Page 1
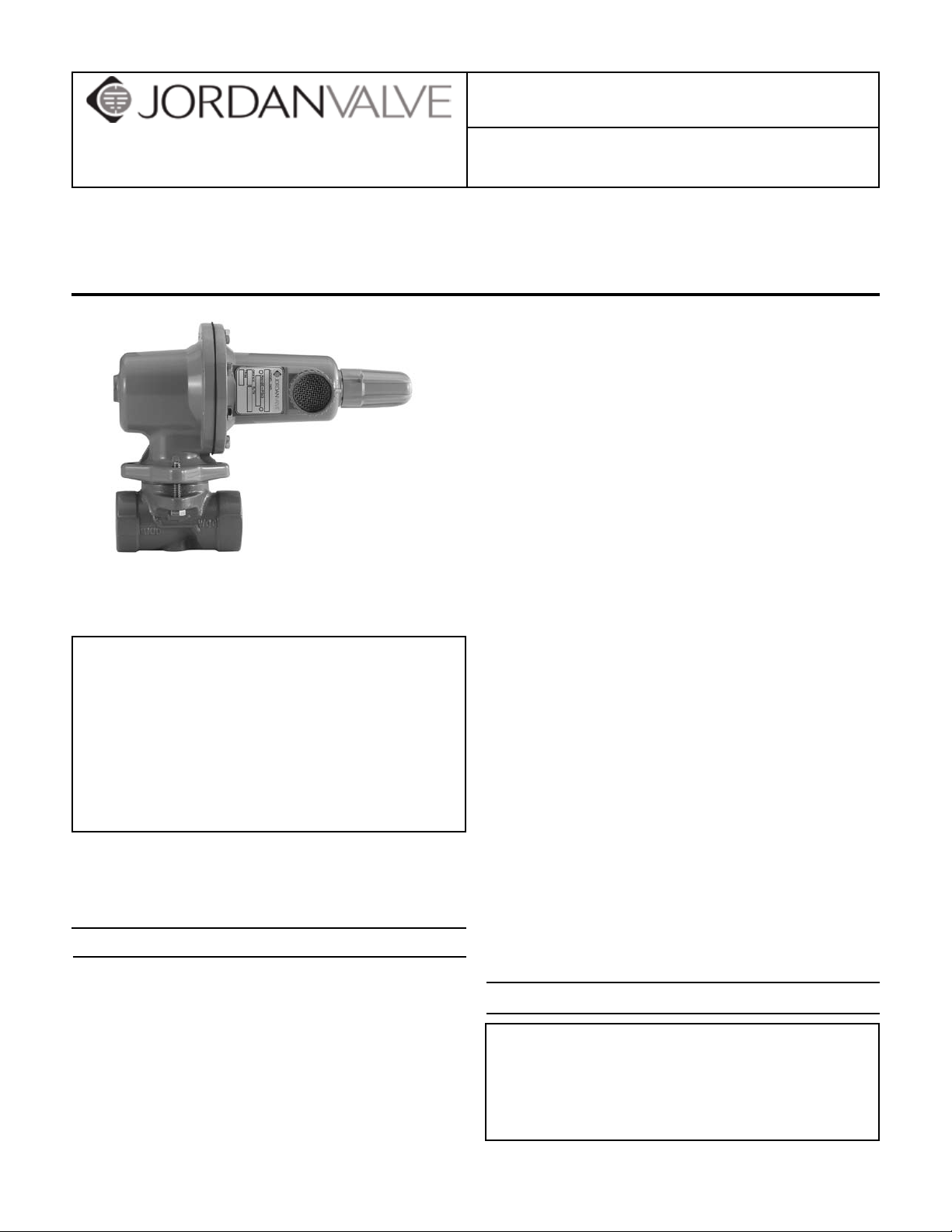
I & M Mark 627
3170 Wasson Road • Cincinnati, OH 45209 USA
Phone 513-533-5600 • Fax 513-871-0105
info@richardsind.com • www.jordanvalve.com
Warning: Jordan Valve Pressure Regulators must only be used, installed and repaired in accordance with these Installation & Maintenance Instructions. Observe all applicable public and company codes and regulations. In the event
of leakage or other malfunction, call a qualied service person; continued operation may cause system failure or a
general hazard. Before servicing any valve, disconnect, shut off, or bypass all pressurized uid. Before disassembling
a valve, be sure to release all spring tension.
Note: This document is to be used in conjunction with
The Mark 627 Series Cut Sheet.
WARNING! Over-pressure of this regulator or
installation of the regulator in applications which
may see pressure levels beyond those for which
the regulator is designed may result in leakage
and/or catastrophic failure. This failure could
result in leaking gas, damage to surrounding
equipment, personal injury or death. To prevent
such damage / injury the regulator should be installed in a safe location and should be chosen
based upon the user’s specic application.
It is highly recommended that suitable pressure relieving
devices, as recommended by appropriate codes or standards, be installed in your system to assure that maximum rated pressures are not exceeded.
Installation
The Mark 627 should be chosen based upon the 1.
maximum, differential and outlet pressures as
described in Table 1. Flow capacities are listed in
Table 2. The operating temperature range is -20°F
to 180°F. When choosing and installing a regulator
one must ensure that the conditions do not exceed
these parameters. Furthermore, large differentials
in pressure across the regulator may result in the
formation of ice in the orice area. The resulting
decrease in orice area may affect the regulators
Installation & Maintenance Instructions for
Mark 627 High Pressure Regulator
ability to ow in sufcient volume for downstream
demand. Therefore, large pressure drop applications may require the use of more than one regulator.
Make sure that line pressure has been eliminated 2.
prior to the installation of any regulator. Prior to
installation the line should be inspected to ensure
that there is no debris that might damage the regulator.
The regulator should be installed with the ow ar-3.
row on the side of the body in the correct orientation to ow - i.e. higher pressure upstream, lower
regulated pressure downstream. As is true with
most regulators, the Mark 627 has an outlet pressure rating that is lower than the inlet pressure rating. Over-pressure protection is needed to avoid
over-pressure if the actual inlet pressure can exceed the outlet pressure rating.
The regulator may be installed in any orientation 4.
as long as the ow is in proper agreement with
the ow arrow on the side of the body. However,
the regulator should be positioned such that the
screened vent will not collect debris or moisture.
Vent Line Option
The Mark 627 includes a vent in the upper housing (24).
If there is concern about build-up of gas in a conned
location, the vent assembly (25) may be removed to allow installation of a remote vent line. With the vent assembly removed, a vent line may be installed into the ¾”
NPT port. This vent line should be as large a diameter as
possible and should utilize minimal bends and elbows.
Furthermore, the vent line opening should be protected
from weather or debris and should be checked regularly
for blockage.
Start-up Operation
WARNING! Release downstream pressure to
prevent a potential over-pressure of the diaphragm. Failure to do so may result in property
damage and/or personal injury. Always employ
upstream and downstream pressure gauges to
monitor startup pressures.
Page 2

Assuming that the regulator is isolated with shutoff
valves on both the upstream and downstream sides,
slowly open upstream valve followed by slowly opening
the downstream valve. Check all connections for leaks
and make necessary output adjustments by manipulating
the adjusting screw (29) per the adjustment procedures
below.
Adjustment
The range of adjustment for a particular regulator is
indicated on the nameplate. Different ranges can be
achieved by substituting a different spring (27).
IMPORTANT: If a new spring is installed the nameplate must be remarked to indicate the new pressure
range.
Refer to Tables 1 and 2 prior to adjustment for pres-1.
sure and ow information, assuring that the chosen
spring will facilitate the desired pressure regulation
and that the maximum pressure output does not
exceed the downstream system pressure limits.
Remove the cap (30) and loosen the jam nut (28). 2.
To INCREASE pressure:3. Turn adjustment screw
clockwise.
To DECREASE pressure:4. Turn adjustment screw
counterclockwise.
Once the desired pressure is achieved, hold adjust-5.
ment screw while securing the jam nut and replace
cap.
Shutdown
the ow will result in accelerated wear on the disc assembly (9) and seat (2).
Replacing the Disk Assembly and Seat
Remove cap screws (3), separating the diaphragm 1.
case (5) and upper housing (24) as a unit.
Inspect the seat (2) and remove / replace if neces-2.
sary. Apply general purpose lubricant to threads of
new seat prior to installation.
Inspect disc assembly (9) for wear / damage. 3.
Should replacement be necessary, remove the hair
pin clip (13) that holds the disc assembly to the
stem (10). Install new disc assembly by aligning the
hole in the disc assembly and stem and reinstalling
the hair pin clip.
Should stem maintenance be required proceed as 4.
follows:
Remove the boost body (6), stabilizer (7) and a.
stem guide (8) form the diaphragm case. Unhook and remove the stem from the lever (15)
and remove the diaphragm case.
Remove and inspect the diaphragm case o-ring b.
(4) and replace as necessary, being sure to liberally lubricate with a general purpose grease
prior to installation in the boost body.
To reassemble, insert the stem into the diaphragm 5.
case and hook into the lever. Be sure to position
the diaphragm case assembly such that the pilot
tube is inserted into the Outlet side of the body.
Secure the diaphragm case assembly to the body
with the two cap screws. Torque the cap screws to
25 ft.-lbs. (34 N•m).
WARNING! Downstream pressure must be released to prevent an over-pressurization of the
diaphragm. Failure to do so may result in property damage and/or personal injury.
Close the upstream block valve followed by closing 1.
the downstream block valve. Open the nearest vent
valve between the regulator and the downstream
block valve.
Maintenance
Routine maintenance should be expected due to normal
wear and tear, damage from external sources or debris.
The regulator components, especially the moving and
sealing parts, should be inspected periodically and replaced as necessary. Frequency of inspection/replacement depends upon severity of conditions, but may also
be required by local/state/federal law or industry standards.
Body Area Maintenance
Large pressure drops or large amounts of particulate in
Diaphragm Assembly and Upper Housing
Maintenance
IMPORTANT! Prior to accessing the spring (27) all
pressure must be released from the diaphragm case.
Remove the cap (30), loosen the jam nut (28) and 1.
turn the adjusting screw (29) counter-clockwise until all spring compression is relieved.
Remove the upper housing cap screws (31) and re-2.
move the upper housing. If changing the spring or
adjusting the upper housing position, do so at this
point and reinstall spring, upper spring seat (26)
and upper housing cap screws and readjust regulator per the instructions under Start-Up Operation
on page one.
If diaphragm assembly maintenance is required, re-3.
move the diaphragm assembly by tilting it such that
the post and pin assembly (19) slips off the lever
(15). If lever replacement is necessary, free it by
removing the lever cap screws (18). Install the new
lever into the lever retainer (16) by inserting the
lever pin (17). Secure the entire assembly into the
diaphragm case by reinstalling the lever cap screws
and torquing them to 7 ft.-lbs. (9 N•m).
-2-
Page 3

Diaphragm and Spring
Remove the diaphragm head cap screw (33), 1.
spring seat (23), diaphragm head (22) and separate
the diaphragm (21) from the post and pin assembly
(19).
After examination and / or replacement, reas-2.
semble by installing diaphragm on post and pin
assembly and reinstalling diaphragm head, spring
seat and cap screw.
Hook the post and pin assembly onto the lever, 3.
rotating the diaphragm assembly until holes match
up with threaded holes in diaphragm case.
Unhook the post and pin assembly from the lever 4.
and torque the diaphragm head cap screw to 7 ftlbs (9 N•m).
Re-hook the post and pin assembly to the lever and 5.
re-check diaphragm hole alignment, loosening and
adjusting as necessary, making sure to re-torque
the diaphragm head cap screw appropriately each
time.
Once proper hole alignment is achieved re-hook 6.
the post and pin assembly to the lever.
Apply lubricant to upper spring seat and install with 7.
the Spring.
Install the upper housing such that the screened 8.
vent assembly is in the preferred orientation.
Install the upper housing cap screws through the 9.
upper housing and diaphragm and screw into the
threaded holes in the diaphragm case nger tight.
Install the adjustment screw into the upper housing, 10.
putting slack into the diaphragm.
Finish tightening the upper housing cap screws, 11.
using a crisscross method, and tightening each to
7 ft.-lbs (9 N•m).
Re-adjust the regulator per the instructions on page 12.
one under Startup Operation.
Mark 627 Regulator Tips
Overpressure protection must always be installed 1.
to protect against overpressure of regulator, as
well as overpressure of downstream equipment in
the event of a regulator failure. Also, downstream
pressure that is substantially higher than the pressure setting may result in damage to the regulator
components.
When sizing regulator you should utilize the small-2.
est orice necessary to accommodate the desired
ow/pressure requirement. Pipe size should preferably be 1”, but no smaller than ¾”.
When picking spring range, if two available spring 3.
ranges will accommodate the preferred pressure
setting, utilize the lower range spring, as it will allow
ner adjustment of the setting.
ADJUSTING SET POINT: Prior to adjustment the 4.
regulator should be owing 5% or higher of the
normal operating ow.
Vent should be oriented such that it is protected 5.
from water and other material which might collect
in the Upper Housing.
It is not uncommon that a small amount of gas may 6.
migrate through the diaphragm material. Proper
venting should be installed to avoid dangerous gas
build up.
Downstream pressure will change to some degree 7.
if upstream pressure changes.
FREEZING: Freezing is a common issue where the 8.
ow of pressurized gas is concerned due to normal
refrigerative effects. It is expected that the user will
realize approximately 1°F in temperature drop for
each 15 psi of differential across the regulator. This
may be particularly problematic during cold weather, when temperatures drop below 45°F (7°C). It is
important that the system be designed to alleviate
this problem by utilizing one or more methods such
as:
Multiple regulated pressure drops
Application of heat to the gas
Removal of water from the gas
Utilizing antifreeze solutions in the ow
Failure to consider the temperature-drop aspect
may result in ice plugging of the orice or erratic
performance due to ice formation on other components within the regulator.
Noise can be generated in regulators with large 9.
pressure drops and high ow volumes, resulting in
premature wear of regulator components.
Regulators inability to maintain published ow rate 10.
may be as a result of inefcient piping on both the
upstream and downstream side of the regulator.
Upstream pressure should be checked at body
inlet.
Table 1
Maximum Spring & Diaphragm Housing Pressure
Maximum pressure to avoid leakage to
atmosphere or possible damage to internal
parts.
Maximum pressure to prevent burst or
possible damage to internal parts.
Maximum diaphragm housing over-pressure
(above set-point) to avoid damage to internal
parts.
Table 2 - Wide-Open Flow Coefcients
Orice Size C
g
C
v
3/32” 6.9 0.24 28.5
1/8” 12.5 0.43 29.4
3/16” 29 0.93 31.2
1/4” 50 1.71 29.3
3/8” 108 3.42 31.6
1/2” 190 5.29 35.9
-3-
250 psi
375 psi
60 psi
C
1
Page 4

Illustration and Parts List
15
17
16
10
11
21
19
18
20
5
7
9
1
22
31
23
33 24
14
12
13
2
27
25 26
8
4
6
29 28
30
Item Description Qty. Item Description Qty.
1 Body 1 18 Lever Cap Screw 2
2* Seat 1 19 Post & Pin Assembly 1
3 Cap Screw (not shown) 2 20 Lock Washer 2
4* O-Ring 1 21* Diaphragm 1
5 Diaphragm Case 1 22 Diaphragm Head 1
6 Boost Body 1 23 Spring Seat 1
7 Stabilizer 1 24 Upper Housing 1
8 Stem Guide 1 25 Vent Assembly 1
9* Disc Assembly 1 26 Upper Spring Seat 1
10 Stem 1 27 Spring 1
11* O-Ring 1 28 Jam Nut 1
12 Back-Up Ring 2 29 Adjusting Screw 1
13 Hair Pin Clip 1 30 Cap 1
14 Pin 1 31 Cap Screw 8
15 Lever 1 32 Name Plate (not shown) 1
16 Lever Retainer 1 33 Cap Screw 1
17 Lever Pin 1 * Recommended Spare Parts
Bulletin IM-MK627-0310
3170 Wasson Road • Cincinnati, OH 45209 USA
Phone 513-533-5600 • Fax 513-871-0105
info@richardsind.com • www.jordanvalve.com
 Loading...
Loading...