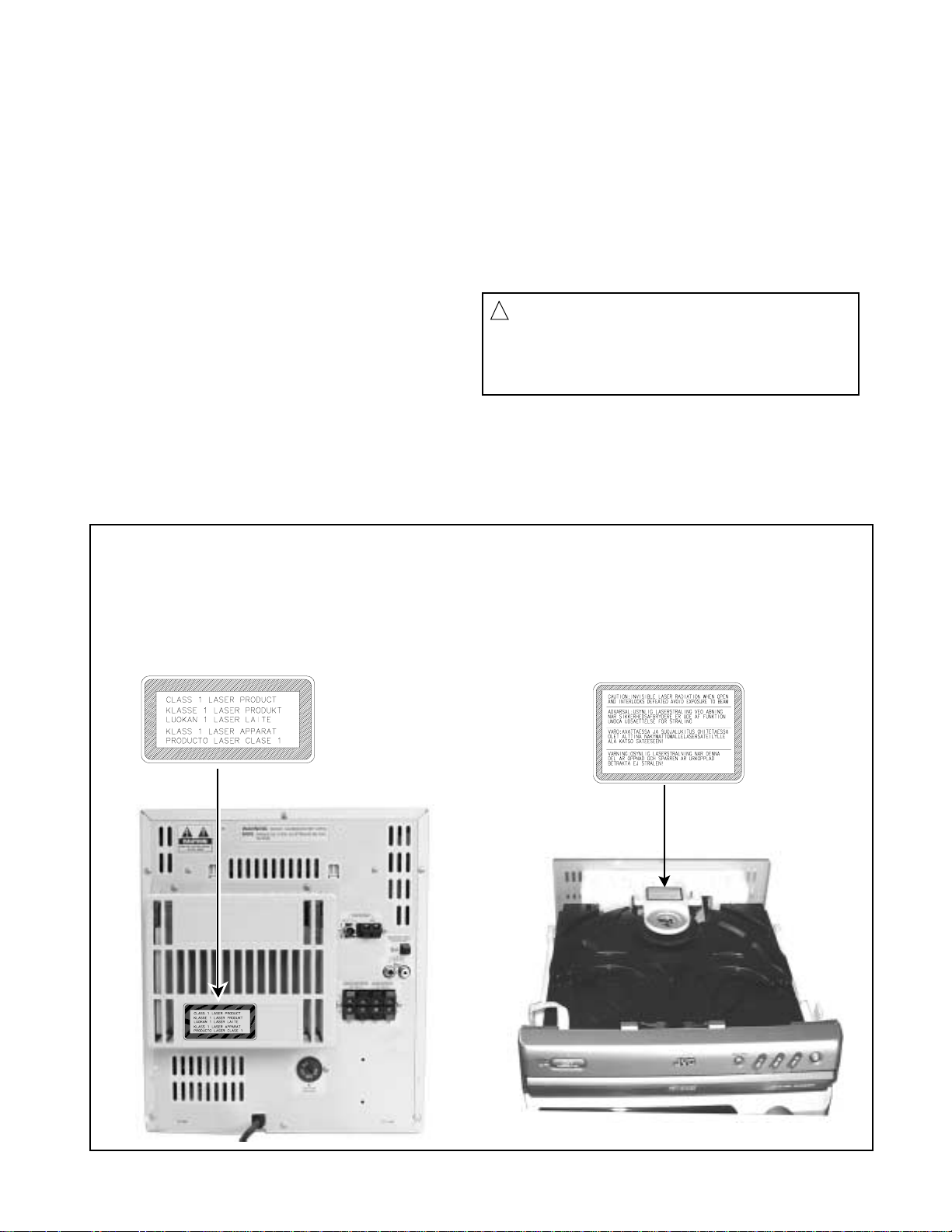
Important for laser products
MX-G50
1.CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
2.DANGER : Invisible laser radiation when open and inter
lock failed or defeated. Avoid direct exposure to beam.
3.CAUTION : There are no serviceable parts inside the
Laser Unit. Do not disassemble the Laser Unit. Replace
the complete Laser Unit if it malfunctions.
4.CAUTION : The compact disc player uses invisible
laserradiation and is equipped with safety switches
whichprevent emission of radiation when the drawer is
open and the safety interlocks have failed or are de
feated. It is dangerous to defeat the safety switches.
Reproduction and position of labels
5.CAUTION : If safety switches malfunction, the laser is able
to function.
6.CAUTION : Use of controls, adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result in
hazardous radiation exposure.
CAUTION
!
Please use enough caution not to
see the beam directly or touch it
in case of an adjustment or operation
check.
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
WARNING LABEL
1-3
Page 4
MX-G50
Preventing static electricity
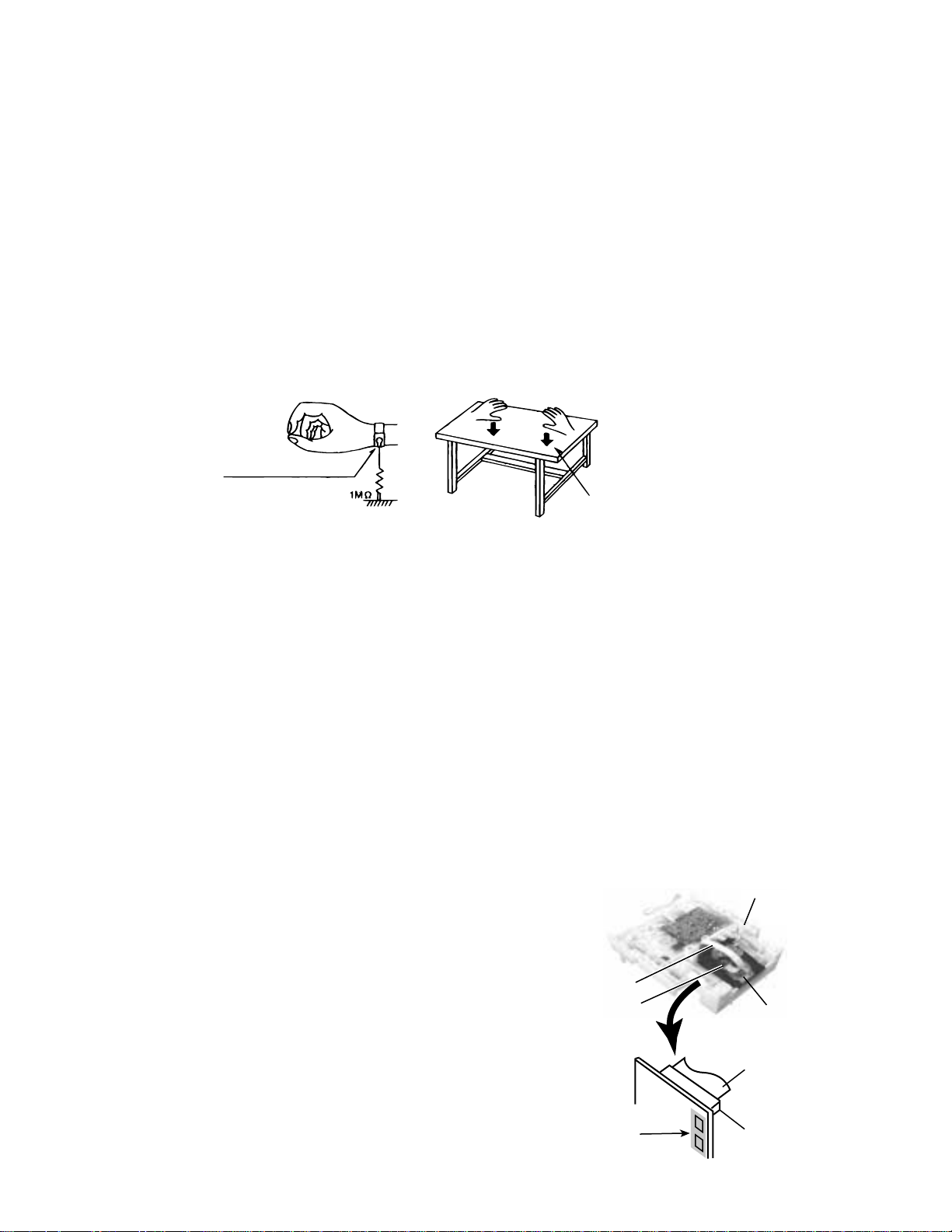
1. Grounding to prevent damage by static electricity
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), which occurs when static electricity stored in the body, fabric, etc. is discharged,
can destroy the laser diode in the traverse unit (optical pickup). Take care to prevent this when performing repairs.
2. About the earth processing for the destruction prevention by static electricity
In the equipment which uses optical pick-up (laser diode), optical pick-up is destroyed by the static electricity of
the work environment.
Be careful to use proper grounding in the area where repairs are being performed.
2-1 Ground the workbench
Ground the workbench by laying conductive material (such as a conductive sheet) or an iron plate over
it before placing the traverse unit (optical pickup) on it.
2-2 Ground yourself
Use an anti-static wrist strap to release any static electricity built up in your body.
(caption)
Anti-static wrist strap
Conductive material
(conductive sheet) or iron plate
3. Handling the optical pickup
1. In order to maintain quality during transport and before installation, both sides of the laser diode on the
replacement optical pickup are shorted. After replacement, return the shorted parts to their original condition.
(Refer to the text.)
2. Do not use a tester to check the condition of the laser diode in the optical pickup. The tester's internal power
source can easily destroy the laser diode.
4. Handling the traverse unit (optical pickup)
1. Do not subject the traverse unit (optical pickup) to strong shocks, as it is a sensitive, complex unit.
2. Cut off the shorted part of the flexible cable using nippers, etc. after replacing the optical pickup. For specific
details, refer to the replacement procedure in the text. Remove the anti-static pin when replacing the traverse
unit. Be careful not to take too long a time when attaching it to the connector.
3. Handle the flexible cable carefully as it may break when subjected to strong force.
4. It is not possible to adjust the semi-fixed resistor that adjusts the laser power. Do not turn it
Attention when CD mechanism assembly is decomposed
*Please refer to "Disassembly method" in the text for pick-up and how to
detach the CD mechanism assembly.
1. Remove the CD changer unit.
2. Remove the CD changer mechanism.
3. Solder is put up before the card wire is removed from the pickup unit
connector on the CD mechanism assembly.
(When the card wire is removed without putting up solder, the CD pick-up
assembly might destroy.)
4. Please remove solder after connecting the card wire with the pickup unit
connector when you install picking up in the substrate.
Card wire
Pickup unit
connector
Soldering
Fig.2
CD changer unit
Fig.1
Card wire
Pickup unit
connector
CD changer
mechanism
1-4
Page 5
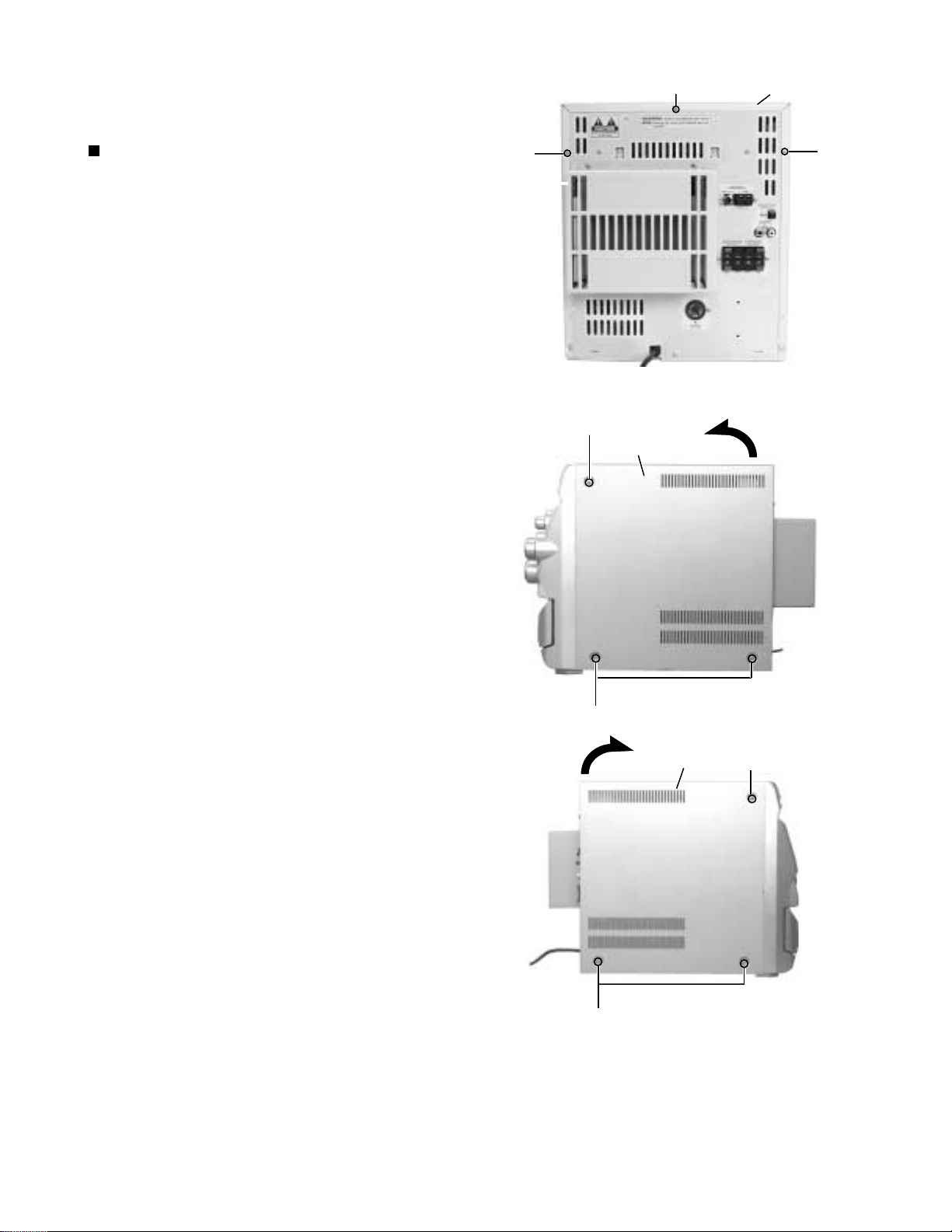
MX-G50
Disassembly method
<Main body>
Removing the metal cover
(See Fig.1 to 3)
1.
Remove the three screws A attaching the metal
cover on the back of the body.
2.
Remove the six screws B attaching the metal cover
on both sides of the body.
3.
Remove the metal cover from the body by lifting the
rear part of the cover.
ATTENTION:
Do not break the front panel tab fitted
to the metal cover.
A
B
A
Fig.1
Metal cover
Metal cover
A
B
B
Fig.2
Metal cover
Fig.3
B
1-5
Page 6
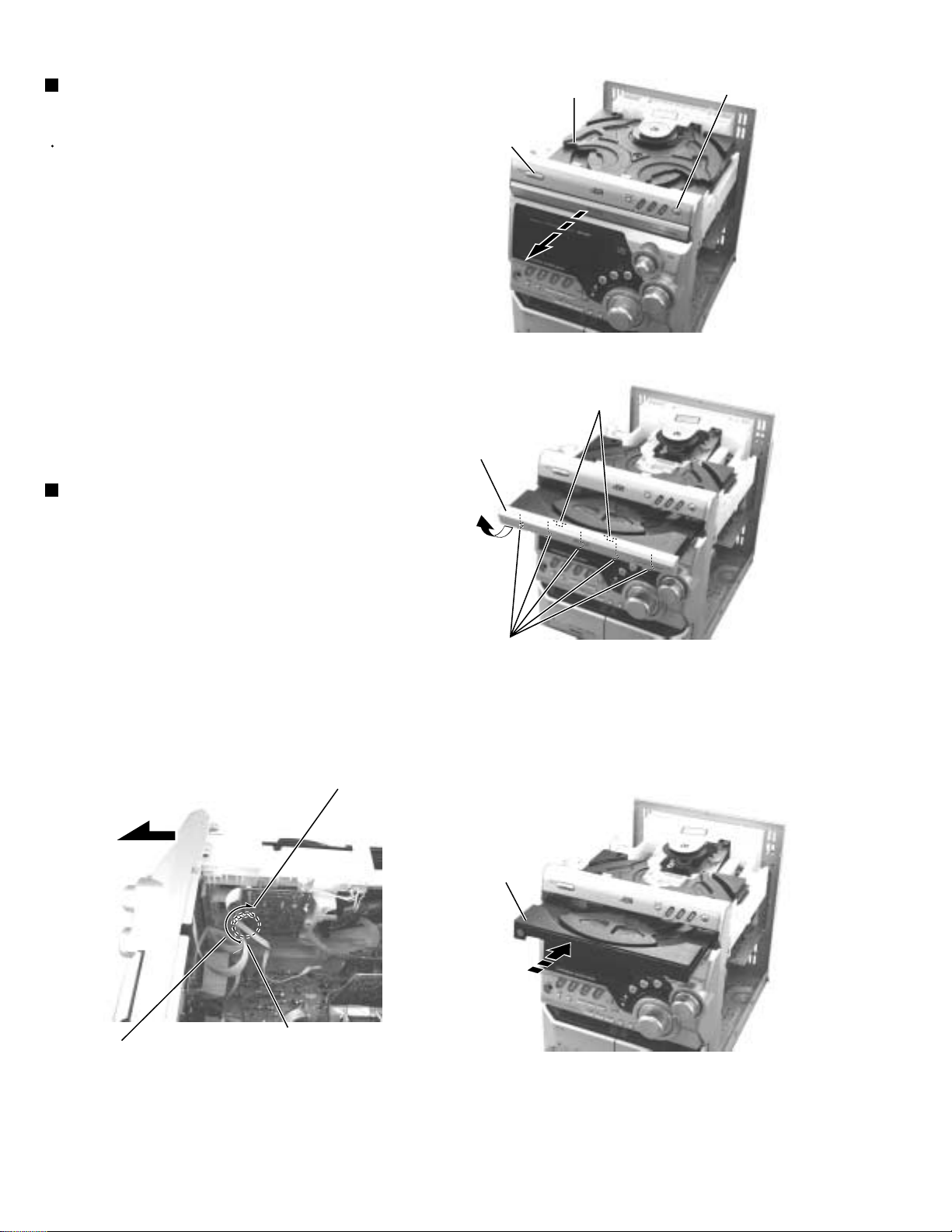
MX-G50
Removing the CD Tray fitting (1)
(See Fig. 4 to 6)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover.
1.
Press the POWER button. Press the OPEN/CLOSE
button to eject the CD tray.
2.
After drawing the lower part of the tray fitting toward
the front, remove the five claws a. Then, while
moving the tray fitting upward, remove it.
3.
Press the OPEN/CLOSE button to insert the tray.
Removing the CD Tray fitting (2)
(See Fig. 5 to 7)
POWER button
CD tray fitting
CD tray
OPEN/CLOSE button
Fig.4
Joint
- How to eject the CD tray without turning on power -
1.
Turn the black loading pulley gear marked b from the
back of the CD changer unit as shown in Fig.7 and
draw the CD tray toward the front.
2.
After drawing the lower part of the tray fitting toward
the front, remove the five claws a. Then, while
moving the tray fitting upward, remove it.
3.
Push and insert the CD tray manually.
(See Fig. 24)
Claw a
Fig.5
CD tray
(Loading pulley gear)
b
1-6
This slot of the board.
Fig.7
Fig.6
Page 7
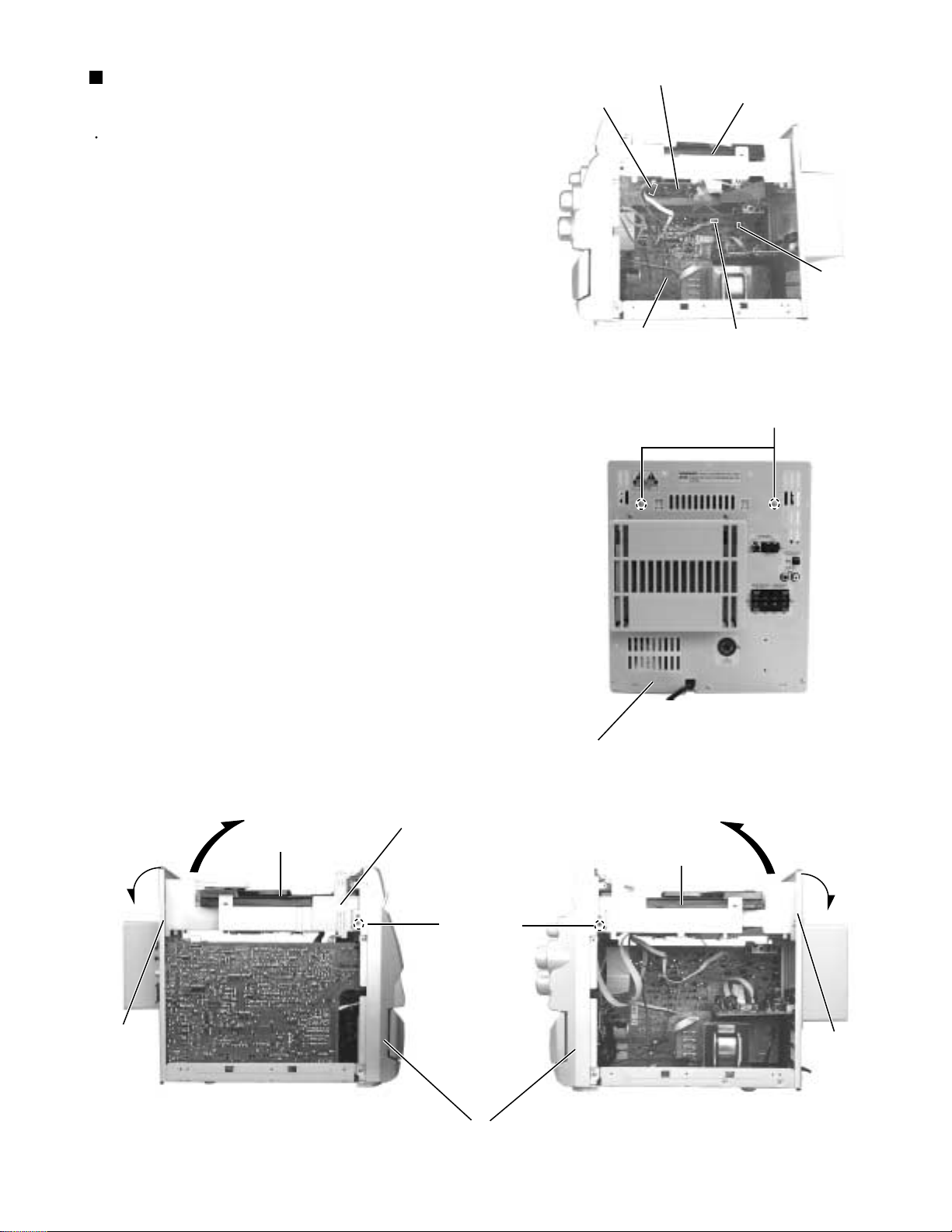
MX-G50
Removing the CD changer unit
(See Fig.8 to 10)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover.
1.
Disconnect the card wire which is attached with
adhesive to the left side of the CD changer unit.
2.
Disconnect the card wire from connector CW105 of
the CD servo board on the back of the CD changer
unit.
3.
Disconnect the harness from connector RCW6 &
OCW on the inner side of the main board in the
body.
4.
Remove the two screws C attaching the CD changer
unit on the back of the body.
5.
Remove the two screws D attaching the CD changer
unit on the both side of the body.
CD servo board
CW105
Main board
CD changer unit
OCW
RCW6
Fig.8
C
6.
Draw the CD changer unit upward from behind while
pulling the rear panel outward.
Adhesive card wire strap
CD changer unit
D
Rear panel
Fig.9
CD changer unit
D
Rear panel
Rear panel
Fig.10 aFig.10 b
Front panel assembly
1-7
Page 8
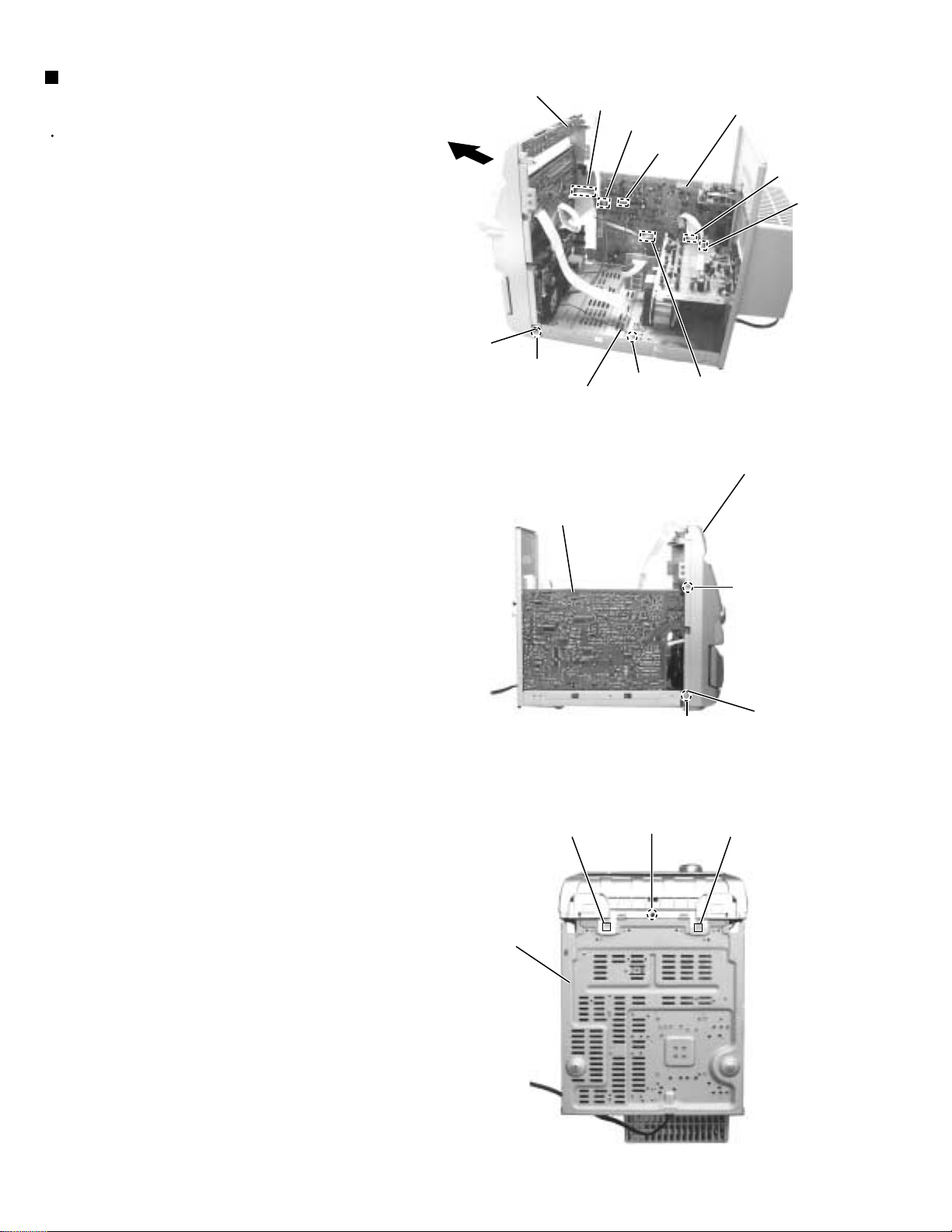
MX-G50
Removing the front panel assembly
(See Fig.11 to 13)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover and the CD changer unit.
1.
Disconnect the card wire from connector FCW3 and
the harness from connector JCW1, JCW2 and
HCW3 on the inner side of the main board in the
body.
2.
Remove the two screws E attaching the front panel
assembly on both sides of the body.
3.
Remove the screw F attaching the earth terminal
extending from the cassette mechanism assembly.
4.
Remove the screw G attaching the front panel
assembly and main board.
5.
Remove the screw H attaching the front panel
assembly on the bottom of the body.
6.
Release the two joints c on both sides and two joints
d on the bottom of the body using a screwdriver.
Front panel assembly
Joint c
E
earth wire
Main board
FCW3
JCW2
F
Fig.11
Main board
JCW1
ACW1
ACW2
HCW3
Front panel assembly
Bottom side
Joint d
Fig.12
H
E
G
Joint c
Joint d
1-8
Fig.13
Page 9
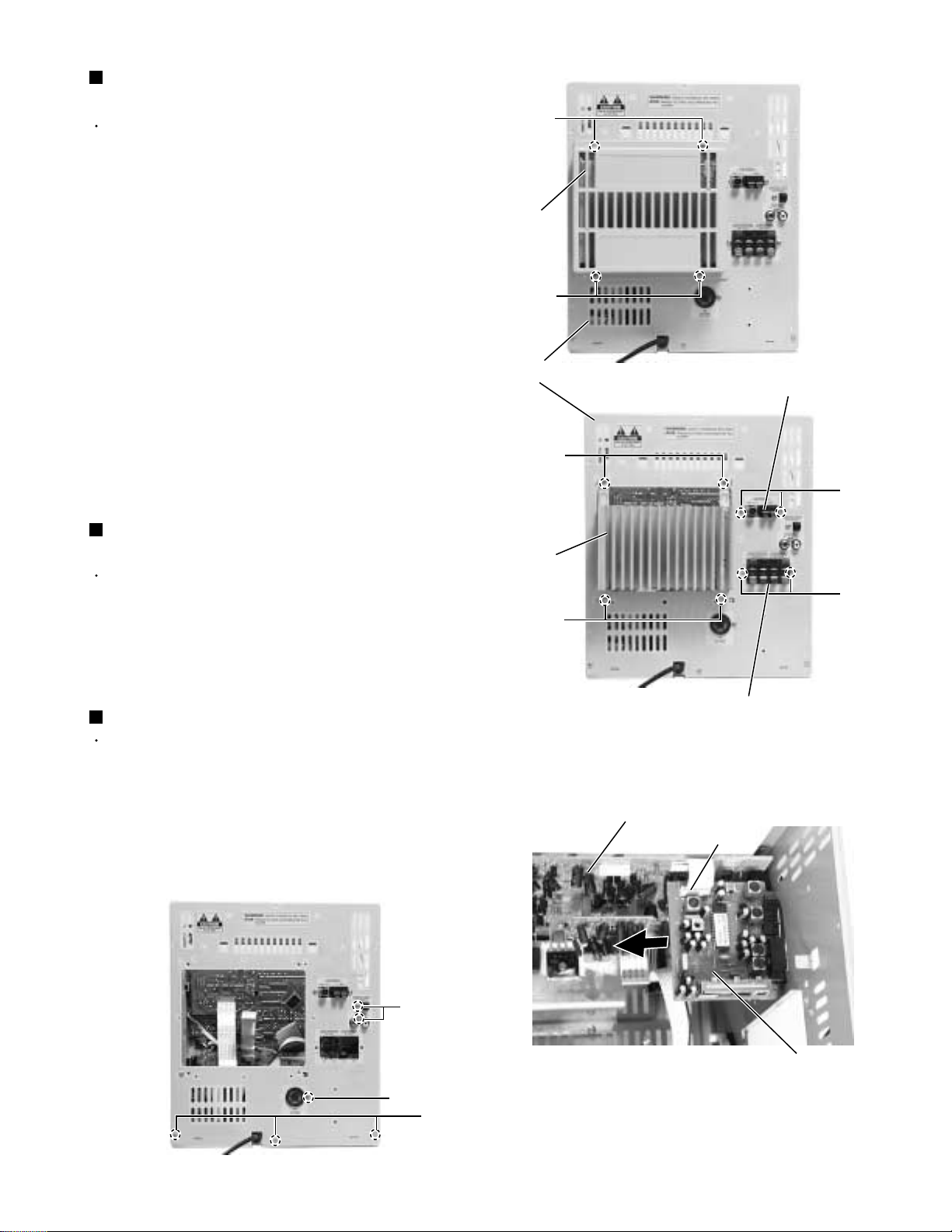
Removing the heat sink & amp. board
(See Fig.14 and 15)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover and the CD changer unit.
1.
Remove the four screws I attaching the heat sink
cover on the back of the body. Remove the heat sink
cover.
2.
Remove the four screws J attaching the heat sink &
amp. board to the rear panel on the back of the
body.
3.
Remove the two screws K attaching the speaker
terminal to the rear panel on the back of the body.
4.
Disconnect the card wire from connector ACW1 and
the harness from connector ACW2 on the amp.
board. (See Fig.11)
I
Heat sink
cover
I
Rear panel
Fig.14
MX-G50
Tuner terminal
5.
After moving the heat sink upward, remove the
claws. Then pull out the heat sink & AMP board
inward.
Removing the tuner board
(See Fig.15 and 16)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover and CD changer unit.
1.
Disconnect the card wire from connector CON01 on
the tuner board.
2.
Remove the two screws L attaching the tuner board.
Removing the rear cover (See Fig.17)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit, heat sink & amp.
board and tuner board.
1.
Remove the five screws M attaching the rear panel.
2.
Remove the screw M' attaching the voltage selector.
(Only US/ UW)
J
L
Heat sink
K
J
Speaker terminal
Fig.15
Main board
CON01
Fig.17
M'
M
M
Fig.16
Tuner board
1-9
Page 10
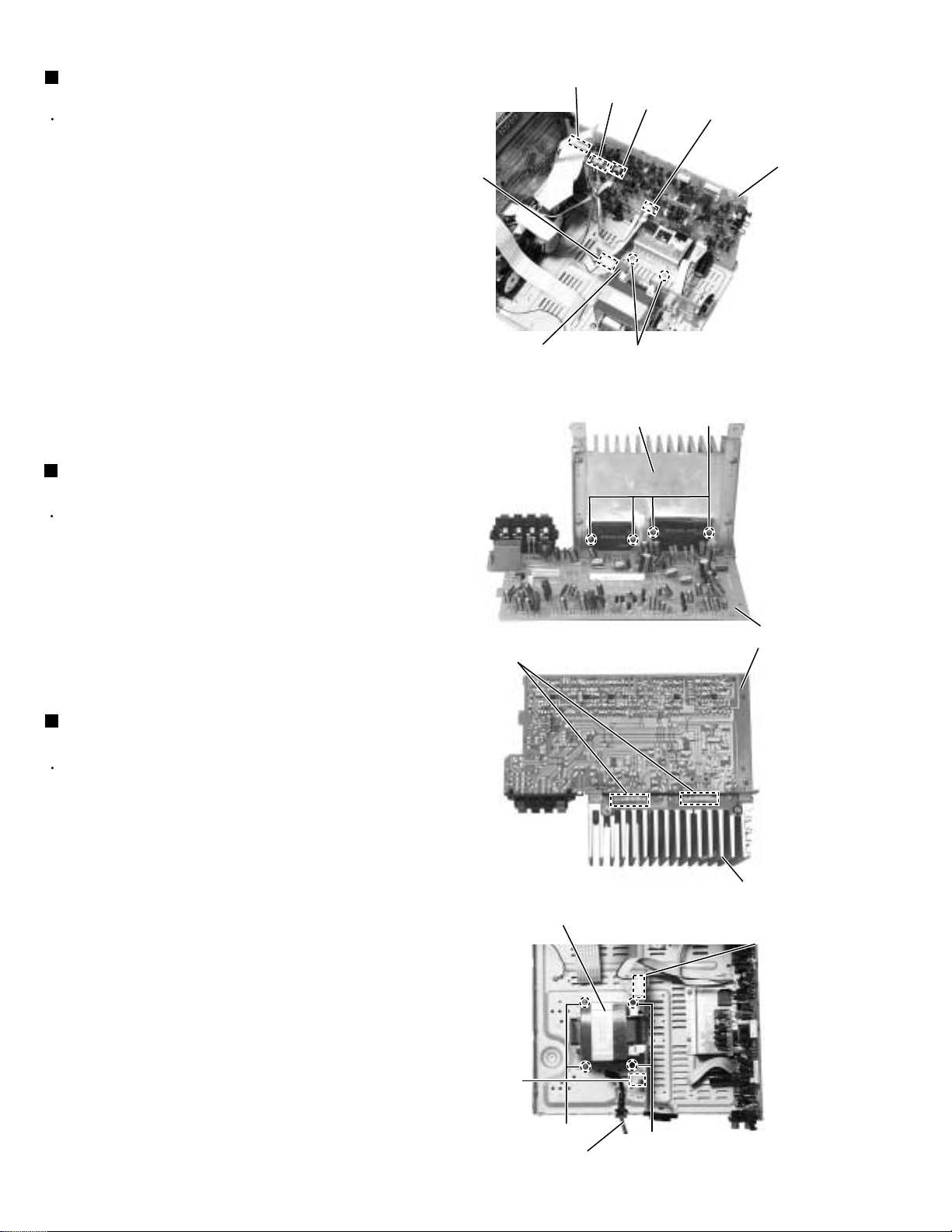
MX-G50
Removing the main board
(See Fig. 18)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit, heat sink & amp.
board tuner board and rear cover.
1.
Disconnect the card wire from connector FCW3 and
the harness from connector JCW1, JCW2 and
HCW3 on the main board.
2.
Disconnect the harness from connector PCW1 on
the power transformer board.
3.
Remove the screw G attaching the main board
holder. (See Fig.12)
4.
Remove the two screws N attaching the heat sink
and bottom chassis.
Removing the power ICs
(See Fig.19 and 20)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, CD changer unit and heat sink &
amp. board.
PCW1
Transformer board
FCW3
JCW2
Fig.18
Heat sink
JCW1
N
HCW3
Main board
P
1.
Remove the four screws P attaching the power ICs
to the heat sink.
2.
Unsolder the power ICs solder point.
Removing the power transformer
(See Fig .21)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, heat sink & amp. board, tuner board
and rear cover.
1.
Disconnect the power cord from connector RCW2 of
the power transformer board.
2.
Disconnect the harness from connector PCW1 of the
power transformer board.
3.
Remove the four screws R attaching the power
transformer and the screw S attaching the earth
terminal.
Power ICs solder point
Power transformer
Fig.19
Fig.20
Amp. board
Heat sink
PCW1
1-10
RCW2
R
Power cord
R
Fig.21
Page 11

MX-G50
<Front panel assembly>
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the metal cover, the CD changer unit and the front
panel assembly.
Removing the power / CD switch board
(See Fig.22)
1.
Disconnect the card wire from connector UCW1 on
the power / CD switch board.
2.
Remove the five screws Q attaching the power / CD
switch board.
Removing the FL display & system
control board (See Fig.22)
1.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector UCW3,
UCW4,UCW5 and UCW6 on the FL display &
system control board.
2.
Remove the five screws R attaching the FL display &
system control board.
3.
Disconnect the card wire from the connector UCW2
on the FL display & system control board.
Power / CD switch board
UCW2
UCW3
UCW4
R
UCW1
Q
R
FL display & system
control board
R
UCW5
UCW6
Fig.22
SOUND MODE knob
ACTIVE BASS EX.
LEVEL knob
VOLUME knob
MIC LEVEL knob
(Only US/ UW)
Removing the front board
(See Fig.23 and 24)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the FL display & system control board.
1.
Pull out the SOUND MODE knob, ACTIVE BASS
EX. LEVEL knob, VOLUME knob and MIC LEVEL
knob(Only US/ UW) from front side.
2.
Remove the ten screws S attaching the front board
and release the two tabs e out ward.
Removing the headphone board & mic
jack board (See Fig.24)
Prior to performing the following procedure remove
the FL display & system control board.
1.
You can pull out the headphone board.
2.
Remove the mic jack board with releasing the tab f.
(Only US/ UW)
Removing the cassette mechanism
assembly (See Fig.24)
Front board
Tab e
Mic jack board
(Only US/ UW)
Tab f
S
Fig.23
S
Headphone
board
S
T
Card wire x
Cassette mechanism assembly
Fig.24
1.
Disconnect the card wire x from the mechanism
board on the cassette mechanism assembly.
2.
Remove the six screws T attaching the cassette
mechanism assembly.
1-11
Page 12
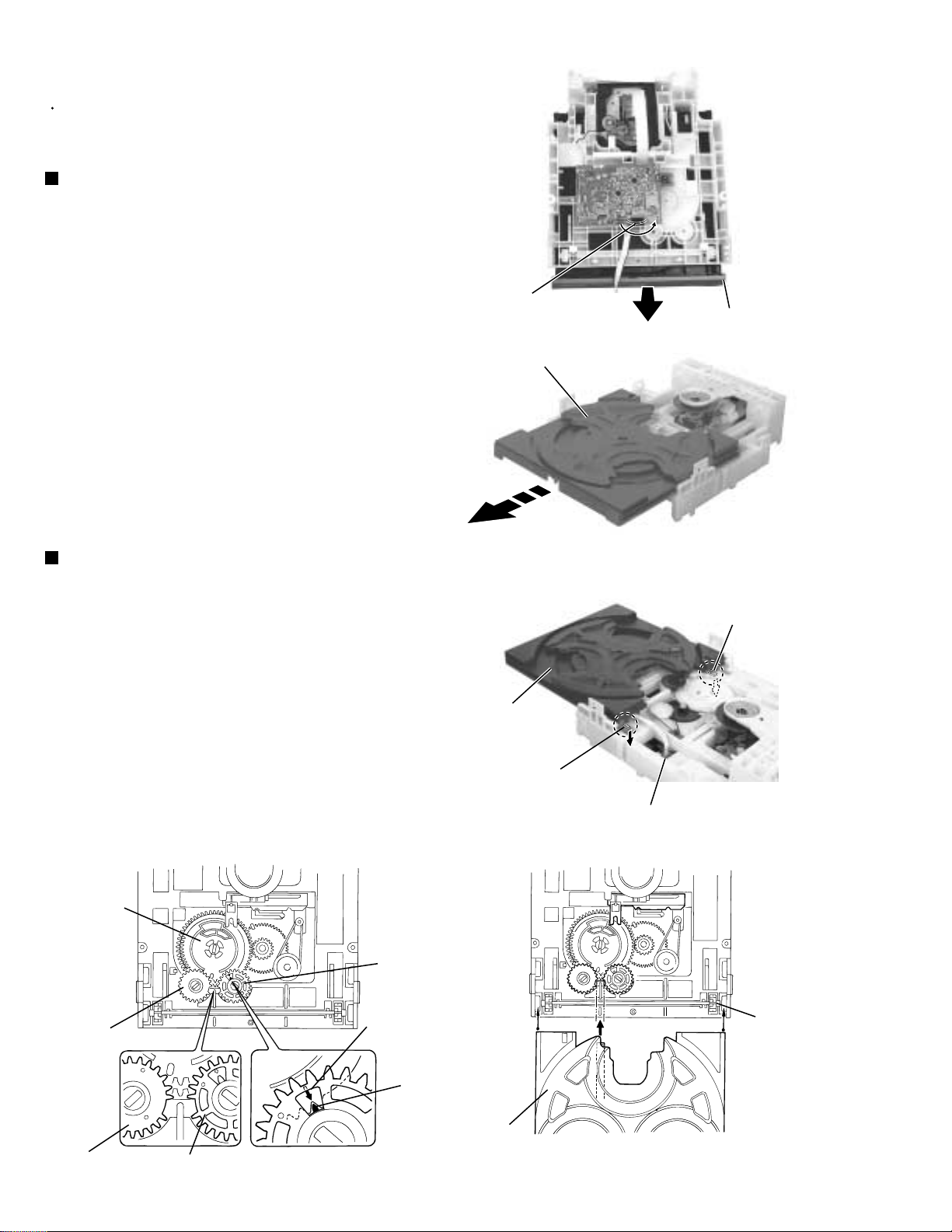
MX-G50
<CD changer unit>
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the CD changer unit.
Removing the CD tray (See Fig.25 to 27)
1.
Turn the black loading pulley gear on the under side
of the CD changer unit in the direction of the arrow
and draw the CD tray toward the front until it stops.
2.
Disconnect the card wire from connector CW103 of
the CD servo board on the upper side of the CD
changer unit.
Loading pulley gear
CD tray
Fig.25
3.
Push down the two tray stoppers marked g and pull
out the CD tray.
Reinstall the CD tray (See Fig.28 to 29)
1.
Align the gear-cam with the gear-tray as shown
fig.27, then mount the CD tray.
2.
When assembling the CD tray, take extreme care not
engage with gear - synchro.
CD tray
Fig.26
g (Tray stopper)
CD tray
g
(Tray stopper)
CD servo board
CW103
Fig.27
Gear-cam
Gear-convert
Gear-convert
1-12
Gear-tray
Gear-tray
Gear-cam
timing point
Gear-tray
CD tray
Fig.28 Fig.29
Gear-synchro
Page 13

Removing the sensor board / the turn
table motor assembly (See Fig.30 to 32)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the CD tray.
MX-G50
X
1.
Remove the screw X attaching the sensor board and
release the two tabs h attaching the sensor board on
the under side of the CD tray.
2.
Disconnect the harness from connector CW1 on the
sensor board and release the harness from the two
hooks i. Remove the sensor board.
3.
Remove the screw Y attaching the turn table. Detach
the turn table from the tray.
4.
Pull outward the tab marked j attaching the turn table
motor assembly on the upper side of the tray and
detach the turn table motor assembly from the tray.
Tray
h
CW1
i
h
Sensor board
Fig.29
Turn table
Y
Turn table motor assembly
Fig.31
j
Fig.32
1-13
Page 14

MX-G50
Removing the belt, the CD servo board
and the switch board (See Fig.33 and 34)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the CD tray.
1.
Detach the belt from the pulley on the upper side of
the CD changer unit (Do not stain the belt with
grease).
2.
Disconnect the card wire from the pickup unit
connector on the under side of the CD changer unit.
Attention : Solder is put up before the card wire is
removed from the pick-up unit
connector on the CD mechanism
assembly.
(When the card wire is removed without
putting up solder, the CD pick-up unit
assembly might destroy.)
3.
Disconnect the motor wire harness from connector
on the CD servo board.
4.
Remove the screw Z attaching the switch board and
release the two tabs k attaching the switch board
outward and detach the switch board.
5.
Remove the two screws A' attaching the CD servo
board and . First release the n side of the two tabs l
and two tabs m attaching the CD servo board motor
to raise the CD servo board slightly, then release the
CD servo board.
Tabs k
Z
Switch board
CW3
CD changer unit
Fig.33
A'
CD servo board
Tabs m
Soldered points
Pickup unit connector
Belt
Motor
Tabs l
CD mechanism board
motor connecter
If the tabs l and m are hard to release, it is
recommendable to unsolder the two soldered points
on the motor terminal of the CD servo board.
Soldering
Card wire
Picup unit
connector
Fig.34
1-14
Page 15

Removing the CD mechanism holder
assembly (mechanism included)
(See Fig.35 to 38)
1.
Disconnect the harness from connector on the CD
mechanism board in the CD mechanism assembly
on the under side of the CD changer unit. Disconnect
the card wire from the pickup unit connector.
Attention : Solder is put up before the card wire is
removed from the pick-up unit
connector on the CD mechanism
assembly. (Refer to Fig. 34)
(When the card wire is removed without
putting up solder, the CD pick-up unit
assembly might destroy.)
MX-G50
Motor connecter
CD changer unit
CD mechanism holder assembly
Pickup unit connector
2.
Remove the screw B' attaching the shaft on the right
side of the CD mechanism holder assembly. Pull
outward the stopper fixing the shaft on the left side
and remove the CD mechanism holder assembly
from behind in the direction of the arrow y.
3.
Turn the CD mechanism holder assembly half
around the lift up slide shaft n of the CD mechanism
holder assembly until the turn table is reversed, and
pull out the CD mechanism holder assembly.
Lift up slide shaft
Fig.35
B'
Stopper
CD mechanism holder assembly
Fig.36
Lift up slide shaft n
CD mechanism holder assembly
Fig.38
y
CD mechanism holder assembly
Fig.37
1-15
Page 16

MX-G50
<CD mechanism section>
•
Removing the CD mechanism holder from the CD
chager unit.
(Refer to "Removing the CD mechanism holder
assembly" )
Removing the pickup unit. (
1. Removing the cut washer c on the feed gear
sleeve and pull out the feed gear.
2. Remove the two screws A fixing the pickup
shaft.
3. Removing the pickup unit.
Removing the motor board.
1. Unsolder the motor terminal on the motor board.
2. Remove the moter board.
Removing the feed motor. (
Remove the two motor fixing screws at B and
removing the feed motor.
Removing the spindle motor.
The spindle motor cannot be removed as a single unit.
When removing the spindle motor, change the chasis
and turntable together as aunit.
See Fig.1)
(See Fig.2)
See Fig.1)
A
Motor board
Shutter
Cut washer
B
Fig.1
Unsolder
Shaft
Pickup unit
A
Feed Gear
Feed motor
Spindle motor
Unsolder
Fig.2
1-16
Page 17

MX-G50
<Cassette mechanism section>
Removing the record/playback mechanism.
Removing the R/P head.
1. Remove the screw A on the right side of the
R/P head.(Fig.1, Fig.2)
2. Remove the screw B on the left side of the
R/P head.(Fig.1, Fig.2)
Remove the erase head.
Remove the screw C fixing the erase head.(Fig.1)
Removing the pinch roller.
1. Pull out the pinch roller by opening the pinch
roller stopper outward to unlock .(Fig.3)
2. When reassembling the pinch roller, refer to
fig. 4 to hook up the spring.
R/P Head
E. Head
Stoppsr
A
B
C
Fig.1
B
Pinch roller
assembly
A
Spring
Pinch roller
Return spring
R/P Head
Fig.2
Pinch roller
stopper
Fig.3
Pinch roller
Pinch roller
spring
Return spring
Return spring
Fig.4
1-17
Page 18

MX-G50
Removing the motor.
1. Remove the two screws D fixing the motor.
Be careful to grease's splash when the
drive belt comes off.(Fig.5, Fig.6)
2. Unsolder the motor terminal.(Fig.5)
Removing the mechanism board.
1.
coil terminal.(Fig.5)
2. Remove the two screws E fixing the board.(Fig.5)
Removing the flywheel.
capstan shaft, then remove the flywheel.
When reassembling the flywheel,
be sure to use new washers as they
cannot be reused.(Fig.8, Fig.9)
Unsolder the four parts a on the solenoid
3. Unhook the three parts b from the board.(Fig.5)
4. Remove the mechanism board.(Fig.5)
Remove the cut-washers at c and d from the
Mecha.
a
Drive belt (Flat)
board
E
b
Motor
Motor
terminal
D
D
Fig.5
Drive belt
Fig.6
E
Drive belt
Motor
b
a
1-18
Sleeve
Flywheel
c
Washer
Sleeve
d
FR belt
Capstan
washer
Flywheel
Fig.7
FR belt
Fig.8Fig.9
Capstan
washer
Flywheel
Page 19

MX-G50
< Speaker section >
Removing the side panel (See Fig. 1)
1.
Remove the five screws A attaching the side panel,
then remove the side panel.
Removing the side speaker
(See Fig. 2 and 3)
Prior to performing the following procedure, remove
the side panel.
B
Side panel
A
B
Fig.1
Side speaker
C
Front panel
1.
Remove the fore screws C attaching the side
speaker.
2.
Pull out the side speaker and remove the speaker
cord from the speaker terminal.
C
Fig.2
Side speaker
Speaker terminal
Fig.3
1-19
Page 20

MX-G50
Wiring connection
Amp board
0
ACW2
ACW1
3809-001224
CD key switch board
UCW1
9
UCW7
Front key switch board
0
9
0
AH39-00254A
AH39-00254A
UCW2
Front / Display board
RCW2
Power transformer
PCW1
UCW3
RFS5
RFS6
UCW4
RFS2
RFS7
RFS8
UCW6
UCW5
AH39-20561P
3809-001121
CD mechanism
CW2
CW1
CW3
0
3809-001185
Color codes are shown below.
1 Brown
2 Red
3 Orange
4 Yellow
5 Green
6 Blue
9
8Gray
7 Violet
0
9 White
0 Black
AAN1
0
2
0
2
16634-502-610
CW102
CW103
9
CW105
CW107
CW101
CW3
CW106
CW104
3809-001034
2
0
9
9
0
AH39-20025S
AH39-00096D
1-20
3809-001228
3708-000258
3708-000122
0
9
2
9
0
0
9
0
FCW1
OCW
9
0
RCW6
FCW2
Main board
Tuner board
HCW3
JW1
JCW1
FCW3
JCW2
FCW3
0
9
RW2
9
0
9
0
0
9
RW1
2
0
0
9
0
HCW2
AH39-00247A
9
E.phone J.board
AH39-00022A
Cassette mechanism
9
0
0
9
9
0
2
88
9
2
0
AH39-20002D
8
2
8
2
Page 21

Adjustment method
1. Tuner
MX-G50
ITEAM
Received FREQ.
Adjustment
point
Output
* Adjustment Location of Tuner PCB
AM(MW) OSC
Adjustment
522~1611 KHz
MO
1~7.0 0.5V
MAIN
PCB
AM(MW) RF
Adjustment
594 KHz
MA
Maximum
Output(Fig1-4)
VT GND
Fig 1-4 OSC Voltage
TESTER
1-21
Page 22

MX-G50
FM THD Adjustment
SSG FREQ.
98 MHz
Adjustment
point
FM DETECTOR COIL
(FM DET)
Output
60 dB
Minimum Distortion (0.4% below)
(Figure 1-1)
FM Search Level Adjustment
SSG FREQ.
Adjustment
point
(SVR1)
Output
BEACON
SENSITIVITY
SEMI-VR(20K )
28 dB(
98 MHz
2dB)
Output
GND
FM S.S.G
FM
Antenna
Terminal
Speaker
Terminal
SET
Input
output
Distortion Meter
Figure1-1 IF CENTER and THD Adjustment
FM Antenna
SET
FM IN
FM S.S.G
28 dB
GND
Oscilloscope
Input
Adjust SVR1 so that "TUNED" of FL T
is lighted (Figure 1-2)
*Adjust FM S.S.G level to 28dB
AM(MW) I.F Adjustment
SSG FREQ.
Frequency
450 kHz
522 kHz
Adjustment
point
AM IF
Maximum output (Figure 1-3)
Figure1-2 FM Auto Search Level Adjustment
60cm
OUTPUT
AM SSG
450KHZ
INPUT
AM ANT
IN
Speaker Terminal
OUTPUT
VTVM Oscilloscope
Figure1-3 AM I.F Adjustment
20 k
AM IF
1-22
Page 23

2 Cassette Deck
To adjust tape speed
MX-G50
Notes
1) Measuring tape: i) VT-712(or equivalent)
(Tapes recorded with 3kHz)
ii) AC-225(or equivalent)
2) Connect the cassette deck to the frequency counter
as in figure 1-5.
Step
Item
Pre-Setup
Condition
Pre-Setup
1) Deck A:VT-712
NOR
1
SPEED
Control
Recording /Play head
OUT
(connected
to the frequency
counter)
2) Press PLAY
SW button
3) Deck B:Same
as above
Cassette Deck
SPK OUT
To Adjust
Turn VSR1 to
left and right
(FRONT PCB)
Cassette Deck
SPK OUT
Figure 1-5
VTVM
Frequency Counter
Standard
3KHz
Oscilloscope
output
Remark
1%
range
AZIMUTH control screw
Figure 1-6
Audio OSC.
SET
(MAIN PCB)
IN
AUX IN
LINE OUT
TP
JCW3
Figure 1-8
VTVM
IN OUT
(GND)
In Out
Figure 1-7
Oscilloscope
1-23
Page 24

MX-G50
To adjust plabyback level/REC
Notes
1) Before the actual adjustment, clean the play/recording
head.
2) Measuring tape :
i) VT-703(or equivalent 10kHz AZIMUTH control)
ii) AC-225(or equivalent)
3) The cassette deck is connections as shown in figure 1-7.
1. Adjust Deck A Play Level
Step
1
Item
AZIMUTH
Pre-Setup
Condition
SPK OUT
(VTVM is
connected to
Pre-Setup
After putting VT703 into Deck A
- Press FWD
PLAY button.
the scope)
2. Adjust Deck B Play Level/REC BIAS
Step
1
Item
AZIMUTH
Pre-Setup
Condition
SPK OUT
(VTVM is
connected to
the scope)
Pre-Setup
After putting VT-703
into Deck B
1)Press FWD PLAY
button.
To Adjust
- Turn the control
screw to as shown
in Figure 1-6.
To Adjust
- Turn the control
screw to as shown
in Figure 1-6.
Standard
Max output
and same phase
(both channels)
Standard
Max output
and same phase
(both channels)
Remark
After
adjustment
secure it with
REGION
LOCK.
Remark
After
adjustment
secure it with
REGION
LOCK.
1-24
2
Recording
Bias
Voltage
Fig 1-8
After putting AC-225
into Deck B
1)Press REC PLAY
button.
2)MAIN PCB JCW3,
connectted to VTVM
Turn JSR2L,JSR2R
to the right and left
7mV(
0.5
mV)
Page 25

Flow of functional operation until TOC read
Power ON
Play Key
RESET a CD LSI
Confirm that the voltage at the pin17
of KB9226(IC101) is "L" "H".
MX-G50
Check Point
LIMIT SW ON
SET Default value of
TE gain, TE balance
Automatic adjusting of
focus bias
Automatic adjusting of
FE offset
Automatic adjusting of
TE offset
LASER power ON
Detection of disk
Confirm that the voltage at the pin33
of KB9226(IC101) is "H" "L" "H".
Confirm that the voltage at the
pin37 of KB9226(IC101) is 3.5V.
Tracking error waveform at TOC reading
Pin 34 of
KB9226
(IC101)
2.50V
Approx
0.4V
Disc states
to rotate
Approx.3.7sec
Disc is rotated
Automatic adjusting of
TE balance
Automatic adjusting of
TE gain
TOC reading
Play a disc
Confirm that the signal from pin24
of KB9226(IC101) is 3.5V as a
accelerated pulse during
approx.1.96s.
Confirm the waveform of
the Tracking error signal
at the pin 34 of KB9226(IC101).
Confirm the eye-pattern
at the pin2 of KB9226(IC101).
1-25
Page 26

MX-G50
Maintenance of laser pickup
(1) Cleaning the pick up lens
Before you replace the pick up, please try to
clean the lens with a alcohol soaked cotton
swab.
(2) Life of the laser diode
When the life of the laser diode has expired,
the following symptoms will appear.
1. The level of RF output (EFM output:ampli
tude of eye pattern) will below.
Is the level of
RFOUT under
1.1V 0.2Vp-p?
YES
O.K
NO
Replace it.
Replacement of laser pickup
Turn off the power switch and,disconnect the
power cord from the ac outlet.
Replace the pickup with a normal one.(Refer
to "Pickup Removal" on the previous page)
Plug the power cord in,and turn the power on.
At this time,check that the laser emits for
about 3seconds and the objective lens moves
up and down.
Note: Do not observe the laser beam directly.
Play a disc.
(3)
Semi-fixed resistor on the APC PC board
The semi-fixed resistor on the APC printed circuit
board which is attached to the pickup is used to
adjust the laser power. Since this adjustment should
be performed to match the characteristics of the
whole optical block, do not touch the semi-fixed
resistor.
If the laser power is lower than the specified value,
the laser diode is almost worn out, and the laser
pickup should be replaced.
If the semi-fixed resistor is adjusted while the pickup
is functioning normally,the laser pickup may be
damaged due to excessive current.
Check the eye-pattern at TP1.
Finish.
1-26
Page 27

Troubleshooting
1. Amplifier
Power malfunction
MX-G50
Front PCB -com
VDD(5V) normal?
UIC1 pin no.18, 46,90
Yes
Front PCB
Does UX1(6MHz)
oscillate?
Yes
Front PCB
When the power is
ON 'H' display at pin
no.15(UIC2)
Yes
Check the main PCB
RIC1(L4959)
No
No
Main PCB RIC1(L4959)
pin No.2, 10 input
voltage normal?
-Check the main PCB
RIC1(L4959)
-Check the front PCB
UD13(IN4002)
Front PCB PWR-SENS
voltage normal?
No
Replase UIC2(M66010)
(pin no.94;5V)
Yes
Replase -com
No
-Check the main PCB;
RBD1(PBL403) RD8(IN5392)
-Check the power PCB;
Fuse P/T, RFS2, RFS5, RFS6
No
-Check the main PCB;
RR7, RC7, RZD4, RR6
RR5, RR4, RC8, RD3
No output
AMP PCB AIC1,
AQ2L, 2R, AQ1,2,3,4
Is mute selected?
Headphone jack short?
UIC1( -com)pin79
check the "H"?
pin no. 4,8,9,12
B+,B- normal?
Yes
Emitter B+?
Yes
No
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Check the B+, B- power source
RBD1, RBD2, RW2
Check the power PCB
Fuse, P/T, RFS2, RFS5,
RFS6, RFS7, RFS8
Check the AMP PCB
AIC1, AIC2
Remove it with remocon
Check headphone jack
soldering condition
Check the front PCB
UIC( -com), UIC2(M66010GP)
No
Check the AMP PCB
AQ2L, 2R, AQ1,5,6,7
1-27
Page 28

MX-G50
2. Tuner malfunction (FM/AM)
3. Tape malfunction
1-28
Page 29

4.CD
MX-G50
1-29
Page 30

MX-G50
Description of major ICs
5L9290 (IC201) : Digital signal processor for CDP
1. Pin layout
VSSA_DAC
VREF
VHALF
VDDA_DAC
LRHOUT
VDDA_PLL
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
VDDD_DAC
RCHOUT
SADTI
VSSD_DAC
LRCKI
BCKI
2. Block diagram
VSSA_PLL
VCO1LF
VSSD_PLL
VDDD_PLL
VDDD1_5V
XIN
XOUT
VSSD1_5V
EFMI
LOCK
SMEF
SMON
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
SMDS
WDCK
S5L9290X
DSP+DAC
48-LQFP-0707
LKFS
TESTV
LKFS
RESETB
MLT
MDAT
SOS1
SQCK
SBCK
SQDT
SBDT
MCK
ISTAT
S0S1
C2PO DATX
SQCK
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
BCKO
LRCKO
SADTO
DATX
C2PO
JITB
SBCK
VDDD3-5V
VSSD2-3V
VDDD2-3V
MUTE
SQDT
1-30
VCO1LF
EFMI
LOCK
SMEF
SMDP
SMDS
WDCK
WFCK
RFCK
C4M
XIN
ISTAT
MLT
MDAT
MCK
MUTE
DPLL
CLV
Servo
Timing
Generator
Micom
Interface
Subcode
Out
EFM
Demodulator
ECC
16K
SRAM
Address
Generator
JITB
Interpolator
Interface
SADTO
LRCKO
BCKO
I/O
Digital
Out
SADTI
LRCKI
BCKI
Digital
Filter
1-bit
DAC
PWM
LPF
LCHOUT
RCHOUT
VHALF
VREF
Page 31

MX-G50
3. Pin function
NO. NAME I/O Pin Description
1 VSSA_PLL - Analog Ground for DPLL
2 VCO1LF O Pump out for VCO1
3 VSSD_PLL - Digital Ground Separated Bulk Bias for DPLL
4 VDDD_PLL - Digital Power Separated Bulk Bias for DPLL (3V Power)
5 VDDD1-5V - Digital Power (5V Power, I/O PAD)
6 XIN I X'tal oscillator input (16.9344MHz)
7 XOUT O X'tal oscillator output
8 VSSD1 - Digital Ground (I/O PAD)
9 EFMI I EFM signal input
10 LOCK O CLV Servo locking status output
11 SMEF O LPF time constant control of the spindle servo error signal
12 SMDP O Phase control output for Spindle Motor drive
13 SMDS O Speed control output for Spindle Motor drive
14 WDCK O Word clock output (Normal Speed : 88.2KHz, Double Speed : 176.4KHz)
(1/2)
15 TESTV I Various Data/Clock Input
16 LKFS O The Lock status output of frame sync
17 C4M O 4.2336MHz clock output
18 RESETB I System Reset at 'L'
19 MLT I Latch signal input from Micom
20 MDAT I Serial data input from Micom
21 MCK I Serial data receiving clock input from Micom
22 ISTAT O The internal status output to Micom
23 S0S1 O Subcode sync signal(S0+S1) output
24 SQCK I Subcode-Q data transfering bit clock input
1-31
Page 32

MX-G50
3. Pin function
NO. NAME I/O Function Description
25 SQDT O Subcode-Q data serial output
26 MUTE I System mute at 'H'
27 VDDD2-3V - Digital Power (3V Power, Internal Logic)
28 VSSD2 - Digital Ground (Internal Logic)
28 VDDD3-5V - Digital Power (5V Power, I/O PAD)
30 SBCK I Subcode data transfering bit clock
31 JITB O Internal SRAM jitter margin status output
32 C2PO O C2 pointer output
33 DATX O Digital audio data output
34 SADTO O Serial audio data output (48 slot, MSB first)
35 LRCKO O Channel clock output
36 BCKO O Bit clock output
37 BCKI I Bit clock input
38 LRCKI I Channel clock input
(2/2)
39 SADTI I Serial audio data input (48 slot, MSB first)
40 VSSD_DAC - Digital Ground for DAC
41 VDDD_DAC - Digital Power for DAC (3V Power)
42 RCHOUT O Right-Channel audio output through DAC
43 VSSA_DAC - Analog Ground for DAC
44 VREF O Referance Voltage output for bypass
45 VHALF O Referance Voltage output for bypass
46 VDDA_DAC - Analog Power for DAC (3V Power)
47 LCHOUT O Left-Channel audio output through DAC
48 VDDA_PLL - Analog Power for PLL (3V Power)
1-32
Page 33

BA4560 (AIC3, AIC4, AIC5, AIC6, AIC7, FIC4, JIC2, UIC3) : Op amp.
1.Pin layout
MX-G50
OUT1
– IN1
+ IN1
1
2
1ch
+
–
3
EE
V
4
2ch
+
V
CC
8
OUT2
7
– IN2
6
–
+ IN2
5
KA9258D (IC301) : 4-ch Motor driver
28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15
10K
VCC VCC
10K
GND
10K
10K
T • S • D
10K
+-
LEVEL SHIFT
REGULATOR
10K
50K
MUTE
LEVEL SHIFT
-+
10K
10K
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
GND
1-33
Page 34

MX-G50
KA22291(JIC1) : PB/REC pre amp.
1.Pin layout
KA22291
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 101112
2.Block diagram
131415161718192021222324
PB OUT(2)
Vcc
Vcc
REC GND
PB OUT(1)
24
16
17
9
1
PB NF(2) PB IN(2) R/P SW SW IN(2) ALC OUT(2)
22 21 8 20
B-IN
A-AN
MODE CONTROL
B-IN
/BIAS CIRCUIT
A-AN
PB.BIAS
INPUT
100k
PRE
RECORE
I.REF
PLAYBACK
I.REF
PRE
100k
23
INPUT
REC.BIAS
N.F
PB NF(1) PB IN(1) A/B SW PB MUTE REC
MUTE MUTE REC
19
R/P SW
A/B SELECT SW
GND IN(1) OUT(1)
18
15
ALC TIME CONSTANT
102 3 4 5 7 6
ALC
DET
100k
PRE
PRE
100k
NF
INPUT
INPUT
N.F
14
13
12
11
REC NF(2)
REC IN(2)
REC IN(1)
REC NF(1)
1-34
Page 35

KA3082 (IC401, IC402) : Bi-directional DC motor driver
1.Pin layout
KA3082
MX-G50
GND V
12345678910
O1
V
V
Z1
CTLVIN1
V
IN2
SV
CC
PV
CCVZ2
2.Pin function
Pin Number Pin Name I/O Pin Function Descriptio n
1 GND - Ground
2V
3V
4V
5V
6V
7SV
8PV
9V
10 V
O1
Z1
CTL
IN1
IN2
CC
CC
Z2
O2
O Output 1
- Phase compensation
I Motor speed control
I Input 1
I Input 2
- Supply voltage (Signal)
- Supply voltage (Power)
- Phase compensation
O Output 2
V
O2
3.Block Diagram
BIAS
1234
GND
O1
V
V
Z1
V
CTL
DRIVER OUT
PRE DRIVER
LOGIC SWITCH
5
V
IN1
678910
V
IN2
SV
CC
TSD
PV
CC
Z2
V
O2
V
1-35
Page 36

MX-G50
KB9226 (IC101) :
1. Pin layout
2. Block diagram
RF amp & Servo signal processor
36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
SLP
37
LD
PD
38
39
PDAC
PDBD
40
PDF
41
PDE
42
DCB
43
MCP
44
DCCI
45
DCCO
46
VREF
47
EQC
48
LPFT
ATSC
RFO
RFM
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
TEIO
TZC/SSTOP
S1L9226X
EQO
EQI
GND
EFMI
FEO
VCC
FEM
FRSH
TEO
FSET
TEM
FLB
FGD
SLO
FSI
SLM
SPO
SPM
ASY
EFM
LOCK
WDCK
CLVI
RESET
MLT
MDATA
MCK
ISTAT
TGU
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
EQO
EFMI
DCCI
DCC0
MCP
DCB
VCC/
VDD
FRSH
FSET
FLB
FGD
FSI
45
46
44
43
10
11
EQI
RFO
RFM
4
5
RF AGC & EQ
Control
Focus OK Detect
Defect Detect Mirror
Gen
Focus Servo Loop
- Gain & Phase
Compensation
- Focus Search
- Offset Adjust
- FZC Gen.
6
7
8
9
EQC
Center
Voltage
APC. Laser
Control &
LPC
Tracking Servo Loop
- Gain & Phase
Compensation
- Track Jump
- Offset Adjust
- TZC Gen.
Hardware Logic
- Auto-Sequencer
- Fast Search
- Febias, Focus Servo,
Tracking Offset ADJ.
VREF
PDE
41 40424748123
Tracking Error
(RW)
I/V AMP
PDF
PDBD
39
RF & Focus
Error (CD-RW)
I/V AMP
Sled Servo &
Kick Gen
PDAC
38
37
35
34
33
36
29
28
27
26
25
PD
LD
LPFT
TEIO
TZC&
SSTOP
ATSC
TEO
TEM
SLP
SLO
SLM
- Tracking Balance & Gain
Adjust
- Interruption Detect
29
FEO
- EFM Muting System
30
FEM
1-36
TGU
12
Micom Data Interface Logic Decoder
Comparator
1413 15 16 17 19 18 20 22 21
ISTAT
MCK
MDATA
MLT
RESET
WDCK
CLVI
LOCK
EFM
ASY
EFM
Spindle
Servo LPF
23
24
SPDLO
SPDLM
Page 37

MX-G50
3. Pin function
Pin No. Symbol I/O Description
1 R FM I RF summing amp. inverting input
2 RFO O RF summing amp. output
3 EQI I RFO DC eliminating input(use by MIRROR, FOK ,AGC & EQ terminal)
4 EQO O RF equalizer output
5 EFMI I EFM slice input. (input impedance 47K)
6 VCC P Main power supply
7 FRSH I Capcitor connection to focus search
8 FSET I Filter bias for focus,tracking,spindle
9 FLB I Capacitor connection to make focus loop rising band
10 FGD I Terminal to change the hign frequency gain of focus loop
11 FSI I Focus servo input
12 TGU I Connect the component to change the high frequency of tracking Loop
13 ISTAT O Internal status output
14 MCK I Micom clock
15 MDATA I Data input
(1/2)
16 MLT I Data latch input
17 RESET I Reset input
18 CLVI I Input the spindle control output from DSP
19 WDCK I 88.2KHz input terminal from DSP
20 LOCK I Sled run away inhibit pin (L: sled off & tracking gain up)
21 EFM O EFM output for RFO slice(to DSP)
22 ASY I Auto asymmetry control input
23 SPM I Spindle amp. inverting input
24 SPO O Spindle amp. output
25 SLM I Sled servo inverting input
26 SLO O Sled servo output
27 SLP I Sled servo noninverting input
28 TEM I Tracking servo amp.inverting input
29 TEO O Tracking servo amp. output
30 FEM I Focus servo amp. inverting input
31 FEO O Focus servo amp. output pin
1-37
Page 38

MX-G50
3. Pin function
Pin No. Symbol I/O Description
32 GND P Main ground
33 TZC/
SSTOP
I Tracking zero crossing input & Check the position of pick-up
not
34 TEIO B Tracking error output & Tracking servo input
35 LPFT I Tracking error integration input (to automatic control)
36 ATSC I Anti-shock input
37 LD O APC amp. output
38 PD I APC amp. input
39 PDAC I Photo diode A & C RF I/V amp. inverting input
40 PDBD I Photo diode B & D RF I/V amp. inverting input
41 PDF I Photo diode F & tracking(F) I/V amp. inverting input
42 PDE I Photo diode E & tracking(E) I/V amp. inverting input
43 DCB I Capacitor connection to limit the defect detection
44 MCP I Capacitor connection to mirror hold
45 DCCI O Output pin to connect the component for defect detect
(2/2)
wherther inside or
46 DCCO I Input pin to connect the component for defect detect
47 VREF O (VCC+GND)/2 Voltage reference output
48 EQC I AGC_equalize level control terminal & capacitor terminal to input in to VCA
BA3837 (IC301) : Mic mixer
1.Block diagram
C B A ROUT LP LP LP RIN
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
–
SW1
+
R
L + R
L – R
L
+
–
+
–
+
+
LOGIC
–
+
–
123456 78
V
CC
MIC LOUT FK TK LIN BIAS GND
–
SW2
+
+
–
1-38
Page 39

L4959 (RIC1) : Voltage regulator
1.Pin layout
MX-G50
TAB CONNECTED TO PIN 6
2.Block diagram
2/10
V
S
EN 8V
EN 12V(a)
EN 12V(b)
8
7
5
REF
GEN
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
D97AU716A
OUT 12V(a)
V
S
OUT 8.6V
EN 8.6V
EN 12V(a)
GND
EN 12V(b)
N.C.
OUT 5.6V
V
S
OUT 12V(b)
5.6V, 250mA
3
OUT 5.6V
REGULATOR
8.6V, 600mA
REGULATOR
9
OUT 8.6V
SWITCHED
12V, 800mA
REGULATOR
11
OUT 12V(a)
SWITCHED
12V, 1.3A
REGULATOR
1
OUT 12V(b)
SWITCHED
D97AU569C
3.Pin function
Pin Pins Description
1 OUT 12V (b) 12V/1.3A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
2V
S
3 OUT 5.6V 5.6V/250mA OUTPUT VOLTAGE
4 N.C. not connected
5 EN 12V (b) Enable 12V/1.3A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
6 GND Ground
7 EN 12V (a) Enable 12V/0.8A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
8 EN 8.6V Enable 8.6V/0.6A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
9 OUT 8.6 8.6V/0.6A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
10 V
S
11 OUT 12V (a) 12V/0.8A SWITCHED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
Supply Voltage
Supply Voltage
GND
6
1-39
Page 40

MX-G50
LC72131M(IC02): PLL frequency synthesizer for electron alignment
1. Pin layout
1
XIN
2
CE
3
DI
4
CL
5
DO
6
BO1
7
BO2
8
BO3
9
BO4
10
I01
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
XOUT
VSS
AOUT
AIN
PD
VDD
FMIN
AMIN
102
IFIN
2. Block diagram
1
20
14
13
2
3
4
5
15
19
CCB
I/F
Power
on
Reset
Reference
Driver
1
2
Swallow
Counter
1/16,1/17 4bits
12bits
Programmable
Divider
Data Shift Register & Latch
Phase
Detector
Charge
Pump
Unlock
Detector
Universal
Counter
16
17
18
11
3.Pin Functions
Symbol
XIN
XOUT
FMIN
AMIN
Pin No.
1
20
14
13
Type
Xtal OSC
Local
oscillator
signal input
Local
oscillator
signal input
6
7
Functions
Crystal resonator connection
(4.5MHz/7.2MHz)
Serial data input : FMIN is selected when DVS is set to 1.
The input frequency range is from 10 to 160MHz.
The signal is passed through a built-in divide-by-two prescaler
and then supplied to the swallow counter.
A1 though the range of divisor setting is from
272 to 65, 535, the actual divisor is twice the setting since
there is also a built-in divide-by-two prescaler.
Serial data input : AMIN is selected when DVS is set to 0.
Serial data input : When SNS is set to 1 :
The input frequency range is form 2 to 40MHz
The signal is supplied directly to the swallow counter.
The range of divisor setting is from 272 to
65, 535 and the actual divisor will be the value set.
Serial data input : When SNS is set to 0 :
The input frequency ranges is from 0.5 to 10MHz.
The signal is supplied directly to a 12-bit
programmable divider.
The range of divisor setting is from 4 to 4,095 and the
actual divisor will be the value set.
9
8
1210
(1/2)
Circuit configuration
1-40
CE
2
Chip enable
Most be set high when serial data is input to the
LC72131M (DI ), or when serial data is output (DO).
S
Page 41

MX-G50
3.Pin Functions
Symbol
CL
DI
DO
VDD
VSS
BO1
BO2
BO3
BO4
Pin No.
15
19
6
7
8
9
4
3
5
Type
Clock
Input data
Output data
Power supply
Ground
Output port
Functions
Used as the synchronization clock when serial data is input
to the LC72131 (DI ), or when serial data is output (DO).
Inputs serial data sent from the controller to the LC72131M.
Output serial data sent from the LC72131M to the controller.
The content of the output data is determined by the serial
data DOCO to DOC2.
The LC72131M power supply (VDD=4.5 to 5/5V)
The power on reset circuit operates when power is first applied.
The LC72131M ground.
Dedicated output pins
The output states are determined by BO1 to BO4 in the
serial data.
'Data"=0:Open
=1:Low
The pins go to the open state after the power-on reset.
An 8Hz time base signal can be output from BO1 when TBC
in the serial data is set to 1.
Note that the ON impedance of the BO1 pin is higher than
that of the other pins (BO2 to BO4)
(2/2)
Circuit configuration
S
S
IO1
IO2
PD
AIN
AOUT
10
12
16
17
18
I/O Port
Charge pump
output
L.P.F
amplifier Tr
Pins used for both input and output
The input or output state is determined by bits IOC1 and IOC2
in the serial state.
'Data"=0:Input port
=1:Output port
When specified for use as an input port :
The input state is transmitted to the controller through the
DO pin.
'Input state"=Low:data value 0
=High:data value 1
When specified for use as an output port :
The output state is determined by bits IO1 and IO2 in the
serial sate.
'Data"=0:Open
=1:Low
These pins go to the input port state after the power-on reset.
PLL Charge pump output
When the frequency generated by dividing the Local oscillator
frequency by N is higher than the reference frequency,
a high level will be output from the PD in. similarly, when that
frequency is lower, a low level will be output.
The PD pin goes to the high impedance state when the
frequencies agree.
The MOS transistor used for the PLL active Low-pass filter.
S
IFIN
11
IF counter
The input frequency range is from 0.4 to 12MHz.
The signal is supplied directly to the IF counter.
The result from the IF counter MBS is output through
the DO pin.
There are four measurement periods: 4, 8, 32 or 64ms.
1-41
Page 42

MX-G50
M66010 (UIC2) : I/O control
1.Pin layout
D0
D1
CLK
CS
Vcc
GND
D24
D23
D22
D21
D20
D19
D18
D17
GND
2.Block diagram
CLOCK INPUT CLK
SET INPUT S
CHIP SELECT CS
INPUT
SERIAL DATA DI
INPUT
DO
1
DI
2
CLK
3
CS
4
5
S
S
6
7
D24
8
D23
9
D22
10
D21
11
D20
12
D19
13
D18
14
D17
15
16
3
6
4
2
D1
32
D2
31
D3
30
D4
29
D5
28
D6
27
D7
26
D8
25
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D16
Control circuit
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
D24 D23 D22 D3 D2 D1
Q24 Q23 Q22 Q3 Q2 Q1
D24 D23 D22 D3 D2 D1
Q24 Q23 Q22 Q3 Q2 Q1
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D16
Shift register 1
Parallel output latch
DI
Shift register 2
DO
GND GND
Vcc
5
DO SERIAL DATA
1
OUTPUT
32
D1
31
D2
30
D3
PARALLEL
DATA I/O
10
D22
9
D23
8
D24
7
16
STK402-040 (AIC1) : 2channel AF power amp.
1.Pin layout
1.Pin layout
+
+
ch.1
ch.1
_
NF
NF
NC
NC
_
STK402-040
STK402-040
1
1
15
15
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
CH1
CH1
CH1
CH1
IN
IN
STK402-090 (AIC2) : 2channel AF power amp.
1.Pin layout
+
ch.1
_
NC
NF
1-42
STK402-090
1
15
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
CH1
CH1
IN
Pre
Pre
Vcc
Vcc
Pre
Vcc
BIAS
BIAS
BIAS
CH1
CH1
VE
VE
CH1
VE
CH1
CH1
-VE
-VE
CH1
-VE
Vcc -Vcc
Vcc -Vcc
Vcc -Vcc
CH2
CH2
+VE
+VE
CH2
+VE
CH2
CH2
-VE
-VE
CH2
-VE
ch.2
ch.2
Pre
Pre
-Vco
-Vco
ch.2
Pre
-Vco
+
+
_
_
SUB
SUB
GND
GND
+
_
SUB
GND
CH2
CH2
NF
NF
CH2
NF
CH2
CH2
IN
IN
CH2
IN
Page 43

TDA7442D (FIC1) : Audio processor
1.Pin layout
MX-G50
R_IN3
R_IN2
R_IN1
L_IN1
L_IN2 V
L_IN3
L_IN4
MUXOUTL
IN(L)
MUXOUT(R)
IN(R)
BIN(R)
BOUT(R)
BIN(L)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2.Block diagram
MUXOUT(L)
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
0.47 F
L-IN1
L-IN2
L-IN3
L-IN4
R-IN1
R-IN2
R-IN3
R-IN4
4
50K
5
50K
6
50K
7
50K
3
50K
2
50K
1
50K
28
50K
31.5dB
control
31.5dB
control
MUXOUT(R)
+
2.2 F
+
2.2 F
28
27
26
25
24
R_IN4
LOUT
ROUT
AGND
S
CREF23
SYMULATED
-
L-R
+
SDA
SCL
DIG-GND
TREBLE(R)
TREBLE(L)
PS1
LP
BOUT(L)
100nF
PS1
17
RPS1
PS1
90Hz
MUSIC
LPF
9KHz
24 25 2316
LP
1.2nF
OFF
V
S
SYMULATED
EFFECT
CONTROL
MUSIC/
SUPPLY
AGND
CREF
22 F
MIXING
AMP
MIXING
AMP
5.6nF
TREBLE-L
18
OFF
SURR
TREBLE
TREBLE
SURR
OFF
Vref
TREBLE-R
5.6nF
5.6K
100nF
100nF
BIN(L)
BOUT(L)
15
14
RB
FIX
BASS
I2C BUS DECODER + LATCHES
BASS
12
BIN(R) BOUT(R)
100nF 100nF
5.6K
FIX
VAR
RB
1319
79dB CONTROL
-
VAR
+
FIX
+
-
SPKR
ATT
MUTE
SPKR
ATT
MUTE
79dB CONTROL
D98AU947A
27
LOUT
21
SCL
22
SDA
20
DIG GND
26
ROUT
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
IN(L)
98
30K
L+R
30K
1110
IN(R)
1-43
Page 44

MX-G50
VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LIMITED
AUDIO & COMMUNICATION BUSINESS DIVISION
PERSONAL & MOBILE NETWORK BUSINESS UNIT. 10-1,1chome,Ohwatari-machi,Maebashi-city,371-8543,Japan
(No.20978)
200107(V)
 Loading...
Loading...