
Juniper Advanced Threat
Prevention Appliance
CLI Command Reference Guide
Release 5.0
March 2018

Juniper Networks, Inc.
1133 Innovation Way
Sunnyvale, California 94089
USA
408-745-2000
www.juniper.net
Juniper Networks, the Juniper Networks logo, Juniper, and Junos are registered trademarks of Juniper Networks, Inc.
and/or its affiliates in the United States and other countries. All other trademarks may be property of their
respective owners.
Juniper Networks assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document. Juniper Networks reserves the
right to change, modify, transfer, or otherwise revise this publication without notice.
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention CLI Command Reference Guide
Copyright© 2018 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
The information in this document is current as of the date on the title page.
YEAR 2000 NOTICE
Juniper Networks hardware and software products are Year 2000 compliant. Junos OS has no known time-related
limitations through the year 2038. However, the NTP application is known to have some difficulty in the year 2036.
END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
The Juniper Networks product that is the subject of this technical document ation consists of (or is intended for
use with) Juniper Networks software. Use of such software is subject to the terms and conditions of the End User
License Agreement (“EULA”) posted at http://www.juniper.net/support/eula/. By downloading, installing or using
such software, you agree to the terms and conditions of that EULA.

Draft for Review - FireEye Confidential - February 15, 2018
CONTENTS
About the Documentation
Documentation and Release Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Requesting Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Opening a Case with JTAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Preface
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Typographical Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Related Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Introduction
Accessing the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Hardware Appliance Access via the Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Configuration Wizard Command Prompt Progressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Hardware, Software and Virtual Appliance Access via SSH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
CLI Help and Keyboard Shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
CLI Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
All-in-One CLI Commands
Basic Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
CM Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Core Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Server Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Collector Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Diagnosis Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
All-in-One CLI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
capture-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
cm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
collector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
copy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
gssreport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
ifrestart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
restart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
set honeypot (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
set traffic-monitoring (for JATP700 Appliances only) (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
set traffic-filter (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
set protocols (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
set proxy (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
set (diagnosis mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
set ip interface (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
set (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
set system-alert (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
setupcheck . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
show (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
show (core mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
show (diagnosis mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
updateimage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Configuration Wizard for the All-in-One Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Core/CM Server CLI Commands
Basic Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
CM Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Core Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Server Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Diagnosis Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
CoreCM CLI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
capture-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
cm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
copy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
gssreport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
ifrestart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
restart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
set (core mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
set system-alert (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
set (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
set (diagnosis mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.

setupcheck . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
show (core mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
show (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
updateimage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Configuration Wizard for the CoreCM Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Mac OS X Engine CLI Commands
Basic Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Core Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Server Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Diagnosis Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Mac OS X Detection Engine CLI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
capture-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
copy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
gssreport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
ifrestart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
restart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
set (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
set (diagnosis mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
setupcheck . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
show (core mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
show (diagnosis mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
show (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
updateimage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Configuration Wizard Command Prompt Responses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Traffic Collector CLI Commands
Basic Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Collector Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Diagnosis Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Server Mode Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
CLI Command Reference Guide
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
Traffic Collector CLI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
capture-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
collector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
copy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
gssreport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
ifrestart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
restart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
set proxy (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
set honeypot (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
set (diagnosis mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
set protocols (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
set (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
set traffic-filter (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
set traffic-monitoring (for JATP700 Appliances only) (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
setupcheck . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
show (collector mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
show (diagnosis mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
show (server mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Configuration Wizard Command Prompt Progressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Glossary of Terms
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Documentation and Release Notes
To obtain the most current version of all Juniper Networks® technical documentation, see the product
documentation page on the Juniper Networks website at http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/.
If the information in the latest release notes differs from the information in the documentation, follow the product
Release Notes. Juniper Networks Books publishes books by Juniper Networks engineers and subject matter
experts. These books go beyond the technical documentation to explore the nuances of network architecture,
deployment, and administration. The current list can be viewed at http://www.juniper.net/books.
Requesting Technical Support
Technical product support is available through the Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center (JTAC). If you are
a customer with an active J-Care or Partner Support Service support contract, or are covered under warranty, and
need post-sales technical support, you can access our tools and resources online or open a case with JTAC.
• JTAC policies—For a complete understanding of our JTAC procedures and policies, review the JTAC User Guide
located at http://www.juniper.net/us/en/local/pdf/resource-guides/7100059-en.pdf.
• Product warranties—For product warranty information, visit http://www.juniper.net/support/warranty/.
• JTAC hours of operation—The JTAC centers have resources available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a
year.
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources
For quick and easy problem resolution, Juniper Networks has designed an online self service portal called the
Customer Support Center (CSC) that provides you with the following features:
• Find CSC offerings: http://www.juniper.net/customers/support/.
• Search for known bugs: https://prsearch.juniper.net/.
• Find product documentation: http://www.juniper.net/documentation/.
• Find solutions and answer questions using our Knowledge Base: http://kb.juniper.net/.
• Download the latest versions of software and review release notes: http://www.juniper.net/customers/csc/
software/.
• Search technical bulletins for relevant hardware and software notifications: http://kb.juniper.net/InfoCenter/.
• Join and participate in the Juniper Networks Community Forum: http://www.juniper.net/company/
communities/.
• Open a case online in the CSC Case Management tool: http://www.juniper.net/cm/.
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. i

Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
To verify service entitlement by product serial number, use our Serial Number Entitlement (SNE) Tool: https://
entitlementsearch.juniper.net/entitlementsearch/.
Opening a Case with JTAC
You can open a case with JTAC on the Web or by telephone.
• Use the Case Management tool in the CSC at http://www.juniper.net/cm/.
• Call 1-888-314-JTAC (1-888-314-5822 toll-free in the USA, Canada, and Mexico).
• For international or direct-dial options in countries without toll-free numbers, see http://www.juniper.net/
support/requesting-support.html
.
ii Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.

This preface contains the following sections:
Preface
• About This Guide on page 1
• Organization on page 1
• Typographical Conventions on page 2
• Related Documentation on page 2
About This Guide
This guide describes the commands that make up the command-line interface (CLI) of the Juniper ATP
Appliance.
This guide is intended for system administrators responsible for deploying, operating, and maintaining the Juniper
ATP Appliance.
Organization
This guide is organized as follows:
• Chapter 1, “Introduction”—Includes an overview of CLI usage, CLI Modes and information about how to
access the Juniper ATP Appliance Command Line Interface.
• Chapter 2, “All-in-One CLI Commands”—Provides information about system commands for updating the
product boot images, setting configurations, and defining system-level settings for Collector and
Detection Engine interfaces and network deployment services.
• Chapter 3, “Core/CM Server CLI Commands”—Provides information about commands available to the
Core and Central Manager for all hardware appliance, software appliance, and virtual appliance models,
including the commands used to manage Detection Engines and Juniper ATP Appliance system
configuration.
• Chapter 4, “Mac OS X Engine CLI Commands”—Provides information about Mac Mini Mac OS X Detection
Engine-specific commands for configuration and status monitoring.
• Chapter 5, “Traffic Collector CLI Commands”—Provides information about the Juniper ATP Appliance
Traffic Collector commands available for identifying, monitoring, and configuring distributed Collector
hardware, software and virtual appliances.
• Chapter 6, “Glossary of Terms”—Provides a set Juniper ATP Appliance-specific as well as cybersecurity
industry terms and definitions.
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
Typographical Conventions
This guide uses the following typographical conventions for special terms and instructions.
Table 4-1 Typographical Conventions
Convention Meaning Example
courier font Coding examples and text to be
entered at the command prompt
Enter the following command:
server set dns
Click A left-mouse button click. Click Download IVP to perform
endpoint infection verification.
Double-click A double-click of the left mouse
button.
Double-click the report name to open
in the integrated SIEM application.
Right-click A right mouse button click. Right-click on the icon to view its
properties.
< | > (text in
angle brackets;
Option for selection of required
parameter and/or value.
interfaces set stp <on | off >
items separated
by the pipe
symbols)
[ ] (text in
square
brackets)
Optional parameters and values,
with selection options separated by
the pipe symbol.
show device alarm [cpu_util | paging]
or
[ | ] (text in
square brackets,
items separated
by pipe
symbols)
Related Documentation
The following is a list of additional Juniper ATP Appliance documentation:
• Juniper ATP Appliance Release Notes— Describes the latest release of the Juniper ATP Appliance software.
• Juniper ATP Appliance Quick Start Guides— Quick Starts describe how to install and initially configure a
Juniper ATP Appliance; refer to the Quick Start for your device or model.
• Juniper ATP Appliance Operator’s Guide— The Operator’s Guide describes usage of all aspect of the Juniper
ATP Appliance All-in-One or distributed defense system.
• Juniper ATP Appliance CEF/SYSLOG Support for SIEM — This guide provides information about Juniper ATP
Appliance CEF and Syslog Logging for SIEM.
• Juniper ATP Appliance Safety and Regulatory Guide—Contains conformance and safety information for
Juniper ATP Appliances.
• Juniper ATP Appliance API Reference Guide— Provides Juniper ATP Appliance HTTP API functions and
information about usage.
2 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.

This chapter explains how to use the Juniper ATP Appliance command line interface (CLI) to configure and
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
administer a Juniper ATP Appliance.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• “Accessing the CLI” in the next section
• CLI Help and Keyboard Shortcuts on page 16
• CLI Modes on page 17
Accessing the CLI
You have the option of accessing the Juniper ATP Appliance CLI in either of two ways:
• Console
• SSH
NOTE Always use the latest version of Putty for SSH operations, if using Putty as an SSH client.
Hardware Appliance Access via the Console
To access the Juniper ATP Appliance CLI using the console port:
1. Connect your computer’s serial port to the DB-9 console port on the Juniper ATP Appliance.
2. Open a terminal program such as Console on Mac OS X, HyperTerminal on Windows, or Minicom on Linux.
3. Configure the terminal program serial communication settings as follows:
› Bits per second: 960
› Data bits: 8
› Stop bit: 1
›Parity: None
4. At the CLI prompt, enter your username and password. By default, the admin user name is admin and the
password is 1JATP234
.
Be sure to change the default password for the admin account after initial setup;
the password must be at least 8 characters in length.
5. To launch the configuration wizard, enter the command
wizard.
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 3
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
# wizard
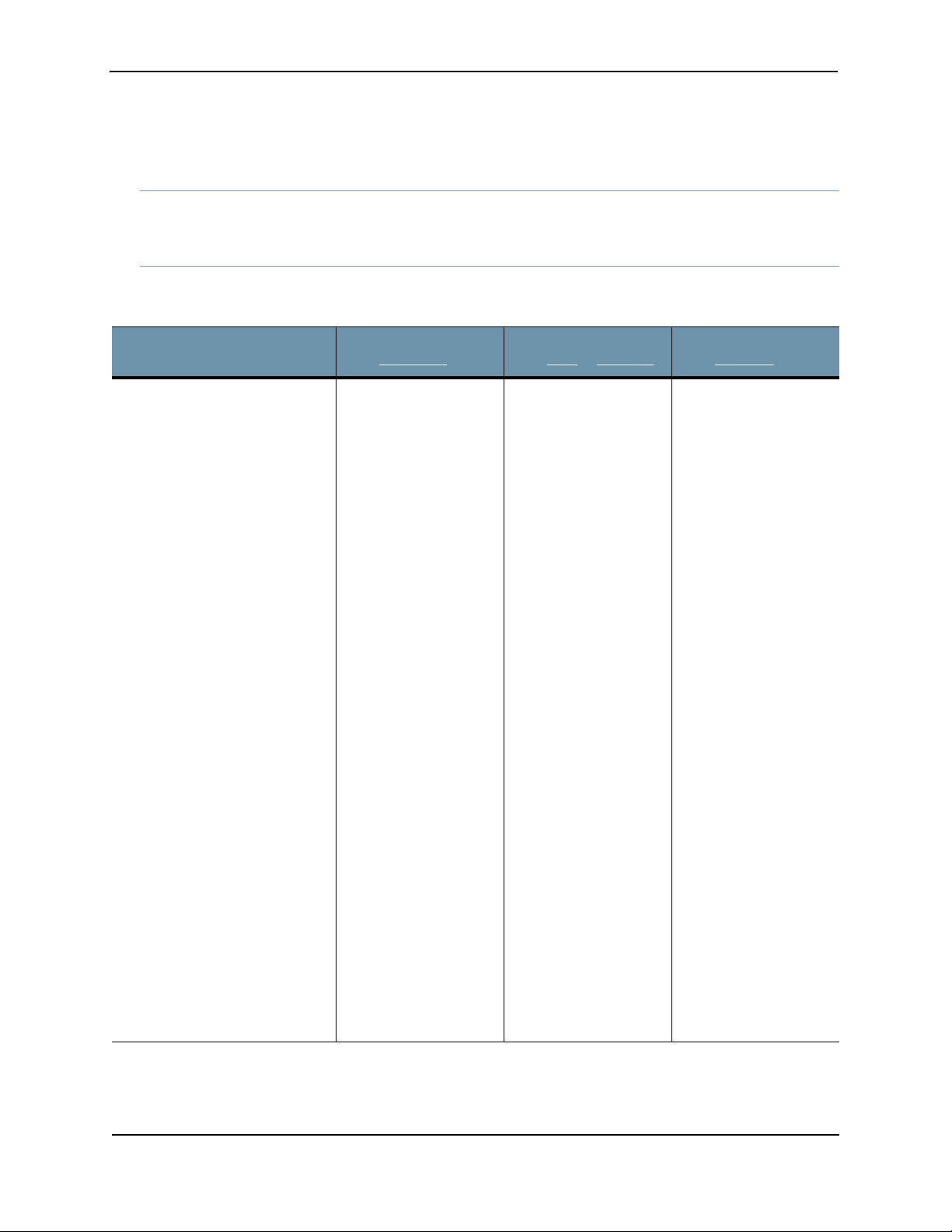
Configuration Wizard Command Prompt Progressions
NOTE Enter CTRL-C to exit the Configuration Wizard at any time. If you exit without completing the
configuration, you will be prompted again whether to run the Configuration Wizard.
You may also rerun the Configuration Wizard at any time with the CLI command wizard.
Configuration Wizard
Prompts
Use DHCP to obtain the IP
address and DNS server
address for the administrative
interface (Yes/No)?
Note: Only if your DHCP
response is no,enter the
following information when
prompted:
a. IP address
b. Netmask
c. Enter a gateway IP
address for this
management
(administrative) interface:
d. Enter primary DNS server
IP address.
e. Do you have a secondary
DNS Server (Yes/No).
Customer Response
from All-in-One
We strongly discourage
the use of DHCP
addressing because it
changes dynamically.
A static IP address is
preferred.
Recommended:
Respond with no:
a. Enter an IP address
b. Enter a netmask
using the form
255.255.255.0.
c. Enter a gateway IP
address.
d. Enter the DNS server
IP address
e. If yes, enter the IP
address of the
secondary DNS server.
Customer Response
from Core
We strongly discourage
the use of DHCP
addressing because it
changes dynamically.
A static IP address is
preferred.
Recommended:
Respond with no:
a. Enter an IP address
b. Enter a netmask
using the form
255.255.255.0.
c. Enter a gateway IP
address.
d. Enter the DNS server
IP address
e. If yes, enter the IP
address of the
secondary DNS server.
or Mac Mini
Customer Response
from Collector
We strongly discourage
the use of DHCP
addressing because it
changes dynamically.
A static IP address is
preferred.
Recommended:
Respond with no:
a. Enter an IP address
b. Enter a netmask
using the form
255.255.255.0.
c. Enter a gateway IP
address.
d. Enter the DNS server
IP address
e. If yes, enter the IP
address of the
secondary DNS server.
f. Do you want to enter the
search domains?
g. Enter the search domain
(separate multiple search
domains by space):
Restart the administrative
interface (Yes/No)?
4 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
f. Enter yes if you want
DNS lookups to use a
specific domain.
g. Enter space
domain(s) separated
by spaces; for
example: example.com
lan.com dom2.com
Enter yes to restart
with the new
configuration settings
applied.
f. Enter yes if you want
DNS lookups to use a
specific domain.
g. Enter space
domain(s) separated
by spaces; for
example: example.com
lan.com dom2.com
Enter yes to restart
with the new
configuration settings
applied.
f. Enter yes if you want
DNS lookups to use a
specific domain.
g. Enter space
domain(s) separated
by spaces; for
example: example.com
lan.com dom2.com
Enter yes to restart
with the new
configuration settings
applied.
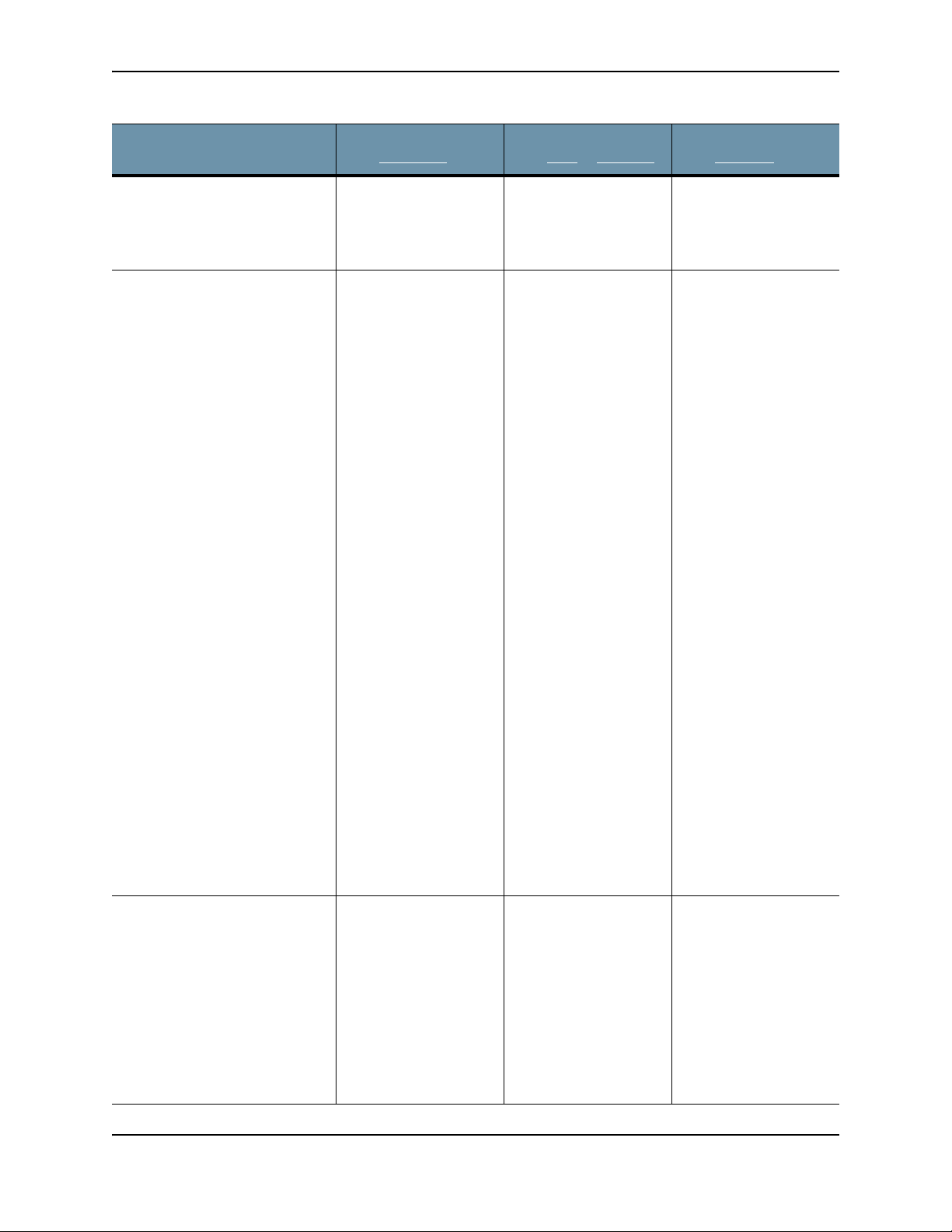
CLI Command Reference Guide
Configuration Wizard
Prompts
Enter a valid hostname (enter a
unique name)
[OPTIONAL]
If the system detects a
Secondary Core with an eth3
port, then the alternate CnC
exhaust option is displayed:
Use alternate-exhaust for the
analysis engine exhaust traffic
(Yes/No)?
Enter IP address for the
alternate-exhaust (eth2)
interface:
Enter netmask for the
alternate-exhaust (eth2)
interface: (example:
255.255.0.0)
Enter gateway IP Address for
the alternate-exhaust (eth2)
interface: (example:10.6.0.1)
Enter primary DNS server IP
Address for the alternateexhaust (eth2) interface:
(example: 8.8.8.8)
Do you have a secondary DNS
server for the alternate-exhaust
(eth2) interface?
Do you want to enter the search
domains for the alternateexhaust (eth2) interface?
Note: A complete network
interface restart can take more
than 60 seconds
Customer Response
from All-in-One
Type a hostname
when prompted; do
not include the
domain; for example:
juniperatp1
Refer to “Configuring
an Alternate Analysis
Engine Interface” in the
Juniper ATP Appliance
Operator’s Guide for
more information.
Enter yes to configure
an alternate eth2
interface.
Enter the IP address for
the eth2 interface.
Enter the eth2
netmask.
Enter the gateway IP
address.
Enter the primary DNS
server IP Address for
the alternate-exhaust
(eth2) interface.
Enter yes or no to
confirm or deny an
eth2 secondary DNS
server.
Enter yes or no to
indicate whether you
want to enter search
domain.
Customer Response
from Core
Type a hostname
when prompted; do
not include the
domain; for example:
juniperatp1
Refer to “Configuring
an Alternate Analysis
Engine Interface” in the
Juniper ATP Appliance
Operator’s Guide for
more information.
Enter yes to configure
an alternate eth2
interface.
Enter the IP address for
the eth2 interface.
Enter the eth2
netmask.
Enter the gateway IP
address.
Enter the primary DNS
server IP Address for
the alternate-exhaust
(eth2) interface.
Enter yes or no to
confirm or deny an
eth2 secondary DNS
server.
Enter yes or no to
indicate whether you
want to enter search
domain.
or Mac Mini
Customer Response
from Collector
Type a hostname
when prompted; do
not include the
domain; for example:
juniperatp1
[Traffic Collectors do
not send or receive
Core analysis engine
CnC network traffic, so
no eth2 interface is
needed.]
Regenerate the SSL self-signed
certificate (Yes/No)?
Enter yes to create a
new SSL certificate for
the Juniper ATP
Appliance Server Web
UI.
If you decline the selfsigned certificate by
entering no, be
prepared to install a
certificate authority
(CA) certificate.
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 5
Enter yes to create a
new SSL certificate for
the Juniper ATP
Appliance Server Web
UI.
If you decline the selfsigned certificate by
entering no, be
prepared to install a
certificate authority
(CA) certificate.
Not applicable to
Collector.
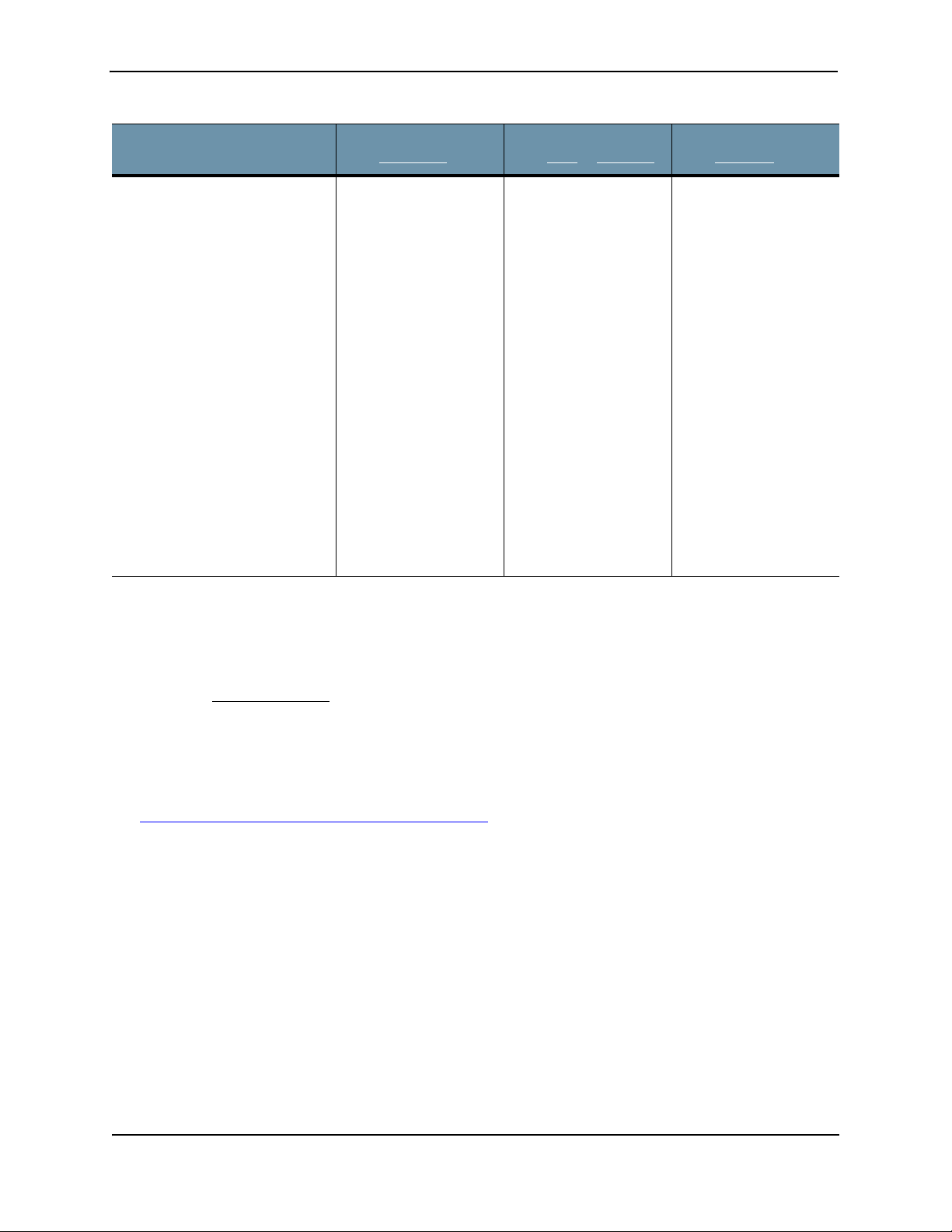
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
Configuration Wizard
Prompts
Enter the following server
attributes:
Is this a Central Manager device:
Device Name: (must be unique)
Device Description
Device Key PassPhrase
NOTE: Remember this
passphrase and use it for all
distributed devices!
Customer Response
from All-in-One
Enter Yes; the system
will auto-set IP
127.0.0.1 as the All-inOne IP address.
Enter the Juniper ATP
Appliance Collector
Host Name; this
identifies the Collector
in the Web UI.
Enter a device
Description
Enter a user-defined
PassPhrase to be used
to authenticate the
Core to the Central
Manager.
Customer Response
from Core
Enter Yes; the system
will auto-set IP
127.0.0.1 as the All-inOne IP address.
Enter a Juniper ATP
Appliance Mac Mini or
Core/CM Host Name;
this identifies the Mac
OS X or Core Engine in
the Web UI.
Enter a device
Description
Enter the same
PassPhrase used to
authenticate the Core
or Mac Mini to the
Central Manager.
or Mac Mini
Customer Response
from Collector
Enter No; the system
will request that you
enter the CM IP
address now.
Enter the Juniper ATP
Appliance Collector
Host Name; this
identifies the Collector
in the Web UI.
Enter a device
Description
Enter the same
PassPhrase used to
authenticate the
Collector to the Central
Manager.
Hardware, Software and Virtual Appliance Access via SSH
To access the Juniper ATP Appliance CLI over the management network:
1. Start a terminal window session and use the ssh command to access the appliance.
For example, if the IP address of the appliance is 10.1.1.2, enter the following command:
xxxxssh admin@10.1.1.2
2. When prompted, enter your password. By default, the admin user name is admin and the password is
1JATP234.
3. To launch the configuration wizard, enter the command
wizard.
# wizard
See Configuration Wizard Command Prompt Progressions for steps.
CLI Help and Keyboard Shortcuts
To display Juniper ATP Appliance CLI help, type the command help to display CLI keys and auto-completion
usage.
For context-sensitive help, alternatively, enter a “?” to display either a list of possible command completions with
summaries, or the full syntax of the current command. A subsequent repeat of this key, when a command has
been resolved, will display a detailed reference, as described below.
• Enter “?” at the prompt to display a list of the available commands in the current mode.
• Enter “?” after you type a command to display its available options and parameters.
• Enter “?” after a partially typed keyword to display command matches for auto-completions
You can enter commands in abbreviated form if you enter enough characters to uniquely identify each keyword.
For example, the show interface command can be abbreviated as:
sh in
6 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
CLI Command Reference Guide
To identify a command’s minimum abbreviation, type a few characters then press Tab. When you have entered
enough characters, the keyword is completed.
The following table outlines the available CLI shortcuts.
Table 1-1 Keyboard Shortcuts
Action Shortcut Description
Auto-Completion Enter, Tab
or Space
Key
Recall Ctrl+P or ↑ Retrieve previous command from CLI history.
Ctrl+N or ↓ Retrieve next command from CLI history.
Ctrl+L or
Ctrl+R
Delete Ctrl+D Delete character.
Ctrl+H Delete character before cursor (Backspace).
Ctrl+K Delete all characters from cursor to end of line.
Ctrl+U or
Ctrl+W
Cursor move Ctrl+A Move cursor to start of line.
Ctrl+B Move cursor back a single character.
Ctrl+E Move cursor to end of line.
Ctrl+F Move cursor forward a single character.
Character
Transpose
Ctrl+T Transpose character at the cursor with preceding character.
Completes a partial command during typing if enough
characters are typed to uniquely identify it.
Clear the screen or Redisplay the current command line.
Delete all characters or words on line.
Interrupt output Ctrl+C Interrupt presentation of the CLI output.
Replace !! Substitute the last command line
!N Substitute the Nth command line (absolute as per 'history'
command)
!-N Substitute the command line entered N lines before
(relative)
Exit mode or
logout
exit Exit current mode or exit the CLI session.
SPECIAL CHARACTER REQUIREMENT
You must enclose non-alphabet characters in double quotes in CLI commands; for example:
Juniper ATP Appliance(server)# set passphrase “kfe$nd#$^S”
CLI Modes
The CLI commands that you can enter depend on your user privileges and the CLI command mode. User roles are
“admin” and “debugging.” The following table describes the CLI command mode.
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 7
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
Note that the prompt in each mode includes the host name of the Juniper ATP Appliance.
Table 1-2 Summary of CLI Modes
Mode Description How to Exit
Basic Mode Monitor system operation and issue basic system
commands. This is the default login mode. The following
prompt is displayed:
JATP#
CM Mode Monitor system history and upgrades from the Core or
vCore in cm (Central Manager) mode.
JATP_Hostname# cm
JATP_Hostname (cm)# ?
Core
Configuration
Mode
Collector
Configuration
Mode
Diagnosis
Packet
Capture,
Monitoring,
GSS Reporting
and
Configuration
Mode
To access Core configuration mode in the Core/CM, All-inOne, and Mac Mini, enter “core” in Basic mode. The prompt
changes to indicate the mode in parentheses:
JATP_Hostname# core
JATP_Hostname (core)# ?
Configure the Juniper ATP Appliance Collector (includes all
commands). To access Collector configuration mode,
enter “collector” in Basic mode. The prompt changes to
indicate the mode in parentheses:
JATP_Hostname# collector
JATP_Hostname (collector)# ?
Check Initial Setup, Diagnose, Monitor, Set GSS, and
Configure the Juniper ATP Appliance (includes all
commands). To access Diagnosis mode, enter
“diagnosis” in Basic mode. The prompt changes to
indicate the mode in parentheses:
JATP_Hostname# diagnosis
JATP_Hostname (diagnosis)# ?
Enter exit to log
out of the CLI.
Enter exit to
leave cm mode.
Enter exit to
leave server
mode.
Enter exit to
leave server
mode.
Enter exit to
leave diagnosis
mode.
Server
Configuration
Mode
Wizard
Configuration
Mode
8 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Set up and monitor the system (includes all Basic
commands plus server-specific commands). To access
Server configuration mode, enter “server” in Basic mode.
The prompt changes to indicate the mode in parentheses:
JATP-Hostname# server
JATP-Hostname (server)# ?
Configure the system during installation and setup the
management network and connected Juniper ATP
Appliance components. To access wizard configuration
mode, enter “wizard” in Basic mode. The prompt changes
to indicate the mode in parentheses:
JATP-Hostname# wizard
JATP-Hostname (wizard)# ?
Enter exit to
leave server
mode.
Enter exit to
leave wizard
mode.

This chapter describes the administration commands for a Juniper ATP Appliance All-in-One server appliance,
CHAPTER 2
All-in-One CLI Commands
software appliance or virtual appliance.
These commands are used to configure the Juniper ATP Appliance All-in-One appliance, manage configurations,
and set system-level settings for interfaces, network services, and SIEM integration.
NOTE You must enclose non-alphabet characters in double quotes in CLI commands.
Basic Mode Commands
Use general system commands to configure the appliance, view appliance history, enter other CLI modes, obtain
help with CLI syntax, and to exit the CLI session.
The general commands are:
• cm on page 12
• core on page 13
• collector on page 12
• diagnosis on page 14
• exit on page 14
• help on page 16
• history on page 17
• server on page 20
• wizard on page 35
Refer to the sections in this guide to review CM Mode, Collector Mode, Core Mode, Diagnosis Mode, Server Mode
and Wizard mode commands per device-- All-in-One, CoreCM, Traffic Collector and Mac OS X Detection Engine
on a Mac Mini.
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 9

Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
CM Commands
• exit on page 14
• help on page 16
• history on page 17
• upgrade on page 34
Core Mode Commands
• exit on page 14
• help on page 16
• history on page 17
• show (core mode) on page 32
• updateimage on page 35
Server Mode Commands
• exit on page 14
• help on page 16
• history on page 17
• ifrestart on page 17
• ping on page 18
• reboot on page 18
• restart on page 19
• restore on page 20
• set ip interface (server mode) on page 26
• set system-alert (server mode) on page 29
• set (server mode) on page 27
• shutdown on page 34
• shutdown on page 34
• traceroute on page 34
Collector Mode Commands
• exit on page 14
• help on page 16
• history on page 17
• set honeypot (collector mode) on page 22
• set traffic-monitoring (for JATP700 Appliances only) (collector mode) on page 22
• set traffic-filter (collector mode) on page 23
• set protocols (collector mode) on page 23
• set proxy (collector mode) on page 24
• set traffic-filter (collector mode) on page 23
• show (collector mode) on page 31 [show proxy inside or show proxy outside]
10 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Diagnosis Mode Commands
• capture-start on page 11
• copy on page 13
• exit on page 14
• gssreport on page 15
• help on page 16
• history on page 17
• set (diagnosis mode) on page 25
• setupcheck on page 30
• show (diagnosis mode) on page 33
All-in-One CLI Commands
capture-start
Table 2-1 capture-start
Starts packet capture as a means for diagnosing and debugging network traffic and
Description
obtaining stats.
See Also: diagnosis
CLI Command Reference Guide
[mode]; collector [mode]; copy
Product(s) CLI
Mode(s)
Syntax
Parameters
Sub-Commands None
All-in-One | Collector
Diagnosis
capture-start
<IP address> <interface_name>
The following example starts a packet capture process on interface eth1 for a
Traffic Collector with IP address 8.8.8.8:
hostname # diagnosis
Example
hostname (diagnosis)# capture-start 8.8.8.8 eth1
NOTE Note: Address 8.8.8.8 need not be a Juniper ATP Appliance. It is just a
host that the capture filters on.
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 11
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
cm
Table 2-2 cm
Enters cm (Central Manager) mode.
Description
See Also: basic
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Core
Mode(s) Basic
[mode];
Syntax
Parameters
Sub-Commands
Example
cm
None
exit | help | history | upgrade
The following command example enters cm configuration mode:
hostname # cm
hostname (cm)#
collector
Table 2-3 collector
Enters the Collector configuration mode.
Description
See Also: server
Product(s) CLI
Mode(s) Basic
Syntax
Parameters None
All-in-One | Collector
collector
[mode]
Sub-Commands exit
Example
; help; history; set (server mode); show (collector mode)
The following example enters collector configuration mode:
hostname # collector
hostname (collector)# ?
12 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
copy
Table 2-4 copy
Description
CLI Command Reference Guide
Uses Secure Copy (SCP) to copy and transfer packet capture or traceback (crash)
data to a remote location, providing the same authentication and level of security
as an SSH transfer.
The copy traceback command, upon Customer Support's request, copies the
traceback files out of the box to a remote location.
See Also: diagnosis
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core-CM | Mac OSX Engine
Mode(s) Diagnosis
[mode]; capture-start
copy capture <scp source_file_name
Syntax
username@destination_host:destination_folder> | traceback
{<tab> | ALL} <string URI as user@hostname:path
copy capture <scp remote filename_location>
Parameters
Sub-Commands None
Example
core
Table 2-5 core
Description
copy traceback <ALL | filename>
copy traceback <tab> [tab displays all available crash filenames]
The following example copies the file "Eth1.txt" from the local host to a remote
host:
hostname (diagnosis)# copy capture Eth1.txt
admin@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory
Enters core mode.
See Also: basic
[mode];
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core | Mac OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Basic
Syntax
Parameters
Sub-Commands
Example
core
None
exit, help, history, show, updateimage
The following command example enters core configuration mode:
hostname # core
hostname (core)#
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 13
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
diagnosis
Table 2-6 diagnosis
Enters the Diagnosis configuration and status check mode.
Description
See Also: collector [mode], server [mode]
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Mac OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Basic
Syntax
Parameters None
Sub-Commands
diagnosis
capture-start; copy; exit; gssreport; help; history; set
(server mode); setupcheck; show (diagnosis mode); shutdown
The following example enters diagnosis configuration and status check mode:
Example
exit
Table 2-7 exit
Description Ends the CLI session.
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Basic | Core | Collector | Diagnosis | Server
Syntax
Parameters None
Example
hostname # diagnosis
hostname (diagnosis)# ?
exit
The following example ends a command mode or CLI session.
JATP# (diagnosis) exit
JATP#
JATP (core) exit
JATP# exit
14 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
gssreport
Table 2-8 gssreport
Use the gssreport command to submit reports to Juniper Global Security Services
Description
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Mac OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) diagnosis
(GSS), and to display the status of the current GSS report.
See Also: gssreport
; diagnosis [mode]
CLI Command Reference Guide
Syntax
Parameters
Sub-Commands None
gssreport status | submit
status - displays the status of the current GSS report.
submit - submits a report to Juniper ATP Appliance GSS.
The following examples display the status of a GSS report submission:
hostname # diagnosis
hostname (diagnosis)# gssreport submit
Successfully started GSS report
Example
hostname (diagnosis)# gssreport status
GSS is currently enabled
Last 5-minute GSS report at 2015-07-28 10:34:24.414322:
successfully submitted
Last hourly GSS report at 2015-07-28 10:34:24.468259:
successfully submitted
Last daily GSS report at 2015-07-28 10:34:28.225512:
successfully submitted
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 15
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
help
Table 2-9 help
Description Displays information about the CLI help system.
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Basic | Core | Collector | Diagnosis | Server
Syntax
Parameters
Example
help
None
The following example shows some of the output of the help command.
CONTEXT SENSITIVE HELP
[?] - Display context sensitive help. This is either a list of
possible command completions with summaries, or the full syntax
of the current command. A subsequent repeat of this key, when a
command has been resolved, will display a detailed reference.
AUTO-COMPLETION
The following keys both perform auto-completion for the current
command line. If the command prefix is not unique then the bell
will ring and a subsequent repeat of the key will display
possible completions.
[enter] - Auto-completes, syntax-checks then executes a command.
If there is a syntax error then offending part of the command
line will be highlighted and explained.
[tab] - Auto-completes
[space] - Auto-completes, or if the command is already resolved
inserts a space.
If “<cr>” is shown, that means that what you have entered so
far is a complete command, and you may press Enter (carriage
return) to execute it.
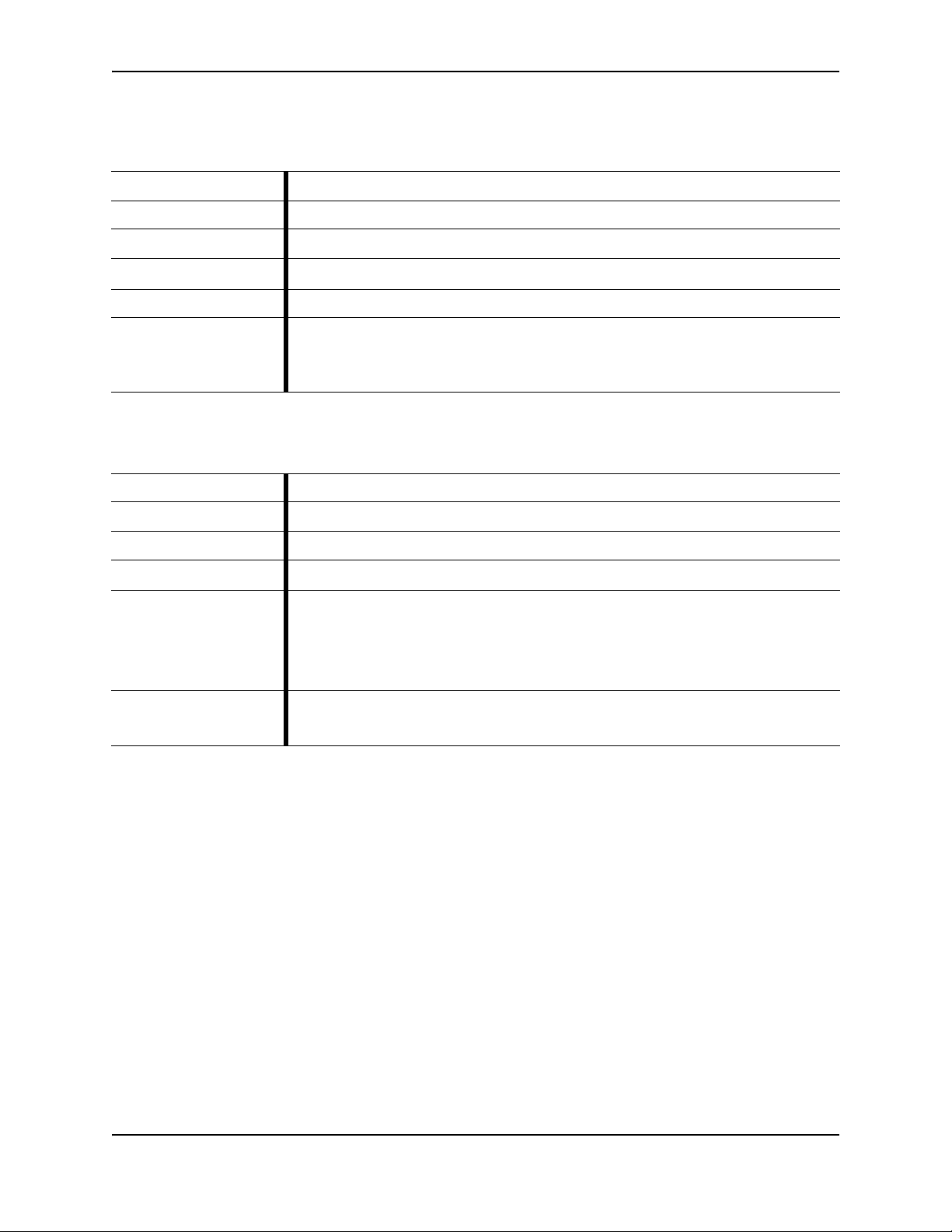
Use ? to learn command parameters and option:
JATP (server)# show f?
firewall Show the firewall configuration settings
interface
JATP (server)# show firewall?
all Show the current iptables settings
whitelist Show the iptables whitelist settings
show firewall whitelist?
<cr>
show firewall whitelist
16 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
CLI Command Reference Guide
eth0 Restarts the management network administra
interface.
eth1 Restarts the monitoring network interface.
history
Table 2-10 history
Description Displays the current CLI session command line history.
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Basic | Core | Collector | Diagnosis | Server
Syntax
Parameters None
Example
history
The following examples returns command line history for the current CLI session.
JATP# (core) history
ifrestart
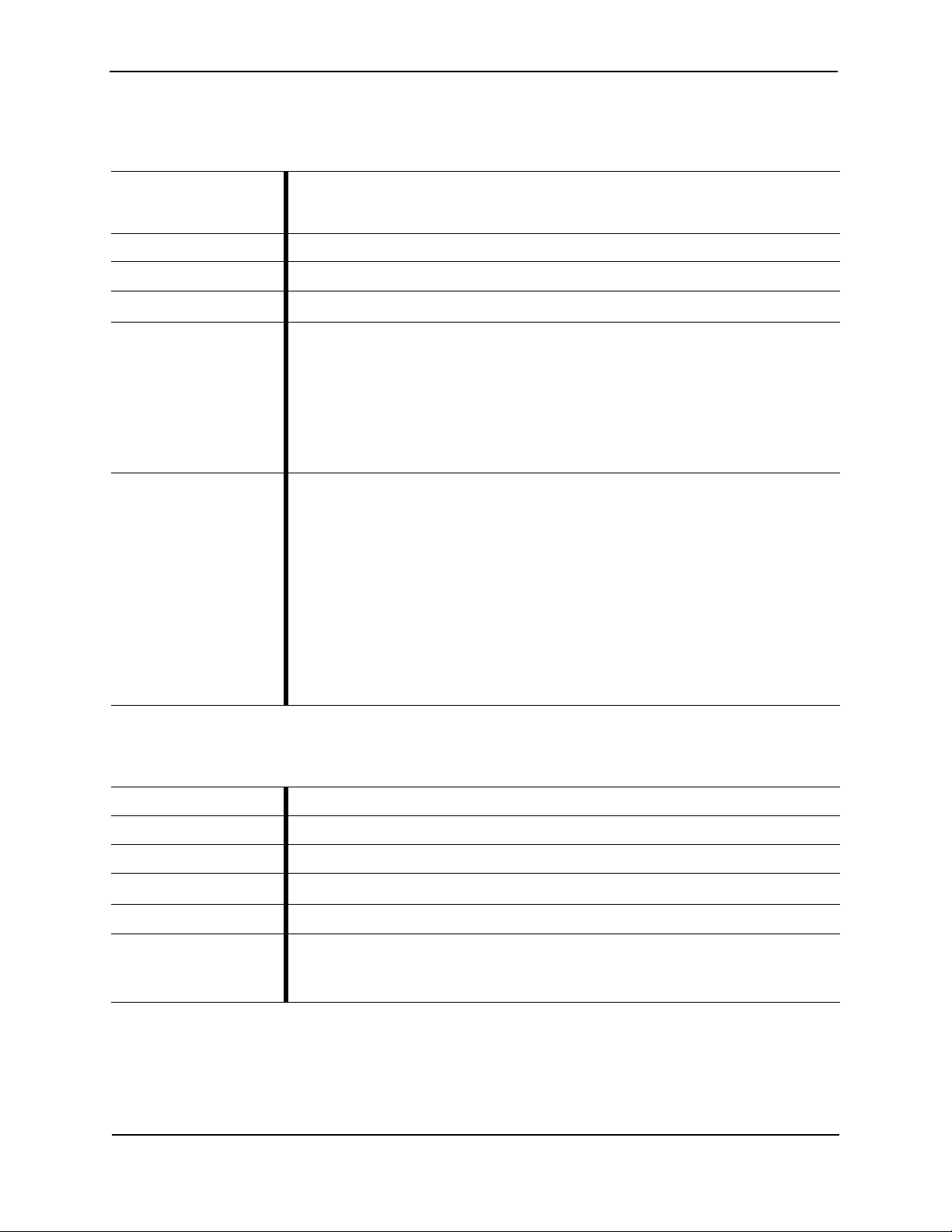
Table 2-11 ifrestart
Description Restarts the interface driver and services using the interface.
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Server
Syntax
Parameters
Example
ifrestart eth0 | eth1
The following example restarts the eth0 interface for the management network.
<FireEye_name># ifrestart eth0
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 17
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
-c count Number of echo requests to send. By default, pings ar
continuously until you press Ctrl+C.
-h hops Number of next hops between pings (default is 1).
string IP address, hostname or interface name used to ping
device address.
ping
Table 2-12 ping
Sends ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) echo request packets to a
Description
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Server
specified host name or IP address to verify that the destination is reachable over
the network.
Syntax
Parameters
Example
reboot
ping [-c count] [-h hops] [string]
The following example sends three echo requests to the device with the IP Address
10.10.10.1
<FireEye_name># ping -c 3 10.10.10.1
PING 10.10.10.1 (10.10.10.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.10.1: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=0.314 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.10.1: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=0.277 ms
64 bytes from v: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=0.274 ms
--- 10.10.10.1 ping statistics --3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time
bbbb1999ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.274/0.288/0.314/0.022 ms
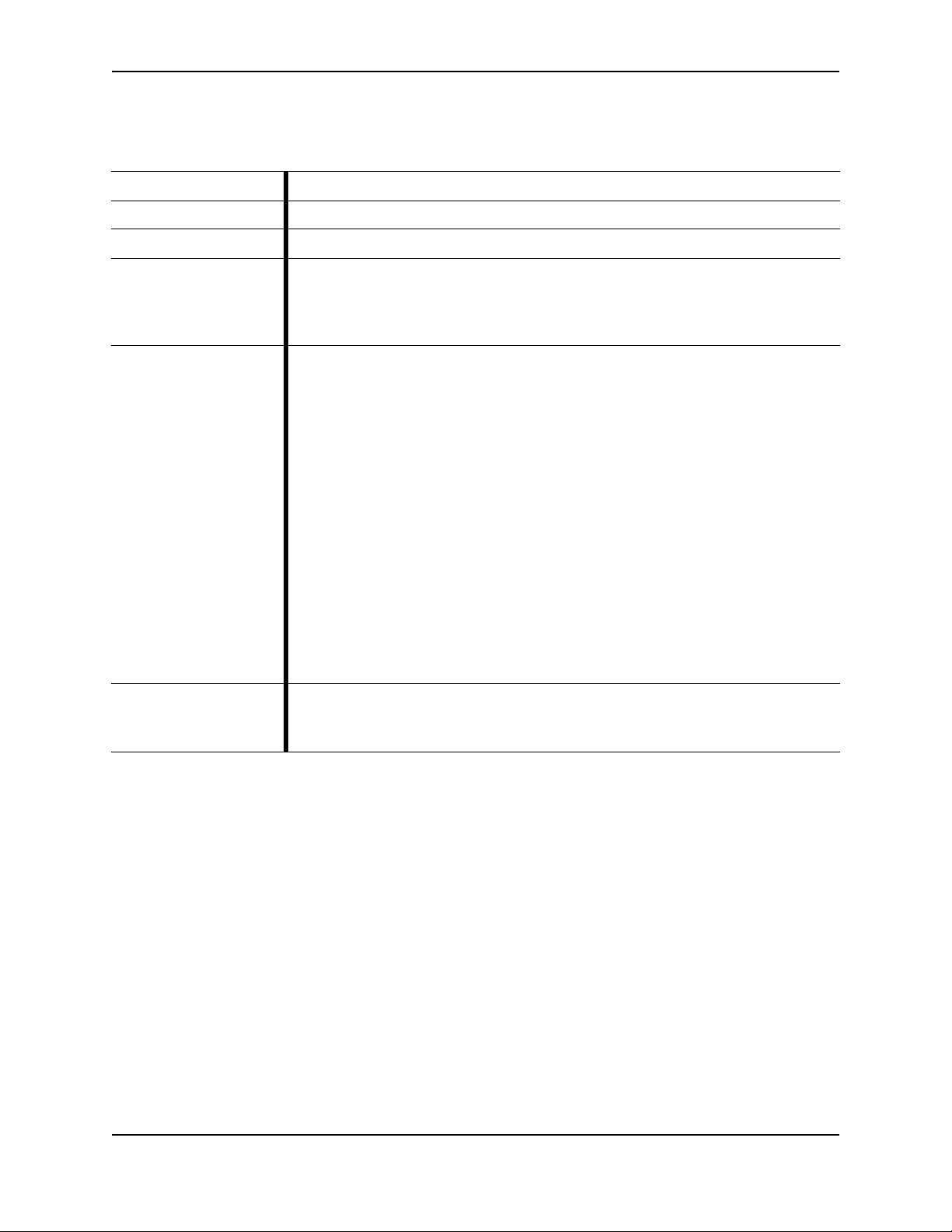
Table 2-13 reboot
Description Reboots the Juniper ATP Appliance.
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Server
Syntax
Parameters
Example
reboot
None
The following example reboots the system.
hostname# reboot
18 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
CLI Command Reference Guide
all
Restarts all Juniper ATP Appliance services.
behaviorengine Restarts the Behavioral Analysis Engine.
cm Restarts the Central Manager Web UI service.
collector
Restarts the Collector service.
core Restarts the Core Detection Engine.
correlationengine Restarts the Correlation Engine.
database Restarts the Database.
ntpserver Restarts the NTP server.
sshserver Restarts the SSH server.
staticengine Restarts the Static Analysis Engine.
webserver Restarts the web server.
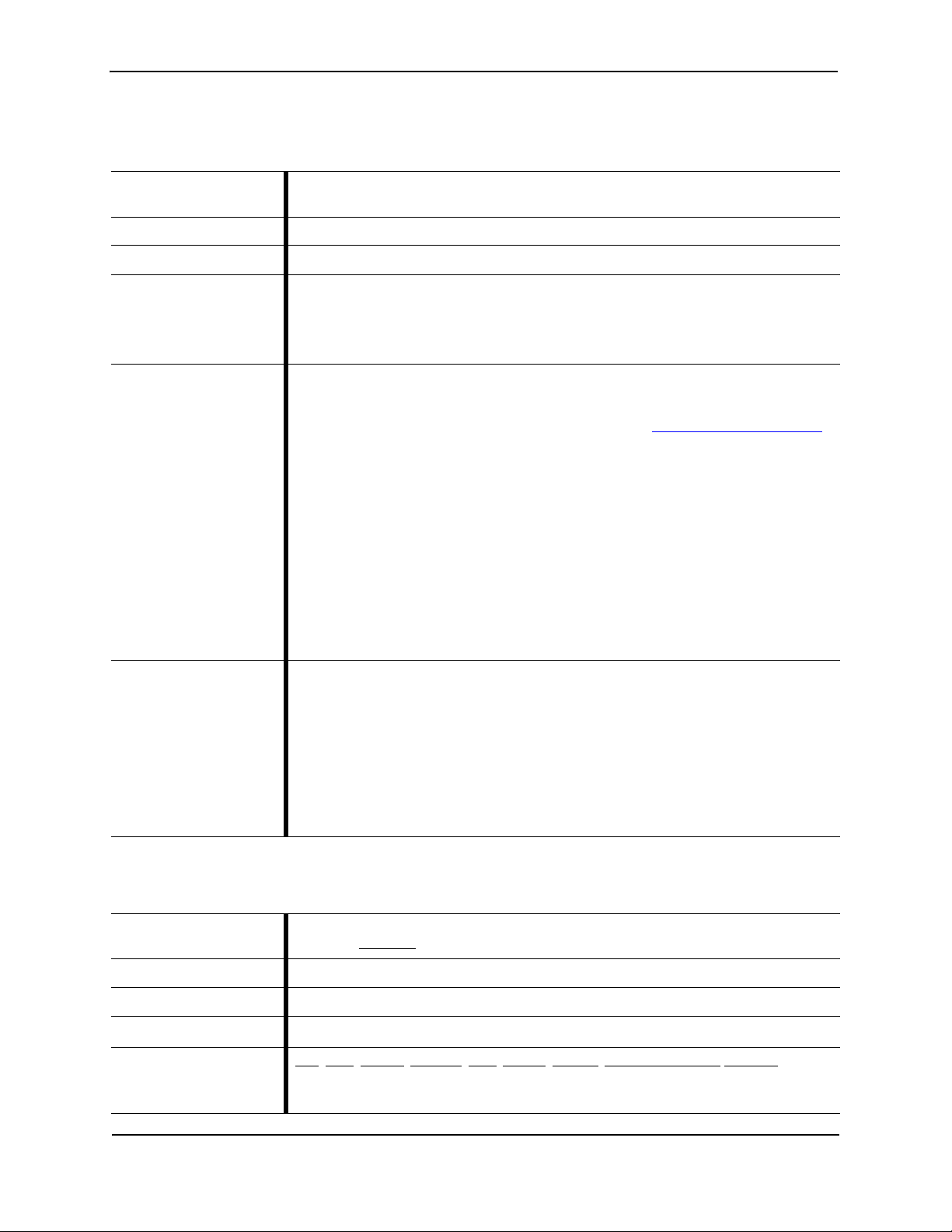
restart
Table 2-14 restart
Description Restarts Juniper ATP Appliance services.
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Server
restart [all | behaviorengine | cm | collector | core |
Syntax
correlationengine | database | ntpserver | sshserver |
staticengine | webserver]
Parameters
The following example restarts the Central manager service.
Example
JATP# restart cm
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 19
Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
support Restores the default support password setting
remote login (set during initial installation per l
See also (server)# set (server mode) support
firewall {backup | default} Restores the firewall settings from either the pr
backup, or from the default factory settings.
hostname Restores the system’s hostname to the factory
hostname.
network Restores the IP address and DNS settings to th
factory default settings.
WARNING: This command option removes the
IP address and DNS settings, and reloads the d
values for these settings.
restore
Table 2-15 restore
Description
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core CM | Mac Mini OS X Detection Engine
Mode(s) Server
Restores the system configuration to the factory default settings.
This will only reset the password to default temporarily.
restore [support | firewall {backup | default} | hostname
Syntax
Parameters
Note: vCore for AWS
does not use the
following CLI
commands:
restore hostname
restore network
| network]
Whitelist rules rely on normal service shutdown to be backed up.Powering off a VM
directly will lose the whitelist state as rules cannot be saved in that case.
The following example restores the system.
JATP# restore
Example
server
Table 2-16 server
Description
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector | Core/CM | Mac Mini Mac OS X
Mode(s) Basic
Syntax
Sub-Commands
20 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
This next example restores the SSH login “support” password to the default.
JATP # restore support password
Restore the default support password? (Yes/No)? yes
support password was restored successfully!
Enters the server configuration mode.
See Also: collector
server
; help; history; ifrestart; ping; reboot; restore; set (server mode);upgrade
exit
Whitelist rules rely on normal service shutdown to be backed up.Powering off a VM
directly will lose the whitelist state as rules cannot be saved in that case.
Table 2-16 server
CLI Command Reference Guide
The following example enters server configuration mode:
Example
hostname # server
hostname (server) # ?
Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc. 21

Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Appliance
set honeypot (collector mode)
Table 2-17 set honeypot
Enables and disables the SSH-Honeypot feature for a Traffic Collector.
A honeypot can be deployed within a customer network to detect network activity
generated by malware attempting to infect or attack other machines in a local area
network. These attempted SSH logins can be used to supplement detection of
lateral spread.
Description
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector
Mode(s) collector
There are two parameters that can be set for a honeypot:
• Enable/disable a honeypot
• Set a Static IP (IP, mask, and gateway) or DHCP of a publicly addressable interface
See Also:
show honeypot command in show (collector mode)
(collector)# set honeypot ssh-honeypot enable dhcp
Syntax
(collector)# set honeypot ssh-honeypot enable address (IP
address) netmask (subnet IP) gateway (IP address)
(collector):# set honeypot ssh-honeypot disable
The following example enables the SMB parser for lateral detections:
(collector)# set honeypot ssh-honeypot enable
address 1.2.3.4 netmask 255.255.0.0 gateway
Example
1.2.3.1
NOTE The static IP configuration does not require configuring DNS.
Honeypots do not require a DNS server at this time.
set traffic-monitoring (for JATP700 Appliances only) (collector mode)
Table 2-18 set traffic-monitoring
Description Sets the traffic monitoring interface on the JATP700
Product(s) CLI All-in-One | Collector
Mode(s) collector
# set traffic-monitoring-ifc 1gb_ifc
Set the traffic monitoring interface to be the 1G interface.
# set traffic-monitoring-ifc 10gb_ifc
Syntax
22 Copyright© 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Set the traffic monitoring interface to be the 10G interface.
NOTE After making an interface type change, the system must be rebooted
for the change to take effect.
 Loading...
Loading...