JS-Technik LSLV-M100 User Manual

JS-Technik GmbH - Lether Gerwerbestrasse 10 - 26197 Großenkneten www.js-technik.de
Safety Information
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in severe injury or
death.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in injury or
death.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result in minor injury or
property damage.
• Do not open the cover of the equipment while it is on or operating. Likewise, do not
operate the inverter while the cover is open. Exposure of high voltage terminals or
charging area to the external environment may result in an electric shock. Do not
remove any covers or touch the internal circuit boards (PCBs) or electrical contacts on
the product when the power is on or during operation. Doing so may result in serious
injury, death, or serious property damage.
• Do not open the cover of the equipment even when the power supply to the inverter
has been turned off unless it is necessary for maintenance or regular inspection.
Opening the cover may result in an electric shock even when the power supply is off.
• The equipment may hold charge long after the power supply has been turned off. Use
a multi-meter to make sure that there is no voltage before working on the inverter,
motor or motor cable.
Read and follow all safety instructions in this manual precisely to avoid unsafe operating
conditions, property damage, personal injury, or death.
Safety symbols in this manual
Safety information

• This equipment must be grounded for safe and proper operation.
• Do not supply power to a faulty inverter. If you find that the inverter is faulty, disconnect
the power supply and have the inverter professionally repaired.
• The inverter becomes hot during operation. Avoid touching the inverter until it has
cooled to avoid burns.
• Do not allow foreign objects, such as screws, metal chips, debris, water, or oil to get
inside the inverter. Allowing foreign objects inside the inverter may cause the inverter to
malfunction or result in a fire.
• Do not operate the inverter with wet hands. Doing so may result in electric shock.
• Check the protection degree of circuits and equipments used in the inverter degree of circuit
protection and the degree of equipment protection.
The following connection terminals and components are electrical protection class 0 devices.
The circuit is protected by the essential insulation and electric shock may occur if the
insulation is done improperly. The same protection measures for electric cables must be
taken when the using or installing the following compornents, or when you connect a cable to
the following terminals or components.
- Multi-function terminals: P1–P3, P4 (Advanced I/O), P5 (Advanced I/O), CM
- Analog terminal inputs and outputs: VR, V1, I2 (Advanced I/O), AO, CM
- Other terminal block connectors: Q1(Standard I/O), EG (Standard I/O), 24, A1, B1, C1, A2
(Advanced I/O), C2 (Advanced I/O)
- Cooling fan
• This inverter is a protection class 1 product.
• Do not modify the interior workings of the inverter. Doing so will void the warranty.
• The inverter is designed for 3-phase motor operation. Do not use the inverter to operate a
single phase motor.
• Do not place heavy objects on top of electric cables. Doing so may damage the cable and
result in an electric shock.
Note
Maximum allowed prospective short-circuit current at the input power connection is defined in
IEC 60439-1 as 100 kA. Depending on the selected MCCB, the LSLV-M100 Series is suitable
for use in circuits capable of delivering a maximum of 100 kA RMS symmetrical amperes at the
drive's maximum rated voltage. The following table shows the recommended MCCB for RMS
symmetrical amperes.
Remarque
Le courant maximum de court-circuit présumé autorisé au connecteur d’alimentation électrique
est défini dans la norme IEC 60439-1 comme égal à 100 kA. Selon le MCCB sélectionné, la
série LSLV-M100 peut être utilisée sur des circuits pouvant fournir un courant RMS symétrique
de 100 kA maximum en ampères à la tension nominale maximale du variateur. Le tableau
suivant indique le MCCB recommandé selon le courant RMS symétrique en ampères.
Working
Voltage
UTE100(E/N)
UTS150(N/H/L)
ABS33c
ABS53c
ABS63c
ABS103c
240V(50/60Hz)
50/65 kA
65/100/150 kA
30 kA
35 kA
35 kA
85 kA
Quick Reference Table
Situation
Reference
I want to configure the inverter to start operating as soon as the power source
is applied.
p.85
I want to configure the motor’s parameters.
p.196
Something seems to be wrong with the inverter or the motor.
p.224
What are the recommended wiring lengths?
p.23
The motor is too noisy.
p.131
I want to apply PID control on my system.
p.122
What are the factory default settings for multi-function terminals?
p. 205,
p. 210
I want to review recent fault trip and warning histories.
p.158
I want to change the inverter’s operation frequency using a potentiometer.
p.69,
p.70
p.72
I want to install a frequency meter using an analog terminal.
p.144
I want to monitor the supply current to motor.
p.58,
p.153
I want to operate the inverter using a multi-step speed configuration.
p. 79
The motor runs too hot.
p.161
The inverter is too hot.
p.163
The cooling fan does not work.
p.152
I want to change the items that are monitored on the keypad.
p.239
I want to operate the inverter using a multi-step speed configuration.
p.153
The following table contains situations frequently encountered by users while working with
inverters. Refer to the typical and practical situations in the table to quickly and easily locate
answers to your questions.

Table of Contents
1 Preparing the Installation
1.1 Product Identification
1.2 Part Names
1.3 Installation Considerations
1.4 Selecting and Preparing a Site for Installation
1.5 Cable Selection
2 Installing the Inverter
2.1 Mounting the Inverter
2.2 Cable Wiring
2.3 Post-Installation Checklist
2.4 Test Run
3 Learning to Perform Basic Operations
3.1 About the Keypad
About the Display
Operation Keys
Control Menu
3.2 Learning to Use the Keypad
Group Selection
Code Selection
Navigating Directly to Different Codes
Switching to a Different Code
Setting Parameter Values
3.3 Actual Application Examples
Acceleration Time Configuration
Frequency Reference Configuration
Frequency Setting
Initializing All Parameters
Frequency Setting (Keypad) and Operation (via Terminal Input)
Frequency Setting (External Potentiometer) and Operation (Terminal
Input)
Frequency Setting (Built-in Potentiometer) and Operation (Keypad)
3.4 Monitoring the Operation
Output Current Monitoring
Fault Trip Monitoring
4 Control Block Diagram
4.1 Setting Frequency
4.2 Setting Run Command
4.3 Controlling Acc/Dec and V/F Voltage
5 Learning Basic Features
5.1 Setting Frequency Reference
Keypad as the Source (KeyPad-1 setting)
Keypad as the Source (KeyPad-2 setting)
Built-in Volume input (V0) 0 – 5 [V] as the Source
V1 Terminal as the Source
Input Current (Terminal I2) as the Source
Input Voltage (Terminal I2) as the Source
Frequency Reference Setting via Built-in Volume (V0) and I2 Terminal
Frequency Reference Setting via Built-in Volume (V0) and I2 Terminal
Frequency Reference Setting via Built-in Volume (V0) and V1 Terminal
Frequency Reference Setting via RS-485 Communication
Frequency Reference Setting via Digital Volume (Up-Down)
5.2 Holding Analog Command Frequency
5.3 Setting Multi-step Frequency
5.4 Command Source Configuration
The Keypad as a Command Input Device
Terminal Block as a Command Input Device (Fwd/Rev Run Commands)
Terminal Block as a Command Input Device (Run and Rotation
Direction Commands)
RS-485 Communication as a Command Input Device
5.5 Forward or Reverse Run Prevention
5.6 Power-on Run
5.7 Reset and Restart
5.8 Setting Acceleration and Deceleration Times
Acc/Dec Time Based on Maximum Frequency
Acc/Dec Time Based on Operation Frequency

Multi-step Acc/Dec Time Configuration
5.9 Acc/Dec Pattern Configuration
5.10 Stopping the Acc/Dec Operation
5.11 V/F(Voltage/Frequency) Control
Linear V/F Pattern Operation
Square Reduction V/F pattern Operation
User V/F Pattern Operation
Output Voltage Setting
5.12 Torque Boost
Manual Torque Boost
Auto Torque Boost
5.13 Stop Mode Setting
Deceleration Stop
Stop After DC Braking
Free Run Stop
5.14 Frequency Limit
Frequency Limit Using Maximum Frequency and Start Frequency
Frequency Limit Using Upper and Lower Limit Frequency Values
Frequency Jump
6 Learning Advanced Features
6.1 DC Braking
Stop After DC Braking
Start After DC Braking
DC Braking During Stop
6.2 Jog operation
Jog Operation 1-Forward Jog by Multi-function Terminal
Jog Operation 2-Fwd/Rev Jog by Multi-function Terminal
6.3 Up-down Operation
6.4 3-Wire Operation
6.5 Dwell Operation
6.6 Slip Compensation Operation
6.7 Simple Sensorless Control
6.8 PID Control
PID Basic Control

6.9 Energy Saving Operation
6.10 Speed Search Operation
6.11 Auto Restart Settings
6.12 Operational Noise Settings (carrier frequency settings)
6.13 2nd Motor Operation
6.14 Frequency Setting and 2nd Operation Mode Setting
6.15 Input Voltage Setting
6.16 Parameter Initialization
6.17 Parameter Lock
6.18 Voltage Trip Prevention During Deceleration
6.19 Brake Control
6.20 Analog Output
6.21 Digital Output
Multi-function Relay Output Terminal Settings
6.22 Draw Operation
6.23 Operation Mode Setting When Cooling Fan is Abnormal
6.24 Operation State Monitor
6.25 I/O Terminal Block State Monitor
6.26 Fault State Monitor
7 Learning Protection Features
7.1 Motor Protection
Electronic Thermal Motor Overheating Prevention (ETH)
Overload Early Warning and Trip
Stall Prevention
7.2 Inverter and Sequence Protection
Output Open-phase Protection
External Trip Signal
Inverter Overload Protection
Speed Command Loss
Dynamic Braking (DB) Resistor Configuration
Initial charging circuit trip(ROT)
8 RS-485 Communication Features
8.1 Communication Standards
8.2 Communication System Configuration

Communication Line Connection
Setting Communication Parameters
Setting Operation Command and Frequency
Command Loss Protective Operation
Parameter Group for Data Transmission
8.3 Communication Protocol
LS INV 485 Protocol
Modbus-RTU Protocol
8.4 Compatible Common Area Parameter
9 Table of Functions
9.1 Operation Group
9.2 Drive Group (PAR → dr)
9.3 Basic Function group (PAR→bA)
9.4 Expanded Function group (PAR→Ad)
9.5 Control Function group (PAR→Cn)
9.6 Input Terminal Block Function group (PAR→In)
9.7 Output Terminal Block Function group (PAR→OU)
9.8 Communication Function group (PAR→CM)
9.9 Application Function group (PAR→AP)
9.10 Protection Function group (PAR→Pr)
9.11 2nd Motor Function group (PAR→M2)
9.12 Config Mode group (PAR→CF)
10 Troubleshooting
10.1 Trips
Fault Trips
10.2 Troubleshooting Fault Trips
10.3 Troubleshooting Other Faults
11 Maintenance
11.1 Regular Inspection Lists
Daily Inspections
Annual Inspections
Bi-annual Inspections
11.2 Storage and Disposal
Storage

Disposal
12 Technical Specification
12.1 Input and Output Specification
12.2 Product Specification Details
12.3 External Dimensions (IP 20 Type)
12.4 Peripheral Devices
12.5 Fuse and Reactor Specifications
12.6 Terminal Screw Specification
12.7 Braking Resistor Specification
12.8 Continuous Rated Current Derating
12.9 Remote Keypad Option
Product Warranty
Index


기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
1 Preparing the Installation
Note
Check the product name, open the packaging, and then confirm that the product is free from
defects. Contact your supplier if you have any issues or questions about your product.
This chapter provides details on product identification, part names, correct installation and
cable specifications. To install the inverter correctly and safely, carefully read and follow the
instructions.
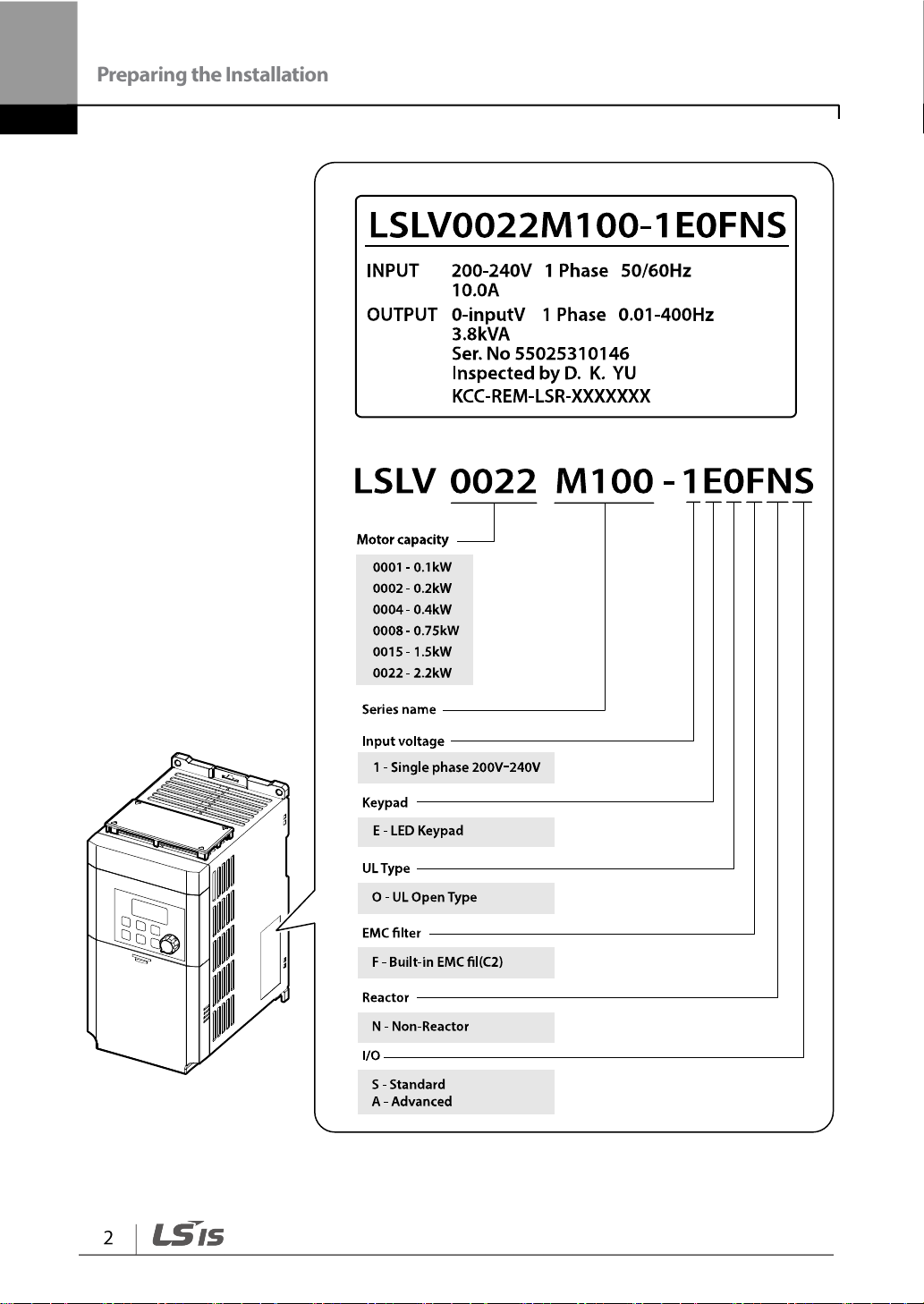
1.1 Product Identification
The M100 Inverter is manufactured in a range of product groups based on drive capacity
and power source specifications. Product name and specifications are detailed on the rating
plate. The illustration on the next page shows the location of the rating plate. Check the
rating plate before installing the product and make sure that the product meets your
requirements. For more detailed product specifications, refer to 12.1 Input and Output
Specification on page 242.
기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
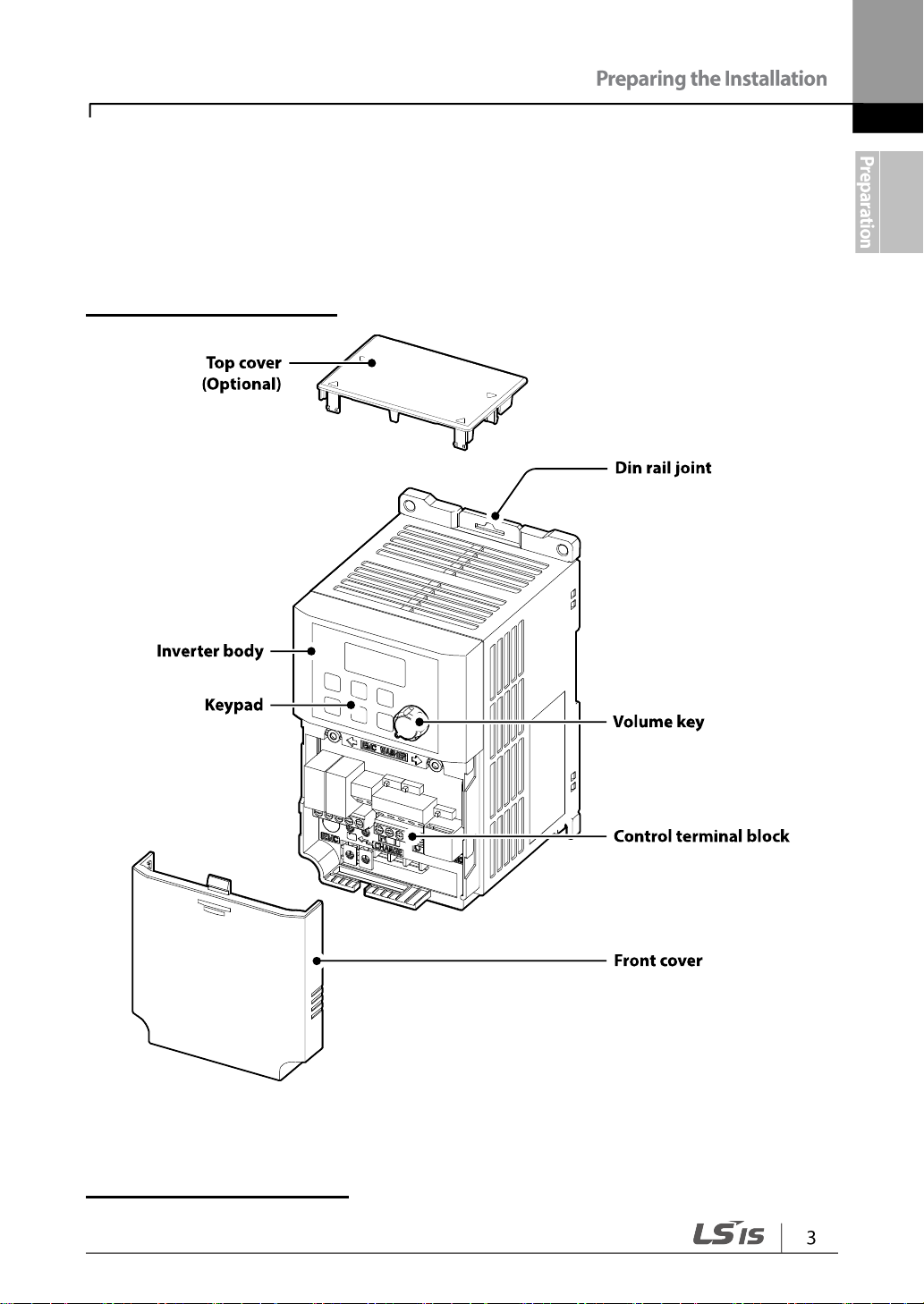
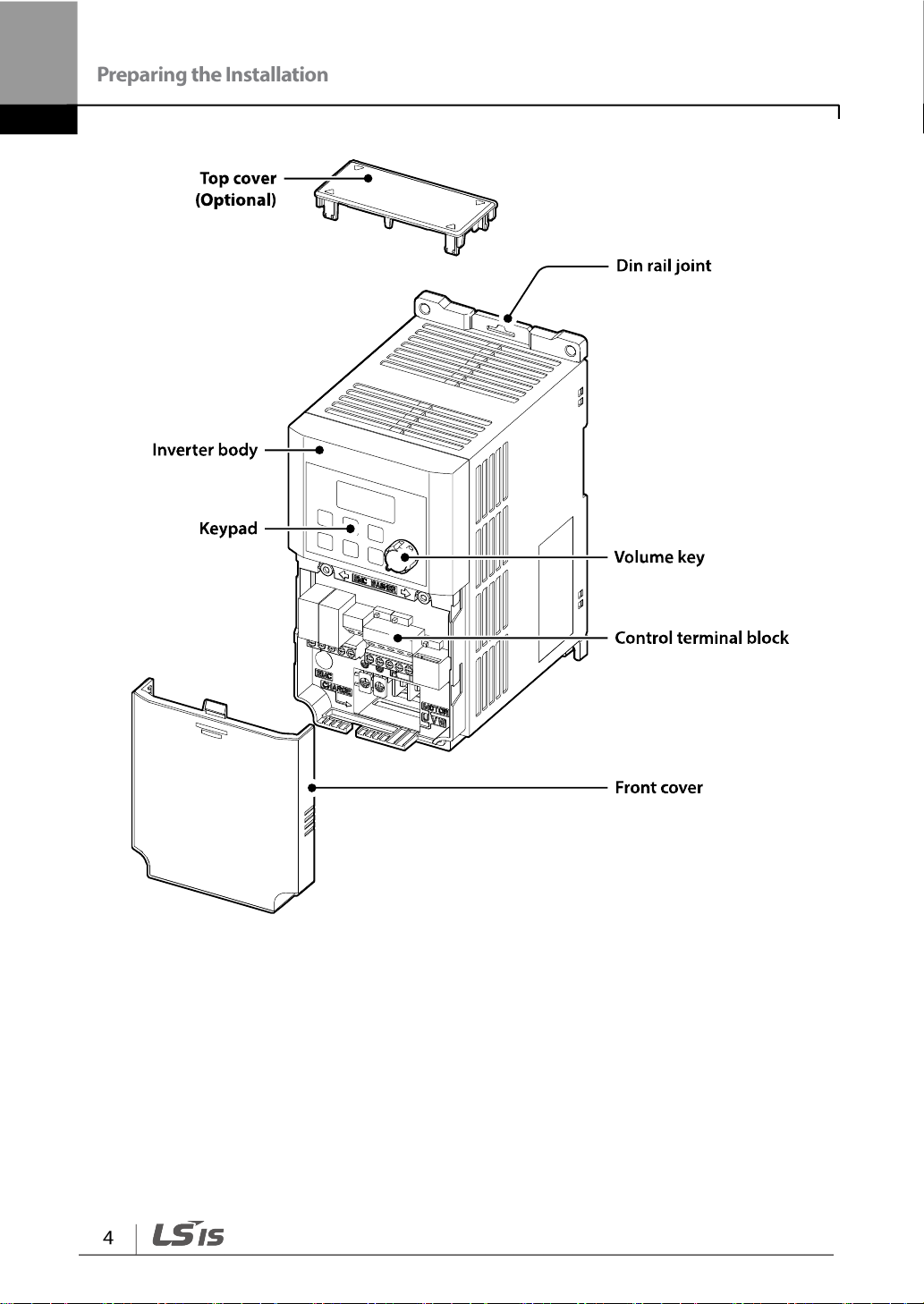
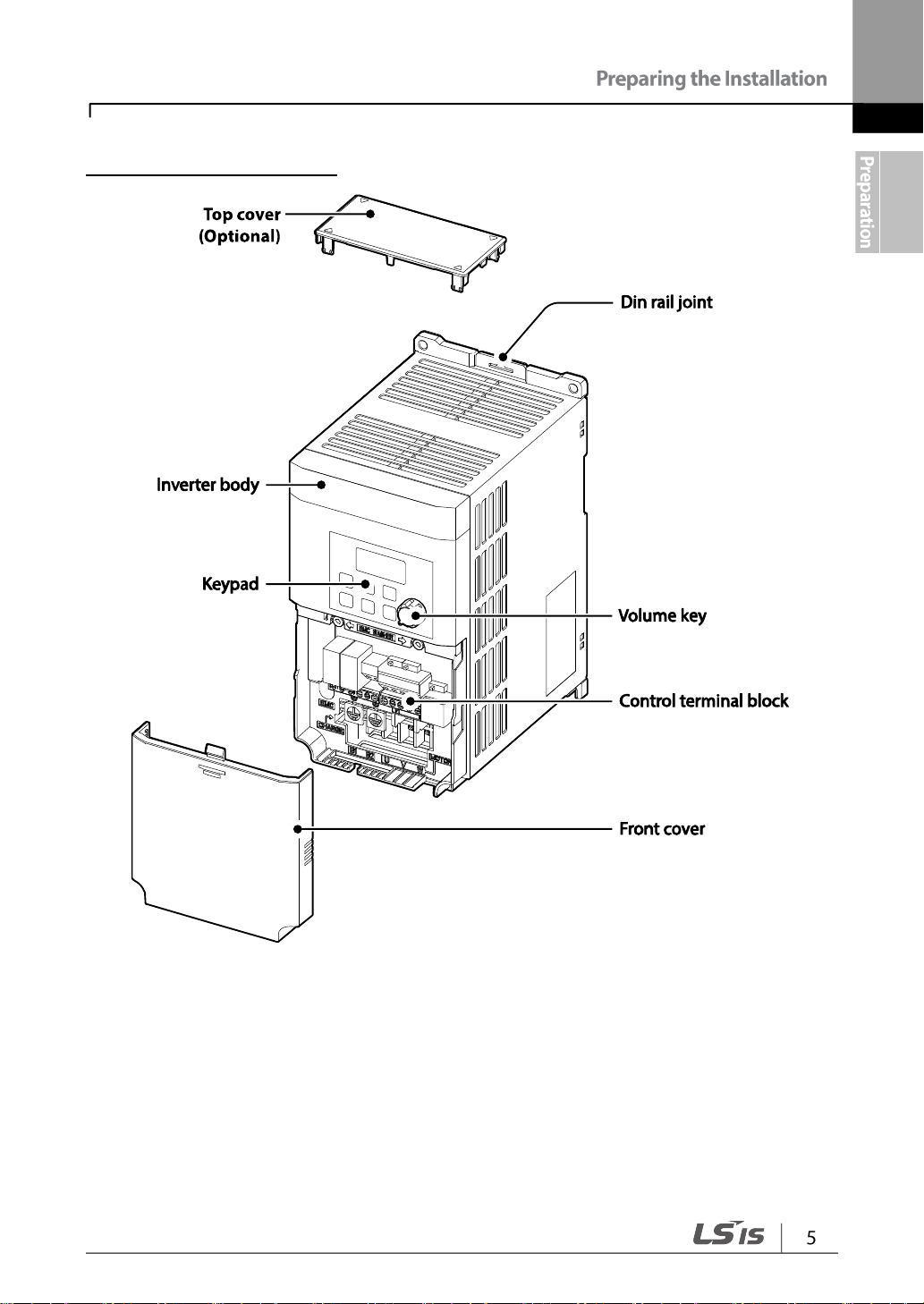
1.2 Part Names
The illustration below displays part names. Details may vary between product groups.
0.1~0.2 kW (Single Phase)
0.4~0.75 kW (Single Phase)
기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
1.5~2.2 kW (Single Phase)
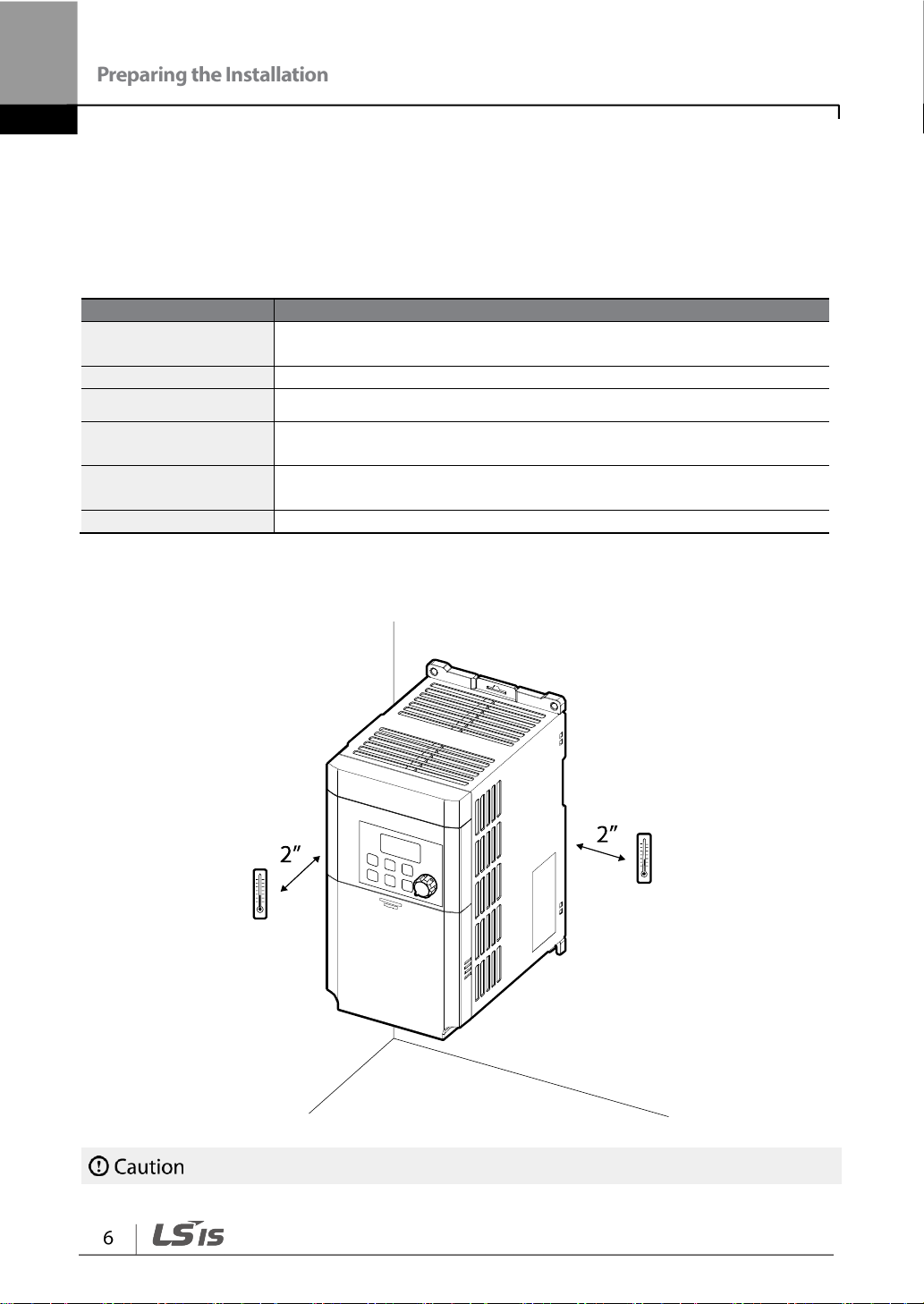
1.3 Installation Considerations
Items
Description
Ambient Temperature
1)
14–122F (-10–50℃)
Ambient Humidity
95% relative humidity (no condensation)
Storage Temperature
- 4–149F (-20–65℃)
Environmental Factors
An environment free from corrosive or flammable gases, oil residue or
dust
Altitude/Vibration
Lower than 3,280 ft (1,000 m) above sea level/less than 1G (9.8
m/sec2)
Air Pressure
70~106 kPa
Inverters are composed of various precision, electronic devices, and therefore the
installation environment can significantly impact the lifespan and reliability of the product.
The table below details the ideal operation and installation conditions for the inverter.
1) The ambient temperature is the temperature measured at a point 2” (5 cm) from the surface of the
inverter.
기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
Do not allow the ambient temperature to exceed the allowable range while operating the
inverter.
1.4 Selecting and Preparing a Site for Installation
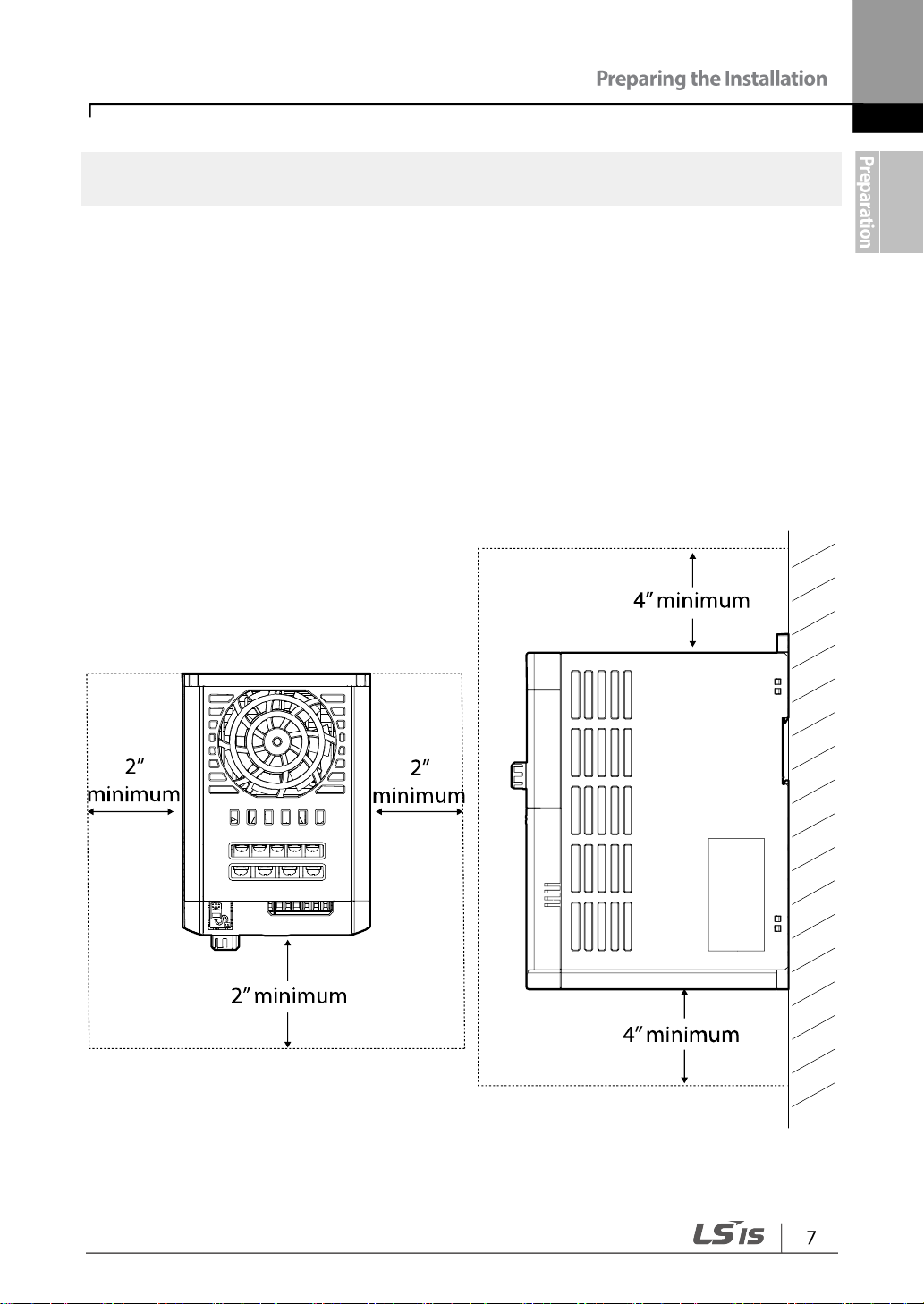
When selecting an installation location consider the following points:
• The inverter must be installed on a wall that can support the inverter’s weight.
• The location must be free from vibration. Vibration can adversely affect the operation of
the inverter.
• The inverter can become very hot during operation. Install the inverter on a surface that
is fire-resistant or flame-retardant and with sufficient clearance around the inverter to
allow air to circulate. The illustrations below detail the required installation clearances.
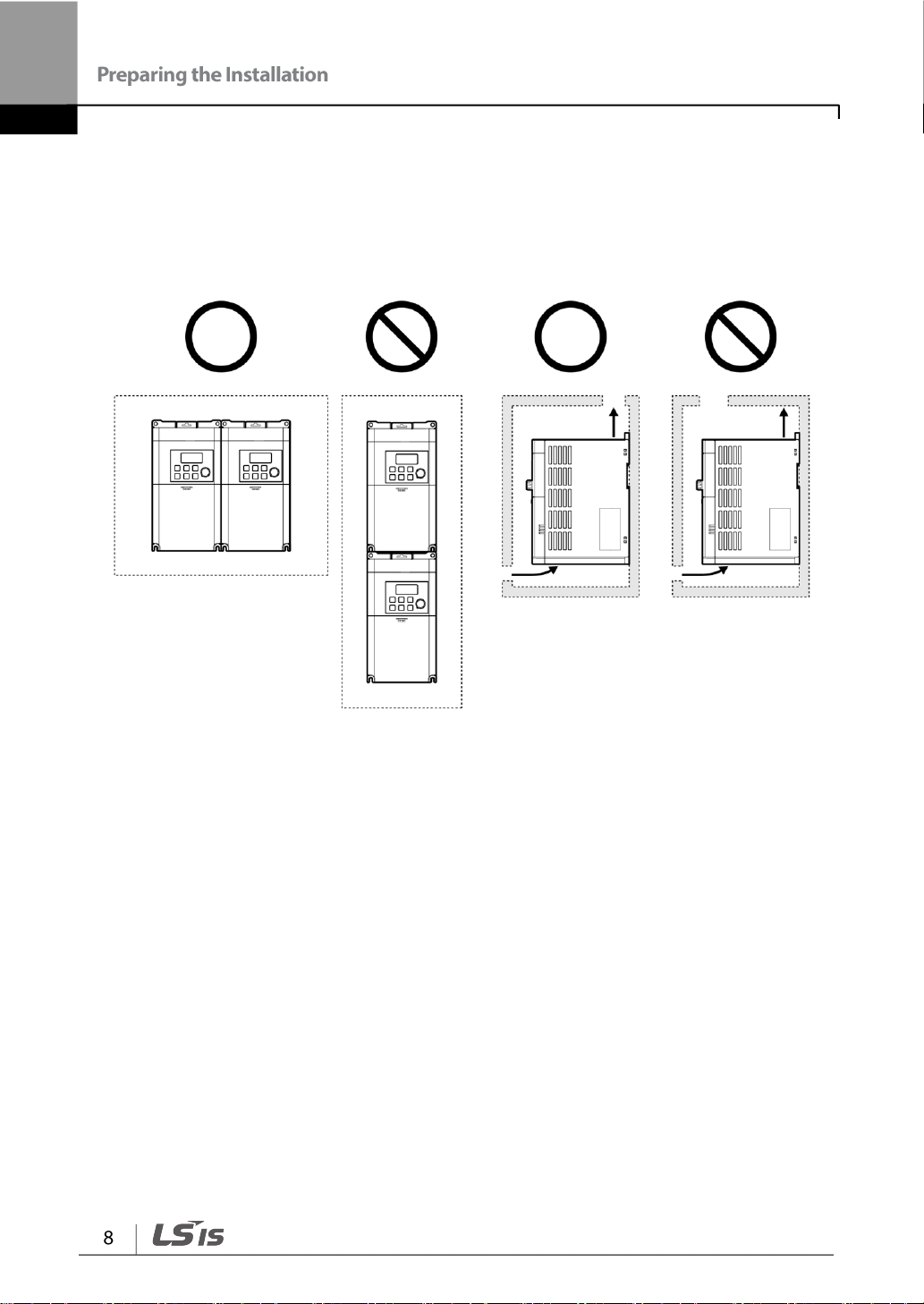
• Ensure sufficient air circulation is provided around the inverter when it is installed. If the
inverter is to be installed inside a panel, enclosure, or cabinet rack, carefully consider the
position of the inverter’s cooling fan and the ventilation louver. The cooling fan must be
positioned to efficiently transfer the heat generated by the operation of the inverter.
기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
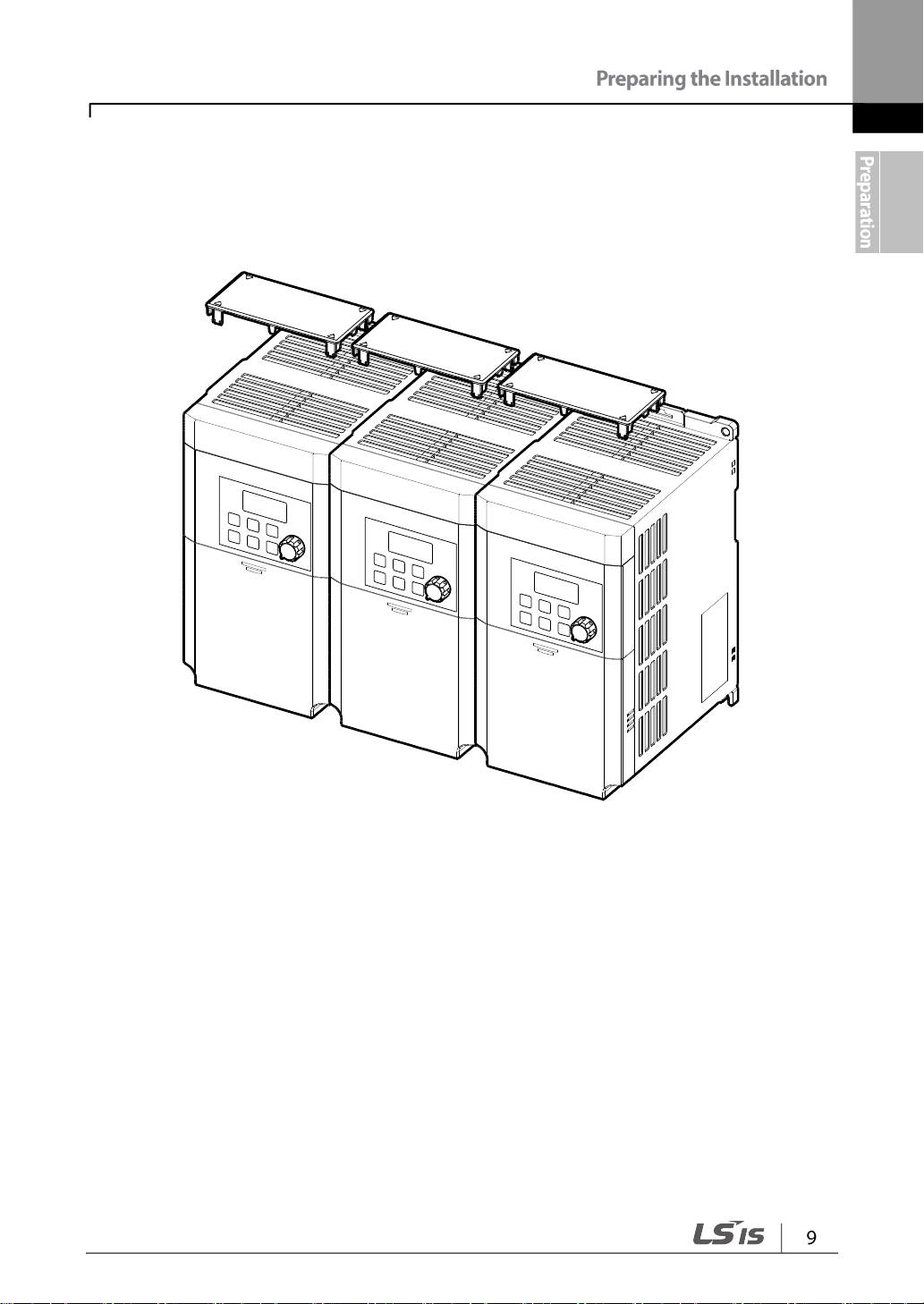
• If you are installing multiple inverters in one location, arrange them side by side and
remove their top covers (optional). The top covers MUST be removed for side-by -side
installations. Use a flat head screwdriver to remove the top covers.
• Keep the distance between inverters at least 0.1’’.
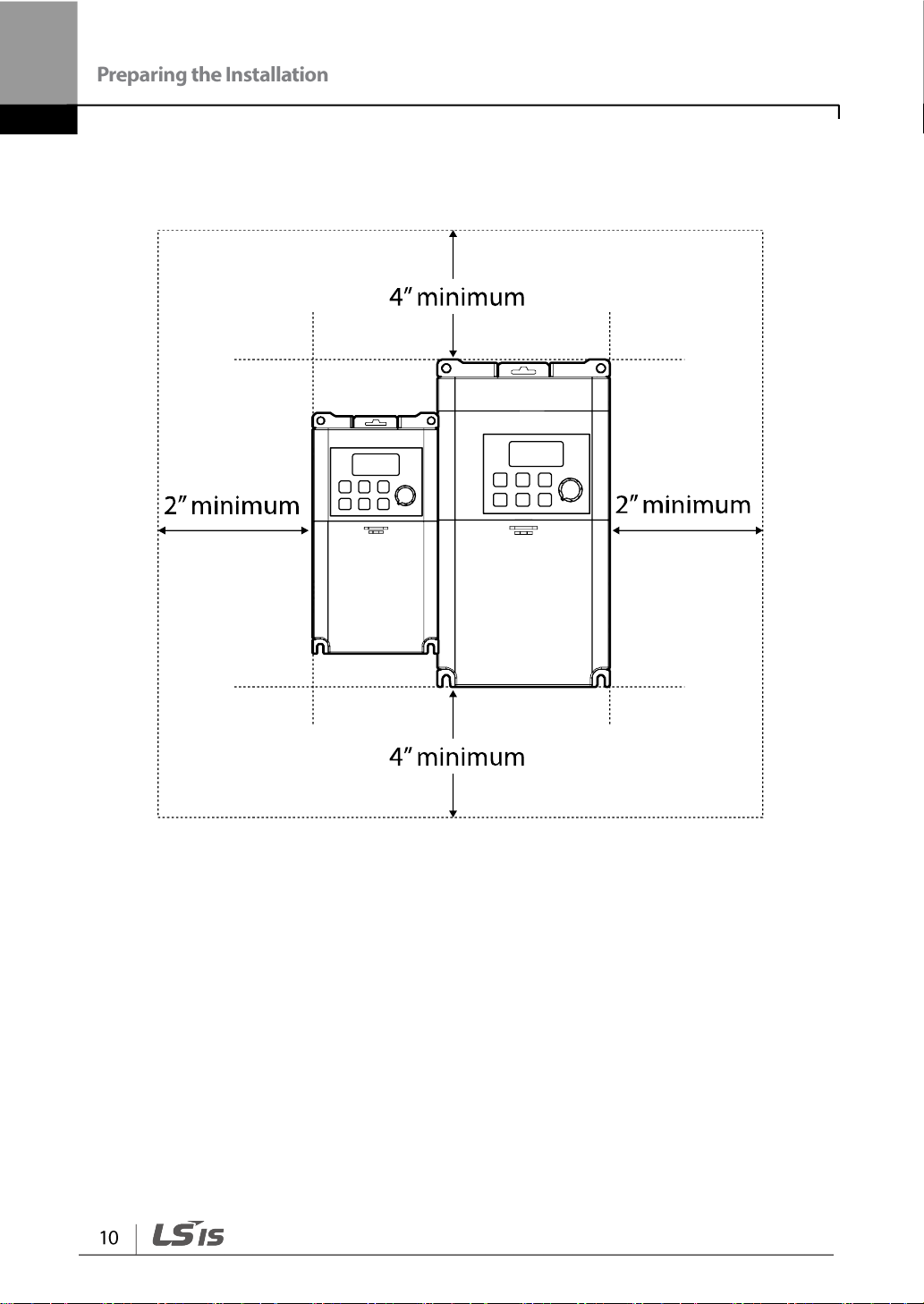
• If you are installing multiple inverters, of different ratings, provide sufficient clearance to
meet the clearance specifications of the larger inverter.
기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
1.5 Cable Selection
• Wherever possible use cables with the largest cross-sectional area for mains power wiring,
to ensure that voltage drop does not exceed 2%.
• Use copper cables rated for 600V, 75℃ for power terminal wiring.
• Use copper cables rated for 300V, 75℃ for control terminal wiring.
Load (kW)
Ground
Power I/O
mm2
AWG
mm2
AWG
R/S/T
U/V/W
R/S/T
U/V/W
Single Phase
200V
0.1
3.5
12 2 2
14
14
0.2
0.4
0.75
1.5
3.5
12
3.5
3.5
12
12
2.2
Terminal
Signal Cable
Without Crimp Terminal
Connectors
(Bare wire)
With Crimp Terminal Connectors
(Bootlace Ferrule)
mm2
AWG
mm2
AWG
P1~P5/CM/VR/V1/I2
/AO/Q1/EG/241)
0.75
18
0.5
20
A1/B1/C1/A2/C21)
1.0
17
1.5
15
When you install power and signal cables in the terminal blocks, only use cables that meet
the required specification for the safe and reliable operation of the product. Refer to the
following information to assist you with cable selection.
Ground Cable and Power Cable Specifications
Signal (Control) Cable Specifications
1) There are no P4, P5, I2, A2, and C2 terminals on the standard I/O, and there are no Q1 and EG
terminals on the Advanced I/O. For more details, refer to 2.2 Cable Wiring Step 4 Control Terminal
Wiring on page 24.

설치 준비
기본조작법
기능알람표
제어블록도
기본 기능
응용 기능
모니터기능
보호 기능
통신 기능
2 Installing the Inverter
This chapter describes the physical and electrical installation methods, including mounting
and wiring of the product. Refer to the flowchart and basic configuration diagram provided
below to understand the procedures and installation methods to be followed to install the
product correctly.
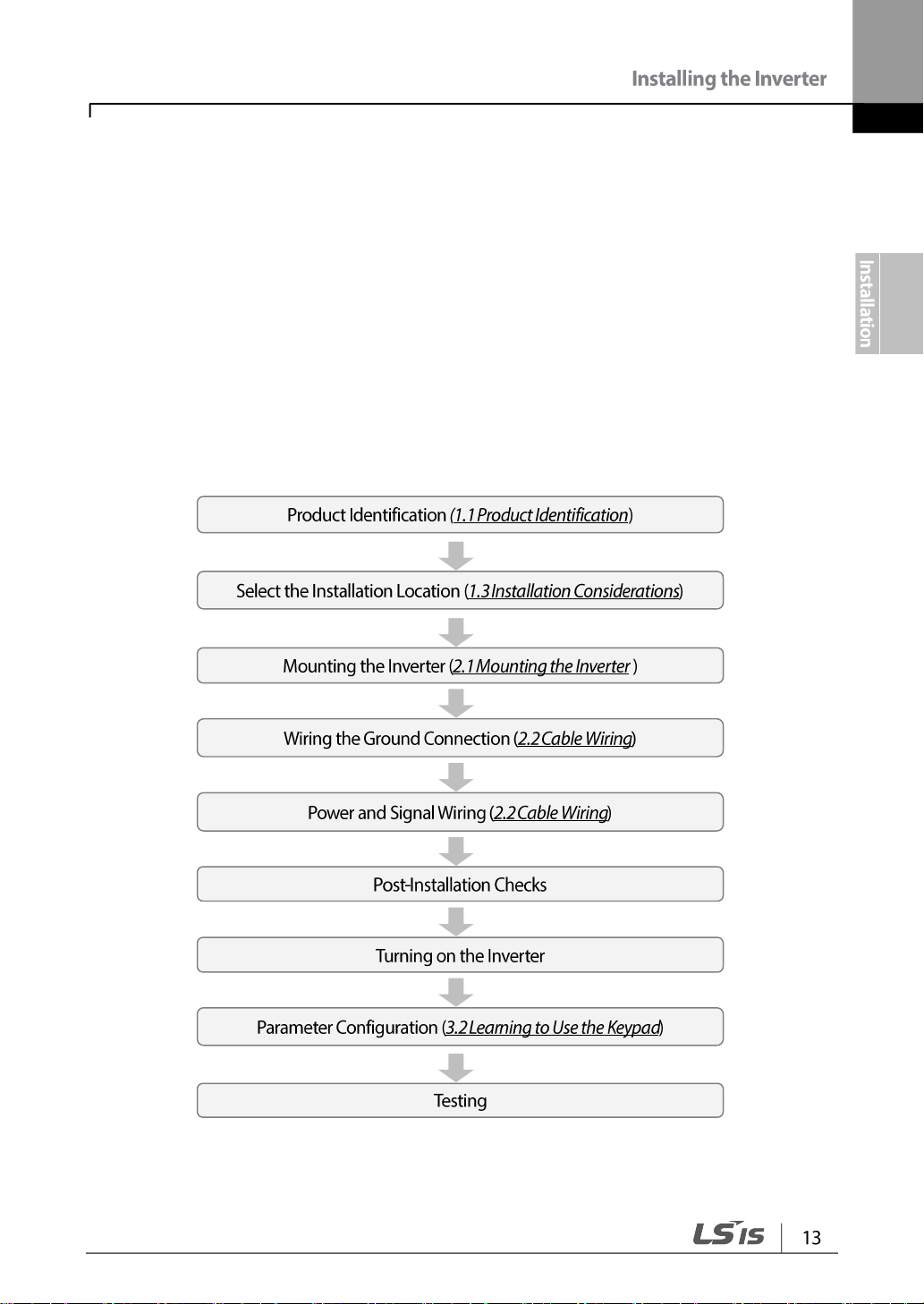
Installation Flowchart
The flowchart lists the sequence to be followed during installation. The steps cover
equipment installation and testing of the product. More information on each step is
referenced in the steps.
Basic Configuration Diagram
• Figures in this manual are shown with covers or circuit breakers removed to show a more
detailed view of the installation arrangements. Install covers and circuit breakers before
operating the inverter. Operate the product according to the instructions in this manual.
• Do not start or stop the inverter using a magnetic contactor, installed on the input power
supply.
• If the inverter is damaged and loses control, the machine may cause a dangerous situation.
Install an additional safety device such as an emergency brake to prevent these situations.
• High levels of current draw during power-on can affect the system. Ensure that correctly
rated circuit breakers are installed to operate safely during power-on situations.
• Reactors can be installed to improve the power factor. Note that reactors may be installed
within 30 ft (9.14 m) from the power source if the input power is 10 times over the inverter’s
power. Refer to 12.5 Fuse and Reactor Specifications on page 247 and carefully select a
reactor that meets the equipment.
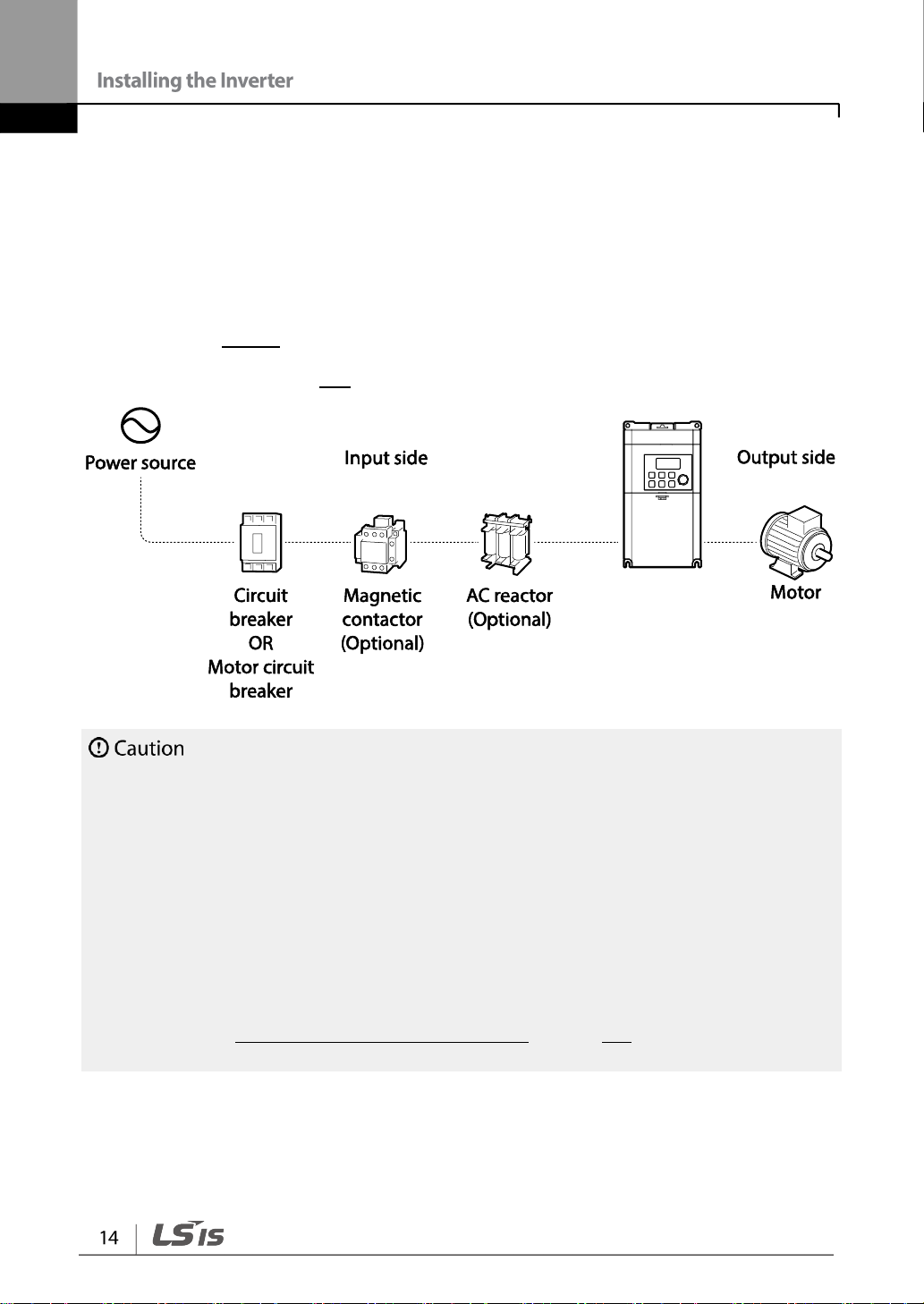
The reference diagram below shows a typical system configuration showing the inverter
and peripheral devices.
Prior to installing the inverter, ensure that the product is suitable for the application (power
rating, capacity, etc). Ensure that all of the required peripherals and optional devices
(resistor brakes, contactors, noise filters, etc.) are available. For more details on peripheral
devices, refer to 0 Unit: mm (inches)
Peripheral Devices on page 247.
설
치
준
비
기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
2.1 Mounting the Inverter
Mount the inverter on a wall or inside a panel following the procedures provided below.
Before installation, ensure that there is sufficient space to meet the clearance specifications,
and that there are no obstacles impeding the cooling fan’s air flow.
Select a wall or panel suitable to support the installation. Refer to 12.3 External Dimensions
(IP 20 Type) on page 245 and check the inverter’s mounting bracket dimensions.
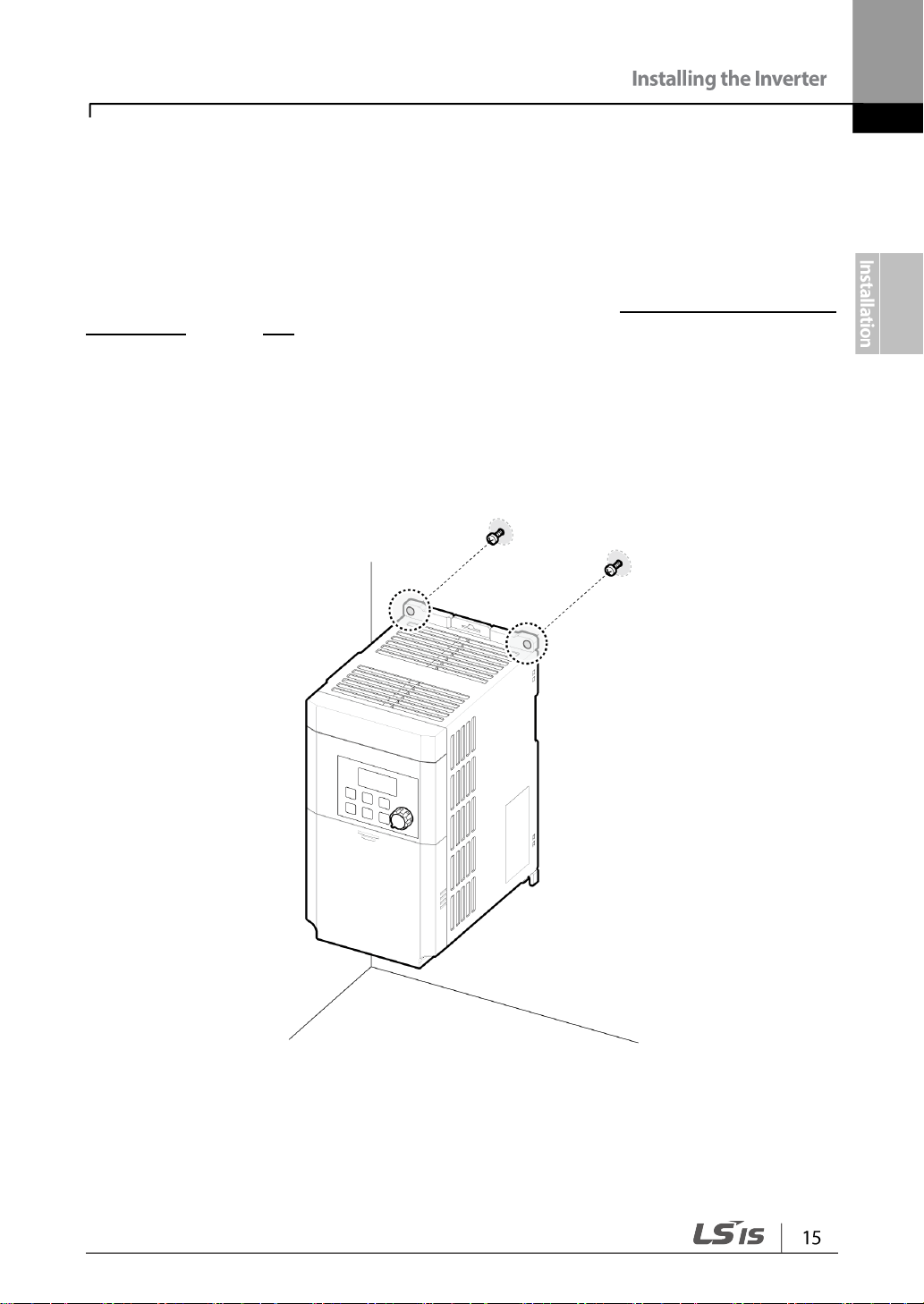
1 Use a level to draw a horizontal line on the mounting surface, and then carefully mark
the fixing points
2 Drill the two upper mounting bolt holes, and then install the mounting bolts. Do not fully
tighten the bolts at this time. Fully tighten the mounting bolts after the inverter has been
mounted.
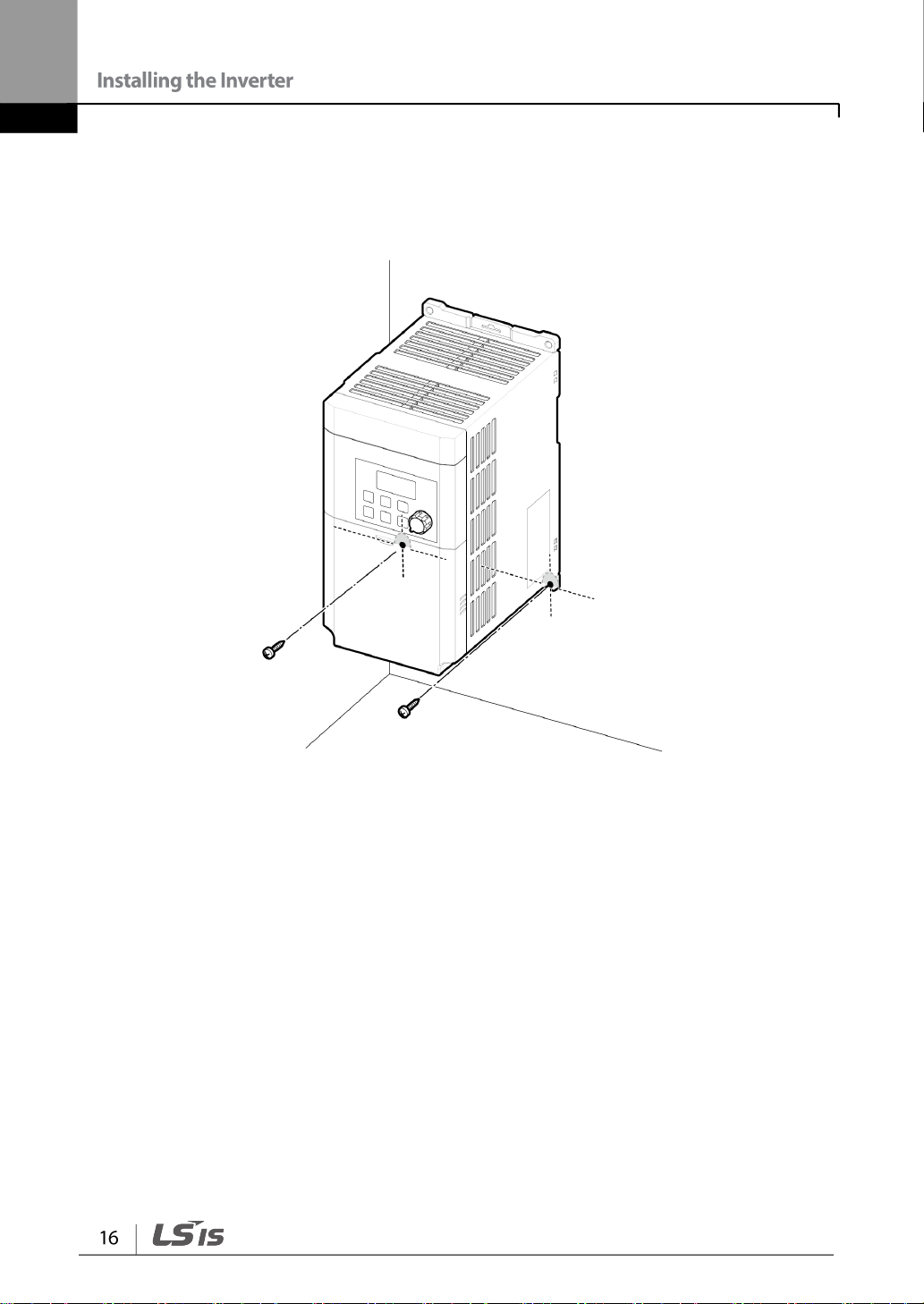
3 Mount the inverter on the wall or inside a panel using the two upper bolts, and then fully
tighten the mounting bolts. Ensure that the inverter is placed flat on the mounting
surface, and that the installation surface can securely support the weight of the inverter.
설
치
준
비
기
본조작법
기
능알
람
표
제
어
블
록도
기
본
기
능
응
용
기
능
모
니터기능
보
호
기
능
통
신
기
능
Note
The quantity and dimensions of the mounting brackets vary based on frame size. Refer to 12.3
External Dimensions (IP 20 Type) on page 245 for detailed information about your model.
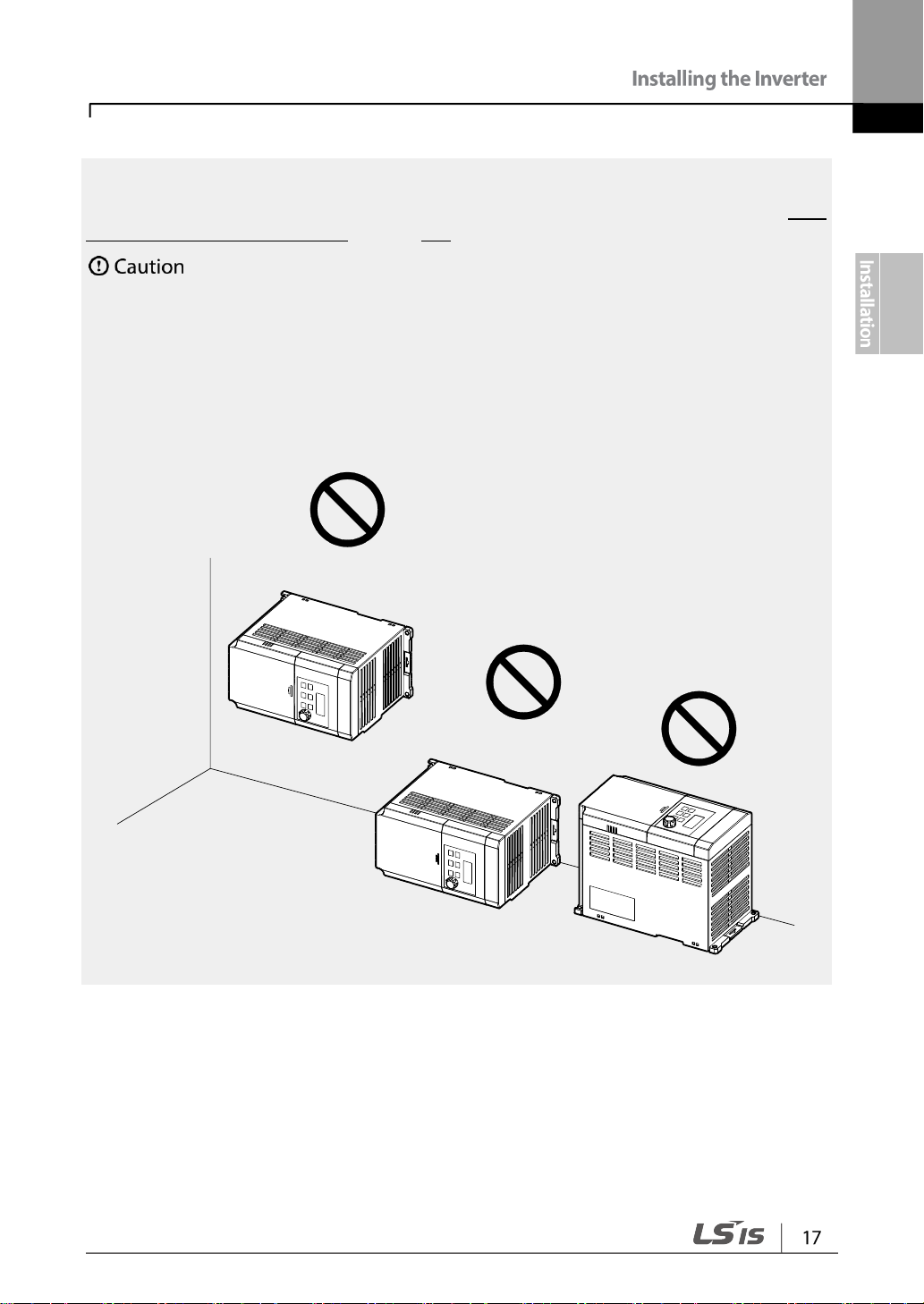
• Do not transport the inverter by lifting with the inverter’s covers or plastic surfaces. The
inverter may tip over if covers break, causing injuries or damage to the product. Always
support the inverter using the metal frames when moving it.
• Use an appropriate transport method that is suitable for the weight.
• Do not install the inverter on the floor or mount it sideways against a wall. The inverter
MUST be installed vertically, on a wall or inside a panel, with its rear flat on the mounting
surface.

2.2 Cable Wiring
• Install the inverter before carrying out wiring connections.
• Ensure that no small metal debris, such as wire cut-offs, remain inside the inverter. Metal
debris in the inverter may cause inverter failure.
• Tighten terminal screws to their specified torque. Loose terminal block screws may allow the
cables to disconnect and cause short circuit or inverter failure. Refer to 12.6 Terminal Screw
Specification on page 248 for torque specifications.
• Do not place heavy objects on top of electric cables. Heavy objects may damage the cable
and result in electric shock.
• The inverter’s power is supplied by the supply grounding system. The TT, TN, IT, and corner-
grounded systems are not suitable for this inverter.
• The inverter may generate direct current to the inverter’s protective ground cable. Only type
B Residual Current Devices (RCD) or Residual Current Monitors (RCM) can be installed.
• Use cables with the largest cross-sectional area, appropriate for power terminal wiring, to
ensure that voltage drop does not exceed 2%.
• Use copper cables rated at 600V, 75℃ for power terminal wiring.
• Use copper cables rated at 300V, 75℃ for control terminal wiring.
• Connect the control terminals separately from the power terminal wiring or high potential
circuit (200 V relay sequence circuit).
• Ensure that there are no control terminal shorts or improper wiring. Control terminal shorts or
improper wiring may damage the inverter or cause malfunction.
• Use a shielded cable while making wiring connections at the control terminal. Unshielded
cables may cause the inverter to malfunction due to interference. Use an STP cable if ground
connections must be installed.
• If you need to re-wire the terminals due to wiring-related faults, ensure that the inverter
keypad display is turned off and the charge lamp under the front cover is off before working
on wiring connections. The inverter may hold a high voltage electric charge long after the
power supply has been turned off.
Remove the control terminal cover, and then install the ground connection as specified.
Complete the cable connections by connecting an appropriately rated cable to the terminals
on the power and control terminal blocks.
 Loading...
Loading...